16th BRICS Summit 2025

- 26 Oct 2025
In News:
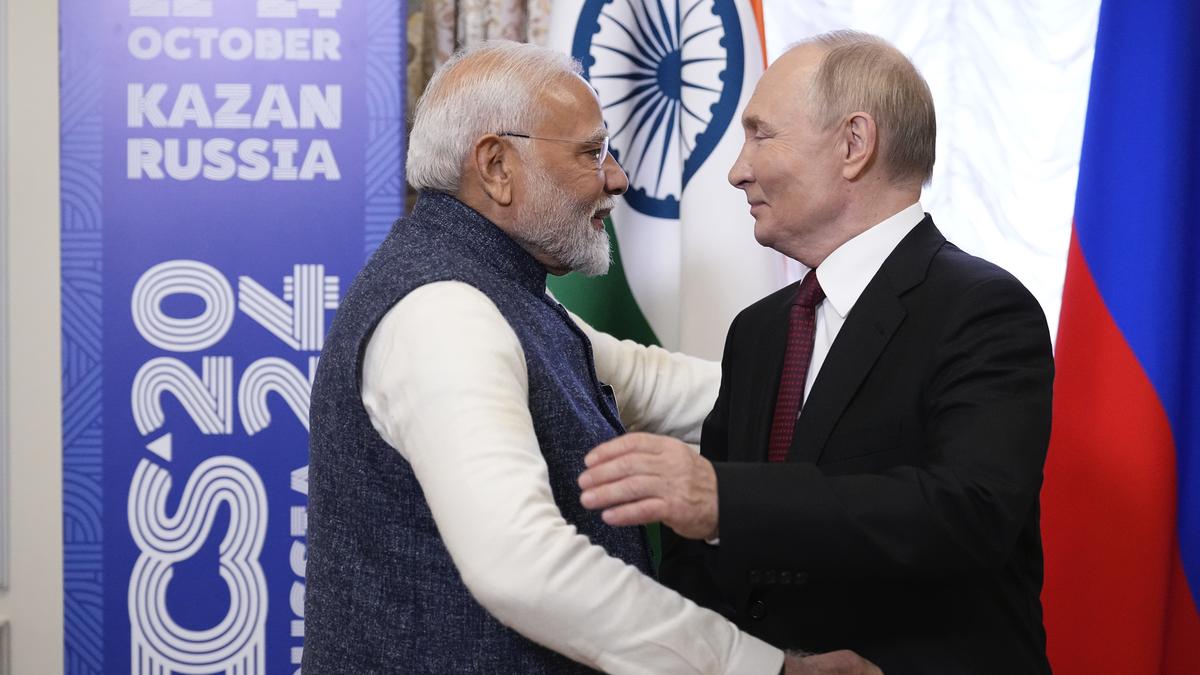
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi attended the 16th BRICS Summit, hosted by Russia in Kazan, under the theme “Strengthening Multilateralism for Just Global Development and Security.”
- The summit brought together leaders from Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, alongside newly inducted members such as Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates, reflecting the bloc’s expanding global footprint.
Background and Evolution of BRICS
- The BRICS grouping originated as BRIC in 2006 following the St. Petersburg meeting between Russia, India, and China, and was later formalized at the Yekaterinburg Summit (2009).
- South Africa joined in 2011, transforming BRIC into BRICS.The most recent expansion in 2024 added five new members, representing a major step toward inclusivity and a stronger collective voice for the Global South.
Initially comprising 42% of the world’s population, 30% of global land area, 23% of GDP, and 18% of global trade, the expanded BRICS seeks to reshape global economic governance and reduce dependence on Western-led institutions.
Objectives and Role
The alliance aims to:
- Promote reform of multilateral institutions such as the UN, IMF, and World Bank to reflect contemporary global realities.
- Foster economic cooperation, technology sharing, and sustainable development.
- Strengthen South-South cooperation and enhance the collective influence of emerging economies in global decision-making.
- Advocate a multipolar world order grounded in equity and mutual respect.
Key Outcomes and Agenda of the 16th Summit
The Kazan summit focused on:
- Financial Independence from Western Systems: Members discussed reducing reliance on the US dollar and the SWIFT network, particularly after sanctions on Russia post-Ukraine conflict.
Countries are increasingly exploring local currency settlements, currency swaps, and building alternative payment systems. - Economic and Development Cooperation: Review of the functioning of the New Development Bank (NDB), which has financed projects worth billions in renewable energy, infrastructure, and social sectors.
The Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA), with a reserve pool of $100 billion, continues to serve as a financial safety net. - Multilateral Reform and Climate Action: Discussions focused on reforming global institutions, promoting resilient supply chains, and strengthening collective action against climate change.
- Technology and Innovation: Members emphasized cooperation in science, innovation, and digital connectivity, enhancing research partnerships through the BRICS Science, Technology, and Innovation Framework.
India’s Priorities
Prime Minister Modi highlighted India’s role as a bridge between the Global South and developed economies. India’s agenda included:
- Strengthening reformed multilateralism and inclusive growth models.
- Deepening economic and technological collaboration within the bloc.
- Promoting people-to-people exchanges and cultural cooperation to enhance mutual understanding.
The visit also reinforced the Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership between India and Russia, marking PM Modi’s second visit to Russia in 2025.
Kazan: Symbolism and Significance
- The summit venue, Kazan, often referred to as Russia’s “third capital”, represents the country’s multi-ethnic and multi-religious identity.
- Located at the confluence of the Volga and Kazanka rivers, Kazan is the capital of Tatarstan and a thriving centre of petrochemicals, IT, and defence industries.
- Its diverse cultural fabric—home to both Orthodox cathedrals and Islamic mosques—embodies Russia’s pluralism and outreach to the Islamic world.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its achievements, BRICS faces internal and external challenges:
- Economic asymmetry among members, with China’s dominance occasionally causing unease.
- Geopolitical frictions, particularly between India and China, complicate consensus-building.
- Slow institutional reforms due to entrenched global power structures.
- Divergent foreign policy orientations toward the West among members.
Conclusion
The 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan reaffirmed the bloc’s commitment to a multipolar, equitable, and inclusive global order.
By advancing financial autonomy, technological cooperation, and institutional reform, BRICS continues to evolve as a platform for the Global South to assert its collective voice.
For India, it remains a vital forum to shape global governance, enhance strategic partnerships, and strengthen its vision of “VasudhaivaKutumbakam”—the world as one family.
H-1B Visa Overhaul and Its Implications for India–US Tech Relations

- 26 Sep 2025
In News:
The United States government has announced a sweeping change to its H-1B visa programme, introducing a $100,000 annual entry fee per visa effective September 21, 2025. Framed as a measure to protect American workers, this move has significant geopolitical and economic implications, particularly for India, whose citizens constitute over 70% of all H-1B beneficiaries annually.
What the New Rule Entails
Under the new proclamation signed by President Donald Trump, no petition filed for an H-1B worker outside the US will be approved unless the sponsoring employer pays the $100,000 fee upfront. Applications without proof of payment will be denied at consular processing. The rule applies to new entrants or those seeking re-entry after travel, though workers already in the US on valid H-1B status are exempt.
The order, valid for 12 months with scope for review, also directs the Department of Labor to raise wage levels for H-1B jobs and asks the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to prioritise petitions offering higher salaries. A discretionary clause empowers DHS to waive the fee for specific individuals, companies, or entire industries if deemed in the “national interest.” However, the proclamation does not define which sectors qualify—though healthcare, defence, and critical technology are likely candidates.
Rationale and Political Context
Immigration has become a central and polarising issue in US politics. Public concern on immigration rose from 2.1% in 2012 to 14.6% in 2024 as a top voter priority. Trump’s political narrative has long linked immigration—both low-skilled and skilled—to job displacement and wage depression among the American working class. The H-1B programme, originally designed to attract top global talent in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields, is now portrayed by nativist factions as a vehicle for outsourcing and wage suppression.
Data from the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) indicate that nearly 70% of H-1B approvals for Indian workers in FY2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median US IT salary was $104,420.
Economic and Industrial Impact
The fee fundamentally alters the cost structure of hiring global talent. The new surcharge, in addition to existing statutory fees, transforms the H-1B from a skill-mobility programme into a premium channel accessible mainly to top-tier corporations or sectors granted exemptions.
Big Tech firms such as Amazon, Microsoft, Meta, Google, and Apple—already the largest H-1B sponsors—face millions in additional costs. Indian IT service giants like Infosys, TCS, Wipro, and HCL, who rely on the visa for onsite client delivery, are particularly vulnerable. The policy may push more work to offshore hubs in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune, reinforcing India’s role as a global back-office and development centre rather than an onsite service provider.
Startups, universities, and research labs, often operating on tight budgets, may scale back recruitment or face disruption to innovation and research projects if waivers are not granted.
Implications for India
For India, this measure could limit opportunities for young professionals transitioning from student visas (OPT) to H-1Bs, while families already in the US may face travel restrictions and uncertainty. However, it may also spur reshoring of tech investment to India, as multinational firms expand local operations to mitigate costs.
Conclusion
The $100,000 H-1B fee marks a decisive shift in US immigration policy—from selective reform to fiscal deterrence. While it may serve short-term political optics of job protectionism, it risks undermining America’s long-standing advantage in global innovation. For India, the challenge lies in turning this disruption into opportunity—by strengthening domestic tech ecosystems, skilling talent, and positioning itself as a preferred global innovation hub amid shifting international labour dynamics.
India-Mauritius Relations
- 17 Sep 2025
In News:
India and Mauritius share deep-rooted historical, cultural, and economic ties, which have been further strengthened through recent diplomatic engagements. In September 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi met Mauritius PM Navinchandra Ramgoolam in Varanasi, reaffirming the partnership as more than a diplomatic arrangement, describing it as a “family bond” rooted in shared history, values, and strategic interests.
Special Economic Package and Development Cooperation
During the meeting, India announced a special economic package worth $680 million, aimed at supporting Mauritius in infrastructure, healthcare, defence preparedness, and maritime security. Key components of the package include:
- Healthcare: Establishment of a 500-bed Sir Seewoosagur Ramgoolam National Hospital, an AYUSH Centre of Excellence, and a Veterinary School and Animal Hospital. The first Jan Aushadhi Kendra outside India was also inaugurated.
- Infrastructure: Development of roads, highways, ring roads, and the ATC Tower at SSR International Airport.
- Strategic and Maritime Security: Assistance in Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) surveillance, hydrographic surveys, navigation charting, and maritime domain awareness over the next five years.
- Chagos Marine Protected Area: India will support Mauritius in monitoring, developing, and protecting the Chagos EEZ, following Mauritius’ sovereignty agreement with the UK.
These initiatives are positioned as hard and soft power diplomacy, enhancing India’s strategic reach in the Indian Ocean while improving Mauritius’ development and security capabilities.
Economic and Technological Cooperation
Mauritius is one of India’s closest economic partners in Africa, ranking as the second-largest source of FDI into India after Singapore. The two nations signed the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) in 2021, India’s first trade deal with an African country. Last year, UPI and RuPay services were launched in Mauritius, and both nations are now exploring trade in local currencies.
India also supports academic and civil service capacity building through collaborations between IIT Madras, Indian Institute of Plantation Management, and the University of Mauritius, as well as the launch of Mission Karmayogi training modules.
Geopolitical and Strategic Significance
Mauritius views India as a trusted partner and net security provider in the Indian Ocean, reinforcing a free, open, and secure maritime domain. India’s support aligns with its Neighbourhood First and Vision Mahasagar policies, countering the growing influence of China, Russia, Iran, and Gulf nations in the region. By assisting Mauritius with EEZ surveillance and maritime capacity building, India strengthens its strategic leverage while bolstering Mauritius’ sovereignty, particularly in the Chagos Archipelago.
Cultural and People-to-People Connect
The bond between the two nations is also cultural and historical. Approximately 70% of Mauritius’ 1.3 million population are of Indian descent, and Indian culture, traditions, and languages are deeply embedded in daily life. During the Varanasi visit, the Mauritian Prime Minister participated in the Ganga Aarti and planned prayers at Shri Kashi Vishwanath Dham, highlighting the symbolic spiritual dimension of bilateral relations.
Conclusion
India’s multi-dimensional engagement with Mauritius demonstrates a blend of strategic foresight, development diplomacy, and cultural affinity. Through the special economic package, maritime cooperation, and people-centric initiatives, India not only strengthens Mauritius’ development and security but also consolidates its influence in a geopolitically vital part of the Indian Ocean, fostering mutual prosperity, stability, and strategic partnership.
India and Iran: Ancient Civilisations and the Shaping of a Multipolar World

- 15 Sep 2025
In News:
The contemporary global order is in the midst of a profound transition. For decades, the international system was dominated by a Western-led order, particularly the United States, which wielded disproportionate influence through control over global finance, technology, media, and international institutions. However, this model now faces a crisis. Blatant violations of international law, unilateral military interventions, trade wars, disregard for multilateralism, and environmental degradation have eroded the credibility of Western dominance.
Rise of the Global South and Civilisational States
Amidst this flux, the Global South—comprising countries across Asia, Africa, and Latin America—has emerged as a collective force asserting strategic autonomy, indigenous development models, and self-reliance in science, technology, and security. Within this, ancient civilisational states like India and Iran occupy a unique position. With their histories of resilience, cultural depth, and governance wisdom, both countries embody values of peace, spirituality, respect for diversity, and sovereignty.
Despite repeated invasions, both civilisations absorbed and reshaped external powers through philosophy, art, and administration. In modern times too, India’s anti-colonial struggle and leadership of the Non-Aligned Movement, and Iran’s oil nationalisation in the 1950s and Islamic Revolution of 1979, underscore their quest for independence.
Contemporary Strategic Convergence
Today, both India and Iran face external pressures but continue to safeguard strategic autonomy. India pursues a balanced foreign policy amidst U.S.-China rivalry, while Iran has withstood sanctions and “economic terrorism” without compromising sovereignty. Their convergence is reflected in:
- Energy and Connectivity: The International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and Chabahar Port enhance Eurasian and Indian Ocean linkages.
- Maritime Security: Cooperation in West Asia underlines their shared interest in regional stability.
- Civilisational Diplomacy: Both uphold dialogue, pluralism, and respect for sovereignty as guiding principles.
Palestine: A Symbol of Global South’s Resistance
The Palestinian struggle epitomises the Global South’s broader resistance to domination and double standards in international law. For India and Iran, support for Palestine reflects their commitment to justice, sovereignty, and peaceful conflict resolution.
Towards a Multipolar World Order
The emerging order is increasingly multipolar, with power distributed across diverse actors like India, China, Brazil, and regional middle powers. This shift emphasises equality, mutual respect, and sovereignty rather than unilateral dominance. India and Iran, by combining civilisational heritage with modern strategic partnerships, can shape this transformation in key ways:
- South-South Cooperation: Deepening BRICS, SCO, and NAM as platforms for financial and technological alternatives.
- Reforming Multilateralism: Advocating UN Security Council reform and inclusive global governance.
- Strategic Autonomy: Maintaining independence while deepening Eurasian, African, and Indo-Pacific linkages.
- Civilisational Values: Promoting peace, sustainability, diversity, and human dignity as anchors of a fairer order.
Conclusion
The erosion of Western hegemony presents both challenges and opportunities. India and Iran, rooted in civilisational resilience and guided by strategic independence, are well placed to contribute to the evolution of a just multipolar order. By advancing cooperative frameworks in connectivity, energy, and regional security, and by upholding values of sovereignty and inclusivity, the two nations can not only strengthen their bilateral partnership but also offer the Global South a vision of shared prosperity, dignity, and stability.
India’s Strategic Autonomy in a Multipolar World

- 13 Sep 2025
In News:
In international relations, few ideas have evolved as dynamically as strategic autonomy. Once a subject of academic debate, it is now central to India’s foreign policy. It reflects the country’s determination to take sovereign decisions without succumbing to external pressures or rigid alliances. Neither isolationism nor neutrality, strategic autonomy embodies flexibility, pragmatism, and the ability to engage with multiple powers on one’s own terms.
Historical Roots and Contemporary Shifts
The roots of strategic autonomy lie in India’s colonial past and its post-independence resolve to safeguard sovereignty. Jawaharlal Nehru’s policy of non-alignment during the Cold War laid the foundation. In the contemporary era, this has transformed into a policy of multi-alignment, where India partners with diverse global actors without being tied to any bloc.
The present world order is far from unipolar. U.S. dominance is contested by China’s assertiveness, Russia’s revisionism, and the West’s internal divisions. For India, this fragmented landscape presents both opportunities and dilemmas. Its national interests — territorial integrity, economic development, technological capacity, and regional stability — must be protected while navigating competing pressures.
India and the United States
Over the last two decades, Indo-U.S. relations have grown significantly. Defence cooperation, joint military exercises, intelligence sharing, and technology transfer mark this partnership. India plays a vital role in forums such as the Quad, Indo-Pacific dialogues, I2U2, and the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC). Shared concerns about China’s rise also drive convergence.
Yet, friction persists. U.S. tariffs, sanctions, and demands to dilute India’s ties with Russia test New Delhi’s resolve. India’s measured response — engaging deeply but resisting external diktats — reflects strategic autonomy in action. It is not anti-Americanism, but an insistence on independent choices.
China: Rivalry and Engagement
China poses the most complex challenge. The 2020 border clashes exposed the fragility of bilateral ties. Despite strained relations, China remains one of India’s largest trading partners and an influential actor in multilateral bodies like BRICS and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO). India’s approach balances deterrence with engagement: strengthening border infrastructure, deepening Indo-Pacific partnerships, and simultaneously keeping communication channels open. Strategic autonomy here means neither capitulation nor reckless confrontation.
Russia: Historical Partnership amid Global Shifts
India’s relationship with Russia has endured since the Cold War, anchored in defence cooperation and shared strategic goals. Despite Moscow’s growing dependence on Beijing and its global isolation after the Ukraine conflict, India continues energy imports and defence ties with Russia. While diversifying suppliers and building indigenous defence industries, India refuses to let external powers dictate its Russia policy — again underscoring strategic autonomy.
Broader Dimensions of Autonomy
Strategic autonomy is not confined to geopolitics. In today’s interconnected world, it extends to economic resilience, technological sovereignty, cyber security, and climate diplomacy. India’s initiatives in digital infrastructure, critical minerals, indigenous platforms, and global technology governance highlight its efforts to secure autonomy in new domains.
Domestic stability is equally critical. Economic vulnerabilities, political polarisation, and institutional capacity influence how effectively India can exercise autonomous choices. True autonomy rests on national strength, innovation, and coherence.
Conclusion
India envisions itself as a sovereign pole in a multipolar world — neither aligning blindly nor withdrawing into isolation. Its foreign policy is assertive, interest-driven, and reflective of civilisational depth. As Prime Minister Narendra Modi asserted during India’s G-20 presidency, India seeks to be the “voice of the Global South,” advocating agency and inclusivity.
Strategic autonomy, therefore, is not a slogan but a strategy — the art of balancing major powers while securing national interest. In an era of shifting power equations, India must continue to engage with the U.S. without dependence, deter China without war, and cooperate with Russia without inheriting its isolation. Standing tall, India seeks not to reject the world but to shape its place within it — on its own terms.
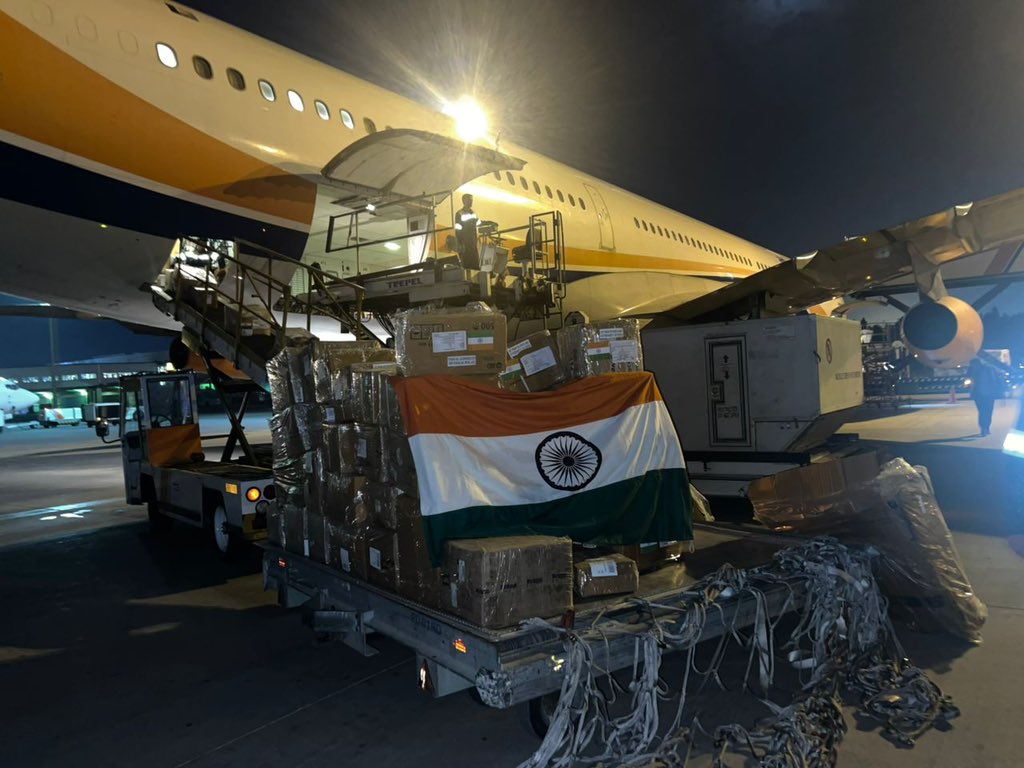
India’s Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) & Soft Diplomacy

- 09 Sep 2025
Introduction
Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) has emerged as a cornerstone of India’s foreign policy and regional engagement. Rooted in the ethos of “VasudhaivaKutumbakam” (the world is one family), India has actively extended aid during natural disasters, reflecting both compassion and strategic foresight. The recent dispatch of 21 tonnes of relief material to Afghanistan after the devastating 6.0-magnitude earthquake, which killed over 1,400 people, underlines India’s commitment to humanitarian outreach and its role as a responsible global actor.
Understanding HADR and Soft Diplomacy
- HADR refers to India’s coordinated relief and rescue operations in disaster-hit regions, at home and abroad. It includes the supply of food, medicines, shelter, sanitation, and technical support.
- Soft Diplomacy implies the use of non-coercive instruments—humanitarian aid, cultural goodwill, and capacity-building initiatives—to enhance India’s global influence and strengthen bilateral trust.
Together, HADR and soft diplomacy enable India to project power through empathy rather than force.
Key Features of India’s HADR Approach
- Rapid Response: The Indian Air Force and Navy ensure swift deployment of relief materials and evacuation missions. For instance, the IAF’s strategic airlift capabilities enable timely supply drops in inaccessible regions.
- Inclusive Relief: Aid packages typically include medicines, food, water, tents, blankets, and water purifiers, focusing on essential survival needs.
- Neutral Assistance: India provides aid without attaching political preconditions, strengthening credibility and neutrality.
- Global Footprint: Beyond neighbours, India has extended assistance to Africa, Pacific Island states, and West Asia, thereby widening its humanitarian outreach.
- Institutional Mechanisms: Agencies like NDMA, NDRF, IAF, Indian Navy, and the Ministry of External Affairs ensure coordination for effective large-scale responses.
Strategic Importance of HADR
- Regional Goodwill: India has earned the reputation of being the “first responder” in South Asia and the Indian Ocean Region. Operations during the Nepal earthquake (2015), Sri Lanka floods, and Maldives water crisis (2014) highlight this proactive role.
- Trust-Building: Humanitarian gestures strengthen bilateral ties, particularly with vulnerable neighbours such as Afghanistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives.
- Soft Power Projection: Such assistance reinforces India’s image as a responsible rising power committed to collective security and humanitarian values.
- Security Dimension: Active engagement through HADR enhances maritime security partnerships and counters external influences in the region, particularly China’s growing footprint in the Indian Ocean.
Contemporary Relevance
In a world marked by climate change, extreme weather events, and fragile states, the frequency of humanitarian crises is increasing. India’s HADR capacity demonstrates both moral leadership and strategic autonomy. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, India’s “Vaccine Maitri” initiative delivered vaccines to over 90 countries, merging humanitarianism with diplomacy.
Furthermore, India’s active participation in multilateral frameworks like BIMSTEC, IORA, and QUAD’s disaster response initiatives showcases its evolving role in shaping global disaster governance.
Challenges
- Logistical hurdles in conflict zones like Afghanistan.
- Resource constraints given India’s vast domestic vulnerabilities.
- The need for greater coordination between civilian and defence agencies.
Conclusion
India’s HADR efforts, anchored in soft diplomacy, reflect a balance of humanitarian compassion and strategic pragmatism. By acting as a credible first responder, India not only saves lives but also nurtures trust, stability, and regional cooperation. In the long run, strengthening institutional mechanisms, enhancing maritime capacity, and integrating climate resilience will further consolidate India’s role as a humanitarian power in a volatile world.
25th SCO Summit 2025

- 05 Sep 2025
In News:
- The 25th Summit of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) was held in Tianjin, China, marking an important milestone in the evolution of the Eurasian grouping.
- Established in 2001 by China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan, the SCO has since expanded to include India and Pakistan (2017), with 10 full members, 17 partners, and representation from Asia, Europe and Africa.
- At Tianjin, Laos was granted partner status, expanding the SCO’s reach and underlining its role as a pan-regional forum.
Major Decisions and Institutional Reforms
The summit adopted over 20 key documents shaping SCO’s long-term trajectory.
- Tianjin Declaration emerged as the central political statement, reaffirming commitments to peace, security and sustainable development.
- A Development Strategy (2026–2035) and Cooperation Programme (2026–2030) to counter extremist ideology were approved.
- A Roadmap for Energy Cooperation (till 2030) and new initiatives in digital economy, AI, climate-friendly industry and education were launched.
- Institutional strengthening included creation of four SCO centres for:
- Countering security threats,
- Combating organised crime,
- Cybersecurity, and
- Anti-drug cooperation.
- Decision was taken to establish an SCO Development Bank to finance infrastructure and social development.
- In a major structural reform, observer states and dialogue partners were merged into a single category of “SCO partners”, streamlining expansion and cooperation mechanisms.
Additionally, Cholpon Ata (Kyrgyzstan) was declared the SCO tourist and cultural capital for 2025–26, reinforcing people-to-people exchanges.
Counter-Terrorism and Security Dimensions
- Terrorism featured prominently in the summit’s deliberations. The Tianjin Declaration explicitly condemned the Pahalgam terror attack (April 2025) in India that killed 26 people, along with the Jaffer Express hijacking and Khuzdar school bus bombing in Pakistan.
- This mention was politically significant, as India had earlier refused to endorse the SCO Defence Ministers’ statement at Qingdao when terrorism concerns were omitted due to Pakistan’s objection.
- India’s firm stance ensured that the leaders’ summit corrected this omission, marking progress in embedding terrorism—including cross-border movement of terrorists—within the SCO’s security agenda. While the declaration avoided naming Pakistan, the acknowledgment of Pahalgam reflected growing recognition of India’s concerns.
India’s Strategic Priorities
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s address outlined India’s SCO vision under three pillars—Security, Connectivity, and Opportunity:
- On security, he reiterated zero tolerance towards terrorism, radicalisation and terror financing, urging collective accountability for states that support cross-border terrorism.
- On connectivity, India reaffirmed support for projects like the Chabahar Port and the International North-South Transport Corridor, vital for regional integration while preserving strategic autonomy.
- On opportunities, India highlighted cooperation in start-ups, innovation, youth empowerment and cultural dialogue, including a proposal for a Civilizational Dialogue Forum to deepen mutual understanding.
India also supported SCO’s reformist agenda, especially new initiatives on organised crime, drug trafficking and cybersecurity, while calling for similar reforms in global institutions like the United Nations, to make them more representative and effective.
Geopolitical Context and India-China Dynamics
The summit was notable for PM Modi’s first visit to China in seven years and his meeting with President Xi Jinping. The inclusion of Pahalgam in the declaration is seen as a potential signal of Beijing’s willingness to recalibrate ties with New Delhi amid its global challenges, though the SCO stopped short of naming Pakistan. The China-Pakistan nexus, particularly through the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, continues to limit consensus on terrorism.
Conclusion
The 25th SCO Summit in Tianjin highlighted the grouping’s evolution into a multidimensional platform addressing security, development, and institutional reforms. For India, it was a diplomatic success to have its terrorism concerns reflected in the final declaration, while also advancing connectivity and reformist goals. However, challenges remain in reconciling divergences within SCO, especially with China’s protective stance towards Pakistan. The summit underlines both the opportunities and limitations of India’s engagement with multilateral Eurasian forums, making it a crucial case study in India’s foreign policy strategy.
India–China Relations

- 25 Aug 2025
In News:
The recent visit of Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi to New Delhi marked the first ministerial-level engagement from China since India and China agreed in October 2024 to complete disengagement at the border. Wang, meeting Prime Minister Narendra Modi, acknowledged that bilateral relations had experienced “ups and downs” and emphasised learning from past experiences. He urged that India and China view each other as partners rather than adversaries, signalling cautious attempts at resetting ties.
Historical Context
Bilateral optimism peaked in October 2019, during the second informal summit between PM Modi and President Xi Jinping at Mahabalipuram. However, eight months later, the Galwan Valley clash in eastern Ladakh resulted in 20 Indian and at least four Chinese casualties, triggering a rupture in relations. Both sides amassed 50,000–60,000 troops along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), leading to a prolonged standoff with frequent confrontations and infrastructure build-ups. Partial disengagement occurred in subsequent years, but the situation remained tense until mid-2024.
The 2024 disengagement agreement at remaining flashpoints in Depsang and Demchok, followed by a Modi–Xi meeting in Kazan, paved the way for a diplomatic thaw. Since then, exchanges at the levels of External Affairs, Defence, and National Security have contributed to restoring dialogue and confidence.
Twin-Track Strategy
India and China have revived the dual-track approach, pursuing border management and broader bilateral cooperation simultaneously. Key mechanisms under the Working Mechanism for Consultation and Coordination (WMCC) include:
- An Expert Group to explore early harvest options in boundary delimitation
- A Working Group for effective border management to maintain peace and tranquillity
- Expansion of General-Level Mechanisms to include Eastern and Middle sectors
This strategy ensures that border issues do not obstruct the development of bilateral ties, while also recognising the need for a political perspective in settling boundary disputes.
Bilateral Cooperation
In the economic and connectivity domain, both sides agreed to:
- Resume direct flights and facilitate visas for tourists, businesses, and media
- Reopen border trade at Lipulekh Pass, Shipki La Pass, and Nathu La Pass
- Promote trade and investment flows through concrete measures
In the water resources sector, China committed to sharing hydrological information on trans-border rivers during emergencies on humanitarian grounds. The Kailash Mansarovar Yatra has resumed, reflecting thawing people-to-people exchanges.
Trust Deficit and Security Concerns
Despite progress, several issues continue to hinder trust:
- Repeated Chinese incursions (Depsang 2013, Chumar 2014, Doklam 2017, and ongoing standoffs)
- Continued deployment of over 50,000 troops in eastern Ladakh
- China–Pakistan military cooperation, including weapon and intelligence support
- Potential risks from China’s mega dam on the YarlungTsangpo (Brahmaputra) affecting downstream states
- Concerns regarding cross-border terrorism and China’s export restrictions on rare earths, fertilisers, and industrial equipment
Strategic Context
The recent thaw also comes amid shifting global dynamics, including strained India–US ties, US tariffs on Indian imports, and broader geopolitical competition. Both India and China aim to maintain stability, enhance economic cooperation, and pursue a multipolar Asia. However, sustainable rapprochement depends on Beijing addressing Indian concerns on security, water, and economic vulnerabilities, alongside constructive engagement on the border.
US–China Trade Truce and the Role of Agricultural Imports in Geoeconomics
- 19 Aug 2025
In News:
The United States and China, the world’s two largest economies, have extended their trade truce for another 90 days until November 10, 2025, averting a sharp escalation of tariffs. The pause keeps US duties on Chinese goods at 30% (against a threatened 145%) and Chinese tariffs on US shipments at 10% (down from an earlier 125%). This temporary reprieve reflects the complex mix of economics, politics, and strategic leverage shaping bilateral relations.
Tariffs and Negotiation Dynamics
Since his return to office, US President Donald Trump has pursued aggressive tariff measures to reduce America’s $300 billion trade deficit with China (2024), arguing that higher duties encourage domestic production and investment. Beijing retaliated with counter-tariffs and restrictions, sparking a tit-for-tat escalation that threatened global supply chains.
The extension of the truce provides space for negotiations over trade imbalances, unfair practices, national security concerns, and market access. It also underscores the challenges of balancing protectionism with the risks of inflation, uncertainty for businesses, and potential disruption to global economic stability.
China’s Leverage: Rare Earths and Agriculture
Beijing has strategically wielded two levers of influence. First, it controls the global supply chain of rare-earth elements and magnets, crucial for the US auto, aerospace, defence, and semiconductor industries. Second, it has employed its role as a major importer of agricultural commodities as a “trump card.”
US farm exports to China fell sharply from $13.1 billion (Jan–June 2024) to $6.4 billion (Jan–June 2025), continuing a downward trend from the 2022 peak of $40.7 billion. The steepest decline has been in soybean exports, dropping from $17.9 billion (2022) to just $2.5 billion (Jan–June 2025). China has redirected much of its soybean imports—74.7 million tonnes in 2024—to Brazil, Argentina, and Canada, significantly hurting American “corn belt” states and livestock producers reliant on feed crops.
Beyond soybeans, imports of US corn, sorghum, barley, cotton, beef, pork, poultry, and tree nuts such as almonds and pistachios have also contracted. This has created pressure on Trump from politically influential farm states, prompting him to publicly urge Beijing to expand soybean purchases.
Impact on the US and India
While American agricultural exports to China have fallen by 51.3% (Jan–June 2025 over 2024), those to India have surged 49.1% in the same period. India has emerged as the largest market for US tree nuts, importing over $1.1 billion in 2024, with a 42.8% year-on-year rise in early 2025. At the same time, the US has become India’s largest buyer of seafood, with frozen shrimp exports worth $1.9 billion in 2024–25.
This divergence highlights India’s growing importance in US agricultural trade, even as tariff disputes persist—Washington recently doubled duties on Indian imports to 50%, citing penalties linked to Russian oil purchases.
Broader Strategic Context
The US–China trade confrontation extends beyond tariffs and agriculture. Issues under negotiation include curbs on semiconductor exports, the role of Chinese platforms like TikTok, and energy security linked to Russian oil purchases. Beijing emphasizes “win-win cooperation,” while Washington continues to pursue coercive tools to address trade imbalances and safeguard national security.
Conclusion
The current trade truce reflects a fragile pause rather than resolution. China’s use of agriculture and rare earths as instruments of economic statecraft illustrates the growing intertwining of trade, technology, and geopolitics. For the US, balancing domestic political pressures from farmers and industries with long-term strategic objectives remains a challenge. For India, the shifting trade landscape offers both opportunities for greater market access and risks of tariff retaliation, underlining the complexity of navigating major power rivalries.
Commemoration of 80 Years Since Hiroshima and Nagasaki
- 11 Aug 2025
In News:
August 2025 marks 80 years since the atomic bombings of Hiroshima (6 August) and Nagasaki (9 August) in 1945, events that not only ended World War II but heralded the beginning of the nuclear age. These bombings remain the only wartime use of nuclear weapons, claiming over 150,000 to 246,000 lives, predominantly civilians, by the end of 1945.
From Stalemate to Nuclear Intervention
- Pearl Harbor (7 December 1941) instigated U.S. entry into WWII and initiated several brutal battles across the Pacific—the likes of Guadalcanal, Iwo Jima, and Okinawa—underscoring the mounting cost of a ground invasion of Japan.
- Japan’s continued resistance despite devastating firebombing campaigns (notably Tokyo in March 1945) and the Potsdam Declaration (July 1945) demanding surrender set the stage for nuclear escalation.
- The Manhattan Project, secret since 1942, culminated in the Trinity test (16 July 1945), proving the atomic bomb's feasibility.
The Bombings Unfold
- Hiroshima (6 August 1945): ‘Little Boy’, a uranium-fission bomb dropped by the B-29 Enola Gay, caused roughly 80,000 immediate deaths; total fatalities reached ~140,000 by end of that year.
- Nagasaki (9 August 1945): ‘Fat Man’, a plutonium-fueled implosion device, dropped amid weather delays on Kokura, killed about 40,000 immediately—totaling ~70,000 by year-end.
Motives Behind the Bombing
- Avoiding invasion casualties: Operation Downfall, the planned invasion, projected massive Allied and Japanese losses.
- Psychological pressure: The bomb's unprecedented devastation aimed to force Japan's surrender.
- Geo-strategic signaling: The bombings demonstrated U.S. might—curbing Soviet advances—and launched the world into a new Cold War dynamic.
- Domestic justification: Following decades and billions invested into the Manhattan Project, prevailing sentiment demanded usage for war-ending impact.
The Aftermath and Long-Term Impact
- Japan surrendered on 14 August 1945, formalizing it on 2 September aboard USS Missouri.
- The nuclear age dawned, introducing doctrines like Mutual Assured Destruction (MAD) and fueling a global arms race visible in treaties and strategic postures to this day.
- Institutions like the Hiroshima Peace Memorial (Genbaku Dome) were later established as symbols for peace and reminders of nuclear risks.
Legacy: Memory and Contemporary Discourse
- Each year, Hiroshima and Nagasaki hold solemn ceremonies—featuring lanterns, peace pledges, and remembrance—to honour victims and renew calls for nuclear disarmament.
- Survivors (hibakusha) testimonials, such as shared during the 80th anniversary, continue to fuel global nuclear abolition movements.
- Contemporary debates persist: while some argue the bombings were a necessary evil to hasten peace, others denounce them as moral travesties — a discourse still evolving with new declassified archival evidence.
Conclusion
The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki were more than wartime events—they ushered in a nuclear epoch marked by existential security threats, ideological competition, and ethical dilemmas. As the world reflects on this 80th anniversary, it must balance historical comprehension with vigilant advocacy for disarmament, remembering that nuclear weapons’ destructive legacy persists, as relevant and grave as ever.
Navigating the New Techno-Capitalist World Order

- 08 Aug 2025
Introduction:
The 21st century is witnessing the rise of a new techno-capitalist world order, where technology and capital converge as key instruments of power. Unlike the earlier developmental model, where states regulated and directed technology for social progress, the current shift—most prominently driven by the United States—places the state as an enabler of private technological monopolies. This transformation has significant implications for global geopolitics, economic security, and India’s technological future.
Understanding Techno-Capitalism
Techno-capitalism refers to a system in which technological innovation and financial capital are co-architects of state power. Its features include:
- Deregulation of critical sectors like AI and fintech.
- Public–private partnerships driving massive investment flows.
- A “tech-broliarchy” of Silicon Valley elites collaborating with state institutions.
- Technology as a geopolitical tool rather than a developmental ideal.
For example, the Trump administration’s AI policy dismantled regulatory barriers, channelled billions into AI-driven manufacturing, and prioritised strategic dominance over global governance norms.
Global Shifts in Tech Ecosystems
United States
The US has transitioned from state-led scientific advancement (e.g., NASA in the 20th century) to private sector-led innovation (e.g., SpaceX, Google DeepMind). Techno-capitalism is now a deliberate strategy blending libertarian individualism with techno-nationalism, reinforcing American primacy in AI, fintech, and crypto.
China
China follows a mission-driven, centralised model, where the state directly steers technological innovation. Its focus areas include AI, digital surveillance, space technology, and the Digital Silk Road. Unlike the US, China treats technology as both a governance tool and an export of state power.
India
India represents a hybrid model, with strong digital public goods (UPI, Aadhaar) and an expanding space programme, but faces systemic challenges:
- Low R&D investment (<0.7% of GDP vs. US 3.5% and China 2.4%).
- Weak linkages between universities and industry.
- Regulatory uncertainty in AI, data, and fintech.
- Limited scaling capacity for start-ups.
India–US Technology Cooperation
Historically, India–US scientific collaboration oscillated between optimism and distrust. The SITE project (1975) reflected Cold War-era cooperation, but the 1974 nuclear test created a trust deficit. Recently, the Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) has revived ties, though divergences on trade, Russia, and US techno-nationalism pose challenges.
Challenges for India in the Techno-Capitalist Era
- AI-driven job displacement in IT-BPO sectors.
- Visa uncertainties in the US affecting skilled migration.
- Underinvestment in R&D, limiting innovation.
- Fragmented regulation, with gaps in AI ethics, crypto, and data governance.
- Start-up ecosystem constraints, including capital shortages and limited government procurement support.
Way Forward for India
- National Tech-Industrial Strategy integrating defence, space, semiconductors, AI, and quantum computing.
- Higher education reform to link universities with mission-mode projects and innovation clusters.
- Balanced regulation that encourages innovation while ensuring consumer rights and systemic safeguards.
- Strategic engagement with the US for co-innovation, while maintaining technological sovereignty.
- Human capital reskilling through a National AI Reskilling Mission and integration of emerging technologies in curricula.
Recognition of Palestine

- 06 Aug 2025
In News:
The Israel–Palestine conflict has once again entered a critical phase, with growing international momentum for recognising Palestinian statehood. British Prime Minister Keir Starmer recently announced that the UK will recognise the State of Palestine at the UN General Assembly in September, unless Israel agrees to a ceasefire in Gaza, allows greater humanitarian access, and recommits to a two-state solution. This announcement marks a dramatic shift in British policy, given its century-old involvement in shaping the conflict.
Growing Global Recognition Drive
The UK’s position is echoed by France, Canada, and Portugal, which have also indicated readiness to recognise Palestine. Out of 193 UN member states, 147 have already extended recognition. Traditionally, major Western powers resisted unilateral recognition, tying it to the outcome of a negotiated peace settlement. However, the ongoing 21-month Gaza conflict has altered this calculus, with Israel facing mounting diplomatic isolation.
Russia and China—both permanent members of the UN Security Council (UNSC)—already recognise Palestine. If the UK and France proceed, the United States will remain the only P5 member opposing recognition, potentially weakening its diplomatic standing. The involvement of key G7 members adds further weight, increasing pressure on other Western nations to reconsider their stance.
Britain’s Historic Role: From Balfour to Partition
Britain’s move is particularly symbolic due to its historic responsibility in the conflict. The Balfour Declaration of 1917, issued by British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour to Zionist leader Lord Rothschild, pledged support for the creation of a “Jewish national home” in Palestine. At that time, Jews constituted only about 9% of the population under Ottoman rule. The declaration was influenced by Britain’s wartime strategy to secure global Jewish support during World War I.
Following the Ottoman Empire’s collapse, Britain assumed control of Palestine under a League of Nations Mandate (1920–1948). It encouraged Jewish immigration and facilitated the creation of parallel institutions, fuelling tensions with the Arab majority. By the end of World War II, Jews made up nearly 30% of the population, and the situation became unmanageable. Britain referred the matter to the UN, which proposed the 1947 Partition Plan. On 14 May 1948, Zionist leaders unilaterally declared the establishment of Israel, immediately recognised by the US. This triggered the First Arab-Israel War, resulting in large-scale displacement of Palestinians—the “Nakba.”
Britain’s Recognition: A Symbolic Shift
Now, 108 years after the Balfour Declaration, Britain’s decision to recognise Palestine signals a historic reversal. While recognition alone may not end Israel’s occupation or resolve the conflict, it carries deep symbolic value. It reflects the erosion of unconditional Western support for Israel, particularly as global outrage grows over civilian casualties in Gaza and accusations of war crimes.
Significance for the International Order
Britain’s recognition could catalyse broader diplomatic shifts. If multiple Western powers formally acknowledge Palestinian statehood, it will strengthen the legitimacy of the two-state solution, long considered the most viable framework for peace. It may also increase pressure on Israel to engage in negotiations under international scrutiny.
At the same time, the development underscores the changing balance of global diplomacy. With the US increasingly isolated on the issue, emerging alignments among Europe, Russia, China, and the Global South highlight a multipolar contest over norms of sovereignty, humanitarian accountability, and conflict resolution.
Conclusion
Britain’s decision to recognise Palestine is not merely a policy adjustment; it is a profound historical reckoning. From endorsing a Jewish homeland through the Balfour Declaration to recognising a Palestinian state more than a century later, Britain’s stance symbolises both continuity and correction in international diplomacy. Whether it translates into tangible progress on the ground depends on Israel’s response, US engagement, and the broader international community’s ability to revive a credible peace process.
China’s Brahmaputra Mega Dam
- 30 Jul 2025
In News:
China’s construction of a $167.8 billion hydropower dam on the Yarlung Zangbo (Brahmaputra) river near the “Great Bend” in Tibet has raised significant geopolitical, ecological, and strategic concerns, particularly for downstream nations like India and Bangladesh. Once completed, this 60,000 MW project—three times the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam—will be the world’s largest.
Strategic and Environmental Concerns
The dam is being built in the seismically active and ecologically fragile Medog region, just before the river enters Arunachal Pradesh as the Siang. The Chief Minister of Arunachal Pradesh has termed the project an “existential threat,” warning that sudden release of water or structural failure could lead to catastrophic flooding and irreversible damage to tribal livelihoods and ecosystems.
Experts reinforce these concerns, citing the risks posed by potential seismic activity, landslides, and unregulated dam operations in a region lacking robust transboundary water governance. Any significant disruption to the river’s natural flow could also affect biodiversity, agriculture, and hydrological patterns in India’s northeast.
The Assam Perspective
Assam, heavily dependent on the Brahmaputra, faces both risks and possible benefits. The state’s Chief Minister has noted that only 30–35% of the river’s flow originates in China, with the majority contributed by monsoon rains and tributaries from Arunachal Pradesh and Bhutan. He suggested that reduced upstream flow might even aid in managing Assam’s annual floods. Nonetheless, the absence of definitive impact assessments necessitates caution.
India’s Diplomatic Position
India, as a lower riparian state, has consistently raised its concerns regarding upstream hydroelectric projects on transboundary rivers. The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) has reiterated the need for transparency, data-sharing, and prior consultation, aligning with global principles of equitable and reasonable use of international rivers.
China, while asserting its sovereign right to develop its rivers, has claimed it is cooperating with downstream nations through hydrological data sharing and disaster mitigation. However, the lack of a legally binding treaty between India and China on water-sharing limits enforceability and fosters mistrust.
Recent diplomatic engagements—including talks in October 2024 and March 2025—have included discussions on river cooperation. India’s decision to resume visas for Chinese tourists and reinitiate the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra indicates a cautious yet strategic engagement policy amid persistent challenges.
Mitigation and Strategic Preparedness
India’s policy response must be comprehensive. Key mitigation measures include:
- Scientific Assessment and Monitoring: Real-time hydrological monitoring and risk modeling are essential.
- Infrastructure Development: Projects like the Upper Siang hydroelectric dam in Arunachal Pradesh, despite environmental concerns, are strategically vital as buffers against sudden flow variations.
- Interlinking of Rivers: Long-term plans to link Brahmaputra tributaries with the Ganga basin can help redistribute water during surplus and scarcity.
- Regional Cooperation: Coordination with other riparian nations such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Myanmar is vital for developing early warning systems and emergency protocols.
Conclusion
The Brahmaputra dam issue encapsulates the complex interplay of sovereignty, ecology, security, and diplomacy in transboundary river management. For India, it presents both a strategic challenge and an opportunity to strengthen its internal preparedness while advancing regional cooperation. A balanced, evidence-driven, and diplomatically assertive approach is critical to safeguarding national interests and promoting regional water security.
PM Modi’s Visit to the Maldives: A Strategic Reset in India’s Indian Ocean Diplomacy

- 28 Jul 2025
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the Maldives in July 2025 marked a significant diplomatic milestone, especially as it came amid shifting regional dynamics. Invited as the Guest of Honour for the 60th Independence Day celebrations, this was his third visit to the Maldives and the first by a foreign Head of Government under President Mohamed Muizzu's tenure. The event also symbolised a remarkable shift from the earlier phase of strained bilateral ties to renewed strategic alignment.
Diplomatic and Developmental Engagements
The visit featured a multifaceted agenda underscoring India’s "Neighbourhood First" and "Vision MAHASAGAR" policies. A commemorative stamp was released jointly by both leaders to mark 60 years of India-Maldives diplomatic relations, symbolised through traditional maritime vessels—India’s Uru boat and Maldives’ Vadhu Dhoni—highlighting shared Indian Ocean heritage.
India handed over two BHISHM Health Cubes—portable medical kits capable of treating 200 casualties and sustaining medical staff for 72 hours—demonstrating commitment to regional humanitarian support. PM Modi also inaugurated the new Ministry of Defence building in Malé, constructed with Indian assistance, enhancing Maldives’ institutional capacity.
A series of high-impact projects were launched, including:
- 3,300 social housing units in Hulhumale under Indian Buyer’s Credit,
- Road and drainage infrastructure in Addu City,
- Six community development initiatives, and
- 72 vehicles and utility equipment to support local governance.
Economic Assistance and Strategic Commitments
India extended a Line of Credit (LoC) worth ?4,850 crore, notably in Indian Rupees—marking the first such transaction for Maldives. This aims to address Maldives’ twin deficit crisis and reduce dependence on foreign currency. Additionally, an agreement was signed to reduce annual debt repayments from $51 million to $29 million, providing significant fiscal relief.
Other announcements included the launch of negotiations for an India-Maldives Free Trade Agreement (IMFTA) and joint climate action through synchronized tree-planting campaigns: India’s Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam and Maldives’ 5 Million Tree Pledge.
Diplomatic Turnaround: From 'India Out' to 'India In'
The symbolism of this visit lies in its contrast to recent tensions. After assuming office in 2023, President Muizzu’s administration aligned more closely with China and ran a vocally anti-India campaign. Early signals—including calls to remove Indian military personnel—suggested a possible strategic rupture. However, India opted for diplomatic engagement over confrontation, facilitating dialogue at COP28 and replacing its military presence with civilian HAL technicians in May 2024.
This calculated patience coincided with Maldives’ economic vulnerabilities, limited Chinese assistance, and the ruling PNC’s consolidation of power. The tide began to turn with high-level Maldivian visits to India and the announcement of a shared vision for maritime and economic cooperation in late 2024.
Conclusion
President Muizzu’s recent statement that "Maldives will not do anything to harm India's security interests" reflects a diplomatic recalibration driven by pragmatism and mutual necessity. The invitation extended to PM Modi for a ceremonial role in Maldives' Independence Day, once unthinkable amid the 'India Out' rhetoric, stands as a testament to the success of India’s calibrated diplomacy in the Indian Ocean region.
U.S. Designation of The Resistance Front (TRF)

- 22 Jul 2025
In News:
India’s sustained diplomatic campaign against cross-border terrorism received a significant fillip with the United States designating The Resistance Front (TRF) as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) and a Specially Designated Global Terrorist (SDGT). The decision, announced by U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio, marks a strong step in countering global terror networks and reaffirms the deepening Indo-U.S. cooperation in counter-terrorism.
The TRF is widely recognized as a proxy outfit of the Pakistan-based Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), formed soon after the abrogation of Article 370 in 2019. Projecting itself as an indigenous, secular “resistance” movement, TRF has sought to legitimize militancy under a veneer of local identity while continuing to rely on the operational, logistical, and financial support of LeT and Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI). Its rebranding strategy is aimed at evading scrutiny by international watchdogs such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
TRF has claimed responsibility for several high-profile terror attacks in Jammu and Kashmir, including the Pahalgam attack in April 2025, which killed 26 tourists. Other attacks attributed to it include the Ganderbal killings (October 2024), Reasi bus attack (June 2024), and a 2020 shooting in Lal Chowk, Srinagar. Its leadership, including current chief Sheikh Sajjad Gul and spokesperson Ahmad Khalid, operate largely from Pakistani soil.
The group also runs an elaborate digital propaganda and recruitment ecosystem. Portals like KashmirFight and Jhelum Media House disseminate extremist narratives, claim responsibility for attacks, and operate as fronts for psychological operations and radicalization. These digital tools further complicate counter-terrorism efforts, allowing TRF to recruit and spread misinformation under the guise of human rights advocacy.
India banned TRF under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967, in January 2023, recognizing its existential threat to national security. India has consistently provided evidence of TRF’s linkages with LeT and other Pakistan-backed outfits like Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) in its submissions to the UN 1267 Sanctions Committee, responsible for imposing sanctions on terror-linked entities.
The U.S. designation of TRF as an FTO and SDGT is not just symbolic. It imposes concrete legal and financial restrictions, making it illegal for U.S. individuals or entities to provide support to the group. The move mandates American financial institutions to block any assets tied to TRF and enables further actions through the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC). These actions aim to globally isolate the outfit and can also trigger secondary sanctions against foreign entities that deal with it.
India has welcomed this move, calling it a “strong affirmation” of India-U.S. cooperation in the fight against terrorism. The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) emphasized that such steps are vital to dismantle terror infrastructure and hold proxy actors accountable. The decision also underscores a growing international consensus on the need for zero tolerance towards terrorism.
This development marks a pivotal moment in India’s counter-terror diplomacy and reinforces the need for global synergy in combating the evolving threat of state-sponsored and hybrid terrorism.
Trump’s Tariff Threats and BRICS

- 17 Jul 2025
In News:
The recent 17th BRICS Summit in Rio de Janeiro (2025) has reignited tensions between the United States and the expanding BRICS grouping. Former U.S. President Donald Trump, who remains a dominant figure in Republican politics, has threatened to impose 10% tariffs on all BRICS nations, framing the bloc as a challenge to American economic hegemony. These threats signal a continuation of Trump's confrontational approach to global trade and reflect deeper anxieties about de-dollarisation efforts emerging from the Global South.
Trump’s concerns stem from what he perceives as an "anti-American" orientation of BRICS. The group's discussions around a common currency, increased use of national currencies, and the development of alternative cross-border payment systems have been interpreted by Trump as an attempt to weaken the U.S. dollar’s central role in international finance. This fear has been intensified post the Russia-Ukraine conflict, which saw several countries reconsider their reliance on dollar-based systems like SWIFT, particularly after Russia’s exclusion from them due to Western sanctions.
In response, Trump has floated punitive trade measures: a 10% tariff on BRICS-aligned nations, 50% on Brazil for its domestic political stance, and 30% on South Africa citing trade disputes and minority rights issues. He is also advocating for the Sanctioning Russia Act, 2025, which proposes an astronomical 500% tariff on Russian oil and related products. Such a move could disrupt oil-importing economies like India and China, both of which have deepened energy ties with Moscow in recent years.
However, BRICS leaders have clarified that de-dollarisation is not about dismantling the dollar-based order but about financial diversification and resilience. The Rio Declaration 2025 stopped short of any anti-U.S. language, instead emphasizing interoperability of payment systems and equitable reform of global institutions. This demonstrates a cautious diplomatic approach aimed at asserting economic agency without triggering direct confrontation.
India, in particular, has taken a measured stance. In Parliament, the Indian government distanced itself from suggestions that BRICS was pursuing an aggressive de-dollarisation agenda. External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar reiterated that India has no official policy to replace the U.S. dollar, and that BRICS decisions are not monolithic but reflect the diversity of its member states. This is crucial, given India’s strategic balancing between the West and the Global South.
Founded in 2009 amid discontent with Western-dominated financial structures, BRICS has expanded to include 10 members, with new entrants like Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, UAE, and Indonesia. While united by frustration over Western dominance, internal diversity—economic, political, and strategic—ensures that BRICS does not function as a rigid anti-West alliance.
At the Rio summit, BRICS condemned unilateral tariff practices and expressed concern over attacks on Iranian civilian infrastructure, showcasing solidarity without directly naming the U.S. or its allies. This signals a shift toward multilateral diplomacy grounded in soft balancing rather than confrontation.
In conclusion, while Trump’s tariff threats underline U.S. anxiety over shifting global power structures, BRICS’ response suggests a nuanced recalibration of the international order—not a radical overhaul. For India, the challenge remains to harness BRICS for strategic autonomy without undermining its multi-aligned foreign policy posture.
India’s Reinvigorated Outreach to the Global South

- 14 Jul 2025
In News:
India’s foreign policy has witnessed a dynamic recalibration with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s expansive visit to Brazil, Ghana, Trinidad & Tobago, Argentina, and Namibia. While participation in the BRICS Summit in Rio de Janeiro was central, the broader aim was to deepen India’s leadership role within the Global South — a diverse group of developing nations in Asia, Africa, Latin America, and Oceania.
Reclaiming Leadership in the Global South
India has long championed the cause of the Global South, grounded in its non-aligned foreign policy legacy and postcolonial solidarity. This identity was rejuvenated through:
- Hosting two Voice of the Global South Summits (2023, 2024), giving a platform to over 125 developing countries.
- Advocating for and securing African Union’s permanent membership in the G20 during its presidency, symbolizing India’s commitment to an inclusive global governance architecture.
These initiatives portray India as a bridge between the Global North and South, positioning itself as a leader that represents the interests of the voiceless in multilateral forums.
Diplomatic Course Correction: The Gaza Challenge
India’s explicit support for Israel during the Gaza conflict (post-October 7, 2023) triggered discomfort among many Global South countries, especially in the Arab and African regions that strongly support the Palestinian cause. Consequences included:
- India’s defeat to Pakistan in the UNESCO Executive Board Vice-Chair election.
- Limited engagement from key Global South nations in the Second Voice of the Global South Summit.
Recognizing these diplomatic setbacks, India recalibrated its stance. At the BRICS Foreign Ministers’ Meeting (2024) and the 2025 Rio BRICS Summit, India joined in expressing grave concern over Israeli military operations in Gaza and condemned strikes on Iran, signaling a return to its balanced, multivector diplomacy.
Strategic Gains at BRICS: Securing Core Interests
India also used the BRICS platform to secure vital national interests. The BRICS Leaders’ Declaration condemned the Pahalgam terror attack in Kashmir and called for combating terrorism, including cross-border terror financing. This was diplomatically significant, given:
- China’s prior reluctance to name Pakistan-based terror actors.
- BRICS’ growing relevance in shaping global narratives.
India’s success in inserting its security concerns into multilateral dialogue marks a maturing assertiveness in diplomacy.
Countering China, Offering Alternatives
India’s proactive outreach also serves to counter China’s rising influence in the Global South. Unlike Beijing’s Belt and Road Initiative, India emphasizes:
- Transparent, demand-driven development assistance.
- Capacity-building and digital partnerships.
- Ethical, sustainable models of cooperation.
Through initiatives like International Solar Alliance, Digital Public Infrastructure partnerships, and humanitarian aid, India offers a democratic, credible alternative to Chinese financing and infrastructure diplomacy.
Conclusion:
India’s current foreign policy trajectory reflects a delicate balancing act—protecting strategic partnerships with global powers while retaining the trust of fellow developing nations. As global multipolarity deepens, India’s role as a consensus builder, ethical voice, and pragmatic actor will shape its success in becoming the leading voice of the Global South.
China-Led Trilateral Nexus: A Strategic Challenge for India

- 01 Jul 2025
Context:
In a significant development, China recently hosted the first China-Pakistan-Bangladesh trilateral dialogue in Kunming, following a similar China-Pakistan-Afghanistan meeting. These efforts signal Beijing’s strategic push to consolidate its influence in South Asia, creating new geopolitical challenges for India.
Understanding the Emerging Nexus
The trilateral arrangements—China-Pakistan-Bangladesh and China-Pakistan-Afghanistan—are part of China’s broader strategic framework to establish deeper regional roots. China drives the agenda, with Pakistan gaining strategic relevance, while Bangladesh and Afghanistan are drawn in for economic, political, and connectivity incentives.
Motivations Behind the Trilateralism
- China aims to dilute India’s regional influence, expand the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and leverage Pakistan to complicate India's neighbourhood strategy.
- Pakistan seeks Chinese economic and strategic backing to offset India, especially after facing diplomatic isolation globally.
- Bangladesh and Afghanistan are attracted by Chinese infrastructure investment, diplomatic weight, and development assurances in a multipolar Asia.
Historical Context
- 1962 Indo-China War: Set the foundation for Sino-Pakistan convergence as a counterweight to India.
- 1965 Siliguri Strategy: Pakistan attempted to encircle India with support from China, Nepal, and East Pakistan, a strategy echoing today.
- China’s Shielding at UNSC: Regular blocking of India’s attempts to designate Pakistan-based terrorists, such as Lashkar-e-Taiba operatives, at the United Nations.
- Operation Sindoor, 2025: Pakistan deployed Chinese drones and radars; Beijing criticized India’s counterstrike, reaffirming its alliance.
Implications for India
- Security Threats: China-Pakistan cooperation now gains a regional sheen, legitimizing their cross-border strategies, e.g., the Pahalgam attack (2025).
- Diplomatic Setbacks: China’s increasing footprint in Dhaka and Kabul limits India’s traditional influence.
- Strategic Encroachment: Enhanced trilateralism boosts BRI's presence in South Asia, undercutting India-led alternatives like BBIN or the Chabahar corridor.
Impact on South Asian Stability
- Regional Polarization: Smaller nations are forced to balance between India and China, causing strategic fragmentation.
- Risk of Proxy Conflicts: Chinese cover may embolden Pakistan’s use of cross-border terrorism.
- Dilution of Regional Forums: SAARC and other platforms may become ineffective under Chinese influence.
Way Forward for India
- Assert Strategic Redlines: India must clearly articulate consequences for neighbours compromising its sovereignty.
- Deepen Regional Cooperation: Utilize BIMSTEC, IORA, and the Indo-Pacific frameworks to counterbalance Chinese presence.
- Economic Diplomacy: Increase targeted investments, credit lines, and market access to offer credible alternatives to BRI.
- Defence Engagement: Expand military and strategic ties with Bangladesh, Maldives, and Afghanistan.
- Narrative Building: Promote India as a cooperative, non-hegemonic regional partner to counter Chinese narratives.
Conclusion
The China-led trilateral dialogues mark a recalibration in South Asia’s geopolitical landscape aimed at constraining India’s rise. India’s response must be multifaceted—merging strategic assertiveness with regional diplomacy and economic outreach. A confident and inclusive India can safeguard its interests and lead a stable, multipolar South Asian order.
Strait of Hormuz Blockade
- 29 Jun 2025
Context:
The recent approval by Iran’s Parliament to potentially close the Strait of Hormuz, pending a final decision by its Supreme National Security Council, has intensified global concerns about energy security and geopolitical stability. This comes in response to U.S. strikes on Iranian military sites, marking a serious escalation in the Gulf region.
Strategic Significance of the Strait of Hormuz
- The Strait of Hormuz is a 33 km-wide maritime chokepoint linking the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and, subsequently, the Arabian Sea. It handles over 25% of global seaborne oil trade, 20% of global oil consumption, and 20% of LNG trade, primarily from Qatar.
- The geographical location of the strait—falling within Iranian and Omani territorial waters—makes it one of the most sensitive energy corridors globally.
- The strait’s vulnerability is compounded by its narrow 3 km-wide navigational channels, making it susceptible to blockades, naval mines, missile strikes, or cyberattacks.
- Historically, Iran has issued such threats without actual closure, even during periods of conflict, largely due to its own dependency on the strait for oil exports, especially to China.
Implications of a Blockade
A complete or even partial blockade could have catastrophic global impacts:
- Disruption of Global Energy Supply: With no alternative sea route, any disruption would curtaildaily movement of 20 million barrels of oil, causingsharp price spikes.
- Limited Overland Alternatives: Saudi Arabia’s East-West pipeline (5 million bpd) and the UAE’s Fujairah pipeline (1.8 million bpd) cannot compensate for the loss of Hormuz transit.
- Higher Shipping and Insurance Costs: Perceived risk increases freight rates, insurance premiums, and logistical expenses globally.
Impact on India
India, the third-largest crude oil consumer, imports over 85% of its oil and 50% of its natural gas. In May 2025 alone, 47% of India’s crude imports passed through the Strait of Hormuz. Disruption would result in:
- Price Volatility: Even if supplies are not entirely blocked, oil and gas prices will spike, stressing the economy.
- Macroeconomic Stress: A surge in energy prices could widen the trade deficit, weaken the rupee, reduce forex reserves, and raise inflation.
- Competitive Pressure: If Iran’s exports to China are blocked, Beijing may seek oil from other producers, increasing global demand and costs, impacting India’s energy budget.
India’s Resilience and Strategic Measures
Despite the vulnerabilities, India has certain buffers:
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Imports from Russia, the U.S., Africa, and Latin America are not dependent on Hormuz. Russian oil arrives via the Suez Canal or Cape of Good Hope, while Qatar’s LNG also uses alternate maritime routes.
- Strategic Reserves: India maintains 9–10 days’ worth of strategic oil reserves for emergencies.
- Government Policy Levers: In case of a prolonged crisis, the government may offer price subsidies for diesel and LPG to contain inflation.
Conclusion
The Strait of Hormuz remains a vital artery of global energy supply and a flashpoint of geopolitical tensions. While India has taken commendable steps toward energy diversification and crisis preparedness, continued diplomatic engagement in West Asia, investments in energy alternatives, and strengthening strategic reserves will be key to mitigating the fallout from any potential blockade.
Reshaping Energy and Geopolitics in West Asia
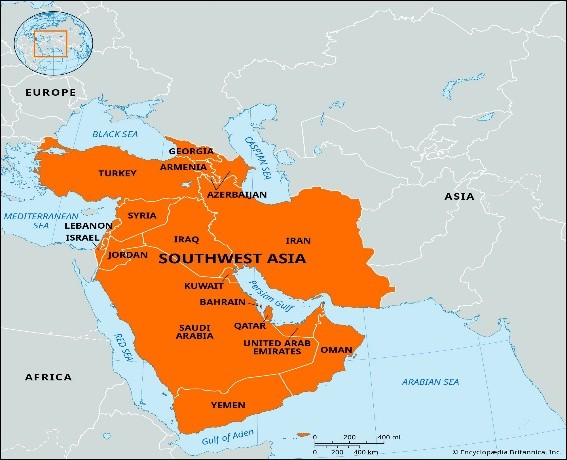
- 24 Jun 2025
In News:
The geopolitical landscape of West Asia is undergoing a profound transformation driven by escalating conflicts, realignments of power, and the increasing weaponisation of energy. The Israel-Iran conflict, rising threats to critical maritime routes, and the shifting allegiances of Gulf states are redefining the region’s strategic and energy equations, with direct implications for global stability and India’s national interests.
West Asia’s Centrality to Global Energy Security
- The Gulf region holds over 50% of global proven oil reserves, producing around 33% of the world’s oil and 17% of global natural gas.
- Despite a global shift to renewables, the world still consumes ~100 million barrels of oil daily, with ~50% used for transport and ~20% for petrochemicals.
- Natural gas accounts for 23% of global energy consumption, supplying a quarter of global electricity.
Geopolitical Flashpoints: Conflict and Energy Disruption
- Israel’s airstrikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities and Iran’s missile retaliation have heightened the risk of regional war.
- Iran may block the Strait of Hormuz, through which ~20% of global oil trade passes. Even the threat has increased insurance and freight rates.
- Charter costs for Very Large Crude Carriers (VLCCs) from the Gulf to China have risen from ~$20,000 to ~$48,000 per day.
- Iran’s oil exports (~2 million barrels/day) form ~2% of global oil supply, difficult to replace due to limited spare capacity among other producers.
- Threat of attacks on energy infrastructure by Iran-backed militias adds to regional instability.
Strategic Realignments in West Asia
- Gulf states (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar) are moving toward multi-polar engagements, strengthening ties with China and Russia, and reducing dependence on the US.
- Historical precedent: The 1973 Arab oil embargo demonstrated the region's ability to influence global politics through oil.
- Arab monarchies’ reluctance to support Western-backed regime change in Iran stems from fears of regional destabilisation and domestic backlash.
- Public sentiment in Gulf nations remains strongly pro-Palestinian and anti-Western, adding internal pressures on ruling elites.
Weaponisation of Energy as a Strategic Tool
- The use of oil embargoes or supply disruptions is re-emerging as a geopolitical instrument.
- Iran could resort to asymmetric warfare or encourage proxy attacks on rival oil facilities, particularly in Iraq (which produces over 4 million barrels/day) and the Gulf.
Implications for India
Opportunities:
- Scope to diversify energy suppliers and enhance strategic petroleum reserves (SPR).
- India’s position in BRICS and SCO offers diplomatic space to act as a moderating influence.
Risks:
- 40–50% of India’s energy imports transit through the Strait of Hormuz—any disruption threatens energy security.
- Surging oil prices can fuel imported inflation, impacting transport, agriculture, and industrial costs.
- Indian projects like Chabahar Port, the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), and the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC) face operational uncertainties.
- Strain on India’s balanced ties with Israel and Iran, with diplomatic fallout possible.
- Gulf remittances (a vital source of foreign exchange) may decline if regional conflict escalates.
Conclusion
West Asia’s reconfiguration is a reminder of the enduring nexus between energy and geopolitics. For India, navigating this complex terrain requires strategic autonomy, energy diversification, and robust regional diplomacy. Balancing relations amid shifting alliances, while securing national interests in energy and trade, must remain central to India’s foreign policy calculus.
India’s uneasy balancing act in the Bay of Bengal

- 19 Jun 2025
In News:
India’s engagement in the Bay of Bengal is increasingly being shaped by the intersection of strategic priorities and economic imperatives. While New Delhi seeks to position itself as the regional integrator and promoter of cooperative regionalism, recent developments — particularly in relation to Bangladesh — underscore the challenges of maintaining this balance.
At the surface, India’s maritime and port infrastructure along the eastern seaboard has seen considerable progress. Cargo throughput at Visakhapatnam, Paradip, and Haldia has steadily risen. Initiatives like the Sagarmala Programme and coastal shipping incentives have doubled cargo movement on the east coast in the last decade. The signing of the BIMSTEC Maritime Transport Cooperation Agreement in early 2025 further aims to harmonise customs procedures and reduce port-related frictions.
Yet, India’s decision to withdraw the transshipment facility granted to Bangladesh in April 2025, which had enabled Dhaka to route exports through Indian ports to third-country destinations, sparked concern. While Indian officials cited logistical congestion, many in Bangladesh interpreted the move as politically motivated — possibly in response to Dhaka’s growing engagement with China and a speech by a Bangladeshi leader in Beijing framing India’s northeast as “landlocked” and dependent on Bangladesh.
This decision, followed by India’s restrictions in May 2025 on the import of seven Bangladeshi product categories via land ports, has fueled bilateral tensions. These developments have particularly impacted Bangladesh’s ready-made garment sector, which constitutes over 85% of its export earnings and had increasingly relied on Indian ports for efficiency. New routing requirements via Kolkata or Nhava Sheva have added delays and costs, weakening the trade facilitation narrative India has long championed.
While Bangladesh has asserted its regional role by diversifying trade partners — including reopening maritime trade with Pakistan — these are sovereign choices. India’s use of trade access as a signaling mechanism, if perceived as coercive, risks undermining the credibility of the neutral and rules-based regional architecture it seeks to build under BIMSTEC.
This is significant beyond bilateral ties. Regional actors like Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, and Thailand observe India's actions closely. If India's trade facilitation appears contingent on political alignment, smaller states may opt to hedge or diversify partnerships, potentially weakening India’s centrality in the Bay of Bengal order.
India remains the region’s best-equipped actor in terms of port capacity, connectivity, and logistics infrastructure, giving it a leadership edge. However, credibility and consistency are equally vital. Without a clear separation between economic cooperation and strategic messaging, India’s regional ambitions risk being derailed.
To restore balance, India could consider reinstating the transshipment facility under a rules-based framework, ensuring transparency and predictability in trade logistics. This would reassure neighbours, revive trust, and reinforce India’s image as a stable anchor in a geopolitically dynamic region.
The Bay of Bengal is at a crossroads. It can evolve into a vibrant economic corridor between South and Southeast Asia, or descend into a fragmented arena of mistrust. India’s choices today will determine whether regional cooperation remains the cornerstone of its foreign policy — or becomes another casualty of strategic competition.
Israel–Iran Strike 2025

- 15 Jun 2025
In News:
On June 13, 2025, Israel launched a large-scale military strike on Iran, targeting nuclear and military sites in Tehran. The attack resulted in the deaths of Iran’s Revolutionary Guard chief and two top nuclear scientists, marking a sharp escalation in the long-running shadow conflict between Israel and Iran.
Backdrop: Iran’s Nuclear Programme and Global Concerns
Iran claims its nuclear programme is peaceful, aimed at energy production and medical research. However, international skepticism remains high. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) recently declared Iran in breach of its non-proliferation obligations for the first time in two decades, citing a lack of transparency, failure to account for undeclared nuclear material, and enrichment of uranium up to 60% purity, dangerously close to weapons-grade (90%). According to reports, Iran possesses enough stockpiled uranium to build up to nine nuclear weapons, raising alarm globally.
Israel’s Strategic Calculus and the Execution of the Strike
Israel has long opposed Iran’s nuclear ambitions and the 2015 nuclear deal (JCPOA). The June 2025 assault was the culmination of years of covert operations, including the 2020 assassination of Mohsen Fakhrizadeh and earlier strikes on Iran-linked targets. The latest strike, targeting nuclear and missile facilities as well as residences of top scientists and generals, is seen as the most severe blow to Iran since the 1979 revolution.
The collapse of Iran’s regional deterrence network—its so-called “axis of resistance”—following the fall of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad in December 2024 played a critical role. With Syria no longer serving as a strategic corridor between Tehran and Hezbollah, Israel perceived an opportune moment to act.
US Foreign Policy Shift and Trump’s Role
The re-election of President Donald Trump in 2024 introduced a more confrontational posture toward Iran. Although the U.S. initially delayed the planned May strike to explore diplomacy, the failure of talks led to U.S. backing for the June operation, using military pressure as leverage for a new nuclear deal demanding Iran's full disarmament.
Regional Fallout and Global Economic Implications
The strike triggered an immediate 8% rise in global oil prices, exposing energy vulnerabilities across oil-importing nations. Particularly affected is India, which imports over 80% of its crude oil. Though India imports little directly from Iran, it depends heavily on Gulf producers like Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, whose exports transit through the Strait of Hormuz—a vital chokepoint now under threat.
Further, disruptions in Red Sea and Suez Canal shipping routes may force Indian exporters to reroute via the Cape of Good Hope, increasing transit times by 15–20 days and pushing shipping costs up by 40–50%.
Market Response and Strategic Concerns
While oil prices are expected to stabilise due to global reserves and supply diversification, gold prices surged above ?1 lakh per 10g as investors moved to safer assets. The broader geopolitical uncertainty may stoke inflationary pressures, affecting global and Indian economic stability.
Conclusion
The Israel–Iran conflict, while regionally contained for now, holds serious global implications—challenging non-proliferation efforts, disrupting energy security, and threatening global economic stability. For India, the crisis underscores the need for diversified energy sourcing, geopolitical agility, and resilient export infrastructure to mitigate such strategic shocks.
Iran’s Non-Compliance with IAEA Safeguards

- 16 Jun 2025
In News:
In a pivotal move, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Board of Governors, recently passed a resolution declaring Iran in breach of its 1974 Comprehensive Safeguards Agreement. This marks the first formal non-compliance declaration since 2006 and signals a possible escalation of Iran’s nuclear issue to the United Nations Security Council (UNSC). The resolution was passed with 19 votes in favour, 3 against (China, Russia, Venezuela), and 11 abstentions.
What led to the resolution?
The IAEA expressed grave concern over Iran’s failure to explain uranium traces found at three undeclared sites—Lavisan-Shian, Varamin, and Turquzabad. These sites, suspected to be part of an undeclared nuclear program until the early 2000s, reflect Iran’s longstanding reluctance to grant the IAEA full access and credible information.
The IAEA resolution cited Iran’s “many failures” since 2019 to provide timely cooperation. This includes Iran’s inability to account for undeclared nuclear material and activities, in violation of its obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and its 1974 Safeguards Agreement.
IAEA Safeguards and Article XII.C
Under the 1974 Safeguards Agreement, Iran is legally required to:
- Declare all nuclear materials and maintain detailed inventories.
- Notify the IAEA about any new nuclear facilities.
- Allow routine and special inspections and surveillance.
The IAEA’s inability to verify the absence of nuclear material diversion for weaponisation constitutes a major safeguard failure.
The resolution was passed under Article XII.C of the IAEA Statute, which grants the Board powers to:
- Demand corrective actions.
- Suspend technical assistance.
- Notify all member states.
- Refer the case to the UNSC.
This rare Article has only been invoked six times before—against Iraq, North Korea, Iran (2006), Libya, Romania, and Syria.
Iran’s Response and Regional Tensions
Iran denounced the resolution as “political” and retaliated by:
- Announcing plans for a new underground uranium enrichment facility.
- Upgrading centrifuges at Fordow.
- Placing air defence systems on alert.
- Threatening “proportional measures” in response to Israeli and Western pressure.
A day after the IAEA resolution, Israel launched preliminary airstrikes on Iranian nuclear sites and declared a state of emergency. Iran reportedly mobilised drones in response, escalating military tensions in the region.
Broader Geopolitical Implications
This development coincides with the October 2025 deadline for the expiration of U.N. sanctions relief under the 2015 Iran Nuclear Deal (JCPOA). The U.S., which exited the JCPOA in 2018, has signaled support for “special inspections” of Iranian sites. Meanwhile, back-channel talks in Oman remain stalled, and the threat of sanctions “snapback” looms large.
The IAEA also maintains $1.5 million worth of peaceful nuclear projects in Iran, including in radiopharmaceuticals and desalination—now potentially at risk.
What lies ahead?
Iran now has a limited window to respond. If it fails to provide adequate clarifications, the Board may escalate the issue to the UNSC, which could result in renewed sanctions or binding resolutions. A follow-up Board meeting and vote is expected in September 2025.
Conclusion
The IAEA’s resolution represents a critical juncture in global non-proliferation diplomacy. It underscores the challenges of verification in the absence of cooperation and the rising tensions in the Middle East nuclear landscape. For India and the world, this raises important questions on nuclear governance, energy diplomacy, and regional stability.
U.K.–EU Reset: A Strategic Gateway for India

- 11 Jun 2025
In News:
The recent diplomatic overture by the United Kingdom under Prime Minister Keir Starmer to reset relations with the European Union (EU) marks a pivotal moment in Euro-Atlantic cooperation. Though the development appears Eurocentric, its implications for India are profound — ranging from trade facilitation and foreign policy realignment to diaspora and talent mobility. For India, this evolving Western convergence offers a unique opportunity to recalibrate its economic and strategic engagements.
Redefining India’s Trade Corridors
The renewed UK-EU cooperation — covering food safety, fisheries, customs, and border controls — has the potential to ease operational frictions for Indian exporters that emerged post-Brexit.
- Current Trade Landscape: In FY2024, India’s exports to the EU stood at $86 billion, and to the U.K. at $12 billion, reflecting the strategic importance of these partners.
- Post-Brexit Challenges: Indian businesses, especially in pharmaceuticals, textiles, and agri-products, faced dual regulatory requirements.
- Reset Opportunities: A harmonised regulatory framework can reduce compliance redundancies and lower costs. India, which meets over 25% of the U.K.’s pharmaceutical demand, could benefit from unified drug approvals.
- Sectoral Impact:
- Indian seafood exports (worth approx. $7.38 billion) could see improved access if sanitary and phytosanitary norms are streamlined.
- However, SMEs may face challenges in adapting to tighter European standards.
Policy Recommendation: India must bolster its export competitiveness through schemes like RoDTEP, PLI, and enhanced certification infrastructure to meet higher technical standards.
Deepening Strategic and Diplomatic Ties
A more aligned U.K.-EU foreign and defence policy creates new avenues for India to build deeper multilateral and trilateral engagements.
- Existing Frameworks:
- India–EU: Strategic Partnership Roadmap to 2025
- India–U.K.: Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (2022), covering cybersecurity, climate, and maritime security
- Potential Synergies:
- Enhanced coordination in forums like the UN, G-20, and WTO
- Scope for defence collaboration in the Indo-Pacific through joint naval exercises, technology transfers, and intelligence sharing
India’s partnerships with France, Germany, and the U.K. already focus on defence modernisation and green technologies. A coordinated U.K.–EU posture could formalise India’s role in shaping Western responses to strategic challenges in Asia, especially China’s assertiveness.
Global South Leadership: India can also leverage this alignment to push for climate finance, digital public infrastructure, and multilateral reform, reinforcing its leadership role post-G20 2023.
Reimagining Talent Mobility and Diaspora Engagement
India possesses the world’s largest diaspora, with significant populations in the U.K. and EU.
- Mobility Trends:
- In 2024, the U.K. issued over 1,10,000 student visas to Indian nationals.
- Post-Brexit, mobility of Indian professionals to the EU was curtailed.
- Potential Reset:
- Renewed U.K.–EU coordination on border and migration policy may enable partial mobility reintegration.
- India’s migration pacts with France, Germany, and Portugal could benefit from a wider U.K.–EU framework.
This realignment could lay the groundwork for a semi-integrated talent corridor, enhancing the movement of students, skilled professionals, and researchers.
Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for India
The U.K.–EU reset is more than a European internal realignment — it is a geostrategic moment that India must strategically exploit. Whether through trade harmonisation, defence diplomacy, or diaspora engagement, India stands to gain significantly. However, to capitalise on this, India must:
- Accelerate trade facilitation and infrastructure modernisation
- Strengthen its regulatory frameworks
- Enhance institutional diplomatic coordination
- Assertively position itself in multilateral platforms
This convergence of economic and diplomatic opportunity presents India with a chance to reshape its place in the evolving global order.
India-China Relations at 75: Navigating the Dragon-Elephant Tango
- 04 Apr 2025
In News:
On April 1, 2025, India and China marked the 75th anniversary of diplomatic relations with the exchange of congratulatory messages between President DroupadiMurmu and President Xi Jinping. Both leaders emphasized the need to deepen cooperation, manage differences strategically, and work jointly for regional and global stability. Xi referred to the bilateral relationship as a “Dragon-Elephant Tango,” symbolizing coordinated progress between two Asian giants.
Significance of the 75th Anniversary
The commemoration marks a diplomatic milestone for two ancient civilizations and modern emerging powers, both key members of the Global South. It offers a timely opportunity to recalibrate relations, especially after recent tensions such as the 2020 Galwan Valley clash. Xi called for enhanced “strategic mutual trust” and deeper coordination on global affairs, reflecting a shared responsibility in shaping the international order.
President Murmu and PM Modi stressed multipolarity, stability, and peaceful coexistence. Notably, over 70,000 visas were issued to Indians in early 2025, indicating a revival in people-to-people exchanges. Talks in March 2025 focused on border management and resumption of cultural and religious exchanges, including the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra.
Historical Overview
India was the first non-socialist country to recognize the People’s Republic of China in 1950. The 1954 Panchsheel Agreement promoted peaceful coexistence. However, the 1962 war over the unresolved border disputes—especially in Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh—remains a lasting legacy of mistrust.
Ties normalized in the 1980s, with Rajiv Gandhi’s 1988 visit paving the way for diplomatic mechanisms like the Special Representatives (SR) dialogue and Working Mechanism for Consultation and Coordination (WMCC). The 2000s saw robust economic engagement, with bilateral trade reaching $138.5 billion by 2024. Both nations became pivotal members of BRICS, SCO, and G20.
Areas of Cooperation
- Multilateral Platforms: India and China coordinate in BRICS, SCO, and on Global South agendas, especially climate finance and equitable development.
- Economic Ties: Despite border frictions, trade remains resilient. China is India’s largest trading partner.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Student exchanges, art exhibitions, and religious pilgrimages continue.
- Public Diplomacy: Diplomatic dialogues, resumed air links, and cooperation on trans-border rivers underscore confidence-building efforts.
Points of Divergence
- Border Dispute: The Line of Actual Control (LAC) remains contentious, especially post-Galwan 2020.
- Strategic Mistrust: China’s ties with Pakistan and presence in the Indian Ocean, as well as its Belt and Road Initiative (excluding India), fuel rivalry.
- Trade Imbalance: India’s import-heavy trade with China leads to a significant deficit.
- Perception Gap: India’s push for strategic autonomy contrasts with China’s assertive regional posturing.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Strategic Dialogue: Revive and regularize SR-level border talks and WMCC meetings.
- Rebuild Trust: Encourage military confidence-building measures and cooperative ventures in non-sensitive areas.
- Balance Trade: Promote diversification and attract Chinese investments aligned with India’s interests.
- Enhance People-to-People Ties: Facilitate educational, cultural, and tourism exchanges.
- Promote Multilateralism: Collaborate on global issues such as climate change, health security, and WTO reforms.
Conclusion
India-China relations remain a blend of cooperation and contestation. The 75th anniversary provides an inflection point to transcend border hostilities and engage in constructive diplomacy. A balanced and long-term perspective, as advocated by both nations, can shift the narrative from conflict to coordinated coexistence—true to the spirit of the “Dragon-Elephant Tango.”
India–US Civil Nuclear Deal

- 01 Apr 2025
Context:
Nearly two decades after the landmark India–US Civil Nuclear Agreement (123 Agreement) was signed in 2007, a major operational milestone has been achieved. In March 2025, the US Department of Energy (DoE) granted regulatory clearance under “10CFR810” of the US Atomic Energy Act (1954), allowing Holtec International, a US-based nuclear engineering firm, to transfer unclassified Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology to three Indian private entities: Holtec Asia (its subsidiary), Tata Consulting Engineers (TCE), and Larsen & Toubro (L&T).
Key Regulatory and Safeguard Provisions
- Authorization Duration: 10 years, subject to a five-year review.
- Safeguards: Technology to be used only for peaceful nuclear activities under IAEA safeguards.
- Restrictions:
- No retransfer to other Indian or foreign entities without US approval.
- Prohibited for military/naval propulsion or enrichment purposes.
- No access to Sensitive Nuclear Technology.
- Compliance: Holtec is required to file quarterly progress reports to the US DoE.
Strategic and Technological Significance for India
- Modernizing India's Nuclear Fleet: India's nuclear program has traditionally relied on Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) using natural uranium. The transfer of SMR technology based on Pressurised Water Reactors (PWRs) represents a shift towards the global mainstream of nuclear reactor technology.
- Boost to Domestic Manufacturing: Collaboration with Indian firms like L&T and TCE can localize manufacturing and engineering, promoting Make in India and self-reliance in nuclear energy technology.
- Entry into Global SMR Supply Chain: This development aligns India with an emerging global trend, as SMRs (30–300 MWe) are increasingly viewed as crucial for decarbonization and energy security.
- Strategic Counterbalance to China: As China advances its SMR technology for energy diplomacy in the Global South, this India–US initiative presents a geopolitical counterweight, especially as both nations face challenges in independently competing with China’s scale and state-led investments.
Legal and Policy Bottlenecks
- Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010: Cited by foreign companies as a barrier due to concerns about supplier liability in case of accidents.
- Atomic Energy Act, 1962: Needs amendments to permit private sector participation in nuclear generation, currently reserved for public sector undertakings like NPCIL and NTPC.
- Despite Holtec's request, these PSUs were not included in the initial authorization due to pending non-proliferation assurances from the Indian government. However, they may be added later, contingent on further diplomatic progress.
Way Forward and Future Prospects
- Holtec’s Expansion Plans: Its non-nuclear manufacturing unit in Dahej, Gujarat is poised for expansion, with a potential doubling of its workforce once SMR manufacturing begins.
- Partnership Pipeline:
- TCE for engineering design.
- L&T for high-precision nuclear component manufacturing.
- Future engagement with NPCIL and NTPC as operators of Holtec’s SMR-300 reactors.
- Clean Energy Strategy: SMRs are positioned as a key component of India's low-carbon energy transition, addressing both rising power demands and global climate commitments.
Conclusion
The US’s clearance for technology transfer to Indian private firms marks a pivotal operational step in the long-stalled India–US civil nuclear partnership. It opens the door for India to enter the global SMR market, boosts its domestic nuclear industry, and strengthens strategic cooperation with the US. However, legal reforms and institutional readiness remain critical for realizing the full potential of this deal.
Kolkata-Northeast Sea Route and the Strategic Highway Project
- 19 May 2025
In News:
India’s northeast has long faced logistical isolation due to its geographical constraints and overdependence on the narrow Siliguri Corridor, also known as the Chicken’s Neck. A recent strategic initiative aims to transform this scenario through the creation of a multi-modal connectivity route that bypasses Bangladesh and directly links the Northeast to the sea via Myanmar and Kolkata. This development gains added relevance in light of recent remarks by Bangladesh’s interim leader Muhammad Yunus, who described Northeast India as “landlocked” and dependent solely on Dhaka for maritime access—a claim that India seeks to counter through tangible connectivity upgrades.
Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP)
At the heart of this initiative lies the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP), a flagship project under India’s Act East Policy, designed to connect the eastern seaport of Kolkata to the landlocked Northeast through Myanmar. The project includes:
- Sea Leg: Kolkata Port to Sittwe Port in Myanmar (~539 km).
- Inland Waterway: From Sittwe to Paletwa via the Kaladan River (~158 km).
- Road Leg in Myanmar: Paletwa to Zorinpui on the India-Myanmar border (~110 km).
- Indian Extension: Zorinpui to Lawngtlai and Aizawl in Mizoram, connecting to the national highway network.
This corridor not only reduces reliance on routes through Bangladesh but also serves as a strategic counterbalance in India’s regional geopolitics, particularly in strengthening ties with Southeast Asia and enhancing its maritime influence in the Bay of Bengal.
Strategic Shillong-Silchar Highway
Complementing the KMTTP is the construction of a 166.8 km four-lane high-speed highway from Mawlyngkhung (near Shillong) to Panchgram (near Silchar) along NH-6. This is the first high-speed corridor in the North-East and the first in a hilly terrain, and is slated for completion by 2030. The project is being developed under the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM) at a cost of ?22,864 crore, with implementation by NHIDCL for the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
The highway will include:
- 19 major bridges, 153 minor bridges, 326 culverts
- 22 underpasses, 26 overpasses, 8 subways, and 34 viaducts
It will reduce travel time between Shillong and Silchar from 8.5 to 5 hours and act as a crucial link to states like Mizoram, Tripura, and Manipur. More significantly, it will integrate with the Kaladan route, offering a direct link to Kolkata via Myanmar and the Bay of Bengal.
Strategic and Economic Significance
This integrated connectivity initiative holds multi-dimensional importance:
- Reduces dependency on Bangladesh and the Siliguri Corridor
- Enhances trade and people-to-people ties with ASEAN nations
- Strengthens regional integration under the Act East Policy
- Boosts economic development in the North-East through improved logistics
- Improves India’s strategic posture in the Indo-Pacific and Bay of Bengal
In conclusion, the Kolkata-Northeast sea route and supporting infrastructure like the Shillong-Silchar highway represent a decisive step towards bridging geographical constraints, boosting regional development, and reinforcing India’s strategic autonomy in the eastern frontier.
US Airstrikes on Houthis
- 22 Mar 2025
In News:
The renewed US military offensive against the Iran-backed Houthi rebels in Yemen reflects intensifying geopolitical tensions in the Red Sea and surrounding West Asian region. In early 2025, the US launched over 40 airstrikes targeting Houthi-controlled areas, including Sanaa, Saada, and the strategic port city of Hodeidah. The escalation follows months of Houthi attacks on international shipping, ostensibly in solidarity with Palestinians during the ongoing Gaza conflict.
Strategic Background and US Objectives
Houthi disruptions to maritime trade in the Red Sea—through drone, missile, and small-boat attacks—have endangered key shipping lanes through Bab-el-Mandeb and the Suez Canal. With nearly 15% of global seaborne trade passing through this corridor, including vital energy supplies, their actions have compelled ships to reroute around Africa, escalating shipping costs and global inflation risks.
Former US President Donald Trump, now leading a second administration, has vowed decisive retaliation. He re-designated the Houthis as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) in early 2025 and emphasized that attacks by the Houthis would be interpreted as attacks by Iran, warning Tehran of dire consequences. Trump’s administration asserts that the airstrikes are aimed at restoring freedom of navigation and deterring Iranian influence in the region. However, critics argue this could be a calibrated signal to avoid direct confrontation with Iran while maintaining pressure ahead of potential nuclear negotiations.
Regional and International Dynamics
The Houthis, officially called Ansar Allah, have displayed remarkable resilience, withstanding over 20,000 airstrikes by the Saudi-led coalition since 2015. Their asymmetric warfare tactics, inspired by groups like Hezbollah, rely on mobility, modular units, and advanced missile and drone technology. Despite repeated bombardments, they retain operational capabilities, evidenced by continued attacks on US naval assets and commercial vessels.
Although Tehran remains the group's principal backer, Houthi ties extend to Russia and China. Beijing, by purchasing nearly 90% of Iran’s oil exports in 2024, indirectly funds the Houthi supply chain. Many of the group’s anti-ship cruise missiles are derivatives of older Chinese designs, while Moscow reportedly provides targeting intelligence and small arms. This triangulation complicates US efforts, making the Houthis part of a broader anti-Western strategic bloc.
Regional Responses and the Humanitarian Toll
Interestingly, major Arab states, including Saudi Arabia—formerly the Houthis' chief adversary—have distanced themselves from the US offensive. Riyadh advised restraint in early 2024 and has reportedly avoided providing logistical support for the strikes. This signals a regional fatigue with military solutions and a possible pivot toward political engagement.
On the ground, the strikes have intensified the humanitarian crisis in Yemen. The Houthi-run health ministry reports at least 31 deaths and over 100 injuries. Yet, the group remains defiant, pledging to continue targeting vessels linked to the US, UK, or Israel until the Gaza blockade is lifted.
Conclusion
The Houthi-US conflict in the Red Sea epitomizes the nexus of regional geopolitics, maritime security, and great power rivalries. For India, which depends heavily on Suez Canal routes for trade and energy imports, developments in this theatre bear close watching. A prolonged conflict could disrupt global supply chains, heighten oil prices, and challenge freedom of navigation principles, central to India’s Indo-Pacific strategy.
India–New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (FTA) Negotiations
- 17 Mar 2025
In News:
India and New Zealand have officially resumed negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) after a prolonged hiatus since 2015. This strategic move aims to enhance bilateral trade, deepen economic interdependence, and strengthen regional cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
Background and Significance
The FTA talks, first initiated in 2010, were stalled due to differences, particularly over India’s high tariffs on New Zealand’s dairy and agricultural exports. The revival of discussions during New Zealand Prime Minister Christopher Luxon's official visit to India in 2025 signals a renewed commitment towards building a balanced, ambitious, and mutually beneficial trade framework.
The bilateral trade relationship, though modest, has shown robust growth. In 2023–24, India exported goods worth $538 million to New Zealand and imported $335 million, generating a trade surplus of $203 million. By December 2024, exports rose by 21.49%, and imports surged by 78.72%, narrowing the trade surplus to $33 million.
Key Objectives of the India–New Zealand FTA
- Enhance supply chain integration.
- Improve market access for goods, services, and investments.
- Strengthen economic resilience and bilateral commercial ties.
- Facilitate trade through the Authorized Economic Operators Mutual Recognition Arrangement (AEO-MRA).
India’s major exports to New Zealand include pharmaceuticals, machinery, textiles, and precious stones, while imports largely consist of wool, aluminum, fruits, and steel products.
Strategic and Geopolitical Dimensions
Beyond economics, the agreement holds strategic significance:
- A defense cooperation MoU was signed to institutionalize military engagements and promote maritime collaboration.
- New Zealand expressed intent to join India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Both nations pledged support for a free, open, inclusive Indo-Pacific, aligning with the UNCLOS-based rules-based international order.
- New Zealand reiterated support for India’s permanent membership in the reformed UNSC and entry into the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
Sectoral Cooperation and Emerging Areas
- Climate Change and Sustainability:
- New Zealand joined India-led initiatives like the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
- Both countries committed to joint action under the Paris Agreement and Sendai Framework.
- Education and Skill Development:
- A renewed Education Cooperation Arrangement was signed to boost academic partnerships, student mobility, and vocational training.
- Plans are underway to commemorate 100 years of sports relations in 2026, coupled with a new MoU on sports cooperation.
- Diaspora and People-to-People Ties:
- The Indian diaspora forms 6% of New Zealand’s population, playing a pivotal role in cultural and economic relations.
- India raised concerns regarding pro-Khalistan activities, and New Zealand assured cooperation in addressing such issues.
Opportunities and Complementarities
India’s Strategic Importance to New Zealand:
- Large market with a growing middle class and rising demand for dairy, meat, and high-value agricultural exports.
- Largest source of skilled migrants and second-largest source of international students.
- Booming digital economy offers collaboration potential in fintech, AI, and digital services.
New Zealand’s Relevance to India:
- Expertise in sustainable farming and dairy technology supports India’s agricultural reforms.
- Recognized climate tech sector aligns with India’s clean energy transition.
- Potential buyer of India’s defense equipment and surveillance systems, enhancing maritime security amid Indo-Pacific tensions.
Challenges in Bilateral Relations
- Stalled FTA negotiations due to tariff sensitivities, particularly in the dairy sector.
- Non-tariff barriers (NTBs) affecting Indian exports like fruits and vegetables.
- Low trade volumes and limited awareness of New Zealand’s economic strengths among Indian businesses.
- Divergences in geopolitical alignments, with New Zealand’s reliance on China creating potential strategic friction.
Way Forward
- Conclude FTA negotiations through dialogue and sectoral agreements in pharmaceuticals, technology, and horticulture.
- Consider an interim Early Harvest Agreement, akin to India–Australia ECTA, to fast-track gains.
- Enhance market access by reducing NTBs, fast-tracking Mutual Recognition Arrangements (MRAs), and organizing trade expos and B2B interactions.
- Leverage climate and renewable energy cooperation, strengthen defense collaboration, and institutionalize maritime security mechanisms.
Conclusion
The renewed India–New Zealand FTA negotiations mark a pivotal step in recalibrating bilateral economic and strategic relations. Anchored in democratic values and shared Indo-Pacific interests, the partnership is poised to evolve into a multi-dimensional engagement encompassing trade, technology, climate resilience, and defense cooperation. The agreement, if concluded, could serve as a model for equitable North–South economic partnerships in a multipolar world order.
India–Mauritius Enhanced Strategic Partnership

- 15 Mar 2025
In News:
India and Mauritius have elevated their bilateral relationship to an Enhanced Strategic Partnership, underscoring deep-rooted historical ties, shared cultural linkages, and growing strategic alignment in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). This elevation came during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Mauritius in March 2025, marking a new phase in India’s engagement with the Global South through the unveiling of the MAHASAGAR Vision—Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions.
Key Agreements and Strategic Cooperation
A total of eight bilateral agreements were signed, focusing on trade, defense, maritime security, financial crimes, and developmental cooperation. A landmark agreement was the signing of India’s first-ever rupee-denominated Line of Credit to Mauritius, worth ?487.6 crore, aimed at upgrading the island’s water supply system. This also complements a broader move toward trade settlement in local currencies, reducing dependence on foreign exchange and enhancing resilience in bilateral commerce.
In the realm of maritime security, the partnership now includes expanded white shipping information sharing, enhanced joint maritime surveillance, and greater utilization of strategic facilities on Agalega Island, developed with Indian assistance. India reaffirmed its commitment to safeguarding Mauritius’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and supporting the establishment of a police academy and a national maritime information-sharing centre.
India also extended support to Mauritius’s claim over the Chagos Archipelago, opposing colonial remnants and reinforcing its consistent stance on sovereignty and decolonization in global forums.
MAHASAGAR Vision and Global South Outreach
The newly unveiled MAHASAGAR initiative builds upon India’s earlier SAGAR doctrine, broadening the framework to include developmental cooperation, technology transfer, capacity building, concessional finance, and joint security across the Global South. It strengthens India’s position as a net security provider and first responder in the IOR, evident from its assistance during Cyclone Chido and the Wakashio oil spill.
The visit also witnessed the inauguration of the Atal Bihari Vajpayee Institute of Public Service and Innovation, a health centre, and 20 community projects built with Indian grants. Further, India announced its support for constructing a new Parliament building in Mauritius, symbolizing democratic solidarity.
Cultural and Economic Pillars
Mauritius hosts a large Indian diaspora (around 70% of its population), maintaining strong cultural, religious, and linguistic ties with India. Historical bonds, such as Mahatma Gandhi’s 1901 visit, continue to influence people-to-people relations. Economically, Mauritius serves as a gateway to Africa, benefiting from India’s rising trade and investment footprint, particularly through the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
India is one of Mauritius’s top trading partners and a major source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), with Mauritius being the second-largest source of FDI into India in FY 2023–24.
Conclusion
The India–Mauritius partnership exemplifies a holistic model of South-South cooperation, driven by shared values, strategic convergence, and mutual development. In the evolving Indo-Pacific framework, it reinforces India's Act East and Extended Neighbourhood policies while bolstering regional stability and economic integration.
USAID Funding in India

- 11 Mar 2025
In News:
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has been a major development partner for India, contributing over $2.8 billion in Official Development Assistance (ODA) since 2001. While initial assistance focused on food aid, recent decades saw a shift toward public health, environmental sustainability, digital infrastructure, and institutional capacity building.
Between 2022 and 2024, India received substantial aid from USAID — $228 million in 2022, $175 million in 2023, and $151 million in 2024 (as of December). A significant portion of this funding targeted health and population programs, including polio eradication, maternal and child health, tuberculosis (TB), HIV/AIDS, and Covid-19 response.
In 2022 alone, $120 million was allocated to Covid-19 control, alongside support for healthcare infrastructure and awareness campaigns.
USAID also supported India’s environmental goals, providing funds for air pollution control, clean water initiatives, and climate resilience, with $17.12 million allocated in 2024. Additionally, USAID backed India's technological advancement by exploring secure 5G Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) systems, aligning with the U.S. Indo-Pacific strategy aimed at countering China’s influence.
However, the January 20, 2025 Executive Order by the U.S. administration directed a halt to foreign aid and restructuring of USAID. Although initially stayed by a U.S. Federal Court in February, the Supreme Court’s March 5 verdict upheld the aid cuts, jeopardizing thousands of ongoing development projects globally, including in India.
This decision critically affects India’s public health landscape. For instance, the ‘Breaking the Barriers’ TB awareness program in Karnataka, Bihar, Telangana, and Assam — funded with $7 million between 2022–23 — is being discontinued. The President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), another major source of HIV/AIDS support, also faces disruption, risking higher infection and mortality rates. The cuts particularly threaten NGOs like Karnataka Health Promotion Trust (KHPT), which relied on USAID for operational continuity.
Beyond health, the withdrawal of USAID support may create a strategic vacuum in South Asia, enabling greater Chinese geopolitical and economic influence. Legal uncertainty around development aid has also raised concerns about the stability of global health and environmental partnerships.
Way Forward for India
- Diversify donor engagement: India must strengthen development ties with consistent partners like Japan ($2.97B in 2022), the EU ($383.5M), and Germany ($235M).
- Increase domestic investments in public health, sanitation, and clean energy to reduce dependence on external aid.
- Boost private sector and philanthropic partnerships to ensure continuity of key health and environmental programs.
- Strengthen indigenous R&D capacity, especially in digital infrastructure and vaccine development.
- Diplomatic dialogue with U.S. policymakers can explore possibilities for reinstating targeted support.
Conclusion
The scaling back of USAID poses significant challenges to India's public health, environmental sustainability, and strategic autonomy. However, it also presents an opportunity for India to reinforce its developmental sovereignty through diversified funding, innovation, and international cooperation.
India-Qatar Relations
- 07 Mar 2025
In News:
India and Qatar have significantly deepened their bilateral relationship, particularly with the recent state visit of Qatar’s Amir, Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al-Thani, to India. This visit marked a pivotal moment, as both countries elevated their ties to a "strategic partnership," exploring avenues for collaboration in energy, trade, and diplomacy.
Evolution of India-Qatar Relations
India's relationship with the Gulf region is multifaceted, encompassing economic, cultural, and people-to-people ties. Qatar holds a special place in India’s foreign policy due to its strategic position in the Middle East, its influence in the LNG market, and its robust ties with both Western powers and regional players such as Israel and Afghanistan. As one of the largest suppliers of LNG to India, Qatar’s energy significance is paramount.
India has consistently prioritized relations with the Gulf, with the Prime Minister placing special emphasis on strengthening ties. The recent visits by India’s External Affairs Minister to Qatar underscore the diplomatic importance of this relationship.
Key Outcomes of the Amir’s Visit
The visit of Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al-Thani resulted in several key agreements and developments:
- Strategic Partnership:India and Qatar upgraded their relationship to a "strategic partnership," signaling enhanced cooperation across various domains such as energy security, trade, and investment. This move aligns Qatar with India’s other strategic Gulf partners like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Oman, reinforcing regional cooperation under the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
- Economic and Trade Cooperation:The two countries committed to doubling bilateral trade from $14 billion to $28 billion over the next five years. Qatar also pledged $10 billion in new investments in India, particularly in the infrastructure, energy, and technology sectors. Several agreements on economic cooperation, youth affairs, and double taxation avoidance were also signed, aimed at facilitating business activities.
- Energy Cooperation:A landmark agreement between QatarEnergy and India’s Petronet LNG extended their LNG supply deal for 20 years, marking the largest-ever LNG agreement. This deal secures India’s long-term energy needs and diversifies its energy sources, ensuring stable pricing for LNG imports.
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA) Possibilities:Discussions were held on a potential India-Qatar Free Trade Agreement (FTA) to boost trade relations. While Qatar has existing FTAs with countries like China, a similar agreement with India could further enhance trade and investment flows. However, India must ensure safeguards to prevent the dumping of third-party goods through Qatar.
- Resolution of Diplomatic Setback:Bilateral relations were strained in 2022 following the arrest of eight Indian Navy personnel in Qatar on espionage charges. The Amir’s decision to pardon these individuals removed a significant diplomatic roadblock, improving goodwill between the two countries.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite the positive developments, challenges persist:
- Economic and Trade Barriers:Non-tariff barriers and bureaucratic hurdles remain significant obstacles to smoother business transactions. Moreover, Qatar’s investments in India are still limited compared to other Gulf nations, despite its substantial sovereign wealth fund. India must encourage greater Qatari participation in sectors like infrastructure, startups, and energy exploration.
- Political and Security Risks:The volatile security situation in the Middle East, particularly tensions between Iran and Israel, poses risks to India’s energy supply chains. Any diplomatic tensions between Qatar and its Gulf neighbors could indirectly affect India’s trade interests.
- Labor and Migration Issues:India must continue to advocate for better working conditions and legal protections for Indian workers in Qatar. Ensuring the welfare of Indian expatriates, including seamless remittance flows and social security benefits, is essential for strengthening bilateral ties.
Conclusion
The elevation of India-Qatar relations to a strategic partnership marks a new chapter in their ties, positioning Qatar as a critical partner in India’s energy security and trade. As India’s influence in the Middle East and global energy markets grows, its relationship with Qatar will play an increasingly important role in shaping the region’s geopolitical landscape. The continued focus on economic cooperation, energy security, and labor welfare will be vital to sustaining and expanding this crucial partnership.
India-EU Strategic Partnership

- 01 Mar 2025
In News:
The recent visit of European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen to India, marked a significant recalibration in India-EU relations. Amid global geopolitical flux—characterized by U.S.-Europe divergences, China’s assertiveness, and disrupted supply chains—India and the EU are deepening cooperation in trade, technology, climate, and security. This partnership is crucial for regional stability and shaping a multipolar, rules-based global order.
Strategic and Economic Dimensions
- Trade and Investment:The EU is India’s largest trading partner, accounting for 12.2% of India’s total trade in 2023. Bilateral goods trade reached $135 billion (FY 2023–24), and services trade stood at $53 billion. The EU is the second-largest source of FDI into India ($117.4 billion since 2000), while Indian FDI to the EU was $40 billion. Free Trade Agreement (FTA) talks, revived in 2021, aim to resolve tariff and regulatory barriers in sectors like automobiles, dairy, pharma, and IT services.
- Technology and Digital Cooperation:The India-EU Trade and Technology Council (TTC), launched in 2022, promotes collaboration in semiconductors, AI, clean energy, and resilient supply chains. Key developments include MoUs on semiconductor R&D and high-performance computing. Challenges remain, particularly around EU data adequacy under GDPR, which affects Indian digital exporters.
- Green Transition and Energy Security:The EU-India Clean Energy and Climate Partnership focuses on renewable energy, smart grids, and sustainable cities. A €1 billion European Investment Bank fund supports green hydrogen projects. India’s participation in European Hydrogen Week 2024 signals growing collaboration in clean energy. Initiatives like SWITCH-Asia promote sustainable consumption and circular economy practices.
- Maritime and Defense Cooperation:Under the ESIWA framework, India and the EU are expanding maritime security ties. The EU has stationed a liaison officer at India’s Information Fusion Centre (Gurugram), and the first joint naval exercise in the Gulf of Guinea (2023) emphasized Indo-Pacific cooperation. However, defense ties remain limited due to India's stronger military relationships with Russia and the U.S.
Institutional and Societal Ties
India-EU relations date back to 1962 and were elevated to a Strategic Partnership in 2004. The Roadmap to 2025, adopted in 2020, prioritizes digital transformation, climate action, and multilateralism. The TTC’s recent meetings reaffirm commitment to tech and trade collaboration.
People-to-people ties are strengthening. Indians received over 20% of EU Blue Cards (2023–24). Over 6,000 Indian students have benefitted from Erasmus scholarships, and 2,700 researchers from Marie Sk?odowska-Curie Actions.
Key Challenges
- Stalled FTA Talks over tariffs and market access.
- Regulatory barriers under SPS and TBT norms.
- Data governance divergence due to lack of EU data adequacy for India.
- Foreign policy misalignments, especially over Russia-Ukraine.
- Fragmented defense engagement due to EU’s limited commitment.
Way Forward
India and the EU must resolve FTA hurdles, negotiate a data-sharing framework, align Indo-Pacific strategies, and invest in alternative supply chains via IMEC. Enhanced cooperation in green tech, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure is key. India must also reform its regulatory landscape to attract EU tech and manufacturing investments.
Conclusion
India-EU ties are entering a transformative phase. Anchored in shared democratic values and strategic interests, the partnership can promote multipolarity, sustainable development, and a resilient global governance architecture.
India–Sri Lanka Fishing Dispute
- 24 Feb 2025
Context:
The recurring arrests of Indian fishermen by the Sri Lankan Navy in the Palk Bay region underscore a complex and unresolved bilateral issue, rooted in historical practices, ecological concerns, and geopolitical sensitivities. The most recent incidents in early 2025 have intensified the diplomatic and political discourse between the two neighbours.
Background and Origin of the Dispute
The core of the India–Sri Lanka fishing dispute lies in the contested fishing rights in the Palk Bay, a narrow strip of sea separating Tamil Nadu from northern Sri Lanka. The 1974 and 1976 maritime boundary agreements, particularly the ceding of Katchatheevu Island to Sri Lanka, formalized the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL). While Indian fishermen were permitted traditional access to the island for specific purposes, the agreements curtailed their fishing activities across the newly delineated boundary.
However, Tamil Nadu fishermen have historically fished in these waters, and the IMBL has not fully erased traditional patterns. The situation is worsened by ecological pressures on Indian fishing grounds, pushing fishermen into Sri Lankan waters.
Key Issues Involved
- Violation of IMBL and Traditional Rights:Indian fishermen often assert customary fishing rights across the IMBL, which clashes with Sri Lanka’s assertion of sovereignty over its territorial waters. Many crossings occur unintentionally due to poor navigation, engine failures, or inclement weather.
- Bottom Trawling and Environmental Concerns:The use of bottom trawlers by Indian fishermen is a major point of contention. This method, which scrapes the seabed, damages marine ecosystems and depletes resources, affecting both nations' long-term fisheries sustainability. Sri Lanka has banned bottom trawling and views it as ecological exploitation and illegal fishing.
- Security and Sovereignty Sensitivities:Sri Lanka perceives these incursions not only as violations of maritime boundaries but also as potential national security threats, recalling past concerns over Tamil militant movements operating from the sea.
- Recurrent Arrests and Humanitarian Concerns:The frequent arrests, imprisonment, and imposition of heavy fines on Indian fishermen have humanitarian and political implications. Often, fishing boats are not returned even after the release of the crew, causing further livelihood losses.
Efforts at Resolution
- Diplomatic Engagement:The issue has prompted high-level political intervention, with the Tamil Nadu government urging the Union Government for effective measures and the convening of a Joint Working Group (JWG) to address the issue diplomatically.
- Livelihood-Based Approaches:Both countries have discussed alternatives to resolve the crisis humanely, including exploring sustainable fishing practices, alternate employment, and deep-sea fishing training.
- Technological Interventions:Use of GPS-based tracking systems and awareness programs aim to prevent inadvertent border crossings and encourage responsible fishing.
- People-to-People Dialogues:Calls for direct interaction between fishermen communities from both nations have been made, suggesting that grassroots engagement may ease tensions and promote mutual understanding.
International Legal Framework
- UNCLOS (1982):Provides legal clarity on maritime boundaries and responsibilities, but emphasizes mutual respect for sovereign rights and sustainable resource use.
- UN Fish Stocks Agreement (1995):Encourages cooperation in conserving transboundary fish stocks, suggesting the role of Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs) in managing shared marine resources.
Conclusion
The India–Sri Lanka fishing dispute in the Palk Bay is not merely a bilateral maritime boundary issue; it is a convergence of historical rights, ecological degradation, livelihood dependence, and strategic concerns. While both countries have taken steps towards conflict management, a long-term solution lies in cooperative marine resource governance, joint monitoring, and community-centric diplomacy. Resolving this issue through dialogue, sustainable practices, and mutual sensitivity is essential to safeguard both bilateral relations and the rights and livelihoods of coastal communities.
Renewed India–US Civil Nuclear Cooperation

- 21 Feb 2025
In News:
Context:
India and the United States have reaffirmed their commitment to fully realise the 123 Civil Nuclear Agreement, marking a major push to revive progress two decades after the pact was signed in 2007.
Key Gains for India
- Technology Transfer & Localisation:The partnership envisions joint construction of US-designed nuclear reactors in India, incorporating large-scale localisation and technology transfer, reversing the US's usual "manufacture-at-home" stance.
- Upgrading India’s Nuclear Capacity:India aims to shift from PHWRs (Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors) to globally dominant PWRs (Pressurised Water Reactors). This will allow India to scale capacity addition and modernise its nuclear fleet.
- Entry into Small Modular Reactors (SMRs):
- SMRs (30–300 MWe) are compact, scalable reactors viewed as essential for future clean energy demands.
- India’s Department of Atomic Energy is exploring collaboration with Holtec International (USA) for joint manufacturing and deployment.
- Holtec's SMR-300, supported by the US Department of Energy with $116 million, is under design review in the UK and Canada.
- Strategic Counter to China:India–US joint ventures in SMRs could counter China’s rising influence in the Global South through its aggressive SMR diplomacy.
Economic & Industrial Impacts
- Holtec plans a nuclear technology campus in Pune and a specialty manufacturing plant in India.
- Existing facility in Dahej, Gujarat, can double workforce if plans are approved.
- Legal reforms in India are being considered to attract investments from Western and Middle Eastern markets into the nuclear sector.
India: Leading the Next Phase of Global Outsourcing (Deloitte Report)
Key Findings from Deloitte’s ‘The Outsourcing Compass’ (2025)
- Growing Demand:
- 81% of global organizations plan to increase outsourcing over the next 3–5 years.
- India continues to lead as a global outsourcing hub, with a projected rise as the world’s 3rd-largest economy by 2027.
- Shift in Outsourcing Models:
- Transition from back-office services to strategic, high-value functions like product development, AI/GenAI support, and brand management.
- 98% of firms depend on Indian service providers for AI and GenAI capabilities.
- Modern Contracting Approaches:
- 36% prefer outcome-based contracts over traditional FTE-based models.
- AI-specific clauses are being added to outsourcing contracts to enhance tracking and cost control.
- Strategic Collaborations & Cost Efficiency:
- Strategic-niche partnerships yield 10–25% annual cost savings; some report 15–35% savings.
- 70% of organizations work with non-traditional providers to access innovative technologies.
- Evolving Operating Models:
- 55% use Global Business Services (GBS) centers for oversight; execution by third-party providers.
- 35% adopt Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) models to scale up while retaining control.
- Robust Governance Structures:
- 45% of mature outsourcing firms operate Vendor Management Offices (VMOs) to manage risks and enhance effectiveness.
Why India Remains Preferred:
- A skilled digital workforce, thriving startup ecosystem, policy stability, and advancements in cybersecurity and vendor governance bolster India’s position.
USAID Freeze and Its Global Implications
- 17 Feb 2025
Context:
On January 20, U.S. President Donald Trump, upon beginning his second term, issued an executive order imposing a 90-day freeze on foreign assistance. The directive aimed to reassess the efficiency and alignment of U.S. foreign development programs with its foreign policy priorities. This decision led to an immediate halt in operations of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), with the majority of its 10,000 personnel placed on administrative leave and project funding suspended worldwide.
What is USAID?
- Established in 1961 under President John F. Kennedy through an Act of Congress, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) functions as an independent agency responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance.
- Its core mission is to promote democratic values, global peace, and prosperity while advancing American national security and economic interests.
- USAID operates in over 100 countries, partnering with governments, NGOs, private firms, and international organizations.
- It offers financial support, technical assistance, and capacity-building across key sectors such as health, education, food security, economic development, humanitarian relief, environmental sustainability, and governance.
- Prominent initiatives include:
- PEPFAR: A flagship HIV/AIDS prevention and treatment program.
- Feed the Future: Focused on combating hunger and improving food security.
- Power Africa: Aimed at expanding electricity access across Africa.
- Water for the World Act: Enhancing water, sanitation, and hygiene infrastructure.
- In 2024, USAID disbursed $44.2 billion globally, which accounted for approximately 0.4% of the U.S. federal budget. Notably, the agency contributed to around 42% of all humanitarian aid tracked by the United Nations that year.
Rationale and Political Overtones
The Trump administration justified the freeze as a review for improving programmatic efficiency and ensuring alignment with U.S. strategic interests. However, critics argue the move is politically motivated, targeting Biden-era programs. Elon Musk, heading the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), labeled USAID a "criminal organization," while Secretary of State Marco Rubio indicated a broader plan for restructuring.
Global Impact of the Freeze
The abrupt suspension of USAID operations threatens development and humanitarian efforts across numerous vulnerable regions. Top recipients like Ukraine, Ethiopia, Somalia, Syria, and Yemen face the sudden withdrawal of critical support in health, food security, disaster relief, and infrastructure.
The United Nations has warned that halting support for HIV/AIDS programs alone could result in over six million deaths within four years. In several African and Middle Eastern nations, the absence of aid could derail long-term projects aimed at poverty alleviation, maternal and child health, vaccination drives, and crisis response mechanisms.
Moreover, the withdrawal risks diminishing the U.S.’s diplomatic influence in the Global South, potentially creating a vacuum for geopolitical competitors such as China, which may expand its presence through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Impact on India
USAID's involvement in India dates back to 1951, when President Truman signed the India Emergency Food Aid Act. Over the decades, it evolved from providing food aid to supporting economic reforms, infrastructure, and public health initiatives. However, India’s dependency on USAID has significantly declined in recent years.
In 2024, USAID allocated approximately $79.3 million to India, primarily focused on healthcare, including HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, maternal and child health, and immunization programs. This constituted only about 0.2% to 0.4% of USAID’s global disbursement.
While the immediate impact on India may be limited due to reduced reliance and growing self-sufficiency, some ongoing health and sanitation projects could face temporary disruptions. The Indian government and implementing agencies have been directed to suspend USAID-funded operations, raising concerns about the continuity of services for vulnerable populations.
Conclusion and the Way Forward
The freeze on USAID funding reflects a shift in U.S. foreign aid philosophy and signals potential isolationist tendencies. While India may be resilient, many developing nations in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia could witness significant humanitarian and developmental setbacks.
To mitigate the impact, affected countries must:
- Enhance domestic resource mobilization to sustain critical development programs.
- Deepen partnerships with multilateral institutions like the UN, World Bank, and WHO.
- Encourage private sector participation through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
- Foster South-South cooperation to promote shared growth models.
The episode underscores the urgent need for the Global South to diversify funding sources and build internal capacities to safeguard developmental progress from geopolitical uncertainties.
India-France AI Summit and Strategic Partnership

- 13 Feb 2025
In News:
India and France, bound by a deep-rooted strategic partnership since 1998, have expanded cooperation across defence, nuclear energy, space, trade, and culture. In a significant move reflecting shared values and mutual respect, Prime Minister Narendra Modi was invited by French President Emmanuel Macron to co-chair the Artificial Intelligence (AI) Action Summit in Paris in 2024—marking a pivotal moment in global AI governance and Indo-French relations.
Enduring Strategic Relations
India-France relations are anchored in the principles of strategic autonomy and reciprocal respect. France has consistently stood by India in challenging times—refusing sanctions post-Pokhran-II nuclear tests in 1998 and maintaining diplomatic engagement during the Emergency in 1976. President Macron’s participation in India’s 2024 Republic Day celebrations underscores the warmth in bilateral ties.
Robust Defence and Technological Cooperation
Defence cooperation forms the backbone of the relationship. Key initiatives include:
- Rafale Fighter Jets: Procurement of 36 Rafales and discussions on 26 Rafale-M jets for the Indian Navy.
- P-75 Scorpene Submarines: Expansion plans include three additional submarines.
- Next-gen Jet Engine Development and a dedicated DRDO office in Paris (2023) to bolster technology collaboration. France’s unique support for Make in India and technology transfer sets it apart, coupled with training programs for Indian personnel.
Expanding Frontiers: AI and Innovation
The Paris AI Summit marked a strategic milestone, with India’s role highlighting its growing global influence in emerging technologies. India presented its flagship IndiaAI Mission—a ?10,371 crore initiative focused on “Making AI in India and Making AI for India,” promoting equitable AI access and innovation.
The Summit, following the UK (2023) and South Korea (2024) AI summits, focused on:
- Public Interest AI
- Future of Work
- Innovation & Culture
- Trust in AI
- Global AI Governance
India advocated responsible AI, inclusive governance, and greater representation of the Global South, emphasizing AI's role in sustainable development and reducing the global AI divide.
Multilateral Engagement and Global Cooperation
India co-chairs the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) for 2024, reinforcing its commitment to ethical and collaborative AI development. Through the Paris Summit, India contributed to the Leaders' Statement, participated in steering committees, and called for AI democratization aligned with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Beyond AI: Economic and Cultural Synergies
Bilateral trade surpassed $15 billion in 2023–24, with Indian exports at $7.14 billion and imports at $7.97 billion. Key developments:
- India-France CEOs Forum: Focus on defence, renewable energy, pharma, and startups.
- India-France Innovation Year 2026 and inauguration of a new Indian consulate in Marseille.
- Triangular Development Cooperation Initiative: Joint projects in the Indo-Pacific focused on climate and SDG targets.
- Joint visit to the ITER fusion energy project, reflecting shared aspirations for clean energy.
Conclusion
The India-France partnership has matured into a multifaceted global alliance—from defence and climate action to AI leadership and sustainable development. The co-chairing of the AI Summit symbolizes India's rising stature in tech diplomacy and affirms the enduring strategic trust between two democratic powers. For UPSC aspirants, this partnership exemplifies strategic depth, technological collaboration, and global engagement driven by shared values and autonomy.
M23 Rebellion
- 11 Feb 2025
In News:
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has once again become the epicenter of a severe humanitarian and geopolitical crisis. In early 2025, the M23 militia, a Tutsi-led rebel group allegedly backed by Rwanda, captured Goma, the capital of North Kivu province.
This strategic and mineral-rich city lies on the eastern border with Rwanda and has historically been a flashpoint in the region. The recent offensive has escalated the violence, displacing over 7,00,000 people, killing more than 2,900, and risking a wider regional conflict.
Historical Roots of the Conflict
The current instability can be traced back to colonial and post-independence ethnic tensions in the Great Lakes region. Under German and Belgian colonial rule, power structures in Rwanda favored the minority Tutsi population, generating long-standing resentment among the Hutus. Following Rwanda’s independence in 1962, a Hutu-majority government took power, culminating in the 1994 Rwandan Genocide, where nearly 800,000 Tutsis and moderate Hutus were killed.
Post-genocide, around 2 million Hutus, including militia members responsible for the killings, fled into eastern Congo (then Zaire), leading to the formation of over 120 armed groups, including the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR), a Hutu militia. Rwanda intervened in Congo in 1996 and 1998, triggering the First and Second Congo Wars, which resulted in millions of deaths and regional destabilization.
Emergence and Role of M23
The M23 (March 23 Movement) was formed in 2012 by former fighters of the Tutsi-led National Congress for the Defence of the People (CNDP), who rebelled after accusing the DRC government of violating a 2009 peace deal meant to integrate them into the national army. Led by SultaniMakenga, M23 initially captured Goma in 2012 but retreated after international pressure.
Resurfacing in 2022, M23 cited non-implementation of the agreement and vowed to protect Tutsi interests against groups like the FDLR. Since then, they have gained control of key mining regions, particularly Rubaya, rich in coltan, a critical mineral used in electronic devices. The UN estimates that M23 earns $800,000 per month from coltan production taxes, indicating that economic motives are as significant as ethnic ones.
The 2025 Escalation
On January 27, 2025, M23 rebels entered Goma and seized control of the airport by the following evening. By January 30, they had captured the city despite sporadic resistance from government forces and allied militias. The group then began advancing southward towards Bukavu, the capital of South Kivu province. The UN has confirmed reports of Rwandan troop incursions into South Kivu, while Burundian forces have joined Congolese troops in resisting the offensive.
Regional Dynamics and Rwanda’s Involvement
The Congolese government, along with the UN and Western powers, accuses Rwanda of backing M23 militarily and logistically. A 2022 UN expert report provided "solid evidence" of Rwandan troops fighting alongside M23, though Rwanda continues to deny these allegations. President Paul Kagame justifies his government's position as defensive, blaming the DRC for its alliance with the FDLR, which threatens Tutsis across the region.
Neighboring Burundi, led by President ÉvaristeNdayishimiye, has warned that Rwanda’s ambitions could spark a wider war, even threatening Burundi’s sovereignty. Uganda, meanwhile, plays a balancing role—supporting Congolese efforts against Islamic State-linked militants, while allegedly allowing M23 safe haven, as per UN reports.
Strategic and Economic Importance of Goma
Goma is not just a city; it is a strategic trade and transport hub at the heart of the DRC’s mineral wealth, particularly coltan, of which the DRC supplies nearly 40% of the world’s demand. The region is crucial for smartphone and electronics manufacturing due to coltan’s utility in capacitors.
Thus, the control of Goma and surrounding territories represents not only a military advantage but also a significant economic resource for M23 and its alleged sponsors.
Humanitarian Impact and Global Concerns
The humanitarian toll of the conflict is staggering. With over a million people displaced since M23’s resurgence, the DRC’s fragile state apparatus is further strained. Corpses reportedly lay unburied in Goma after the assault, reflecting a deep crisis of governance, security, and human rights.
Given the ethnic complexities, resource conflicts, and regional rivalries, there are growing fears of the conflict escalating into a full-fledged regional war, drawing in Rwanda, Burundi, and Uganda.
India and the Middle East
- 10 Feb 2025
In News:
India's foreign policy has undergone a strategic shift towards West Asia, driven by imperatives of energy security, economic integration, and geopolitical balance.
The launch of theIndia-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)at the G20 Summit 2023 marks a key initiative aimed at reshaping global trade while deepening India’s engagement with the Middle East and Europe.
Importance of the Middle East for India
- Energy Security:The Middle East supplies over 53% of India’s crude oil (as of January 2025). Long-term energy agreements, such as the LNG deal with Qatar (until 2048) and India-UAE green hydrogen MoUs, ensure stable energy flows. Strategic ties mitigate disruptions due to OPEC+ cuts and geopolitical tensions.
- Trade and Economic Ties: India’s trade with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) reached USD 161.59 billion in FY 2023–24. The UAE is India’s third-largest trading partner, with exports worth USD 35.6 billion. A proposed India-GCC Free Trade Agreement and operationalization of IMEC can enhance regional integration.
- Diaspora and Remittances:Over 66% of India’s 1.34 crore NRIs live in Gulf nations. India was the world’s top remittance recipient in 2022, with USD 111 billion, a major share from the Middle East. Labor reforms in the region (e.g., Saudi Arabia’s Nitaqat) influence migrant welfare.
- Geopolitical and Strategic Autonomy: India balances relations across regional fault lines — Iran-Saudi and Israel-Arab states — while maintaining strategic autonomy. Defense cooperation includes naval exercises (e.g., Al-Mohed Al-Hindi with Saudi Arabia) and connectivity via Chabahar Port in Iran.
- Food and Maritime Security: The Gulf is a major destination for Indian agricultural exports (e.g., UAE imports worth USD 1.9 billion in FY 2022–23). Strategic waterways like the Red Sea and Arabian Sea are crucial for trade, though increasingly vulnerable to piracy and regional conflict.
IMEC: A Strategic Connectivity Corridor
- IMECenvisions linking India to Europe through the Middle East via multimodal transport and digital-energy corridors, bypassing the Suez Canal. It aims to counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Key stakeholders include India, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel, and the EU. The Intergovernmental Framework Agreement (2024) lays the foundation for implementation, targeting USD 600 billion in infrastructure investment by 2027.
- Objectives include trade facilitation, supply chain diversification, digital connectivity, and green energy collaboration. However, the Israel-Gaza conflict and regional instability have delayed execution.
Challenges
- Energy volatility due to OPEC+ decisions and Red Sea disruptions.
- Geopolitical unrest in Yemen, Gaza, and Iran-Israel tensions.
- Maritime insecurity, with piracy and Houthi attacks raising shipping costs.
- Labor rights issues, including migrant exploitation.
- Strategic competition from China, with over USD 273 billion invested in the region since 2005.
Policy Recommendations
- Co-develop energy infrastructure (e.g., Saudi Aramco’s stake in Indian refineries).
- Diversify trade via an India-GCC FTA and sectoral cooperation (IT, defense, fintech).
- Enhance maritime and digital connectivity through IMEC and joint port development.
- Secure labor migration with skill pacts and expanded protection schemes.
- Strengthen counter-terrorism and defense cooperation, including intelligence sharing.
Conclusion
India’s West Asia strategy is multifaceted—balancing energy diplomacy, trade, diaspora ties, and strategic connectivity. IMEC offers a transformative opportunity to position India as a central link in global supply chains, but its success depends on stable regional geopolitics and coordinated implementation.
Darfur Crisis: Humanitarian Emergency in Western Sudan
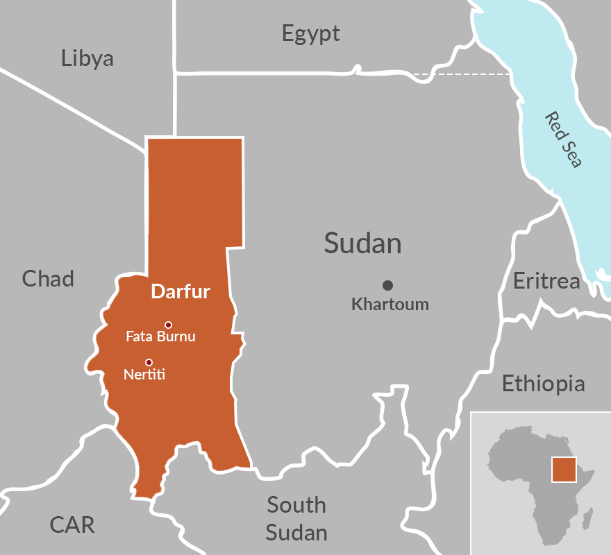
- 31 Jan 2025
Context:
Sudan’s Darfur region is once again in global focus following a deadly drone attack on the last functional hospital in El-Fasher, killing at least 67 people and injuring dozens. The International Criminal Court (ICC) has called for urgent UN Security Council intervention as the humanitarian situation deteriorates.
Geographical and Historical Background
- Location: Western Sudan, bordering Chad, Libya, Central African Republic, and South Sudan.
- Area: Approximately 493,000 sq. km, nearly the size of France.
- Topography: Predominantly arid and semi-arid terrain, with desert in the north and savanna in the south. Key physical features include:
- Jebel Marra Mountains: Volcanic highlands and key water source.
- Wadi Howar: Seasonal river vital for agriculture.
- Baggara Belt: Grazing zone, often contested.
- Historical Significance: Once an independent Islamic sultanate ruled by the Fur tribe, Darfur was annexed by Anglo-Egyptian Sudan in 1916. The name "Darfur" means "land of the Fur" in Arabic.
Ethnic Composition and Demographics
- Home to over 80 ethnic groups, including the Fur, Zaghawa, Beja, Nubians, and Arabs.
- Long-standing ethnic tensions exist between Arab nomadic groups and non-Arab farming communities, which have been a root cause of conflict.
Conflict Timeline and Key Actors
- Conflict Origins: Armed conflict began in 2003, led by rebel groups such as the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and Justice and Equality Movement (JEM), demanding political autonomy and better representation.
- Government Response: The Sudanese government armed Janjaweed militias—now rebranded as the Rapid Support Forces (RSF)—who were accused of widespread atrocities, including genocide, mass killings, and rape.
- Recent Escalation:
- In 2023, violence surged amid civil war between Sudan's national army and RSF.
- RSF has seized much of Darfur and has besieged El-Fasher, capital of North Darfur, since May 2023.
- A January 2025 drone attack destroyed the Saudi Hospital in El-Fasher, killing 67 people. The hospital was one of the last with surgical capacity in the region.
Humanitarian Impact
- Health Crisis:
- 80% of healthcare facilities in Sudan are non-functional.
- Attacks on medical infrastructure have been rampant; El-Fasher’s Saudi Hospital was hit multiple times by suspected RSF drones.
- Displacement and Starvation:
- Over 12 million people displaced.
- Tens of thousands killed.
- Famine has already gripped camps like Zamzam, Abu Shouk, and Al-Salam, and is expected to spread to additional regions, including El-Fasher, by May 2025 (UN Assessment).
Global and Regional Implications
- The Darfur conflict has destabilized the region, affecting neighboring countries like Chad and the Central African Republic.
- ICC has issued warrants for several individuals including former President Omar al-Bashir, citing war crimes and crimes against humanity.
- The conflict highlights the intersection of climate stress, ethnic rivalries, political marginalization, and international accountability failures.
India-Indonesia Relations

- 27 Jan 2025
In News:
The President of Indonesia, visited India as the Chief Guest for the 76th Republic Day in January 2025. This marked the 75th anniversary of diplomatic ties, reaffirming the commitment to deepen cooperation in economic, strategic, cultural, and defense domains.
Historical Foundations
- Ancient Civilizational Links: Trade and cultural exchanges date back to the 2nd century BCE, reflected in the influence of Hinduism and Buddhism on Indonesian society (e.g., Ramayana, Mahabharata, Borobudur, Prambanan).
- Modern Diplomatic Ties:
- Formalized in 1950, with a Treaty of Friendship in 1951.
- Collaborated in the 1955 Bandung Conference and co-founded the Non-Aligned Movement (1961).
- Indonesia’s first President Sukarno was the Guest of Honour at India’s first Republic Day in 1950.
- Cold War and Beyond:
- Relations cooled in the 1960s but revived in the 1980s.
- The 1991 'Look East' Policy and the 2014 'Act East' Policy revitalized ties.
- Strategic Partnership in 2005; upgraded to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2018.
Key Pillars of Cooperation
- Economic and Trade Relations
- Trade Volume: Reached USD 38.8 billion (2022–23), targeted to increase to USD 50 billion by 2025.
- Key Imports: India imports coal, palm oil, and nickel.
- Investment: Indian investments in Indonesia total USD 1.56 billion in infrastructure, textiles, and energy.
- New Developments:
- MoU on Local Currency Settlement Systems to reduce dependency on USD.
- Focus on resolving trade barriers via forums like WGTI and BMTF.
- Cooperation in critical minerals like nickel and bauxite.
- BPCL to invest USD 121 million in the Nunukan gas block.
- Military Exercises: Garuda Shakti (Army), Samudra Shakti (Navy), and participation in Milan, Komodo, Super Garuda Shield, etc.
- Key Agreements:
- 2018 Defense Cooperation Agreement.
- White Shipping Information Exchange (WSIE).
- Proposal for Bilateral Maritime Dialogue and Cyber Security Dialogue.
- Joint vision on maritime cooperation under SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
- BrahMos Deal: Talks underway for Indonesia’s acquisition of BrahMos missiles (~USD 450 million).
- Cultural Diplomacy: Shared heritage of Hindu-Buddhist traditions; India assisting in restoring Prambanan temple.
- Tourism & Connectivity: Direct flights since 2023; India is the second-largest source of tourists to Bali.
- New Initiatives:
- Cultural Exchange Programme (2025–2028).
- India reaffirmed the Kashi Cultural Pathway for heritage restoration and repatriation of artifacts.
- Science, Technology, and Space
- ISRO supports Indonesia’s satellite ambitions; agreement on Biak Tracking Station.
- Renewed MoU on STEM cooperation.
- Areas of collaboration: Quantum tech, high-performance computing, and digital public infrastructure.
- Energy and Health Security
- Collaboration on biofuels under the Global Biofuels Alliance.
- Joint initiatives on mid-day meals and public distribution systems.
- MoUs on digital health, capacity building, and traditional medicine.
Multilateral and Regional Cooperation
- ASEAN & Indo-Pacific: Commitment to ASEAN centrality and cooperation through IPOI, India-Indonesia-Australia Trilateral, and ASEAN-India outlook.
- Global Platforms: Collaboration in BRICS, G20, IORA, and advocacy for the Global South.
- Climate & Disaster Resilience:
- Joint efforts under CDRI.
- Indonesia invited to the International Solar Alliance and Big Cat Alliance.
Key Challenges
- Trade Imbalance: Heavy reliance on limited imports (coal, palm oil); imbalance persists as Indonesia’s trade with China is far greater (~USD 139 billion).
- Bureaucratic & Regulatory Barriers: Slow progress on infrastructure and investment due to permit and regulatory issues.
- Geopolitical Pressures: Indo-Pacific instability and China's expanding influence pose strategic challenges.
- Logistical Constraints: Inadequate connectivity infrastructure hinders deeper integration.
Way Forward
- Trade Diversification: Include sectors like tech, agriculture, and green energy.
- Defense Deepening: Expand joint exercises, maritime patrols, and intelligence-sharing.
- Enhance Connectivity: Boost air, sea, and digital linkages for trade and tourism.
- Green Collaboration: Advance renewable energy and sustainable mining ventures.
- Cultural & Educational Engagement: Promote student exchanges, scholarships (e.g., ITEC), and diaspora involvement.
Conclusion
India and Indonesia share deep-rooted civilizational links and are strategically aligned in the Indo-Pacific. Their evolving Comprehensive Strategic Partnership encompasses trade, defense, technology, and cultural diplomacy. Strengthening this partnership will not only boost bilateral growth but also ensure a stable, multipolar, and cooperative regional order.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- 20 Jan 2025
Context:
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), announced at the G20 Summit 2023 in New Delhi, is a transformative multi-modal connectivity initiative aiming to link India, the Middle East, and Europe through railways, ports, roads, energy pipelines, and digital infrastructure.
- Seen as a strategic counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), IMEC marks a significant step in reshaping global trade routes and enhancing economic cooperation across continents.
Structure and Components of IMEC
- Corridors:
- Eastern Corridor: Connects India to the Arabian Peninsula
- Northern Corridor: Links the Gulf to Europe
- Key Infrastructure:
- Rail and road networks
- Shipping routes from Indian ports (e.g., Mumbai, Mundra, Kandla, JNPT) to UAE and onwards via rail to Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Israel (Haifa Port)
- Maritime link from Haifa to Piraeus Port in Greece, and further into Europe
- Electricity grids, green hydrogen pipelines, and high-speed data cables
- Participating Nations: India, US, Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, Italy, European Union
- Support Mechanism: US-led Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII)
Significance of IMEC
For India
- Enhanced Global Connectivity:
- Provides faster, cost-effective access to European markets
- Reduces dependence on the Suez Canal, a known chokepoint
- Economic Gains:
- Boosts the Make in India initiative through expanded market access
- Enhances maritime security and tourism opportunities in the Mediterranean
- Strategic Leverage:
- Strengthens ties with Middle East, US, and Europe
- Reinforces India’s image as a global strategic partner
- Energy Security and Green Growth:
- Facilitates the Green Grid Concept via power lines and hydrogen pipelines
- Aligns with India’s clean energy and decarbonisation goals
- Digital and Cyber Infrastructure:
- Supports data flow and communication resilience across the corridor
For the United States
- Strategic Counter to BRI:
- Offers democratic nations an alternative to China’s BRI
- Reinforces Transatlantic Unity:
- Addresses trust deficits post Ukraine war
- Reaffirms US commitment to European allies
- Energy and Supply Chain Security:
- Reduces reliance on adversarial energy routes
- Diversifies regional supply chains
- Geopolitical Stability:
- Encourages peaceful engagement among West Asian rivals
- Deters alignment with China-led blocks
- Job Creation and Economic Growth:
- Infrastructure investments boost local economies and employment
Strategic and Geopolitical Implications
- Acts as a balancing mechanism in global geopolitics against the influence of China’s BRI
- Built on diplomatic breakthroughs such as the Abraham Accords
- Promotes economic cooperation between traditional rivals (e.g., Israel, Saudi Arabia, UAE)
- Supports a rules-based international order centered on transparency, sustainability, and democratic values
Challenges to Implementation
- Geopolitical Instability: Conflicts such as Israel-Hamas, Iran-Saudi tensions, or political instability in West Asia can delay progress
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks:
- High capital requirement and complexity of cross-border integration
- Varying timelines and priorities among participating nations
- Competing Regional Interests:
- Exclusion of key players like Turkey, Iran, and China may trigger pushback
- Turkey’s rivalry with Greece and Israel may create diplomatic hurdles
Security Concerns: Risk of terrorism, piracy, and cyber threats in unstable regions
Israel-Hamas Ceasefire

- 19 Jan 2025
In News:
After 15 months of war triggered by Hamas' October 2023 attack on Israel, a ceasefire agreement has been brokered by Qatar, Egypt, and the US, marking a fragile but significant pause in one of the most destructive phases of the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Key Features of the Ceasefire Agreement
The agreement is based on a three-phase framework proposed by US President Joe Biden in June 2024 and endorsed by the UN Security Council:
Phase I (42 days)
- Complete ceasefire and withdrawal of Israeli forces from all populated areas in Gaza.
- Release of 33 Israeli hostages (women, elderly, injured) by Hamas.
- Release of 900–1,650 Palestinian prisoners, including minors and those detained since October 7, 2023.
- Daily entry of 600 humanitarian aid trucks into Gaza.
- Partial Israeli withdrawal from key corridors like Netzarim (splitting Gaza) and parts of the Philadelphi Corridor (Gaza-Egypt border).
Phase II
- Release of remaining hostages, primarily male soldiers.
- Complete Israeli military withdrawal from Gaza.
- Details to be negotiated during Phase I; no written guarantees for its execution.
Phase III
- Return of the remains of deceased hostages.
- Initiation of a multi-year reconstruction plan for Gaza under international supervision.
Challenges to Implementation
Fragile Political Consensus in Israel
- Far-right ministers (e.g., Itamar Ben-Gvir) oppose the deal, threatening to quit the government.
- Prime Minister Netanyahu faces pressure from both hawks demanding a full military victory and moderates seeking peace.
Hamas' Demands
- Seeks permanent ceasefire and complete Israeli withdrawal, making it unwilling to release all hostages without guarantees.
- Israel, in contrast, insists on neutralizing Hamas militarily.
Unclear Future Governance of Gaza
- Israel rejects both Hamas and the Palestinian Authority (PA) as future administrators.
- Global consensus supports Palestinian-led governance, but viable alternatives remain elusive.
Wider Geopolitical Impact
Reshaping West Asia
- Conflict escalated tensions with Hezbollah (Lebanon) and drew Israel into direct conflict with Iran.
- Iran’s influence weakened due to losses in Hezbollah and Syria.
- Assad regime in Syria collapsed, altering regional power dynamics.
Diplomatic Repercussions for Israel
- Despite military dominance, Israel faces global condemnation over civilian casualties.
- PM Netanyahu is under scrutiny at the ICC (war crimes) and ICJ (genocide allegations).
- Israel is now diplomatically isolated, particularly after the humanitarian toll in Gaza.
Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza
- Over 64,000 Palestinians killed (The Lancet, 2024), including large numbers of civilians.
- Massive destruction of infrastructure—schools, hospitals, homes—rendering Gaza nearly uninhabitable.
- Reconstruction hinges on sustained peace and international aid.
Conclusion
The ceasefire presents a rare opportunity for de-escalation in a deeply entrenched conflict. However, distrust between parties, domestic political constraints, and regional rivalries pose significant risks to its sustainability. A durable peace can only emerge through inclusive political dialogue, humanitarian prioritization, and movement toward a two-state solution.
Implications of China’s Mega-Dam Project on the Brahmaputra River Basin
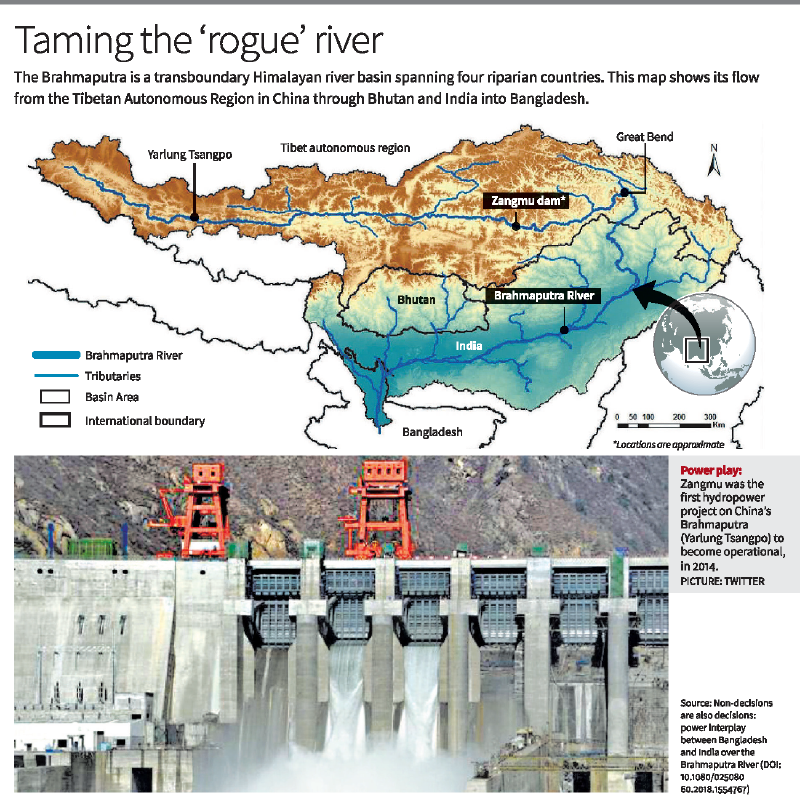
- 07 Jan 2025
Introduction:
China has approved the construction of the Yarlung Tsangpo hydropower project, the world's largest hydropower project, with a capacity of 60,000 MW, on the Brahmaputra River in Tibet. This mega-dam, located at the Great Bend in Medog county, has significant geopolitical, environmental, and socio-economic implications for India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh, the downstream riparian countries.
Geographical and Geopolitical Context:
- The Brahmaputra is a transboundary river system flowing through China, India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- China, located at the river’s source in Tibet, is the uppermost riparian nation, controlling water flow into India and Bangladesh.
- All riparian countries, including China, India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh, have proposed major water infrastructure projects in the river basin, which has become a site for geopolitical rivalry, with mega-dams symbolizing sovereignty.
China’s Hydropower Ambitions:
- The Yarlung Tsangpo project is part of China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) and aims to address the country's energy needs while moving towards net carbon neutrality by 2060.
- The river's steep descent from Tibet provides an ideal location for hydroelectricity generation.
- China’s previous mega-projects, like the Three Gorges Dam, highlight the scale of these ambitions but also raise concerns about environmental and social consequences, including ecosystem disruption, displacement, and seismic risks.
Impact on Downstream Communities:
- Water Flow and Agriculture: China’s mega-dam may significantly alter water flow to India, particularly affecting agriculture and water availability in the northeastern regions. India, reliant on the Brahmaputra for irrigation and drinking water, could face disruptions.
- Silt and Biodiversity: The blocking of silt essential for agriculture could degrade soil quality and damage biodiversity in the river basin.
- Seismic Risks: The region’s seismic activity, coupled with the construction of large dams, heightens the risk of catastrophic events such as landslides and Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), which have previously caused devastation in the Himalayas.
Hydropower Competition Between China and India:
- Both China and India are competing to harness the Brahmaputra's potential for hydropower, with India planning its own large project at Upper Siang.
- Bhutan has also proposed several medium-sized dams, raising concerns in downstream countries about cumulative impacts.
- No comprehensive bilateral treaty exists between India and China to regulate shared transboundary rivers, though they have mechanisms for data sharing and discussions on river issues.
Environmental and Regional Concerns:
- The Brahmaputra river basin is an ecologically sensitive region. The construction of large dams threatens the fragile ecosystem, including agro-pastoral communities, biodiversity, and wetlands.
- Tibet’s river systems are vital for the global cryosphere, affecting climate systems, including monsoon patterns. Disruption to these systems could have broader implications for regional and global climate stability.
Challenges in Bilateral Cooperation:
- India and China have struggled with effective coordination on river management. China has shown reluctance to share critical hydrological data, a concern amplified by the lack of a binding agreement.
- The ongoing geopolitical tensions between the two countries, particularly over the border dispute, further complicate cooperation on transboundary water issues.
Recommendations for India:
- Enhanced Cooperation: India should push for renewed agreements and mechanisms for real-time data exchange with China to prevent ecological and socio-economic damage.
- Public Challenges: India needs to challenge China’s claims that its hydropower projects will have minimal downstream impact, ensuring that India's concerns are addressed in international forums.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Water issues should be prioritized in India’s diplomatic engagement with China, emphasizing the importance of transparency and cooperation to ensure mutual benefit and regional stability.
Conclusion:
The Yarlung Tsangpo mega-dam project poses significant risks to the entire Brahmaputra river basin. A collaborative approach, involving transparent dialogue and cooperation among riparian countries, is essential to mitigate the potential adverse impacts on downstream communities and the fragile Himalayan ecosystem.
India-Kuwait Ties

- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's two-day visit to Kuwait marks a significant milestone in India-Kuwait relations, being the first visit by an Indian Prime Minister in over four decades. This visit, undertaken at the invitation of Emir Sheikh Meshal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, aims to strengthen bilateral ties in key areas like trade, defense, energy, and cultural cooperation.
Strategic Partnership and Key Agreements
The visit elevated India-Kuwait relations to a 'Strategic Partnership,' with agreements covering diverse sectors. A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defense cooperation was signed, focusing on joint military exercises, coastal defense, and training. Furthermore, the two countries signed a Cultural Exchange Programme for 2025-2029 and an Executive Programme on Sports Cooperation for 2025-2028, enhancing cultural and people-to-people ties.
The establishment of a Joint Commission on Cooperation (JCC) will monitor bilateral relations, and new Joint Working Groups (JWGs) have been set up in areas like education, trade, and counter-terrorism. Both nations also agreed to deepen collaboration in emerging sectors such as semiconductors, artificial intelligence, e-governance, and technology sharing.
Economic and Energy Cooperation
India and Kuwait share strong economic ties, with bilateral trade reaching USD 10.47 billion in 2023-24. Kuwait is India’s sixth-largest crude oil supplier, meeting 3% of India's energy needs. The countries have also agreed to transition from a buyer-seller relationship in energy to a more comprehensive partnership, with focus areas including oil, gas, refining, and renewable energy. Kuwait’s membership in the International Solar Alliance (ISA) was welcomed by India, reflecting their growing collaboration in the energy sector.
Indian Diaspora and Labour Cooperation
The Indian community, numbering over 1 million, forms the largest expatriate group in Kuwait and plays a pivotal role in the country’s economy. Their contribution spans various sectors, including healthcare, engineering, retail, and business. Kuwait’s Vision 2035, which seeks to diversify its economy beyond oil, presents significant opportunities for collaboration with India, particularly in infrastructure, renewable energy, and technology.
The skilled workforce from India also aligns with Kuwait's developmental goals, offering further opportunities for labor cooperation, especially in sectors like healthcare, technology, and infrastructure.
Geopolitical and Multilateral Cooperation
India-Kuwait relations hold regional significance, particularly in West Asia. Kuwait's role in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) amplifies its geopolitical importance. India’s engagement with Kuwait helps maintain a balanced presence in the region, essential for its energy security and broader geopolitical interests. The GCC, which includes six Arab states, remains a key partner for India, contributing to significant trade and remittances. India also seeks to conclude a Free Trade Agreement with the GCC to enhance economic collaboration.
Cultural and Historical Ties
India and Kuwait’s relationship has deep historical roots, dating back to the pre-oil era when maritime trade was a cornerstone of Kuwait’s economy. Over the years, this relationship has grown, with India being a major trading partner and Kuwait contributing significantly to India's energy needs. The Indian Rupee was once the legal tender in Kuwait, underscoring the strength of their historical ties.
In conclusion, PM Modi's visit to Kuwait sets the stage for enhanced cooperation across several domains, reinforcing the strategic partnership between the two nations. It also highlights India's broader objectives in the West Asia region, balancing economic, geopolitical, and cultural interests.
Revitalization of India-China Relations: A Diplomatic Turning Point

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The 23rd meeting between India’s National Security Adviser (NSA) and China’s Foreign Minister, held as Special Representatives (SRs), marks a pivotal moment in the complex bilateral relationship between the two nations. This dialogue, which follows years of strain exacerbated by the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, signals a renewed commitment to restoring stability and fostering peace along the border.
Special Representatives Mechanism: A Foundation for Dialogue
The SR mechanism, established in the early 2000s, has long served as a key platform for addressing bilateral disputes, particularly the contentious boundary issue. Past rounds of discussions have facilitated troop disengagement and efforts to maintain peace along the Line of Actual Control (LAC). The recent meeting, following the 2023 BRICS summit discussions between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping, demonstrates a positive step towards de-escalation, with the resumption of talks providing hope for progress.
Key Outcomes of the 23rd SR Meeting
Several significant developments emerged from the meeting, focusing on cultural, economic, and strategic cooperation:
- Cultural and Economic Cooperation:
- Kailash-Mansarovar Yatra: The resumption of this religious pilgrimage represents a significant cultural exchange, fostering people-to-people ties.
- Border Trade Revival: Border trade in Sikkim has been reestablished, potentially revitalizing local economies and improving trade relations.
- Scientific and Environmental Cooperation:
- Trans-boundary River Data Sharing: China’s commitment to sharing crucial river data with India will aid in flood management, directly addressing India’s long-standing concerns over water security, particularly in light of China's upstream dam projects.
- Connectivity and Exchange Programs:
- Discussions on restarting direct flights and visa easements for students and businesses, along with enhanced journalist exchanges, signal a move toward greater normalization of relations.
- Commitment to Border Peace:
- Both sides have reiterated their intent to maintain peace along the border, a critical factor in reducing tensions. While China expressed a six-point consensus, India has cautiously framed the outcome as “positive directions,” reflecting a reserved optimism.
Challenges in India-China Relations
Despite the positive momentum, numerous challenges persist in the bilateral relationship:
- Boundary Dispute:
- The core irritant remains the unresolved border issue, with divergent perceptions of the LAC. While some disengagement has occurred, full de-escalation and demilitarization across the entire border have not yet been achieved.
- Trust Deficit:
- The 2020 Galwan clash has left a lasting scar on mutual trust. Additionally, China’s aggressive patrolling and policy shifts continue to raise concerns in India, necessitating vigilance in future negotiations.
- Economic Imbalances:
- India’s trade relationship with China remains lopsided, with a significant trade deficit. Moreover, China’s growing influence in India’s neighborhood, particularly in Pakistan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, challenges India’s strategic interests.
- Global Power Dynamics:
- India’s evolving alliances, particularly with the U.S., QUAD, and I2U2 group, alongside China’s assertive stance in Taiwan and the South China Sea, complicate bilateral relations and influence global perceptions.
The Way Forward
To navigate the challenges and harness opportunities, India must adopt a balanced approach, combining diplomatic engagement, economic resilience, and strategic vigilance:
- Confidence-Building Measures:
- Continued disengagement and de-escalation at the LAC, coupled with increased transparency in military activities, will be critical to maintaining peace.
- Broadening Cooperation:
- Exploring areas of mutual interest, such as climate change, public health, and infrastructure development, could foster deeper cooperation and help transcend contentious issues.
- Economic Realignment:
- India must address its trade deficit by pushing for greater market access for Indian products in China. Additionally, diversifying supply chains and promoting joint ventures in renewable energy and technology can reduce dependency.
- Multilateral Engagement:
- Engaging through global forums like BRICS, SCO, and G20, and strengthening regional alliances, will help mitigate tensions and counterbalance China's regional influence.
- Strategic Vigilance:
- Strengthening ties with regional allies, particularly in the Indo-Pacific, and enhancing military preparedness will safeguard India’s strategic interests in the face of China’s assertiveness.
Conclusion
The recent meeting between India and China represents a cautious but constructive step toward stabilizing their fraught relationship. By focusing on diplomacy, strengthening economic ties, and maintaining strategic vigilance, India can navigate its complex relationship with China in a rapidly shifting global context. A careful balance of engagement and vigilance will be crucial for India’s future dealings with its powerful neighbor.
India-Sri Lanka Diplomatic Engagement

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent visit of Sri Lankan President Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD) to India marked a significant moment in bilateral relations, as it was his first foreign trip since assuming office. The visit underscored key diplomatic exchanges and collaborations between the two countries, showcasing both areas of agreement and divergence.
Key Takeaways from AKD's Visit
Assurance on Anti-India Activities: One of the primary concerns for India was the use of Sri Lankan territory for activities detrimental to its security, particularly the presence of Chinese “research vessels” at Sri Lankan ports. President AKD assured Prime Minister Narendra Modi that Sri Lanka would not allow its territory to be used in ways that threaten India’s interests. This assurance is crucial, as it signals Sri Lanka's stance on maintaining regional stability, despite AKD’s perceived pro-China inclinations.
Tamil Minority Issue: Divergent Views: A notable divergence in their discussions was the issue of the Tamil minority in Sri Lanka. India has long advocated for the full implementation of the 13th Amendment to Sri Lanka’s Constitution, which would grant greater autonomy to the Tamil minority. However, AKD resisted this, reaffirming his opposition to the amendment’s full implementation. While India emphasized the importance of reconciliation and holding provincial elections, AKD focused on unity, sustainable development, and social protection, sidestepping any definitive commitments on the Tamil issue.
Sri Lanka's Assertive Diplomatic Posture: AKD’s strong parliamentary mandate has allowed him to adopt a more assertive diplomatic stance. This is evident not only in his handling of the Tamil issue but also in his approach to dealing with major powers like India and China. His administration appears to be prioritizing a more independent foreign policy, signaling a shift from previous administrations.
Bilateral Cooperation and Development Initiatives
The visit saw significant agreements on bilateral cooperation, particularly in development and connectivity. Both nations acknowledged the positive impact of India’s assistance in Sri Lanka’s socio-economic growth. Key projects discussed include:
- Indian Housing Project: Phases III and IV.
- Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects across three islands.
- High-Impact Community Development Projects.
- Digital collaborations, such as the implementation of Aadhaar and UPI systems in Sri Lanka.
Additionally, discussions focused on enhancing energy cooperation, including the supply of LNG, development of offshore wind power in the Palk Strait, and the high-capacity power grid interconnection. The resumption of passenger ferry services between key Indian and Sri Lankan ports was also a priority.
Defence and Security Cooperation
The two leaders agreed to explore a Defence Cooperation Framework and intensify collaboration on maritime surveillance, cyber security, and counter-terrorism. This aligns with India’s strategic interests in the region, as it seeks to ensure stability in the Indian Ocean and strengthen its defense ties with Sri Lanka.
Strategic Continuity Amid Leadership Change
Despite a change in leadership, the core strategic interests between India and Sri Lanka remain aligned. India views Sri Lanka’s stability as crucial to regional security, and both countries are focused on a mutually beneficial partnership. AKD’s emphasis on economic recovery and tackling corruption within Sri Lanka, as seen in his actions against political figures like Speaker Asoka Ranwala, further signals his determination to build a strong foundation for his government’s future.
Conclusion
President AKD’s visit highlighted the evolving dynamics of Sri Lanka’s foreign policy, marked by a more confident and independent approach in engaging with India. While challenges remain, especially regarding the Tamil issue, both countries have reaffirmed their commitment to deepening bilateral ties, with a focus on development, connectivity, and strategic cooperation.
India-Bhutan Relations

- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The December 2023 visit of Bhutan’s King and Queen to India highlights the enduring and strategic partnership between the two nations. Amidst growing Chinese influence and Bhutan’s domestic challenges, the visit holds significant geopolitical relevance, reinforcing India-Bhutan relations and underscoring Bhutan's critical role in India’s regional security.
Reaffirmation of India-Bhutan Relations
The visit reaffirmed the strong, time-tested partnership between India and Bhutan, rooted in mutual trust and cooperation. India reiterated its commitment to Bhutan's socio-economic development, increasing its financial aid for the 2024-2029 period from ?5,000 crore to ?10,000 crore. Notably, Bhutan’s flagship Gelephu Mindfulness City Project, championed by King Jigme Khesar, received strong Indian backing, reflecting India’s willingness to align with Bhutan’s developmental priorities.
Strategic Areas of Cooperation
Clean Energy and Hydropower
Bhutan remains central to India’s renewable energy strategy, particularly in hydropower, a vital part of Bhutan's economy. Bhutan exports the majority of its hydropower to India, reinforcing bilateral ties in the energy sector. This cooperation aligns with India’s regional energy security goals, with both nations seeking to strengthen clean energy initiatives.
Infrastructure Development
The visit also emphasized infrastructure projects, vital for enhancing Bhutan's connectivity. These projects are strategically significant, considering Bhutan's geostrategic importance in the Himalayas. Infrastructure development further strengthens the ties between the two nations, with a focus on mutual benefits and regional stability.
Geopolitical Context: China’s Growing Influence
China-Bhutan Border Disputes
The border issue with China has been ongoing since 1984. In 2023, Bhutan and China signed an agreement to expedite the settlement and demarcation of their borders. China’s push for resolution is part of its broader strategy to reduce India’s influence in Bhutan. The disputed areas, particularly those near India’s Siliguri Corridor, hold strategic importance for New Delhi. Any territorial adjustments could undermine India’s access to its Northeastern states.
Chinese Influence and Economic Engagement
China has been constructing villages along disputed border areas, altering ground realities and establishing civilian hubs that could serve as military outposts. Additionally, China is offering economic incentives to Bhutan, including promoting tourism and investing in Bhutan’s telecom sector, seeking to draw the country into closer economic and diplomatic alignment.
India’s Role in Bhutan’s Security and Sovereignty
Strategic Dependence on India
Bhutan's small military relies heavily on Indian support for training and defense. The 2017 Doklam standoff, where Indian forces intervened to prevent China from constructing a road in disputed territory, underscored India's crucial role in safeguarding Bhutan’s territorial integrity.
Friendship Treaty
The India-Bhutan Friendship Treaty is the cornerstone of their bilateral relations, ensuring Bhutan's sovereignty while reinforcing India's role in Bhutan’s foreign and defense policies. India's increased financial support aims to counter China’s economic influence in Bhutan.
Challenges for Bhutan
Balancing India and China
Bhutan is navigating a delicate balance between preserving its historical ties with India and engaging with China, which offers economic benefits. However, Bhutan’s sovereignty concerns limit its ability to make independent diplomatic decisions.
Domestic Issues
Bhutan faces challenges such as youth migration and limited economic diversification. Over-reliance on hydropower and a lack of industrial development make it vulnerable to external pressures, particularly from China.
The Strategic Importance of Bhutan to India
Geopolitical Buffer
Bhutan's location is vital for India’s security, especially in relation to the Siliguri Corridor, a narrow land link connecting India’s Northeast. Any Chinese presence in Bhutan’s disputed regions could disrupt access to this crucial corridor.
Hydropower Collaboration
Bhutan’s hydropower exports are central to India’s renewable energy strategy, and their cooperation in this area ensures mutual benefits.
Way Forward
India must continue to prioritize Bhutan’s development needs, ensuring robust financial and infrastructural support. Proactive engagement is necessary to address Bhutan’s concerns, particularly in light of China’s growing influence. Additionally, India should support Bhutan’s economic diversification to reduce reliance on external actors.
How Minilateralism is Reshaping Global Order

- 09 Dec 2024
Introduction
Minilateralism refers to the growing trend of smaller, more focused international groupings of countries that cooperate on specific issues or regional challenges. It contrasts with the traditional multilateral frameworks, which are often large, slow-moving, and bogged down by lengthy debates and consensus-building. Today, minilateral platforms are increasingly driving global decision-making and shaping the future of international relations.
Rise of Minilateralism
Failure of Multilateralism
- Multilateralism's Decline: Traditional multilateral institutions like the United Nations (UN) are increasingly seen as ineffective due to their bureaucratic nature and the challenges in building consensus among a large number of diverse nations.
- Global Challenges: Emerging global issues, such as climate change, terrorism, and cybersecurity, require faster and more effective responses. The inability of multilateral platforms to address these challenges efficiently has led to a preference for smaller, more agile groupings.
Emergence of New Powers
- Multipolar World: The rise of new powers such as China, India, and Brazil has contributed to the formation of minilateral groupings. These rising powers desire a greater role in global governance but may not yet have the ability or desire to reshape the international order through large, cumbersome institutions.
- Minilateralism as "Multipolarity Lite": Minilateralism allows these countries to assert themselves as regional or global poles without the need for the complexities of full-scale multilateralism.
India's Role in Minilateralism
Strategic Positioning
- Geopolitical Context: India’s strategic location in South Asia, its status as part of the Global South, and its proximity to a rising China have all influenced its approach to minilateralism. India’s multi-aligned approach reflects its desire for flexibility in navigating the complex and shifting global geopolitical landscape.
- Diverse Partnerships: India is a key player in various minilateral arrangements, balancing its relationships with both traditional Western powers and rising Eastern nations, often serving as a bridge between competing geopolitical interests.
Minilateralism as a Solution
- Diversification Over Alignment: India's preference for minilateralism stems from the desire to avoid over-reliance on any single bloc or country. By engaging in multiple minilateral platforms, India seeks to hedge its interests, balancing its strategic objectives between competing global forces.
The Role of Minilateral Forums
Decision-making and Action
- Faster Action: Minilateral groupings facilitate quicker decision-making by bringing together like-minded countries to focus on specific issues, allowing for more decisive action than traditional multilateral bodies.
- Conflict Resolution: While minilateral platforms may not directly resolve conflicts, they offer indirect pathways for addressing geopolitical tensions by fostering dialogue and cooperation among countries with divergent interests.
Examples of Minilateral Groupings
- BRICS: The grouping of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa is an example of a minilateral arrangement where emerging powers cooperate on shared economic and political interests.
- Quad: The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (comprising the United States, India, Japan, and Australia) is a prominent example of minilateralism focused on regional security, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Other Regional Groupings: Minilateralism also manifests in regional arrangements such as the ASEAN-led East Asia Summit or the India-Japan-Australia trilateral forum, each addressing specific regional and global concerns.
Conclusion
Shaping the Future of Global Order
Minilateralism is reshaping the international order by fostering closer, more flexible cooperation between countries on a wide range of issues. As multilateralism faces growing challenges, smaller, more focused partnerships offer a faster and more efficient means of addressing global problems. India's pivotal role in these groupings reflects its desire to navigate a complex geopolitical landscape while maintaining strategic autonomy. The rise of minilateralism marks a significant shift in global governance, one that could define the future of international relations.
Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
Need for modification of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) amidst changing geopolitical, environmental, and demographic realities.
Background of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- About IWT:
- Signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank.
- Governs the sharing of the Indus River system waters.
- Historical Context:
- Origin in the Inter-Dominion Accord of 1948 post-partition.
- Finalized after negotiations facilitated by the World Bank in 1951.
- Key Provisions:
- Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) allocated to India.
- Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) allocated to Pakistan, with limited use allowed for India (e.g., hydropower, irrigation).
- Establishment of the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC) for cooperation and dispute resolution.
India’s Perspective
- Rationale for Modification:
- Increased demographic and agricultural demands.
- Need for sustainable water management.
- Acceleration of hydropower projects on western rivers permitted by the treaty.
- Security Concerns: Cross-border terrorism impacting trust in treaty operations.
Pakistan’s Concerns
- Dependence on Indus System: Critical for agriculture and drinking water as the lower riparian state.
- Potential Impacts of Modification:
- Fear of reduced water availability.
- Concerns over India’s hydropower projects altering water flow.
Current Challenges
- Hydropower Projects: Disputes over compliance with treaty provisions regarding hydropower construction.
- Technical Disputes: Divergent interpretations of treaty terms.
- Political Tensions: Strained bilateral relations with minimal diplomatic engagement.
- Climate Change Impacts: Altered precipitation patterns and glacial melt affecting water availability.
Arguments for Modifying the Treaty
- Addressing Contemporary Challenges: Climate change, technological advancements, and increased water demand.
- Securing National Interests:
- Clarifications on hydropower construction.
- Improved dispute resolution mechanisms.
Risks of Modifying the Treaty
- Escalation of Tensions: Perceived unilateral actions by Pakistan.
- Political Sensitivities: Domestic opposition in both countries.
Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
- Engagement and Dialogue: Bilateral discussions with potential third-party mediation (e.g., World Bank).
- Cooperation over Conflict: Recognizing mutual benefits of collaboration in water management.
- Adaptation Measures: Incorporate provisions addressing climate change and technological advances.
16th BRICS Summit
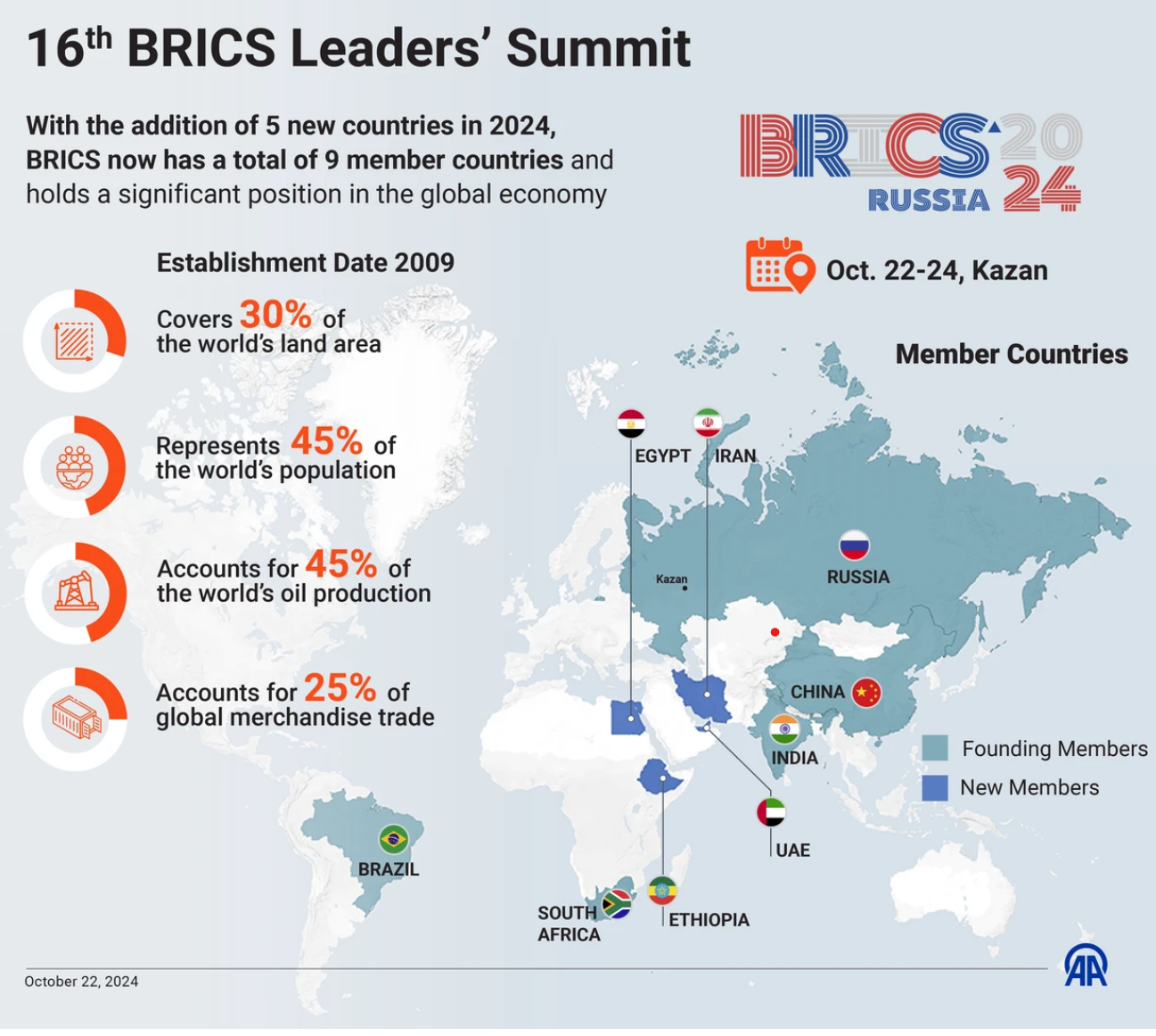
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the 16th BRICS Summit was held in Kazan, Russia.
Key Highlights:
Overview of the Bilateral Meeting between PM Modi and President Xi
- Location & Context: The meeting took place on the sidelines of the 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan, Russia (October 23, 2024), marking the first bilateral interaction between PM Modi and President Xi Jinping in nearly five years.
- Significance: The meeting focused on India-China relations, specifically the border dispute that arose following the 2020 standoff in Ladakh.
- Agreement on Border Disengagement: Both leaders welcomed an agreement for "complete disengagement" along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), which could pave the way for the resolution of issues that emerged after the Galwan Valley clashes in June 2020.
Key Points of the India-China Border Pact
- Resolution of Border Issues: The agreement addresses longstanding disputes, including in Depsang Plains and Demchok, where Chinese forces had encroached on Indian territory.
- Restoration of Patrolling: Both nations agreed to restore patrols to old patrolling points (PPs) along the LAC in these disputed areas.
- Next Steps: The Special Representatives (SRs) on the India-China boundary will meet soon to oversee the management of peace and tranquility in the border areas and explore mutually acceptable solutions.
- Diplomatic Mechanisms: Dialogue mechanisms at the foreign ministers and other official levels will be utilized to stabilize and rebuild bilateral relations, contributing to regional and global stability.
Strategic Importance of the Bilateral Meeting
- Maintaining Peace and Stability: PM Modi emphasized that differences between India and China should be managed carefully to ensure that broader peace and tranquility are maintained.
- Global Impact: Both leaders affirmed that stable India-China relations would have a positive impact on regional and global peace and contribute to a multipolar world.
- Long-Term Strategic Perspective: The leaders discussed progressing bilateral relations from a strategic perspective, enhancing communication, and exploring cooperation to address developmental challenges.
Key Takeaways from the 16th BRICS Summit
- Expansion and New Membership: The summit saw the inclusion of five new members—Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia (pending formalization). This expansion reflects BRICS’s growing influence as a forum representing the Global South.
- Focus on Multilateralism: Leaders emphasized multilateral cooperation to address challenges such as global security, economic growth, and sustainable development.
- Kazan Declaration: The declaration touched upon key issues:
- Geopolitical Conflicts: It called for dialogue and diplomacy to resolve disputes like the Ukraine crisis and the West Asia conflict.
- Sanctions and Trade: Criticized unilateral sanctions and their disruptive effects on global trade and development goals.
- Grain Exchange: A proposal was made to establish a BRICS Grain Exchange, aimed at improving agricultural trade among member states.
- Financial Integration: There was a push for greater financial integration through the use of local currencies for trade, exemplified by India’s UPI system as a successful model.
Importance of BRICS in the Global Context
- Global Influence: BRICS continues to be a key player in global geopolitics, representing 40% of the world’s population and 26% of global GDP (as of 2023).
- Strategic Goals: BRICS has consistently called for reform of international institutions like the UNSC, IMF, and World Bank, advocating for a more equitable global governance structure.
- Economic Collaboration: The New Development Bank (NDB), established in 2015, continues to play a vital role in funding development projects across BRICS countries, though the group’s influence in global finance remains limited compared to the World Bank.
Challenges Facing BRICS Expansion
- Geopolitical Contradictions: The inclusion of diverse new members (e.g., UAE, Egypt, Iran) could complicate decision-making due to geopolitical rivalries.
- Decision-Making Hurdles: Achieving consensus among an expanding membership will become more challenging. The expansion may dilute the cohesiveness of the group, as seen in other multilateral forums like the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and G77.
- De-Dollarisation Efforts: While BRICS aims to de-dollarize trade and reduce reliance on the SWIFT system, efforts to develop alternatives like a BRICS payment system and BRICS currency are still in nascent stages.
- Economic Disparities: Economic gaps among members—China’s GDP is significantly larger than the combined GDP of other members—could also create imbalances in decision-making.
India’s Role and Strategic Positioning in BRICS
- Geopolitical Balancing: India's participation in BRICS is a strategic maneuver to balance its global position and strengthen ties with emerging economies, particularly in the Global South.
- Diplomatic Relations with Russia: India continues to prioritize its relationship with Russia, which remains crucial for regional security and energy cooperation.
- India-China Ties: The agreement on the India-China border represents a significant shift in relations, with potential for a reset in Sino-Indian ties.
Key Themes in the Kazan Declaration
- Global Governance: Calls for reforming global institutions to give developing nations more representation.
- Energy and Sustainability: Proposals for strengthening energy cooperation, including the creation of energy corridors and the promotion of sustainable energy practices.
- Security: Emphasized the need for universal security by addressing the security concerns of all nations and promoting dialogue over confrontation.
Conclusion: Future of India-China and BRICS Relations
- India-China Relations: The border disengagement pact is a critical step towards stabilizing the India-China relationship, with potential positive impacts on regional security and global geopolitics.
- BRICS’s Growing Influence: As BRICS expands, it faces internal challenges but remains a potent voice for the Global South, aiming to reshape global governance and financial systems.
- India’s Strategic Positioning: India is likely to play a pivotal role in BRICS, especially as the group’s focus shifts towards regional stability, economic cooperation, and de-dollarization in the coming years.
India - Canada Relations

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
India-Canada relations have recently faced serious setbacks following allegations of India's involvement in the killing of Khalistani leader Hardeep Singh Nijjar in Canada. These claims have led to escalating diplomatic tensions and mutual expulsions of diplomats between the two countries.
Recent Developments in India-Canada Relations
- Assassination of Hardeep Singh Nijjar:
- Nijjar, a prominent Khalistani leader, was assassinated in British Columbia, Canada.
- The Canadian Prime Minister accused Indian officials of involvement, which India has denied as "absurd."
- Diplomatic Fallout:
- Both nations expelled each other's diplomats, reducing diplomatic staff and freezing consular services, exacerbating the tensions.
- Support from the Five Eyes Alliance:
- Canada enlisted the Five Eyes intelligence alliance to gain international backing amid the escalating diplomatic crisis with India.
What is the Five Eyes Alliance?
- About:
- The Five Eyes is a multilateral intelligence alliance composed of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- These countries cooperate on signals intelligence under the UK-USA Agreement.
- Expansion:
- The alliance later grew into the Nine Eyes and Fourteen Eyes alliances, incorporating additional countries like the Netherlands, Denmark, France, Norway, and others.
Key Areas of India-Canada Relations
- Political Relations:
- Diplomatic ties began in 1947, with both countries sharing democratic values, human rights, and pluralism.
- Collaborative efforts in global forums like the UN, G20, and Commonwealth focus on climate change, security, and sustainable development.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Bilateral trade in 2023 was worth USD 9.36 billion.
- Canada is the 18th largest investor in India with investments totaling USD 3.3 billion (2000-2023).
- Ongoing Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) negotiations aim to boost trade in goods, services, and investments.
- Diaspora Connections:
- Over 1.8 million people of Indian origin in Canada, contributing significantly to cultural and economic exchanges.
- Canada is home to one of the largest Indian diaspora populations globally.
- Education and Space Innovation:
- IC-IMPACTS promotes joint research in healthcare, agricultural biotechnology, and waste management.
- Space collaboration includes partnerships between ISRO and the Canadian Space Agency.
- Indian students represent nearly 40% of Canada's international student population.
- Nuclear Cooperation:
- A 2010 nuclear agreement allows the supply of uranium to India and establishes a Joint Committee for oversight.
- Strategic Importance:
- India’s role is key in Canada’s Indo-Pacific strategy, including collaboration on maritime security, counter-terrorism, and regional stability.
Challenges in India-Canada Relations
- Diplomatic Immunity Issues:
- Canada invoked the Vienna Conventions to protect its diplomatic staff amid tensions, with both sides highlighting the importance of maintaining diplomatic norms.
- Khalistan Issue:
- India views Canada’s tolerance of Khalistani separatist groups as a threat to its territorial integrity.
- Canada’s investigation into India’s alleged role in Nijjar’s assassination has exacerbated diplomatic mistrust.
- Economic and Trade Barriers:
- The political rift has stalled negotiations for the CEPA and slowed bilateral trade.
- Canadian investments in India face increased uncertainty due to deteriorating relations.
- Visa and Immigration Delays:
- Reduced Canadian diplomatic staff in India has caused significant delays in visa processing, especially for students.
- Geopolitical Implications:
- Tensions between India and Canada risk damaging India’s reputation on the global stage, particularly if allegations of intelligence overreach are substantiated.
- Canada’s membership in the G7 and ties with the Five Eyes make the situation complex, affecting relations with other strategic partners of India, including the US, UK, Australia, and Japan.
The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Immunity
- Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961): Establishes the framework for the treatment and protection of diplomatic missions and their personnel.
- Diplomatic Immunity: Diplomats are protected from arrest and detention by the host country.
- Inviolability of Diplomatic Premises: Diplomatic missions cannot be entered without permission.
- Protection of Consular Officers: Ensures consular officers can assist their nationals without interference.
Way Forward for India-Canada Relations
- Address the Khalistan Issue: Engage in active dialogue to resolve concerns about the Indian diaspora and the Khalistan movement, respecting each other’s sovereignty.
- Strengthen Economic Ties:
- Revitalize CEPA negotiations, with a focus on sectors like technology, renewable energy, and infrastructure.
- Enhance trade and investment frameworks for mutually beneficial opportunities.
- Balance Geopolitical Interests:
- Both nations should navigate relationships with major powers like the US, China, and Russia with care.
- A cautious approach is necessary to maintain strategic partnerships without further conflict.
- Leverage Multilateral Platforms: Utilize forums like the G7 and Five Eyes to address global challenges and promote shared values, while working to stabilize bilateral ties.
Conclusion
India-Canada relations are at a critical juncture due to recent tensions. While historical ties and shared interests provide a strong foundation, the diplomatic fallout requires careful management. Both nations must seek ways to restore dialogue, address sensitive issues like the Khalistan movement, and focus on economic cooperation to stabilize and strengthen the relationship moving forward.
INDUS WATERS: INDIA FREEZES TALKS WITH PAKISTAN
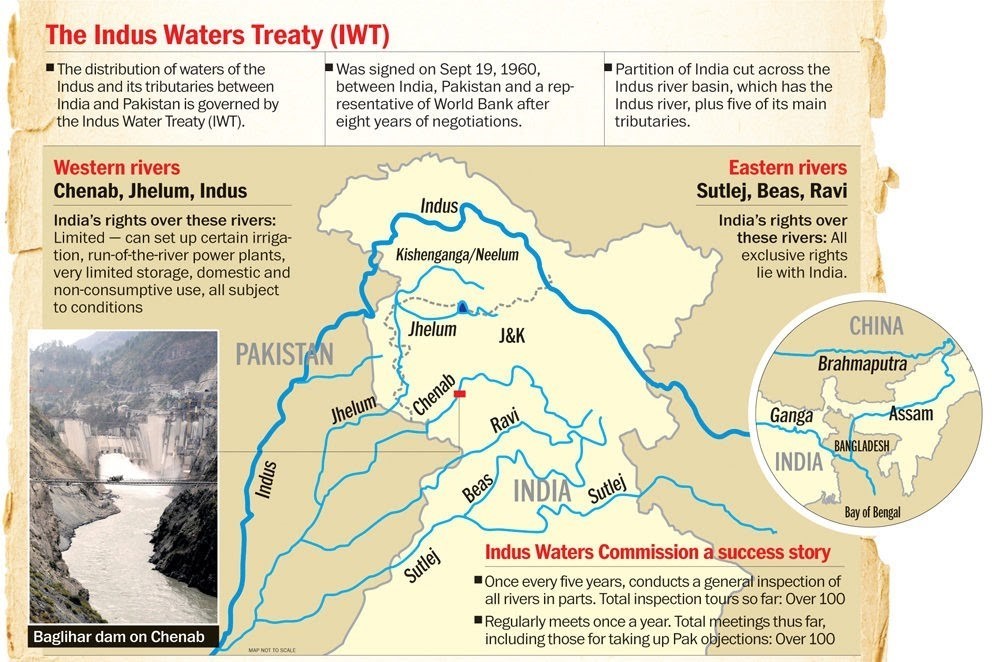
- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
India has decided to halt all meetings of the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC) until both governments engage in discussions to renegotiate the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT), a decision communicated by a senior official. The last PIC meeting occurred in May 2022, and since January 2023, India has made four attempts to initiate talks with Pakistan, but these efforts have not received satisfactory responses.
The IWT, established in 1960 with the mediation of the World Bank, governs the sharing of six rivers between India and Pakistan. Under this treaty, India controls the waters of the Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas rivers, while Pakistan has rights to the Sindh, Jhelum, and Chenab rivers. The treaty mandates annual meetings of the PIC, which have continued despite ongoing conflicts between the two nations. However, India’s recent push for renegotiation threatens the stability of this long-standing arrangement.
India's Notice for Review of the Indus Waters Treaty
India formally issued a notice to Pakistan on August 30, 2023, seeking modifications to the IWT, citing "fundamental and unforeseen changes" that necessitate a reassessment of the agreement. This is not an isolated instance; India had previously requested a review in January 2023, attributing the need for change to Pakistan’s persistent intransigence regarding its obligations under the treaty.
Key reasons for India’s demand include:
- Changes in population demographics and environmental challenges.
- The necessity for clean energy development to meet emissions targets.
- The impact of ongoing cross-border terrorism, which India argues affects water management and security.
The notification highlights issues related to two contentious hydroelectric projects in Jammu & Kashmir—the Kishanganga and Ratle projects—over which Pakistan has raised objections, claiming they violate the IWT. India asserts that these projects are "run-of-the-river" schemes that do not significantly impede river flow.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms Under the Treaty
The IWT outlines a structured dispute resolution mechanism, as detailed in Article IX. This mechanism involves three levels:
- First Level: Initial discussions occur at the PIC, where either party must inform the other of planned projects.
- Second Level: If differences remain unresolved, a Neutral Expert, appointed by the World Bank, is engaged to mediate.
- Third Level: Should the Neutral Expert fail to resolve the issue, the dispute escalates to the Court of Arbitration.
Historically, both countries have used these mechanisms, although recent years have seen significant contention. After a Pakistan-backed terror attack in Uri in 2016, India’s Prime Minister expressed the sentiment that “blood and water cannot flow together,” leading to the suspension of routine talks.
The World Bank has navigated a complex situation, receiving requests from both nations for adjudication on overlapping disputes. In December 2016, it paused these processes to encourage direct negotiations. Despite attempts to resume dialogue between 2017 and 2022, Pakistan’s reluctance to engage has further complicated matters.
Current Status and Future Implications
India’s formal notification and its call for renegotiation may set a precedent that challenges the existing framework of the IWT. The continuation of the PIC's activities hinges on a willingness from both governments to address these evolving concerns collaboratively. As tensions persist and environmental needs grow, the future of water-sharing arrangements in the region remains uncertain. The overarching goal for both nations will be to find a sustainable resolution that addresses emerging challenges while honoring the historical framework established by the IWT.
Can Sheikh Hasina be Extradited?

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The chief prosecutor of Bangladesh’s International Crimes Tribunal (ICT), Mohammad Tajul Islam, announced plans to seek the extradition of former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina from India. The ICT was established in 2010 to investigate crimes committed during the 1971 independence war from Pakistan.
Background on Sheikh Hasina's Exile
Ms. Hasina sought refuge in India in early August after a mass uprising forced her to resign. Following her departure, numerous criminal cases have been filed against her and her aides, with charges including murder, torture, abduction, crimes against humanity, and genocide. The interim government in Dhaka has revoked her diplomatic passport, and the existing bilateral extradition treaty between India and Bangladesh may allow for her return to face trial.
Extradition Treaty Overview
Key Provisions
- Under the International Crimes (Tribunals) Act of 1973, Bangladeshi courts can proceed with trials in Ms. Hasina’s absence, raising concerns about the fairness and adherence to due process. Thus, her extradition is deemed crucial.
- The extradition treaty between India and Bangladesh was executed in 2013 and amended in 2016 to facilitate the exchange of fugitives. The treaty has allowed the transfer of several political prisoners, including two involved in the 1975 assassination of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, Ms. Hasina’s father, and Anup Chetia, the former general secretary of the banned United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA).
Extradition Conditions
- The treaty mandates the extradition of individuals charged with crimes punishable by at least one year’s imprisonment. It follows the principle of dual criminality, meaning the offense must be punishable in both countries. Since the charges against Ms. Hasina are prosecutable in India, she qualifies for extradition. The treaty also covers attempts to commit crimes and complicity in such offenses.
- The 2016 amendment significantly lowered the evidentiary threshold for extradition, requiring only an arrest warrant from a competent court in the requesting country to initiate proceedings.
Grounds for Refusal of Extradition
Political Nature of Offenses
Article 6 of the treaty allows for extradition to be refused if the offense is deemed of a “political nature.” However, many offenses, including murder and terrorism-related crimes, are explicitly excluded from this classification. Given that several charges against Ms. Hasina fall outside this exemption, it is unlikely India could justify denying extradition on these grounds.
Good Faith Clause
Article 8 permits denial of extradition requests if the accusations are not made in good faith or involve military offenses not recognized under general criminal law. India could argue that the charges against Ms. Hasina are politically motivated and may lead to her facing unfair trials or persecution upon her return. Recent reports indicate that some of Ms. Hasina’s former ministers faced violent arrests, raising further concerns about the political climate in Bangladesh.
Potential Implications of Extradition Request
Dr. Sreeradha Datta, a professor of international relations at O.P. Jindal Global University, commented that the treaty does not guarantee Ms. Hasina’s extradition, emphasizing that the final decision will depend on diplomatic negotiations and political factors. Even if India declines the request, it may only serve as a minor political irritant rather than significantly damaging bilateral relations.
Economic Considerations
Bangladesh is India’s largest trade partner in South Asia, with bilateral trade estimated at $15.9 billion for the fiscal year 2022-23. Before Ms. Hasina’s ouster, both countries were set to discuss a comprehensive economic partnership agreement (CEPA) to strengthen economic ties. Following the regime change in Dhaka, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi has engaged with Chief Adviser Muhammad Yunus of the interim government, pledging continued support for ongoing development projects.
India’s Approach to the Russia-Ukraine Conflict and Economic Ties

- 11 Sep 2024
India’s Four-Point Principle on the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
- Principles for Resolution: External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar outlined India's four key principles regarding the Russia-Ukraine conflict:
- Peace as a Priority: Emphasis on the need for peace and the belief that the conflict cannot be resolved through continued warfare.
- Negotiation Requirement: Asserted that any resolution must involve Russia in the dialogue process.
- No Battlefield Solutions: Stressed that solutions cannot be achieved on the battlefield.
- Active Engagement: India is actively engaged and concerned about finding a resolution, with ongoing discussions with both Russia and Ukraine.
- Hosting Peace Conference: Jaishankar noted that while suggestions for India to host a peace conference have been made, there is no commitment from India to propose or host such a conference.
- Recent Diplomacy: Referenced Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visits to Moscow and Kyiv and highlighted National Security Adviser Ajit Doval's current visit to Russia.
Diplomatic Discussions with Germany
- Bilateral Meeting: Jaishankar met with German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock in Berlin to prepare for German Chancellor Olaf Scholz’s visit to New Delhi on October 24-25.
- Topics of Discussion:
- Global Issues: Discussed the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the Gaza conflict, and coordination for the UN Summit of the Future.
- UN Security Council Expansion: India and Germany are jointly advocating for the expansion of the UN Security Council.
- Ongoing Engagement: Both ministers will reconvene later this month at the UN General Assembly.
India-Germany Relations
- Germany’s Role: Baerbock acknowledged ongoing discussions with India and other countries about their roles in peace efforts, despite differing positions on the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Economic and Trade Relations:
- Migration and Mobility: Plans to enhance the India-Germany migration and mobility partnership, aiming to increase the number of skilled Indian workers in Germany. Currently, 125,000 Indian nationals work and 50,000 students study in Germany.
- Military Cooperation: Discussed expanding military partnerships, including joint air force exercises and upcoming naval exercises in Goa.
- Trade and Investment: Efforts to boost annual bilateral trade to $30 billion and attract about $25 billion in investment from Germany. New Delhi will host the Asia Pacific Conference of German Business next month.
Economic Ties with China
- Business Relations: Jaishankar addressed concerns about economic ties with China amidst a four-year military stand-off and related restrictions.
- Business Sectors: India is open to Chinese business but emphasizes the need for clarity on sectors and business terms.
Summary
India’s approach to the Russia-Ukraine conflict emphasizes peace, negotiation, and active engagement. Diplomatic efforts with Germany focus on global issues, military cooperation, and economic growth. Jaishankar also highlighted a nuanced stance on economic ties with China amid ongoing tensions.
India's Balancing Act: Navigating Iran Relations in the Face of Regional Turmoil and Leadership Transition

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The death of Iran’s President Ebrahim Raisi in a helicopter accident on May 20 has added another layer of uncertainty in a region already wracked by political tensions and war.
Context:
- In the wake of President Ebrahim Raisi's unexpected passing in a helicopter accident on May 20, the geopolitical landscape of the region faces heightened uncertainty.
- Despite the tragic event, the enduring influence of Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei suggests minimal immediate impact on Iran's policies.
- However, this event prompts a closer examination of the evolving dynamics between India and Iran, amidst recent geopolitical shifts.
A Historical Perspective on India-Iran Relations:
- Historical Background: India and Iran share a rich historical tie woven with deep-rooted cultural and economic connections spanning centuries.
- From ancient times, both civilizations have influenced each other in language, culture, and commerce, fostering enduring ties.
- Following India's independence in 1947, formal diplomatic relations were swiftly established between the two nations.
- Despite the divergence of their Cold War alliances—India with the Non-Aligned Movement and Iran aligning with the United States—mutual respect characterized their interactions.
- The Iranian Revolution in 1979 heralded a shift in Iran's ideological stance, yet India remained committed to nurturing bilateral relations, recognizing the significance of regional stability and economic collaboration.
- Economic and Energy Collaboration: Central to the India-Iran partnership is their robust energy cooperation, with Iran serving as a vital supplier of oil and natural gas to India.
- In addressing India's burgeoning energy demands, Iranian resources have played a pivotal role in sustaining India's economic growth.
- The early 2000s witnessed landmark agreements, including long-term oil supply pacts and discussions on strategic pipeline projects like the Iran-Pakistan-India (IPI) gas pipeline.
- Strategic Imperatives; Strategically, India has recognized Iran's pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of the broader West Asian region.
- Both nations have shared interests, notably in fostering stability in Afghanistan.
- Iran's geographic position offers India a strategic gateway to Central Asia, circumventing Pakistan—a factor underscored by India's investments in projects such as the Chabahar port, aimed at bolstering connectivity to Afghanistan and beyond.
Recent Shifts and Implications for India-Iran Relations:
- The Abraham Accords and Evolving Regional Dynamics: The 2020 Abraham Accords, facilitated by the US, introduced a new layer of complexity to regional geopolitics.
- These agreements, which normalized ties between Israel and several Arab nations including the UAE and Bahrain, were perceived as part of a broader US strategy to counterbalance Iran's influence.
- India's active involvement in the I2U2 coalition (India, Israel, UAE, and the US) signals its alignment with this strategy, potentially signalling a departure from traditional bilateral collaborations, a shift Iran has taken note of.
- India-Middle-East Economic Corridor (IMEC) Initiative: The unveiling of the IMEC project during the 2023 G20 summit in New Delhi marks a pivotal development.
- This initiative proposes a transportation network linking India to Israel via the UAE and Saudi Arabia, presenting a strategic alternative route that bypasses Iran.
- The IMEC underscores India's commitment to integrating into evolving economic and strategic frameworks in West Asia, potentially reshaping traditional ties with Iran.
- Impact of US Sanctions: The reinstatement of US sanctions on Iran following the Trump administration's withdrawal from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) in 2018 had profound implications for India-Iran economic relations.
- These sanctions triggered a significant reduction in India's oil imports from Iran, prompting India to seek alternative energy sources.
- While this strained the economic aspect of bilateral ties, India remained interested in advancing projects like the Chabahar port despite the challenges posed by the sanctions.
Strategic Implications and Hurdles with the Chabahar Project:
Strategic Importance:
- The Chabahar endeavour stands as a linchpin within India's regional connectivity and strategic framework.
- Nestled along Iran's southeastern coast, the port furnishes India with direct access to the Arabian Sea, offering a vital alternative to China's Gwadar port under its Belt and Road Initiative.
- Positioned as a gateway to Afghanistan and Central Asia, Chabahar bolsters India's geopolitical foothold, circumventing historical barriers imposed by Pakistan.
- Envisioned as a nucleus of economic activity, the port holds the promise of catalyzing trade and investment between India, Iran, and Afghanistan, unlocking the vast potential of Central Asian markets.
- By fostering Chabahar's development, India aims to provide a counterbalance to China's Gwadar port, positioning itself as a pivotal player in reshaping regional trade dynamics.
Navigating Challenges Amid Strategic Imperatives:
- Despite its strategic allure, the Chabahar project grapples with multifaceted challenges.
- US sanctions have cast a pall over international investments and hindered crucial financial transactions vital for the port's advancement.
- The seismic shift in Afghanistan's political landscape following the Taliban's resurgence has cast uncertainty over the project's trajectory.
- The original tripartite agreement, contingent upon the stability offered by the erstwhile US-backed Ghani regime, now faces an altered reality.
- The enduring viability of Chabahar hinges on regional stability and collaboration, factors further complicated by Iran's economic woes amidst ongoing sanctions.
- Persistent geopolitical tensions pose formidable obstacles to the sustained success of this ambitious undertaking, underscoring the need for adept navigation amid strategic imperatives.
Future Trajectories for India-Iran Relations:
- Pursuing Strategic Autonomy: Chabahar demonstrates India's pursuit of strategic autonomy, allowing it to navigate geopolitical landscapes and assert regional influence.
- Balancing relations with Iran, the US, and other regional players enables India to maintain a multifaceted foreign policy that serves its strategic objectives.
- Leveraging International Cooperation: India could explore collaborations with international partners like the EU to mitigate the impact of US sanctions and garner diplomatic and economic support.
- Strengthening ties with Central Asian countries may enhance Chabahar's economic prospects.
- Commitment to Regional Stability: India's continued engagement with Afghanistan, including humanitarian aid, underscores its commitment to regional stability and connectivity through Chabahar.
- Maintaining a presence in Afghanistan highlights the strategic importance of Chabahar as a key node for regional diplomacy and economic activity.
Conclusion
The sudden demise of Iran's President Ebrahim Raisi exacerbates uncertainty in an already tumultuous region. India must deftly balance its strategic interests amidst competing regional powers and the intricate landscape of geopolitical rivalries and international sanctions. The revival of the Chabahar project exemplifies India's strategic adaptability but also underscores the precarious nature of its regional engagements. India's ability to exhibit strategic foresight and diplomatic finesse will be crucial in effectively navigating the ever-changing geopolitical environment.
India’s Nuanced Approach in the South China Sea
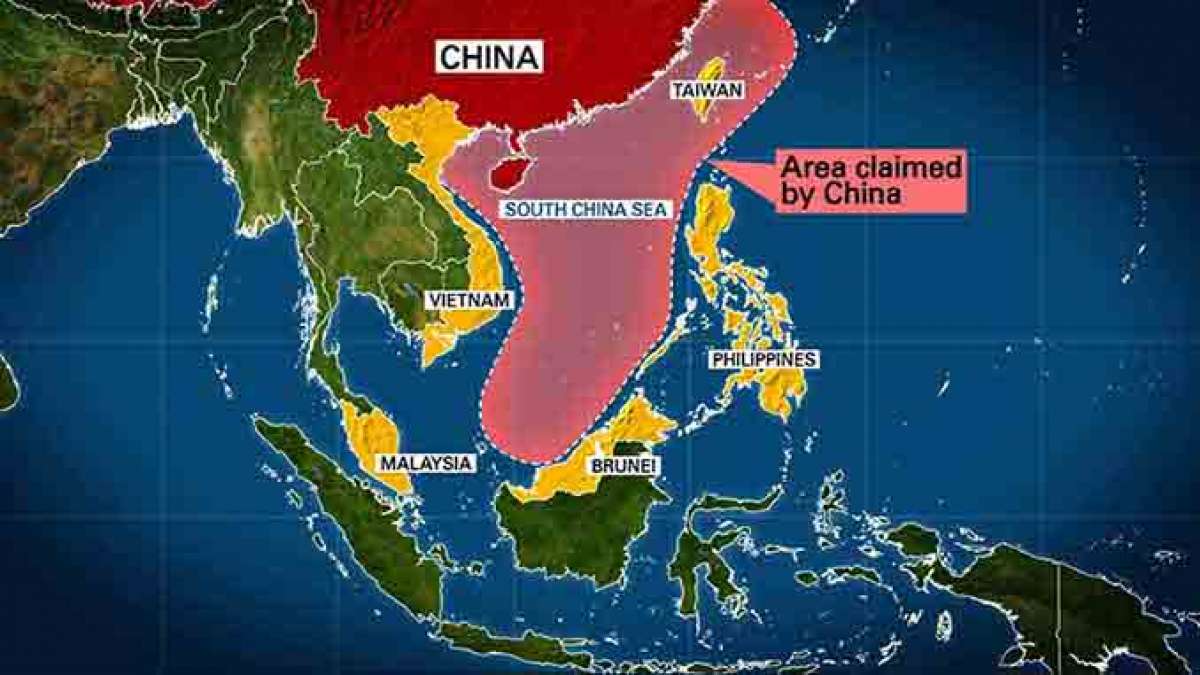
- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In March 2024, India’s External Affairs Minister, S. Jaishankar, articulated, in a joint statement during his visit to Manila, India’s full support for the Philippines in upholding its national sovereignty concerning the South China Sea.
Context:
- During his visit to Manila in March 2024, India's External Affairs Minister reiterated India's steadfast support for the Philippines in safeguarding its national sovereignty amidst the ongoing South China Sea dispute.
- This statement came against the backdrop of heightened tensions and frequent maritime incidents in the region throughout 2023.
- Furthermore, a joint statement issued in 2023 by India and the Philippines emphasized the importance of China adhering to the rules-based maritime order and recognizing the 2016 ruling by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in favor of the Philippines.
- These statements reflect a notable shift in India's approach towards the South China Sea issue, departing from its previous stance of caution and neutrality.
- India's evolving position on the South China Sea underscores its broader strategic and economic interests on the global stage, with a renewed emphasis on upholding international maritime law, sovereignty, and sovereign rights in the region.
About the South China Sea (SCS):
- The South China Sea (SCS) is a pivotal body of water located in Southeast Asia, bordered by China to the north, Vietnam to the east and south, the Philippines to the west, and Borneo to the south.
- It encompasses a myriad of shoals, reefs, atolls, and islands, with notable features including the Paracel Islands, the Spratly Islands, and the Scarborough Shoal.
- Strategically situated, the SCS serves as a crucial maritime passage connecting the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean via the Strait of Malacca.
- It plays a vital role in global trade, with approximately one-third of all shipping traversing its waters annually, facilitating trillions of dollars in trade and serving as a linchpin for geopolitical dynamics.
- Rich in marine biodiversity, the SCS harbors a third of the world's marine species, providing essential fisheries that contribute to the food security of Southeast Asian nations.
- Additionally, the region is believed to possess vast reserves of oil and gas beneath its seabed, further heightening its economic significance.
- With an estimated $3.4 trillion worth of ship-borne commerce passing through its lanes each year, including crucial energy supplies to nations like the United States, Japan, and South Korea, the South China Sea stands as one of the busiest and most consequential waterways on the planet.
Various Ongoing Disputes in the South China Sea (SCS):
There are multiple ongoing disputes in the South China Sea (SCS) involving several countries. These disputes revolve around territorial and maritime claims over islands, reefs, banks, and other features in the region.
- Spratly Islands Dispute: The Spratly Islands are claimed by China, Taiwan, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei.
- These islands are strategically important due to their location in the middle of the South China Sea, as well as potential oil and gas reserves.
- Paracel Islands Dispute: The Paracel Islands are claimed by China, Taiwan, and Vietnam.
- China currently controls the islands, but Vietnam also asserts its sovereignty over them.
- Scarborough Shoal Dispute: The Scarborough Shoal is a disputed territory between China, Taiwan, and the Philippines.
- The shoal is rich in fishing resources and is strategically located near important shipping lanes.
- Gulf of Tonkin Dispute: This dispute involves China, Taiwan, and Vietnam, who have overlapping claims over the boundaries in the Gulf of Tonkin.
- Natuna Islands Dispute: Although geographically a part of the South China Sea, Indonesia claims sovereignty over the Natuna Islands, while China's "Nine-Dash Line" claim overlaps with Indonesia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) near the Natuna Islands.
- Senkaku Islands Dispute: In the East China Sea, the Senkaku Islands are disputed between China, Taiwan, and Japan, with Japan currently administering them.
- These disputes stem from historical claims, economic interests, and strategic considerations, leading to tensions between the involved parties.
India’s Policy Shift:
- Initially, India's engagement in the region was primarily motivated by economic considerations, in line with its Look East Policy.
- This policy sought to strengthen economic linkages with Southeast Asia and secure vital energy resources essential for India's growing economy.
- Demonstrating this economic focus, Indian state-owned enterprises like ONGC Videsh participating in oil and gas ventures in Vietnam's exclusive economic zones highlighted India's economic imperatives and its adherence to the principles of maritime resource exploration and exploitation within the framework of international law, particularly UNCLOS.
- India's policy trajectory has since evolved from Look East to Act East, indicating a shift towards a more proactive and strategic stance in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This shift reflects India's acknowledgment of the changing geopolitical landscape and the imperative for a comprehensive foreign policy approach.
- The Act East Policy places greater emphasis on economic integration and underscores the importance of forging strategic partnerships and enhancing security cooperation with countries in the Indo-Pacific, including Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, and the Philippines.
- Concurrently, India has augmented its capabilities through various measures such as forward deployment, mission-based operations, heightened maritime domain awareness, and the establishment of deep-water maritime infrastructure.
India's intricate dynamic with China:
- The assertive behavior exhibited by China in the South China Sea (SCS) and its gradual encroachment strategy across various maritime domains, including the Indian Ocean, have sparked apprehension within India.
- Chinese intelligence-gathering activities in the Eastern Indian Ocean have heightened India's vigilance, prompting a more proactive stance to address perceived threats to its maritime security.
- Against the backdrop of escalating geopolitical tensions in the SCS, largely driven by China's assertive territorial assertions and militarization efforts, India's approach has undergone a nuanced yet less cautious evolution.
- This transformation in India's stance toward the SCS is closely interlinked with its complex relationship with China.
- Both nations have a history of longstanding border disputes, which escalated following the Galwan Valley clash in 2020.
- China's periodic incursions into Indian territory and recent actions such as renaming Indian villages in Arunachal Pradesh further exacerbate these tensions.
- The Galwan Valley incident prompted India to deploy a frontline warship to the SCS, showcasing India's asymmetric deterrence capabilities.
- China's assertive stance and territorial claims in both the SCS and along India's land border pose significant challenges to regional stability.
- India's strategic engagements, including regular naval exercises and enhanced military cooperation with Southeast Asian nations, serve dual purposes: reaffirming India's commitment to regional security and acting as a counterbalance to China's contentious assertions.
The ASEAN Perspective:
- New Delhi's strategic recalibration stems from recognizing the critical importance of the South China Sea (SCS) for regional security and the global maritime order.
- The disputes involving China and various ASEAN nations in the SCS directly impact the principles of freedom of navigation and overflight, which are essential not only for India's trade and energy transport but also for countries worldwide.
- As an active participant in the Indo-Pacific region, India cannot afford to remain indifferent to such significant issues.
- Its central role in the Indo-Pacific extends beyond the Indian Ocean to the broader maritime domain, where China's rise challenges the established order in unforeseen ways.
- India's Indo-Pacific strategy prioritizes ASEAN centrality, despite internal differences within the regional grouping presenting challenges.
- India's advocacy for a rule-based international maritime order, particularly its steadfast support for UNCLOS, stands in opposition to unilateral actions that undermine regional stability.
- This principled stance, deeply rooted in India's foreign policy framework, indirectly counters China's expansive territorial claims and activities in the SCS, underscoring India's dedication to regional stability and security as a responsible stakeholder.
Navigating Challenges and Choices for India:
- India encounters complexities in managing the South China Sea (SCS) disputes, especially given the divergent interests within ASEAN.
- While ASEAN nations adopt varying approaches to disputes, India aims to strike a delicate balance between supporting regional partners and steering clear of direct entanglement in confrontational situations.
- India is exploring a spectrum of options, including initiatives to bolster capacity, cooperation in defense matters, infrastructure development, and advocating for the preservation of international law in the SCS.
Conclusion:
India's recalibrated approach to the South China Sea disputes arises from strategic necessities, evolving geopolitical landscapes, and regional intricacies. The nuanced stance adopted by India towards the South China Sea is emblematic of its broader strategy, aimed at safeguarding its interests while actively participating in collective endeavors to uphold peace, stability, and the rule of international law across the Indo-Pacific region.
A Reformed UNSC is not Possible Without India as a Permanent Member

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At a time when India is seriously advocating structural and functional reforms in the United Nations, the global forum’s president, Dennis Francis, has expressed optimism about India’s potential to secure a permanent seat on the UN Security Council.
Context:
- Amid India's active promotion of structural and functional reforms within the United Nations, Dennis Francis, the president of the global forum, has voiced optimism regarding India's ability to secure a permanent seat on the UN Security Council.
- The US and other Western countries sound extremely hollow when they pontificate on strengthening democracy and the fight against terrorism even as they keep India out of P5.
What is P5 Nations in the United Nations?
- P5 refers to the Permanent Five or Permanent Members of the United Nations Security Council.
- These are the five countries that have a permanent seat on the Security Council, granting them significant power within the UN.
The P5 members are:
-
- China
- France
- Russia
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Most of these countries were major victors of World War II and were seen as key players in maintaining international peace and security.
- They hold a special privilege within the Security Council: the right to veto any resolution.
- This means any one of these countries can single-handedly block a resolution, regardless of how many other countries support it.
- The P5's power and influence is a subject of some debate. Some argue that it's necessary to maintain stability, while others believe it gives these countries too much control and hinders the UN's effectiveness.
Urgent Need for Overhauling the United Nations (UN):
- Addressing the 76th UNGA in 2021, the Prime Minister of India underscored the imperative for 'comprehensive UN reforms,' stressing that 'outmoded structures' are inadequate to tackle contemporary challenges.
- Issues such as climate change, counterterrorism efforts, and the attainment of sustainable development goals (SDGs) were not prioritized when the UN was established seven decades ago.
- Today, they demand urgent attention.
- The aftermath of World War 2 has spawned numerous conflicts that persist, undermining global peace and economic advancement.
- The Covid-19 pandemic has laid bare the fragility of the world's healthcare systems.
- In today's multipolar world, the UN's polarized and antiquated structure is ill-suited to meet the demands of global governance.
- Cooperation among nations is essential to prevent the abuse of selective veto power by members pursuing hegemonic agendas.
Inconsistencies in Global Perceptions of India's UNSC Candidacy:
- In 2023, as India's G20 presidency drew to a close, the country's foreign minister noted a positive international reception to India's bid for a permanent seat on the UNSC.
- During bilateral discussions between the Prime Minister of India and the President of the USA, a joint statement emphasized India's stance on the need for a more inclusive and representative global governance structure through UN Security Council reform.
- In the same statement, the US expressed support for India's candidacy for a non-permanent seat on the UNSC for the term 2028-2029.
- Beyond the US, other voices echo the call for expanding non-permanent UNSC membership.
- The Uniting for Consensus (UFC) group, comprising twelve nations, advocates for increasing the number of non-permanent elected UNSC members from 15 to 26.
- Formed in 1990, the UFC opposes creating new permanent national seats, arguing that the current P5 arrangement stems from post-World War 2 circumstances, and creating additional privileged positions would be detrimental to UN membership's general interests.
- Critics point out the inconsistency of Western nations, notably the US, a permanent UNSC member, advocating for democracy and counterterrorism while simultaneously excluding India, one of the oldest UN members and the largest democracy, from the P5.
- China presents the primary obstacle to India's pursuit of a permanent UNSC seat.
China's Influence on UNSC Reform Efforts:
- Italy-China Collaboration within UFC: In 2023, the Deputy Prime Minister of Italy engaged in discussions with his Chinese counterpart, focusing on bilateral agreements and the situation in Ukraine.
- During this exchange, the Deputy Prime Minister of Italy commended the productive and consistent cooperation between China and Italy concerning UNSC reform, particularly their coordination within the Uniting for Consensus (UFC) group, where China holds an observer status.
- The presence of China as an observer suggests dim prospects for those advocating genuine reforms and expansion of the P5.
- China's Opposition to the G4 Group: Also in 2023, the G4 Group, consisting of India, Brazil, Japan, and Germany, convened during the 78th UNGA to deliberate on the UN reform process, particularly focusing on expanding the P5.
- Their objective is to modernize the UN's structure, which has its roots in the aftermath of World War 2.
- However, opposition from China, Russia, and South Korea regarding Japan's participation in the G4 due to historical issues stemming from World War 2 has caused friction and disagreement among the countries involved.
- Acknowledging India's Role: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru played a pivotal role in advocating for China's inclusion as a permanent member of the UN Security Council. Notably, both the US and the Soviet Union informally offered India the UNSC seat in the early 1950s.
- Nehru emphasized China's significance within the framework of his foreign policy.
- However, China's actions in Tibet and its conflict with India in 1962 shattered Nehru's perception of China's global role.
- India now stresses the importance of resolving issues such as Tibet and territories like Xinjiang and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- As a permanent UNSC member, China should remember the circumstances that led to its membership and acknowledge its responsibilities to India.
Conclusion
The international community must acknowledge that without comprehensive restructuring and democratization, untethered from its historical constraints, the United Nations (UN) will struggle to address the complexities of contemporary geopolitics and foster genuine multilateralism. Without these reforms, the aspirations for peace and prosperity will remain elusive. What's urgently required is a revamped, credible, and inclusive UN 2.0 that can effectively safeguard global peace and security.
United Nations Security Council:
- The Security Council has primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- It has 15 Members, and each Member has one vote.
- Under the Charter of the United Nations, all Member States are obligated to comply with Council decisions.
- The Security Council takes the lead in determining the existence of a threat to the peace or act of aggression.
- It calls upon the parties to a dispute to settle it by peaceful means and recommends methods of adjustment or terms of settlement.
- In some cases, the Security Council can resort to imposing sanctions or even authorizing the use of force to maintain or restore international peace and security.
Prioritizing Africa in India's Global South Perspective
- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As Africa houses three-fourths of humanity and over 39 percent of the global GDP, there's a growing call to reform existing structures towards a more inclusive and representative system focused on development.
Context:
- President of India, Droupadi Murmu's trip to Mauritius underscored the significance of India's ties with African nations, particularly emphasizing Mauritius' role as a pivotal partner in the Indian Ocean Region.
- This visit reflects India's expanding involvement in Africa, characterized by joint initiatives in community development and the inauguration of critical infrastructure projects.
- As India endeavors to bolster its standing within the Global South, it becomes imperative to comprehend the diverse facets of the India-Africa relationship, analyzing the potential opportunities it offers and the necessity for enhanced collaboration.
Analyzing India's Comprehensive Engagement with Africa:
- Investments and Trade: India's commitment to Africa is evidenced by its burgeoning investments, which soared to $98 billion in 2023, reflecting its confidence in Africa's economic potential and its dedication to nurturing enduring partnerships.
- Bilateral trade between India and Africa has surged to $100 billion, spanning diverse sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, technology, and services, catalyzing economic growth and diversification in both regions.
- Developmental Projects: India's involvement in Africa extends to diverse developmental initiatives, encompassing infrastructure, healthcare, education, agriculture, and renewable energy sectors.
- By spearheading such projects, India not only fosters economic progress in Africa but also cements diplomatic ties and goodwill.
- Export of Scalable Solutions: Drawing on its expertise in cost-effective and scalable solutions, India has played a pivotal role in addressing various challenges confronting African nations.
- Through initiatives spanning from eco-friendly housing to solar energy technology, Indian entities contribute to poverty alleviation and sustainable development, bolstering India's reputation as a dependable partner committed to mutual progress.
- Mutual Prosperity and Development: India and Africa mutually benefit by capitalizing on each other's strengths and resources.
- While India's investments stimulate economic growth, generate employment, and facilitate technology transfer in Africa, African markets offer India access to vital natural resources, new markets, and strategic collaborations.
- This symbiotic relationship fosters economic resilience, innovation, and inclusive growth in both regions.
The Strategic Significance of India's Advocacy for Africa's Representation in Global Arenas:
- Enhancing Africa's Representation and Influence India's active advocacy for Africa's presence in global governance platforms underscores its dedication to amplifying the voices of developing nations.
- Recognizing Africa's substantial population and economic contribution, India emphasizes the necessity of its representation for a fairer and more inclusive international system.
- Initiatives like supporting the African Union's inclusion in the G20 highlight India's acknowledgment of Africa's pivotal role in shaping global agendas.
- Driving Reform and Adaptation Amidst evolving global challenges, there's a growing impetus for adapting governance structures to address emerging issues and foster sustainable development.
- India's push for Africa's participation in global forums reflects its commitment to reforming institutions like the United Nations, International Monetary Fund, and World Bank to better reflect the interests of developing nations.
- Fostering Strategic Partnerships India's advocacy for Africa's representation in global governance is not only driven by altruism but also strategic considerations.
- Recognizing Africa's increasing influence, India seeks to cultivate strategic partnerships with African nations to advance its global interests.
- By supporting Africa's involvement in decision-making processes, India enhances its diplomatic influence and strengthens its position as a leading voice in the Global South.
- Advancing Development Goals: Aligned with its broader development agenda, India's advocacy for Africa's representation in global governance focuses on priorities such as poverty alleviation, sustainable development, and inclusive growth.
- By championing Africa's interests in international forums, India aims to address systemic inequalities and advocate for policies benefiting vulnerable populations.
- This advocacy spans various domains, including trade, finance, climate change, and peace and security, reflecting India's commitment to fostering a more equitable world order.
Exploring India Africa's Rich Historical Bonds and Charting a Path for Future Collaboration:
- Legacy of Colonialism and Struggle for Liberation: India's historical relationship with Africa is deeply rooted in its fight against colonialism, with both regions sharing similar experiences of exploitation and oppression under European rule.
- India's support for African liberation movements during the colonial era solidified a bond based on shared values of freedom and sovereignty.
- Cultural Exchange and People-to-People Connections: Centuries of interaction between Indian traders, scholars, and missionaries with African societies have left enduring cultural legacies, enriching both regions' traditions and languages.
- Today, vibrant Indian communities contribute to Africa's cultural diversity and economic vitality, fostering mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Commitment to Development and Capacity-Building: India's engagement with Africa in development cooperation dates back to its early days of independence, with a focus on providing technical assistance and capacity-building support.
- Continued collaboration in sectors such as education, healthcare, agriculture, and infrastructure underscores India's enduring commitment to Africa's progress and prosperity.
- Exploring Economic Opportunities and Innovation: With Africa emerging as a dynamic economic hub, India stands poised to deepen its economic ties by leveraging historical bonds and cultural affinities.
- Opportunities abound for enhanced trade, investment, and technology exchange, benefiting both regions and driving sustainable development.
- Forging Strategic Partnerships in a Changing Global Landscape: Amid geopolitical shifts, India and Africa have the chance to strengthen strategic alliances grounded in shared values and interests.
- By aligning diplomatic efforts and leveraging their collective strengths, both regions can wield greater influence on global issues like climate change, terrorism, and pandemics, fostering a more equitable and inclusive world order.
Conclusion
The multifaceted partnership between India and Africa presents abundant prospects for economic, political, and social collaboration. In India's pursuit of leadership within the Global South, fostering closer ties with African nations emerges as imperative. Amidst the swiftly evolving global landscape, the alignment between India and Africa signifies a potential for mutual prosperity and advancement
India's Bhutan Policy: Balancing Regional Allies in the Shadow of Dragon
- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Bhutan decided on Wednesday to postpone a state visit by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Thimphu this week because of bad weather.
Context:
- The planned visit to Bhutan on 21-22 March by the Indian prime minister however had to be postponed due to inclement weather conditions over Paro airport.
- Notwithstanding the sudden intervention by nature, the visit which was otherwise planned amid an electioneering time, showcases the importance that New Delhi is imparting to an important friend and neighbour.
- The importance of Bhutan for India can be immediately gauged from the manner in which China is seeking to woo its southern neighbour away from the ambit of Indian influence.
Background of India-Bhutan Relations:
- India and Bhutan have maintained a special bilateral relationship based on mutual trust, goodwill, and understanding.
- This unique partnership is founded upon the Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation, first signed in 1949 and subsequently renewed in 2007.
- The treaty has provided a strong framework for the two nations to develop close political, economic, and cultural ties.
- A significant aspect of the enduring bond between India and Bhutan lies in their spiritual kinship.
- Bhutan regards India as the "gyagar," acknowledging its role as the sacred birthplace of Buddhism.
- This deep cultural and religious connection has helped foster resilience and camaraderie between the two nations, further cementing their historical friendship.
Why does Bhutan Hold Significant Importance for India?
- India and Bhutan have maintained strong bilateral relations rooted in shared cultural heritage, political cooperation, economic ties, and social connections.
Cultural Bonds:
- Buddhist Heritage: With India being the birthplace of Lord Buddha, Bhutanese monks frequently visit significant Buddhist sites such as Nalanda, Bodh Gaya, and Rajgir, fostering spiritual connections.
- Open Border Policy: The open border encourages regular exchanges of travellers for work, tourism, shopping, and medical care, further strengthening cultural ties.
Political Cooperation:
- High-Level Visits: Frequent political exchanges at the ministerial level, including visits by the Indian Prime Minister and the King of Bhutan, sustain and strengthen bilateral relations.
- Doklam Crisis: During the 2017 crisis, Bhutan granted access to Indian army personnel to resist Chinese incursions, demonstrating mutual trust and cooperation.
- Civilian Award: Bhutan conferred its highest civilian award on Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2021, recognizing his contributions to the friendship between the two nations.
Economic Partnerships:
- Financial Assistance: India has provided financial aid to Bhutan since the 1960s, supporting its five-year plans, for agriculture, irrigation, health, industrial development, road transport, energy, and education.
- Trade and Commerce: The 1972 Agreement on Trade and Commerce, revised in 2016, promotes free trade, with India being Bhutan's largest trading partner, exceeding $1422 million in bilateral trade in 2021-22.
- Vaccine Maitri Initiative: Bhutan was the first country to receive Indian-made Covishield vaccines, with 550,000 doses gifted during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Hydropower Collaboration: A vital cooperation area generating significant revenue, hydroelectric projects are covered under a 2006 bilateral agreement, with four operational projects supplying 2136 MW of electricity to India and two more under construction.
Social Connections:
- Education: Approximately 1,000 scholarships are provided annually to Bhutanese students in Indian universities for engineering and medicine, fostering knowledge exchange.
- Indian Diaspora: 50,000 Indians working in Bhutan contribute to fields such as education, arts, and health.
Environmental Importance:
- Carbon-Neutral Commitment: As one of the few countries committed to carbon neutrality, Bhutan has found a key partner in India to achieve this goal through renewable energy, forest conservation, and sustainable tourism initiatives.
New Cooperation Areas:
- Space: Joint development of the India-Bhutan SAT small satellite aims to help manage Bhutan's natural resources, promoting scientific collaboration.
- Fintech: Launching the RuPay Card enables full interoperability, with Bhutan as the second country to launch India's BHIM app for cashless payments.
- E-learning: Integrating Bhutan's DrukRen with India's National Knowledge Network facilitates information access for universities and research institutions in both countries, fostering educational cooperation.
What are the Challenges in India-Bhutan Relations?
- Despite their close ties, India-Bhutan relations face several challenges that must be addressed to maintain a strong partnership.
China's Growing Influence:
- Chinese Presence: China's increasing influence in Bhutan, particularly near the disputed Bhutan-China border, has raised concerns in India, traditionally Bhutan's closest ally.
- While Bhutan and China have not established diplomatic relations, their friendly exchanges can potentially shift the balance of power in the region.
Border Disputes:
- Incidents of Incursions: While the 699 km India-Bhutan border has been largely peaceful, recent incursions by Chinese forces have created flashpoints, such as the 2017 Doklam standoff in the India-China-Bhutan tri-junction.
- Any escalation of these border disputes could strain India-Bhutan relations and challenge their traditional security cooperation.
Hydropower Projects:
- Bhutan's hydropower sector is a key economic pillar, with India playing a significant role in its development.
- However, some Bhutanese have expressed concerns over the perceived disproportionate benefits for India.
- These concerns have led to public opposition in Bhutan against Indian involvement in the sector, which could impact bilateral relations.
Trade Issues:
- Trade Imbalance: India accounts for over 80% of Bhutan's imports and exports, raising concerns about the significant trade deficit.
- Bhutan seeks greater access to the Indian market for its products to reduce the trade deficit, which could require further negotiation and collaboration between the two countries.
- To navigate these challenges, both India and Bhutan must address these concerns through open dialogue, strategic cooperation, and mutually beneficial agreements to maintain their strong and enduring partnership.
Strategies for Strengthening Indo-Bhutan Relations:
- To further enhance the bilateral ties between India and Bhutan, several approaches can be adopted to address potential challenges and promote mutual growth such as:
- Diplomatic Engagement: India should regularly discuss with Bhutan to comprehend its evolving foreign policy objectives and concerns.
- Continual support for Bhutan's sovereignty and development needs is vital to allay any apprehensions of India as a threat.
- Expanded Economic Assistance: India can provide increased economic aid, trade advantages, and infrastructural development to shield Bhutan from succumbing to China's debt-trap tactics.
- Fortifying Defense Collaboration: India should address existing impediments in the relationship and reinforce defence and security cooperation with Bhutan to ensure mutual safety and counter potential Chinese influence effectively.
- Promoting Regional Cooperation: India and Bhutan are members of various regional organizations like SAARC, BIMSTEC, and BBIN.
- Strengthening regional cooperation mechanisms will ensure Bhutan's interests are adequately represented in these forums, enhancing overall regional stability and prosperity.
Conclusion
Bhutan is perhaps one of the most important allies that India has in its neighbourhood. Time has proven its relationship with India. However, recent times have witnessed changing dynamics in the Himalayan kingdom’s polity. Focusing on diplomatic engagement, bolstering economic support, strengthening military ties, and fostering regional cooperation will pave the way for a prosperous and secure future. Also, corrective and course-correction measures that are being undertaken by India to implement its Neighbourhood First policy are laudable.
Key Facts about Bhutan:
- Geography: Nestled between India and China, Bhutan is a landlocked country characterized by majestic mountains and verdant valleys.
- Thimphu is the capital city of Bhutan.
- Political System: Bhutan transitioned to democracy in 2008, following its inaugural democratic elections. The King of Bhutan serves as the Head of State.
- Official Name: Referred to as the 'Kingdom of Bhutan', its Bhutanese name is Druk Gyal Khap, translating to the 'Land of the Thunder Dragon'.
- River: The Manas River, stretching over 376 km, holds the title of Bhutan's longest river. It flows through the Himalayan foothills, forming a transboundary river between southern Bhutan and India.
- Government system: Bhutan follows a parliamentary monarchy system.
- Borders: Bhutan shares borders with only two countries: India and Tibet (an autonomous region of China).
Greece’s gateway to Asia, India’s gateway to Europe

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The state visit by Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis to India will be another important step in building a strategic relationship between India and Greece — a process which began with the historic visit of the Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, to Greece in August 2023.
Context:
- The upcoming state visit of Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis to New Delhi signifies a pivotal milestone in the ongoing initiatives to forge a strategic partnership between Greece and India.
- This diplomatic initiative follows the landmark visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Greece in August 2023, which generated enthusiasm among Greek political and business circles.
- The anticipation surrounding the visit of the Greek Prime Minister underscores the mutual dedication to enhancing bilateral relations and collaboration across diverse sectors.
Historical Connections:
- India and Greece share a rich historical bond spanning more than 2500 years, characterized by cultural exchanges and a mutual embrace of democratic values.
- Presently, their bilateral relations are multifaceted, covering political, economic, and military cooperation.
- Trade Routes: Ancient maritime trade routes linked the Indus Valley Civilization with the Aegean region, facilitating the exchange of commodities such as spices, textiles, and intellectual ideas.
- Archaeological evidence, including the discovery of Indus seals in Mesopotamia, suggests the existence of trade connections between the two civilizations.
- Alexander the Great (326 BCE): Alexander's conquest of parts of northwest India fostered cultural and diplomatic exchanges between Greece and India.
- Greek philosophies and ideologies potentially influenced various aspects of Indian art, mathematics, and astronomy during this period.
- Indo-Greek Kingdoms (2nd century BCE – 1st century CE): Hellenistic kingdoms established in northwest India witnessed a fusion of Greek and Indian cultures.
- This blending is evident in Gandhara art, which exhibits Greco-Buddhist influences and serves as a testament to the cultural interplay between the two civilizations.
The Current Status of Bilateral Relations between India and Greece:
- Steady Progress in Bilateral Relations: While India and Greece share a historical connection and mutual enthusiasm, the pace of their bilateral cooperation has been characterized by gradual progress.
- In this context, it is essential to delve into the various facets of collaboration, recognizing both the positive developments and the need for enhanced momentum.
- Military Cooperation: Over time, military collaboration between the two nations has witnessed notable advancements.
- Joint exercises involving the Indian Navy, Indian Air Force, and the Greek armed forces have been conducted, underscoring a shared commitment to fostering mutual understanding and coordination.
- Reciprocal exercises are in the pipeline, illustrating an ongoing endeavour to deepen military bonds.
- These joint military endeavours not only bolster regional security but also signify an increasing level of confidence and collaboration between the armed forces of Greece and India.
- Economic Engagement: On the economic front, there have been significant instances of collaboration signalling a burgeoning partnership.
- For instance, an Indian construction company has joined forces with a prominent Greek construction firm to undertake a significant project: the construction of a new airport on the island of Crete.
- Such initiatives highlight the potential for cross-border investments and partnerships that can contribute to economic development and diversification.
Advancing Economic Reforms And Greece's Role:
- Greece's proactive stance in promoting deeper EU-India relations adds another layer of importance to ongoing economic reforms.
- As Greece endeavours to swiftly finalize the EU-India bilateral trade and investment agreement (BTIA), it underscores its dedication to establishing a conducive environment for heightened economic cooperation.
- The BTIA is poised to act as a catalyst, providing a structured framework for trade and investment, thereby nurturing closer economic bonds between the EU and India.
A Path to Closer Ties: Economic Reforms in Greece
- The economic facet of the Greece-India relationship assumes greater prominence as Greece, under the leadership of Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis, embarks on substantial economic reforms.
- Over the past half-decade, the Mitsotakis administration has implemented measures aimed at steering the Greek economy towards a more sustainable growth trajectory.
- This transformation positions Greece not only as a dependable eastern frontier of the European Union (EU) but also as a potential linchpin in broader geopolitical and economic strategies.
IMEEC Corridor: A Vision of Significance
- As Greece solidifies its role in the Eastern Mediterranean, the concept of establishing the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) emerges as a compelling vision.
- The IMEEC embodies a comprehensive economic initiative aimed at seamlessly connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe, thereby stimulating trade, investment, and economic collaboration.
- This ambitious proposition aligns with the shared vision of both nations to deepen their economic bonds and explore novel avenues for cooperation.
The Geopolitical Significance of the Indo-Greek Relationship:
- A Robust Foundation Rooted in Historical Bonds: The historical backdrop of the evolving ties between Greece and India (with diplomatic relations established in 1950) enriches their contemporary diplomatic endeavours.
- Furthermore, these diplomatic exchanges acquire significance amidst India's ascent as a global power, being perceived not only as an enduring ally but also as a dynamic and influential player on the world stage.
- Contemporary Diplomacy: The momentous visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Greece in August 2023 served as a watershed, laying the groundwork for enhanced collaboration.
- The enthusiasm witnessed in Greece, particularly among political and business circles, underscores the perceived opportunities in forging a strategic partnership with India.
- Strategic Importance of Both Nations' Locations: The geopolitical relevance of this burgeoning relationship is amplified by the strategic locations of Greece and India.
- Situated in regions pivotal to the global system, both nations grapple with geopolitical complexities and volatility.
- Recent events in the Red Sea highlight the interconnectedness of the East Mediterranean, where Greece is positioned, and the Indian Ocean region, accentuating the imperative for collaboration to promote security, stability, and prosperity.
- A Strategic Vision: Gateway to Europe and Asia: The Greek Prime Minister's assertion that "India will find no better gateway to Europe than my country, and for Greece, there is no better gateway to Asia than a close strategic relationship with India" encapsulates the acknowledgement of each nation's unique role in bridging the other's region.
- This pragmatic understanding not only acknowledges geographical realities but also reflects a strategic vision to leverage mutual strengths for collective advancement.
Way Forward to Enhance Indo-Greek Relations:
- Promoting Cross-Cultural Understanding: By expanding university student exchange programs, deliberate steps will be taken to familiarize the younger generation with the cultures, traditions, and educational systems of both nations.
- This fosters not only cross-cultural appreciation but also establishes a groundwork for future collaborations and friendships.
- Fostering Cultural Exchanges: Cultural exchanges serve as a cornerstone in fortifying the bonds between Greece and India.
- Through the promotion of cultural events, exhibitions, and festivals, both countries create platforms for their citizens to immerse themselves in and celebrate the richness of each other's cultural heritage.
- These initiatives act as bridges, connecting hearts and minds, and nurturing a sense of shared identity and mutual respect for cultural diversity.
- Media Collaboration: Bridging Information Gaps: Media collaboration emerges as a pivotal avenue to bridge geographical distances and keep the citizens of both nations abreast of developments, cultural nuances, and societal trends.
- Joint efforts in media, including co-productions, cultural documentaries, and news coverage, facilitate a nuanced understanding of each other's realities.
Conclusion
The swift exchange of visits between the political leadership of Greece and India underscores their commitment and the urgency in advancing their strategic partnership. As the world navigates through a pivotal year in 2024, the onus lies on policymakers and businesses to capitalize on this momentum and fortify the strategic partnership between Greece and India.
Inauguration of BAPS Temple in UAE by PM Modi: Exploring Its Unique Features, Architecture, and Significance (Indian Express)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
During his two-day visit to UAE, Prime Minister Modi will inaugurate the BAPS Swaminarayan temple in Abu Dhabi, the first Hindu temple in the Gulf nation.
Context:
- Prime Minister Modi on Wednesday inaugurated the (BAPS) temple, the first-ever Hindu temple in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- The iconic stone temple is located in Abu Mureikhah, near Al Rahba off the Dubai-Abu Dhabi Sheikh Zayed Highway.
- The inauguration of the 108-ft high temple marks a significant moment for the Hindu community in UAE and the two countries’ bilateral ties.
What is BAPS?
- Bochasanwasi Shri Akshar Purushottam Swaminarayan Sanstha (BAPS) is a socio-spiritual Hindu organisation founded on the principles of practical spirituality.
- The temple was built by the organisation, a denomination of the Swaminarayan Sampradaya, a Vaishnav sect of Hinduism.
- With over 3,850 centres globally, BAPS has garnered national and international recognition, including affiliation with the United Nations.
- Through vows of abstinence and purity, BAPS fosters a foundation for humanitarian endeavours, caring for societies, families, and individuals.
What Does BAPS Do?
- The BAPS Swaminarayan Sanstha views spirituality as its core mission. Through gradual steps, it strives to draw individuals closer to God.
- In collaboration with BAPS Charities, the organization extends its outreach globally, addressing diverse humanitarian needs.
- From education to healthcare and environmental concerns, practical solutions are offered to real-world problems, impacting lives on both macro and micro scales.
- BAPS has a network of around 1,550 temples across the world, including the Akshardham temples in New Delhi and Gandhinagar, and Swaminarayan temples in London, Houston, Chicago, Atlanta, Toronto, Los Angeles, and Nairobi.
Who is Swami Narayan?
- Bhagwan Swaminarayan’s life and work have not only influenced communities in Gujarat, India but have affected change throughout the world.
- He reestablished Hindu Sanatan Dharma, cleansing traditions and rituals of the impurities that had seeped in over time.
- His contributions have been hailed by Hindus and dignitaries of other faiths as truly transforming the lives of millions of individuals.
- He improved societal standards and, most importantly, the innate nature of people, eradicating them from lust, anger, greed, and envy.
- Bhagwan Swaminarayan’s teachings transcended borders, rejuvenating Hindu traditions worldwide.
What are the Features of the (BAPS) Temple?
- The Abu Dhabi temple is a traditional stone Hindu temple with seven shikhars.
- Built in the traditional Nagar style, the temple’s front panel depicts universal values, stories of harmony from different cultures, Hindu spiritual leaders and avatars.
- Spread over 27 acres, the temple complex is on 13.5 acres
- The 13.5 acres of land was gifted by Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the President of the UAE in 2019.
- The height of the temple is 108 ft, its length 262 ft and its width 180 ft.
- While the external facade uses pink sandstone from Rajasthan, the interior uses Italian marble.
- A total of 20,000 tonnes of stones and marble were shipped in 700 containers for the temple.
- More than Rs 700 crore was spent on the temple’s construction.
- The temple has two central domes, Dome of Harmony and Dome of Peace, emphasizing human coexistence through the carvings of earth, water, fire, air, and plants.
- A Wall of Harmony, one of the largest 3D-printed walls in the UAE, features a video showcasing key milestones of the temple’s construction.
- The word ‘harmony’ has been written in 30 different ancient and modern languages.
- The seven shikhars (spires) are representative of the seven Emirates of the UAE.
- Other amenities include an assembly hall with a capacity of 3,000 people, a community centre, exhibitions, classrooms, and a majlis venue.
What are the Key Architectural Features?
- The temple was judged the Best Mechanical Project of the Year 2019 at the MEP Middle East Awards, and the Best Interior Design Concept of the Year 2020.
- Among the key architectural features are 96 bells and galumphs installed around the path leading to the temple.
- These 96 bells are a tribute to Pramukh Swami Maharaj’s 96 years of life.
- Nano tiles have been used, which will be comfortable for visitors to walk on even in the hot weather.
- On the top left of the temple is a stone carving of the scene of Pramukh Swami Maharaj envisioning the temple in Abu Dhabi in 1997.
- Non ferrous material (which is more vulnerable to corrosion) has been used in the temple.
- While many different types of pillars can be seen in the temple, such as circular and hexagonal, there is a special pillar, called the ‘Pillar of Pillars’, which has around 1,400 small pillars carved into it.
- Buildings surrounding the temple are modern and monolithic, with their colour resembling sand dunes.
- Deities from all four corners of India have been featured in the temple.
- These include Lord Ram, Sita, Lakshman and Hanuman, Lord Shiv, Parvati, Ganpati, Kartikeya, Lord Jagannath, Lord Radha-Krishna, Akshar-Purushottam Maharaj (Bhagwan Swaminarayan and Gunatitanand Swami), Tirupati Balaji and Padmavati and Lord Ayappa.
- The temple also has some special features, like a ‘holy river’ surrounding it, for which waters from Ganga and Yamuna have been brought in.
- The river Saraswati has been depicted in the form of white light.
- A Varanasi-like ghat has been created where the ‘Ganga’ passes.
- Apart from 15 value tales from Indian civilisation, stories from the Maya civilisation, Aztec civilisation, Egyptian civilisation, Arabic civilisation, European civilisation, Chinese civilisation and African civilisation have been depicted.
What is the Significance of the Temple?
- A Muslim king donated land for a Hindu Mandir, where the lead architect is a Catholic Christian, the project manager a Sikh, the foundational designer a Buddhist, the construction company a Parsi group, and the director comes from the Jain tradition.
Religious Significance:
- First Hindu stone temple in Abu Dhabi: This marks a historic milestone for the Hindu community in the UAE, providing them with a dedicated place of worship and cultural centre.
- Symbol of religious tolerance: The temple's inauguration signifies the UAE's growing acceptance and appreciation of religious diversity, fostering interfaith dialogue and understanding.
Cultural Significance:
- Strengthens India-UAE ties: The temple stands as a symbol of the strong cultural and diplomatic relations between India and the UAE, promoting mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Promotes Indian culture: The temple serves as a platform to educate the UAE community about Indian art, architecture, and traditions, fostering cultural exchange and appreciation.
Social Significance:
- Provides a sense of belonging: The temple offers a space for the Hindu community to gather, celebrate festivals, and connect with their cultural roots, fostering a sense of belonging and identity.
- Promotes social integration: The temple's open-door policy welcomes people of all faiths, encouraging social interaction and understanding between different communities in the UAE.
- Strengthens social fabric: The temple's emphasis on values like compassion, service, and community engagement contributes to strengthening the social fabric of UAE society.
Overall, the BAPS Swaminarayan Mandir in Abu Dhabi represents a significant step forward in religious tolerance, cultural exchange, and community building in the UAE. It serves as a testament to the growing understanding and appreciation between India and the UAE, and its impact will be felt for generations to come.
