Gaganyaan Human Spaceflight Mission (The Hindu)
- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully carried out two more hot tests on the Gaganyaan Service Module Propulsion System (SMPS) at ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC), Mahendragiri (Tirunelveli District), Tamil Nadu.
About Gaganyaan Mission:
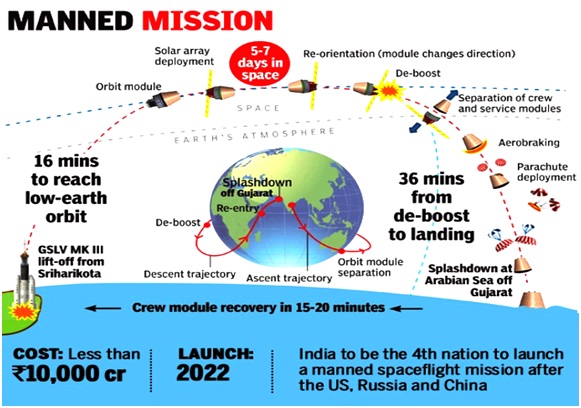
- The Gaganyaan program is an indigenous manned mission aiming to send Indian astronauts to space.
- As part of the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme, this Indian crewed orbital spacecraft plans to carry 3 astronauts to space by the end of 2023 or in 2024.
- Upon its successful execution, India will become the 4th nation after US, Russia and China to achieve a Human Spaceflight Mission.
- It is launched by ISRO's Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle GSLV Mk III (3 stages heavy-lift vehicle).
What is the Significance of Gaganyaan Mission for India:
- Self-reliance and Make in India: The Gaganyaan mission contributes to India's aspiration of achieving self-reliance by boosting the Make in India initiative, reducing reliance on external support for satellite launches.
- Advancing R&D and Robotics: The mission propels scientific and technological research and development, especially in space exploration, facilitating India's long-term and cost-effective plans for robotic and human exploration beyond the solar system.
- Addressing Regional Demands: Gaganyaan's focus on regional requirements becomes essential, given the limited availability of International Space Stations (ISS) worldwide, making it a relevant initiative for regional space exploration.
- Strengthening International Ties: By promoting collaborative and peaceful endeavors, the Gaganyaan mission fosters international partnerships and contributes to global security.
- Boost to Academic Organizations: The Gaganyaan Programme is a collective national endeavor, fostering active involvement from academia and National Agencies. It will establish an extensive framework for collaboration, uniting ISRO, academia, industry, national agencies, and other scientific organizations in a collaborative effort.
- Elevated Prestige: Gaganyaan's successful mission will position India as the 4th country to achieve human spaceflight, elevating the nation's prestige on the global stage. Also, it will solidify India's significant role as a key player in the space industry.
Challenges in the Mission:
- Launch Reliability: The GSLV Mk III requires significant modifications to meet human-rated and fail-safe criteria, with the challenge of achieving a reliability of 98% or higher, posing a daunting task.
- Crew Escape System: Developing a reliable crew escape system is crucial to prepare for emergencies from the launch phase onwards. The Environmental Control & Life Support System (ELCSS), space suit, and crew support systems are still in the developmental stage.
- Astronaut Training: India lacks facilities for comprehensive training, including centrifuges to simulate g-forces and aircraft for zero-gravity simulations, posing a hurdle in preparing astronauts adequately.
- Threat of Space Debris: The increasing threat of space debris in low earth orbits raises concerns about potential collisions with small debris, leading to cabin depressurization in the crew module.
- Financial Implications: Human space flight missions are not one-time investments but an ongoing pursuit with national benefits, raising financial concerns regarding long-term funding requirements.
Problems Faced by Gaganyaan Astronauts:
- Environmental Hazards: Astronauts encounter radiation risks and navigate a hostile space environment devoid of gravity and atmosphere.
- Artificial Atmosphere: Two primary options for creating a suitable atmosphere are pure oxygen or a combination of oxygen and an inert gas like nitrogen, helium, or argon.
- Medical Issues: Microgravity can impact hand-eye and head-eye coordination, orientation, vision, muscle strength, aerobic capacity, etc. Additionally, isolation and reliance on limited resources may lead to behavioral issues such as depression, cabin fever, fatigue, sleep disorders, and psychiatric disorders.
- Aerospace Technology Challenges: Space travel demands significantly higher speeds than regular air travel, with rockets accelerating to approximately 25,000 km per hour within minutes. Launch, pre-launch, and post-launch periods pose potential risks, including rocket malfunctions.
Way Forward for India's Space Programme:
- Private Sector Involvement: Encouraging the participation of the private sector in supporting ISRO and developing critical space technologies is vital.
- Promoting Youth Engagement: Initiating campaigns and media outreach to stimulate the interest of young individuals in space activities will help nurture future talent.
- Continued Government Support: The government should persist in its encouragement and support of ISRO's endeavors, while also engaging the private sector in space activities.
Pursuing a manned space programme becomes the logical progression for India. Gaganyaan's success will elevate India to the elite club of space superpowers and pave the way for developing its own space station. Overcoming technological challenges is crucial for ensuring the safety and success of future manned missions.
International Collaboration: Collaboration with other nations will be essential for acquiring the necessary technologies and expertise to further India's space exploration goals.
