Does Data Justify Subdivision of Quotas?
- 05 Nov 2024
Context
India's reservation system has long been a tool for uplifting historically marginalized communities, especially Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs). However, recent debates have questioned whether the system serves its intended purpose, particularly in light of disparities within the SC groups. The need for a ‘quota-within-quota’ system has been raised to ensure more equitable outcomes across different SC subgroups.
The Reservation System: Origins and Objectives
Purpose of Reservations
- Historical Background: Established to correct centuries of social and economic exclusion faced by SCs and STs.
- Mechanism for Equality: Aimed to create opportunities in education, government employment, and public offices for historically marginalized groups.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s Vision: Reservations were designed to transition from formal legal equality to substantive equality.
Challenges of the Current System
- Despite progress, certain SC subgroups seem to have benefited more than others.
- A Supreme Court ruling has led to calls for a 'quota-within-quota' to address intra-SC disparities.
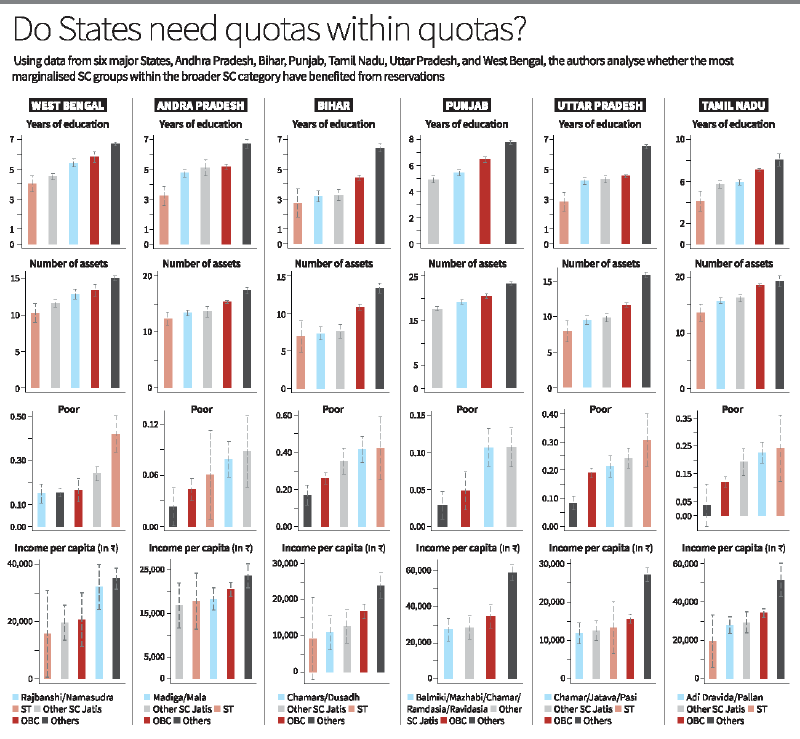
Exploring Intra-SC Disparities: The Data Analysis
States Examined
- Key States: Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- Objective: To investigate whether some SC subgroups have disproportionately benefited from the reservation system.
Findings Across States
- Andhra Pradesh: Minor differences between SC groups (Malas vs. Madigas), with both groups showing similar socio-economic progress.
- Tamil Nadu: No significant disparity between Adi Dravida and Pallan groups, both benefiting equally from reservations.
- Punjab: Subdivision of quotas since 1975 has led to better outcomes for disadvantaged groups like Mazhabi Sikhs and Balmikis.
- Bihar: The Mahadalit category, introduced in 2007, failed due to political intervention, undermining the policy’s goals.
Key Insights
- In some states (e.g., Punjab), a subdivision of quotas has been effective in addressing intra-SC disparities.
- In other states, like Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, the benefits of reservations are already distributed fairly evenly among SC subgroups.
- The gap between SCs and upper-caste groups remains much larger than the gap within SCs.
The Issue of Access to Reservations
Caste Certificates as a Proxy for Access
- Data from IHDS: Less than 50% of SC households in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar report having caste certificates, limiting access to reserved positions.
- Better Access in Some States: Over 60-70% of SC households in Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh have caste certificates.
Core Issue: Ensuring Access
- Access Challenges: Without proper access to caste certificates, many SCs are excluded from the benefits of the reservation system.
- Priority Area: Ensuring that all eligible SCs have access to reservations is a critical concern before considering subdivision.
The 'Quota-within-Quota' Proposal
Concept and Potential Benefits
- Targeted Assistance: A ‘quota-within-quota’ would provide more focused help to the most disadvantaged SC subgroups, as seen in Punjab.
- Political Considerations: However, the political motivations behind quota subdivision, as seen in Bihar, can undermine the policy’s effectiveness.
Criticism and Limitations
- Uneven Need for Subdivision: In many states, the need for further subdivision is minimal, as the benefits of reservations are already fairly distributed.
- Political Exploitation: The policy risks becoming a political tool rather than a genuine means of achieving social justice, as political influence often determines who is categorized as the most disadvantaged.
Addressing Inequality Beyond Reservations
Income-Based Criteria and Monetary Benefits
- Current Approach: Monetary benefits (e.g., scholarships, lower fees) are a part of the affirmative action system.
- Income Criterion: Should be used to determine eligibility for monetary benefits to focus assistance on those most in need.
The "Creamy Layer" Debate
- Supreme Court’s Suggestion: The introduction of a "creamy layer" exclusion for SCs, akin to the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) model, remains contentious and requires stronger evidence.
Challenges of Economic Mobility
- Stigma and Discrimination: Economic progress does not necessarily eliminate social stigma or discrimination, especially for historically marginalized groups.
- Long-Term Goal: While reservations have contributed to creating a Dalit middle class, addressing stigma will require a gradual process.
The Need for Updated Data and Evidence-Based Policy
Data Deficiency
- Lack of Comprehensive Data: The absence of updated, reliable data on caste-based disparities limits the effectiveness of any policy reform.
- National Census Delay: India’s national Census, the only source of comprehensive data on caste, has been delayed, exacerbating the problem.
Evidence-Driven Reform
- Importance of Data: Robust and up-to-date data is essential to assess the true impact of reservations and to make informed policy decisions.
Conclusion: Reforming the Reservation System
- Reservations’ Success: The reservation system has played a significant role in improving the socio-economic status of SCs and STs.
- Intra-SC Disparities: While some subgroups benefit more than others, the broader gap between SCs and upper-caste groups remains far more pronounced.
- Focus on Access: The primary focus should be on improving access to reservations, ensuring that all eligible SCs benefit fully from affirmative action.
