What are the Pollutants in Our Air, and How They Impact Health (Indian Express)
- 08 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Rising pollution levels in north India have led to focus returning on the Air Quality Index (AQI) score, a measure of air pollution.
Context:
- The escalating pollution in northern India has once again drawn attention to the Air Quality Index (AQI) score, which gauges air pollution levels.
- On Monday, Delhi, for instance, registered an AQI score exceeding 400.
- This categorizes the air quality as 'severe,' with any reading above 100 indicating at least a moderate level of pollution on the index.
What is the Air Quality Index (AQI)?
- AQI is a number, which is a measure of air quality.
- The higher the AQI, the worse the air.
- The color-coded AQI index was launched in India in 2014, and it helps the public and the government understand the condition of the air and what subsequent measures are to be taken to combat the situation, based on its severity.
- According to the Central Pollution Control Board, part of the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change, the AQI transforms complex air quality data of various pollutants into a single number (index value), nomenclature, and color.
- The pollutants measured include PM 10, PM 2.5, Nitrogen Dioxide, Ozone, Carbon, etc.
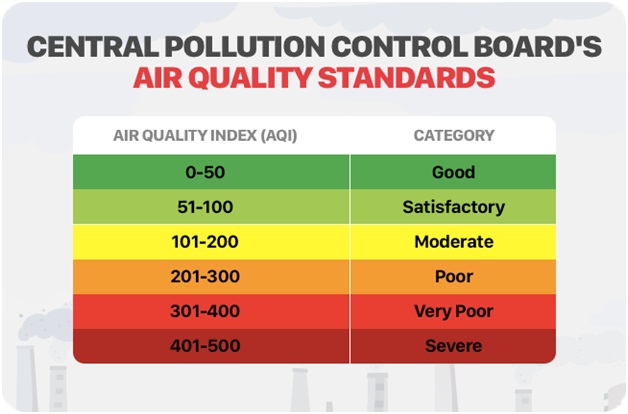
- There are six categories of AQI, namely ‘Good’ (0-50), ‘Satisfactory’ (51-100), ‘Moderately polluted’ (101-200), ‘Poor’ (201-300), ‘Very Poor’ (301-400), and ‘Severe’ (401-500).
How Pollutants Impact Our Health?
PM 10 and PM 2.5
- These are extremely fine particulate matter (PM) particles, with the digits accompanying them referring to their diameter.
- So, PM 10 and PM 2.5 are smaller than 10 and 2.5 microns in their diameter, respectively.
- One micron is about a thousandth of a millimeter and this tiny size has a role to play in how they impact human health.
- The finer the particles are, the more difficult it gets to protect oneself from them.
- Due to their size, the PM 2.5 particles can easily bypass the nose and throat and can enter the circulatory system.
- The particles can also lead to chronic diseases such as asthma, heart attack, bronchitis, and other respiratory problems.
- Byproducts of emissions from factories, vehicular pollution, construction activities, and road dust, such particles are not dispersed and stay suspended in the air that we breathe.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) gets in the air from the burning of fuel, with sources including emissions from vehicles and power plants.
- Short-term exposure to high levels of NO2 can aggravate respiratory diseases like asthma, and lead to other problems such as coughing or difficulty in breathing.
- Long-term exposure may also contribute to the development of asthma and could increase susceptibility to respiratory infections.
Ozone (O3)
- Ozone is a gas that is present in the upper layers of the atmosphere, protecting human health from the impact of the Sun’s UV rays.
- However, surface-level ozone is among the most significant air pollutants. It is formed by the reaction of atmospheric pollutants in the presence of sunlight.
- According to the International Journal of Medical Public Health, with the increase in surface ozone levels, there is a likelihood of an increase in the risk of hospital admissions for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD) and the number of cardiovascular and respiratory deaths.
Sulphur Dioxide (SO2)
- The largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels by power plants and other industrial facilities.
- Additional sources are industrial processes and natural sources such as volcanoes.
- As with other gases, SO2 exposure is harmful to the cardiovascular system and can lead to the development of respiratory illnesses.
- SO2 can also react with other compounds to form particulate matter.
- At high concentrations, gaseous SOx can harm trees and plants by damaging foliage and decreasing growth.
Ammonia (NH3)
- A 2017 NASA-funded study said that in India, “A broad increase in fertilizer use coupled with large contributions from livestock waste have resulted in the world’s highest concentrations of atmospheric ammonia.”
- While gaseous ammonia is a natural part of Earth’s nitrogen cycle, excess ammonia is harmful to plants and reduces air and water quality.
- In the troposphere –where all weather takes place and where people live – ammonia gas reacts with nitric and sulfuric acids to form nitrate-containing particles.
- Those particles contribute to aerosol pollution that is damaging to human health.
- Ammonia gas can also fall back to Earth and enter lakes, streams, and oceans, where it contributes to harmful algal blooms and “dead zones” with dangerously low oxygen levels.
Lead (Pb)
- Lead is a naturally occurring toxic metal found in the Earth’s crust. But in increased quantities, exposure to it becomes extremely dangerous to health.
- Important sources of environmental contamination come from mining, smelting, manufacturing and even recycling activities.
- Young children are particularly vulnerable to lead poisoning because they absorb four to five times as much ingested lead as adults from a given source.
- Children who survive severe lead poisoning may be left with permanent intellectual disability and behavioral disorders.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- A toxic, colorless, and odorless gas, it is given off when fuel containing carbon, such as wood, coal, and petrol, is burned.
- If CO levels are high enough, a person may become unconscious and die. Long-term exposure has been linked with an increased risk of heart disease.
