NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
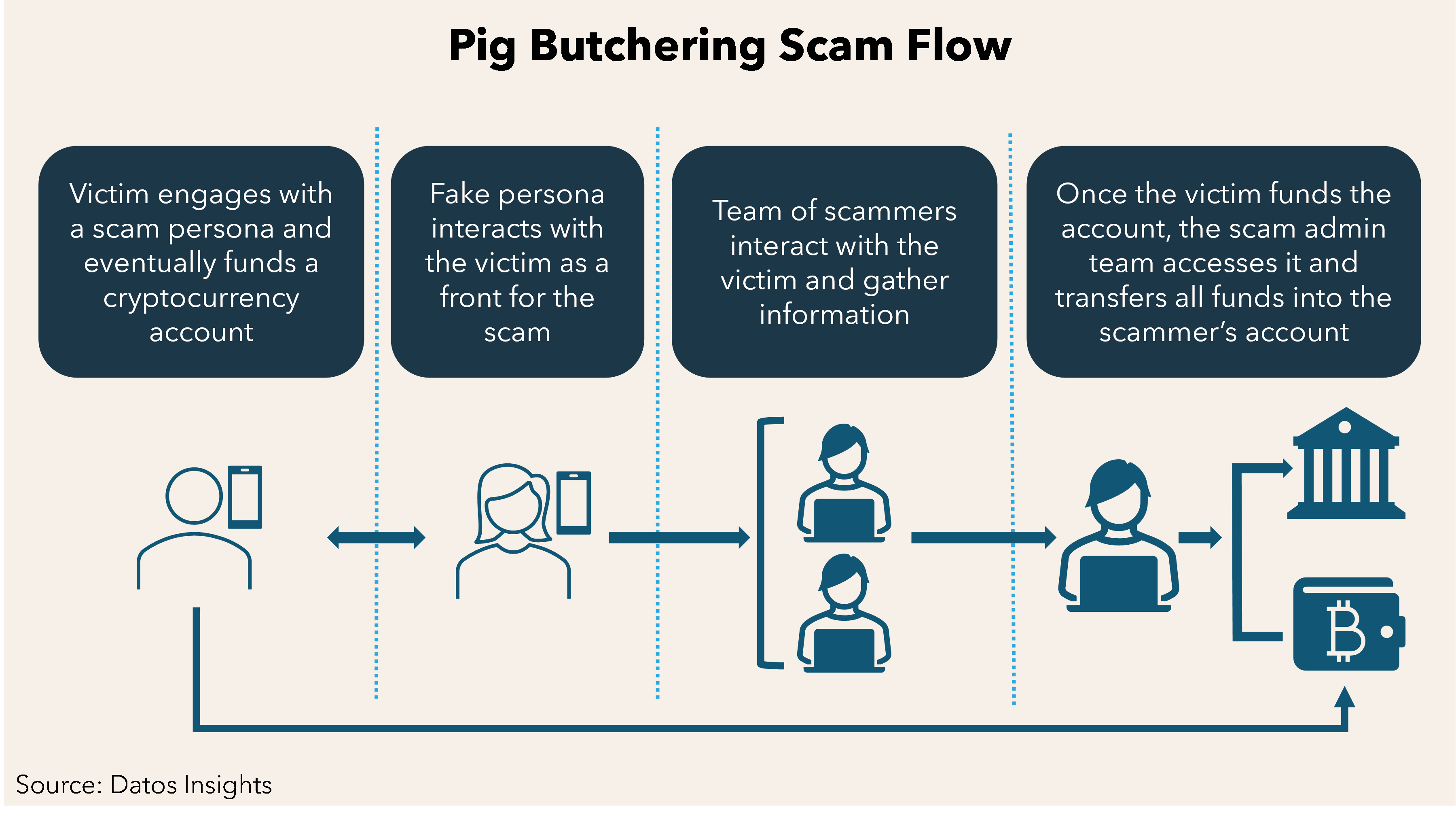
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
61st Raising Day

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 20, 2024, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah attended the 61st Raising Day function of the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) in Siliguri, West Bengal. During the event, he e-inaugurated the Integrated Check Point (ICP) Agartala and a newly constructed residential complex for the Border Guard Force (BGF) at Petrapole. The event was attended by several dignitaries, including the Director of Intelligence Bureau (IB), Secretary of Border Management (MHA), and the Director-General of SSB.
Key Highlights from the Speech:
- Tributes to Martyrs: Shri Shah paid tributes to SSB martyrs, highlighting their sacrifices in protecting the country's borders and eliminating Left Wing Extremism in the eastern region. He acknowledged the 4 Padma Shri, 1 Kirti Chakra, and other national awards received by SSB for their exceptional service.
- Role in Connecting Borders: The Home Minister praised SSB’s role in connecting the culture, language, and heritage of border villages with mainstream India. He emphasized that the SSB has fulfilled its motto of "Service, Security, and Brotherhood" while maintaining a strong relationship with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Security and Vigilance: SSB is responsible for securing a 2,450 km border with Nepal and Bhutan. Shri Shah noted that SSB's vigilance has helped in stopping narcotics, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Additionally, the force has worked to ensure that Bihar and Jharkhand are now Naxal-free.
- Zero-Tolerance Policy: The SSB has a zero-tolerance policy on encroachments, narcotics, and smuggling. Over the last three years, the SSB successfully removed more than 1,100 encroachments from government land and seized significant amounts of narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit currency.
- Impact in Jammu & Kashmir: SSB has played a critical role in combating terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, killing more than 19 terrorists and arresting 14 through various operations.
- Humanitarian Efforts: Besides security, SSB has actively participated in disaster relief operations during floods and landslides, often at great personal risk.
- Government Schemes for CAPF Personnel: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, various welfare schemes like Ayushman Cards, CAPF e-Housing, and scholarships have been launched to support CAPF personnel and their families.
- Self-Employment Initiatives: SSB has promoted self-employment for border youth, training them in areas like beekeeping, mobile repairing, and driving. They have also contributed significantly to the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, creating awareness about drug addiction among 36,000 youth.
- Environmental Contribution: The force has planted over 6 crore trees as part of its environmental efforts.
Pegasus Spyware

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
For the first time, a court in the US has held Israel’s NSO Group liable for its intrusive spyware Pegasus, which could set up a measure of accountability for the company that it has, for long, allegedly downplayed.
Overview:
- Pegasus is a spyware developed by the Israeli company NSO Group.
- It has been used for surveillance, allegedly targeting journalists, activists, politicians, and government officials across the world, including India.
Recent Legal Developments:
- US Court Ruling (2024):
- A US court held NSO Group liable for using Pegasus to surveil 1,400 WhatsApp users, including 300 from India.
- NSO Group violated the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the California Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA).
- The ruling may revive debates on the accountability of spyware use and its implications on privacy.
Use of Pegasus in India:
- Targeted Individuals (2021):
- 300 Indian numbers allegedly targeted, including journalists, politicians, Union Ministers, and civil society members.
- High-profile targets included opposition leaders, constitutional authorities, and activists.
- Government Denial:
- The Indian government denied involvement, stating allegations lacked substance.
- In Parliament, IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw rejected claims, asserting India’s surveillance laws prevent unauthorized surveillance.
- NSO Group Response:
- NSO Group denied the allegations, calling them “false and misleading” and citing doubts about the sources.
Investigations and Legal Actions:
- Supreme Court Inquiry:
- The Supreme Court appointed a committee of technical experts in 2021 to investigate claims.
- August 2022 Report: Found no conclusive evidence of spyware use on examined devices but noted lack of cooperation from the government.
- State-Level Investigations:
- West Bengal: Set up a Commission of Inquiry into Pegasus surveillance, later halted by the Supreme Court.
- Andhra Pradesh: The issue became political, with allegations that the previous government used Pegasus to monitor opposition figures.
Pegasus Spyware Features:
- Capability: Can hack iOS and Android devices to collect data, record conversations, capture photos, and access app data.
- Exploitation Method: Uses zero-day vulnerabilities to exploit iOS and Android devices covertly.
- Invisibility: Operates without user knowledge, often only detected through signs like browser closings after phishing links are clicked.
Controversial Use of Pegasus:
- Global Use: Though intended for fighting terrorism and crime, Pegasus has been misused for spying on journalists, politicians, human rights activists, and opposition leaders.
- India Specifics:
- Pegasus Project: Targeted Indian citizens, including activists, journalists, and politicians.
- Amnesty International: Confirmed use of Pegasus to target Indian phones.
India's Legal Framework for Surveillance:
- Telecommunications Act (2023): Empowers the government to control telecom services during emergencies, but requires authorization for lawful interceptions.
- IT Act (2000): Allows the government to monitor, intercept, or decrypt information through computer resources under certain conditions.
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act (2023): Aims to protect personal data, including provisions on surveillance, data breaches, and rights of individuals over their data.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns:
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- Surveillance infringes on the right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Freedom of speech and expression (Article 19) may be curtailed, with surveillance being used to suppress dissent.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Surveillance often occurs without judicial or parliamentary oversight, leading to potential executive overreach.
- Inability to Seek Legal Remedies:
- Citizens targeted by surveillance cannot challenge it due to lack of awareness, undermining constitutional rights.
- Executive Overreach and Suppression of Free Expression:
- Pegasus revelations have raised concerns about surveillance targeting constitutional functionaries, suppressing free speech, and stifling open discourse.
Reimposition of Protected Area Permit (PAP) in Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of the Government of India has recently reinstated the Protected Area Regime (PAR) for the states of Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland, which are strategically located along the international border with Myanmar. This move comes amid growing security concerns, particularly the influx of migrants from Myanmar, which has been cited as a significant factor in the ongoing conflicts in the region.
What is Protected Area Permit (PAP)?
A Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permission required for foreign nationals to visit certain areas of India deemed sensitive due to their proximity to international borders or other security-related concerns. The regulations governing the PAP are laid down under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958, which restricts the entry of foreigners to designated regions within India.
Purpose of PAP:
The PAP regime serves multiple critical objectives:
- National Security: It ensures the monitoring and regulation of foreign nationals in sensitive border areas.
- Preservation of Local Communities: The regime safeguards indigenous populations and their unique cultural heritage.
- Environmental Conservation: The permit helps minimize ecological disturbances in fragile regions, ensuring sustainable tourism and development.
Key Features of PAP Regime:
- Eligibility: All foreign nationals, excluding Bhutanese citizens, must obtain a PAP to enter these designated areas. The permit can be granted for specific regions, routes, and time periods.
- Validity: The PAP is typically valid for 10 days with the possibility of extension.
- Restricted Areas: Certain foreign nationals, particularly those from Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, require prior approval from the MHA to enter these regions.
- Tourism and Other Permits: While foreign nationals can visit these regions for tourism purposes under the PAP, non-touristic visits require special permission from the MHA.
- Registration: Foreigners must register with the Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) within 24 hours of arrival in the protected area.
Historical Context and Reimposition:
The PAP regime was lifted for Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland in 2011, as part of efforts to boost tourism in the region. However, due to rising security concerns related to illegal immigration and ethnic tensions, the MHA reimposed the PAP in 2025. The government’s move aligns with its broader national security strategy to better control foreign movements in sensitive border regions, particularly those with Myanmar, where the Free Movement Regime (FMR) had previously allowed easier cross-border travel.
Background on Security Concerns:
The influx of individuals from Myanmar, particularly members of the Chin community, which shares ethnic ties with the Kuki-Zomi communities in India, has been a source of tension. The Manipur government has repeatedly emphasized that uncontrolled migration has contributed to the unrest in the state. Additionally, the decision to end the FMR between India and Myanmar has further intensified the debate over border security and migration.
Impact on Tourism and Local Communities:
While the reimposition of the PAP is seen as a measure to strengthen security, it has raised concerns in states like Mizoram and Nagaland, which have been actively promoting tourism. For example, Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival recently attracted over 200,000 visitors, including foreign nationals. The reintroduced restrictions may dampen tourism in these states, which were previously exempt from the PAP to encourage foreign visits.
Key Legal Provisions Under the PAP Regime:
- Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958: This order mandates the requirement of a PAP for foreigners visiting areas close to international borders.
- Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963: This order covers areas that require a Restricted Area Permit (RAP) for foreign nationals, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
States Affected by the PAP Regime:
The PAP regime affects regions close to India’s international borders, including the entire states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand.
Smuggling in India Report 2023-24
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The annual ‘Smuggling in India - Report 2023-24’ report, which highlights DRI’s performance and experience over the last financial year as well as trends in the field of anti-smuggling and commercial fraud, will be released during the celebration.
Major Narcotics Hubs and Routes:
- Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan (The Death Crescent):
- Primary source of heroin trafficked into India.
- Routes via Africa, the Gulf, and India-Pakistan border.
- Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand (The Death Triangle):
- Significant source of synthetic drugs and heroin.
- Drugs often enter India through porous northeastern borders (e.g., Assam, Mizoram).
- Vulnerable regions: Moreh, Churachandpur, Zokhawthar.
- Maritime Routes:
- India’s vast coastline provides opportunities for drug trafficking, often through concealed shipping containers and fishing vessels.
- Air Routes:
- Increased trafficking due to international air traffic.
- Smuggled drugs often concealed in luggage, courier packages, or ingested by mules.
Major Narcotics Trends and Seizures (FY24):
- Cocaine:
- Significant increase in trafficking, particularly from South America and Africa.
- 47 seizures, up from 21 in the previous year.
- Seized quantity: 107 kg.
- Methamphetamine:
- Spiked in northeastern states like Assam and Mizoram.
- Seized quantity in FY24: 136 kg; increased in the first half of FY25 with 123 kg.
- Hydroponic Marijuana:
- Increasing smuggling from the US, Thailand, and other countries.
- Black Cocaine:
- New form of cocaine coated with substances like charcoal or iron oxide to evade detection.
- Contraband Cigarettes:
- Smuggling through sea routes, especially from Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- Seizures increased by 19% in FY25, reaching 3.95 crore sticks.
- Illicit Gold:
- Significant destination for gold smuggling from West Asia (UAE, Saudi Arabia).
- Seized quantity fell slightly (1,319 kg in FY24), with land and air routes being primary methods.
- Wildlife Smuggling:
- Seizures included 53.5 kg of elephant tusks, leopard skins, live pangolins, and more.
Challenges and Issues:
- Porous Borders:
- Smuggling across eastern borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal remains a significant challenge.
- Difficult terrain in these regions aids traffickers.
- Air and Sea Routes:
- Growing use of air and maritime routes due to faster movement of goods.
- Technology and Detection:
- Emergence of “black cocaine” challenges traditional detection methods.
Anti-Smuggling and Drug Control Efforts:
- International Cooperation:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) lead global efforts.
- Paris Pact Initiative targets Afghan opiate trafficking.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) provides legal framework.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) work together for enforcement.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan focus on awareness and rehabilitation.
ABOUT DRI
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is the premier intelligence and enforcement agency on anti-smuggling matters under the aegis of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC), Government of India.
- It came into existence on 4th December 1957.
- With its Headquarters at New Delhi, 12 Zonal Units, 35 Regional Units and 15 Sub-Regional Units, DRI has been carrying out its mandate of preventing and detecting cases of smuggling of narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances, gold, diamonds, precious metals, wildlife products, cigarettes, arms, ammunitions & explosives, counterfeit currency notes, foreign currency, SCOMET Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) items, hazardous & environmentally sensitive materials, antiques etc. and taking punitive action against the organised crime groups engaged therein.
- DRI is also engaged in unearthing commercial frauds and instances of customs duty evasion.
Operation Kawach

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Delhi Police recently initiated Operation Kawach, arresting and detaining around 1,000 people in an attempt to crack down on various gangs and their operations in the wake of the recent incidents of shootings reported in the city.
Overview of Operation Kawach
- Objective: A crackdown on gang-related violence, drug trafficking, and other illegal activities like possession of firearms, banned drugs, and liquor.
- Agencies Involved:Delhi Police (Local Police, Special Cell, and Crime Branch)
- Duration: Initiated on November 12, 2024 (5 PM) and continued until November 13, 2024 (5 PM).
Key Details of the Operation
- Arrests and Detentions:
- Around 1,000 people detained.
- 486 people apprehended in Outer North Delhi (20% juveniles).
- Arrests made in Dwarka, Southwest, and North Delhi.
- Key Gangs Targeted:
- Associated with notorious gangs led by Lawrence Bishnoi, Neeraj Bawana, Kaushal Chaudhary, TilluTajpuria, Kala Jatheri, Manjeet Mahal, and Nandu gangs.
- Charges: Involvement in activities like:
- Possession of illegal firearms.
- Trafficking of liquor and banned drugs (NDPS Act).
- Theft and other criminal activities.
Significance of Operation Kawach
- Public Safety: Aimed at dismantling organized crime networks to enhance safety and reduce violence in Delhi.
- Impact on Gangs: Directly targets high-profile criminals, including those involved in gang wars and drug trafficking.
- Strategic Law Enforcement: Strengthens law enforcement capabilities, working in coordination across multiple police units.
Cyberfraud Losses and Economic Impact

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- ?1.2 lakh crore is the projected financial loss due to cyber frauds in India over the next year (2024), according to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Union Home Ministry.
- This could amount to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Mule Accounts:
- Mule accounts are a significant contributor to cyber frauds. These accounts are used to facilitate money laundering and illegal transactions.
- On average, around 4,000 mule accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- Mule accounts typically facilitate the transfer of funds out of India, often through cryptocurrency transactions.
- Sources of Cyber Scams:
- A majority of frauds are linked to Chinese entities or China-based operations, with about half of the cybercrime complaints originating from China.
- Other major hubs for cyber frauds include Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, which house call-centre-like scam compounds.
- Azerbaijan has also been identified as a new hotspot for such scams.
- International Dimension:
- Fraudulent withdrawals have been reported from ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia using mule accounts.
- The international nature of these scams often involves routing stolen funds through various countries, using methods like cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Cybercrime and Terror Financing:
- Cyber scams have potential ramifications beyond financial losses; they can be used for terror financing and money laundering.
- Cryptocurrency is a common medium for laundering money, with an example cited of ?5.5 crore laundered through 350 transactions in a short span.
- ATM Hotspots and Fraudulent Withdrawals:
- 18 ATM hotspots have been identified across India where fraudulent withdrawals occur.
- Fraudsters exploit these locations to withdraw money, often using mule bank accounts and cross-border ATM networks.
- Government Response:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is working to combat these frauds by convening meetings with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The objective is to curb the operation of mule accounts and strengthen the banking system to prevent such frauds.
- Banks are being urged to flag unusually high-value transactions or accounts with low balances that are engaging in suspicious activity.
- Fraudulent Calls and Scam Compounds:
- Indian fraudsters, in collaboration with international scam rings, use Indian mobile phone numbers to deceive citizens.
- Countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, and Azerbaijan have been identified as hubs for investment scams involving fraudulent calls.
- Helpline and Cyber Fraud Reporting System:
- The Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (part of I4C) and the 1930 helpline provide mechanisms to report financial frauds.
- ?11,269 crore in financial frauds was reported during the first half of 2024 via these channels.
- The system also involves cooperation with over 200 financial intermediaries, including banks and wallets.
Z-Morh Tunnel Project in Kashmir

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
Seven people were killed in Jammu and Kashmir when suspected militants targeted the workers of infrastructure company APCO Infratech, which is constructing the Z-Morh tunnel on the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway. This is the first militant attack on a key infrastructure project in Jammu and Kashmir. In the past, militants have not targeted such infrastructure projects in the region.
What is the Z-Morh Tunnel?
- Length: 6.4 kilometers
- Connection: Links Sonamarg (a popular tourist destination) with Kangan town in central Kashmir’s Ganderbal district.
- Construction Site: Located near Gagangir village, ahead of Sonamarg.
- Naming: The tunnel gets its name from the Z-shaped road near the construction site.
Importance of the Z-Morh Tunnel
- All-Weather Connectivity: The tunnel is crucial for year-round access to Sonamarg, particularly in the winter when the road is often blocked by snow avalanches.
- Location: Situated at 8,500 feet above sea level, the tunnel provides a safe, all-weather route for tourists and locals, especially during winter months when access to Sonamarg is typically limited.
Strategic Importance
- Part of Zojila Tunnel Project:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is integral to the larger Zojila tunnel project, which aims to provide all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh.
- The Zojila Tunnel, under construction at an altitude of around 12,000 feet, will connect Sonamarg (Kashmir) to Drass (Ladakh) and is expected to be completed by December 2026.
- Military and Strategic Significance:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is crucial for rapid military mobilization between Srinagar, Kargil, Leh, and Drass regions.
- It ensures quick access for military personnel to the Ladakh border, particularly in areas of heightened security like Siachen Glacier and the Turtuk sub-sector (on the Pakistan border).
- The tunnel will reduce dependence on air transport for troop and supply movements to forward areas, leading to cost savings and extended aircraft lifespan.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Manipur government has extended the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in the hill districts of the State for another six months.
- Effective October 1, the provisions of the Act will be extended to the whole State, except 19 police station limits in seven valley districts, thus maintaining the status quo, since three such notifications were passed since March 2023.
- It added that the “disturbed area” status could not be reviewed and a detailed ground assessment could not be done as “the sister security agencies are preoccupied with maintenance of law and order” and “it will be premature to arrive at any conclusion or decision on such sensitive matter without detailed assessment.”
Overview of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA)
- Enactment: The AFSPA was passed by Parliament and approved by the President on September 11, 1958.
- Context: It was introduced in response to rising violence in the North-eastern States, which state governments struggled to control.
Key Provisions of AFSPA
- Powers Granted:
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Kill anyone acting against the law.
- Arrest and search premises without a warrant.
- Receive protection from prosecution and legal action without Central government sanction.
- The Act empowers armed forces and Central Armed Police Forces in "disturbed areas" to:
- Issuance of Notifications:
- Both State and Union governments can issue notifications regarding AFSPA.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs issues "disturbed area" notifications for Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
Definition of Disturbed Areas
- Criteria:
- A disturbed area is declared under Section 3 of AFSPA, indicating the need for armed forces' assistance in maintaining civil order.
- Factors leading to the declaration can include:
- Conflicts among different religious, racial, linguistic, or regional groups.
- Authority to Declare:
- The Central Government, the Governor of the State, or the administrator of a Union Territory can declare an area as disturbed.
- Duration:
- Once designated as disturbed, the area remains classified as such for three months, as per The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
- State Government Input:
- State governments can recommend whether AFSPA should continue in their region.
Grey-zone Warfare Latest Entry in Lexicon of Warfare

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the last day of the 2024 Raisina Dialogue (February 24), India’s Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan said that “grey zone warfare” is the latest in informal warfare.
What is the Grey Zone Warfare?
- Grey zone warfare refers to a strategic approach where a nation seeks to gain advantages over others without engaging in overt conflict.
- It involves a series of tactics, including cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and economic pressures, aimed at subtly undermining or destabilizing adversaries.
- China has notably employed this strategy against India and neighboring countries.
What are the China's Grey Zone Tactics Against India?
- South China Sea Activities: China asserts its dominance in the South China Sea using naval and civilian vessels, raising tensions with neighboring countries like India.
- Infrastructure Near Borders: China constructs infrastructure and settlements near India's borders, bolstering territorial claims and strategic positioning.
- Digital Investments: China invests in Indian digital platforms and media, influencing public narratives and perceptions.
India's Counter-Measures:
- Inter-Agency Collaboration: India promotes collaboration among defense, intelligence, and law enforcement agencies to devise comprehensive strategies to counter grey zone threats.
- Enhanced Vigilance: India increases surveillance and presence in border areas and strategic locations to detect and respond to covert Chinese activities.
- Regulating Foreign Investments: India scrutinizes foreign investments in critical sectors, particularly technology, to safeguard national security interests.
Long-Term Implications for India:
- Information Warfare: Grey zone conflicts often involve digital misinformation, influencing public opinion and perceptions.
- Economic Leverage: Dependency on foreign investments poses vulnerabilities if used as leverage by investing nations.
- Technology Dependency: Heavy reliance on foreign technology exposes India to risks, emphasizing the need to bolster indigenous technological capabilities.
Conclusion
Grey zone warfare encompasses a multifaceted strategic landscape, blending digital, economic, and geopolitical tactics. India recognizes these challenges and is actively devising strategies to navigate this complex terrain.
Bengaluru's Rameshwaram cafe blast puts the spotlight on IEDs

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least nine people were injured after an explosion at the bustling Rameshwaram Cafe in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area recently, possibly by an improvised explosive device (IED).
What is Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)?
- An Improvised Explosive Device (IED) refers to a makeshift explosive device constructed and deployed unorthodoxly or improvised.
- These devices are typically crafted using commonly available materials, including explosives, triggers, and containers, often to cause destruction, injury, or death.
- IEDs can vary widely in design and complexity, ranging from simple pipe bombs to more intricate devices incorporating timers, remote controls, or even cellular communication for activation.
- IEDs can be deployed using a vehicle, carried, placed, or thrown by a person, delivered in a package, or concealed on the roadside.
- Due to their adaptable nature, IEDs are commonly used by insurgents, terrorists, and other malicious actors to carry out attacks against both military and civilian targets.
- Their unpredictable nature and often concealed placement make them particularly challenging for security forces to detect and mitigate.
- Efforts to counter IED threats involve a combination of technological advancements, intelligence gathering, and counterinsurgency strategies aimed at identifying and neutralizing these devices before they can cause harm.
Types of IEDs:
- Vehicle-Borne IEDs: Among the most destructive forms of IEDs are those concealed within vehicles. These can be driven to specific locations and detonated, causing massive explosions capable of levelling buildings.
- Suicide Bombings: Suicide bombings involve individuals strapping IEDs to their bodies, becoming human carriers of destruction. This method inflicts maximum damage in densely populated areas.
- Package IEDs: Package IEDs are small devices hidden in innocuous-looking packages. They are often placed in public spaces, targeting unsuspecting victims.
Methods of IED Initiation:
- Remote Control: IEDs can be remotely triggered using various methods, such as cell phones or radio signals, allowing attackers to maintain a safe distance from the explosion.
- Pressure Activation: Pressure-sensitive IEDs detonate when a certain amount of pressure is applied, making them lethal traps for those who inadvertently trigger them.
- Timers: IEDs can also be equipped with timers, which delay the explosion to occur at a specific time, further complicating detection and prevention.
The Devastating Impact of IEDs:
- The aftermath of IED explosions is often catastrophic, leading to loss of life, severe injuries, and widespread damage to infrastructure.
- The psychological impact on survivors and affected communities can be long-lasting.
Detection Technologies and Challenges:
- Detection technologies such as (Metal Detectors, X-ray and Imaging Scanners, Explosive Trace Detection (ETD), and Sniffer Dogs) play a critical role in countering the threat of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), but they also face numerous challenges due to the evolving nature of these devices.
Cabinet approves Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for the period 2021-26

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of “Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)” with a total outlay of Rs. 4,100 crore for a period of 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
About the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP):
- The FMBAP Scheme is being implemented throughout the country for effective flood management, erosion control and anti-sea erosion and to help in maintaining peace along the border.
- The scheme benefits towns, villages, industrial establishments, communication links, agricultural fields, infrastructure etc. from floods and erosion in the country.
- The catchment area treatment works will help in the reduction of sediment load into rivers.
- The Scheme aims at the completion of the ongoing projects already approved under FMP.
The Scheme has two components:
- Under the Flood Management Programme (FMP) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 2940 crore, central assistance will be provided to State Governments for taking up critical works related to flood control, anti-erosion, drainage development and anti-sea erosion, etc.
- The pattern of funding to be followed is 90% (Centre): 10% (State) for Special Category States (8 North-Eastern States and Hilly States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and UT of Jammu & Kashmir) and 60% (Centre):40% (State) for General/ Non-Special Category States.
- Under the River Management and Border Areas (RMBA) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 1160 crore, flood control and anti-erosion work on common border rivers with neighbouring countries including hydrological observations and flood forecasting, and investigation & pre-construction activities of joint water resources projects (with neighbouring countries) on common border rivers will be taken up with 100% central assistance.
- The Scheme has the provision of incentivizing the States which implement flood plain zoning, recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Importance:
- While the primary duty of flood management lies with the State Governments, the Union Government actively promotes and advocates for the adoption of modern technology and innovative approaches.
- Additionally, projects executed under the RMBA component serve to safeguard critical installations of security agencies and border outposts situated along border rivers from the perils of floods and erosion.
- Furthermore, the scheme includes provisions for incentivizing states that implement flood plain zoning, a recognized and effective non-structural measure for flood management.
