Nobel Peace Prize 2024

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Peace Prize has been awarded to Nihon Hidankyo, an organisation of survivors of the Hiroshima-Nagasaki bombings. In doing so, the Nobel Committee has highlighted the power of their testimonies and the need for disarmament.
Key Points about Nihon Hidankyo and the Hibakusha Movement
- Nihon Hidankyo:
- Established on August 10, 1956, as the nation-wide organization for survivors of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings.
- Focuses on the welfare of Hibakusha (A-bomb survivors), promoting nuclear disarmament, and advocating for compensation for victims.
- Works to share the stories and experiences of Hibakusha, both within Japan and globally.
- Hibakusha (Bomb-affected People):
- Survivors of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
- Played a pivotal role in the global nuclear disarmament movement.
- Their testimonies have helped create the "nuclear taboo," ensuring nuclear weapons have not been used since 1945.
Role of Hibakusha in Nuclear Disarmament
- Global Impact:
- The bombings ignited a global movement for nuclear disarmament.
- Hibakusha's advocacy has highlighted the human cost of nuclear weapons, shaping international policy and promoting the nuclear taboo.
- Nihon Hidankyo’s Advocacy:
- The organization has been instrumental in documenting the effects of nuclear weapons and advocating for their abolition.
- Testimonies from Hibakusha have been key in raising awareness about the catastrophic humanitarian consequences of nuclear warfare.
Nobel Committee's Recognition and Current Nuclear Challenges
- Recognition of Hibakusha's Work:
- The Nobel Committee awarded the Peace Prize to Nihon Hidankyo for its role in promoting nuclear disarmament and for contributing to the nuclear taboo.
- The nuclear taboo is under increasing pressure as new countries seek nuclear weapons and existing powers modernize their arsenals.
- Current Nuclear Landscape:
- The US and Russia continue to maintain large nuclear stockpiles, with the US planning to spend over $1 trillion on upgrading its nuclear capabilities by the 2040s.
- New Threats: Geopolitical tensions, including regional conflicts, raise concerns about the resurgence of nuclear arms races.
Previous Nobel Peace Prizes for Disarmament
- Past Laureates:
- 1974: Former Japanese Prime Minister Eisaku Sato awarded for Japan's commitment to non-nuclear weapons policy.
- 2017: International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN) awarded for its efforts to draw attention to the humanitarian consequences of nuclear weapons and push for a nuclear ban treaty.
- Link with Alfred Nobel’s Vision:
- Alfred Nobel, the founder of the Peace Prize, made his fortune with the invention of dynamite and sought to use his wealth to promote peace, especially through disarmament.
Onset of Monsoon
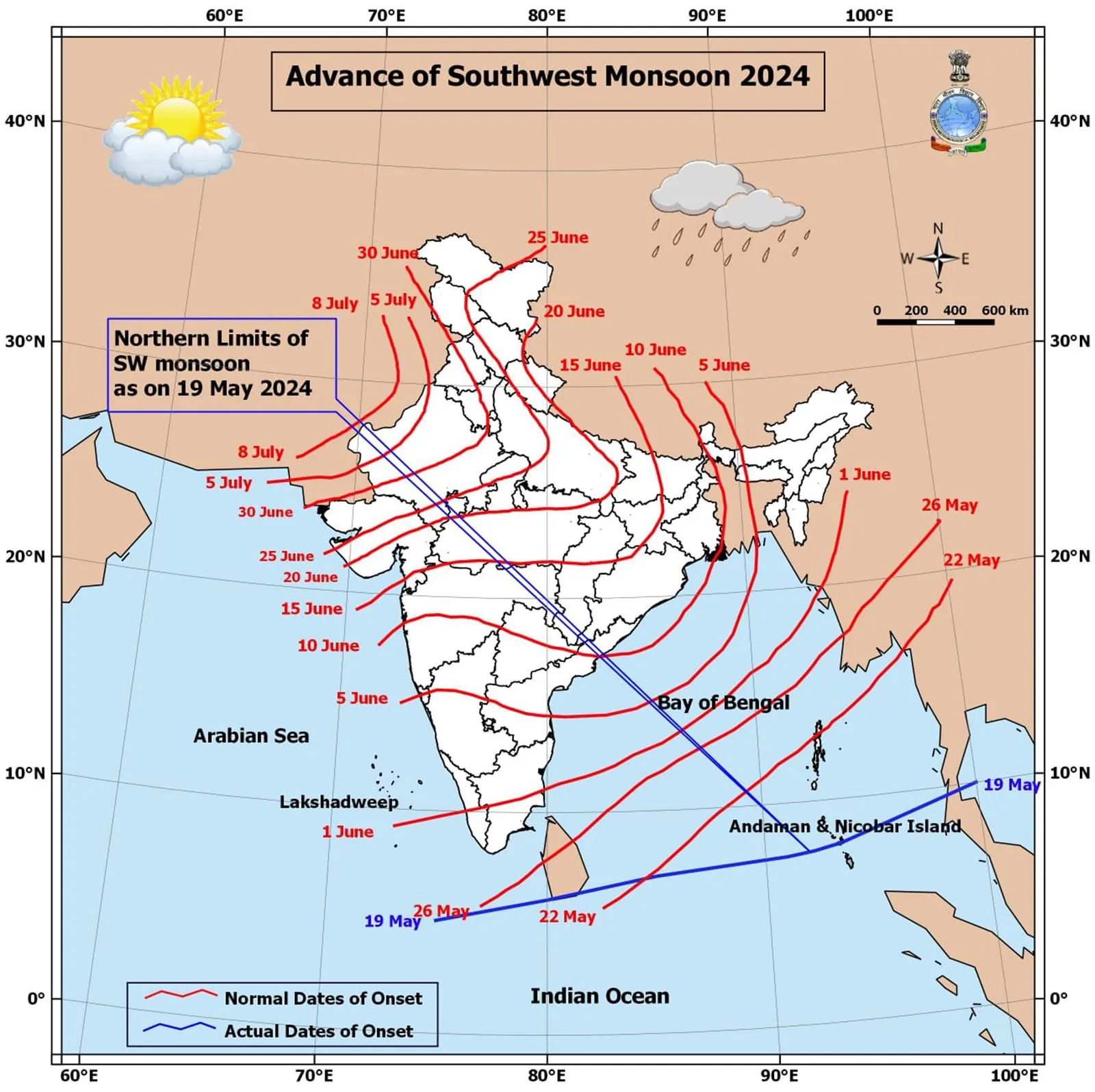
- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The southwest monsoon is progressing normally, and conditions are suitable for its onset on the Kerala coast in the next five days, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said on Monday (May 27).
What does the ‘onset of monsoon’ Mean?
- The onset of the monsoon over Kerala marks the beginning of the four-month, June-September southwest monsoon season over India, which brings more than 70% of the country’s annual rainfall.
- The onset of the monsoon is a significant day in India’s economic calendar.
- According to the IMD, the onset of the monsoon marks a crucial transition in the large-scale atmospheric and ocean circulations in the Indo-Pacific region, and the Department announces it only after certain defined and measurable parameters, adopted in 2016, are met.
Onset & Advance of Monsoon:
- Broadly, the IMD checks for the consistency of rainfall over a defined geography, its intensity, and wind speed.
- Rainfall: The IMD declares the onset of the monsoon if at least 60% of 14 designated meteorological stations in Kerala and Lakshadweep record at least 2.5 mm of rain for two consecutive days at any time after May 10. In such a situation, the onset over Kerala is declared on the second day, provided specific wind and temperature criteria are also fulfilled.
- The 14 enlisted stations are Minicoy, Amini, Thiruvananthapuram, Punalur, Kollam, Alappuzha, Kottayam, Kochi, Thrissur, Kozhikode, Thalassery, Kannur, Kasaragod, and Mangaluru.
- Wind field: The depth of westerlies, prevailing winds that blow from the west at midlatitudes — should be up to 600 hectopascals (1 hPa is equal to 1 millibar of pressure) in the area bound by the equator to 10ºN latitude and from longitude 55ºE to 80ºE.
- The zonal wind speed over the area bound by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-80ºE longitude should be of the order of 15-20 knots (28-37 kph) at 925 hPa.
- Heat: According to IMD, the INSAT-derived Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR) value (a measure of the energy emitted to space by the Earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere) should be below 200 watts per sq m (wm2) in the box confined by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-75ºE latitude.
- Northern Limit of Monsoon (NLM): Southwest monsoon normally sets in over Kerala around 1st June.
- It advances northwards, usually in surges, and covers the entire country around the 15th of July.
- The NLM is the northernmost limit of monsoon up to which it has advanced on any given day.
In general, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands start receiving monsoon rainfall between May 15 and May 20 every year, and it usually starts raining along the Kerala coast in the last week of May.
ZIG Currency

- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To address its long-standing economic instability, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe (RBZ) has launched a new gold-backed currency called the ZiG, short for Zimbabwe Gold, replacing the Zimbabwean dollar on April 5, 2024.
What is a ZiG Currency?
- Zimbabwe Gold, or ZIG, is the world's newest currency that was introduced by Zimbabwe to replace the Zimbabwe dollar in April.
- It is backed by the country's gold reserves and was launched in an effort to reduce currency instability and hyperinflation.
- It is the sixth currency Zimbabwe has used since the 2009 collapse of the Zimbabwe dollar amid hyperinflation of 5 billion per cent.
Features of ZiG currency:
- Gold-Backed: The ZiG is unique as it is backed by gold reserves, ensuring its value is supported by the physical gold held by the government.
- Denominations: ZiG notes and coins are issued in denominations of 1ZiG, 2ZiG, 5ZiG, 10ZiG, 20ZiG, 50ZiG, 100ZiG, and 200ZiG. This gold backing aims to provide stability and prevent currency devaluation.
Reasons for Launching a New Currency:
- High Inflation: Zimbabwe has struggled with extreme inflation, with rates exceeding 500% in recent years.
- Currency Instability: The Zimbabwean dollar, introduced in 1980, lost its value due to hyperinflation. The country's reliance on various foreign currencies, mainly the US dollar, has limited economic control.
- Historical Collapse: The collapse of the Zimbabwean dollar in 2009, with hyperinflation peaking at 5 billion per cent, is one of the worst currency crashes in history.
Economic Control: Converting the previous national currency, the Zimbabwe dollar, into ZiGs is intended to simplify monetary matters and provide certainty and predictability in the financial system.
AI Agents

- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Known as ‘AI agents’, GPT-4o and Project Astra have been touted as far superior to conventional voice assistants such as Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant.
What are AI Agents?
- AI agents are sophisticated AI systems that can engage in real-time, multi-modal (text, image, or voice) interactions with humans.
- Unlike conventional language models, which solely work on text-based inputs and outputs, AI agents can process and respond to a wide variety of inputs including voice, images, and even input from their surroundings.
- AI agents are designed to perceive their environment and take actions in order to achieve specific goals.
- They perceive their environment through sensors, process the information using algorithms or models, and then take actions using actuators or other means.
- AI agents can range from simple systems that follow predefined rules to complex, autonomous entities that learn and adapt based on their experiences.
- They're utilized in various fields, including robotics, gaming, virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, and more.
- These agents can be reactive (responding directly to stimuli), deliberative (planning and making decisions), or even have learning capabilities (adapting their behaviour based on data and experiences).
How are they Different From Large Language Models?
- While large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and GPT-4 have the ability only to generate human-like text, AI agents make interactions more natural and immersive with the help of voice, vision, and environmental sensors.
- Unlike LLMs, AI agents are designed for instantaneous, real-time conversations with responses much similar to humans.
- LLMs lack contextual awareness, while AI agents can understand and learn from the context of interactions, allowing them to provide more relevant and personalised responses.
- Also, language models do not have any autonomy since they only generate text output.
- AI agents, however, can perform complex tasks autonomously such as coding, data analysis, etc.
- When integrated with robotic systems, AI agents can even perform physical actions.
What are the Potential Uses of AI Agents?
- AI agents can serve as intelligent and highly capable assistants.
- They are capable of handling an array of tasks, from offering personalised recommendations to scheduling appointments.
- AI agents can be ideal for customer service as they can offer seamless natural interactions, and resolve queries instantly without actually the need for human interventions.
- In the field of education and training, AI agents can act as personal tutors, customise themselves based on a student’s learning styles, and may even offer a tailored set of instructions.
- In healthcare, they could assist medical professionals by providing real-time analysis, diagnostic support, and even monitoring patients.
Risks and Challenges Associated With AI Agents:
- While AI agents showcase immense potential for the future, they are not without risks.
- Privacy and security are a key area of concern as AI agents gain access to more personal data and environmental information.
- Just like any AI model, AI agents can carry forward biases from their training data or algorithms, leading to harmful outcomes.
As these systems become more common, appropriate regulations and governance frameworks should be laid out to ensure their responsible deployment.
Paris Principles on NHRIs

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the second year in a row, an organisation affiliated with the UN human rights office has deferred accreditation for India’s human rights body, the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC).
What are the Paris Principles?
- The Paris Principles, formally Principles Relating to the Status of National Human Rights Institutions, which were adopted by the UN General Assembly on December 20, 1993, set out minimum standards that NHRIs must meet in order to be considered credible and to operate effectively.
- The Paris Principles lay down six main criteria to determine which NHRIs are functioning effectively and would receive accreditation from GANHRI.
- They are
- broad mandate based on universal human rights norms and standards
- autonomy from the government
- independence guaranteed by the statute or Constitution
- pluralism, including membership that broadly reflects their society
- adequate resources and
- adequate powers of investigation
- These Principles also say that NHRIs should be equipped to receive complaints and cases brought by individuals, third parties, NGOs, trade unions, or other organisations representative of professionals such as lawyers and journalists.
Accreditation:
- Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI), which represents about 120 national human rights institutions, is responsible for reviewing and accrediting these institutions in compliance with the Paris Principles every five years.
- GANHRI acts through its Subcommittee on Accreditation (SCA), which categorises member NHRIs into two groups, ‘A’ and ‘B’. As of November 29, 2023, 120 NHRIs were accredited by GANHRI, 88 of which were given an ‘A’ rank, indicating full compliance with the Paris Principles; the remaining 32 were put under ‘B’, indicating partial compliance.
Why has India’s Accreditation Been Put on Hold?
- India’s accreditation status was put on hold after the Sub-Committee on Accreditation (SCA) meeting on May 1 in Geneva.
- The SCA, which meets twice a year, scrutinizes each country’s human rights institution.
- The May 1 meeting, chaired by New Zealand with participation from South Africa, Sri Lanka, and Spain, highlighted several concerns about the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India.
- Issues raised include a lack of transparency in NHRC appointments, conflicts of interest with police overseeing investigations, and no minority or female representation on the panel.
- Additionally, nine human rights organizations, including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, expressed concerns about India’s human rights record, citing increasing restrictions on civic space and discrimination against minorities.
- UN human rights experts also highlighted “attacks on minorities, media, and civil society” in India.
What Happens if India Loses Accreditation?
- If India loses its 'A' status accreditation, its National Human Rights Institution (NHRI) will face significant limitations. With 'A' status, NHRIs can participate in the UN Human Rights Council, its subsidiary bodies, and some UNGA bodies and mechanisms, and hold full membership in the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) with voting and governance rights.
- With 'B' status, NHRIs can attend GANHRI meetings but cannot vote or hold governance positions. Without proper accreditation, India’s NHRC cannot represent the country at the UN Human Rights Council, vote, or hold governance roles.
- India’s review has been deferred, and a final decision is yet to be made.
What is India’s Record of Accreditation with GANHRI?
- India’s National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) was established in 1993 and first accredited by the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) in 1999.
- It achieved 'A' status in 2006 and retained it in 2011.
- However, in 2016, accreditation was deferred due to issues like the appointment of political representatives and lack of gender balance and pluralism in the NHRC staff.
- Despite these concerns, the NHRC regained 'A' status in 2017.
- In 2023, the Sub-Committee on Accreditation (SCA) withheld India’s accreditation again, citing six reasons, including the NHRC’s inability to operate without government interference and the presence of too many government officials and individuals affiliated with the ruling party in the commission.
Salas y Gómez
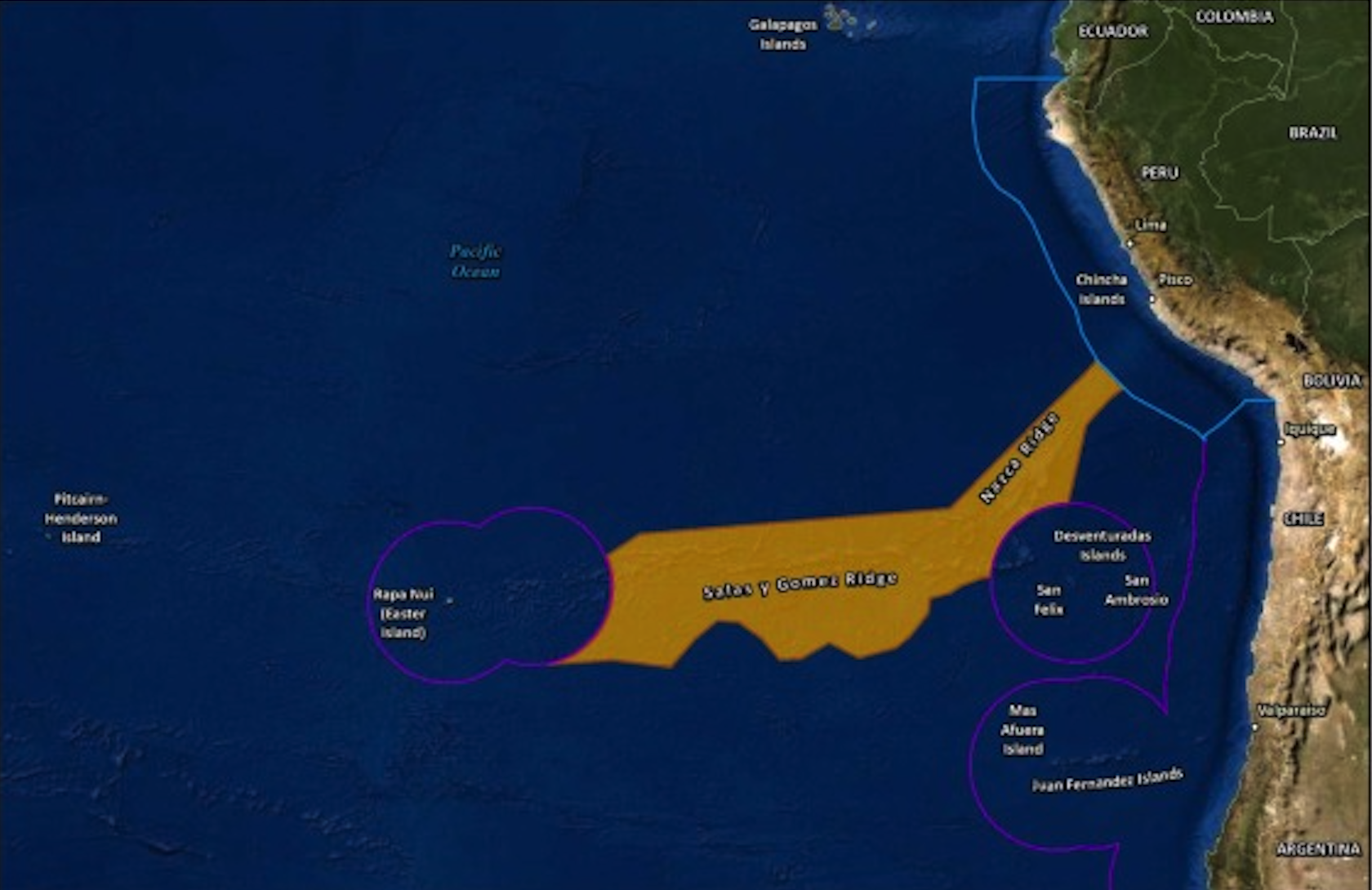
- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of scientists last week announced they discovered 160 species when exploring 10 seamounts and two islands on the 2,900-kilometre-long ocean ridge Salas y Gómez.
What is ‘Salas y Gomez’?
- Salas y Gómez is a remarkable underwater mountain chain in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean.
- This 2,900-kilometer-long range stretches in a west-east orientation, connecting the East Pacific Rise and the Nazca Ridge.
- The western end of the chain lies within Chile's Exclusive Economic Zone near the Easter Islands, while the eastern part extends into areas beyond national jurisdiction and touches upon the national waters of Chile and Peru.
- The region is characterized by unique ecosystems isolated by the Atacama Trench, the Humboldt Current System, and an extreme oxygen minimum zone.
- Salas y Gómez and Nazca ridges are known for their extraordinary biodiversity, hosting some of the highest levels of marine endemism on Earth.
- Given the ecological significance of this underwater mountain range, there is a growing interest in designating Salas y Gómez and its surrounding areas as high-seas marine protected areas upon the ratification of the UN High Seas Treaty.
- This initiative aims to safeguard the region's unique ecosystems and contribute to global marine conservation efforts.
About the United Nations High Seas Treaty:
- The United Nations High Seas Treaty is a legal framework, or a set of legal tools, designed to protect the oceans that are beyond any country’s territory.
- The high seas are defined as the waters that are 200 nautical miles from any national jurisdiction; they are international open waters that all countries can use for marine business such as shipping, fishing, and marine research.
- The treaty’s formal name is the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction Treaty, or BBNJ Treaty for short.
Key Facts About the High Seas Treaty:
- The treaty was to be negotiated under the United Nations Convention on Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS) of 1982.
- It took 19 years to reach an agreement on it.
- Before now, laws to protect ocean waters and biodiversity beyond countries’ territorial boundaries only protected 1.2% of the high seas.
Added Sugars/Free Sugars

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nestlé’s products for babies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America were found to contain added sugars, while the same products sold in Europe did not have it, according to a recent report.
Highlights of the Report on Nestle:
- A report by the Swiss organization Public Eye titled 'How Nestlé gets children hooked on sugar in lower-income countries' scrutinized Nestlé for employing varying nutritional standards across its products depending on the country, with unclear sugar content labeling.
- The report highlighted Nestlé's Cerelac, the world's largest baby cereal brand, which contains significantly higher sugar levels in markets like India, Ethiopia, and Thailand compared to Germany and the UK.
- Despite sugar not being recommended for infants, Nestlé's baby food products with added sugars are allowed under some countries' national legislation, conflicting with WHO guidelines.
- WHO recommends reducing daily free sugar intake to less than 10% of total energy intake, preferably less than 5% (around 25 grams per person per day), for better health.
- Nestlé India claims to have reduced added sugars by up to 30% in their infant cereals portfolio over the last five years, depending on the variant.
What are Added Sugars?
- Sugar is a simple carbohydrate.
- Some food items have sugar that is naturally occurring.
- It is “found in milk (lactose) and fruit (fructose) or any product that contains milk (such as yogurt, milk, or cream) or fruit (fresh, dried) contains some natural sugars.
- Free sugar or added sugar is added separately to a food item during preparation or processing.
- It can “include natural sugars such as white sugar, brown sugar, and honey, as well as other caloric sweeteners that are chemically manufactured (such as high fructose corn syrup).
Why is Added Sugar Bad?
- Excessive consumption of added sugars poses several health risks.
- Limiting sugar intake is essential for maintaining a healthy diet and preventing various diseases.
The following are some reasons why added sugars can be harmful:
- Poor Nutritional Balance: Consuming too much-added sugar can lead to increased overall energy intake, often replacing nutritionally adequate calories from healthier food sources.
- This results in an unbalanced diet lacking essential nutrients, increasing the risk of malnutrition and other health problems.
- Increased Risk of Non-Communicable Diseases: Excessive sugar consumption is associated with a higher risk of developing non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular ailments.
- These diseases can have severe long-term consequences on overall health and well-being.
- Unnecessary for Infants and Children: Adding sugar to foods offered to babies and young children is unnecessary and can be highly addictive, establishing unhealthy eating habits that continue into adulthood.
- Early exposure to sugar is also associated with tooth decay and can contribute to nutrition-based disorders later in life.
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Eight years after Parliament passed the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs is in the process of reviewing the functioning of the Act, including by holding regular meetings with homebuyers and setting up a data collection unit within the Ministry.
What Is Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)?
- The Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 is an act of the Parliament of India that strives to protect home buyers and helps escalate the investment made in the real estate industry.
- It was established under this Act to regulate the real estate sector.
- Additionally, it acts as the adjudicating body for faster dispute resolution related to the real estate industry.
The Primary Objectives of the Act:
- Ensuring Transparency: Promoting transparency in the real estate sector regarding the sale of flats, apartments, plots, buildings, or any real estate project.
- Establishing Dispute Resolution: Setting up an adjudicating mechanism to swiftly resolve disputes.
- Protecting Buyer Interests: Safeguarding the interests of buyers/allottees in the real estate domain.
- Building Trust: Fostering trust between buyers and promoters by leveraging regulatory authority.
- Furthermore, the Act mandates that Real Estate Regulatory Authorities establish and maintain a web portal containing pertinent details of all registered real estate projects for public access.
Reasons for RERA Implementation:
- The introduction of RERA was necessitated by challenges faced by the Indian real estate sector since 2012, including factors such as unemployment, recession, low rental yield, inventory pile-up, and ambiguous tax and arbitration frameworks.
Projects Covered by RERA:
- RERA covers commercial and residential projects, including plotted developments, that exceed 500 square meters or comprise more than 8 units.
- Additionally, projects lacking a Completion Certificate prior to the Act's commencement are subject to its provisions.
Benefits of RERA Implementation:
- Standardization: RERA ensures uniformity in the real estate sector concerning aspects like carpet areas and common areas, thereby preventing malpractices such as alterations in layout, area, agreements, and specifications.
- It also mandates disclosure of details regarding brokers, architects, and contractors.
- Timely Delivery: Developers are obligated to adhere to scheduled delivery timelines for office spaces or homes.
- Failure to comply may result in stringent penalties or imprisonment for the developer.
- Regulatory Compliance: RERA mandates obtaining clearance from government departments before the sale of any residential or commercial property.
- Financial Transparency: Developers are required to maintain separate bank accounts for each project, enhancing financial transparency and accountability.
- Warranty Protection: Buyers are empowered to report any structural defects in the building to the developer within one year of possession, with the developer obligated to rectify them free of charge.
Challenges Associated with RERA:
- Limited Scope: The regulations of RERA do not extend to ongoing projects or those stalled due to clearance issues, potentially leaving certain projects outside its jurisdiction.
- Approval Delays: Delays in approval and clearance from government agencies may impede the timely completion and delivery of real estate projects, affecting both developers and buyers.
- Exemption for Small Developers: Small-scale developers overseeing projects smaller than 500 square meters are exempt from RERA's provisions, and registration with the regulatory authority is not compulsory for them.
- Project Launch Delays: Projects cannot be launched without necessary clearances, which may result in delays in the commencement of new projects.
Warming up to climate change: How does climate change impact extreme weather events?

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Extreme weather is becoming more frequent and more intense in many places around the world because of climate change.
How Does Climate Change Impact Extreme Weather Events?
- The Earth's average temperature has gone up by at least 1.1 degrees Celsius since 1850, mostly because of human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
- This temperature rise has led to more frequent and stronger extreme weather events worldwide, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires.
- It's hard to directly blame one single weather event on climate change because there are many factors involved.
- However, studies can tell us if climate change made a particular event worse or more likely to happen.
- For example, after a deadly heatwave in Western Europe in 2019, a study found that climate change made that heatwave five times more likely to occur.
- In India, heatwaves have become longer because of global warming, and they're expected to get even worse in the future.
- Climate models predict that by the 2040s, heatwaves might become 12 times more common.
- Higher temperatures also make droughts worse.
- In East Africa, for instance, a severe drought happened between 2020 and 2022, leading to famine and displacing millions of people.
- A report found that climate change made droughts like this at least 100 times more likely in that region.
- Warmer temperatures also contribute to wildfires by drying out land and making it easier for fires to start and spread.
- In Canada, for example, a study showed that climate change doubled the chances of extreme fire conditions.
- This was particularly concerning because Canada recently faced its worst wildfire season ever.
- As temperatures rise, the air can hold more moisture, leading to heavier rainfall and more flooding during storms.
- Warm air can also dry out the soil, making droughts worse. But when warm, moist air meets cooler air, it can lead to more intense storms and flooding.
- There's also evidence that climate change is making hurricanes stronger and more frequent.
- Warmer oceans provide more energy for hurricanes to form and intensify.
- The oceans have absorbed a lot of the extra heat from greenhouse gases, making them warmer.
- This, in turn, leads to stronger storms and more damage when they hit land.
- So, while climate change doesn't directly cause any single weather event, it's making extreme weather events more common and more severe, putting people and ecosystems at risk.
Key aspect in poll bond case still alive: Money Bill route

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court struck down the electoral bonds scheme as unconstitutional recently, it saved one aspect of the challenge for another day and a larger bench – the issue of the government using the money Bill route to bring in the laws that introduced the electoral bonds.
News Summary:
- A recent ruling by a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court invalidated the electoral bonds scheme, citing it as unconstitutional.
- However, the court reserved one aspect of the challenge for further review by a larger bench – specifically, the government's use of the money Bill route to enact the laws introducing the electoral bonds.
The Supreme Court highlighted that:
- The examination of introducing these amendments through a money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution was not addressed.
- The interpretation of Article 110 of the Constitution has been referred to a seven-judge Bench and remains pending judicial review.
What are Money Bills?
- According to Article 110, a money Bill encompasses provisions related to taxes, government borrowing, and expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India, among other financial matters.
- Article 109 outlines the process for the passage of such Bills, granting predominant authority to the Lok Sabha in their enactment.
- The Speaker is responsible for certifying a Bill as a Money Bill, with the Speaker's decision being final.
- In the past seven years, the government has utilised the money Bill route to introduce various legislations, notably including the Aadhaar Act, 2016, and the Finance Act, 2017.
Other Instances of Government Utilising Money Bill Route:
- Several significant legislations have been enacted by the government through the money Bill route, including:
- The Finance Acts of 2016 and 2018, introduced amendments to the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, of 2010.
- The Tribunals Reforms Act was passed as a money Bill in 2017.
- The rigorous amendments to the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) in 2022, alongside the enactment of the Aadhaar Act in 2018.
- The Supreme Court has upheld the validity of the PMLA amendments and the legality of the Aadhaar Act.
- Notably, Chief Justice of India Chandrachud dissented in the five-judge bench decision that upheld the Aadhaar Act, criticising the government's use of the money Bill route as a subversion of the Constitution.
- However, these laws may still face scrutiny and potential invalidation if the court determines that they were enacted through improper procedure, namely, utilising the money Bill route.
Difference Between Money Bills and Financial Bills:
- While every Money Bill is categorised as a Financial Bill, not every Financial Bill qualifies as a Money Bill.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely dedicated to tax proposals is deemed a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Financial Bill may include provisions on taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects.
- The Compensatory Afforestation Fund Bill, 2015, which establishes funds under the Public Account of India and states, serves as an example of a Financial Bill.
The process for passing these two types of bills varies considerably.
-
- The Rajya Sabha lacks the authority to reject or amend a Money Bill.
- Following passage by the Lok Sabha, Money Bills are referred to the Rajya Sabha for recommendations.
- Within 14 days, the Rajya Sabha must return the Bill to the Lok Sabha with its suggestions, which are not binding.
- Should the Lok Sabha reject the recommendations, the Bill is considered passed by both Houses in its original form from the Lok Sabha.
- If the Rajya Sabha fails to provide recommendations within 14 days, the same outcome applies.
- However, both Houses of Parliament must approve a Financial Bill.
- While an ordinary Bill can originate in either House, a Money Bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha, per Article 117(1).
- Moreover, only on the President's recommendation can anyone introduce or propose Money Bills in the Lok Sabha.
- Amendments related to reducing or abolishing any tax are exempt from requiring the President's recommendation.
- The essential conditions for a Financial Bill to attain Money Bill status are that it must solely originate in the Lok Sabha, not the Rajya Sabha, and must be introduced upon the President's recommendation.
INCOIS, ISRO to study rip currents for safer beaches

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) have embarked on a project to continuously monitor and issue operational forecast alerts of rip currents.
What is a Rip Current?
- Rip currents are channelled currents of water flowing away from shore at surf beaches.
- They typically extend from near the shoreline, through the surf zone and past the line of breaking waves. (The surf zone is the area between the high tide level on the beach to the seaward side of breaking waves.)
Formation of Rip Currents:
- Rip currents form when waves break near the shoreline, piling up water between the breaking waves and the beach.
- One of the ways this water returns to sea is to form a rip current, a narrow stream of water moving swiftly away from shore, often perpendicular to the shoreline.
Size of the Rip Currents:
- Rip currents can be as narrow as 10 or 20 feet in width though they may be up to ten times wider.
- The length of the rip current also varies.
- Rip currents begin to slow down as they move offshore, beyond the breaking waves, but sometimes extend for hundreds of feet beyond the surf zone.
Speed of the Rip Current:
- Rip current speeds can vary. Sometimes they are too slow to be considered dangerous.
- However, under certain wave, tide, and beach-shape conditions the speeds can quickly become dangerous.
Are All Rip Currents Dangerous?
- Rip currents are present on many beaches every day of the year, but they are usually too slow to be dangerous to beachgoers.
- However, under certain wave, tide, and beach-shape conditions they can increase to dangerous speeds.
- The strength and speed of a rip current will likely increase as wave height and wave period increase.
How Do Rip Currents Result in the Drowning of Swimmers?
- Drowning deaths occur when people pulled offshore are unable to keep themselves afloat and swim to shore.
- This may be due to any combination of fear, panic, exhaustion, or lack of swimming skills.
- Rip currents are the greatest surf zone hazard to all beachgoers. They can sweep even the strongest swimmer out to sea.
- Rip currents are particularly dangerous for weak and non-swimmers.
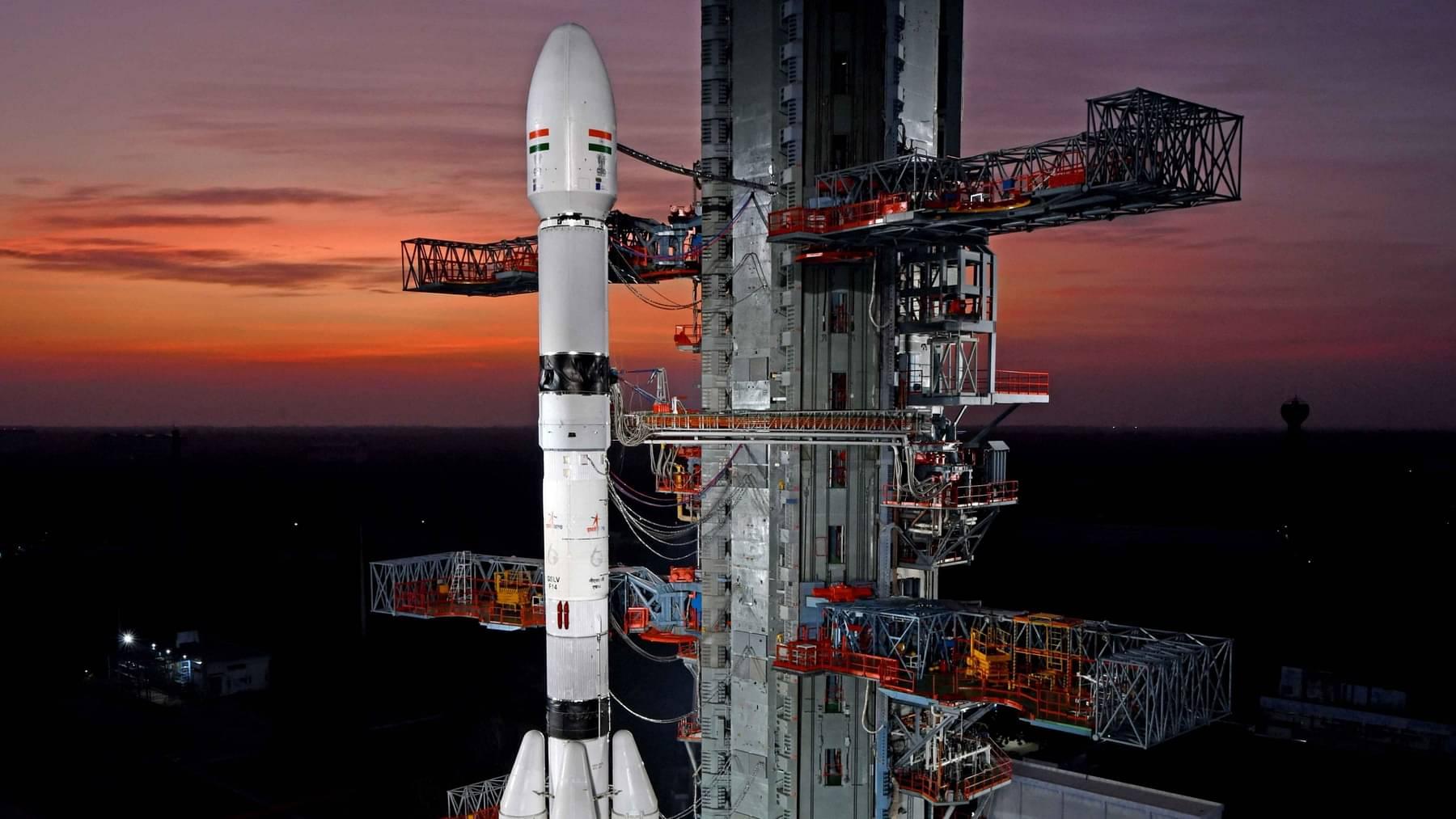
ISRO’s ‘Naughty Boy’ Rocket Launches INSAT-3DS (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently launched its weather satellite INSAT-3DS board spacecraft Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) F14, nicknamed the ‘naughty boy’ for its spotty record.
What is the GSLV-F14?
- The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), standing at a height of 51.7 metres, is a three-stage launch vehicle with a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes.
- First stage: Its first stage (GS1) features a solid propellant (S139) motor with 139 tons of propellant and four earth-storable propellant stages (L40) strapons, each carrying 40 tons of liquid propellant.
- Second Stage: The second stage (GS2) also utilises an earth-storable propellant system with a 40-ton propellant load.
- Third Stage: The third stage (GS3) is equipped with a cryogenic system containing 15 tons of propellant, consisting of liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
- GSLV-F14 serves as a versatile launch vehicle, capable of deploying various types of spacecraft for communication, navigation, earth resource surveys, and other specialised missions.
GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission Overview and Key Goals:
- INSAT-3DS Satellite marks a significant advancement in the Third Generation of Meteorological Satellite series from Geostationary Orbit, with substantial contributions from Indian industries.
- Fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), the mission aims to enhance meteorological services, complementing the existing capabilities of INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR satellites.
Key Objectives:
- Earth Observation and Oceanic Monitoring: Utilise various spectral channels to monitor Earth's surface, conduct oceanic observations, and assess environmental conditions critical for meteorology.
- Atmospheric Parameter Profiling: Provide vertical profiles of essential meteorological parameters within the atmosphere, enhancing our understanding of atmospheric dynamics.
- Data Collection and Dissemination: Facilitate the collection and dissemination of data from Data Collection Platforms (DCPs), ensuring timely access to crucial meteorological information.
- Satellite Aided Search and Rescue (SAR) Services: Enable Satellite Aided Search and Rescue services, enhancing emergency response capabilities through advanced satellite technology.
Significance of the GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission:
- The launch of INSAT-3DS holds a lot of significance for India's space agency as it is equipped to provide extremely accurate weather forecast information by studying the surface of the ocean, also being helpful in disaster prevention.
- The GSLV has encountered challenges in the past, with four out of 15 launches facing setbacks, contrasting with the higher success rates of ISRO's PSLV and LVM-3.
- The success of this mission is critical, especially considering the upcoming launch of the Earth observation satellite, NISAR, later this year, a collaborative effort between NASA and ISRO.
- INSAT-3DS, with a mission lifespan of 10 years, will assume the roles of INSAT-3D (2013) and INSAT-3DR (2016), which have reached the end of their operational lives.
- This mission will enhance meteorological forecasting capabilities, enabling better prediction of extreme weather events like thunderstorms, providing visibility assessments for aviation, and facilitating research on forest fires, smoke, snow cover, and climate dynamics.
What Is Nazool Land Which Is At The Heart Of Haldwani Violence? (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Violence erupted in Uttarakhand’s Haldwani district recently after the administration conducted a demolition drive at the site of a mosque and madrasa, allegedly on Nazool land, killing five and injuring many more.
What is Nazool Land?
- Nazool land is owned by the government but most often not directly administered as state property.
- The state generally allots such land to any entity on lease for a fixed period, between 15 and 99 years.
- In case the lease term is expiring, one can approach the authority to renew the lease by submitting a written application to the Revenue Department of the local development authority.
- The government is free to either renew the lease or cancel it — taking back Nazool land.
- In almost all major cities of India, Nazool land has been allotted to different entities for a variety of different purposes.
How did Nazool Land Emerge?
- During British rule, kings and kingdoms which opposed the British frequently revolted against them, leading to several battles between them and the British Army.
- Upon defeating these kings in battle, the British would often take their land away from them.
- After India gained Independence, the British vacated these lands.
- But with kings and royals often lacking proper documentation to prove prior ownership, these lands were marked as Nazool land — to be owned by the respective state governments.
How Does the Government Use Nazool Land?
- The government generally uses Nazool land for public purposes like building schools, hospitals, Gram Panchayat buildings, etc.
- Several cities in India have also seen large tracts of land denoted as Nazool land used for housing societies, generally on lease.
- Very often, the state does not directly administer Nazool land but rather leases it to different entities.
- While several states have brought in government orders for framing rules for Nazool land, The Nazool Lands (Transfer) Rules, 1956 is the law mostly used for Nazool land adjudication.
New Education Policy Taking Forward Swami Dayanand’s Vision (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Education Policy 2020 is taking forward the vision of social reformer Swami Dayanand Saraswati, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said recently.
Who was Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati?
- Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati, born on February 12, 1824, in Tankara, Gujarat, was a pioneering social reformer.
- He established the Arya Samaj in 1875 with the aim of addressing prevailing social injustices.
Religious and Social Reforms:
- Rejection of Idolatry and Ritualism: Dayanand Saraswati staunchly opposed idol worship and ritualistic practices, advocating instead for the worship of a formless, attributeless God as outlined in the Vedas.
- Shuddhi Movement: He initiated the Shuddhi Movement to reclaim individuals who had converted to religions like Islam or Christianity, aiming to reintegrate them into Hinduism.
- Back to Vedas: Recognizing the importance of Vedic wisdom, he spearheaded a movement to revive the teachings of the Vedas, emphasizing their relevance in modern society.
- Women’s Rights: Dayanand Saraswati championed women’s rights, advocating for their education and equal participation in social and religious spheres alongside men.
- Opposition to Child Marriage and Sati: He vehemently opposed practices like child marriage and sati, viewing them as detrimental to society and antithetical to Vedic principles.
Educational Reforms:
- Dayanand Saraswati established several Gurukuls to impart Vedic knowledge to his followers and empower them to disseminate this wisdom further.
- Influenced by his philosophy and vision, his disciples founded the Dayanand Anglo Vedic (DAV) College Trust and Management Society following his demise in 1883.
- The first DAV High School was founded in Lahore on June 1, 1886, under the leadership of Mahatma Hans Raj.
Literary Contributions:
- Dayanand Saraswati's philosophical ideas are encapsulated in his notable works like "Satyartha Prakash" and "Veda Bhashya," shedding light on his vision for Hindu reform.
- His thoughts were further disseminated through the journal "Arya Patrika," which he edited, reflecting his philosophical convictions.
Arya Samaj:
- Founded by Dayanand Saraswati in Bombay in 1875, the Arya Samaj, meaning "society of the nobles," aimed to reform Hinduism by steering it away from superstition.
- With the motto "Krinvanto Vishwam Aryam" meaning "Make this world noble," the Samaj advocated for a return to the true essence of Hinduism, rejecting ritualistic practices like idol worship, pilgrimage, and animal sacrifice.
- In the 1880s, the Samaj actively supported widow remarriage, promoting social reforms aligned with its principles.
- The Arya Samaj's influence extends beyond India, with active branches worldwide.
Polygamy in India: Insights and debates surrounding Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly recently passed the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill, 2024 after a two-day discussion. The Bill brings uniformity in personal laws, governing things such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance, across communities in the state (excluding tribals).
What is Polygamy?
- Polygamy involves the practice of having multiple spouses simultaneously, which can include either wives or husbands.
- It manifests in two primary forms:
- Polygyny, where a man is married to several women concurrently, and
- Polyandry, where a woman is married to multiple men concurrently.
Who can have "multiple wives"?
- Under Hindu law, which applies to Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists, the practice of polygamy is prohibited.
- Individuals governed by Hindu law can face criminal proceedings under Sections 494 and 495 of the Indian Penal Code.
- The Special Marriage Act, as well as Christian and Parsi laws, also outlaw bigamy.
- However, the Shariat Protection Act exempts Muslims in India from the ban on polygamy.
- Additionally, due to the protection granted to cultural practices of scheduled tribes, polygynous marriages can be found in tribal groups across northeastern states, Odisha, Telangana, and other regions.
- Courts have had to face cases where a man converted to Islam from other religions to marry a second wife.
- While the Supreme Court, in its 1994 Sarla Mudgal verdict, declared that conversion solely for a second marriage is invalid, the Law Commission reports from 1961 and 2009 have emphasized the need to clarify the legal position of the "second wife" in a converted Muslim marriage and address the rights of any children born from such a union.
What does the data say?
- Government data on polygamy can be obtained from two main sources — the decadal census and the National Family Health Survey (NFHS). Both have certain limitations.
- The census does not directly collect data on polygamy.
- Rather its incidence is inferred from the difference in the number of married men and the number of married women in the country.
- More married women than men point to the prevalence of situations where men have married more than once.
- Rather its incidence is inferred from the difference in the number of married men and the number of married women in the country.
What does the census data say?
- According to the census of 2011, there are 28.65 crore married men in India, compared to 29.3 crore married women.
- The difference between the two numbers — 65.71 lakh — can be explained either by the incidence of polygamy or men going abroad.
- The highest discrepancy in the population of married men and women can be found among Hindus (who make up the largest number of Indians), followed by Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Sikhs, and Buddhists.
- However, when compared to their respective shares in the total population, Muslims and Christians report the greatest difference.
What does NFHS data say?
- The NFHS-5 showed the prevalence of polygamy (the percentage of women who reported their husbands had other wives) was highest among Christians (2.1%), followed by Muslims (1.9%), and Hindus (1.3%), looking at religion.
- Overall, Scheduled Tribes reported the highest incidence at 2.4%.
- A June 2022 study by the International Institute of Population Sciences (IIPS) showed that polygynous marriages (one man married to more than one woman at a time) have decreased from 1.9% in 2005-06 to 1.4% in 2019-21, among the whole population.
- Buddhists, who reported a 3.8% incidence of polygyny in 2005-06, saw the sharpest dip of 65.79% to 1.3% in 2019-21.
- The incidence of polygyny in the total population fell by 26.31%.
Constitutional Perspective and Supreme Court's Insights:
- India, as a secular state, upholds the principle of equality among religions, ensuring that no religion holds superiority or inferiority over another.
- The Indian Constitution guarantees fundamental rights to all citizens, and any legislation conflicting with these rights is considered unconstitutional.
- Article 13 of the Constitution invalidates any law inconsistent with Part III of the Constitution.
- Article 14 ensures equal treatment and protection under the law for every individual within India's territory.
- In a 2021 verdict, the Supreme Court highlighted India's recognition of a plural legal system, allowing different religious communities to abide by distinct 'personal laws.'
- However, these personal laws must adhere to constitutional validity and morality, ensuring they do not infringe upon Articles 14, 15, and 21 of the Constitution.
Bharat Ratna for former PMs Charan Singh and PV Narasimha Rao, scientist Swaminathan (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union government on February 9, 2024, announced former Prime Ministers Chaudhary Charan Singh, P.V. Narasimha Rao and agriculture scientist M.S. Swaminathan will be honoured with the country’s highest civilian honour, the Bharat Ratna posthumously.
News Summary:
- The government recently conferred the Bharat Ratna for former Prime Ministers Chaudhary Charan Singh and PV Narasimha Rao and agricultural scientist MS Swaminathan, who is known for his leading role in India's 'Green Revolution', posthumously.
- Earlier, the government had announced Bharat Ratna, for veteran BJP politician LK Advani and socialist icon and former Bihar Chief Minister Karpoori Thakur.
Who was PV Narasimha Rao?
- Pamulaparthi Venkata Narasimha Rao (28 June 1921 – 23 December 2004) was a lawyer and a towering Congress leader in undivided Andhra Pradesh, who became the 9th prime minister of India.
- He ruled the country between 1991 and 1996.
- In 1991, when India was facing a foreign reserves crisis, Narasimha Rao's government brought about three big-ticket economic reforms -- globalisation, liberalisation and privatisation.
- PV Narasimha Rao was the first person from South India to become the prime minister of India.
- He was born in a Telugu Niyogi Brahmin family in the Laknepalli village of Narsampet mandal, Warangal.
- The district is currently in Telangana.
- He was a freedom fighter who took part in Hyderabad's Vande Mataram movement in the late 1930s.
- After Independence, PV Narasimha Rao became a full-time politician.
- He was elected as an MLA for the first time in 1957.
- Till 1971, he assumed many ministerial positions in the state government. He became the chief minister of Andhra Pradesh in 1971.
- He was known as an Indira Gandhi loyalist and supported her in 1969 when the Congress vertically split into two parts.
- Rao also served as a member of parliament from Andhra Pradesh and handled home, defence and foreign affairs portfolios as a central minister.
- In 1991, he had almost retired, however, he came back to active politics after the assassination of Congress President and Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi's assassination.
- He was also the first Congress PM outside the Nehru-Gandhi family.
- He broke several conventions as the prime minister.
- He appointed economist Manmohan Singh as his finance minister.
- Together, they brought about economic reforms.
Who was Chaudhary Charan Singh?
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was born in a middle-class farmer family in Meerut in 1902.
- He started his political career with the Congress.
- He was first elected to the Uttar Pradesh assembly in 1937 from Chhaprauli and later got re-elected in 1946, 1952, 1962 and 1967.
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was appointed as a parliamentary secretary in Govind Ballabh Pant's government in 1946.
- He worked in several departments before being appointed a cabinet minister for justice and information in 1951.
- In 1967, he quit the Congress and became the chief minister of Uttar Pradesh for the first time after being elected as the leader of the Sanyukta Vidhayak Dal coalition.
- He became the chief minister for the second time in 1970.
- In 1979 after the Jana Sangh (BJP's predecessor) pulled out of the 18-month-old Morarji Desai-led Janata Party government.
- Congress (I) decided to extend support to Chaudhary Charan Singh who took oath as prime minister on July 28, 1979.
- But before he could prove his majority in the Lok Sabha, Indira Gandhi withdrew support to his government and Singh resigned.
- He continued to remain as caretaker PM till January 14, 1980.
Who was MS Swaminathan?
- M.S. Swaminathan is an eminent Indian agricultural scientist and geneticist hailed as the "Father of the Green Revolution" in India.
- Born on August 7, 1925, Swaminathan's groundbreaking research and advocacy have significantly contributed to India's agricultural development and food security.
- He played a crucial role in introducing high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice, which revolutionized agricultural productivity in the country during the 1960s and 1970s.
- Swaminathan has received numerous awards and honours for his contributions to agriculture and sustainable development, and he continues to be a leading voice in global efforts to address food security and environmental sustainability.
Prithvi Vigyan Scheme to Bolster Earth Science Research Approved by Cabinet (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet has approved a Rs 4,797 crore research scheme to boost and maintain research momentum in the fields of ocean, atmospheric and polar sciences.
What is PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI)?:
- The PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI) will be an umbrella scheme spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences to help continue many of the ongoing research projects covering the period from 2021 to 2026.
- This scheme encompasses five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training and Outreach (REACHOUT)
- The principal objectives of the comprehensive PRITHVI Scheme are as follows:
- Enhancing and maintaining long-term observations across the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere to monitor critical indicators of the Earth System and its changes.
- Developing modelling systems to comprehend and forecast weather patterns, ocean dynamics, and climate-related hazards, while advancing the understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring the polar and high seas regions to uncover new phenomena and resources.
- Innovating technology for the exploration and sustainable utilization of oceanic resources benefits society at large.
- Translating insights from Earth systems science into services that contribute to societal well-being, environmental preservation, and economic prosperity.
- This scheme is poised to foster the development of integrated, multidisciplinary earth science research and innovative initiatives across various institutes under the MoES umbrella.
Significance of the PRITHVI Scheme:
- Under the PRITHVI Scheme, the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) plays a pivotal role in delivering vital services concerning weather, climate, oceanography, coastal conditions, hydrology, seismology, and natural hazards.
- These services play a crucial role in issuing forecasts, warnings, and alerts for a wide array of natural disasters, including tropical cyclones, floods, tsunamis, and earthquakes.
- By facilitating disaster preparedness and risk mitigation, they contribute significantly to safeguarding lives and property.
- Earth System Sciences encompass a comprehensive study of the interconnected components of the Earth, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere, along with their intricate interactions.
- The PRITHVI Scheme is designed to address these components comprehensively, enhancing our understanding of Earth System Sciences and delivering dependable services for the nation's benefit.
- Through integrated research and development endeavours across diverse MoES institutes, the scheme is poised to tackle major challenges in weather forecasting, climate science, oceanography, cryospheric studies, and seismology.
- These efforts aim to explore sustainable methods for harnessing both biological and non-biological resources, ensuring responsible utilization of our planet's resources.
Govt To Sell Bharat Rice At Rs 29/Kg in Retail Market (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will launch retail sales of Bharat Rice at ?29 per kg from next week to provide relief to consumers. It has also directed traders to disclose rice stock to control prices.
Context:
- The recent announcement by the Union government regarding the retail sale of rice at Rs 29 per kg through three cooperatives has garnered attention in the news.
- This initiative, known as 'Bharat Rice,' seeks to address the upward trend in rice prices.
- Over the past year, retail prices have surged by 14.5%, while wholesale prices have seen a 15.5% increase.
- This move aims to mitigate the impact of rising rice prices on consumers and ensure the affordability and accessibility of this staple food item.
Recent Developments:
- In response to escalating domestic rice prices and to ensure food security within the country, the Union government implemented measures in 2023.
- These included a ban on the export of white (non-basmati) rice and the imposition of a 20% export duty on par-boiled rice.
- The decision to restrict rice exports was driven by the need to stabilize domestic prices and guarantee an ample food supply for the nation.
- Experts predict that these restrictions are likely to remain in place until the upcoming general election scheduled for April-May 2024.
- Challenges in rice production during the 2023-24 kharif season, exacerbated by dry weather conditions attributed to El Nino, have further complicated the supply situation.
- Despite these trade limitations, local rice prices have remained firm, prompting government warnings to retailers.
Government Intervention:
- Union Food Secretary Sanjeev Chopra highlighted a 14.51% increase in retail rice prices over the past year.
- In response to rising rice prices, the government has mandated traders, wholesalers, retailers, and processors to report their rice and paddy stocks every Friday to manage food inflation and curb speculative activities.
- To counter inflationary pressures, the government has initiated the retail sale of 'Bharat Rice' to the general populace.
- Initially, 5 lakh tonnes of rice will be allocated for retail sale under this brand through agencies like NAFED, NCCF, and Kendriya Bhandar, priced at ?29 per kilogram in 5 kg and 10 kg bags.
- Furthermore, the Food Corporation of India (FCI) has ample stocks of good-quality rice available for sale to traders and wholesalers under the open market sales scheme at a reserve price of ?29 per kilogram.
Status of India’s Rice Exports:
- India holds the position of the world's largest rice exporter, accounting for 45% of the global rice market share.
- During April-May 2023, overall rice exports witnessed a notable increase of 21.1% compared to the previous fiscal year.
- Basmati rice exports in May 2023 alone surged by 10.86% compared to May 2022, reflecting a sustained upward trend.
- The export of non-Basmati rice has been steadily rising over the past three years, with Basmati rice exports in 2022-2023 surpassing the previous year's figures.
- Recent data provided by the government indicates a 15% increase in total rice exports (excluding broken rice) by August 17 compared to the corresponding period in the previous year.
- Regional Dynamics: Thailand anticipates a nearly 25% decrease in rice production for the 2023-2024 season, while Myanmar has halted raw rice exports.
- Similarly, rice availability is expected to be limited in Iraq and Iran.
- India annually exports more than 4 million tons of basmati - a premium long-grain variety famed for its aroma - to Iran, Iraq, Yemen, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and the United States, among others.
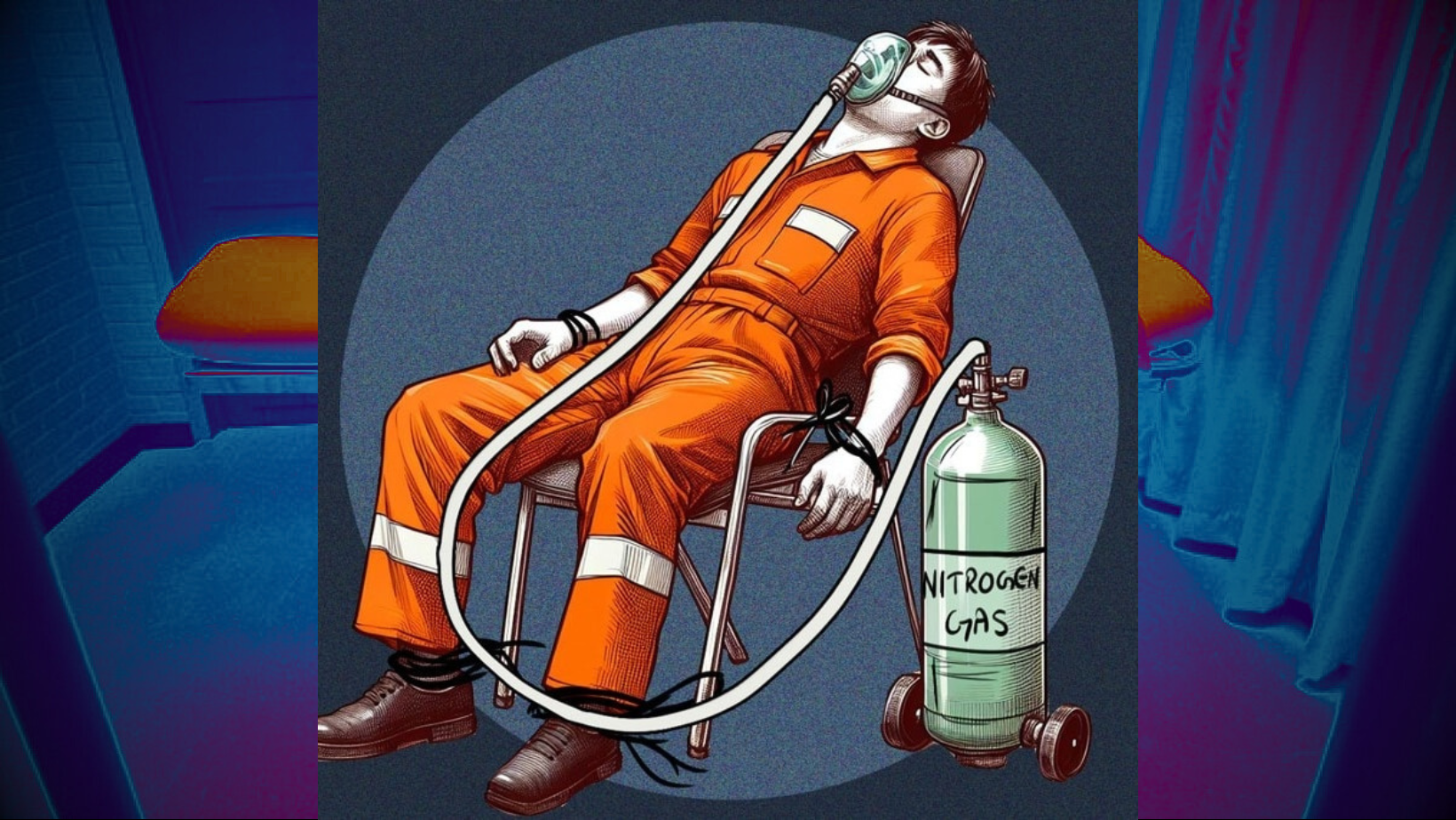
Alabama in USA Carried Out the First Ever Execution Using Nitrogen Gas (Indian Express)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Alabama inmate Kenneth Smith was executed on January 25 by nitrogen hypoxia, marking the United States’ first execution using the method, and the first time in over four decades that a new method of execution was introduced since lethal injection was first used in 1982.
News Summary:
- An Alabama death row inmate has been put to death by nitrogen gas, in the first known execution of its kind in the US.
- His case marks the first known execution by nitrogen hypoxia, which his lawyers had argued amounted to a form of “cruel and unusual punishment”.
- Death by nitrogen gas is an untested procedure, and its opponents say it can cause unnecessary suffering.
- Kenneth Smith, 58, was a contract killer who had been on the death row since 1996.
What is Nitrogen Hypoxia?
- Nitrogen hypoxia is a style of execution wherein an inmate is made to inhale nitrogen instead of oxygen, leading to gradual asphyxiation.
- To achieve this, a respirator mask is placed over the head of the inmate on death row.
- While the air we breathe is made up of 80 per cent nitrogen, it exists in combination with oxygen, rendering the colourless, odourless gas harmless.
- However, if a person is deprived of oxygen and made to breathe in just nitrogen, the gas proves lethal.
- When a high concentration of nitrogen is inhaled, it replaces the oxygen in the body and disables the respiratory system, causing death.
Why Nitrogen Hypoxia?
- Nitrogen hypoxia is the first new method of execution to be introduced since 1982 when lethal injections began being used.
- The drug needed to administer lethal injections to inmates on death row became harder to access over time, pushing authorities to scout for alternatives.
- Further, there were reports of a surge in complications associated with the procedure as well.
- As of now, only three states in the United States have approved the use of nitrogen gas to execute death row inmates, namely, Alabama, Oklahoma, and Mississippi.
Is Nitrogen Hypoxia Ethical?
- There is little research regarding death by nitrogen hypoxia.
- When the State is considering using a novel form of execution that has never been attempted anywhere, the public has an interest in ensuring the State has researched the method adequately and established procedures to minimise the pain and suffering of the condemned person.
- The risks associated with this method of execution include the risks surrounding the chances of a gas leak if the mask is not secured well on the inmate.
- The law requires that this execution not be cruel.
Key facts about Nitrogen:
- The air around us, the atmosphere, is made up of about 78% nitrogen and only 21% oxygen.
- The rest comprises water vapour, argon, neon, helium, hydrogen and xenon.
- Those are known as "permanent gases".
- There is also a range of "variable gases" in the atmosphere.
- They include methane, ozone and carbon dioxide — with concentrations that can vary from day to day and region to region.
- At a concentration of 78% in the atmosphere, nitrogen is safe to breathe.
- But it grows dangerous and potentially fatal once levels of nitrogen reach 80% or more.
- Nitrogen has no odour, is tasteless, and colourless.
- Nitrogen gas is inert, but certain soil bacteria can "fix" nitrogen into a usable form for plants and animals.
- French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavoisier named nitrogen azote, meaning without life.
- Nitrogen was sometimes referred to as 'burnt' or 'dephlogisticated' air.
- Nitrogen compounds are found in foods, fertilizers, poisons, and explosives.
- It is responsible for the orange-red, blue-green, blue-violet, and deep violet colours of the aurora.
- Nitrogen has a valence of 3 or 5.
- Discovery: Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772
- Nitrogen is the fifth most abundant element in the universe.
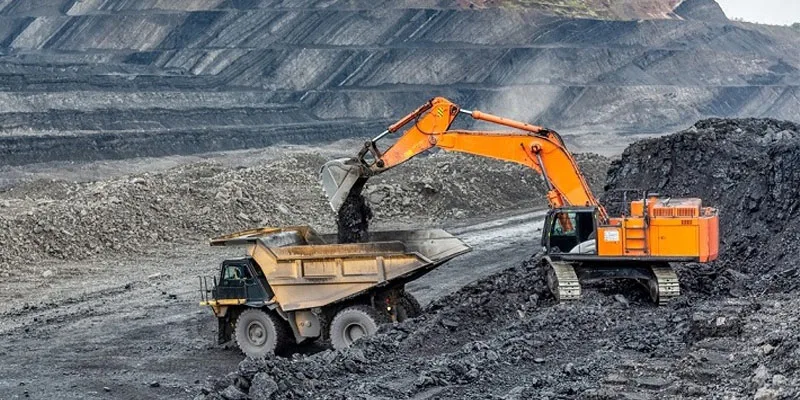
Centre approves incentive of Rs 8,500 crore for coal gasification projects (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to achieve the target of coal gasification of 100 million tonnes (MT) of coal by 2023 in India, the government recently approved Rs 8,500 crore incentives.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a thermo-chemical procedure wherein the pressure and heat of the gasifier disintegrate coal into its chemical components.
- The resulting "syngas" are mostly carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen, with some other gaseous substances thrown in for good measure.
- Coal gasification is an in-situ method wherein oxygen is infused into the seam together with water and ignited at high temperatures, causing coal to partly oxidised into hydrogen, CO, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
- Ex-situ reactors are designed to simulate the gasification process above the ground's surface.
- Sulphur in coal is transformed to H2S and trace volumes of carbonyl sulphide during the gasification process (COS).
- Acid gas removal technology can easily and cost-effectively discard these sulphur compounds.
- There is no scrubber sludge produced by coal gasification plants, which necessitates careful and expensive disposal.
- The majority of the wash water is reprocessed, and residual wastewater from gasification plants can be treated effectively.
- As a result, coal gasification is regarded as a cleaner coal technology when compared to coal combustion.
- Furthermore, coal could be used to generate a range of products using clean coal innovations such as hydrogen, methanol, and fertilisers via coal gasification.
- Carbon fibres and plastic composites made from coal power plant ash/residue.
How can it be used?
- Syngas, according to proponents of coal gasification, can be used to generate power, in energy-efficient fuel cell technology, or as chemical "building components" for industrial applications.
- The hydrogen can also be extracted and used to power a hydrogen economy.
- Coal gas can also be transformed into a transportation fuel to be used in automobiles as a replacement for gasoline, but it is less efficient than the current output and combustion of petroleum-based gasoline.
- Coal gasification is said to be more efficient than traditional coal burning since it can use the gases two times: the coal gases are first purified of contaminants before being fired inside a turbine to produce energy.
- The gas turbine exhaust heat can be then collected and used to produce steam for a steam turbine generator.
- This is known as a combined process, and according to DOE, a coal gasification processing facility using this dual method can possibly attain an efficiency of 50% or higher, compared to the customary coal power plant, which is typically just above 30%.
Significance of Coal Gasification:
- India announced environmental targets as its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement in 2016.
- In order to meet these objectives, coal gasification aids in the decrease of emission levels and the advancement of non-fossil fuel-based energy resources.
- The syngas produced by coal gasification can be used to generate urea and a variety of products such as methanol, Dimethyl ether (DME), and olefins, allowing India to minimise imports and become self-sufficient.
- Syngas CO and H2 are essential reducing agents for steel production and are regarded as an environmentally friendly technique of steel production because they reduce the import of furnace oil.
- India has ambitious plans to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) domestically rather than importing them from China.
- As a result, the potential of Syngas requirement for making APIs, as well as methanol as a solvent, is being investigated.
- The synthesis gas can be used in an Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) system to generate electricity in an efficient and environmentally friendly manner.
Initiatives taken by India:
- The Ministry of Coal, through Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan, has taken the initiative, National Coal Gasification Mission, that is to utilise coal through coal gasification, with the goal of achieving 100 MT coal gasification by 2030.
- It has also been recommended that all coal companies assign a nodal officer and formulate a plan for gasifying at least 10 per cent of their coal production.
- SHAKTI policy was implemented in coal gasification projects to minimise operating costs by allocating long-term coal linkages through auction.
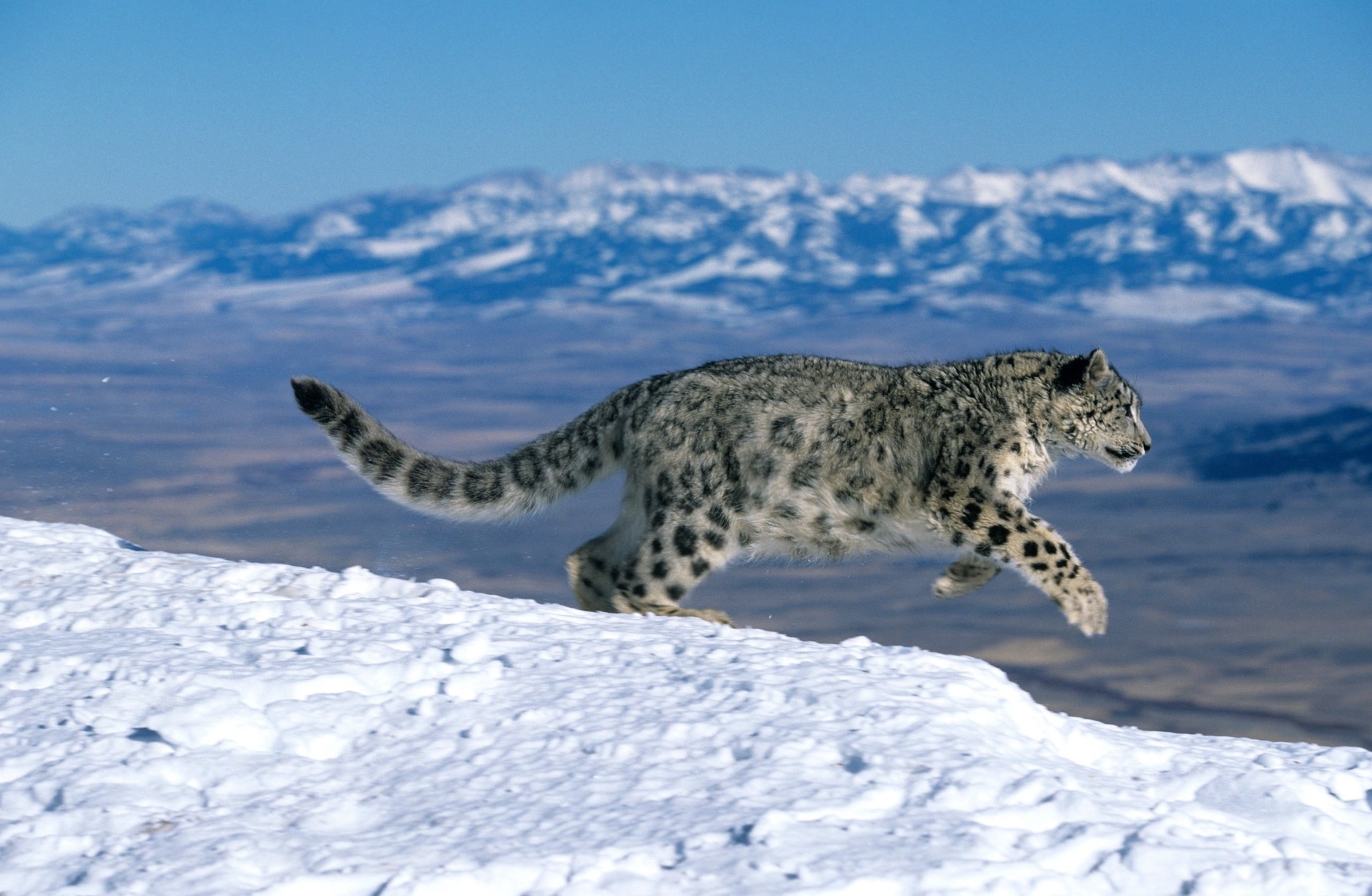
Darjeeling zoo’s success with snow leopards: Why wild cats are fussy breeders (Indian Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP) in Darjeeling has made headlines for successfully breeding 77 snow leopards since the 1980s, placing it next only to New York’s Bronx Zoo, which has produced 80 snow leopard cubs since it started breeding experiments with the species in the 1960s.
About Snow Leopard:
- The snow leopard, also known as the ounce, is a large Asian cat belonging to the family Felidae, classified as Panthera uncia.
- It preys on various animals, including marmots, wild sheep, ibex, and domestic livestock. As the apex predator in the mountain ecosystem, snow leopards serve as vital indicators of ecosystem health.
- Habitat: Native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia, snow leopards are found in India, specifically in the western Himalayas covering Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh in the eastern Himalayas.
- Threats to Survival: With an estimated 4,000 to 6,500 snow leopards remaining in the wild, around 500 of them are in India.
- Human settlement expansion, particularly livestock grazing, has escalated conflicts.
- Climate change, causing a rise in average temperatures across their habitat, poses an additional threat.
- Poaching, driven by illegal trades in pelts and body parts used in traditional Chinese medicine, further endangers their lives.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Conservation Efforts: The Government of India initiated Project Snow Leopard in 2009 to safeguard and conserve the snow leopard population and their habitats through participatory policies.
- Under the UNDP's SECURE Himalaya project in 2020, India's first Snow Leopard Conservation Centre was launched in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand, promoting conservation efforts in the region.
About Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP):
- Formerly known as the Himalayan Zoological Park, the PNHZP was established in August 1958 in Darjeeling, West Bengal.
- Dedicated to the preservation of ecological balance in the Eastern Himalayas, the park pursues the following objectives:
- Ex-situ Conservation and Captive Breeding: The park focuses on the ex-situ conservation and captive breeding of endangered Himalayan animal species.
- Awareness and Education: Aiming to educate and motivate both local residents and visitors, the park conducts awareness campaigns highlighting the significance of Himalayan ecosystem conservation.
- Applied Research: The PNHZP initiates applied research in animal biology, behaviour, and healthcare, contributing to a better understanding of these aspects.
- Conservation Pioneering: Recognized as a conservation pioneer, the zoo initiated the first ex-situ conservation breeding program in 1986, commencing with the Snow Leopard conservation breeding project.
- The Red Panda project followed suit in 1990.
- High-Altitude Zoo: The PNHZP holds the distinction of being the largest high-altitude zoo in the country, making significant strides in the conservation of endangered Eastern Himalayan species in India.
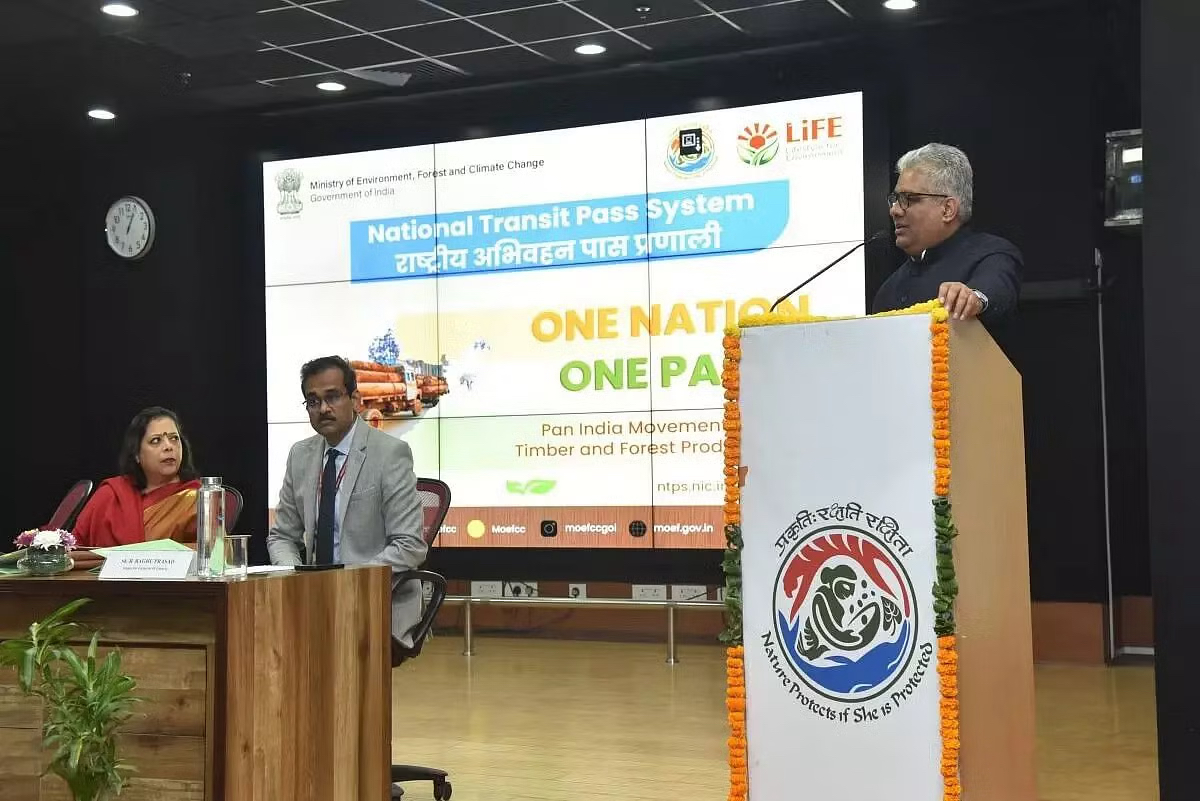
Minister Bhupendra Yadav launches NTPS, a unified system for forest goods’ transport across India (Indian Express)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The central government on Friday launched the National Transit Pass System (NTPS) to facilitate seamless transit of forest goods across the country through a single permit.
About the National Transit Pass System (NTPS):
- The National Transit Pass System (NTPS) is established to facilitate the smooth transit of timber, bamboo, and other forest produce across the country.
- Currently, transit permits are issued based on state-specific rules, leading to a fragmented system.
- The NTPS aims to implement a "One Nation-One Pass" regime, ensuring seamless transit across the entire nation.
- This initiative streamlines the issuance of timber transit permits by providing a unified online platform for tree growers and farmers engaged in agroforestry, contributing to a more business-friendly environment.
Key Features of NTPS:
- Unified Online Platform: The NTPS offers a unified, online mode for obtaining timber transit permits, simplifying the process for tree growers and farmers involved in agroforestry nationwide.
- Record Management: It manages records for both inter-state and intra-state transportation of timber, bamboo, and other forest produce from various sources, including private lands, government-owned forests, and private depots.
- QR Coded Transit Permits: The system generates QR coded transit permits, enabling check gates across states to verify the permits' validity and ensure seamless transit.
- User-Friendly Applications: NTPS provides desktop and mobile applications for easy registration and permit applications, enhancing user convenience.
- Regulated Species and Exemptions: Transit permits are issued for regulated tree species, while users can self-generate No Objection Certificates for exempted species.
- State Participation: Presently, 25 States and Union Territories have adopted the unified permit system, simplifying interstate business operations for producers, farmers, and transporters.
- Nodal Ministry: The NTPS operates under the guidance of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
The Supreme Court directed the governments to provide details on “the estimated inflow of illegal migrants into India.. after March 25, 1971”. (Indian Express)
- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Thursday asked the Centre and Assam government to provide details on the “estimated inflow of illegal migrants” to Assam and other Northeastern states after March 25, 1971, and the status of border fencing.
News Summary:
- During the hearing of petitions, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court expressed concerns about the perceived 'unlimited influx' of illegal migrants from Bangladesh, impacting demographics and straining resources for Indian citizens.
- The court questioned the application of Section 6A, granting Indian citizenship benefits to illegal migrants, solely in Assam and not in West Bengal, which shares a larger border with Bangladesh.
- The Supreme Court directed the Home Secretary to submit an affidavit by May 11, 2023, detailing the estimated inflow of illegal migrants, steps taken to address illegal immigration, and specifics on border-fencing extent and timelines.
- The government was also instructed to provide information on illegal immigration along the West Bengal border post on March 25, 1971.
Why Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955 is Under Challenge?
- Presently, a Supreme Court bench is reviewing petitions from indigenous Assamese groups challenging Section 6A of the Citizenship Act.
- These groups assert that the special provision serves as a 'beacon' for illegal entrants to settle in Assam, gain Indian citizenship, and subsequently deprive locals of political, and economic rights, jeopardizing Assamese cultural identity.
- The petitioners question the constitutional validity of Section 6A, claiming it is arbitrary, specifically singles out Assam, violates Article 14, and has led to an influx of illegal migrants from Bangladesh.
- They advocate for establishing 1951 as the cutoff date for inclusion in the National Register of Citizens instead of 1971.
- The primary petitioner, Assam Sanmilita Mahasangha (ASM), argues that Section 6A is discriminatory, arbitrary, illegal, and infringes upon the rights of indigenous Assamese people by establishing a different citizenship cutoff date for Assam compared to the rest of India (July 1948).
What are the Arguments of the Central Government?
- The central government refutes the accusation of unfairly burdening the state with the responsibility of handling illegal migrants, contending that different states of India can be classified differently based on historical and geographical factors.
- According to the government, the classification implied in Section 6-A is founded on intelligible differentia.
- Dismissing claims of arbitrariness, the Centre asserts that the guarantee against non-arbitrariness under Article 14 does not mandate universal application for every law, irrespective of dissimilarity or the nature of the individuals it pertains to.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which is marking its 75th anniversary? (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Seventy-five years ago on Sunday, the UN General Assembly approved the Universal Declaration of Human Rights at a meeting in Paris – laying one of the foundation stones of the international order that emerged following the horrors of World War II.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)?
- On 10 December 1948, during a session in Paris, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously endorsed the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), marking a pivotal moment in shaping the post-World War II international order.
- The UDHR emerged as a response to wartime atrocities and aimed to establish a shared understanding of the fundamental rights and freedoms inherent to all individuals.
- A concise yet impactful document, the declaration comprises a preamble and 30 articles that delineate essential rights and freedoms.
- These 30 articles encompass a comprehensive spectrum of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Emphasizing their universality, these rights are deemed applicable to all individuals, irrespective of nationality, ethnicity, gender, religion, or any other status.
- While not legally binding, the UDHR has functioned as a guiding force inspiring the development of international human rights law.
Key Features:
- Preamble: The preamble elucidates the reasons behind adopting the declaration, underscoring the inherent dignity and the equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family.
- Articles: The UDHR articulates 30 articles outlining a wide array of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights. Examples of these rights include:
- The right to life, liberty, and security of person.
- The right to freedom of religion, expression, and assembly.
- The right to work and education.
- The right to an adequate standard of living.
- The declaration asserts that "all are equal before the law" and emphasizes the entitlement of everyone to "a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal."
- It also affirms the right of "everyone to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution.
Achievements of UNDHR:
- The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UNDHR) is acknowledged for its significant impact, having served as the inspiration and foundation for over 70 human rights treaties at both global and regional levels, as noted by the United Nations.
- It played a pivotal role in inspiring movements such as decolonization, the anti-apartheid movement, and various struggles for freedom worldwide, including those related to gender, LGBTIQ+ rights, and opposition against racism.
What is the Current Situation?
- As the 75th anniversary is commemorated, human rights face challenges amid conflicts such as the Israel-Hamas war, Russia's actions in Ukraine, internal strife in Myanmar and Sudan, and numerous other global situations.
- UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has remarked that the Universal Declaration has been frequently misused and abused, exploited for political gain, and often ignored by those who should uphold it.
- Contrastingly, Amnesty International asserts that the declaration serves as living proof that a global vision for human rights is attainable and can be realized.
- Despite instances of neglect or exploitation, the declaration remains relevant, and the world is encouraged to recognize its successes while learning from its failures.
AGARTALA-AKHAURA RAIL LINK PROJECT (Indian Express)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Bangladesh counterpart Sheikh Hasina will jointly inaugurate the Agartala-Akhaura cross-border rail link project on Wednesday.
Facts About:
- The rail line between Agartala in Tripura and Akhaura in Bangladesh would pave the way for the first train to run from the northeastern region of India to Bangladesh.
- The project is significant from an international as well as from a domestic point of view.
- At present, the rail route from Agartala to Kolkata is around 1600 kilometres and takes about 38 hours.
- The footfall of passengers from Agartala to Kolkata is significantly very high due to the linguistic similarity between the two states.
Both states also share age-old cultural and business relations and Agartala depends on Kolkata from the medical tourism point of view as well.
- Upon operationalisation of the Agartala-Akhaura Rail link project the distance will be reduced by around 500 kilometres and the travel time will be 16 hours between Agartala and Kolkata.
- In addition, this rail link will also provide direct access between landlocked northeastern India and the Chittagong port of Bangladesh.
- The Ministry for Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) has funded the railway line from Agartala to Nischintpur;
whereas the Ministry of External Affairs has funded the rail line from Nischintpur to Gangasagar which is in Bangladesh.
- The project is part of India's 'Act East Policy', which aims to promote economic cooperation and develop strategic ties with countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
EJECTA HALO (Indian Express)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Chandrarayaan-3 Lander Module produced an amazing 'ejecta halo' of lunar material, according to recent information released by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
Facts About:
An ejecta halo is a bright, irregular patch of lunar material that surrounds a lander after it has landed on the Moon.
- It is caused by the thrust from the lander's engines and the impact of the lander on the lunar surface, which displaces and ejects lunar regolith (soil) and dust.
- The ejecta halo can be several meters in diameter and can extend tens of meters from the lander.
The Vikram lander of the Chandrayaan-3 mission created a spectacular ejecta halo when it landed on the Moon in August 2023.
- Scientists from the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) estimate that about 2.06 tonnes of lunar regolith were ejected and displaced over an area of 108.4 square meters around the landing site.
Ejecta halos can be studied to learn more about the composition and structure of the lunar regolith.
- They can also be used to calibrate remote sensing instruments and to develop new methods for landing spacecraft on the Moon.
SATELLITE INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (Indian Express)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Reliance Jio recently declared that it had effectively tested the first gigabit internet service in India, based on satellite technology.
Facts About:
- Satellite Internet operates in a way similar to satellite TV.
- It begins with an internet service provider launching satellites into space to orbit the Earth.
These satellites, placed in low- or high-Earth orbit, transmit a signal.
- A receiver dish, positioned in your home or business, captures this signal.
It should have an unobstructed view of the sky.
- You connect a modem to this dish to convert the received signal into usable internet connectivity.
- High-speed satellite internet is typically delivered through constellations of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- LEO satellites orbit the planet at altitudes ranging from 250 to 2,000 kilometers.
- Communication between these satellites and Earth occurs using radio waves.
Advantages of Satellite Internet:
- Satellite Internet is ideal for users residing in rural or remote areas, far from urban centers or cable/phone offices.
- It relies on a satellite dish for two-way communication and doesn't require telephone cables or lines.
- When compared to other internet options, satellite internet experiences fewer or minimal network outages.
CYCLONE HAMOON (Indian Express)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The severe cyclonic storm “Hamoon” weakened into a deep depression and is likely to weaken further into a depression in the next six hours, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said Wednesday.
Facts About:
- Presently situated over the west-central Bay of Bengal, it is anticipated to intensify shortly and proceed north and northeastward towards the coastal regions of Bangladesh and West Bengal.
- Named by: Iran gave the cyclonic storm its name after it formed.
Inland desert lakes and marshlands are referred to as "hamoon" in Persian.
They developed as yearly natural reservoirs in regions that border the Helmand basin.
- Projected Landfall: After weakening into a deep depression, it is predicted to make landfall between Khepupara and Chittagong on the coast of Bangladesh.
- Potential Effects: Parts of India are predicted to receive rainfall from the Hamoon, despite its decreased intensity.
- The northeastern states of Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, south Assam, and Meghalaya are expected to experience light to moderate rainfall, with isolated heavy rains (64.5 mm-115.5 mm) according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Because of the anticipated effects of the cyclone, the (IMD) has also issued a yellow alert for coastal districts in West Bengal and Odisha.
How are Cyclones Given Their Names?
- Cyclones receive their names through a process managed by regional specialized meteorological centers (RSMCs) and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers (TCWCs).
- There are a total of six RSMCs and five regional Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers responsible for this naming process.
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) serves as an RSMC and is responsible for naming cyclones that form over the north Indian Ocean, encompassing the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
- Additionally, the IMD is tasked with issuing advisories to 12 other countries in the region regarding cyclone and storm development.
DUST SUPPRESSANT (Indian Express)
- 25 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Dust suppressants will be used in Delhi to mitigate pollution from dust. This, however, is not the first time it has been used in the Capital and parts of NCR.
Facts About:
- Magnesium or calcium salts with moisture-absorbing properties can act as dust suppressants.
- For longer-lasting dust control, water and dust suppressant powder are combined and sprayed on roads.
- Efficacy: In 2019, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) advised using them, citing a study that discovered a 30% decrease in dust concentration, including PM10, PM2.5, and PM1, when dust suppressants were used in conjunction with water.
- Dust suppressants combined with water are significantly more effective at reducing particulate matter emissions than plain water sprinkling, according to a 2019 advisory from the Delhi Public Works Department (PWD).
- Magnesium chloride and bio-additives have been found to be particularly effective as a dust suppressant.
- To reduce dust emissions, the Delhi Pollution Control Committee and the CPCB both released guidelines recommending the use of dust suppressants during construction and in areas with high levels of dust.
WHITE PHOSPHOROUS BOMBS (Indian Express)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent reports, Israeli forces have been using white phosphorous against the civilian population of Gaza.
Facts About:
It is a waxy solid that is colorless, white, or yellow.
Occurrence:
- It does not occur naturally. Phosphate rocks are used to make it.
- It is a highly flammable substance that reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere.
- As little as 10 to 15 degrees above room temperature can cause it to catch fire.
Every country has strict regulations regarding its manufacturing and handling due to its combustible nature.
Applications:
- It is primarily used in the military, but it may also be used as a component in fertilizers, food additives, and cleaning compounds.
- It was originally used in pesticides and fireworks, but many countries have banned its use in a variety of industries.
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), an intergovernmental organization and the implementing body for the Chemical Weapons Convention, has not included White Phosphorus in any of the three Chemical Weapons Schedules.
CALIPSO Mission (Indian Express)
- 30 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, NASA declared the conclusion of the CALIPSO mission, which conducted assessments of climate, weather, and air quality.
Facts About:
- CALIPSO (Cloud-Aerosol LIDAR and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations), is a dedicated mission aimed at understanding the influence of clouds and aerosols on Earth's climate.
- A collaborative endeavor between NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) and CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales), the French space agency, CALIPSO took to the skies in 2006 as a satellite-based observatory.
- Scientists have harnessed CALIPSO's data to construct three-dimensional atmospheric models, enhancing our capacity to forecast future climate changes.
- CALIPSO has been an integral part of the "A-Train" constellation of spacecraft, which includes Aqua, Aura, and PARASOL, all dedicated to the study of Earth's weather and environment.
Key Instrumentation:
- The mission is equipped with CALIOP, a lidar system that operates at two wavelengths and is sensitive to polarization.
Additionally, it carries two passive sensors functioning in the visible and thermal infrared spectral ranges.
- CALIOP emits laser pulses and measures the light scattered back by clouds and aerosols, enabling the creation of vertical profiles detailing properties such as height, thickness, and optical depth.
- Notably, CALIOP is the first lidar to provide continuous atmospheric measurements from Earth's orbit.
- This invaluable data aids scientists in generating comprehensive three-dimensional profiles of cloud and aerosol distributions.
- Throughout its 17 years of operation, the mission amassed over 10 billion LIDAR measurements and contributed to the creation of numerous scientific reports.
e-Cabinet System (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Tripura inaugurated an e-cabinet system in Agartala, aimed at advancing digital infrastructure and enhancing the digitization of government services and information.
Facts About:
- The e-Cabinet system is a robust software portal designed for State Governments to facilitate electronic and online Cabinet meetings.
- It has been developed by the National Information Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY).
- Tripura is now the fourth state, and the second in the Northeast region, to implement the e-cabinet system, following in the footsteps of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Key Features:
- Enhances the utilization of technology in meetings and reduces paper consumption.
- Streamlines workflow activities for meetings, covering pre-meeting, during the meeting, and post-meeting phases.
- Offers a user-friendly interface designed for smart tablets, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Incorporates a secure push and pull mechanism to safeguard sensitive Cabinet matters.
- Establishes an institutional memory and knowledge repository, facilitating quick searches and retrieval of information.
- For virtual meetings, eCabinet seamlessly integrates with the Bharat VC solution of NIC.
Benefits and Impact of eCabinet:
- Substantial savings in paper, fuel, and manpower resources.
- Real-time data updates.
- Enhanced information accessibility, promoting coordinated actions.
- Improved decision-making processes and swift retrieval of meeting decisions and action taken.
- Enables virtual participation of Ministers in Cabinet proceedings.
Conocarpus Tree (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the government of Gujarat has instituted a prohibition on the planting of Conocarpus trees in both forested and non-forested areas, citing concerns regarding their detrimental effects on the environment and human well-being.
Facts About:
- The Conocarpus tree is a flowering plant belonging to the Combretaceae family.
- It is categorized as an invasive mangrove species.
- These trees bloom during the winter season, releasing pollen into their surroundings.
- In India, public authorities have commonly used Conocarpus for landscaping purposes, including road medians, roadsides, and public gardens.
- In the Arabian Peninsula, it has been employed to combat desert storms and pollution.
- This tree is renowned for its year-round dark green leaves and its ability to thrive in harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures.
- It exhibits adaptability, even in areas with high salinity.
- The Conocarpus tree absorbs a significant amount of water from the soil, posing a threat to groundwater levels.
- Its extensive root system can damage communication cables, drainage lines, and drinking water pipelines.
- This species is native to various regions in North and South America, as well as parts of Africa.
Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Gems and Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) has made a plea to the diamond industry, urging them to halt the importation of rough diamonds.
Facts About:
- GJEPC serves as the apex organization representing India's Gem and Jewellery industry, operating under the sponsorship of the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India.
- Primary Role: The Council's primary mission is to introduce Indian gem and jewellery products to global markets and facilitate their exports.
It achieves this by furnishing its members with crucial information on foreign trade inquiries, trade regulations, tariff rates, and updates on jewellery fairs and exhibitions.
- Location: Headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, GJEPC maintains a presence through regional offices nationwide, boasting a membership exceeding 7,500.
Additional Functions:
- Collaborating in international jewellery showcases.
- Encouraging countries to explore opportunities for cooperation in the supply of rough diamonds, colored gemstones, and finished jewellery.
- Identifying potential partners and buyers in international markets through buyer-seller meetings.
- Administering the Kimberly Process Certification Scheme as India's Nodal Agency.
- Advocating for export-related matters with the Government, Ministries, Regulatory Authorities, and Agencies.
- Conducting image-building campaigns via international advertisements, publications, and audio-visuals.
- Establishing training institutes across six cities (Mumbai, Delhi, Surat, Jaipur, Varanasi, and Udupi) to impart manufacturing skills and promote technical and design excellence.
- Initiating the establishment of Jewellery Parks throughout the country.
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) (Indian Express)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has made changes to the regulations for Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA). They now require these NGOs to furnish information about assets, both movable and immovable, that have been established using foreign funds in their annual returns.
Facts About:
- FCRA is a law governing foreign contributions, especially monetary donations, to NGOs and entities in India.
- Originally passed in 1976 and significantly amended in 2010.
- Aims to prevent foreign organizations from influencing India's politics, society, economy, or religion for harmful purposes.
- Administered by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Defines 'foreign contribution' as donations, currency, or securities from foreign sources.
- Allows individuals, associations, companies, and others to receive foreign contributions with FCRA registration.
- Funds must be used for the intended purpose, with a maximum of 20% for administrative expenses.
- Requires NGOs to open a designated bank account with the State Bank of India, Delhi.
- Registration is mandatory for NGOs and can be renewed if they meet requirements.
- Cancellation is possible for false statements or illegal activities.
- Suspension and fund-freezing authority were also granted to the Ministry.
- Challenges to government orders can be filed in the High Court.
Armed Forces Tribunal (Indian Express)
- 27 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) Chandigarh Bench Bar Association has taken the step of going on an unlimited strike. This strike is a response to the decision made by the AFT chairperson to move a judicial member from Chandigarh to Kolkata.
Facts About:
- The Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) is like a special court in India for military matters, and it started in 2009 under the Armed Forces Tribunal Act, 2007.
- What it does: It deals with arguments and complaints about things like appointments, jobs, and the rules for people who are part of the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- It handles appeals when someone disagrees with the decisions made by military courts.
- If the military court's decision seems right, the Tribunal can say so.
But if it's not right, the Tribunal can change it.
- If someone doesn't agree with what the Tribunal says, they can only go to the Supreme Court to argue their case.
- The AFT has its main office in New Delhi, and there are eight other offices in different cities.
- Each office has two important people:
A Judicial Member who is a retired High Court Judge and
An Administrative Member who is a retired Armed Forces officer with a high rank.
- Sometimes, a Judge Advocate General (JAG) who has been in the job for at least a year can also be an Administrative Member.
- How it works:
The Tribunal follows certain rules for how they do things, and they use English for all their work.
They usually do things the way High Courts in India do them.
Emerging Markets Bond Index (Indian Express)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
JP Morgan Chase & Co will add Indian government bonds to its emerging markets bond index starting in June 2024.
Facts About:
- This index serves as a benchmark for measuring how well international government and corporate bonds from emerging market countries perform.
These countries must meet specific liquidity and structural requirements.
- Emerging market bonds are debt instruments issued by developing nations.
They usually offer higher yields compared to bonds from developed countries.
- A total of 23 Indian Government Bonds (IGBs) with a combined notional value of $330 billion are eligible for inclusion.
They are all categorized as "fully accessible" for non-residents.
- Advantages of this inclusion:
This development is expected to lead to higher demand for the Indian rupee, potentially protecting it from depreciation.
Lower borrowing costs could support important infrastructure projects.
Increased liquidity may result in more efficient trading conditions.
- India's local bonds will become part of JP Morgan's Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) index.
- They are expected to make up a maximum of 10 percent of the GBI-EM Global Diversified Index (GBI-EM GD).
World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) (Indian Express)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) of India has recently earned a 10-year recognition status from the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME).
Facts About:
WFME is a worldwide organization dedicated to the training and education of medical doctors.
Their mission is to work towards better healthcare for all people.
WFME's primary goal is to elevate the quality of medical education on a global scale by promoting the highest scientific and ethical standards.
They achieve this goal through several means, including:
- Establishing standards in medical education
- Advocating for the accreditation of medical schools
- Developing databases related to medical education
- Initiating projects focused on the future of medicine and medical education
- Publishing informative materials and forming partnerships
WFME was established in 1972 and has its headquarters in Ferney-Voltaire, France.
Notably, WFME is the organization that officially represents medical teachers and medical teaching institutions on a global scale, serving as their voice before the World Health Organization (WHO).
WFME's accreditation program plays a crucial role in ensuring that medical institutions meet and uphold the highest international standards in education and training.
Adi Shankaracharya (IndianExpress)
- 23 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh recently revealed a 108-feet tall statue of Adi Shankaracharya, an ancient Vedic scholar and teacher from the 8th century, in Omkareshwar.
Facts About:
- Adi Shankaracharya, also known as Shankara, was an ancient Indian philosopher and theologian who lived around the 8th century CE.
- Birthplace: He was born in Kalady, a village in what is now Kerala.
His Philosophical Contributions:
- His most famous achievement was his role in developing and spreading Advaita Vedanta, a school of Hindu philosophy that emphasizes non-duality.
- He brought together the ideas of 'Advaita Vedanta' and explained the core concepts of the Upanishads.
- Shankaracharya's significant work involved uniting six sub-sects known as 'Shanmata,' which translates to 'six religions.' This concept recognized six supreme deities, all part of one divine power.
- He also established the 'Dashanami Sampradaya,' which promotes a monastic way of life.
- While he strongly believed in ancient Hinduism, he criticized the 'Mimamsa school of Hinduism,' which focused primarily on rituals.
- Founding of Four Mathas: He founded four important monastic centers in India, each associated with one of the cardinal directions:
Sringeri in the south
Dwarka in the west
Puri in the east, and
Badrinath in the north.
Bima Sugam Platform (Indian Express)
- 20 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has established a steering committee, which will serve as the highest authority responsible for developing its ambitious Bima Sugam platform.
Facts About:
- This platform will empower individuals to purchase life, health, motor, or property insurance policies online, providing a convenient digital solution.
- It aims to offer a one-stop destination for insurance companies, agents, brokers, banks, and aggregators, streamlining accessibility.
- Serving as a centralized database, it will assist consumers with all their insurance-related needs, ensuring efficiency.
- The platform will facilitate the swift introduction of new or experimental insurance products.
- Cyril Amarchand Mangaldas (CAM) has been appointed as the legal counsel for this project, responsible for establishing a Section 8 not-for-profit company that will own the Bima Sugam platform.
- It will cater to both personal and commercial/business insurance needs, aiding users in identifying and comparing the best-suited products within specified timelines.
- The platform will encompass a comprehensive range of insurance offerings, including life insurance and its various forms such as term plans, savings (Par and Non-Par), annuities, pension plans, and more.
- Furthermore, it will showcase a fully digital onboarding process for all insurance products, eliminating manual interventions.
Gold Exchange-traded Funds (Indian Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In August, Gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs) saw an impressive inflow of Rs 1,028 crore, marking the highest influx in the past 16 months.
Facts About:
- These are investment funds linked to the value of gold.
- Gold ETFs are passive investments that track the price of gold and invest in physical gold bullion.
- They represent gold in a form that can be paper-based or dematerialized.
- Each unit of a Gold ETF is equivalent to 1 gram of highly pure physical gold.
- Gold ETFs are listed and traded on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd. (BSE).
- They offer complete transparency regarding their gold holdings, thanks to direct gold pricing.
International Organisation of Legal Metrology (OIML) (Indian Express)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Secretary of the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs announced that India has achieved the status of being an OIML certificate-issuing authority.
Facts About:
- OIML, short for the International Organisation of Legal Metrology, was established in 1955 as an international body.
- Its primary role is to develop model regulations, standards, and related documents that are used by legal metrology authorities and industry worldwide.
- OIML plays a vital part in aligning national laws and regulations concerning the accuracy of measuring instruments such as clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analyzers, radar speed measuring devices, ship tanks at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India joined the OIML in 1956 and simultaneously signed the metric convention.
- Headquartered in Paris, France.
C-295 MW Aircraft (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Airbus delivered the first C-295MW transport aircraft to the Indian Air Force in Seville, Spain.
Facts About:
- C-295 MW Aircraft a versatile transport aircraft with a capacity of 5-10 tonnes.
- Replacing the 1960s Avro aircraft in the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- Suitable for various missions.
- Contract includes 16 fly-away aircraft from Seville and 40 to be jointly manufactured with Tata Advanced Systems Ltd. (TASL).
Key Features:
- Up to 11-hour flight endurance.
- All-weather, day and night operations.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL) capability.
- Rear ramp door for troop and cargo drops.
- Air tanker conversion with a detachable refueling kit.
- Airborne Early Warning (AEW) variant with 360-degree radar coverage.
- Water bomber capability (7,000 liters).
- Close-air support and Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR).
- Suitable for medical evacuation, airdropping, and special missions.
Skill India Digital (SID) Platform (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Skill Development has just introduced the Skill India Digital (SID) platform.
Facts About:
- Skill India Digital (SID) is India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for skill development, education, employment, and entrepreneurship.
- It consolidates various skilling initiatives, offering over 264 courses from 42,623 centers nationwide.
- Developed by the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) in partnership with industry players.
- Part of the World Bank-assisted Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion (SANKALP) program.
- Supports multiple Indian languages and uses Aadhaar-based eKYC for secure access.
- Features user-friendly interface, adaptable to various devices.
- Utilizes AI and facial recognition for personalized course recommendations.
- Integrates government training programs from Central and State governments.
- Introduces Digitally Verified Credentials (DVCs) for secure skill showcasing.
- Offers Digital CVs with personalized QR Codes for easy access to qualifications and skills.
eCourts Project (Indian Express)
- 15 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Cabinet recently gave the green light to the third phase of the eCourts Projects, allocating a budget of ?7,210 crore for it.
Facts About:
- The eCourts Project is a nationwide initiative aimed at modernizing the Indian judiciary by using technology.
- It all began with the 'National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary – 2005,' proposed by the eCommittee of the Supreme Court of India.
- This committee was formed by the Government of India in response to a suggestion from the Chief Justice of India.
- Its purpose is to develop a national strategy for computerizing the Indian judiciary and advise on technological and management-related improvements.
- This project covers all District Courts across India and is overseen and funded by the Department of Justice under the Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India
The eCourts Project has several key goals:
- Providing efficient and citizen-centric services in a timely manner.
- Implementing decision support systems in courts.
- Automating processes to increase transparency and access to information.
- Boosting judicial productivity to make the justice system affordable, accessible, cost-effective, predictable, reliable, and transparent.
- Phase I of the eCourts Project was completed in 2015, computerizing 14,249 court sites. Phase II expanded this effort, computerizing 18,735 District and Subordinate courts.
Vidya Samiksha Kendra (Indian Express)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
As part of the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), the Ministry of Education is encouraging states to establish Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs).
Facts About:
- Vidya Samiksha Kendra, abbreviated as VSKs, serves as a comprehensive data repository housing information from all Ministry of Education (MoE) initiatives.
- These Kendras operate control rooms responsible for collecting data, monitoring key performance indicators, and employing AI and machine learning to analyze data sourced from government schemes.
This repository regularly updates data from various sources, including:
- The PM-POSHAN mid-day meal programs.
- Teacher training data sourced from the National Initiative for School Heads' and Teachers' Holistic Advancement portal.
- Textbook content originating from Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing.
- School attendance and dropout statistics accessible through the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE+).
- Students' learning outcomes as determined by the National Achievement Survey.
- The Performance Grading Index, evaluating the state and union territory-level school education systems.
Funding for this initiative includes a central allocation ranging from 2 to 5 crore rupees to each state for the adoption and establishment of VSKs.
Self Regulatory Organisation for Fintech (Indian Express)
- 12 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has requested fintech organizations to establish a Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO).
Facts About:
- A Self-Regulatory Organization is an independent entity, not affiliated with the government, responsible for formulating and enforcing industry-specific rules and standards that govern the behavior of its member entities.
- The primary objectives are safeguarding customers' interests and fostering a culture of ethics, fairness, and professionalism within the industry.
Key Functions of an SRO:
- Facilitating Communication: A recognized SRO serves as a vital bridge for communication between its members and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
This ensures a seamless flow of information and feedback.
- Setting Standards: SROs play a pivotal role in establishing and upholding minimum benchmarks and standards.
This helps in cultivating professional and ethical conduct among their member entities.
- Education and Awareness: SROs contribute to enhancing industry expertise by providing training to the staff of their members and other relevant stakeholders.
They also organize awareness programs to disseminate knowledge.
- Grievance Resolution: An important function of an SRO is to create a uniform framework for addressing grievances and managing disputes across its member organizations, promoting fairness and transparency.
Konark Temple Wheel (Indian Express)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
At the G20 summit venue, Bharat Mandapam, the Prime Minister of India greeted the leaders with a backdrop featuring a replica of the Konark Wheel from Odisha's Sun Temple in Puri.
Facts About:
- The Konark Wheel was created in the 13th century when King Narasimhadeva-I ruled.
- This wheel, with 24 spokes, is also seen on India's national flag.
- It represents India's ancient knowledge, advanced civilization, and great architecture.
- The spinning motion of the Konark Wheel represents time, Kalachakra, and the idea of constant progress and change.
- It's a strong symbol of democracy, reflecting the endurance of democratic values and dedication to societal progress.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Indian EXpress)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of India recently declared the start of a massive economic corridor connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Facts About:
- The project involves India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, France, Italy, Germany, and the US.
- Its goal is to boost trade between these countries, especially in energy products.
- The IMEC has two parts:
An Eastern Corridor linking India to the Gulf region and
A Northern Corridor connecting the Gulf region to Europe.
- It includes railways, ship-rail transit, and road routes.
- This corridor will have a railway, an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline, and a high-speed data cable.
- In the future, it will play a big role in connecting India, West Asia, and Europe economically.
- This rail and shipping corridor is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII).
- Why is it important?
- It will increase prosperity by enhancing energy and digital communications flow among these nations.
- The project will also address the infrastructure needs of developing countries in terms of growth.
Central Empowered Committee (Indian Express)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Supreme Court of India has transferred its environmental oversight committee, the Central Empowered Committee, to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Facts About:
- The Supreme Court created this committee in 2002, and it was restructured in 2008.
- Its main job was to keep an eye on environmental issues and make sure everyone followed the rules.
- Now, there have been some changes. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change says the CEC shouldn't be a temporary group anymore; it should become a permanent team that deals with environmental stuff.
Here's how the new CEC will be set up:
- It will have a chairperson who has 25 years of experience in environment, forests, and wildlife or 25 years of big-time government work.
- They can't be older than 66 years and should be at least an additional secretary in rank.
- The member secretary will be a full-time government officer, at least a Deputy Inspector General of forests or a director in the Government of India.
- They need to know a lot about the environment, forests, or wildlife and have 12 years of experience.
- There will be three expert members, one each for environment, forests, and wildlife. They should have 20 years of experience.
- The central government will pick these members for a three-year term.
Varicella Zoster Virus (Indian Express)
- 09 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Scientists from the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology have made a historic discovery in India. They have identified the Clade 9 variant of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) here for the first time.
Facts About:
- Varicella-zoster is a type of herpes virus that gives you chickenpox, which is a common illness when you're a kid.
- This virus only infects humans and belongs to the α-herpesvirus family.
- It's found all over the world and spreads easily.
- When you first get infected with this virus, you get chickenpox, which is also called acute varicella.
- In some cases, this virus can even affect your central nervous system and lead to serious problems.
One-hour Trade Settlement (Indian Express)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which previously stated its intention to introduce real-time settlement of trades in July, is now considering implementing one-hour settlement of trades as the initial step.
Facts About:
In a one-hour settlement, when an investor sells a share, the money will be deposited into their account within an hour, and the buyer will have the shares in their demat account within an hour.
Trade settlement is a process that involves the transfer of funds and securities on the settlement date.
- It's considered complete when the purchased securities from a listed company are delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the money.
- Previously, trade settlements followed the T+1 cycle, meaning they occurred within one day or 24 hours of the actual transactions.
This changed in January 2023 when India shifted to the T+1 settlement cycle, making it the second country globally, after China, to adopt this cycle for top-listed securities.
Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Authorities from the Ministry of Union Housing and Urban Affairs have indicated that the initial installment of loans for supporting ongoing projects in tier-2 and tier-3 cities through the Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) is expected to be released shortly.
Facts About:
The UIDF is created by utilizing the priority sector lending shortfall.
Objective:
- This fund serves as a resource for public agencies to develop urban infrastructure in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Emphasis is placed on essential services such as sewage and solid waste management, water supply, sanitation, construction, and improvement of drainage systems, with a priority on projects that have a significant impact.
The National Housing Bank manages this fund.
It initially has a corpus of ?10,000 crore and is modeled after the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF).
States are encouraged to harness resources from the 15th Finance Commission's grants and existing schemes, while also considering user charges when accessing the UIDF.
Currently, it covers 459 tier-2 cities and 580 tier-3 cities.
UIDF Loans:
- nterest rate: Bank Rate minus 1.5%
- The loan principal is repayable in five equal annual installments within seven years from the draw date, including a two-year moratorium period.
- Interest payments are made on a quarterly basis.
Stump-tailed Macaque (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Delhi Zoo has recently welcomed eight stump-tailed macaques, which were transferred from the Aizawl Zoological Park in Mizoram.
Facts About:
The stump-tailed macaque, also known as the bear macaque, is an Old-World monkey species native to South Asia.
Scientific Name: Macaca arctoides
Natural Habitat: These monkeys inhabit tropical and subtropical evergreen forests.
Geographic Range:
- They are indigenous to regions including Cambodia, southwest China, northeast India, Laos, Myanmar, northwest Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- In India, they are predominantly found south of the Brahmaputra River, primarily in the northeastern states.
Their Indian range extends from Assam and Meghalaya to eastern Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, and Tripura.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule II
Adopt a Heritage 2.0 Scheme (Indian Express)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Archaeological Survey of India is ready to introduce its new and innovative program called "Adopt a Heritage 2.0.
Facts About:
- This initiative is a joint effort of the Ministry of Tourism in partnership with the Ministry of Culture and the Archaeological Survey of India.
- It was inaugurated on World Tourism Day in September 2017.
- Under this program, the government invites various entities, including public and private sector companies, as well as individuals, to undertake the development of selected historical monuments and tourist sites throughout India.
- The primary goal is to encourage these entities to become 'Monument Mitras' and assume the responsibility of enhancing both basic and advanced tourist facilities at these locations.
- The corporate sector is encouraged to utilize corporate social responsibility (CSR) funds for site maintenance.
- In return, Monument Mitras receive limited visibility on-site and on the official Incredible India website.
US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (Indian Express)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform under the US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
Facts About:
In August 2023, the U.S.-India Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP) was launched under the Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
RETAP was established to take bilateral collaboration further with a result-oriented, time-bound technology focus.
It is intended to advance new and emerging renewable technologies with a view toward deployment and scaling.
RETAP’s initial focus is to be on green/clean hydrogen, wind energy, long long-duration energy storage, and to explore geothermal energy, ocean/tidal energy and other emerging technologies as mutually determined in the future.
The initial work plan is guided by the following five themes:
- Research & Development
- Piloting & Testing of Innovative Technologies
- Advanced Training & Skill Development
- Policy and Planning for Advancing RET and Enabling Technologies
- Investment, Incubation and Outreach programmes
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1940523
Cauvery Water dispute (Indian Express)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Cauvery Water Authority fixes quantum to be released by Karnataka.
Facts About:
- The current outflow rate into the river is 4,398 cubic feet per second (cusecs), whereas the inflow stands at 2,300 cusecs as of Wednesday.
- The outflow rate was 2,292 cusecs on Tuesday at 8 p.m. but was increased after 11 p.m.
- The Kabini Reservoir in Mysuru district also contributes to the outflow, currently standing at 2,000 cusecs.
- Cumulatively, both reservoirs will release around 6,398 cusecs of water.
Cauvery Water Sharing Dispute: Historical Background
- 1892 Onset: The water dispute originates from 1892 between British-ruled Madras Presidency and the princely state of Mysore (now Karnataka).
- 1924 Agreement: A 50-year agreement mediated by the British aimed to ease tensions but set the stage for future conflicts.
- Post-Independence Battles: Karnataka’s dam constructions in the 1960s-80s triggered Tamil Nadu’s Supreme Court appeal, leading to the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT).
- Interim Measures: The Cauvery River Authority (CRA) implemented interim orders in 1998. Contentious issues persisted despite CWDT’s 2013 award.
- Final Award: CWDT’s 2013 award allocated water quantities for Tamil Nadu (419 TMC), Karnataka (270 TMC), Kerala (30 TMC), and Puducherry (7 TMC).
Water Sharing Criteria
- Monthly Schedule: Karnataka, the upper riparian state, must provide Tamil Nadu a specified monthly water quantity.
- Annual Allocation: In a “normal” year, Karnataka provides 177.25 TMC to Tamil Nadu, with 123.14 TMC during the southwest monsoon.
- Challenges: Monsoon disagreements arise due to varying rainfall during this period.
Constitutional Provisions for Water Sharing
- Article 262: Empowers Parliament to address inter-State river disputes; IRWD Act, 1956 enacted under this article.
- Seventh Schedule: Defines legislative authority over water resources in Entry 17 (State List) and Entry 56 (Union List).
Resolving Cauvery Water Sharing
(A) Supreme Court’s 2018 Verdict:
- Cauvery as National Asset: The Supreme Court declared Cauvery a “national asset,” upholding inter-State river water equality.
- Allocation Adjustments: The Court noted deficiencies in CWDT’s assessment, resulting in marginal relief for Karnataka and reduced allocation for Tamil Nadu.
- Formation of CMB: The Court directed the establishment of the Cauvery Management Board (CMB) for effective implementation.
(B) Cauvery Water Management Scheme:
- CWMA Establishment: Formed to regulate water releases with CWRC’s assistance.
- Permanent and Technical Bodies: CWMA oversees regulation, while CWRC ensures data collection and award implementation.
Current Status and Future Implications:
- Ongoing Challenge: The Cauvery water dispute remains a historical and legal challenge.
- Resource Management: CWMA and CWRC aim to address the dispute through effective water management.
- Continued Struggle: The dispute underscores the complexity of water sharing in a federal system and the need for equitable solutions.
Tamil Nadu’s Contention
- CWMA’s Decision: CWMA sought 10,000 cusecs for 15 days from Karnataka, but Karnataka proposed 8,000 cusecs up to August 22.
- Previous Agreement: Karnataka’s refusal to adhere to the earlier agreement of 15,000 cusecs for 15 days at the CWRC meeting angered Tamil Nadu.
- Distress-sharing Formula: Tamil Nadu supports distress-sharing, but Karnataka hasn’t embraced it.
Karnataka’s Perspective
- Rainfall Deficit: Karnataka claims lower rainfall in Cauvery’s catchment areas, including Kerala, leading to reduced inflow.
- Challenging Situation: Karnataka cites reduced reservoir inflow as the reason for not releasing water this year.
- Lack of Consistency: Despite endorsing distress-sharing, Karnataka declined to accept the formula.
Future Scenario
- Tamil Nadu’s Concerns: Mettur reservoir’s critically low storage affects farmers and upcoming kuruvai crop.
- Water Shortage: Current water availability may last only 10 days, considering dead storage and drinking water needs.
- Awaiting Supreme Court: The case’s outcome depends on the Supreme Court’s interpretation and decision.
- Need for Resolution: The need for a mutually acceptable distress-sharing formula is evident.
Ongoing Challenges and Factors Prolonging the Dispute:
- Erratic Water Levels: Flood-drought cycles, pollution, and groundwater depletion cause unpredictable water levels.
- Idealistic Calculations: SC’s verdict relies on favorable conditions often misaligned with reality.
- Dependency and Population: Both states heavily rely on the river, causing conflicting urban and agricultural water needs.
- Inefficient Water Use: Inefficient irrigation methods lead to low crop productivity per unit of water used.
- Hydropolitics and Delays: Water disputes are used for political mobilization. Prolonged tribunal processes contribute to delays.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/bangalore/cauvery-water-dispute-siddaramaiah-says-tn-causing-unnecessary-nuisance-8934747/
Seethakali folk art (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 20-member group is going to perform Seethakali folk art, outside Kerala for the first time as to revive one of the fading dance forms of Kerala.
Facts About:
- In the early times, Seethakali was performed as part of the harvest festival Onam.
- From Atham star till the 28th day after Onam, the performers who belong to the subaltern communities go from one house to another performing this art.
Key Features of Seethakali:
- Folk Dance Drama: Seethakali is a traditional folk dance drama that was once performed during the festival days in erstwhile Desinganad (Kollam, Kerala), primarily during the Onam festivities.
- Dalit Artists: The performance was carried out by Dalit artists belonging to the Veda and Pulaya communities, focusing on presenting episodes from the Ramayana from Sita’s perspective.
- Vanayatra to Andardhanam: Seethakali portrays the journey from “vanayatra” (exile to the forest) to “andardhanam” (descend into the earth) of Sita, featuring a blend of songs, storytelling, and fast movements.
- Instruments: The dance drama is accompanied by instruments such as ganjira, manikatta, chiratta, and kaimani.
- Narrative through Songs: Seethakali’s story is conveyed through songs, with 28 collected over three years, featuring a folk style influenced by Vallappaattu, Kuthirappaattu, and Rakshasappattu.
- Oral Tradition: Seethakali songs were orally transmitted from one generation to the next, which led to a pause in the tradition.
- Basic Movements: The dance involves basic steps, striving to preserve the original essence of the art form.
- Character Ensemble: The performance includes key characters such as Sita, Ram, Lakshman, Ravan, and Hanuman.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/artistes-breathe-a-new-life-into-seethakali-folk-art/article67234768.ece
RIGHT TO REPAIR (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In recent years, several states in the U.S. have enacted ‘right to repair’ laws.
Facts About:
- It refers to government measures that forbid manufacturers to impose barriers that deny consumers the ability to repair consumer products.
- The sectors identified for the right to repair include farming equipment, mobile phones/tablets, consumer durables, and automobiles/automobile equipment.
- Government has launched a unified portal, https://righttorepairindia.gov.in, to onboard leading brands and reliable third-party technicians to provide easy access to overhauling services.
- The portal has on boarded leading brands such as Apple, Samsung, Honda, Kent RO Systems, Havells, Hewlett Packard, and Hero MotoCorp.
- The portal seeks to streamline trade between original equipment manufacturers and third-party sellers.
- The right to repair has been recognized in many countries across the globe, including the USA, UK, and European Union.
Significance of Right to repair for India:
- Lowering costs for consumers: By providing access to third-party technicians, the right to repair can reduce costs for consumers who may not be able to afford expensive repairs or replacement devices.
- Reducing electronic waste: India is one of the largest generators of electronic waste in the world, and the right to repair can help reduce e-waste by extending the lifespan of electronic devices and appliances.
- Supporting small businesses: The right to repair can also support small businesses that provide repair services, by creating a level playing field with manufacturers who may have previously had a monopoly on repairs.
- Empowering consumers: By giving consumers the ability to repair their own devices or choose where to have them repaired, the right to repair empowers consumers to make informed choices and take control of their own devices.
- Promoting transparency and collaboration: The right to repair framework aims to build a consumer-centric ecosystem that promotes transparency and collaboration between manufacturers, sellers, and consumers.
Challenges associated with implementing right to repair in India
- Limited Access to Information: Many manufacturers do not provide adequate information to consumers about repair options or how to repair devices, which can make it difficult for consumers to exercise their right to repair.
- Lack of Awareness: Consumers lack awareness about their rights to repair and the benefits of repairing their devices leading to a lack of demand for repair services, limiting the growth of the repair industry.
- Opposition from manufacturers: Some manufacturers may oppose the right to repair, arguing that it could compromise their intellectual property rights or lead to safety concerns making it difficult to pass legislation or regulations to support the right to repair.
- Limited availability of spare parts: The availability of spare parts is often limited in India, particularly for older or less common models of devices makes it difficult for repair technicians to perform repairs or for consumers to find reliable repair services.
- Lack of regulatory mechanism: Currently, there is no comprehensive regulation in India that governs the right to repair which can lead to confusion among consumers and repair technicians about their rights and responsibilities, and may limit the growth of the repair industry.
Way Forward:
Many countries around the world have been attempting to pass effective ‘right to repair’ laws. But the movement has faced tremendous resistance from tech giants such as Apple and Microsoft over the years.
The New York legislation is a reminder that it is time to not only acknowledge the right to repair of consumers but also respond to the corresponding rights of the manufacturers. This warrants some expedited policy changes to recognise the ‘right to repair’, be it through amendments in the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 or through a separate law.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-the-right-to-repair-movement-7400287/
G20 ministers agree to map global value chains, link MSMEs (Indian Express)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations agreed recently to map global value chains, integrate small businesses with them and ease trade documentation.
Facts About:
What are important parts of outcome document from Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations?
- Comprehensive framework within the G20 context for the purpose of mapping out global value chains is suggested.
The objective is to comprehend the existing issues and identify the necessary actions to enhance the inclusivity, sustainability, and resilience of these value chains.
- It focuses on MSMEs. The declaration from Jaipur emphasizes the imperative of reinforcing the capabilities of MSMEs.
Due to their small scale, MSMEs face limitations in accessing critical information, financial resources, and market-related data points.
A worldwide trade assistance platform, overseen by theInternational Trade Centre, will be consistently upgraded through consultation with UNCTAD and the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
This evolution aims to make the platform more inclusive and to offer comprehensive data to MSMEs.
- The principles associated with the digitization of trade documents is important part of outcome document. The aim is to minimize the reliance on paper documents and remove obstacles that hinder the seamless movement of goods and services.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/g20-trade-meet-ends-ministers-priority-areas-value-chains-msmes-8909647/
National Medical Commission (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has put on hold the regulations that make it mandatory for doctors to prescribe generic drugs.
Facts About:
- In light of the criticism received by the Indian Medical Association (IMA) as well as the as the Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance (IPA), the National Medical Commission put on hold the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023.
- Even the country’s apex drug regulator, the Central Drugs Standard Drug Control Organisation (CDSCO), questioned the language in the notification.
- The participating bodies suggested that the guidelines be kept in abeyance until the WHO’s good manufacturing practices are implemented.
- The participants said that prescribing only generic drugs will prompt pharmacies to sell generic drugs at high-profit margins, disincentivising firms that manufacture quality branded generics
National Medical Commission:
- The National Medical Commission is a statutory body established under the National Medical Commission Act, 2019.
- The NMC replaced the erstwhile Medical Council of India (MCI) which was established in 1934.
Objectives of NMC –
- Improve access to quality and affordable medical education;
- Ensure availability of adequate and high-quality medical professionals in all parts of the country;
- Promote equitable and universal healthcare that encourages community health perspective and makes services of medical professionals accessible to all the citizens;
- Encourages medical professionals to adopt latest medical research in their work and to contribute to research;
- Objectively assess medical institutions periodically in a transparent manner;
- Maintain a medical register for India;
- Enforce high ethical standards in all aspects of medical services;
- Have an effective grievance redressal mechanism.
Composition of NMC –
- NMC is a 25-member body, majority of them being nominated by the Central government.
- Tenure of NMC members is four years (except for part-time members whose tenure is two years).
- The NMC has 11 part-time members representing states or state medical councils.
- The NMC chairpersons and other members, nominated by the Central government, cannot be renominated.
- Any decision requires approval of the majority (minimum 13 out of 25) of the Commission.
Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023:
- On August 2nd, the National Medical Commission had published the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023 aimed at reshaping prescription practices.
- It mandated that registered medical practitioners prescribe medications using “generic”, “non-proprietary”, or “pharmacological” names.
- The guidelines define a generic drug as a “drug product that is comparable to brand/reference listed product in dosage form, strength, route of administration, quality and performance characteristics, and intended use.”
- It says branded generic drug is one which has come off patent and is manufactured by drug companies and sold under different companies’ brand names.
- The guidelines say, “Every RMP (Registered Medical Practitioner) should prescribe drugs using generic names written legibly and prescribe drugs rationally, avoiding unnecessary medications and irrational fixed-dose combination tablets.”
- The guidelines have also talked about punitive measures against those violating the directive.
- Besides the instructions on generic drugs, the NMC guidelines included directives on issues ranging from continued medical education, usage of social media platforms and maintaining a dynamic register of doctors.
- It also barred doctors from attending events sponsored by pharmaceutical companies.
- However, the NMC guidelines have not gone down well with the Indian Medical Association (IMA).
Issued Raised by the Indian Medical Association (IMA):
- The IMA issued a statement in response to the regulations introduced by the NMC.
- The IMA says the biggest impediment to generic drugs is the uncertainty about its quality.
- IMA said that the quality control in the nation being very weak, there’s practically no guarantee of the quality of drugs and prescribing drugs without assured quality would be detrimental to patient health.
- The statement added that less than 0.1% of the drugs manufactured in India are tested for quality.
- The IMA said that step should be deferred till the Government can assure the quality of all the drugs released into the market.
- The statement says patient care and safety are not negotiable.
- The IMA says it has been demanding for long that only good quality drugs should be made available in the country and prices should be uniform and affordable.
- It urges the Government to have ‘one drug, one quality, one price’ system whereby all brands should either be sold at the same price or banned and only generics allowed while ensuring highest quality of these drugs.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/nmc-hold-regulations-mandating-doctors-prescribe-generic-drugs-bar-them-endorsing-drug-brand-8907964/
Gene-Edited Mustard (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Indian scientists have developed the first ever low-pungent mustard that is pest and disease-resistant. It is based on CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing.
Facts About:
- Among India’s domestically grown oilseeds, rapeseed-mustard stands out.
- However, its pungent oil and unpalatable meal have posed challenges for both consumers and livestock.
- Scientists have undertaken breeding efforts to create Canola-quality (white) mustard with reduced pungency and improved meal quality.
About Rapeseed-Mustard
- Rapeseed-Mustard: India’s significant oilseed is rapeseed-mustard, contributing significantly to vegetable oil production and meal availability.
- Pungency: Mustard seeds contain glucosinolates, compounds that give the oil and meal their pungent flavor and odor.
Quest for Canola-Quality Mustard
- Canola-Quality Pursuit: Scientists aimed to breed mustard lines with low glucosinolate content similar to Canola.
- Reducing Pungency: Efforts to create low-pungency oil and meal have faced challenges due to the necessity of glucosinolates in plant defense.
- Vulnerability to Pests and Diseases: Canola-quality mustard lines have not been cultivated extensively due to their susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Role of Gene Editing
- Innovative Research: Gene editing emerges as a solution to balance glucosinolate levels for improved quality and plant defence.
- CRISPR/Cas9 Approach: Researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing tool to target and modify 10 out of 12 GTR genes in Indian mustard.
- Achieving Desired Changes: Editing GTR genes led to lower glucosinolate content in seeds while preserving higher levels in leaves and pod walls.
Benefits of GE Mustard
- Easy Synthesis: Glucosinolates are synthesized in mustard leaves and pod walls before translocation to seeds.
- Dual Benefit of Glucosinolates: The study revealed that edited mustard lines with low-seed glucosinolates exhibited improved defence against pests and diseases.
Distinction between GE and GM
- GE Mustard: The new mustard lines are genome-edited (GE), not genetically modified (GM).
- Transgene-Free Solution: Unlike GM crops with foreign genes, GE lines have no foreign DNA and no residual gene-editing tools.
Regulatory Considerations and Future Prospects
- Regulation Changes: India’s regulatory environment is shifting, exempting GE plants free of exogenous introduced DNA from stringent approval requirements.
- Potential Field Trials: Scientists are preparing for open field trials of GE mustard, with expectations to conduct them in the upcoming planting season.
- Importance of Self-Reliance: With massive edible oil imports, domestic oilseed production through breeding advancements like GE mustard becomes vital for self-reliance.
Economic Implications and Self-Sufficiency
- Importance of Oilseeds: India’s substantial edible oil imports highlight the need for boosting domestic oilseed production.
- Mustard’s Role: Mustard’s high oil content and protein-rich meal position it as a significant oilseed crop.
- Potential Benefits: Both GE mustard and GM hybrid mustard have the potential to reduce dependence on imported vegetable oils.
Conclusion
- The journey of rapeseed mustard from its pungent state to a potentially improved, self-sufficient crop demonstrates the power of innovative breeding techniques.
- The breakthrough in gene editing opens doors to balancing quality and plant defence.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/gene-edited-mustard-less-pungent-more-useful-8901549/
Fujiwhara Effect (Indian Express)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, powerful winds tormented the Bay Area and other parts of Central and Southern California, uprooting trees and disrupting the power supply due to Fujiwhara effect.
Facts About:
- It was identified by a Japanese meteorologist Sakuhei Fujiwhara.
- It was observed for the first time over the western Pacific Ocean, when typhoons Marie and Kathy merged in 1964.
What is it?
- When two hurricanes (or cyclones, depending on where you live), spinning in the same direction, are brought close together, they begin ‘an intense dance around their common center’ – this interaction between two cyclones is called the Fujiwhara effect.
When it Occur?
- If one hurricane’s intensity overpowers the other, then the smaller one will orbit it and eventually crash into its vortex to be absorbed.
- On the other hand, if two storms of similar strengths pass by each other, they may gravitate towards each other until they reach a common center and merge, or merely spin each other around for a while before shooting off on their own paths.
- In rare instances, the two ‘dancing’ cyclones, if they are intense enough, may merge with one another, leading to the formation of a mega cyclone capable of wreaking havoc along coastlines.
Experts have noted the rising frequency of this unusual effect, attributing it to a rapidly warming world and the subsequent heating of ocean waters.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwia1b_gj6OBAxXpSmwGHVb_DTQQFnoECBUQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Findianexpress.com%2Farticle%2Fexplained%2Fexplained-climate%2Ffujiwhara-effect-cyclones-dance-8905398%2F&usg=AOvVaw0_moE3dRI3IZbhz8XqmBkl&opi=89978449
Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap (Indian Express)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a new report ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’, was published by the anti-debt campaigners Debt Justice and partners.
Facts About:
Key Takeaways from ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’ report:
- Debt-Reliant Economies and Fossil Fuel Dependence:Poor countries burdened with heavy debts are compelled to rely on fossil fuel revenue to repay loans borrowed from wealthier nations, multilateral creditors like the World Bank and IMF, or private lenders.
For Example: Argentina has been supporting fracking projects in the Vaca Muerta oil and gas field in Northern Patagonia to generate revenues to ease the country’s debt crisis. Notably, the IMF has also backed these projects.
- Surging External Debt Payments in Global South:The external debt payments of Global South countries have surged by 150% between 2011 and 2023, reaching the highest levels in 25 years.
- Debt Crisis and Constrained Public Spending:Around 54 countries are facing a debt crisis, resulting in reduced public spending during the pandemic to meet loan repayment obligations.
- Climate Challenges Amplify Borrowing in Global South:Many of these indebted countries lack adequate resources for climate adaptation, mitigation, and addressing loss and damage, forcing them to borrow more money.
- Natural Disasters Escalate Debt-to-GDP Ratio:After events like natural disasters, countries can see their debt as a percentage of GDP rise significantly, such as Dominica’s experience after Hurricane Maria in 2017.
- Unfulfilled Pledges: Despite promises to discontinue investing in fossil fuels in Global South countries, richer nations and lenders continue to finance fossil fuel projects through loans, perpetuating fossil fuel production.
- Resource Backed Loans (RBLs):Resource backed loans (RBLs) are a mechanism through which repayment is tied to natural resources or future income streams derived from those resources.
Recommendations for a Sustainable Path Forward:
- Implementing ambitious debt cancellation for countries in need without economic conditions
- Rejecting repayments from fossil fuel projects.
- Aligning bilateral and multilateral finance with a 1.5-degree warming scenario while avoiding fossil fuel financing.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/rich-countries-force-poor-nations-rely-fossil-fuels-8904371/
ICMR study on post COVID mortality (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) study reported that 17.1% of those hospitalized since September 2020 experience post-Covid conditions.
Facts About:
What were the main findings of the ICMR study?
- The study, encompassing 14,419 Covid-19 patients hospitalized since September 2020, revealed a 6.5% mortality rate within a year after hospitalization. Around 17.1% experienced post-Covid-19 conditions. It also highlighted the increased mortality risk associated with comorbidities, age, and gender.
How did the study define “post-Covid-19 conditions”?
- The study defined “post-Covid-19 conditions” as the persistence or new onset of fatigue, breathlessness, or cognitive abnormalities, due to the lack of established definitions from organizations like the World Health Organization or the CDC during patient enrollment.
What impact did a single vaccine dose have on mortality?
- The study indicated that a single vaccine dose prior to Covid-19 infection reduced one-year mortality by 60%, emphasizing the importance of vaccination even before exposure.
Who faced a higher risk of mortality according to the study?
- The study revealed that individuals with comorbid conditions were at the highest risk of mortality, being more than 9 times likely to die within a year. Men were 1.3 times more likely to die, while those above 60 years were 2.6 times more likely.
What risk did children face in terms of mortality?
- Children between 0 and 18 years had a 5.6-fold higher risk of death in the year following infection, with a 1.7-fold increase in the immediate four weeks post-hospitalization. Severe comorbidities among admitted children were hypothesized as a reason for the higher odds of death.
Can mild Covid-19 variants lead to long Covid?
- The long Covid might occur even in individuals with mild Covid-19. While symptoms improve with therapy, over-diagnosis of long Covid may be occurring, warranting consideration of alternative causes for reported symptoms.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/explained-the-debate-over-indias-smartphone-manufacturing-dreams/article67220769.ece
Marine Heat Waves (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Extreme Heat waves are harming marine life in the Mediterranean Sea.
Facts About:
Why are high sea temperatures a problem?
- Lesser dissolution of gases: Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolve better at colder temperatures, so that means the warmer the water; the less oxygen is available to breathe.
- Higher rate of respiration in marine organism: Higher temperatures also cause an increase in metabolism, which in turn means animals have to breathe even more than usual.
- The rise in temperature accelerates metabolism, and the organisms need more food to maintain this metabolic rate.
- More Algal blooms: They are more common in hotter waters. Such blooms can further deplete oxygen levels and produce toxins harmful for fish, marine mammals and birds.
What species and ecosystems are worst hit by marine heat waves?
- High water temperatures are most harmful for animals living at the bottom of oceans, lakes or rivers.
- These benthic species include corals, mussels, sponges, starfish and plants like sea grasses, and are often attached to rock or solid ground.
- Scientists observed mass deaths of benthic species along thousands of kilometers of Mediterranean coastline between 2015 and 2019.
What does extreme heat in the Mediterranean mean for people?
- Affecting fishing activities in the area: Fishermen are catching fewer familiar species and instead are finding more invasive fish which they have difficulty selling.
- Increase in invasive fishes: Some are even poisonous, like the puffer fish migration is seen in the region.
- Habitat loss: It could also lead to an overall decline in fish populations, while disappearing seagrass.
What is the phenomenon behind heat trap in oceans?
- Ocean Heat Content (OHC): It is the amount of energy absorbed by and stored in the oceans. It is measured in joules.
- When sunlight reaches the earth, oceans absorb this energy and store it as heat.
- While the heat is first absorbed at the surface of the water body, some of it is eventually disbursed throughout.
- Water has a higher heat capacity than air, which means that it can store much larger amounts of heat.
- GHG emissions - These gases trap heat in a blanket around the earth, not allowing it to escape, thus raising the temperature of the earth’s surface and leading to global warming.
Why Mediterranean Sea is significant for global temperatures?
The Mediterranean Sea has significant implications for global temperatures due to its role as a "climate amplifier." This phenomenon is referred to as the "Mediterranean Effect" or "Mediterranean Climate Amplification." Here are the reasons:
- Heat Absorption and Release: The Mediterranean Sea has a lower heat capacity compared to the vast oceans, such as the Atlantic or Pacific.
- As a result, it heats up and cools down more quickly. During the summer months, the Mediterranean Sea absorbs heat from the sun, leading to warming of the surrounding land areas.
- In winter, it releases the stored heat, moderating temperatures in nearby regions.
- Warm and Dry Summers: The Mediterranean region experiences warm and dry summers, which are conducive to high evaporation rates from the sea's surface.
- This process results in the release of latent heat into the atmosphere, contributing to the warming of the air.
- Atmospheric Circulation: The temperature contrast between the relatively warm Mediterranean Sea and the cooler landmasses during summer leads to the development of low-pressure systems over land.
- This creates a pressure gradient that drives winds from the sea to the land, bringing warm, moist air with it. This warm air can further increase temperatures over land areas.
- Feedback Loops: The warming effect of the Mediterranean Sea can lead to feedback loops. Warmer land areas result in higher evaporation rates, which in turn contribute to the amplification of temperature rise.
- This cycle of heat absorption, release, and evaporation intensifies the Mediterranean Climate Amplification.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/extreme-heatwaves-mediterranean-sea-8901948/
Vegetated Canopies (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In a recent development in Spain, tensioned sail-like vegetated awnings or canopies known as “Greenshades” have been strategically installed on the facades of buildings.
Facts About:
- Vegetated canopies are innovative structures designed to reintroduce greenery into urban landscapes.
- Inspired by the natural canopies found in forests and diverse plant ecosystems, these canopies play a crucial role in mitigating the urban heat island effect and enhancing the overall environmental quality of urban areas.
- This installation approach not only adds an aesthetic dimension to the urban architecture but also serves as a practical solution for reintroducing green elements in areas where traditional planting is challenging.
Emulating Nature’s Canopies:
- Mimicking the canopy formations observed in forest ecosystems, these vegetated awnings recreate a semblance of natural green cover.
- By doing so, they provide shade, reduce direct sunlight exposure, and create a more pleasant atmosphere in commercial streets and public spaces.
- This is particularly valuable in areas where the presence of trees and vegetation is limited.
Hydroponic Growth System:
- The vegetation integrated within these awnings grows using a hydroponic growth system.
- This method utilises a water supply point to provide the plants with the necessary moisture and nutrients. Additionally, a water outlet is incorporated into the design to facilitate efficient drainage.
- This innovative approach ensures that the greenery thrives even in non-traditional planting environments.
BENEFITS OF VEGETATED CANOPIES
Cooling Effects via Evapotranspiration
- Singular Green’s innovative canopy design efficiently reduces temperatures in both immediate areas and beneath the awnings.
- Achieved through evapotranspiration, where plants transfer water to the atmosphere, this cooling process enhances comfort.
Air Quality Improvement through Plant Selection
- Carefully chosen plants possess a special ability to absorb gases, including pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide.
- This contributes to better urban air quality and healthier living conditions.
Noise Reduction with Sound Wave Absorption
- Vegetated canopies excel at absorbing sound waves, minimising noise pollution and creating a more serene urban environment.
- Incorporating sound-absorbing substrates enhances the auditory experience.
Oxygen Generation and Gas Filtration
- Surprisingly, a single square metre of these canopies produces a year’s worth of oxygen for an individual.
- Moreover, they serve as natural filters, removing harmful gases from the air and thus improving overall air quality.
Efficient Water and Lighting Integration
- Beyond their green benefits, these canopies facilitate centralised water and lighting installations.
- Integrated lights equipped with motion sensors respond to real-time needs, promoting energy-efficient urban infrastructure.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
- Introducing these canopies into urban spaces fosters biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse wildlife.
- This initiative aligns with the vision of sustainable, nature-friendly cities, nurturing a harmonious urban ecosystem.
In the face of climate change-induced challenges, our response must be proactive, multifaceted, and holistic. The success of vegetated canopies as a means to combat extreme heat waves demonstrates that nature-inspired solutions have the power to transform urban environments into havens of sustainability, resilience, and well-being. By embracing such strategies and embarking on a collective journey, we can build cities that thrive in harmony with the planet.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/vegetated-canopies-green-spaces-urban-spain-8893918/
Expansion of BRICS (Indian Express)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently there have been internal conflicts about the nature and scope of the potential expansion of BRICS.
Facts About:
- BRICS is an acronym for five regional economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- The first four were initially grouped as “BRIC” in 2001 by an economist Jim O’Neill, who coined the term to describe fast-growing economies that would collectively dominate the global economy by 2050.
- Summits: The governments of the BRICS states have met annually at formal summits since 2009.
- India hosted the 13th BRICS summit in 2021 virtually.
- China hosted the 14th BRICS summit in 2022.
- South Africa will host the 15th summit 2023.
- BRICS is an important grouping bringing together the major emerging economies from the world, comprising:
- 41% of the world population,
- 24% of the world GDP
- Over 16% share in world trade.
- Total combined area of 29.3% of the total land surface of the world
- Over a period of time, BRICS countries have come together to deliberate on important issues under the three pillars of:
- political and security,
- economic and financial and
- Cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
- New Development Bank and BRICS: Formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states.
- The Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments.
The need for BRICS expansion
- Economic strength: The economic strength of the five members of the grouping is not as promising as it was when the platform was first announced in 2009.
- Though the BRICS nations certainly represent 43% of the world’s population and around 30% of the global economy, their economic weaknesses are certain.
- China’s anti-western orientation: China is focused on a quick expansion of BRICS with the aim of giving the platform a distinctly anti-western orientation.
- Prevailing Anti-Western sentiment: Many realize that the doors of other groupings are closed to them.
- The clamour reflects prevailing anti-western sentiments and a pervasive desire to create a sizeable forum of the Global South.
- Global challenges: Russia is being marginalised in the global economy, while China is facing a difficult economic environment with the west turning against it.
Challenges with expanding BRICS grouping:
- An increase in membership is likely to weigh the group in favour of Chinabecause some countries waiting to join are also part of the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative.
- This raise concerns that an expanded BRICS could be seen as a Chinese-led anti-American bloc.
- India, which has been strengthening its bilateral relationship with the US, has been concerned about expansion.
- India views China’s role in driving these countries for membership of BRICS along with the support of Russia.
- India also raised its concern in last year’s BRICS that any addition of new members must follow the carefully thought-out objective criteria for membership.
- This should be mutually discussed among the present members, so that all are of the same view regarding expansion.
- Further, at the BRICS foreign ministers’ meeting last month, India’s External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar emphasized the need to consider the ways in which existing BRICS countries collaborate with each other and engages with non-BRICS countries.
Way Forward:
The 15th BRICS summit holds multifaceted importance for India, offering a platform for addressing geopolitical concerns, facilitating bilateral talks, and advancing economic collaborations. As the global landscape continues to evolve, BRICS remains a critical forum for emerging economies to engage and collaborate on key global challenges. The outcomes of this summit will not only affect the member nations but also shape the broader trajectory of international relations and cooperation.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/brics-expansion-significance-for-india-8907925/
RBI allows switch from ‘floating to fixed rate’ regime (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) asked all regulated entities (REs), including banks and NBFCs, to give personal loan borrowers an option to switch over from a floating rate to a fixed rate regime at the time of resetting interest rates.
Facts About:
- When a customer takes a loan, the interest rate reset clause in the loan agreement allows the lender to review the interest rate after a certain period, as per the occurrence of a scheduled reset date of the loan.
- The reset rate is the new interest rate that a borrower must pay effective from the scheduled reset date.
- EMI of a floating rate loan changes with periodical changes in reset interest rates.
- These rates and the calculation are not uniform for all the banks as the cost of funds differs from banks.
Changes made by RBI:
The RBI asked banks to implement the following regulations:
- For Regulated entities (RE) :
- At the time of sanction, REs will have to clearly communicate to the borrowers about the possible impact of a change in benchmark interest rate on the loan leading to changes in EMI and/or tenor or both.
- Any increase in the EMI/ tenor or both will have to be communicated to the borrower immediately through appropriate channels.
- At the time of reset of interest rates, REs will have to give the option to borrowers to switch over to a fixed rate as per their board-approved policy.
- The policy will also specify the number of times a borrower will be allowed to switch during the tenor of the loan.
- REs will have to disclose all applicable charges for switching loans from floating to fixed rate and any other service charges/ administrative costs in the sanction letter and also at the time of revision of charges or costs from time to time.
- For EMI or Elongation of tenor:
- The borrowers will also be given the choice to opt for enhancement in EMI or elongation of tenor or for a combination of both options, and to prepay, either in part or in full, at any point during the tenor of the loan, with foreclosure charges.
- The RBI said REs will have to ensure that these instructions are extended to the existing as well as new loans by December 31, 2023.
Why has RBI issued new regulations?
- RBI's Supervisory Reviews: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has conducted supervisory reviews and received feedback from the public.
- Unreasonable Tenor Elongation: Instances of banks significantly extending tenors of floating rate loans without proper borrower consent and communication have been identified.
- Interest Rate Changes: Banks can alter interest rates by adjusting the internal benchmark rate and spread during the loan term, potentially harming borrowers' interests and monetary transmission.
- Arbitrary EMI Resets: Borrowers complain of banks arbitrarily resetting Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) and extending tenors without adequate notification.
- Hidden Foreclosure Charges: Borrowers are often unaware of foreclosure charges, adding to borrower dissatisfaction.
- Stress Concealment: RBI notes that prolonged tenor elongation may obscure underlying stress in banks' financial health.
- Refinancing Challenges: While theoretically possible, refinancing floating rate loans across different banks with distinct internal benchmarks is complex due to varying benchmark adjustment methods.
- Limited Borrower Options: Borrowers might feel compelled to stay with their original bank, paying higher charges, as refinancing is often impractical due to benchmark disparities.
Possible impacts:
- Interest rate of borrowers: Banks can change the interest rate by changing the internal benchmark rate and the spread during the term of the loan which could harm the interest of the borrower and also impair monetary transmission.
Benefits of Fixed rate regime:
- For borrowers:
- Protection from Rate Hikes: Shifting to a fixed rate provides protection against potential future increases in interest rates. This can be particularly beneficial if interest rates are expected to rise in the near future.
- Budgeting and Financial Planning: Fixed payments make it easier for borrowers to budget and plan their finances since they know exactly how much they need to allocate for their loan payments.
- Potential Cost: Fixed interest rates tend to be initially higher than prevailing floating rates. Borrowers opting for a fixed rate might end up paying more initially compared to what they would have paid with a floating rate if rates remain relatively stable or decrease.
- For lenders:
- Interest Rate Risk Mitigation: Lenders are less exposed to interest rate risks when borrowers opt for fixed rates. They can better manage their own interest rate risk since they know the interest income they'll receive remains constant.
- Lending Profitability: Fixed-rate loans typically come with higher initial interest rates compared to floating-rate loans. This can lead to increased lending profitability for lenders, especially if rates remain stable or decline.
- Potential Lower Loan Demand: Higher initial fixed rates might deter some potential borrowers who are attracted to lower initial payments offered by floating rates.
- Limited Flexibility: Lenders might have less flexibility in adjusting loan terms for borrowers with fixed-rate loans, as the interest rate remains constant regardless of market conditions.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/rbi-fixed-rate-regime-personal-loan-8898445/
Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
New data from the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of World Resources Institute (WRI) has been released.
Facts About:
What does it mean for a country to be exposed to extreme water stress?
- Extreme water stress signifies that a country uses more than 80% of its renewable water supply for activities such as irrigation, livestock, industry, and domestic needs. This reliance makes them vulnerable to water scarcity during periods of drought.
How does the WRI define the term ‘water stress’?
- A region is deemed ‘water stressed’ when the demand for water surpasses the available volume or when water quality limitations restrict its use for various purposes.
Which regions and countries are the most water-stressed according to the report?
- The most water-stressed regions are West Asia, North Africa, and South Asia. Notable water-stressed countries include Bahrain, Cyprus, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, and others.
How is global water demand projected to change by 2050?
- Global water demand is estimated to increase by 20-25% by 2050. Additionally, watersheds facing unpredictable water supplies are expected to rise by 19%. This could result in 100% of West Asia and North Africa’s population facing extreme water stress by 2050.
What are the implications of high water stress beyond immediate concerns?
- The report emphasizes that extreme water stress affects not only consumers and industries but also has far-reaching political implications. Water stress can impact political stability, making it a critical issue to address for global leaders.
What are the economic implications of solving global water challenges?
- According to WRI’s findings, addressing global water challenges would cost around 1% of the global GDP or 29 cents per person per day from 2015 to 2030. Despite the costs, the potential economic benefits and stability improvements make it a worthwhile investment.
Source: https://chinawaterrisk.org/useful-links/aquaduct-water-risk-atlas/
Artificial Intelligence Index 2023 (Indian Express)
- 18 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India ranked fifth in Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based investments according to Stanford University’s annual AI Index report 2023.
Facts About:
- AI Index is an independent project at Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI).
Purpose:
- The annual report compiles, analyzes, and visually presents AI-related data to empower responsible and ethical AI advancements in collaboration with human interests
Global AI Investment Rankings
- United States
- China
- United Kingdom
- Israel
- India
India's Remarkable Growth
- India secured the fifth position in AI investments received by startups worldwide in 2022.
- AI startups in India attracted $3.24 billion in funding, surpassing countries like South Korea, Germany, Canada, and Australia.
Investment Revival amidst Recession
- Despite a global AI investment dip since 2021 due to economic challenges, a resurgence in Venture Capital (VC) funding is anticipated this year.
- Enterprises and consumers' heightened interest in generative AI products like Open AI's ChatGPT is expected to drive this revival.
Global Contribution to LLM Development
- 54% of researchers involved in advancing large language models (LLMs) hail from American institutions.
- Significant progress observed as researchers from Canada, Germany, and India joined the LLM development landscape in the past year.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/artificial-intelligence/key-takeaways-from-stanford-ai-index-report-2023-8539812/
National Medical Commission’s New Guidelines (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to the National Medical Commission’s Registered Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations or NMC RMP Regulations 2023, doctors can now refuse treatment to the unruly and violent patients.
Facts About:
The National Medical Commission Act, 2019:
- It was introduced to address various issues and challenges in the medical field, including improving the quality of medical education, enhancing access to healthcare services, and ensuring ethical and transparent practices.
- Key Provisions include:
- Ethical and Professional Conduct: The Act emphasizes maintaining ethical and professional conduct among medical practitioners and includes provisions to address any deviations from these standards.
- Community Health Providers: The Act introduces the concept of Community Health Providers who are allowed to practice limited medicine in underserved rural areas to address the shortage of doctors.
- Formation of the National Medical Commission (NMC): NMC is an regulatory body which regulates medical education and medical professionals.
- Establishment of Medical Advisory Council.
- Reforms in Medical Education.
Refusing treatment is a complex issue that involves various stakeholders viz. doctors and healthcare professionals, patients and their families, healthcare institutions, medical associations and regulatory bodies, legal authorities, ethics committees, public opinion and media, religious and cultural communities, etc.
Arguments in Favour of the Regulation:
- Unruly Behaviour
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- For example, a 21-year-old patient attacked a doctor with a knife during consultation at Delhi’s Sir Ganga Ram Hospital.
- Dignity and Integrity: Unruly behaviour can sometimes cross ethical boundaries, leading to disrespectful or abusive treatment of healthcare staff. Doctors have a right to work in an environment that respects their dignity and professional integrity.
- For example, a 40-year-old doctor on duty in a hospital in Faridabad was assaulted by attendants of a patient as the doctor was attending to another patient, he could not immediately attend to the patient.
- Brings Deterrence: Allowing unruly behaviour to go unchecked might enable a cycle of disruptive or non-compliant behaviour, which could negatively impact the patient’s overall health outcomes. By refusing treatment, the doctor may communicate that certain standards of behaviour are expected for a therapeutic relationship to proceed.
- Right to Freedom to practise any profession: The regulations give the doctors the right to choose whom they will serve, except in case of a life-threatening emergency.
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- Financial Constraints
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- If a patient cannot afford the treatment, the doctor might argue that proceeding with treatment without full financial transparency could undermine the patient’s autonomy and informed consent.
- In extreme cases, relatives of patients have been known to hold doctors or hospital staff hostage, demanding treatment.
- Professional Boundaries: Some proponents of this perspective argue that doctors have a professional duty to provide medical care and expertise, but they are not obligated to address broader societal issues such as patients’ financial difficulties.
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- Ethical Boundaries: Doctors have ethical responsibilities not only toward their patients but also toward themselves, their families and the healthcare community.
- For example, potential threats and violence have long-lasting impacts which manifests in the degradation of personal and professional relations.
- Objectivity: Taking decisions which are free from subjectivity caused by emotions, perceptions and individual bias is necessary for long term sustainability.
- For example, Free medical care for a desperate patient may be ethical, but providing it to many patients may not be feasible for one provider.
- Selfless Duty: Medical practitioners often prioritize the well-being of their patients above their own comfort, personal time and space. However, the job can be thankless at times.
- For example, During COVID-19 despite their selfless dedication, medical professionals were subjected to regular assaults and verbal abuse throughout the country.
Arguments against the Regulation
- Dedication and the Duty of Care: Dedication is the sense of deep rooted commitment to devote oneself to a cause.. This includes a duty to provide care to those in need, regardless of their financial status.
-
- In India, out-of-pocket health expenditure accounts for more than half of total health expenditure pushing many households into poverty. This shows the dire need for empathy and compassion towards those in need.For example, Dr Ramanand Singh has been treating his patients for just Rs 50 for the past 35 years in Bihar. He even waives off his fees in cases where the patients cannot afford medical treatment.
- Justice and Equity: The principle of justice requires that healthcare be distributed fairly and equitably.Denying treatment to a patient solely based on their inability to pay could be seen as unjust, perpetuating disparities in healthcare access.
- Hippocratic Oath: Physicians pledge to do what is in the best interest of their patients and to avoid causing harm.
- Physicians promise to treat all patients fairly, regardless of their background, and to provide care to the best of their abilities without bias.
- Unholy Nexuses: Many doctors form nexuses with drugmakers to prescribe specific drugs from their brand instead of generic drugs leads to considerable rise in treatment costs for patients.
- For example, freebies given to doctors including travel expenses, gifts etc. by drugmakers is a common practice.Beneficence: It means kindness or generosity and this principle refers to the moral obligation to act in a manner that will benefit others.The principle of beneficence obligates doctors to act in the best interests of their patients and to promote their well-being.
- Compassion: It is the desire to end someone’s suffering which forms the core principle of a medical practitioner. Refusing treatment to individuals on certain grounds could lead to the possibility of crisis of conscience among several practitioners.
- Loss of Trust and Credibility: The medical profession relies on public trust, and denying treatment to those in need could erode that trust and damage the reputation of the medical community.
- Responsibility: Some argue that healthcare professionals have a broader social responsibility to address systemic issues in healthcare, including affordability and access. Refusing treatment might be seen as abdicating this responsibility.
- Undermining Right to Life: Providing a legal caveat for the registered physicians to refuse treatment is against the fundamental right guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Further, there is no specific definition of “abusive” in law as it is purely a subjective interpretation that may depend on the personal opinion of any individual.
- Subjective interpretation may further lead to exclusion on the basis of race, religion, caste, sex etc.
What Should be Done?
- Persuasion: Influencing patients to follow prescribed norms for behaviour and ensuring smooth functioning.
- For example, during COVID-19 pandemic, voice messages were circulated using caller tune to make people aware of the importance of vaccination and prevent attacks on health workers.
- Emotional Intelligence: Equipping and training medical personnel with necessary skills so that they can manage their emotions and try to avoid escalation of situation and providing practical solutions to the given problems.
- Transparent Approaches: Consider alternative approaches before refusing treatment. This might involve social workers, mental health professionals, or conflict resolution experts to address the underlying issues contributing to the unruly behaviour.
- For example, Doctors in San Diego (USA)refer patients to low-cost family health centersthat provide caring, affordable, high-quality health care and supportive services to everyone.
- Ethical Principles Balancing: Weigh the principles of patient autonomy, duty of care, patient safety, and respect for healthcare personnel’s well-being. Consider how refusing treatment aligns with these principles and what potential consequences might arise from the decision.
- For example, Doctors Without Borders is a Nobel Peace Prize receiver charity that provides humanitarian medical care in conflict zones to all those in need of medical care, irrespective of the role played by them in the conflict.
- Tolerance: Accepting actions and practices which may be considered to be incorrect but still tolerable to some extent that they should not be prohibited or penalised heavily.
- For example, a significant number of the cases of unruly behaviour arises in situations which may not be considered as “common” and even the most well-behaved might behave in a way which is not acceptable in society due to the shock or intensity of the moment which one may not be able to handle.
- Consent: Communicating the decision clearly to the patient, and explaining the reasons behind it thus ensuring that the patient understands the potential consequences of their behaviour on their health and the doctor-patient relationship.
- Offering Continuity of Care: If possible, provide recommendations for alternative sources of care, whether within your healthcare institution or elsewhere. Ensure the patient’s ongoing health needs are addressed.
Conclusion
We must protect those who heal. Ethical decisions in healthcare are rarely black and white. It’s important to approach each situation with sensitivity, professionalism, and a commitment to upholding the well-being of patients, healthcare staff, and the broader community. Consulting with colleagues, supervisors, and ethics committees can provide valuable guidance in making these difficult decisions
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/doctors-new-national-medical-commission-guidelines-8890632/#:~:text=The%20guidelines%20say%20that%20doctors,but%20at%20least%20three%20credits.
Urea Gold (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi officially launched Urea Gold fertiliser.
Facts About:
- In a significant development, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled Urea Gold, a novel fertiliser product, created by Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF), a state-owned entity. This pioneering formulation involves enhancing urea with sulphur to address crucial agricultural challenges.
What is Urea Gold?
- Traditional urea primarily consists of 46% nitrogen (N). Urea Gold represents a leap forward by combining 37% nitrogen and 17% sulphur.
- This innovative composition serves two primary purposes: bolstering soil quality and boosting nitrogen utilization efficiency.
Soil Deficiencies Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE)
- Soil Deficiencies in India
- Indian soils suffer from deficiencies, particularly in key nutrients like sulphur (S).
- This deficiency is particularly crucial for certain crops such as oilseeds and pulses, which play a significant role in India’s agricultural output. These crops require adequate sulphur for healthy growth and optimal yield.
- The deficiency in sulphur can hinder their productivity and affect the overall agricultural landscape.
- Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE) Challenge
- NUE refers to the proportion of applied nitrogen fertilisers that is effectively taken up by crops for growth and yield production.
- Only about 35% of the nitrogen from urea, a commonly used fertiliser, is utilized by crops in India.
- The rest, roughly 65%, is lost through various processes, including ammonia volatilisation into the atmosphere and leaching into the ground as nitrate.
Challenges in Urea Consumption in India
- Import Dependency: India heavily relies on imported urea due to insufficient domestic production. Around 7.6 million tonnes of urea were imported out of the total 35.7 million tonnes sold last fiscal year.
- Feedstock Dependency: The feedstock for domestic urea production, natural gas, is predominantly imported. This adds to the overall import dependence for the fertiliser.
- High Consumption: Urea is India’s most widely used fertiliser, with consumption rising from 26.7 million tonnes to 35.7 million tonnes between 2009-10 and 2022-23.
- Environmental Impact: Excessive urea usage contributes to environmental problems such as air and water pollution. Ammonia emissions and nitrate leaching are associated with these environmental challenges.
- Higher Input Costs: Inefficient fertiliser use due to low NUE leads to higher input costs for farmers. They need to apply more fertiliser to achieve desired yields.
Significance of Urea Gold
- Nutrient Enrichment: Urea Gold is a novel fertiliser fortified with sulphur (S). It contains 37% nitrogen (N) and 17% sulphur, addressing soil deficiencies that are critical for crops like oilseeds and pulses.
- Targeted Improvement: The sulphur content in Urea Gold addresses the specific nutrient requirements of oilseeds and pulses, which are crucial components of Indian agriculture and are significantly import-dependent.
- Packaging and Pricing Shift: Urea Gold’s introduction might entail packaging in 40-kg bags, adapting to the preferences of farmers.While exact pricing remains undisclosed, market trends suggest Urea Gold could be priced between Rs 400 to Rs 500 per 40-kg bag.
- Enhanced NUE: The sulphur-coated urea granules in Urea Gold facilitate a controlled and gradual release of nitrogen. This extended nutrient availability improves NUE, leading to reduced fertiliser application frequency and better crop health.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Urea Gold’s dual focus on addressing soil deficiencies and improving NUE contributes to more sustainable agricultural practices. It reduces excessive fertiliser use and associated environmental impact.
- Economic Benefit: The improved NUE offered by Urea Gold has the potential to reduce input costs for farmers, as they can achieve similar or better yields with lower fertiliser quantities.
- Potential Yield Boost: The sustained nitrogen release mechanism of Urea Gold can potentially lead to increased crop yields due to longer periods of vibrant foliage and enhanced nutrient availability.
Potential Hurdles
- Pricing Uncertainty: Lack of clear pricing details for Urea Gold could impact its adoption among farmers.
- Subsidy Disparity: The current additional rates offered by the government may not sufficiently incentivize companies to promote fortified fertilisers like Urea Gold.
- Limited Farmer Incentives: Farmers might perceive fortified fertilisers as more expensive compared to traditional options, leading to reluctance in adoption.
- Distribution Challenges: Ensuring uniform distribution and application of fortified fertilisers presents logistical complexities.
- Regulatory Influence: Regulatory aspects, such as pricing controls and subsidy structures, can affect the feasibility of fortified fertiliser products.
- Awareness Gap: Limited farmer awareness regarding the benefits and correct usage of fortified fertilisers might hinder their willingness to switch.
- Production Scalability: Scaling up fortified fertiliser production to meet demand and ensure availability poses a significant hurdle.
Way Forward
- Price Rationalization: The government could consider revisiting subsidy rates to make fortified fertilisers economically attractive for both companies and farmers. This would encourage the adoption of innovative products like Urea Gold.
- Subsidy Structure: Tailoring subsidies to reflect the enhanced benefits of fortified fertilisers, such as improved NUE and reduced environmental impact, could encourage their adoption.
- Education Campaigns: Launching awareness campaigns about the advantages of fortified fertilisers, like Urea Gold, can educate farmers and dispel misconceptions about their higher costs.
- Field Demonstrations: Organizing on-field demonstrations of the benefits of fortified fertilisers could provide tangible evidence to farmers, boosting their confidence in making the switch.
- Long-Term Perspective: Encouraging farmers to consider the long-term economic and environmental benefits of fortified fertilisers could shift their focus from initial cost concerns.
- Market Diversification: Exploring partnerships with private sector players and agribusinesses to promote fortified fertilisers could enhance market penetration.
- Gradual Transition: Gradually phasing in fortified fertilisers while continuing to offer traditional options at subsidized rates can ease farmers into adopting the new products.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/how-to-make-urea-more-efficient-as-a-fertiliser-and-why-thats-needed-8891183/
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Kerala Legislative Assembly has unanimously adopted a resolution expressing its concern over the Union Government move to impose a Uniform civil code (UCC).
Facts About:
- The Kerala Assembly resolution essentially strikes a cautious note that a proposed “UCC could harm the secular nature of the country. “
- The resolution also talks about federalism – that the Centre could make a unilateral move on the contentious issue without consulting states.
- The resolution also argued that, it is critical to note that the Uniform Civil Code was limited to Directive Principles.
What does Constitution say about UCC?
- The Constitution refers to civil code only in its Directive Principles.
- Implementation of Directive Principles is not mandatory.
- The court may order to enforce Fundamental rights. But the Directive Principles of Article 44 of the Constitution cannot be enforced even by the courts.
Can the state legislate on UCC?
- Article 162 of the Constitution:
- The issue of personal laws falls in List III —the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution.
- While subjects in the Union lists fall within the purview of the Parliament, states can legislate on subjects in the State List.
- For entries in the ‘Concurrent List’, Article 162 of the Constitution gives state governments the power to legislate on subjects where a central law does not occupy the field.
- If there is a central law, it automatically gains precedence over the state law on the subject.
- Entry 5 of Concurrent List:
- Also the Entry 5 of the Concurrent lists “Marriage and divorce; infants and minors; adoption; wills, intestacy and succession; joint family and partition; all matters in respect of which parties in judicial proceedings were immediately before the commencement of this Constitution subject to their personal law.
- This allows states the power to legislate on the subject but only in the absence of a central law.
Do states can bring their own personal laws again?
The answer to it is NO, due to following cases;
- State laws on the issues mentioned in Entry 5 of the Concurrent List will not have precedence over central legislation.
- On specific areas not covered by central legislation, states can legislate.
- But central legislation already covers all aspects of marriage, divorce, inheritance and succession.
Supreme Court’s stand:
- The Court mentioned that Article 162 of the Constitution indicates that the executive power of a State extends to matters with respect to which the Legislature of the State has power to make laws.
- In view of the provisions of Entry 5 of the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule, the constitution of a Committee per se cannot be challenged as ultra vires.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/kerala-assembly-resolution-against-uniform-civil-code-8885558/#:~:text=The%20Kerala%20Legislative%20Assembly%20on,a%20common%20personal%20law%20code.
Bill on Election Commission members’ Appointments (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Bill is set to be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with the view of overturning the effect of the Supreme Court’s (SC) verdict on the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners (ECs).
Facts About:
- The Bill seeks to establish a committee of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM for selecting members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Current Procedure: Currently, the Law Minister suggests a pool of suitable candidates to the Prime Minister for consideration.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the PM.
- As per the Bill, a Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary and comprising two other members, not below the rank of Secretary to the government, having knowledge and experience in matters relating to elections, shall prepare a panel of five persons who can be considered for appointment.
- Then, as per the Bill, a Selection Committee consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister will appoint the CEC and other ECs.
Present structure to appoint CEC and ECs:
- Under Article 324 (2), the President appoints the CEC and other ECs.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.
- The Constitution does not prescribe any qualifications, academic or otherwise, for appointment to these offices.
- Tenure:
- The tenure of office and the conditions of service of all the commissioners is determined by the President.
- The tenure of commissioners is 6 years or up to the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CEC and the two other ECs have the same powers and emoluments, including salaries, which are the same as a Supreme Court judge.
- All three commissioners have the same right of taking a decision. In case of a difference of opinion amongst the three members, the matter is decided by the Commission by a majority.
Process of removal:
- Article 324 of the Constitution of India mentions the provisions to safeguard and ensure the independent and impartial functioning of the Election Commission.
- The CEC is provided with security of tenure. He cannot be removed from his office except in the same manner and on the same grounds as a judge of the Supreme Court.
- Any other election commissioner or a regional commissioner cannot be removed from office except on the recommendation of the CEC.
Supreme Courts’ Judgment:
- On March 2, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court unanimously ruled that a high-power committee consisting of the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India must pick the CEC and ECs.
- The judgement by a bench came in 2015, challenging the constitutional validity of the practice of the Centre-appointed members of the Election Commission.
- According to the judgement, the SC has now given the Opposition and the judiciary a say in the matter, ruling that the CEC and ECs must be appointed by the President on the advice of a committee comprising the PM, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India.
- Also, in 2018, a two-judge bench of the SC referred the case to a larger bench since it required a close examination of Article 324 of the Constitution, which deals with the role of a Chief Election Commissioner.
Debate around appointment of CEC and ECs:
- Article 324(2) reads that “The Election Commission shall consist of the Chief Election Commissioner and such number of other Election Commissioners, if any, as the President may from time-to-time fix and the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners shall, subject to the provisions of any law made in that behalf by Parliament, be made by the President.”
- The Parliament has the power to nullify the effect of a Court ruling by addressing the concerns flagged in the judgment.
- In this case, the arrangement prescribed by the Supreme Court was specifically because the Court noted that there was a “legislative vacuum.” Filling that vacuum is well within the purview of the Parliament.
- However, the idea of an independent body that conducts elections permeates through the judgement.
- The Court repeatedly stated that to be the objective of the framers of the Constitution.
- The composition of the Selection Committee in the Bill raises questions on whether the process is now independent or still rigged in favour of the Executive.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/bill-election-commission-members-appointment-process-explained-8885676/#:~:text=The%20Centre%27s%20Bill%20seeks%20to,Commission%20of%20India%20(ECI).
India takes first step to remove animals from Drug-testing (Indian Express)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an amendment to the New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules (2023) passed by the Government of India, aims to replace the use of animals in research, especially in drug testing.
Facts About:
What is the reason behind shifting to Alternative testing modes?
- The drug development journey involves rigorous testing to assess the efficacy and unintended effects.
- The first step of this process has been to test the candidate molecule in at least two animal species: a rodent (mouse or rat) and a non-rodent, such as canines and primates
- Lack of accuracy: Human response is influenced by factors like genetics and diet, leading to a significant mismatch between animal models and human responses.
- This mismatch contributes to the high failure rate during human clinical trials, highlighting the need for more accurate testing methods.
- Animals cannot consent to their own participation in research.
- Welfare of animals: Critics argue that animal testing can cause suffering and harm to animals. Animals are held in sterile, isolated cages, forced to suffer disease and injury, and typically euthanized at the end of each study.
What are Alternative testing modes?
- Organoids: These technologies encompass three-dimensional cellular structures, known as "organoids" or "mini-organs," which closely replicate the functions of specific body organs at a miniature scale.
- Organ-on-a-chip: The "organ-on-a-chip" technology employs small chips with human cells and microchannels to simulate physiological processes.
- organ-on-a-chip are AA-battery-sized chips lined with human cells connected to microchannels, to mimic blood flow inside the body.
- Additive manufacturing: 3D bioprinters use human cells as 'bio-ink' to build tissues. This could help make personalized drug tests and change how we create drugs.
What are Global regulatory frameworks that have adopted non-animal methods to test the effect and potential side-effects of new drug candidates?
- European Union: In 2021, the European Union adopted a resolution for an action plan promoting non-animal technologies in research, regulatory testing, and education.
- USA: The U.S. passed the FDA Modernization Act 2.0 in December 2022, permitting the use of these methods for drug safety and efficacy testing.
- South Korea: South Korea introduced a Bill for advancing alternatives to animal testing in December 2022.
- Canada: In June 2023, Canada amended its Environmental Protection Act to minimize vertebrate animal use in toxicity testing.
India
- In March 2023, the Indian government incorporated non-animal alternatives for drug testing and development into the drug development process by modifying the New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules 2019.
- This step followed public input and consultation with the Drug Technical Advisory Board, which advises governments on drug-related technical issues at both the Central and State levels.
What are the challenges with these alternate methods?
- Multidisciplinary: Developing an organ-on-a-chip system requires multidisciplinary knowledge in the fields of cell biology, materials science, fluid dynamics, electronics, engineering, and pharmacology/toxicology to accurately replicate organ behavior and assess drug effects.
- At present there is a lack of focused training and expertise in India.
- Dependence of Imports: Most of the reagents, cell-culture related materials, and instruments for these technologies are currently imported from the U.S., Europe, and Japan.
- Managing Complexity: Researchers simplify recreating human tissues in the lab by minimizing components for disease simulation.
- No universal approach due to disease-specific variations; for example, a liver-on-a-chip won't fit all liver diseases.
- Variability arises from differences in lab protocols, expertise, and specific research goals. Regulators express concerns about data consistency due to these variations.
Suggestions
- Establishment of specialized institutes: Recently, a meeting organized by the Centre for Predictive Human Model Systems and Humane Society International India called for the need of specialized institutes similar to the Wyss Institute.
- WyssInsitute in Boston is a dedicated center that focuses on innovations that emulate human biology.
- The dedicated institute will facilitate effective communication and collaboration across various fields.
- Promoting innovation: Developing a comprehensive and self-sustaining ecosystem in India to address this gap in the fields of cell culture, material science, and electronics.
- Guidelines: Urgent need for guidelines establishing minimal quality criteria and standards for these systems.
- Existing guidelines on animal testing requirements need re-evaluation and updating to accommodate advancements in cell-based and gene-editing therapies.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/animal-trials-drug-development-india-amendment-2019-rules/article67019288.ece
ECOWAS and Niger Coup: Challenges and Potential Responses (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Context: Recently there was apprehension of intervention by the ECOWAS( Economic Community of West African States) in Niger following a military coup in the country.
Facts About:
- The recent coup in Niger has brought the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) into the spotlight as it grapples with responding to the political crisis in the region.
- As Niger faces economic hardships and military intervention by regional players looms, the role of ECOWAS is under scrutiny.
Understanding ECOWAS
- Formation and Membership: Established in 1975, ECOWAS aims to foster economic integration among its 15 member countries, including Benin, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Nigeria, and more.
- Objective: The organization envisions a borderless region based on democratic principles and good governance.
- Economic Goals: ECOWAS seeks to create a unified trading bloc, single currency, and enhanced cooperation in sectors such as industry, energy, and telecommunications.
ECOWAS in Conflict Resolution
- Regional Peacekeeping: ECOWAS has played a role in resolving conflicts by deploying peacekeeping missions. Notable examples include ECOMOG’s involvement in Liberia and Sierra Leone during the 1990s and early 2000s.
- Gambia Crisis: In 2017, ECOWAS intervened in Gambia, ensuring the peaceful transfer of power after then-President Yahya Jammeh refused to step down following an election defeat.
- Challenges and Successes: While ECOWAS has effectively resolved conflicts in some cases, it faces challenges due to differing interests among member countries and evolving security threats.
ECOWAS’s Response to Niger Coup
- Potential Military Intervention: ECOWAS has hinted at possible military intervention in Niger. However, regional challenges, including shared borders with other military-led nations, could complicate intervention plans.
- Support for Coups: Some military coups in West Africa have been justified by leaders citing terrorism and security challenges, accusing civilian governments of inadequacy.
- Security Situation: The ECOWAS Commission President reported a significant rise in terrorist attacks in the region, with a substantial death toll and refugees fleeing the violence.
Economic Measures and Sanctions
- Economic Sanctions: ECOWAS has previously imposed economic sanctions on countries undergoing political turmoil. However, the efficacy of these measures is questionable, especially when nations are grappling with economic difficulties.
- France’s Role: France’s historical ties to Niger and the presence of foreign troops have fueled local sentiments against foreign involvement, creating complexities for potential interventions.
Challenges and Dilemmas
- Leadership Dynamics: The current chairman of ECOWAS, Nigerian President Bola Ahmed Tinubu, advocates for military intervention in Niger. However, internal opposition and conflicting interests within ECOWAS member states complicate decision-making.
- Complexity of the Situation: The unique circumstances of each nation undergoing turmoil require tailored responses. The Niger coup’s leader, Gen. Abdourahmane Tchiani, has a history with ECOWAS peacekeeping missions.
Conclusion
- ECOWAS’s response to the Niger coup underscores the complexity of regional dynamics, the challenges of military intervention, and the delicate balance between security and democratic governance.
- As the organization grapples with finding an effective solution, its role as a mediator and peacekeeping force in West Africa continues to evolve in response to the changing geopolitical landscape.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/ecowas-west-africa-niger-coup-explained-8882492/
State of Elementary Education in Rural India Report (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan launched the first State of Elementary Education in Rural India report.
Facts About:
Key Highlight of the Report:
Pan-India survey was conducted by the Development Intelligence Unit (DIU), across 6,229 rural households in 20 states, focussing on 6 to 16-year-old children in rural communities.
Equality Among Gender: Parents from rural communities believe that a child’s gender, whether a boy or a girl, should not hinder their educational aspirations.
- Total of 78 percent of parents of girls and 82 per cent of parents of boys wanted to educate their children to graduation and above.
Parental participation: About 84 percent of parentsregularly attend parent-teacher meetings, demonstrating their active involvement in their children’s education.
Role of Parents: Majority of children (62.5 per cent) are under the supervision of their mothers when it comes to their studies, while 49 per cent are supervised by their fathers.
- Over 38 per cent of parents opt for private tutors to further enhance their children’s education.
- About 26 per cent of the children study under the supervision of a private tutor.
Drop Outs: Out of the total dropped-out children, around one-fourth of male children discontinued their education during primary schooling, due tolack of interest in studies.
- Dropout rate for female children is high at 35 per cent, due to the need to contribute to the family’s earnings.
- A higher proportion of both boys and girls dropped out of school after completing the primary school education (75 per cent for boys and 65 per cent for girls).
Increased access to smartphones: Nearly half, 49.3 percent of students in rural India have access to smartphones.
- 76.7 percent of these students primarily use their phones for entertainment purposes, such as playing video games and watching movies.
- Only 34 percent of smartphone-accessible students use their devices for study-related downloads, while 18 percent access online learning through tutorials.
Learning Environment at Home: 40 percent of parents have age-appropriate reading materials available at home, beyond school books.
- Only 40 percent of parents engage in daily conversations with their children about their school learning, while 32 percent have such discussions a few days a week.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/education/78-parents-in-rural-india-want-their-daughters-to-study-till-graduation-and-beyond-report-8885528/#:~:text=in%20family's%20earnings.- ,According%20to%20the%20survey%2C%20one%2Dfourth%20of%20male%20children%20dropped,after%20completing%20primary%20school%20education.
Revised manufacturing rules for drug firms (Indian Express)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently the center government directed all pharmaceutical companies in the country to implement the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Facts About:
Directions by the Government:
- Larger companies with a turnover of over Rs 250 crore have been asked to implement the changes within six months.
- The medium and small-scale enterprises with turnover of less than Rs 250 crore have been asked to do so within a year.
About Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP):
- Quality Management: It is a set of guidelines and quality management principles which ensure pharmaceutical products, as well as other products in the food and healthcare industries, are consistently produced and controlled to meet quality standards appropriate for their intended use.
- Aspects Include: It covers all aspects of the manufacturing process, including the premises, equipment, personnel, materials, production, quality control, documentation, and storage of finished products.
Need for the Improved Standards:
- To match up with the Global Standards: Implementation of the new norms will bring the Indian industry on par with global standards.
- Only 2,000 of the 10,500 drug manufacturing units in the country at present meet global standards, being WHO-GMP certified.
- The improved standards will ensure that pharmaceutical companies follow standard processes, quality control measures, and do not cut corners, improving the quality of medicines available in India as well as sold in the global market.
- To improve Indian Products Image: There have been a string of incidents where other countries have reported alleged contamination in India-manufactured syrups, eye-drops, and eye ointments.
- The deaths of 70 children in the Gambia, 18 children in Uzbekistan, three persons in the United States, and six deaths in Cameroon have been linked to these products.
- To rectify the Deficiencies: A risk-based inspection of 162 manufacturing units by the government found several deficiencies — incoming raw materials not being tested before use, product quality not being reviewed , absence of quality failure investigation, infrastructure deficiency to prevent cross-contamination, faulty design of manufacturing and testing areas, missing qualified professionals, and poor documentation.
- To Provide a Structure to the Draft: Implementation of the revised good manufacturing practices (GMP) as listed in the 2018 draft schedule M of the drugs and cosmetics rules.
Major Changes & Significance:
- Standard & Reliable Quality: The revised GMP guidelines focus on quality control measures, proper documentation, and IT backing to maintain quality of medicines produced.
- Review & Validation: It introduces pharmaceutical quality systems, quality risk management, product quality review and validation of equipment.
- Thorough Investigation: Carrying regular quality reviews of all its products, verify consistency of the quality and the processes, thorough investigation of any deviation or suspected defect and implementation of any preventive actions.
- Evaluation of Changes: It also suggests a change control system to evaluate all changes that may affect the production or quality of the product.
- Maintenance of Stability & Required Conditions:The companies will also be needed to mandatorily maintain the drugs in a stability chamber, set the proper temperature and humidity, and carry out an accelerated stability test as well.
- Data Safety & Security: The guidelines also state that companies should have GMP-related computerized systems, which ensure that there is no tampering of data related to the processes.
- In case sensitive data is entered manually to the system, there will be additional checks to validate the accuracy of the data. Backups would also be created to ensure there is no loss of data.
Conclusion:
The step taken is a required and desirable one. Instituting the same quality across the industry will give confidence to regulators from other countries and will improve the quality of drugs in the domestic markets.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/revised-manufacturing-rules-for-drug-firms-what-changes-and-why-8879305/
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) recently addressed the Manipur DGP, urging the filing of an FIR against three individuals.
About the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
Composition of NCPCR:
- This commission has a chairperson and six members of which at least two should be women.
- All of them are appointed by Central Government for three years.
- The maximum age to serve in commission is 65 years for Chairman and 60 years for members.
Functions and responsibilities of NCPCR:
- Examine and assess current safeguards for child rights and propose effective implementation strategies.
- Submit periodic reports to the central government on the efficacy of these safeguards.
- Conduct investigations into child rights violations and recommend legal action when appropriate.
- Raise awareness about child rights and available safeguards through diverse channels, such as publications, media, and seminars.
- Conduct inspections of institutions housing children, including juvenile homes, and suggest remedial measures if required.
- Investigate complaints and proactively address issues related to child rights deprivation, violation, and non-implementation of protective laws.
