Economic Survey 2024–25
- 01 Feb 2025
In News:
- Released on 31st January 2025, a day before the Union Budget.
- Prepared by the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance.
- Provides a comprehensive review of India’s macroeconomic trends, sectoral developments, and key policy challenges.
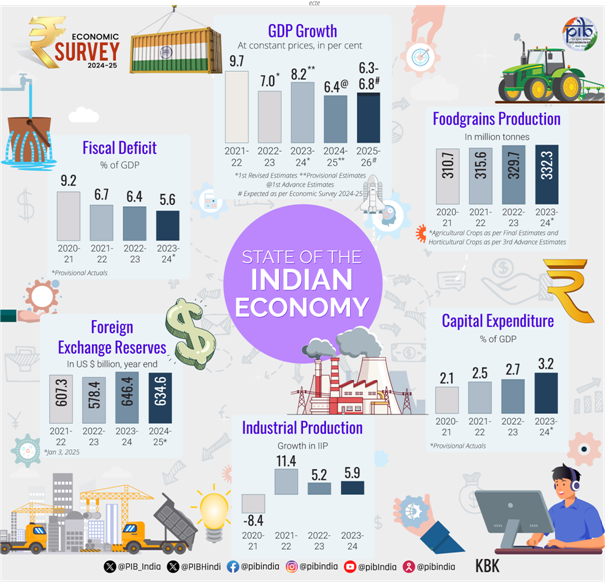
- Real GDP growth estimated at 6.4% in FY25 (close to decadal average); projected between 6.3–6.8% in FY26.
- Reflects India's resilience amidst global slowdown, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical uncertainties.
Sector-wise Performance
Agriculture:
- Expected growth: 3.8% in FY25.
- Record Kharif foodgrain production: 1647.05 LMT (+5.7% YoY).
- Growth driven by horticulture, livestock, and fisheries.
- Supported by above-normal monsoons and robust reservoir levels.
Industry:
- Estimated growth: 6.2% in FY25.
- Construction, utilities, and mining contribute significantly.
- Challenges: Sluggish export demand, climate disruptions, and festival timing variations.
- Manufacturing PMI remains in the expansionary zone.
Services:
- Robust growth: 7.2% in FY25.
- Services exports up by 12.8% (April–Nov FY25) vs 5.7% in FY24.
- Growth led by finance, real estate, public administration, and professional services.
Inflation and Price Stability
- Retail inflation eased to 4.9% (Apr–Dec 2024) from 5.4% (FY24).
- Food inflation remains high at 8.4%, driven by pulses and vegetables.
- CPI expected to align with RBI's 4% target by FY26.
Investment and Infrastructure
- Capital Expenditure grew 8.2% YoY (Jul–Nov 2024); sustained increase since FY21.
- Infrastructure momentum:
- 2031 km railways commissioned (Apr–Nov 2024).
- 17 Vande Bharat trains introduced.
- Port efficiency improved; container turnaround time reduced from 48.1 to 30.4 hours.
- Renewable energy capacity rose by 15.8% YoY (Dec 2024).
External Sector and Trade
- Overall exports grew by 6% (Apr–Dec 2024); merchandise exports up 1.6%.
- Services exports surged; India now 7th largest globally.
- FDI inflows: $55.6 billion (Apr–Nov FY25), +17.9% YoY.
- Forex reserves at $640.3 billion (Dec 2024), covering 10.9 months of imports and 90% of external debt.
- CAD contained at 1.2% of GDP in Q2 FY25.
- Strong remittance inflows support BOP stability.
Fiscal Health
- Gross Tax Revenue rose 10.7% YoY (Apr–Nov 2024).
- Stable deficit indicators allowed for developmental expenditure.
- State revenue expenditure grew 12%, with subsidies increasing by 25.7%.
Banking, Credit, and Financial Markets
- Gross NPAs dropped to 2.6% (lowest in 12 years).
- CRAR of scheduled banks at 16.7% (Sept 2024), well above regulatory norms.
- Stock market cap to GDP ratio: 136%, higher than China (65%) and Brazil (37%).
- Credit-GDP gap reduced to -0.3% in Q1 FY25 (from -10.3% in Q1 FY23).
Employment and Labour Market
- Unemployment rate declined to 3.2% (2023-24) from 6.0% (2017-18).
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) and Worker-Population Ratio (WPR) improved.
- Emphasis on AI skill development to future-proof labour markets.
Health, Education & Social Sector
- Government health expenditure rose from 29% to 48% of total health spending (FY15–FY22).
- Out-of-pocket expenditure dropped from 62.6% to 39.4% in the same period.
- Education reforms aligned with NEP 2020 via programs like Samagra Shiksha, DIKSHA, PM SHRI, etc.
- Social services spending grew at 15% CAGR (FY21–FY25).
- Decline in Gini coefficient indicates improving consumption equality.
Policy Recommendations and Reform Agenda
- Deregulation as central theme to boost productivity and EoDB.
- Advocates Ease of Doing Business 2.0, led by states, targeting:
- Simplification of compliance norms.
- Risk-based regulation.
- Reduction in tariffs and licensing hurdles.
- ?50,000 crore Self-Reliant India Fund launched for MSME equity support.
- Need for long-term infrastructure investment to achieve Viksit Bharat@2047.
Global Backdrop
- Global GDP grew by 3.3% in 2023, with an average 3.2% growth projected over next five years (IMF).
- Weak global manufacturing; services sector remains stronger.
- Risks: Geopolitical tensions, trade policy fragmentation, energy transition dependence on China.
Way Forward
- Balanced outlook for FY26 with upside from:
- Strong rural demand.
- Agricultural recovery.
- Easing food inflation.
- Challenges include:
- Geopolitical tensions.
- Global trade and commodity price volatility.
- Delay in private investment materialisation.
