Smart Cities Mission (SCM)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
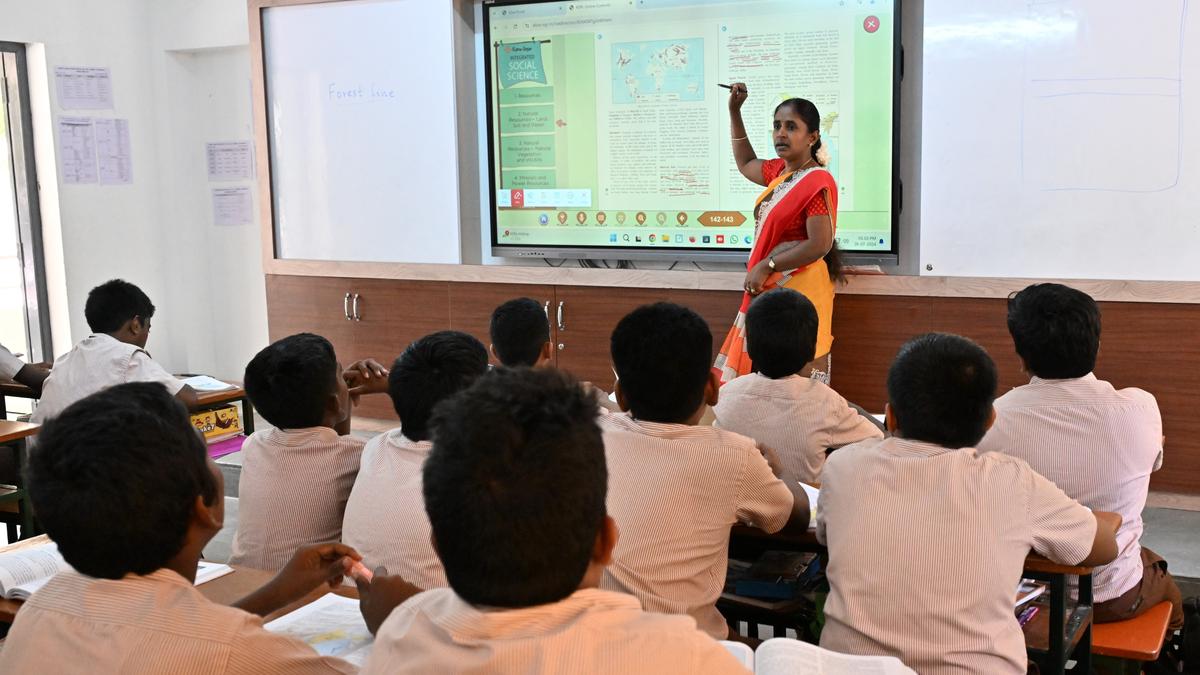
The introduction of smart classrooms as part of the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has had a significant impact on education, leading to a 22% increase in enrolment across 19 cities, according to a report from the Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B). The study covers the period from 2015-16 to 2023-24 and highlights several key benefits of this initiative, which aims to improve the overall learning environment in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Increased Enrolment: The introduction of smart classrooms has been linked to a 22% increase in student enrolment across 19 cities, suggesting that the initiative has made education more appealing and accessible.
- Smart Classroom Development: By 2023-24, 71 cities had developed 9,433 smart classrooms in 2,398 government schools. The states with the most smart classrooms are:
- Karnataka (80 classrooms)
- Rajasthan (53 classrooms)
- Tamil Nadu (23 classrooms)
- Delhi (12 classrooms)
- West Bengal has a very limited number, with just two classrooms.
- Improved Learning Experience: Teachers have expressed positive feedback, agreeing that the smart classrooms have improved learning experiences and attendance among students. Additionally, the smart classroom setup has contributed to increased comfort for teachers and higher preference for these modern facilities.
- Teacher Training: Special training provided to teachers has enhanced their comfort with using the smart classroom tools, with senior secondary teachers showing the highest comfort levels.
- Digital Libraries: The study also found that 41 cities have developed Digital Libraries with 7,809 seating capacity, offering essential resources for students. Cities like Raipur (Chhattisgarh) and Tumakuru (Karnataka) have seen positive outcomes from these libraries, particularly in supporting students preparing for competitive exams.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission aims to promote cities that offer core infrastructure, a decent quality of life, a sustainable environment, and the application of smart solutions. As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the mission have been completed.
SAAR Platform and Research
- In 2022, the Smart Cities Mission introduced the SAAR (Smart Cities and Academia towards Action and Research) platform to bridge the gap between academia and the government. Under this platform, 50 impact assessment studies have been initiated by 29 premier institutions, including six Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), and 12 specialized research institutes.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)

- 24 Dec 2024
In News
Justice V. Ramasubramanian, a retired Supreme Court judge, has been appointed as the new chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC). This decision was made by President Droupadi Murmu, and it comes following the completion of Justice Arun Kumar Mishra's tenure as NHRC chairperson in June 2023. After Justice Mishra's retirement, Vijaya Bharathi Sayani served as the acting chairperson. Alongside Justice Ramasubramanian, Priyank Kanoongo and Dr. Justice Bidyut Ranjan Sarangi (Retd.) have also been appointed as members of the commission.
Justice Ramasubramanian had been appointed a judge of the Supreme Court in September 2019 and retired in June 2023. His appointment to the NHRC is seen as a significant development for human rights advocacy and protection in India.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
Establishment and Legal Framework
- Formation Date: The NHRC was established on October 12, 1993, under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Paris Principles: It was created in alignment with the Paris Principles (1991), which were endorsed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, aimed at setting standards for national human rights institutions.
- Statutory Body: NHRC is a statutory body, meaning it is established by law, with a primary function to safeguard human rights in India.
Objectives
The NHRC's primary objective is to promote and protect human rights as defined in Section 2(1)(d) of the PHRA, which include fundamental rights such as:
- Right to Life
- Right to Liberty
- Right to Equality
- Right to Dignity
These rights are guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and are essential to the protection of individuals' freedoms and welfare.
Composition of NHRC
- Chairperson: A former Chief Justice of India or a former Supreme Court judge serves as the chairperson.
- Members:
- One former or sitting Supreme Court judge.
- One former or sitting Chief Justice of a High Court.
- Three members, with at least one woman, who have experience in human rights matters.
- Ex-Officio Members: The chairpersons of various National Commissions (e.g., SC/ST, Women, Minorities) and the Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities are also part of the NHRC.
Functions and Powers
The NHRC has several crucial functions and powers to ensure the protection and promotion of human rights:
- Inquiry into Human Rights Violations: The commission can inquire into violations of human rights by public servants or negligence in protecting rights.
- Recommendations: It can make recommendations on how to protect, promote, and effectively implement human rights within India.
- Review of Laws: NHRC assesses various laws, treaties, and international instruments related to human rights.
- Research and Awareness: It promotes research, publications, and awareness about human rights issues, including educating the public about their rights and safeguards.
- Inspection of Institutions: NHRC has the authority to visit and inspect institutions such as jails, detention centers, and other places of confinement to ensure the humane treatment of individuals.
Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) Mission
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
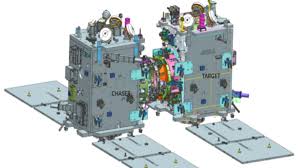
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission, a key milestone in India’s space capabilities. The mission will deploy two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into a 740 km orbit using the PSLV-C60 rocket. SpaDeX aims to demonstrate the technology for satellite docking, a critical component for future space missions such as lunar exploration and the development of India's own space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
Key Objectives of SpaDeX Mission:
- Primary Objective: To demonstrate the rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft (SDX01 and SDX02) autonomously.
- Secondary Objectives: Include testing electric power transfer between the docked spacecraft, composite spacecraft control, and post-docking payload operations.
The mission will see the two spacecraft gradually approach each other, performing a series of maneuvers, starting at a 20 km distance and closing to millimeter-scale distances before docking. Once docked, they will execute secondary tasks, such as scientific payload operations, using advanced technologies including high-resolution cameras, multi-spectral payloads, and radiation monitors.
Technological Innovations:
- Docking Mechanism: An indigenous, motor-driven, low-impact, androgynous docking system with capture, extension/retraction, and rigidization mechanisms. Both spacecraft are equipped with identical docking systems to simplify operations.
- Advanced Sensors: The spacecraft will use a Laser Range Finder (LRF), Proximity & Docking Sensors (PDS), and Rendezvous Sensors for precise distance measurement and to guide the docking process.
- Inter-Satellite Communication: The spacecraft will employ autonomous inter-satellite links (ISL) for real-time communication and data sharing.
- RODP Processor: This system, based on GNSS, ensures accurate position and velocity determination for the spacecraft during the docking procedure.
Significance of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Technological Milestone: SpaDeX positions India as the fourth country, after the US, Russia, and China, to develop space docking technology.
- Space Exploration: The successful demonstration will facilitate future space exploration, including Chandrayaan-4 and interplanetary missions.
- Modular Space Infrastructure: Space docking is essential for building multi-modular space stations, which allows the construction of large structures in space and enhances flexibility for future missions.
- Satellite Servicing: Docking enables satellite servicing, including repairs, refueling, and upgrades, which increases the operational lifespan of satellites.
SpaDeX Mission for India’s Space Station:
The SpaDeX mission is a crucial step towards India’s plans for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). This will be India’s first modular space station, designed to conduct advanced scientific research, including in life sciences and medicine. BAS is expected to begin operations by 2035, and the development of docking technology is pivotal for its assembly and operation.
Mission Launch Details:
The PSLV-C60 rocket is set to launch the SpaDeX mission from Sriharikota. The mission is a demonstration of India's growing space capabilities and its indigenous technologies, including the Bharatiya Docking System (BDS).
Challenges and Technological Requirements:
The docking process requires extremely precise maneuvering, as the two spacecraft will be traveling at speeds of 28,800 km/h and must reduce their relative velocity to just 0.036 km/h before docking. This level of precision is crucial for future missions involving spacecraft servicing, crew transfers, and the construction of space infrastructure like BAS.
In addition to the docking demonstration, SpaDeX will carry 24 academic and startup payloads aboard the PSLV’s fourth stage, POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4), offering a valuable platform for microgravity research.
Future Prospects:
The success of SpaDeX will pave the way for more complex missions, such as India’s lunar and Mars exploration programs, the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and international collaborations in satellite servicing and space infrastructure.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
Mission Shukrayaan
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
ISRO received approval for its first Venus mission, Shukrayaan. The probe will undertake a detailed investigation of Venus, including its surface, atmosphere and geological structure.
Shukrayaan Mission (Venus Orbiter Mission):
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for 2028.
- Objective: Investigate Venus to gather data on its surface, atmosphere, and geological structure.
- Scientific Focus: Study weather patterns, geological activities, and atmospheric composition (e.g., carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds).
- Instrumentation: Equipped with synthetic aperture radar, infrared, and ultraviolet imaging devices to study Venus’s ionosphere.
- Significance: Offers global coverage of Venus, addressing gaps in previous missions' spatial coverage.
- Cost: Estimated at Rs 1,236 crore.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO plans to use the LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) rocket to launch the mission into an elliptical parking orbit (170 km x 36,000 km).
- Mission Data Processing: Data will be archived and disseminated through the Indian Space Science Data Center (ISSDC).
Chandrayaan 4 Mission:
- Collaborative Effort: Joint mission between India (ISRO) and Japan.
- Launch Objective: Land on the moon's south pole, with a focus on the region at 90°S (compared to previous missions at 69.3°S).
- Mission Details:
- Includes a rover weighing 350 kg (12 times heavier than previous rover).
- The rover will be equipped with advanced scientific tools for lunar exploration.
- Government Approval: Awaiting approval, with a target execution date of 2030.
Gaganyaan Mission (Human Spaceflight Program):
- Timeline: Unmanned flight in 2026, followed by a manned mission.
- Indian Space Station: Construction approved; to be completed by 2035, comprising five modules.
- Purpose: To serve as a transit facility for deep space exploration, including future lunar missions.
Mars Exploration Plans:
- Future Missions: Plans to send satellites to Mars and attempt a landing on the Martian surface.
- Significance: Demonstrates India’s growing ambitions in interplanetary exploration.
INSAT-4 Series of Satellites:
- Goal: Launch of new meteorological and oceanographic sensors to improve weather forecasts and disaster management.
- Technological Advancements: Need for India to catch up with global advancements in space-based sensors.
International Collaboration in Space:
- Chandrayaan 4: A collaboration between ISRO and Japan to explore the moon’s south pole, showcasing India's growing international cooperation in space exploration.
Strategic Importance of Shukrayaan:
- Contribution to Science: The mission’s global dataset will provide unique insights into Venus, enhancing the understanding of planetary atmospheres and geological processes.
- Potential for Discoveries: Research on Venus’s ionosphere and possible volcanic activity.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the launching of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) as a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare.
Key Highlights
Objective & Focus:
- Launch of NMNF by the Union Cabinet to promote chemical-free farming in India.
- Aim to improve soil health, reduce input costs, and produce nutritious food.
- Support the shift to natural farming (NF), emphasizing local knowledge and agro-ecological principles.
Financial Allocation:
- Total Outlay: ?2481 crore (Government of India share ?1584 crore, State share ?897 crore) until FY 2025-26.
Key Features of NMNF:
- Coverage: Targeting 15,000 clusters in Gram Panchayats, covering 7.5 lakh hectares and impacting 1 crore farmers.
- Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs): 10,000 BRCs to supply ready-to-use natural farming inputs.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and Agricultural Universities (AUs): Establishment of 2,000 model demonstration farms for hands-on training in natural farming techniques.
- Farmer Training: 18.75 lakh farmers to be trained in NF practices such as preparation of organic inputs like Jeevamrit and Beejamrit.
- Krishi Sakhis/CRPs: Deployment of 30,000 workers for farmer mobilization and awareness.
Implementation Strategy:
- Farmer Certification System: Providing easy, simple certification for marketing natural farming produce with dedicated branding.
- Monitoring: Real-time, geo-tagged monitoring of implementation through an online portal.
- Convergence with other government schemes and organizations for market linkages and support.
Natural Farming Practices:
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): Promote sustainable farming by using local livestock and diverse crop systems.
- Benefits: Reduce dependence on external inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, rejuvenate soil quality, and increase resilience to climate risks (e.g., drought, floods).
- Encourage biodiversity, and improve soil carbon content and water-use efficiency.
Targeted Areas and Farmer Support:
- Focus on areas where NF practices are already being followed or where farmer producer organizations (FPOs) or self-help groups (SHGs) are active.
- Training through model demonstration farms will focus on practical, location-specific NF techniques tailored to regional agro-ecologies.
Impact on Agriculture and Environment:
- Environmental Impact: Encourages sustainable farming by reducing chemical exposure, improving soil health, and promoting climate resilience.
- Farmer Well-being: By reducing input costs and promoting nutritious food, it aims to improve farmer incomes and family health.
- Contributing to the long-term health of the environment, ensuring a healthy Mother Earth for future generations.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Soil Nutrient Compromise: Concerns that some crops, like rice, might require chemical fertilizers (e.g., NPK) for optimal growth, which may not be sufficiently replaced by organic manure alone.
- The shift to natural farming requires significant awareness and training to ensure sustainable and productive yields.
Institutional Framework:
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is the implementing body.
- Collaboration with KVKs, AUs, and farmer organizations ensures grassroots level support and knowledge dissemination.
ISRO's Analogue Space Mission in Ladakh

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
In a significant leap for the country’s space exploration aspirations, India has embarked on its first analogue space mission in Leh, a landmark step that will attempt to simulate life in an interplanetary habitat to tackle the challenges of a base station beyond Earth.
Mission Overview:
- Objective: To simulate living conditions in an interplanetary habitat, addressing challenges astronauts may face during deep-space missions (e.g., Moon, Mars).
- Goal: Study long-term isolation, habitat design, resource management, and psychological effects on astronauts.
- Partners: ISRO’s Human Spaceflight Centre, AAKA Space Studio, University of Ladakh, IIT Bombay, Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council.
Rationale for Ladakh:
- Geological Similarities: Ladakh’s terrain mirrors Martian and lunar surfaces, making it ideal for testing space technologies.
- Climate: Cold, dry, high-altitude conditions simulate the extreme environments of space.
- Focus Areas: Testing habitat construction, microbial studies, and survival strategies for long-duration space travel.
What are Analogue Space Missions?
- Definition: Simulated space missions on Earth designed to replicate the conditions of space exploration.
- Purpose:
- Test technologies (e.g., life support, habitat design, in-situ resource utilization).
- Study human behavior, psychological impacts of isolation, and operational readiness for extended space travel.
- Relevance: Crucial for preparing astronauts for missions to the Moon, Mars, or asteroids.
Significance of Analogue Missions:
- Technological Testing: Analogue missions help in evaluating systems for habitat design, life support, and health monitoring.
- Human Factors: They provide insights into crew health, teamwork under pressure, and performance during isolation.
- Psychological Studies: Address the impact of confinement, isolation, and communication delays on astronauts.
- Training: Participants (analogue astronauts) are trained for real-world space missions by conducting scientific experiments and managing emergencies.
Global Examples of Analogue Missions:
- NASA’s NEEMO: An underwater mission simulating microgravity conditions to train astronauts for space tasks.
- SIRIUS Program (UAE): Focuses on the psychological impacts of long-duration space isolation, featuring international collaborations.
- Arctic Mars Analogue Svalbard Expedition (AMASE): Uses the extreme Arctic environment of Svalbard to test Mars exploration technologies and procedures.
Relation to India’s Space Aspirations:
- Gaganyaan Mission: ISRO’s human spaceflight mission aiming to send Indian astronauts into space.
- Interplanetary Exploration: The analogue mission supports India’s broader goal of advancing human space exploration and technology development for Mars and beyond.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has decided to introduce four new components under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), aimed at promoting modern farming techniques:Hydroponics, Aquaponics, Vertical Farming&Precision Agriculture
Key Features of MIDH:
- MIDH is a Central Sponsored Scheme (CSS) aimed at the integrated development of various horticulture crops, including:
- Fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa, and bamboo.
- The scheme focuses on pre-production, production, post-harvest management, processing, and marketing activities.
Revision of Operational Guidelines and Cost Norms:
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare is revising the MIDH operational guidelines and cost norms, which were last updated in April 2014.
- The revised guidelines are expected to be released within one month.
- Cost norms are likely to increase by 20% compared to the existing rates, addressing concerns from various states about outdated guidelines.
Reason for Revision:
- Several states, including Odisha, have raised concerns over the old rates under MIDH. For example, Odisha’s Agriculture Minister highlighted that the state was still using 10-year-old rates.
- The Union Cabinet had already approved the rationalization of all CSS operating under the Ministry into two umbrella schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (PM-RKVY)
- Krishonnati Yojana (KY)
Growth in India's Horticulture Sector:
- India’s horticulture production has significantly increased in recent years:
- Total production reached 334.60 million metric tonnes in 2020-21, up from 240.53 million metric tonnes in 2010-11.
- India is now the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, surpassing food grain production.
- MIDH Annual Budget:The annual allocation for MIDH in the current financial year (2024-25) is ?2,000 crore.
National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Ministry of Culture plans to revive and relaunch the National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) to enhance the preservation and accessibility of India’s ancient texts.
- The mission’s objective is to document, conserve, digitize, and disseminate India’s rich manuscript heritage, ensuring their protection and public access.
Formation of a New Autonomous Body:
- The National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) is likely to be restructured into an autonomous body called the National Manuscripts Authority, which will be under the Ministry of Tourism and Culture.
- The new body will address the challenges and gaps in manuscript preservation and management, offering more focused and flexible governance.
Background and Achievements:
- Established in 2003, the NMM has been part of the Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts (IGNCA).
- Key achievements:
- 52 lakh manuscripts have had metadata prepared.
- Over 3 lakh manuscripts have been digitized, though only one-third have been uploaded for public access.
- Preventive and curative conservation of over 9 crore folios of manuscripts has been undertaken over the last 21 years.
- The NMM has set up 100 Manuscripts Resource Centres and Manuscripts Conservation Centres across India.
Current Challenges and Gaps:
- Data Uploading and Access:
- Of the 130,000 digitized manuscripts, only 70,000 are accessible online due to the absence of a comprehensive access policy.
- A significant portion (around 80%) of manuscripts areprivately owned, restricting public access and usage.
- Digitization Mismatch:
- There have been concerns about discrepancies between the digitized data and the original manuscripts, which requires correction to ensure authenticity and accuracy.
- Lack of Comprehensive Access Policy:
- Limited public access to manuscripts due to policy restrictions hinders further research and public engagement with this rich heritage.
Scope and Future of NMM:
- India's Manuscript Heritage: India is believed to have around 10 million manuscripts, spread across various regions, languages, scripts, and topics.
- Digitization and Accessibility: Moving forward, the key challenge will be ensuring that a larger proportion of the manuscripts are digitized, uploaded, and made publicly available, particularly from private collections.
- The establishment of the National Manuscripts Authority is expected to streamline efforts and enhance coordination between government bodies, private institutions, and scholars.
India's Mission Mausam and the Cloud Chamber

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
Mission Mausamaims to not just improve weather forecasting in the country but also ‘manage’ certain weather events, and on demand, enhance or suppress rainfall, hail, fog and, later, lightning strikes.
- Focus Areas:
- Enhancing or suppressing rainfall, hail, fog, and later, lightning strikes on demand.
- Strengthening cloud physics research to better understand and modify weather conditions.
- Establishment of Cloud Chamber:
- Location: The cloud chamber is being built at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune.
- Purpose: To study cloud physics in detail and develop methods for weather modification.
- Key Feature: It will be a convective cloud chamber, capable of simulating conditions specific to Indian monsoon clouds.
What is a Cloud Chamber?
- A scientific apparatus that mimics the conditions required for cloud formation.
- Function: Water vapour, aerosols, and other particles are injected into the chamber, and under controlled temperature and humidity conditions, clouds can be formed.
- Global Context: While many countries have cloud chambers, India is building one with convection properties, which are essential for studying monsoon clouds. Only a few such chambers exist globally.
Why India Needs a Convective Cloud Chamber?
- Cloud Physics: The chamber will allow scientists to study various phenomena such as:
- Cloud behaviour under normal and extreme conditions.
- Formation of rain droplets and ice particles.
- Influence of moisture from cyclones or low-pressure systems.
- Interactions between different cloud layers.
- Objective: To gain insights into cloud formation specific to the Indian monsoon and develop strategies for weather modification.
Applications for Weather Modification:
- The cloud chamber will help scientists simulate and understand how to influence weather events like rain and fog, particularly in monsoon systems.
- It will allow testing of new ideas and theories under controlled conditions, adjusting temperature, humidity, and convection parameters to suit Indian weather conditions.
India’s Experience with Cloud Seeding:
- Cloud Seeding: A technique tested in India to enhance rainfall by introducing particles (seeds) into clouds.
- CAIPEEX Program: India conducted the Cloud Aerosol Interaction and Precipitation Enhancement Experiment (CAIPEEX) over a decade to study cloud seeding's effectiveness.
- Findings: Cloud seeding increased rainfall by up to 46% in some regions, showing its potential under specific conditions.
- Limitations: Cloud seeding is not a one-size-fits-all solution and is effective only under certain conditions.
Significance for India’s Weather Forecasting:
- Improved Weather Modification: The cloud chamber and insights from it could lead to better management of weather events, especially in regions affected by monsoon rains, cyclones, and droughts.
- Tailored Strategies: India will be able to implement targeted weather interventions, especially in agricultural regions, to reduce the negative impacts of extreme weather.
???????Global and Regional Relevance:
- Cloud Chamber: The Pune facility will be one of the few globally with the specific focus on convective properties needed to study Indian monsoon systems.
- Role in Climate Science: India’s investment in cloud physics research positions it at the forefront of developing technologies to manage climate variability and extreme weather events.
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission

- 15 Oct 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has officially launched its first two initiatives: the Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG) and the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission. These initiatives aim to enhance India’s research landscape and support innovation in critical sectors.
Prime Minister Early Career Research Grant (PMECRG)
- Objective: The PMECRG is designed to empower early career researchers by providing flexible funding and support for high-quality innovative research. It aims to foster creativity and drive technological progress, positioning India as a global leader in science and technology (S&T).
- Significance: This grant recognizes the essential role of young researchers in advancing India's scientific agenda. By investing in their development, ANRF aims to cultivate a vibrant research ecosystem that encourages groundbreaking discoveries.
Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission
- Focus: The MAHA-EV Mission targets the development of key technologies for electric vehicles, specifically in areas such as tropical EV batteries, power electronics, machines and drives (PEMD), and charging infrastructure.
- Goals:
- Reduce Import Dependency: By fostering domestic innovation in EV components.
- Global Leadership: Positioning India as a leader in the electric vehicle sector, aligning with the government's Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision.
- Collaboration: The mission is designed to encourage multi-institutional and multi-disciplinary collaboration to address critical scientific challenges, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of India's EV sector.
Significance of Both Initiatives
- Bridging Gaps: Both initiatives aim to bridge the gap between academic research and industrial applications, a key goal of ANRF. This alignment is crucial for translating research into practical applications that benefit society.
- Strategic Interventions: These programs reflect the discussions held during the ANRF's Governing Board meeting, which emphasized global positioning in key sectors, capacity building, and fostering an innovation ecosystem.
- Long-term Vision: The initiatives contribute to India's goal of achieving a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047, accelerating the country's progress toward a sustainable and technologically advanced future.
The launch of the PMECRG and MAHA-EV Mission marks a significant step in enhancing India's research ecosystem. By supporting early career researchers and advancing electric vehicle technologies, ANRF is poised to drive innovation, foster collaboration, and strengthen India’s position on the global scientific stage. These initiatives reflect a commitment to sustainable development and technological leadership, paving the way for transformative advancements in various sectors.
USCIRF Report on India: Key Highlights

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), a Washington DC-based bipartisan U.S. federal government agency, has released a country update on India, flagging “collapsing religious freedom conditions”.
- Agency Overview:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is an independent, bipartisan U.S. federal commission established under the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Its primary functions include reviewing global religious freedom violations, providing policy recommendations to U.S. leaders, and publishing annual reports.
- Current Concerns:
- USCIRF's latest report indicates a “collapse” in religious freedom conditions in India, particularly worsening throughout 2024, especially around national elections.
- Legal and Policy Changes:
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- State-level anti-conversion and anti-terrorism laws.
- Implementation rules for the 2019 Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA).
- Passage of a State-level Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in Uttarakhand.
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- Violations and Incidents:
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Authorities have facilitated the construction of Hindu temples on former mosque sites.
- Increased attacks on religious minorities, particularly following the consecration of the Ayodhya temple in January 2024.
- Targeting of Religious Minorities:
- Arrests of Christians accused of forced conversions under anti-conversion laws.
- Anti-cow slaughter laws exploited by vigilante groups to target Muslims, Christians, and Dalits, often with little to no legal repercussions for perpetrators.
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Recommendations:
- USCIRF urges the U.S. State Department to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern” due to severe violations of religious freedom.
About USCIRF
- Composition: Comprised of nine commissioners appointed by the U.S. President or Congressional leaders, supported by non-partisan staff.
- Objective: To monitor and recommend actions on religious freedom violations aligned with international human rights standards.
National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds)

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
Cabinet Approves National Mission on Edible Oils – Oilseeds (NMEO-Oilseeds) (2024-25 to 2030-31).
Objective:
- Achieve self-reliance in edible oil production in seven years.
Financial Outlay:
- ?10,103 crore for the mission period.
Key Goals:
- Increase primary oilseed production from 39 million tonnes (2022-23) to 69.7 million tonnes by 2030-31.
- Boost domestic edible oil production to 25.45 million tonnes, meeting 72% of projected requirements.
Focus Areas:
- Enhance production of key oilseed crops: Rapeseed-Mustard, Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Sesamum.
- Improve extraction efficiency from secondary sources (e.g., Cottonseed, Rice Bran).
Strategies:
- Promote high-yielding, high oil content seed varieties.
- Extend cultivation to rice fallow areas and encourage intercropping.
- Use advanced technologies like genome editing for seed development.
SATHI Portal:
- Launch of an online 5-year rolling seed plan for timely seed availability.
- Coordination with cooperatives, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and seed corporations.
Infrastructure Development:
- Establish 65 new seed hubs and 50 seed storage units.
- Develop over 600 Value Chain Clusters across 347 districts, covering over 1 million hectares annually.
Support for Farmers:
- Access to high-quality seeds, training on Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), and pest management advisory.
Environmental Benefits:
- Promote low water usage, improve soil health, and utilize crop fallow areas.
Background Context:
- India relies on imports for 57% of its edible oil demand.
- Previous initiatives include the National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) and significant increases in Minimum Support Price (MSP) for oilseeds.
- Imposition of 20% import duty on edible oils to protect local producers.
The NMEO-Oilseeds mission aims to enhance domestic oilseed production, reduce import dependency, and improve farmers' incomes while contributing to environmental sustainability.
Cruise Bharat Mission

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The central government launched the five-year Cruise Bharat Mission, aiming to boost cruise tourism in India to 1 million passengers and create 400,000 jobs by 2029.
Mission Goals
- Passenger Traffic: Increase from 0.5 million to 1 million sea cruise passengers by 2029.
- River Cruise Passengers: Grow from 0.5 million to 1.5 million.
- Job Creation: Generate 400,000 jobs in the cruise sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion:
- International cruise terminals: From 2 to 10.
- River cruise terminals: From 50 to 100.
- Marinas: From 1 to 5.
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1 (2024-2025):
- Conduct studies and master planning.
- Form alliances with neighboring countries.
- Modernize existing cruise terminals and destinations.
- Phase 2 (2025-2027):
- Develop new cruise terminals and marinas.
- Activate high-potential cruise locations.
- Phase 3 (2027-2029):
- Integrate cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Continue developing infrastructure and enhancing cruise experiences.
Strategic Focus Areas
- Sustainable Infrastructure:
- Develop world-class terminals, marinas, and water aerodromes.
- Emphasize digitalization (e.g., facial recognition) and decarbonization (shore power).
- Create a National Cruise Infrastructure Masterplan 2047.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations using digital solutions (e.g., e-clearance and e-visa facilities).
- Cruise Promotion & Circuit Integration:
- Focus on international marketing and investment.
- Host events like the "Cruise India Summit."
- Form alliances with neighboring countries (UAE, Maldives, Singapore).
- Regulatory and Financial Policies:
- Establish tailored fiscal and financial policies.
- Launch a National Cruise Tourism Policy.
- Capacity Building & Employment:
- Create a Centre of Excellence for cruise-related economic research.
- Develop National Occupational Standards to enhance youth employment opportunities.
Expected Outcomes
- Tourism Growth: Position India as a global cruise destination.
- Cultural Promotion: Highlight the cultural, historical, and natural heritage of Bharat through cruise circuits.
- Community Benefits: Ensure inclusive growth for local communities and stakeholders in the cruise sector.
The Cruise Bharat Mission is set to redefine India's cruise tourism landscape, focusing on infrastructure development, operational efficiency, and promoting cultural heritage, while ensuring economic growth and job creation for the future.
Digital Agriculture Mission

- 03 Sep 2024
Introduction
India's digital revolution has significantly transformed governance and service delivery in recent years by creating digital identities, secured payments and transactions. This progress has paved the way for a thriving digital ecosystem across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and retail, positioning India as a leader in citizen-centric digital solutions.
For a similar transformation of the Agriculture Sector, the Union Cabinet Committee, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the 'Digital Agriculture Mission' with a substantial financial outlay of Rs. 2,817 Crore, including a central government share of Rs. 1,940 Crore, on September 2, 2024.
The Digital Agriculture Mission is designed as an umbrella scheme to support various digital agriculture initiatives. These include creating Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), implementing the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), and supporting IT initiatives by the Central Government, State Governments, and Academic and Research Institutions.
The scheme is built on two foundational pillars:
- Agri Stack
- Krishi Decision Support System.
Additionally, the mission includes ‘Soil Profile Mapping’ and aims to enable farmer-centric digital services to provide timely and reliable information for the agriculture sector.
AgriStack: Kisan ki Pehchaan
AgriStack is designed as a farmer-centric Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to streamline services and scheme delivery to farmers. It comprises three key components:
1. Farmers' Registry
2. Geo-referenced village maps
3. Crop Sown Registry
- A crucial feature of AgriStack is the introduction of a 'Farmer ID', similar to Aadhaar card, serving as a trusted digital identity for farmers.
- These IDs, created and maintained by the State Governments/ Union Territories, will be linked to various farmer-related data, including land records, livestock ownership, crops sown, and benefits availed.
- The implementation of AgriStack is progressing through partnerships between the Central and State Governments, with 19 states having signed MoUs with the Ministry of Agriculture. Pilot projects have been conducted in six states to test the creation of Farmer IDs and the Digital Crop Survey.
- The six states include Uttar Pradesh (Farrukhabad), Gujarat (Gandhinagar), Maharashtra (Beed), Haryana (Yamuna Nagar), Punjab (Fatehgarh Sahib), and Tamil Nadu (Virudhnagar).
Key targets include:
- Creating digital identities for 11 crore farmers over three years (6 crore in FY 2024-25, 3 crore in FY 2025-26, and 2 crore in FY 2026-27)
- Launching the Digital Crop Survey nationwide within two years, covering 400 districts in FY 2024-25 and all districts in FY 2025-26
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- The Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) will integrate remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources into a comprehensive geospatial system.
3. Soil Profile Mapping
Under the mission, detailed soil profile maps on a 1:10,000 scale for approximately 142 million hectares of agricultural land have been envisaged, with 29 million hectares of soil profile inventory already being mapped.
- Further under the Digital Agriculture Mission, the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) will be used for crop-cutting experiments to provide precise yield estimates, enhancing agricultural production accuracy.
- The mission is expected to create direct and indirect employment in agriculture, providing opportunities for around 2,50,000 trained local youth and Krishi Sakhis.
- By leveraging modern technologies like data analytics, AI, and remote sensing, the mission will improve service delivery for farmers, including streamlined access to government schemes, crop loans, and real-time advisories.
Key Components of the Mission
The Digital Agriculture Mission focuses on grassroots implementation, targeting farmers as the primary beneficiaries. Some of the key benefits of the mission include:
- Digital authentication for accessing services and benefits, reducing paperwork and the need for physical visits.
- Enhanced efficiency and transparency in government schemes, crop insurance, and loan systems through accurate data on crop area and yield.
- Crop map generation and monitoring for better disaster response and insurance claims.
- Development of digital infrastructure to optimize value chains and provide tailored advisory services for crop planning, health, pest management, and irrigation.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 that the Government, in partnership with states, will implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture over the next three years.
- This initiative will cover farmers and their lands, with a digital crop survey for Kharif planned for 400 districts this year. The goal is to update registries with details of 6 crore farmers and their lands.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 had previously introduced the DPI for agriculture, which aims to provide comprehensive data on farmers, including demographic details, land holdings, and crops sown. The DPI will integrate with state and central digital infrastructures to offer a range of farmer-centric services, including information on livestock, fisheries, soil health, and available benefits.
Conclusion
- The Union Cabinet also approved six major schemes alongside the Digital Agriculture Mission, with a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 crore.
- These initiatives include Rs 3,979 crore for Crop Science aimed at ensuring food security and climate resilience by 2047, and Rs 2,291 crore for strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences to support students and researchers. Rs 1,702 crore is allocated for Sustainable Livestock Health and Production to boost incomes from livestock and dairy, while Rs 1,129.30 crore is designated for Sustainable Development of Horticulture to increase income from horticulture. Additionally, Rs 1,202 crore will be invested in strengthening Krishi Vigyan Kendra, and Rs 1,115 crore towards Natural Resource Management.
- These comprehensive approaches leverage digital technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in India's agricultural sector, potentially transforming the lives of millions of farmers across the country. By extending the digital revolution to agriculture, India aims to further solidify its position as a global leader in innovative, technology-driven solutions for critical sectors of the economy.
AYUSHMAN BHARAT DIGITAL MISSION (ABDM)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) have been created in the past three years under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM). The digital healthcare mission marked its three-year anniversary.
Key Highlights:
- Launch Date: September 27, 2021.
- Vision: Establish a robust digital health infrastructure to enhance healthcare accessibility, efficiency, and transparency.
- Duration: A transformative three-year journey aimed at revolutionizing India’s digital healthcare ecosystem.
Objectives and Background
- Alignment with National Health Policy: The mission stems from the National Health Policy (2017), emphasizing accessibility and the integration of digital technologies.
- Building Blocks:
- National Health Stack (2018) introduced unique health identifiers and verified registries.
- National Digital Health Blueprint (2019) provided guidance for implementing ABDM.
Key Features of ABDM
- Unique Health Identifier (ABHA ID): Assigns a unique ID to every individual for managing health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): Comprehensive database of healthcare professionals across all systems of medicine.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): Repository of public and private health facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies.
- Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM): Allows secure access and sharing of health records based on informed consent.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Facilitates the discovery and delivery of health services.
- National Health Claims Exchange (HCX): Standardizes the insurance payment process for quicker claims.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensures confidentiality and security of health-related information in compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Interoperability: Enables seamless data exchange among stakeholders, supported by key gateways (HIE-CM, NHCX, UHI).
- Transparency: Offers individuals access to both public and private health services, ensuring transparent pricing and accountability.
Key Initiatives
- Scan and Share: QR-code based OPD registration reduces wait times and improves data accuracy.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Financial incentives to encourage participation in the ABDM ecosystem, launched on January 1, 2023.
- Microsites for Private Sector Adoption: Operationalized 106 microsites to facilitate ABDM adoption among private providers.
- End-to-End ABDM Adoption Pilot: Aimed at digitizing healthcare facilities across India, with 131 selected for participation.
Achievements
- Health Accounts Creation: Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) established, linking 42 crore health records.
- Ecosystem Participation: Involvement of 236 private entities and leading public institutions, enhancing interoperability.
- Healthcare Facility Registration: 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals registered.
Moving Towards Transformation
- Collaborations: Partnerships with IIT Kanpur and Maharashtra University of Health Sciences to drive digital health education and public goods development.
- Training Initiatives: Introduction of a WhatsApp Chatbot for stakeholder training on digital health practices.
- Digital Health Standards: Launched by the National Accreditation Board of Hospitals to promote digital health technology adoption.
- Integration of eSwasthya Dham Portal: Extends ABDM benefits to Char Dham Yatris.
Vision for the Future
ABDM aims to create a seamless digital health ecosystem, ensuring every Indian citizen has access to their health records through a unique ABHA ID. The initiative includes:
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS): Aids healthcare professionals in improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
INDIA’s FIRST MISSION TO VENUS

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
India is set to launch its first mission to Venus in March 2028, following the recent approval from the Union Cabinet. This mission, led by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), marks India’s second interplanetary endeavor after the successful Mars Orbiter Mission in 2013.
Importance of Studying Venus
- Earth's Twin: Venus is often referred to as Earth’s twin due to its similar mass, density, and size. Understanding Venus can provide insights into Earth’s own evolution.
- Extreme Conditions: The planet has a surface temperature around 462°C and an atmospheric pressure similar to that found deep under Earth’s oceans. Its atmosphere consists primarily of 96.5% carbon dioxide and features clouds of sulfuric acid.
- Historical Water Presence: Venus may have had water in the past, leading scientists to explore how it transitioned to its current hostile environment, likely due to a runaway greenhouse effect.
Mission Overview
- Launch Timeline: The mission will utilize a strategic launch window when Earth and Venus are closest, occurring every 19 months. It was initially planned for 2023 but is now set for 2028.
- Payload: The mission will carry around 100 kg of scientific instruments, including 17 Indian and 7 international experiments.
- Journey to Venus: After exiting Earth's orbit, the spacecraft will take about 140 days to reach Venus.
Aero-Braking Technique
- First-time Use: This mission will employ aero-braking, a technique to adjust the spacecraft’s orbit by skimming through Venus's atmosphere, creating drag that reduces altitude.
- Target Orbit: The satellite will initially be in a highly elliptical orbit of 500 km x 60,000 km and will be gradually lowered to an orbit of either 300 x 300 km or 200 x 600 km over about six months.
Scientific Payloads
- Synthetic Aperture Radar: For imaging the surface of Venus.
- Thermal Camera: To study temperature variations.
- Interplanetary Dust Analysis: Investigating dust particle flow.
- High-Energy Particle Studies: Examining particles entering the atmosphere and their ionization effects.
- Atmospheric Composition Study: Assessing the structure, variability, and thermal state of Venus’s atmosphere.
Which countries are trying to study Venus?
- There have been several missions to Venus in the past by the United States, the erstwhile USSR, Japan, and a collaborative mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) with Japan.
- The US has planned at least two more missions to Venus in the future — DaVinci in 2029 and Veritas in 2031 — and the ESA has planned the EnVision mission for 2030.
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION 2.0

- 24 Sep 2024
Mission Overview:
- Launched on October 1, 2021, as the second phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Aims for "Garbage-Free Status" in all urban areas by 2026.
- Focuses on 100% source segregation, door-to-door waste collection, and scientific waste management.
Legacy Waste Issues:
- Legacy waste consists of improperly collected and stored solid waste, often found in landfills and abandoned sites.
- Approximately 15,000 acres of prime land are buried under nearly 16 crore tonnes of legacy waste in India.
- The mission seeks to convert legacy dumpsites into green zones and establish scientific landfills to manage untreated waste.
Current Progress:
- Of 2,424 identified dumpsites (each with over 1,000 tonnes of waste), only 470 have been fully remediated (16% reclaimed).
- 1,224 sites are under ongoing remediation, while 730 remain untouched.
- Out of 28,460 acres of affected land, 4,552 acres have been reclaimed, with 23,908 acres still to be addressed.
State Performance:
- Tamil Nadu: 837 acres reclaimed (42% of its total dumpsite area).
- Gujarat: Leads in percentage, reclaiming 75% of its landfill area (698 out of 938 acres).
Financial Aspects:
- Central assistance of ?3,226 crore has been approved for remediation efforts.
- States and Union Territories must provide a matching share to access these funds.
Challenges:
- Legacy waste management involves complexities such as radiological characterization, leachate management, and fire control.
- Current municipal solid waste generation in India is around 150,000 tonnes per day.
Historical Context:
- The original Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-U 1.0) launched on October 2, 2014, focused on making urban areas Open Defecation Free (ODF).
EUROPA CLIPPER MISSION

- 21 Sep 2024
In news:
NASA is preparing to launch the Europa Clipper mission, which aims to investigate Jupiter's icy moon, Europa.
Key Details:
- Objective: This mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter to conduct a thorough study of Europa, focusing on its potential habitability.
- Significance: Europa Clipper will be NASA's first mission specifically designed to explore an ocean world beyond Earth. Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean beneath its icy surface, which raises the possibility of supporting life.
- Spacecraft Specifications:
- The spacecraft measures 100 feet (30.5 meters) from end to end and 58 feet (17.6 meters) across, making it the largest NASA spacecraft ever built for a planetary mission.
- Mission Plan:
- Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and conduct 49 close flybys of Europa to gather critical data regarding its environment and potential habitability.
- Instrumentation:
- Equipped with nine scientific instruments and a gravity experiment that leverages its telecommunications system, the spacecraft will maximize data collection by operating all instruments simultaneously during each flyby. This approach will allow scientists to compile comprehensive data layers, creating an in-depth understanding of Europa.
- Power Source:
- The spacecraft is outfitted with large solar arrays to harness sunlight for its energy needs while operating in the challenging environment of the Jupiter system.
Solar Array
A solar array is a collection of solar panels interconnected to generate electrical power. When combined with other components like an inverter and battery, it forms a complete solar energy system.
TRISHNA MISSION

- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
During a recent event, the President of the French Space Agency, Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), addressed various topics, celebrating 60 years of collaboration between France and India in space exploration, alongside discussions on the Gaganyaan and TRISHNA missions.
Overview of the TRISHNA Mission
The Thermal Infrared Imaging Satellite for High-resolution Natural Resource Assessment (TRISHNA) is a joint initiative by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and CNES.
Mission Objectives
TRISHNA aims to provide high-resolution, timely observations of Earth's surface temperature, monitor vegetation health, and analyze water cycle dynamics. It will facilitate:
- Assessment of urban heat islands
- Detection of thermal anomalies related to volcanic activity and geothermal resources
- Monitoring of snowmelt runoff and glacier behavior
- Collection of data on aerosol optical depth, atmospheric water vapor, and cloud cover
Satellite Payloads
TRISHNA is equipped with two main payloads:
- Thermal Infra-Red (TIR) Payload: Supplied by CNES, this payload includes a four-channel long-wave infrared imaging sensor that enables high-resolution mapping of surface temperature and emissivity.
- Visible-Near Infra-Red-ShortWave Infra-Red (VNIR-SWIR) Payload: Developed by ISRO, this payload consists of seven spectral bands aimed at detailed mapping of surface reflectance, which is crucial for calculating biophysical and radiation budget variables.
The data retrieved from both payloads will aid in solving surface energy balance equations to estimate heat fluxes.
Operational Details
- TRISHNA will operate in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 761 km, with a scheduled overpass time of 12:30 PM at the equator.
- This orbit will achieve a spatial resolution of 57 meters for land and coastal regions, and 1 km for oceanic and polar areas.
- The mission is expected to have an operational lifespan of five years.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, approved the proposal of Kaynes Semicon Pvt Ltd to setup a semiconductor unit in Sanand, Gujarat, with an investment of Rs 3,300 crore.
Key Highlights:
- The proposed unit, under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), will produce nearly 60 lakh chips per day.
- The chips produced in this unit will cater to a wide variety of applications which include segments such as industrial, automotive, electric vehicles, consumer electronics, telecom and mobile phones, etc.
- The initiative aligns with India’s goal of developing indigenous semiconductor capabilities.
- As per the reports, India’s semiconductor market is projected to reach $64 billion by 2026, positioning the country as a major global semiconductor hub.
- The first indigenously-developed chip is set to arrive in the country by the end of this year.
- In March, PM Modi laid the foundation stone of three semiconductor projects worth Rs 1.25 lakh crore.
- Tata Electronics is setting up a semiconductor fab in Dholera, Gujarat and one semiconductor unit in Morigaon, Assam.
- CG Power is setting up one semiconductor unit in Sanand. These units will produce lakhs of direct and indirect jobs.
- These four units will bring an investment of almost Rs 1.5 Lakh crore. The cumulative capacity of these units is about 7 crore chips per day, according to the Ministry of Electronics & IT.
- The Programme for Development of Semiconductors and Display Manufacturing Ecosystem in India was notified in 2021 with a total outlay of Rs 76,000 crore.
About India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- It is a specialized and independent Business Division within the Digital India Corporation that aims to build a vibrant semiconductor and display ecosystem to enable India’s emergence as a global hub for electronics manufacturing and design.
- ISM has all the administrative and financial powers and is tasked with the responsibility of catalysing the India Semiconductor ecosystem in manufacturing, packaging, and design.
- ISM has an advisory board consisting of some of the leading global experts in the field of semiconductors.
- ISM has been working as a nodal agency for the schemes approved under the Semicon India Programme.
Semicon India Programme:
- Launched in 2021 with a total budget of Rs. 76,000 crore, the ISM is overseen by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), Government of India. This initiative is part of a broad effort to develop a sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem within the country.
- The programme is designed to offer financial support to companies involved in semiconductor and display manufacturing and design. It also aims to foster the creation of domestic Intellectual Property (IP), and to promote and incentivize the Transfer of Technologies (ToT).
- Under this programme, four key schemes have been introduced:
- Scheme for establishing Semiconductor Fabs in India.
- Scheme for establishing Display Fabs in India.
- Scheme for setting up Compound Semiconductors/Silicon Photonics/Sensors Fabs and Semiconductor Assembly, Testing, Marking, and Packaging (ATMP)/OSAT facilities in India.
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme.
Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT)

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
The Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT) has recently unveiled a groundbreaking web portal, ‘shabd.education.gov.in,’ which is set to be a significant resource for technical terminology across all 22 official Indian languages. This initiative, supported by the Union Education Ministry, aims to consolidate and digitize scientific and technical terminologies, making them accessible to users in multiple languages.
Key Features of the Portal:
- Central Repository: The website serves as a central repository for glossaries developed by CSTT and other institutions. It currently hosts 322 glossaries with approximately 2.2 million words, with a goal to expand to 450 glossaries.
- Search Functionality: Users can search for technical terms using various criteria, including language, subject, type of dictionary, or specific language pairs. This comprehensive search capability allows for targeted and efficient access to information.
- Feedback Mechanism: The portal enables users to provide feedback on the terminologies, helping to refine and update the database based on real-world use and expert input.
- Expanding Technical Education: The launch of this platform supports the broader goal of enhancing technical education in Indian languages, which is crucial for fields like medicine and engineering.
Historical Context and Support:
- CSTT's Role: Established in 1961, CSTT is tasked with developing and defining scientific and technical terms in Hindi and other Indian languages. The commission also publishes textbooks, monographs, and journals, and organizes various academic events to promote standardized terminology.
- Process of Compilation: Terminologies are compiled through specialized committees for each subject area, with separate language committees ensuring the standardization of terms. The CSTT has been assisted by the National Translation Mission in this effort.
Impact and Usage:
- Since its launch in March 2024, the portal has seen significant engagement, with over 122,000 hits from both domestic and international users. This reflects the growing interest and need for accessible technical terminology in multiple languages.
- The portal is poised to play a crucial role in standardizing and disseminating technical knowledge across diverse linguistic communities in India, facilitating better understanding and education in various scientific and technical fields.
23rd Law Commission of India

- 06 Sep 2024
Constitution and Tenure:
- Notification and Term:
- The 23rd Law Commission of India was notified by the Union government on September 2, with effect from September 1.
- The commission will have a three-year term, concluding on August 31, 2027.
- The tenure of the previous Law Commission, chaired by former Karnataka High Court Chief Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi, ended on August 31.
Role and Importance of the Law Commission:
- Purpose:
- The Law Commission is a non-statutory body formed by the Union Ministry of Law and Justice through a gazette notification.
- Its role includes reviewing the functioning of laws, recommending the repeal of obsolete legislation, and providing recommendations on issues referred by the government.
- Composition:
- Typically chaired by a retired Supreme Court or High Court judge.
- Includes legal scholars and can also have serving judges.
- Impact:
- Over the years, 22 Law Commissions have submitted 289 reports.
- Their recommendations have influenced significant legislation, such as the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (CrPC), and the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act).
Constitution of the 23rd Law Commission:
- Structure:
- The commission will consist of:
- A full-time chairperson.
- Four full-time members, including a member-secretary.
- Up to five part-time members.
- Ex officio members including the secretaries of the Legal Affairs and Legislative departments.
- The commission will consist of:
- Appointment and Remuneration:
- Chairperson and full-time members can be serving Supreme Court or High Court judges or other experts chosen by the government.
- The chairperson will receive a monthly salary of ?2.50 lakh, while members will receive ?2.25 lakh.
- The member-secretary must be an officer of the Indian Legal Service of the rank of Secretary.
- Serving judges appointed to the commission will serve until retirement or the end of the commission’s term, without additional remuneration.
Terms of Reference:
- Primary Tasks:
- Identify and recommend the repeal of obsolete or irrelevant laws.
- Create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for periodic review and simplification of existing laws.
- Identify laws that are misaligned with current economic needs and suggest amendments.
- Directive Principles and Reforms:
- Examine laws in light of Directive Principles of State Policy and suggest improvements and new legislation to achieve constitutional objectives.
- Address laws affecting the poor, conduct post-enactment audits of socio-economic legislation, and review judicial administration for responsiveness.
Previous Commission's Contributions:
- Reports and Recommendations:
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
- A report in April 2023 recommending retention of Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code (sedition law), with suggested amendments for clarity.
- A report recommending a new law to protect trade secrets.
- A report on simultaneous elections, though it was not submitted to the government before the commission’s chairperson assumed office as a Lokpal member.
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
Upcoming Focus:
- The 23rd Law Commission is expected to continue examining key issues, including the implementation of a uniform civil code, which was also considered by the 22nd Commission but whose recommendations remain unpublished.
Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM)

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Securing water for the future as the mantra, the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) in the latest intervention has taken up the Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM) model on a pilot basis in the city.
What is an Aquifer?
- An aquifer is a body of porous rock or sediment that is saturated with groundwater.
- Groundwater enters an aquifer through precipitation that seeps down through the soil.
- It can then move through the aquifer and emerge at the surface via springs and wells.
- Aquifers are classified into two types:
- Deep Aquifers
- Shallow Aquifers
What is Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM)?
- In 2022, the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) launched a Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM) pilot program in ten cities across nine states:
- Bengaluru (Karnataka), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Dhanbad (Jharkhand), Gwalior (Madhya Pradesh), Hyderabad (Telangana), Jaipur (Rajasthan), Kolkata (West Bengal), Pune and Thane (Maharashtra), and Rajkot (Gujarat).
- The SAM pilot is overseen by the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and supported by the Advanced Center for Water Resources Development and Management (ACWADAM) in Pune and the Biome Environmental Trust in Bengaluru.
- Under SAM, the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) has identified five municipal parks for implementation this year.
How does it work?
- The project involves drilling shallow water injection borewells to depths of 100-120 feet to extract water from shallow aquifers.
- This process helps recharge the underlying layers during rainfall events by collecting water from the surrounding watershed and directing it through recharge pits.
- Consequently, underground water layers are replenished, leading to a rise in the water table.
Boeing Starliner
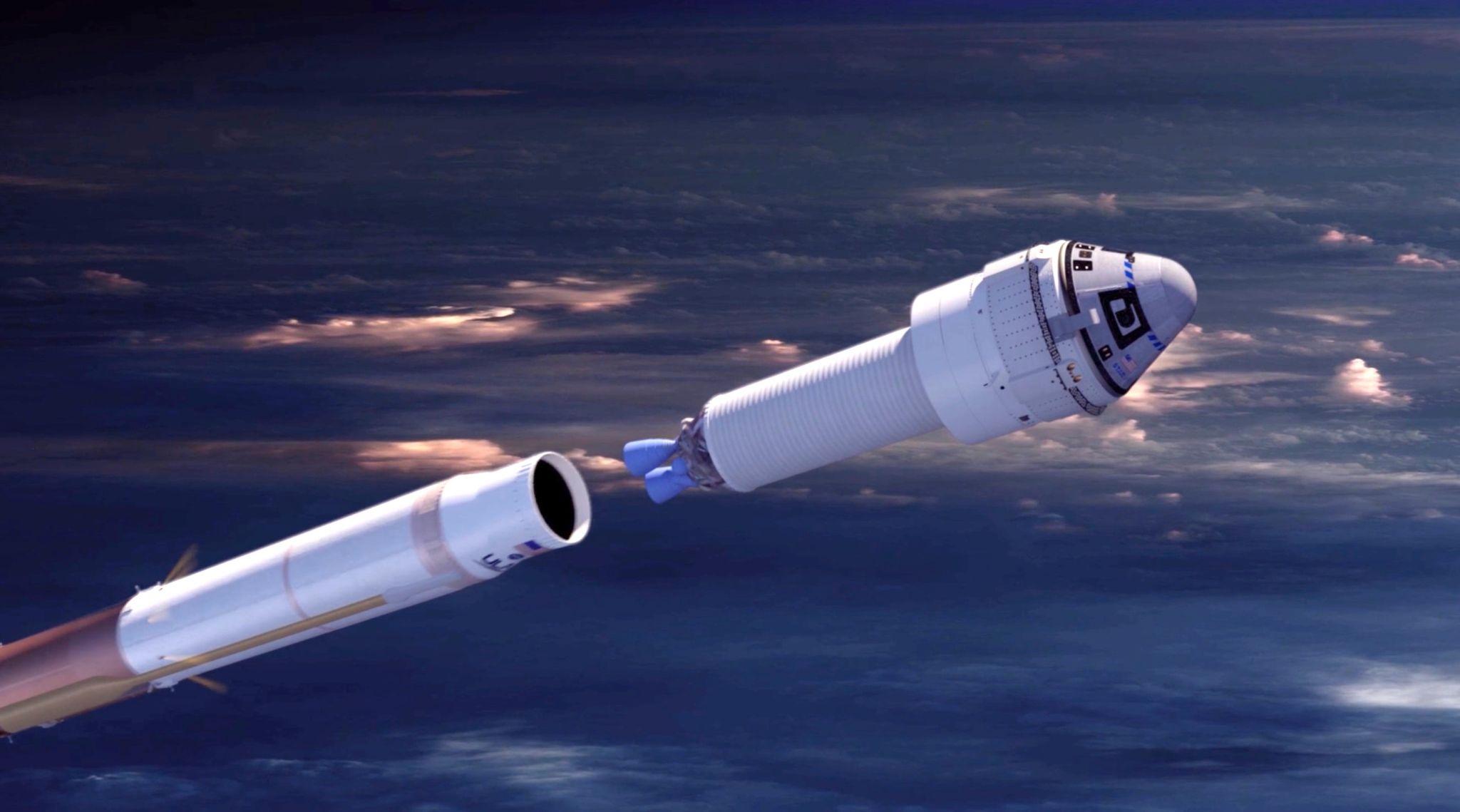

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft, carrying two NASA astronauts, will be launched by an Atlas V rocket from the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, to the International Space Station (ISS).
What is Boeing’s Starliner?
- Starliner, a reusable spacecraft, has a pusher abort system.
- This allows the crew to safely escape throughout the launch and the ascent phases of the mission.
- In addition to being software-driven, the Starliner has wireless internet that will help with “crew communication, entertainment and docking with the International Space Station”
- The spacecraft can fly and course-correct on its own.
- It operates like advanced self-driving cars, with features similar to sophisticated cruise control and hands-free driving, allowing astronauts to simply enjoy the ride without intervention.
- It also allows astronauts to choose their level of control.
- Consisting of a crew capsule and a service module, the Starliner aims to revolutionize space travel with its advanced features and capabilities.
Crew Capsule:
- The crew capsule is the heart of the spacecraft, providing housing for astronauts during their journey.
- Designed to withstand the rigours of reentry, the capsule ensures a safe return to Earth for its occupants.
Service Module:
- The service module is equipped with essential systems for astronaut survival, such as air and temperature control, water supply, and sanitation facilities.
- Additionally, it contains the necessary engines and fuel required for manoeuvring the spacecraft in space.
- This module is not reusable and is designed for single use.
Starliner Specifications:
- With a width of over 4 meters, the Starliner can accommodate up to seven astronauts at once.
- The spacecraft boasts a unique weldless structure, making it both durable and reusable, with a potential for up to 10 missions and a six-month turnaround time between launches.
- Furthermore, the Starliner incorporates modern technologies like wireless internet and tablet interfaces for enhanced crew interaction.
Launch Vehicle:
- The Starliner is compatible with the Atlas V rocket, operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin.
- This collaboration ensures the seamless integration of the spacecraft and launch vehicle, optimizing mission success.
Why is the mission significant?
- In 2014, NASA selected Boeing and SpaceX to develop spacecraft for transporting astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS).
- While SpaceX has already conducted multiple successful missions with its Dragon crew capsule, the Starliner's success would mark the first time the United States has two domestically produced spacecraft capable of carrying astronauts to space.
- Once operational, Boeing and SpaceX will alternate missions to the ISS, with each crew's expedition lasting up to six months.
- This partnership will continue until the ISS is decommissioned in the next decade.
China’s Chang’e-6 Mission
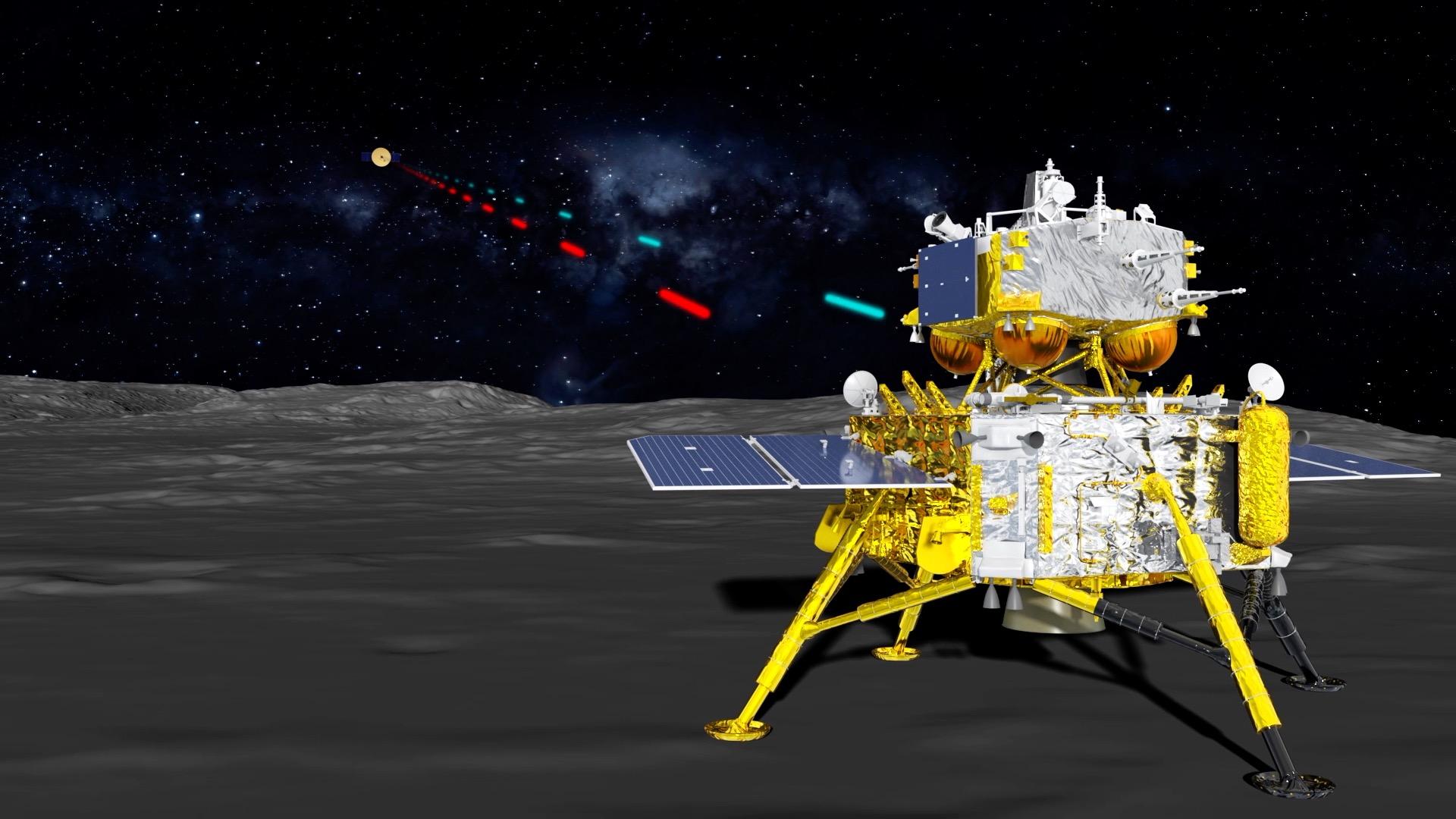

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, China launched its second mission to the far side of the Moon. If successful, it will be the world’s first mission to bring back samples from the part of the Moon that the Earth never gets to see.
What is Chang’e-6 Mission?
- China's Chang'e-6 spacecraft launched recently, on a mission to collect samples from the far side of the Moon.
- The mission aims to grab samples containing material ejected from the lunar mantle and thus provide insight into the history of the Moon, Earth, and Solar System.
- It is a 53-day-long mission. After reaching the Moon’s orbit, the mission’s orbiter will circle the natural satellite while its lander will descend into the 2,500-kilometre-wide South Pole-Aitken basin on the lunar surface.
- The impact that created the basin, among the largest in the history of the solar system, is thought to have dug up material from the lunar mantle.
- If that material can be retrieved, scientists can learn more about the history of the Moon’s insides.
- After collecting samples through scooping and drilling, the lander will launch an ascent vehicle, which will transfer the samples to the orbiter’s service module.
- This module will then return to the Earth.
- China is the only country to achieve a soft landing on the far side of the Moon.
- In 2019, its Chang’e-4 mission landed on the region and explored the Moon’s Von Karman crater with the help of a rover.
Why is the Far Side of the Moon Important?
- The Moon’s far side is often referred to as the dark side because it cannot be seen from the Earth, not because it does not catch the Sun’s rays.
- The Moon is tidally locked with the Earth and therefore, we see only one side of the Moon, also known as the near side.
- The far side has been under the spotlight in recent years as it is very different from the near side.
- It has a thicker crust, more craters and fewer maria, or plains where lava once flowed.
- Examining the samples from the far side can help scientists solve mysteries about the origin and evolution of the Moon — till now, scientists have only been able to analyse samples from the near side.
- The far-side samples can also give answers to the longstanding question: why is it different from the near side?
- Going to the far side, getting samples and doing different kinds of geophysical measurements is really important to figuring out this really long, long-standing mystery.
Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto.
About Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC):
- The Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC) is a national forum established in 1919, comprising creators, custodians, and users of records.
- Its primary purpose is to advise the Government of India on matters related to record management and their utilization for historical research.
Secretariat:
- The National Archives of India, New Delhi, serves as the Secretariat for the IHRC, formerly known as the Indian Historical Records Committee since 1911.
Leadership and Membership:
- Led by the Union Minister of Culture, the IHRC consists of 134 members, including government agencies, government-appointed nominees, representatives from State/UT Archives, universities, and learning institutions.
- Over the years, the IHRC has convened 62 sessions.
Committee Structure: The IHRC operates with two adjunct bodies:
- Editorial Committee: Responsible for reviewing and approving papers based on archival sources for presentation at committee sessions.
- Standing Committee: Tasked with reviewing the implementation of committee recommendations and providing input on meeting agendas.
- The Secretary of the Ministry of Culture chairs the Standing Committee of IHRC.
- The Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto recently.
- The logo signifies the theme and uniqueness of IHRC entirely.
- The pages in the shape of lotus petals represent IHRC as the resilient nodal institution for maintaining historical records.
- The Sarnath pillar in the middle represents India's glorious past.
- Brown as the colour theme reinforces the organization's mission of preserving, studying, and honouring India's historical records.
- The motto translates as "Where history is preserved for the future."
- The IHRC plays a vital role in identifying, collecting, cataloging, and maintaining historical documents, manuscripts other sources of historical information.
- By doing so the Commission ensures that valuable historical knowledge is conserved for future generations.
- The motto, therefore, reflects the Commission's commitment to ensuring the safeguarding of historical documents and making these accessible for the benefit of present and future generations.
United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women)

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to a recent report by UN Women, six months into the war, Gaza is facing a humanitarian crisis disproportionately impacting women and girls.
What is UN Women?
- Founded in 2010 by the United Nations General Assembly as part of the UN reform agenda.
- Merges resources and mandates to create a more significant impact on gender equality and women's empowerment.
- Serves as a global advocate for women and girls, addressing their needs and accelerating progress.
Key Roles:
- Supports intergovernmental bodies like the Commission on the Status of Women in developing policies, global standards, and norms for gender equality.
- Assists member states in implementing these standards and offers technical and financial support upon request.
- Builds effective partnerships with civil society organizations.
- Leads and coordinates the UN system's work on gender equality while promoting accountability through regular monitoring of progress.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Works globally to realize the SDGs for women and girls.
- Promotes women's equal participation in all aspects of life.
Country-level Support:
- Collaborates with government and non-governmental partners in countries that request assistance.
- Helps implement policies, laws, services, and resources to advance gender equality.
Grant-making Funds:
- Fund for Gender Equality: Provides grants to support innovative, high-impact programs by government agencies and civil society groups.
- UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women: Finances initiatives that address violence against women and girls.
Commission on the Status of Women (CSW):
- A global policy-making body focused on gender equality and women's advancement.
- Operates as a functional commission of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
Information and Advocacy:
- Regularly provides information on women's rights issues to the General Assembly, ECOSOC, and the Security Council.
- Maintains the UN Secretary-General's database on violence against women, tracking measures taken by UN Member States and organizations.
- UN Women plays a vital role in advancing gender equality and women's empowerment worldwide by providing crucial support, resources, and advocacy through its various initiatives and collaborations.
Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT)

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Congress has hailed as an “important first step” the Supreme Court’s notice to the Election Commission and the Centre on a plea seeking a complete count of VVPAT slips and said the matter should be decided before the Lok Sabha polls commence.
What is the Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT)?
- The Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail, or VVPAT system, was first introduced in 2014 for the first time during the 2014 Lok Sabha Elections.
- The ECI conducted pilot tests of VVPAT systems in a few constituencies in 2011, and after successful trials, VVPAT was gradually deployed across all polling stations in subsequent elections.
- It is connected to Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) and enables voters to confirm that their votes were cast as intended.
- The concept of VVPAT was to enhance the credibility and transparency of EVMs.
What are VVPAT Slips?
- VVPAT slips are an integral part of the EVMs used in elections.
- It provides a physical paper trail for voters to verify that their vote has been correctly recorded by the EVM.
- It ensures transparency and accountability in the electoral process by allowing voters to verify their vote before casting it finally.
- The VVPAT produces a paper slip that permits the voter to confirm the accuracy of their vote on the EVM.
- This slip displays the name and symbol of the party chosen by the voter.
- Additionally, the machine features a transparent window through which the voter can observe the printed slip.
- Subsequently, the slip is securely deposited into a sealed compartment within the machine.
- However, in the event of a dispute, this sealed box can be opened for further examination.
Controversies Surrounding VVPAT:
- Despite its intended purpose of enhancing transparency, VVPAT has been subject to several controversies over the years.
- Some critics have raised concerns about the reliability of VVPAT systems, citing instances of malfunctioning printers, paper jams, and discrepancies between electronic and paper records.
- The Opposition parties within the INDIA bloc have been advocating for the full counting of VVPATs, to bolster public trust in the EVMs, which itself has been subjected to intense scrutiny recently.
- Their concern has mostly stemmed from allegations of delay in the printing and displaying of VVPAT slips for every vote, which they claim can significantly increase the time required for vote counting.
Supreme Court’s intervention in VVPATs:
- In April 2019, the SC asked the poll panel to increase the number of EVMs that undergo VVPAT physical verification from one to five per assembly segment in a parliamentary constituency.
- In the month of May the same year, the Supreme Court dismissed a writ petition seeking 100 percent counting of VVPAT in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections.
- Earlier in the same month, the Supreme Court had also dismissed the review petition filed by opposition parties to increase verification of VVPAT-EVM to 50 percent.
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
Vision for Edible Oil Self-Reliance takes root in the North-East

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has reiterated the Government’s commitment to move towards self-sufficiency in edible oils production and harped on the importance of oil palm cultivation in the northeast region.
About the National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP):
- The National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) is an initiative launched by the Government of India in August 2021 to significantly enhance oil palm cultivation and crude palm oil production.
- This centrally sponsored scheme prioritizes the North East region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, aiming to boost the area and productivity of oilseeds and Oil Palm.
- The targets of NMEO-OP include expanding the oil palm area to 10 lakh hectares by 2025-26, a substantial increase from 3.5 lakh hectares in 2019-20, along with elevating Crude Palm Oil production to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26 from 0.27 lakh tonnes in 2019-20.
- Furthermore, the mission seeks to enhance consumer awareness to maintain a consumption level of 19.00 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
- Implementation of NMEO-Oil Palm involves various stakeholders such as the State Departments of Agriculture and Horticulture, Central University, ICAR-Institutions, CDDs, SAUs, KVKs, Central Agencies/Cooperatives, Oil palm processors/ Associations, DD Kisan, AIR, DD, TV channels.
- The salient features of NMEO-OP encompass assistance for planting material, inputs for intercropping up to a gestation period of 4 years, the establishment of seed gardens and nurseries, micro-irrigation, bore well/pump set/water harvesting structure, vermicompost units, solar pumps, harvesting tools, custom hiring center cum harvester groups, farmers and officers training, and replanting of old oil palm gardens, among others.
Oil Palm Production in India:
- Originating in West Africa, Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis) is a relatively recent crop in India known for its high vegetable oil yield per hectare.
- It yields two main oils, palm oil, and palm kernel oil, utilized in both culinary and industrial applications.
- The primary oil palm-growing states in India include Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Kerala, which collectively contribute to 98% of the total production.
- Additionally, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Mizoram also have significant areas dedicated to oil palm cultivation.
Mission Divyastra: India's Agni-V missile makes maiden flight with MIRV

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India on Monday announced the successful testing of an Agni missile capable of carrying multiple warheads meant to hit multiple targets simultaneously.
What are Agni-5 Missiles?
- Agni is a long-range missile developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation, DRDO.
- The family of Agni missiles has been in the arsenal of the Indian armed forces since the early 1990s.
- This latest variant of the missile is equipped with what is known as MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) technology, first developed at least five decades ago but in possession of only a handful of countries.
Salient Features of Agni-5:
- Powered by a three-stage solid-fuel engine, Agni-5 boasts a range exceeding 5,000km.
- The Agni series encompasses medium to Intercontinental variants, spanning Agni-1 to Agni-5, with ranges varying from 700 km to over 5,000 km.
- DRDO’s successful June 2021 test of Agni P, a canisterized missile, demonstrated a range capability ranging between 1,000 and 2,000 km.
- With its ability to be launched from both road and rail platforms, Agni-5 ensures ease of deployment and swift launch capabilities.
What is MIRV Technology?
- The MIRV have revolutionized the concept of ballistic missile payloads by enabling a single missile to carry multiple warheads, each capable of targeting enemies at different locations.
- The technology was first introduced in the US with the successful test of the Minuteman III in 1968, which brought the technology into actual use in the 1970.
- The Soviet Union developed their own MIRV-enabled ICBM and SLBM technology by the end of the 1970s.
- The strategic shift started by MIRV has enabled many nations to greater target damage and reduce the effectiveness of enemy missile systems, altering the landscape of global nuclear deterrence.
- The warheads on MIRVs can be launched at different speeds and in different directions.
- Some MIRVed missiles can hit targets as far as 1,500 km apart.
- The technology requires a delicate combination of large missiles, small warheads, precise guidance, and a complex mechanism for releasing warheads sequentially during flight.
How does MIRV Work?
- The MIRV-equipped missile follows a trajectory into space similar to other ballistic missiles.
- After the boost phase, the missile’s upper stage, known as ‘bus’, reaches suborbital spaceflight, and aligns itself based on designated targets.
- The ‘bus’ sequentially deploys multiple warheads along with decoys and countermeasures.
- Each warhead can be assigned a different target or trajectory.
- After the deployment, the warheads re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere and proceed to their respective targets.
What are the Challenges?
- The MIRV technology enhances first-strike proficiency and complicates the calculus of mutual assured destruction.
- With the ability to deploy multiple warheads from a single missile, nations can achieve a broader spread of targets, making the defense system less effective and more costly.
- Although MIRVs were not initially made to defeat ballistic missile defenses, they are much more difficult to defend against than traditional missiles.
- Possession of MIRV technology not only exhibits a country’s nuclear prowess but plays a crucial role in shaping international security and nuclear deterrence strategies.
UGC notifies framework for private universities to set up off-campus centers

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with the “future academic vision” instead of “commercial interests”, the UGC has notified modalities on March 6 for state private universities to set up off campus centers within their respective states.
News Summary:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) recently permitted private universities to establish off-campus centers and outlined regulations for the same.
- Previously, private universities in the country were restricted from opening off-campus centers in other states.
- In a meeting held on March 5, the UGC decided to authorize state private universities to establish off-campus centers across the country, provided they meet specific criteria.
- Criteria include a minimum of five years of establishment and accreditation from the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), without requiring an A or B grade.
- Universities seeking to establish off-campus centers must meet staff, infrastructure, and financial requirements mandated by the commission and obtain approvals from statutory and regulatory bodies.
- These universities must ensure the provision of infrastructure, faculty, and courses offered at the main campus to students at their off-campus centers.
- A one-time establishment fee of Rs 10 lakh is required to be paid to the UGC by the universities.
- The UGC reserves the right to conduct inspections and take punitive actions against universities in case of irregularities or complaints.
- Additionally, the UGC may order the closure of a university’s off-campus center for violations, with the university responsible for relocating affected students to the main campus.
About University Grants Commission (UGC):
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) of India operates as a statutory body established under the UGC Act, 1956.
- Its primary mandate encompasses coordinating, determining, and upholding standards within higher education institutions across India.
- UGC holds the authority to grant recognition to universities and colleges within the country and allocates funds to these recognized institutions.
- Nodal Ministry: Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education.
Mandate of UGC:
- Facilitating and coordinating university education initiatives.
- Establishing and maintaining standards in teaching, examination, and research activities within universities.
- Formulating regulations to define minimum education standards.
- Monitoring advancements in collegiate and university education while disbursing grants to these institutions.
- Serving as a crucial intermediary between the Union and State governments and higher education institutions.
- Providing advisory services to the Central and State governments concerning measures aimed at enhancing university education standards.
Conclusion
Academic experts said that this decision may prove beneficial for students as they will get more options to choose from. However, it also means that the 16 government-run universities in the state will face more competition. More students may shift to these centers, leaving a large number of approved seats in the public universities vacant every year.
Union Cabinet approves India AI Mission with 10,372 cr outlay

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
India has made its first move to address a key shortcoming it currently has in unlocking opportunities around generative artificial intelligence (AI) – that of computing hardware.
What is IndiaAI Mission?
- India's AI Mission entails the launch of an artificial intelligence (AI) initiative, announced by the Prime Minister at the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi, with implementation overseen by the 'IndiaAI' Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- Led by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the mission aims to establish a computing capacity exceeding 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) and develop foundational models trained on datasets encompassing major Indian languages, focusing on priority sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Additionally, the mission will involve the establishment of AI Curation Units (ACUs) in 50-line ministries and the creation of an AI marketplace to provide AI services and pre-trained models to AI application developers.
- Implementation of the AI computer infrastructure will follow a public-private partnership model, with 50% viability gap funding, with Rs 4,564 crore allocated from the total outlay of Rs 10,372 crore for building computing infrastructure.
Key Features of the IndiaAI Mission:
- IndiaAI Compute Capacity: Establishing a scalable AI computing ecosystem to meet the growing demands of India's burgeoning AI start-ups and research community.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre: Focusing on the development and deployment of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and domain-specific foundational models in critical sectors.
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: Streamlining access to high-quality non-personal datasets to fuel AI innovation.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative: Promoting the adoption of AI applications in critical sectors, addressing problem statements sourced from Central Ministries, State Departments, and other entities.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: Mitigating barriers to entry into AI programs by expanding AI courses at undergraduate, master's, and Ph.D. levels.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Supporting and accelerating deep-tech AI startups by providing streamlined access to funding for futuristic AI projects.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Ensuring the responsible implementation of AI projects through the development of indigenous tools and frameworks to foster trust and safety in AI applications.
The Significance of the IndiaAI Mission:
- The IndiaAI Mission aligns with the vision of fostering indigenous AI development and leveraging AI technology for the benefit of India.
- It aims to demonstrate to the international community the positive impact of AI technology on society, thereby enhancing India's global competitiveness.
- By establishing a comprehensive ecosystem for AI innovation through strategic partnerships across public and private sectors, the mission will catalyze AI-driven advancements.
- It will foster creativity and bolster internal capabilities, ensuring India's technological sovereignty.
- Furthermore, the mission is poised to create employment opportunities that demand advanced skills, leveraging India's demographic advantage.
PM Modi launches India’s first hydrogen-powered ferry built at Cochin Shipyard

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Modi recently virtually launched India’s first indigenously developed hydrogen fuel cell ferry manufactured by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), which will be deployed for service at Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh.
What is the "Harit Nauka" (Green Boat) Initiative?
- Initiated by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways, "Harit Nauka" aims to facilitate a sustainable transition of inland vessels.
- In January 2024, the shipping ministry introduced the "Harit Nauka" guidelines, outlining the path towards environmentally friendly practices for inland vessels.
- According to these guidelines, all states are mandated to progressively adopt green fuels for 50% of their inland waterway-based passenger fleets within the next decade, to achieve 100% adoption by 2045. This initiative aligns with the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- The implementation of this initiative not only contributes to reducing emissions but also paves the way for replicating such environmentally friendly ferry models across the country to enhance urban mobility.
- Furthermore, it serves as a significant catalyst for advancing the objectives of the National Green Hydrogen Mission.
What are Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
- Hydrogen fuel cells harness the chemical energy of hydrogen to generate electricity, offering a clean energy solution with electricity, heat, and water as the sole products and by-products.
Functioning:
- Similar to batteries, fuel cells continuously produce electricity and heat as long as fuel is supplied. A typical fuel cell comprises two electrodes—an anode (negative electrode) and a cathode (positive electrode)—surrounding an electrolyte.
- Hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode, while air is directed to the cathode. At the anode, a catalyst separates hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons, which then travel different paths.
- Electrons create an electric current through an external circuit, while protons migrate through the electrolyte to the cathode, combining with oxygen and electrons to form water and heat.
Challenges in India:
- High Cost: Fuel cell systems remain relatively expensive compared to conventional energy sources.
- Infrastructure Deficiency: India currently lacks the necessary infrastructure for the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology, including hydrogen production and distribution networks.
- Technical Hurdles: Despite ongoing advancements, fuel cell technology is still in its nascent stages, facing persistent technical challenges.
- Policy Constraints: The absence of a comprehensive policy framework from the Indian government has constrained the development and adoption of fuel cell technology, impeding research and investment.
India's Initiatives:
- In response to these challenges, India has formulated the National Green Hydrogen Policy, delineating a vision for the growth of the hydrogen and fuel cell industry.
- The policy aims to position India as a global hub for the production, utilization, and export of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives, signalling a strategic commitment to advancing sustainable energy solutions.
Characteristics of the Hydrogen-Powered Ferry:
- Length and Capacity: The hydrogen fuel cell vessel is a 24-meter-long catamaran, capable of accommodating up to 50 passengers in its air-conditioned passenger area.
- Battery-Free Operation: Distinguished by its innovative design, this ferry does not rely on conventional batteries for storing electrical energy.
- Instead, it utilizes hydrogen fuel, stored in cylinders onboard the vessel. With five hydrogen cylinders capable of carrying 40kg of hydrogen, the ferry can sustain operations for eight hours. Additionally, it features a 3-kW solar panel to complement its power source.
- Fuel Cell Technology: Equipped with a 50-kW PEM (proton-exchange membrane) fuel cell, coupled with Lithium-Ion Phosphate batteries, the ferry boasts adaptability in response to varying power demands.
- PEM fuel cells, renowned for their lower operating temperature, lightweight, and compactness, are commonly employed in automotive applications.
- Environmental Sustainability: With zero emissions and noise, coupled with enhanced energy efficiency, the hydrogen fuel cell-powered ferry stands as an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Its minimal moving parts contribute to reduced maintenance requirements compared to combustion vessels.
- Additional Advantages: While hydrogen fuel cell technology has been in development for maritime purposes, only a handful of countries worldwide have executed demonstration projects.
- Thus, this ferry positions India at the forefront, providing an early advantage in harnessing the potential of hydrogen as an emerging green fuel within the marine sector.
An initiative to improve nutrition in adolescent girls using Ayurveda under Mission Utkarsh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The project for anemia control under Mission Utkarsh will be a joint public health initiative by the Ministries of Ayush and Women and Child Development and will be launched in five aspirational districts first as a pilot project.
About Mission Utkarsh:
- Mission Utkarsh was launched in January 2022, a new initiative of “rapid improvement of selected Districts” to improve.
- Under this mission, 15 central ministries and departments are working to bring select key performance indicators in bottom districts to the state and national average.
- Over 94,000 adolescent girls between the age group of 14-18 years registered under Poshan Tracker at approximately 10,000 Anganwadi Centres will benefit in 12 12-month periods of the program.
- The coordinating agency for the project will be the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS).
- Classical Ayurveda medicines (Drakshavaleha and Punarnavadi mandoor) for better nutrition to improve the health of the anemic adolescent girls will be provided for a period of 3 months.
- These five districts are Dhubri in Assam, Bastar in Chhattisgarh, Paschimi Singhbhum in Jharkhand, Gadchiroli in Maharashtra, and Dholpur in Rajasthan.
- Building research capacity through training, conferences, workshops, and seminars with the active participation of researchers of integrative healthcare would be enhanced.
What is Anaemia?
- According to WHO, anemia occurs when there is a lower-than-normal count of red blood cells or a reduced hemoglobin concentration within them, crucial for oxygen transport throughout the body.
Symptoms
- This condition leads to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath due to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common nutritional cause, although deficiencies in folate, vitamins B12 and A can also contribute.
- Chronic diseases like kidney or liver disease, cancer, and genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia further exacerbate anemia.
Significance:
- Anaemia has significant implications, particularly affecting vulnerable populations like pregnant women and children under five, impacting reproductive health and reducing work capacity, thus posing an economic burden.
Anaemia in India:
- India faces a substantial anemia burden, with recent surveys indicating alarming prevalence rates among women aged 15-49 and children aged six months to five years, highlighting the urgent need for public health interventions.
First moon-landing by private company

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fifty-two years after the last successful Apollo mission, a US-made spacecraft landed on the Moon recently which also marks the arrival of private space companies on the lunar surface.
What is Odysseus Lunar Exploration?
- Odysseus is a spacecraft built by Intuitive Machines, embarked on its journey from Earth aboard a Falcon 9 rocket by SpaceX recently.
- Intuitive Machines, headquartered in Houston, USA, boasts a decade-long legacy in space exploration endeavours.
- Loaded with six NASA payloads, Odysseus set its course for the Moon.
- Its lander module, Nova-C, achieved the milestone of landing in the Moon's south pole region, following Chandrayaan-3's similar feat last year.
- This marks the third successful moon-landing event in under a year, alongside Chandrayaan-3 and Japan's SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon).
Mission Objectives:
- The primary aim of the lunar lander is to assess the environmental conditions at the Moon's south pole.
- This assessment holds significant importance as NASA gears up for a crewed mission in September 2026 with Artemis III.
- Before sending astronauts to this area, NASA seeks to gather crucial data, including insights into water presence and accessibility, to inform mission planning.
Funding:
- Under the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, NASA allocated $118 million to Intuitive Machines for this mission.
- CLPS has engaged at least 14 private companies to ferry NASA payloads to the Moon, fostering a collaborative environment aimed at nurturing the private space industry's capabilities in lunar exploration technology and science.
The Significance of Odysseus:
- Advancing Long-Term Lunar Presence: Odysseus' successful landing heralds a transformative phase in lunar exploration, aiming to establish infrastructure and a technological ecosystem capable of sustaining extended human presence.
- Diverging from Past Lunar Missions: In contrast to the moon landings of the 1960s and 1970s spearheaded by the US and the Soviet Union, Odysseus' mission focuses on leveraging lunar resources for sustained exploration.
- While historic moon landings were remarkable feats, technological limitations of the time hindered the immediate utilisation of lunar resources such as mining.
- Supporting US Commitment to Moon Exploration via Artemis Program: Odysseus' touchdown aligns with the US commitment to rekindle lunar exploration through the ambitious Artemis program.
- This endeavour transcends mere lunar landing missions, aiming to establish essential infrastructure and a thriving lunar economy conducive to comprehensive exploration.
- Unlocking Lunar Potential as a Gateway to Deep Space: By laying the groundwork for lunar infrastructure and economic activity, missions like Odysseus pave the way for leveraging the Moon as a springboard for deeper space exploration, offering nations unprecedented opportunities for cosmic discovery.
About 400 Smart Cities Mission Projects are Likely to Miss June 30 Deadline (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Housing and Urban Affairs Secretary Manoj Joshi told the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Housing and Urban Affairs that Some projects under the Smart Cities Mission would not be able to meet the June 30 deadline and the respective state governments would be responsible for completing them thereafter.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Approximately 400 Smart City Mission (SCM) projects are facing challenges in meeting the extended deadline of June 2024, according to a recent report by the Parliamentary committee.
- These projects, being implemented by around ten cities under the Center's flagship SCM, are at risk of not being completed within the timeframe.
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) has granted a second extension to the Smart Cities Mission, giving it until June 2024 to finalize pending work.
- However, if these projects are not completed by then, the respective state governments will be responsible for completing them at their own expense.
- The role of the ministry extends beyond merely transferring funds; it also involves overseeing project execution and ensuring successful completion.
- Despite the challenges, the ministry has emphasized that there will be no further extensions to the mission.
- Delays have been attributed to various factors, including difficulties in relocating local populations, legal hurdles such as land procurement issues, frequent turnover of smart cities' CEOs, and delays in projects requiring coordination with other government entities.
- In light of these challenges, the committee has proposed extending the Smart Cities Mission to Tier-2 cities located within 50-100 km of capital cities and tourist destinations.
- Additionally, the committee has highlighted the importance of protecting privacy rights, especially given the extensive deployment of surveillance technology like CCTV cameras and Integrated Command and Control Centers across all 100 cities involved in the mission.
What is the Smart Cities Mission (SCM)?
- The Smart Cities Mission (SCM) was initiated on 25th June 2015, to foster urban centers that offer essential infrastructure and a sustainable, clean environment.
- Through a competitive process spanning from 2016 to 2018, 100 cities were selected for development as Smart Cities, each receiving five years from their selection to complete designated projects.
- Administered as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), the program entails financial support from the Central Government amounting to Rs. 48,000 crores over five years, equating to an average of Rs. 100 crore per city per year, matched by an equivalent contribution from the State or Urban Local Body (ULB).
- Guided by six core principles, the Smart Cities initiative aims to enhance the quality of life for residents through the implementation of innovative solutions, fostering economic growth, and addressing social, economic, physical, and institutional aspects of urban development. It prioritizes sustainable and inclusive progress, endeavouring to establish scalable models that can serve as beacons for other cities aspiring for advancement.
- Financing for the Smart Cities Mission entails shared responsibilities between the Central Government, state governments, and ULBs, requiring equal contributions for project implementation.
- As of December 1, 2023, significant progress has been made, with 6,419 projects worth Rs. 1,25,105 crore completed out of a total of 7,970 projects valued at Rs. 1,70,400 crore.
- An additional 1,551 projects worth Rs. 45,295 crore are currently in progress, though certain cities, particularly those in the North-Eastern and Himalayan regions, as well as small Union Territories, face challenges in keeping pace.
- Budget allocations for the Smart Cities proposal have seen adjustments, with a reduction in the outlay from Rs. 7,634 crores to Rs. 7,535 crores in the revised budget for 2023-24, and a further decrease to Rs. 2,236 crores for the 2024-25 fiscal year.
: Law Commission of India (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 22nd Law Commission of India led by Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi has recommended that the offense of criminal defamation should be retained in the new criminal laws.
About the Law Commission of India:
- The Law Commission of India is a non-statutory body, constituted by the Government of India from time to time.
- The commission's function is to research and advise the government on legal reform, and is composed of legal experts, and headed by a retired judge.
- The commission is established for a fixed tenure and works as an advisory body to the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- The first Law Commission was established during colonial rule in India by the East India Company under the Charter Act of 1833 and was presided over by Lord Macaulay.
- After that, three more commissions were established in British India.
- The first Law Commission of independent India was established in 1955 for a three-year term.
- Since then, twenty-one more commissions have been established.
- The 22nd Law Commission has been notified with effect from 21st February 2020 for a term of 3 years.
- Cabinet approves the extension of the term of the 22nd Law Commission of India up to 31st August 2024.
- Justice Rituraj Awasthi (Former Chief Justice of the Karnataka HC) was appointed as the chairperson of the current 22nd Law Commission.
- The last chairman of the 21st Law Commission was retired Supreme Court judge Justice B.S. Chauhan.
The Responsibilities of the Law Commission:
- Identification of laws which are no longer relevant and recommending the repeal of obsolete and unnecessary enactments;
- Suggesting enactment of new legislations as may be necessary to implement the Directive Principles and to attain the objectives set out in the Preamble of the Constitution;
- Considering and conveying to the Government its views on any subject relating to law and judicial administration that may be specifically referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Considering the requests for providing research to any foreign countries as may be referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Preparing and submitting to the Central Government, from time to time, reports on all issues, matters, studies and research undertaken by it and recommending such reports for effective measures to be taken by the Union or any State; and
- Performing such other functions as may be assigned to it by the Central Government from time to time.
Ganga mission gets the power to allow treated sewage into water bodies (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), the Centre’s nodal agency responsible for the abatement of pollution in river Ganga and its tributaries, has assumed new powers under which it may now permit the discharge of treated sewage and effluent that conforms to the prescribed “norms” into the river, canal or water bodies.
About the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The National Clean Ganga Mission (NMCG) is a flagship programme developed by the National Council for the Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of the Ganga River, also known as the National Ganga Council.
- It is registered as a society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- It came into existence on August 12th 2011 and is supported by the State-Level Program Management Groups (SPMGs) in Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- The Government of India established this body to encourage a coordinated effort by the listed states to tackle the contamination of the Ganga River by offering financial and technological assistance.
Key objectives of the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The project entails rehabilitating and boosting existing STPs and immediate short-term action to reduce pollution at the exit points on the riverfront in order to control the inflow of sewage.
- To preserve the consistency of the water cycle without altering the fluctuations of the natural season.
- Restore and control surface and groundwater supply.
- Regenerate and preserve the natural flora of the city.
- To preserve and invigorate the aquatic biodiversity and the riparian biodiversity of the Ganga River basin.
- Enable the public to engage in the process of protecting, rejuvenating and maintaining the water.
Major functions of the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- Execution of the National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA) work program
- Integration of the National Ganga River Basin Project supported by the World Bank
- Supervise and manage the execution of projects approved by the Government of India under NGRBA
- To perform some additional research or duties as may be delegated by MoWR, RD & GJ in the context of restoration of the Ganga River
- Layout regulations and procedures for the conduct of NMCG affairs and contribute or revise, vary or amend them as and when required
- Grant or accept financial aid, loan securities or properties of any kind, and undertake and approve the management of any endowment trust, fund or gift that is not incompatible with the objectives of the NMCG.
- Take all such action and take any other action that might seem appropriate or relevant to the accomplishment of the goals of the NGRBA.
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module Retraces Steps to Earth Orbit (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have brought the Propulsion Module (PM) of the Chandrayaan-3 mission , which initially brought the Vikram lander to within 100 km of the Moon's surface before detaching and executing a historic controlled descent on August 23, back into Earth orbit.
What is a Propulsion Module in Chandrayaan-3?
- The Propulsion Module is a rectangular component of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft, equipped with solar panels for power.
- Its primary purpose was to transport the Lander module to the lunar polar circular orbit and facilitate its separation.
- Following separation, the SHAPE payload within the Propulsion Module was activated.
- Initially intended for a three-month operation during the mission, the ISRO announced on December 4th that the Chandrayaan-3's Propulsion Module had been manoeuvred out of lunar orbit.
- Placed high above Earth for an additional mission, the module is currently sustained by residual fuel.
- This bonus mission will showcase technologies crucial for future lunar sample retrieval, according to ISRO.
- As of now, the ISRO has not disclosed its plans for the spacecraft once it depletes its fuel.
Importance of Propulsion Module's Return to Earth's Orbit:
- ISRO highlighted the key achievements resulting from the return manoeuvres conducted on the Propulsion Module (PM) in connection to upcoming missions:
- Planning and executing the trajectory and manoeuvres for the return journey from the Moon to Earth.
- Developing a software module for planning such manoeuvres, along with its initial validation.
- Planning and executing a gravity-assisted flyby around a planet or celestial body.
- Preventing uncontrolled crashing of the PM onto the Moon's surface at the end of its life, aligning with the requirement of avoiding debris creation.
What is Chandrayaan-3 Mission?
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) (PIB)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) has recently praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
About Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):
- The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body created by WHO and FAO of the United Nations with 188 member countries.
- It is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular session once a year alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO with all work subject to approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organizations.
- The Commission works in the six UN official languages.
- India has been a member of this commission since 1964.
- The 46th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was held from 27 November to 2 December (2023) in Rome, Italy.
- In the current session, India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millet, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet, and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
Good Governance Day: Govt launches 3 new features on iGOT Mission Karmayogi platform (TOI)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Good Governance Day, Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched the Extended Version of Mission Karmayogi by introducing three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform that include My iGOT, Blended Programs and Curated Programs..
About Mission Karmayogi:
- Mission Karmayogi, the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), is geared towards equipping Civil Servants with enhanced creativity, constructiveness, and innovation, utilising transparency and technology to prepare them for future challenges.
- This innovative program serves as a cornerstone for the country's civil servants, emphasizing a balanced approach between 'on-site learning' and traditional 'off-site learning.'
- Approved by the Government on September 2, 2020, Mission Karmayogi encompasses six key pillars:
- Policy Framework
- Institutional Framework
- Competency Framework
- Digital Learning Framework (iGOT-Karmayogi)
- The electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS), and
- The Monitoring and Evaluation Framework.
- Encompassing all civil servants, including contractual employees, across various ministries, departments, organizations, and agencies of the Union Government, the program introduces three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform:
- My iGOT: Delivers targeted training courses on the home page of individual officers, directly addressing their unique capacity-building needs identified in the Capacity-Building Plan for their Ministries/Departments.
- Blended Programs: Facilitates equitable access to training methodologies across all levels by integrating traditional offline (in-person) classroom courses with online learning components.
- This approach enables officers and faculty to benefit from both the flexibility of online courses and the invaluable interactions of face-to-face classroom sessions.
- Curated Programs: Designed to cater to diverse learning needs of Ministries/Departments and Training Institutions, offering a custom approach to address the specific requirements of different segments within the civil services.
Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission (HT)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Dr Aroh Barjatya, an Indian-origin scientist is set to lead the multi-institution NASA rocket mission on October 14.
About Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission:
- The APEP mission entails the launch of three rockets, each equipped with scientific instruments, to explore changes in the upper atmosphere during a solar eclipse, particularly during the critical phase of sudden light reduction.
- Mission Objective: To investigate alterations in the ionosphere induced by the abrupt decrease in sunlight during an eclipse, leading to the generation of waves in this atmospheric layer.
- Measurements will encompass changes in electric and magnetic fields, as well as variations in density and temperature.
- Launch Details: The launch site is the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, with a specific focus on studying the ionosphere's response during an eclipse.
- Potential Impact on Communications: NASA notes projections indicating a temperature and density reduction in the ionosphere during the eclipse, potentially causing disruptive wave disturbances that could affect GPS and satellite communications.
- Process: Rockets will be strategically positioned just beyond the path of annularity, where the Moon directly aligns with the Sun.
- Each rocket will deploy four compact scientific instruments designed to capture data on electric and magnetic fields, density, and temperature changes.
- NASA's primary objective is to achieve unprecedented simultaneous measurements from multiple ionospheric locations during a solar eclipse.
- Rationale for Rocket Selection: Sounding rockets were chosen for their precision in pinpointing and measuring specific regions of space.
- Their ability to investigate lower altitudes, inaccessible to satellites, makes them ideal for this mission.
- Sounding rockets offer precise data recording as they ascend and descend during suborbital flights, covering altitudes ranging from 45 to 200 miles (70 to 325 kilometres) above Earth's surface along their flight path.
Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) (PIB)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, GoI is organizing the 19th Working Party on Data Collection and Statistics (WPDCS19) of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) from 28th November to 2nd December 2023.
About the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission:
- The Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for the management of tuna and tuna-like species in the Indian Ocean.
- It works to achieve this by promoting cooperation among its Contracting Parties (Members) and Cooperating Non-Contracting Parties in order to ensure the conservation and appropriate utilisation of fish stocks and encouraging the sustainable development of fisheries.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations adopted the Agreement for the Establishment of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission during its 105th Session in Rome on 25 November 1993.
- The Indian Ocean holds the position as the second-largest tuna fishery globally, making it a crucial focus for the IOTC.
- Currently, the IOTC boasts 31 contracting parties, including countries and two cooperating non-contracting parties, Liberia and Senegal.
- Membership is open to Indian Ocean coastal countries, countries or regional economic integration organizations that are UN members, countries that are members of UN special organizations, and countries involved in tuna fishing in the Indian Ocean.
- India is an active member of the IOTC, with its headquarters located in Victoria, Seychelles.
Psyche Mission (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A NASA experiment on the Psyche spacecraft has beamed back a near-infrared laser that contains test data from almost 16 million kilometers away.
About the Psyche Mission:
- Psyche is a NASA mission to study a metal-rich asteroid ‘Psyche’, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- The mission launched on October 13, 2023, from Kennedy Space Center and will arrive at Psyche in August 2029.
- The spacecraft will orbit the asteroid for about two years, studying its geology, composition, and magnetic field.
- Scientists believe that Psyche may be the exposed core of an early planet that never fully formed.
- If so, studying Psyche could provide important insights into the formation of our solar system.
- It is also the first in a series of NASA science missions to be the primary payload launched on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
- The goals of the Psyche mission are to:
- Understand the composition and structure of a metallic asteroid.
- Determine how Psyche formed and evolved.
- Learn more about the formation of planetary cores.
- The Psyche spacecraft is a solar-powered spacecraft that uses Hall effect thrusters for propulsion.
- The spacecraft also carries a suite of scientific instruments, including:
- A magnetometer to measure Psyche's magnetic field.
- A spectrometer to measure the composition of Psyche's surface.
- A gamma-ray spectrometer to measure the abundance of elements on Psyche's surface.
PM PVTG Development Mission (NewsOnAir)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi is going to launch the PM PVTG (Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups) Development Mission in a huge step to empower tribal people.
About PM PVTG Development Mission:
- The PM PVTG Development Mission plans to saturate PVTG families and habitations with basic facilities such as road and telecom connectivity, electricity, safe housing, clean drinking water, and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, and sustainable livelihood opportunities.
- The Mission will be implemented through the convergence of 11 interventions of nine Ministries.
- In addition, saturation will be ensured for schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojna, Sickle Cell Disease Elimination, TB Elimination, 100 percent immunisation, PM Surakshit Matritva Yojana, PM Matru Vandana Yojana, PM Poshan, and PM Jan Dhan Yojana.
Who are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- PVTGs, or Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, represent the most vulnerable subsets within India's diverse tribal communities, requiring heightened support and development efforts.
- There are 75 PVTGs in 18 States and Union Territories living in 22 thousand 544 villages having a population of around 28 lakhs.
- These tribes stay in scattered, remote, and inaccessible habitations, often in forest areas.
- The Government of India employs specific criteria for their identification, encompassing pre-agricultural technological levels, low literacy rates, economic disadvantages, and either a declining or stagnant population.
- The origin of the PVTG category dates back to 1975 when the government identified 52 vulnerable tribal groups, later augmented by an additional 23 in 1993.
- Notable examples of PVTGs include:
- the Cholanaikayan in Kerala
- Kathodi in Gujarat
- Jarawas in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands and
- Koraga in Karnataka
- The distinctive classification of PVTGs underscores a commitment to addressing the unique challenges faced by these marginalized tribal communities, aiming to uplift them through targeted support and development initiatives.
Euclid Mission (NASA)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Euclid mission, which will investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, released its first five science images recently.
About Euclid Mission:
- Euclid is a European mission, built and operated by European Space Agency (ESA), with contributions from NASA.
- Euclid is designed to give important new insights into the "dark side" of the universe -- namely dark matter and dark energy, both thought to be key components of our cosmos.
- It was launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, (USA) on 1 July 2023 and the launch vehicle used was ‘SpaceX Falcon 9’.
- The mission derives its name from Euclid of Alexandria, an ancient Greek mathematician from around 300 BC, who laid the foundations of geometry.
- Euclid Mission Objective: The primary goal of the Euclid mission is to create a three-dimensional map of the universe, with time as the third dimension.
- This will be achieved by observing billions of galaxies, extending up to 10 billion light-years away, and covering over a third of the celestial sphere.
- Euclid will explore how the Universe has expanded and how structure has formed over cosmic history, revealing more about the role of gravity and the nature of dark energy and dark matter.
- The Euclid Consortium – consisting of more than 2,000 scientists from 300 institutes in 13 European countries, the U.S., Canada, and Japan – is responsible for providing the scientific instruments and scientific data analysis.
- NASA provided the detectors of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer, NISP.
- Euclid is a medium-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme.
NASA all set to launch of PACE mission to study air quality, key climate factors and more (NASA)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
NASA is ready to enhance our understanding of Earth’s atmosphere with the upcoming Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission, scheduled for launch in early 2024.
What is NASA's PACE Mission?
- The mission will leverage advanced polarimeters to investigate the intricate interactions of light, aerosols, and clouds, enhancing our understanding of their impact on both air quality and climate.
- Beyond aerosol analysis, the PACE mission will delve into the study of ocean colour.
- At its core, the Ocean Colour Instrument (OCI) serves as the primary science instrument for PACE, designed to measure the ocean's colour across a spectrum ranging from ultraviolet to shortwave infrared.
- The mission includes two polarimeters:
- The Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and
- The Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2)
- Working in tandem, these instruments offer complementary spectral and angular sampling, ensuring polarimetric accuracy and extensive spatial coverage.
- This integrated approach aims to deliver enhanced atmospheric correction and a comprehensive dataset on aerosols and clouds, surpassing the capabilities of OCI alone.
- The collaborative payload of OCI, SPEXone, and HARP2 is poised to achieve significant breakthroughs in aerosol-cloud-ocean research.
What are Aerosols and their Effect?
- Aerosols are comprised of liquid or solid particles suspended in a gaseous or liquid medium.
- In the atmosphere, these particles are predominantly found in the lower layers (< 1.5 km) since aerosol sources are terrestrial.
- However, specific aerosols may extend into the stratosphere, particularly those ejected by volcanoes at high altitudes.
- Sources of Aerosols:
- Natural Sources: Generated from breaking waves (sea salt), wind-blown mineral dust from the surface, and volcanic emissions.
- Anthropogenic Aerosols: These include sulphate, nitrate, and carbonaceous aerosols, primarily originating from fossil fuel combustion.
- Effects of Aerosols:
- Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry.
- Reduction of Visibility.
- Significance for Air Quality and Human Health: Aerosols can adversely affect the heart and lungs.
- Role as Nuclei: Serve as nuclei for cloud droplets or ice crystals in ice clouds.
ISRO’s Gaganyaan TV-D1 test flight tomorrow: Everything you need to know (Indian Express)

- 20 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is preparing to launch its first-ever test flight, TV-D1, for the Gaganyaan mission, marking a watershed moment in the country's pursuit of human spaceflight.
About the TV-D1 Mission:
- Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1) will assess the crew module's readiness for the Gaganyaan mission.
- It is a single-stage liquid rocket designed specifically for this abort mission.
- The payloads include the Crew Module (CM) and Crew Escape Systems (CES) with their fast-acting solid motors, as well as the CM fairing (CMF) and Interface Adapters.
- This flight will simulate the abort condition encountered during the Gaganyaan mission's ascent trajectory, which corresponds to a Mach number of 1.2.
- The Crew Escape System is designed to operate automatically at various altitudes if the onboard computer detects any problems.
Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (LiveMint)
- 28 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RoDTEP scheme, which initially lasted until September 30, 2023, will now continue until June 30, 2024, with the same rates for products that are already being exported.
Facts About:
- The RoDTEP Scheme, officially known as the Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products, plays a crucial role in helping Indian exporters.
- It became operational on January 1, 2021, replacing the earlier export incentive program called Merchandise Exports from India (MEIS).
- This change was necessary because the World Trade Organization (WTO) found that the MEIS scheme violated WTO rules by providing export subsidies for a wide range of goods.
- How it Works: Under the RoDTEP Scheme, exporters receive a rebate based on a percentage of the value of their exports (known as FOB or Freight On Board value).
This rebate is given in the form of a transferable duty credit/electronic scrip (e-scrip), and the details of these credits are maintained digitally by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
The RoDTEP Committee, which operates within the Department of Revenue, is responsible for reviewing and recommending the maximum rates for different export sectors under this scheme.
- Main Objective: The primary goal of the RoDTEP Scheme is to offer comprehensive support to exporters by refunding the duties and taxes incurred during the production and distribution of exported products.
Importantly, it covers taxes, duties, and levies imposed at the central, state, and local levels, which are not reimbursed through other existing mechanisms.
- Financial Support: In the fiscal year 2023-24, the Indian Government has allocated a substantial budget of Rs. 15,070 crores to support the RoDTEP Scheme.
- Engaging with Stakeholders: The RoDTEP Committee has recently started its work by collaborating with Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) and Chambers of Commerce.
Competition Commission of India (CCI) (TOI)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Competition Commission of India has recently unveiled preliminary rules for overseeing mergers and acquisitions involving significant India-based operations, particularly those in the technology sector, thereby extending the authority of the antitrust regulator.
Facts About:
- CCI is a government-established statutory body founded in March 2009 under the Competition Act, 2002.
- The primary objective of CCI is to foster fair competition in the economy, ensuring a level playing field for producers and promoting market dynamics that benefit consumers.
- The Commission's key focus areas include eradicating practices detrimental to competition, fostering and maintaining competitive environments, safeguarding consumer interests, and upholding the freedom of trade in India's markets.
Mandate: CCI enforces the provisions of The Competition Act, 2002, which:
- Prohibits anti-competitive agreements and the abuse of dominant positions by enterprises.
- Regulates mergers and acquisitions (M&A) that could potentially harm competition within India. Hence, deals exceeding certain thresholds require clearance from CCI.
- Monitors the activities of large enterprises to ensure they do not misuse their 'dominant position' by controlling supply, setting high purchase prices, or engaging in unethical practices that may harm emerging businesses.
Composition: CCI functions as a quasi-judicial body, consisting of one chairperson and six additional members, all appointed by the Central Government.
Headquarters: The Commission is headquartered in New Delhi.
Malaviya Mission (PIB)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Malaviya Mission - Teachers Training Programme, initiated by the University Grants Commission, was recently unveiled at Kaushal Bhawan in New Delhi by the Union Minister for Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship.
Facts About:
- The primary objective is to offer customized training programs for educators.
- This initiative is focused on enhancing the capabilities of faculty members in higher education institutions (HEI).
- It is dedicated to achieving continuous professional development and strengthening the skills of 15 lakh HEI teachers across India through 111 Malaviya Mission centers within a specific timeframe.
- The program is designed to elevate the quality of teacher training, foster leadership qualities among educators, and align with the objectives of the National Education Policy (NEP).
- Capacity building activities under this Mission will be aligned with a credit framework to facilitate career advancement opportunities for teachers.
- Notably, the Indian Knowledge System has been incorporated into the program's modules.
- As part of this initiative, Human Resource Development Centers will undergo a transformation and be renamed as Madan Mohan Malaviya Teachers Training Centers.
Bill on Election Commission members’ Appointments (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Bill is set to be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with the view of overturning the effect of the Supreme Court’s (SC) verdict on the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners (ECs).
Facts About:
- The Bill seeks to establish a committee of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM for selecting members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Current Procedure: Currently, the Law Minister suggests a pool of suitable candidates to the Prime Minister for consideration.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the PM.
- As per the Bill, a Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary and comprising two other members, not below the rank of Secretary to the government, having knowledge and experience in matters relating to elections, shall prepare a panel of five persons who can be considered for appointment.
- Then, as per the Bill, a Selection Committee consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister will appoint the CEC and other ECs.
Present structure to appoint CEC and ECs:
- Under Article 324 (2), the President appoints the CEC and other ECs.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.
- The Constitution does not prescribe any qualifications, academic or otherwise, for appointment to these offices.
- Tenure:
- The tenure of office and the conditions of service of all the commissioners is determined by the President.
- The tenure of commissioners is 6 years or up to the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CEC and the two other ECs have the same powers and emoluments, including salaries, which are the same as a Supreme Court judge.
- All three commissioners have the same right of taking a decision. In case of a difference of opinion amongst the three members, the matter is decided by the Commission by a majority.
Process of removal:
- Article 324 of the Constitution of India mentions the provisions to safeguard and ensure the independent and impartial functioning of the Election Commission.
- The CEC is provided with security of tenure. He cannot be removed from his office except in the same manner and on the same grounds as a judge of the Supreme Court.
- Any other election commissioner or a regional commissioner cannot be removed from office except on the recommendation of the CEC.
Supreme Courts’ Judgment:
- On March 2, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court unanimously ruled that a high-power committee consisting of the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India must pick the CEC and ECs.
- The judgement by a bench came in 2015, challenging the constitutional validity of the practice of the Centre-appointed members of the Election Commission.
- According to the judgement, the SC has now given the Opposition and the judiciary a say in the matter, ruling that the CEC and ECs must be appointed by the President on the advice of a committee comprising the PM, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India.
- Also, in 2018, a two-judge bench of the SC referred the case to a larger bench since it required a close examination of Article 324 of the Constitution, which deals with the role of a Chief Election Commissioner.
Debate around appointment of CEC and ECs:
- Article 324(2) reads that “The Election Commission shall consist of the Chief Election Commissioner and such number of other Election Commissioners, if any, as the President may from time-to-time fix and the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners shall, subject to the provisions of any law made in that behalf by Parliament, be made by the President.”
- The Parliament has the power to nullify the effect of a Court ruling by addressing the concerns flagged in the judgment.
- In this case, the arrangement prescribed by the Supreme Court was specifically because the Court noted that there was a “legislative vacuum.” Filling that vacuum is well within the purview of the Parliament.
- However, the idea of an independent body that conducts elections permeates through the judgement.
- The Court repeatedly stated that to be the objective of the framers of the Constitution.
- The composition of the Selection Committee in the Bill raises questions on whether the process is now independent or still rigged in favour of the Executive.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/bill-election-commission-members-appointment-process-explained-8885676/#:~:text=The%20Centre%27s%20Bill%20seeks%20to,Commission%20of%20India%20(ECI).
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) recently addressed the Manipur DGP, urging the filing of an FIR against three individuals.
About the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
Composition of NCPCR:
- This commission has a chairperson and six members of which at least two should be women.
- All of them are appointed by Central Government for three years.
- The maximum age to serve in commission is 65 years for Chairman and 60 years for members.
Functions and responsibilities of NCPCR:
- Examine and assess current safeguards for child rights and propose effective implementation strategies.
- Submit periodic reports to the central government on the efficacy of these safeguards.
- Conduct investigations into child rights violations and recommend legal action when appropriate.
- Raise awareness about child rights and available safeguards through diverse channels, such as publications, media, and seminars.
- Conduct inspections of institutions housing children, including juvenile homes, and suggest remedial measures if required.
- Investigate complaints and proactively address issues related to child rights deprivation, violation, and non-implementation of protective laws.
National Dental Commission Bill, 2023 (TIO)
- 24 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently witnessed the introduction of the National Dental Commission Bill, 2023, by the government.
About National Dental Commission Bill, 2023:
- The primary objective of the Bill is to revoke the Dentists Act of 1948, ushering in new regulations and reforms.
- With a focus on affordability, the bill strives to enhance dental education accessibility and ensure quality oral healthcare services.
- In place of the existing Dental Council of India, the Bill proposes the establishment of the National Dental Commission (NDC) to oversee dental education and related matters effectively.
What is National Dental Commission (NDC)?
- The establishment of the new commission entails the formulation of policies and the maintenance of quality standards in dental education and the dental profession.
- A key responsibility of the commission will be to regulate fees for 50% of seats in private dental colleges.
Composition of NDC:
- The structure of the NDC will mirror that of the National Medical Commission (NMC), which replaced the Medical Council of India.
- The head office of the National Dental Commission will be located in New Delhi, consisting of a chairperson, eight ex officio members, and 24 part-time members and the appointment of members will be done by the central government.
- The Bill mandates that all members of the commission must declare their assets and liabilities upon entering and leaving office, along with disclosing any professional and commercial engagements they are involved in.
