C Raja Mohan writes: A time for para diplomacy
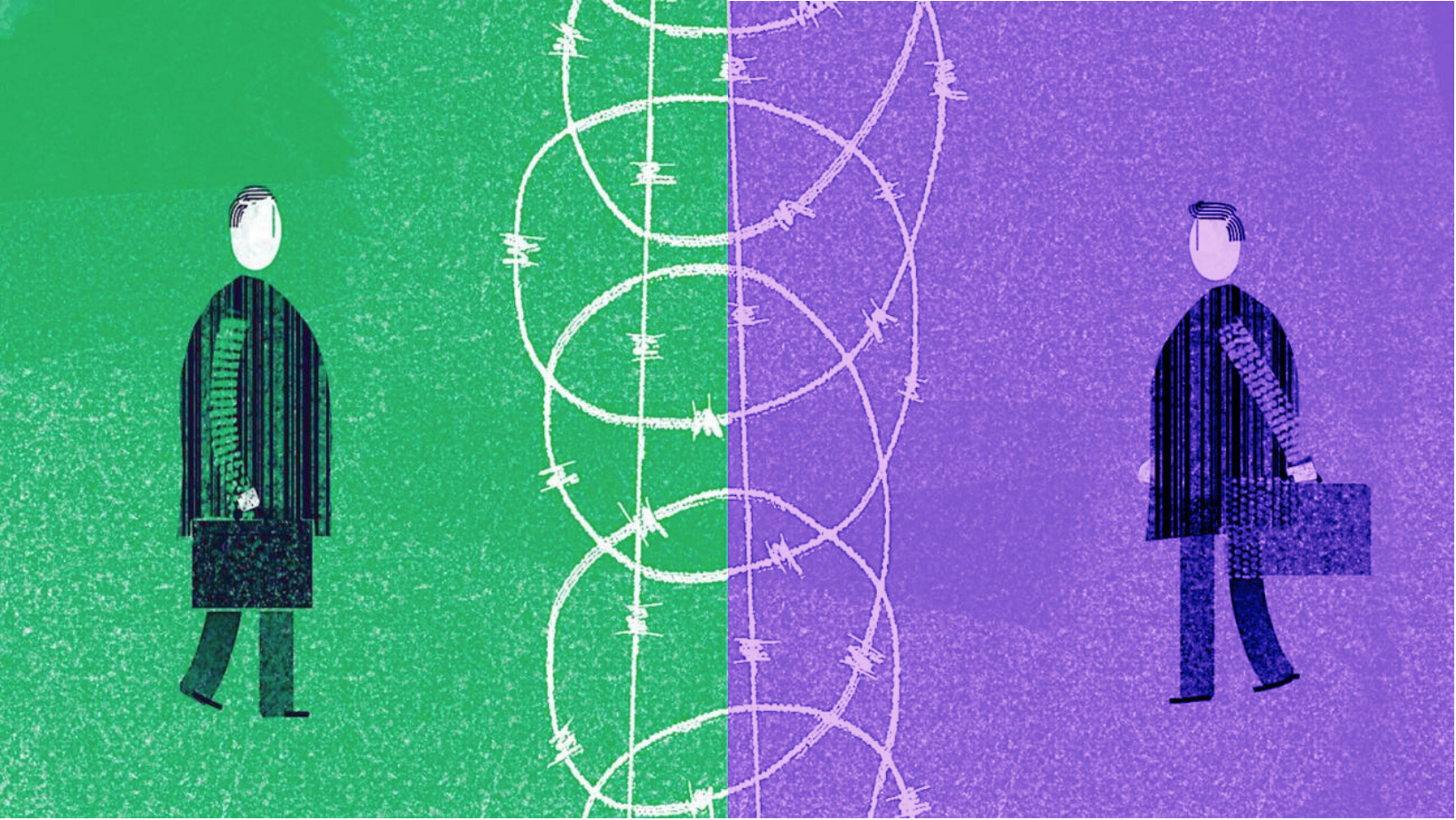
- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Shiromani Akali Dal came out with its poll manifesto and said it would seek the transfer of Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan to India through mutual land exchange between the two countries.
Context:
- The Shiromani Akali Dal's (SAD) proposal to retrieve Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan through a negotiated territory exchange reflects a growing desire to transform the India-Pakistan border from a zone of conflict to one of cooperation and economic integration.
- This idea might appear as unlikely as the Bharatiya Janata Party's (BJP) pledge to integrate Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) into India.
- Nonetheless, it signifies a profound aspiration to transform the India-Pakistan border from a contentious zone into one characterized by cooperation and economic integration.
What is Para Diplomacy?
Origins of Paradiplomacy:
- The concept of para-diplomacy was first proposed in 1990 by John Kincaid, an American scholar who outlined a foreign policy role for local governments within a democratic federal system.
- Economic para diplomacy related to trade and investment in particular has become an institutionalised practice across the world – in federal states like the United States, Canada and Belgium, quasi-federal states like Spain, non-federal states like Japan and even non-democratic states like the People’s Republic of China.
Aims and Objectives of Paradiplomacy:
- Paradiplomacy can be employed with a variety of aims which can range from bringing in a decentralised dimension to international debates to internationalisation of domestic issues by bringing regional issues onto the global stage, promoting trade, tourism, cultural ties and even post-conflict reconciliation to local political activism being sought for international support.
- Subnational relations can also be conducted to promote and attract investments seeking region-specific economic advantages.
Drivers of Paradiplomacy:
- In more ways than one, paradiplomacy owes its origins to globalisation.
- As the world economy has become increasingly global and increasingly integrated in a variety of ways, sub-national units (regions, states, provinces and even cities) find their functions and activities circumscribed by the global system.
- Federalism is also a key contributor to the growth of paradiplomacy.
- Sub-national actors such as states and provinces that have a formal legal personality are necessarily more likely to engage in international activities designed to promote and protect local and international interests and prerogatives.
What are the Challenges Associated with BJP and SAD’s Territorial Ambitions?
- Practical Hurdles in BJP and SAD's Territorial Objectives: The proposals put forth by the SAD to renegotiate the Radcliffe Line in Punjab or the BJP's assertion to reclaim PoK face numerous challenges.
- Altering the territorial status quo in Punjab or reclaiming PoK, whether through diplomatic negotiations or by force, presents formidable obstacles.
- Complexities and Resistance: Such endeavours would not merely disrupt the already delicate territorial equilibrium but also provoke substantial opposition, given the deep-rooted historical and ongoing tensions between India and Pakistan.
- Pursuing a Pragmatic Approach: A more viable alternative lies in reimagining these borders as conduits for trade and collaboration rather than confrontation.
- This pragmatic stance resonates with the SAD's additional proposal to reopen the Attari and Hussainiwala borders with Pakistan for trade and tourism, with the aim of fostering economic prosperity in the region.
Obstacles Hindering Economic Cooperation Between India and Pakistan:
- Political and Military Resistance in Pakistan: One of the foremost barriers to economic cooperation stems from the entrenched position of Pakistan's military and political establishment.
- Over the years, the Pakistani military's steadfast opposition to economic engagement with India, primarily due to unresolved issues surrounding Kashmir, has been a significant deterrent.
- Despite occasional signs of thaw, such as the February 2021 ceasefire agreement, internal resistance has consistently impeded progress.
- Even Prime Minister Imran Khan's tentative consideration of resuming trade ties with India faced vehement opposition, highlighting the deep-seated reluctance to normalize relations without addressing the Kashmir dispute.
- Historical Context and Suspicion: The historical animosities dating back to the traumatic partition of 1947 and subsequent wars have entrenched mutual suspicion and distrust between the two nations.
- These historical grievances have not only shaped national narratives but also influenced contemporary policy decisions.
- Addressing underlying political tensions becomes imperative for either country to fully commit to economic cooperation.
- Lack of Reciprocal Trade Policies: On the trade front, Pakistan's refusal to grant India the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status remains a significant hurdle.
- While India extended this status to Pakistan in 1996 to foster trade ties, the gesture was not reciprocated.
- Subsequent events, such as India's withdrawal of MFN status post the Pulwama terror attack and the revocation of Jammu and Kashmir's special constitutional status, have further strained bilateral trade relations.
- Economic Rationality vs. Political Baggage: Despite the evident economic benefits of trade, Pakistan's establishment remains wary of engaging with India due to historical conflicts and the overarching Kashmir issue.
- While there have been instances where the Pakistani business community advocated for resuming trade ties, such appeals often faced resistance from the political and military elite, who prioritize geopolitical concerns over economic pragmatism.
- Regional Stability and Security Concerns: Security concerns, including allegations of cross-border terrorism, complicate the economic relationship between India and Pakistan.
- Heightened military vigilance and frequent skirmishes along the border hinder trade and perpetuate an environment of hostility and mistrust.
- The ongoing conflict and the threat of terrorist activities cast a shadow over efforts to normalize trade relations.
Proposing a New Strategy for Improving India-Pakistan Relations:
- Introduction of Special Economic Zones: A significant aspect of the SAD's manifesto is the proposition to convert the Punjab border into a special economic zone, aiming to nurture small and medium enterprises and potentially revolutionize India-Pakistan relations.
- This innovative vision encompasses the idea of Pakistan establishing a parallel zone on its side, fostering integrated development and economic interdependence.
- Drawing inspiration from successful models of cross-border economic zones in Southeast Asia and China's collaborative initiatives with neighbouring countries, such an endeavour holds promise for fostering mutual prosperity.
- Leveraging Para Diplomacy: At the heart of these proposals lies the concept of para diplomacy, or sub-state diplomacy, wherein provincial and local governments engage in formal interactions to advance national interests.
- This approach offers a novel means to navigate around the entrenched positions often held by national governments, presenting fresh avenues for cooperation.
- While historical attempts at para diplomacy between East and West Punjab have surfaced intermittently, they have struggled to endure amidst overarching national conflicts.
- Embracing these innovative strategies could pave the way for a constructive dialogue and sustainable cooperation between India and Pakistan, fostering mutual understanding and prosperity in the region.
Fostering Consensus and Cooperative Federalism for Sustainable India-Pakistan Relations:
- To foster sustainable and productive economic cooperation between India and Pakistan, nurturing a robust consensus between the central government and state governments, particularly those in the border regions, is imperative.
- This collaborative approach, known as cooperative federalism, holds the key to innovative diplomatic strategies that prioritize the interests of local populations.
- India's federal structure has historically grappled with tensions between the central and state governments, particularly concerning foreign policy and cross-border cooperation.
- The diverse political landscapes across Indian states often give rise to conflicting interests and priorities.
- For example, West Bengal's interactions with Bangladesh have been marked by complexities stemming from differing perspectives between the state leadership and the central government.
- Similarly, Tamil Nadu's influence on India's policies towards Sri Lanka has been substantial, occasionally complicating bilateral relations due to the state's concerns for the Tamil population in Sri Lanka.
- Cooperative federalism entails the harmonious collaboration of national and state governments to achieve shared objectives while respecting the autonomy of state governments.
- By aligning state objectives with national interests, this approach offers a pragmatic framework for managing border relations and fostering economic cooperation with neighbouring countries.
- Embracing consensus and cooperative federalism is paramount for forging a path towards peace, stability, and prosperity in the region, laying the groundwork for enduring and mutually beneficial relations between India and Pakistan.
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Shiromani Akali Dal came out with its poll manifesto and said it would seek the transfer of Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan to India through mutual land exchange between the two countries.
Context:
- The Shiromani Akali Dal's (SAD) proposal to retrieve Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan through a negotiated territory exchange reflects a growing desire to transform the India-Pakistan border from a zone of conflict to one of cooperation and economic integration.
- This idea might appear as unlikely as the Bharatiya Janata Party's (BJP) pledge to integrate Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) into India.
- Nonetheless, it signifies a profound aspiration to transform the India-Pakistan border from a contentious zone into one characterized by cooperation and economic integration
What is Para Diplomacy?
Origins of Paradiplomacy:
- The concept of para-diplomacy was first proposed in 1990 by John Kincaid, an American scholar who outlined a foreign policy role for local governments within a democratic federal system.
- Economic para diplomacy related to trade and investment in particular has become an institutionalised practice across the world – in federal states like the United States, Canada and Belgium, quasi-federal states like Spain, non-federal states like Japan and even non-democratic states like the People’s Republic of China.
Aims and Objectives of Paradiplomacy:
- Paradiplomacy can be employed with a variety of aims which can range from bringing in a decentralised dimension to international debates to internationalisation of domestic issues by bringing regional issues onto the global stage, promoting trade, tourism, cultural ties and even post-conflict reconciliation to local political activism being sought for international support.
- Subnational relations can also be conducted to promote and attract investments seeking region-specific economic advantages.
Drivers of Paradiplomacy:
- In more ways than one, paradiplomacy owes its origins to globalisation.
- As the world economy has become increasingly global and increasingly integrated in a variety of ways, sub-national units (regions, states, provinces and even cities) find their functions and activities circumscribed by the global system.
- Federalism is also a key contributor to the growth of paradiplomacy.
- Sub-national actors such as states and provinces that have a formal legal personality are necessarily more likely to engage in international activities designed to promote and protect local and international interests and prerogatives.
What are the Challenges Associated with BJP and SAD’s Territorial Ambitions?
- Practical Hurdles in BJP and SAD's Territorial Objectives: The proposals put forth by the SAD to renegotiate the Radcliffe Line in Punjab or the BJP's assertion to reclaim PoK face numerous challenges.
- Altering the territorial status quo in Punjab or reclaiming PoK, whether through diplomatic negotiations or by force, presents formidable obstacles.
- Complexities and Resistance: Such endeavours would not merely disrupt the already delicate territorial equilibrium but also provoke substantial opposition, given the deep-rooted historical and ongoing tensions between India and Pakistan.
- Pursuing a Pragmatic Approach: A more viable alternative lies in reimagining these borders as conduits for trade and collaboration rather than confrontation.
- This pragmatic stance resonates with the SAD's additional proposal to reopen the Attari and Hussainiwala borders with Pakistan for trade and tourism, with the aim of fostering economic prosperity in the region.
Obstacles Hindering Economic Cooperation Between India and Pakistan:
- Political and Military Resistance in Pakistan: One of the foremost barriers to economic cooperation stems from the entrenched position of Pakistan's military and political establishment.
- Over the years, the Pakistani military's steadfast opposition to economic engagement with India, primarily due to unresolved issues surrounding Kashmir, has been a significant deterrent.
- Despite occasional signs of thaw, such as the February 2021 ceasefire agreement, internal resistance has consistently impeded progress.
- Even Prime Minister Imran Khan's tentative consideration of resuming trade ties with India faced vehement opposition, highlighting the deep-seated reluctance to normalize relations without addressing the Kashmir dispute.
- Historical Context and Suspicion: The historical animosities dating back to the traumatic partition of 1947 and subsequent wars have entrenched mutual suspicion and distrust between the two nations.
- These historical grievances have not only shaped national narratives but also influenced contemporary policy decisions.
- Addressing underlying political tensions becomes imperative for either country to fully commit to economic cooperation.
- Lack of Reciprocal Trade Policies: On the trade front, Pakistan's refusal to grant India the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status remains a significant hurdle.
- While India extended this status to Pakistan in 1996 to foster trade ties, the gesture was not reciprocated.
- Subsequent events, such as India's withdrawal of MFN status post the Pulwama terror attack and the revocation of Jammu and Kashmir's special constitutional status, have further strained bilateral trade relations.
- Economic Rationality vs. Political Baggage: Despite the evident economic benefits of trade, Pakistan's establishment remains wary of engaging with India due to historical conflicts and the overarching Kashmir issue.
- While there have been instances where the Pakistani business community advocated for resuming trade ties, such appeals often faced resistance from the political and military elite, who prioritize geopolitical concerns over economic pragmatism.
- Regional Stability and Security Concerns: Security concerns, including allegations of cross-border terrorism, complicate the economic relationship between India and Pakistan.
- Heightened military vigilance and frequent skirmishes along the border hinder trade and perpetuate an environment of hostility and mistrust.
- The ongoing conflict and the threat of terrorist activities cast a shadow over efforts to normalize trade relations.
Proposing a New Strategy for Improving India-Pakistan Relations:
- Introduction of Special Economic Zones: A significant aspect of the SAD's manifesto is the proposition to convert the Punjab border into a special economic zone, aiming to nurture small and medium enterprises and potentially revolutionize India-Pakistan relations.
- This innovative vision encompasses the idea of Pakistan establishing a parallel zone on its side, fostering integrated development and economic interdependence.
- Drawing inspiration from successful models of cross-border economic zones in Southeast Asia and China's collaborative initiatives with neighbouring countries, such an endeavour holds promise for fostering mutual prosperity.
- Leveraging Para Diplomacy: At the heart of these proposals lies the concept of para diplomacy, or sub-state diplomacy, wherein provincial and local governments engage in formal interactions to advance national interests.
- This approach offers a novel means to navigate around the entrenched positions often held by national governments, presenting fresh avenues for cooperation.
- While historical attempts at para diplomacy between East and West Punjab have surfaced intermittently, they have struggled to endure amidst overarching national conflicts.
- Embracing these innovative strategies could pave the way for a constructive dialogue and sustainable cooperation between India and Pakistan, fostering mutual understanding and prosperity in the region.
Fostering Consensus and Cooperative Federalism for Sustainable India-Pakistan Relations:
- To foster sustainable and productive economic cooperation between India and Pakistan, nurturing a robust consensus between the central government and state governments, particularly those in the border regions, is imperative.
- This collaborative approach, known as cooperative federalism, holds the key to innovative diplomatic strategies that prioritize the interests of local populations.
- India's federal structure has historically grappled with tensions between the central and state governments, particularly concerning foreign policy and cross-border cooperation.
- The diverse political landscapes across Indian states often give rise to conflicting interests and priorities.
- For example, West Bengal's interactions with Bangladesh have been marked by complexities stemming from differing perspectives between the state leadership and the central government.
- Similarly, Tamil Nadu's influence on India's policies towards Sri Lanka has been substantial, occasionally complicating bilateral relations due to the state's concerns for the Tamil population in Sri Lanka.
- Cooperative federalism entails the harmonious collaboration of national and state governments to achieve shared objectives while respecting the autonomy of state governments.
- By aligning state objectives with national interests, this approach offers a pragmatic framework for managing border relations and fostering economic cooperation with neighbouring countries.
- Embracing consensus and cooperative federalism is paramount for forging a path towards peace, stability, and prosperity in the region, laying the groundwork for enduring and mutually beneficial relations between India and Pakistan.
Conclusion
Irrespective of its political orientation, the upcoming Indian government should regard para-diplomacy as a strategic asset in its foreign policy arsenal. This approach demands not only robust dialogue between the central government and the border provinces but also concerted efforts to align the interests of the inhabitants of these regions with broader national objectives. By embracing para diplomacy, India can lay the groundwork for a more harmonious and economically fruitful relationship with Pakistan, turning contentious borders into conduits of cooperation.
Critical Times Call for Strong Judicial Adjudication

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The process of judicial review should be strong, immediate, and unambiguous in the case of statutes that are obviously unconstitutional or divisive.
Context:
- The role of judicial review has become increasingly significant in contemporary times.
- The Supreme Court of India is currently examining a crucial case regarding the constitutionality of the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) and its associated rules.
- The ambiguity in these rules has raised concerns, especially for applicants whose citizenship requests have been denied, highlighting the urgent need for redress.
- Additionally, the issue of dual citizenship for foreign applicants, without renouncing their original citizenship, has created a conflict with the law.
- This ambiguity goes against the Parent Act's spirit, as some petitioners pointed out.
Legislative Malice, Judicial Review, and the Challenge of Populist Regimes:
- Constitutional courts do not routinely interdict statutes or statutory rules, as laws passed by Parliament are generally presumed valid unless proven to contravene constitutional provisions.
- Moreover, the legal doctrine maintains that malice cannot typically be attributed to the legislative process, as established in Manish Kumar vs Union of India (2021).
- In Gurudevdatta Vikoos Maryadit vs State Of Maharashtra (2001), the Supreme Court further emphasized that "legislative malice is beyond the pale of jurisdiction of the law courts."
- However, this conventional wisdom may be insufficient when addressing the unique challenges posed by populist regimes employing motivated legislation.
- As populist governments worldwide increasingly weaponize legislation to further their political agendas, the question arises as to whether constitutional courts should reconsider their stance on legislative malice.
- Given the potential for populist regimes to undermine democratic principles and erode the rule of law, the need for robust judicial review has never been greater.
- In light of these challenges, a careful reevaluation of the limits of judicial intervention may be necessary to ensure that the rights and freedoms enshrined in constitutional democracies are protected from malicious legislative actions.
Judicial Challenges and Lessons from the Recent Cases:
- Recent cases have highlighted the pressing need for a more proactive judiciary in safeguarding democratic principles and the rule of law.
- In Vivek Narayan Sharma vs Union of India (2023), the irreversible consequences of the absence of judicial intervention regarding Kashmir's special status were brought to the forefront.
- The Anoop Baranwal vs Union of India (2023) case underscored the necessity for an independent body to select the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- However, the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023, reintroduced the "Prime Minister's Committee" system for ECI appointments, raising concerns about the impartiality of the selection process.
- When this Act was challenged in Jaya Thakur vs Union of India (2024), the Court declined to halt its implementation, citing the presumption of validity.
- This decision exemplifies how an overly deferential approach to legislative actions can potentially jeopardize democratic institutions and processes.
Case Studies and Implications of Targeted Legislation:
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA): CAA exemplifies targeted legislation, as it explicitly excludes Muslims from the citizenship application process, demonstrating a clear case of legislative malice through religious categorization.
- Tripple Talaq case: Another instance of targeted legislation is the Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Marriage) Act (2019), which criminalized instant triple talaq.
- Despite the Supreme Court declaring instant triple talaq void in Shayara Bano (2017), the Act's criminalization of an already legally invalid practice appears excessive and unnecessary.
- Unintended effects: Unintended consequences have arisen from the triple talaq legislation, as some individuals now resort to alternative divorce methods or desertion to avoid potential legal repercussions.
- Although the law aimed to protect Muslim women, it has paradoxically worsened their situation.
- Furthermore, such divisive measures have inspired similar legislation in other states, such as anti-conversion laws, perpetuating social divisions.
- These cases reveal the need for a vigilant judiciary to scrutinize targeted legislation and ensure that laws do not perpetuate discrimination or undermine fundamental rights.
- Addressing legislative malice is essential for preserving the integrity of democratic institutions and upholding constitutional principles.
Judicial Scrutiny in Contemporary Politics: International Perspectives and Indian Precedents
- The Evolution of Judicial Scrutiny in Modern Politics: Traditionally, the United States has been cautious about judicial nullification of statutes based on malicious intent.
- John Hart Ely argued that using the Constitution to penalize perceived ill intentions of political leaders is inappropriate.
- Susannah W. Pollvogt's Viewpoint on Discriminatory Law: However, in today's political climate, where legislative actions driven by malice are increasingly common, a growing need for more rigorous judicial scrutiny has emerged.
- Scholar Susannah W. Pollvogt contends that animus, or hostility, can never justify discriminatory state actions under equal protection analysis.
- She cites the United States Dept. of Agriculture vs Moreno (1973) to illustrate how legislation targeting specific groups reflects discriminatory intent and a desire to cause harm.
- Indian Legal Precedents for Judicial Intervention: In India, there are instances where the Supreme Court has intervened to halt the implementation of parliamentary legislation.
- In Ashoka Kumar Thakur vs Union of India (2007), the Court issued a judicial injunction regarding the allocation of a 27% quota for Other Backward Community (OBC) candidates in professional colleges.
- More recently, in Rakesh Vaishnav vs Union of India (2021), the Supreme Court's stay order on three controversial farm laws effectively prevented their enforcement.
- This intervention eventually led to the government's withdrawal of the laws amidst widespread farmer protests.
- These cases demonstrate the vital role of the judiciary in safeguarding fundamental rights and democratic principles.
- As legislative malice becomes more prevalent, judicial scrutiny must evolve to ensure that laws do not perpetuate discrimination or undermine constitutional values.
Conclusion
To protect constitutional principles and democratic values, judicial review must be prompt, vigorous, and unambiguous when confronted with divisive or unconstitutional statutes. The Supreme Court should learn from its past decisions and recognize the political impact of its actions, particularly during critical moments. Delayed adjudication can render constitutional review ineffective, making time-sensitive intervention essential in addressing malicious and unconstitutional legislation.
India's Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2023 (TOI)

- 04 Aug 2023
- The central government will notify countries where data fiduciaries may transfer personal data.
- Such transfers will be subject to prescribed terms and conditions.
- Exemptions:
- Certain specified cases will be exempt from certain rights of data principals and obligations of data fiduciaries, excluding data security. These cases include:
- Prevention and investigation of offenses.
- Enforcement of legal rights or claims.
- The central government may, through notification, exempt certain activities from Bill's application, such as
- Processing by government entities for national security and public order.
- Data processing for research, archiving, or statistical purposes.
- Data Protection Board of India:
- The central government will establish the Data Protection Board of India.
- Key functions of the Board include:
- Monitoring compliance and imposing penalties.
- Directing data fiduciaries to take necessary measures in the event of a data breach.
- Addressing grievances made by affected individuals.
- Penalties:
- The Bill outlines penalties for various offenses, including
- Fines of up to Rs 200 crore for non-compliance with obligations related to children's data.
- Fines of up to Rs 250 crore for failure to implement adequate security measures to prevent data breaches.
Importance of the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023:
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2023 holds significant value as it aims to ensure the safety and privacy of users’ personal data while granting them greater control over its portability. The bill sets forth stringent measures and norms that will hold big corporations and consumers accountable, imposing substantial fines on those who fail to comply.
- The primary objective of the bill is to enhance the accountability of entities, including internet companies, mobile apps, and businesses, in their collection, storage, and processing of citizens' data, safeguarding the citizens' "Right to Privacy." Once approved, various public and private entities will be obligated to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting and processing their data.
- This landmark legislation signifies a major step towards valuing and protecting the privacy of each consumer, ensuring that their personal data is handled with utmost care and responsibility, creating a safer and more secure digital environment for all.
Concerns regarding the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023, include several contentious issues:
- The government and its agencies are granted wide-ranging exemptions.
- The powers of the data protection board might be diluted.
- The proposed amendment to the Right to Information Act, of 2005, is causing worries, particularly due to the removal of the public interest caveat that could restrict sharing of government officials' personal information.
- The bill overrides Section 43A of the Information Technology Act, 2000, which mandates compensation for mishandling user data by companies. The new compensation mechanism has been questioned, as it may impact users' ability to seek adequate redress.
- Addressing these concerns is essential to ensure a comprehensive and balanced approach to safeguarding personal data in the digital realm.
What are Data Privacy Regulations in Other Countries?
- Approximately 70% of countries worldwide have implemented data protection legislation, as reported by the United Nations trade agency UNCTAD.
- The EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enforced in 2018, is considered the most stringent privacy and security law globally and serves as a benchmark for data protection regulations.
- Several countries, such as China and Vietnam, have recently strengthened their laws concerning the cross-border transfer of personal data to enhance data privacy.
- In 2018, Australia passed a bill granting police access to encrypted data.
In conclusion, the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023, offers extensive rights to individuals, granting them enhanced visibility, awareness, decision-making autonomy, and control over their data. It imposes strict obligations on companies to adhere to individual rights and establishes robust redressal mechanisms, backed by significant penalties for non-compliance.
Moreover, the Bill reinforces the landmark judgment of the Supreme Court in the case of Justice K. S. Puttaswamy (Retd) Vs Union of India (2017). In this judgment, a nine-judge bench unanimously recognized the constitutionally protected fundamental right to privacy for Indians, affirming that privacy is an intrinsic aspect of life and liberty under Article 21 of the Constitution. The Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023, is a crucial step towards upholding this fundamental right and ensuring better protection of personal data in the digital age.
Mains Question:
- Examine the provisions and significance of the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023, comparing it to global data privacy regulations and its alignment with the Indian Supreme Court's right to privacy ruling. (15M)
India is in Dire need of Police Reforms (LiveMint)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The outbreak of communal violence in the Delhi region raises concerns over the role of law enforcement; police forces need structural autonomy and revised incentives.
About Police and Policing Framework in India:
Police forces play a crucial role in upholding and enforcing laws, investigating crimes, and providing security to the nation's people. Given India's large population, well-equipped police forces with adequate personnel, weaponry, forensic, communication, and transport support are essential for effective performance.
The existing legal and institutional framework for police matters in India was inherited from the British, but it lacks accountability in establishing a responsible police force. Despite multiple reform proposals acknowledged by the Government of India and the Supreme Court, comprehensive implementation remains elusive. Consequently, India must revise the legal and institutional framework to advance towards smart policing.
Constitutional and Legal Provisions:
- As per the Constitution of India, 'Police' and 'Public Order' fall under state subjects in the Seventh Schedule, granting each state its own police force.
- The central government is also permitted to maintain its police forces to assist states in maintaining law and order.
- The foundational framework for policing in India was established through the Police Act, of 1861, during the pre-independence era.
- Additionally, several other laws and regulations, such as the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC), Indian Penal Code (IPC), Evidence Act, and state-specific laws, govern the functioning of the police in India.
Issues and challenges in Police Forces:
- Colonial Legacy: The current police system in India is still rooted in colonial-era laws, with past misuse of police as a tool to suppress dissent, which sometimes continues in the present government.
- Shortage of Police Personnel: Despite a sanctioned strength of 181 police per lakh persons in 2016, the actual strength was only 137 police, well below the United Nations' recommended standard of 222 police per lakh persons, leading to overburdened police personnel.
- Custodial Death: Instances of custodial death due to torture or pressure in police/judicial custody remain a concern, despite the Supreme Court's guidelines against it.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Modern policing requires robust communication support, modern weapons, and high mobility, but funds allocated for police infrastructure often face underutilization.
- Lack of Torture Law: While India has signed the "United Nations Convention Against Torture," a specific domestic law against torture is yet to be enacted.
- Political Interference: Political interference hampers police officers' ability to perform their duties effectively, with insufficient tenure and posting security for higher-ranking officers.
- Promotion and Working Conditions: Qualifications and training for police personnel, especially at lower levels, need improvement. Verbal abuse from superiors and inhumane working conditions for lower ranks impact their relationship with the public negatively.
Significance of Police Reforms:
- Police-Population Ratio: India's low ratio of 120 police per 100,000 people, compared to the global average of 270, results in inadequately equipped and politically oriented police, posing a security challenge for its citizens.
- Tackling Corruption: A significant rise in vigilance inquiries against police personnel in 2016 and a decrease in corruption from 66% (2014) to 34% (2015) highlight the need for reforms to address corruption within the police force.
- Adapting to Changing Crime Patterns: Evolving social and technological changes, driven by the internet and social media, have transformed crime, necessitating reforms to effectively combat lawlessness and global terrorism.
- Ensuring Inclusivity: Underrepresentation of women and marginalized castes can lead to insensitivity towards these groups, highlighting the importance of reforms to promote inclusivity within the police force.
- Addressing Caste-Based Violence: Reforms are crucial to tackling escalating violence arising from caste conflicts, including recent Dalit uprisings and farmers' issues across the country.
Various Committees for Police Reforms:
- Gore Committee on Police Training (1971-73): Reviewed police training from constabulary to IPS officers.
- National Police Commission (1977): Produced eight Reports on various aspects of police administration.
- Ribeiro Committee (1998): Recommended setting up Police Performance and Accountability Commissions at the state level and a District Complaints Authority, and replacing the Police Act, of 1861.
- Padmanabhaiah Committee (2000): Studied police force recruitment, training, duties, investigations, and prosecution.
- Soli Sorabjee Committee (2005).
- Vohra Committee Report: Exposed the nexus between criminals, politicians, and government officials, suggesting the establishment of an institution to address the issue.
Way Forward for Police Reforms: Seven Supreme Court Directives
- Curbing Political Control: Ensure state governments do not exert undue influence or pressure on the police.
- Merit-Based Appointments: Implement a transparent and merit-based process for appointing the Director-General of Police, ensuring a minimum tenure of 2 years.
- Tenure Stability: Provide a minimum tenure of 2 years to police officers handling operational duties, including district Superintendents of Police and Station House Officers.
- Separation of Functions: Separate the roles of investigation and law enforcement to enhance efficiency and transparency.
- Police Establishment Board: Establish a Police Establishment Board to address transfers, postings, promotions, and service-related matters for officers up to the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police.
- State and District Police Complaints Authority: Set up independent Police Complaints Authorities at the state and district levels to address serious misconduct complaints against police officers.
- National Security Commission: Establish a National Security Commission at the union level to facilitate the selection and placement of chiefs of Central Police Organizations with a minimum tenure of 2 years.
Preserving tribal culture: Odisha’s Special Development Councils model is worth emulating (The Hindu)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
In Odisha's development model driven by the 5T principles (transparency, technology, teamwork, time limit, and transformation), the vision of inclusive growth and community-led development goes beyond being a mere idea; it stands as an actionable strategy with tangible outcomes.
Tribal population in India:
- India encompasses a significant tribal population of 8.6%, possessing a vast repository of indigenous knowledge that holds the potential to offer sustainable solutions through recognition, adoption, and integration into mainstream practices.
- As per Article 342 of the Indian Constitution, the President has the authority to specify, with respect to any State or Union territory, the tribes, tribal communities, parts of, or groups within tribes or tribal communities as Scheduled Tribes.
Tribal Culture: A Glimpse
- Communal Bond: Many tribal communities in India embrace a strong sense of communal living, where resources are shared, and decisions are collectively made within close-knit communities.
- Connection with Nature: Tribals deeply connect with nature, embracing traditional beliefs and practices centered around forests and animals.
- Self-Sufficiency: A tribe embodies self-reliance, forming relatively closed societies where their self-sufficiency pursuits define their openness to the outside world.
- Spiritual Traditions: Tribals nurture distinct spiritual beliefs, often venerating ancestors, nature spirits, or deities, adding uniqueness to their cultural tapestry.
- Expressive Artistry: Tribals are celebrated for their exquisite art forms, such as pottery, weaving, and jewelry making. These crafts hold spiritual and cultural significance, passing down through generations.
Tribal Lifestyle and Sustainable Development:
- Harmony with Nature: The tribal lifestyle upholds profound respect for the natural environment, incorporating sustainable practices like using natural materials for housing, food, and medicine, and living in sync with nature's cycles.
- Community-Centric Decision-Making: Their collective decision-making process prioritizes the needs of the entire community, ensuring sustainable and equitable choices.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Tribals actively promote biodiversity by employing traditional agricultural techniques like intercropping and seed saving, as well as safeguarding sacred sites vital for biodiversity conservation.
- Resource Conservation: Sustainable practices involve judicious resource usage, such as rotational farming and allowing forests to regenerate before harvesting timber, ensuring their long-term availability.
- Intergenerational Knowledge Transfer: Passing down knowledge to future generations includes traditional wisdom about the natural environment and sustainable resource management.
- Water Resource Protection: Tribal communities have devised practices to safeguard water resources, guaranteeing their availability for future generations while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Regenerative Agriculture: For centuries, tribal communities have practiced regenerative agriculture, incorporating crop rotation, intercropping, and organic matter to enrich soils and sequester carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Embracing Renewable Energy: Traditional reliance on renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower offers a model for expanding and modernizing clean energy solutions for broader communities.
Challenges Confronting Tribal Lifestyles:
- Discrimination: Tribal communities frequently encounter discrimination and bias from the dominant society, leading to restricted access to education, healthcare, and essential services.
- Land Rights: Displacement from ancestral lands due to industrialization and mining has led to the loss of cultural identity and socio-economic marginalization among tribal communities.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Adverse effects of climate change, such as altered rainfall patterns, more frequent natural disasters, biodiversity loss, deforestation, pollution, and habitat destruction, have severely impacted their traditional livelihoods and ways of life.
- Socioeconomic Marginalization: Limited access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities has resulted in poverty and social exclusion for many tribal communities.
- Lack of Political Representation: Tribal communities often lack political representation, depriving them of a voice in decision-making processes that directly influence their lives.
- Cultural Assimilation: Pressures to conform to the dominant culture impose a risk of losing traditional knowledge, language, and cultural practices within many tribal communities.
What is Odisha's Special Development Councils (SDCs) Initiative?
- In a momentous stride towards preserving, promoting, and celebrating tribal culture while advancing the trajectory of development, the Odisha government introduced the Special Development Councils (SDCs) initiative in 2017.
- The primary objective is to safeguard the rich culture and heritage of 62 tribes in the State under a unified approach while ensuring continued economic progress in the regions.
- Originally encompassing 9 tribal-dominated districts and benefiting 60 lakh tribal households across 117 blocks, the initiative has now expanded to cover 23 districts, extending its benefits to over 84 lakh tribal individuals.
Government Initiatives for Tribal Culture Conservation:
- National Scheduled Tribes Finance and Development Corporation (NSTFDC): Established in 2001 under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, NSTFDC aims to uplift Scheduled Tribes economically through concessional financial assistance under various schemes.
- TRIFED's Tribal Initiatives: The government plans to establish 50,000 Van Dhan Vikas Kendras and 3,000 Haat Bazaars, fostering economic opportunities for tribal populations.
- Central Sector Scheme: Supporting Institutional Development & Marketing of Tribal Products/Produce.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Ensuring a sustainable mechanism for Marketing Minor Forest Produce (MFP) through Minimum Support Price (MSP) and developing value chains, providing social safety for MFP gatherers.
- Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana: A market-linked tribal entrepreneurship development program promoting the formation and strengthening of Tribal Producer Companies through clusters of tribal Self Help Groups (SHGs).
- Scholarships: Government-funded scholarships for pre-matric, post-matric, and overseas education, facilitating educational access for tribal students.
- Support to NSTFDC: Assistance to the National Scheduled Tribes Finance and Development Corporation for further empowerment initiatives.
- Development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs): Comprehensive support encompassing housing, land distribution, agricultural and animal husbandry development, link road construction, and more.
- Vocational Training in Tribal Areas: Focused on enhancing the skills of ST youth for diverse job opportunities and self-employment, elevating their socio-economic status.
Mains Question:
- Examine the challenges faced by tribal lifestyles and evaluate the effectiveness of government initiatives for tribal culture conservation in improving socio-economic conditions and preserving cultural heritage among tribals. (15M)
