Satellite Docking Experiment (SpaDeX)

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) achieved a historic milestone by successfully executing a satellite docking experiment, making India the fourth country after the United States, Russia, and China to accomplish this feat. This advancement represents a significant leap in India's space capabilities, positioning the nation at the forefront of space exploration and in-orbit servicing.
Key Highlights:
- The Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) is a critical technological demonstration by ISRO aimed at developing autonomous docking and undocking capabilities in space.
- The mission involves two satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), which were launched aboard PSLV C60 on December 30, 2024.
- The docking maneuver was overseen by the Mission Operations Complex (MOX) at the ISRO Telemetry, Tracking, and Command Network (ISTRAC) and was successfully completed in the early hours of January 18, 2025.
Key Steps in the Docking Process:
- Manoeuvre from 15m to 3m hold point.
- Precision docking initiation, leading to spacecraft capture.
- Retraction and rigidization for stability.
- Successful control of the docked satellites as a single object.
Significance of the Mission
- Technological Advancement: The docking of two spacecraft in orbit is a crucial capability that paves the way for:
- Autonomous spacecraft operations
- Refueling and maintenance of satellites
- Space station development
- Lunar and interplanetary missions
Future Applications
- Manned Missions: Enables India to develop technology for manned lunar missions and future space station operations.
- Satellite Servicing: Allows repair, maintenance, and extension of satellite lifespan, reducing costs and space debris.
- Sample Return Missions: Essential for lunar and planetary sample retrieval, crucial for deep-space exploration.
Challenges and Overcoming Setbacks
The SpaDeX docking was initially scheduled for January 7, 2025, but was postponed due to the need for further ground validation and an unexpected drift between the satellites. The issue was later resolved, and the docking was executed with precision.
The Road Ahead
Undocking and Power Transfer Demonstration
- ISRO will follow up with power transfer checks between the docked satellites.
- The satellites will later undock and operate separately for the remaining mission duration of up to two years.
Expanding Space Capabilities
- The successful execution of SpaDeX aligns with India’s plans for an independent space station by the 2030s.
- Strengthens India’s position in international space collaborations and commercial space services.
Conclusion
The SpaDeX mission represents a landmark achievement for India’s space program, placing it among the elite nations capable of satellite docking. This breakthrough will serve as a foundation for India’s ambitious future missions, including deep-space exploration, human spaceflight, and interplanetary research. As ISRO continues to develop advanced space technologies, India is set to play a crucial role in the future of global space exploration.
Digital Governance in India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
India is making significant strides toward digital governance, an initiative aimed at enhancing both citizen services and the capabilities of government employees. This transition to a digitally-driven framework is designed to improve the efficiency, transparency, and accountability of government operations, positioning India as a global leader in modern governance practices.
What is Digital Governance?
Digital governance refers to the application of technology to enhance the functioning of government processes. By integrating digital tools and platforms, it aims to streamline administrative operations, reduce inefficiencies, and improve public service delivery. This approach also extends to ensuring greater transparency and accountability in government dealings.
Key Initiatives in Digital Governance
India has launched several critical initiatives to modernize governance through digital means. Some of the key programs include:
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform: The iGOT Karmayogi platform is a government initiative to provide online training to public employees. It aims to enhance public administration skills, foster expertise in data analytics, and equip employees with the necessary tools in digital technologies. This initiative aims to prepare government personnel to handle the challenges of a digitally evolving governance landscape.
- e-Office Initiative: The e-Office program is designed to reduce paper-based work by digitizing workflows within government departments. This initiative facilitates real-time communication among offices and ensures more efficient and transparent management of tasks. It also helps streamline decision-making processes and improves the speed of governance operations.
- Government e-Marketplace (GeM): The Government e-Marketplace (GeM) is an online platform developed to optimize procurement processes. It allows government agencies to procure goods and services efficiently, transparently, and with accountability. This platform has contributed to reducing corruption and ensuring that government purchases represent the best value for public money.
- Cybersecurity Training for Employees: As digital operations increase, ensuring the safety of sensitive data is paramount. The cybersecurity training program for government employees is designed to enhance their ability to recognize and respond to potential cyber threats. This initiative ensures data protection, safe online practices, and cyber resilience across digital governance platforms.
Challenges in Implementing Digital Governance
Despite its benefits, India faces several challenges in the successful implementation of digital governance. These obstacles must be addressed to unlock the full potential of technology-driven governance.
- Resistance to Technological Change: One of the key barriers to digital transformation in government is the resistance among employees to adopt new technologies. Many government officials remain accustomed to traditional, paper-based processes and are reluctant to transition to digital systems due to concerns about complexity and job security.
- Digital Divide in Rural Areas: While urban regions in India have better access to high-speed internet and digital infrastructure, many rural areas face significant digital divide challenges. Limited access to technology hampers the successful implementation of digital governance in these regions, restricting equitable service delivery across the country.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The rise of digital operations in governance increases the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. With government data being digitized, the threat of cybercrimes becomes more pronounced, making it critical to implement robust cybersecurity measures and data protection strategies to safeguard sensitive information.
- Lack of Incentives for Training Outcomes: Although government employees are encouraged to take part in training programs such as iGOT Karmayogi, the absence of clear incentives to complete these programs can undermine their effectiveness. Establishing tangible rewards or career progression linked to the successful completion of training would encourage employees to fully engage in capacity-building initiatives.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges
To ensure the success of digital governance, several strategies must be put in place to address the challenges identified.
- Foster Innovation-Friendly Environments: Promoting an innovation-friendly culture within government offices can help reduce resistance to new technologies. Encouraging employees to engage with digital tools, offering regular training, and providing ongoing support will facilitate a smoother transition to a technology-driven governance system.
- Invest in Digital Infrastructure for Rural Areas: Addressing the digital divide requires significant investment in digital infrastructure in rural and remote areas. Ensuring that these regions have reliable internet access and the necessary technological resources will empower citizens across India to benefit from digital governance.
- Continuous Capacity-Building Programs: Establishing continuous training programs for government employees will ensure that they remain up-to-date with the latest technological trends. Regular updates to training content will help employees stay prepared to handle emerging challenges in digital governance.
- Strengthen Cybersecurity Protocols: To mitigate cybersecurity risks, it is essential to implement stringent cybersecurity measures across all levels of government operations. This includes regular cybersecurity awareness programs, proactive threat management systems, and rigorous data protection protocols to safeguard both government data and citizens’ personal information.
Conclusion
India’s shift towards digital governance represents a significant step toward modernizing administrative systems, enhancing transparency, and improving service delivery to citizens. However, challenges such as resistance to change, the digital divide, cybersecurity risks, and the lack of clear incentives for training must be addressed. By investing in digital infrastructure, offering continuous training programs, and reinforcing cybersecurity measures, India can create an effective and secure framework for digital governance that benefits both its citizens and the government workforce.
India’s Startup Revolution

- 15 Jan 2025
Context
India has solidified its position as one of the most dynamic startup ecosystems globally, emerging as a hub for innovation, entrepreneurship, and technological progress. However, realizing its ambition of becoming the top startup ecosystem requires addressing critical challenges and leveraging available opportunities.
Current Landscape of Indian Startups
Growth and Innovation
India ranks as the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world, following the U.S. and China. As of January 15, 2025, over 1.59 lakh startups have been officially recognized by DPIIT, with more than 120 attaining unicorn status (valuation exceeding $1 billion).
Investment Trends
Despite economic fluctuations, India's startups continue to attract significant investments. In 2022, venture capitalists infused $25 billion into the ecosystem, reaffirming India’s position as a preferred destination for global investors. Although there was a slowdown in 2023, domains like Software as a Service (SaaS) and climate tech continue to secure substantial funding.
Government Support
India’s startup-friendly policies, including Startup India, Digital India, and Atmanirbhar Bharat, have created an enabling environment. Notable initiatives include:
- Tax incentives, faster patent approvals, and regulatory relaxations.
- The launch of a ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) in 2023 to improve capital accessibility.
- The Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry (BHASKAR) to streamline collaboration among startups and investors.
Regional Growth
- Tier II and III Expansion: Nearly 50% of startups are now based in emerging hubs such as Indore, Jaipur, and Ahmedabad.
- Tamil Nadu: The state boasts a $28 billion startup ecosystem, growing at 23%. Chennai alone houses around 5,000 startups, significantly contributing to employment generation.
- Kerala: With a $1.7 billion startup ecosystem, Kerala exhibits a compound annual growth rate of 254%, emphasizing cost-effective tech talent hiring.
Key Challenges Faced by Startups
1. Funding Constraints
The global economic downturn, coupled with rising interest rates, has limited venture capital inflows, resulting in layoffs and operational cutbacks.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Barriers
Despite government support, startups grapple with complex tax structures, evolving data protection laws, and stringent compliance requirements, including ESOP taxation policies.
3. Scaling and Market Adaptability
Many startups struggle with operational inefficiencies, limited market penetration, and inadequate infrastructure, hampering growth potential.
4. High Failure Rate
Approximately 90% of Indian startups fail within five years due to poor product-market fit, lack of financial planning, and insufficient adaptation to market needs.
5. Talent Shortages
India faces stiff competition in acquiring skilled professionals in areas like AI, cybersecurity, and machine learning, making retention increasingly difficult amid economic uncertainties.
Strategic Measures to Strengthen India’s Startup Ecosystem
1. Enhancing Policy Frameworks
- Simplified Regulations: Streamline startup registration, funding approvals, and international business operations.
- IP Protection: Strengthen intellectual property laws to boost R&D investment.
- Sector-Specific Initiatives: Develop targeted policies for AI, deep tech, healthcare, and green technologies.
2. Expanding Funding Access
- Encouraging Domestic Investment: Leverage pension and sovereign wealth funds to invest in startups.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster large-scale government-industry collaboration to finance emerging ventures.
- Decentralized Funding: Expand angel investor networks and micro-investment opportunities, particularly in Tier II and III cities.
3. Building Robust Infrastructure
- Tech Parks and Incubation Centers: Establish state-of-the-art facilities with mentorship programs.
- Improved Digital Connectivity: Ensure high-speed internet access in underserved regions.
- Enhanced Logistics and Supply Chains: Strengthen infrastructure to support startup scalability.
4. Developing a Skilled Workforce
- STEM and Entrepreneurial Education: Introduce curriculum enhancements in technical and business disciplines.
- Upskilling Programs: Collaborate with industry leaders to train professionals in high-demand skills.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Promote initiatives encouraging women and marginalized communities in entrepreneurship.
5. Fostering Innovation and Risk-Taking
- Strengthened R&D Funding: Increase allocations to universities and private research sectors.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship: Reduce societal stigma surrounding startup failures to promote risk-taking.
- Leveraging Domestic Challenges: Address local issues like climate change and urbanization through innovation.
6. Expanding Global Reach
- International Collaborations: Partner with foreign accelerators and governments.
- Ease of Cross-Border Trade: Simplify export and import regulations for startups.
- Engaging the Indian Diaspora: Encourage successful overseas entrepreneurs to mentor and invest in Indian startups.
7. Advancing Sustainability Goals
- Green Tech Promotion: Support startups focusing on renewable energy and circular economy initiatives.
- Eco-Friendly Incentives: Offer financial support to ventures aligning with sustainability targets.
- Inclusive Growth Strategies: Expand agritech, edtech, and health-tech startups in rural areas, supporting platforms like the Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) by NITI Aayog.
Building a Resilient Digital Economy
To fortify India's digital economy, startups should leverage existing infrastructure like UPI and Aadhaar while capitalizing on emerging technologies such as AI, 5G, and blockchain. A robust cybersecurity framework and data protection policies will be essential to ensure investor confidence.
Genome India Project

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Genome India Project is an ambitious national initiative aimed at decoding the genetic diversity of India’s population. Launched in January 2020 by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), the project seeks to create a comprehensive map of India’s genetic variations, offering insights that can revolutionize public health, medicine, and our understanding of human genetics.
What is Genome Sequencing?
Genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome. The human genome, composed of about 3 billion base pairs of DNA, contains all the genetic instructions necessary for the growth, development, and functioning of the human body. The process involves extracting DNA from a sample (often blood), breaking it into smaller fragments, and using a sequencer to decode these fragments. The data is then reassembled to reconstruct the full genome.
Key Aims and Objectives
The Genome India Project aims to address several crucial scientific and healthcare challenges:
- Create an Exhaustive Catalog of Genetic Variations: This includes common, low-frequency, rare, and structural variations (such as Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms or SNPs).
- Establish a Reference Haplotype Structure: This reference panel will be used for imputing missing genetic variations in future genetic studies.
- Design Affordable Genome-wide Arrays: These arrays will be useful for research and diagnostics at a lower cost, making genetic analysis accessible.
- Create a Biobank for Future Research: The collected DNA and plasma will be preserved for future studies to facilitate ongoing genetic research.
Genome India Project: Phase 1 and Key Findings
The project’s Phase 1 focused on sequencing the genomes of 10,074 individuals from 99 ethnic groups across India. This initiative provides a critical baseline for studying the country’s genetic diversity. Some of the key findings include:
- 459 plant species have been identified as part of genetic diversity studies.
- 135 million genetic variations have been uncovered, including 7 million that are unique to India, not found in global databases.
- The project has revealed several genetic risks specific to Indian populations, such as the MYBPC3 mutation (linked to cardiac arrest) and the LAMB3 mutation (associated with a lethal skin condition), which are not commonly seen in global datasets.
This database will serve as a vital resource for researchers, contributing to the development of precision medicine, better disease diagnosis, and more personalized treatments.
Second Phase: Expanding the Scope
The second phase of the Genome India Project will focus on sequencing the genomes of individuals suffering from specific diseases. This will enable researchers to:
- Compare the genomes of healthy individuals with those having diseases, helping identify genetic mutations responsible for conditions like cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Investigate rare diseases specific to Indian populations and develop therapies tailored to these conditions.
By sequencing the genomes of individuals with various conditions, the project aims to pinpoint genetic factors that contribute to the pre-disposition or causation of diseases.
Data Sharing and Security
To ensure data security and privacy, the genetic information will be made available only through managed access. Researchers interested in using the data will need to submit a proposal and collaborate with the Department of Biotechnology. The data will be stored securely at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC) in Faridabad, Haryana, and anonymized to maintain confidentiality.
Why Does India Need Its Own Genetic Database?
India is home to a highly diverse population, with over 4,600 distinct ethnic groups and varying genetic backgrounds. The country’s genetic diversity, shaped by its geographical, cultural, and historical context, cannot be fully understood through datasets derived from other countries. The Genome India Project helps:
- Identify Genetic Risk Factors: For various diseases, paving the way for developing targeted diagnostic tools and therapies.
- Uncover Unique Variants: Some genetic mutations found in India, such as the Vaishya community’s resistance to anaesthetics, are absent in global databases.
- Address Population-specific Health Issues: Genetic mapping enables the identification of prevalent diseases and health conditions specific to Indian populations.
Global Context and Comparison
India’s genome sequencing effort is part of a larger global movement in genomics:
- Human Genome Project (2003): The first international effort to decode the human genome.
- 1,000 Genome Project (2012): Published 1,092 human genome sequences.
- UK 100,000 Genome Project (2018): Sequenced 100,000 genomes for health research.
- European Genome Project: Aims to sequence over 1 million genomes across 24 countries.
The Genome India Project fills a crucial gap by focusing on the genetic diversity of Indian populations, which differs significantly from the genetic profiles studied in Western or European genomes.
Applications of Genome India Project
The Genome India Project has the potential to impact multiple areas:
- Advancements in Medicine: Understanding genetic variations can lead to the development of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles.
- Genetic and Infectious Disease Control: The project helps identify genetic resistance to diseases, and aids in understanding how certain populations may respond differently to drugs or vaccines.
- Public Health Policies: Data from the project can inform health policies, especially in tackling diseases prevalent in specific regions or communities.
- International Research Collaboration: The project aims to foster collaboration with global research communities, enhancing India’s presence in the field of genomics.
Conclusion:
The Genome India Project is a landmark initiative for India’s scientific community, enabling better understanding of the country’s genetic diversity and paving the way for breakthroughs in medicine, healthcare, and disease prevention. The ability to analyze genetic variations on such a large scale provides immense opportunities for precision medicine and personalized treatments.
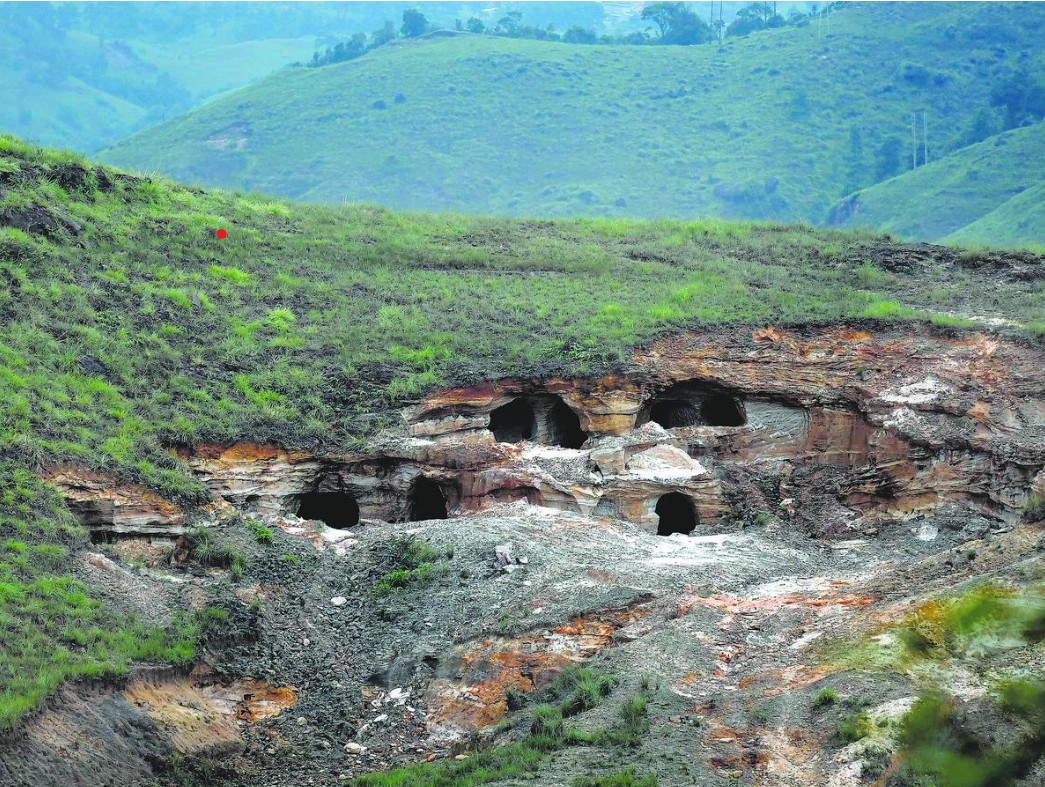
Rat-hole mining

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
In Dima Hasao district of Assam, at least nine workers aged between 26 and 57 were trapped in a coal “rat-hole” mine after it was flooded with water. Three miners trapped in a flooded coal mine were confirmed dead, while six remained stuck. Later an Indian Navy team, including deep-sea divers, arrived at the site, where the water level inside the pit is 200 feet deep.
Key Takeaways:
- Rat-hole mining is a method of extracting coal from narrow, horizontal seams, prevalent in Meghalaya. The term “rat hole” refers to the narrow pits dug into the ground, typically just large enough for one person to descend and extract coal.
- Once the pits are dug, miners descend using ropes or bamboo ladders to reach the coal seams. The coal is then manually extracted using primitive tools such as pickaxes, shovels, and baskets.
- Types of Rat-hole mining:
- Side-cutting mining: In the side-cutting procedure, narrow tunnels are dug on the hill slopes and workers go inside until they find the coal seam. The coal seam in the hills of Meghalaya is very thin, less than 2 m in most cases.
- Box-cutting mining: In the other type of rat-hole mining, called box-cutting, a rectangular opening is made, varying from 10 to 100 sqm, and through that a vertical pit is dug, 100 to 400 feet deep. Once the coal seam is found, rat-hole-sized tunnels are dug horizontally through which workers can extract the coal.
- Concerns associated with Rat-hole mining: Rat-hole mining poses significant environmental and safety hazards. This method of mining has faced severe criticism due to its hazardous working conditions, and numerous accidents leading to injuries and fatalities.
- The mines are typically unregulated, lacking safety measures such as proper ventilation, structural support, or safety gear for the workers. Additionally, the mining process can cause land degradation, deforestation, and water pollution. Despite attempts by authorities to regulate or ban such practices, they often persist due to economic factors and the absence of viable alternative livelihoods for the local population.
- Notably, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned Rat-hole mining in 2014, and retained the ban in 2015, on grounds of it being unscientific and unsafe for workers. The order was in connection with Meghalaya, where this remained a prevalent procedure for coal mining. The state government then appealed the order in the Supreme Court.
Role of Rat-Hole Mining in Uttarkashi Tunnel Rescue
- The rat-hole mining practice, banned for being unsafe, helped in the rescue operation of 41 workers trapped in the collapsed Silkyara-Barkot tunnel in Uttarakhand in 2023.
- Rat-hole miners were called in after the auger machine that was drilling through the debris broke. Rescuers then tried cutting through the blade stuck inside the rescue pipes and removing it piece by piece. As large metal pieces hindered the machine drilling, the rescuers went ahead with rat-hole mining.
- It was a test of grit and perseverance – for men on both sides of the 57 metres of debris – as the rescue operation suffered one setback after another. In the end, it was miners who dug through the last 12 metres and reached the trapped men.
Selection Process for Chief Election Commissioner (CEC)

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023 represents a significant shift in the process of selecting the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and other Election Commissioners (ECs) in India. Traditionally, the senior-most Election Commissioner automatically ascended to the position of CEC. However, the new law introduced in December 2023 widens the scope for selection, allowing for a more transparent process with an expanded pool of candidates.
Key Features of the Act:
- Election Commission Structure: The Election Commission of India is constituted by the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and two other Election Commissioners (ECs). The President of India appoints these members, with the number of ECs fixed periodically.
- Appointment Process: The Act mandates that the CEC and ECs are appointed by the President based on recommendations from a Selection Committee. This committee comprises:
- The Prime Minister (Chairperson),
- The Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha (or leader of the largest opposition party),
- A Union Cabinet Minister appointed by the Prime Minister.
- Search Committee: A Search Committee, chaired by the Minister of Law and Justice, prepares a panel of five candidates. The Selection Committee may choose from this panel or opt for someone outside of it.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Candidates must have integrity and experience in election management.
- They should be or have been Secretary-level officers or equivalent.
- Term and Reappointment:
- The term of CEC and ECs is six years or until they turn 65 years.
- They cannot be re-appointed after their term.
- Salary and Pension: The salary, allowances, and conditions of service of CEC and ECs are equivalent to those of a Cabinet Secretary.
- Removal Process:
- The CEC can be removed in the same manner as a Supreme Court Judge.
- ECs can be removed only on the recommendation of the CEC.
Departure from Tradition:
Traditionally, the next CEC was the senior-most Election Commissioner. However, the new law opens the process, allowing the Search Committee to consider candidates outside the current pool of Election Commissioners. This widens the net and may lead to a more transparent and inclusive selection.
Concerns and Criticisms: While the Act aims to improve the selection process, it has faced scrutiny and concerns, particularly about the independence of the Election Commission:
- Government Influence: The inclusion of the Leader of Opposition in the Selection Committee is a positive step, but critics argue that the final decision may still be influenced by the government. The government’s dominance in the Selection Committee could potentially affect the neutrality of the Commission.
- Exclusion of the Chief Justice of India (CJI): The Supreme Court's 2023 ruling had recommended including the CJI in the committee, but the new Act excludes the CJI. This has raised concerns about the balance of power and the credibility of the Election Commission.
- Risk of Partisanship: Former CEC O.P. Rawat expressed concerns that political changes might influence decisions, leading to a compromised credibility of the Election Commission.
Legal Challenges: Petitions challenging the exclusion of the CJI from the Selection Committee are currently pending before the Supreme Court, which is expected to address them in February 2025.
Historical Context and Legal Backdrop:
- Article 324 of the Indian Constitution provides for the appointment of CEC and ECs by the President, but this is subject to laws passed by Parliament.
- In 2023, the Supreme Court intervened in response to the growing concerns over the executive's unilateral control over these appointments. The Court's ruling in the Anoop Baranwal v. Union of India case led to the formation of a committee comprising the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition, and CJI until Parliament could enact a law. This resulted in the Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners Act, 2023, which was aligned with the Court's directions.
Implications and Way Forward:
- Potential Government Influence: While the law aims to reduce executive control, the dominant role of the Prime Minister and the Leader of the Opposition could still allow the government to influence appointments, especially in contentious times.
- Suggestions for Reform: The Law Commission had recommended a broader selection committee, including the CJI, to ensure a balanced and impartial selection process. The National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (NCRWC) also suggested a committee comprising key political figures, including the Leader of Opposition in the Rajya Sabha and the Speaker of Lok Sabha.
- Integrity of the Election Commission: The credibility and impartiality of the Election Commission are vital for ensuring free and fair elections. It is crucial to ensure that the appointment process not only appears fair but is also free from political interference.
Conclusion:
The Chief Election Commissioner and Other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023 introduces a reformed approach to the selection of the Election Commission members. While the law aims for greater transparency, it also raises concerns regarding government influence and independence. The Supreme Court’s review of the exclusion of the CJI from the Selection Committee will be pivotal in determining the future trajectory of the Election Commission’s appointment process. The evolving legal and institutional dynamics will play a significant role in shaping the electoral reforms in India.
Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) Report

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
The Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) report for 2023-24 reveals a significant decline in school enrolment across India, highlighting critical challenges in the education sector. The total enrolment in grades 1-12 fell by over 1.55 crore students, from 26.36 crore (2018-2022 average) to 24.8 crore in 2023-24. This represents a 6% drop, with the biggest declines occurring in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Enrolment Decline:
- In 2023-24, enrolment decreased from 25.17 crore in 2022-23 to 24.8 crore.
- The drop was not only in government schools (5.59%) but also in private schools (3.67%).
- States like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Maharashtra saw the largest decreases.
- The decline in enrolment is despite an increase in the number of schools, from 14.66 lakh in 2022 to 14.72 lakh in 2023.
- Methodology Change:
- A significant change in the data collection methodology occurred in 2022-23, including linking enrolment to Aadhaar numbers, aimed at reducing data duplication.
- While this has improved data accuracy, it has also led to the removal of inflated figures, explaining part of the enrolment drop.
- Despite these changes, there has been a notable decline of 37 lakh students from 2022-23 to 2023-24, which remains unexplained in the report.
- Gender and Age Trends:
- Boys’ enrolment declined by 6.04%, and girls’ by 5.76%, reflecting a uniform drop across gender groups.
- The dropout rates increase as students progress through school, with the highest dropout at the secondary level.
- Infrastructure and Facilities:
- While most schools have basic facilities like electricity and gender-specific toilets, advanced infrastructure like functional computers (57%) and internet access (53%) is lacking in nearly half of schools.
- This technological gap exacerbates regional disparities and affects educational quality, particularly in rural areas.
- State-Specific Impact:
- Jammu and Kashmir, Assam, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh saw the highest reductions in the number of schools.
- Many school closures or mergers have led to increased distances for students, causing further dropouts during re-admission processes.
Socio-Economic Barriers:
- Economic hardships, migration, and inadequate facilities contribute to the enrolment decline.
- Low-income families and backward regions struggle to prioritize education, further affecting enrolment and retention.
Government Initiatives:
- Initiatives like the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, and Right to Education Act (RTE) have made strides in primary education but face challenges in secondary education.
- Education spending has hovered around 4-4.6% of GDP, which is insufficient to meet the needs of the education system.
Moving Forward:
- Targeted Interventions: Focus on expanding vocational training, incentivizing school attendance, and improving digital infrastructure in schools.
- Address Regional Disparities: Conduct audits to address school shortages in densely populated areas and consolidate underutilized urban schools.
- Enhancing Teacher Quality: Invest in teacher training and encourage innovative teaching methods.
- Community Engagement: Promote local participation in school management to address specific educational needs.
Conclusion:
The UDISE+ 2023-24 report underscores the need for urgent reforms in India's education system, focusing on increasing enrolment, reducing dropout rates, and ensuring equitable access to quality education. By addressing these challenges with targeted policies, India can move closer to achieving its educational goals.
Why Farmers Deserve Price Security
- 11 Jan 2025
Introduction:
The future of Indian agriculture is at a crossroads. With the shrinking of the agricultural workforce and the diversion of fertile farmlands for urbanization, ensuring the sustainability of farming is a strategic imperative. Among the various support mechanisms for farmers, the Minimum Support Price (MSP) remains a central point of debate. Should there be a legal guarantee for MSP? This question has gained prominence, especially with the rising challenges in agriculture, from unpredictable climate patterns to volatile market prices.
The Decline of Agriculture and Its Impact
India’s agricultural sector faces a dual crisis: loss of both land and human resources. Prime agricultural lands across river basins, such as the Ganga-Yamuna Doab or the Krishna-Godavari delta, are being repurposed for real estate, infrastructure, and industrial projects. Additionally, the number of "serious farmers" – those deriving at least half of their income from agriculture – is dwindling. The number of operational holdings may be 146.5 million, but only a small fraction of these farmers remains committed to agriculture.
This decline threatens the future of India’s food security, as the country will need to feed a population of 1.7 billion by the 2060s. To sustain farming and ensure long-term food security, we must secure farmers' livelihoods. Price security, particularly through MSP, plays a crucial role in this context.
The Role of MSP in Securing Farmers
MSP is the government-mandated price at which it guarantees the purchase of crops if market prices fall below a certain threshold. It provides a safety net for farmers against price volatility. The process of fixing MSP involves recommendations by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), which takes into account factors such as the cost of production and market trends. Once approved by the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), MSP is set for various crops, including rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
For farmers to stay in business, there must be a balance between production costs and returns. Farming is a risky business – yield losses can occur due to weather anomalies, pest attacks, or other natural factors. However, price risks can be mitigated with a guaranteed MSP. This would encourage farmers to invest in their land and adopt modern farming technologies, which would boost productivity and reduce costs.
Arguments for and Against Legal MSP Guarantee
Supporters of a legal MSP guarantee argue that it would provide financial security to farmers, protecting them from unpredictable market conditions. It would also promote crop diversification, encourage farmers to shift from water-intensive crops to those less dependent on irrigation, and inject resources into rural economies, thus addressing distress in rural areas.
However, critics highlight several challenges with a legal guarantee for MSP. The most significant concern is the fiscal burden it would impose on the government, potentially reaching Rs. 5 trillion. Furthermore, such a system could distort market dynamics, discouraging private traders and leading to a situation where the government becomes the primary buyer of agricultural produce. This could be economically unsustainable, especially for crops with low yields. Additionally, legal MSP guarantees could violate World Trade Organization (WTO) subsidy principles, adversely impacting India’s agricultural exports.
The Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
Given the challenges associated with a legal MSP guarantee, alternative measures should be explored. Price Deficiency Payment (PDP) schemes, such as those implemented in Madhya Pradesh and Haryana, could be expanded at the national level. These schemes compensate farmers for the difference between market prices and MSP, ensuring price security without the fiscal burden of procurement.
Additionally, the government can focus on improving agricultural infrastructure, such as cold storage facilities, to help farmers better access markets and increase price realization. Supporting Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) could also help farmers by enhancing collective bargaining power and ensuring better prices for their produce. Moreover, gradual expansion of MSP coverage to include a wider range of crops would encourage diversification, reducing the dominance of rice and wheat.
River Interlinking: Environmental Disaster or Solution?
- 09 Jan 2025
Overview of the River Interlinking Concept
The concept of river interlinking in India traces its origins to the 19th century, when Sir Arthur Cotton first proposed inter-basin water transfer to address irrigation issues. Over time, this idea was refined by other experts. It evolved into the National Water Grid and, later, the River-Interlinking Project (ILR) under the Ministry of Water Resources. The goal is to transfer surplus water from rivers to drought-prone areas, aiming for water security, irrigation, and power generation.
Key Projects and Initiatives
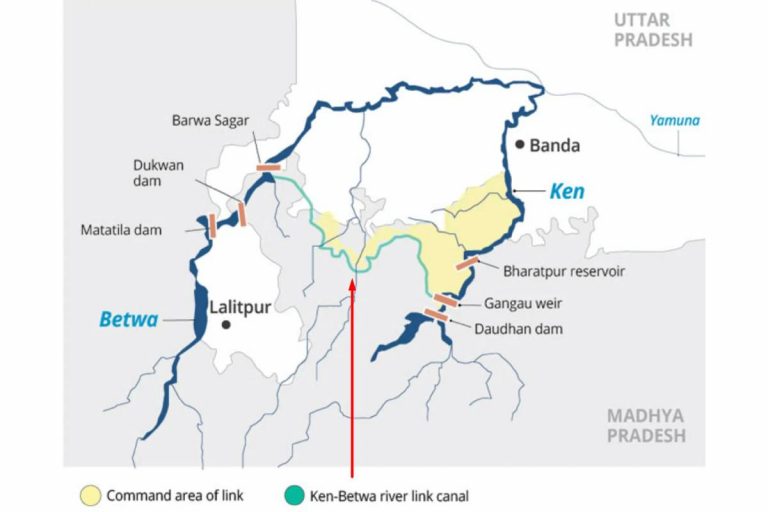
- Ken-Betwa River Link Project (KBLP): Launched in December 2024, the KBLP will link the water-surplus Ken River with the drought-stricken Betwa River. It aims to irrigate over 10 lakh hectares, supply drinking water to 62 lakh people, and generate hydropower and solar power. However, concerns over the environmental impact of building a dam within the Panna Tiger Reserve have been raised.
- National River Linking Project (NRLP): The NRLP, formally known as the National Perspective Plan, is an ambitious proposal that includes 30 river links—14 Himalayan and 16 Peninsular—to connect India's rivers and create a giant South Asian Water Grid.
Benefits of Interlinking Rivers
- Flood and Drought Mitigation: Redistributing water from surplus areas to drought-prone regions, such as Bundelkhand, will reduce the severity of floods and droughts.
- Agriculture and Irrigation: Expanding irrigation systems across 35 million hectares of land could significantly boost agricultural productivity and food security.
- Hydropower Generation: The interlinking project has the potential to generate up to 34 GW of hydropower, contributing to India's renewable energy targets.
- Economic Growth: Improving water availability can boost industries, provide drinking water, and support economic development in underdeveloped regions.
- Inland Waterways: The project will also contribute to the expansion of inland waterways, benefiting trade and reducing transportation costs.
Challenges and Concerns
- Environmental Impact:
- Biodiversity Loss: Projects like the Ken-Betwa project raise alarms about the destruction of ecologically sensitive areas, such as the Panna Tiger Reserve.
- River Ecosystem Disruption: Altering natural river courses can harm aquatic life, disrupt deltaic ecosystems, and degrade water quality. For instance, the Sardar Sarovar Dam's impact on the Narmada river system shows the long-term consequences of such projects.
- Pollution: The mixing of cleaner and more polluted rivers could exacerbate water contamination issues.
- Social and Financial Costs:
- Displacement: Large-scale interlinking projects will displace millions, especially marginalized communities and indigenous people, and disturb local livelihoods.
- High Financial Burden: The total estimated cost of the NRLP is ?5.5 lakh crore, which does not include environmental rehabilitation costs or the long-term maintenance of the infrastructure.
- Climate Change: Predictions suggest that climate change could affect river flows and the availability of surplus water. This might render the interlinking project ineffective in the long term.
- Inter-State Conflicts: Water-sharing disputes, like the long-standing issues over the Cauvery and Krishna rivers, could intensify with more interlinking projects.
- Infrastructural Challenges: Maintaining vast canal networks and reservoirs, managing sedimentation, and acquiring land for construction are logistical hurdles.
Alternative Approaches and Solutions
- Efficient Water Management:
- Integrated Watershed Management: Implementing a comprehensive approach to manage existing water resources can reduce the need for large-scale river transfers.
- Groundwater Recharge: Focusing on efficient groundwater management by identifying recharge mechanisms and regulating water use is crucial for sustainability.
- Modern Irrigation Techniques:
- Drip Irrigation: Israel’s success with drip irrigation, which reduces water use by 25%-75%, provides an example of how modern technologies can save significant amounts of water.
- Virtual Water: Emphasizing the import of water-intensive goods (like wheat) could save local water resources, which would otherwise be used for domestic agriculture.
- National Waterways Project (NWP): An alternative to the interlinking project, NWP aims to improve water management by creating navigation channels that double as water distribution networks with a fraction of the land use.
Way Forward
- Comprehensive Impact Assessments: The need for multidisciplinary studies to evaluate the environmental, social, and economic impacts of river interlinking projects cannot be overstated. Stakeholder engagement is crucial for equitable decision-making.
- Sustainable Water Policies: A national water policy should prioritize sustainable water practices, focusing on local solutions, such as water harvesting, watershed management, and smart irrigation.
- Focus on Regional Solutions: Smaller, state-specific projects should be prioritized to address water scarcity issues without triggering large-scale environmental degradation.
The Impact of Climate Change on Earth’s Water Cycle

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Climate change is significantly affecting Earth's water cycle, leading to extreme weather events such as intense floods and prolonged droughts. According to the 2024 Global Water Monitor Report, this disruption is increasingly evident, as seen in the devastating weather patterns experienced worldwide in 2024. The report, based on data from international researchers, highlights how these changes are directly linked to rising global temperatures and the resulting shifts in precipitation patterns.
Understanding the Water Cycle
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water in various forms—solid, liquid, and gas—throughout the Earth's atmosphere, land, and bodies of water. This cycle involves processes such as:
- Evaporation: Water from the surface of oceans, lakes, and rivers turns into vapor.
- Transpiration: Water is absorbed by plants from the soil and released as vapor.
- Precipitation: Water vapor condenses into clouds and falls as rain or snow, replenishing the Earth's surface.
- Runoff and Infiltration: Precipitation either flows into rivers or infiltrates the soil, contributing to groundwater.
The water cycle is vital for maintaining the planet’s ecosystems, regulating weather patterns, and providing water for all living organisms. However, climate change is intensifying these natural processes, with far-reaching consequences.
Impact of Climate Change on the Water Cycle
As global temperatures rise, climate change is having a profound impact on the water cycle. Warmer temperatures lead to:
- Increased evaporation: As air temperatures soar, more water evaporates into the atmosphere. For every 1°C rise in temperature, the atmosphere can hold about 7% more moisture, which exacerbates storms and increases the intensity of rainfall.
- More intense precipitation: With more moisture in the atmosphere, storms have become more intense, leading to severe flooding in various regions.
- Increased droughts: Warmer air also dries out the soil. This reduces the amount of water available for crops and plants, while also increasing the evaporation rate from soil, leading to longer and more intense droughts.
This disruption of the water cycle is already causing erratic weather patterns, as some regions face severe droughts, while others are experiencing extreme rainfall and floods.
Key Findings from the 2024 Global Water Monitor Report
The 2024 report presents several alarming statistics that highlight the growing impact of climate change on the water cycle:
- Water-related disasters: In 2024, these disasters caused over 8,700 fatalities, displaced 40 million people, and resulted in economic losses exceeding $550 billion globally.
- Dry months: There were 38% more record-dry months in 2024 than the baseline period (1995-2005), underlining the growing frequency of droughts.
- Intense rainfall: Record-breaking rainfall occurred 27% more frequently in 2024 compared to 2000, with daily rainfall records set 52% more often. This shows the growing intensity of precipitation events.
- Terrestrial water storage (TWS): Many dry regions faced ongoing low TWS levels, reflecting the scarcity of water in these areas, while some regions, such as parts of Africa, saw an increase in water storage.
- Future predictions: Droughts may worsen in regions like northern South America, southern Africa, and parts of Asia, while areas like the Sahel and Europe could experience increased flood risks in the coming years.
Conclusion
The findings of the 2024 report underscore the alarming impact of climate change on the global water cycle. As temperatures continue to rise, we can expect more frequent and severe weather events, including extreme flooding and devastating droughts. These changes will affect billions of people worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for action to mitigate climate change and adapt to its consequences. Addressing this challenge requires global cooperation to reduce emissions, enhance water management systems, and protect vulnerable regions from the intensifying effects of climate change.
Implications of China’s Mega-Dam Project on the Brahmaputra River Basin
- 07 Jan 2025
Introduction:
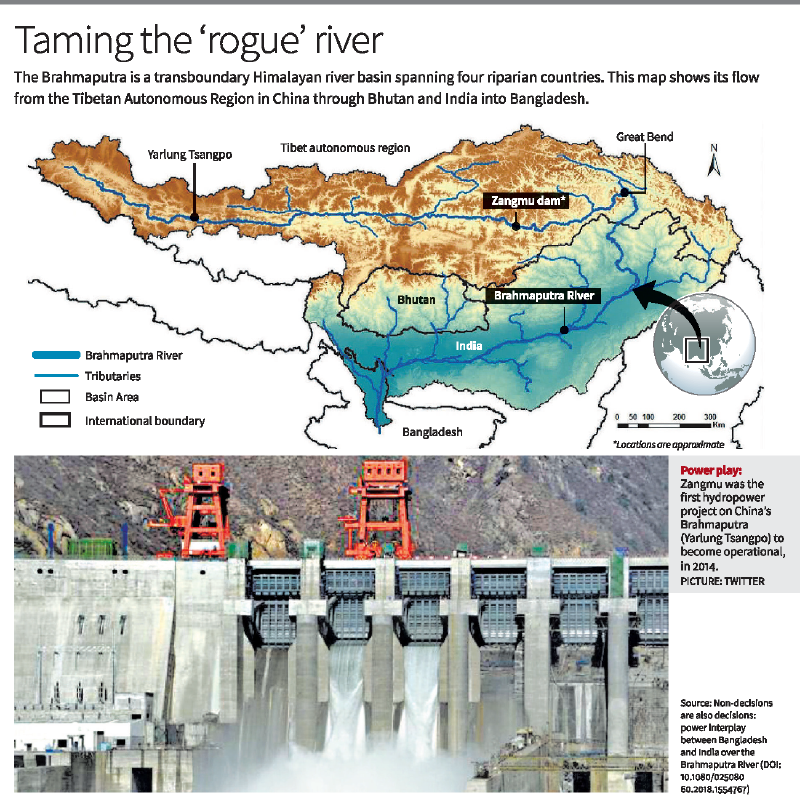
China has approved the construction of the Yarlung Tsangpo hydropower project, the world's largest hydropower project, with a capacity of 60,000 MW, on the Brahmaputra River in Tibet. This mega-dam, located at the Great Bend in Medog county, has significant geopolitical, environmental, and socio-economic implications for India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh, the downstream riparian countries.
Geographical and Geopolitical Context:
- The Brahmaputra is a transboundary river system flowing through China, India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- China, located at the river’s source in Tibet, is the uppermost riparian nation, controlling water flow into India and Bangladesh.
- All riparian countries, including China, India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh, have proposed major water infrastructure projects in the river basin, which has become a site for geopolitical rivalry, with mega-dams symbolizing sovereignty.
China’s Hydropower Ambitions:
- The Yarlung Tsangpo project is part of China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) and aims to address the country's energy needs while moving towards net carbon neutrality by 2060.
- The river's steep descent from Tibet provides an ideal location for hydroelectricity generation.
- China’s previous mega-projects, like the Three Gorges Dam, highlight the scale of these ambitions but also raise concerns about environmental and social consequences, including ecosystem disruption, displacement, and seismic risks.
Impact on Downstream Communities:
- Water Flow and Agriculture: China’s mega-dam may significantly alter water flow to India, particularly affecting agriculture and water availability in the northeastern regions. India, reliant on the Brahmaputra for irrigation and drinking water, could face disruptions.
- Silt and Biodiversity: The blocking of silt essential for agriculture could degrade soil quality and damage biodiversity in the river basin.
- Seismic Risks: The region’s seismic activity, coupled with the construction of large dams, heightens the risk of catastrophic events such as landslides and Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), which have previously caused devastation in the Himalayas.
Hydropower Competition Between China and India:
- Both China and India are competing to harness the Brahmaputra's potential for hydropower, with India planning its own large project at Upper Siang.
- Bhutan has also proposed several medium-sized dams, raising concerns in downstream countries about cumulative impacts.
- No comprehensive bilateral treaty exists between India and China to regulate shared transboundary rivers, though they have mechanisms for data sharing and discussions on river issues.
Environmental and Regional Concerns:
- The Brahmaputra river basin is an ecologically sensitive region. The construction of large dams threatens the fragile ecosystem, including agro-pastoral communities, biodiversity, and wetlands.
- Tibet’s river systems are vital for the global cryosphere, affecting climate systems, including monsoon patterns. Disruption to these systems could have broader implications for regional and global climate stability.
Challenges in Bilateral Cooperation:
- India and China have struggled with effective coordination on river management. China has shown reluctance to share critical hydrological data, a concern amplified by the lack of a binding agreement.
- The ongoing geopolitical tensions between the two countries, particularly over the border dispute, further complicate cooperation on transboundary water issues.
Recommendations for India:
- Enhanced Cooperation: India should push for renewed agreements and mechanisms for real-time data exchange with China to prevent ecological and socio-economic damage.
- Public Challenges: India needs to challenge China’s claims that its hydropower projects will have minimal downstream impact, ensuring that India's concerns are addressed in international forums.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Water issues should be prioritized in India’s diplomatic engagement with China, emphasizing the importance of transparency and cooperation to ensure mutual benefit and regional stability.
Conclusion:
The Yarlung Tsangpo mega-dam project poses significant risks to the entire Brahmaputra river basin. A collaborative approach, involving transparent dialogue and cooperation among riparian countries, is essential to mitigate the potential adverse impacts on downstream communities and the fragile Himalayan ecosystem.
NITI Aayog Celebrates 10 Years

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
- NITI Aayog, the National Institution for Transforming India, completed its 10th anniversary on January 1, 2025.
- Established to replace the Planning Commission, NITI Aayog was designed to address contemporary challenges such as sustainable development, innovation, and decentralization in a dynamic, market-driven economy.
About NITI Aayog
Establishment and Mandate
- Formation: Created through a Union Cabinet resolution in 2015.
- Primary Mandates:
- Overseeing the adoption and monitoring of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Promoting competitive and cooperative federalism between States and Union Territories.
Composition
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India.
- Governing Council: Includes Chief Ministers (CMs) of all States and UTs, Lt. Governors, the Vice Chairperson, full-time members, and special invitees.
- CEO: Appointed by the PM for a fixed tenure.
Key Achievements
Policy Advisory and Decentralized Governance
- Shifted focus from financial allocation to policy advisory roles.
- Promoted decentralized governance through data-driven initiatives like the SDG India Index and the Composite Water Management Index.
Innovative Initiatives
- Aspirational Blocks Programme (2023): Focused on 500 underdeveloped blocks for 100% coverage of government schemes.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): Trained over 1 crore students through Atal Tinkering Labs and incubation centres.
- Initiatives like e-Mobility, Green Hydrogen, and the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme were conceptualized to drive innovation and sustainability.
Role and Functions of NITI Aayog
Strategic Advice and Federal Cooperation
- Provides policy formulation and strategic advice to both central and state governments.
- Fosters cooperative federalism by encouraging collaboration between the central and state governments.
Monitoring and Evaluation
- Plays a crucial role in monitoring and evaluating policies and programs to ensure alignment with long-term goals.
Promoting Innovation and SDGs
- NITI Aayog contributes to aligning national development programs with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), focusing on innovation, research, and technology in critical sectors.
Key Differences Between Planning Commission and NITI Aayog
Aspect Planning Commission NITI Aayog
Purpose Centralized planning and resource allocation. Focus on cooperative federalism and policy research.
Structure Led by the PM, with Deputy Chairman and full-time members. Led by the PM, with Vice-Chairperson, CEO, and Governing Council.
Approach Top-down, centralized. Bottom-up, encouraging state participation.
Role in Governance Executive authority over policies. Advisory body without enforcement power.
Five-Year Plans Formulated and implemented. Focus on long-term development, no Five-Year Plans.
Challenges Faced by NITI Aayog
- Limited Executive Power: Lacks authority to enforce its recommendations, restricting its influence.
- Coordination Issues: Achieving effective collaboration between central and state governments remains challenging.
- Data Gaps: Inconsistent state-level data hampers accurate policymaking and evaluation.
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources hinder full implementation of initiatives.
- Resistance to Change: Some states resist NITI Aayog's initiatives due to concerns over autonomy and alignment with local needs.
Future Vision and Planning
- Agenda for 2030: Focus on achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in areas like poverty alleviation, education, healthcare, clean energy, and gender equality.
- Vision for 2035: NITI Aayog's 15-year vision document aims for sustainable, inclusive growth, with an emphasis on economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability.
- Innovation and Digitalization: Promotes digitalization and innovation through data-driven policymaking and regional focus on tribal and hilly areas.
Conclusion: Reflections on the First Decade
- Despite significant achievements, NITI Aayog’s influence remains limited by its advisory role and resource constraints.
- The shift away from centralized planning, evident since the dissolution of the Planning Commission, has sparked debate about the effectiveness of such a model in ensuring long-term development and inclusive growth.
Draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India has introduced the long-awaited draft Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025 to operationalize the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023. These rules contain several significant provisions, including the controversial reintroduction of data localisation requirements, provisions for children's data protection, and measures to strengthen data fiduciaries' responsibilities.
This development holds substantial implications for both Indian citizens' data privacy and global tech companies, especially with respect to compliance, security measures, and data processing.
Data Localisation Mandates
Key Provision: The draft rules propose that certain types of personal and traffic data must be stored within India. Specifically, "significant data fiduciaries", a category that will include large tech firms such as Meta, Google, Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon, will be restricted from transferring certain data outside India.
- Committee Oversight: A government-appointed committee will define which types of personal data cannot be transferred abroad, based on factors like national security, sovereignty, and public order.
- Localisation Re-entry: This provision brings back data localisation, a contentious issue previously removed from the 2023 Data Protection Act after heavy lobbying by tech companies.
- Impact on Big Tech: Companies like Meta and Google had previously voiced concerns that strict localisation rules could hinder their ability to offer services in India, with Google arguing for narrowly tailored data localisation norms.
Role and Responsibilities of Data Fiduciaries
Key Provision: The rules lay out a clear framework for data fiduciaries, defined as entities that collect and process personal data.
- Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs): This subcategory will include entities that process large volumes of sensitive data, such as health and financial data. These companies will be held to higher standards of compliance and security.
- Data Retention: Personal data can only be stored for as long as consent is valid; after which, it must be deleted.
- Security Measures: Data fiduciaries must implement stringent measures such as encryption, access control, unauthorized access monitoring, and data backups.
Parental Consent for Children's Data
Key Provision: The draft rules include provisions aimed at protecting children's data, including mechanisms to ensure verifiable parental consent before children under 18 can use online platforms.
- Verification Process: Platforms must verify the identity of parents or guardians using government-issued identification or digital locker services.
- Exceptions: Health, mental health institutions, educational establishments, and daycare centers will be exempted from needing parental consent.
Data Breach Reporting and Penalties
Key Provision: In the event of a data breach, data fiduciaries are required to notify affected individuals without delay, detailing the breach's nature, potential consequences, and mitigation measures. Failure to comply with breach safeguards can result in penalties.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Entities that fail to adequately protect data or prevent breaches could face fines of up to Rs 250 crore.
- Breach Notification: The rules mandate timely reporting of all breaches, whether minor or major, and an emphasis on transparency in the breach notification process.
Safeguards for Government Data Processing
Key Provision: The draft rules seek to ensure that the government and its agencies process citizen data in a lawful manner with adequate safeguards in place.
- Exemptions for National Security and Public Order: The rules also address concerns that the government may process data without adequate checks by stipulating lawful processing and protections when data is used for national security, foreign relations, or public order.
Compliance Challenges for Businesses
Key Challenges: The introduction of these rules will impose several challenges for businesses, particularly tech companies:
- Consent Management: Companies will need to implement robust systems to handle consent records, allowing users to withdraw consent at any time. This will require significant infrastructure changes.
- Data Infrastructure Overhaul: Organizations will need to invest in data collection, storage, and lifecycle management systems to ensure compliance.
- Security Standards: Experts have raised concerns about the vagueness of certain security standards, which could lead to inconsistent implementation across sectors.
Penalties and Enforcement
Key Provisions:
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Entities failing to adhere to the rules may face significant financial penalties, including fines up to Rs 250 crore for serious breaches.
- Repeat Violations: Consent managers who repeatedly violate rules could have their registration suspended or cancelled.
Conclusion:
The Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025 bring important changes to India’s data privacy framework, particularly the reintroduction of data localisation and more stringent requirements for data fiduciaries. These rules aim to strengthen citizen privacy and ensure greater accountability from businesses. However, the challenges in compliance, especially for global tech firms, and the potential impact on service delivery, will need to be closely monitored as the final rules take shape.
Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) 2023-24 Report
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
The UDISE+ report for 2023-24, released by the Ministry of Education, presents key insights into India’s school education system. UDISE+ serves as a comprehensive database, tracking student enrolment, school infrastructure, and other educational parameters, enabling efficient policy implementation and gap identification.
Key Findings:
- Decline in School Enrolment: Enrolment figures in Indian schools have witnessed a significant decline for the first time in recent years. The total enrolment dropped from 26.36 crore (2018-22 average) to 25.17 crore in 2022-23 and further to 24.8 crore in 2023-24, marking a fall of 1.55 crore students or nearly 6%. This drop is attributed to the improved data collection methods which helped eliminate duplicate entries, especially students enrolled in both government and private schools.
- Gender and School Type-wise Trends: The enrolment drop was observed across both government and private schools. Government schools saw a decline of 5.59%, whereas private schools experienced a 3.67% reduction. Gender-wise, the enrolment of boys decreased by 6.04%, while girls’ enrolment dropped by 5.76%, compared to the 2018-22 average.
- State-wise Data: The enrolment drop was not uniform across states. Bihar recorded the largest decline, with a loss of 35.65 lakh students, followed by Uttar Pradesh (28.26 lakh) and Maharashtra (18.55 lakh). In contrast, states like Andhra Pradesh, Delhi, Jammu & Kashmir, and Telangana saw an increase in enrolment during the same period.
- Level-wise Trends: The most significant declines were recorded at the primary (Classes 1-5), upper primary (Classes 6-8), and secondary (Classes 9-10) levels. However, enrolment in pre-primary and higher secondary (Classes 11-12) levels showed an increase in 2023-24 compared to the previous average.
- Impact of Data Refinement: The implementation of Aadhaar-linked student data collection has enhanced the accuracy of enrolment figures. The de-duplication process helped remove cases of students being enrolled in both government and private schools. This revision is expected to provide more accurate data for targeted educational schemes and improve the effectiveness of government programs like Samagra Shiksha and PM POSHAN.
Challenges in Education
Despite the improvements in data collection, several systemic issues persist:
- Access and Retention: High dropout rates, especially at the secondary level, remain a challenge for sustained student retention.
- Disparities among Marginalized Groups: Enrolment among SC, ST, OBC, and minority communities showed a notable decline, reflecting existing inequities in the education system.
- Infrastructure and Teacher Training: Uneven distribution of resources and insufficient teacher training continue to hamper educational outcomes, affecting quality and student engagement.
Way Forward
To address these challenges, the following steps are critical:
- Strengthening NEP 2020: The National Education Policy aims for universal Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) by 2030, with a focus on skill-based learning and inclusive education.
- Teacher Capacity Building: There is a need for targeted interventions to improve teacher quality and address gaps in the student-teacher ratio.
- Infrastructure Optimization: Schools should optimize their resources based on enrolment trends to improve access and address disparities.
- Data-Driven Monitoring: Continuous monitoring using student-specific data will help identify dropouts and allocate resources efficiently.
Government Extends Special Subsidy on DAP

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian government has decided to extend the special subsidy on Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) fertilizer for another year, a decision aimed at stabilizing farmgate prices and addressing the challenges posed by the depreciation of the Indian rupee.
Key Government Decision
- Extension of Subsidy: The Centre has extended the Rs 3,500 per tonne special subsidy on DAP from January 1, 2025 to December 31, 2025.
- Objective: This extension aims to contain farmgate price surges of DAP, India’s second most-consumed fertilizer, which is being impacted by the fall in the rupee's value against the US dollar.
Fertilizer Price Dynamics and Impact
- MRP Caps on Fertilizers: Despite the decontrol of non-urea fertilizers, the government has frozen the maximum retail price (MRP) for these products.
- Current MRPs:
- DAP: Rs 1,350 per 50-kg bag
- Complex fertilizers: Rs 1,300 to Rs 1,600 per 50-kg bag depending on composition.
- Current MRPs:
- Subsidy on DAP: The subsidy includes Rs 21,911 per tonne on DAP, plus the Rs 3,500 one-time special package.
- Impact of Currency Depreciation:
- The rupee's depreciation has made imported fertilizers significantly more expensive.
- The landed price of DAP has increased from Rs 52,960 per tonne to Rs 54,160 due to the rupee falling from Rs 83.8 to Rs 85.7 against the dollar.
- Including additional costs (customs, port handling, insurance, etc.), the total cost of imported DAP is now Rs 65,000 per tonne, making imports unviable without further subsidy or MRP adjustments.
- The rupee's depreciation has made imported fertilizers significantly more expensive.
Industry Concerns and Viability Issues
- Import Viability:
- Fertilizer companies face significant cost pressures due to rising import prices and the current MRP caps.
- Without an increase in government subsidies or approval to revise MRPs upwards, imports will be unviable.
- Even with the extended subsidy, companies estimate a Rs 1,500 per tonne shortfall due to currency depreciation.
- Stock Levels and Supply Challenges:
- Current stock levels for DAP (9.2 lakh tonnes) and complex fertilizers (23.7 lakh tonnes) are below last year's levels.
- With inadequate imports, there are concerns about fertilizer supply for the upcoming kharif season (June-July 2025).
Government’s Strategy and Fiscal Implications
- Compensation for Imports:
- In September 2024, the government approved compensation for DAP imports above a benchmark price of $559.71 per tonne, based on an exchange rate of Rs 83.23 to the dollar.
- With the rupee falling below Rs 85.7, these previous compensation calculations have become outdated.
- Fiscal Impact:
- The extended subsidy will cost the government an additional Rs 6,475 crore. Despite this, political implications of raising the MRP are minimal, as only non-major agricultural states are facing elections in 2025.
Future Outlook and Priorities
- Immediate Priority: The government’s primary concern is securing adequate fertilizer stocks for the kharif season, focusing on ensuring sufficient imports of both finished fertilizers and raw materials.
- Balancing Factors: The government will need to navigate the complex balance of maintaining fertilizer affordability for farmers, ensuring the viability of fertilizer companies, and managing fiscal constraints.
As the subsidy extension is implemented, all eyes will be on the government's ability to ensure a stable supply of fertilizers while safeguarding both farmer interests and economic sustainability in the face of an increasingly challenging exchange rate environment.
Caste-Based Discrimination in Prisons

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Ministry of Home Affairs has recently introduced significant revisions to the Model Prison Manual, 2016, and the Model Prisons and Correctional Services Act, 2023. These changes aim to eliminate caste-based discrimination in Indian prisons and establish a standardized approach to defining and treating habitual offenders across the country.
Background
In October 2024, the Supreme Court of India expressed concerns over the persistence of caste-based discrimination within prisons and the lack of consistency in how habitual offenders are classified. In response, the Court instructed the government to amend prison regulations to promote equality and fairness. The newly introduced reforms are in line with the Court's directives and focus on aligning prison practices with constitutional principles.
Addressing Caste-Based Discrimination in Prisons
The recent amendments take specific steps to combat caste-based discrimination within correctional facilities:
- Ban on Discrimination: Prison authorities are now mandated to ensure there is no caste-based segregation or bias. All work assignments and duties will be distributed impartially among inmates.
- Legal Provision Against Discrimination: A new clause, Section 55(A), titled "Prohibition of Caste-Based Discrimination in Prisons and Correctional Institutions", has been added to the Model Act, establishing a formal legal framework to address caste discrimination.
- Manual Scavenging Ban: The amendments extend the provisions of the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013 to include prisons, prohibiting the degrading practice of manual scavenging or any hazardous cleaning within correctional facilities.
Redefining Habitual Offenders
The updated amendments also standardize the classification and treatment of habitual offenders, in accordance with the Supreme Court’s directions:
- Uniform Definition: A habitual offender is now officially defined as an individual convicted and sentenced to imprisonment for two or more separate offences within a continuous five-year period, provided the sentences were not overturned on appeal or review. Importantly, time spent in jail under sentence is excluded from this five-year period.
- National Consistency: States that do not have specific Habitual Offender Acts must amend their laws within three months to ensure consistency with the new national framework.
Importance of the Reforms
- Promoting Equality: These amendments seek to uphold the constitutional rights of prisoners, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of caste or background, are treated equally and with dignity.
- Eliminating Degrading Practices: The extension of the manual scavenging prohibition to prisons is a vital step in eliminating degrading and inhumane practices, ensuring a more humane environment for prisoners.
- Uniform Framework: The establishment of a standardized definition of habitual offenders ensures a consistent approach in handling repeat offenders across all states, reducing the possibility of arbitrary classifications.
Conclusion
The reforms introduced by the Union Home Ministry mark a significant milestone in India’s prison reform journey. By addressing caste-based discrimination and standardizing the classification of habitual offenders, these amendments reaffirm the country’s commitment to human rights and the rule of law. These changes not only improve the conditions within prisons but also set the stage for future reforms aimed at creating a fairer and more equitable correctional system.
Introduction to Dr. Manmohan Singh's Economic Reforms
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Dr. Manmohan Singh, a distinguished economist, played a crucial role in shaping India’s economic trajectory. His leadership, as Finance Minister (1991–96) and Prime Minister (2004–14), is particularly noted for the economic liberalization and reform policies that transformed India’s economy.
India’s Economic Crisis of 1991
- Economic Collapse: India faced a severe balance of payments crisis, with dwindling foreign reserves and rising inflation.
- Key Challenges: Fiscal deficit, industrial stagnation, and trade imbalances worsened by the collapse of the Soviet Union.
- Urgent Measures: Dr. Singh was appointed Finance Minister during this crisis and initiated bold reforms to stabilize and grow the economy.
Key Reforms in 1991
- Devaluation of the Rupee
- Aimed at making Indian exports competitive in global markets.
- Reduced import tariffs and liberalized foreign trade.
- Industrial Policy Reforms
- Abolition of Licence Raj: Deregulated the industrial sector, promoting private enterprises.
- Reduced state control and encouraged foreign investment, leading to industrial growth.
- Banking and Financial Reforms
- Reduced the statutory liquidity ratio (SLR) and cash reserve ratio (CRR).
- Allowed for more credit flow, fostering economic expansion and banking sector efficiency.
- Global Integration
- Introduced economic liberalization policies, integrating India with the global economy and attracting foreign investments.
Economic Growth and Social Welfare Initiatives
- Poverty Reduction: Reforms helped lift millions out of poverty by fostering job creation and industrial growth.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): Launched in 2005, providing 100 days of wage employment to rural households.
- Right to Information (RTI) and Right to Education (RTE)
- Empowered citizens by ensuring transparency and access to government information.
- RTE guaranteed free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14.
- Financial Inclusion: Aadhar project introduced to facilitate welfare delivery and financial inclusion.
Legacy of Economic Liberalization and Growth
- Economic Growth: Under his leadership, India’s GDP grew at an average rate of 8%, establishing India as one of the fastest-growing economies.
- Shift to a Market-Driven Economy: Reforms dismantled socialist controls, facilitating the rise of the private sector.
- Attracting Foreign Investment: Economic liberalization and policy reforms made India an attractive destination for foreign capital.
Leadership During Political and Economic Challenges
- Reluctant Prime Minister
- In 2004, Singh became Prime Minister despite initial reluctance, emerging as a unifying figure during coalition politics.
- His tenure saw India’s rise as a global economic power, particularly from 2004–2009.
- Challenges
- Singh’s second term was marred by allegations of corruption and policy paralysis, leading to criticism of his administration.
- However, his personal integrity remained intact, and he maintained focus on governance.
- Historic India-US Nuclear Deal (2008)
- The deal marked a significant shift in India’s foreign relations and energy policies, enabling civilian nuclear trade.
Conclusion
Dr. Manmohan Singh’s economic policies are central to India's modern economic framework. His vision transformed India from a closed, socialist economy to a vibrant, globalized economy, promoting inclusive growth and institutional reforms. Despite facing challenges and criticisms, his legacy remains a testament to strategic policymaking that continues to influence India’s economic landscape.
Sustainable Groundwater Management in India’s Agriculture

- 30 Dec 2024
Introduction: Groundwater Crisis and Agriculture
- India's Agricultural Dependence on Groundwater: India is a leading producer of water-intensive crops like rice, wheat, and pulses. The country’s agricultural sector heavily depends on groundwater for irrigation, especially for paddy cultivation.
- Over-exploitation of Groundwater: Groundwater extraction for irrigation is increasingly unsustainable, threatening agricultural sustainability in the long term.
Rising Groundwater Usage and Its Implications
- Population Growth and Groundwater Use: Between 2016 and 2024, global population grew from 7.56 billion to 8.2 billion, and India’s population rose from 1.29 billion to 1.45 billion. Concurrently, groundwater used for irrigation increased from 38% in 2016-17 to 52% in 2023-24, exacerbating the water crisis.
- Over-extraction in Major Paddy-Producing States: States like Rajasthan, Punjab, and Haryana have witnessed severe over-exploitation of groundwater for irrigation.
- Rajasthan: Highest groundwater salinisation (22%) despite receiving the highest average rainfall (608 mm) among these states.
- Punjab and Haryana: Lesser groundwater salinity due to canal irrigation and micro-irrigation systems.
Impact of Excessive Fertilizer Use on Groundwater Quality
- Soil Salinity and Groundwater Contamination: Excessive use of fertilizers, particularly for paddy cultivation, increases soil salinity and contributes to groundwater contamination.
- Toxic Chemicals in Groundwater: Nitrate contamination, caused by nitrogen-based fertilizers, and uranium contamination due to phosphate fertilizers are key concerns in states like Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Health Risks: Contaminated groundwater poses health risks such as thyroid disorders, cancer, and dental fluorosis, along with reduced agricultural productivity.
Projected Impact on Future Groundwater Availability
- Unsustainable Groundwater Levels: The Central Groundwater Board (CGWB) reports that if current practices continue, over half of the districts in Punjab could face groundwater depletion. Similarly, 21-23% of districts in Haryana and Rajasthan may experience a similar crisis.
- Population Growth and Water Scarcity: With India’s population expected to reach 1.52 billion by 2036, the need for sustainable groundwater management becomes even more critical.
Government Initiatives for Groundwater Management
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (2014): Promotes sustainable practices like zero tillage, cover cropping, and micro-irrigation for efficient water and chemical use.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (2015): Aims to boost irrigation efficiency through drip and sprinkler irrigation methods.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana (2019): Targets efficient groundwater management in water-stressed states like Gujarat, Haryana, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Success of Government Initiatives: CGWB data shows that the percentage of districts with unsustainable groundwater levels dropped from 23% in 2016-17 to 19% in 2023-24.
Role of State Governments in Groundwater Management
- State-Level Initiatives: States with unsustainable groundwater levels must take proactive measures to manage water resources efficiently.
- Example - Odisha: Odisha's Integrated Irrigation Project for Climate Resilient Agriculture emphasizes irrigation efficiency and climate-smart practices, supported by World Bank funding.
- Encouraging Resource-Efficient Agriculture: States with safe groundwater levels, like Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Telangana, and Odisha, should adopt water-efficient practices to protect groundwater resources.
Conclusion: Ensuring Agricultural Sustainability and Water Security
- Need for Urgent Action: Scaling up efforts to improve irrigation practices and groundwater management is crucial to securing India’s agricultural future.
- Global Food Security: Protecting groundwater resources will not only ensure water security within India but also contribute to global food security amid climate challenges.
- Blueprint for Sustainable Agriculture: States like Odisha are providing a model for sustainable water management, which can be replicated across water-stressed regions in India.
Surge in E-Waste Generation in India
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
India has seen a significant increase in electronic waste (e-waste) generation, rising by 72.54% from 1.01 million metric tonnes (MT) in 2019-20 to 1.751 million MT in 2023-24. The sharpest rise occurred between 2019-20 and 2020-21, driven by increased electronic consumption due to the COVID-19 pandemic's work-from-home and remote learning arrangements.
Environmental and Health Concerns
E-waste contains hazardous substances like arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury. If not properly managed, these materials can severely impact human health and the environment, contaminating soil and water sources.
Government Efforts: E-Waste Management Rules, 2022
- Introduction of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): The government introduced the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, effective from April 1, 2023. These rules focus on making producers responsible for the recycling of e-waste. Producers are assigned recycling targets based on the quantity of e-waste generated or products sold and must purchase EPR certificates from authorized recyclers to meet these targets.
- Integration of Bulk Consumers: Public institutions and government offices, categorized as bulk consumers, are mandated to dispose of e-waste only through registered recyclers or refurbishers, ensuring proper treatment and recycling of the waste.
- Expansion of E-Waste Coverage: The updated rules expanded the scope to include 106 Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) items from FY 2023-24, up from 21 items previously covered under the 2016 E-Waste Rules.
Challenges in E-Waste Recycling and Disposal
- Low Recycling Rates: Although the share of e-waste recycled in India has increased from 22% in 2019-20 to 43% in 2023-24, a significant 57% of e-waste remains unprocessed annually. Informal sector practices, which dominate e-waste handling, often lack the necessary environmental safeguards, leading to improper disposal and environmental contamination.
- Lack of Infrastructure and Awareness: India faces challenges in building adequate infrastructure for e-waste collection and recycling, resulting in improper disposal in landfills. Furthermore, a lack of public awareness regarding proper disposal methods exacerbates the problem.
Global Context and India’s Position
- India ranks as the third-largest e-waste generator globally, following China and the United States. With an increasing rate of e-waste generation, the country faces an urgent need to improve recycling efficiency and adopt sustainable disposal methods.
International and National Conventions on E-Waste
- India is a signatory to several international conventions that govern hazardous waste management, including the Basel Convention, which regulates the transboundary movement of hazardous wastes, and the Minamata Convention, which focuses on mercury. At the national level, India has established the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, and other frameworks to manage and reduce e-waste effectively.
Strategic Recommendations for Effective E-Waste Management
- Harnessing the Informal Sector: India’s informal sector, which handles a significant portion of e-waste, must be integrated into the formal recycling systems. This can be achieved through training and financial support to ensure safe and environmentally responsible recycling practices.
- Technological Innovations: Encouraging research into advanced recycling technologies, such as AI and IoT-based solutions for efficient e-waste collection and tracking, will be crucial for improving the e-waste management system.
- Learning from Global Practices: Countries like the European Union (EU) and Japan have set strong examples. The EU’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive and Japan’s Home Appliance Recycling Law emphasize Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and provide models for India to adapt.
Conclusion
To address the growing e-waste challenge, India must improve its recycling infrastructure, integrate the informal sector, and adopt best practices from international models. With sustainable and effective strategies, India can mitigate the environmental and health risks posed by e-waste while promoting a circular economy.
Glass Ceiling Cracks: Women's Rising Role in the 2024 Lok Sabha Elections
- 28 Dec 2024
Introduction:
The 2024 Lok Sabha elections marked a significant step forward for women’s participation in Indian politics. With 800 women candidates contesting across 390 constituencies, this was the highest ever since the 1957 general elections. This surge in women candidates has been a positive reflection of the evolving role of women in India's democratic processes.
Increase in Women Candidates:
- A total of 800 women candidates participated in the 2024 elections, up from 726 in 2019.
- The number of constituencies with no female candidate dropped to a historic low of 152, from 171 in 2019.
- However, despite the rise in participation, only 74 women won, while 629 forfeited their deposits.
Regional Variations:
- The highest number of women candidates were from Maharashtra (111), followed by Uttar Pradesh (80) and Tamil Nadu (77).
- Some constituencies, like Baramati, Secunderabad, and Warangal, saw the highest participation of women, with eight candidates each.
Voter Turnout and Gender Dynamics:
- Women voters surpassed men in voter turnout for the second consecutive time, with 65.78% women casting their vote in 2024, compared to 65.55% of men.
- Assam’s Dhubri recorded the highest female voter turnout at 92.17%, reflecting increased female engagement in the electoral process.
Electoral Data and Gender Insights:
- In 2024, there were 47.63 crore female electors out of 97.97 crore total voters, making up 48.62% of the electorate, a slight increase from 2019.
- The number of female electors per 1,000 male voters reached 946, up from 926 in 2019, showing growing electoral inclusivity.
Challenges and Progress:
- Despite the gains in women’s representation, there remain several constituencies without any female candidates, notably in states like Uttar Pradesh (30 constituencies), Bihar (15), and Gujarat (14).
- Though women's participation has risen, the number of women who win remains disproportionately low, reflecting the challenges they face in a patriarchal political landscape.
Inclusion and Diversity:
- The 2024 elections also saw greater inclusivity, with a rise in third-gender electors, which increased by 23.5% to 48,272.
- Voter turnout among transgender voters nearly doubled, reaching 27.09% compared to 14.64% in 2019.
- Additionally, the number of persons with disabilities (PwD) electors increased to 90.28 lakh, showcasing broader electoral inclusivity.
Conclusion:
The 2024 Lok Sabha elections witnessed a remarkable increase in women’s participation, both as voters and candidates. While the journey toward full gender parity in politics continues, the trends from these elections indicate a growing shift toward more inclusive electoral processes. The data released by the Election Commission further underlines this progress, showing the increasing role of women in shaping India’s democratic future.
Free Movement Regime
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government, through the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), has recently issued new guidelines to regulate the movement of people between India and Myanmar, especially along the border regions. These guidelines come after the suspension of the Free Movement Regime (FMR), which had previously allowed residents within a specified range of the border to move freely. The new protocol aims to enhance internal security and address concerns related to demographic shifts in India's northeastern states.
Background of the Free Movement Regime (FMR)
What is FMR?
The Free Movement Regime (FMR) is a bilateral arrangement between India and Myanmar that permits residents living in border areas to cross the international boundary without a visa. This agreement was established in 1968 to facilitate familial, cultural, and economic exchanges between people living on either side of the border.
Territorial Limits and Evolution
Initially, the FMR allowed free movement within a 40 km radius from the border. However, in 2004, this limit was reduced to 16 km, and additional regulations were introduced in 2016. The most recent development sees the limit further reduced to 10 km, with stricter regulations implemented to regulate the movement.
Recent Developments and New Guidelines
Suspension of FMR
In February 2023, Union Home Minister Amit Shah announced the suspension of the FMR along the India-Myanmar border, citing concerns about internal security and demographic changes, particularly in India's northeastern states. This decision came in the context of growing ethnic violence and political pressures, especially from states like Manipur.
Despite the announcement, the formal scrapping of the FMR is yet to be officially notified by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA). However, the MHA has issued new guidelines to regulate cross-border movement, focusing on enhancing security without completely discontinuing the regime.
Key Features of the New Guidelines
The updated protocols issued by the MHA include several measures aimed at improving the security and regulation of movement across the border:
- Reduced Movement Limit: The new guidelines reduce the free movement limit from 16 km to 10 km from the border on both sides.
- Border Pass System: Residents wishing to cross into Myanmar or return to India must obtain a "border pass" from the Assam Rifles. This pass allows a stay of up to seven days in the neighboring country.
- Document and Health Checks: Upon entry into India, individuals will undergo a document inspection by the Assam Rifles, followed by security and health checks conducted by state police and health authorities. Biometrics and photographs will be collected, and a QR code-enabled border pass will be issued for verification.
- Designated Entry Points: There will be 43 designated entry and exit points across the border, with biometric verification and health screening required at all points.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: The Assam Rifles will oversee the movement, ensuring that individuals comply with the new regulations. Violations of the movement protocol will result in legal action.
Infrastructure and Technology Implementation
The government plans to establish infrastructure, such as biometric machines and software for border pass issuance. Pilot entry and exit points will be operational soon, with a phased implementation for the remaining points.
Political Reactions and Opposition
Regional Concerns and Opposition
The suspension of the FMR has been a contentious issue in India's northeastern states. The governments of Nagaland and Mizoram have raised objections to the scrapping of the regime, citing the cultural and familial ties of border communities. The Nagaland Assembly passed a resolution opposing the government's decision, while political leaders in Manipur argued that the unregulated movement of people had contributed to ethnic violence in the region.
Specific Concerns in Manipur
The chief minister of Manipur, N. Biren Singh, attributed ongoing ethnic conflicts in the state to the unchecked movement of people across the border. This was particularly evident in the violent ethnic clashes that broke out in 2023. As a result, Singh urged the Home Ministry to cancel the FMR along the India-Myanmar border, and the new guidelines reflect the state's concerns.
Conclusion
The suspension of the Free Movement Regime along the India-Myanmar border, followed by the introduction of stricter guidelines, marks a significant shift in India's border management policy. While the formal scrapping of FMR is yet to occur, the new protocols aim to balance security concerns with the region's long-standing cultural ties. The implementation of biometric checks and designated entry points signifies the government’s focus on modernizing border control while addressing regional concerns. The outcome of this policy shift will have important implications for internal security, demographic dynamics, and bilateral relations between India and Myanmar.
Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 26, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi presided over the Veer Bal Diwas celebrations at the Bharat Mandap in New Delhi. This annual event commemorates the martyrdom of the sons of Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji and highlights the importance of nurturing the next generation. During the occasion, PM Modi also launched the ‘Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan,’ an initiative aimed at improving nutrition and well-being in rural India.
Veer Bal Diwas: Commemorating Sacrifice and Courage
Veer Bal Diwas was declared on January 9, 2022, by PM Modi to honor the sacrifices made by the young sons of Guru Gobind Singh Ji — Sahibzada Baba Zorawar Singh and Baba Fateh Singh — who were martyred in 1704. During the Mughal-Sikh battles, these two brave boys were captured and offered safety if they converted to Islam, which they refused. Their refusal to abandon their faith led to their brutal martyrdom by being bricked alive in the walls of a fort in Sirhind (Punjab). This act of resilience and unwavering faith is a cornerstone of Sikh history and culture.
Veer Bal Diwas not only commemorates their sacrifice but also serves as a reminder of the strength, faith, and courage demonstrated by all four of Guru Gobind Singh Ji’s sons. It underscores the Sikh ideals of sacrifice, courage, and dedication to faith.
Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan: Addressing Malnutrition in Rural Areas
On the same day, PM Modi launched the 'Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan', a nationwide mission focused on improving nutritional outcomes in rural areas. The initiative aims to enhance nutrition-related infrastructure and promote active community participation in tackling malnutrition. By encouraging village-level involvement, the program seeks to ensure that nutrition becomes a community-driven effort.
Key Objectives
- Malnutrition Eradication: The initiative focuses on combating malnutrition in rural communities by improving access to better nutrition.
- Healthy Competition: Encourages competition among villages to adopt best practices for nutrition and overall health.
- Sustainable Development: Promotes long-term, sustainable health practices that align with India's broader goals, such as the Poshan Abhiyan and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The program aims to make rural populations active participants in improving their own well-being, strengthening community-driven initiatives for better nutritional outcomes.
Engaging Children and Fostering Patriotism
In line with Veer Bal Diwas, various events were organized to engage young minds across the nation. These initiatives not only raised awareness about the significance of the day but also fostered a culture of courage, dedication, and patriotism.
- Online Competitions: Interactive quizzes were conducted through platforms like MyGov and MyBharat to encourage participation and understanding of Veer Bal Diwas.
- Creative Activities: Schools, Child Care Institutions, and Anganwadi centers organized storytelling, creative writing, and poster-making contests to engage children and promote nationalistic values.
Honoring Young Achievers: PMRBP Awardees
The event also saw the presence of the recipients of the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar (PMRBP), which recognizes children who have demonstrated exceptional abilities in various fields. The awardees, 17 in total, were presented with medals, certificates, and citation booklets by President Droupadi Murmu. These young achievers served as a source of inspiration, reinforcing the theme of celebrating youth potential on Veer Bal Diwas.
Conclusion: Strengthening the Foundation of India’s Future
The celebrations of Veer Bal Diwas and the launch of the Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan highlight the government’s commitment to nurturing India’s future by investing in its children and rural communities. By honoring historical sacrifices and fostering community-driven health and nutrition initiatives, these efforts contribute to building a resilient, prosperous India that can meet global challenges head-on. The twin focus on children’s development and rural well-being underscores India’s vision of a healthier, more inclusive society, aligned with national and global development goals.
India-Kuwait Ties

- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's two-day visit to Kuwait marks a significant milestone in India-Kuwait relations, being the first visit by an Indian Prime Minister in over four decades. This visit, undertaken at the invitation of Emir Sheikh Meshal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, aims to strengthen bilateral ties in key areas like trade, defense, energy, and cultural cooperation.
Strategic Partnership and Key Agreements
The visit elevated India-Kuwait relations to a 'Strategic Partnership,' with agreements covering diverse sectors. A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defense cooperation was signed, focusing on joint military exercises, coastal defense, and training. Furthermore, the two countries signed a Cultural Exchange Programme for 2025-2029 and an Executive Programme on Sports Cooperation for 2025-2028, enhancing cultural and people-to-people ties.
The establishment of a Joint Commission on Cooperation (JCC) will monitor bilateral relations, and new Joint Working Groups (JWGs) have been set up in areas like education, trade, and counter-terrorism. Both nations also agreed to deepen collaboration in emerging sectors such as semiconductors, artificial intelligence, e-governance, and technology sharing.
Economic and Energy Cooperation
India and Kuwait share strong economic ties, with bilateral trade reaching USD 10.47 billion in 2023-24. Kuwait is India’s sixth-largest crude oil supplier, meeting 3% of India's energy needs. The countries have also agreed to transition from a buyer-seller relationship in energy to a more comprehensive partnership, with focus areas including oil, gas, refining, and renewable energy. Kuwait’s membership in the International Solar Alliance (ISA) was welcomed by India, reflecting their growing collaboration in the energy sector.
Indian Diaspora and Labour Cooperation
The Indian community, numbering over 1 million, forms the largest expatriate group in Kuwait and plays a pivotal role in the country’s economy. Their contribution spans various sectors, including healthcare, engineering, retail, and business. Kuwait’s Vision 2035, which seeks to diversify its economy beyond oil, presents significant opportunities for collaboration with India, particularly in infrastructure, renewable energy, and technology.
The skilled workforce from India also aligns with Kuwait's developmental goals, offering further opportunities for labor cooperation, especially in sectors like healthcare, technology, and infrastructure.
Geopolitical and Multilateral Cooperation
India-Kuwait relations hold regional significance, particularly in West Asia. Kuwait's role in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) amplifies its geopolitical importance. India’s engagement with Kuwait helps maintain a balanced presence in the region, essential for its energy security and broader geopolitical interests. The GCC, which includes six Arab states, remains a key partner for India, contributing to significant trade and remittances. India also seeks to conclude a Free Trade Agreement with the GCC to enhance economic collaboration.
Cultural and Historical Ties
India and Kuwait’s relationship has deep historical roots, dating back to the pre-oil era when maritime trade was a cornerstone of Kuwait’s economy. Over the years, this relationship has grown, with India being a major trading partner and Kuwait contributing significantly to India's energy needs. The Indian Rupee was once the legal tender in Kuwait, underscoring the strength of their historical ties.
In conclusion, PM Modi's visit to Kuwait sets the stage for enhanced cooperation across several domains, reinforcing the strategic partnership between the two nations. It also highlights India's broader objectives in the West Asia region, balancing economic, geopolitical, and cultural interests.
Revitalization of India-China Relations: A Diplomatic Turning Point

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The 23rd meeting between India’s National Security Adviser (NSA) and China’s Foreign Minister, held as Special Representatives (SRs), marks a pivotal moment in the complex bilateral relationship between the two nations. This dialogue, which follows years of strain exacerbated by the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, signals a renewed commitment to restoring stability and fostering peace along the border.
Special Representatives Mechanism: A Foundation for Dialogue
The SR mechanism, established in the early 2000s, has long served as a key platform for addressing bilateral disputes, particularly the contentious boundary issue. Past rounds of discussions have facilitated troop disengagement and efforts to maintain peace along the Line of Actual Control (LAC). The recent meeting, following the 2023 BRICS summit discussions between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping, demonstrates a positive step towards de-escalation, with the resumption of talks providing hope for progress.
Key Outcomes of the 23rd SR Meeting
Several significant developments emerged from the meeting, focusing on cultural, economic, and strategic cooperation:
- Cultural and Economic Cooperation:
- Kailash-Mansarovar Yatra: The resumption of this religious pilgrimage represents a significant cultural exchange, fostering people-to-people ties.
- Border Trade Revival: Border trade in Sikkim has been reestablished, potentially revitalizing local economies and improving trade relations.
- Scientific and Environmental Cooperation:
- Trans-boundary River Data Sharing: China’s commitment to sharing crucial river data with India will aid in flood management, directly addressing India’s long-standing concerns over water security, particularly in light of China's upstream dam projects.
- Connectivity and Exchange Programs:
- Discussions on restarting direct flights and visa easements for students and businesses, along with enhanced journalist exchanges, signal a move toward greater normalization of relations.
- Commitment to Border Peace:
- Both sides have reiterated their intent to maintain peace along the border, a critical factor in reducing tensions. While China expressed a six-point consensus, India has cautiously framed the outcome as “positive directions,” reflecting a reserved optimism.
Challenges in India-China Relations
Despite the positive momentum, numerous challenges persist in the bilateral relationship:
- Boundary Dispute:
- The core irritant remains the unresolved border issue, with divergent perceptions of the LAC. While some disengagement has occurred, full de-escalation and demilitarization across the entire border have not yet been achieved.
- Trust Deficit:
- The 2020 Galwan clash has left a lasting scar on mutual trust. Additionally, China’s aggressive patrolling and policy shifts continue to raise concerns in India, necessitating vigilance in future negotiations.
- Economic Imbalances:
- India’s trade relationship with China remains lopsided, with a significant trade deficit. Moreover, China’s growing influence in India’s neighborhood, particularly in Pakistan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, challenges India’s strategic interests.
- Global Power Dynamics:
- India’s evolving alliances, particularly with the U.S., QUAD, and I2U2 group, alongside China’s assertive stance in Taiwan and the South China Sea, complicate bilateral relations and influence global perceptions.
The Way Forward
To navigate the challenges and harness opportunities, India must adopt a balanced approach, combining diplomatic engagement, economic resilience, and strategic vigilance:
- Confidence-Building Measures:
- Continued disengagement and de-escalation at the LAC, coupled with increased transparency in military activities, will be critical to maintaining peace.
- Broadening Cooperation:
- Exploring areas of mutual interest, such as climate change, public health, and infrastructure development, could foster deeper cooperation and help transcend contentious issues.
- Economic Realignment:
- India must address its trade deficit by pushing for greater market access for Indian products in China. Additionally, diversifying supply chains and promoting joint ventures in renewable energy and technology can reduce dependency.
- Multilateral Engagement:
- Engaging through global forums like BRICS, SCO, and G20, and strengthening regional alliances, will help mitigate tensions and counterbalance China's regional influence.
- Strategic Vigilance:
- Strengthening ties with regional allies, particularly in the Indo-Pacific, and enhancing military preparedness will safeguard India’s strategic interests in the face of China’s assertiveness.
Conclusion
The recent meeting between India and China represents a cautious but constructive step toward stabilizing their fraught relationship. By focusing on diplomacy, strengthening economic ties, and maintaining strategic vigilance, India can navigate its complex relationship with China in a rapidly shifting global context. A careful balance of engagement and vigilance will be crucial for India’s future dealings with its powerful neighbor.
India-Sri Lanka Diplomatic Engagement

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent visit of Sri Lankan President Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD) to India marked a significant moment in bilateral relations, as it was his first foreign trip since assuming office. The visit underscored key diplomatic exchanges and collaborations between the two countries, showcasing both areas of agreement and divergence.
Key Takeaways from AKD's Visit
Assurance on Anti-India Activities: One of the primary concerns for India was the use of Sri Lankan territory for activities detrimental to its security, particularly the presence of Chinese “research vessels” at Sri Lankan ports. President AKD assured Prime Minister Narendra Modi that Sri Lanka would not allow its territory to be used in ways that threaten India’s interests. This assurance is crucial, as it signals Sri Lanka's stance on maintaining regional stability, despite AKD’s perceived pro-China inclinations.
Tamil Minority Issue: Divergent Views: A notable divergence in their discussions was the issue of the Tamil minority in Sri Lanka. India has long advocated for the full implementation of the 13th Amendment to Sri Lanka’s Constitution, which would grant greater autonomy to the Tamil minority. However, AKD resisted this, reaffirming his opposition to the amendment’s full implementation. While India emphasized the importance of reconciliation and holding provincial elections, AKD focused on unity, sustainable development, and social protection, sidestepping any definitive commitments on the Tamil issue.
Sri Lanka's Assertive Diplomatic Posture: AKD’s strong parliamentary mandate has allowed him to adopt a more assertive diplomatic stance. This is evident not only in his handling of the Tamil issue but also in his approach to dealing with major powers like India and China. His administration appears to be prioritizing a more independent foreign policy, signaling a shift from previous administrations.
Bilateral Cooperation and Development Initiatives
The visit saw significant agreements on bilateral cooperation, particularly in development and connectivity. Both nations acknowledged the positive impact of India’s assistance in Sri Lanka’s socio-economic growth. Key projects discussed include:
- Indian Housing Project: Phases III and IV.
- Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects across three islands.
- High-Impact Community Development Projects.
- Digital collaborations, such as the implementation of Aadhaar and UPI systems in Sri Lanka.
Additionally, discussions focused on enhancing energy cooperation, including the supply of LNG, development of offshore wind power in the Palk Strait, and the high-capacity power grid interconnection. The resumption of passenger ferry services between key Indian and Sri Lankan ports was also a priority.
Defence and Security Cooperation
The two leaders agreed to explore a Defence Cooperation Framework and intensify collaboration on maritime surveillance, cyber security, and counter-terrorism. This aligns with India’s strategic interests in the region, as it seeks to ensure stability in the Indian Ocean and strengthen its defense ties with Sri Lanka.
Strategic Continuity Amid Leadership Change
Despite a change in leadership, the core strategic interests between India and Sri Lanka remain aligned. India views Sri Lanka’s stability as crucial to regional security, and both countries are focused on a mutually beneficial partnership. AKD’s emphasis on economic recovery and tackling corruption within Sri Lanka, as seen in his actions against political figures like Speaker Asoka Ranwala, further signals his determination to build a strong foundation for his government’s future.
Conclusion
President AKD’s visit highlighted the evolving dynamics of Sri Lanka’s foreign policy, marked by a more confident and independent approach in engaging with India. While challenges remain, especially regarding the Tamil issue, both countries have reaffirmed their commitment to deepening bilateral ties, with a focus on development, connectivity, and strategic cooperation.
Bank Credit to Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs)

- 21 Dec 2024
Introduction
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) is a flagship program by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) that aims to reduce poverty by empowering women, especially through Self-Help Groups (SHGs). These SHGs have been instrumental in improving financial inclusion, providing access to credit, and enhancing the economic and social status of women across India. The program has made significant strides in mobilizing women, improving their access to financial services, and facilitating entrepreneurial ventures in rural areas.
Key Features and Initiatives of DAY-NRLM
- Self-Help Groups (SHGs):
- Formation: DAY-NRLM supports the creation and strengthening of SHGs, primarily focusing on rural women from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Mobilization: As of 2024, over 10.05 crore women have been mobilized into 90.87 lakh SHGs across India.
- Objective: The main goal is to reduce poverty through empowerment by providing access to financial services and sustainable livelihoods.
- Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP):
- Support for Rural Enterprises: SVEP, a sub-scheme under DAY-NRLM, encourages SHG women and their families to set up small-scale businesses.
- Impact: As of October 2024, 3.13 lakh rural enterprises have been supported under this initiative.
- State-wise Distribution: The program has supported enterprises across various states, with notable contributions from Andhra Pradesh (27,651 enterprises), Kerala (34,569), and Uttar Pradesh (28,904).
- Banking Correspondent Sakhis:
- Role: Women in SHGs are trained as Banking Correspondent Sakhis to enhance access to banking services such as deposits, credit, remittances, pensions, and insurance in rural areas.
- Current Deployment: 1,35,127 Sakhis have been deployed under DAY-NRLM, empowering women to be financial intermediaries in their communities.
- Financial Support for SHGs:
- Revolving Fund: SHGs receive funds ranging from Rs. 20,000 to Rs. 30,000 to boost their operations and financial stability.
- Community Investment Fund: SHGs can avail of up to Rs. 2.50 lakh under the Community Investment Fund to strengthen their financial position.
- Interest Subvention: To make bank loans more affordable, DAY-NRLM provides interest subvention to SHGs, reducing their overall credit costs.
- Online Marketing Platform:
- www.esaras.in: This online platform allows SHGs to market their products, improving their access to broader markets and enhancing their income-generating potential.
Impact of DAY-NRLM and SHGs
- Financial Inclusion: SHGs play a vital role in financial inclusion by providing access to banking services, loans, and insurance to women, especially in rural and remote areas.
- Credit Mobilization: As of November 2024, SHGs have leveraged Rs. 9.71 lakh crore in bank credit, thanks to the capitalization support provided by DAY-NRLM, including Revolving Funds and Community Investment Funds.
- Empowerment of Women: SHGs have significantly contributed to the empowerment of women, providing them with financial independence, social support, and the ability to make decisions in their households and communities.
Challenges Faced by SHGs
- Beneficiary Identification: Ensuring that the most marginalized individuals are included in SHGs can be challenging.
- Training Gaps: There is a lack of quality training programs and expert trainers to build the capacity of SHG members.
- Financial Literacy: Many SHG members have limited knowledge of formal financial services, hindering effective financial management.
- Market Linkages: Poor integration with markets limits the growth potential of SHGs, especially in terms of product sales and business expansion.
- Community Support: Insufficient business environment support and value chain linkages pose challenges to SHG sustainability and growth.
Government Initiatives Supporting SHGs
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP): Launched by NABARD in 1992, this initiative aims to link SHGs with formal banking institutions, facilitating financial inclusion.
- Mission for Financial Inclusion (MFI): A broader initiative to ensure that rural populations have access to affordable financial services such as savings, credit, insurance, and pensions.
- Lakhpati Didi Initiative: Launched in 2023, this initiative empowers SHG women to adopt sustainable livelihood practices and aim for an annual household income exceeding Rs. 1 lakh.
Role of SHGs in Rural Development
- Women Empowerment: SHGs have emerged as a powerful tool for empowering women through financial independence, social security, and the ability to make informed decisions.
- Economic Growth: SHGs foster small-scale entrepreneurship, thereby creating local businesses that contribute to rural economic growth.
- Social Cohesion: By promoting collective action, SHGs provide a social support system that helps in addressing common issues faced by their members, such as health, education, and safety.
Future Prospects and Way Forward
- Technological Integration: SHGs should leverage advanced digital platforms for transaction management, record-keeping, and communication, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
- Reducing Informal Borrowing: Linking SHGs with formal financial institutions will reduce reliance on informal lenders, promoting financial inclusion.
- Inclusive Approach: SHGs should adopt an inclusive model to ensure that members from diverse socio-economic backgrounds are fairly represented and benefit equally.
- Training and Capacity Building: There is a need for more Community Resource Persons (CRPs) who can guide SHGs in beneficiary identification, financial management, and scaling their activities.
Supreme Court Directs Policy for Sacred Groves Protection

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court of India issued a significant judgment directing the Union Government to formulate a comprehensive policy for the protection and management of sacred groves across the country. These natural spaces, traditionally safeguarded by local communities, play a crucial role in preserving both ecological diversity and cultural heritage.
What are Sacred Groves?
Sacred Groves are patches of virgin forests that are protected by local communities due to their religious and cultural significance. They represent remnants of what were once dominant ecosystems and serve as key habitats for flora and fauna. Typically, sacred groves are not just ecological reserves, but also form an integral part of local traditions, often protected due to spiritual beliefs.
Key Features of Sacred Groves:
- Ecological Value: Sacred groves contribute significantly to biodiversity conservation.
- Cultural Significance: These groves are revered in various religious practices and are central to local traditions.
- Geographical Presence: Sacred groves are found in regions like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and parts of Rajasthan.
Supreme Court's Directive
The court's judgment was based on a plea highlighting the decline of sacred groves in Rajasthan, particularly those being lost due to deforestation and illegal land-use changes. While the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 empowers state governments to declare community lands as reserves, the court recognized the need for a unified national policy to protect sacred groves as cultural reserves.
Recommendations:
- Nationwide Survey: The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) was instructed to conduct a nationwide survey to map and assess sacred groves, identifying their size and extent.
- Legal Protection: Sacred groves should be recognized as community reserves and protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- State-Specific Measures: The Rajasthan government was specifically directed to carry out detailed mapping (both on-ground and satellite) of sacred groves within the state, ensuring that the groves are recognized for their ecological and cultural significance.
The Role of Sacred Groves in Conservation
Sacred groves play a pivotal role in the conservation of biodiversity. They serve as refuges for various plant and animal species, and the traditional practices associated with these groves, such as tree worship, discourage destructive activities like logging and hunting.
Ecological and Cultural Importance:
- Sacred groves often act as critical biodiversity hotspots, preserving rare and indigenous species.
- They help maintain clean water ecosystems and act as carbon sinks, contributing to climate mitigation.
- Practices of non-interference with these areas have allowed flora and fauna to thrive over centuries.
Cultural Significance Across India
The importance of sacred groves is deeply embedded in India's diverse cultural heritage. They are considered the abode of deities, and various regions have unique names and rituals associated with these groves.
Examples of Sacred Groves in India:
- Himachal Pradesh: Devban
- Karnataka: Devarakadu
- Kerala: Kavu
- Rajasthan: Oran
- Maharashtra: Devrai
Piplantri Village Model
A key example highlighted in the judgment was the Piplantri village in Rajasthan, where the community undertook a remarkable transformation of barren land into flourishing groves. The initiative, driven by local leadership, involves planting 111 trees for every girl child born, which has led to several environmental and social benefits.
Impact of Piplantri's Community Efforts:
- Over 40 lakh trees have been planted, which has recharged the water table by 800-900 feet and lowered the local climate by 3-4°C.
- The initiative has contributed to the reduction of female foeticide and empowered women's self-help groups.
- The village now enjoys economic growth, better education opportunities, and increased local income.
Legal and Statutory Framework
Sacred groves are already recognized under existing Indian laws, notably the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, which allows states to declare sacred groves as community reserves. Additionally, the National Forest Policy of 1988 encourages the involvement of local communities in the conservation of forest areas, a principle supported by the Godavarman Case of 1996.
Key Legal Provisions:
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Empowers state governments to declare sacred groves as community reserves.
- National Forest Policy, 1988: Encourages community involvement in the conservation and protection of forests, including sacred groves.
- Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006: Suggests empowering traditional communities as custodians of sacred groves.
Looking Ahead: The Need for Action
The Supreme Court has scheduled further hearings to assess the progress of the survey and mapping efforts by Rajasthan. The court also stressed the importance of empowering traditional communities to continue their role as custodians of sacred groves, ensuring their sustainable protection for future generations.
By recognizing the ecological and cultural significance of sacred groves and encouraging community-driven conservation efforts, the Supreme Court’s ruling sets a precedent for more inclusive environmental policies in India. This could also inspire similar initiatives in other parts of the world, promoting the protection of sacred natural spaces for their critical role in maintaining biodiversity and fostering sustainable communities.
The Costly Push for 100% Electrification of Indian Railways

- 19 Dec 2024
Introduction
RITES Ltd., the consultancy arm of the Indian Railways, has secured two contracts to repurpose six broad gauge diesel-electric locomotives for export to African railways. These locomotives, originally designed for India’s broad gauge of 1,676 mm, will be modified for use on railways with the narrower Cape Gauge of 1,067 mm. While this is a commendable re-engineering effort, it also highlights a larger issue within Indian Railways: the unnecessary redundancy of functional diesel locomotives, leading to significant wastage of resources.
The Growing Problem of Idle Diesel Locomotives
As of March 2023, there were 585 diesel locomotives idling across the Indian Railways network due to electrification. This number has now reportedly grown to 760 locomotives, many of which still have more than 15 years of serviceable life. The root cause of this redundancy lies in the government’s mission to electrify the entire broad gauge network at an accelerated pace. This electrification push has resulted in the premature retirement of locomotives that could still serve the network for years, raising questions about the economic and environmental logic behind this decision.
The Justification for Electrification: Foreign Exchange and Environmental Concerns
The Indian government’s electrification drive is often justified on two primary grounds: saving foreign exchange by reducing the import of crude oil and reducing environmental pollution. Additionally, electrification is framed as a step toward a “green railway” powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind. However, the reality of these claims is more complicated.
Foreign Exchange Savings: A Small Impact on National Diesel Consumption
While electrification may reduce India’s diesel consumption, the impact on national fuel use is minimal. Railways account for just 2% of the country’s total diesel consumption. A report by AC Nielsen in 2014 indicated that the transport sector consumed 70% of the total diesel, with railways accounting for only 3.24%. Even with 100% electrification, the savings in foreign exchange would have little impact on the country’s overall diesel consumption, leaving other sectors like trucking and agriculture as the main contributors.
Environmental Concerns: Shifting Pollution, Not Reducing It
The environmental argument for electrification is also flawed. Electricity in India is still largely generated from coal-fired power plants, with nearly 50% of the country’s electricity coming from coal. Since the Indian Railways is heavily involved in transporting coal, switching from diesel to electric locomotives simply shifts pollution from the tracks to the power plants. This means that the transition to electric traction will not result in a cleaner environment unless the country significantly reduces its reliance on coal. Without a substantial increase in renewable energy generation, the push for a “green railway” remains unrealistic.
The Dilemma of Retaining Diesel Locomotives for Strategic Purposes
Despite the goal of 100% electrification, a significant number of diesel locomotives will remain in service. Reports indicate that 2,500 locomotives will be kept for “disaster management” and “strategic purposes,” although it is unclear why such a large fleet is necessary for these purposes. Additionally, about 1,000 locomotives will continue to operate for several more years to meet traffic commitments. This suggests that even with a fully electrified network, Indian Railways will continue to rely on thousands of diesel locomotives, many of which have substantial residual service life left.
Financial Sustainability and Coal Dependency
The financial sustainability of this transition remains a concern. Currently, the Indian Railways generates a significant portion of its freight revenue from transporting coal—40% of its total freight earnings in 2023-24. If the railways become fully electrified, it will need to find alternative revenue sources, as coal is a primary contributor. Until non-coal freight options can replace this income, the financial health of the railways may be at risk.
Conclusion: Wasted Resources and Unmet Goals
The mission to electrify the Indian Railways, while ambitious, is an example of how vanity projects can lead to colossal waste. Thousands of diesel locomotives are being discarded prematurely, despite their potential to continue serving the network. The environmental and financial justifications for 100% electrification, while appealing in theory, fail to account for the complexities of India’s energy landscape. As a result, the drive to create a “green railway” is likely to fall short, leaving behind a legacy of wasted taxpayer money and unfinished goals.
Arctic Tundra: From Carbon Sink to Carbon Source

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The Arctic tundra, a frozen, treeless biome, has historically been a vital carbon sink, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO?) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). However, recent findings suggest that, for the first time in millennia, this ecosystem is emitting more carbon than it absorbs, a change that could have significant global consequences. This alarming shift was highlighted in the 2024 Arctic Report Card published by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The Arctic Tundra’s Role as a Carbon Sink
The Arctic tundra plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. In typical ecosystems, plants absorb CO? through photosynthesis, and when they die, carbon is either consumed by decomposers or released back into the atmosphere. In contrast, the tundra’s cold environment significantly slows the decomposition process, trapping organic carbon in permafrost—the permanently frozen ground that underpins much of the region.
Over thousands of years, this accumulation of organic matter has resulted in the Arctic storing an estimated 1.6 trillion metric tonnes of carbon. This figure is roughly double the amount of carbon in the entire atmosphere. As such, the tundra has served as a critical carbon sink, helping to mitigate global warming by trapping vast quantities of CO?.
Shifting Dynamics: Emission of Greenhouse Gases
Recent reports indicate a dramatic shift in the Arctic tundra’s role in the carbon cycle. Rising temperatures and increasing wildfire activity have disrupted the tundra’s balance, leading it to transition from a carbon sink to a carbon source.
Impact of Rising Temperatures
The Arctic region is warming at a rate approximately four times faster than the global average. In 2024, Arctic surface air temperatures were recorded as the second-warmest on record since 1900. This rapid warming is causing permafrost to thaw, which in turn activates microbes that break down trapped organic material. As this decomposition accelerates, carbon in the form of CO? and methane (CH?)—a more potent greenhouse gas—are released into the atmosphere.
The experts, explained the process by comparing thawing permafrost to meat left out of the freezer. Similarly, thawing permafrost accelerates the breakdown of trapped carbon.
The Role of Wildfires
In addition to warming temperatures, the Arctic has experienced a surge in wildfires in recent years. 2024 marked the second-highest wildfire season on record in the region, releasing significant amounts of GHGs into the atmosphere. Wildfires exacerbate the thawing of permafrost, creating a feedback loop where increased carbon emissions contribute further to warming, which, in turn, leads to more emissions.
Between 2001 and 2020, these combined factors caused the Arctic tundra to release more carbon than it absorbed, likely for the first time in millennia.
The Global Consequences of Emission
The transition of the Arctic tundra from a carbon sink to a carbon source is alarming, as it represents a significant amplification of global climate change. The release of additional CO? and CH? into the atmosphere further accelerates the greenhouse effect, leading to higher global temperatures. This warming is already having visible consequences around the world, from extreme weather events to rising sea levels.
If the Arctic tundra continues to emit more carbon than it absorbs, it could significantly exacerbate the climate crisis. The report underscores the urgency of addressing global emissions, as reducing greenhouse gases remains the most effective way to prevent further destabilization of this sensitive ecosystem.
Mitigating the Impact: The Path Forward
Despite the alarming trends, the Arctic Report Card suggests that it is still possible to reverse this process. By reducing global GHG emissions, it may be possible to slow the thawing of permafrost and allow the Arctic tundra to regain its role as a carbon sink. Scientists emphasize that mitigating climate change on a global scale is essential to prevent further emissions from the Arctic ecosystem.
Scientists, stressed the importance of emission reductions, stating, “With lower levels of climate change, you get lower levels of emissions from permafrost… That should motivate us all to work towards more aggressive emissions reductions.”
However, current trends suggest that achieving this goal may be challenging. A recent report from the Global Carbon Project indicates that fossil fuel emissions are likely to rise in 2024, with total CO? emissions projected to reach 41.6 billion tonnes, up from 40.6 billion tonnes in 2023.
Commitment to Eradicating Naxalism in Chhattisgarh by 2026

- 17 Dec 2024
Overview
Union Home Minister Amit Shah has reiterated India's commitment to eliminate Naxalism in Chhattisgarh by March 31, 2026. He emphasized the progress made in the fight against Naxalism, highlighting key successes and outlining the strategy for the coming years.
Key Pointers
- Government Commitment: Amit Shah emphasized the joint commitment of the Government of India and the Chhattisgarh state leadership to rid the state of Naxalism by 2026.
- Security Forces’ Success: Over the past year, Chhattisgarh police neutralized 287 Naxalites, arrested around 1,000, and saw 837 surrenders.
- Top Naxal Cadres Neutralized: The state forces successfully neutralized 14 high-ranking Naxal cadres.
- President’s Police Colour Award: Chhattisgarh Police received the President's insignia within 25 years, a significant achievement for the state.
The Three-Pronged Strategy for Eliminating Maoist Insurgency
- Security Measures (Force)
Deployment of Security Forces
- Enhanced Presence: Increased deployment of Central and State police forces in Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) areas.
- Joint Operations: Coordinated operations between state and central forces, including CRPF and COBRA units.
- Upgraded Technology: Incorporation of UAVs, solar lights, and mobile towers to enhance operational efficiency.
Operation SAMADHAN
- Key Elements:
- Smart Leadership: Leading with innovative strategies.
- Aggressive Strategy: Swift, decisive action against insurgents.
- Motivation and Training: Strengthening the capabilities of forces.
- Actionable Intelligence: Real-time intelligence for effective operations.
- Harnessing Technology: Using modern tech for strategic advantage.
2. Development Initiatives
Focused Development Schemes
- PMGSY: Rural road connectivity under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana.
- Aspirational Districts Program: Improving infrastructure in Naxal-affected areas.
- Skill Development: Targeted schemes in 47 LWE-affected districts to reduce unemployment.
Infrastructure Development
- Special Infrastructure Schemes: Building schools, roads, and bridges in remote areas to integrate them into the mainstream economy.
- Rehabilitation: Focus on providing rehabilitation for former Naxals through education and vocational training.
3. Empowerment (Winning Hearts and Minds)
Public Engagement
- Tribal Empowerment: Strengthening communication with tribal communities to reduce alienation and mistrust.
- Rehabilitation Policies: Surrender schemes offering incentives like education and financial aid to reintegrate former insurgents into society.
Maoism: Ideology and Background
What is Maoism?
- Origin: A form of communism developed by Mao Tse Tung, focusing on armed insurgency to capture state power.
- Core Beliefs: Maoists believe in violence and insurrection as legitimate means to overthrow the state and establish a People’s Democratic Republic.
- Indian Maoism: The Communist Party of India (Maoist), formed in 2004, leads the largest Maoist insurgency in India.
Recent Achievements in Combatting Maoist Insurgency
Key Successes in 2023
- Maoist-Free Villages: Villages in Dantewada declared "Maoist-free," a significant victory for the state.
- Reduction in Security Forces’ Casualties: 14 deaths in 2024, a dramatic decrease from 198 deaths in 2007.
- Infrastructure and Logistical Support: Enhanced use of helicopters and fortified police stations.
Government’s Commitment to Rebuilding
- Rehabilitation and Welfare: The government is implementing policies to improve the living standards of affected families, including 15,000 houses for Naxal-affected regions.
- Economic Development: Focus on building infrastructure and providing employment through skills training programs.
Challenges in Eliminating Naxalism
Socio-Economic Issues
- Exploitation of Tribals: Marginalization of tribals due to displacement for mining and forestry.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Basic amenities like roads, schools, and healthcare are absent in many areas.
- Centralized Naxal Command: The CPI (Maoist) retains a strong leadership, despite fragmentation of its forces.
Governance and Trust Issues
- Alienation of Local Populations: Ineffective governance and poor implementation of welfare schemes fuel local support for Naxal groups.
- Resource Conflict: The Naxals exploit rich mineral resources in the region to fund their insurgency.
Way Forward
Governance and Economic Reforms
- Tribal Empowerment: Form Tribal Advisory Councils as per the Fifth Schedule for better resource management.
- Land Redistribution: Enforce the Land Ceiling Act to reduce inequality.
- Livelihood Programs: Offer alternative livelihoods to reduce dependency on illegal activities.
Security Measures
- Paramilitary Deployment: Specialized forces to secure tribal areas and enable local governance.
- Resource Management: Ensure sustainable exploitation of natural resources, involving tribal communities in the decision-making process.
Peace Dialogues
- Inclusive Policies: Engage in dialogue with Naxals to facilitate their reintegration into mainstream society.
Conclusion
Naxalism in India, particularly in Chhattisgarh, is a complex issue rooted in socio-economic inequalities, lack of development, and historical alienation of tribal communities. The government's approach, encapsulated in the SAMADHAN strategy, combines security operations with developmental initiatives and a focus on empowerment to tackle the problem. With a clear commitment to eliminate Naxalism by 2026, the Indian government is making significant strides in reducing violence, improving governance, and integrating affected communities into the mainstream.
How would a carbon market function?

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
COP29, the ongoing climate conference in Azerbaijan’s capital Baku, has given a fillip to the idea of using carbon markets to curb carbon emissions by approving standards that can help in the setting up of an international carbon market as soon as the coming year.
Introduction to Carbon Markets
- Carbon markets allow the buying and selling of the right to emit carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
- Governments issue certificates known as carbon credits, each representing the right to emit 1,000 kilograms of CO2.
- The total number of credits issued is capped to control carbon emissions. Companies and individuals who don’t have credits cannot emit CO2.
Trading of Carbon Credits
- Carbon Credit Trading: Companies holding more carbon credits than needed can sell them to others who need more, with the price determined by market forces.
- Carbon Offsets: Businesses can also purchase carbon offsets, often provided by environmental NGOs, which promise to reduce emissions (e.g., by planting trees). These offsets counterbalance the firm’s carbon emissions.
- The trading of both credits and offsets is designed to create financial incentives for companies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Advantages of Carbon Markets
- Addressing Externalities: Carbon emissions are a classic example of an economic externality, where the costs of pollution are not reflected in market prices.
- Market Efficiency: By allowing firms to buy and sell carbon credits, the system internalizes the cost of carbon emissions, encouraging businesses to reduce emissions to avoid higher costs.
- Incentive for Emission Reduction: Carbon markets aim to create a financial reason for companies to lower their emissions, thus helping mitigate climate change.
Voluntary vs. Government-Mandated Carbon Markets
- Voluntary Carbon Reporting: Many corporations prefer voluntary systems like the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) for reporting their emissions, fearing government-imposed restrictions.
- Market Flexibility: Corporations like ExxonMobil and General Motors argue that carbon markets with freely traded credits allocate carbon allowances more efficiently than government-imposed limits. This allows firms to purchase credits from others, optimizing resource allocation without restricting output.
- Corporate Resistance to Government Intervention: Firms are often reluctant to accept strict government budgets for carbon emissions, fearing increased operational costs and production limitations due to diverse supply chains.
Issues and Criticisms of Carbon Markets
- Government Manipulation of Credit Supply: Governments may increase the number of carbon credits issued, leading to lower prices and reduced incentives for emission reductions.
- Lack of Accountability in Carbon Offsets: Critics argue that some companies buy carbon offsets as a form of virtue signalling, without genuine concern for their environmental impact. This undermines the effectiveness of the offsets.
- Government Mismanagement: Political decision-making may lead to the over-restriction of carbon credits, potentially slowing economic growth by limiting available emissions allowances. The ability of governments to accurately determine the optimal supply of carbon credits is a contentious issue.
The Concept of Carbon Credits and Their History
- Introduction of Carbon Credits: Carbon credits were first introduced in the 1990s in the U.S., specifically through a cap-and-trade model designed to control sulfur dioxide emissions. This approach later expanded to include carbon emissions.
- Role of Carbon Markets: In essence, these markets aim to create a financial mechanism where firms can trade the right to pollute, ensuring a balance between economic growth and environmental protection.
Criticism of Carbon Offsets
- Effectiveness of Offsets: Experts are critical of carbon offsets, arguing that they do not always lead to meaningful reductions in emissions. For example, some companies may purchase offsets without ensuring that the projects are genuinely offsetting their emissions.
- Moral Hazard: Critics suggest that offset programs may lead to firms simply paying for the right to pollute, rather than actually reducing emissions in their operations.
Conclusion
- Carbon Markets as a Tool for Emission Reduction: Despite the criticisms, carbon markets remain a promising tool for mitigating climate change, provided they are carefully regulated and implemented.
- The Future of Carbon Trading: As discussions at COP29 evolve, the development of international standards for carbon trading could potentially enhance the effectiveness of these markets, offering a viable path to global emission reductions.
Agrarian Crisis in India

- 15 Dec 2024
Introduction
- Supreme Court Committee Report: A high-level committee, appointed by the Supreme Court in September 2024, submitted its interim report on November 21, 2024, highlighting the severe distress in India's agricultural sector.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Income crisis faced by farmers
- Rising debt burden
- Farmer suicides
- Stagnation in agricultural growth
- Impact of climate change
Key Findings of the Supreme Court Committee Report
Income Crisis in Indian Agriculture
- Daily Earnings: Farmers earn an average of just Rs 27 per day from agricultural activities, a meager income that makes it impossible to sustain a decent standard of living.
- Average Household Income: Agricultural households have an average monthly income of Rs 10,218, far below the basic threshold for a decent life.
Escalating Debt Burden
- Institutional Debt: In 2022-23, Punjab's institutional debt was Rs 73,673 crore, and Haryana's was Rs 76,630 crore.
- Non-Institutional Debt: This burden is further exacerbated by non-institutional debt, contributing 21.3% of total debt in Punjab and 32% in Haryana.
Farmer Suicides
- High Suicide Rates: Over 400,000 farmers and agricultural workers have committed suicide since 1995, primarily due to escalating debt and financial despair.
- Survey Findings: In Punjab, a survey found 16,606 suicides among farmers and farm workers between 2000 and 2015.
Stagnation in Agricultural Growth
- Growth Rates: Between 2014-15 to 2022-23, Punjab's agricultural growth was a mere 2% per year, and Haryana’s was 3.38%, far below the national average.
Disproportionate Employment
- Workforce Participation: 46% of India’s workforce is employed in agriculture, but it contributes only 15% to national income. Many farmers face disguised unemployment and underemployment.
Impact of Climate Change
- Environmental Degradation: Climate change, water depletion, erratic rainfall, and soil degradation are further destabilizing the agricultural sector and threatening food security.
Challenges Faced by the Agricultural Sector
1. Limited Access to Credit and Finance
- Small Farmers: 86% of Indian farmers are small and marginal, struggling to access institutional credit, which limits their ability to invest in modern agricultural inputs.
2. Fragmented Landholdings
- Small Landholdings: The average landholding is 1.08 hectares, insufficient for large-scale, efficient farming, limiting the adoption of modern agricultural techniques.
3. Outdated Farming Practices
- Traditional Methods: Many farmers continue using traditional, inefficient farming practices due to limited access to modern technology.
4. Water Scarcity and Irrigation Issues
- Dependence on Monsoons: 60% of cropped area is rainfed, and only 52% of gross sown area is irrigated, exacerbating vulnerability to droughts and erratic rainfall.
5. Soil Degradation and Erosion
- Degraded Land: 30% of India's agricultural land is affected by soil degradation, leading to lower productivity and reduced resilience to pests.
6. Inadequate Agricultural Infrastructure
- Post-Harvest Losses: Insufficient storage, cold chain, and rural infrastructure result in 15-20% post-harvest losses, further reducing farmers' income.
Government Schemes for Farmers' Welfare
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana: Direct income support for farmers.
- PM Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Crop insurance scheme.
- PM Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY): Irrigation schemes to enhance water availability.
- e-NAM: National electronic market for better price realization.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund: Financial support for infrastructure development.
- Promotion of Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): Empowering farmers through collective marketing and production.
Recommendations for Addressing the Crisis
1. Loan Waivers and Debt Relief
- Debt Alleviation: Immediate measures to reduce the crushing debt burden through loan waivers, a key factor behind farmer suicides.
2. Legal Recognition of Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- MSP Protection: Granting legal backing to MSP to ensure farmers receive a fair price for their produce, reducing price volatility and income insecurity.
3. Promotion of Sustainable Farming
- Organic Farming: Encouraging organic farming and crop diversification to improve soil health and reduce dependency on a few staple crops.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Adopting water-efficient practices, drought-resistant crops, and sustainable farming techniques.
4. Agricultural Marketing Reforms
- Market Efficiency: Improving the agricultural marketing system by establishing farmer-friendly markets and reducing intermediaries to ensure better price realization.
5. Rural Employment Generation
- Diversification: Creating non-agricultural employment opportunities in rural areas through skill development and promoting agro-based industries.
6. Climate Adaptation Measures
- Water Management: Enhancing water management systems and promoting rainwater harvesting.
- Resilience to Climate Change: Investing in climate-resilient infrastructure and farming technologies.
Implications of the Findings
Economic Impact
- Agricultural Decline: Continued neglect of the agricultural sector poses a risk to India's economy, potentially leading to long-term economic instability and increased rural-urban migration.
Food Security
- Threat to National Food Security: Declining agricultural productivity, exacerbated by climate change and inadequate reforms, threatens the country’s ability to meet food demands.
Social Stability
- Farmer Suicides and Unrest: The ongoing crisis, marked by widespread suicides and growing despair, risks social instability and unrest, particularly in rural regions.
Conclusion: Urgent Need for Reform
The committee’s report underscores the critical need for comprehensive reforms in India’s agricultural sector to alleviate the crisis. Immediate action is required to address the debt burden, improve incomes, and ensure sustainable agricultural practices. Legal reforms like MSP recognition and debt relief, along with investments in infrastructure and climate resilience, are key to securing a stable future for Indian agriculture.
Artificial Solar Eclipse: Why Are Satellites Trying to Block the Sun?
- 14 Dec 2024
Introduction
The European Space Agency (ESA) has launched Proba-3, a mission that will create an artificial solar eclipse to study the Sun's atmosphere, known as the corona. This mission aims to demonstrate new technology and address unresolved questions about the Sun's outer layers.
What is an Artificial Solar Eclipse?
- Definition: An artificial solar eclipse mimics the natural phenomenon where the moon blocks sunlight, allowing detailed observation of the Sun’s corona.
- Created By: The eclipse is created by two satellites, which align to block the Sun's light and generate a controlled shadow for scientific study.
- Purpose: The goal is to study the Sun’s corona, particularly to understand why it is significantly hotter than the Sun’s surface.
How Does the Proba-3 Create an Eclipse?
Launch and Spacecraft
Proba-3 was launched on December 5 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India. The mission uses two satellites:
- Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC): This spacecraft guides the other satellite.
- Occulter Spacecraft (OSC): This satellite has a disk that creates a controlled shadow onto the CSC.
Formation Flying
Using Precise Formation Flying (PFF) technology, the two spacecraft maintain a precise distance of 150 meters (492 feet) apart, aligning perfectly with the Sun. This alignment mimics the effect of a solar eclipse.
Precision Requirements
The eclipse will need to maintain millimetre-level accuracy for up to six hours per orbit to provide scientists with stable observational conditions.
Mission Goals
- Demonstrating PFF Technology: One of the primary objectives of the Proba-3 mission is to demonstrate PFF technology. This involves using GPS and inter-satellite radio links for positioning, as well as maintaining a precise distance between the two spacecraft.
- Studying the Sun’s Corona: Another goal is to understand why the corona is hotter than the Sun's surface. The onboard instruments, including a coronagraph, will help with this research. The coronagraph will block out the Sun’s bright light, enabling clearer observations of the corona.
- ASPICCS Coronagraph: The Proba-3 coronagraph, named the Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun (ASPICCS), is designed to observe the corona in high detail, mimicking the observational conditions of a total solar eclipse.
Why Is This Such a Big Deal?
- Revealing the Sun’s Corona: The Sun’s corona is typically invisible because it is much less bright than the Sun’s surface. It can only be seen during a solar eclipse when the Moon blocks the Sun's light.
- Predicting Space Weather: Studying the corona helps scientists predict space weather and geomagnetic storms, which can disrupt satellites and other systems on Earth.
- Extended Observations: Unlike natural solar eclipses, which last only a few minutes, Proba-3 can provide six hours of observation time in each orbit (approximately 19 hours and 36 minutes), allowing for continuous study of the corona.
What is Precise Formation Flying (PFF) Technology?
- Definition: PFF technology allows satellites to maintain exact positions and orientations relative to each other in orbit.
- Mechanism: The technology uses GPS, inter-satellite radio links, and automated control systems to ensure alignment.
- Implementation in Proba-3: In the Proba-3 mission, the Coronagraph and Occulter spacecraft stay 150 meters apart, using PFF to maintain millimetre-level precision, which is crucial for simulating a solar eclipse.
- Benefits: PFF enhances mission accuracy and provides a platform for advanced observational techniques that will enable more detailed studies of the Sun's corona.
Conclusion
Proba-3 is a groundbreaking mission that will offer unprecedented insights into the Sun’s corona by simulating solar eclipses using advanced satellite technology. By studying the Sun’s outer layers, scientists aim to improve our understanding of space weather and the mysterious temperature anomaly of the corona.
India-Bhutan Relations

- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The December 2023 visit of Bhutan’s King and Queen to India highlights the enduring and strategic partnership between the two nations. Amidst growing Chinese influence and Bhutan’s domestic challenges, the visit holds significant geopolitical relevance, reinforcing India-Bhutan relations and underscoring Bhutan's critical role in India’s regional security.
Reaffirmation of India-Bhutan Relations
The visit reaffirmed the strong, time-tested partnership between India and Bhutan, rooted in mutual trust and cooperation. India reiterated its commitment to Bhutan's socio-economic development, increasing its financial aid for the 2024-2029 period from ?5,000 crore to ?10,000 crore. Notably, Bhutan’s flagship Gelephu Mindfulness City Project, championed by King Jigme Khesar, received strong Indian backing, reflecting India’s willingness to align with Bhutan’s developmental priorities.
Strategic Areas of Cooperation
Clean Energy and Hydropower
Bhutan remains central to India’s renewable energy strategy, particularly in hydropower, a vital part of Bhutan's economy. Bhutan exports the majority of its hydropower to India, reinforcing bilateral ties in the energy sector. This cooperation aligns with India’s regional energy security goals, with both nations seeking to strengthen clean energy initiatives.
Infrastructure Development
The visit also emphasized infrastructure projects, vital for enhancing Bhutan's connectivity. These projects are strategically significant, considering Bhutan's geostrategic importance in the Himalayas. Infrastructure development further strengthens the ties between the two nations, with a focus on mutual benefits and regional stability.
Geopolitical Context: China’s Growing Influence
China-Bhutan Border Disputes
The border issue with China has been ongoing since 1984. In 2023, Bhutan and China signed an agreement to expedite the settlement and demarcation of their borders. China’s push for resolution is part of its broader strategy to reduce India’s influence in Bhutan. The disputed areas, particularly those near India’s Siliguri Corridor, hold strategic importance for New Delhi. Any territorial adjustments could undermine India’s access to its Northeastern states.
Chinese Influence and Economic Engagement
China has been constructing villages along disputed border areas, altering ground realities and establishing civilian hubs that could serve as military outposts. Additionally, China is offering economic incentives to Bhutan, including promoting tourism and investing in Bhutan’s telecom sector, seeking to draw the country into closer economic and diplomatic alignment.
India’s Role in Bhutan’s Security and Sovereignty
Strategic Dependence on India
Bhutan's small military relies heavily on Indian support for training and defense. The 2017 Doklam standoff, where Indian forces intervened to prevent China from constructing a road in disputed territory, underscored India's crucial role in safeguarding Bhutan’s territorial integrity.
Friendship Treaty
The India-Bhutan Friendship Treaty is the cornerstone of their bilateral relations, ensuring Bhutan's sovereignty while reinforcing India's role in Bhutan’s foreign and defense policies. India's increased financial support aims to counter China’s economic influence in Bhutan.
Challenges for Bhutan
Balancing India and China
Bhutan is navigating a delicate balance between preserving its historical ties with India and engaging with China, which offers economic benefits. However, Bhutan’s sovereignty concerns limit its ability to make independent diplomatic decisions.
Domestic Issues
Bhutan faces challenges such as youth migration and limited economic diversification. Over-reliance on hydropower and a lack of industrial development make it vulnerable to external pressures, particularly from China.
The Strategic Importance of Bhutan to India
Geopolitical Buffer
Bhutan's location is vital for India’s security, especially in relation to the Siliguri Corridor, a narrow land link connecting India’s Northeast. Any Chinese presence in Bhutan’s disputed regions could disrupt access to this crucial corridor.
Hydropower Collaboration
Bhutan’s hydropower exports are central to India’s renewable energy strategy, and their cooperation in this area ensures mutual benefits.
Way Forward
India must continue to prioritize Bhutan’s development needs, ensuring robust financial and infrastructural support. Proactive engagement is necessary to address Bhutan’s concerns, particularly in light of China’s growing influence. Additionally, India should support Bhutan’s economic diversification to reduce reliance on external actors.
Impeachment of Judges
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent controversy surrounding remarks made by Justice Shekhar Kumar Yadav of the Allahabad High Court has prompted calls for his impeachment. During an event organized by the Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP), Justice Yadav made statements that were perceived as communal, leading to concerns over judicial impartiality. This incident has reignited discussions about the impeachment process for judges in India, highlighting the delicate balance between judicial independence and accountability.
Impeachment Process for Judges in India
In India, the impeachment process for judges, although not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution, serves as a mechanism to ensure judicial accountability while safeguarding judicial independence. The process is outlined under Articles 124 and 218 of the Indian Constitution, which govern the removal of Supreme Court and High Court judges, respectively.
Grounds for Impeachment
Judges in India can be removed on two grounds:
- Proved Misbehavior: Conduct that breaches the ethical standards of the judiciary.
- Incapacity: A judge’s inability to perform judicial duties due to physical or mental infirmity.
These grounds are clearly specified to prevent arbitrary removal, ensuring that the process remains fair and just.
Steps in the Impeachment Process
- Initiation of Motion: The process begins when a motion for impeachment is introduced in Parliament, either in the Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha. The motion must be supported by at least 100 members of the Lok Sabha or 50 members of the Rajya Sabha. This ensures significant parliamentary backing before the motion proceeds.
- Formation of an Inquiry Committee: If the motion is admitted, a three-member inquiry committee is constituted. This includes a Supreme Court judge, the Chief Justice of a High Court, and a distinguished jurist. The committee conducts a thorough investigation into the allegations.
- Committee Report and Parliamentary Debate: Following the investigation, the committee submits its findings. If the judge is found guilty, the report is debated in Parliament. Both Houses must approve the motion by a special majority, which requires a two-thirds majority of members present and voting, as well as a majority of the total membership.
- Final Removal by the President: Once the motion is passed in both Houses, it is presented to the President, who issues the removal order.
Safeguards Against Misuse
The impeachment process includes several safeguards to prevent misuse:
- High Threshold for Initiation: The requirement for significant support from Parliament ensures that the process cannot be initiated frivolously.
- Objective Inquiry: The inquiry committee, comprising legal experts, guarantees an impartial investigation.
- Parliamentary Scrutiny: Both Houses of Parliament are involved, ensuring that the process undergoes democratic scrutiny.
Challenges and Precedents
Despite the rigorous process, no Supreme Court judge has been successfully impeached to date. Past attempts, such as those against Justice V. Ramaswami (1993) and Chief Justice Dipak Misra (2018), were unsuccessful. These instances demonstrate the complexities involved in the impeachment process.
Guidelines for Judges’ Public Statements
Judges in India are entitled to freedom of speech, but they are expected to exercise caution in public statements to maintain the dignity of their office. The Bangalore Principles of Judicial Conduct (2002) and the Restatement of Values of Judicial Life (1997) outline key principles for judicial conduct, including:
- Non-Interference in Political Matters: Judges should refrain from commenting on political issues to avoid any perception of bias.
- Impartiality: Judges must avoid statements that could prejudice ongoing cases or align them with specific ideologies.
Upholding Judicial Impartiality in a Diverse Society
To maintain impartiality, judges must interpret laws based on constitutional values of justice, equality, and secularism. Furthermore, the judiciary must ensure representation from diverse backgrounds to foster inclusivity and reduce systemic biases. Training programs focused on cultural competence and social diversity are essential to ensure that judges are sensitive to the needs of marginalized communities.
Conclusion
The impeachment process, while stringent, plays a critical role in maintaining judicial accountability in India. As seen in the case of Justice Yadav, judicial conduct, particularly public statements, must be carefully scrutinized to preserve the integrity of the judiciary. Upholding impartiality and adhering to constitutional values are paramount in ensuring that the judiciary continues to function as a neutral arbiter in India’s democracy.
Analysis of Female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) Trends in India: 2017-2023
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) recently released a working paper revealing critical insights into the trends of female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in India from 2017-18 to 2022-23. The report highlights an overall increase in female LFPR, with rural areas experiencing more significant growth compared to urban areas. This article delves into the key findings, regional disparities, influencing factors, and government initiatives aimed at promoting female workforce participation.
Key Findings on Female LFPR
The period between 2017-18 and 2022-23 witnessed a notable rise in female LFPR, both in rural and urban regions, though rural areas saw higher gains.
Rural female LFPR surged by approximately 69%, from 24.6% to 41.5%, while urban female LFPR increased from 20.4% to 25.4%. This consistent growth was observed even after excluding unpaid family workers or household helpers, reinforcing the long-term trend of increased female workforce participation across India.
However, a significant point of discussion in the report was the regional variations in female LFPR. States like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana have consistently reported low female LFPR, which is noteworthy considering that Punjab and Haryana are among India's wealthiest states, while Bihar is the poorest. This regional disparity suggests that economic prosperity does not automatically translate into higher female labour force participation, highlighting deeper socio-cultural and structural barriers.
Regional Disparities in Female LFPR
The report emphasizes the persistent challenges in northern and eastern India. Punjab and Haryana, despite their affluence, have struggled with low female LFPR. Cultural and societal norms in these regions may contribute to the underrepresentation of women in the workforce, particularly in rural areas where traditional gender roles are more entrenched.
On the other hand, Bihar, the poorest state in India, had the lowest female LFPR in the country, particularly in rural areas. However, there has been a significant improvement in recent years, especially among rural married women. This indicates a slow but positive shift in attitudes towards female employment in these states.
In contrast, northeastern states such as Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh have shown significant improvements in female LFPR, particularly in rural areas. These states have demonstrated that regional and cultural factors can also create conducive environments for female workforce participation.
Demographic Factors Affecting Female LFPR
Several demographic patterns influence female LFPR, including marital status and age. The report notes that married men consistently exhibit higher LFPR compared to women. Marriage, however, has a detrimental impact on female LFPR, particularly in urban areas, where women often face greater familial and societal pressures to prioritize domestic responsibilities over formal employment.
Age dynamics also play a crucial role in female LFPR trends. The data reveals a bell-shaped curve for female participation, peaking around the age of 30-40 years and sharply declining thereafter. This is in stark contrast to male LFPR, which remains almost universally high between the ages of 30-50 before gradually declining. These trends underscore the challenges women face in sustaining their participation in the workforce due to familial responsibilities, especially after marriage and childbirth.
Government Initiatives and the Rise in Female LFPR
The government's focus on women-led development is evident through various schemes aimed at increasing female workforce participation. Programs like Mudra Loans, the Drone Didi Scheme, and the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana have been particularly instrumental in empowering women, especially in rural areas. These initiatives provide women with access to financial resources, skill development opportunities, and avenues for entrepreneurship, all of which contribute to the rise in female LFPR.
The EAC-PM's analysis acknowledges the positive impact of these government schemes, but it also stresses the need for further research to evaluate their long-term effectiveness. While the descriptive analysis highlights a substantial increase in female LFPR between 2017-18 and 2022-23, especially in rural areas, there remains a need for continuous monitoring and assessment of these schemes to ensure their sustained impact.
Conclusion: A Positive Shift, but Challenges Remain
The increase in female LFPR across India from 2017-18 to 2022-23 signals a positive shift in employment trends, particularly in rural areas. However, regional disparities, societal norms, and demographic factors continue to pose challenges. The rise in female LFPR is encouraging, but it is essential to understand the deeper socio-economic factors that shape women's participation in the workforce.
Government schemes have contributed to this growth, but future research is necessary to gauge their long-term effects and ensure that women’s participation in the workforce is not just a short-term trend. It is crucial that the government continues to refine policies that support women in overcoming socio-cultural and economic barriers, especially in less prosperous states like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana. Sustained efforts, including education, skill development, and gender-sensitive policies, will be key to ensuring that the rise in female LFPR is both inclusive and long-lasting.
The analysis by the EAC-PM provides an essential framework for policymakers to design more targeted interventions to address regional disparities and create a more inclusive labor market for women in India.
No-Confidence Motion Against Rajya Sabha Chairman

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
In December 2024, around 60 opposition MPs from the INDIA (Indian National Developmental, Inclusive Alliance) bloc submitted a notice to the Rajya Sabha Secretariat, seeking the removal of Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar from his position as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. This unprecedented move has sparked significant political debate, with the opposition accusing Dhankhar of partisanship and bias in the conduct of parliamentary proceedings.
The Charges Against Jagdeep Dhankhar
Allegations of Bias and Partisanship
The opposition has raised several allegations against Dhankhar since his appointment as the Rajya Sabha Chairman in August 2022. These include:
- Partiality towards the ruling government: The opposition claims that Dhankhar has shown bias in favor of the BJP, with accusations of repeatedly denying the Leader of the Opposition, Mallikarjun Kharge, the opportunity to respond to statements made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and BJP President J.P. Nadda.
- Interference in Parliamentary Debates: Opposition MPs have accused Dhankhar of disrupting their speeches and allowing ruling party members to dominate parliamentary discussions.
- Unbecoming Remarks: The notice also refers to comments made by Dhankhar, including praising the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) and recalling his association with "so-called cultural organizations." These actions, according to the opposition, violate the non-partisan nature expected of the Chairman.
The Constitutional Framework for Removal of the Vice-President
Legal Provisions for Impeachment
The Vice-President of India, who also serves as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, is elected for a five-year term. Article 67 of the Indian Constitution outlines the procedure for his removal:
- Notice Requirement: A motion for the removal of the Vice-President must be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with a prior 14-day notice.
- Approval Process: The resolution must be passed by a majority in the Rajya Sabha and then approved by the Lok Sabha.
- Grounds for Removal: The Vice-President can only be removed through a resolution that is supported by a majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Opposition’s Plan and Challenges
Despite lacking the necessary numbers in the Rajya Sabha to succeed in the impeachment motion, the opposition's move is aimed at sending a political message to the BJP, expressing dissatisfaction with the functioning of the Parliament under Dhankhar’s leadership.
The current session of Parliament is scheduled to end on December 20, 2024, leaving little time for the motion to gain traction. The opposition also does not have the numbers needed for a majority in the Rajya Sabha, which complicates the chances of success for the motion.
Historical Precedents for Similar Resolutions
The last notable attempt to remove a parliamentary officer occurred in 2020 when the opposition moved a no-confidence motion against Rajya Sabha Deputy Chairman Harivansh. This motion was prompted by his decision to extend the session during the contentious farm Bills debate. Although the motion was discussed, it did not result in any significant change.
Similarly, there have been instances where motions to remove Lok Sabha Speakers have been moved but not passed, such as against G.V. Mavalankar in 1951, Sardar Hukam Singh in 1966, and Balram Jakhar in 1987.
Role and Significance of the Vice-President in India
Constitutional Role
The Vice-President of India holds the second-highest constitutional office, primarily functioning as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. His duties include:
- Presiding over Rajya Sabha Sessions: The Vice-President ensures the smooth functioning of the Rajya Sabha and maintains order during debates. He does not typically vote except in the case of a tie.
- Acting President: In the absence, resignation, or death of the President, the Vice-President assumes the role of the Acting President.
Removal Process Under Article 67
- Article 67(b) of the Constitution specifies the process for the removal of the Vice-President, requiring a 14-day notice and approval from both Houses of Parliament. This provision ensures that any such resolution receives due consideration and is not moved hastily.
Implications for Parliamentary Democracy
- Risks to Parliamentary Integrity: Opposition leaders have expressed concern that the current political environment is eroding the integrity of India’s parliamentary system. They argue that by misusing constitutional offices for partisan ends, the ruling government risks undermining the democratic foundations of the country.
Significance of the Move
- Although the opposition may not succeed in removing Dhankhar, the notice serves as a powerful symbol of resistance. The move underscores the opposition’s commitment to defending the principles of parliamentary democracy and the need for impartiality in the conduct of parliamentary affairs.
Conclusion
The opposition’s push to remove Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar from his position as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha highlights the growing political tensions in India’s Parliament. While the move may not succeed due to the lack of numerical support, it brings to the forefront critical issues regarding the independence of constitutional offices and the functioning of parliamentary democracy in India. The developments around this notice will continue to be a significant point of discussion as the winter session of Parliament draws to a close.
How Minilateralism is Reshaping Global Order

- 09 Dec 2024
Introduction
Minilateralism refers to the growing trend of smaller, more focused international groupings of countries that cooperate on specific issues or regional challenges. It contrasts with the traditional multilateral frameworks, which are often large, slow-moving, and bogged down by lengthy debates and consensus-building. Today, minilateral platforms are increasingly driving global decision-making and shaping the future of international relations.
Rise of Minilateralism
Failure of Multilateralism
- Multilateralism's Decline: Traditional multilateral institutions like the United Nations (UN) are increasingly seen as ineffective due to their bureaucratic nature and the challenges in building consensus among a large number of diverse nations.
- Global Challenges: Emerging global issues, such as climate change, terrorism, and cybersecurity, require faster and more effective responses. The inability of multilateral platforms to address these challenges efficiently has led to a preference for smaller, more agile groupings.
Emergence of New Powers
- Multipolar World: The rise of new powers such as China, India, and Brazil has contributed to the formation of minilateral groupings. These rising powers desire a greater role in global governance but may not yet have the ability or desire to reshape the international order through large, cumbersome institutions.
- Minilateralism as "Multipolarity Lite": Minilateralism allows these countries to assert themselves as regional or global poles without the need for the complexities of full-scale multilateralism.
India's Role in Minilateralism
Strategic Positioning
- Geopolitical Context: India’s strategic location in South Asia, its status as part of the Global South, and its proximity to a rising China have all influenced its approach to minilateralism. India’s multi-aligned approach reflects its desire for flexibility in navigating the complex and shifting global geopolitical landscape.
- Diverse Partnerships: India is a key player in various minilateral arrangements, balancing its relationships with both traditional Western powers and rising Eastern nations, often serving as a bridge between competing geopolitical interests.
Minilateralism as a Solution
- Diversification Over Alignment: India's preference for minilateralism stems from the desire to avoid over-reliance on any single bloc or country. By engaging in multiple minilateral platforms, India seeks to hedge its interests, balancing its strategic objectives between competing global forces.
The Role of Minilateral Forums
Decision-making and Action
- Faster Action: Minilateral groupings facilitate quicker decision-making by bringing together like-minded countries to focus on specific issues, allowing for more decisive action than traditional multilateral bodies.
- Conflict Resolution: While minilateral platforms may not directly resolve conflicts, they offer indirect pathways for addressing geopolitical tensions by fostering dialogue and cooperation among countries with divergent interests.
Examples of Minilateral Groupings
- BRICS: The grouping of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa is an example of a minilateral arrangement where emerging powers cooperate on shared economic and political interests.
- Quad: The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (comprising the United States, India, Japan, and Australia) is a prominent example of minilateralism focused on regional security, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Other Regional Groupings: Minilateralism also manifests in regional arrangements such as the ASEAN-led East Asia Summit or the India-Japan-Australia trilateral forum, each addressing specific regional and global concerns.
Conclusion
Shaping the Future of Global Order
Minilateralism is reshaping the international order by fostering closer, more flexible cooperation between countries on a wide range of issues. As multilateralism faces growing challenges, smaller, more focused partnerships offer a faster and more efficient means of addressing global problems. India's pivotal role in these groupings reflects its desire to navigate a complex geopolitical landscape while maintaining strategic autonomy. The rise of minilateralism marks a significant shift in global governance, one that could define the future of international relations.
Beware of Digital Wedding Invites

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
In the peak wedding season, cyber fraudsters are increasingly exploiting digital wedding invitations to hack into mobile phones. These fraudulent invites, often disguised as PDF wedding cards shared on WhatsApp, contain embedded malware that allows cybercriminals to gain full access to the victim's phone. This includes access to sensitive financial data, making individuals vulnerable to fraud. The Lucknow Police Cyber Cell has issued a public warning, urging citizens to be cautious and avoid opening suspicious files.
How the Scam Works
The scam involves cybercriminals sending out malware-laden wedding invitations. Once the recipient opens the file, the malware infects their phone, enabling the fraudsters to remotely control the device. From there, they can access sensitive information, including bank account details, and may even transfer funds without the victim’s consent.
Preventive Measures and Cyber Hygiene
To protect against such scams, individuals should follow these preventive steps:
- Avoid Suspicious Files: Do not open files from unknown senders, particularly those with extensions like APK, PIF, or VBS. It is crucial to verify the sender's number—legitimate Indian numbers typically begin with +91.
- Turn Off Auto-Download: Disabling automatic downloads on platforms like WhatsApp can prevent files from being opened unknowingly.
- Enable Two-Step Verification: Strengthen security by activating two-step verification on your digital accounts and setting strong passwords.
- Report Fraud Immediately: In case of suspicious activity, contact the cybercrime helpline at 1930 or file a complaint on the official cybercrime portal (www.cybercrime.gov.in).
The Lucknow Police’s “Cyber Pathshala” campaign aims to raise awareness and educate the public on digital scams, particularly during the wedding season when these frauds are at their peak.
Cybersecurity Challenges in India
This emerging digital threat is part of a broader trend of sophisticated cybercrimes in India. Cyber fraudsters are increasingly using manipulative tactics, such as phishing, fake digital arrests, and malware attacks. In 2024, India witnessed a significant rise in ransomware attacks, frauds targeting financial institutions, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
India's legislative and institutional frameworks are evolving to address these challenges. Key measures include:
- The Information Technology Act, 2000, which lays the foundation for tackling cybercrimes.
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, which focuses on protecting personal data.
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), which coordinates national responses to cyber incidents.
Additionally, new frameworks like the National Cyber Security Policy, 2013, and initiatives such as Cyber Surakshit Bharat and the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), aim to fortify India's digital landscape and promote cybersecurity.
Emerging Cyber Threats
As India becomes more digitally connected, the threat landscape continues to evolve:
- Digital Arrest Scams: Fraudsters impersonate law enforcement to extort money from victims, claiming they are under investigation for fictitious crimes.
- Ransomware: Attacks on critical infrastructure, such as financial institutions and healthcare systems, have led to operational disruptions and financial losses.
- Deepfake Technology: The rise of AI-generated deepfakes poses significant risks, including misinformation and financial fraud.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities: The rapid adoption of IoT devices has created new security challenges, with many devices lacking adequate protection.
Strategic Recommendations for Enhancing Cybersecurity
To counter these evolving threats, India must focus on several strategic areas:
- Digital Literacy Campaigns: Nationwide efforts to improve digital literacy, particularly targeting vulnerable groups such as rural populations and senior citizens.
- Stronger IoT Security Protocols: Mandating secure design and certification for IoT devices.
- AI-Driven Threat Intelligence: Implementing AI-based tools for early threat detection and response in critical sectors.
- Mandatory Cybersecurity Audits: Regular audits of critical infrastructure, especially in sectors like healthcare, banking, and utilities.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships to address challenges such as cryptocurrency fraud, ransomware, and dark web-enabled crimes.
Conclusion
The rise of digital fraud, including the manipulation of wedding invitations for malicious purposes, highlights the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures in India. By improving public awareness, investing in technological solutions, and reinforcing legal and institutional frameworks, India can better protect its citizens from the growing threat of cybercrime. A proactive and informed approach is essential to secure the digital future of the nation.
Building on the Revival of the Manufacturing Sector
- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s manufacturing sector has shown remarkable signs of recovery and growth, thanks to strategic policy initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. To fully capitalize on this momentum and become a global manufacturing hub, however, deeper reforms are needed.
The Success of the PLI Scheme: A Catalyst for Growth
The government’s PLI scheme has been instrumental in revitalizing key sectors like electronics, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and textiles. It has not only boosted production but also increased exports and job creation. According to the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) 2022-23, manufacturing output grew by an impressive 21.5%, while gross value added (GVA) increased by 7.3%. Sectors such as basic metals, refined petroleum products, food products, and motor vehicles, which are beneficiaries of the PLI scheme, contributed 58% of total manufacturing output, registering growth of 24.5%.
This success underlines the potential of India’s manufacturing sector, with the PLI scheme acting as a key enabler. However, while the recovery is promising, there are significant challenges to overcome to sustain long-term growth.
Expanding PLI Incentives to New Sectors
The PLI scheme has largely benefitted traditional industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing. To further accelerate growth, the scope of the scheme must be extended to labour-intensive sectors such as apparel, footwear, and furniture, which hold immense potential for job creation. Additionally, emerging sectors like aerospace, space technology, and maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services offer new avenues for growth. By diversifying the incentive structure to these sectors, India could establish a more robust and resilient manufacturing ecosystem.
In sectors like capital goods, where India is heavily import-dependent, the potential for reducing supply chain vulnerabilities is significant. Moreover, promoting green manufacturing and advanced technologies could further bolster India’s competitiveness in global markets.
Addressing the Divergence Between Output and Value Addition
Despite a surge in production, India’s gross value added (GVA) has not kept pace with output growth. The ASI data shows that input prices soared by 24.4% in 2022-23, indicating that while production volumes are up, industries are grappling with high input costs. A more streamlined import regime could mitigate these costs. Simplifying tariffs into a three-tier system (for raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods) would reduce input costs, enhance competitiveness, and improve integration into global value chains.
Regional Imbalance: A Barrier to Inclusive Growth
The manufacturing sector’s growth is heavily concentrated in a few states such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Uttar Pradesh, which account for over 54% of manufacturing GVA. This concentration not only restricts equitable development but also hampers the overall growth potential of the sector. To address this, it is crucial that states actively participate in India's manufacturing growth story by implementing market reforms in land, labour, and power. Additionally, infrastructure development and investment promotion in less industrialized regions could help balance growth and ensure that the benefits of manufacturing reach all corners of the country.
Fostering MSME Growth and Enhancing Female Workforce Participation
Micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) contribute about 45% of India’s manufacturing GDP and employ around 60 million people. To scale these businesses and integrate them into global value chains, PLIs should be tailored to accommodate their needs, such as lowering capital investment thresholds and reducing production targets.
Equally important is the enhancement of female workforce participation. Studies suggest that India’s manufacturing output could increase by 9% if more women enter the workforce. The development of supportive infrastructure, such as hostels and childcare facilities, can play a pivotal role in enabling women’s participation, thus driving inclusive growth.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
To transform into a developed economy by 2047, India must continue to focus on strengthening its manufacturing sector. According to industry estimates, manufacturing’s share in Gross Value Added (GVA) can rise from 17% to 25% by 2030 and further to 27% by 2047. Achieving this will require sustained efforts to enhance competitiveness through business reforms, cost reduction, and policy support. India is well-positioned to harness its manufacturing potential, but timely and focused interventions are necessary to turn this vision into reality.
Reflections on Baku’s ‘NCQG Outcome’ at COP29
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The recently concluded COP29 in Baku, Azerbaijan, has brought the spotlight back to climate finance, particularly in relation to the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG). As the global community grapples with the escalating climate crisis, the discussions and outcomes from the COP29 summit are pivotal in shaping future climate action. However, the agreed-upon financial targets, which were expected to be a step towards transformative climate justice, have sparked significant concern, particularly among developing nations.
The Need for Climate Finance: A Global Responsibility
Climate finance is essential for supporting developing countries, which bear the brunt of climate change despite contributing minimally to global emissions. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has stressed the need to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, yet current policies could lead to a rise of up to 3.1°C. To counter this, developing nations require financial assistance to transition to green energy, adapt to climate impacts, and implement their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
The upfront costs of green technologies, such as renewable energy, are high, and while they offer long-term savings, their initial investments remain a significant barrier. Additionally, many developing countries face fiscal constraints, making it even more difficult to adopt climate-friendly technologies without external financial support.
The Role of NCQG in Addressing Climate Finance Gaps
The NCQG, an evolution of the 2010 $100 billion annual commitment, aims to provide clarity and accountability in climate financing. Established as a framework to ensure financial resources for climate action, the NCQG should ideally focus on the evolving needs of the Global South. However, at COP29, the target agreed upon was a mere $300 billion annually by 2035, far from the $1.3 trillion that developing countries had requested. This amount falls drastically short of what is necessary to meet the ambitious climate goals and fails to represent a transformative shift in financial flows.
Key Challenges and Discontent with the Outcome
Several challenges have been raised regarding the COP29 outcome:
- Equity and Responsibility: Developed nations are expected to bear a larger share of the financial burden, in line with the principle of 'Common but Differentiated Responsibilities' (CBDR). However, the NCQG outcome bypasses this principle, offering insufficient funds for climate action in developing countries.
- Types of Finance: There is debate over whether private finance should count towards the goal. Developing countries have stressed the importance of public finance over loans, which add to their debt burdens.
- Insufficient Commitment: While the $300 billion annual pledge is a step forward, it is far from adequate. The global climate finance needs, estimated at $5 trillion to $7 trillion by 2030, require bolder commitments from developed nations.
India's Position and Domestic Efforts
At COP29, India emphasized the need for developed countries to fulfill their financial commitments, advocating for at least $1.3 trillion annually until 2030. India, despite being a developing country, has also made significant strides in climate action through domestic policies. The 2024-25 Union Budget allocated substantial funds to renewable energy projects, including ?19,100 crore for the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy. These efforts demonstrate India’s commitment to climate goals, though the financial flow remains insufficient.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
The NCQG outcome at COP29 highlights the ongoing disparities in global climate finance commitments. While the $300 billion annual target is a step forward, it does not align with the urgency or scale required to tackle the climate crisis. To achieve a just and equitable transition to a sustainable future, future climate finance discussions must prioritize transparency, accountability, and fairness, ensuring that developed nations shoulder their fair share of the responsibility. The path forward requires unwavering international cooperation to ensure that developing countries receive the necessary support to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Scrapping of Windfall Gains Tax

- 05 Dec 2024
Introduction
On December 2, 2024, the Indian government withdrew the windfall gains tax on domestic crude oil production and fuel exports (diesel, petrol, and aviation turbine fuel - ATF). This tax, initially imposed in July 2022, was introduced in response to the surge in global oil prices following Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Its removal reflects the current global oil market stability and the improved fuel supply situation in India.
What is Windfall Gains Tax?
Definition
A windfall tax is a levy imposed on unexpected profits that result from extraordinary events, such as geopolitical crises or market disruptions. In the case of India, the tax was applied to the super-normal profits of oil producers and fuel exporters due to the global energy turmoil.
Key Features
- Domestic Crude Oil: The Special Additional Excise Duty (SAED) was imposed on domestic crude oil production.
- Fuel Exports: A combination of SAED and Road and Infrastructure Cess (RIC) was levied on diesel, petrol, and ATF exports.
Rationale Behind the Windfall Gains Tax
Immediate Context
The tax was introduced during a period of soaring global crude oil prices, driven by the Russia-Ukraine conflict. India, which imports over 85% of its oil, faced concerns about the availability of fuels and the impact of rising prices on domestic consumption. The tax was seen as a way to:
- Ensure Domestic Fuel Supply: By discouraging excessive fuel exports during a period of global supply chain disruptions.
- Increase Government Revenue: The tax aimed to capture windfall profits and offset the duty cuts on domestic fuel sales.
Global Context
Other countries also implemented similar windfall taxes during this period, as energy companies saw record profits due to the price surge.
Decline in Windfall Gains Tax Revenue
Revenue Collection
The windfall gains tax initially raised significant revenue, but the amount has decreased over time due to falling global oil prices:
- FY 2022-23: Rs 25,000 crore
- FY 2023-24: Rs 13,000 crore
- FY 2024-25 (so far): Rs 6,000 crore
This decline, combined with reduced oil prices, led to the tax being effectively inactive before its formal withdrawal.
Withdrawal of the Windfall Gains Tax
Reasons for the Withdrawal
- Global Stabilization: Crude oil prices, which had exceeded $100 per barrel, have now stabilized under $75 per barrel, with no immediate signs of a significant price surge.
- Domestic Fuel Availability: There is now a robust fuel supply in the domestic market, making the tax less necessary.
- Declining Revenues: With the tax generating diminishing returns, it was no longer economically viable for the government to maintain it.
Impact of the Scrapping
The government's move to scrap the windfall gains tax is seen as a signal of stability and predictability in the taxation regime. It assures the oil industry that the government is confident in the stability of global oil prices and supply chains.
Criticism of the Windfall Tax
Industry Opposition
The windfall tax faced opposition from the oil industry, which argued that it:
- Reduced Profitability: The tax limited the profits of publicly listed companies like ONGC and Reliance Industries.
- Discouraged Oil Production: By making the taxation environment unpredictable, it deterred investment in oil exploration and production in a country that is heavily dependent on oil imports.
- Created Uncertainty: Frequent revisions of the tax led to an unstable business environment.
Conclusion
The scrapping of the windfall gains tax is a significant policy shift. It not only provides relief to oil companies but also signals a more predictable and stable taxation regime. By withdrawing the tax, the government is fostering a conducive environment for future investments in domestic oil production and signaling its confidence in the stability of global oil prices. This move is a crucial step in ensuring that India’s energy policies remain adaptable and aligned with the evolving global market conditions.
Current Representation of Women in CAPFs

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) of India, comprising forces like CRPF, BSF, CISF, and others, play a crucial role in maintaining internal security. Women’s participation in these forces has been historically limited, but recent efforts have focused on increasing their representation. As of 2024, women constitute only 4.4% of the total personnel in CAPFs, highlighting the slow progress despite various initiatives.
Current Representation and Changes Over Time
- Overall Representation: Women make up 4.4% of the 9.48 lakh-strong CAPFs. Within this, the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) has the highest representation at 7.02%, followed by the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) at 4.43%, Border Security Force (BSF) at 4.41%, Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) at 4.05%, Assam Rifles at 4.01%, and Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) at 3.38%.
- Growth of Women Personnel: From 15,499 women in 2014, the number has tripled to 42,190 in 2024, reflecting a steady increase in recruitment. However, the percentage remains low despite these gains.
- Recruitment Trends: In 2024, 835 women were recruited, with 5,469 more in the process. In 2025, 4,138 women are expected to be recruited.
Government Efforts and Parliamentary Committee Recommendations
- Policy Measures: The government has introduced several steps to encourage women’s participation in CAPFs, such as reservations in constable-level positions: one-third for CRPF and CISF, and 14-15% for border forces like BSF, SSB, and ITBP.
- Challenges in Recruitment: Despite these policies, recruitment has not kept pace with the targets. The 2022 Parliamentary Committee on Home Affairs expressed disappointment over the “abysmally low” number of women in CAPFs, noting that women made up only 3.68% of the forces at that time.
- Recommendations by Parliamentary Committees:
- The Home Affairs Committee recommended fast-tracking phase-wise recruitment of women, particularly in CISF and CRPF.
- The Standing Committee on Personnel (2023) suggested “soft postings” for women to avoid difficult working conditions, especially in remote or strenuous terrains. It also called for reservations for transgender individuals.
- In 2024, further steps like fee waivers, relaxed physical standards, and provisions for maternity and child care leave were introduced to make the work environment more inclusive.
Reasons Behind Low Representation
- Cultural Barriers: Traditional gender roles and societal expectations deter many women from pursuing careers in security forces.
- Work Environment: The demanding nature of the job, which includes postings in remote areas and high-risk operations, makes it less appealing, especially for women with family responsibilities.
- Infrastructure Issues: Lack of adequate accommodation, sanitation facilities, and safety measures for women are deterrents to joining and retaining female personnel.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Although the representation of women in CAPFs has seen improvement, it remains below expectations due to persistent challenges. The government’s continuous focus on recruitment reforms, better working conditions, and policy incentives will be crucial to achieve gender parity in these forces. As societal attitudes evolve and the infrastructure improves, more women may be encouraged to serve in these vital security roles. Future efforts must include targeted recruitment drives and creating a more inclusive and supportive environment to enhance women’s participation in CAPFs.
India's Gig Economy: Growth and Impact on Employment

- 03 Dec 2024
Introduction
India’s gig economy is experiencing rapid growth, with projections indicating it will significantly contribute to the national economy and employment generation. A recent report by the Forum for Progressive Gig Workers estimates the gig economy could reach $455 billion by the end of 2024, growing at a 17% compounded annual growth rate (CAGR). By 2030, it may add 1.25% to India’s GDP and create 90 million jobs.
What is the Gig Economy?
- Definition: The gig economy refers to a labor market based on short-term, flexible jobs, typically facilitated by digital platforms. Gig workers, also called freelancers or independent contractors, are compensated for each task they complete.
- Key Features:
- Flexibility in work schedule and location.
- Task-based employment through digital platforms.
- Common sectors: e-commerce, transportation, delivery services, and freelance work.
Status of the Gig Economy in India
- Market Growth:
- In 2020-21, India had 7.7 million gig workers, which is expected to grow to 23.5 million by 2029-30.
- Key sectors contributing to growth include e-commerce, transportation, and delivery services.
- Driving Factors:
- Digital Penetration: With over 936 million internet subscribers and 650 million smartphone users, digital infrastructure is a key enabler of the gig economy.
- Startup and E-commerce Growth: The rise of startups and e-commerce platforms has increased demand for flexible labor.
- Changing Work Preferences: Younger generations seek work-life balance, opting for flexible gig work.
Gig Economy and Employment Generation
- Contribution to GDP: The gig economy is expected to contribute 1.25% to India’s GDP by 2030.
- Job Creation:
- The gig economy could create up to 90 million jobs by 2030.
- It is estimated that by 2030, gig workers will comprise 4.1% of India’s total workforce.
- Benefits:
- Women’s Empowerment: Gig work provides financial independence and flexibility, especially benefiting women in the workforce.
- Regional Growth: Tier-II and Tier-III cities are seeing accelerated growth in gig work opportunities.
Challenges Faced by Gig Workers
- Job Insecurity: Many gig workers experience instability in their employment, especially in low-skilled jobs.
- Income Volatility: Earnings are unpredictable, and workers face difficulty in financial planning.
- Regulatory Gaps: There is no comprehensive legal framework to protect gig workers’ rights and ensure fair working conditions.
- Delayed Payments: A significant number of workers face delayed payments, affecting their financial well-being.
- Skill Development: Many workers report a lack of opportunities for career advancement and skill development.
Government Initiatives for Gig Workers
- Code on Social Security, 2020: Recognizes gig workers and aims to extend social security benefits, though it lacks comprehensive coverage.
- e-Shram Portal & Welfare Schemes: Initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana and PMJJBY aim to provide financial security to gig workers.
- State-level Initiatives:
- Rajasthan’s Platform-Based Gig Workers Act (2023) focuses on registration and welfare.
- Karnataka’s bill mandates formal registration and grievance mechanisms.
The Way Forward
- Legal Reforms: India can draw from international models like California and the Netherlands, where gig workers are reclassified as employees to ensure protections such as minimum wages and regulated working hours.
- Portable Benefits System: Implementing a system where gig workers can access benefits like healthcare and retirement plans regardless of their employer.
- Skill Development: Strengthening collaborations with vocational institutions to enhance skills and improve earning potential.
- Technological Solutions: Establishing robust feedback mechanisms for workers to report exploitation and ensure fairness within the gig economy.
Conclusion
The gig economy in India is poised to become a significant driver of economic growth and job creation. However, addressing challenges such as income volatility, job insecurity, and regulatory gaps is crucial to ensuring sustainable growth.
NITI Aayog’s Framework for Future Pandemic Preparedness
- 02 Dec 2024
Introduction
In response to the evolving threat of pandemics, NITI Aayog has released an Expert Group report titled "Future Pandemic Preparedness and Emergency Response — A Framework for Action." The report offers a strategic blueprint for India to enhance its pandemic preparedness, drawing from the lessons learned during the COVID-19 crisis and global best practices. This framework aims to create a rapid, well-coordinated response system for future public health emergencies.
Rationale Behind the Expert Group
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of global and national health systems to emerging infectious diseases. As future pandemics are inevitable, especially with increasing zoonotic threats, India has taken a proactive step in planning for such eventualities. The WHO has warned that 75% of future pandemics may be zoonotic, caused by pathogens transmitted from animals to humans.
Key Findings from COVID-19 Response
India's response to COVID-19 highlighted several strengths and weaknesses in the public health system. Key efforts included developing vaccines, enhancing research and development frameworks, and deploying digital tools for data management across its 1.4 billion population. However, gaps were identified in governance, data management, and cross-sectoral coordination. These lessons have been integrated into the expert group’s framework for future preparedness.
The 100-Day Response Framework
A crucial aspect of the report is the emphasis on the first 100 days of a pandemic. The expert group argues that a rapid response within this period is essential for minimizing the impact of any outbreak. The framework outlines a detailed roadmap for preparedness, which includes tracking, testing, treating, and managing outbreaks efficiently. A robust system for quick deployment of countermeasures, including vaccines and treatments, is pivotal during these critical days.
Four Pillars of Pandemic Preparedness
The report's recommendations are organized around four pillars:
- Governance, Legislation, Finance, and Management:
- Proposes a new Public Health Emergency Management Act (PHEMA) to address modern pandemic needs.
- Creation of an empowered group of secretaries (EGoS) for rapid decision-making and coordination.
- Data Management, Surveillance, and Predictive Tools:
- Calls for a unified data platform to aggregate and analyze data for timely decision-making.
- Emphasizes strengthening genomic surveillance and establishing a national biosecurity network.
- Research, Innovation, and Infrastructure:
- Recommends a high-risk innovation fund to support research on diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics.
- Suggests enhancing manufacturing capacity and building biosafety containment facilities.
- Partnerships and Community Engagement:
- Stresses the importance of private sector involvement and community engagement in managing pandemics.
- Proposes a risk communication unit at the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) to manage public information and prevent misinformation.
International and National Collaboration
The report underscores the need for cross-border collaboration, aligning India’s efforts with international frameworks such as the WHO’s revised International Health Regulations and the Pandemic Accord negotiations. Collaboration with global institutions, academia, and the private sector is essential for sharing data, technology, and expertise during health crises.
Lessons from Past Epidemics
The report draws lessons from several past epidemics, including SARS, H1N1, and Ebola, which revealed the importance of timely diagnostics, coordinated surveillance, and rapid response. These lessons highlight the need for stronger international regulations, integrated data systems, and enhanced public-private partnerships in tackling future pandemics.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The framework offers actionable recommendations to strengthen India’s pandemic preparedness. From institutionalizing governance structures and creating a dedicated pandemic fund to enhancing surveillance and fostering innovation, these steps are designed to ensure rapid response and minimize the impact of future health crises. By focusing on governance, data management, research, and community partnerships, India aims to build a resilient health system capable of facing future challenges effectively.
Digital Arrests

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
In 2024, India has witnessed an alarming rise in cybercrime, particularly a new scam called "digital arrests." This type of fraud involves criminals impersonating law enforcement officials to extort money from victims. With more than 92,000 people targeted and ?2,141 crore defrauded from victims, these scams are rapidly becoming a significant concern for the public and law enforcement.
Nature of ‘Digital Arrests’
The modus operandi of digital arrest scams is sophisticated and emotionally manipulative. Cybercriminals contact victims through video calls, often using fake police officers' profiles and official documents to build credibility. They accuse victims of serious crimes such as money laundering or drug trafficking, claiming urgent action is needed to avoid arrest. The scammers create a false atmosphere of fear and urgency, convincing the victim to transfer large sums of money under the pretext of settling legal dues.
A notable example involves Ruchi Garg, who was targeted by scammers posing as police officers, falsely claiming her son was involved in a major scam. She was coerced into transferring ?80,000 before realizing it was a scam. Similar cases have affected hundreds, with perpetrators using AI-generated voices and fake visuals to amplify the deception.
The Growth of Cybercrime in India
Digital arrest scams are part of a broader increase in cybercrime in India. The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) has reported a rise in cyber fraud, with financial losses exceeding ?27,900 crore between 2021 and 2024. The most significant sources of these losses include stock trading scams, Ponzi schemes, and digital arrest frauds. As criminals adapt to emerging technologies and use social engineering tactics, the scale and complexity of scams are growing.
The surge in cybercrimes is fueled by vulnerabilities in India's digital landscape. With over 95 crore Internet users, many people, particularly the elderly or less tech-savvy, remain susceptible to such fraud. Cybercriminals often exploit this lack of awareness, combining fear and confusion to manipulate victims.
International Scope and Challenges
One of the challenges in combating digital arrests is the transnational nature of cybercrime. Scams often originate from countries like China, Cambodia, and Myanmar, where "scam compounds" run operations to train individuals in fraudulent techniques. These groups use virtual private networks (VPNs) and encrypted apps to conceal their identities and locations, making it difficult for Indian authorities to trace them.
Moreover, the involvement of mule bank accounts to launder defrauded money complicates investigations. Thousands of such accounts are identified and blocked regularly, but the flow of money continues through multiple channels, including cryptocurrencies.
Government Efforts and Preventive Measures
To address the growing menace of digital frauds, the Indian government has initiated several measures. The I4C, launched in 2020, aims to strengthen the response to cybercrimes by coordinating with various law enforcement agencies. The National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal allows citizens to report cyber fraud, while real-time alerts are sent to banks to prevent financial losses.
Additionally, the Cyber Crime Coordination Centre and other initiatives like Cyber Surakshit Bharat and CERT-In are working to enhance cybersecurity awareness and support victims. The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, also aims to regulate data security, which can reduce the sale of personal data on the dark web, a key enabler of these scams.
Conclusion
‘Digital arrests’ exemplify the evolving nature of cybercrimes in India. As digital threats become more complex and widespread, it is essential for citizens to remain vigilant and informed. Effective law enforcement, technological innovations, and public awareness are critical to reducing the impact of these scams and safeguarding the digital economy.
Biomedical Waste Regulations

- 30 Nov 2024
The Emergence of HIV and Global Panic
In 1983, scientists Luc Montagnier and Robert Gallo independently identified the virus responsible for AIDS. By the mid-1980s, HIV/AIDS was perceived as a biological death sentence, with the virus primarily attacking immune cells, making medical intervention difficult. The epidemic quickly became associated with fear, ignorance, and stigma, as it was often linked to marginalized groups.
The "Syringe Tide" Incident and Public Outrage
In August 1987, the U.S. faced a public health crisis when discarded medical waste, including syringes and blood vials, washed up on beaches along the Atlantic coast. Known as the "Syringe Tide," this incident shocked the public and fueled anxiety, especially when children were seen playing with syringes. Traced to improper waste disposal in New York City, the event highlighted the hazardous nature of medical waste, which had been previously underestimated. Combined with the HIV/AIDS epidemic, this incident amplified public fear and economic losses of up to $7.7 billion due to the decline in tourism.
U.S. Response: Medical Waste Tracking Act of 1988
The widespread outrage led to the U.S. government passing the Medical Waste Tracking Act in 1988. This was the first law to formally categorize hospital waste as hazardous. The Act introduced stringent guidelines for the handling, transportation, and disposal of medical waste, establishing systemic regulation and oversight. It marked a significant turning point in both public health and environmental safety, changing how medical waste was managed in the healthcare sector.
India’s Journey in Biomedical Waste Management
Initial Steps and Delays
While the U.S. responded swiftly to the crisis, India’s approach to managing biomedical waste was slower. In 1986, India enacted the Environmental Protection Act, which marked the country’s first significant step towards environmental conservation. That same year, India identified its first HIV case. However, biomedical waste was not yet recognized as hazardous, and the Hazardous Waste (Management and Handling) Rules of 1989 failed to address the issue. As a result, local bodies were left to manage waste disposal, leading to inefficiencies.
Judicial Intervention and Legislative Action
In the 1990s, as pollution levels rose, particularly in urban areas like Delhi, the inadequacies of the system became apparent. In the landmark case Dr. B.L. Wadehra vs. Union of India (1996), the Supreme Court criticized Delhi’s waste management system, calling the city an "open garbage dump." This judgment led to a nationwide conversation on waste management and resulted in the Biomedical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules of 1998, marking the formal recognition of hospital waste as hazardous. The rules empowered the Central and State Pollution Control Boards to regulate waste disposal, ensuring accountability.
The Link Between HIV and Biomedical Waste Regulations
The HIV crisis highlighted the need for safe disposal practices to protect the environment and healthcare workers. While India charted its own course, the global response to HIV, particularly the U.S. model, influenced India’s approach to biomedical waste management. Over the years, India has made significant progress, with amendments to the rules in 2016 and 2020 to improve waste management technology and ensure safe disposal.
Current Challenges and Progress
- Ongoing Issues in Biomedical Waste Management: Despite significant progress, challenges remain, especially in rural and resource-limited areas. Mishandling of biomedical waste continues to pose risks, and healthcare professionals still face occupational hazards. Gaps in compliance and awareness persist, but the system’s progress is undeniable.
Conclusion
The HIV/AIDS epidemic, while tragic, indirectly led to significant improvements in healthcare waste management. As the crisis highlighted the dangers of improper waste disposal, it spurred legislative and systemic changes that have contributed to safer healthcare environments. The progress in biomedical waste management demonstrates that crises can often lead to long-term improvements.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet recently approved the launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF), marking a significant shift in the government's approach to agriculture. This initiative, a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, aims to promote natural farming across India, focusing on reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and promoting environmentally sustainable practices.
What is Natural Farming?
Natural farming, as defined by the Ministry of Agriculture, is a chemical-free agricultural method that relies on inputs derived from livestock and plant resources. The goal is to encourage farmers to adopt practices that rejuvenate soil health, improve water use efficiency, and enhance biodiversity, while reducing the harmful effects of fertilizers and pesticides on human health and the environment. The NMNF will initially target regions with high fertilizer consumption, focusing on areas where the need for sustainable farming practices is most urgent.
Evolution of Natural Farming Initiatives
The NMNF is not an entirely new concept but a scaled-up version of the Bhartiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhti (BPKP) introduced during the NDA government's second term (2019-24). The BPKP was part of the larger Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojna (PKVY) umbrella scheme, and natural farming was also promoted along the Ganga River under the NamamiGange initiative in 2022-23. With the renewed focus on natural farming following the 2024 elections, the government aims to extend the lessons learned from BPKP into a comprehensive mission mode, setting a clear direction for sustainable agriculture.
In Budget speech for 2024-25, it was announced a plan to initiate one crore farmers into natural farming over the next two years. The mission will be implemented through scientific institutions and willing gram panchayats, with the establishment of 10,000 bio-input resource centers (BRCs) to ensure easy access to the necessary inputs for natural farming.
Key Objectives
The NMNF aims to bring about a paradigm shift in agricultural practices by:
- Expanding Coverage: The mission plans to bring an additional 7.5 lakh hectares of land under natural farming within the next two years. This will be achieved through the establishment of 15,000 clusters in gram panchayats, benefiting 1 crore farmers.
- Training and Awareness: The mission will establish around 2,000 model demonstration farms at Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), Agricultural Universities (AUs), and farmers' fields. These farms will serve as hubs for training farmers in natural farming techniques and input preparation, such as Jeevamrit and Beejamrit, using locally available resources.
- Incentivizing Local Inputs: The creation of 10,000 bio-input resource centers will provide farmers with easy access to bio-fertilizers and other natural farming inputs. The mission emphasizes the use of locally sourced inputs to reduce costs and improve the sustainability of farming practices.
- Farmer Empowerment: 30,000 Krishi Sakhis (community resource persons) will be deployed to assist in mobilizing and guiding farmers. These trained individuals will play a key role in generating awareness and providing on-ground support to the farmers practicing natural farming.
- Certifications and Branding: A major aspect of the mission is to establish scientific standards for natural farming produce, along with a national certification system. This will help in creating a market for organically grown produce and encourage more farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
Targeting High Fertilizer Consumption Areas
The Ministry of Agriculture has identified 228 districts in 16 states, including Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Maharashtra, and West Bengal, where fertilizer consumption is above the national average. These districts will be prioritized for the NMNF rollout, as they have high fertilizer usage but low adoption of natural farming practices. By focusing on these areas, the mission seeks to reduce the over-dependence on chemical fertilizers and foster a transition to more sustainable farming practices.
Benefits of Natural Farming
The NMNF aims to deliver multiple benefits to farmers and the environment:
- Cost Reduction: Natural farming practices can significantly reduce input costs by decreasing the need for costly chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Soil Health and Fertility: By rejuvenating the soil through organic inputs, natural farming improves soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity, leading to long-term agricultural sustainability.
- Climate Resilience: Natural farming enhances resilience to climate-induced challenges such as drought, floods, and waterlogging.
- Healthier Produce: Reduced use of chemicals results in safer, healthier food, benefitting both farmers and consumers.
- Environmental Conservation: The promotion of biodiversity, water conservation, and carbon sequestration in soil leads to a healthier environment for future generations.
Conclusion
The launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming represents a critical step toward transforming India's agricultural practices into a more sustainable and environmentally friendly model. By targeting regions with high fertilizer usage, providing farmers with the tools and knowledge for natural farming, and creating a system for certification and branding, the government hopes to make natural farming a mainstream practice. As India continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, soil degradation, and health risks from chemical inputs, the NMNF provides a promising framework for sustainable agriculture that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.
India’s Urban Infrastructure

- 28 Nov 2024
Introduction
India’s urban population is projected to double from 400 million to 800 million by 2050. This demographic shift presents both challenges and opportunities for transforming the country’s urban infrastructure. To meet the growing needs of urban areas, India will require an investment of approximately ?70 lakh crore by 2036, a figure significantly higher than current spending levels.
Financial Challenges in Urban Infrastructure
- Investment Gap
- The current annual investment in urban infrastructure stands at ?1.3 lakh crore, which is only 28% of the ?4.6 lakh crore needed annually.
- A large portion of the existing investment, around 50%, is directed towards basic urban services, with the remainder allocated to urban transport.
- Municipal Finances
- Municipal finances have remained stagnant at 1% of GDP since 2002.
- Despite increased transfers from the central and state governments, municipal bodies face financial strain.
- The contribution of municipal own-revenue has decreased from 51% to 43%, indicating a reduced financial independence.
- Revenue Collection Inefficiencies
- Urban local bodies (ULBs) are collecting only a small fraction of their potential revenues, with property tax collections representing just 0.15% of GDP.
- Cost recovery for essential services like water supply and waste management ranges between 20% and 50%, pointing to a significant funding gap.
- Underutilization of Resources
- Cities like Hyderabad and Chennai utilized only 50% of their capital expenditure budgets in 2018-19.
- Central schemes such as AMRUT and the Smart Cities Mission also showed suboptimal fund utilization, with utilization rates of 80% and 70%, respectively.
- Decline in Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
- Investments through PPPs in urban infrastructure have seen a sharp decline, from ?8,353 crore in 2012 to ?467 crore in 2018.
- This drop is attributed to limited project-specific revenues and inadequate funding mechanisms.
Structural and Administrative Challenges
- Weak Governance and Fragmented Management
- Fragmented governance and limited administrative autonomy hinder effective urban planning and resource allocation.
- Municipal bodies often lack the ability to undertake long-term planning and project execution due to these governance challenges.
- Climate Vulnerability and Sustainability: Urban areas are increasingly vulnerable to climate risks like floods and heatwaves. However, many urban infrastructure projects fail to incorporate climate resilience in their planning, exacerbating the long-term vulnerability of investments.
- Inadequate Land Management
- There is poor coordination between land use planning and infrastructure development, resulting in urban sprawl and inefficient transportation systems.
- Opportunities to capitalize on the land value generated by metro and rail projects remain underutilized.
Measures for Transforming Urban Infrastructure
- Streamline Revenue Collection: Leverage technology to improve property tax collection systems and enhance cost recovery in essential services.
- Enhance Fund Utilization: Strengthen municipal capacities for effective project planning and incentivize the timely use of allocated grants.
- Scale Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Investments: Develop a pipeline of bankable projects and create risk-sharing mechanisms to attract private sector investments.
- Decouple Project Preparation from Funding: Ensure that infrastructure projects are thoroughly prepared for financial, social, and environmental sustainability before seeking funding.
- Promote Urban Innovation: Establish urban innovation labs and encourage public-private-academic collaborations to foster the adoption of advanced technologies.
- Empower Municipalities: Grant municipalities greater financial autonomy, enabling them to raise capital through municipal bonds and other debt mechanisms.
- Integrated Urban Planning: Align infrastructure development with land use, transport, and housing requirements, while integrating climate resilience into planning.
- Capacity Building: Invest in the training of municipal staff to improve governance and financial management capabilities.
Conclusion
India’s expanding urban population presents a major opportunity for economic growth. However, addressing the financial and structural challenges in urban infrastructure is crucial for harnessing this potential. By adopting a combination of short-term actions, medium-term strategies, and long-term reforms, India can create sustainable, resilient urban infrastructure that meets the growing needs of its cities, fostering inclusive development and long-term prosperity.
The Controversy around the Sambhal Mosque

- 27 Nov 2024
Introduction
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has become a flashpoint in a larger religious and legal dispute after a petition was filed questioning its historical origins. Alleging that the mosque was built on the site of an ancient Hindu temple, the case has triggered both legal challenges and violent clashes, raising concerns about communal harmony and the protection of religious sites.
Background of the Dispute
On November 19, 2024, a petition was filed in the Sambhal district court, claiming that the 16th-century Jama Masjid was constructed over the site of an ancient Hari Har Mandir. This claim mirrors similar petitions filed in other parts of India, including Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have sought to alter the religious character of mosques they believe were built on temple sites. The petitioners in the Sambhal case include advocate Hari Shanker Jain, a key figure in the Gyanvapi and Mathura disputes.
Survey and Clashes
The Sambhal court ordered a survey of the mosque on November 19, 2024, to investigate the historical claims. The initial phase of the survey, conducted peacefully, involved mosque authorities and local police. However, a second survey on November 24 escalated tensions, as it was accompanied by a procession led by a local priest chanting Hindu slogans. Protests soon turned violent, leading to stone-pelting, police firing, and at least five deaths, including two teenagers. Locals accused the police of excessive force, while the police denied allegations of shooting.
The Mosque’s Historical Context
The Shahi Jama Masjid was built by Mughal Emperor Babur's general, Mir Hindu Beg, around 1528. It is one of the three mosques constructed during Babur's reign, the other two being in Panipat and Ayodhya. Architectural studies suggest it was constructed using stone masonry with plaster, and while some historians believe it was built on a pre-existing structure, the mosque’s historical context is complex. Local Hindu tradition holds that the site was originally a Vishnu temple, with the belief that Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu, will arrive there.
Legal Implications: The Places of Worship Act, 1991
The dispute touches upon the Places of Worship Act, 1991, which mandates the preservation of the religious character of all places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947. The Act was designed to prevent further disputes over religious sites, except for the Babri Masjid case, which was already under litigation at the time. The petitioners in the Sambhal case argue that the religious character of the mosque should be altered, contradicting the Act’s provisions.
Challenges to the Places of Worship Act
The Places of Worship Act has been criticized for barring judicial review and preventing any changes to the religious status of sites that existed before India’s independence. Some legal experts suggest that while an inquiry into the religious nature of a place might be permissible, changing that character would violate the Act. The ongoing legal challenges in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, and now Sambhal, highlight the complexities of reconciling India’s legal framework with communal sensitivities.
Conclusion
The Sambhal mosque dispute underscores the challenges in balancing India’s legal framework with religious and communal dynamics. While the Places of Worship Act aims to preserve the status quo, petitions challenging it have revived contentious debates over historical monuments and their religious significance. As the legal proceedings continue, the case will likely have far-reaching implications for India’s secular fabric and the preservation of communal harmony.
29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The 29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29), held in Baku, Azerbaijan, focused on enhancing climate finance, adaptation measures, and global cooperation.
Key Outcomes of COP29:
- Climate Finance: A new goal was set to triple climate finance for developing countries to USD 300 billion annually by 2035. The total climate finance target aims for USD 1.3 trillion annually by 2035.
- Carbon Markets: The conference operationalized Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, which establishes frameworks for carbon credit trading between countries. It also launched the Paris Agreement Crediting Mechanism, ensuring safeguards for human rights and the environment.
- Transparency and Adaptation: COP29 saw 13 countries submit their Biennial Transparency Reports, promoting greater accountability. The Baku Adaptation Roadmap was launched to speed up National Adaptation Plans (NAPs) in Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
- Gender and Inclusivity: A new Gender Action Plan was developed, and the Lima Work Programme on Gender was extended for another 10 years. Over 55,000 people, including civil society, Indigenous peoples, and youth, participated.
- Global Climate Action: The 2024 Yearbook of Global Climate Action highlighted the role of non-Party stakeholders like businesses and sub-national actors in combating climate change.
India’s Role at COP29: India played an active role in highlighting resilient infrastructure initiatives like the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) and advocated for financial resources to support Small Island Developing States (SIDS). India also pushed for solar energy adoption through the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and promoted gender-inclusive climate policies. India co-hosted the LeadIT summit with Sweden, focusing on industrial decarbonization.
Challenges at COP29:
- Inadequate Finance: Despite ambitious targets, many countries felt the financial commitments were insufficient and distant.
- Private Sector Dependency: The reliance on private sector contributions raised concerns about the reliability of funding.
- Emission Reduction Gaps: There was a lack of sufficient pledges to meet the 1.5°C global warming target, with rising emissions.
- Geopolitical Conflicts: Disputes over issues like the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) hindered progress.
India’s Carbon Credit Framework:
India introduced the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022, establishing a domestic carbon market and setting a legislative framework for carbon credit trading. This aligns with India’s NDCs and aims to support sustainable growth while reducing emissions. However, concerns about the integrity of carbon credits and potential "greenwashing" need to be addressed through rigorous verification systems.
Conclusion:
COP29 marked progress in scaling up climate finance, carbon markets, and adaptation efforts, but significant challenges remain, especially in finance, emission reductions, and geopolitical cooperation. India's initiatives in carbon credit frameworks and resilience are steps toward a sustainable future. Moving forward, a collaborative, transparent, and adaptive approach is crucial to meet global climate goals.
Challenges in Municipal Financing

- 25 Nov 2024
Introduction
Municipal corporations (MCs) in India are essential service providers in urban areas, but they face severe financial constraints, which hinder their ability to provide quality services. While urban India contributes almost 60% of the nation's economic output, MCs are heavily reliant on state and central government transfers, limiting their financial autonomy and operational capacity.
Key Issues in Municipal Financing
- Limited Revenue Generation
- Low Property Tax Revenues: Property tax, the main source of municipal revenue, contributes only 0.12% of GDP, a figure that reflects poor tax collection mechanisms and outdated property valuation systems.
- Revenue Concentration: Over 58% of municipal revenue comes from the top 10 cities, highlighting fiscal disparity between urban areas.
- Dependence on Government Transfers: Municipalities rely significantly on state and central transfers, constituting a large portion of their revenue. This reduces their ability to plan and execute long-term projects independently.
- Inefficiency in Tax and Fee Collection
- Ineffective Property Tax Systems: Existing tax formulas do not reflect actual property valuations, leading to under-taxation and revenue loss.
- Inadequate User Charges: Fees for essential services like water supply, sanitation, and waste management are not regularly adjusted, impacting cost recovery and service quality.
Strategies for Strengthening Urban Local Bodies (ULBs)
- Enhancing Revenue Sources
- Property Tax Reforms: Implementing GIS-based property tax mapping and linking tax rates to actual property valuations can improve tax compliance and revenue generation.
- Rationalising User Charges: Regular adjustments to service fees for water, sanitation, and waste management can ensure cost recovery and better service delivery.
- Reducing Dependence on Transfers
- State and Central Transfers: A rule-based framework for government transfers, accounting for inflation and city growth, can ensure predictability and adequate compensation for MCs.
- Boosting Non-Tax Revenues: MCs can increase income from user fees (e.g., for urban transport and waste management) and explore public-private partnerships (PPPs) to enhance service delivery.
- Leveraging Technology for Efficiency
- Digitalisation and Automation: Streamlining processes through technology can reduce inefficiencies, cut down on waste, and free up resources for capital expenditure.
- Monitoring Systems: Improved monitoring and reporting can reduce pilferage, enhance revenue collection, and ensure accountability.
Fiscal Management and Innovative Financing
- Municipal Bonds and Innovative Financing
- Larger MCs are already using municipal bonds to fund infrastructure projects. Smaller cities can adopt similar financing instruments to diversify funding sources and attract private investment.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Fostering partnerships in sectors like urban transport and waste management can attract private investment and reduce the financial burden on MCs.
- Resource Pooling for Infrastructure Projects
- MCs can collaborate to pool resources for large-scale projects, such as renewable energy or urban transport initiatives, overcoming fiscal constraints that individual corporations face.
Government Initiatives for Urban Governance
- Citizen-Centric Programs
- Swachh Sarvekshan (2017) promotes citizen participation to improve urban cleanliness.
- Swachh Bharat Idea Book empowers citizens to propose innovative solutions to urban challenges.
- Performance-Based Indices
- Ease of Living Index (2017) and the Municipal Performance Index (2019) assess urban quality of life, service delivery, and governance, encouraging better performance in ULBs.
Conclusion
Empowering urban local bodies is crucial for effective urban governance and development. By improving revenue generation through reforms, reducing dependence on transfers, and adopting innovative financing mechanisms, municipal corporations can enhance their capacity to meet the growing demands of urbanization. Collaborative efforts between the government, civil society, and academia are essential to ensure sustainable urban development and better living conditions for urban residents.
The Fight for Accessibility and Dignity in Indian Prisons

- 24 Nov 2024
Introduction
Prisons in India face numerous systemic issues, with overcrowding, abuse, and neglect being prevalent. For prisoners with disabilities, these challenges are magnified, as they struggle with basic needs and lack necessary accommodations. This issue is not only a human rights violation but also a failure in the implementation of legal protections.
Prison Conditions and Accessibility Issues for Disabled Inmates
- Challenges Faced by Disabled Prisoners: Disabled prisoners, such as Professor G.N. Saibaba, who spent a decade in prison before being exonerated, face severe challenges in performing everyday tasks like using toilets or taking baths. His experience of being physically lifted by fellow inmates due to the lack of wheelchair accessibility highlights the systemic neglect.
- Exclusion and Abuse: Prisoners with disabilities are particularly vulnerable to abuse, as their specific needs are ignored. The government does not track the number or conditions of disabled prisoners, which leads to neglect and mistreatment. Notably, Father Stan Swamy, who had Parkinson's disease, was denied essential items like a straw, affecting his ability to eat and drink.
Legal Framework and International Obligations
- Constitutional Protections: The Indian Constitution guarantees rights to prisoners, including protection from torture (Article 21) and the right to fair legal processes (Article 22). The Supreme Court has reinforced the need for humane treatment in prisons through various judgments.
- International Commitments: India has committed to international conventions such as the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and the Nelson Mandela Rules, which require reasonable accommodations for disabled prisoners. Despite these commitments, the practical enforcement of such rights remains minimal.
- Domestic Legislation: The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, mandates the protection of disabled individuals from abuse and exploitation. However, violations like the denial of basic assistive devices to prisoners show a gap in enforcement. The Ministry of Home Affairs has issued guidelines for prison accessibility, but they have yet to be widely implemented.
Systemic Failures and Lack of Political Will
- Overcrowding and Inadequate Infrastructure: Indian prisons house over 5.73 lakh prisoners, far exceeding their capacity. This overcrowding exacerbates the challenges faced by disabled prisoners, as the infrastructure is inadequate to meet their needs. A 2018 audit of Delhi’s prisons revealed significant accessibility gaps, such as inaccessible cells and toilets, making daily life for disabled prisoners even more difficult.
- Political Apathy and Public Indifference: Many believe that prisoners deserve their suffering, fueling a lack of urgency in addressing prison reforms. However, the state is responsible for ensuring the rights and dignity of all prisoners, including those with disabilities. There is a need for a shift in societal attitudes to ensure that these rights are upheld.
Reforms and the Way Forward
- Infrastructure and Accessibility: Prisons must implement universal design principles, ensuring that infrastructures are accessible to all, especially prisoners with disabilities. This includes accessible cells, toilets, and common areas, as well as functional wheelchairs.
- Judicial and Legal Reforms: The judicial system must expedite trials, especially for undertrials, and ensure that all prisoners have access to legal representation. This would help alleviate the overcrowding crisis and improve the overall functioning of the prison system.
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation and Welfare Programs: Prison systems need to focus on rehabilitation rather than mere punishment. Programs for skill development, education, and mental health support should be integrated into prison routines, providing prisoners with opportunities for personal growth and reintegration into society.
- Strengthening Oversight Mechanisms: There must be greater transparency in prison management through independent oversight bodies and regular audits. A whistleblower mechanism can help report violations of prisoner rights, ensuring greater accountability.
India’s Agricultural Sector

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
India’s agricultural sector, which employs 42.3% of the population, is crucial to the nation’s economy. However, it faces a range of challenges that need to be addressed to ensure long-term stability, food security, and sustainable growth.
Current Performance of India’s Agricultural Sector
- Key Agricultural Metrics and Growth
- Foodgrain Production: India produced 330.5 million metric tonnes (MT) of foodgrains in 2022-23, maintaining its position as the world’s second-largest producer.
- Horticulture Production: A record high of 351.92 million tonnes in horticultural production was achieved, marking a 1.37% increase from the previous year.
- Market Outlook
- India’s agricultural market is projected to reach USD 24 billion by 2025.
- The food and grocery retail sector is ranked as the sixth-largest globally, with 70% of its sales generated from retail.
- Investment and Export Trends
- FDI in Agriculture: From April 2000 to March 2024, the agricultural services sector attracted USD 3.08 billion in foreign direct investment, while the food processing industry garnered USD 12.58 billion.
- Agricultural Exports: India’s agricultural and processed food exports reached USD 4.34 billion in 2024-25, including products like marine products, rice, and spices.
Key Challenges Confronting India’s Agriculture
- Climate Change and Environmental Impact:Extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and erratic rainfall, continue to impact agricultural productivity. In 2023, India experienced its second-warmest year on record, contributing to crop damage and rising food prices.
- Water Stress and Irrigation Inefficiency: Agriculture consumes the majority of India’s water resources, but irrigation efficiency is still low. The country relies heavily on flood irrigation, which leads to significant water wastage. Only 11% of agricultural land is under micro-irrigation, far below global standards.
- Land Fragmentation and Declining Farm Sizes: The average size of agricultural farms has decreased from 1.08 hectares in 2016-17 to 0.74 hectares in 2021-22, hindering the adoption of modern farming practices and mechanization.
- Market Access and Price Realization: Farmers continue to face challenges in accessing fair market prices due to the dominance of intermediaries and inadequate market infrastructure. Despite reforms like e-NAM, price gaps between farm-gate and retail prices persist, leaving farmers with a smaller share of the final price.
- Technology Adoption and Digital Divide: Although agritech is growing in India, only 30% of farmers use digital tools in agriculture, and rural digital literacy is just 25%, which limits the widespread adoption of modern farming solutions.
Addressing Structural Issues in Indian Agriculture
- Soil Health and Sustainability:The excessive use of chemical fertilizers and mono-cropping practices has led to soil degradation. Approximately 30% of agricultural land in India is experiencing degradation, impacting productivity and sustainability. Stubble burning further exacerbates this issue, worsening air quality and soil health.
- Crop Diversification Challenges:Many farmers are locked into the wheat-rice cycle due to Minimum Support Price (MSP) guarantees, limiting the cultivation of other crops like pulses and oilseeds. Although India is the largest producer of pulses, the domestic production is insufficient to meet the growing demand.
- Feminisation of Agriculture:Women make up 63% of agricultural workers but own only 11-13% of the operational land, limiting their access to resources and decision-making power. This gender disparity hampers their economic security and limits their participation in agricultural development.
Conclusion
India’s agricultural sector holds immense potential but is facing significant structural challenges that must be addressed to ensure its long-term growth and sustainability. Urgent reforms are needed to address issues like climate vulnerability, inefficient irrigation, land fragmentation, and limited market access. Additionally, fostering technology adoption, improving infrastructure, and addressing gender disparities will be crucial for improving the sector's performance and securing India’s food security needs.
Janaagraha’s Report on Urban Local Bodies
- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
46% of councillors in urban local bodies are women, says a report by Janaagraha, a not-for-profit organisation working to strengthen systems of governance in India’s cities.
Overview: Gender Representation in Urban Local Bodies
- Women Councillors in India: Around 46% of councillors in urban local bodies (ULBs) are women, according to a recent report by Janaagraha, a non-profit organization focused on strengthening urban governance systems.
- Capital Cities: In 19 out of 21 capital cities with active ULBs (such as Patna, Shimla, Ranchi, and Bhubaneswar), women councillors exceed 60% of the total councillor count.
Top States for Women Councillors
- Tamil Nadu stands out with the highest number of women councillors in the country, according to the "Roadmap for India’s City Systems Reforms" report by Janaagraha.
- Other States in the Top 10:
- Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, Bihar, and Chhattisgarh.
Women’s Reservation and Empowerment
- 50% Reservation: 17 states have legislated 50% women’s reservation in urban local bodies, surpassing the constitutional minimum of 33%.
Pathways for Urban Transformation
- Three Key Recommendations:
- Place-Based Governance: Advocates for governance focused on regional economies and local governments rather than sector-driven policies.
- Decentralised Participatory Governance: Emphasizes the need to strengthen urban local governments and increase citizen participation through the 74th constitutional amendment.
- Building State Capacities: Calls for a more effective role of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs and state urban departments focused on local self-government.
Rural-Urban Transition and Policy Reforms
- Urbanization of Villages: The report highlights that about 1,000 villages have already transitioned into urban areas since the 2011 Census, urging the need for a rural-urban transition policy.
- Reimagine Urban Ministries: Recommends restructuring urban ministries to focus on regional economies and the strengthening of local governance institutions.
Key Challenges in Urban Governance
- Delays in Elections: 61% of ULGs in 15 states have delayed council elections.
- Disempowered Local Bodies: Mayors and ULGs often lack autonomy, with control over only four out of 18 functions.
- Citizen Participation Gaps: There is a lack of formal platforms for citizen involvement in governance.
Skilling and Capacity Building
- Certification-Based Training: Proposes skilling programs for ULG staff, with a focus on improving municipal efficiency and project implementation.
- Shared Service Centres: Recommends creating municipal service centres to benefit smaller cities and enhance urban management.
Conclusion: Need for Place-Based Governance
- Strategic Shift: Srikanth Viswanathan, CEO of Janaagraha, emphasized the need to shift away from a sector-based governance model to a place-based governance approach, better suited to the urban challenges of modern India.
Earning Instead of Burning
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Paddy straw burning, prevalent in Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, contributes to severe air pollution, especially during the post-harvest period in October and November. Despite various government measures and subsidies to reduce stubble burning, it continues due to economic and operational constraints faced by farmers. To address this issue, innovative technologies for the productive use of paddy straw need to be explored.
Stubble Burning: Causes and Consequences
Reasons for Stubble Burning
- Short Crop Cycles: The narrow window between paddy harvest and wheat sowing forces farmers to burn straw to prepare fields quickly.
- Economic Constraints: High costs of alternative residue management methods.
- Lack of Awareness: Farmers are often unaware of sustainable alternatives.
- Limited Mechanization: Availability of crop residue management machinery is inadequate.
- Policy Gaps: Ineffective enforcement of regulations and insufficient incentives.
Consequences of Stubble Burning
- Air Pollution: Emission of harmful pollutants like PM2.5, CO2, and CO contributes to air quality degradation.
- Health Hazards: Increased respiratory illnesses due to the inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Soil Degradation: Loss of essential nutrients and organic matter.
- Climate Change: Stubble burning releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Economic Costs: Increased health care costs and loss of soil fertility.
Technologies for Paddy Straw Utilization
Large-Scale Technologies
- Direct Combustion:Burns rice straw under controlled conditions to generate heat for cooking and industrial uses. While its calorific value is lower than that of petrol and diesel, it is still viable for local energy generation.
- Pyrolysis and Gasification:
- Pyrolysis: Converts rice straw into bio-oil through heating at 200-760°C in the absence of oxygen.
- Gasification: Converts rice straw into syngas at higher temperatures (480-1,650°C) with limited oxygen. Challenges include low gas production and tar accumulation.
- Biochar Production:Rice straw is incinerated at lower temperatures to produce biochar, which is used as a soil conditioner to improve fertility, water retention, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Power Generation:Biomass-based power plants use rice straw to generate electricity, providing a sustainable energy source, especially for rural areas. States like Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh are scaling up such plants.
- Pellet Production:Rice straw is compressed into compact pellets, improving its density, transportability, and combustion efficiency. These pellets can partially replace coal in power plants, offering an alternative use for crop residue.
- Biofuels:Conversion of rice straw into biofuels like ethanol and biogas helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels and supports the renewable energy transition.
- Paper Production:Rice straw, with its high cellulose content, is used as an eco-friendly alternative to wood in the paper and pulp industry, reducing environmental impact.
Small-Scale Technologies
- Composting:Rice straw can be composted to produce organic fertilizer, enhancing soil health. Vermicomposting is another effective method, though awareness among farmers remains low.
- Mushroom Cultivation:Rice straw serves as an ideal substrate for growing mushrooms, particularly species like Volvariellavolvacea. This practice provides an additional income source for farmers.
- Silica Extraction:Rice straw contains high silica content, which can be extracted for industrial applications like construction and electronics.
- Fodder for Ruminants:Though rice straw is low in digestibility due to high silica content, it can be used as animal feed after pre-treatment, such as drying, grinding, or chemical processes to enhance its nutritional value.
- Adsorbent for Pollution Control:Rice straw can be used to remove heavy metals and toxins from contaminated water, showing promise in environmental cleanup efforts.
- Soil Incorporation:Instead of burning, rice straw can be incorporated directly into the soil to improve fertility, moisture retention, and crop yield. This practice is already being adopted in regions like Punjab and Haryana.
Conclusion: Path Forward
Stubble burning continues to be a significant environmental challenge, but the development and adoption of technologies for utilizing paddy straw can offer viable solutions. Both large- and small-scale technologies can convert rice straw into valuable products like biofuels, power, and fertilizers. To ensure widespread implementation, efforts must be made to increase awareness among farmers and stakeholders, coupled with strong policy support and infrastructural investment. A collaborative approach involving the government, industries, and farmers is essential for sustainable management of rice straw, benefiting both the environment and the economy.
Reimagining Governance with AI: The Promise of GovAI

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
India's rapid digital transformation, coupled with the advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), presents a unique opportunity to reimagine governance. The concept of GovAI—using AI to enhance public administration—holds the potential to revolutionize governance, improve efficiency, and create more responsive and inclusive public systems.
Digital Transformation in Governance
- Evolution of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- Over the past decade, India has made significant strides in digital governance through the development of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). DPI has reduced inefficiencies, enhanced transparency, and improved service delivery, transforming India's governance landscape.
- Impact of AI on Governance
- As AI becomes a critical enabler in various sectors, its application to governance promises to deliver more efficient, inclusive, and responsive government services. The potential of AI lies in its ability to provide more with less, driving innovation across key public services.
Key Trends Driving GovAI
- Rapid Digitalization of India
- Currently, 90 crore Indians are connected to the Internet, with projections indicating 120 crore by 2026, positioning India as the most connected country globally.
- Digitalization serves as the backbone for AI-driven governance, enabling efficient data collection, analysis, and informed policy-making.
- Data as a Valuable Resource
- The rapid digitalization of India has led to the generation of vast amounts of data. This data serves as the fuel for AI models, which can be used to enhance governance.
- Programs like the IndiaDatasetsProgramme aim to harness government datasets for AI development while safeguarding data privacy through legislation.
- Demand for Efficient Governance
- The post-COVID world has underscored the need for governments to deliver better outcomes with fewer resources. AI has the potential to optimize the use of public resources, enabling more efficient and targeted governance.
India’s Leadership in AI-Driven Governance
- Positioning India as a Global Leader
- India’s digital governance initiatives have placed it at the forefront of AI adoption in the public sector. Through GovAI, India can solidify its position as a global leader in using technology for public good.
- As the Chair of the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI), India is advocating for the inclusive development of AI to ensure that it benefits all nations, not just a select few.
- Role of Innovation Ecosystem
- India’s innovation ecosystem, comprising startups, entrepreneurs, and tech hubs, can play a crucial role in driving the development of AI models, platforms, and apps for governance.
- A strong partnership between the government and private sector is essential to successfully deploy AI solutions across various sectors of governance.
Potential Benefits of GovAI
- Enhanced Efficiency and Service Delivery
- AI-powered tools, such as chatbots, can provide citizens with 24/7 assistance, streamlining public service delivery and reducing waiting times.
- AI can help in automating processes and improving the overall efficiency of government operations.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making
- AI can analyze large datasets to make informed policy decisions and design targeted interventions in sectors like healthcare, education, and social welfare.
- Data-driven insights can enhance the effectiveness of welfare schemes, improving outcomes for marginalized communities.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability
- AI can enhance transparency in governance by minimizing human intervention in processes, thus reducing corruption and ensuring efficient use of public resources.
- Predictive analytics and real-time data monitoring can enable proactive governance, preventing issues before they escalate.
Challenges and Drawbacks of GovAI
- Privacy Concerns
- The use of AI in governance requires the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about data privacy and surveillance.
- Robust data protection laws must be enforced to ensure citizens' data is handled responsibly.
- Accountability and Bias
- AI systems may produce biased outcomes depending on the data they are trained on. Ensuring accountability for decisions made by AI systems remains a challenge, particularly when errors or biases occur.
- Transparent mechanisms must be established to hold AI systems accountable for their actions.
- Increased State Control and Surveillance
- The integration of AI in governance could lead to increased state control, potentially compromising individual freedoms. Ensuring that AI is used responsibly to balance power between the government and citizens is critical.
- Digital Divide
- The benefits of AI in governance may not be evenly distributed across the population, exacerbating the digital divide.
- Efforts must be made to ensure that marginalized communities, without access to digital technologies or skills, are not left behind.
Conclusion
- Balancing Benefits and Risks
- The integration of AI into governance systems presents significant benefits, including enhanced efficiency, transparency, and proactive governance. However, there are challenges related to privacy, accountability, and state control.
- To ensure AI serves the public good, India must implement strong regulatory frameworks, promote transparency, and develop ethical AI systems that respect citizens’ rights and freedoms.
- Moving Toward Maximum Governance
- AI can help realize the vision of maximum governance, enabling more effective and targeted interventions across sectors like healthcare, security, education, and disaster management.
- The success of GovAI will depend on a trusted partnership between the government, private sector, and innovation ecosystem, ensuring that AI technology serves the larger public interest.
Sustainable Path to Net-Zero for India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
India's commitment to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070 presents a significant challenge, with only 45 years remaining to reach this ambitious target. The path to net-zero requires a balancing act between economic development, energy security, and climate adaptation. India’s efforts to meet its climate goals will be shaped by multiple factors, including resource constraints, land use, and financial limitations.
Why Net-Zero at All?
- Scientific Consensus on Climate Change
- Climate change is a growing concern, with the global temperature rise already reaching 1.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- To avoid catastrophic impacts, the world needs to limit the temperature rise to 1.5°C. The remaining global carbon budget for this target is around 400-500 billion tonnes of CO?.
- Necessity of Sharp Emission Reductions
- Countries must drastically reduce emissions to stay within the carbon budget. Achieving net-zero emissions is essential for maintaining global climate stability.
Equity in Net-Zero Transitions
- Developed vs. Developing Countries
- Developed nations, historically responsible for a large share of emissions, are expected to lead the transition. However, they have not met the financial and technological support commitments for developing countries.
- Developing nations like India, with low per capita emissions, are under pressure to balance climate action with economic development.
- Climate Justice
- India’s per capita emissions are among the lowest globally, but the richest 10% of Indians contribute significantly to national emissions, exacerbating inequality.
- The impacts of climate change disproportionately affect the economically weaker sections, making the transition to net-zero not only an environmental challenge but a social justice issue as well.
The Challenge of Balancing Development and Sustainability
- Limits of India’s Resources
- India faces resource constraints, including land, water, and biodiversity, which limit the feasible expansion of renewable energy capacity.
- Meeting energy demands while ensuring food security, forest cover, and biodiversity preservation becomes increasingly challenging as energy requirements rise.
- Sustainable Consumption vs. Aspirational Lifestyles
- India’s aspiration to emulate the developed world’s lifestyle is unsustainable due to limited resources, which could lead to severe consequences like groundwater depletion, heat stress, and biodiversity loss.
- The focus should be on sufficiency consumption corridors, ensuring that consumption meets developmental goals without exceeding sustainable limits.
Projected Power Demand and Renewable Energy Targets
- Rising Power Demand
- India’s power demand could increase nine to ten-fold by 2070. Meeting this demand entirely via renewable energy requires significant expansion in energy generation capacity:
- 5,500 GW of solar energy
- 1,500 GW of wind energy
- India’s power demand could increase nine to ten-fold by 2070. Meeting this demand entirely via renewable energy requires significant expansion in energy generation capacity:
- Land Use Constraints
- To meet these targets, India must address land-use trade-offs. Expanding beyond 3,500 GW of solar and 900 GW of wind would require significant compromises in land availability for other uses, including agriculture and conservation.
Strategic Pathways to Net-Zero: Demand and Supply Measures
- Demand-Side Measures
- Energy-efficient construction: Use of better materials and passive designs to reduce cooling energy demand.
- Urban transport: Shift to public and non-motorized transport to reduce energy consumption in cities.
- Dietary choices: Promoting sustainable dietary practices to reduce the carbon footprint of food systems.
- Electrification: Focus on alternative fuels and energy-efficient appliances.
- Supply-Side Measures
- Decentralization of Energy Production: Expanding rooftop solar panels and solar pumps for agriculture.
- Nuclear Power Expansion: Increase nuclear energy to provide a low-carbon baseload and complement renewable sources like solar and wind, which are intermittent.
The Role of International Cooperation and Financial Support
- Global Cooperation
- Global climate action requires alignment between national interests, which may not always coincide, as seen in the context of the U.S. presidential election potentially influencing global climate policy.
- India’s path to net-zero depends heavily on international climate financing, technology transfer, and collaborative efforts to address climate justice.
- Equitable Financing for Developing Countries
- Developed countries are expected to provide financial support to developing nations like India to achieve climate goals. However, this support has been insufficient to date.
Conclusion: India’s Balancing Act
India faces a challenging balancing act as it seeks to provide quality of life for its growing population while achieving its climate adaptation and mitigation goals. The path to net-zero will require careful management of economic growth, energy production, and resource conservation. India must focus on demand-side strategies to reduce energy consumption and increase efficiency while expanding renewable energy infrastructure in a sustainable manner. Additionally, international cooperation and financial support will be crucial in ensuring that India’s transition to net-zero is equitable, efficient, and aligned with its developmental priorities.
Andhra Pradesh's Natural Farming Model

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
Andhra Pradesh's (AP) natural farming model presents a transformative opportunity to reshape the state’s agricultural landscape by 2050. An analysis by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in collaboration with the AP government, reveals how scaling natural farming could employ more farmers, increase incomes, and foster sustainable agricultural practices, potentially surpassing the benefits of conventional industrial agriculture.
AgroEco2050: Exploring Two Agricultural Futures
The AgroEco2050 initiative aimed to envision two possible futures for Andhra Pradesh’s agricultural systems by 2050:
- Industrial Agriculture Path: Focusing on intensification of conventional farming, relying heavily on chemicals, machinery, and monocultures.
- Natural Farming Path: Expanding agroecological practices, relying on regenerative, chemical-free farming methods to create more jobs, better livelihoods, and improve the environment.
The study compared these pathways, analyzing their impacts on employment, income, food production, biodiversity, and land use.
Key Findings: Natural Farming’s Impact on Employment and Income
- Employment Growth
- By 2050, natural farming would employ twice as many farmers as industrial agriculture: 10 million compared to 5 million.
- Unemployment in natural farming would decrease to 7%, in stark contrast to a projected 30% unemployment rate in the industrial agriculture scenario.
- Farmer Income
- Natural farming is expected to be more profitable for farmers due to lower input costs (seeds, fertilizers, machinery) and higher market prices for high-quality produce.
- The income gap between farmers and non-farmers, which stood at 62% in 2019, would decrease to 22% under natural farming by 2050, a sharp improvement compared to the 47% gap predicted under industrial agriculture.
What is Natural Farming?
Natural farming is an ecological, chemical-free farming system that emphasizes the use of locally available resources. Key practices include:
- Biodiversity-based pest management
- On-farm biomass recycling (e.g., mulching)
- Indigenous techniques like using cow dung and urine for soil fertility.
Globally recognized as a form of regenerative agriculture, it offers a sustainable alternative to industrial agriculture by sequestering carbon and restoring soil health.
Global Adoption
States like Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, and others are already adopting natural farming. While still evolving, its acceptance among farmers is steadily growing.
Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) in Andhra Pradesh
Origin and Growth
- In 2016, Andhra Pradesh launched the Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) initiative to offer a sustainable alternative to capital-intensive agriculture.
- This program, implemented by RythuSadhikaraSamstha, targets covering 6 million farmers across 6 million hectares.
National Recognition
The ZBNF approach gained national attention when it was featured in the 2019 Union Budget, aimed at doubling farmers' incomes by 2022. The central government now promotes this model under the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY).
Challenges in Scaling Natural Farming
- Farmer Training and Support
- Farmers need ongoing education and support to transition effectively to natural farming. Current training systems often fail to address the full scope of their needs.
- Certification Barriers
- The certification process for organic farming, including Participatory Guarantee Systems (PGS) and third-party certifications, is complex and costly, presenting a barrier for small-scale farmers.
- Marketing and Procurement Challenges
- There is a lack of effective marketing systems for organic products, which hampers the ability of farmers to sell their produce at fair prices.
- Without strong procurement or buy-back systems, farmers may struggle to find markets for their products.
- Policy and Funding Gaps
- Organic and natural farming programs still receive minimal funding compared to subsidies for chemical fertilizers, impeding large-scale adoption.
- Slow state-level implementation and a continued reliance on chemical inputs also delay the widespread shift to natural farming.
Moving Forward
- Scientific Research on Yields
- To address concerns about lower yields for staple crops, more scientific research is needed to assess the long-term viability of natural farming, especially for crops like wheat and rice, which are crucial for India’s food security.
- Localized Adoption
- Natural farming may be best suited for non-staple crops or localized farming, balancing sustainability with the need for food security.
- Risk Mitigation for Food Security
- Careful evaluation of natural farming’s impact on staple crop yields is necessary to avoid the food security risks witnessed in countries like Sri Lanka, where a sudden shift to organic farming led to reduced yields and increased prices.
Conclusion
The Andhra Pradesh natural farming model offers a promising alternative to industrial agriculture, with the potential to create jobs, improve farmers' incomes, and promote environmental sustainability. However, for this vision to become a reality, significant efforts must be made to address challenges related to training, certification, marketing, and funding. With continued research, policy support, and community involvement, natural farming can play a crucial role in feeding the future and promoting a more sustainable agricultural system.
Khap Panchayats: Evolving Towards Modern Governance and Justice

- 17 Nov 2024
Why in the News?
Khap Panchayats have attracted attention due to their evolving role in addressing key socio-economic issues like unemployment, education, and rural development. Modernization efforts are underway to regulate these traditional councils, integrating them into formal Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) systems for better governance, accountability, and social justice.
What are Khap Panchayats?
Definition and Origin:
Khap Panchayats are community-based councils primarily found in North India, particularly in Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan. These informal bodies, composed of elders from kinship groups (Khaps), have historically served as local governance bodies that resolve disputes within their communities. Their origins trace back centuries and they function alongside formal legal systems, often prioritizing customary norms over constitutional law.
Historical Role:
Historically, Khap Panchayats have maintained social order in rural areas, acting as forums for dispute resolution related to marriage, property, and community matters. While their decisions were respected within their communities, they operated parallel to formal courts, and their influence was often seen as a stabilizing force in rural society. However, their structure has also contributed to the perpetuation of patriarchal practices and social exclusion.
Issues with Khap Panchayats
- Patriarchal Practices:Khap Panchayats have often been associated with gender inequality. They enforce rigid social norms that limit women's autonomy, particularly in matrimonial matters, inheritance rights, and personal freedoms. This has led to criticism for their role in suppressing women's rights.
- Honor Killings and Social Conservatism:Khap Panchayats are notorious for opposing inter-caste and same-gotra marriages, at times even endorsing honor killings to preserve social order. Such practices are violations of fundamental rights and personal freedoms guaranteed by the Indian Constitution.
- Legality Concerns:The decisions of Khap Panchayats often clash with constitutional values such as equality, personal liberty, and dignity. Their informal judgments lack legal validity and frequently violate the rule of law, raising significant concerns about their adherence to India’s legal framework.
- Caste-based Discrimination:Khap Panchayats have been criticized for reinforcing caste hierarchies, which leads to discrimination and exclusion of marginalized communities. Their focus on preserving traditional caste structures often results in the oppression of the vulnerable, particularly lower-caste groups.
Gender Dynamics and Evolving Roles of Khap Panchayats
In recent years, some Khap Panchayats have started to show more progressive and inclusive stances, particularly in promoting gender justice:
- Support for Women Athletes:Khap Panchayats have begun to recognize and celebrate the achievements of women, particularly in sports. Several Khap bodies have felicitated women sportspersons, contributing to a growing culture of sports among rural women. This marks a shift from their traditionally patriarchal stance.
- Promoting Gender Justice:Notably, the MehamChaubisiKhap in Haryana has played a significant role in advocating for women’s rights and gender equality. It was involved in supporting the 2023 wrestlers' protest against sexual harassment, demonstrating a shift towards gender-related activism and social reform.
Supreme Court Ruling on Khap Panchayats:
In the landmark Shakti Vahini v. Union of India case (2018), the Supreme Court of India addressed the issue of honor killings and inter-caste marriages. The Court emphasized that honor killings violate fundamental rights and called for strict measures to prevent such crimes. The Court further directed state governments to establish special protection cells for couples facing threats from their families and communities. This ruling underscored the importance of personal liberty and freedom of choice, regardless of community or caste.
What is Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)?
Definition and Importance:
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) refers to methods of resolving disputes without resorting to formal litigation. These methods include mediation, arbitration, and conciliation, all of which encourage cooperative problem-solving and mutually agreeable solutions. ADR is particularly important in India due to the overburdened judicial system, which faces a backlog of cases and delays.
ADR offers several advantages, including:
- Cost-effectiveness
- Confidentiality
- Flexibility
- Improved relationships between parties involved
Types of ADR Mechanisms:
- Arbitration: A formal process where an arbitrator resolves disputes and their decision is legally binding.
- Conciliation: A third-party neutral assists the parties in reaching an agreement, and the recommendations can be accepted or rejected.
- Mediation: A mediator facilitates communication between disputing parties, helping them reach a voluntary and mutually agreeable resolution.
- Negotiation: A direct negotiation between the parties without third-party involvement, aiming for a mutually acceptable settlement.
Integrating Khap Panchayats into the Formal ADR System
Given the potential of Khap Panchayats as community-based governance bodies, integrating them into the formal ADR framework can significantly enhance their role in dispute resolution. Here are some strategies for modernizing Khap Panchayats:
- Legal Recognition of ADR Role:Khap Panchayats can be legally recognized within the ADR framework, formalizing their role in mediation and dispute resolution, ensuring their decisions align with constitutional norms and human rights.
- Training and Capacity Building:Khap leaders can undergo training in ADR techniques such as mediation and arbitration, equipping them with skills to resolve conflicts impartially and in line with legal standards. This would help transition Khaps from informal bodies to more structured and legally compliant dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Legal Regulation and Oversight:Regulations can be put in place to define the scope and limitations of Khap Panchayats' authority, ensuring their decisions do not violate human rights or the constitution. Oversight mechanisms should be established to monitor their actions and prevent practices like honor killings or forced marriages.
- Shift Towards Developmental Roles:Some Khap Panchayats are already advocating for progressive reforms in areas like unemployment, education, and rural development. By focusing on these issues, Khap Panchayats can serve as agents of social change and contribute to community development.
- Awareness and Accountability:Awareness campaigns can educate rural communities about constitutional rights and the legal system, emphasizing the importance of formal legal frameworks and human rights. At the same time, Khap Panchayats should be held accountable for actions that undermine justice or equality.
- Collaboration with Formal Institutions:Khap Panchayats can collaborate with local governance bodies and judicial institutions, ensuring that their decisions align with the rule of law and contribute to social justice. This would enhance their role in inclusive decision-making and legally sound governance.
Conclusion
Khap Panchayats, with their deep-rooted history and influence, have the potential to evolve into modern governance institutions. By integrating them into the formal ADR framework, aligning their practices with constitutional values, and focusing on community development, they can contribute positively to dispute resolution and social reform in rural India. This transformation will require legal regulation, training, oversight, and awareness to ensure that Khap Panchayats function as effective, equitable bodies that respect the fundamental rights of all individuals.
Net Borrowing Ceiling

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
- In 2023, the central government imposed a Net Borrowing Ceiling (NBC) on Kerala, limiting its borrowing capacity to 3% of the projected Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) for the fiscal year 2023-24.
- Impact on Kerala’s Finances: This ceiling has significantly impacted Kerala’s ability to meet its expenditure needs and fund developmental activities, triggering political and legal disputes. Kerala has approached the Supreme Court of India, arguing that the imposition of NBC infringes upon its constitutional rights under Article 293 of the Indian Constitution.
Constitutional Provisions on Borrowing Powers
Article 292: Borrowing Powers of the Centre
- Central Government’s Borrowing: Article 292 grants the Central Government the authority to borrow money on the security of the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Limits on Borrowing: The extent of borrowing by the Centre is determined by laws enacted by Parliament.
Article 293: Borrowing Powers of the States
- State Borrowing: Article 293 allows State Governments to borrow within India against the Consolidated Fund of the State. However, it imposes certain conditions:
- If a State has outstanding loans or guarantees given by the Centre, the Centre’s consent is required to raise further loans.
- The Central government can impose conditions when granting such consent.
Centre’s Role in State Borrowing
- Article 293(3) allows the Centre to impose conditions on a state’s borrowing if it has existing liabilities or guarantees outstanding.
- The Centre has wide discretion in granting or denying consent, which has been a point of contention in Kerala’s case.
The Imposition of Net Borrowing Ceiling (NBC)
Scope of the NBC
- Comprehensive Coverage: The NBC encompasses all borrowing avenues, including open market loans, loans from financial institutions, and liabilities from State public accounts. To curb circumventing of the borrowing cap via State-owned enterprises, the NBC also covers borrowings by these entities.
Purpose of NBC
- Fiscal Discipline: The NBC is designed to regulate borrowing and prevent states from accumulating unsustainable levels of debt, thus ensuring financial stability.
- Transparency: By including all borrowing avenues, including off-budget borrowings by state-owned enterprises, the NBC aims to provide a clearer picture of a state’s financial health.
Arguments for the NBC
- Macroeconomic Stability: The NBC helps maintain macroeconomic stability by controlling the borrowing levels of states, thus protecting the national economy.
- Compliance with FRBM Act: The NBC aligns with the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, aiming to keep the fiscal deficit within prescribed limits.
- Equitable Resource Distribution: The NBC ensures that wealthier states do not disproportionately borrow, thus promoting balanced regional development.
Arguments Against the NBC
- Erosion of Fiscal Autonomy: Critics argue that the NBC undermines the fiscal autonomy of states, as guaranteed by Article 293, by restricting their ability to make independent financial decisions.
- Impact on Developmental Activities: States, particularly Kerala, contend that the borrowing cap restricts their ability to fund key infrastructure projects and social welfare activities.
- Legal Concerns: The NBC’s impact on the interpretation of Article 293 raises legal questions regarding the extent of the Centre’s authority over state borrowing powers.
Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act
Overview of the FRBM Act
- Objective: The FRBM Act, 2003 was enacted to promote fiscal discipline and ensure long-term financial stability in India.
- Key Features:
- Targets a 3% fiscal deficit of GDP for the Centre.
- Requires states to enact similar laws to control their fiscal deficit.
Amendments to FRBM Act
- 2018 Amendment: The FRBM Amendment Act required the central government to ensure that the fiscal deficit did not exceed 3% of GDP and total public debt remained under 60% of GDP.
- Fiscal Deficit Reduction: By 2025-26, the fiscal deficit is expected to be reduced to below 4.5% of GDP.
Way Forward: Strengthening Article 293
Guidelines for Borrowing Powers
- Transparency in Decision-Making: The Centre should ensure that the borrowing process is transparent, with clear standards and procedures for accepting or rejecting state borrowings.
- Consultative Process: The Centre should engage in consultations with states before imposing borrowing caps or conditions, fostering a cooperative federal structure.
- Equitable Treatment: Borrowing restrictions should apply uniformly to all states to avoid bias or favoritism.
Strengthening Fiscal Federalism
- Fiscal Autonomy: States should be given the flexibility to manage their finances in a way that reflects their unique economic needs and challenges.
- Periodic Reviews: The Net Borrowing Ceiling should be reviewed periodically to account for changing economic conditions and developmental priorities.
The Need for More Women in Politics
- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
India, the world's largest democracy, is at a crucial juncture where women’s active political participation is essential for holistic development and true democratic engagement. The year 2024 demands increased involvement of women in politics to address issues of gender inequality and ensure comprehensive policy representation.
Current Status of Women’s Political Representation in India
Women in Parliament
- Initial Representation: In 1952, women accounted for only 4.41% of the Lok Sabha. This gradually rose to around 14.36% in the 2019 elections.
- Recent Trends: In the 2024 elections, women made up approximately 16% of the Lok Sabha, with 74 women MPs, 43 of whom are first-time representatives.
Women in State Legislatures
- Representation in state legislative assemblies remains low, with the highest percentages in Chhattisgarh (14.4%), West Bengal (13.7%), and Jharkhand (12.4%).
Global Comparison
- According to the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), India ranks lower than many countries in terms of female representation in parliament, with global averages standing at 26.1%. India lags behind several African and South Asian nations.
Importance of Women’s Political Empowerment
- Enhancing Governance and Accountability: Political empowerment of women ensures better representation of gender-sensitive issues, promoting accountability in governance.
- Breaking Patriarchal Norms: Increasing women’s participation helps challenge the patriarchal structure that dominates Indian politics and promotes inclusive governance.
- Policy and Social Impact: Women in politics are more likely to advocate for policies that address issues like health, education, and gender equality, leading to improved societal welfare.
- Economic Benefits: Studies suggest that women in political leadership tend to improve economic outcomes for their constituencies by prioritizing social infrastructure.
Barriers to Women’s Political Participation
- Gender Gaps in Political Ambition: Women are less likely to pursue political careers due to gender conditioning, family pressures, and stereotypes about leadership abilities.
- Patriarchal Culture: A deeply ingrained patriarchal society hampers women’s political involvement, with male-dominated party structures and social norms limiting opportunities.
- High Election Costs: The financial burden of running for office often discourages women from contesting elections due to unequal access to resources.
- Male Gatekeepers in Politics: Political parties often show a preference for male candidates, especially for higher-profile positions, hindering the rise of women leaders.
- Criminalisation and Corruption in Politics: Growing criminalisation in politics and lack of political education further alienates women from the political process.
Key Legislative and Constitutional Measures for Women’s Political Empowerment
Legislative Measures
- Nari Shakti VandanAdhiniyam (2023): Provides 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and state assemblies.
- 73rd and 74th Amendments (1992): Introduced 33% reservation for women in Panchayats and Municipalities.
- Gender-Neutral Rules: Lok Sabha adopted gender-neutral rules in 2014, promoting inclusivity in legislative procedures.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 14 and 15: Ensure equality and non-discrimination, fundamental to women’s political participation.
- Article 243D: Mandates 33% reservation for women in Panchayats.
International Commitments
- CEDAW (1979): Advocates for women’s participation in political and public life.
- Beijing Platform (1995) and SDGs (2015): Call for removing barriers to women’s participation in politics.
Measures for Promoting Women’s Political Participation
- Quotas and Reservations: Ensuring mandatory quotas for women candidates in party tickets and legislative bodies can help bridge gender gaps.
- Capacity Building and Training: Offering political training programs for women can empower them with the skills and resources necessary for effective political participation.
- Strengthening Grassroots Movements: Support for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) can build leadership among women at the local level.
- Supportive Political Ecosystem: Political parties should be encouraged to nominate women for higher office positions, such as the Rajya Sabha or state legislative councils.
- Raising Public Awareness: Public awareness campaigns focusing on the importance of women in politics can shift societal attitudes and garner wider public support.
Conclusion:
As India moves forward, the active participation of women in politics is not merely a matter of equity but an essential building block for a vibrant, inclusive, and effective democracy. Through structural reforms, public awareness, and the promotion of female leadership, India can strengthen its democratic framework, ensuring that all citizens, regardless of gender, have an equal stake in shaping the nation's future.
Inter-State Council

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
The Inter-State Council, which works for Centre-State and interstate coordination and cooperation, has been reconstituted with Prime Minister Narendra Modi as its chairman, all chief ministers and nine Union ministers as members and 13 Union ministers as permanent invitees.
About the Inter-State Council (ISC)
Formation of ISC
- Establishment: Created on May 28, 1990, through a Presidential Order following the recommendations of the Sarkaria Commission (1988).
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
- Meetings: The Council has convened 12 times since its formation.
Constitutional Provisions
- Not a Constitutional Body: It was established under Article 263 of the Constitution, making it a non-permanent advisory body.
- Role: Article 263 empowers the President to create the ISC for improving coordination between States and the Union.
Powers and Functions
- Investigate and Discuss: The ISC discusses subjects of common interest between the Centre and States.
- Recommendations: It recommends measures for better coordination and addressing inter-state issues.
- Deliberations: The ISC also deliberates on matters referred by the Chairman.
Composition of the ISC
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India.
- Members:
- Chief Ministers of all States and Union Territories with legislative assemblies.
- Lieutenant Governors/Administrators of Union Territories without assemblies.
- 6 Union Cabinet Ministers nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Governors of States under President’s rule.
- Standing Committee:
- Chaired by the Union Home Minister.
- Includes 5 Union Cabinet Ministers and 9 Chief Ministers.
Functions and Role of the ISC
Role in Centre-State Cooperation
- Facilitates better coordination and cooperation between the Centre and States.
- Addressing disputes related to Centre-State and Inter-State relations.
Additional Functions
- Make Recommendations: Based on discussions, it recommends actions to align policies.
- Promote Social Legitimacy: Through consensus-driven decisions, ISC strengthens policy acceptance among states.
Key Bodies Related to Centre-State Relations
Zonal Councils
- Purpose: Promote interstate cooperation and coordination.
- Constitution: There are five Zonal Councils (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, Southern) and a separate North Eastern Council established in 1972.
River Water Dispute Tribunals
- Function: Set up under the Inter-State River Water Disputes Act, 1956, these tribunals resolve disputes over river water sharing between States.
GST Council
- Constitution: Established under Article 279A, the GST Council is responsible for decisions related to GST implementation, ensuring cooperative federalism.
Chief Justice of India

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
On November 11, 2024, Justice Sanjiv Khanna was sworn in as the 51st Chief Justice of India (CJI) at the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Delhi, marking a significant milestone in the Indian judiciary. He succeeds Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, who retired on November 10, 2024. Justice Khanna's term as CJI will last until May 13, 2025.
Background of Justice Sanjiv Khanna
Early Life and Legal Career
- Legal Practice: Justice Khanna began his legal career in 1983 after completing his law degree from Delhi University. He practiced in the District Courts of Delhi and handled cases in constitutional law, taxation, arbitration, and environmental law.
- Career in Delhi High Court: He was appointed as an Additional Judge to the Delhi High Court in 2005 and became a Permanent Judge in 2006.
- Appointment to the Supreme Court: Justice Khanna was appointed as a Supreme Court Judge in January 2019, without having served as a Chief Justice of a State High Court, and superseding 32 senior High Court judges.
Key Judicial Rulings of Justice Sanjiv Khanna
Major Constitutional Bench Decisions
- Abrogation of Article 370: Justice Khanna was part of the Bench that upheld the abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution, which revoked Jammu and Kashmir’s special status.
- Electoral Bonds Scheme: He also contributed to the ruling that struck down the 2018 Electoral Bonds scheme, raising questions about the transparency of political funding.
Support for EVMs
- Justice Khanna defended the use of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) and rejected calls to revert to paper ballots, emphasizing the need for technological progress and institutional trust.
Personal Liberty and Bail Decisions
- Arvind Kejriwal’s Interim Bail: Justice Khanna granted interim bail to Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal in the liquor policy case, underscoring personal liberty as a fundamental right.
- Judicial Review of Bail Conditions: He also initiated discussions on setting standards for bail conditions in cases involving significant political figures.
Role of the Chief Justice of India (CJI)
Appointment Process
- Article 124(2): A Supreme Court judge is appointed by the President of India, with the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court traditionally becoming the CJI.
- Qualifications: The CJI must be a citizen of India and have served as a judge in a High Court for at least five years or as an advocate in a High Court for ten years.
Powers and Responsibilities
- Master of the Roster: The CJI is the "Master of the Roster," responsible for assigning cases to specific benches and determining the court's schedule.
- Collegium System: The CJI, along with four senior judges, forms the Collegium that recommends judicial appointments for the Supreme Court and High Courts.
- Ad-Hoc Appointments: The CJI can also appoint ad-hoc judges to the Supreme Court under Article 127 of the Constitution.
Removal
- A CJI can only be removed through a process initiated in Parliament, requiring a special majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Appointment of CJI in Other Countries
United States
- The Chief Justice of the United States serves for life, with tenure continuing until impeachment or voluntary retirement.
United Kingdom
- The Lord Chief Justice in the UK is appointed by a special panel from the Appeal Court or the Supreme Court. The tenure is life, but mandatory retirement is set at 75 years of age.
Conclusion
Justice Sanjiv Khanna’s appointment as the 51st Chief Justice of India represents a significant moment in the country's judicial history. With his extensive experience and legal acumen, he faces numerous challenges, from dealing with case pendency to navigating sensitive constitutional issues. His tenure will likely shape the future trajectory of the Indian judiciary, with a focus on upholding justice and personal liberty while addressing the evolving needs of a democratic society.
Significance of LignoSat
- 12 Nov 2024
Introduction
- LignoSat is the world's first satellite constructed with wood, developed to test the viability of using timber as a sustainable material in space exploration.
- Launched on November 5, 2024, the satellite was sent to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard a SpaceX Dragon cargo capsule and will be released into orbit after a month for a six-month test.
What is LignoSat?
- Dimensions: LignoSat measures 4 inches (10 cm) on each side and weighs 900 grams.
- Material Composition: The satellite features panels made from magnolia wood using traditional Japanese craftsmanship, without screws or glue.
- Development Collaboration: LignoSat was developed by Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry, in collaboration with various researchers and space organizations.
Purpose and Objectives of the Mission
- Testing Timber in Space:
- The primary goal is to study how wood performs in the extreme conditions of space, where temperatures fluctuate dramatically between -100°C to 100°C.
- The satellite will also assess how wood interacts with space radiation and its potential to reduce the impact of radiation on sensitive electronics, such as semiconductors.
- Space Sustainability:
- LignoSat aims to demonstrate that wood can be a sustainable, renewable alternative to metals (like aluminium) traditionally used in spacecraft construction.
- The satellite will help determine if wood can be used in future space missions, potentially reducing reliance on non-renewable materials.
Testing the Durability of Wood in Space
- Challenges of Space Environment:
- Space is an extremely harsh environment with extreme temperature variations, exposure to radiation, and the lack of water and oxygen, all of which affect material durability.
- Unlike Earth, where wood decomposes due to moisture and oxygen, space's vacuum conditions could potentially preserve the wood's integrity, providing valuable insights into its durability.
- Previous Use of Wood in Space:
- Wood has already been tested in space applications: cork has been used on spacecraft to withstand re-entry conditions.
- The LignoSat mission builds on this knowledge, aiming to test wood's performance in space's high-radiation and vacuum environment.
Potential Advantages of Using Wood in Space Exploration
- Sustainability and Environmental Benefits:
- Unlike conventional aluminium satellites, which generate harmful pollutants upon re-entry (e.g., aluminium oxides), LignoSat's wooden components will degrade in a more environmentally friendly manner, minimizing atmospheric pollution.
- As space exploration increases, particularly with mega-constellations (e.g., SpaceX’s Starlink), space debris management becomes critical. Using wood could reduce the environmental impact of satellite disposal.
- Renewable Resource:
- Wood is a renewable resource, which offers a potential solution to the growing demand for materials used in space technology.
- Kyoto University researchers have long been exploring the idea of building habitats on the Moon and Mars using timber, with LignoSat seen as a stepping stone to proving the material's space-grade capabilities.
LignoSat's Design and Construction
- Hybrid Construction:
- While the outer panels of LignoSat are made from magnolia wood, the satellite still incorporates traditional aluminium structures and electronic components inside.
- The hybrid construction allows researchers to compare the performance of wood against conventional materials used in spacecraft.
- Testing Methods:
- LignoSat will orbit Earth for six months and monitor the wood’s reaction to space conditions, providing valuable data for future space missions.
- Sensors embedded in the satellite will track various environmental factors, such as radiation exposure, temperature fluctuations, and the structural integrity of the wood.
The Long-Term Vision: Building Timber Habitats in Space
- The research team, led by Takao Doi (astronaut and Kyoto University professor), envisions a future where timber is used for constructing space habitats on the Moon and Mars.
- The team’s ultimate goal is to plant trees in space and develop timber houses on extraterrestrial bodies, providing a sustainable, self-sufficient environment for humans in space.
Broader Implications for Space Exploration
- Sustainability in Space Missions:
- LignoSat represents an innovative step toward more sustainable space technologies by investigating eco-friendly materials that can minimize the environmental impact of space missions.
- It aligns with global efforts to make space exploration more sustainable, especially as space tourism and colonization plans grow.
- Future Prospects:
- If successful, LignoSat could pave the way for wood-based materials being used in spacecraft construction, not only for satellites but also for space stations and future human habitats in space.
Conclusion
- LignoSat’s mission marks a significant milestone in space exploration by exploring wood as a sustainable material in space technology.
- As the first wooden satellite, its results could pave the way for more eco-friendly, renewable materials in future space missions, aligning with global goals for sustainability and reducing space-related pollution.
What are the costs of population decline?

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
India has been witnessing significant demographic changes due to decades of family planning policies. This has led to declining fertility rates in certain States, particularly in the southern and smaller northern regions.
Introduction: Demographic Shift in India
- Southern States’ Fertility Trends: States like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana have fertility rates below the replacement level (around 1.4–1.5), while Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh have higher fertility rates (2.6–3).
- Ageing Population: Southern States face the challenge of an ageing population, with Kerala projected to have 22.8% of its population aged 60+ by 2036, while Bihar will have only 11%.
Economic and Health Impact of Population Decline
- Economic Consequences:
- Dependency Ratio: The old-age dependency ratio (the number of elderly for every 100 working-age individuals) has increased significantly in some States. Kerala, for example, had a ratio of 26.1 in 2021, signaling a crisis point.
- Loss of Demographic Dividend: States with declining fertility rates face the loss of a demographic dividend, i.e., the economic benefit from a large working-age population, which is increasingly burdened by elderly dependents.
- Health Expenditure: Rising healthcare costs, especially for cardiovascular diseases in southern States, will strain public health systems. The southern States, although comprising one-fifth of India's population, spent 32% of the country’s total out-of-pocket expenditure on cardiovascular diseases in 2017-18.
- Challenges of Low Fertility:
- Declining Labour Force Participation: Policies encouraging higher fertility may also reduce women’s labour force participation, undermining the economic growth of these States.
- Economic Pressures: Southern States, despite higher tax contributions, face a diminished share of central resources due to slower population growth. This is a point of concern in inter-State fiscal relations.
Political Implications of Uneven Population Growth
- Impact on Federal Structure:
- The uneven population growth across States will lead to significant changes in the delimitation of constituencies after the current freeze on seat allocation in Parliament expires in 2026.
- Redistribution of Lok Sabha Seats: Northern States like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar will likely gain more seats, while southern States like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh will lose seats due to their declining population shares.
- Challenges in Federal Relations:
- Southern States’ economic contributions through taxes are disproportionate to the resources they receive from the central pool, leading to growing tensions between high-growth and slow-growth regions.
- The shift in political power post-delimitation could increase regional disparities, potentially leading to political tensions between States.
Solutions and Policy Recommendations
- Pro-Natalist Policies:
- Southern States are considering pro-natalist policies to incentivize higher fertility rates. However, such measures have been largely unsuccessful internationally, especially when women’s economic independence and educational choices are restricted.
- International Experience: Attempts to incentivize childbearing, without addressing broader socio-economic factors like gender equality, have generally failed in other nations. Maternity benefits, gender-neutral parental leave, and childcare support are key to increasing fertility sustainably.
- Gender Equity and Work-Family Balance:
- Work-family policies that support paid maternity and paternity leaves, affordable childcare, and gender-neutral employment policies are essential to empower women to balance family and career.
- Studies indicate that countries with higher gender equity have better fertility rates because women are less likely to forgo childbearing for career reasons.
- Increasing Retirement Age:
- One way to reduce the old-age dependency ratio is to increase the retirement age, which would allow older workers to remain employed longer and support a sustainable economy.
- Social Security and pension reforms should also be considered to accommodate the ageing workforce and reduce the economic burden on younger generations.
- Managing Migration:
- Migration policies should be adjusted to manage the influx of economic migrants into southern States, who contribute to the economy but continue to be counted in their home States for fiscal and political purposes.
- Migration-based policy reforms could address the challenge of an ageing population in states with declining fertility while ensuring equitable resource distribution across States.
Bharat 6G Mission
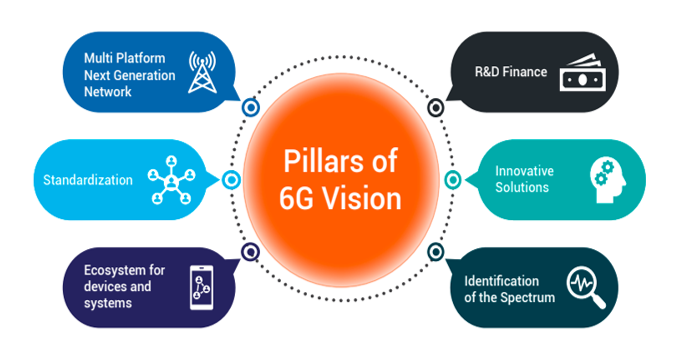
- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
India aspires to lead the world in 6G technology by 2030 through the Bharat 6G Mission. This initiative builds upon the successful rollout of 5G, which reached 98% of districts in just 21 months.
Key Features of 6G Technology
- Terahertz (THz) Frequencies: 6G will utilize THz waves capable of transmitting significantly more data than 5G, offering ultra-fast data rates.
- Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output): Supports a large number of devices and simultaneous connections using multiple antennas, improving data transmission and reception.
- Network Slicing: Creates specialized, smaller networks tailored to specific traffic types, such as video streaming or industrial automation.
- Enhanced Security: Incorporates advanced encryption and authentication protocols to safeguard sensitive data.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC): Ensures ultra-low latency, critical for applications like industrial automation, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR).
- Integrated Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IIRS): Enhances signal strength and quality, particularly in areas with poor reception.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Supports data communication over hundreds of GHz or THz frequencies, facilitating faster transfer rates.
Government Initiatives for 6G Development
Bharat 6G Vision and Strategy
- Goal: To design, develop, and deploy 6G technologies, ensuring secure, intelligent, and pervasive global connectivity.
- Core Principles:
- Affordability, sustainability, and ubiquity aligned with the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India).
- Strategic Objectives:
- Promote R&D through startups, universities, and industries.
- Develop affordable 6G solutions and global IP contributions.
- Focus on transformative applications to enhance quality of life.
Technology Innovation Group (TIG) on 6G
- Established: November 1, 2021.
- Task Forces:
- Focus on multidisciplinary solutions, spectrum management, devices and networks, international standards, and R&D funding.
Bharat 6G Alliance
- A collaborative effort between Indian industry, academia, and research institutions to develop 5G advancements, 6G products, and patents.
- Global Alignment: Partners with organizations like the Next G Alliance (US), 6G Flagship (Finland), and South Korea’s 6G Forum.
Applications of 6G Technology
Application Area
Description
Healthcare
Real-time patient monitoring and AI-connected devices.
Agriculture
IoT and AI-driven predictive systems for crop health and irrigation.
Defense & Internal Security
Enhanced surveillance, communication, and unmanned operations.
Disaster Response
High-volume communication for emergency coordination.
Transportation
Ultra-low latency for urban air mobility and traffic management.
Education
High-speed remote learning, immersive AR/VR-enabled classrooms.
Metaverse
3D holographic displays and seamless virtual interactions.
Industrial Automation
Smart factories with enhanced operational efficiency through real-time data.
Smart Cities
Efficient urban infrastructure and real-time monitoring using IoT.
Entertainment & Media
Higher-quality streaming, immersive content delivery.
Environmental Monitoring
Real-time data collection for resource management and conservation.
Challenges in 6G Development
- Technical Complexity: Development of advanced components and subsystems makes 6G technology highly complex.
- Infrastructure Deployment: Significant investment and regulatory support are required for the necessary infrastructure upgrades.
- Spectrum Allocation: The limited availability of spectrum poses challenges in balancing competing demands for bandwidth.
- Security Concerns: High-speed data transmission increases vulnerability to cyber threats, necessitating robust security protocols.
- Standardization Issues: Achieving global consensus on standards for 6G interoperability can be slow and contentious.
- Global Collaboration: Effective international cooperation is critical for technological and regulatory alignment.
Conclusion
India’s Bharat 6G Mission represents a visionary approach to maintaining technological leadership in the rapidly evolving global digital landscape. By investing in research, fostering international collaborations, and pursuing policies aligned with Atmanirbhar Bharat, India can harness 6G to fuel socio-economic growth and strengthen global connectivity.
Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education Act, 2004

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
The Supreme Court recently upheld the constitutional validity of the Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education Act, 2004 (also called the Madarsa Act), while striking down certain provisions related to the granting of higher education degrees. The Court overturned the Allahabad High Court's previous decision, which had deemed the Act unconstitutional on the grounds that it violated the principle of secularism.
What is the Madarsa Act?
The Madarsa Act provides a legal framework for regulating madrasas (Islamic educational institutions) in Uttar Pradesh. The Act:
- Establishes the Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education, which oversees the curriculum and examinations for madrasas.
- Ensures that madrasas follow the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) curriculum for mainstream secular education alongside religious instruction.
- Empowers the state government to create rules for regulating madrasa education.
Allahabad High Court's Ruling
In March 2024, the Allahabad High Court declared the Madarsa Act unconstitutional, citing:
- Violation of secularism: The Court argued that the Act's emphasis on compulsory Islamic education, with modern subjects being optional, discriminated on religious grounds, violating the secular nature of the Constitution.
- Right to Education: The Court also claimed that the Act denied quality education under Article 21A, which guarantees free and compulsory education to children.
- Higher Education Degrees: The Act's provisions allowing the granting of Fazil and Kamil degrees were found to conflict with the University Grants Commission Act, 1956, which regulates higher education.
Supreme Court's Ruling
The Supreme Court overturned the Allahabad High Court's decision on several grounds:
- Basic Structure Doctrine: The Court clarified that the basic structure doctrine, which applies to constitutional amendments, does not apply to ordinary legislation like the Madarsa Act. Therefore, a law cannot be struck down simply for violating secularism unless explicitly prohibited by the Constitution.
- State's Authority to Regulate Education: The Court held that the state has the right to regulate education in minority institutions, as long as the regulation is reasonable and rational. It emphasized that the Madarsa Act does not deprive these institutions of their minority character.
- Right to Education for Minority Institutions: Referring to a 2014 decision, the Court ruled that the Right to Education Act (RTE) does not apply to minority institutions, as it would undermine their right to impart religious education and self-administer.
Striking Down Higher Education Provisions
While upholding most of the Act, the Supreme Court struck down the provisions related to higher education degrees (Fazil and Kamil). It ruled that:
- Section 9 of the Act, which allowed the Board to grant these degrees, is in conflict with the University Grants Commission Act, which only permits degrees to be awarded by universities recognized by the UGC.
Implications of the Ruling
- Regulation of Madrasa Education: The ruling affirms the state's authority to ensure quality education in madrasas, balancing religious instruction with secular subjects.
- Protection of Minority Rights: By upholding the Madarsa Act, the Court protected the rights of religious minorities to run educational institutions while ensuring they meet educational standards.
- Focus on Inclusivity: The judgment emphasizes the integration of madrasas within the broader educational framework, ensuring that madrasa students receive quality education.
In conclusion, the Supreme Court's decision supports the regulation of madrasa education while safeguarding the rights of minority institutions, except in areas related to the granting of higher education degrees, which remain under the jurisdiction of the UGC Act.
Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
Need for modification of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) amidst changing geopolitical, environmental, and demographic realities.
Background of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- About IWT:
- Signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank.
- Governs the sharing of the Indus River system waters.
- Historical Context:
- Origin in the Inter-Dominion Accord of 1948 post-partition.
- Finalized after negotiations facilitated by the World Bank in 1951.
- Key Provisions:
- Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) allocated to India.
- Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) allocated to Pakistan, with limited use allowed for India (e.g., hydropower, irrigation).
- Establishment of the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC) for cooperation and dispute resolution.
India’s Perspective
- Rationale for Modification:
- Increased demographic and agricultural demands.
- Need for sustainable water management.
- Acceleration of hydropower projects on western rivers permitted by the treaty.
- Security Concerns: Cross-border terrorism impacting trust in treaty operations.
Pakistan’s Concerns
- Dependence on Indus System: Critical for agriculture and drinking water as the lower riparian state.
- Potential Impacts of Modification:
- Fear of reduced water availability.
- Concerns over India’s hydropower projects altering water flow.
Current Challenges
- Hydropower Projects: Disputes over compliance with treaty provisions regarding hydropower construction.
- Technical Disputes: Divergent interpretations of treaty terms.
- Political Tensions: Strained bilateral relations with minimal diplomatic engagement.
- Climate Change Impacts: Altered precipitation patterns and glacial melt affecting water availability.
Arguments for Modifying the Treaty
- Addressing Contemporary Challenges: Climate change, technological advancements, and increased water demand.
- Securing National Interests:
- Clarifications on hydropower construction.
- Improved dispute resolution mechanisms.
Risks of Modifying the Treaty
- Escalation of Tensions: Perceived unilateral actions by Pakistan.
- Political Sensitivities: Domestic opposition in both countries.
Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
- Engagement and Dialogue: Bilateral discussions with potential third-party mediation (e.g., World Bank).
- Cooperation over Conflict: Recognizing mutual benefits of collaboration in water management.
- Adaptation Measures: Incorporate provisions addressing climate change and technological advances.
Zeroing in on Methane Diplomacy, at COP29

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
From November 11 to 22, 2024, global leaders will gather in Baku, Azerbaijan, for the 29th Conference of Parties (COP29) under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). This year’s summit, known as the Finance COP, will focus on setting a new global climate finance target—the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG).
A key focus of the summit is the reduction of methane emissions, as countries aim to curb near-term temperature increases, which buys critical time for long-term CO2 reductions necessary for stabilizing climate change.
U.S.-China Collaboration and Methane Reduction
US-China Collaboration Despite Geopolitical Tensions
Despite ongoing geopolitical tensions, the United States and China have found common ground on the issue of methane reduction. Both nations recognize the importance of addressing methane emissions, which are more potent in the short term than CO2. They, along with the United Arab Emirates, organized a summit at COP28 to discuss methane and other non-CO2 pollutants.
China’s National Plan for Methane Emissions
In November 2023, China launched its first national methane reduction plan, emphasizing capacity-building efforts over explicit reduction targets. This plan marked a significant step in China’s climate policy, underscoring its commitment to mitigating methane emissions alongside the U.S.
Given that China and the U.S. are the two largest contributors to methane emissions globally, their collaboration presents a significant opportunity for global climate mitigation efforts. India, the third-largest emitter of methane, could benefit from this partnership by seeking financial support and technical expertise to address its methane challenges.
India’s Methane Emissions Profile and Challenges
Emissions Breakdown
India’s Third Biennial Update Report to the UNFCCC indicates that in 2016, India emitted approximately 409 million tons of CO2-equivalent methane. The major sources of these emissions include:
- Agriculture: 74% (mainly from livestock and rice cultivation)
- Waste: 14% (unmanaged organic waste in landfills and dumpsites)
- Energy: 11%
- Industrial processes: 1%
Due to the dominant role of agriculture, India has been cautious about committing to stringent methane reduction targets. Initiatives like the Global Methane Pledge, which calls for a 30% reduction from 2020 levels by 2030, have not been fully embraced.
Environmental and Health Impact of Methane Emissions
Methane-related fires at waste dumpsites, such as the Bhalswa dump in Delhi (2022), have highlighted the broader environmental and health risks of methane emissions. These fires contribute significantly to air pollution, making it urgent for India to address methane in its waste management and agricultural sectors.
India’s Initiatives for Methane Reduction
Waste Management Programs
- Comprehensive Waste Management Framework India’s waste management sector is a significant source of methane, contributing 14% of the nation’s total emissions. Although a comprehensive regulatory framework for waste management has been developed, implementation remains slow due to local capacity constraints and financial limitations.
- Innovative Solutions Indore, a city in Madhya Pradesh, has pioneered waste sorting and biomethane production. The city's initiative includes:
- Sorting organic waste
- Converting it into biogas to fuel city buses
This model has gained national attention and is being considered for replication in other cities.
- GOBARdhan Scheme Launched as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0, the Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) scheme encourages rural communities to convert cattle manure and other organic waste into biogas and compost, reducing methane emissions from livestock waste while providing additional income to rural households.
Agricultural and Livestock Emission Reduction
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) The NMSA promotes climate-resilient agricultural practices that reduce methane emissions. For example, Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) is a water-saving technique used in rice farming that reduces methane emissions by limiting anaerobic decomposition.
- National Livestock Mission Under the National Livestock Mission, practices such as improved fodder management, silage making, and Total Mixed Ration (TMR) feeding are being promoted. These practices reduce methane emissions from livestock by improving digestion and feed efficiency.
Opportunities for India at COP29
Leveraging U.S.-China Methane Partnership
COP29 offers India an opportunity to leverage the U.S.-China collaboration on methane reduction. By engaging with these two major emitters, India can seek:
- Financial support
- Technical assistance
- Capacity-building resources, particularly for its waste sector, which is a significant source of methane emissions.
Accurate data on methane emissions, such as satellite-based monitoring, can help India refine its emission inventories and enhance the effectiveness of its methane mitigation efforts.
Fast-Tracking India’s Methane Reduction Efforts
Although methane is not the primary focus at COP29, India has an opportunity to fast-track its efforts in methane reduction. The country's existing policies and initiatives, such as waste management programs and agricultural missions, provide a foundation upon which international collaboration can build.
Recent data from satellite monitoring in cities like Delhi and Mumbai shows that actual methane emissions from waste dumpsites may be 50%-100% higher than previously estimated, highlighting the urgency of addressing this issue.
Conclusion
Although methane may not dominate the COP29 agenda, it represents a critical pathway for India to accelerate its climate action. With the groundwork already laid through domestic policies and innovative solutions, India now requires enhanced financial and technical backing to scale up its methane reduction initiatives. By engaging proactively at COP29, India has a unique opportunity to secure the resources needed to tackle methane emissions, benefiting both its citizens and the global fight against climate change.
Supreme Court Ruling on Property and Redistribution

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
A crucial 9-judge bench of the Supreme Court ruled on the scope of government powers over private property, with a focus on Articles 39(b) and 31C of the Constitution.
Key Issues Considered by the Court
- Article 31C: Whether it still protects laws giving effect to Articles 39(b) and 39(c), even after amendments and past rulings.
- Interpretation of Article 39(b): The meaning of “material resources of the community” and the limits on government acquisition.
Legal and Constitutional Background
- Article 31C and 39(b) Overview:
- Article 31C was introduced by the 25th Amendment (1971) to protect laws related to the distribution of resources for the common good.
- Article 39(b) (Directive Principle of State Policy) mandates that resources should be distributed to best serve the common good.
- Historical Context:
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973): The Supreme Court affirmed the Constitution’s "basic structure," impacting the interpretation of amendments to Article 31C.
- Minerva Mills Case (1980): The Court struck down further amendments to Article 31C.
The Supreme Court’s Ruling in 2024
- Restoration of the Post-Kesavananda Position: The Supreme Court clarified that the interpretation of Article 31C is restricted, and the protection under this article applies only to laws implementing Articles 39(b) and 39(c), not all directive principles.
- On Redistributing Private Property:
- The majority opinion held that not all privately owned properties can be considered “material resources of the community” for redistribution under Article 39(b).
- The Court dismissed the broad interpretation of "material resources" used in previous rulings (e.g., Justice Krishna Iyer’s dissent in the Ranganatha Reddy case, 1977).
Dissenting and Concurring Opinions
- Justice Nagarathna’s Concurring Opinion:
- Acknowledged that certain privately owned resources could be considered material resources (e.g., forests, wetlands), but emphasized a balanced approach.
- Distinguished between personal belongings and resources that could be considered part of the public domain.
- Justice Dhulia’s Dissent:
- Argued for a broader interpretation, in line with past rulings, that private resources could be considered material resources if they served the public good.
Interpretation of Article 39(b)
- Scope of the Article:
- Article 39(b) directs the State to ensure that the ownership of material resources is distributed to serve the common good.
- It imposes a positive obligation on the State to create policies for resource distribution, but does not authorize arbitrary expropriation of private property.
- Private Property as Material Resources:
- The Court clarified that private property cannot be deemed a material resource of the community unless specific conditions are met (e.g., scarcity, public welfare implications).
- The judgment emphasized a case-by-case analysis rather than a blanket approach.
Criteria for Assessing Material Resources
The Court provided criteria to evaluate whether a private property could be considered a “material resource of the community”:
- Nature of the Resource: What is the resource’s fundamental characteristic?
- Impact on Public Welfare: Does the resource impact the common good or public interest?
- Ownership Type: Is the resource privately owned or under state control?
- Scarcity: Is the resource scarce or in finite supply?
- Concentration of Ownership: Are the resources concentrated in the hands of a few private entities?
Implications of the Ruling
- Protection of Private Property Rights: The ruling strengthens protections against arbitrary State acquisition of private property, reinforcing the constitutional safeguards for property rights.
- Economic Implications: The Court noted that India’s economic trajectory has shifted from socialism to a market-based economy, and that resource redistribution policies should reflect this change.
- Policy Shifts: The ruling marks a shift away from a socialist economic ideology towards one that emphasizes private property rights, while still considering public welfare in resource distribution.
Conclusion
- Balancing Individual Rights with Public Welfare: The ruling underscores the importance of balancing private property rights with the need for equitable resource distribution to serve the common good.
- Implications for Constitutional Interpretation: This judgment marks a pivotal moment in the interpretation of property rights in India, affirming the evolving nature of the Constitution in response to dynamic economic and social policies.
Does Data Justify Subdivision of Quotas?
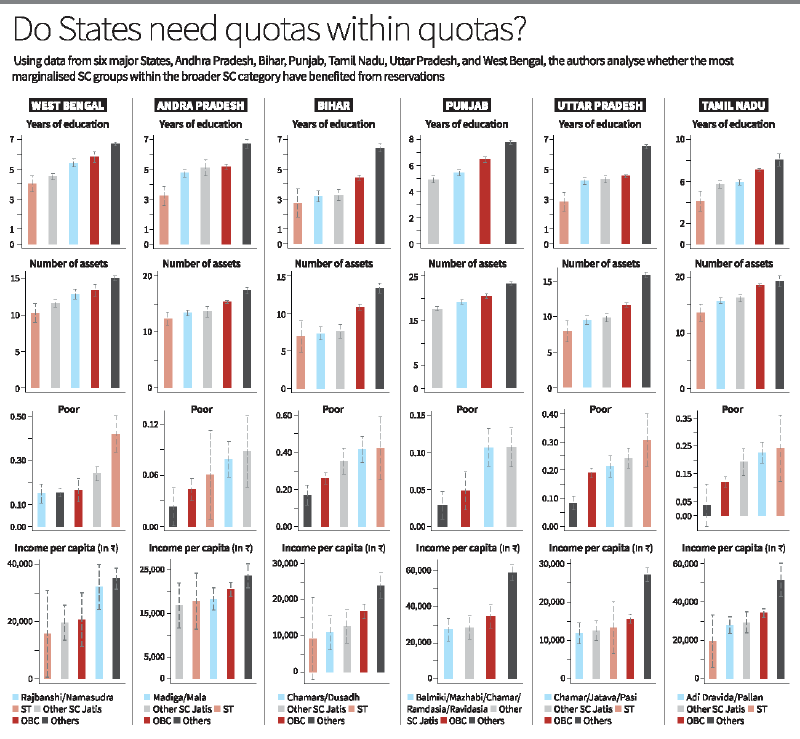
- 05 Nov 2024
Context
India's reservation system has long been a tool for uplifting historically marginalized communities, especially Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs). However, recent debates have questioned whether the system serves its intended purpose, particularly in light of disparities within the SC groups. The need for a ‘quota-within-quota’ system has been raised to ensure more equitable outcomes across different SC subgroups.
The Reservation System: Origins and Objectives
Purpose of Reservations
- Historical Background: Established to correct centuries of social and economic exclusion faced by SCs and STs.
- Mechanism for Equality: Aimed to create opportunities in education, government employment, and public offices for historically marginalized groups.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s Vision: Reservations were designed to transition from formal legal equality to substantive equality.
Challenges of the Current System
- Despite progress, certain SC subgroups seem to have benefited more than others.
- A Supreme Court ruling has led to calls for a 'quota-within-quota' to address intra-SC disparities.
Exploring Intra-SC Disparities: The Data Analysis
States Examined
- Key States: Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- Objective: To investigate whether some SC subgroups have disproportionately benefited from the reservation system.
Findings Across States
- Andhra Pradesh: Minor differences between SC groups (Malas vs. Madigas), with both groups showing similar socio-economic progress.
- Tamil Nadu: No significant disparity between Adi Dravida and Pallan groups, both benefiting equally from reservations.
- Punjab: Subdivision of quotas since 1975 has led to better outcomes for disadvantaged groups like Mazhabi Sikhs and Balmikis.
- Bihar: The Mahadalit category, introduced in 2007, failed due to political intervention, undermining the policy’s goals.
Key Insights
- In some states (e.g., Punjab), a subdivision of quotas has been effective in addressing intra-SC disparities.
- In other states, like Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, the benefits of reservations are already distributed fairly evenly among SC subgroups.
- The gap between SCs and upper-caste groups remains much larger than the gap within SCs.
The Issue of Access to Reservations
Caste Certificates as a Proxy for Access
- Data from IHDS: Less than 50% of SC households in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar report having caste certificates, limiting access to reserved positions.
- Better Access in Some States: Over 60-70% of SC households in Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh have caste certificates.
Core Issue: Ensuring Access
- Access Challenges: Without proper access to caste certificates, many SCs are excluded from the benefits of the reservation system.
- Priority Area: Ensuring that all eligible SCs have access to reservations is a critical concern before considering subdivision.
The 'Quota-within-Quota' Proposal
Concept and Potential Benefits
- Targeted Assistance: A ‘quota-within-quota’ would provide more focused help to the most disadvantaged SC subgroups, as seen in Punjab.
- Political Considerations: However, the political motivations behind quota subdivision, as seen in Bihar, can undermine the policy’s effectiveness.
Criticism and Limitations
- Uneven Need for Subdivision: In many states, the need for further subdivision is minimal, as the benefits of reservations are already fairly distributed.
- Political Exploitation: The policy risks becoming a political tool rather than a genuine means of achieving social justice, as political influence often determines who is categorized as the most disadvantaged.
Addressing Inequality Beyond Reservations
Income-Based Criteria and Monetary Benefits
- Current Approach: Monetary benefits (e.g., scholarships, lower fees) are a part of the affirmative action system.
- Income Criterion: Should be used to determine eligibility for monetary benefits to focus assistance on those most in need.
The "Creamy Layer" Debate
- Supreme Court’s Suggestion: The introduction of a "creamy layer" exclusion for SCs, akin to the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) model, remains contentious and requires stronger evidence.
Challenges of Economic Mobility
- Stigma and Discrimination: Economic progress does not necessarily eliminate social stigma or discrimination, especially for historically marginalized groups.
- Long-Term Goal: While reservations have contributed to creating a Dalit middle class, addressing stigma will require a gradual process.
The Need for Updated Data and Evidence-Based Policy
Data Deficiency
- Lack of Comprehensive Data: The absence of updated, reliable data on caste-based disparities limits the effectiveness of any policy reform.
- National Census Delay: India’s national Census, the only source of comprehensive data on caste, has been delayed, exacerbating the problem.
Evidence-Driven Reform
- Importance of Data: Robust and up-to-date data is essential to assess the true impact of reservations and to make informed policy decisions.
Conclusion: Reforming the Reservation System
- Reservations’ Success: The reservation system has played a significant role in improving the socio-economic status of SCs and STs.
- Intra-SC Disparities: While some subgroups benefit more than others, the broader gap between SCs and upper-caste groups remains far more pronounced.
- Focus on Access: The primary focus should be on improving access to reservations, ensuring that all eligible SCs benefit fully from affirmative action.
RBI brings back 102 tonnes gold from BoE; 60 per cent reserves in India

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
England over the past two-and-a-half years, reflecting a strategic shift in its approach to safeguarding gold reserves. This move marks a significant increase in the RBI's domestic gold holdings.
Rise in the RBI's Domestic Gold Holdings
- Current Status (September 2024):The RBI's domestic gold reserves have grown to 510.46 metric tonnes, up from 295.82 metric tonnes in March 2022.
- Reduction in Gold Held Abroad:The gold held under the custodianship of the Bank of England has decreased to 324 metric tonnes from 453.52 metric tonnes in March 2022.
- Gold as a Share of Foreign Exchange Reserves:The proportion of gold in India's total foreign exchange reserves increased from 8.15% in March 2024 to 9.32% in September 2024.
Gold Kept in the Bank of England
- Overview of the Bank of England's Gold Vault:The Bank of England is home to one of the largest gold vaults in the world, second only to the New York Federal Reserve, housing around 400,000 bars of gold.
- India’s Gold Held Abroad:The RBI continues to retain 324 metric tonnes of its gold with the Bank of England and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS).
- Additional Gold Management:Around 20 tonnes of gold are managed through gold deposit schemes.
- Strategic Role of London’s Gold Market:Storing gold in London provides immediate access to the global London bullion market, enhancing liquidity for India’s gold assets.
Historical Context of India’s Gold Holdings
- 1991 Balance of Payments Crisis:During a financial crisis in 1991, India had to send 47 tonnes of gold to the Bank of England to secure loans for repaying international creditors.
RBI’s Strategy to Bring Gold Back to India
- Global Trend of Central Banks Buying Gold:Since the imposition of U.S. sanctions on Russia in 2022, central banks globally have been increasing their gold reserves as a hedge against inflation and to reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar. India has outpaced other G20 nations in this trend, surpassing Russia and China in gold purchases.
- De-dollarisation:This shift is part of a broader strategy of de-dollarisation, aiming to diversify away from the U.S. dollar amidst rising gold prices and growing geopolitical tensions.
Significance of Repatriating Gold to India
- Sign of Economic Strength
- Recovery from the 1991 Crisis:The decision to repatriate gold reflects a significant improvement in India's economic position, a stark contrast to the 1991 economic crisis when India had to pledge gold for financial survival.
- Optimizing Financial Resources
- Reducing Storage Costs:Storing gold domestically allows the RBI to save on storage fees paid to foreign custodians, such as the Bank of England.
- Strategic Significance
- Enhanced Resilience Amid Global Instability:By repatriating its gold, India enhances its strategic autonomy and strengthens its economic position in a world of rising uncertainties and currency volatility.
RBI's Capacity to Safeguard Gold Domestically
- Increasing Domestic Storage Capacity:The RBI has been increasing its domestic capacity for gold storage to accommodate rising reserves and reduce dependence on foreign gold safekeeping facilities.
- Current Foreign Exchange Reserves:As of October 2024, India’s total foreign exchange reserves stand at $684.8 billion, sufficient to cover over 11.2 months of imports.
Diversification of Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Mitigating Currency Risks:By increasing gold reserves, India diversifies its foreign exchange holdings, reducing reliance on any single currency and shielding itself from global currency fluctuations and economic volatility.
- Gold as a Stable Asset:Gold serves as a stable asset, providing a safeguard against global economic shocks, and balances India’s reserves portfolio.
Gold as a Hedge against Inflation
- Preserving Wealth amid Inflation:Gold is traditionally viewed as a hedge against inflation, maintaining or appreciating in value when other currencies weaken. By increasing its gold reserves, India positions itself to better withstand the adverse effects of inflation and ensure long-term financial stability.
Conclusion
The repatriation of gold by the RBI reflects a strategic move to bolster India's economic strength and diversify its financial assets. The decision to bring gold back to India not only signifies an improvement in India's economic fundamentals but also aligns with global trends of central banks increasing their gold reserves to ensure long-term stability and reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar.
Key Takeaways from COP-16: Convention on Biological Diversity

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The 16th edition of the Convention of Biological Diversity (CBD) in Cali, Colombia was concluded.
Key Agreements at COP-16
- Establishment of the Cali Fund
- Purpose: To ensure equitable benefit-sharing from the use of Digital Sequence Information (DSI) on genetic resources.
- Focus on Indigenous Communities: At least 50% of the Cali Fund will support Indigenous peoples and local communities, with special emphasis on women and youth.
- Creation of a Permanent Subsidiary Body
- Inclusion of Indigenous Peoples: A new body will ensure the active participation of Indigenous groups in biodiversity conservation and policy discussions.
- Resource Mobilisation Strategy
- Target Funding: The conference agreed on a strategy to secure USD 200 billion annually by 2030 to support global biodiversity initiatives.
- Kunming Biodiversity Fund: A contribution of USD 200 million from China to support biodiversity funding.
- Management of Invasive Alien Species
- New Guidelines: Proposals for databases, cross-border trade regulations, and enhanced coordination with e-commerce platforms to manage invasive species.
- Identification of Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Areas (EBSAs)
- Enhanced Process: COP-16 agreed on an evolved process for identifying EBSAs, a critical aspect of marine conservation.
- Global Action Plan on Biodiversity and Health
- One Health Approach: Approval of a global action plan to curb zoonotic diseases, promote health, and safeguard ecosystems.
India’s Contribution at COP-16
Updated National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP)
- Financial Commitment: India plans to invest ?81,664 crore (USD 9.8 billion) from 2025-30 on biodiversity conservation.
- Focus Areas: India highlighted efforts such as the establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance, expansion of Ramsar sites, and increased spending on biodiversity from 2018-2022.
International Finance Support
- Global Partnerships: India emphasized the need for international finance to meet biodiversity targets, particularly under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Outcomes from COP-16
- New Mechanisms for Biodiversity Conservation
- Cali Fund: Ensures equitable benefit-sharing from genetic resources.
- Permanent Subsidiary Body: Facilitates the inclusion of Indigenous peoples in policy-making.
- Funding and Resource Mobilization
- USD 200 Billion Annually: Strategy to secure funding for biodiversity initiatives.
- Redirecting Harmful Subsidies: Agreement to redirect USD 500 billion in harmful subsidies by 2030.
- Biodiversity and Human Health
- Global Action Plan on Biodiversity and Health: Aimed at preventing zoonotic diseases and promoting human, animal, and environmental health.
Challenges in Biodiversity Protection
Key Threats to Biodiversity
- Population Growth and Resource Demand: Increasing population and demand for biological resources lead to over-exploitation.
- Habitat Degradation and Climate Change: Destruction of ecosystems and climate change threaten species globally.
- Invasive Species: Introduction of non-native species harms local biodiversity.
- Government Policies: Policies that prioritize development without environmental safeguards contribute to biodiversity loss.
Gaps in Global Biodiversity Framework
- Weak Legal Language: Concerns about insufficient legal protection for critical ecosystems.
- Lack of Implementation Mechanisms: Absence of mandatory review mechanisms for biodiversity targets.
Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF)
Framework Overview
- Adoption: Adopted at COP-15 in 2022, the KMGBF sets 23 action-oriented targets for biodiversity by 2030.
- Key Goals: Includes restoring 30% of degraded ecosystems and reducing the risk of invasive species by 50%.
- Living in Harmony with Nature: The framework envisions achieving biodiversity targets and living sustainably with nature by 2050.
Way Forward: Moving from Agreements to Action
- Participation of Stakeholders - Inclusive Approach: Ensuring the involvement of all relevant stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and local communities, in biodiversity conservation.
- Integrated Resource Management - Ecosystem Approach: Promoting a holistic approach to managing biodiversity and natural resources.
- Strengthening Governance - Good Governance Practices: Encouraging better governance to prevent unregulated exploitation of natural resources.
- International Financial Support - Alignment with Financial Institutions: Aligning global financial institutions and multilateral development banks with biodiversity conservation goals.
WWF Living Planet Report 2024

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- The WWF Living Planet Report 2024 highlights a drastic 73% decline in the average size of monitored wildlife populations globally from 1970 to 2020.
- The report underscores the urgent need for biodiversity conservation to maintain ecological balance, food security, and human health.
Key Findings of the 2024 Report
Wildlife Population Decline
- 73% Decline in monitored wildlife populations over the past 50 years (1970-2020).
- Freshwater species: Declined by 85%, the most significant drop.
- Terrestrial species: Declined by 69%.
- Marine species: Declined by 56%.
Main Threats to Wildlife
- Habitat Loss: Primary driver, particularly due to the expansion of food systems.
- Overexploitation: Over-hunting, fishing, and resource extraction.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species disrupt local ecosystems.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil contamination, especially in Asia-Pacific.
- Disease: Emerging diseases impacting wildlife populations.
Ecosystem Risks and Tipping Points
- Decline in wildlife signals risks of ecosystem tipping points.
- Critical ecosystems, like the Amazon and coral reefs, face potential irreversible damage.
- Impact on global food security and livelihoods due to ecosystem collapse.
India’s Wildlife Status
- Vulture populations in India remain critically endangered.
- Tiger populations have increased to 3,682 (2022).
- Snow leopards have been successfully monitored with 718 individuals recorded.
Case Study: Chennai’s Wetland Loss
- 85% reduction in Chennai’s wetlands due to urban expansion, exacerbating flood and drought risks.
- Initiatives like the Tamil Nadu Wetland Mission aim to restore these wetlands to improve ecosystem resilience.
Impacts of Wildlife Decline
- Ecosystem Imbalance
- Disruption in predator-prey relationships, pollination, and nutrient cycles due to species decline.
- Leads to ecosystem instability and potential collapse.
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Reduced genetic diversity makes ecosystems less resilient to environmental changes.
- Increases vulnerability to diseases, natural disasters, and climate change.
- Threats to Food Security
- Pollinators like bees and insects are essential for crop yields.
- Loss of pollinators threatens global food supply and agriculture.
- Human Health Implications
- Healthy ecosystems regulate disease by controlling pest populations.
- Declining biodiversity increases the risk of zoonotic diseases, such as COVID-19.
- Economic Consequences
- Agriculture, fisheries, and tourism industries depend on healthy ecosystems.
- Decline in wildlife can lead to job losses and economic instability.
- Cultural and Social Impacts
- Wildlife holds cultural, spiritual, and recreational value for societies worldwide.
- Loss of iconic species diminishes cultural identities and opportunities for nature-based tourism.
Challenges in Biodiversity Conservation
- Inadequate National Actions
- Despite global commitments (e.g., Global Biodiversity Framework, Paris Agreement, UN SDGs), national actions are insufficient to meet 2030 biodiversity targets.
- Risk of crossing tipping points that could lead to irreversible ecosystem degradation.
- Key Drivers of Biodiversity Loss
- Habitat Loss: Driven by agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure development.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, extreme weather, and altered precipitation patterns.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable hunting, fishing, logging, and resource extraction.
- Pollution: Industrial, agricultural, and plastic pollution disrupt natural habitats.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species outcompeting and threatening native populations.
- Lack of Funding: Inadequate financial resources for effective conservation.
- Weak Policy and Enforcement: Poorly implemented habitat protection laws.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Increased interactions between expanding human populations and wildlife.
- Genetic Diversity Loss: Reduced genetic diversity makes species vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes.
- Awareness Gaps: Insufficient public awareness on the importance of biodiversity.
Conclusion and Way Forward
Policy and Action Recommendations
- Expand protected areas and restore ecosystems to halt biodiversity loss.
- Engage Indigenous communities in conservation and land management practices.
- Promote sustainable farming, reduce food waste, and encourage plant-based diets to lessen food production impacts.
- Shift to renewable energy and reduce fossil fuel use to mitigate climate change.
- Redirect investments from environmentally harmful sectors to nature-friendly industries.
WWF-India’s Call for Collective Action
- WWF-India advocates for collective action to align climate, conservation, and sustainable development policies.
- The goal is to ensure a resilient and thriving future for both biodiversity and human societies.
Tackling Judicial Pendency and Adjournments in India

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
The issue of judicial delays and adjournments has become a significant concern in India’s judicial system. President Droupadi Murmu, while addressing the National Conference of District Judiciary in September 2024, emphasized the need to eliminate the culture of adjournments. These delays particularly affect the poor and rural populations, who often suffer in silence, avoiding court due to the fear of protracted justice.
Background of the Indian Judicial System
India’s judicial system has evolved under various legal frameworks, including the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC) and the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC). Initially, civil courts dealt with a wide range of cases, while criminal courts focused on criminal offenses. The establishment of the Supreme Court and High Courts further strengthened India’s judicial architecture to handle constitutional and appellate cases.
To address the growing caseload, the Indian government introduced the tribunal system through the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1976, aiming to manage specialized disputes. However, despite these reforms, case pendency continues to rise.
Key Issues Contributing to Judicial Delay and Pendency
- Judge-to-Population Ratio - India currently has 21 judges per million people, far below the recommended 50 judges per million as per the 120th Law Commission Report. The shortage of judges directly contributes to the growing backlog of cases.
- Vacant Judicial Positions - As of late 2024, 30% of High Court positions remain vacant, exacerbating the case pendency crisis. The delay in filling these vacancies has resulted in overburdened judges, further delaying case resolution.
- Legislative Overload - The enactment of laws without conducting prior judicial impact assessments leads to an increase in the number of cases, often without considering the capacity of the judiciary to handle them. This lack of foresight results in excessive pressure on courts.
- Overworked Judiciary - Judges often face a heavy workload, with some handling multiple responsibilities across different courts. This overburdening leads to mental fatigue, increased errors, and prolonged decision-making.
- Witness Delays - The absence of witnesses and delays in their appearance in court can significantly prolong the judicial process, contributing to case pendency.
Government Initiatives and Challenges
-
- National Judicial Infrastructure Plan (NJIP): The NJIP aims to modernize judicial infrastructure, improving court functioning and case processing. However, its full implementation across the country remains a work in progress.
- E-Courts Project: The E-Courts project aims to digitize the judicial process, including e-filing and virtual hearings. This initiative has shown promise in reducing procedural delays but still requires wider application.
- Tribunal System: While tribunals were introduced to reduce the burden on regular courts, their success has been limited, and the abolition of six tribunals in 2021 has added additional pressure on High Courts.
- Case Timeline Legislation: Laws prescribing time-bound adjudication for sensitive cases have been enacted, but due to inefficiencies in the system, deadlines are rarely met.
Recommendations for Reform
-
- Enhance Judicial Strength
-
- Increase the Judge-to-Population Ratio: The government should prioritize the appointment of judges to meet the 50 judges per milliontargets.
- Fill Vacant Positions: High Courts should fill vacant positions six months in advance to ensure a steady supply of judges.
-
- Judicial Impact Assessment
- Implement Judicial Impact Assessments: The Justice M. Jagannadha Rao Committee’s recommendation for judicial impact assessments should be made mandatory. Every new Bill should assess the likely increase in judicial workload, the required number of judges, and the necessary infrastructure.
- Promote Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
-
- Encourage ADR Mechanisms: Mediation and arbitration should be promoted as cost-effective alternatives to court proceedings. Public awareness campaigns and legal reforms can encourage the use of ADR.
-
- Strengthen Infrastructure and Technology
- Modernize Court Infrastructure: The judiciary should invest in technology such as e-filing and virtual hearings to reduce administrative burdens and expedite case resolutions.
- Streamline Administrative Processes: Technology can also help automate administrative tasks, thereby reducing the workload on judges and speeding up case processing.
- Limit Adjournments
- Stricter Norms for Adjournments: Judicial bodies should enforce stricter norms for granting adjournments, ensuring that they are not used excessively.
- Oversight Mechanism: An independent body can monitor the frequency of adjournments and take corrective action if needed.
Conclusion
Addressing the issue of judicial adjournments and case pendency requires a comprehensive approach involving structural reforms, better resource allocation, and the adoption of technology. Strengthening the judiciary’s infrastructure, increasing judicial appointments, and promoting alternative dispute resolution are vital steps toward ensuring quicker, fairer justice. The collaborative efforts of the judiciary, government, and society at large are essential to ensuring that India’s judicial system can meet the demands of justice in a timely and efficient manner.
Analysis of Election Expenditure in India

- 30 Oct 2024
Overview
Election expenditure has become a pressing issue in modern democracies, with growing concerns about its implications for political integrity and fair competition. In India, the skyrocketing costs of elections—both in terms of candidate spending and political party expenditure—pose significant challenges to electoral transparency, governance, and equity.
Current State of Election Expenditure in India
The total expenditure on elections in India has risen dramatically in recent years. For the 2024 Lok Sabha elections, the total expenditure by various political parties is estimated to reach around ?1,00,000 crores. This is a significant jump from the ?9,000 crores spent in the 1998 general elections. The expenditure per vote has also risen substantially, from ?25,000 in 1951 to ?1,400 in 2024.
The election expenditure limits for individual candidates are capped by the Election Commission of India (ECI):
- ?95 lakh for larger states (Lok Sabha constituencies)
- ?75 lakh for smaller states
- ?40 lakh for legislative assembly elections in larger states
- ?28 lakh for smaller states
However, these caps apply only to individual candidates. Political parties are not subject to any expenditure limits, allowing them to spend unlimited amounts during campaigns. This discrepancy leads to considerable financial disparities between well-funded national parties and regional or smaller parties, undermining the principle of equitable competition.
Global Comparisons: Election Financing and Spending Limits
Election financing varies widely across democracies, with countries like the United States and the United Kingdom adopting specific limits and regulations to curb excessive spending.
- United States: U.S. elections are financed largely through contributions from individuals, corporations, and Political Action Committees (PACs). Notably, Super PACs—which can raise and spend unlimited funds—have exacerbated concerns over money's influence on political outcomes. The 2024 U.S. presidential election is expected to cost around $16 billion (approximately ?1,36,000 crores).
- United Kingdom: Political parties are subject to strict expenditure limits. Each political party is allowed to spend £54,010 for each constituency, with an overall cap of £35 million for contests across all constituencies. This is aimed at ensuring that elections are not swayed by wealth alone and that smaller parties have a fighting chance.
Despite these measures, the United States still faces issues with unlimited corporate donations and the growing influence of wealthy donors, highlighting the complexities in curbing money in politics.
Challenges Posed by Rising Election Expenditure
The rising costs of elections present multiple challenges in India, exacerbating corruption, unfair competition, and political inequality.
a) Political Corruption and Influence
Large election expenditures are often funded by corporate donations and other private entities, creating a nexus between politicians and donors. This can lead to a quid-pro-quo relationship, where politicians may prioritize the interests of their donors over public welfare. This undermines public trust in the political system.
b) Unaccounted Money and Illegal Practices
A significant portion of the election expenditure is unaccounted for. The Centre for Media Studies (CMS) reports that in the 2019 general elections, around 25% of the total expenditure was spent on illegally distributing cash to voters. This practice, coupled with the absence of strict regulations on third-party campaigners, enables the use of black money in elections, further skewing the electoral process.
c) Uneven Playing Field
The absence of limits on party spending creates a situation where well-funded national parties have an inherent advantage over smaller regional parties and independent candidates. This financial inequality reduces the ability of under-funded candidates to compete based on ideas and merit rather than financial muscle. Furthermore, the growing influence of digital advertising and media campaigns has further widened this gap, with larger parties investing heavily in digital platforms like Google and Facebook, marginalizing those without the resources to do so.
Proposed Reforms to Address Election Expenditure Issues
To address these challenges, several reforms have been suggested by experts, committees, and the Election Commission. These reforms aim to curb excessive spending, ensure fairness, and increase accountability in the electoral process.
a) Capping Expenditure by Political Parties
There is a pressing need to introduce expenditure ceilings for political parties, in addition to those imposed on individual candidates. According to the 2016 Electoral Reforms Report by the Election Commission, political party spending should be capped at a level not exceeding the total expenditure limit for all candidates fielded by the party. This would level the playing field, ensuring that the influence of money is curtailed during elections.
b) State Funding of Elections
Recommendations for state funding of elections have been made by the Indrajit Gupta Committee (1998) and the Law Commission Report (1999). The state could partially finance the campaigns of recognized political parties, ensuring that candidates are not solely reliant on private donations. However, this reform faces challenges in terms of feasibility and implementation, especially regarding the mechanism for allocation of funds.
c) Regulation of Third-Party Campaigners
India should follow the example of countries like Australia, where third-party campaigners are formally registered and required to disclose their funding sources. This would help in tracking illegal contributions and ensure that election spending is transparent.
d) Ban on Government Advertisements During Election Periods
The use of government advertisements by the ruling party during the run-up to elections often leads to an uneven playing field. A ban on government-funded ads during the six months before elections would ensure that the ruling party does not gain an unfair advantage through public resources.
e) Strengthening Electoral Oversight
An independent electoral oversight body could be established to oversee campaign financing and ensure that all parties comply with spending limits. This would include measures to audit party finances, track donations, and verify spending claims, making it more difficult for parties to evade rules or use black money.
Conclusion: The Need for Comprehensive Electoral Reforms
The rising costs of elections in India present significant challenges to the democratic process. While expenditure limits for candidates exist, the lack of restrictions on party spending creates financial inequalities that undermine fair competition. The increasing role of corporate donations, illegal cash distribution, and unregulated third-party spending further complicates the situation.
To ensure fair elections, it is crucial that India adopts reforms such as capping political party expenditures, state funding of elections, and stronger oversight mechanisms. These steps, coupled with bipartisan political will, could help create a more equitable, transparent, and accountable electoral system, fostering greater public trust in the democratic process.
By addressing these challenges head-on, India can work toward an election system that encourages political participation based on ideas and policies rather than financial clout, ultimately strengthening the foundations of democracy.
Analysis of Growing Economic Divide in India
- 29 Oct 2024
Overview
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM)'s report titled "Relative Economic Performance of Indian States: 1960-61 to 2023-24" highlights an alarming trend of widening economic disparities across India's states, which is increasingly threatening the principles of federalism and national unity. The findings reveal significant regional imbalances in terms of contributions to the national income, per capita income, and overall economic development. This analysis delves into the key insights from the report and explores the broader implications for India's federal structure, governance, and policy approaches.
Key Insights from the Report
- Regional Economic Disparities:
- Western and Southern States' Dominance: States such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka have consistently outperformed others. These states have benefited from higher private investments, better infrastructure, and a more business-friendly environment. They also enjoy proximity to international markets, especially coastal regions like Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, which have access to ports and export markets.
- Underperformance of Northern and Eastern States: On the other hand, northern states (with exceptions like Delhi and Haryana) and eastern states like Bihar, Odisha, and West Bengal lag behind in economic performance. These regions face challenges such as poor infrastructure, low levels of investment, and weak governance structures, which hinder their growth potential.
- Impact of Liberalization (1991):
- The 1991 economic reforms marked a shift toward market-oriented growth, benefiting states that were already more industrialized or had better urban infrastructure. Southern states, in particular, adapted well to the liberalized environment, attracting higher levels of private investment and expanding their economies.
- The liberalization process disproportionately favored urban centers like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Bengaluru, where investments were channelized into growing service sectors, technology, and industries, creating a feedback loop of wealth accumulation in these hubs. Meanwhile, the hinterland remained underdeveloped due to insufficient public investment and the lack of private sector interest in these regions.
- Investment Disparities:
- Private Investment: Wealthier states attract a disproportionate share of private investment, which is driven by profitability and market opportunities. These states have better infrastructure, which reduces transaction costs and increases returns on investment. In contrast, underdeveloped states struggle to attract investment due to poor governance, inadequate infrastructure, and perceived higher risks.
- Public Investment: While the public sector still plays a role in investment, the New Economic Policies (NEP) since 1991 have shifted the focus towards private sector-driven growth. This has further widened the investment gap, as the poorer states receive less public investment relative to their needs.
- Role of Infrastructure and Governance:
- The availability and quality of infrastructure are significant determinants of economic performance. States with better roads, energy supply, ports, and communication networks tend to attract more investments. Additionally, good governance, characterized by reduced corruption, better policy implementation, and transparency, also plays a critical role in fostering economic development.
- In contrast, states with weaker governance structures and poor infrastructure struggle to create an enabling environment for businesses, further compounding regional disparities.
- Impact on Federalism:
- The growing economic divide is leading to tensions between the Centre and state governments, particularly in wealthier states that contribute significantly to national income but feel short-changed in resource allocation. These states argue that they are not receiving a fair share of national resources in return for their contributions, leading to growing dissatisfaction with the federal system.
- The tension is exacerbated by political factors, such as accusations from opposition-led states that the Centre uses public investment to favor states aligned with the ruling party. The growing perception of politicization of resource allocation has the potential to undermine the spirit of cooperative federalism.
Structural Causes of Regional Inequality
- Economic and Investment Magnetism:
- Wealthier states attract more private investments, as they offer better returns due to established markets, skilled labor, and urbanization. Cities like Mumbai, Delhi, and Bengaluru serve as economic magnets, drawing talent, technology, and capital, which further consolidates their economic dominance.
- In contrast, states without such economic hubs or access to global markets struggle to attract investment. The absence of urban agglomerations and the concentration of wealth and resources in a few states perpetuate regional disparities.
- Policy and Investment Bias:
- Post-liberalization policies have disproportionately benefited the organized sector, often at the expense of the unorganized sector, which is more prevalent in poorer states. The emphasis on industrial growth and infrastructure development has largely bypassed the rural and informal sectors, which are critical in underdeveloped states.
- The organized sector has also benefited from government support, such as tax concessions and subsidized infrastructure, which have enabled these industries to thrive in already developed regions. This has widened the gap between the haves and the have-nots.
- Cronyism and the Black Economy:
- Crony capitalism and the prevalence of the black economy in poorer states further exacerbate regional imbalances. In some cases, political patronage and corruption divert resources and investments from areas that need them most. This weakens the investment climate, especially in states with higher levels of informal and illegal economic activity.
Implications for Federalism
The growing economic disparity poses a serious threat to India's federal structure. The increasing dissatisfaction of wealthier states with the current fiscal arrangements and the growing demand for fairer resource allocation challenge the spirit of cooperative federalism. A well-functioning federal system relies on equitable distribution of resources and opportunities for all regions to develop.
Policy Recommendations
To address these disparities and strengthen India's federal framework, several policy measures need to be implemented:
- Enhancing Governance and Infrastructure in Lagging States:
- Improved governance and reducing corruption are essential in attracting both private and public investments. Additionally, there must be a focus on developing critical infrastructure, such as roads, energy, and health facilities, which are essential for economic growth.
- States need to increase public investment in sectors like education, healthcare, and social security to improve human capital and productivity.
- Focus on the Unorganized Sector:
- A significant portion of the labor force in poorer states is employed in the unorganized sector. Policies should aim to formalize this sector by providing social security benefits, improving labor rights, and increasing productivity through skill development. This could help raise incomes and stimulate local demand, attracting more private investment.
- Balancing the Organized and Unorganized Sectors:
- While the organized sector has benefited from liberalization, more attention should be given to the unorganized sector, which forms the backbone of the economy in many poorer states. A balanced approach to economic growth, which includes both organized and unorganized sectors, can help reduce disparities.
- Shifting Focus from Urban Centers to Hinterlands:
- Private sector investment must be incentivized in underdeveloped regions through tax breaks, subsidies, and targeted infrastructure projects. This will encourage businesses to expand beyond the major urban centers, thus promoting a more balanced distribution of economic activities.
Conclusion
The widening economic divide in India, as revealed by the EAC-PM report, poses a significant challenge to the country's federalism and unity. To ensure inclusive and balanced development, policy reforms must focus on reducing regional disparities by improving governance, infrastructure, and investment in lagging states. A shift towards equitable growth, addressing the needs of both the organized and unorganized sectors, is essential to promoting national cohesion and ensuring sustainable economic progress across all regions.
Strengthening the Anti-Defection Law to Uphold India's Democratic Integrity

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The Anti-Defection Law, introduced in 1985 through the 52nd Constitutional Amendment, aims to curb political instability caused by legislators switching parties for personal or financial reasons. While the law has helped maintain political stability, it faces several challenges, including delays in decision-making, potential bias in adjudication, and lack of transparency in party directives. These issues undermine its effectiveness in safeguarding democratic integrity.
Historical Context and Genesis
The issue of political defections, exemplified by the term "Aaya Ram, Gaya Ram," traces its origins to the 1960s when frequent party-switching destabilized governments. To address this, the Anti-Defection Law was enacted in 1985, disqualifying members who voluntarily gave up their party membership or defied party whips on critical votes. Initially effective in reducing defections, the law has faced challenges due to emerging loopholes, particularly regarding party "splits" and "mergers."
Gaps and Loopholes in the Current Law
One major loophole was the provision allowing a party split if one-third of its members defected, exploited until the 91st Amendment in 2003, which increased the threshold for mergers to two-thirds. Despite this change, defections continue, particularly through "mergers." Another issue is the role of the Speaker in deciding disqualification petitions. Given that the Speaker is often affiliated with the ruling party, their decisions are sometimes seen as biased, leading to delays in resolving defection cases. Additionally, the lack of transparency in issuing party whips has caused disputes regarding their legitimacy.
Proposed Reforms
To address these challenges, two key amendments are proposed:
- Fixed Time Frame for Decision-Making: A clear time frame—such as four weeks—should be established for the Speaker or an adjudicatory body to resolve defection cases. If no decision is made within this period, defecting members should automatically be disqualified.
- Transparency in Whips: Political parties should be required to make the issuance of whips public, either through newspaper publications or electronic communication, to ensure that members are fully informed of party positions on critical votes.
Ethical Concerns and Impact on Democracy
While the Anti-Defection Law was introduced to promote political stability, it has inadvertently stifled internal dissent within parties. Legislators are often forced to follow party lines, even when their personal convictions or constituents' interests conflict. This limits their freedom of expression and undermines the representative nature of democracy. Furthermore, the law has not fully curbed unethical practices such as "poaching" of members or defectors seeking personal gain, which continue to destabilize governments and erode public trust in the system.
The Way Forward: Political Will and Comprehensive Reforms
To strengthen the Anti-Defection Law, reforms must balance party discipline with individual freedoms. Key steps include:
- Independent Adjudication: Establishing an independent tribunal to handle defection cases can reduce political bias and expedite the decision-making process.
- Clear Timeframes: Setting a fixed timeline for resolving defection cases will prevent delays and ensure accountability.
- Transparency in Whip Issuance: Ensuring public notice of party whips will reduce ambiguity and disputes.
- Promoting Ethical Conduct: Strengthening ethical guidelines to discourage "poaching" and protect the integrity of the electoral process.
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
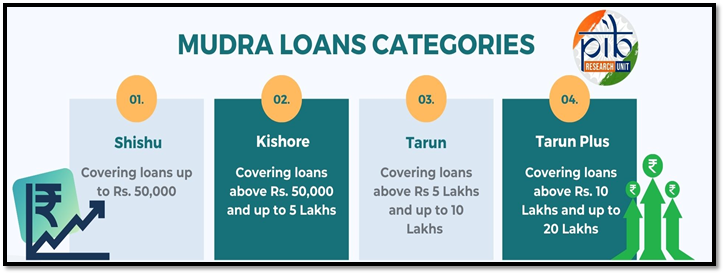
- 27 Oct 2024
Introduction
The Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 8, 2015, with the aim of providing financial support to non-corporate, non-farm small and micro enterprises in India. Through this initiative, loans are provided to individuals and small businesses who are unable to access formal institutional finance.
In the Union Budget 2024-25, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced an increase in the loan limit under PMMY from ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh, with the introduction of a new loan category, Tarun Plus, aimed at fostering growth in the entrepreneurial sector.
Key Features of the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
Loan Limit Increase
- Loan Limit Raised: The loan limit has been increased from ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh for eligible entrepreneurs.
- New Loan Category: The newly introduced Tarun Plus category caters to entrepreneurs who have previously availed and successfully repaid loans under the Tarun category.
- Credit Guarantee: The Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU) will cover these enhanced loans, further ensuring the security of micro-enterprises.
Categories of MUDRA Loans
PMMY provides collateral-free loans through financial institutions like Scheduled Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks (SFBs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), and Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs). These loans are provided for income-generating activities in sectors like manufacturing, trading, services, and allied agriculture activities.
Objectives of PMMY
- Financial Inclusion: PMMY targets marginalized and socio-economically neglected sections of society, promoting financial inclusivity.
- Support to Small Businesses: By providing affordable loans, the scheme encourages small-scale entrepreneurs, particularly women and minority groups, to establish and expand their businesses.
- Fostering Entrepreneurship: PMMY aims to unlock the potential of India’s entrepreneurial spirit, especially in rural and underserved areas.
MUDRA: The Institutional Backbone
Role of Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd. (MUDRA)
MUDRA is the primary institution set up by the Government of India to manage and implement the Mudra Yojana. It acts as a refinancing agency that provides financial support to small and micro-enterprises by working through financial intermediaries, such as banks and micro-finance institutions.
Funding Sources
- Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
Application Process
Applicants can avail loans through any of the aforementioned financial institutions or apply online via the Udyami Mitra Portal.
Benefits of Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
- Collateral-free Loans: No security is required to obtain loans, which reduces the financial burden on borrowers.
- Easily Accessible: PMMY loans are available across India, making them accessible to entrepreneurs in both rural and urban areas.
- Quick and Flexible Loans: Loans can be disbursed quickly with flexible repayment terms (up to 7 years).
- Empowering Women Entrepreneurs: The scheme offers special incentives for women entrepreneurs, helping them to establish and grow their businesses.
- Support to Rural Areas: Special emphasis on empowering rural enterprises and reducing regional disparities.
- MUDRA Card: The MUDRA Card is a RuPay debit card that allows borrowers to access funds through an overdraft facility, enhancing liquidity for businesses.
- No Default Penalty: In case of loan defaults due to unforeseen circumstances, the government will step in to reduce the burden on entrepreneurs.
Categories of Loans Under PMMY
1. Shishu Category: Loans up to ?50,000
- Targeted at micro-enterprises at the initial stage of their business journey.
2. Kishore Category: Loans between ?50,000 and ?5 lakh
- Targeted at enterprises looking to expand their operations and upgrade their infrastructure.
3. Tarun Category: Loans between ?5 lakh and ?10 lakh
- For established businesses that are in need of funds to scale up.
4. Tarun Plus: Loans between ?10 lakh and ?20 lakh
- A new category designed for entrepreneurs who have repaid loans under the Tarun category and wish to further expand their business.
Achievements of PMMY (2023-24)
- Total Loans Sanctioned: ?5.4 trillion across 66.8 million loans in FY 2023-24.
- Loans Disbursed: Significant amounts were disbursed under each category:
- Shishu: ?1,08,472.51 crore
- Kishore: ?1,00,370.49 crore
- Tarun: ?13,454.27 crore
- Women Borrowers: A large share of loans have gone to women entrepreneurs, ensuring gender inclusivity.
- Minority Borrowers: The scheme also emphasizes financial empowerment of minority communities.
- NPA Reduction: The Non-Performing Assets (NPA) in Mudra loans have reduced to 3.4% in FY 2024, compared to higher levels in earlier years.
Digital Tools and Support Systems
MUDRA MITRA App
The MUDRA MITRA mobile app helps users access information about the PMMY scheme, loan application procedures, and other resources. The app is available for download on Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
Online Loan Application
Entrepreneurs can apply for loans online via portals such as PSBloansin59minutes and Udyamimitra, providing greater convenience and accessibility.
Steps to Improve Implementation
- Handholding Support: Assistance in submitting loan applications is available for applicants.
- Intensive Awareness Campaigns: The government conducts publicity campaigns to raise awareness about PMMY.
- Simplified Loan Process: The loan application forms have been simplified to encourage wider participation.
- Performance Monitoring: Regular monitoring of PMMY implementation to ensure its success.
- Interest Subvention: A 2% interest subvention is offered for prompt repayment of Shishu loans.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana has been a transformative scheme in fostering entrepreneurship and ensuring financial inclusion for small and micro-businesses across India. With the recent increase in loan limits and the addition of the Tarun Plus category, the scheme continues to empower emerging entrepreneurs and provides a crucial lifeline for business growth and sustainability. By supporting women, minorities, and new entrepreneurs, PMMY has contributed significantly to economic upliftment and inclusive growth in the country.
The right to die with dignity

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare's draft guidelines (October 2024) aim to implement the Supreme Court's 2018 and 2023 orders on the right to die with dignity.
Legal Context: Supreme Court Rulings and Constitutional Rights
- Right to Refuse Treatment:
- Common Law & Article 21: The right to refuse medical treatment is grounded in common law and is now recognized as a fundamental right under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, following the 2018 Supreme Court judgment in Common Cause v. Union of India.
- Supreme Court Rulings: The court's rulings in 2018 and 2023 affirmed that individuals have the constitutional right to refuse life-sustaining treatment and to die with dignity.
Withholding and Withdrawing Life-Sustaining Treatment
- Definition and Meaning:
- What Is Life-Sustaining Treatment? Life-sustaining treatments, such as ventilators and feeding tubes, artificially replace vital bodily functions to sustain life.
- Withholding/Withdrawal: This refers to discontinuing these treatments when they no longer improve the patient's condition or merely prolong suffering.
- When Is It Done?
- End-of-Life Care: Withholding or withdrawing treatment is considered when further medical intervention is futile and would only artificially prolong the dying process.
- Focus on Comfort: After withdrawing life-sustaining measures, the focus shifts to palliative care to alleviate pain and suffering.
Understanding Euthanasia and Misconceptions
- What Is Euthanasia?
- Definition: Euthanasia refers to the intentional ending of a terminally ill patient’s life by medical professionals to relieve suffering.
- Passive Euthanasia Misconception: In India, the term "passive euthanasia" is often mistakenly used to describe withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatment, but this does not involve the active killing of the patient.
- Legal Framework: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) clarified in 2018 that "passive euthanasia" is not a legally accepted practice in the country.
The Role of Doctors: Ethical Dilemmas and Shared Decision-Making
- Is Withdrawing Treatment "Giving Up" on the Patient?
- Not Abandonment: Withdrawing life-sustaining treatment is not about abandoning the patient but recognizing when further interventions would cause unnecessary suffering.
- Palliative Care: The patient’s comfort and dignity are prioritized through palliative care, which focuses on pain management and emotional support for both the patient and family.
- Doctors' Ethical Responsibility:
- Shared Decision-Making: The process encourages a collaborative approach between doctors and the patient’s family or surrogate decision-makers. This joint decision-making ensures that the wishes of the patient are respected and relieves the doctor from bearing sole responsibility for life-and-death decisions.
Living Wills and Advance Medical Directives
- What Is a Living Will?
- Definition: A living will is a legal document where a person outlines their medical preferences in the event they lose decision-making capacity.
- Eligibility and Process: Individuals aged 18 or older, who are capable of making decisions, can draft a living will, naming at least two trusted surrogate decision-makers.
- Legal Requirements: The document must be signed in the presence of an executor, two witnesses, and notarized to be legally binding.
- 2023 Supreme Court Guidelines: The Court simplified the procedure for making living wills to ensure that the right to die with dignity is upheld.
Medical Procedure for Withholding or Withdrawing Treatment
- Supreme Court Guidelines
- The Supreme Court laid out a clear procedure for withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatment, emphasizing patient autonomy, expert assessments, and family consent.
- Primary and Secondary Medical Boards:
- Primary Medical Board: The treating hospital sets up a Primary Medical Board, consisting of the treating doctor and two subject-matter experts, to assess the patient's condition and determine if life-sustaining treatment is appropriate.
- Secondary Medical Board: A Secondary Medical Board, comprising independent experts, reviews the Primary Board's decision for added oversight.
- Consent from Family/Surrogate Decision-Makers:
- The patient’s wishes, as outlined in an advance directive or by a surrogate, must be respected, and their consent is essential for proceeding with treatment withdrawal.
- Judicial Oversight:
- Once the decision to withdraw treatment is made, the hospital is required to notify the local judicial magistrate, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Conclusion: Legal and Ethical Clarity in End-of-Life Care
- Shared Decision-Making: The process ensures that medical teams, families, and surrogate decision-makers collaborate, preventing any medical professional from facing moral or legal dilemmas alone.
- Protection of Autonomy: These frameworks and guidelines uphold patient autonomy, offering a legal and ethical pathway for terminally ill patients to exercise their right to die with dignity.
16th BRICS Summit
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the 16th BRICS Summit was held in Kazan, Russia.
Key Highlights:
Overview of the Bilateral Meeting between PM Modi and President Xi
- Location & Context: The meeting took place on the sidelines of the 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan, Russia (October 23, 2024), marking the first bilateral interaction between PM Modi and President Xi Jinping in nearly five years.
- Significance: The meeting focused on India-China relations, specifically the border dispute that arose following the 2020 standoff in Ladakh.
- Agreement on Border Disengagement: Both leaders welcomed an agreement for "complete disengagement" along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), which could pave the way for the resolution of issues that emerged after the Galwan Valley clashes in June 2020.
Key Points of the India-China Border Pact
- Resolution of Border Issues: The agreement addresses longstanding disputes, including in Depsang Plains and Demchok, where Chinese forces had encroached on Indian territory.
- Restoration of Patrolling: Both nations agreed to restore patrols to old patrolling points (PPs) along the LAC in these disputed areas.
- Next Steps: The Special Representatives (SRs) on the India-China boundary will meet soon to oversee the management of peace and tranquility in the border areas and explore mutually acceptable solutions.
- Diplomatic Mechanisms: Dialogue mechanisms at the foreign ministers and other official levels will be utilized to stabilize and rebuild bilateral relations, contributing to regional and global stability.
Strategic Importance of the Bilateral Meeting
- Maintaining Peace and Stability: PM Modi emphasized that differences between India and China should be managed carefully to ensure that broader peace and tranquility are maintained.
- Global Impact: Both leaders affirmed that stable India-China relations would have a positive impact on regional and global peace and contribute to a multipolar world.
- Long-Term Strategic Perspective: The leaders discussed progressing bilateral relations from a strategic perspective, enhancing communication, and exploring cooperation to address developmental challenges.
Key Takeaways from the 16th BRICS Summit
- Expansion and New Membership: The summit saw the inclusion of five new members—Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia (pending formalization). This expansion reflects BRICS’s growing influence as a forum representing the Global South.
- Focus on Multilateralism: Leaders emphasized multilateral cooperation to address challenges such as global security, economic growth, and sustainable development.
- Kazan Declaration: The declaration touched upon key issues:
- Geopolitical Conflicts: It called for dialogue and diplomacy to resolve disputes like the Ukraine crisis and the West Asia conflict.
- Sanctions and Trade: Criticized unilateral sanctions and their disruptive effects on global trade and development goals.
- Grain Exchange: A proposal was made to establish a BRICS Grain Exchange, aimed at improving agricultural trade among member states.
- Financial Integration: There was a push for greater financial integration through the use of local currencies for trade, exemplified by India’s UPI system as a successful model.
Importance of BRICS in the Global Context
- Global Influence: BRICS continues to be a key player in global geopolitics, representing 40% of the world’s population and 26% of global GDP (as of 2023).
- Strategic Goals: BRICS has consistently called for reform of international institutions like the UNSC, IMF, and World Bank, advocating for a more equitable global governance structure.
- Economic Collaboration: The New Development Bank (NDB), established in 2015, continues to play a vital role in funding development projects across BRICS countries, though the group’s influence in global finance remains limited compared to the World Bank.
Challenges Facing BRICS Expansion
- Geopolitical Contradictions: The inclusion of diverse new members (e.g., UAE, Egypt, Iran) could complicate decision-making due to geopolitical rivalries.
- Decision-Making Hurdles: Achieving consensus among an expanding membership will become more challenging. The expansion may dilute the cohesiveness of the group, as seen in other multilateral forums like the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and G77.
- De-Dollarisation Efforts: While BRICS aims to de-dollarize trade and reduce reliance on the SWIFT system, efforts to develop alternatives like a BRICS payment system and BRICS currency are still in nascent stages.
- Economic Disparities: Economic gaps among members—China’s GDP is significantly larger than the combined GDP of other members—could also create imbalances in decision-making.
India’s Role and Strategic Positioning in BRICS
- Geopolitical Balancing: India's participation in BRICS is a strategic maneuver to balance its global position and strengthen ties with emerging economies, particularly in the Global South.
- Diplomatic Relations with Russia: India continues to prioritize its relationship with Russia, which remains crucial for regional security and energy cooperation.
- India-China Ties: The agreement on the India-China border represents a significant shift in relations, with potential for a reset in Sino-Indian ties.
Key Themes in the Kazan Declaration
- Global Governance: Calls for reforming global institutions to give developing nations more representation.
- Energy and Sustainability: Proposals for strengthening energy cooperation, including the creation of energy corridors and the promotion of sustainable energy practices.
- Security: Emphasized the need for universal security by addressing the security concerns of all nations and promoting dialogue over confrontation.
Conclusion: Future of India-China and BRICS Relations
- India-China Relations: The border disengagement pact is a critical step towards stabilizing the India-China relationship, with potential positive impacts on regional security and global geopolitics.
- BRICS’s Growing Influence: As BRICS expands, it faces internal challenges but remains a potent voice for the Global South, aiming to reshape global governance and financial systems.
- India’s Strategic Positioning: India is likely to play a pivotal role in BRICS, especially as the group’s focus shifts towards regional stability, economic cooperation, and de-dollarization in the coming years.
Stubble Burning and the Supreme Court's Ruling: Protecting the Right to a Pollution-Free Environment

- 24 Oct 2024
Introduction
Recently, the Supreme Court of India expressed serious concerns about the ongoing issue of stubble burning in the states of Punjab and Haryana. The Court criticized the selective enforcement of penalties for stubble burning and emphasized that such practices violate citizens' fundamental right under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, which guarantees the right to live in a pollution-free environment.
Court’s Observations on Stubble Burning
- The Supreme Court highlighted the failure of state governments in effectively implementing laws against stubble burning.
- Selective Enforcement: The Punjab and Haryana governments were accused of prosecuting only a few violators while allowing many others to escape punishment by paying a nominal fine.
- The Court observed that this approach is a blatant violation of the right to live in a pollution-free environment, which is guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
Right to a Pollution-Free Environment
- The Court emphasized that every citizen has the fundamental right to live in an environment free from pollution, as mandated by Article 21 of the Constitution.
- The Court questioned the effectiveness of current environmental regulations, specifically pointing out the lack of proper machinery to collect fines under Section 15 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Impact of Stubble Burning
Stubble burning, primarily in the northern states of India, exacerbates air pollution, especially in Delhi and surrounding regions. The seasonal spike in air pollution during the months of October and November is largely attributed to farm fires. This not only worsens the air quality but also has severe implications for public health.
Environmental and Health Consequences
- Air Pollution: The burning of crop residues significantly contributes to the rise in PM2.5 and PM10 levels, leading to hazardous air quality.
- Soil Health: Burning crop residues depletes essential nutrients from the soil, reducing organic carbon content and harming soil fertility.
Health Risks
- Exposure to pollutants like particulate matter (PM) can lead to respiratory problems, heart diseases, and other health complications for the population, especially in densely populated areas like Delhi.
Legal and Institutional Shortcomings
- Inadequate Implementation: Despite laws and penalties being in place, the lack of an effective enforcement mechanism has resulted in the persistence of stubble burning.
- Toothless Penalties: The Supreme Court criticized the amended Section 15 of the Environment Protection Act, 1986, which replaced criminal penalties with financial fines for environmental violations. However, the lack of rules and appointed adjudicating officers has rendered this provision ineffective.
- No Serious Enforcement: The failure of the Central government and state authorities to implement effective penalties has led to widespread non-compliance with environmental laws.
Government Actions and Responses
Centre’s Efforts:
- The Central Government has introduced a Central Sector Scheme to promote agricultural mechanization for in-situ management of crop residue in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Delhi.
- The government provides financial assistance of up to 50% for the purchase of machinery, such as the Happy Seeder, to manage paddy stubble without burning.
- A total of ?3,062 crore has been released from 2018 to 2023 to tackle stubble burning.
State-Level Actions:
- The Punjab government has introduced cash incentives for farmers who refrain from burning stubble. Additionally, the state is offering non-fiscal incentives, such as access to panchayat land for storing paddy straw.
- The Pusa Decomposer, developed by the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), is a bio-enzyme used to decompose crop residue. It helps in turning the stubble into manure within 20-25 days, enhancing soil health.
Challenges for Farmers:
- Many farmers still prefer burning stubble due to high costs associated with alternative methods of residue management.
- The Happy Seeder and other machinery remain expensive and are not affordable for most small-scale farmers, leading them to resort to burning as the most cost-effective option.
Court’s Directive and the Way Forward
- The Supreme Court directed the Centre and state governments to ensure better enforcement of laws related to air pollution, vehicular emissions, and industrial pollution.
- The Court also urged the Union Government to consider Punjab’s request for additional funds to tackle the stubble burning issue and to strengthen the enforcement mechanism.
- Urgency for Action: The Court’s observations suggest that the existing framework needs urgent reforms to protect citizens’ right to a pollution-free environment.
Constitutional Provisions Related to Environmental Protection
India’s Constitution provides several provisions to ensure the protection of the environment:
Article 21: Right to Life and Environment
- In the landmark case Subhash Kumar v. State of Bihar (1991), the Supreme Court held that the right to life under Article 21 includes the right to a wholesome environment.
- This view was reiterated in Virender Gaur v. State of Haryana (1994), further strengthening the legal framework for environmental protection.
Directive Principles of State Policy
- Article 48A: The State is mandated to protect and improve the environment and safeguard forests and wildlife.
- Article 39(e) and 47: These Articles place a duty on the State to promote public health and ensure environmental protection.
Fundamental Duties
- Article 51A(g) places a duty on citizens to preserve and protect the environment.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s ruling highlights the urgent need for better implementation of environmental laws and the protection of citizens’ fundamental rights under Article 21. While government schemes are in place, a more robust and consistent approach is required to address the issue of stubble burning and air pollution. Immediate reforms in the enforcement mechanisms and incentives for farmers are crucial to achieve a sustainable, pollution-free environment in India.
Biodiversity COP16

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), while historically overshadowed by climate change discussions, is now gaining increasing attention due to the growing recognition of the global biodiversity crisis. This evolving prominence highlights the need for urgent action to preserve ecosystems and halt biodiversity loss, which is intimately linked with the climate crisis.
Overview of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Origins and Objectives:
- The CBD emerged from the 1992 Rio Earth Summit, alongside the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Main Goals:
- Protect global biodiversity.
- Restore ecosystems.
- Ensure equitable distribution of the benefits derived from biological resources.
- COP16 and the Kunming-Montreal Framework:
- The 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) marks the first meeting following the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework adopted at COP15 in 2022.
- The framework sets out four key goals and 23 targets to be achieved by 2030, including:
- Protect 30% of global lands and oceans by 2030.
- Restore 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030.
The Growing Convergence Between Climate Change and Biodiversity
- Interlinkages Between Climate Change and Biodiversity:
- Mutual Impact:
- Climate change accelerates biodiversity loss by altering habitats and threatening species.
- In turn, ecosystem degradation contributes to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases (GHGs) from deforestation and soil degradation.
- Shared Drivers:
- Both crises are driven by unsustainable human activities, including over-exploitation of natural resources, deforestation, over-consumption, and pollution.
- Increasing Synergy:
- There is a growing realization of the need for integrated solutions that address both climate change and biodiversity loss simultaneously.
- Momentum for 30 x 30 Targets
- The 30 x 30 Commitment:
- The 30 x 30 targets are central to the Kunming-Montreal Framework, which includes:
- Conservation of 30% of the world's lands and oceans.
- Restoration of 30% of degraded ecosystems.
- These targets aim to ensure the preservation of biodiversity-rich areas and the restoration of degraded ecosystems globally by 2030.
- National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs):
- Countries are required to develop and submit their NBSAPs (akin to Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for climate change).
- As of now, only 32 countries have submitted their NBSAPs, with more expected during COP16.
- High Seas Treaty:
- A crucial agreement for achieving 30 x 30 targets is the High Seas Treaty (also called Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdictions (BBNJ)), which focuses on:
- Establishing protected marine areas in biodiversity-rich regions beyond national jurisdictions.
- Ensuring regulation of human activities in these areas.
Access and Benefit Sharing: The Case of Genetic Resources
- Genetic Resources and Their Exploitation:
- The oceans, along with terrestrial ecosystems, harbor a wide variety of genetic resources that can be exploited for medical, commercial, and scientific purposes.
- Advances in biotechnology and digital sequencing of genetic material have raised issues about the equitable sharing of benefits from these resources.
- Nagoya Protocol and Benefit Sharing:
- The Nagoya Protocol (2010) set out guidelines for the access and fair sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources.
- At COP16, discussions will center on how genetic sequences (used in products such as medicines, crops, etc.) can be used fairly, ensuring that indigenous communities, who may be the original custodians of these resources, benefit equitably.
Finance Mechanisms for Biodiversity Conservation
- Financial Targets:
- One of the key goals of the Kunming-Montreal Framework is to mobilize $200 billion per year by 2030 for biodiversity conservation globally.
- Developed countries are expected to contribute $20 billion annually to developing nations, increasing to $30 billion by 2030.
- Phasing Out Harmful Subsidies:
- Countries are urged to eliminate perverse incentives that harm biodiversity, such as subsidies for:
- Over-fishing.
- Deforestation.
- Fossil fuel consumption.
- The goal is to repurpose such incentives to support sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
- New Financial Mechanisms:
- COP16 discussions will also focus on creating innovative financial mechanisms, such as:
- A biodiversity fund.
- Biodiversity credits, similar to carbon credits, which would allow countries or organizations to offset their biodiversity loss by investing in conservation projects elsewhere.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Implementation of 30 x 30 Targets:
- The main challenge lies in translating ambitious goals into actionable plans at the national and local levels. Countries must not only submit action plans but also implement and monitor them effectively.
- Increased Global Cooperation:
- Addressing biodiversity loss requires collaboration between countries, industries, and local communities to ensure that efforts are comprehensive and inclusive.
- Public Awareness and Engagement:
- It is crucial to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation and the urgent need for collective action to mitigate the combined threats of biodiversity loss and climate change.
Conclusion: The Need for Urgent Action
The discussions at COP16 signal an important shift in how the world addresses biodiversity and its links to climate change. As countries continue to recognize the interconnectedness of these two crises, the outcome of the CBD negotiations could play a pivotal role in shaping global environmental policy. However, meeting the ambitious goals set forth by the Kunming-Montreal Framework requires strong political will, adequate financing, and effective global cooperation.
What are the stress factors for Indian Railways?

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
On October 17, eight coaches of the Agartala-Lokmanya Tilak Express derailed in Assam with no casualties. On October 11, a passenger train rear-ended a stationary goods train near Chennai, also with no casualties. Indian trains have been involved in multiple accidents of late. The Balasore accident on June 2, 2023, had the greatest death toll, more than 275, yet pressure on the Railways to improve safety competes with pressures straining its subsistence.
Railway Accident Trends
- Decline in Accidents Over Time:
- From 1,390 accidents per year in the 1960s, railway accidents have reduced to about 80 accidents per year in the last decade.
- Recent Consequential Accidents:
- 34 accidents in 2021-2022
- 48 accidents in 2022-2023
- 40 accidents in 2023-2024
- Primary Causes of Accidents:
- 55.8% due to staff errors (railway personnel).
- 28.4% due to non-staff errors.
- 6.2% due to equipment failure.
- Role of Signalling Failures:
- Major accidents, such as Balasore and Kavaraipettai, were attributed to signalling system failures.
Key Safety Technologies and Measures
- Kavach System:
- Kavach is an automatic train protection system designed to prevent collisions by monitoring train positions and activating alarms or braking.
- As of February 2024, Kavach was implemented on only 2% (1,465 route km) of the railway network, limiting its effectiveness.
- Signalling System Overhaul:
- Outdated and faulty signalling systems contribute significantly to accidents. Both Balasore and Kavaraipettai incidents were linked to failures in signalling infrastructure.
Financial Strain on Indian Railways
- Operating Ratio (OR):
- The Operating Ratio (OR) in 2024-2025 is estimated to be ?98.2, indicating that the Railways spends ?98.2 for every ?100 earned.
- A higher OR reduces available funds for safety improvements and infrastructure upgrades.
- Budgetary Constraints:
- The 2023-24 budget showed a 7.2% reduction in capital outlay for track renewal and a 96% decrease in the Depreciation Reserve Fund, which is used to replace aging assets.
- Revenue Imbalance:
- Freight services account for 65% of Railways’ revenue but face capacity constraints, with 30% of the network operating at over 100% capacity.
- Passenger services, however, continue to incur significant losses, with ?68,269 crore loss in 2021-22.
Challenges in Rail Infrastructure
- Slow Infrastructure Development:
- The government's Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs), intended to alleviate congestion, are severely delayed:
- The Eastern DFC is the only fully operational corridor.
- Other corridors, including the Western DFC and additional planned routes, remain incomplete.
- Track and Equipment Maintenance:
- Ongoing delays in upgrading and maintaining essential infrastructure (tracks, wagons, signalling) contribute to the rising number of accidents.
Loco Pilot Working Conditions
- Extended Working Hours:
- Loco pilots often work 12-hour shifts due to manpower shortages, leading to fatigue and increased risk of human error.
- Stress and exhaustion are significant contributors to accidents caused by human error, including Signal Passed at Danger (SPAD).
Recommendations for Improving Railway Safety
- Loco Pilot Vacancies:Immediate recruitment to fill the 18,799 vacant loco pilot positions to prevent overworking and reduce fatigue-related errors.
- Expand Kavach Deployment:Accelerate the nationwide installation of the Kavach system, particularly on high-risk and high-traffic routes, to enhance safety.
- Complete Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs):Expedite the completion of DFCs to ease congestion and increase freight movement efficiency.
- Independent Railway Safety Authority:Establish an independent Railway Safety Authority with statutory powers, as recommended by the Kakodkar Committee (2012), to enforce safety standards and monitor implementation.
- Improve Signal Infrastructure:Invest in advanced and reliable signalling systems to prevent errors stemming from outdated or malfunctioning infrastructure.
- Regulate Working Hours:Enforce strict work hour limits to reduce fatigue among railway staff and ensure proper rest between shifts.
- Strengthen Trackside Infrastructure:Install fencing along tracks in high-risk areas to prevent cattle run-overs, a common cause of derailments in rural and semi-urban areas.
Conclusion
- Indian Railways faces a complex set of challenges, balancing safety requirements with financial constraints. Despite technological advancements like Kavach, its limited deployment and outdated infrastructure continue to present significant risks.
- A holistic approach to reform is needed, including addressing manpower shortages, upgrading safety technologies, and investing in infrastructure development. This will be essential for reducing accidents, improving safety, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of India’s vast railway network.
Fortified Rice: A Strategic Initiative to Combat Micronutrient Deficiencies in India

- 21 Oct 2024
Introduction to Rice Fortification
Fortification refers to the process of adding micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, to food products that are not naturally present in sufficient amounts. In India, rice fortification has been identified as a cost-effective strategy to address widespread micronutrient deficiencies, particularly iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12. These deficiencies contribute to various health problems such as anemia, stunted growth, and cognitive impairments, particularly among women and children.
Background: India’s Fortified Rice Program
India has one of the highest rates of malnutrition globally, with anemia affecting every second woman and every third child in the country. Rice is a staple food for approximately 65% of India’s population, making it an ideal vehicle for micronutrient fortification. In 2019, the Indian government launched the rice fortification initiative as part of its broader strategy to improve public health and nutrition outcomes.
In July 2024, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of the fortified rice program under key welfare schemes, including the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY). This initiative will run until December 2028, and aims to make fortified rice a common feature of the Public Distribution System (PDS), mid-day meals, and anganwadis, reaching millions of beneficiaries across the country.
Fortification Process and Standards
The fortification of rice involves adding essential micronutrients—iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12—to rice grains. This can be done by either coating the rice with a premix or producing extruded rice kernels that are enriched with nutrients before blending them with regular rice. According to the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), every kilogram of fortified rice should contain:
- Iron: 28 mg - 42.5 mg
- Folic Acid: 75 - 125 micrograms
- Vitamin B12: 0.75 - 1.25 micrograms
Scientific Safety and Efficacy of Iron Fortified Rice
The safety and effectiveness of iron-fortified rice have been under close scrutiny. Concerns were raised about whether individuals with hemoglobinopathies (such as Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Anemia) might be adversely affected by the added iron. Initially, the packaging of fortified rice carried health advisories for these individuals, but a 2023 scientific review and committee assessment concluded that there were no health risks from iron fortification for such individuals. The iron levels in fortified rice are minimal compared to the levels of iron patients with Thalassemia receive through blood transfusions, and Sickle Cell patients have naturally elevated levels of hepcidin, which limits iron absorption.
Following the review, the advisory was removed in July 2024, aligning with global practices where similar advisories are not required in countries that fortify rice.
Expansion of Fortified Rice Infrastructure
India’s rice fortification program has scaled up rapidly. As of 2024, over 21,000 rice mills have installed blending equipment to produce fortified rice, with a monthly capacity of 223 lakh metric tons (LMT). Additionally, 232 premix suppliers have the capacity to produce 75 LMT annually, significantly surpassing the requirements of the PMGKAY, which mandates the procurement of 5.2 LMT of fortified rice annually.
To ensure quality, NABL-accredited labs conduct rigorous testing on fortified rice products across the country. This infrastructure expansion supports the goal of fortifying rice distributed through welfare schemes and public safety nets.
Global Context: Rice Fortification Worldwide
Fortification of staple foods, including rice, is a globally recognized practice aimed at addressing micronutrient deficiencies in populations with limited access to diverse diets. As of 2024, 18 countries globally are actively involved in rice fortification. The World Health Organization (WHO) has endorsed rice fortification as an effective means to combat iron deficiency anemia, especially in countries like India where rice is a primary dietary staple.
Countries such as the U.S. have been fortifying rice since the late 1950s, and WHO recommends iron fortification where rice constitutes a major part of the diet.
Benefits of Iron Fortification of Rice
- Improved Cognitive Development: Iron is crucial for brain development and cognitive function. Adequate iron intake during early childhood is linked to better cognitive performance, which can improve educational outcomes.
- Enhanced Maternal and Infant Health: Iron deficiency during pregnancy is associated with risks such as maternal anemia and poor fetal development. Fortified rice helps reduce these risks by improving iron intake among pregnant women.
- Reduction in Prevalence of Anemia: Regular consumption of fortified rice has been shown to improve hemoglobin levels in populations suffering from iron deficiency anemia. This has been particularly evident in pilot districts in India, where iron fortification has led to improved health outcomes among both adults and children.
Potential Risks and Challenges
- Bioavailability of Iron: Iron bioavailability refers to the body's ability to absorb and utilize the iron from fortified foods. While iron from rice is absorbed to a lesser extent compared to meat, its fortification still contributes significantly to overall iron intake, especially in populations that consume rice regularly.
- Overload of Iron: Excessive iron intake can lead to iron toxicity, causing oxidative stress, liver damage, and increased risk of infections. Special care must be taken to ensure that individuals with conditions like hemochromatosis or those receiving other forms of iron supplementation do not experience iron overload.
- Technical and Social Barriers: While India has made substantial progress in infrastructure for rice fortification, challenges remain in ensuring the quality, stability, and safety of fortified rice. Moreover, ensuring affordability, accessibility, and acceptance of fortified rice among diverse population groups remains a critical concern.
Future Directions for Rice Fortification
- Nanotechnology for Enhanced Iron Absorption: To improve the bioavailability of iron, exploring the use of nanotechnology could help encapsulate iron particles, enhancing their absorption and effectiveness in the body.
- Biofortification Integration: Combining iron fortification with biofortification—the process of breeding rice varieties with naturally higher iron content—could provide a sustainable solution for long-term micronutrient deficiency.
- Public-Private Partnerships: To scale up rice fortification, there is a need for collaborations between the government, private sector, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). These partnerships can help improve distribution networks, technology development, and financial sustainability.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Rigorous evaluation studies, such as those being conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and NITI Aayog, will help assess the effectiveness of the rice fortification program and ensure its continuous improvement.
Conclusion: A Path to Nutritional Security
The fortification of rice in India represents a powerful tool to address the growing problem of micronutrient deficiencies, particularly iron deficiency anemia, which affects millions of people, especially women and children. By ensuring that fortified rice is integrated into government welfare schemes, India can take a significant step toward improving public health and achieving its nutritional goals.
While challenges related to bioavailability, iron overload, and implementation remain, ongoing research, technological innovation, and collaborative efforts can help mitigate these risks. As India continues to expand its rice fortification program, it offers a model for other countries facing similar nutritional challenges, reinforcing the role of fortified foods in achieving global sustainable development goals (SDGs) related to health and nutrition.
Mission Mausam

- 20 Oct 2024
Introduction: The Need for Advanced Weather Forecasting
India is increasingly facing extreme weather events such as flooding and droughts, which have become more frequent and intense in recent years. According to a 2021 study by the Council on Energy, Environment, and Water (CEEW), 40% of districts in India face alternating climatic hazards, where flood-prone areas also experience droughts, and vice versa. Moreover, a 64% increase in heavy rainfall days during the monsoon season has been recorded over the last decade.
Despite these challenges, India’s weather forecasting systems remain underdeveloped, particularly in flood-prone regions. While cyclone-prone areas benefit from comprehensive early warning systems, flood-prone regions are largely under-covered. To address these gaps and to prepare for more frequent climate risks, the Mission Mausam, launched in September 2024, aims to transform India's weather forecasting capabilities.
Key Objectives of Mission Mausam
Mission Mausam focuses on three main pillars:
- Increasing Weather Observation Networks
- Improving Weather Forecasting Models
- Investigating Weather Modification Techniques
This initiative is led by three institutions under the Ministry of Earth Sciences:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF)
- Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM)
The mission is backed by an investment of ?2,000 crore and aims to address the growing complexity of India’s climate challenges.
1. Gaps in India's Current Weather Observation Network
Despite significant advances, India’s existing weather observation system has several gaps, particularly in terms of coverage and data accessibility.
Weather Radar Coverage
India currently operates 39 Doppler Weather Radars (DWRs), but their distribution is not optimal. Key regions that are highly vulnerable to extreme weather events are under-monitored:
- Western Coast: Only 5 radars monitor the entire western coastline, where cyclones are becoming more frequent and intense.
- Urban Centres: Cities like Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, and Jodhpur — which have experienced repeated flooding — lack adequate radar coverage.
Action Required:
- Expand Radar Coverage: Prioritise the installation of weather radars along the western coast and in urban centres with high climate risks.
- Improve Observation Platforms: In addition to radars, install other weather observation platforms such as wind profilers and radiometers to provide more comprehensive data.
Limited Data Access
At present, the data from India’s weather observation network is not fully accessible to researchers and innovators. This limits the ability to develop localised early warning systems and innovative solutions for climate resilience.
Action Required:
- Open Data Access: Make weather data available to researchers, academic institutions, and private sector innovators. This will encourage the development of analytical tools and localized solutions for extreme weather events.
- Global Best Practices: Following the examples of countries like the United States, United Kingdom, and France, which openly share weather data, India can foster innovation and improve its forecasting capabilities.
2. Strengthening Weather Forecasting Models
Improved weather forecasting models are essential for accurately predicting extreme weather events, including heavy rainfall, floods, and cyclones.
Machine Learning and Atmospheric Physics
Mission Mausam will enhance weather forecasting models through:
- Integration of Machine Learning: By incorporating machine learning techniques, India can improve prediction accuracy and lead times.
- Better Understanding of Atmospheric Physics: Improved scientific understanding of the atmosphere can lead to more accurate and reliable weather forecasts.
Action Required:
- Enhance Forecasting Capabilities: Focus on improving long-term and short-term weather predictions, especially for regions prone to extreme weather.
- Incorporate Technology: Leverage advanced technologies, including AI and machine learning, to predict weather patterns more accurately.
3. Improving Communication and Dissemination of Weather Information
Effective communication of weather warnings is essential for timely action by governments, businesses, and citizens.
Enhancing Warning Systems
Currently, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) disseminates weather warnings through various channels, including mobile applications and web portals. However, the effectiveness of these warnings can be improved.
Action Required:
- User-Friendly Warnings: Improve the interface of weather apps and websites, providing users with guidance on how to interpret warnings and take necessary precautions.
- Capacity Building: Create informational videos, media campaigns, and easy-to-understand guides to help citizens act upon warnings effectively.
Wider Use of Localised Decision Tools
Localized decision tools can be used to help communities in specific regions take proactive steps before, during, and after extreme weather events.
Action Required:
- Localized Early Warning Systems: Develop region-specific warning tools that integrate local knowledge with scientific forecasts, making them more effective for local populations.
4. Integrating Mission Mausam with Sectoral Planning
The success of Mission Mausam will depend on its integration with various sectoral policies, particularly in areas such as agriculture, water management, and energy.
Use Cases for Climate-Resilient Sectors
Data from the enhanced weather observation system can be used to:
- Support Agriculture: Weather forecasts can inform crop planning and irrigation management, helping farmers mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events.
- Water Resource Management: Improved forecasting can assist in flood management, water storage, and distribution planning.
- Energy Sector Planning: Accurate weather predictions can help the energy sector plan for weather-related disruptions, such as extreme temperatures or storms that affect power grids.
Action Required:
- Sectoral Integration: Ensure that the weather data generated by Mission Mausam is shared with relevant ministries (e.g., Agriculture, Water Resources, Energy) to develop climate-resilient policies and strategies.
Conclusion: Moving Towards a Climate-Smart India
Mission Mausam is a critical initiative to make India more weather-ready and climate-smart. By improving weather observation networks, enhancing forecasting models, and promoting data-sharing, India can mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events that have become increasingly unpredictable and severe. The success of Mission Mausam will depend on:
- Investing in technology
- Expanding weather coverage
- Engaging local communities and sectors
As India continues to face the challenges posed by climate change, Mission Mausam holds the potential to revolutionize how the country prepares for and responds to extreme weather events, ultimately reducing the toll on lives and livelihoods.
Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
A Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court, in a majority judgment of 4:1 ratio, upheld the constitutionality of Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955, which permits immigrants from Bangladesh residing in Assam to secure Indian citizenship, as a valid piece of legislation aligned to the Preambular value of fraternity.
Background:
- Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955, deals with the citizenship status of immigrants from Bangladesh who entered Assam before March 25, 1971.
- Introduced as part of the 1985 Assam Accord, it provides a special provision for Assam due to the unique demographic challenges posed by large-scale migration from Bangladesh.
Key Aspects of the Supreme Court Ruling
Majority Opinion
- Constitutional Validity: The Court reaffirmed that Section 6A does not violate Articles 6 and 7 of the Constitution. These Articles set the cut-off for granting citizenship to migrants from East and West Pakistan. Section 6A, operating from a later date, is distinct and does not interfere with these earlier constitutional provisions.
- Justification of Cut-off Date: The March 25, 1971 cut-off date is upheld as reasonable. This date coincides with Operation Searchlight, launched by the Pakistani Army to suppress the Bengali nationalist movement. Migrants arriving before this date are considered part of India's post-partition demographic landscape.
- Fraternity and Equal Treatment: The Court emphasized that the principle of fraternity, as enshrined in the Preamble, cannot be selectively applied. Immigrants who arrived before March 25, 1971, are entitled to citizenship, while those arriving after are considered illegal immigrants. The ruling aims to balance the humanitarian aspect of migration with the state's right to protect its cultural and economic integrity.
- Historical Context: The judgment also invoked the Assam Accord, which was designed to address the issue of large-scale migration from Bangladesh, providing a political solution to Assam’s concerns. The Court held that the special provisions for Assam under Section 6A do not violate Article 14 (equality before the law) due to the distinct situation in Assam compared to the rest of India.
Section 6A of the Citizenship Act: Provisions and Purpose
- Section 6A was introduced under the 1985 Citizenship (Amendment) Act following the Assam Accord. It allows migrants who entered Assam before January 1, 1966, to automatically gain citizenship. For those entering between January 1, 1966, and March 25, 1971, citizenship can be granted after fulfilling specific conditions.
- Exclusion of Post-1971 Migrants: Migrants arriving in Assam after March 25, 1971, are not eligible for Indian citizenship under Section 6A and are considered illegal immigrants.
- Assam Accord Context: The Assam Accord sought to resolve the issue of illegal immigration from Bangladesh and address the political, cultural, and economic concerns of the indigenous Assamese population. It set the cut-off date of March 25, 1971, as a landmark for distinguishing between legal and illegal migrants.
Implications of the Supreme Court Judgment
Impact on Immigrant Recognition
- Continued Citizenship: By upholding Section 6A, the Court grants continued citizenship rights to immigrants from Bangladesh who entered Assam before the cut-off date of March 25, 1971. This decision affirms India's commitment to protect those displaced by the Bangladesh Liberation War.
Assamese Identity Preservation
- Cultural Protection: The majority opinion dismissed concerns that the presence of immigrants would infringe upon the cultural and linguistic rights of the Assamese people. The Court emphasized that existing constitutional safeguards (e.g., Article 29(1)) are sufficient to preserve the unique identity of the Assamese community, even in the face of demographic changes.
Demographic and Economic Impact
- Tensions on Demographic Shift: Critics argue that the continued influx of migrants, though legally recognized, may strain Assam’s demographic balance, potentially threatening its cultural identity and economic resources. This could fuel local demands for stricter immigration controls and increase political mobilization around cultural preservation.
- Resource Allocation Challenges: The judgment implies that immigrants who are granted citizenship will have access to public resources, adding pressure on Assam's limited economic resources. This may necessitate the implementation of more robust policies for equitable resource distribution.
Pressure on Immigration Laws and Enforcement
- Immigration Law Enforcement: The judgment stresses the need for more effective enforcement of immigration laws, particularly regarding the detection and deportation of illegal immigrants who entered Assam post-1971. The inefficiencies in the current mechanisms for detecting such immigrants were criticized, and the Court called for judicial oversight to improve the enforcement process.
Regional and International Implications
- Bangladesh Relations: The decision, by excluding post-1971 immigrants from citizenship, may strain India-Bangladesh relations, as it could be perceived as India pushing responsibility for these migrants onto Bangladesh. This has the potential to complicate regional cooperation on issues like border management, migration control, and security.
Conclusion: Balancing Humanitarian and Political Interests
The Supreme Court’s decision to uphold Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955, reflects a delicate balance between humanitarian concerns—acknowledging the plight of displaced persons—and the political necessity of protecting Assam’s cultural and demographic integrity. While the judgment provides clarity on the legal status of immigrants in Assam, it also highlights the need for efficient immigration enforcement, greater judicial oversight, and equitable resource management to address the ongoing challenges posed by migration in the region.
India - Canada Relations

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
India-Canada relations have recently faced serious setbacks following allegations of India's involvement in the killing of Khalistani leader Hardeep Singh Nijjar in Canada. These claims have led to escalating diplomatic tensions and mutual expulsions of diplomats between the two countries.
Recent Developments in India-Canada Relations
- Assassination of Hardeep Singh Nijjar:
- Nijjar, a prominent Khalistani leader, was assassinated in British Columbia, Canada.
- The Canadian Prime Minister accused Indian officials of involvement, which India has denied as "absurd."
- Diplomatic Fallout:
- Both nations expelled each other's diplomats, reducing diplomatic staff and freezing consular services, exacerbating the tensions.
- Support from the Five Eyes Alliance:
- Canada enlisted the Five Eyes intelligence alliance to gain international backing amid the escalating diplomatic crisis with India.
What is the Five Eyes Alliance?
- About:
- The Five Eyes is a multilateral intelligence alliance composed of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- These countries cooperate on signals intelligence under the UK-USA Agreement.
- Expansion:
- The alliance later grew into the Nine Eyes and Fourteen Eyes alliances, incorporating additional countries like the Netherlands, Denmark, France, Norway, and others.
Key Areas of India-Canada Relations
- Political Relations:
- Diplomatic ties began in 1947, with both countries sharing democratic values, human rights, and pluralism.
- Collaborative efforts in global forums like the UN, G20, and Commonwealth focus on climate change, security, and sustainable development.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Bilateral trade in 2023 was worth USD 9.36 billion.
- Canada is the 18th largest investor in India with investments totaling USD 3.3 billion (2000-2023).
- Ongoing Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) negotiations aim to boost trade in goods, services, and investments.
- Diaspora Connections:
- Over 1.8 million people of Indian origin in Canada, contributing significantly to cultural and economic exchanges.
- Canada is home to one of the largest Indian diaspora populations globally.
- Education and Space Innovation:
- IC-IMPACTS promotes joint research in healthcare, agricultural biotechnology, and waste management.
- Space collaboration includes partnerships between ISRO and the Canadian Space Agency.
- Indian students represent nearly 40% of Canada's international student population.
- Nuclear Cooperation:
- A 2010 nuclear agreement allows the supply of uranium to India and establishes a Joint Committee for oversight.
- Strategic Importance:
- India’s role is key in Canada’s Indo-Pacific strategy, including collaboration on maritime security, counter-terrorism, and regional stability.
Challenges in India-Canada Relations
- Diplomatic Immunity Issues:
- Canada invoked the Vienna Conventions to protect its diplomatic staff amid tensions, with both sides highlighting the importance of maintaining diplomatic norms.
- Khalistan Issue:
- India views Canada’s tolerance of Khalistani separatist groups as a threat to its territorial integrity.
- Canada’s investigation into India’s alleged role in Nijjar’s assassination has exacerbated diplomatic mistrust.
- Economic and Trade Barriers:
- The political rift has stalled negotiations for the CEPA and slowed bilateral trade.
- Canadian investments in India face increased uncertainty due to deteriorating relations.
- Visa and Immigration Delays:
- Reduced Canadian diplomatic staff in India has caused significant delays in visa processing, especially for students.
- Geopolitical Implications:
- Tensions between India and Canada risk damaging India’s reputation on the global stage, particularly if allegations of intelligence overreach are substantiated.
- Canada’s membership in the G7 and ties with the Five Eyes make the situation complex, affecting relations with other strategic partners of India, including the US, UK, Australia, and Japan.
The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Immunity
- Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961): Establishes the framework for the treatment and protection of diplomatic missions and their personnel.
- Diplomatic Immunity: Diplomats are protected from arrest and detention by the host country.
- Inviolability of Diplomatic Premises: Diplomatic missions cannot be entered without permission.
- Protection of Consular Officers: Ensures consular officers can assist their nationals without interference.
Way Forward for India-Canada Relations
- Address the Khalistan Issue: Engage in active dialogue to resolve concerns about the Indian diaspora and the Khalistan movement, respecting each other’s sovereignty.
- Strengthen Economic Ties:
- Revitalize CEPA negotiations, with a focus on sectors like technology, renewable energy, and infrastructure.
- Enhance trade and investment frameworks for mutually beneficial opportunities.
- Balance Geopolitical Interests:
- Both nations should navigate relationships with major powers like the US, China, and Russia with care.
- A cautious approach is necessary to maintain strategic partnerships without further conflict.
- Leverage Multilateral Platforms: Utilize forums like the G7 and Five Eyes to address global challenges and promote shared values, while working to stabilize bilateral ties.
Conclusion
India-Canada relations are at a critical juncture due to recent tensions. While historical ties and shared interests provide a strong foundation, the diplomatic fallout requires careful management. Both nations must seek ways to restore dialogue, address sensitive issues like the Khalistan movement, and focus on economic cooperation to stabilize and strengthen the relationship moving forward.
Global Hunger Index 2024
- 17 Oct 2024
Why in the news?
India is ranked 105th among 127 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024, indicating a ‘serious’ level of hunger, along with Afghanistan and Pakistan, which also face hunger challenges.
According to the Global Hunger Index released on 10th October 2024, the hunger levels in 42 countries are at alarming levels, making the goal of Zero Hunger by 2030 unattainable. At this pace of progress, the world will not even attain a low hunger level until 2160. The world’s GHI score is 18.3, which is considered moderate in the severity of hunger scale.
Key Takeaways:
1. The GHI is published by Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe annually to measure and track hunger at global, regional, and national levels. The purpose of the report is to create awareness and understanding of the struggle against hunger and call attention to those areas of the world where hunger levels are highest and there is a need for additional efforts.
2. GHI is calculated based on a formula that combines four indicators that together capture the multidimensional nature of hunger:
- Undernourishment: the share of the population whose caloric intake is insufficient;
- Child stunting: the share of children under the age of five who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition;
- Child wasting: the share of children under the age of five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition; and
- Child mortality: the share of children who die before their fifth birthday, reflecting in part the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments.
3. The 2024 GHI reflects that multiple factors are posing challenges in attaining Zero Hunger. The challenges include large-scale armed conflicts, climate change indicators that are worsening faster than expected, high food prices, market disruptions, economic downturns, and debt crises in many low- and middle-income countries.
4. The report highlights the link between Gender inequality, climate change, and hunger. Gender is intertwined with climate and food security challenges in ways that respective policies and interventions often ignore. Women and girls are typically hardest hit by food insecurity and malnutrition. They also suffer disproportionately from the effects of weather extremes and climate emergencies.
5. Six countries – Somalia, Yemen, Chad, Madagascar, Burundi, and South Sudan- have levels of hunger considered alarming. This is the result of widespread human misery, undernourishment, and malnutrition.
What is Hunger?
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) defines hunger as food deprivation, or undernourishment, as the habitual consumption of too few calories to provide the minimum dietary energy an individual requires to live a healthy and productive life, given that person’s sex, age, stature, and physical activity level.
6. India ranked 105th out of 125 countries in the Global Hunger Index 2024, with a score of 27.3, indicating a serious level of hunger. Child wasting is particularly high in India. Child undernutrition in India goes hand in hand with the poor nutritional status of mothers, suggesting an intergenerational pattern of undernutrition and underscoring the need for attention to maternal health nutrition and infant feeding.
7. India’s GHI score of 27.3 is a cause for concern, especially when compared to its South Asian neighbours like Bangladesh, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, which fall into the “moderate” category
8. The performance of India on various parameters of GHI:
- 13.7 per cent of India’s population suffers from undernourishment,
- 35.5 per cent of children under the age of five are stunted
- 18.7 per cent experience child wasting and
- 2.9 per cent of children do not reach their fifth birthday.
9. The policy recommendations made in the document include strengthening accountability to international law and the enforceability of the right to adequate food, promoting gender-transformative approaches to food systems and climate policies and programs, and making investments that integrate and promote gender, climate, and food justice.
National Family Health Survey
1. The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) in India provides estimates of underweight, (low weight for age), stunting (low height for age), and wasting (low weight for height). These conditions affect preschool children (those less than 6 years of age) disproportionately and compromise a child’s physical and mental development while also increasing the vulnerability to infections.
2. According to the NFHS 5, the percentage of stunted, wasted, and underweight children is 36 per cent, 19 per cent and 32 per cent respectively.
(Thought Process: These data can be incorporated in your Mains Answer Writing to enrich your content.)
3. NFHS 5 highlighted that among mothers with a child between ages 6-23 months, 18 per cent reported that their child did not eat any food whatsoever — referred to as “zero-food” — in the 24 hours preceding the survey. The zero-food prevalence was 30 per cent for infants aged 6-11 months, remains worryingly high at 13 per cent among the 12-17 months old, and persists even among 18-23 months-old children at 8 per cent.
Hidden Hunger
In India, we suffer largely from “hidden hunger” which does not always manifest itself in an emaciated appearance. It is a hunger caused by the constant or recurrent lack of food of sufficient quality and quantity. It is the deprivation of vitamins and minerals, essential micronutrients that are necessary for proper growth, physical fitness, and mental development.
4. Going without food for an entire day at this critical period of a child’s development raises serious concerns related to severe food insecurity. According to the World Health Organisation, at six months of age, 33 per cent of the daily calorie intake is expected to come from food. This proportion increases to 61 per cent at 12 months of age. The recommended calorie percentages mentioned here are the minimum amount that should come from food.
5. India has a challenging task in attaining the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 2 of “zero hunger”. Mission Poshan 2.0, the overarching flagship programme dedicated to maternal and child nutrition, has evolved in the right direction by targeting SDG 2 “zero hunger” and focusing on food-based initiatives, including its flagship supplementary nutrition programme service as mandated by the 2013 National Food Security Act.
Climate Change and Methane Emissions in the Amazon Rainforest

- 16 Oct 2024
Overview
Recent research from the University of São Paulo reveals that climate change is poised to significantly disrupt the methane cycle in the Amazon rainforest, with potential global repercussions. Rising temperatures and increased flooding are impacting microbial activity in both floodplain and upland forest soils, leading to contrasting changes in methane dynamics.
Key Findings
- Methane Uptake Reduction: The study indicates that methane absorption in upland forest soils could decrease by as much as 70% in warmer, drier conditions. This reduction diminishes the forest's role as a methane sink.
- Floodplain Contributions: Floodplains, which cover over 800,000 square kilometers during the rainy season, contribute up to 29% of global wetland methane emissions. Here, methane-producing microbes thrive due to the breakdown of organic matter.
Understanding the Methane Cycle
- Definition: The methane cycle encompasses the processes that control the production, consumption, and release of methane (CH4) in the environment.
- Microbial Roles:
- Methanogens produce methane, primarily in waterlogged conditions.
- Methanotrophs consume methane, living in drier, oxygen-rich soils. These interactions are critical in regulating methane levels in the atmosphere.
- Sources and Sinks: While wetlands and other environments release methane, hydroxyl radicals (OH) in the troposphere act as a natural sink, helping to oxidize methane into carbon dioxide.
Climate Change Impacts on the Methane Cycle
- Imbalance of Sources and Sinks: As global temperatures rise, the release of methane from soils may increase, exacerbating climate change effects.
- Melting Clathrates: Methane clathrates, trapped in cold sediments, are at risk as warming causes them to release methane, further contributing to greenhouse gas concentrations.
Global Consequences of Methane Disruption
- Climate Change Amplifier: Methane is the second most significant greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential 28 times greater than carbon dioxide over a century.
- Air Quality and Health: Increased methane emissions can lead to higher levels of tropospheric ozone, resulting in respiratory health issues and reduced air quality.
- Biodiversity Threats: The changes in methane dynamics can destabilize ecosystems, leading to shifts in species distributions and loss of biodiversity.
Balancing the Methane Cycle
To mitigate the impacts of methane emissions, various strategies can be employed:
- Enhanced Landfill Design: Utilizing gas collection systems to capture methane for energy rather than allowing it to escape.
- Livestock Management: Introducing feed additives to reduce methane emissions from ruminants.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Implementing techniques like alternative wetting and drying in rice cultivation to lower methane output.
- Soil Health Improvements: Promoting organic fertilization and crop rotation to foster aerobic conditions in soils.
Research Insights
The study involved subjecting soil samples from floodplains and upland forests to elevated temperatures and varying humidity levels. Results indicated:
- Stable methane emissions in floodplains alongside an increase in methane-producing microbes.
- A significant decline in methane uptake in upland soils due to temperature sensitivity, with higher temperatures reducing microbial diversity.
Conclusion
The Amazon rainforest plays a crucial role in regulating global methane levels, and its response to climate change is vital for understanding future greenhouse gas emissions. As these ecosystems face increased pressure from rising temperatures and changing hydrological conditions, it becomes imperative to enhance our understanding and management of methane dynamics to mitigate broader climate impacts.
Asset Monetisation
- 15 Oct 2024
In News
The NITI Aayog has recently increased the asset monetisation target for the fiscal year 2024-25 (FY25) by ?23,000 crore, bringing the total to ?1.9 trillion. This adjustment aligns with the broader target of ?6 trillion set under the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) for the period from FY 2022 to FY 2025.
Understanding Asset Monetisation
Definition
Asset monetisation refers to the process of converting public assets into revenue-generating assets without selling them outright. This includes using assets to generate profit or cash, thereby unlocking their economic value.
Importance
- Revenue Generation: Monetisation creates new revenue streams for governments by leveraging underutilised public assets.
- Focus on Public Assets: The emphasis is on monetising existing infrastructure such as roads, airports, railways, and pipelines, primarily targeting brownfield assets—those that can be improved or repurposed.
Monetisation vs. Privatisation
While privatisation involves complete ownership transfer to the private sector, asset monetisation allows public authorities to retain ownership while benefiting from private sector efficiencies through structured partnerships.
The National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP)
Overview
The NMP is an initiative aimed at promoting sustainable infrastructure financing through the monetisation of operational public assets. It envisions a monetisation potential of ?6 lakh crore, focusing on leasing core assets from the Central government and public sector entities.
Preparation and Coverage
- Collaborative Approach: Developed by NITI Aayog in consultation with infrastructure ministries such as Roads, Railways, and Power.
- Sector Coverage: Encompasses various sectors including roads (27% of the total value), railways (25%), power (15%), and telecom (6%).
Framework for Monetisation
- Retention of Rights: The government retains ownership, with assets reverting to public authorities post-transaction.
- Stable Revenue Streams: Focus on de-risked brownfield assets that provide consistent revenue.
- Defined Partnerships: Establishment of contractual frameworks with strict performance indicators.
Alignment with National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
The NMP is integrated with the NIP, which seeks to attract investments in both greenfield and brownfield projects across all sectors.
Current Status of the NMP
Revenue Generation
As of FY24, the NMP has generated ?3.9 trillion, slightly below the original target of ?4.3 trillion for the initial three years.
Successful Monetisation Examples
- The Ministry of Coal exceeded its target, raising ?1.54 trillion against a goal of ?80,000 crore.
- Mining assets have also been monetised significantly, surpassing their revised targets.
Sectors Lagging
- Railways: Only ?20,417 crore monetised, achieving just 30% of the target.
- Civil Aviation: A mere 14% of its targeted monetisation has been achieved.
Challenges Facing the NMP
- Low Monetisation Potential: The NMP's ?6 lakh crore target represents only a small fraction (5-6%) of the total capital expenditure under the NIP.
- Disinvestment Issues: Many sectors chosen for monetisation have consistently fallen short of their disinvestment targets, raising doubts about achieving future goals.
- Long-Term Rights Concerns: Granting private entities long-term operational rights may be perceived as a form of privatisation, potentially leading to public distrust.
- Budget Clarity: There is a lack of transparency regarding how monetisation proceeds will be allocated within the government budget.
- Potential for Monopolies: Consolidation of asset ownership could lead to monopolistic practices, especially in critical infrastructure sectors.
- Taxpayer Concerns: Taxpayers are wary of the potential for double charges on public assets they initially funded.
Way Forward
- Accelerating Monetisation: The government should expedite contract-based monetisation through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP), particularly in sectors like railways and airports.
- Land Monetisation Initiatives: Engaging real estate companies to develop multi-storey buildings can generate additional revenue while enhancing housing options.
- Establishing Budget Guidelines: Clear budgeting guidelines should be developed to clarify the allocation of funds generated from monetisation, ensuring they are used for infrastructure development rather than operational expenses.
Navigating the Middle-Income Trap: Challenges and Solutions for India

- 14 Oct 2024
Introduction
The World Development Report 2024 addresses the phenomenon of the middle-income trap, where countries struggle to maintain growth as they transition from low to middle-income status. This report advocates for a "3i" approach—Investment, global Technology infusion, and domestic Innovation—to overcome this challenge. India faces specific hurdles, including stagnant exports, rising protectionism, and premature deindustrialization.
Understanding the Middle-Income Trap
Definition and Characteristics
- A middle-income trap occurs when a country, after achieving middle-income status, fails to progress to high-income status.
- This phenomenon typically arises when a country's per capita income reaches about 11% of US levels, leading to:
- High wage levels that diminish competitiveness against low-wage economies.
- Insufficient technological advancement to compete with high-income nations.
Economic Implications
- Traditional growth drivers become ineffective.
- Rising wages in labor-intensive sectors decrease competitiveness, while innovation and productivity remain stagnant.
Historical Context: India’s Income Evolution
1. Post-Independence Era (1950s-1970s)
- Per Capita Income: ?265 in 1950-51.
- Growth Rate: 3.5%, dominated by agriculture.
- Economic Structure: Heavy state intervention and public sector focus.
2. Liberalization Phase (1980s-1990s)
- Per Capita Income Growth: Accelerated to 5.6%.
- Major Shift: 1991 liberalization led to a rise in the services sector and an expanding middle class.
3. High Growth Phase (2000-2010)
- GDP Growth: 8-9% annually.
- Per Capita Income: Increased from ?16,173 in 2000-01 to ?24,295 in 2007-08.
- Sectoral Dominance: Surge in software and services exports.
4. Mixed Growth Phase (2010-2020)
- Growth Volatility: Average of 6-7%.
- Wealth Inequality: Top 1% owned 40.5% of national wealth by 2021.
5. Post-Covid Recovery (2020-Present)
- GDP: Reached $3.75 trillion.
- Current Issues: Unemployment at 8.1%, while digital payment systems expanded.
Challenges in Overcoming the Middle-Income Trap
1. Premature Deindustrialization
- The manufacturing sector's GDP share has stagnated at 15-17%, far below the target of 25%.
- Limits potential productivity gains and innovation.
2. Limitations of Services-Led Growth
- Over-reliance on the services sector hampers mass employment and inclusive growth.
3. Declining Total Factor Productivity (TFP)
- TFP growth has been declining, indicating a shift toward input-driven growth rather than efficiency-driven growth.
4. Informal Sector Dominance
- The informal economy comprises about 90% of the workforce, leading to low productivity and limited access to technology.
5. Risk of a Demographic Burden
- Youth unemployment is rising, with only 2.3% of the workforce receiving formal skill training.
6. Global Economic Headwinds
- Slowing global growth affects India’s export-led strategies, with a recent contraction in merchandise exports.
7. Infrastructure and Logistics Bottlenecks
- India ranks 38th in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index, highlighting significant infrastructure gaps.
Strategic Measures for India
1. Enhance Manufacturing Competitiveness
- Targeted Industrial Policies: Refine the Production-Linked Incentive scheme and extend it to emerging sectors like green hydrogen.
2. Accelerate Digital Infrastructure and Skills Development
- Leverage India's digital platforms to create a skills ecosystem and modernize vocational training.
3. Boost R&D Expenditure
- Increase public R&D spending to 2% of GDP by 2030, focusing on key sectors like renewable energy.
4. Foster an Innovation-Driven Manufacturing Policy
- Shift focus to high-value specialized manufacturing rather than competing in mass production.
5. Integrate Skills and Education
- Align educational curricula with industry needs and establish centers of excellence in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
6. Lead in Green Technology
- Scale initiatives like the International Solar Alliance and create a national carbon market.
7. Reform Market Regulations
- Liberalize product and factor markets to enhance competition and efficiency.
Conclusion
India's path out of the middle-income trap necessitates a concerted effort to boost manufacturing, foster innovation, and address productivity challenges. By leveraging digital infrastructure and enhancing skills, alongside adopting green technologies, India can create a sustainable framework for growth. Effective execution of targeted policies will be crucial for transitioning to a high-income economy.
ASEAN SUMMIT

- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
The 21st ASEAN-India Summit took place in Vientiane, Lao PDR, on 10 October 2024. This summit coincided with the 10th anniversary of India’s Act East Policy. Prime Minister Narendra Modi joined ASEAN leaders to assess the progress of the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership and set the course for future collaboration.
In his address, Prime Minister Modi reaffirmed India's strong support for ASEAN Unity, ASEAN Centrality, and the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific. Referring to the 21st century as the “Asian century,” he emphasized the pivotal role of India-ASEAN relations in shaping Asia’s future. He highlighted the success of India’s Act East Policy, noting that in the last decade, trade between India and ASEAN had doubled to over USD 130 billion, with ASEAN becoming one of India’s top trade and investment partners. He also pointed out direct flight connections with seven ASEAN countries, advancements in Fin-tech collaborations, and efforts to restore shared cultural heritage in five ASEAN nations. PM Modi also stressed the importance of completing the review of the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement (AITIGA) promptly to unlock greater economic potential. He spoke about the progress made in the India-ASEAN knowledge partnership, particularly through scholarships for ASEAN students at Nalanda University.
In line with the summit’s theme of ‘Enhancing Connectivity and Resilience", PM Modi announced a 10-point plan, which includes:
- Celebrating 2025 as the ASEAN-India Year of Tourism, with USD 5 million allocated for joint initiatives.
- Marking a decade of the Act East Policy through people-centric activities like a Youth Summit, Start-up Festival, Hackathon, Music Festival, ASEAN-India Network of Think Tanks, and Delhi Dialogue.
- Organizing an ASEAN-India Women Scientists Conclave under the ASEAN-India Science and Technology Development Fund.
- Doubling scholarships at Nalanda University and offering new scholarships for ASEAN students at Indian agricultural universities.
- Reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement by 2025.
- Enhancing disaster resilience, with India contributing USD 5 million.
- Initiating a new Health Ministers’ track for building health resilience.
- Establishing a regular ASEAN-India Cyber Policy Dialogue to strengthen digital and cyber resilience.
- Hosting a workshop on Green Hydrogen.
- Inviting ASEAN leaders to join the ‘Plant a Tree for Mother’ campaign to promote climate resilience.
During the summit, leaders agreed to develop a new ASEAN-India Plan of Action (2026-2030) to guide future cooperation and adopted two joint statements:
- Joint Statement on Strengthening ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership for Peace, Stability, and Prosperity in the Indo-Pacific, highlighting the role of India’s Act East Policy in advancing the ASEAN-India relationship.
- ASEAN-India Joint Statement on Advancing Digital Transformation, recognizing India’s leadership in digital transformation and embracing a partnership in digital public infrastructure.
Prime Minister Modi expressed his gratitude to the Prime Minister of Laos for successfully hosting the summit and to Singapore for its role as Country Coordinator over the past three years. He looked forward to working with the Philippines, the new Country Coordinator for India.
ABOUT Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- ASEAN is a political and economic organization focused on fostering economic growth and regional stability among its member countries.
- The member states include Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN was founded in 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand, with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by its original members: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand. Brunei Darussalam joined in 1984, followed by Vietnam in 1995, Lao PDR and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999.
ASEAN Summit:
- This is ASEAN’s highest decision-making body, consisting of the heads of state or government of member nations. The summit is held twice a year.
- The first ASEAN Summit took place in 1976 in Bali, Indonesia.
The Mental Health Crisis in India

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
India faces a significant mental health crisis, driven by various factors including economic disparities, social isolation, and changing family dynamics. The pandemic further worsened these issues, leading to detrimental effects on mental well-being.
Causes of Mental Illness
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, violence, inequality, and environmental deprivation contribute to rising mental health issues.
- Pandemic Impact: Lockdowns and uncertainties have heightened stress levels and anxiety.
- Adverse Life Experiences: Trauma, abuse, and dysfunctional family relationships can severely impact mental health.
- Cultural Pressures: The urban focus on consumerism and status can lead to feelings of inadequacy and dissatisfaction.
The Shortage of Mental Health Professionals
India's mental health services are severely lacking, with only 0.75 psychiatrists per 100,000 population—far below the World Health Organization's recommendation of three. This shortage underscores the need for policy interventions and incentives to increase the supply of mental health professionals.
Government Initiatives for Mental Health
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to improve mental health care:
- National Mental Health Programme (NMHP): Launched in 1982 to enhance community-based mental health services.
- Mental Healthcare Act, 2017: Decriminalized suicide attempts and introduced advanced directives for treatment choices.
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2017: Recognizes mental illness as a disability, enhancing rights for affected individuals.
- Manodarpan Initiative: Provides psycho-social support to students.
- Kiran Helpline: A suicide prevention helpline for crisis management.
- National Tele-Mental Health Programme: Launched in 2022 to expand access to mental health services, particularly in underserved areas.
Economic Survey 2023-24
For the first time, the Economic Survey emphasized the importance of mental health in policy recommendations, calling for effective implementation of mental health initiatives to address existing gaps.
Understanding Healthy Workplaces
Defining a Healthy Workplace
A healthy workplace fosters collaboration between employers and employees to promote physical and psychological safety. It encompasses open communication, respect, and a supportive environment, crucial for addressing workplace stress, anxiety, and burnout.
Current Crisis: Overwork and Mental Health
The phenomenon of ‘Karoshi’ (death from overwork) highlights the severe consequences of workplace stress. In India, 40% of employees report high stress levels due to excessive work demands.
Ethical Perspectives on Healthy Workplaces
Creating a healthy workplace involves:
- Fairness and Equity: Ensuring all employees have equal access to resources and opportunities.
- Respect for Individual Dignity: Acknowledging contributions and fostering psychological safety.
- Moral Responsibility of Employers: Providing a safe working environment and promoting mental health initiatives.
- Transparency and Accountability: Building trust through open communication about policies and practices.
- Promoting Work-Life Balance: Encouraging a balance between professional and personal life to prevent burnout.
Global Precedents for Work-Life Balance
Countries like Australia and France have introduced regulations, such as the ‘right to disconnect,’ allowing employees to disengage from work communications after hours.
Conclusion and Way Forward
Establishing healthy workplaces is not merely a regulatory compliance issue but an ethical commitment to employee well-being. Both employers and employees must collaborate to create an environment of psychological safety, open communication, and mutual respect. By prioritizing these principles, organizations can foster workplaces that enhance productivity and support mental health, ultimately driving innovation and improving overall well-being.
MeitY relaxes AI compute procurement norms for Start-ups

- 09 Oct 2024
Overview
The Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) has relaxed certain provisions related to the procurement of computing capacity for artificial intelligence (AI) solutions. This decision is part of the Rs 10,370 crore IndiaAI Mission, aimed at enhancing the country’s AI capabilities.
Key Relaxations
Annual Turnover Requirements
- Primary Bidders: Turnover requirement reduced from ?100 crore to ?50 crore.
- Non-Primary Consortium Members: Requirement halved from ?50 crore to ?25 crore.
Computing Capacity Adjustments
- The performance threshold for successful bidders has been revised:
- FP16 Performance: Reduced from 300 TFLOPS to 150 TFLOPS.
- AI Compute Memory: Reduced from 40 GB to 24 GB.
Importance of the Changes
These adjustments respond to concerns raised by smaller companies about exclusionary requirements that favored larger firms. The aim is to create an inclusive environment that allows start-ups to participate in the AI landscape.
AI Mission Goals
- Establish a computing capacity of over 10,000 GPUs.
- Develop foundational models with capacities exceeding 100 billion parameters.
- Focus on priority sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
New Technical Criteria
- Companies must demonstrate experience in offering AI services over the past three financial years.
- Minimum billing of ?10 lakh required for eligibility.
Local Sourcing Requirements
- Components for cloud services must be procured from Class I or Class II local suppliers as per the ‘Make in India’ initiative:
- Class I Supplier: Domestic value addition of at least 50%.
- Class II Supplier: Local content between 20-50%.
Data Sovereignty and Service Delivery
- All AI services must be delivered from data centres located in India.
- Data uploaded to cloud platforms must remain within India's sovereign territory.
Implementation Strategy
- The Rs 10,370 crore plan will be implemented through a public-private partnership model.
- 50% viability gap funding has been allocated for computing infrastructure development.
Conclusion
The relaxations in AI compute procurement norms aim to support the growth of start-ups in India, fostering an environment conducive to innovation in artificial intelligence. With these changes, smaller companies are better positioned to contribute to the country's ambitious AI goals.
How India can harness the power of AI to become a Trailblazer

- 08 Oct 2024
Introduction
India stands at the forefront of an AI revolution, poised to leverage its unique position for unprecedented growth and innovation. With a robust economic outlook, the nation is ready to transform its AI capabilities.
Economic Landscape
Projected Growth
- Nomura estimates India's economy will grow at an average rate of 7% over the next five years, surpassing the IMF's global growth forecast of 3.2% for 2024.
- Hosting the G20 and Global Partnership on AI meetings in 2023 has created a favorable geopolitical environment.
Market Potential
- India’s AI market is expected to reach $17 billion by 2027, with a growth rate of 25-35% annually from 2024 to 2027 (Nasscom).
- The country leads Asia Pacific in the use and adoption of Generative AI, with significant engagement from students and employees.
The Role of Industry
Driving Transformation
- Similar to historical industrial leaders, India Inc has the potential to drive significant change across various sectors.
- The goal is to transition from participation to leadership in the global AI ecosystem.
Sector-Specific Strategies
- Industries must align AI capabilities with specific sectoral goals by mapping challenges, opportunities, and ambitions.
Case Study: Logistics Sector
Historical Inefficiencies
- A decade ago, the logistics sector in India faced significant inefficiencies.
AI Integration
- Traditional AI introduced automation and basic forecasting. Companies like PandoAI have leveraged AI to consolidate supply chain data and provide valuable analytics.
- The integration of Generative AI can further enhance predictive capabilities and innovative solutions.
Infrastructure and Investment
Current Challenges
- India generates 20% of the world’s data but has only 2% of global data centers, limiting technological advancement.
Government Initiatives
- Plans to procure 10,000 GPUs in the next 18-24 months and a National Semiconductor Mission to establish a domestic chip industry.
Need for Industry Investment
- Collaboration between government and industry is crucial to meet the growing demands for computing power.
Talent Development
Workforce Dynamics
- Hiring of AI talent increased by 16.8% in 2023, indicating a rising focus on AI capabilities.
- Many Indian-origin AI professionals work for international companies, highlighting the need for local opportunities.
Educational Initiatives
- Programs like FutureSkills PRIME should be expanded to enhance talent development in AI.
Ethical Standards and Governance
Importance of Trust
- Establishing trustworthy AI standards is essential for consumer confidence and sustainable operation.
- Challenges such as bias and data security require robust governance frameworks.
Operationalizing Ethics
- Develop AI governance frameworks addressing ethical concerns and data security.
- Ensure transparency in AI algorithms and decision-making processes.
- Promote inclusive AI development by engaging diverse perspectives.
- Invest in ethical AI research through collaborations with academic institutions.
Conclusion
India’s commitment to a strategic vision, substantial investment, and adherence to trustworthy AI practices can position it as a global leader in the AI landscape. This is a pivotal moment for India to harness AI's transformative power, paving the way for a new era of economic prosperity.
National Agriculture Code (NAC)

- 07 Oct 2024
Introduction
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is in the process of developing the National Agriculture Code (NAC), which aims to establish standardized practices across the agricultural sector. This initiative mirrors existing frameworks such as the National Building Code and the National Electrical Code.
Purpose of the National Agriculture Code
The NAC seeks to standardize agricultural practices throughout the entire agricultural cycle, ensuring consistency and quality in farming operations. It will serve as a comprehensive guide for farmers, agricultural institutions, and policymakers.
Structure of the NAC
The NAC will be divided into two main parts:
- General Principles: Applicable to all crops, providing a foundational framework.
- Crop-Specific Standards: Tailored standards for key crops such as paddy, wheat, oilseeds, and pulses.
Coverage of the NAC
The code will encompass a wide range of agricultural processes, including:
- Agricultural Cycle: From crop selection to post-harvest operations.
- Post-Harvest Operations: Including standards for storage, processing, and traceability.
- Emerging Practices: Guidelines for natural and organic farming, as well as the integration of Internet-of-Things (IoT) technologies.
- Input Management: Recommendations for the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and weedicides.
Objectives of the National Agriculture Code
The BIS outlines several key objectives for the NAC:
- Standardization: Create a national code that reflects the diverse agro-climatic zones and socio-economic conditions across India.
- Quality Culture: Act as a reference for policymakers and regulators to enhance agricultural quality.
- Guidance for Farmers: Provide a practical guide to assist farmers in making informed decisions.
- Integration of Standards: Combine existing Indian standards with agricultural practices.
- Modernization: Emphasize aspects such as SMART farming, sustainability, and documentation.
- Capacity Building: Support training programs conducted by agricultural extension services.
Implementation Timeline
The BIS has established working panels comprising university professors and research organizations to draft the NAC, with a target completion date set for October 2025. Following this, training programs for farmers will be organized, facilitated by universities with financial assistance from the BIS.
Standardized Agriculture Demonstration Farms (SADF)
In conjunction with the NAC, the BIS is launching Standardized Agriculture Demonstration Farms (SADFs) at select agricultural institutions. These farms will serve as experimental sites to test and implement agricultural practices aligned with Indian standards. Partnerships with prominent agricultural institutes are being formalized through Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs), with two agreements already signed, including one with Govind Ballabh Pant University of Agriculture and Technology.
Significance of the NAC
- Uniform Standards: Promotes best practices in diverse agricultural environments.
- Stakeholder Guidance: Provides a structured framework for informed decision-making.
- Support for Modern Techniques: Encourages the adoption of innovative practices and technologies.
- Farmer Empowerment: Facilitates training and capacity building for enhanced productivity.
Challenges and Limitations
- Implementation Barriers: Standardizing practices across varied climates and soil conditions may prove challenging.
- Adoption Resistance: Smaller farmers might struggle with resource availability or awareness of new practices.
- Dynamic Agricultural Needs: The need for frequent updates to the NAC to keep pace with evolving agricultural trends.
- Infrastructure Constraints: Rural areas may lack the necessary infrastructure to effectively implement NAC guidelines.
Conclusion
The National Agriculture Code represents a pivotal move towards modernizing and standardizing agricultural practices in India. While it aims to enhance productivity and sustainability, its success hinges on effective implementation, farmer engagement, and ongoing updates to meet the changing landscape of agriculture.
Fairwork India Report
- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
The Fairwork India Ratings 2024 report, which analyses the work conditions of platform workers on digital labour platforms in India, draws a picture of aggregators who are non-committal to ensuring that workers earn the local living wage and unwilling to recognise collectivisation of workers.
Key Findings:
- Overall Performance: No platform scored above six out of ten, and none achieved top points across the five assessed principles: Fair Pay, Fair Conditions, Fair Contracts, Fair Management, and Fair Representation.
- Study Background: This report is the sixth annual analysis conducted by the Fairwork India Team, in collaboration with the Centre for IT and Public Policy (CITAPP), IIIT-Bangalore, and Oxford University.
Analysis of Welfare Legislation
- The report discusses the evolving nature of platform work and its implications for proposed legislation affecting gig workers in Karnataka and Jharkhand.
- Political interest in gig workers' welfare has increased, but the effectiveness of these initiatives remains uncertain.
- Professors Balaji Parthasarathy and Janaki Srinivasan highlight the importance of ongoing research and advocacy for improving gig worker conditions.
Methodology
- Principles of Assessment: Platforms were evaluated based on five principles, each consisting of two points—one that could only be awarded if the first point was fulfilled.
- Data Collection: Worker interviews were conducted across multiple cities, including Bengaluru, Chennai, Delhi, Kochi, and Thiruvananthapuram.
- Platforms Analyzed: The study included 11 platforms from various sectors, such as logistics, food delivery, and personal care.
Detailed Findings by Principle
Fair Pay
- First Point: Bigbasket and Urban Company were recognized for implementing a minimum wage policy ensuring workers earn at least the local minimum wage.
- Second Point: No platform met the criteria for committing to a local living wage after work-related costs.
Fair Conditions
- First Point: Platforms such as Amazon Flex, BigBasket, and Swiggy provided adequate safety equipment and training.
- Second Point: BigBasket, Swiggy, Urban Company, Zepto, and Zomato offered additional protections, including accident insurance and compensation for medical-related work absences.
Fair Contracts
- First Point: BigBasket, BluSmart, and others ensured contract accessibility and data protection protocols.
Fair Management
- First Point: Amazon Flex, BigBasket, and several others provided due process in disciplinary decisions.
- Second Point: BluSmart, Swiggy, Urban Company, and Zomato were noted for regular external audits and anti-discrimination policies.
Fair Representation
- Despite increased collectivization efforts among platform workers, no platform showed a willingness to recognize collective bodies, underscoring a critical gap in worker representation.
Conclusion
The Fairwork India Ratings 2024 report highlights significant challenges in ensuring fair work conditions for platform workers in India, stressing the need for continuous advocacy and reform in the gig economy.
National Urban Livelihood Mission (NULM)

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
The Government is set to launch NULM 2.0, the latest iteration of the National Urban Livelihood Mission (NULM), aimed at enhancing the livelihoods of urban poor and vulnerable populations. This version will specifically target six key groups: construction workers, gig workers, waste management workers, care workers, domestic workers, and transportation workers.
Overview of DAY-NULM
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM) was initiated in 2014 by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs to replace the Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rozgar Yojana. It aims to uplift urban poor through organized self-help groups (SHGs), skill development, and access to credit.
Key Features:
- Funding Structure: DAY-NULM operates as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, with a funding ratio of 75:25 between the central and state governments, adjusted to 90:10 for North Eastern and Special Category states.
- Mobilization of Women: The mission has successfully formed over 831,000 SHGs, mobilizing more than 8.4 million urban poor women by 2023.
- Objectives: It focuses on sustainable livelihoods through skill development, financial access, and entrepreneurship, particularly for women.
Components and Achievements
DAY-NULM includes various initiatives such as:
- Skill training programs.
- Support for self-employment.
- Rehabilitation for street vendors.
Performance Highlights:
- Over 89.33 lakh women have joined SHGs, with 6.12 lakh receiving initial funds.
- Approximately 15 lakh individuals have undergone skill training, leading to employment for 8.20 lakh.
- Surveys have identified 53.76 lakh street vendors, resulting in significant documentation and support.
Introduction of NULM 2.0
NULM 2.0 is a revamped initiative designed to further support urban livelihoods through financial aid and infrastructure enhancements.
Key Features:
- Microcredit Access: Eligible individuals can obtain microcredit of up to ?4 lakh, while groups can access up to ?20 lakh, with a subsidized interest rate of 5%.
- Support for Enterprises: The funding aims to assist beneficiaries in starting small businesses, creating social infrastructure, and providing grants for innovative projects, such as sanitation machinery.
Pilot Initiative
To effectively implement NULM 2.0, the government will conduct a pilot program in 25 cities. This will focus on:
- Identifying urban poor populations.
- Ensuring targeted assistance to improve beneficiaries’ earnings and living conditions.
Conclusion
The rollout of NULM 2.0 represents a significant step in addressing the needs of the urban poor, with a comprehensive framework designed to provide financial support and improve livelihoods. By focusing on critical worker groups and leveraging microcredit, the initiative aims to foster sustainable development and enhance the quality of life for urban vulnerable communities.
Bihar Under Water: An Analysis of Recurring Floods
- 04 Oct 2024
Overview
Bihar is one of India's most flood-prone states, with 11.84 lakh people affected by annual flooding. The state grapples with the devastation of homes, crops, and livestock, prompting a cycle of recovery only to face similar disasters each year.
Geographical Vulnerabilities
Flood-Prone Conditions
- Demographics: 76% of North Bihar’s population lives under the threat of floods.
- River Systems: The state is crisscrossed by multiple snow-fed and rain-fed rivers, contributing to various flood types:
- Flash Floods: Rapid onset due to rainfall in Nepal (lead time: 8 hours).
- River Floods: Slower onset with a lead time of 24 hours, lasting over a week.
- Drainage Congestion: Extended flooding throughout the monsoon season (lead time: over 24 hours).
- Permanent Waterlogging: Caused by various factors including sedimentation and encroachments.
Factors Contributing to Flooding
- Himalayan Rivers: Rivers like Kosi, Gandak, and Bagmati carry significant sediment, leading to overflow during heavy rains.
- Waterlogging Causes: Silted rivers, encroachment of drainage channels, and local topographical features called Chaurs contribute to permanent waterlogging.
Historical Management Efforts
Embankments and Their Impact
- Kosi River: Known as the "sorrow of Bihar," embankments built in the 1950s to control the Kosi’s flow have led to unintended consequences.
- Sediment Accumulation: Narrowing of the river’s course has caused sediment to build up, increasing the riverbed height and flood risks.
- Current Crisis: Recent flooding was exacerbated by the release of 6.6 lakh cusec of water from the Birpur barrage in Nepal, leading to multiple embankment breaches.
Economic and Social Effects
Impact on Livelihoods
- While annual flooding may not always lead to significant loss of life, the economic repercussions are severe:
- Damage to crops and infrastructure.
- Loss of livestock and economic migration outside the state.
- Government Spending: Approximately Rs 1,000 crore is allocated annually for flood management and relief efforts.
Proposed Solutions
Structural vs. Non-Structural Approaches
- Dam Construction: Proposals for new barrages on the Kosi and other rivers have been discussed, but require cooperation from Nepal.
- Need for Comprehensive Strategies: Experts suggest a dual approach:
- Structural Solutions: Dams and embankments.
- Non-Structural Solutions: Policy development, risk mitigation, and improved community awareness.
Emphasis on Risk Reduction
- The Flood Atlas of Bihar advocates for minimizing flood risk rather than relying solely on structural measures.
- Focus on enhancing early warning systems and community preparedness is crucial for effective flood management.
Conclusion
Bihar’s unique geographical and socio-economic landscape necessitates a multifaceted approach to flood management. While structural solutions like dams are important, the state must also invest in non-structural measures that promote resilience and reduce vulnerability among its population.
Tax Crackdown on NGOs: Overview and Allegations
- 03 Oct 2024
Introduction
In recent months, the Income Tax (I-T) Department has intensified scrutiny of several non-governmental organizations (NGOs) in India, linking them to allegations of misconduct, particularly in relation to foreign funding and activities that allegedly stall economic development. The investigation, which began with searches on September 7, 2022, targets prominent NGOs such as Oxfam, the Centre for Policy Research (CPR), and others.
Background of the Investigation
Triggering Events
The I-T probe was initiated following extensive searches at the premises of five major NGOs, including Oxfam, CPR, Environics Trust (ET), the Legal Initiative for Forest and Environment (LIFE), and Care India Solution for Sustainable Development (CISSD).
Key Allegations
The investigation highlights several critical allegations:
- Foreign Funding: Over 75% of funding for four of the NGOs during a five-year period was sourced from abroad, which is claimed to shape their activities in India.
- Interconnections: There are allegations of overlapping personnel and funding connections between these NGOs.
- Legal Challenges: Following the cancellation of their Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) licenses, these organizations have filed legal challenges that are currently under review by the Delhi High Court.
Violations of the FCRA
The I-T department asserts that these NGOs violated multiple provisions of the FCRA, including discrepancies in annual returns and misappropriation of foreign funds. The cancellation of their FCRA licenses has led to heightened scrutiny and legal ramifications.
Specific NGO Allegations
- Oxfam India
- Accused of supporting foreign entities in efforts to halt mining projects by the Adani Group, violating its stated charitable objectives.
- Allegations include attempts to redirect funds through other NGOs post-FCRA cancellation.
- Centre for Policy Research (CPR)
- Charged with mishandling foreign donations and involvement in environmental litigation, notably the Hasdeo movement against coal mining in Chhattisgarh.
- Received substantial funding for its Namati-Environmental Justice Programme, purportedly to facilitate legal actions rather than educational initiatives.
- Environics Trust (ET)
- Allegedly funded protests against significant industrial projects, including JSW’s Utkal Steel Plant.
- Claims of collaboration with international organizations to impede development projects, particularly coal initiatives.
- Legal Initiative for Forest and Environment (LIFE)
- Accused of being used as a conduit by the US-based Earth Justice to obstruct coal mining and thermal projects in India.
- Internal communications allegedly reveal awareness of their controversial activities.
Interconnected Operations
The investigation indicates that these NGOs may be working in concert, as highlighted by the I-T department:
- Funding Networks: For instance, Oxfam is cited as a primary funder of ET, allegedly to mobilize local communities against coal industries.
- Personnel Links: Relationships between key figures in these organizations, such as the former president of CPR, who is also associated with Care India, raise concerns about coordinated efforts.
Responses from NGOs
Denial of Allegations
The allegations have been met with strong denials from the NGOs involved. Ritwick Dutta, founder of LIFE, characterized the claims of interlinking as baseless, asserting that his organization operates independently and has no financial ties to Oxfam or CPR.
Lack of Official Responses
Other NGOs, including Oxfam and CPR, have not officially responded to the I-T department's accusations, leaving some questions unanswered regarding their operational practices.
The Role of Civil Society Organizations (CSOs) in India
Definition and Importance
CSOs encompass a range of nonprofit organizations that operate independently from the government. In India, these include:
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs): Primarily focused on community welfare and development across various sectors.
- Community-Based Organizations (CBOs): Grassroots entities that directly serve local needs and interests.
Impact and Challenges
CSOs play a crucial role in advocating for vulnerable populations and addressing social issues. However, they face significant challenges, including scrutiny over funding sources and operational transparency, especially amid increasing governmental oversight.
Conclusion
The ongoing investigation into these NGOs raises critical questions about the relationship between civil society and government regulation in India. While the I-T department's crackdown aims to ensure compliance with foreign funding regulations, the implications for activism and public participation in developmental issues remain contentious. As the legal proceedings unfold, the future of these organizations and their missions may be at stake.
Women Entrepreneurship Platform

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
Telangana has become the first state in India to establish a chapter of NITI Aayog’s Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP), aimed at promoting and supporting women entrepreneurs across various sectors.
Overview of WEP
- Objective: To provide women entrepreneurs access to resources, tools, and networks for business growth.
- Previous Operation: WEP was primarily a Central Government initiative before this chapter's establishment.
Launch Details
- Event: The WEP Telangana Chapter was launched in Hyderabad.
- Key Figures:
- NITI Aayog CEO BVR Subrahmanyam
- State IT and Industries Secretary Jayesh Ranjan
- Co-chair of WEP Sangeetha Reddy
Customised Support for Women Entrepreneurs
- Services Offered:
- Digital skilling
- Access to financial services
- Mentorship
- Market linkages
- Implementation Body: WE Hub will serve as the nodal body for the scheme in the state, leveraging its expertise to empower women entrepreneurs.
Importance of Women Entrepreneurship
- Economic Impact: Emphasis the crucial role of women entrepreneurship in India's economic future.
- Challenges Addressed: The initiative aims to overcome barriers faced by women entrepreneurs in finances, mentoring, and marketing.
Future Expansion Plans
- Vision for Growth:
- Principal Economic Advisor Anna Roy outlined plans to expand WEP to tier 2 and 3 cities.
- The initiative aims to build an inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem through a hub-and-spoke model.
WE Bridge Initiative
- Leadership: WE Hub CEO Sita Pallacholla appointed as mission director for the WEP Telangana Chapter.
- State’s Advantages: Telangana was chosen for its supportive environment for entrepreneurship in Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and its robust innovation ecosystem.
- WE Bridge: Introduced as a single-window platform for women entrepreneurs in the state.
Benefits of the Partnership
- Access to Resources: The collaboration with NITI Aayog will enhance opportunities for women, providing access to funding, technology, and networks.
- Mentoring Emphasis: Sangeetha Reddy highlighted the critical role of mentoring in business success.
Objectives of WEP Telangana
- Skill Empowerment: Enhance digital technology and financial literacy among women entrepreneurs.
- Mentorship Connections: Link women entrepreneurs with industry leaders for guidance in business development, marketing, and scaling.
- Market Access: Facilitate connections with potential investors and industry partners through WE Hub’s extensive network.
What is the Unified Lending Interface by the RBI?

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), as part of its strategy to create digital public infrastructure in the country, has announced that a new technology platform called the Unified Lending Interface (ULI) would be introduced by the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub, Bengaluru which will enable friction-less credit to farmers and MSME borrowers to begin with.
What is ULI?
The ULI platform, aims to revolutionize the credit underwriting process by enabling a streamlined and consent-based transfer of both financial and non-financial data from various sources to lenders.
- Seamless Data Flow: ULI facilitates an efficient flow of digitized data, including crucial records like land titles, directly to lenders, enhancing the credit appraisal process.
- Faster Credit Appraisal: The platform is particularly beneficial for smaller and rural borrowers who may lack extensive credit histories, significantly reducing the time required for credit assessments.
- Standardized APIs: ULI employs common, standardized Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that allow for a plug-and-play integration, simplifying the technical requirements for lenders and ensuring easy access to diverse data sources.
- Access to Diverse Data: Lenders can access a wealth of information from various databases, including government records and satellite imagery, which can provide deeper insights into potential borrowers.
- Opportunities for FinTechs: The platform also opens up opportunities for FinTech companies by connecting them with multiple lenders, thereby enhancing their ability to deliver tailored financial solutions.
ULI aims to create a more inclusive and efficient lending ecosystem, ultimately improving access to credit for a wider range of borrowers.
How will it work?
The ULI platform transforms the loan application process, especially for first-time borrowers and those without traditional credit histories. Here’s how it works:
- Centralized Data Access: ULI acts as a single point of access for lenders to retrieve crucial economic data about loan applicants. This reduces the need for applicants to gather extensive documentation themselves.
- Plug-and-Play Integration: Financial institutions can easily connect to the ULI platform through standardized APIs, allowing them to quickly access various data sources relevant to the borrower’s financial history and status.
- Automated Data Retrieval: Instead of borrowers spending weeks collecting documents, lenders can automatically fetch necessary information from the platform. For instance, data for a dairy farmer may include:
- Cash Flow Information: Sourced from local milk cooperatives.
- Land Ownership: Verified through state land records.
- Financial Insights: Derived from the farmer’s historical farming patterns.
- Enhanced Visibility: This comprehensive data access turns what were previously blind spots for lenders into clear insights, allowing them to assess applicants more accurately.
- Rapid Decision-Making: With immediate access to essential data, lenders can quickly determine the borrower’s income and creditworthiness. This streamlines decision-making, enabling loans to be sanctioned and disbursed within minutes.
- Supporting Tenant Farmers: Tenant farmers, who typically struggle to obtain loans due to lack of land titles, can also benefit. ULI can facilitate loans by allowing banks to verify identity and eligibility based on the intended use of funds for agricultural inputs rather than land ownership.
In summary, ULI simplifies the loan process, making it faster and more inclusive for diverse borrowers by leveraging digital data access and automation.
How did it start?
The ULI platform, officially launched by the RBI on August 10, 2023, emerged from the need for a streamlined approach to credit appraisal in an increasingly digital landscape. Here’s how it all began:
- Identification of Need: The RBI recognized that with rapid digitalization, there was a pressing need for a centralized platform to provide access to the data necessary for credit assessments. This was essential for facilitating frictionless digital credit delivery.
- Pilot Project: To test the concept, the RBI initiated a pilot project focused on the digitalization of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans under ?1.6 lakh in September 2022. This pilot was launched in select districts across Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Encouraging Results: The initial outcomes of the KCC pilot were promising, showcasing the potential for seamless loan disbursement. The pilot demonstrated that loans could be disbursed at the doorstep, either through assisted or self-service modes, all without the need for extensive paperwork.
- Development of ULI: Building on the success of the KCC pilot, the RBI moved forward with the establishment of the ULI platform to broaden the scope of digital credit accessibility for a wider range of borrowers.
Drone Technology in Agriculture

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Farmers in Bhagthala Khurd, Kapurthala, and Amritsar are increasingly using drones to apply pesticides to their maize and moong crops. Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are advanced flying machines that can be operated either autonomously or via remote control.
Drone Technology in Agriculture
While the use of drones in Indian agriculture is still emerging, it shows great potential. In Punjab, 93 out of the 100 drones provided to farmers by the Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO) under the Centre’s ‘NAMO Drone Didi’ scheme are already in operation. Each drone, costing Rs 16 lakh, is equipped with a 12-litre water tank.
Benefits
- Health Protection: Drones minimize farmers' direct exposure to harmful pesticides, reducing the risk of health issues like cancer and kidney problems.
- Efficiency: Drones can spray an acre in just 5-7 minutes, significantly faster than the several hours required for manual application. They ensure a uniform application, which can enhance crop yields.
- Data Collection: Drone data helps pinpoint areas requiring attention, leading to better crop management and increased profits.
- Nano Fertilisers: Drones effectively handle nano fertilisers, ensuring even distribution of these small quantities that are difficult to spread manually.
- Pest Control: Drones enable timely application of pesticides during infestations of pests such as pink bollworms, locusts, and whiteflies.
- Environmental Benefits: Drones improve nutrient absorption from nano fertilisers by up to 90%, reducing runoff and pollution. Leaf-based application is also less polluting than soil-based methods.
- Water Conservation: Drones reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional methods.
- Cost Reduction: They decrease the need for manual labor and reduce pesticide and chemical use, lowering overall costs.
- Additional Uses: Drones are also used to drop seed balls (a mix of soil and cow dung with seeds) for potential reforestation projects.
Challenges
- Job Loss: The use of drones may reduce demand for manual labor, affecting job opportunities for laborers.
- Knowledge and Training: Farmers may lack the necessary skills and training to operate drones effectively.
- Cost: The high cost of drones can be a significant barrier for many farmers.
- Regulatory Barriers: Regulatory challenges may complicate the adoption of drones in agriculture.
Initiatives
- Digital India Campaign: Aims to enhance digital infrastructure and provide training.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR): Promotes precision agriculture technologies, including drones.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: Offers Rs. 120 crore (US$ 14.39 million) to incentivize domestic drone manufacturing and reduce import reliance.
- Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM): Provides financial aid to farmers purchasing drones, making technology more accessible.
- NAMO Drone Didi Scheme: Launched to empower women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and provide access to modern agricultural technology.
- Support and Training: Efforts are underway to offer training and support to farmers to overcome adoption barriers.
Conclusion and Way Forward
Drone technology holds the promise of transforming agriculture by boosting efficiency, yields, and cost-effectiveness. In Punjab, where traditional manual methods have prevailed, drones offer a new approach to pesticide and fertiliser application. It is essential for farmers and policymakers to work together to address challenges and ensure that the benefits of drones are fully realized while mitigating any potential drawbacks.
What does spaceflight do to the human body?
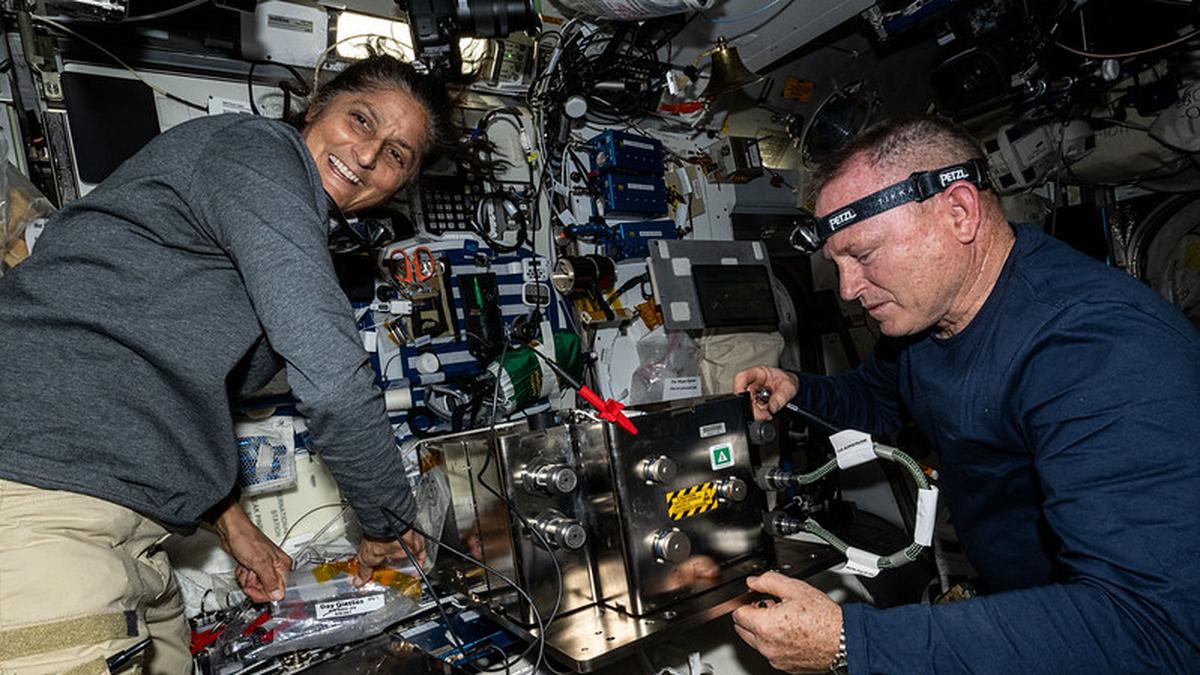

- 01 Sep 2024
In News:
- On August 24, 2023, NASA announced that Boeing’s Starliner crew capsule was deemed unsafe for the return of astronauts Sunita Williams and Barry Wilmore from the International Space Station (ISS).
- Williams and Wilmore’s stay onboard the ISS has been extended until February 2025, with their return planned via a SpaceX crew capsule in September 2024.
- Starliner will undock and return uncrewed.
Understanding Space
Definition and Characteristics
- What is Space?
- Space is defined as the area above the Karman line (100 km above sea level), transitioning from ‘earth-like’ to ‘space-like’ conditions.
- Microgravity Explained
- Astronauts experience microgravity due to the diminishing force of gravity, not complete absence, leading to various physiological effects.
Environmental Challenges
- Radiation in Space
- The Van Allen radiation belts, located above the Karman line, pose a significant challenge, exposing astronauts to charged particles.
- Historical research during the Apollo program determined that exposure levels in these belts are not harmful.
Effects of Space on the Human Body
Physiological Changes
- Bone Health: Microgravity leads to bone weakening, potentially causing renal stones due to excess mineral deposition.
- Digestive Issues: Food movement slows, contributing to potential weight gain.
- Eye Health: Spaceflight-associated neuro-ocular syndrome (SANS) affects about 20% of astronauts, with 70% of long-duration astronauts affected, causing vision impairment.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Reduced workload on the heart can result in muscle shrinkage.
- Muscle and Blood Changes: Muscle mass and strength decline; increased loss of red blood cells necessitates dietary adjustments.
Cognitive and Psychological Factors
- Balance and Orientation: Altered signals in microgravity challenge the brain's ability to maintain balance.
- Psychological Impacts: Isolation, fatigue, and stress from family separation contribute to mental health challenges.
Mitigating the Effects of Space
Strategies and Research
- Exercise and Routines: Strict exercise regimens and predictable routines are critical for maintaining astronaut health during missions.
- Nutritional Adjustments: Research is ongoing into how nutrients and drugs are metabolized in space.
- Monitoring and Countermeasures: Development of portable optical coherence tomography machines for SANS detection is underway, alongside potential countermeasures like lower body negative pressure and artificial gravity exposure.
Ongoing Research Initiatives
- Understanding Spaceflight Effects: The "space omics" studies aim to identify how space environments affect human biology, exemplified by NASA’s Twins Study.
- International Collaboration: Programs like Japan’s KAKENHI and Europe’s Space Omics Topical Team, along with U.S. research protocols, are exploring biological responses to space conditions.
Duration of Human Space Missions
Historical Context and Current Trends
- Increased Duration: The average time spent in space has risen from one month in the 1960s to six months in the 2020s.
- Current Missions
- Williams and Wilmore will potentially spend 256 days in orbit.
- Record holders: Valeri Polyakov (437 days), Frank Rubio (370 days), and Oleg Kononenko (over 1,000 days across missions).
Future Aspirations
- Long-Duration Missions: The shift from lunar missions to potential permanent moon bases and human missions to Mars presents new challenges in safety and health for astronauts.
DRAFT GUIDELINES ON PASSIVE EUTHANASIA IN INDIA

- 30 Sep 2024
Introduction
The Union Health Ministry of India has released new draft guidelines regarding passive euthanasia, aiming to address the complexities surrounding the withdrawal of life support for terminally ill patients. This move is significant, as it provides clarity for both medical professionals and patients regarding end-of-life care. The guidelines represent an effort to bridge the existing regulatory gap, ensuring ethical practices in sensitive medical decisions.
Understanding Euthanasia
Definition and Types
Euthanasia refers to the practice of intentionally ending a patient's life to alleviate suffering. The term originates from Greek, meaning "good death." Euthanasia can be categorized into several types:
- Active Euthanasia: Actively causing death, such as administering a lethal injection.
- Passive Euthanasia: Withholding life-sustaining treatments, allowing death to occur naturally.
- Voluntary Euthanasia: Conducted with the patient’s consent.
- Involuntary Euthanasia: Performed without patient consent, often in cases where the patient’s wishes are unknown.
Legal Context
While active euthanasia remains illegal in India, passive euthanasia was legalized by the Supreme Court in March 2018. This legal framework allows for the withdrawal of life support under specific circumstances.
Key Provisions of the Draft Guidelines
Conditions for Withdrawal of Life Support
The guidelines stipulate four critical conditions under which life support may be withdrawn:
- Brainstem Death: The patient must be declared brainstem dead as per the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act (THOA) of 1994.
- Medical Prognosis: The patient's condition must be advanced, indicating that aggressive therapeutic interventions are unlikely to yield benefits.
- Informed Refusal: The patient or their surrogate must document an informed refusal of continued life support following an understanding of the prognosis.
- Legal Compliance: Procedures must align with the legal principles established by the Supreme Court.
Decision-Making Process
The decision to withdraw life support requires a multi-tiered approach:
- Primary Medical Board (PMB): A group of at least three physicians must reach a consensus and explain the medical situation to the patient’s surrogate.
- Secondary Medical Board (SMB): A further validation by another set of three physicians, including one appointed by the district’s Chief Medical Officer, is necessary to confirm the PMB’s decision.
Advance Medical Directives
The guidelines emphasize the importance of advance medical directives, allowing individuals to document their healthcare preferences in case they lose decision-making capacity.
Ethical Considerations
Concerns from the Medical Community
While the guidelines aim to provide clarity, there are concerns regarding the legal scrutiny that doctors may face. The Indian Medical Association (IMA) has raised issues about the potential for undue stress on medical professionals, who historically have made these decisions in good faith without formal guidelines. They argue that placing such decisions within a regulatory framework might misinterpret standard medical practices.
Patient Autonomy and Dignity
The guidelines uphold the fundamental rights to autonomy, privacy, and dignity. Patients capable of making healthcare decisions can refuse life-sustaining treatments, even if such refusals may lead to death. The emphasis on informed decision-making seeks to ensure that patients can navigate their end-of-life choices with dignity.
Implications for Policy and Practice
Need for Stakeholder Feedback
The Health Ministry has solicited feedback from stakeholders, including healthcare professionals and the public, by October 20, 2024. This participatory approach aims to refine the guidelines and address any concerns regarding their implementation.
Balancing Ethical and Practical Considerations
The draft guidelines represent a significant step towards formalizing the process of passive euthanasia in India. They attempt to balance ethical considerations surrounding patient autonomy with the practical realities faced by healthcare providers.
Conclusion
The introduction of draft guidelines on passive euthanasia marks a pivotal moment in India's healthcare landscape. By clarifying the legal and ethical frameworks surrounding end-of-life decisions, these guidelines aim to enhance the dignity of terminally ill patients while providing essential support to healthcare professionals. The ongoing discourse surrounding these guidelines will be crucial in shaping their final form and ensuring their alignment with societal values and ethical norms.
CONCERNS OVER JUDICIAL CONDUCT

- 29 Sep 2024
Background
A recent incident involving Justice V Srishananda of the Karnataka High Court has raised serious concerns regarding judicial comments and conduct. During a hearing, Justice Srishananda referred to a locality in Bengaluru as being “in Pakistan” and made an objectionable remark against a female lawyer. Although he subsequently apologized, the Supreme Court, led by Chief Justice D Y Chandrachud, expressed serious concern, highlighting the rarity of such judicial reproach.
Constitutional Framework for Judicial Discipline
Impeachment: The Sole Recourse
Judges of constitutional courts, including the Supreme Court and High Courts, enjoy substantial protections to maintain independence from executive interference. However, this raises the question of accountability: who oversees the judiciary?
- Article 124(4): This article outlines that judges can only be removed through impeachment, which requires a political process involving both Houses of Parliament. The grounds for impeachment are limited to "proved misbehaviour" or "incapacity."
- High Standards for Impeachment: The necessity for a two-thirds majority in both Houses makes successful impeachment exceedingly rare. Historically, only five impeachment proceedings have been initiated, with only one resulting in successful impeachment (Justice Soumitra Sen).
Challenges in Addressing Judicial Misconduct
Certain actions, such as indiscipline or bias, may not meet the impeachment standard but still warrant attention. The Supreme Court faces a dilemma: how to address these issues without the option of impeachment.
Mechanisms for Judicial Accountability
Judicial Intervention
The Supreme Court can intervene through judicial action, as evidenced by past cases:
- Contempt of Court: In 2017, the Supreme Court sentenced Calcutta High Court’s Justice C S Karnan to six months’ imprisonment for contempt. This case raised concerns about one constitutional court punishing judges of another, as it set a precarious precedent.
Transfer Policy
The Supreme Court also influences High Court judges through its Collegium system:
- Collegium Recommendations: The Collegium recommends the transfer of judges, which can serve as a disciplinary tool. The case of Justice P D Dinakaran illustrates this practice. Facing allegations of corruption, he was transferred from Karnataka to Sikkim, a move criticized as merely “transferring corruption.”
Conclusion
The incident involving Justice Srishananda underscores the complexities of judicial accountability in India. While the Constitution provides for impeachment as the only formal recourse against errant judges, the high threshold for such proceedings necessitates alternative mechanisms for maintaining judicial integrity. The Supreme Court's ability to intervene and the use of transfer policies are critical components in addressing judicial misconduct, but they also raise questions about the balance between accountability and judicial independence.
SOUTH CHINA SEA
- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
In recent years, maritime East Asia has emerged as a battleground for intensified power politics, particularly in the East China Sea and the South China Sea. These regions involve complex territorial disputes and geopolitical tensions, particularly concerning China, Japan, Taiwan, and several Southeast Asian nations.
Geographic and Strategic Significance
East China Sea
- Territorial Claims: The East China Sea borders China, Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea, with the Senkaku/Diaoyu islands being a focal point of contention.
- Crises: Multiple crises have erupted over these islands, reflecting deep-seated national interests.
South China Sea
- Key Players: Located between China, Taiwan, and five Southeast Asian countries—Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, the Philippines, and Indonesia.
- Flashpoint: This area has become a critical flashpoint in the Indo-Pacific, with China aggressively asserting its claims.
China's Motivations
Naval Exercises and Claims
- Naval Collaboration: China has conducted naval exercises with Russia in the South China Sea, showcasing military capabilities and reinforcing territorial claims.
- Legal Standing: Despite a 2016 ruling by a permanent court of arbitration declaring China's claims to lack legal basis, Beijing has rejected this decision.
Regional Responses to China's Actions
1. Enhancing Defence Capabilities
- Increased Defence Spending: Countries like Japan and the Philippines are significantly boosting their defence budgets, with Japan aiming to double its spending by 2027.
- Acquisition of Technology: The Philippines has acquired anti-ship BrahMos missiles from India as part of its defence enhancement efforts.
2. Addressing Maritime Activities
- Shift in Policy: The Philippines has pivoted from a conciliatory approach to actively publicizing confrontations with Chinese vessels.
- Public Diplomacy: The Philippines employs social media to document and share encounters with Chinese ships, shaping public perceptions.
3. Strengthening Alliances
- U.S. Cooperation: The Philippines, Japan, and South Korea are reinforcing their defence relationships with the U.S., expanding cooperation in various domains including joint exercises.
- Trilateral Meetings: The U.S., Japan, and South Korea have deepened their trilateral cooperation, addressing concerns about unilateral changes to the status quo in the Indo-Pacific.
U.S. Credibility and Strategic Implications
Despite efforts to bolster alliances, concerns remain regarding U.S. credibility and the impact of domestic politics on its international commitments. There is ongoing debate over whether U.S. engagement balances Chinese power or exacerbates tensions.
China’s Sovereignty Perspective
National Security Framework
- Defence White Paper: China's 2019 Defence White Paper emphasizes that the South China Sea islands and Diaoyu Islands are integral parts of its territory.
- Infrastructure Development: China claims its actions are defensive, building infrastructure and conducting patrols, while regional nations view these actions as provocative.
Economic Importance of the Seas
- Maritime Trade Routes: Key maritime trade routes in East Asia traverse these waters, with the Taiwan Strait being a critical choke point.
- Resource Richness: The region contains vast reserves of untapped oil and natural gas, making it economically significant.
China's Aggressive Tactics
Infrastructure and Militarization
- Building Facilities: China is constructing military installations and artificial islands in both the East and South China Seas.
- Conflict with Japan: China has frequently contested Japanese claims, resulting in significant diplomatic and military tensions.
South China Sea Belligerence
- Power Asymmetry: China's navy is the largest in the world, enabling it to project power effectively in the South China Sea.
- Aggressive Maneuvers: Tactics include harassment of resupply missions, ramming vessels, and the use of military-grade lasers.
Recent Escalations in the South China Sea
- Increased Incidents: Since 2022, clashes between China and the Philippines have intensified, especially around Second Thomas Shoal and Sabina Shoal.
- Dangerous Encounters: China's larger Coast Guard vessels pose significant risks during confrontations, raising concerns about potential miscalculations.
Conclusion
The evolving power dynamics in maritime East Asia highlight the interplay of national interests, regional security, and international cooperation. The situation remains fluid, with significant implications for global trade, security, and diplomatic relations. Understanding these complexities is essential for addressing the challenges posed by an assertive China and fostering stability in the region.
ARMED FORCES (SPECIAL POWERS) ACT (AFSPA)

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) is a controversial law that grants extraordinary powers to the armed forces in designated "disturbed areas." Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs extended AFSPA for six months in parts of Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh, highlighting ongoing security concerns in these regions.
Current Status of AFSPA
Extended Areas
- Nagaland: AFSPA has been extended to eight districts—Dimapur, Niuland, Chumoukedima, Mon, Kiphire, Noklak, Phek, and Peren—along with 21 police stations in additional districts.
- Arunachal Pradesh: The Act continues in Tirap, Changlang, and Longding districts, as well as in certain areas of Namsai district.
Duration of Extension
The current extension is effective from October 1, 2024, lasting for six months unless revoked earlier. These areas were initially declared "disturbed" on April 1, 2024.
About AFSPA
Objective
AFSPA aims to maintain law and order in regions affected by insurgency or unrest, providing armed forces with necessary powers to perform their duties.
Key Provisions
- Section 3: Empowers the Governor or the Central Government to declare areas as "disturbed."
- Section 4: Grants special powers for arrests and searches without warrants.
- Section 6: Mandates that arrested individuals and seized property be handed over to the police.
- Section 7: Prosecution of armed forces personnel requires prior approval from the Central Government.
Rationale for Implementation
- To enable effective counter-insurgency operations.
- To ensure the protection of armed forces members.
- To uphold national security and sovereignty.
Criticisms and Issues
AFSPA has faced significant backlash for:
- Violating Fundamental Rights: Critics argue it undermines Articles 14, 19, and 21 of the Constitution.
- International Law Conflicts: It is perceived as contrary to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
- Erosion of State Autonomy: The Act is viewed as an infringement on state powers, even in peaceful contexts.
Ineffectiveness and Atrocities
Reports of human rights abuses and the ineffectiveness of AFSPA in genuinely countering insurgency raise questions about its continued application.
Government's Position
Union Home Minister Amit Shah has noted that AFSPA has been lifted from 70% of the northeastern states, but it remains in force in certain areas, including Jammu and Kashmir, where revocation is also being considered.
Jeevan Reddy Committee
On November 19, 2004, the Central Government established a five-member committee led by Justice B.P. Jeevan Reddy to assess the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in northeastern states. The committee was tasked with reviewing the law's implications and effectiveness.
Key Findings
In its 2005 report, the Jeevan Reddy Committee made several critical observations and recommendations:
- Complete Repeal: The committee advocated for the complete repeal of AFSPA, labeling it a "symbol of hate and oppression" and describing it as an "instrument of high-handedness."
- Incorporation into Other Legislation: It suggested that relevant provisions of AFSPA be integrated into the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967, with necessary modifications to delineate the powers of armed and paramilitary forces.
- Establishment of Grievance Cells: The committee recommended the creation of grievance cells in each district where armed forces are deployed, aimed at addressing public complaints and concerns regarding military actions.
Additional Recommendations
- The 5th report of the Second Administrative Reforms Commission also echoed the call for repealing AFSPA, reinforcing the need for legislative reform in addressing security issues.
- In 2016, the Supreme Court ruled that the armed forces cannot evade investigation for alleged excesses committed during their duties, even in "disturbed areas." This ruling clarified that the legal protections offered by AFSPA are not absolute, emphasizing accountability.
Conclusion
AFSPA remains a contentious issue with significant implications for civil rights, regional stability, and national security. A careful review and possible reform of the Act are essential to balance security needs with the protection of fundamental rights.
PLFS REPORT 2023-24
- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) conducted by the National Statistical Office (NSO) from July 2023 to June 2024 provides crucial insights into the employment landscape in India.
Key Findings from the PLFS Report 2023-24
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR):
- The LFPR for individuals aged 15 years and above rose to 60.1%, an increase from 57.9% the previous year.
- For males, LFPR is at 78.8%, while for females, it increased to 41.7%, up from 37.0%.
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR):
- The WPR for the same age group stands at 58.2%. This is composed of 76.3% for males and 40.3% for females.
- Female WPR improved from 35.9% to 40.3% during the reporting period.
- Unemployment Rate (UR):
- The overall unemployment rate is 3.2%. It slightly declined for males from 3.3% to 3.2%, while it increased for females from 2.9% to 3.2%.
Overview of the PLFS
The PLFS, initiated in April 2017, aims to provide timely and accurate labor market data. It focuses on two main objectives:
- Short-term Employment Indicators: Measure key employment metrics every three months in urban areas using the Current Weekly Status (CWS) approach.
- Annual Estimates: Gather employment and unemployment data for both urban and rural areas, assessing them in terms of Usual Status and CWS.
Methodology and Sample Design
- The survey employs a rotational panel sampling design in urban areas, where households are visited multiple times to ensure comprehensive data collection.
- During the 2023-24 period, a total of 12,800 Field Sampling Units (FSUs) were designated, with 12,743 successfully surveyed.
Conceptual Framework
Key indicators measured include:
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): Percentage of the population working or actively seeking work.
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): Percentage of employed individuals in the total population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR): Proportion of unemployed individuals among the labor force.
Challenges in Job Creation
India continues to face significant challenges in generating formal jobs. Key factors contributing to this issue include:
- Informalization of Employment: Growth in sectors like agriculture and construction is leading to increased informal employment, lacking social security and job protections.
- Technological Advancements: Automation and AI threaten job opportunities, even for skilled workers, as evidenced by layoffs in the IT sector.
- Skill Mismatch: Despite a push for skill development, the share of skilled jobs has declined, highlighting a growing disconnect between training programs and labor market needs.
- Policy Impacts: Past policies, such as demonetization and poorly implemented GST, have negatively impacted small and medium enterprises (SMEs), which are vital for job creation.
Way Forward:
To address these challenges, several strategies are proposed:
- Sectoral Diversification: Fostering investments in manufacturing, renewable energy, and technology can generate productive jobs.
- Support for MSMEs: Targeted financial aid and regulatory relief for micro, small, and medium enterprises are crucial for boosting their employment potential.
- Skill Development: Aligning training initiatives with current industry demands, particularly in emerging sectors, is essential.
- Focus on New-Age Services: Encouraging growth in sectors like e-commerce and online education could create diverse job opportunities.
Conclusion
The PLFS 2023-24 reveals an encouraging increase in labor force participation, particularly among women, while also highlighting persistent challenges in unemployment and gender disparities. The findings underscore the need for continued efforts to enhance job creation and improve employment conditions in both formal and informal sectors.
TRIPURA'S INSURGENCY RESOLUTION: A LANDMARK DECLARATION

- 25 Sep 2024
In News:
Recent Developments
Insurgency-Free Declaration
Tripura Chief Minister Manik Saha has officially declared the state "insurgency-free" following a significant surrender ceremony where 584 militants from the National Liberation Front of Tripura (NLFT) and the All-Tripura Tiger Force (ATTF) laid down their arms.
Memorandum of Settlement
This milestone follows a Memorandum of Settlement signed on September 4 between the central government and various insurgent groups, witnessed by the union home minister. The Tripura government has successfully facilitated 12 peace accords over the last decade, leading to over 10,000 insurgents surrendering.
Understanding Insurgency in Tripura
Historical Context
Tribal Composition
Tripura is home to 19 indigenous tribes, including the Tripra, Reang, and Jamatia, with Kok Borok as the primary language alongside other Tibeto-Burmese dialects.
Journey to Statehood
- Accession: Tripura became part of the Indian Union on October 15, 1949.
- Union Territory: It was designated as a Union Territory on November 1, 1956.
- Statehood: Tripura attained full statehood on January 21, 1972.
Causes of Insurgency
- Demographic Changes: A significant influx of Bengali refugees from East Pakistan resulted in the indigenous population declining from 95% in 1931 to 31% by 1991.
- Tribal Discontent: The tribal population lost control over land and resources, leading to widespread grievances.
- Socio-Economic Factors: Issues such as geographic isolation, socio-economic challenges, corruption, and tribal land alienation fueled unrest.
Evolution of Political Movements and Insurgency
Formation of Political Organizations
- TUJS: Established in 1967 to advocate for tribal rights and autonomy.
- Armed Struggle: The Tripura Sena emerged in 1970, followed by the Tripura National Volunteers (TNV) in 1978, both pushing for an independent tribal state.
Rise of Insurgent Groups
Key groups involved include:
- TUJS: Formed in 1971.
- TNV: Established in 1981.
- NLFT: Founded in 1989.
- ATTF: Formed in 1990.
Communal Clashes and Military Response
- Opposition from Bengali Population: Groups like Amra Bangali emerged in opposition to tribal demands, leading to violent clashes with over 1,800 fatalities.
- Military Intervention: The Indian Army was deployed in 1980 to restore order.
Attempts at Peace and Resurgence of Militancy
TNV Settlement
The TNV signed a peace agreement with the state government in 1988, focusing on restoring tribal lands. However, issues with implementation led to the rise of new militant groups.
Resurgence of Insurgency
Between 1996 and 2004, insurgency gained traction, supported by logistics from Bangladesh and external networks, leveraging the region's challenging geography.
Strategic Response to Insurgency
- Counter-Insurgency Operations
- The state focused on effective counter-insurgency operations involving local police and paramilitary forces, minimizing the need for military deployment.
- Psychological Operations
- Efforts were made to shift perceptions among tribal communities, exposing the exploitative nature of insurgents.
- Confidence-Building Measures
- Rehabilitation packages and public appeals by state leaders encouraged insurgents to reintegrate into society.
- Civic and Developmental Initiatives
- Comprehensive development initiatives were implemented, enhancing healthcare, connectivity, and job opportunities, alongside civic action programs by security forces.
- Political and Governance Reforms
- Strengthening local governance through autonomous councils and encouraging tribal participation aimed to foster a more inclusive development process.
Conclusion
Tripura's journey to overcome insurgency highlights the effectiveness of a multi-faceted approach, combining socio-economic development with strategic military and political initiatives. The state's experience illustrates that insurgency can be addressed through sincere leadership and a balanced focus on military and socio-economic challenges.
INDIA'S STRATEGIC PUSH FOR A DOMESTIC SEMICONDUCTOR ECOSYSTEM
- 24 Sep 2024
Introduction
India is actively pursuing the establishment of a domestic semiconductor ecosystem to lessen dependence on imports and tackle global supply chain vulnerabilities. This initiative, launched under the Semiconductor Mission in 2021 with a USD 10 billion investment, is vital for national security, particularly in defense and telecommunications.
Current Status of the Semiconductor Industry in India
Market Overview
- 2022 Market Size: USD 26.3 billion
- Projected Growth: Expected to reach USD 271.9 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 26.3%.
Import-Export Dynamics
- Imports: USD 5.36 billion in 2021; efforts are underway to reduce this reliance.
- Exports: USD 0.52 billion in 2022, marking the highest level to date.
Government Initiatives
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM): Part of the Digital India Corporation, focused on developing a strong semiconductor ecosystem.
- Financial Support: Covers 50% of project costs for semiconductor and display manufacturing facilities.
- Semicon India Programme: Launched in December 2021 with ?76,000 crore (around USD 9.2 billion) dedicated to semiconductor manufacturing.
- FY24 Budget Increase: Allocated ?6,903 crore (approximately USD 833.7 million) for further development.
International Collaborations
- MoU with the European Commission: Aims to enhance semiconductor ecosystems.
- MoC with Japan: Focused on improving supply chain resilience in the semiconductor sector.
Importance of Semiconductors for India
Economic Growth and Industrial Development
- Semiconductors are crucial for enhancing India's electronics manufacturing, targeting a notable share of the projected USD 1 trillion global semiconductor market by 2030.
- The Semiconductor Mission is projected to generate 35,000 direct jobs and 100,000 indirect jobs, potentially raising electronics manufacturing to USD 300 billion by 2026.
National Security and Strategic Autonomy
- Essential for defense and telecommunications, semiconductors ensure reliable supplies for critical defense systems and secure communication networks.
Technological Self-Reliance and Innovation
- With around 65-70% of electronic components currently imported, primarily from China, initiatives aim to foster domestic innovation and reduce this reliance.
Global Supply Chain Integration
- The objective is to position India as a key player in the global electronics supply chain, increasing its current 3% share of the global electronics manufacturing value.
Job Creation and Skill Development
- The semiconductor industry is anticipated to drive job creation and skill development, enhancing STEM education and research in advanced technologies.
Challenges Facing India's Semiconductor Aspirations
Infrastructure Issues
- India faces significant infrastructure challenges, including unreliable power supply and water shortages that impact semiconductor production.
Talent Shortage
- There is a projected need for 250,000 to 300,000 skilled professionals in semiconductor fields by 2027.
High Manufacturing Costs
- Semiconductor manufacturing is capital-intensive, and operational costs in India are generally higher compared to established hubs like Taiwan and South Korea.
Global Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
- Global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by events such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, present risks to India's semiconductor goals.
Environmental Challenges
- The energy-intensive nature of semiconductor manufacturing raises concerns about its environmental impact, particularly regarding greenhouse gas emissions.
Competition from Other Emerging Markets
- India faces competition from countries like Vietnam and Malaysia, which are successfully attracting semiconductor investments with favorable conditions and incentives.
Strategies for Advancing India's Semiconductor Vision
Enhance Education and Training
- Expand semiconductor engineering programs and collaborate with global companies to develop relevant curricula and hands-on training.
Develop Domestic Chip Design Capabilities
- Invest in chip design by establishing dedicated centers in technology hubs to encourage innovation.
Build a Comprehensive Supply Chain
- Create a robust domestic supply chain by attracting investments across all segments, from raw materials to advanced packaging.
Establish a Sovereign Semiconductor Fund
- Launch a dedicated fund for semiconductor projects to provide long-term investment and reduce reliance on foreign funding.
Implement a "Chip Diplomacy" Approach
- Use India's geopolitical position to negotiate technology transfers and partnerships with leading semiconductor nations.
Launch a "Green Semiconductor" Initiative
- Aim to become a leader in sustainable semiconductor manufacturing by minimizing environmental impacts.
Create a National Semiconductor Commons
- Establish shared infrastructure for research and prototyping to lower barriers for startups and promote innovation.
Conclusion
To fulfill its semiconductor aspirations, India must enhance education and training, develop a strong supply chain, and foster strategic collaborations. By addressing infrastructure challenges and skill gaps while promoting sustainable practices, India can secure its position as a significant player in the global semiconductor industry and strive for technological self-reliance.
ANALYSIS OF INDIA'S TRADE DEFICIT
- 23 Sep 2024
Overview of the Trade Deficit
India experienced a notable increase in its trade deficit during July and August 2024, primarily due to declining exports and rising imports. This trend is indicative of both domestic challenges and global economic conditions.
Understanding Trade Deficit
A trade deficit occurs when a country's imports surpass its exports, leading to a negative trade balance. While not inherently detrimental, sustained trade deficits can result in issues such as currency depreciation, rising national debt, and pressure on local industries.
Factors Influencing India's Trade Deficit
Several key elements have contributed to the widening of India’s trade deficit in recent months:
- Decline in Exports
- Oil Exports: A sharp decline was observed in petroleum exports, which dropped by 22.2% in July and 37.6% in August, influenced by both weakened global demand and falling oil prices.
- Gems & Jewellery: This sector saw a reduction exceeding 20% in exports during both months, adversely affecting overall trade performance.
- Pharmaceuticals and Electronics: These sectors also faced slower growth due to ongoing weak global demand.
- China's Economic Slowdown
- Exports to China, particularly in materials such as stone and iron ore, diminished as China grappled with internal economic challenges and reduced infrastructure spending, negatively impacting India's export revenue.
- Surge in Gold Imports
- August saw a record $10.1 billion in gold imports, more than doubling previous figures. This increase was driven by lowered import duties and heightened domestic demand for the festive season, significantly contributing to the trade deficit.
- Decline in Oil Imports
- On a more positive note, India’s oil import bill decreased by nearly a third due to falling global oil prices, marking the lowest petroleum trade deficit in three years. However, this reduction did not sufficiently counterbalance deficits in other areas.
Implications of the Trade Deficit
- Currency Depreciation: A growing trade deficit may exert downward pressure on the Indian rupee, making imports costlier and potentially worsening the deficit further, given India's heavy reliance on imported commodities.
- Impact on Economic Growth: Prolonged trade deficits can hinder economic growth by reflecting diminished export competitiveness and excessive reliance on imports.
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: While India’s foreign exchange reserves are currently robust, a sustained deficit could deplete these reserves, complicating efforts to stabilize the rupee in the future.
Long-term Challenges and Outlook
India's trade deficit is shaped by a mixture of global and domestic influences:
- Weak Global Demand: Economic sluggishness in developed markets, such as the U.S. and EU, reduces demand for Indian exports, particularly in pharmaceuticals and textiles.
- China’s Economic Issues: As China seeks to offload surplus goods, India may face increased competition from cheaper imports, which could challenge domestic industries.
- Trade Barriers and Regulations: New international trade policies, particularly in the EU regarding environmental standards, impose additional compliance burdens on Indian exporters.
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
While India's escalating trade deficit poses challenges, it is not an insurmountable issue. Policymakers need to adopt strategic measures to tackle underlying structural problems:
- Boosting Exports: Enhancing the competitiveness of export sectors through technological investment and market expansion is vital. Strengthening trade agreements can also improve market access.
- Reducing Non-essential Imports: Minimizing reliance on luxury imports, particularly gold, while promoting domestic manufacturing can help in balancing the trade deficit.
- Developing Domestic Industries: Fostering growth in sectors such as electronics and renewable energy will not only reduce import dependence but also enhance export capacity.
- Managing Currency and Debt: Careful management of the rupee's valuation and maintaining adequate foreign exchange reserves are crucial in mitigating trade deficit impacts.
Achieving the ambitious goal of $1 trillion in exports for both goods and services by 2030 is attainable but requires overcoming current global economic hurdles, adapting to new trade regulations, and building a self-sufficient economy. By strategically addressing these challenges, India can work toward reducing its trade deficit while maintaining economic growth.
INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENT OF WILDLIFE HABITATS (IDWH) SCHEME

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet has approved the continuation of the Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats (IDWH) scheme for the 15th Finance Commission cycle, with a total outlay of ?2,602.98 crore. This scheme aims to enhance the conservation of wildlife and their habitats across India, building upon the earlier "Assistance for the Development of National Parks and Sanctuaries."
Overview of the Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats (IDWH)
IDWH is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme designed to support various components critical to wildlife conservation. Key aspects of the scheme include:
- Support to Protected Areas: This encompasses national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, conservation reserves, and community reserves.
- Protection of Wildlife Outside Protected Areas: This aims to safeguard wildlife habitats and corridors beyond designated reserves.
- Recovery Programs: These initiatives focus on critically endangered species and their habitats.
Key Projects Under IDWH
The scheme integrates several prominent conservation projects:
- Project Tiger: Launched in 1973, this initiative seeks to ensure a viable population of Bengal tigers in their natural habitats. It employs advanced technologies such as the M-STrIPES application for effective management and monitoring.
- Project Elephant: Initiated in 1992, this project focuses on elephant conservation, addressing human-elephant conflicts, and promoting the welfare of domesticated elephants.
- Development of Wildlife Habitat: This includes Project Dolphin, which utilizes technology like Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) for monitoring dolphin populations, and Project Lion, aimed at strengthening lion conservation efforts in line with the “Lion @ 2047” vision.
Significance of the Scheme
The IDWH scheme promises significant ecological and economic benefits:
- It is projected to generate over 50 lakh man-days of direct employment, alongside indirect job opportunities through eco-tourism and related activities.
- A total of 55 tiger reserves, 33 elephant reserves, and 718 protected areas will benefit from the scheme, enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- By supporting keystone species such as tigers, elephants, cheetahs, snow leopards, and lions, the scheme contributes to the overall integrity of these ecosystems.
The overall outlay for the three components for the 15th Finance Commission cycle as well as its remaining period:
S.No. Name of the Scheme Central Share State Share Total
1. Project Tiger 1575.00 955.00 2530.00
2. Project Elephant 182.58 54.00 236.58
3. Development of Wildlife Habitat 845.4 273.02 1118.42
*All figures in Rs. Crores Total 2602.98 1282.02 3885.00
Component of EFC 2024-25 2025-26
Project Tiger 365.00 365.00
Project Elephant 40.00 40.12
Development of Wildlife Habitat 195.00 183.16
*All figures in Rs. Crores Total 600 588.28
SRI LANKA’S PRESIDENTIAL ELECTIONS: IMPORTANCE AND IMPLICATIONS FOR INDIA

- 21 Sep 2024
Overview of the Elections
Sri Lanka is gearing up for its first presidential election since the significant protests of 2022 and an unprecedented economic crisis. Scheduled for September 21, the election comes at a critical juncture for the nation, following the ousting of the Rajapaksa regime.
Context of the Crisis
The protests were ignited by severe economic difficulties, including inflation soaring to 70% and shortages of essential goods like food, fuel, and medicine. While some improvements have been noted, a full recovery remains elusive, with economic concerns at the forefront of voters' minds.
Electoral Landscape
Voting System
- Candidates: 38 candidates are contesting, all men.
- Voting Process: Each of the 17 million eligible voters can select up to three candidates. A candidate needs over 50% of the votes to win outright; otherwise, a run-off will occur between the top two contenders.
India's Strategic Interests
Concerns over Regional Influence
India is closely monitoring the elections due to strategic interests, particularly in countering China's expanding influence in Sri Lanka. The previous administrations have leaned towards China, which has raised concerns in New Delhi.
Key Candidate Positions
- Sajith Premadasa: Historically skeptical of China; supports the implementation of the 13th Amendment for provincial power devolution, aligning with Indian interests.
- Anura Kumara Dissanayake: Has a pro-China background and has criticized Indian business interests in Sri Lanka, raising potential tensions with India.
Economic Recovery and Voter Sentiment
Current Economic Situation
Post-crisis, the economy has shown signs of stabilization, with no food or fuel shortages and reduced inflation. However, many Sri Lankans continue to struggle financially, feeling the impact of increased taxes and electricity rates mandated by the IMF bailout conditions.
Voter Priorities
The election marks a shift in voter focus, with economic recovery taking precedence over traditional ethnic or religious considerations. Skepticism about political promises is high, as citizens recall previous failures to deliver on reforms.
Conclusion: The Path Ahead
As Sri Lanka heads into this pivotal election, the outcome will be crucial for both the nation and its international relations, particularly with India. The next president's ability to navigate economic recovery and regional dynamics will significantly influence Sri Lanka's trajectory.
INDUS WATERS: INDIA FREEZES TALKS WITH PAKISTAN
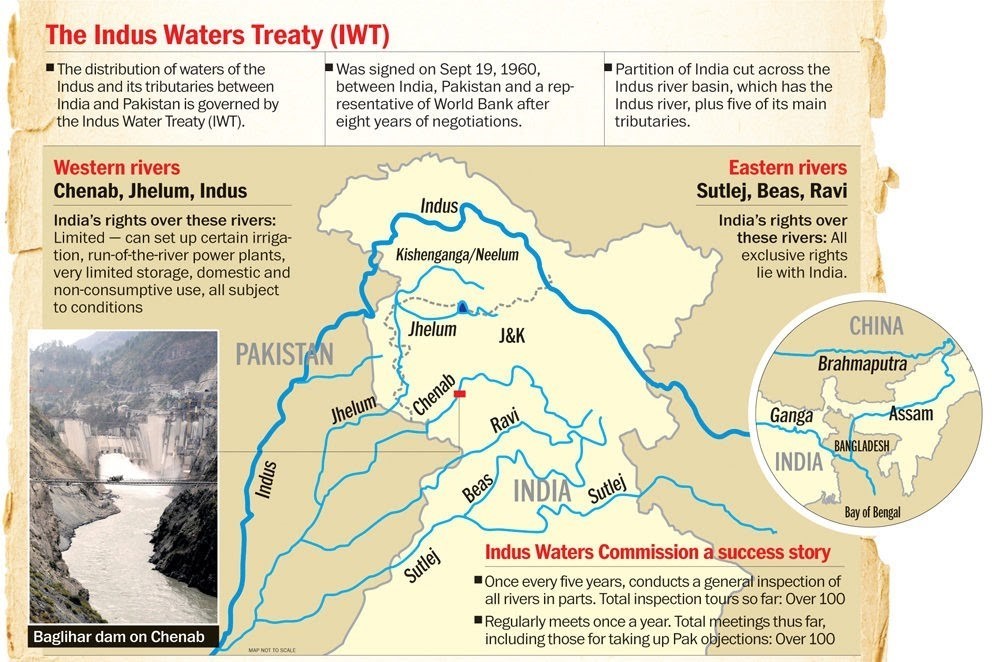
- 20 Sep 2024
In News:
India has decided to halt all meetings of the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC) until both governments engage in discussions to renegotiate the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT), a decision communicated by a senior official. The last PIC meeting occurred in May 2022, and since January 2023, India has made four attempts to initiate talks with Pakistan, but these efforts have not received satisfactory responses.
The IWT, established in 1960 with the mediation of the World Bank, governs the sharing of six rivers between India and Pakistan. Under this treaty, India controls the waters of the Ravi, Sutlej, and Beas rivers, while Pakistan has rights to the Sindh, Jhelum, and Chenab rivers. The treaty mandates annual meetings of the PIC, which have continued despite ongoing conflicts between the two nations. However, India’s recent push for renegotiation threatens the stability of this long-standing arrangement.
India's Notice for Review of the Indus Waters Treaty
India formally issued a notice to Pakistan on August 30, 2023, seeking modifications to the IWT, citing "fundamental and unforeseen changes" that necessitate a reassessment of the agreement. This is not an isolated instance; India had previously requested a review in January 2023, attributing the need for change to Pakistan’s persistent intransigence regarding its obligations under the treaty.
Key reasons for India’s demand include:
- Changes in population demographics and environmental challenges.
- The necessity for clean energy development to meet emissions targets.
- The impact of ongoing cross-border terrorism, which India argues affects water management and security.
The notification highlights issues related to two contentious hydroelectric projects in Jammu & Kashmir—the Kishanganga and Ratle projects—over which Pakistan has raised objections, claiming they violate the IWT. India asserts that these projects are "run-of-the-river" schemes that do not significantly impede river flow.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms Under the Treaty
The IWT outlines a structured dispute resolution mechanism, as detailed in Article IX. This mechanism involves three levels:
- First Level: Initial discussions occur at the PIC, where either party must inform the other of planned projects.
- Second Level: If differences remain unresolved, a Neutral Expert, appointed by the World Bank, is engaged to mediate.
- Third Level: Should the Neutral Expert fail to resolve the issue, the dispute escalates to the Court of Arbitration.
Historically, both countries have used these mechanisms, although recent years have seen significant contention. After a Pakistan-backed terror attack in Uri in 2016, India’s Prime Minister expressed the sentiment that “blood and water cannot flow together,” leading to the suspension of routine talks.
The World Bank has navigated a complex situation, receiving requests from both nations for adjudication on overlapping disputes. In December 2016, it paused these processes to encourage direct negotiations. Despite attempts to resume dialogue between 2017 and 2022, Pakistan’s reluctance to engage has further complicated matters.
Current Status and Future Implications
India’s formal notification and its call for renegotiation may set a precedent that challenges the existing framework of the IWT. The continuation of the PIC's activities hinges on a willingness from both governments to address these evolving concerns collaboratively. As tensions persist and environmental needs grow, the future of water-sharing arrangements in the region remains uncertain. The overarching goal for both nations will be to find a sustainable resolution that addresses emerging challenges while honoring the historical framework established by the IWT.
Can Sheikh Hasina be Extradited?

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The chief prosecutor of Bangladesh’s International Crimes Tribunal (ICT), Mohammad Tajul Islam, announced plans to seek the extradition of former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina from India. The ICT was established in 2010 to investigate crimes committed during the 1971 independence war from Pakistan.
Background on Sheikh Hasina's Exile
Ms. Hasina sought refuge in India in early August after a mass uprising forced her to resign. Following her departure, numerous criminal cases have been filed against her and her aides, with charges including murder, torture, abduction, crimes against humanity, and genocide. The interim government in Dhaka has revoked her diplomatic passport, and the existing bilateral extradition treaty between India and Bangladesh may allow for her return to face trial.
Extradition Treaty Overview
Key Provisions
- Under the International Crimes (Tribunals) Act of 1973, Bangladeshi courts can proceed with trials in Ms. Hasina’s absence, raising concerns about the fairness and adherence to due process. Thus, her extradition is deemed crucial.
- The extradition treaty between India and Bangladesh was executed in 2013 and amended in 2016 to facilitate the exchange of fugitives. The treaty has allowed the transfer of several political prisoners, including two involved in the 1975 assassination of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, Ms. Hasina’s father, and Anup Chetia, the former general secretary of the banned United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA).
Extradition Conditions
- The treaty mandates the extradition of individuals charged with crimes punishable by at least one year’s imprisonment. It follows the principle of dual criminality, meaning the offense must be punishable in both countries. Since the charges against Ms. Hasina are prosecutable in India, she qualifies for extradition. The treaty also covers attempts to commit crimes and complicity in such offenses.
- The 2016 amendment significantly lowered the evidentiary threshold for extradition, requiring only an arrest warrant from a competent court in the requesting country to initiate proceedings.
Grounds for Refusal of Extradition
Political Nature of Offenses
Article 6 of the treaty allows for extradition to be refused if the offense is deemed of a “political nature.” However, many offenses, including murder and terrorism-related crimes, are explicitly excluded from this classification. Given that several charges against Ms. Hasina fall outside this exemption, it is unlikely India could justify denying extradition on these grounds.
Good Faith Clause
Article 8 permits denial of extradition requests if the accusations are not made in good faith or involve military offenses not recognized under general criminal law. India could argue that the charges against Ms. Hasina are politically motivated and may lead to her facing unfair trials or persecution upon her return. Recent reports indicate that some of Ms. Hasina’s former ministers faced violent arrests, raising further concerns about the political climate in Bangladesh.
Potential Implications of Extradition Request
Dr. Sreeradha Datta, a professor of international relations at O.P. Jindal Global University, commented that the treaty does not guarantee Ms. Hasina’s extradition, emphasizing that the final decision will depend on diplomatic negotiations and political factors. Even if India declines the request, it may only serve as a minor political irritant rather than significantly damaging bilateral relations.
Economic Considerations
Bangladesh is India’s largest trade partner in South Asia, with bilateral trade estimated at $15.9 billion for the fiscal year 2022-23. Before Ms. Hasina’s ouster, both countries were set to discuss a comprehensive economic partnership agreement (CEPA) to strengthen economic ties. Following the regime change in Dhaka, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi has engaged with Chief Adviser Muhammad Yunus of the interim government, pledging continued support for ongoing development projects.
How do emergency provisions impact Centre-State relations?

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
The recent spate of renewed violence in Manipur has once again triggered the discussion around Centre-State relations and the use of emergency provisions by the Centre.
What is our federal set-up?
India is a federation with governments at the Centre and the States. The Seventh Schedule to the Indian Constitution distributes the power between the Union and States. Under this scheme, it is the domain of the State governments to maintain law and order in their respective States.
What are emergency provisions?
The emergency provisions are provided in Part XVIII of the Constitution. Articles 355 and 356 deal primarily with the affairs of government in a State under this part.
Article 355 imposes a duty on the Centre to protect every State from external aggression and internal disturbance. It also specifies that the Centre should ensure that every State government operate according to the Constitution.
Article 356 allows for the imposition of the President’s rule if a State’s government cannot function in accordance with constitutional provisions. While in the U.S. and Australia, federal government functions also involve protecting States, their constitutions do not contain provisions for removing State governments.
B.R. Ambedkar explained the purpose of Article 355, keeping in mind the federal character of our polity, that if the Centre is to interfere in the State’s administration under Article 356, it must be by or under some obligation which the Constitution imposes on the Centre. Hence, Article 355 was incorporated to check any arbitrary or unauthorised use of Article 356.
What have the courts ruled?
Dr. Ambedkar again in the constituent Assembly wished that Articles 355 and 356 would never be called into operation and would remain a dead letter. However, it was a travesty of the Constitutional principles and federalism that Article 356 was misused on several occasions removing elected governments that enjoyed majority in the States. Reasons varied from loss in Lok Sabha elections to deterioration of law and order in the States. It was only after the Supreme Court’s categorical judgement in the S R Bommai case (1994) that such misuse was restricted. The court held that Article 356 should be imposed only in the event of a breakdown of constitutional machinery, as distinguished from an ordinary breakdown of law and order. It also held that the imposition of the President’s rule is subject to judicial review and should not be misused for political reasons.
On the other hand, the scope of Article 355 has been widened by various Supreme Court rulings. In State of Rajasthan Vs Union of India (1977), the court had a narrow interpretation of Article 355 as justifying the employment of Article 356. However, in subsequent cases such as Naga People’s Movement of Human Rights Vs Union of India (1998), Sarbananda Sonowal Vs Union of India (2005), and H.S.Jain Vs Union of India (1997), the legal position with respect to Article 355 has shifted. The scope of actions under this article has been widened to permit all statutorily and constitutionally available actions by the Union to discharge its duties of protecting the State and ensuring that its governance is in accordance with the Constitution.
What are the suggestions?
The Sarkaria Commission on Centre-State Relations (1987), the National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2002), and the Punchhi Commission on Centre-State Relations (2010) have all opined that Article 355 not only imposes a duty on the Union but also grants it the power to take necessary actions for the effective performance of that duty. Imposition of the President’s rule under Article 356 must be used as a last resort in situations of utmost gravity and urgency.
The situation in Manipur is grave. Large-scale violence against innocent civilians, women and children; looting of ammunition from police armoury; drone and missile attacks targeting civilians cannot be viewed as just an ordinary breakdown of law and order. Constitutional as well as political expediency, considering that the same party is in power at the Centre and the State, has resulted in Article 356 not being invoked. However, under Article 355, all possible instructions and actions should continue to be pursued to restore normalcy at the earliest.
The Shock of Crumbling Infrastructure and the Path Forward

- 15 Sep 2024
Infrastructure is a cornerstone of economic development, and in a rapidly growing economy like India’s, its robustness is vital. Recent incidents, particularly the collapse of several under-construction bridges in Bihar, have cast a spotlight on significant issues within the Indian infrastructure sector, particularly in terms of quality control and project management. With the country's aim to become a developed nation by 2047, addressing these challenges is crucial for sustaining economic growth and ensuring safety.
Current Challenges
- Cost Overruns and Delays: One of the most pressing issues is the frequent occurrence of cost overruns and delays. According to a report by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, 431 infrastructure projects with investments exceeding ?150 crore each have faced cost overruns totaling ?4.82 lakh crore as of December 2023. Additionally, a significant percentage of projects are delayed, with 36% running behind schedule by 25 to 60 months and 15% delayed for over 60 months.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Infrastructure projects often face delays due to the complex maze of clearances required. The implementation status of many projects indicates a lack of comprehensive planning and coordination, especially in urban infrastructure projects managed by local bodies that may lack sufficient capacity and expertise.
- Project Management Deficiencies: Traditional project management practices in India are often outdated. There is a need for an overhaul to incorporate modern tools and techniques for real-time data management and analysis. Insufficient attention during the planning stages of projects exacerbates these issues, leading to increased costs and project failures.
Path Forward
1. Integrating Modern Practices: Adopting modern project management practices is essential. This includes real-time data management, use of advanced analytics, and adopting global best standards. For example, in the United Kingdom, the Infrastructure and Projects Authority focuses on refining project processes, while countries like China and Saudi Arabia have established agencies dedicated to end-to-end project delivery.
2. PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan: India has initiated the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, aimed at integrating various government departments and stakeholders into a unified platform. This GIS-based ERP portal is designed to monitor real-time progress and enhance coordination among departments. While this initiative is promising, the effectiveness will depend on the quality of implementation and oversight.
3. Holistic Program Management Approach: The “Program Management Approach” used in industrial corridor development projects, like the Shendra-Bidkin in Aurangabad, exemplifies effective management of multiple projects simultaneously. This disciplined approach, involving systematic coordination of resources and information, can be applied more broadly across infrastructure projects.
4. Professional Training and Certification: To build a capable workforce, there is a need to establish agencies for professional training in project management. Similar to the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, such agencies can focus on developing professional ethics and responsibilities in project execution and oversight.
Conclusion
With substantial taxpayer money allocated for infrastructure development, it is imperative to prevent the pitfalls of cost overruns and project failures. A robust program management system, incorporating modern practices and professional training, will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of infrastructure projects. This approach will not only support India’s high-growth trajectory but also contribute to creating a safer, more affluent future for its citizens.
The Path to Universal Health Coverage: Embracing Data and Digital Technology

- 13 Sep 2024
The expansion of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) represents a complex but crucial endeavor. The integration of data and digital technology stands out as a pivotal factor in smoothing the way towards achieving this goal.
Understanding Universal Health Coverage
Universal Health Coverage means ensuring that every individual has access to the full spectrum of quality health services when and where they need them, without facing financial hardship. This concept encompasses a broad range of essential health services, including health promotion, prevention, treatment, rehabilitation, and palliative care throughout an individual's life.
UHC as a Sustainable Development Goal
Achieving UHC is a key target of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) established by the global community in 2015. However, despite this commitment, progress towards this goal remains off-track. Since 2015, improvements in health services coverage have stalled, and the proportion of people facing catastrophic out-of-pocket health expenses has been rising steadily since 2000.
Challenges to Universal Health Coverage
Several challenges hinder the advancement of UHC:
- Global Stagnation: Progress in health coverage has stagnated globally, affecting regions and countries alike.
- Manpower Shortages: Many Western and Central Asian countries face severe healthcare manpower shortages.
- Pandemic Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic has further disrupted essential health services, with 92% of countries experiencing interruptions at the pandemic's peak in 2021, and 84% still reporting disruptions in 2022.
- Inequality in Healthcare Spending: The disparity between poor and non-poor households has widened, with lower-income families often forced to deplete their resources or sell assets to cover healthcare costs. According to the WHO, 55 million people fall into poverty annually due to catastrophic health expenditures.
- Insufficient Spending: India’s healthcare spending, currently at 3.2% of its GDP, is lower than the average spending of 5.2% observed in lower and middle-income countries (LMICs). The government’s health expenditure is also lower compared to other countries like China, Thailand, Vietnam, and Sri Lanka.
Opportunities Through Digital Health
To address these challenges, leveraging digital health solutions is critical. India's leadership in digital health is exemplified by the Global Initiative on Digital Health, launched under India’s G20 presidency. This initiative aims to drive investments into digital health and facilitate regional and international collaboration.
India’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, which precedes this global initiative, highlights the country's commitment to using digital technology to manage the complexities of UHC expansion. Digital health tools can play a transformative role in managing contracts, implementing value-based provider reimbursements, and streamlining healthcare delivery.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds significant promise for revolutionizing healthcare. AI-powered diagnostic tools can improve the accuracy and speed of medical diagnoses, leading to better patient outcomes. AI can also predict disease outbreaks, analyze healthcare data, optimize treatment plans, and enhance drug discovery, making healthcare more personalized and effective.
Building Digital Infrastructure
India’s experience in expanding digital health infrastructure can serve as a model for other low- and middle-income countries. Many of these nations are seeking to build and enhance their healthcare systems, and India’s approach may offer valuable policy insights.
The Need for Private Sector Participation
Achieving UHC in India cannot rely solely on the public sector. Integrating the private sector into the public healthcare framework is essential. Addressing modern health challenges requires a collaborative effort that includes both public and private sectors, creating a multifaceted and synergistic approach to healthcare.
WHO’s Recommendations
To strengthen health systems, the WHO recommends reorienting them with a primary health care (PHC) approach. Implementing PHC can deliver up to 90% of essential UHC interventions, potentially saving 60 million lives and increasing global life expectancy by 3.7 years by 2030.
Looking Ahead
It is crucial to balance national interests with international ambitions and leverage digital technologies to create inclusive solutions. Countries should build on their existing systems, gradually implementing reforms and best practices. With dedicated effort and a commitment to excellence, it is possible to build a healthier and more prosperous future for generations to come.
India’s sickle cell challenge
- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
Last year, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission to eliminate sickle cell disease as a public health problem by 2047, from Shahdol, Madhya Pradesh.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
- It is a genetic blood disorder that affects the shape of red blood cells. Normally, red blood cells are round and flexible, but in sickle cell disease, they become stiff and crescent-shaped, resembling a sickle.
- This abnormal shape makes it difficult for these cells to travel smoothly through blood vessels, leading to blockages and various health problems.
- It is caused by a mutation in the gene that tells the body how to make hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
- Both parents must pass down the defective gene for a child to develop the disease.
- If a person inherits the gene from just one parent, they have sickle cell trait and can pass the gene to their children but usually do not experience symptoms.
- Symptoms:
- Episodes of severe pain, called pain crises, typically in the chest, joints, and bones.
- Fatigue and anemia, due to the rapid breakdown of red blood cells.
- Swelling in the hands and feet, caused by the sickle-shaped cells blocking blood flow.
- Frequent infections, as the spleen, which helps fight infection, may be damaged by the disease.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children, due to chronic anemia.
- Diagnosis:
- It is usually diagnosed through a blood test. Newborns are routinely screened for the disease in many countries.
- The test checks for the presence of hemoglobin S, the defective form of hemoglobin that causes sickle cell disease.
- Treatment:
- While there is no universal cure for sickle cell disease, treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce complications.
- Pain relief medications for pain crises.
- Blood transfusions to treat anemia and prevent stroke.
- Hydroxyurea, a medication that can reduce the frequency of pain crises and the need for blood transfusions.
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplants, which can potentially cure the disease but are not suitable for all patients due to risks and availability of donors.
- Challenges in India
- India, with over a million affected individuals, faces the world’s second largest burden of sickle cell disease, primarily affecting tribal regions across Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra. Only 18% of those affected receive consistent treatment due to significant drop-offs at diagnosis and adherence stages. Diagnosis is hindered by stigma and reliance on traditional healers, with a lack of trust in the public healthcare system. Treatment adherence is also poor due to the absence of a permanent cure, inadequate supply of essential medications like hydroxyurea, and logistical challenges, including long travel distances for medicine. Additionally, vaccination coverage, which helps improve patients' quality of life, remains insufficient.
The way ahead
- It is important to reduce the stigma related to the disease and build trust in public health institutions. Awareness should be raised through targeted media campaigns to bust specific myths (which vary by region and tribe).
- Second, given that cases are often missed and diagnosis delayed, there could be increasing screening for newborns. This strategy is low-cost with a high pay-off and would especially be effective in areas where the condition is endemic.
- Third, drugs as well as adherence support must be available close to patients, in the nearest health and wellness centres. For complications, interdisciplinary centres of excellence at the district/division levels should be made operational.
- Fourth, ensuring that all known patients receive approved vaccines will be crucial; this may require catch-up vaccination programmes.
- Fifth, health in tribal areas should be operationally strengthened by factoring in conditions unique to these areas. Healthcare should also be adequately funded.
- Finally, research should be conducted to better understand the disease and its pathways in India, and to develop new treatments. Philanthropists and members of civil society must play a catalytic role, and work with the Central and State governments.
India’s Approach to the Russia-Ukraine Conflict and Economic Ties

- 11 Sep 2024
India’s Four-Point Principle on the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
- Principles for Resolution: External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar outlined India's four key principles regarding the Russia-Ukraine conflict:
- Peace as a Priority: Emphasis on the need for peace and the belief that the conflict cannot be resolved through continued warfare.
- Negotiation Requirement: Asserted that any resolution must involve Russia in the dialogue process.
- No Battlefield Solutions: Stressed that solutions cannot be achieved on the battlefield.
- Active Engagement: India is actively engaged and concerned about finding a resolution, with ongoing discussions with both Russia and Ukraine.
- Hosting Peace Conference: Jaishankar noted that while suggestions for India to host a peace conference have been made, there is no commitment from India to propose or host such a conference.
- Recent Diplomacy: Referenced Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visits to Moscow and Kyiv and highlighted National Security Adviser Ajit Doval's current visit to Russia.
Diplomatic Discussions with Germany
- Bilateral Meeting: Jaishankar met with German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock in Berlin to prepare for German Chancellor Olaf Scholz’s visit to New Delhi on October 24-25.
- Topics of Discussion:
- Global Issues: Discussed the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the Gaza conflict, and coordination for the UN Summit of the Future.
- UN Security Council Expansion: India and Germany are jointly advocating for the expansion of the UN Security Council.
- Ongoing Engagement: Both ministers will reconvene later this month at the UN General Assembly.
India-Germany Relations
- Germany’s Role: Baerbock acknowledged ongoing discussions with India and other countries about their roles in peace efforts, despite differing positions on the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Economic and Trade Relations:
- Migration and Mobility: Plans to enhance the India-Germany migration and mobility partnership, aiming to increase the number of skilled Indian workers in Germany. Currently, 125,000 Indian nationals work and 50,000 students study in Germany.
- Military Cooperation: Discussed expanding military partnerships, including joint air force exercises and upcoming naval exercises in Goa.
- Trade and Investment: Efforts to boost annual bilateral trade to $30 billion and attract about $25 billion in investment from Germany. New Delhi will host the Asia Pacific Conference of German Business next month.
Economic Ties with China
- Business Relations: Jaishankar addressed concerns about economic ties with China amidst a four-year military stand-off and related restrictions.
- Business Sectors: India is open to Chinese business but emphasizes the need for clarity on sectors and business terms.
Summary
India’s approach to the Russia-Ukraine conflict emphasizes peace, negotiation, and active engagement. Diplomatic efforts with Germany focus on global issues, military cooperation, and economic growth. Jaishankar also highlighted a nuanced stance on economic ties with China amid ongoing tensions.
Arctic Sea Ice Changes May Alter India's Monsoon Patterns

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
A study by researchers from India’s National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) has found that seasonal variations in Arctic Sea ice are impacting the Indian monsoon.
What is the Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall?
The Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall (ISMR), occurring from July to September, is one of the most significant monsoon systems globally. During the summer, the Central Asian and Indian landmasses heat up more quickly than the surrounding oceans. This temperature difference creates a low-pressure zone at the Tropic of Cancer known as the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ). Trade winds from the southeast are then deflected toward the Indian subcontinent due to the Coriolis effect and the low pressure they encounter after crossing the equator. As these winds pass over the Arabian Sea, they pick up moisture and bring rain to India. The southwest monsoon divides into two branches over the Indian landmass. The Arabian Sea branch delivers rain to the west coast, while the Bay of Bengal branch brings rain to the eastern and northeastern parts of India. These branches converge over Punjab and Himachal Pradesh, with the Arabian Sea branch moving inward and the Bay of Bengal branch following the Himalayas.
Complexity of the Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall
Recent climate models have revealed that the ISMR is influenced by the surface temperatures of the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific Oceans. Additionally, the circum-global teleconnection (CGT), a large-scale atmospheric wave at mid-latitudes, also plays a significant role in affecting the monsoon.
Influence of Arctic Sea Ice on the Indian Monsoon
The study indicates that reduced sea ice in the central Arctic results in decreased rainfall in western and peninsular India, but increased rainfall in central and northern India. Conversely, lower sea ice levels in the upper latitudes, especially in the Barents-Kara Sea region, delay the onset of the monsoon and make it more unpredictable.
Other Atmospheric Systems Influencing the Pattern
When sea ice levels in the central Arctic rise, the heat transferred from the ocean to the atmosphere triggers cyclonic circulation at lower latitudes, such as the North Atlantic. This process enhances Rossby waves—fast-moving air currents created by Earth's rotation and temperature differences—which move from west to east. These waves cause high pressure over northwest India and low pressure over the Mediterranean region, strengthening the Asian jet stream over the Caspian Sea and shifting the subtropical easterly jet northward. This shift leads to increased rainfall in western and peninsular India. On the other hand, decreased sea ice in the Barents-Kara Sea generates an anticyclonic circulation (clear skies) over northwest Europe. This disturbance affects the upper atmosphere over subtropical Asia and India, resulting in increased rainfall in northeastern India while leaving central and northwest regions drier.
Role of Climate Change
Climate change accelerates the reduction of Arctic sea ice, which intensifies the variability and unpredictability of the ISMR. Lower Arctic sea ice contributes to more frequent and severe droughts in some areas, while causing excessive rainfall and flooding in others. The study underscores the urgent need for expanded research on climate dynamics and more accurate monsoon forecasts to address these changing patterns.
The role of district agro-met offices in supporting farmers

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
- Last week, PTI reported that the India Meteorological Department (IMD) is planning to revive District Agro-Meteorology Units (DAMUs) under the Gramin Krishi Mausam Sewa (GKMS) scheme.
Background:
- The IMD established 199 DAMUs in 2018 in collaboration with the Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
- The aim was to use weather data to prepare and disseminate sub-district level agricultural advisories. In March, DAMUs were shut down following an order issued by the IMD.
Why are agro-met units important?
- Around 80% of farmers in India are small and marginal. They largely practise rain-fed agriculture in the backdrop of a decades-long farm crisis that is now overlaid with climate change-related weather variability.
- The DAMUs were located within Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs). Scientists and researchers trained in meteorology and agriculture were recruited as DAMU staff. They used weather data provided by the IMD like rainfall, temperature and wind speeds to prepare agricultural advisories related to sowing and harvesting, usage of fertilizers and pesticides, irrigation etc.
- These advisories were sent to millions of farmers across the country free-of-cost in local languages twice a week. They were shared via text messages, WhatsApp groups, newspapers and also through in-person communication from DAMU staff and KVK officers.
- Since these advisories provided weather information in advance, they helped farmers plan activities like irrigation. They also served as early warnings for extreme events like droughts and heavy rainfall. Many studies conducted over the years have stressed the benefits of agro-met advisories.
Why were DAMUs shut down?
- According to an Article-14 report, the NITI Aayog misrepresented the role of District Agricultural Management Units (DAMUs) and advocated for their privatization. The report claims that NITI Aayog inaccurately stated that agro-met data was automated, thereby diminishing the role of DAMU staff. In reality, DAMU staff were crucial in creating agricultural advisories based on IMD weather data, which were disseminated to farmers in local languages. NITI Aayog also proposed monetizing these services, contrasting with the current free provision of agro-met information to all farmers.
- A policy brief from the National Institute of Advanced Studies (NIAS), Bangalore, released in August, highlights that localized and accessible advisories from District Agricultural Management Units (DAMUs) have significantly improved farmers' responses to climatic variations in the Kalyana-Karnataka region. This has led to increased yields and incomes. The brief recommends reconsidering the decision to discontinue DAMUs and suggests exploring ways to enhance their effectiveness and presence.
What about private players?
Currently, a few private companies offer weather advisories, but their services are often too costly for small and marginal farmers. Dr. M. N. Thimmegowda, a professor at the University of Agricultural Sciences noted that annual subscriptions can cost ?10,000 per crop, leading to expenses of ?20,000-40,000 for vegetable and cereal growers, and up to ?60,000-80,000 for specialized advisories. Additionally, there is concern that these companies may provide biased recommendations for fertilizers and pesticides, favoring certain brands.
How can biotechnology be harnessed for economic development?

- 04 Sep 2024
The Centre unveiled its BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) policy last week.
On the face of it, the policy appears to be a routine attempt to create incentives and opportunities to energise growth in the biotech sector. But it is, in fact, about transforming existing industrial and manufacturing processes across various sectors to make them more sustainable and environment-friendly, and less wasteful.
The policy seeks to achieve this by harnessing the power of biotechnology, and developing new manufacturing methods that replicate, or mimic, processes found in natural biological systems.
Potential Benefits of Biotechnology:
- Medical Science:
- Cures for genetic disorders.
- Development of targeted therapies and treatments.
- Agriculture:
- Creation of new plant varieties with desirable traits.
- Increased crop yields and resistance to pests and diseases.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Bioplastics: Eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics (e.g., polylactic acid from corn starch).
- Carbon Capture: Micro-organisms capture and convert CO2 into biofuels, reducing the need for CO2 storage.
- Synthetic Biology:
- Design of novel organisms for specific functions.
- Laboratory-grown organs for transplantation, reducing reliance on organ donors.
- Industrial Processes:
- Replacement of chemical processes with biological ones, reducing pollution.
- Production of sustainable materials and fuels.
BioE3 Policy Benefits for India:
- Economic Impact:
- Expected $2-4 trillion from biomanufacturing over the next decade.
- Prepares India for future economic opportunities in biotechnology.
- Research and Development:
- Promotes competencies, research, and talent development.
- Supports technology development and maturation.
- Biomanufacturing Hubs:
- Establishes facilities for producing bio-products: chemicals, enzymes, functional foods, and more.
- Focus areas: bio-based chemicals, smart proteins, precision therapeutics, climate-resilient agriculture, carbon capture, and marine/space research.
- Future Technologies:
- Supports development of life support systems for space and innovative marine-based products.
- Encourages collaboration among multiple government departments for effective implementation.
State changes in rape law

- 05 Sep 2024
The recent legislative changes in rape laws across West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra represent significant shifts towards more stringent punishments and expedited judicial processes.
West Bengal: Aparajita Bill
Features:
- Death Penalty: The Bill introduces the death penalty as the mandatory punishment for rape where the victim dies or is left in a permanent vegetative state. It also extends the death penalty to all cases of rape, including gang rape of women above 18.
- Special Institutions: It mandates the creation of Special Task Forces in each district for investigating rape cases, and Special Courts for expedited trials.
- Changes to Existing Laws: The Bill amends the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, Bharatiya Nyaya Suraksha Sanhita, and the Protection of Children Against Sexual Offences Act (POCSO), introducing rigorous imprisonment and increasing penalties for repeat offenders and for disclosing victim identities.
- Acid Attacks: The Bill increases punishment for acid attacks to rigorous imprisonment for life.
Special Provisions:
- Establishes strict timelines for investigation and trial, aiming for efficiency.
- Includes amendments to the POCSO Act to align with the new death penalty provisions.
Andhra Pradesh: Disha Bills
Features:
- Death Penalty: The Disha Act introduces the death penalty for rape, including for minors below 16, gang rape, and repeat offenders.
- Special Courts and Teams: Similar to the Aparajita Bill, it creates Special Police Teams and Exclusive Special Courts in each district to handle these cases.
- Women and Children Offenders Registry: Proposes a registry to track offenders, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Special Provisions:
- Focuses on speeding up the investigation and trial process.
- Proposes comprehensive measures including a registry to maintain offender data, although this may have privacy implications.
Maharashtra: Shakti Bill
Features:
- Death Penalty: The Shakti Bill also introduces the death penalty for rape cases, with an emphasis on “heinous” cases such as acid attacks.
- Shortened Timelines: Like the other bills, it reduces the timeframes for investigations and trials.
- Web Platform Obligations: Imposes penalties on social media and internet platforms for failing to provide data requested by investigators in cases of crimes against women.
Special Provisions:
- Includes specific provisions for acid attacks with potential death penalty in severe cases.
- Addresses the role of web platforms in aiding investigations, reflecting concerns over digital evidence.
Comparative Summary
Death Penalty:
- West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh both introduce the death penalty for various rape offenses, including cases involving minors and gang rapes.
- Maharashtra includes the death penalty but emphasizes "heinous" acid attack cases more explicitly.
Special Institutions:
- All three states create special investigative teams and courts to handle rape cases more swiftly, though the exact mechanisms and timelines differ slightly.
Amendments to Existing Laws:
- West Bengal and Maharashtra both amend the POCSO Act to include the death penalty.
- Andhra Pradesh also makes amendments but with a broader focus on creating a comprehensive registry.
Additional Provisions:
- Maharashtra uniquely addresses the role of web platforms in investigations, an aspect not covered by the other states.
- Andhra Pradesh includes the establishment of an offender registry, which may have broader implications for data privacy and offender tracking.
Council of Europe’s Convention on Artificial Intelligence

- 06 Sep 2024
- The United States, the European Union, and the United Kingdom are anticipated to sign the Council of Europe’s new convention on artificial intelligence (AI), marking it as the first “legally binding” international treaty on AI.
- The treaty, officially named the Council of Europe Framework Convention on Artificial Intelligence and Human Rights, Democracy and the Rule of Law, was opened for signature during a Council of Europe Ministers of Justice conference in Vilnius, Lithuania.
Purpose and Approach:
- Human Rights Focus:
- The convention prioritizes human rights in regulating both public and private-sector AI systems.
- It seeks to address concerns that fragmented regulations by individual countries could impede the development of AI technology.
- Risk-Based Framework:
- The treaty adopts a risk-based approach to the design, development, use, and decommissioning of AI systems.
- It is applicable to AI systems used across public sectors, including entities acting on behalf of the government, and private sectors, covering multiple geographies.
Key Provisions and Obligations:
- Accountability:
- Signatories are accountable for harmful and discriminatory outcomes resulting from AI systems.
- They must ensure AI outputs respect equality and privacy rights and provide legal recourse for victims of AI-related rights violations.
- Human Rights and Democratic Integrity:
- AI systems must be consistent with obligations to protect human rights.
- They must not undermine democratic institutions, including judicial independence and access to justice.
- Measures must be implemented to safeguard democratic processes, including fair access to public debate and freedom of opinion.
- Exemptions:
- Exemptions include national security and research and development activities.
- Parties are obligated to address risks related to the lifecycle of AI activities by both public and private actors.
International Context:
- Related Agreements:
- The treaty complements other AI regulations and agreements, such as the G7 pact on AI (October 2023), Europe’s AI Act, and the Bletchley Declaration signed by 28 countries (November 2023).
Challenges and Concerns:
- Enforcement Issues:
- Despite being termed “legally binding,” the treaty lacks specific provisions for punitive sanctions like penalties or fines.
- Compliance is primarily monitored, which may not be a strong deterrent for enforcement.
- Initial Approvals:
- Hanne Juncher, Director of Security, Integrity and Rule of Law at the Council, indicated that 10 participants are expected to be among the first to approve the convention.
- This early support reflects the significant investment and satisfaction of these participants in the treaty’s outcome.
Conclusion:
- The Council of Europe’s convention represents a pioneering step towards a globally coordinated approach to AI regulation, emphasizing human rights and democratic principles. However, its effectiveness will depend on the development of robust enforcement mechanisms and broader adoption by key international stakeholders
La Niña Delays and Its Impact on India’s Weather
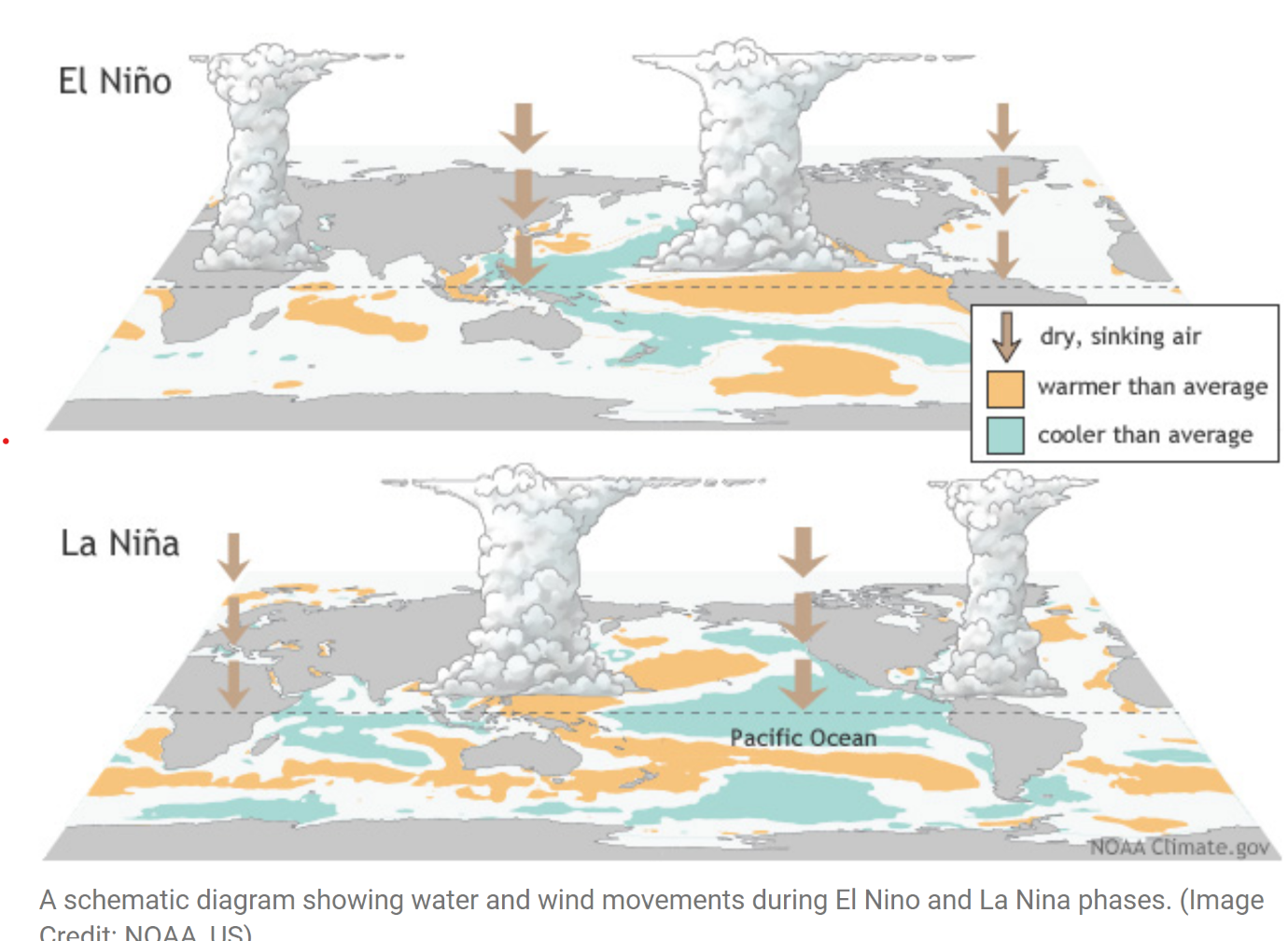
- 07 Sep 2024
- Current Conditions:
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported neutral Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) conditions.
- La Niña is expected to develop towards the end of the monsoon season, around the end of this month.
- Forecasting Challenges:
- Major global agencies have struggled with accurate forecasts for La Niña’s onset this year.
- Initial predictions suggested La Niña would start around July, but it has been delayed.
- Understanding La Niña:
- La Niña, meaning "The Little Girl" in Spanish, is a phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- ENSO influences global climate through changes in tropical Pacific Ocean sea surface temperatures.
- ENSO phases:
- El Niño (warm phase)
- La Niña (cool phase)
- Neutral
- ENSO Phases Explained:
- Neutral Phase: Eastern Pacific is cooler; trade winds drive warm water westward, causing upwelling of cooler waters.
- El Niño Phase: Weakened trade winds result in warmer eastern Pacific waters.
- La Niña Phase: Strengthened trade winds push more warm water to the western Pacific, cooling the eastern Pacific.
- Impact on India:
- El Niño typically reduces monsoon rainfall; La Niña generally enhances it.
- The previous El Niño occurred from June 2023 to May 2024.
- La Niña episodes can influence severe weather patterns and are linked to higher temperatures, heavy precipitation, and droughts.
- Weather Model Predictions:
- A strong El Niño ended in June, transitioning ENSO to neutral.
- Global models initially forecasted La Niña for July but revised this to August-October.
- IMD’s forecast since April predicted La Niña in the latter half of the monsoon season, aiming for enhanced rainfall in August and September.
- Reasons for Delayed Onset:
- The expected La Niña might be weak, complicating predictions.
- Other atmospheric factors, including the Madden-Julian Oscillation, impact weather models.
- Current and Future Impacts:
- La Niña's first signs are expected by late September or early October.
- It is projected to peak in November and continue through the northern hemisphere winter.
- Monsoon Impact: La Niña’s delayed onset means it won’t significantly affect the current southwest monsoon, though India saw a 16% surplus in August rainfall and a forecast of 109% “above normal” rain for September.
- Potential Effects:
- Northeast Monsoon: La Niña could influence the northeast (winter) monsoon (October-December), impacting Tamil Nadu, coastal Andhra Pradesh, Rayalaseema, south interior Karnataka, and Kerala. While La Niña typically doesn’t favor northeast monsoon rainfall, exceptions have occurred.
- Cyclone Activity: La Niña years often see increased cyclone activity in the north Indian Ocean, with higher intensity and longer-lasting storms.
- Winter Weather: Historically, La Niña years lead to harsher and colder winters, suggesting a potentially severe winter ahead.
India Becomes Leading Plastic Polluter

- 08 Sep 2024
India has emerged as the top global plastic polluter, releasing 9.3 million tonnes (Mt) of plastic annually, accounting for nearly 20% of the world's total plastic emissions.
Top Plastic Polluters:
- India: 9.3 Mt
- Nigeria: 3.5 Mt
- Indonesia: 3.4 Mt
- China: Previously first, now fourth, due to improvements in waste management practices such as incineration and controlled landfills.
Understanding Plastic Emissions
Plastic emissions refer to plastic that escapes from managed systems into unmanaged or uncontrolled environments. These emissions can occur throughout the lifecycle of plastic, from production through to disposal.
Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC)
The INC, established by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) in 2022, is working towards creating a global binding treaty on plastic pollution. The committee addresses the entire plastic lifecycle:
- INC Sessions:
- INC-1: Punta del Este, Uruguay (November 2022)
- INC-2: Paris, France (May – June 2023)
- INC-3: Nairobi, Kenya (December 2023)
- INC-4: Ottawa, Canada (2024)
- INC-5: Scheduled for South Korea (November 2024)
Status of Waste Generation in India
- Underreported Waste Generation: Official figures estimate 0.12 kilograms per person per day, which may be higher in reality.
- Excluded Data:
- Waste from rural areas.
- Waste recycled by the informal sector.
- Open burning of uncollected waste.
Global Trends in Plastic Pollution
- Sources of Pollution:
- Global North: Littering is a major contributor.
- Global South: Uncollected waste is the primary source of plastic pollution.
- Top Polluting Countries: 69% of global plastic waste emissions come from 20 countries, mostly low- and middle-income nations.
- High-Income Countries: Although these countries produce more plastic waste, their advanced waste management systems prevent them from being top polluters.
India's Initiatives to Address Plastic Waste
- UNDP India’s Plastic Waste Management Program (2018-2024): Focuses on improving plastic waste management practices.
- Ban on Single-Use Plastics (SUP): Prohibits the manufacture, import, sale, and use of plastic bags thinner than 120 microns.
- Plastic Waste Management Rules (2022): Introduces Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for plastic packaging, with targets for recycling, reusing, and using recycled plastic.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Launched in 2014 to improve waste management and eliminate open defecation.
- India Plastics Pact: Aims to transform the plastic lifecycle.
- Project REPLAN: Focuses on creating carry bags from a blend of plastic waste and cotton fibers.
- Un-Plastic Collective: Promotes a circular economy to reduce unnecessary plastic use and environmental impact.
- GoLitter Partnerships Project: Targets reducing marine plastic litter from fisheries and shipping.
Global Initiatives to Combat Plastic Pollution
- Closing the Loop: A UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific project to develop policies addressing plastic waste.
- Global Tourism Plastics Initiative: Aims to reduce plastic pollution from the tourism sector by 2025.
- EU Single-Use Plastics Directive (2021): Seeks to minimize plastic waste in the environment.
Heat Waves Impact on Informal Workers and India's Heat Action Plans

- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Crowded urban areas exacerbate the heat island effect, heightening risks for informal workers due to their unstable employment, lack of safety nets, and existing socio-economic vulnerabilities.
Context:
- Nowadays, Northern India is experiencing an intense heat wave, with workers, particularly those involved in hard physical labour, being the most vulnerable.
- In Delhi, temperatures have exceeded 50 degrees Celsius, posing severe and life-threatening conditions for labourers.
- The recent death of a 40-year-old worker due to extreme heat has prompted the Lieutenant Governor's office to issue guidelines, underscoring the urgency and gravity of the situation for those working under the scorching sun.
What is a Heat Action Plan?
- Heat Action Plan or HAP is a policy document prepared to effectively understand and respond to the harmful effects of heat waves.
- HAPs are prepared by the government authorities at various levels and serve as a comprehensive guide, outlining measures to prepare for, respond to, recover from and learn from extreme heat events.
- It is an advisory document that’s put forward by state and local governments that explains what needs to be done to prepare for a heat wave, what is to be done after a heat wave is declared, and puts forth a range of emergency responses and course corrective actions to learn from the heat wave experience so that the HAP can be refined.
- The primary purpose of these plans is to protect vulnerable populations and direct essential resources, including healthcare, financial support, information, and infrastructure, to those most at risk during extreme heat conditions.
- These plans are multi-sectoral in nature. They involve implementation from multiple government departments simultaneously before enduring heat waves and the main idea behind them is to make sure that during extreme temperatures, there is no loss of life.
- HAPs play a crucial role in raising awareness and providing guidance for individuals and communities to proactively safeguard their well-being against heat waves through a balanced mix of short and long-term actions.
What are the Flaws in Existing Heat Action Policies?
- Inadequate Coverage and Implementation: Despite NDMA mandates, many regions lack comprehensive HAPs.
- Where HAPs do exist, implementation is often inconsistent, leading to uneven protection for vulnerable populations, especially in urban areas.
- Insufficient Focus on Informal Workers: HAPs largely overlook the specific needs of informal workers, who make up a significant portion of the urban workforce.
- This group includes construction labourers, street vendors, domestic workers, and home-based workers, all facing unique challenges during heat waves.
- When workers are mentioned, it's usually in a generic "outdoor workers" category, resulting in insufficient and inappropriate interventions.
- Short-Term, Reactive Approach: Many HAPs focus on immediate relief rather than long-term solutions, evidenced by temporary measures like water provision and altered work hours.
- While these provide immediate relief, they do not address the underlying vulnerabilities that exacerbate the impact of heat waves on workers.
- There is a need for HAPs to integrate with broader urban planning and climate action plans for sustainable, resilient solutions.
- Rural Bias in Planning: HAPs often have a rural bias, neglecting the unique challenges of urban environments.
- Urban areas experience the "heat island effect," where dense infrastructure and reduced vegetation lead to higher temperatures.
- Informal urban settlements, where many workers live, are particularly vulnerable due to poor housing conditions and limited access to basic services.
- Lack of Integration with Urban Planning: HAPs often operate in isolation from other urban planning and development initiatives.
- There is little coordination between HAPs and urban design, housing policies, or infrastructure development.
- This lack of integration means missed opportunities to create more heat-resilient urban environments.
- Urban greening, improved housing designs, and better urban mobility can significantly reduce heat exposure and improve life quality for informal workers, but these measures are rarely considered in HAPs.
- Absence of Worker Participation: A critical gap is the lack of participation from worker communities in developing and implementing HAPs.
- Informal workers, who are most affected by heat waves, often have valuable insights into their working conditions and specific challenges.
- Excluding them from the planning process results in measures that may not be practical or effective.
Recommended Policies to Mitigate the Impact of Heat Waves:
- Reconceptualizing Heat Waves: Heat waves should be treated as prolonged disasters rather than isolated events, integrating Heat Action Plans (HAPs) with long-term urban planning and climate action strategies.
- The NDMA should collaborate with urban stakeholders such as the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) and the Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE).
- Worker Participation: It's essential to include worker communities in the preparation of action plans.
- The government should involve worker welfare boards and committees, like the Town Vending Committees (TVC) for street vendors, in drafting and implementing HAPs.
- Engaging these groups can lead to more tailored and effective interventions.
- Gender-Specific Needs: The impact of heat waves is not gender-neutral. Women workers, who constitute a significant part of the informal workforce, face unique challenges often overlooked in HAPs.
- These include increased care responsibilities, reproductive health risks, and greater exposure to heat in domestic and care work settings.
- HAPs should incorporate gender-specific measures to address these challenges, ensuring equitable and inclusive interventions.
- Economic and Health Protection: Heat waves profoundly affect the economic and health conditions of informal workers, yet HAPs often lack comprehensive measures to mitigate these effects.
- Informal workers frequently face income loss due to reduced working hours and increased healthcare expenses.
- HAPs should include provisions for income protection, such as compensation for lost wages and access to affordable healthcare.
- Strengthening social protection systems is also crucial to provide a safety net for workers during extreme heat events.
- Rethinking Labor Laws: As labour laws and Labor Codes are reformed, they should integrate considerations of climate change and its impact on work.
- This ensures that labour laws are responsive to new challenges posed by extreme heat and other climate-related events.
- Extending legal protections to informal workers is necessary, ensuring they receive the same rights and benefits as formal workers, including safe working conditions, fair wages, and social security access.
- Urban Reimagining: The government should redesign urban spaces to prioritize the needs of informal workers.
- This includes ensuring access to water, shade, and rest areas in public and work spaces.
- Additionally, investing in urban infrastructure to mitigate the impact of heat waves is essential.
- This involves increasing green spaces, improving housing conditions in informal settlements, and enhancing public transportation.
Conclusion
The recent severe heat wave in northern India highlights the pressing need for comprehensive and inclusive measures to safeguard the most vulnerable workers. By integrating long-term planning, inclusive policies, and active worker participation, India can effectively protect its informal workforce from the devastating impacts of extreme heat. Prioritizing the design of cities to meet the needs of workers is essential for fostering a more resilient and equitable urban environment.
Dispelling Population Myths Triggered by a Working Paper

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The working paper released by the Economic Advisory Council (EAC) to the Prime Minister makes an erroneous assertion regarding the growth of the Muslim population.
Context:
- The discussion on India's religious demographics is frequently marred by sensationalism and misinterpretation, often driven by media and political narratives.
- A recent working paper by the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM), titled "Share of Religious Minorities: A Cross-Country Analysis (1950-2015)," has been a particular target of such distortions.
- Hence, it is crucial to critically examine the findings and interpretations of the EAC-PM's working paper, placing them within the broader socio-economic dynamics and demographic trends.
Composition of the Population of various communities highlighted by EAC:
- The population composition of various communities in the region has changed between 1950 and 2015, as highlighted by the data:
- In terms of absolute numbers, the Hindu population saw a substantial increase of 701 million individuals, while the Muslim population grew by 146 million.
- However, when looking at proportional changes, the Hindu population experienced a decrease of 6.64 percentage points, from 84.7% in 1950 to 78.06% in 2015.
- Conversely, the Muslim population's proportion increased by 4.25, rising from 9.84% in 1950 to 14.09% in 2015.
- Despite these shifts in proportions, the Hindu population remains numerically larger than the Muslim population as of 2015.
What does the 2011 census say?
According to the 2011 census, the following changes in the proportions of various religious communities were observed in comparison to the 2001 census:
- The Hindu population's proportion relative to the total population decreased by 0.7 percentage points.
- The Sikh population's proportion saw a decline of 0.2 percentage points.
- The Buddhist population's proportion decreased by 0.1 percentage points.
- On the other hand, the Muslim population's proportion relative to the total population increased by 0.8 percentage points.
- The proportions of the Christian and Jain communities underwent no significant change during the 2001-2011 period.
A Study on Socio-Economic Aspects and Population Growth in the Muslim Communities:
The Impact of Education:
- Education significantly influences fertility rates and overall population growth. Communities with higher educational attainment, particularly among women, generally exhibit lower fertility rates.
- Education equips individuals with knowledge about family planning, reproductive health, and the economic implications of large families.
- In India, disparities in educational attainment among different religious communities contribute to variations in population growth rates.
- Historically, the Muslim community has encountered barriers to accessing quality education, leading to higher fertility rates compared to the Hindu community.
- This indicates that the higher population growth rate among Muslims is due to limited educational opportunities rather than religious doctrine.
Economic Conditions:
- Economic stability plays a crucial role in determining family size and population growth.
- Economically stable families tend to have fewer children, enabling them to invest more resources in each child's health, education, and overall well-being.
- In contrast, economically disadvantaged communities often exhibit higher fertility rates as a response to economic insecurity, viewing children as contributors to household income.
- The higher growth rate of the Muslim population in India can be attributed to lower average income levels and limited access to economic opportunities within the community.
- Addressing economic disparities is essential for moderating population growth and enhancing overall human development.
Access to Healthcare:
- Healthcare access, especially reproductive health services, is a key determinant of fertility rates.
- Communities with better access to healthcare services, including contraception and maternal healthcare, typically have lower fertility rates.
- The Muslim community in India has historically faced challenges in accessing healthcare services, contributing to higher fertility rates.
- Improving healthcare access for all communities is vital for achieving balanced population growth and improving quality of life.
Cultural Factors and Gender Norms:
- Cultural factors and gender norms also influence fertility rates. Traditional norms valuing large families and early marriage can lead to higher fertility rates in some communities.
- Promoting gender equality and empowering women to make informed reproductive choices are crucial for moderating population growth.
- Programs aimed at changing cultural attitudes towards family size and encouraging later marriages can significantly impact reducing fertility rates.
Urbanization and Migration:
- Urbanization and migration patterns affect population growth, with urban areas generally exhibiting lower fertility rates than rural areas due to better access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
- Migration from rural to urban areas can lead to a decline in fertility rates as individuals adapt to urban socio-economic conditions.
- In India, the Muslim population is more concentrated in rural areas, which tend to have higher fertility rates.
- Promoting urbanization and integrating rural communities into urban settings can contribute to balanced population growth.
Human Development Indicators:
- Human development indicators, such as life expectancy, child mortality rates, and literacy rates, are closely linked to population growth.
- Communities with higher human development indicators tend to have lower fertility rates.
- The lag in human development indicators among the Muslim community compared to the Hindu community underscores the need for targeted interventions to improve education, healthcare, and economic opportunities for all.
Religious Demography in a Broader Context:
Historical Stability in Religious Composition:
- Historical data indicates that India's religious composition has remained relatively stable over the decades.
- The 2021 Pew Research Centre report, which analyzed Census data from 1951 to 2011, reveals that the proportions of India's major religious groups have shown remarkable stability since Partition.
- This stability counters claims of dramatic demographic shifts. The Hindu population has consistently constituted a large majority, while the proportions of other religious groups, including Muslims, have grown at a predictable rate.
- This historical perspective underscores that changes in religious demography are gradual and not indicative of sudden or alarming shifts.
Projections and Future Trends:
- Projections by leading demographers offer a nuanced understanding of future demographic trends.
- In a 2005 study, P. N. Mari Bhat and Francis Zavier projected that the proportion of Muslims in India’s total population would peak at around 18.8% by 2101.
- This projection is based on historical trends and factors such as declining fertility rates and improvements in socio-economic conditions.
- Recent data from the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) shows a significant decline in Muslim fertility rates, suggesting that the peak proportion might be even smaller if similar studies were conducted today.
- These projections highlight that fears of Muslims overtaking Hindus in population numbers are unfounded and not supported by empirical evidence.
Socio-Economic Development and Demographic Trends:
- Socio-economic development plays a critical role in shaping demographic trends. Improved education, healthcare, and economic opportunities lead to lower fertility rates across all communities.
- The decline in Muslim fertility rates, as observed in the NFHS data, is a direct result of better access to education and healthcare.
- This trend is expected to continue as development efforts reach more communities.
- Therefore, socio-economic development is essential for achieving balanced population growth and should be the focus of policy interventions.
Conclusion
The sensationalism and misinterpretation of the EAC-PM working paper's findings can obstruct informed public discourse. Achieving an accurate understanding of population dynamics demands a nuanced examination of socio-economic conditions and demographic data. As India awaits updated Census data, it's imperative to promote a discourse on religious demography that is informed and balanced, free from divisive political narratives.
Still No Sign of the Language of Equity and Inclusion

- 29 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Equity in education, health care, and rights in India cannot succeed unless the ableist barriers that exclude Deaf and hard-of-hearing citizens are removed.
Context:
- As the 2024 general election in India concludes, the absence of sign language interpreters during the Election Commission of India's announcement in March highlights the ongoing exclusion of Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) citizens.
- This incident reflects the broader societal neglect and ableism that marginalize the DHH community in daily life.
- It is crucial to examine the everyday challenges faced by DHH individuals, the limited opportunities available to them, and the necessary steps to address these issues.
Promoting Equity and Recognizing Exclusive Practices:
- India's goals for equitable education, healthcare, and rights are fundamentally compromised by persistent ableist barriers that exclude Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) individuals.
- The National Programme for Prevention and Control of Deafness exemplifies this issue.
- Although it addresses hearing impairment prevention and treatment, it fails to improve the quality of life for DHH individuals.
- The program emphasizes theoretical aspects like screening and hearing aids but neglects Indian Sign Language (ISL), essential for deaf communication.
- Despite the Social Justice Ministry establishing the ISL Research and Training Centre in 2015 and the National Education Policy 2020 recommending ISL standardization in schools, ISL remains unrecognized as an official language and is rarely used in educational systems, even in schools for the deaf.
The Debate Over Oralism and Educational Exclusion:
Historical Context and Pedagogical Approaches:
- The debate between oralism and the use of sign language in educating deaf individuals has deep historical roots, reflecting broader societal attitudes toward disability and communication.
- Emerging in the late 19th century, oralism emphasizes teaching deaf individuals to use their voices and read lips rather than relying on sign language.
- Proponents believed that integrating deaf individuals into the hearing world was best achieved by encouraging them to mimic spoken language as closely as possible, assuming this would enable them to function more effectively in a predominantly hearing society.
Criticisms of Oralism:
- Despite its intentions, oralism has faced widespread criticism for its limitations and negative impacts on deaf individuals.
- One major criticism is that oralism often leads to linguistic deprivation, especially in children.
- Learning to speak and read lips can be extremely challenging and time-consuming, resulting in delays in language acquisition and cognitive development.
- Without early and consistent exposure to a natural language like sign language, deaf children risk not developing the foundational language skills necessary for effective communication and learning.
- Additionally, oralism can create significant social isolation, as the pressure to conform to oral communication can undermine the development of a strong, positive deaf identity and sense of belonging within the deaf community.
The Case for Sign Language:
- In contrast, using sign language as the primary mode of instruction for deaf students has numerous benefits.
- Sign language is a natural and fully developed language that enables deaf individuals to communicate effectively from an early age.
- Research shows that early exposure to sign language supports cognitive development and academic achievement, allowing deaf children to develop language skills on par with their hearing peers.
- Furthermore, sign language fosters a sense of community and cultural identity among deaf individuals, providing a strong sense of belonging and self-worth.
The Indian Context:
- In India, the education system has largely adhered to the oralist approach, significantly impacting deaf students.
- Most educators in schools for the deaf are not trained in Indian Sign Language (ISL), perpetuating exclusion and limited accessibility.
- The current educational framework focuses on "rehabilitation," expecting deaf individuals to adapt to their surroundings rather than addressing the societal barriers impeding their inclusion.
- This approach fails to recognize the value of sign language and the importance of providing deaf students with a language-rich environment that supports their linguistic and cognitive development.
Everyday Challenges and Opportunities for the Invisible Deaf Population:
The Invisible Population:
- India's hearing-impaired population is substantial, with the 2011 Census reporting five million people, the National Association of the Deaf estimating 18 million, and the World Health Organization suggesting nearly 63 million Indians have significant hearing impairment.
- Despite these numbers, Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) individuals remain largely invisible in society.
- Only 5% of deaf children attend school, often facing prolonged educational timelines due to an oralist curriculum.
- Employment opportunities for the deaf are limited, with government recruitment sometimes favouring those with lesser impairments, leading to protests.
- Despite petitions for Indian Sign Language (ISL) recognition, the government resists, citing the adequacy of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act (RPDA) 2016, which falls short in practical implementation.
Lack of Accessibility in Public Transport:
- DHH individuals face numerous every day challenges due to a lack of accessibility in public transport, media, public structures, and emergency services.
- Basic activities, such as following public announcements or accessing customer service, become insurmountable tasks.
- While some progress has been made with accessible options in films and sports, much remains to be done.
- Employment opportunities for the deaf are often restricted to low-skill jobs, and the government sector lags in accessibility and inclusion initiatives.
- Protests by the deaf community demanding better education and employment opportunities have often been met with force or empty promises.
Healthcare and Mental Health Accessibility:
- Access to healthcare poses additional challenges for the deaf community, as most hospitals lack interpreters, complicating communication.
- This is especially problematic in mental healthcare, where a lack of ISL-trained professionals further marginalizes DHH individuals.
- Although the Mental Healthcare Act of 2017 promises universal mental healthcare, its implementation is ineffective, with only 250 certified sign language interpreters available and no clear data on ISL-trained mental health professionals.
Way Forward:
- To address these issues, recognizing Indian Sign Language (ISL) as an official language and integrating it into schools and colleges for both hearing and Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) students is crucial.
- This approach would also create employment opportunities for DHH individuals as educators.
- Additionally, healthcare systems need to be updated to ensure easy and accessible communication for DHH patients, including employing language-concordant physicians.
- Regulatory commissions in medical fields must reduce barriers for DHH individuals aspiring to healthcare professions, fostering a more inclusive workforce.
- Media channels should consistently offer deaf programming, and government event announcements should include live ISL interpreters, as seen in many other countries.
- Timely interventions in these areas could lead to significant improvements, potentially ensuring real-time ISL interpretations in future elections.
Conclusion
The challenges faced by the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) community in India are complex and deeply rooted in societal ableism. While some progress has been made, much more needs to be done. It is crucial for authorities to actively engage with the DHH community and address their specific needs. By recognizing and implementing necessary changes, India can move towards a more inclusive society where the rights and needs of DHH individuals are fully acknowledged and met.
Geopolitical Significance of Chabahar Port: Opportunities and Challenges for India
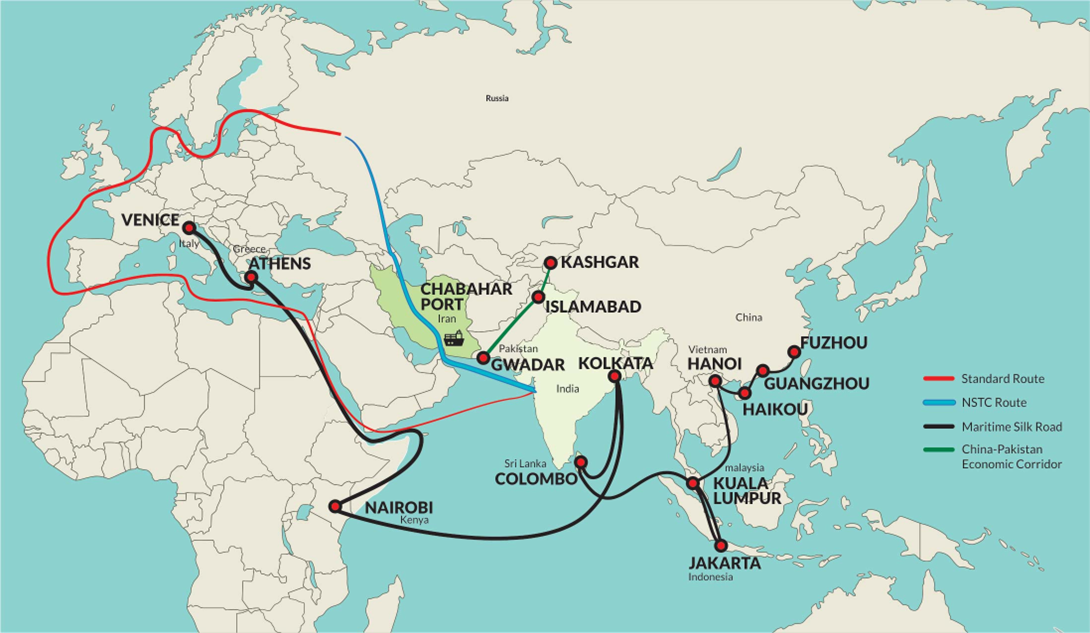
- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India secured rights to invest in and operate the Shahid-Behesti terminal at Chabahar Port for another 10 years.
Context:
- The recent extension of the contract between India and Iran, granting New Delhi continued investment and operational rights at the Shahid-Beheshti terminal within Chabahar Port for another ten years, underscores the project's strategic and economic significance.
- This development occurs amid a turbulent period in West Asia, characterized by ongoing conflict in Gaza, escalating tensions between Israel and Iran, and a destabilizing helicopter crash resulting in the loss of Iran’s President and Foreign Minister.
- Nevertheless, the Chabahar project retains its pivotal role in cementing economic ties between India and Iran despite these formidable challenges.
Significance of the Chabahar Project for India:
- Economic Connectivity and Trade Advancement: Chabahar Port serves as a vital node in the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), streamlining India's trade routes with Central Asia, Russia, and beyond.
- By offering a direct sea-land route that circumvents Pakistan, Chabahar substantially cuts transportation time and costs for Indian exports bound for these regions.
- This heightened connectivity fosters increased trade, economic convergence, and access to fresh markets, augmenting India's export potential and economic prosperity.
- Geopolitical Influence and Strategic Independence: Chabahar represents a strategic asset for India to assert its influence in the region and diminish reliance on Pakistani transit routes, often fraught with geopolitical tensions.
- Through investment in Chabahar, India solidifies a strategic foothold in Iran, a nation wielding significant sway in West and Central Asia.
- The port empowers India to project strength and maintain a strategic presence in a landscape where China, through its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and Pakistan, vie for dominance.
- This strategic autonomy is pivotal for India's foreign policy, enabling adept navigation of intricate regional dynamics.
- Regional Security and Harmony: Chabahar Port assumes a crucial role in India's efforts towards regional security and stability, particularly concerning Afghanistan.
- Endorsed by the Taliban and with their financial commitment, Chabahar emerges as a key conduit for humanitarian aid and economic provisions to Afghanistan, thereby fostering stability in a strife-ridden region.
- By promoting economic growth and offering alternatives to Pakistani ports, Chabahar helps mitigate the peril of economic isolation for Afghanistan, fostering regional tranquillity.
- Countervailing Chinese Influence: Strategically positioned to counterbalance Chinese presence, Chabahar offers a distinct avenue to offset Chinese influence, notably vis-à-vis the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and Gwadar Port.
- While Gwadar, under China's dominion, lies proximate to Chabahar, the latter furnishes an alternative route pivotal for diversifying regional supply chains.
- By fortifying Chabahar, India not only mitigates the strategic risks of Chinese infrastructure dominance but also offers a viable alternative for international trade routes evading Chinese control.
- Diplomatic Collaboration and Multilateralism: Chabahar Port epitomises India's dedication to diplomatic collaboration and multilateral engagement.
- Through this venture, India showcases its adeptness in partnering with diverse international stakeholders, including Iran, Afghanistan, and Central Asian nations, nurturing a collaborative regional milieu.
- The port aligns with broader international endeavours to bolster connectivity and economic amalgamation across Eurasia, positioning India as a pivotal player in regional developmental endeavours.
- Energy Security: Given Iran's substantial energy reserves, Chabahar Port holds promise in bolstering India's energy security.
- By serving as a strategic ingress point for Iranian oil and gas, the port facilitates energy imports, diversifies India's energy sources, and diminishes dependence on any single nation or route.
- This diversification is instrumental in securing a stable and resilient energy supply, indispensable for India's burgeoning economy.
Challenges in India-Iran Relations Amidst Chabahar Port Dynamics:
- Sanctions and Global Pressures: The imposition of international sanctions, particularly by the United States, has significantly disrupted economic ties between India and Iran.
- Projects like the Farzad-B gas field and the Irano Hind Shipping Company bore the brunt of these sanctions directly.
- The Chabahar Port project itself has faced intricacies due to U.S. sanctions, necessitating periodic exemptions for India to sustain its development efforts.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: India's strategic partnership with the United States sometimes clashes with its engagements with Iran, creating geopolitical complexities.
- During the Obama administration, India curtailed its oil imports from Iran in line with U.S. policies on Tehran’s nuclear program, impacting bilateral trade and diminishing Iran's standing as a major oil supplier to India.
- Competing Regional Agendas: India and Iran harbour divergent regional interests that occasionally conflict.
- While Iran aims to bolster its influence in West Asia and deepen ties with nations like China and Russia, India’s regional focus includes countering China’s Belt and Road Initiative and safeguarding its interests in Afghanistan.
- These disparate priorities can lead to friction and curtail the extent of bilateral cooperation.
Recommendations for Future Engagement:
Diversification of Economic Cooperation: While the Chabahar Port remains crucial, India and Iran should broaden their economic collaboration beyond it.
-
- Exploring sectors like energy, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and technology through revived projects like the Farzad-B gas field or new joint ventures can enhance economic ties.
- Establishing a comprehensive trade framework involving tariff reduction, streamlined customs procedures, and investment incentives can stimulate bilateral commerce.
Enhancement of Diplomatic Engagement: Regular high-level visits and dialogues are essential to address misunderstandings and align strategic interests.
-
- Institutionalizing such engagements ensures continuous and structured communication between the two nations.
- Leveraging participation in multilateral forums like the United Nations and regional organizations can facilitate joint initiatives, amplifying diplomatic influence and fostering closer ties.
- Balancing Geopolitical Alignments: India should navigate its strategic partnership with the United States while engaging with Iran, emphasizing the significance of projects like Chabahar.
- Diplomatic efforts should prioritize securing exemptions from sanctions hindering critical projects, necessitating transparent communication with the U.S.
- Strengthening ties with other regional actors such as Afghanistan, Central Asian countries, and Russia can reinforce India-Iran relations and regional stability.
- By implementing these recommendations, India and Iran can foster a more robust and diversified partnership, enhancing mutual prosperity and geopolitical stability in the region.
Conclusion
The Chabahar port project symbolizes the intricate fabric of India-Iran relations, intertwining economic ambitions with strategic considerations. Amidst the shifting tides of geopolitics, Chabahar emerges as a symbol of the enduring collaboration between the two nations.
Maintaining this foundational project while expanding economic collaboration and diplomatic finesse will be pivotal in fortifying and advancing the India-Iran relationship in the years ahead.
A Door to a Housing Scheme, Tribals Find Hard to Open

- 27 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to a recent report, the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN) is facing challenges in implementation.
Context:
- India is home to numerous tribal groups, including 75 identified as Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) across various states.
- To address their socio-economic backwardness, the Government of India launched the Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development Mission in 2023-24.
- Despite this initiative, both PVTGs and frontline officials encounter significant challenges when using a mobile application to register for the housing scheme.
What is the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya MahaAbhiyan (PM JANMAN)?
- The Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya MahaAbhiyan (PM JANMAN) is an initiative launched by the Government of India to uplift and empower the Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
Its key objectives and implementation aspects:
- The PM JANMAN initiative aims to ensure that PVTGs have access to essential services and improved living standards by addressing their critical needs through a comprehensive set of interventions.
- One of the flagship programs under this initiative is the Housing scheme, a Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) scheme designed to provide secure and habitable housing to PVTG households.
- The Housing scheme targets to reach 4.90 lakh PVTG households by the year 2026, with each household entitled to receive ?2.39 lakh in three instalments.
- This financial assistance is intended to enable these vulnerable communities to construct safe and durable houses, protecting them from environmental challenges and providing a sense of security and dignity.
- By addressing the critical need for safe housing, along with other interventions focused on clean drinking water, sanitation, and other essential services, the PM JANMAN initiative aims to uplift the living conditions of PVTGs and empower them to overcome the challenges they face.
- This comprehensive approach seeks to create a supportive environment for the overall development and well-being of these marginalized communities. CopyRetry
What are the Challenges Associated with PM JANMAN Housing Scheme Implementation?
Data Mismatch and Ineligibility Issues:
- A significant challenge in the registration process is the widespread deletion of job cards, essential for registering for the PM JANMAN Housing scheme.
- Over the past two years, more than eight crore MGNREGA workers' job cards, including those of PVTG members, have been deleted. This massive data purge has prevented many eligible households from registering for the scheme, thereby excluding them from receiving benefits.
- Additionally, incorrect registrations have been reported, where individuals register using others' job cards.
- This not only deprives rightful owners of their entitlements but also creates administrative burdens in correcting these errors.
Discrepancies in Data Collection Systems:
- The 'Awaas+' registration app, used by block/panchayat-level officials, is critical for data collection but has significant discrepancies with other official records.
- For instance, in Vanjari Panchayat, Alluri Sitharama Raju district, Andhra Pradesh, the app lists only 22 villages, while the MGNREGA Management Information System (MIS) lists 31 villages.
- These discrepancies confuse beneficiaries and officials and may lead to the exclusion of eligible households.
App Usability and Confusion:
- The 'Awaas+' app's user interface and functionality present several challenges. The app collects beneficiaries' data in three main areas: geographical location, household profiles, and bank account details.
- However, its design and operational issues make the process cumbersome.
- The app includes pre-populated village lists that often do not match official records, leading to incorrect registrations or an inability to register certain households.
Geo-tagging and Network Issues:
- The app’s geo-tagging feature, meant to accurately record household locations and planned construction sites, faces issues due to network problems in remote areas.
- These network issues hinder the geo-tagging process, resulting in incomplete or incorrect data entries, which affects registration and service delivery planning.
Financial Inclusion Barriers:
- The app's bank selection functionality is another significant hurdle. Beneficiaries must choose from three categories of banks (Cooperative Bank, Commercial Bank, or Regional Rural Bank), each presenting numerous options.
- For instance, selecting 'Commercial Bank' can display over 300 options, and choosing 'State Bank of India' can show over 500 branch options.
- This complexity is overwhelming for beneficiaries and officials, especially those with limited digital literacy.
- Despite the Government of India’s push for India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) to enhance financial inclusion in remote areas, the app does not list IPPB, limiting access to convenient banking services for many PVTG households.
Inclusivity and Accessibility Issues:
- The app also fails to capture specific information about PVTGs, defaulting to a general 'ST' (Scheduled Tribe) category.
- This oversight results in non-PVTG registrations, complicating the process further. Local officials sometimes require PVTG members to obtain certification from village leaders, problematic in areas where PVTGs and non-PVTGs coexist.
- Additionally, network issues exacerbate the geo-tagging feature's challenges, adding to the difficulties faced by officials and beneficiaries alike.
Recommendations for Policymakers to Improve the PM JANMAN Scheme:
User-Friendly Application Interface:
- Redesign the ‘Awaas+’ mobile app to simplify navigation with intuitive menus and clear instructions.
- This will assist both beneficiaries and frontline officials who may not be tech-savvy. Include detailed guidelines on entering names and other details, especially when Aadhaar information is unavailable or differs from official records.
Accurate and Comprehensive Data Lists:
- Ensure the app’s pre-populated lists of villages and other data fields are regularly updated and synchronized with other government databases, such as the MGNREGA Management Information System (MIS), to eliminate discrepancies.
- Additionally, include explicit fields for PVTGs within the app to prevent incorrect registration of non-PVTG households.
Include IPPB in Banking Options:
- Add the India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) to the list of available banks in the registration app.
- Given IPPB’s extensive reach in rural and remote areas, this inclusion would significantly enhance financial access for PVTG households.
- Simplify the bank selection process by implementing a search function or categorizing banks more effectively to facilitate easier selection by users.
Improve Technical Infrastructure:
- Invest in improving network connectivity in remote areas to support geo-tagging and other app functionalities.
- Partner with telecom companies to extend coverage to underserved regions and develop offline capabilities for the registration app, allowing data collection without immediate internet access and subsequent synchronization when connectivity is available.
Provide Comprehensive Training and Support:
- Implement comprehensive training programs for frontline officials and community volunteers on using the app and managing the registration process efficiently.
- Establish dedicated technical helplines or support centres to assist with real-time troubleshooting and provide guidance for users facing difficulties.
Conclusion
While various initiatives have targeted the vulnerabilities of PVTGs, accessing government benefits remains a substantial challenge for these marginalized communities. The PM JANMAN initiative stands as a potential avenue to enhance the well-being of PVTGs. However, it is imperative to address the existing obstacles in the registration process and prioritize inclusivity and accessibility. The PM JANMAN scheme presents an opportunity to shift the paradigm for PVTGs, but its success hinges on effectively tackling implementation challenges and fulfilling the commitments made.
Religion Should Not be the Sole Reason for Granting Reservation
- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Calcutta High Court has struck down a series of orders passed by the West Bengal government between March 2010 and May 2012 by which 77 communities (classes), 75 of which were Muslim, were given reservation under the Other Backward Classes (OBC) category.
Context:
- In a significant ruling on Wednesday, the Calcutta High Court dismissed all Other Backward Classes (OBC) certificates issued in West Bengal since 2010.
- A division bench of Justice Tapabrata Chakraborty and Justice Rajasekhar Mantha made this decision while addressing a public interest litigation (PIL) that challenged the process of granting OBC certificates.
- The court directed that a new list of OBCs should be created based on the West Bengal Commission for Backward Classes Act of 1993.
What is the Issue With OBC Certificates?
- In 2010, the West Bengal (WB) government issued notifications, on the recommendations of the West Bengal Backward Classes Commission, including 42 classes (41 from the Muslim community) as Other Backward Classes (OBCs), entitling them to reservation and representation in government employment under Article 16(4) of the Constitution.
- Also in 2010, an order was issued sub-categorizing the 108 identified OBCs in the state (66 pre-existing and 42 newly identified) into 56 OBC-A (more Backward) and 52 OBC-B (Backward) categories.
- In 2012, the West Bengal government included 35 classes (34 from the Muslim community) as OBCs.
- In 2013, the West Bengal Backward Classes (Other than Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) (Reservation of vacancies and posts) Act 2012 gave recognition to all 77 new OBCs.
- These orders and legislation were challenged in the Calcutta High Court on the grounds that the declaration of classes as OBCs was based purely on religion, the categorization was not based on any acceptable data, and the survey conducted by the Commission was unscientific.
The Calcutta High Court's Ruling on West Bengal's Reservation Policies:
- The court found that religion had been the sole basis for the state government to provide reservation, which is prohibited by the Constitution and court orders.
- The High Court heavily relied on the Supreme Court's judgment in Indra Sawhney v Union of India (Mandal judgment).
- In 1992, a nine-judge Bench held that OBCs cannot be identified and given reservation solely based on religion.
- The Supreme Court also held that all states must establish a Backward Classes Commission to identify and recommend classes of citizens for inclusion and exclusion in the state OBC list.
- The High Court noted that the Commission's recommendation had been made with "lightning speed" and without using any objective criteria to determine the backwardness of these classes.
- The court stated that there is no question that the said communities have been used as a political prop for vote bank politics.
- The court struck down some provisions of West Bengal's 2012 Act, including:
- The provision allowed the state government to sub-classify OBC reservations into OBC-A and OBC-B categories.
- The provision allows the state to amend the Schedule of the 2012 Act to add to the list of OBCs.
- The court held that sub-classification is meant to address different levels of deprivation faced by different communities and could only be done based on scientific data.
- Since the Commission acknowledged that the government did not consult it prior to sub-classification within OBC, the court ruled that the state government must consult the Commission to create a fair and unbiased classification.
The Position on Religiously-Based Reservations in the Constitution and Court Orders:
The Constitution of India:
- Article 15(1) specifically prohibits the state from discriminating against citizens on grounds only of religion and caste (along with sex, race, and place of birth).
- Article 16(2) specifically prohibits the state from discriminating against citizens on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth, residence or any of them, in respect of any employment or office under the State.
The Observations of the Supreme Court:
- In M R Balaji (1962), the SC held that while castes among Hindus may be an important factor to take into account when assessing the social backwardness of certain groups or classes of citizens, it cannot be the only test in this regard.
- In E P Royappa vs State Of Tamil Nadu (1973), the SC held that equality is a dynamic concept and cannot be confined within traditional limits.
- In State of Kerala vs N M Thomas (1975), the SC held that the crucial word 'only' in Articles 15 and Article 16 implies that if a religious, racial, or caste group constitutes a weaker section (under Article 46) or constitutes a backward class, it would be entitled to special provisions for its advancement.
- The SC in Indra Sawhney (1992) laid down that any social group if found to be backward under the same criteria as others, will be entitled to be treated as a backward class.
What are the Current Provisions of Reservation?
- The current provisions of reservation in India stem from the Constituent Assembly's decision to provide employment reservations for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes under Article 16(4A) of the Constitution.
- Initially approved for a period of 10 years, these reservations have been renewed annually ever since.
- Notably, Christian and Muslim communities within the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes do not receive reservation benefits.
- The decision not to extend reservation to religious minorities was influenced by the partition, as reflected in Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel's presentation of a special sub-committee report in 1949, addressing the issues faced by minority populations in East Punjab and West Bengal.
- The committee, which included Nehru, Rajendra Prasad, KM Munshi, and Ambedkar, concluded that the country's conditions had changed to such an extent that "in the context of independent India and the present circumstances, it is no longer appropriate to reserve seats for Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, or any other religious minority."
- They believed that reservations for religious communities "may lead to some degree of separatism and, to an extent, contradict the concept of a secular democratic state."
- They argued that the fundamental rights of freedom of religion and the right of minorities to maintain their own educational institutions were sufficient safeguards for protecting minorities.
- However, the Advisory Committee agreed that "the specific situation of the Scheduled Castes would make it necessary to grant them reservation for the originally decided ten-year period."
- Ambedkar attempted to resolve several positions on the caste question by introducing the concept of backwardness and reservation as methods of creating a society beyond caste.
Arguments Related to Religion-based Reservation in India:
Arguments in Favour of Religion-Based Reservations in India:
- Socio-Economic Backwardness: According to the Sachar Committee Report, Muslims in India lag behind other communities in terms of socio-economic indicators such as education, employment, and income.
- Reservations can help in bridging this gap.
- Constitutional Mandate: The Indian Constitution provides for affirmative action for socially and educationally backward classes irrespective of religious and cultural denomination.
- Ensuring Adequate Representation: Reservations can ensure adequate representation of underrepresented religious groups in employment, education, and other fields.
Arguments Against Religion-Based Reservations in India:
- Secularism: Critics argue that providing reservations based on religion goes against the principle of secularism enshrined in the Indian Constitution, which advocates equal treatment of all religions by the state.
- Undermining National Unity: Religion-based reservations could undermine national unity as it could lead to resentment and division among different communities.
- Economic Criteria: Reservations should be based solely on economic criteria rather than religion, to ensure that benefits reach those who are truly economically disadvantaged, irrespective of their religion.
- Administrative Challenges: Implementing reservations based on religion could pose administrative challenges, such as determining the criteria for identifying beneficiaries and preventing misuse of the system.
Way Forward:
- Socio-Economic Criteria: Instead of religion, reservations could be based on socio-economic criteria, ensuring that benefits reach the most disadvantaged individuals regardless of their religion.
- Empowerment Through Education: Focus on improving educational infrastructure and providing skill development programs to empower the backward communities and enhance their socio-economic status.
- Inclusive Policies: Implement inclusive policies that address the specific needs of the backward religious communities in areas such as education, employment, and healthcare, without resorting to religious-based reservations.
- Dialogue and Consensus: Engage in a dialogue involving all stakeholders to arrive at a consensus to address the socio-economic challenges faced by the various communities, ensuring that any measures taken are in line with constitutional values and principles.
Conclusion
While recognizing the socio-economic disparities faced by various religious communities in India, the emphasis on inclusive policies based on socio-economic criteria emerges as pivotal. By prioritizing education empowerment, promoting dialogue, and fostering consensus, India can navigate towards a more equitable and inclusive society. By steering away from religion-based reservations and focusing on holistic development, India can uphold its constitutional values while addressing the diverse needs of its population.
A Message on the Model Code of Conduct for Leaders – From Mahabharata and Beyond

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a democracy, while elections are imperative, it's equally crucial for both the populace and our leaders to retain their moral integrity, as a loss of ethical grounding could result in repercussions that extend far beyond the periodic act of political selection.
Context:
- Satyameva Jayate ("Truth alone triumphs") from the Mundaka Upanishad was adopted as the national motto on January 26, 1950, the day India became a Republic.
- A day earlier, the country's Election Commission was formed with the primary responsibility of enabling citizens to exercise their democratic right to choose a government.
- The Election Commission is expected to provide a level playing field so that candidates, political parties, and their campaigners do not unduly influence voters through excessive use of money, force, or dishonesty.
About The Model Code of Conduct (MCC):
- The Election Commission of India introduced the Model Code of Conduct with the hope that it would encourage self-control among political stakeholders.
- The 2019 Manual emphasized that those seeking public office should behave in a way worthy of being emulated by others.
- The Commission considers the Code an important contribution by political parties to democracy.
- It expects parties to exhibit model behaviour in their actions and rhetoric.
- However, reality often deviates from this expectation. Political discourse sometimes degrades into coarse and ignoble exchanges.
- This has led to debates on whether it should be called a moral code rather than just a model code.
The Complexity of Truth from a Philosophical Perspective:
- Francis Bacon's Essay of Truth commences with Pilate's profound questioning, "What is truth?" - a query that resonates through the ages, its answer shrouded in layers of complexity.
- This intricate nature finds symbolic representation in the Ashokan pillar's trio of visible lions, embodying the three dimensions of truth: my viewpoint, your perspective, and an objective third-person narrative.
- Yet, there exists a fourth, unseen dimension - that of absolute truth, often perceived as knowable only to a higher power.
- Amidst this philosophical labyrinth, the Election Commission of India (ECI) navigates the realm of human imperfection, striving to enforce the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) – a framework designed to curb dishonest practices during the electoral process.
- However, expecting individuals to adhere to this model solely for the duration of elections, if they have not upheld such principles in their daily lives, could be considered a naive endeavor.
The Intersection of Morality and Law in the Electoral Process:
- Foundations of the Model Code of Conduct (MCC):
- At the core of the Model Code of Conduct lies a fundamental interplay between legal requirements and moral expectations.
- Morality governs individual behaviour based on notions of right and wrong, often rooted in cultural, religious, or personal beliefs.
- Law, conversely, comprises rules established by a governing authority to regulate conduct and ensure order and justice within society.
- Philosophical perspectives offer valuable insights into this dynamic. Immanuel Kant's philosophy distinguishes between morality and law, viewing moral actions as those driven by a sense of duty, while societal rules govern legal actions.
- Utilitarianism, advocated by thinkers like Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill, evaluates actions based on their consequences and their contribution to the overall well-being of society.
- In the context of the Model Code of Conduct, this perspective suggests that political behaviour should be assessed not only against legal standards but also by its broader impact on societal harmony and democratic health.
- Legal Framework and Enforcement:
- The legal framework encompassing the Model Code of Conduct includes specific provisions in the Indian Penal Code and the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- These laws define actions that constitute corrupt practices and electoral offences, providing a legal basis for enforcing the Code.
- However, the intersection of morality and law within this framework presents unique challenges.
- In legal terms, "mens rea" refers to the intention or knowledge of wrongdoing, and establishing mens rea is crucial for proving guilt in many cases.
- The Model Code of Conduct implicitly addresses mens rea by prohibiting actions intended to manipulate or deceive voters, such as false promises or appeals to communal sentiments.
- Sections 123(3) and 123(3A) of the Representation of the People Act classify appeals to caste or communal feelings as corrupt practices, punishable under the law.
- Similarly, Section 125 prohibits promoting enmity between different groups in connection with elections.
- These legal provisions aim to curb divisive tactics and uphold the ethical conduct envisioned by the Model Code of Conduct.
- However, enforcement requires clear evidence linking the actions to the intent of influencing electoral outcomes.
Ethical Reflection in the Electoral Process & Lesson from Mahabharata:
- Upholding Integrity: The imperative for ethical reflection in the electoral process stems from the need to uphold the integrity of democracy itself.
- The conduct of elections must align with the core values of truth and fairness that underpin the democratic ethos.
- Ethical Lesson from Mahabharata: The story of Yudhishthira in the Mahabharata, who lost his moral high ground despite technically telling the truth, underscores the importance of ethics over mere adherence to rules.
- Ethics in elections transcends simply following the law; it involves adhering to higher standards of honesty, integrity, and fairness.
- Moral Soundness over Legal Compliance: Ethical reflection ensures that political actions and decisions are not just legally compliant but also morally sound.
- This is particularly crucial in a democracy, where the legitimacy of the government is derived from the consent of the governed, and this consent must be obtained through fair means.
- Safeguarding Democratic Norms: When ethical standards are compromised, democratic norms such as transparency, accountability, and fairness are weakened.
- This erosion can lead to a governance crisis where the authority of elected officials is questioned, undermining the very foundation upon which democracy rests.
Conclusion
“Satyameva Jayate” is not just India’s motto however it encapsulates a guiding principle that should permeate the conduct of individuals and institutions alike. The Election Commission of India's efforts to enforce the Model Code of Conduct reflect an ongoing struggle to strike a delicate balance between legal enforcement and moral persuasion. For a truly democratic society to thrive, this equilibrium must be continually sought and maintained. The pursuit of political power must never be allowed to erode the foundational value of truth upon which the democratic edifice rests. By upholding the principle of Satyameva Jayate, not just in rhetoric but in action, the integrity of the electoral process and the sanctity of democratic norms can be safeguarded, ensuring that the will of the people remains the cornerstone of governance.
India's Balancing Act: Navigating Iran Relations in the Face of Regional Turmoil and Leadership Transition

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The death of Iran’s President Ebrahim Raisi in a helicopter accident on May 20 has added another layer of uncertainty in a region already wracked by political tensions and war.
Context:
- In the wake of President Ebrahim Raisi's unexpected passing in a helicopter accident on May 20, the geopolitical landscape of the region faces heightened uncertainty.
- Despite the tragic event, the enduring influence of Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei suggests minimal immediate impact on Iran's policies.
- However, this event prompts a closer examination of the evolving dynamics between India and Iran, amidst recent geopolitical shifts.
A Historical Perspective on India-Iran Relations:
- Historical Background: India and Iran share a rich historical tie woven with deep-rooted cultural and economic connections spanning centuries.
- From ancient times, both civilizations have influenced each other in language, culture, and commerce, fostering enduring ties.
- Following India's independence in 1947, formal diplomatic relations were swiftly established between the two nations.
- Despite the divergence of their Cold War alliances—India with the Non-Aligned Movement and Iran aligning with the United States—mutual respect characterized their interactions.
- The Iranian Revolution in 1979 heralded a shift in Iran's ideological stance, yet India remained committed to nurturing bilateral relations, recognizing the significance of regional stability and economic collaboration.
- Economic and Energy Collaboration: Central to the India-Iran partnership is their robust energy cooperation, with Iran serving as a vital supplier of oil and natural gas to India.
- In addressing India's burgeoning energy demands, Iranian resources have played a pivotal role in sustaining India's economic growth.
- The early 2000s witnessed landmark agreements, including long-term oil supply pacts and discussions on strategic pipeline projects like the Iran-Pakistan-India (IPI) gas pipeline.
- Strategic Imperatives; Strategically, India has recognized Iran's pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of the broader West Asian region.
- Both nations have shared interests, notably in fostering stability in Afghanistan.
- Iran's geographic position offers India a strategic gateway to Central Asia, circumventing Pakistan—a factor underscored by India's investments in projects such as the Chabahar port, aimed at bolstering connectivity to Afghanistan and beyond.
Recent Shifts and Implications for India-Iran Relations:
- The Abraham Accords and Evolving Regional Dynamics: The 2020 Abraham Accords, facilitated by the US, introduced a new layer of complexity to regional geopolitics.
- These agreements, which normalized ties between Israel and several Arab nations including the UAE and Bahrain, were perceived as part of a broader US strategy to counterbalance Iran's influence.
- India's active involvement in the I2U2 coalition (India, Israel, UAE, and the US) signals its alignment with this strategy, potentially signalling a departure from traditional bilateral collaborations, a shift Iran has taken note of.
- India-Middle-East Economic Corridor (IMEC) Initiative: The unveiling of the IMEC project during the 2023 G20 summit in New Delhi marks a pivotal development.
- This initiative proposes a transportation network linking India to Israel via the UAE and Saudi Arabia, presenting a strategic alternative route that bypasses Iran.
- The IMEC underscores India's commitment to integrating into evolving economic and strategic frameworks in West Asia, potentially reshaping traditional ties with Iran.
- Impact of US Sanctions: The reinstatement of US sanctions on Iran following the Trump administration's withdrawal from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) in 2018 had profound implications for India-Iran economic relations.
- These sanctions triggered a significant reduction in India's oil imports from Iran, prompting India to seek alternative energy sources.
- While this strained the economic aspect of bilateral ties, India remained interested in advancing projects like the Chabahar port despite the challenges posed by the sanctions.
Strategic Implications and Hurdles with the Chabahar Project:
Strategic Importance:
- The Chabahar endeavour stands as a linchpin within India's regional connectivity and strategic framework.
- Nestled along Iran's southeastern coast, the port furnishes India with direct access to the Arabian Sea, offering a vital alternative to China's Gwadar port under its Belt and Road Initiative.
- Positioned as a gateway to Afghanistan and Central Asia, Chabahar bolsters India's geopolitical foothold, circumventing historical barriers imposed by Pakistan.
- Envisioned as a nucleus of economic activity, the port holds the promise of catalyzing trade and investment between India, Iran, and Afghanistan, unlocking the vast potential of Central Asian markets.
- By fostering Chabahar's development, India aims to provide a counterbalance to China's Gwadar port, positioning itself as a pivotal player in reshaping regional trade dynamics.
Navigating Challenges Amid Strategic Imperatives:
- Despite its strategic allure, the Chabahar project grapples with multifaceted challenges.
- US sanctions have cast a pall over international investments and hindered crucial financial transactions vital for the port's advancement.
- The seismic shift in Afghanistan's political landscape following the Taliban's resurgence has cast uncertainty over the project's trajectory.
- The original tripartite agreement, contingent upon the stability offered by the erstwhile US-backed Ghani regime, now faces an altered reality.
- The enduring viability of Chabahar hinges on regional stability and collaboration, factors further complicated by Iran's economic woes amidst ongoing sanctions.
- Persistent geopolitical tensions pose formidable obstacles to the sustained success of this ambitious undertaking, underscoring the need for adept navigation amid strategic imperatives.
Future Trajectories for India-Iran Relations:
- Pursuing Strategic Autonomy: Chabahar demonstrates India's pursuit of strategic autonomy, allowing it to navigate geopolitical landscapes and assert regional influence.
- Balancing relations with Iran, the US, and other regional players enables India to maintain a multifaceted foreign policy that serves its strategic objectives.
- Leveraging International Cooperation: India could explore collaborations with international partners like the EU to mitigate the impact of US sanctions and garner diplomatic and economic support.
- Strengthening ties with Central Asian countries may enhance Chabahar's economic prospects.
- Commitment to Regional Stability: India's continued engagement with Afghanistan, including humanitarian aid, underscores its commitment to regional stability and connectivity through Chabahar.
- Maintaining a presence in Afghanistan highlights the strategic importance of Chabahar as a key node for regional diplomacy and economic activity.
Conclusion
The sudden demise of Iran's President Ebrahim Raisi exacerbates uncertainty in an already tumultuous region. India must deftly balance its strategic interests amidst competing regional powers and the intricate landscape of geopolitical rivalries and international sanctions. The revival of the Chabahar project exemplifies India's strategic adaptability but also underscores the precarious nature of its regional engagements. India's ability to exhibit strategic foresight and diplomatic finesse will be crucial in effectively navigating the ever-changing geopolitical environment.
C Raja Mohan writes: A time for para diplomacy
- 22 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Shiromani Akali Dal came out with its poll manifesto and said it would seek the transfer of Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan to India through mutual land exchange between the two countries.
Context:
- The Shiromani Akali Dal's (SAD) proposal to retrieve Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan through a negotiated territory exchange reflects a growing desire to transform the India-Pakistan border from a zone of conflict to one of cooperation and economic integration.
- This idea might appear as unlikely as the Bharatiya Janata Party's (BJP) pledge to integrate Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) into India.
- Nonetheless, it signifies a profound aspiration to transform the India-Pakistan border from a contentious zone into one characterized by cooperation and economic integration.
What is Para Diplomacy?
Origins of Paradiplomacy:
- The concept of para-diplomacy was first proposed in 1990 by John Kincaid, an American scholar who outlined a foreign policy role for local governments within a democratic federal system.
- Economic para diplomacy related to trade and investment in particular has become an institutionalised practice across the world – in federal states like the United States, Canada and Belgium, quasi-federal states like Spain, non-federal states like Japan and even non-democratic states like the People’s Republic of China.
Aims and Objectives of Paradiplomacy:
- Paradiplomacy can be employed with a variety of aims which can range from bringing in a decentralised dimension to international debates to internationalisation of domestic issues by bringing regional issues onto the global stage, promoting trade, tourism, cultural ties and even post-conflict reconciliation to local political activism being sought for international support.
- Subnational relations can also be conducted to promote and attract investments seeking region-specific economic advantages.
Drivers of Paradiplomacy:
- In more ways than one, paradiplomacy owes its origins to globalisation.
- As the world economy has become increasingly global and increasingly integrated in a variety of ways, sub-national units (regions, states, provinces and even cities) find their functions and activities circumscribed by the global system.
- Federalism is also a key contributor to the growth of paradiplomacy.
- Sub-national actors such as states and provinces that have a formal legal personality are necessarily more likely to engage in international activities designed to promote and protect local and international interests and prerogatives.
What are the Challenges Associated with BJP and SAD’s Territorial Ambitions?
- Practical Hurdles in BJP and SAD's Territorial Objectives: The proposals put forth by the SAD to renegotiate the Radcliffe Line in Punjab or the BJP's assertion to reclaim PoK face numerous challenges.
- Altering the territorial status quo in Punjab or reclaiming PoK, whether through diplomatic negotiations or by force, presents formidable obstacles.
- Complexities and Resistance: Such endeavours would not merely disrupt the already delicate territorial equilibrium but also provoke substantial opposition, given the deep-rooted historical and ongoing tensions between India and Pakistan.
- Pursuing a Pragmatic Approach: A more viable alternative lies in reimagining these borders as conduits for trade and collaboration rather than confrontation.
- This pragmatic stance resonates with the SAD's additional proposal to reopen the Attari and Hussainiwala borders with Pakistan for trade and tourism, with the aim of fostering economic prosperity in the region.
Obstacles Hindering Economic Cooperation Between India and Pakistan:
- Political and Military Resistance in Pakistan: One of the foremost barriers to economic cooperation stems from the entrenched position of Pakistan's military and political establishment.
- Over the years, the Pakistani military's steadfast opposition to economic engagement with India, primarily due to unresolved issues surrounding Kashmir, has been a significant deterrent.
- Despite occasional signs of thaw, such as the February 2021 ceasefire agreement, internal resistance has consistently impeded progress.
- Even Prime Minister Imran Khan's tentative consideration of resuming trade ties with India faced vehement opposition, highlighting the deep-seated reluctance to normalize relations without addressing the Kashmir dispute.
- Historical Context and Suspicion: The historical animosities dating back to the traumatic partition of 1947 and subsequent wars have entrenched mutual suspicion and distrust between the two nations.
- These historical grievances have not only shaped national narratives but also influenced contemporary policy decisions.
- Addressing underlying political tensions becomes imperative for either country to fully commit to economic cooperation.
- Lack of Reciprocal Trade Policies: On the trade front, Pakistan's refusal to grant India the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status remains a significant hurdle.
- While India extended this status to Pakistan in 1996 to foster trade ties, the gesture was not reciprocated.
- Subsequent events, such as India's withdrawal of MFN status post the Pulwama terror attack and the revocation of Jammu and Kashmir's special constitutional status, have further strained bilateral trade relations.
- Economic Rationality vs. Political Baggage: Despite the evident economic benefits of trade, Pakistan's establishment remains wary of engaging with India due to historical conflicts and the overarching Kashmir issue.
- While there have been instances where the Pakistani business community advocated for resuming trade ties, such appeals often faced resistance from the political and military elite, who prioritize geopolitical concerns over economic pragmatism.
- Regional Stability and Security Concerns: Security concerns, including allegations of cross-border terrorism, complicate the economic relationship between India and Pakistan.
- Heightened military vigilance and frequent skirmishes along the border hinder trade and perpetuate an environment of hostility and mistrust.
- The ongoing conflict and the threat of terrorist activities cast a shadow over efforts to normalize trade relations.
Proposing a New Strategy for Improving India-Pakistan Relations:
- Introduction of Special Economic Zones: A significant aspect of the SAD's manifesto is the proposition to convert the Punjab border into a special economic zone, aiming to nurture small and medium enterprises and potentially revolutionize India-Pakistan relations.
- This innovative vision encompasses the idea of Pakistan establishing a parallel zone on its side, fostering integrated development and economic interdependence.
- Drawing inspiration from successful models of cross-border economic zones in Southeast Asia and China's collaborative initiatives with neighbouring countries, such an endeavour holds promise for fostering mutual prosperity.
- Leveraging Para Diplomacy: At the heart of these proposals lies the concept of para diplomacy, or sub-state diplomacy, wherein provincial and local governments engage in formal interactions to advance national interests.
- This approach offers a novel means to navigate around the entrenched positions often held by national governments, presenting fresh avenues for cooperation.
- While historical attempts at para diplomacy between East and West Punjab have surfaced intermittently, they have struggled to endure amidst overarching national conflicts.
- Embracing these innovative strategies could pave the way for a constructive dialogue and sustainable cooperation between India and Pakistan, fostering mutual understanding and prosperity in the region.
Fostering Consensus and Cooperative Federalism for Sustainable India-Pakistan Relations:
- To foster sustainable and productive economic cooperation between India and Pakistan, nurturing a robust consensus between the central government and state governments, particularly those in the border regions, is imperative.
- This collaborative approach, known as cooperative federalism, holds the key to innovative diplomatic strategies that prioritize the interests of local populations.
- India's federal structure has historically grappled with tensions between the central and state governments, particularly concerning foreign policy and cross-border cooperation.
- The diverse political landscapes across Indian states often give rise to conflicting interests and priorities.
- For example, West Bengal's interactions with Bangladesh have been marked by complexities stemming from differing perspectives between the state leadership and the central government.
- Similarly, Tamil Nadu's influence on India's policies towards Sri Lanka has been substantial, occasionally complicating bilateral relations due to the state's concerns for the Tamil population in Sri Lanka.
- Cooperative federalism entails the harmonious collaboration of national and state governments to achieve shared objectives while respecting the autonomy of state governments.
- By aligning state objectives with national interests, this approach offers a pragmatic framework for managing border relations and fostering economic cooperation with neighbouring countries.
- Embracing consensus and cooperative federalism is paramount for forging a path towards peace, stability, and prosperity in the region, laying the groundwork for enduring and mutually beneficial relations between India and Pakistan.
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Shiromani Akali Dal came out with its poll manifesto and said it would seek the transfer of Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan to India through mutual land exchange between the two countries.
Context:
- The Shiromani Akali Dal's (SAD) proposal to retrieve Kartarpur Sahib from Pakistan through a negotiated territory exchange reflects a growing desire to transform the India-Pakistan border from a zone of conflict to one of cooperation and economic integration.
- This idea might appear as unlikely as the Bharatiya Janata Party's (BJP) pledge to integrate Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) into India.
- Nonetheless, it signifies a profound aspiration to transform the India-Pakistan border from a contentious zone into one characterized by cooperation and economic integration
What is Para Diplomacy?
Origins of Paradiplomacy:
- The concept of para-diplomacy was first proposed in 1990 by John Kincaid, an American scholar who outlined a foreign policy role for local governments within a democratic federal system.
- Economic para diplomacy related to trade and investment in particular has become an institutionalised practice across the world – in federal states like the United States, Canada and Belgium, quasi-federal states like Spain, non-federal states like Japan and even non-democratic states like the People’s Republic of China.
Aims and Objectives of Paradiplomacy:
- Paradiplomacy can be employed with a variety of aims which can range from bringing in a decentralised dimension to international debates to internationalisation of domestic issues by bringing regional issues onto the global stage, promoting trade, tourism, cultural ties and even post-conflict reconciliation to local political activism being sought for international support.
- Subnational relations can also be conducted to promote and attract investments seeking region-specific economic advantages.
Drivers of Paradiplomacy:
- In more ways than one, paradiplomacy owes its origins to globalisation.
- As the world economy has become increasingly global and increasingly integrated in a variety of ways, sub-national units (regions, states, provinces and even cities) find their functions and activities circumscribed by the global system.
- Federalism is also a key contributor to the growth of paradiplomacy.
- Sub-national actors such as states and provinces that have a formal legal personality are necessarily more likely to engage in international activities designed to promote and protect local and international interests and prerogatives.
What are the Challenges Associated with BJP and SAD’s Territorial Ambitions?
- Practical Hurdles in BJP and SAD's Territorial Objectives: The proposals put forth by the SAD to renegotiate the Radcliffe Line in Punjab or the BJP's assertion to reclaim PoK face numerous challenges.
- Altering the territorial status quo in Punjab or reclaiming PoK, whether through diplomatic negotiations or by force, presents formidable obstacles.
- Complexities and Resistance: Such endeavours would not merely disrupt the already delicate territorial equilibrium but also provoke substantial opposition, given the deep-rooted historical and ongoing tensions between India and Pakistan.
- Pursuing a Pragmatic Approach: A more viable alternative lies in reimagining these borders as conduits for trade and collaboration rather than confrontation.
- This pragmatic stance resonates with the SAD's additional proposal to reopen the Attari and Hussainiwala borders with Pakistan for trade and tourism, with the aim of fostering economic prosperity in the region.
Obstacles Hindering Economic Cooperation Between India and Pakistan:
- Political and Military Resistance in Pakistan: One of the foremost barriers to economic cooperation stems from the entrenched position of Pakistan's military and political establishment.
- Over the years, the Pakistani military's steadfast opposition to economic engagement with India, primarily due to unresolved issues surrounding Kashmir, has been a significant deterrent.
- Despite occasional signs of thaw, such as the February 2021 ceasefire agreement, internal resistance has consistently impeded progress.
- Even Prime Minister Imran Khan's tentative consideration of resuming trade ties with India faced vehement opposition, highlighting the deep-seated reluctance to normalize relations without addressing the Kashmir dispute.
- Historical Context and Suspicion: The historical animosities dating back to the traumatic partition of 1947 and subsequent wars have entrenched mutual suspicion and distrust between the two nations.
- These historical grievances have not only shaped national narratives but also influenced contemporary policy decisions.
- Addressing underlying political tensions becomes imperative for either country to fully commit to economic cooperation.
- Lack of Reciprocal Trade Policies: On the trade front, Pakistan's refusal to grant India the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status remains a significant hurdle.
- While India extended this status to Pakistan in 1996 to foster trade ties, the gesture was not reciprocated.
- Subsequent events, such as India's withdrawal of MFN status post the Pulwama terror attack and the revocation of Jammu and Kashmir's special constitutional status, have further strained bilateral trade relations.
- Economic Rationality vs. Political Baggage: Despite the evident economic benefits of trade, Pakistan's establishment remains wary of engaging with India due to historical conflicts and the overarching Kashmir issue.
- While there have been instances where the Pakistani business community advocated for resuming trade ties, such appeals often faced resistance from the political and military elite, who prioritize geopolitical concerns over economic pragmatism.
- Regional Stability and Security Concerns: Security concerns, including allegations of cross-border terrorism, complicate the economic relationship between India and Pakistan.
- Heightened military vigilance and frequent skirmishes along the border hinder trade and perpetuate an environment of hostility and mistrust.
- The ongoing conflict and the threat of terrorist activities cast a shadow over efforts to normalize trade relations.
Proposing a New Strategy for Improving India-Pakistan Relations:
- Introduction of Special Economic Zones: A significant aspect of the SAD's manifesto is the proposition to convert the Punjab border into a special economic zone, aiming to nurture small and medium enterprises and potentially revolutionize India-Pakistan relations.
- This innovative vision encompasses the idea of Pakistan establishing a parallel zone on its side, fostering integrated development and economic interdependence.
- Drawing inspiration from successful models of cross-border economic zones in Southeast Asia and China's collaborative initiatives with neighbouring countries, such an endeavour holds promise for fostering mutual prosperity.
- Leveraging Para Diplomacy: At the heart of these proposals lies the concept of para diplomacy, or sub-state diplomacy, wherein provincial and local governments engage in formal interactions to advance national interests.
- This approach offers a novel means to navigate around the entrenched positions often held by national governments, presenting fresh avenues for cooperation.
- While historical attempts at para diplomacy between East and West Punjab have surfaced intermittently, they have struggled to endure amidst overarching national conflicts.
- Embracing these innovative strategies could pave the way for a constructive dialogue and sustainable cooperation between India and Pakistan, fostering mutual understanding and prosperity in the region.
Fostering Consensus and Cooperative Federalism for Sustainable India-Pakistan Relations:
- To foster sustainable and productive economic cooperation between India and Pakistan, nurturing a robust consensus between the central government and state governments, particularly those in the border regions, is imperative.
- This collaborative approach, known as cooperative federalism, holds the key to innovative diplomatic strategies that prioritize the interests of local populations.
- India's federal structure has historically grappled with tensions between the central and state governments, particularly concerning foreign policy and cross-border cooperation.
- The diverse political landscapes across Indian states often give rise to conflicting interests and priorities.
- For example, West Bengal's interactions with Bangladesh have been marked by complexities stemming from differing perspectives between the state leadership and the central government.
- Similarly, Tamil Nadu's influence on India's policies towards Sri Lanka has been substantial, occasionally complicating bilateral relations due to the state's concerns for the Tamil population in Sri Lanka.
- Cooperative federalism entails the harmonious collaboration of national and state governments to achieve shared objectives while respecting the autonomy of state governments.
- By aligning state objectives with national interests, this approach offers a pragmatic framework for managing border relations and fostering economic cooperation with neighbouring countries.
- Embracing consensus and cooperative federalism is paramount for forging a path towards peace, stability, and prosperity in the region, laying the groundwork for enduring and mutually beneficial relations between India and Pakistan.
Conclusion
Irrespective of its political orientation, the upcoming Indian government should regard para-diplomacy as a strategic asset in its foreign policy arsenal. This approach demands not only robust dialogue between the central government and the border provinces but also concerted efforts to align the interests of the inhabitants of these regions with broader national objectives. By embracing para diplomacy, India can lay the groundwork for a more harmonious and economically fruitful relationship with Pakistan, turning contentious borders into conduits of cooperation.
Critical Times Call for Strong Judicial Adjudication

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The process of judicial review should be strong, immediate, and unambiguous in the case of statutes that are obviously unconstitutional or divisive.
Context:
- The role of judicial review has become increasingly significant in contemporary times.
- The Supreme Court of India is currently examining a crucial case regarding the constitutionality of the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) and its associated rules.
- The ambiguity in these rules has raised concerns, especially for applicants whose citizenship requests have been denied, highlighting the urgent need for redress.
- Additionally, the issue of dual citizenship for foreign applicants, without renouncing their original citizenship, has created a conflict with the law.
- This ambiguity goes against the Parent Act's spirit, as some petitioners pointed out.
Legislative Malice, Judicial Review, and the Challenge of Populist Regimes:
- Constitutional courts do not routinely interdict statutes or statutory rules, as laws passed by Parliament are generally presumed valid unless proven to contravene constitutional provisions.
- Moreover, the legal doctrine maintains that malice cannot typically be attributed to the legislative process, as established in Manish Kumar vs Union of India (2021).
- In Gurudevdatta Vikoos Maryadit vs State Of Maharashtra (2001), the Supreme Court further emphasized that "legislative malice is beyond the pale of jurisdiction of the law courts."
- However, this conventional wisdom may be insufficient when addressing the unique challenges posed by populist regimes employing motivated legislation.
- As populist governments worldwide increasingly weaponize legislation to further their political agendas, the question arises as to whether constitutional courts should reconsider their stance on legislative malice.
- Given the potential for populist regimes to undermine democratic principles and erode the rule of law, the need for robust judicial review has never been greater.
- In light of these challenges, a careful reevaluation of the limits of judicial intervention may be necessary to ensure that the rights and freedoms enshrined in constitutional democracies are protected from malicious legislative actions.
Judicial Challenges and Lessons from the Recent Cases:
- Recent cases have highlighted the pressing need for a more proactive judiciary in safeguarding democratic principles and the rule of law.
- In Vivek Narayan Sharma vs Union of India (2023), the irreversible consequences of the absence of judicial intervention regarding Kashmir's special status were brought to the forefront.
- The Anoop Baranwal vs Union of India (2023) case underscored the necessity for an independent body to select the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- However, the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Act, 2023, reintroduced the "Prime Minister's Committee" system for ECI appointments, raising concerns about the impartiality of the selection process.
- When this Act was challenged in Jaya Thakur vs Union of India (2024), the Court declined to halt its implementation, citing the presumption of validity.
- This decision exemplifies how an overly deferential approach to legislative actions can potentially jeopardize democratic institutions and processes.
Case Studies and Implications of Targeted Legislation:
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA): CAA exemplifies targeted legislation, as it explicitly excludes Muslims from the citizenship application process, demonstrating a clear case of legislative malice through religious categorization.
- Tripple Talaq case: Another instance of targeted legislation is the Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Marriage) Act (2019), which criminalized instant triple talaq.
- Despite the Supreme Court declaring instant triple talaq void in Shayara Bano (2017), the Act's criminalization of an already legally invalid practice appears excessive and unnecessary.
- Unintended effects: Unintended consequences have arisen from the triple talaq legislation, as some individuals now resort to alternative divorce methods or desertion to avoid potential legal repercussions.
- Although the law aimed to protect Muslim women, it has paradoxically worsened their situation.
- Furthermore, such divisive measures have inspired similar legislation in other states, such as anti-conversion laws, perpetuating social divisions.
- These cases reveal the need for a vigilant judiciary to scrutinize targeted legislation and ensure that laws do not perpetuate discrimination or undermine fundamental rights.
- Addressing legislative malice is essential for preserving the integrity of democratic institutions and upholding constitutional principles.
Judicial Scrutiny in Contemporary Politics: International Perspectives and Indian Precedents
- The Evolution of Judicial Scrutiny in Modern Politics: Traditionally, the United States has been cautious about judicial nullification of statutes based on malicious intent.
- John Hart Ely argued that using the Constitution to penalize perceived ill intentions of political leaders is inappropriate.
- Susannah W. Pollvogt's Viewpoint on Discriminatory Law: However, in today's political climate, where legislative actions driven by malice are increasingly common, a growing need for more rigorous judicial scrutiny has emerged.
- Scholar Susannah W. Pollvogt contends that animus, or hostility, can never justify discriminatory state actions under equal protection analysis.
- She cites the United States Dept. of Agriculture vs Moreno (1973) to illustrate how legislation targeting specific groups reflects discriminatory intent and a desire to cause harm.
- Indian Legal Precedents for Judicial Intervention: In India, there are instances where the Supreme Court has intervened to halt the implementation of parliamentary legislation.
- In Ashoka Kumar Thakur vs Union of India (2007), the Court issued a judicial injunction regarding the allocation of a 27% quota for Other Backward Community (OBC) candidates in professional colleges.
- More recently, in Rakesh Vaishnav vs Union of India (2021), the Supreme Court's stay order on three controversial farm laws effectively prevented their enforcement.
- This intervention eventually led to the government's withdrawal of the laws amidst widespread farmer protests.
- These cases demonstrate the vital role of the judiciary in safeguarding fundamental rights and democratic principles.
- As legislative malice becomes more prevalent, judicial scrutiny must evolve to ensure that laws do not perpetuate discrimination or undermine constitutional values.
Conclusion
To protect constitutional principles and democratic values, judicial review must be prompt, vigorous, and unambiguous when confronted with divisive or unconstitutional statutes. The Supreme Court should learn from its past decisions and recognize the political impact of its actions, particularly during critical moments. Delayed adjudication can render constitutional review ineffective, making time-sensitive intervention essential in addressing malicious and unconstitutional legislation.
Hyperpoliticisation of Indian Higher Education

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The hyperpoliticisation of Indian higher education is a grave threat to academic institutions, the academic profession, and intellectual life in general.
Context:
- The higher education system in India is one of the largest globally, showcasing its rich historical legacy and future ambitions.
- The country is home to an impressive range of institutions, including the globally renowned Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), as well as a vast network of universities and colleges.
- Notably, the QS World University Rankings for Asia 2024 highlight India as having the most represented higher education system.
- However, this expansive framework faces numerous challenges and opportunities that shape the current higher education landscape in India.
- While access has significantly expanded, concerns about quality, relevance, and the ability to prepare youth for the 21st century remain.
- Additionally, recent reports have pointed to a troubling trend of increasing politicization within Indian higher education institutions, which threatens academic freedom, intellectual discourse, and overall educational quality.
Current Status of Higher Education in India:
As per the All India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE) 2021-22, released in January 2024:
- Student Enrolment: Higher education institutes have seen a significant rise in student enrolment, reaching 4.33 crore in 2021-22 from 4.14 crore in 2020-21 and 3.42 crore in 2014-15.
- Notably, women's enrolment has surged by 32% to 2.07 crore in 2021-22 from 1.5 crore in 2014-15, with the highest proportion enrolled at the postgraduate level (55.4%).
- Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) and Gender Parity Index (GPI): India's estimated GER for the age group 18-23 years stands at 28.4%.
- The GPI, reflecting the female GER to male GER ratio, is 1.01 at the national level, indicating gender parity.
- Discipline-wise Enrolment: At the undergraduate level, the Bachelor of Arts (BA) programme leads with 34.2% enrolment, followed by science (14.8%), commerce (13.3%), and engineering and technology (11.8%).
- Social science dominates postgraduate enrolment, with around 10.8 lakh students.
- Primacy of Government Institutions: Government universities attract 73.7% of all students, despite comprising only 58.6% of all universities.
- State public universities hold the largest share of enrolment, accounting for approximately 31% of government-owned universities.
Current Challenges in India's Higher Education System:
- Politicization and Lack of Autonomy: Concerns arise regarding the growing politicization of higher education institutions, including allegations of political interference in appointments and curriculum decisions.
- Many institutions lack autonomy in crucial areas like faculty recruitment and curriculum design, hindering innovation and adaptability.
- Inequitable Access and Low GER: Access to higher education remains unequal, with disparities based on socio-economic status, gender, and geography.
- Although India's Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) has improved (currently 28.4%), it still falls below the global average of 36.7%.
- Limited Funding: Budget cuts in the education sector, including a 7% reduction in the Interim Budget 2024-25 and a 61% decrease in the allocation for the University Grants Commission, pose significant challenges.
- Despite rising Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD), India's R&D investment as a percentage of GDP lags behind other countries.
- Shortage of Faculty and Brain Drain: There is a severe shortage of qualified faculty members in Indian higher education institutions, with over 30% of teaching positions vacant in 45 Central Universities as of 2023.
- The brain drain of talented academics to other countries or the private sector exacerbates this issue.
- Inadequate Industry-Academia Collaboration: Insufficient collaboration between higher education institutions and industries leads to a skill gap among graduates, with a significant demand-supply gap in key roles such as ML engineer and data scientist.
- Uneven Regional Development: Higher education institutions' development varies across regions and states, with states like Delhi, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra hosting more reputed institutions compared to northeastern and central regions, which face challenges in terms of quality and access.
How Can the Higher Education System in India Be Revamped?
- Redefine Universities' Role: Shift focus from rote learning to practical skill development through project-based learning, internships, and industry collaborations.
- Encourage universities to engage with local communities on social development projects, promoting social responsibility among students.
- Transform institutes from "Degree Issuers" to "Skill Generators."
- Open Educational Resources (OER): Enhance the National Digital Library of India and promote the development and adoption of open educational resources, like MIT OpenCourseWare, providing free access to quality educational materials.
- This approach could reduce costs, enhance access, and foster a culture of knowledge sharing.
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation Centers: Establish dedicated centres within universities, inspired by Stanford University's StartX program, offering mentorship, funding opportunities, and a supportive ecosystem for students and faculty to transform innovative ideas into successful ventures.
- Dual Study Programs: Implement phase-wise dual study programs, inspired by Germany's apprenticeship model, where students combine theoretical learning at universities with practical training in companies.
- This approach ensures industry-relevant skill development and enhances employability.
- Competency-based Credentialing and Blockchain Certificates: Implement a competency-based credentialing system that recognizes skills and competencies acquired through various learning pathways.
- Leverage blockchain technology to issue tamper-proof, verifiable digital certificates and credentials, promoting lifelong learning, skill-based education, and recognition of diverse learning experiences.
- Transnational Education Partnerships: Promote collaborations with reputed international universities for joint degrees, twinning programs, or branch campuses.
- This approach could enhance global exposure, facilitate knowledge transfer, and improve the international competitiveness of Indian higher education.
Key Government Initiatives in Higher Education:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Aims to transform the education system, focusing on multidisciplinary learning, skill development, and promoting research and innovation.
- It proposes increasing the Gross Enrollment Ratio in higher education to 50% by 2035.
- Institutions of Eminence (IoE) Scheme: Launched in 2018, this scheme selects 20 institutions to enjoy complete autonomy, aiming to improve their global rankings and enhance higher education quality.
- National Credit Framework: Designed to integrate training and skill development into the education system.
- Credits earned by students will be stored digitally in the Academic Bank of Credits, accessible via a linked Digilocker account.
- Revamped Accreditation and Ranking Systems: The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) ranks higher education institutions across categories, while the revamped National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) ensures quality standards among institutions.
- Digital Initiatives: SWAYAM, an online learning platform, offers courses from school to postgraduate levels.
- The National Digital Library of India provides access to educational resources.
- SHE under INSPIRE: The Scholarship for Higher Education (SHE) program, part of the Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE) by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), supports deserving students in basic and natural sciences at undergraduate, postgraduate levels and encourages research careers through scholarships.
- Study in India Program: Launched in 2018, this program attracts international students by offering scholarships and streamlining admission processes.
- Foreign Institutions in India: The University Grants Commission's 2023 regulations allow foreign universities ranked among the world's top 500 to establish branch campuses in India.
Conclusion
India's higher education sector is undergoing significant reforms and initiatives aimed at enhancing quality, accessibility, and global competitiveness. Through policies like the National Education Policy 2020 and programs such as Institutions of Eminence, the government is prioritizing multidisciplinary learning, skill development, and research promotion. Digital initiatives like SWAYAM and the Study in India Program further contribute to modernizing and internationalizing higher education, while efforts to attract foreign institutions and scholarships underscore India's commitment to fostering innovation and excellence in education.
Challenges in the Way to Achieve Green Growth and Solutions

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The recent heatwave has reminded us of the stark risks posed by climate change and highlighted the criticality of the efforts taken by the Conference of Parties (COP).
Context:
- The recent heatwave highlights the escalating threats of climate change, emphasizing the urgent need for robust climate action.
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) confirmed that 2023 was the warmest year on record, drawing renewed attention to carbon-intensive sectors like power and industry.
- As the third-largest carbon emitter globally, India faces increased scrutiny over its emissions.
- To address these challenges, significant efforts are being made to transition towards green energy, bolstered by various government initiatives and policies.
India's Green Growth Landscape: A Shift Towards Sustainable Practices
- Indian industries, particularly those in high-carbon emitting sectors, are increasingly acknowledging the importance of embracing sustainable practices.
- Many companies are taking proactive measures to transition towards renewable energy sources.
- For example, leading firms in refining, chemical production, and fertilizers are exploring the potential of Green Hydrogen to reduce their carbon emissions.
- These sectors are crucial in India's decarbonization efforts due to their significant contribution to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Although there are no mandatory regulations for green technology adoption, many entities are voluntarily adopting these technologies.
- This shift is driven by stakeholder expectations and the recognition of transition risks, such as policy, regulatory, technology, market, reputation, and legal challenges.
- Among these risks, technological risk is the most pressing concern for entities adopting green technologies.
Challenges in India's Transition to Green Growth:
Shifting from Fossil Fuels to Renewable Energy
- Fossil fuel-based power is India's primary source of carbon emissions.
- To meet the government's climate target of increasing non-fossil power to 50% by 2030, several schemes have been launched to boost renewable energy.
- ICRA projects that India will achieve this goal, with the share of non-fossil fuel-based installed capacity rising from 41% in 2022-23 to 59% by 2029-30.
- However, this transition requires significant investment, with an estimated Rs 11-12 lakh crore needed for renewable energy power and over Rs 5-6 lakh crore for transmission infrastructure and storage capabilities.
Ensuring Continuous Renewable Energy Supply:
- Ensuring a steady supply of renewable energy is crucial to reach the targeted level, given its intermittent nature.
- Hybrid renewable energy projects (wind and solar) complemented by energy storage systems can help achieve this.
- For sectors like steel and cement, the government must explore more carbon sequestration methods, such as installing carbon capture utilisation and storage (CCUS), which is inevitable for these hard-to-abate sectors.
Challenges in the Cement Sector:
- Cement manufacturing is resource and energy-intensive, producing an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide per tonne of cement.
- CCUS can reduce 60-70% of emissions during cement manufacturing, as most emissions are generated during clinker production.
- Niti Aayog's report estimates that the cement sector needs a CCUS capacity of two million tonnes per annum by 2030, with a capital cost of Rs 1,600-1,800 crore.
Challenges in the Steel Sector:
- Due to the abundance of virgin iron ore and limited domestic scrap, the domestic steel industry primarily uses coal as a reducing agent, resulting in high emissions.
- With India's 2070 net-zero target and carbon tax policies in some countries, domestic steelmakers are focusing on reducing their carbon footprint by 25-30% through technological interventions by 2030.
Government Efforts in India's Green Energy Transition and Carbon Reduction:
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: The PLI scheme offers financial incentives to manufacturers, encouraging them to establish production facilities in India.
- This strengthens the local solar manufacturing industry, making solar energy more affordable and accessible.
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF) for Offshore Wind and Battery Storage Projects: VGF schemes make large-scale renewable energy projects more financially viable, attracting private investment.
- Offshore wind and battery storage projects particularly benefit from this support, addressing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources.
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) Scheme: The FAME scheme provides subsidies for electric vehicle (EV) purchases and supports the development of charging infrastructure.
- This initiative aims to reduce vehicular emissions, decrease oil dependency, and promote sustainable urban mobility.
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy, has the potential to significantly reduce emissions in hard-to-abate sectors.
- The mission supports research, pilot projects, and production facilities, positioning India as a global leader in green hydrogen technology.
- Amendments to the Energy Conservation Act: The amendments include provisions for energy efficiency standards and energy management systems.
- These measures aim to reduce energy consumption, lower emissions, and promote sustainable industrial practices.
Recommendations for Overcoming Green Growth Challenges in India:
- Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs): The government should enforce mandatory percentages of electricity consumption from renewable sources.
- RPOs require power distribution companies and large consumers to purchase a specific proportion of energy from renewables, ensuring consistent demand and promoting sector growth.
- Implementation of the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): Policymakers should devise strategies that promote sustainable development while tackling climate change.
- The NAPCC encompasses eight missions focusing on solar energy, energy efficiency, sustainable agriculture, and water conservation, enabling cross-sectoral efforts to integrate climate resilience and sustainability into national policies.
- Tax Incentives and Subsidies: Financial incentives should be provided to support renewable energy and green technologies.
- Tax benefits such as accelerated depreciation and tax holidays reduce investment burdens.
- Subsidies for solar power, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems make these technologies more accessible and appealing to consumers and businesses.
- Increased Viability Gap Funding (VGF): The government should address financial gaps in economically viable projects lacking initial investment.
- VGF schemes make large-scale renewable energy projects, like offshore wind farms and battery storage systems, more financially viable and reduce investment risks.
Conclusion
India's journey towards embracing green energy and sustainability is characterized by both formidable hurdles and promising prospects. The proactive steps taken by the government and the enthusiastic participation of diverse stakeholders are laying the groundwork for a more environmentally friendly tomorrow. Yet, reaching the ambitious climate goals demands persistent backing, significant financial injections, and a surge in technological advancements. In a world grappling with the intensifying effects of climate change, India's resolute pledge to slash carbon emissions and shift towards renewable energy stands as both an imperative and an inspiration for nations worldwide.
Redefining India's Poverty Threshold: Embracing New Perspectives

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
It is important to recognize India’s progress in alleviating poverty based on norms established in the 1970s. However, there is a need to update the poverty threshold to reflect contemporary notions of a ‘decent standard of living’.
Context:
- The recent release of the Household Consumer Expenditure Survey (HCES) data by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) has sparked renewed debates on poverty estimation in India.
- According to estimates derived from the methodologies proposed by the Tendulkar and Rangarajan Committees, poverty levels have reportedly decreased significantly since 2011-12, with figures standing at approximately 6.3% and 10% respectively for the year 2022-23.
Evolution of Consumption-Based Poverty Measurement in India:
- India's consumption-based poverty measurement has evolved since its inception in the 1960s.
- The approach was first introduced by the 1962 Working Group and further refined by the 1979 Task Force.
The 1979 Task Force:
- The task force defined the poverty line as the per-capita consumption expenditure level that could satisfy the average daily calorie requirement of 2,400 kcal in rural areas and 2,100 kcal in urban areas.
- This included associated non-food expenditures, and the monetary value of this norm became the foundation for subsequent poverty line revisions.
Tendulkar and Rangarajan Committees:
- These committees revisited the calorie norms and expenditure levels established by the 1979 Task Force.
- However, they did not adequately address non-food components.
- The committees argued that if expenditures on specific necessities meet nutritional requirements, they should also cover other essential non-food needs.
Implications of the estimates:
- The estimates indicate a notable decrease in poverty since 2011-12.
- However, some commentators advocate for a reassessment of the poverty line in light of changes in survey methodology.
- They contend that recent alterations in survey methodology in the Household Consumer Expenditure Survey (HCES) make previous methodologies unsuitable for analyzing HCES data.
- Surjit S. Bhalla, an economist and former member of the Economic Advisory Council, has provided comprehensive counterarguments to such assertions.
- Nevertheless, none of these discussions have addressed the suitability of current methodologies for monitoring poverty using consumption data.
Historical Background of Poverty Measurement:
- Early approaches: Consumption-based poverty measurement was initiated with a Working Group established by the Planning Commission in 1962 and further refined by a task force in 1979.
- This task force meticulously outlined its rationale for establishing a poverty line specific to India.
- Definition of poverty line: It was delineated as the per-capita consumption expenditure required to fulfil average daily calorie needs (2,400 Kcal in rural areas, 2,100 Kcal in urban areas) along with associated non-food expenses.
- This average calorie standard was derived from an analysis of the demographic and activity-based composition of the population during that period.
- The monetary value assigned to this standard became the foundation for subsequent revisions of poverty lines.
- However, the fundamental methodology underpinning this calculation was not critically reassessed.
Reevaluating Poverty Measurement Norms in India:
- The Tendulkar and Rangarajan Committees acknowledged the evolving demographic and activity composition in India, leading them to propose adjustments to calorie norms and expenditure levels for poverty measurement.
- However, these committees did not adequately reconsider the non-food components of the poverty line.
- At the core of their argument was the assertion that if spending within an expenditure class is sufficient to meet nutritional requirements, it should also be adequate to cover associated non-food needs.
- This assumption is questionable in the context of modern India, as the country has undergone significant changes since the 1970s when the Task Force on Poverty was established.
Demographic and Educational Indicators in India Since the 1970s:
Several significant demographic and educational shifts have taken place in India since the 1970s:
- Life Expectancy: Life expectancy at birth has improved from 49.7 years in 1970 to 69.4 years in 2018, reflecting advancements in healthcare and overall quality of life.
- Ageing Population: The proportion of individuals aged 60 and above has grown from 6.1% in the 1970s to 10.1% by 2021.
- This shift highlights the need for policies and programs that address the unique needs of an ageing population.
- Primary Education: The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in primary education has experienced substantial growth, increasing from 62% in 1971 to universal enrolment today.
- This progress demonstrates a stronger emphasis on ensuring access to basic education for all children.
- Higher Education: The Gross Enrolment Ratio for higher education has also seen significant growth, rising from below 6% in the 1970s to approximately 28% in recent years.
- This development signals a greater focus on providing opportunities for advanced education and skill development.
Implications of Demographic and Educational Changes in India:
- The demographic and educational shifts observed in India since the 1970s have significant implications for out-of-pocket expenditures on health and education, as revealed by National Sample Survey (NSS) data. Key implications include:
Education Expenditures:
- The increase in primary and higher education enrolment has led to stiffer competition for aspirational jobs.
- This competition has driven higher spending on private tuition, leading to 'education poverty' among families with young children.
- Addressing this issue requires a change in the approach to education, as outlined in the National Education Policy (2020).
Health Expenditures:
- The rise in life expectancy and an ageing population have led to increased health expenditure needs, especially among the elderly.
- Changes in household composition and a growing elderly population living independently have further highlighted the need for better healthcare provisions.
- Political parties, like the ruling party with its Ayushman Bharat promise, recognize the importance of addressing these healthcare needs, indicating a potential shift in policy focus.
Elderly Population and Household Composition:
- The increase in life expectancy and decline in mortality rates have created a more age-diverse population with a larger elderly population.
- This ageing population necessitates greater attention to healthcare and financial support for the elderly, an issue that may not be adequately captured by current poverty measurement norms.
Redefining Poverty Norms for a Changing India:
- Current consumption-based poverty measures capture average population attributes but face limitations when accounting for increased population heterogeneity.
- As the population structure evolves, using averages to describe poverty becomes problematic.
- For example: Elderly households may meet nutrition expenditure requirements but struggle with healthcare costs.
- Households with young children might cover food needs yet face challenges in meeting aspirational education expenses, like private tuition.
- These examples highlight how households could surpass extreme poverty thresholds yet lack resources for a decent living standard.
- Consequently, updating poverty norms is essential to accurately capture the realities of diverse household needs.
- To achieve the Sustainable Development Goal of eradicating poverty in all forms, India must redefine its poverty norms, moving away from outdated standards based on 1970s data.
- By establishing fresh norms for the Amrit Kaal, India can better address the unique challenges faced by its population and make significant strides towards alleviating poverty.
Conclusion
India has made remarkable progress in alleviating poverty based on existing norms. However, to ensure a decent living standard for all citizens, it is crucial to update poverty measures to reflect current demographic and economic changes. By acknowledging the evolving needs of its population, India can continue making significant strides in poverty reduction and work towards a more inclusive and prosperous future.
Evaluating India's Current Competition Law Amid Proposed Digital Framework

- 15 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
It stated that due to the swift evolution of digital markets, the current competition law framework may not timely address the anti-competitive conduct by large digital enterprises.
Context:
- The Committee on Digital Competition Law (CDCL), recently released its report recommending a new Digital Competition Law for India alongside the Draft Digital Competition Bill (DCB).
- The genesis of the report goes back to the 53rd Report of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance (PSC), released in December 2022.
- The PSC Report acknowledged the unique dynamics of digital markets, noting their strong network effects and concentration.
- It highlighted that the current competition law framework may not address anti-competitive conduct by large digital enterprises in a timely manner due to the rapid evolution of digital markets.
- Consequently, the report emphasized the need for a new law to restrict certain leading players from engaging in specific anti-competitive activities that could distort competition.
- Activities such as self-preferencing, bundling and tying, and deep discounting were highlighted as areas of concern.
Key Proposals of the Draft Digital Competition Bill:
Predictive regulation:
- The dynamic nature of digital markets, characterized by constant evolution and interconnected offerings, necessitates a shift from traditional ex-post regulation to a forward-looking, preventive, and presumptive ex-ante framework.
- The draft Bill proposes this proactive approach as the way forward, acknowledging the limitations of regulating market abuse after it has already occurred.
- India's current Competition Act of 2002 follows an ex-post antitrust framework, which has faced criticism for its delayed response to market abuse.
- By the time penalties are imposed, market conditions may have already changed, further disadvantaging smaller competitors.
- To effectively navigate the complexities of the digital realm, it is crucial to implement predictive regulation that identifies potential antitrust issues and establishes clear guidelines to mitigate harm and maintain a level playing field.
Significant entities:
- In the Bill, certain "core digital services," such as search engines and social media platforms, prompt the Competition Commission of India (CCI) to designate companies as "Systematically Significant Digital Enterprises (SSDEs)."
- This designation hinges on diverse quantitative and qualitative criteria, encompassing turnover, user base, and market influence.
- The quantitative thresholds for SSDE designation include:
- A turnover in India of at least Rs 4,000 crore over the last three financial years or a global turnover of at least $30 billion.
- A gross merchandise value in India of at least Rs 16,000 crore, or a global market capitalization of at least $75 billion.
- Additionally, the relevant core digital service should have a minimum of 1 crore end users or 10,000 business users.
- Entities falling outside these parameters may still be designated as SSDEs if the CCI deems their presence significant in any core digital service.
- SSDEs are prohibited from practices such as self-preferencing, anti-steering, and restricting third-party applications.
- Violations of these regulations may result in fines of up to 10% of their global turnover.
Associate Digital Enterprises:
- Recognizing the potential benefits of data sharing among entities within a major technology conglomerate, the Bill proposes to identify Associate Digital Enterprises (ADEs).
- Under this provision, if an entity within a group is identified as an associate entity, it would bear similar obligations as SSDEs, contingent upon its involvement with the core digital service provided by the primary company.
- For instance, consider the relationship between Google Search and Google Maps, where data flow from the former informs the functionalities of the latter.
- In this scenario, Google Maps could potentially be classified as an ADE.
- Similarly, the extent of data exchange between Google Search and YouTube could determine the classification of the latter as an ADE, depending on the recommendations provided to users.
Key Challenges with the Digital Competition Bill:
- Regulatory Approach: While the Digital Competition Bill (DCB) draws inspiration from international frameworks such as the UK's Digital Markets, Competition and Consumers Bill (DMCC) and the EU's Digital Markets Act, it could benefit from considering alternative approaches like Japan's "co-regulation" strategy.
- Integrating such an approach might foster a better balance between competition and innovation.
- Timeline: The current May 15, 2024 deadline for submitting comments may not provide sufficient time for a thorough analysis of the complex issues addressed by the DCB and its potential impacts on various stakeholders.
- A further extension of the consultation period should be considered.
- Inter-Regulatory Mechanisms: Overlaps between the DCB and existing sector-specific policy instruments need to be addressed.
- Implementing an inter-regulatory consultation mechanism will ensure clarity and a harmonized approach across regulatory bodies.
- Capacity Building: Strengthening the capacity of the Competition Commission of India (CCI) and its Digital Markets and Data Unit (DMDU) is crucial, particularly through the integration of technology sector experts.
- The DCB should outline specific measures to bolster the Commission's capacity and resources in order to effectively navigate the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Need to Foster Digital Competition:
- Advocating for a Presumptive Framework: Government officials propose a shift towards a presumptive regulatory framework to address the entrenched pattern of anti-competitive behaviour by major tech companies.
- Notably, Google faced a substantial fine of Rs 1.337 crore from the CCI for its anti-competitive practices within the Android ecosystem.
- Concerns Over Tech Monopolies: Officials express apprehension over the dominance of a handful of US-based tech giants, which has stifled innovation over the past decade.
- High market barriers deter new entrants from challenging the dominance of established players, perpetuating a cycle of market concentration.
- Challenges for Emerging Players: Once a company secures a significant market share, its product often becomes the default choice for users, making it challenging for competitors to challenge its dominance.
- Even prominent entities like Spotify have raised concerns about the restrictive policies enforced by industry giants like Apple and Google.
- Niche Alternatives and Market Dynamics: While niche alternatives such as Signal for messaging and DuckDuckGo for search engines exist, they remain niche preferences rather than mainstream choices.
- The proliferation of big tech companies has facilitated affordable advertising rates for smaller businesses, but it has also intensified surveillance and data tracking practices, compromising user privacy.
Conclusion
The proposed DCB marks a notable stride towards regulating India’s digital markets. However, certain concerns persist about its content and policymaking mechanism. The timeline for stakeholder consultation is inadequate, necessitating an extension to ensure comprehensive feedback. Additionally, implementing inter-regulatory mechanisms and capacity building for the CCI remains critical to effectively navigating the evolving digital landscape. Therefore, addressing these issues will be pivotal in ensuring a progressive digital competition framework in India.
Need for a Farmer-Friendly Agri-Export Policy

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The current government policy, skewed towards consumers, unfavourably impacts farmers, necessitating a shift to enhance farmers' incomes.
Current State of India‘s Agricultural Exports:
- The current status of India's agri exports highlights a notable shortfall in achieving government targets.
- Despite aiming for $60 billion in 2022, actual exports in 2023-24 amounted to $48.9 billion, showing an 8% decrease from the previous year's $53.2 billion.
- Between 2004-05 and 2013-14, agricultural exports witnessed remarkable growth, expanding nearly fivefold from $8.7 billion to $43.3 billion.
- However, this growth trajectory slowed significantly in the period from 2014-15 to 2023-24, with an annual growth rate of merely 1.9%.
- Key exports include rice ($10.4 billion), marine products ($7.3 billion), spices ($4.25 billion), bovine meat ($3.7 billion), and sugar ($2.8 billion).
What is Agricultural Export Policy?
- The Agricultural Export Policy, commonly known as an agri-export policy, encompasses a range of governmental regulations, strategies, and incentives aimed at facilitating and encouraging the export of agricultural commodities from a specific nation.
- It encompasses diverse measures such as export subsidies, tariff adjustments, quality benchmarks, market access arrangements, financial support, and promotional efforts to assist agricultural producers and exporters in accessing global markets, enhancing their competitiveness, and broadening their export horizons.
- The Government of India introduced a comprehensive Agriculture Export Policy in December 2018, with the following objectives:
- To diversify our export basket, and destinations and boost high-value and value-added agricultural exports, including focus on perishables.
- To promote novel, indigenous, organic, ethnic, traditional and non-traditional Agri products exports.
- To provide an institutional mechanism for pursuing market access, tackling barriers and dealing with sanitary and phytosanitary issues.
- To strive to double India’s share in world agri exports by integrating with global value chains.
- Enable farmers to get the benefit of export opportunities in overseas markets.
What is the Need for an Agri-Export Policy?
- Economic Contribution: India's agricultural exports, totalling around USD 53 billion in the fiscal year 2022-2023, constitute a significant portion of overall exports, yet the country's global share in agricultural exports remains low at 2.2% as of 2016.
- Food Security Enhancement: Despite catering to a substantial portion of the world's population with limited resources, a well-designed export policy can generate additional revenue to invest in bolstering food security and augmenting farmers' incomes.
- Inflation Control: Agricultural exports have the potential to stabilize domestic prices, benefiting consumers and producers, particularly during periods of abundant harvests.
- Job Creation: With approximately 45% of the workforce engaged in agriculture, promoting agricultural exports can foster employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas where agriculture is predominant.
- Balance of Payments Support: Agricultural exports significantly contribute to India's foreign exchange reserves, helping to offset trade deficits and maintain currency stability.
- Crop Diversity Utilization: India's diverse agricultural production offers substantial export potential, which can be tapped into through a well-structured export policy.
- Trade Relations Strengthening: Agricultural exports are pivotal in fostering and reinforcing trade ties with countries like the United States, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Addressing Structural Challenges: The policy framework can effectively tackle obstacles such as low farm productivity, inadequate infrastructure, global price fluctuations, and limited market access.
What are the Challenges in India's Agri-Export Policy?
Several challenges hamper the effectiveness of India's agricultural export policy, requiring strategic interventions to unleash the sector's full potential:
- Restrictive Export Policies: Favoring domestic consumers over farmers often impedes the achievement of export targets.
- Restrictions on commodities like Basmati rice, such as the Minimum Export Price (MEP) of USD 1,200, can limit export volumes.
- Subsidy-Centric Schemes: Increased subsidies during election periods, including food and fertilizer subsidies, strain fiscal discipline.
- Populist measures like loan waivers and free power for farmers impact the financial health of the agricultural sector.
- Insufficient R&D Investment: Low investment in agricultural R&D, approximately 0.5% of agricultural GDP, hinders growth prospects.
- Doubling or tripling R&D investments is essential for India to excel in agricultural production and exports.
- Quality and Standards: Maintaining consistent quality and meeting international standards is challenging.
- Variability in quality, compliance issues, and difficulties in meeting Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures due to pests and diseases impede exports.
- Infrastructure: Inadequate infrastructure for storage, transportation, and processing results in post-harvest losses, reducing export competitiveness.
- Environmental and Sustainability Concerns: Balancing the growth of agricultural exports with environmental sustainability is crucial.
- Over-exploitation of resources may have long-term consequences, necessitating careful resource management and sustainable practices.
Government Initiatives Promoting Agri-Export in India:
To unlock the full potential of India's agricultural exports, the government has launched several initiatives to enhance productivity, modernise infrastructure, and promote sustainable practices. Key schemes include:
- E-NAM (National Agriculture Market): A pan-India electronic trading portal, E-NAM enables farmers to sell directly to buyers, reducing intermediaries and ensuring fair prices.
- E-NAM has integrated 1,000 wholesale markets and 585 mandis across 18 states and 3 Union Territories.
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM): Promoting sustainable horticulture practices, including organic farming and precision farming, NHM supports the establishment of over 100 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) for horticultural products.
- The mission also backs the production of high-value horticultural products for export.
- Market Access Initiative (MAI): Supporting export promotion activities, such as participation in trade fairs, capacity building, and market research, MAI has facilitated Indian exporters' participation in over 100 international trade fairs annually.
- Operation Greens: With an allocation of INR 500 crores in the Union Budget 2023-2024, Operation Greens stabilizes the supply and prices of essential agricultural commodities like fruits and vegetables.
- The scheme reduces price volatility, ensures fair prices for farmers, and fosters sustainable agri-exports.
- Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters (SAMPADA): With a budgetary allocation of INR 6,000 crores for the period 2020-2021 to 2024-2025, SAMPADA modernizes infrastructure for agro-processing clusters.
- This reduces post-harvest losses and increases shelf life, improving the overall export potential.
- APEDA: Promoting the export of scheduled products, APEDA provides guidelines for sustainability and quality.
- APEDA facilitated exports of agricultural products worth USD 22.17 billion during the financial year 2022-2023.
- Agri Export Zones (AEZs): AEZs provide infrastructure development and technology adoption for sustainable agri-exports.
- Established for commodities like mangoes, grapes, and spices, AEZs have contributed to increased export volumes.
- Promotion of Organic Farming: Initiatives promoting organic farming for environmental sustainability and the export potential of organic products have resulted in increased organic farming area, reaching 3.90 million hectares in 2022-2023, with exports of organic products totalling USD 1.04 billion.
Way Forward for a Stable Agricultural Export Policy in India:
To establish a stable and prosperous agri-export policy in India, several strategic actions and considerations must be taken into account. These include:
- Prioritizing Farmer Welfare: Ensuring that farmers receive fair prices for their produce is crucial for the success of agricultural exports and the well-being of the farming community.
- Supporting Domestic Consumers: Implementing targeted income policies to support vulnerable populations and maintain food security for domestic consumers.
- Enhancing Productivity: Increasing agricultural productivity through investments in R&D, seeds, irrigation, fertilizers, and improved farming practices to bolster global competitiveness.
- Diversifying Export Basket: Expanding the range of agricultural exports, focusing on value-added products, and targeting a wide array of international markets to minimize reliance on a select few commodities.
- Quality Assurance: Implementing strict quality standards and certification mechanisms to ensure that exported agricultural products meet international norms.
- Establishing uniform quality and standardization protocols is vital, particularly for horticultural items.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in modern infrastructure, such as cold storage, processing facilities, transportation, and logistics, to reduce post-harvest losses and enhance export competitiveness.
- Offering financial incentives, subsidies, and credit facilities can encourage investments in agriculture, infrastructure, and processing facilities.
- Technology Adoption: Promoting the use of advanced agricultural technologies, precision farming, and efficient irrigation techniques to boost productivity.
- Encouraging the growth of agri-startups and fostering innovative solutions can enhance agricultural production and export efficiency.
- Environmentally Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable farming practices, including organic farming, to ensure environmental sustainability in agriculture.
- Learning from Global Best Practices: Gaining insights from successful agricultural export policies and best practices in other countries can inform India's approach.
- Strengthening diplomatic efforts to negotiate favourable trade agreements and reduce trade barriers will provide better access to international markets.
Conclusion
To ensure India's continued growth in global agricultural trade, a stable export policy is crucial, embodying dynamism, responsiveness, and adaptability. It must prioritize agricultural sustainability, environmental responsibility, and farmer welfare, securing India's position in international trade. Balancing economic growth with farmer well-being and environmental concerns is key to unleashing India's agricultural potential. Forward-looking policies and innovative solutions will strengthen the agri-export sector, fostering a prosperous and sustainable future for all.
Evaluating the Enhancement of State-run Companies Under Modi Government and Realities

- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Wednesday said the government's focus on capital expenditure and infrastructure development has directly benefited state-run companies and led to substantial growth in their stock performance.
Context:
- In a democratic system, robust opposition plays a vital role in upholding accountability and fostering balanced governance.
- However, the absence of an effective opposition can impede democratic processes, resulting in unfounded criticisms and ineffective checks and balances.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi's government has encountered such obstacles, especially concerning its oversight of public sector enterprises (PSEs).
- Thus, it is imperative to evaluate the performance of PSEs during the Modi administration, juxtaposing it with historical contexts, and elucidating the government's strategic initiatives aimed at their revitalization.
Strategic Divestment Initiatives by the Modi Government:
- The divestment strategy adopted by the Modi government involves a well-thought-out approach to balance fiscal objectives and national interests.
- This is exemplified through the decisions made regarding Air India and Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd (BPCL).
- Air India Privatisation: Air India's transition from a loss-making entity reliant on government subsidies to a privately-owned enterprise signifies a strategic move to enhance efficiency and competitiveness in the aviation sector.
- Privatisation aims to inject agility and market responsiveness into Air India's operations, fostering growth and profitability amidst intense industry competition.
- Post-privatisation, Air India's ambitious expansion plans underscore its renewed focus on capturing market opportunities and improving financial performance.
- Retaining Stake in BPCL: Contrary to Air India, the government's decision to maintain ownership of Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd (BPCL) reflects strategic considerations linked to energy security and sectoral importance.
- BPCL's extensive retail network and expertise in areas like ethanol blending align with the government's objectives in sustainable energy transition.
- By retaining control over BPCL, the government ensures influence over critical sectors while leveraging the company's capabilities to advance national priorities such as sustainability and energy resilience.
- Strategic Decision-Making: The government's divestment strategy goes beyond immediate financial gains, considering broader strategic implications and long-term national interests.
- Factors like sectoral significance, market dynamics, and alignment with development goals inform divestment decisions, ensuring they contribute to India's economic growth and strategic objectives.
- Through a strategic divestment approach, the government aims to strike a balance between fiscal imperatives and broader developmental priorities, driving sustainable and inclusive growth.
An In-depth Review of PSE Performance During the Modi Era:
- Under Prime Minister Narendra Modi's leadership, Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs) have experienced notable growth and transformations across various sectors. This comprehensive analysis showcases the strides made by PSEs under the current administration:
- Financial Sector: The Modi government's intervention and reforms revitalized public sector banks (PSBs), inherited with significant non-performing assets (NPAs).
- PSBs reported their highest-ever profits and lowest-ever NPAs in the fiscal year 2022-23, indicating a substantial improvement in their financial health and investor trust.
- Oil and Gas Sector: Oil India Ltd, an upstream oil company, achieved its highest-ever crude and natural gas production, contributing to India's energy security.
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL) reported record-high refinery throughput, sales volume, and net profit, highlighting its operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
- Energy Generation: Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL) achieved its highest-ever profit for the first nine months of any fiscal year, demonstrating resilience and adaptability in a dynamic market.
- Coal India registered its highest-ever production, underscoring the government's emphasis on maximizing domestic coal output to meet growing demand.
- Infrastructure Development and Expansion: National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) set a new record for the highest-ever electricity generation in a year, strengthening India's power infrastructure.
- PSEs like Indian Railways and Ports have undertaken ambitious plans to modernize and expand infrastructure capacity, supporting economic growth and development.
Notable Differences Between the Current Government's Strategy and Results and Those of its Predecessors:
- Comparing the current government's approach to managing Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs) with that of its predecessors reveals significant differences:
- UPA Era Mismanagement: During the UPA regime, PSEs were frequently subjected to political interference and corruption, resulting in inefficiency and stagnation.
- Sectors like Indian Railways faced systemic challenges, such as bureaucratic hurdles and lack of accountability, leading to suboptimal performance and reduced contributions to the economy.
- Corruption and Cronyism During Past Administrations: The UPA era was tainted by major corruption scandals, damaging the credibility of PSEs and eroding public trust in the government's capacity to manage public resources.
- Political-corporate alliances further undermined the integrity and efficiency of PSEs, compromising their capacity to serve the public interest.
- Policy Paralysis and Inefficiency: The UPA government's policy paralysis and administrative inefficiencies hindered innovation and growth in the public sector.
- Delayed projects and bureaucratic obstacles led to missed economic opportunities and job creation constraints.
- Modi Government's Transformative Reforms: The Modi government has pursued a reform agenda to revitalize and enhance the competitiveness of the public sector through strategic vision, decisive action, and an emphasis on transparency and accountability.
- Prime Minister Modi's leadership has emphasized accountability and performance, with measures to streamline decision-making processes, reduce red tape, and hold PSEs accountable.
- Proactive governance and strategic initiatives, including divestment, strategic partnerships, and infrastructure investments, have unlocked new growth opportunities, improved operational efficiency, and positioned PSEs for long-term success in a global market.
Conclusion
- The governance of Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs) under Prime Minister Modi's leadership marks a transformative era characterized by forward-thinking reforms, efficient management, and a clear vision for national development.
- In the face of opposition critique, the government's strategic interventions have successfully positioned PSEs as significant contributors to India's growth trajectory, ultimately fostering a brighter and more prosperous future for the nation and its citizens.
- Through a combination of bold decision-making, transparency, and a commitment to accountability, the Modi government has revitalized the public sector and enhanced its competitiveness.
- By addressing the challenges inherited from previous administrations, the current leadership has demonstrated its dedication to promoting sustainable growth and development while effectively managing PSEs for the greater good of the country.
Freshwater Quest: The Emergence of the New Gold Rush
- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India can take the lead in shaping non-controversial legislative text that addresses the gaps in the laws of the sea, especially in exploratory activities that concern freshwater extraction.
Context:
- Recent statistics reveal that the vast majority of Earth's water is saline, leaving only a small portion as freshwater. Surprisingly, just 0.3% of this freshwater exists in liquid form on the surface, highlighting the significance of subterranean freshwater reserves, including those beneath the ocean floor.
- This emphasizes the growing importance of underground freshwater resources amid the escalating scarcity of surface water.
What are Undersea Freshwater Reserves?
- Undersea freshwater reserves are large volumes of fresh water found beneath the ocean floor.
- In the 1960s, the U.S. Geological Survey made an unexpected discovery of freshwater reserves beneath the ocean floor while drilling off the coast of New Jersey.
- This finding has since been followed by international scientific teams uncovering additional sources of underwater freshwater across the globe, notably including a deep river at the bottom of the Black Sea.
- This particular underwater river is over 100 feet deep, flows at a rate of about four miles per hour, and boasts a volume comparable to some of the world's largest land-based rivers.
- As freshwater resources on land become increasingly scarce, countries are turning their attention towards exploring and potentially exploiting both surface and subsurface freshwater reserves within their maritime zones.
- It is anticipated that these efforts may eventually extend beyond national Exclusive Economic Zones into regions governed by the United Nations Law of the Sea Convention, highlighting the significance of this valuable resource and the increasing need for its sustainable management.
Legal and Policy Framework of Ocean Governance:
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS): The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) serves as the primary legal framework governing the management and constitution of the world's oceans.
- It incorporates most internationally recognized maritime laws while also acknowledging the importance of customary international law in sea governance.
- UNCLOS designates the "Area" beyond national jurisdiction as the seabed, ocean floor, and subsoil, defining it as the common heritage of mankind.
- This classification underscores the notion that these regions should be available for the benefit of current and future generations.
- 1958 Geneva Conventions: The 1958 Geneva Conventions on the Law of the Sea also play a vital role in maritime legal doctrine.
- These include the Convention on the Territorial Sea and the Contiguous Zone, the Convention on the High Seas, the Convention on Fishing and Conservation of the Living Resources of the High Seas, and the Convention on the Continental Shelf.
- These Geneva Conventions address many issues similar to those covered by UNCLOS and draw their principles from customary international law, reinforcing the essential foundations of maritime legal norms.
- Exclusive Economic Zones and the "Area" under UNCLOS: UNCLOS delineates Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) extending up to 200 nautical miles from coastal boundaries, granting states exclusive rights to marine resources within this zone.
- Beyond the EEZ lies the "Area," designated as the common heritage of mankind, managed collectively for sustainable utilization.
Navigating Complexities in UNCLOS and Geneva Conventions:
- The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the 1958 Geneva Conventions on the Law of the Sea present complex legal interplays due to varying degrees of ratification and overlapping jurisdictions.
- For instance, UNCLOS supersedes the Geneva Conventions for its signatories but does not apply to non-signatory states.
- This divergence in international agreements is exemplified by the United States, which is a signatory to the Geneva Conventions but not UNCLOS.
- The term "resources" under UNCLOS is limited to solid, liquid, or gaseous mineral resources found in the Area.
- However, it remains unclear whether this definition extends to freshwater. Given the increasing scarcity of freshwater resources, potential conflicts may arise over its exploration and extraction in the "Area," particularly in the absence of specific legislation governing resources beyond national jurisdiction.
- The complex legal landscape is further exacerbated by the presence of multiple pieces of maritime legislation that fail to address emerging challenges effectively.
- Additionally, the regulatory authority of the International Seabed Authority (ISA) under UNCLOS adds another layer of complexity, as it remains unclear who regulates state parties to the Geneva Conventions regarding mining and exploratory activities in the "Area.
Significance of Freshwater Exploration for the Future:
- Addressing Scarcity: Given that merely 0.3% of Earth's freshwater is readily available on the surface, the exploration of underground and underwater sources emerges as imperative to satisfy future water demands.
- Conflict Prevention: As freshwater scarcity intensifies, the exploration and protection of underwater sources serve as proactive measures to mitigate potential conflicts over water resources.
- Promoting Sustainability: Engaging in responsible freshwater exploration aligns with Sustainable Development Goals, fostering the sustainable utilization of natural resources to ensure their availability for future generations.
Way Forward:
- Legislative Clarity: It is crucial to create a thorough legal framework that addresses the difficulties of discovering freshwater reserves outside of national borders.
- This framework should harmonize UNCLOS provisions with customary international law, ensuring clarity and consistency in governing maritime activities.
- International Collaboration: Engaging in constructive dialogue and negotiation forums, nations can strive to reconcile divergent legal interpretations and foster mutual understanding.
- Establishing multilateral agreements and protocols can enhance cooperation and coordination in managing underwater freshwater resources.
- Research and Technological Advancement: Investment in research and technological innovation is crucial for unlocking the full potential of underwater freshwater reserves.
- Advanced exploration techniques and sustainable extraction methods can optimize resource utilization while minimizing environmental impact.
- India's Leadership Role: As a pivotal stakeholder in maritime affairs, India can spearhead international discourse on freshwater exploration.
- By advocating for inclusive and equitable approaches, India can contribute to the development of global norms and standards governing underwater resource management.
Conclusion
The increasing scarcity of freshwater underscores the urgent need for an internationally recognized legislative framework to govern the exploration and exploitation of underground freshwater resources. The establishment of such a framework would not only help prevent potential conflicts but also ensure the sustainable utilization of this vital resource for the benefit of both present and future generations on a global scale. By proactively addressing these challenges, nations can work together to secure the long-term availability and equitable distribution of freshwater, fostering stability and prosperity in an increasingly water-scarce world.
An AI-infused World Needs Matching Cybersecurity
- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
As generative AI technology becomes more prevalent, safeguarding consumers' ability to navigate digital environments securely has become increasingly imperative.
Context:
- In recent times, the integration of generative artificial intelligence (AI) across industries has significantly transformed operational processes.
- However, this rapid advancement has also led to the emergence of new cyber threats and safety concerns.
- With incidents such as hackers exploiting generative AI for malicious purposes, including impersonating kidnappers, it is evident that a comprehensive analysis and proactive approach are required to address and mitigate the potential risks associated with this technology.
- A study by Deep Instinct revealed that 75% of professionals observed a surge in cyberattacks over the past year, with 85% attributing this escalation to generative AI.
- Among surveyed organizations, 37% identified undetectable phishing attacks as a major challenge, while 33% reported an increase in the volume of cyberattacks.
- Additionally, 39% of organizations expressed growing concerns over privacy issues stemming from the widespread use of generative AI.
Significant Impact of Generative AI & Growing Cybersecurity Challenges:
- Transformative Impact: Generative AI has revolutionized various sectors like education, banking, healthcare, and manufacturing, reshaping our approach to operations.
- However, this integration has also redefined the landscape of cyber risks and safety concerns.
- Economic Implications: The generative AI industry's projected contribution to the global GDP, estimated between $7 to $10 trillion, underscores its significant economic potential.
- Yet, the development of generative AI solutions, such as ChatGPT introduced in November 2022, has introduced a cycle of benefits and drawbacks.
- Rising Phishing and Credential Theft: An alarming surge of 1,265% in phishing incidents/emails and a 967% increase in credential phishing since late 2022 indicates a concerning trend.
- Cybercriminals exploit generative AI to craft convincing emails, messages, and websites, mimicking trusted sources to deceive unsuspecting individuals into divulging sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
- Emergence of Novel Cyber Threats: The proliferation of generative AI has expanded the cyber threat landscape, enabling sophisticated attacks.
- Malicious actors leverage AI-powered tools to automate various stages of cyber-attacks, accelerating their pace and amplifying their impact.
- This automation poses challenges for detection and mitigation, making attacks more challenging to thwart.
- Challenges for Organizations: Organizations across sectors face escalating cyber threats, including ransomware attacks, data breaches, and supply chain compromises.
- The interconnected nature of digital ecosystems exacerbates the risk, as vulnerabilities in one system can propagate to others, leading to widespread disruption and financial losses.
- Additionally, cybercriminals' global reach and anonymity pose challenges for law enforcement and regulatory agencies.
The Bletchley Declaration: Addressing AI Challenges
- Global Significance: The Bletchley Declaration represents a pivotal global initiative aimed at tackling the ethical and security dilemmas associated with artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI.
- Named after Bletchley Park, renowned for its British code-breaking endeavours during World War II, the declaration embodies a collective resolve among world leaders to shield consumers and society from potential AI-related harms.
- Acknowledgement of AI Risks: The signing of the Bletchley Declaration at the AI Safety Summit underscores the mounting awareness among global leaders regarding AI's inherent risks, notably in the cybersecurity and privacy realms.
- By endorsing coordinated efforts, participating nations affirm their dedication to prioritizing AI safety and security on the international agenda.
- Inclusive Engagement: The Bletchley Declaration's inclusive nature is evident in the involvement of diverse stakeholders, including major world powers like China, the European Union, India, and the United States.
- By fostering collaboration among governments, international bodies, academia, and industry, the declaration facilitates cross-border and cross-sectoral knowledge exchange, essential for effectively addressing AI challenges and ensuring equitable regulatory frameworks.
- Consumer Protection Focus: At its heart, the Bletchley Declaration underscores the imperative of safeguarding consumers against AI-related risks.
- Participating countries commit to formulating policies and regulations that mitigate these risks, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and oversight in AI development and deployment.
- Additionally, mechanisms for redress in cases of harm or abuse are prioritized.
- Ethical AI Promotion: A core tenet of the Bletchley Declaration is the promotion of ethical AI practices.
- Participating nations pledge to uphold principles of fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI development and usage, striving to prevent discriminatory or harmful outcomes.
- This commitment aligns with broader endeavours to ensure responsible AI deployment for the betterment of society.
Alternative Measures for AI Risk Mitigation:
- Institutional-Level Strategies: Governments and regulatory bodies can enact robust ethical and legislative frameworks to oversee the development, deployment, and utilization of generative AI technologies.
- These frameworks should prioritize consumer safeguarding, transparency, and accountability, all while fostering innovation and economic prosperity.
- Furthermore, the integration of watermarking technology can aid in the identification of AI-generated content, empowering users to discern between authentic and manipulated information.
- This proactive approach can substantially mitigate the prevalence of misinformation and cyber threats stemming from AI-generated content.
- Continuous Innovation and Adaptation: Sustained investment in research and development is imperative to proactively address emerging cyber threats and devise innovative solutions to counter them.
- By bolstering support for cutting-edge research in AI security, cryptography, and cybersecurity, governments, academia, and industry can drive technological progress that fortifies cybersecurity resilience and mitigates the inherent risks associated with generative AI.
Conclusion
Effectively tackling the challenges presented by generative AI demands a comprehensive strategy encompassing regulatory, collaborative, and educational efforts across institutional, corporate, and grassroots domains. Through the enactment of robust regulatory frameworks, stakeholders can collaboratively mitigate the risks posed by AI-driven cyber threats, fostering a safer and more secure digital environment for all.
Balancing Fundamental Rights (FR) and the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP)

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The top court has a chance, in Property Owners Association vs State of Maharashtra, to resolve the clash between fundamental rights and Directive Principles of State Policy.
Context:
- In a recent hearing before a nine-judge Bench of the Supreme Court of India in Property Owners Association vs State of Maharashtra, two crucial questions have surfaced concerning the interpretation and implementation of constitutional provisions.
- The initial query revolves around elucidating the concept of "material resources of the community" as articulated in Article 39(b) of the Indian Constitution.
- The subsequent issue delves into the potential discord between legislation crafted to fulfil the objectives delineated in Article 39(b) and the fundamental rights to equality and liberty enshrined in Part III of the Constitution.
The Conflict Between Fundamental Rights (FR) and Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP):
- Inherent Dilemma: At the core of India's constitutional framework lies a significant tension between fundamental rights and directive principles of state policy (DPSP).
- Part III guarantees citizens' fundamental rights, while Part IV outlines DPSPs as guiding principles for state action.
- This tension stems from the divergent nature of these provisions:
- fundamental rights are legally enforceable
- whereas DPSPs serve as moral and political directives without judicial enforceability.
- Clash of Objectives: The conflict between fundamental rights and DPSPs arises from conflicting priorities: individual liberties versus collective welfare.
- While fundamental rights focus on safeguarding individual autonomy and limiting state interference, DPSPs underscore the state's responsibility to foster social and economic justice for citizens' well-being.
- This tension is compounded by India's diverse societal fabric, marked by varying social, economic, and cultural landscapes.
- Historical Discourse: The conflict between fundamental rights and DPSPs has sparked considerable debate and legal scrutiny throughout India's constitutional history.
- Courts have grappled with striking a balance between state intervention for societal welfare and safeguarding individual freedoms, especially when legislative measures aimed at fulfilling DPSPs impinge on fundamental rights.
- The Supreme Court's pivotal role in adjudicating these conflicts has significantly shaped India's constitutional democracy.
- Intensified Debate: During the 1970s, the conflict between fundamental rights and DPSPs reached a zenith, prompting amendments to shield certain laws from judicial review.
- The landmark Kesavananda Bharati vs State of Kerala (1973) case sought to address this conflict, yet it persisted, reflecting the ongoing struggle to reconcile competing constitutional imperatives.
What is the Article 31C of the Indian Constitution?
- The 25th Amendment (Birth of Article 31C): Enacted through the 25th amendment to the Indian Constitution, Article 31C was introduced to shield laws aimed at actualizing Article 39(b) and (c) from judicial scrutiny concerning potential violations of fundamental rights.
- This constitutional provision sought to safeguard legislative measures crafted to secure the material resources of the community, shielding them from challenges under Articles 14 and 19, which safeguard equality and various freedoms, respectively.
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (Challenging Article 31C): The landmark Kesavananda Bharati vs State of Kerala (1973) case questioned the validity and breadth of Article 31C.
- The Supreme Court deliberated on whether Article 31C, by immunizing certain laws from fundamental rights challenges, infringed upon the basic structure of the Constitution.
- While affirming the principle of judicial review and the supremacy of the Constitution's basic structure, the ruling left uncertainties about the extent to which Article 31C could restrict fundamental rights.
- Expansion via the 42nd Amendment: Despite judicial scrutiny in Kesavananda, Parliament expanded Article 31C's reach through the 42nd Amendment in 1976.
- This amendment aimed to widen the immunity granted to laws furthering directive principles, extending beyond Article 39(b) and (c) to encompass any directive principle.
- The 42nd Amendment marked a significant shift in the equilibrium between fundamental rights and directive principles, sparking concerns over potential encroachments on individual liberties.
- Minerva Mills Case (Judicial Intervention): The constitutionality of the expanded Article 31C faced judicial scrutiny in Minerva Mills vs Union of India (1980).
- In a seminal verdict, the Supreme Court struck down the 42nd Amendment, emphasizing the symbiotic relationship between fundamental rights and directive principles within the constitutional framework.
- Chief Justice Y.V. Chandrachud's assertion regarding fundamental rights serving as a check against unchecked state authority underscored the significance of this ruling.
- Ambiguities and Pending Matters: Following the Minerva Mills case, ambiguities persisted regarding the status of Article 31C and its alignment with the Constitution's basic structure.
- Justice Y.V. Chandrachud's divergent opinions in Minerva Mills and Waman Rao vs Union of India added complexity to the issue.
- The absence of a definitive Supreme Court ruling on the validity of Article 31C has perpetuated the tension between fundamental rights and directive principles.
Property Owners Association Vs State of Maharashtra: Resolving a Constitutional Conundrum
- Comprehensive Legal Examination by the Supreme Court: At the heart of this case lies a critical examination of a law granting a state government board full control over dilapidated buildings, contingent upon the consent of at least 70% of residents.
- The legality of this law is under scrutiny, particularly regarding its potential infringement on fundamental rights enshrined in Articles 14 and 19, which ensure equality and various freedoms, respectively.
- Rebalancing Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles: The verdict in the Property Owners case holds profound significance for recalibrating the equilibrium between fundamental rights and directive principles in India's constitutional fabric.
- It will delineate whether laws designed to uphold directive principles, such as acquiring dilapidated buildings for the common good, can withstand challenges based on fundamental rights.
- This raises fundamental questions regarding the hierarchy of rights and duties within the constitutional framework and the extent to which the state can limit individual liberties for the collective welfare.
- Addressing Ambiguities and Pending Issues: The Property Owners case offers an opportunity for the judiciary to clarify ambiguities surrounding the interpretation and implementation of Article 31C, considering previous judicial precedents.
- Prior conflicting rulings in cases like Kesavananda Bharati and Minerva Mills have left unresolved queries regarding the validity and scope of Article 31C, particularly concerning its alignment with the Constitution's basic structure.
- Despite subsequent judgments like Waman Rao and Sanjeev Coke vs Bharat Coking Coal (1982), which followed, the Supreme Court has yet to provide a definitive analysis of Article 31C introduced by the 25th amendment and its compatibility with the Constitution's foundational principles.
- By offering clarity on these matters, the Supreme Court can foster a more coherent and uniform approach to reconciling the divergent demands of fundamental rights and directive principles.
Conclusion
The verdict in the Property Owners case stands as an opportunity to reinforce the core tenets of equality, liberty, and social justice embedded within the Indian Constitution. By delicately reconciling the safeguarding of individual rights with the advancement of societal well-being, the judiciary holds the key to preserving the integrity of India's constitutional democracy. Such a decision would ensure that principles of justice and fairness remain paramount in the governance of the nation, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society.
Elevating India's Online Gaming Industry

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Prime Minister’s vision to establish India as a prominent global gaming hub has received renewed attention as he engaged with seven of the top gamers in the country.
Context:
- The Prime Minister of India has envisioned the nation as a leading global gaming hub, recognising the potential of the online gaming industry to drive economic growth and innovation.
- In a recent engagement with top gamers, key areas of focus were identified, including regulatory clarity, cultural integration, and diversity in the gaming landscape.
- As India's gaming industry experiences rapid growth, it is essential to address existing challenges and devise effective strategies to propel the nation to the forefront of the global gaming arena.
- By establishing clear regulatory guidelines, fostering partnerships, promoting skill development, encouraging original Indian content, and leveraging the country's digital infrastructure, India can unlock its full potential and emerge as a global gaming powerhouse.
Factors Driving the Growth of India's Gaming Industry:
- Enhanced Internet Infrastructure and Connectivity: The expansion of broadband services in Tier-II and Tier-III cities via initiatives like BharatNet and the National Broadband Mission has widened the accessibility of online gaming beyond urban areas.
- The proliferation of 4G and forthcoming 5G networks has further bolstered internet speeds and reduced latency, crucial for seamless gaming experiences.
- Affordable Data and Smartphone Access: Decreasing costs of mobile data plans, spurred by intense competition among telecom providers, have made data more affordable and accessible for gaming enthusiasts across socio-economic segments.
- With India's smartphone base exceeding 680 million, predominantly comprising 4G devices, mobile phones have emerged as the primary gaming platform, capturing a significant share of the market.
- Emergence of E-sports: The inclusion of e-sports in prestigious events like the Commonwealth Games and Asian Games has elevated its status as a legitimate sporting activity.
- The success of Indian teams on global platforms has further propelled industry growth, enhancing its profile and inspiring aspiring gamers.
- Government Support and Regulatory Clarity: Regulations like the IT Rules 2021 have established a regulatory framework for online gaming, addressing concerns regarding content and addiction.
- The formation of self-regulatory bodies and initiatives like the AVGC Promotion Task Force have fostered industry growth.
- Additionally, liberalized FDI norms and government recognition of gamers have attracted international investments.
- Robust Start-up Ecosystem: India's thriving start-up ecosystem has fostered the growth of numerous gaming companies, driving innovation and catering to diverse consumer preferences.
- The emergence of gaming unicorns like Game 24X7, Dream11, and Mobile Premier League underscores the sector's potential and attractiveness to investors.
- Cultural Shift and Pandemic Impact: The Covid-19 lockdown accelerated the adoption of online gaming as a virtual entertainment and socializing avenue.
- With Indians spending an average of 4.5 hours per week on gaming post-lockdown, perceptions have evolved, recognizing gaming not just as a leisure activity but also as a viable career option.
- Integration of Advanced Technologies: Adoption of technologies such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), cloud gaming, and blockchain has enriched gaming experiences and spurred innovation.
- AR and VR offer immersive gameplay, while cloud gaming ensures device-agnostic access.
- Blockchain integration facilitates asset ownership and tokenized economies, enhancing engagement.
Key Challenges Facing India's Gaming Sector:
The Indian gaming industry faces several obstacles that must be addressed to foster sustainable growth and innovation:
- Regulatory Ambiguity and Fragmented Policies: The absence of a cohesive regulatory framework creates uncertainty for industry players.
- Varying state laws and regulations leads to a fragmented policy landscape, with some states banning certain online games while others adopt a more liberal approach.
- Taxation Concerns and Sustainability Challenges: The recent imposition of a 28% Goods and Services Tax (GST) on the total face value of bets raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of the industry, particularly for smaller startups.
- High tax rates may force smaller companies out of business, stifling innovation and hampering industry growth.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity Challenges: Despite progress, reliable and high-speed internet connectivity remains a challenge in rural and remote areas.
- Only 31% of the rural population uses the internet compared to 67% of urban dwellers (India Inequality Report 2022).
- Content Localization and Cultural Relevance: Developing games and content that resonate with India's diverse cultural and linguistic landscapes presents a challenge for game developers.
- While some games like Ludo King have successfully adapted to local tastes, many international games struggle to find similar cultural resonance.
- Responsible Gaming and Addiction Concerns: As the gaming industry expands, concerns about gaming addiction, particularly among younger populations, must be addressed.
- The prevalence of internet gaming disorder in Indian students ranges from 1.3% to 19.9% for the adolescent group (source).
- The "Beware of Smartphone Zombies" signboards in Bengaluru serve as a reminder of the growing issue of digital distraction and the need for responsible gaming practices.
Strategies to Boost India's Gaming Industry:
Several measures can be adopted to enhance the gaming industry in India:
- Regulatory Clarity: Improving regulatory clarity is crucial, particularly regarding the implementation of self-regulatory bodies mandated by the IT Rules of 2021.
- Prompt action is needed to establish a clear and supportive framework for industry growth.
- Dedicated Gaming Hubs and Incubators: Establishing specialized gaming hubs and incubators in major cities can foster innovation, collaboration, and talent development.
- These hubs can provide cutting-edge infrastructure, mentorship, and resources for game developers, startups, and professionals.
- Promote Game Development based on Indian Culture and Mythology: Encouraging and incentivizing game developers to create games inspired by India's rich cultural heritage, mythology, and folklore can help build a unique identity for Indian games, catering to both domestic and international audiences.
- Games like "Raji: An Ancient Epic" have successfully blended Indian cultural elements with engaging gameplay.
- Innovative Funding and Investment Models: Supporting alternative funding models like crowdfunding, venture capital investments, and public-private partnerships can assist game development and startups.
- Global gaming companies like Ubisoft have experimented with blockchain-based assets and in-game economies, presenting opportunities for Indian companies to explore innovative funding models.
- Empowering Women in Gaming: With women constituting 40% of India's gaming populace, they are well-positioned to lead the country's gaming revolution.
- Supporting and empowering women in the gaming industry can unlock diverse talent, fresh perspectives, and innovative ideas to drive sector growth.
- Cross-Industry Collaborations: Fostering collaborations between the gaming industry and other sectors, such as tourism, education, and hospitality, can help explore the potential of gamification and serious games.
- These partnerships can lead to innovative applications of gaming technology across various domains.
- By implementing these strategies, India can create a thriving and globally competitive gaming industry, unlocking significant economic, creative, and technological potential.
Conclusion
India's gaming industry holds immense potential for growth and innovation. To capitalize on this opportunity, it is crucial to address key challenges such as regulatory ambiguity and infrastructure limitations while promoting cultural integration and diversity in the gaming landscape. By fostering cross-industry collaborations, leveraging cutting-edge technologies, and empowering underrepresented groups, India can become a global gaming powerhouse, driving economic development and shaping the future of the gaming industry.
Constructed Wetlands: Solution for Wastewater Treatment in India

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Constructed wetlands ecosystems can significantly contribute to sustainable industrial progress and the preservation of water resources.
Context:
- Industrial growth in India has led to major environmental issues, especially in managing industrial wastewater.
- Untreated or improperly treated industrial discharge into water sources causes severe threats to ecosystems, public health, and water security.
- With diverse sectors like manufacturing, textiles, chemicals, and mining, pollution is substantial.
- Traditional treatment methods often fail to address the complex pollutants in industrial wastewater, demanding a shift to comprehensive, nature-based solutions.
- Constructed wetlands offer a promising solution, providing effective treatment and significant environmental and economic benefits.
- These unique ecosystems combine the efficiency of natural processes with human innovation, presenting an eco-friendly alternative to conventional treatment methods.
What are Constructed Wetlands?
- A constructed wetland is a type of sustainable wastewater treatment system that is designed to look and function as a natural wetland does.
- Constructed wetlands are created for the purpose of treating wastewater from small, rural communities in an environmentally friendly way before allowing it to return to the water system safely.
- They are usually made up of a primary settlement tank where wastewater from the community is collected and from that, several ponds follow which are planted with wetland plants including reeds, rushes and sedges.
- The ponds are usually gently sloped towards a river to allow water to flow very slowly through the wetland before flowing away.
- Any particles that have been carried in the water will settle on the bottom and the plants and natural microorganisms (e.g. bacteria, algae and fungi) in the wetlands will break down and remove certain pollutants and elements e.g. phosphorus in the water.
- Constructed wetlands are typically divided into two categories: Subsurface flow (SSF) and surface flow (SF).
- Subsurface flow (SSF) wetlands direct wastewater through gravel beds or porous media, promoting microbial activity that degrades organic matter.
- In contrast, surface flow (SF) wetlands demonstrate their aesthetic appeal above the water’s surface, with gently flowing streams and lush vegetation.
- While each design exhibits distinct advantages, both variants share a unified objective: to convert pollutants into benign compounds through natural processes.
- Plant Selection: Plants like cattails, bulrushes, and sedges are crucial for nutrient absorption and provide habitat for beneficial bacteria.
- Their roots oxygenate the soil and support microbial processes, aiding in pollutant removal.
- Microbial Activity: Beneath the water's surface, a complex microbial community breaks down pollutants, converting toxic substances like ammonia into benign compounds like nitrate.
- This microbial activity occurs naturally, without external intervention.
- Mutual Benefit: Plants and microbes engage in a symbiotic relationship where plants absorb nutrients and contaminants are trapped, while microbes break down pollutants.
- This mutually beneficial interaction fosters a thriving ecosystem within constructed wetlands.
Nature’s Filtration System:
- Constructed wetlands replicate the functionalities of natural wetlands but are purposefully designed to treat wastewater efficiently.
- They comprise shallow basins adorned with wetland vegetation such as reeds, rushes and sedges.
- As wastewater traverses through these basins, a series of physical, chemical and biological processes unfold, effectively eliminating contaminants and enhancing water quality.
Constructed wetlands present numerous benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness: In contrast to traditional treatment facilities, constructed wetlands frequently offer a more economical option for construction and upkeep.
- Their construction and maintenance entail minimal energy consumption and lower operational expenses, rendering them especially appropriate for settings with limited resources.
- Versatility: Constructed wetlands can be customised to address diverse forms of industrial wastewater, effectively managing a broad spectrum of pollutants and contaminants.
- These wetlands can be configured as either free-water surface or subsurface flow systems, chosen based on the particular needs of the location and the characteristics of the pollutants present.
- Environmental benefits: In addition to their primary role in wastewater treatment, constructed wetlands offer supplementary environmental advantages.
- They function as habitats for a wide array of plant and animal species, promoting biodiversity conservation.
- Moreover, they contribute to ecosystem services such as flood control and carbon sequestration, further enhancing their ecological significance.
- Scalability and adaptability: Constructed wetlands are flexible in their scalability, and able to be adjusted to fit various industrial operations and spatial limitations.
- They are versatile, accommodating both centralised and decentralised wastewater treatment methods, thereby providing adaptability in their deployment.
Constructed Wetlands Across India:
- India boasts several remarkable locations where constructed wetlands are utilised for wastewater treatment.
- In Delhi's Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary, a constructed wetland system purifies sewage from adjacent settlements while providing a habitat for diverse flora and fauna, contributing to regional biodiversity conservation.
- Chennai's Perungudi and Kodungaiyur regions have integrated constructed wetlands into their decentralised wastewater treatment strategy.
- These wetlands treat local community sewage, reducing pollutant levels and easing pressure on centralised treatment plants.
- The Kolkata East Wetlands in West Bengal, a Ramsar site, comprises an extensive network of natural and constructed wetlands treating Kolkata's wastewater.
- These wetlands offer livelihoods for local fishing and agricultural communities while improving water quality.
- Palla village in Haryana uses constructed wetlands to treat wastewater from Delhi before releasing it into the Yamuna River, improving water quality and mitigating downstream pollution.
- Auroville, a sustainable international township in Tamil Nadu, employs decentralised wastewater treatment systems featuring constructed wetlands, demonstrating a community-driven approach to wastewater management.
- The Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan utilises constructed wetlands for treating village wastewater.
- This initiative addresses sanitation needs while preserving the reserve's ecological integrity and wildlife habitats.
Opportunities and Challenges in the Indian Context:
Potential for Adoption:
- In India, the potential for utilising constructed wetlands in industrial wastewater treatment is immense.
- With its rich biodiversity and abundance of wetland ecosystems, the country presents favourable conditions for their widespread adoption.
- The decentralised nature of industries makes constructed wetlands an appealing option for on-site or cluster-level wastewater treatment.
Challenges to Overcome:
- Establishment of clear policies and regulatory frameworks to encourage the adoption of constructed wetlands in industrial wastewater treatment.
- Provision of incentives and subsidies to incentivize industries to invest in sustainable wastewater management practices.
- Raising awareness and enhancing technical expertise among stakeholders, including industry professionals, regulators, and local communities.
- Continuous monitoring and research efforts to evaluate the performance of constructed wetlands in diverse industrial settings, including optimizing design parameters and addressing emerging challenges such as new contaminants and the impacts of climate change.
Community Involvement:
- Engagement of local communities in the planning, design, and management of constructed wetlands fosters a sense of ownership and ensures the long-term sustainability of these systems.
- Active participation from community members is essential for the success of constructed wetland projects.
Conclusion
Constructed wetlands present a promising solution for combating industrial wastewater pollution in India. By addressing policy, capacity-building initiatives, and community involvement, constructed wetlands have the potential to significantly contribute to sustainable industrial progress and the preservation of water resources for future generations.
Challenges Faced by MSME Sector in India & Its Solution

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new provision in the Income-Tax Act from Budget 2023-24 ensures prompt payments to MSMEs however, it's causing a problem: large companies are cancelling orders from registered MSMEs and giving them to unregistered ones.
Context:
- The Union Budget 2023-24 brought in a fresh provision in the Income-Tax (IT) Act to ensure timely payments to micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) within 45 days of supplying goods or services.
- Yet, this measure has led to an unusual issue: big corporations are cancelling orders from registered MSMEs and redirecting them to unregistered ones.
What is the Latest Tax Compliance Guidelines for MSMEs:
- In India, businesses typically record expenses as they occur (accrual basis), regardless of whether payment has been made.
- However, under Section 15 of the MSMED Act 2006 and the newly enacted Section 43B(h) of the IT Act, businesses are obligated to settle payments with MSME Registered Enterprises within 15 days or up to 45 days if stipulated in an agreement.
- Failure to adhere to this regulation results in the inability to deduct these payments as expenses in the same fiscal year, potentially increasing taxable income and business taxes.
- Moreover, delayed payments to MSME-registered units incur interest liabilities, placing the responsibility on the payer to fulfil outstanding dues.
What is MSME?
- MSMEs are Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises that are usually involved in the manufacture and production of goods and commodities.
- These business enterprises are the backbone of a country’s development and provide holistic development to the rural and urban population of the country.
- The MSME sector in India makes a contribution of around 30% to the nation’s GDP.
- Moreover, it contributes about 40% to the total exports of India, and
- It provides more than 110 million job opportunities in the country.
- The Government of India introduced the MSME under the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act of 2006.
- MSMEs are managed under the Ministry of MSMEs.
- The objective of MSMEs is to primarily engage in manufacturing, processing, production, and preservation of goods and commodities.
- These business enterprises play an important role in the socio-economic development of the country.
- Thus, the importance of MSME in the growth and development of India is vital.
MSME Classification:
- Businesses are classified as micro, small or medium enterprises based on their turnover and the sector they operate in (manufacturing/services).
Types of MSME:
According to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act 2006, MSMEs are of 2 types:
- Manufacturing Enterprises: Business enterprises that are involved in the manufacturing of goods, as stated under Schedule I of the IDRA 1951, are categorised as MSMEs.
- Additionally, all business enterprises that contribute value to the finished products by making use of plants and machinery also come under MSMEs.
- Service Enterprises: Business enterprises that provide services and come under the category of ‘enterprises’ as stated in the MSMED Act are service enterprises and come under MSMEs.
- However, individual service providers do not qualify as service enterprises.
Importance of MSME in the Indian economy:
- Export: MSMEs’ contribution to the exports from India was recorded at 45.56% till Sept. 2023.
- Such high volumes of exports facilitate international trade and contribute to industrial growth within the country.
- Employment: MSMEs create employment in rural and urban areas of the country.
- These business enterprises are the second largest employment sector in India after agriculture.
- By setting up units in rural and underdeveloped areas, MSMEs contribute to the better living standards of people from lower socioeconomic and rural areas as well.
- Innovation: MSMEs bring innovation to various processes in the manufacturing of goods and commodities.
- They provide the necessary skills, tools, and technology for automation and advancement in their sectors.
- It contributes to the overall technological upgradation of the country and promotes research and development.
- Entrepreneurship: MSMEs promote inclusiveness in the country by facilitating the entry of aspiring entrepreneurs in various sectors.
- They promote healthy competitiveness among entrepreneurs, which fuels industrial growth.
Challenges faced by the MSME sector in India:
- Financial: Access to finance is a significant hurdle for MSMEs, with only 16% receiving timely finance.
- This forces them to rely on their own resources, hindering their growth prospects.
- Even larger firms struggle to access cheaper credit from formal banks.
- Regulatory issues: MSMEs face challenges with tax compliance and labour law changes, which have proven costly.
- Despite attempts to make the sector more competitive, compliance with regulations and tax registration remains difficult, leading to low capital and business closures.
- Infrastructure: India's infrastructure is crucial for the MSME sector, especially in the outsourcing industry.
- However, inadequate infrastructure affects their efficiency and ability to compete globally, limiting their growth potential.
- Low productivity & Lack of innovation: MSMEs may lack high productivity but offer value through cost efficiency and providing goods at lower prices.
- However, their small-scale production and low margins put them at a disadvantage compared to larger firms.
- Indian MSMEs often rely on outdated technologies and lack entrepreneurs who embrace new tools and technologies.
- This hampers their productivity and competitiveness, especially when compared to larger firms in sectors like e-commerce and call centres.
- Technical changes: MSMEs have faced significant technical changes over time, impacting their growth potential.
- Changes in land ownership rights have led to mismanagement and reduced productivity, highlighting the need for adaptability.
- Competition & Skills: MSMEs face fierce competition from larger firms, exacerbated by the rise of e-commerce and globalization.
- While competition is not new, MSMEs struggle to withstand the pressure in areas such as agriculture, garments, and tourism.
- MSMEs lag behind in terms of skills compared to their counterparts in other countries.
- Dependence on informal workers with limited technical skills hampers productivity and forces smaller firms into low-skilled jobs, hindering long-term growth.
- Lack of professionalism: Many Indian MSMEs lack professionalism, making them vulnerable to corruption and abuse of power.
- This significantly impacts their business productivity and overall growth.
- Lack of standardized policies: India lacks consistent MSME policies, resulting in inconsistent development and entrepreneurship promotion programs.
- While progress has been made in Delhi, nationwide efforts are necessary for Indian firms to compete globally.
Government MSME Schemes and Policies in India:
- FIRST: Keeping in view the crucial role MSMEs play in the development of the country, the central government announced the launch of FIRST (Forum for Internet Retailers, Sellers, and Traders).
- The program aligns with the government’s Digital India movement and educates and informs MSMEs about opportunities to become self-reliant and digitally capable.
- MSME Innovation Scheme: Under this scheme, MSMEs can enjoy reimbursement of the cost of Intellectual Property Rights applications for new ideas and designs.
- The programme provides financial and other resources to MSMEs to encourage innovation.
- CGTMSE: The Credit Guarantee Trust Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises scheme provides financial assistance of up to ?2 Crore to new businesses.
- CLCSS: The Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme provides capital subsidies to MSMEs operating in the khadi, village, and coir sectors.
- The subsidy allows these businesses to acquire technological innovation and upgradation.
- ASPIRE: ASPIRE, or A Scheme for Promotion of Innovation, Rural Industries, and Entrepreneurship, fosters innovation and entrepreneurship in rural and agricultural sectors by establishing advanced technology networks.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): The PMMY scheme provides loans up to Rs. 10 lakhs to MSMEs.
- The scheme has three categories of loans: Shishu (up to Rs. 50,000), Kishore (up to Rs. 5 lakhs), and Tarun (up to Rs. 10 lakhs).
- The loans do not require collateral and are available to both new and existing MSMEs.
- Stand-Up India: The Stand-Up India scheme provides loans up to Rs. 1 crore to SC/ST and women entrepreneurs for setting up new ventures in the manufacturing, services, or trading sectors.
- The scheme aims to promote entrepreneurship among these communities and provides support through the entire loan process.
Way Forward:
- Creating awareness about government schemes and initiatives: Stakeholders should take active measures to educate MSMEs about the various schemes and initiatives launched by the government to promote SME financing.
- This will help MSMEs take advantage of these schemes and secure financing for their businesses.
- Developing innovative financing solutions: Financial institutions should develop innovative financing solutions that cater to the unique needs of MSMEs.
- These solutions can include alternative credit scoring mechanisms, digital lending platforms, and other innovative solutions that reduce the reliance on collateral and traditional credit histories.
- Encouraging private-public partnerships: Private-public partnerships can be a powerful tool to promote SME financing.
- Governments and private sector companies can work together to develop financing solutions that are tailored to the needs of MSMEs.
- Reducing the cost of credit: High interest rates on loans can be a significant barrier for MSMEs to secure financing.
- Stakeholders should take measures to reduce the cost of credit for MSMEs, which will make it easier for them to invest in their businesses and drive growth.
- Leveraging technology: Technology can play a crucial role in improving SME financing.
- Stakeholders should leverage technology to develop digital lending platforms, credit scoring mechanisms, and other solutions that can reduce the cost and time involved in securing financing.
Conclusion
MSMEs are vital to India's economy, driving exports, employment, innovation, and entrepreneurship. Although they face financial, regulatory, and infrastructure hurdles, fostering a supportive environment through awareness, innovative financing, partnerships, cost reduction, and technology can empower MSMEs to overcome challenges and significantly contribute to India's socio-economic growth.
Get the Sustainable Development Goals Back on Track

- 04 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
2024 is an election year across the world and newly elected governments need to focus on the all-important sustainability issue.
Context:
- The United Nations Summit on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) held in September in New York presented a chance to assess progress toward the lofty Agenda 2030 goal.
- The COVID-19 pandemic and other worldwide crises have made progress towards these goals difficult, despite the fact that they are part of a framework that has been widely agreed upon.
- It is critical to evaluate the state of SDG implementation, investigate critical areas that call for immediate attention, talk about the results of academic studies on the SDGs' political influence, and suggest ways to advance sustainable development.
What is Sustainable Development?
- Sustainable development entails fostering development that fulfils present needs while safeguarding the capacity of future generations to meet their own needs.
- Coined by the Brundtland Commission in its 1987 report, "Our Common Future," this definition remains widely embraced.
- Embracing sustainable development involves collaborative endeavours aimed at constructing an inclusive, sustainable, and resilient future for both humanity and the environment.
What is the Progress and Emerging Challenges in SDG Implementation?
- Slow Progress and Growing Concerns: The path toward achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) has been marred by sluggish progress and mounting concerns, casting doubt on the world's ability to attain the 2030 targets.
- Despite initial optimism following the adoption of Agenda 2030 by the UN General Assembly in 2015, reports indicate inadequate progress and deviation from the intended trajectory.
- While there were modest improvements noted between 2015 and 2019, particularly in areas like poverty reduction and access to essential services, they fell significantly short of the necessary benchmarks outlined in the agenda.
- Challenges Amplified by Global Crises: The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic and other global crises has compounded the hurdles in SDG achievement.
- The pandemic, in particular, has triggered profound socioeconomic repercussions, disrupting economies, widening inequalities, and propelling millions into poverty.
- The diversion of resources and attention toward addressing immediate health and economic exigencies has further impeded advancements toward long-term sustainable development objectives.
- Concerns Over Environmental Sustainability: A notable concern arises from the insufficient emphasis on goals related to environmental sustainability and biodiversity conservation.
- Critical objectives such as sustainable consumption and production, climate action, and marine and terrestrial biodiversity preservation have been overlooked, jeopardising the welfare of present and future generations.
- Neglecting these environmental imperatives not only undermines progress toward specific SDGs but also poses existential threats to humanity and the planet.
- Fragmented Approach to SDG Pursuit: Furthermore, the prevailing approach to SDG pursuit often disregards the interconnected and indivisible nature of the goals.
- The SDGs are interlinked, with progress in one goal intricately linked to advancements in others.
- Yet, the disjointed strategies adopted by many nations and stakeholders fail to acknowledge these interconnections, leading to isolated efforts unlikely to yield substantive outcomes.
- Without a holistic and cohesive approach to sustainable development, achieving the overarching objective of harmonising human well-being with environmental health remains elusive.
International Promises and Real-World Execution:
Renewed Pledges from International Leaders:
- Amidst these developments, the UN SDG Report 2023 underscored five critical areas necessitating immediate attention:
- The government's commitment to seven years of accelerated, sustained, and transformative actions to fulfil SDG promises;
- Concrete, comprehensive, and targeted governmental policies to eradicate poverty, mitigate inequality, and combat environmental degradation, prioritising the empowerment of women, girls, and marginalised communities;
- Enhancement of national and subnational capacities, institutional accountability, and governance mechanisms to expedite progress;
- Reaffirmation of the international community's commitment to provide assistance and mobilise resources for developing nations, alongside fortifying the UN development system.
- Acknowledging the gravity of the situation, world leaders reiterated their commitments and pledged intensified efforts to achieve the SDGs, envisioned as the global pathway out of crises by 2030.
- However, the extent to which these global declarations translate into action at the grassroots level remains uncertain.
Challenges in National Implementation:
- Despite governments' global vows, significant disparities often exist between rhetoric and practical implementation on the national stage.
- Political considerations, competing agendas, and resource limitations can impede the effective execution of SDG-related policies.
- Furthermore, inadequate coordination and coherence among various government departments and administrative tiers may lead to fragmented initiatives, diminishing the overall efficacy of SDG implementation efforts.
Academic Perspectives and Suggestions:
- Limited Political Influence: The research highlights that while the SDGs have sparked discussions and prompted some normative and institutional adjustments, their direct political impact at national and local levels remains constrained.
- Despite international endorsement, the SDGs have yet to yield significant political outcomes in many nations, underscoring the necessity for a nuanced understanding of the factors shaping SDG implementation and the pathways for driving political transformation.
- Systemic Strategies for SDG Achievement: The study underscores the significance of embracing a systemic approach to unlock the transformative potential of the SDGs.
- This entails identifying and managing trade-offs while maximising synergies across diverse goals.
- By addressing interconnected challenges comprehensively, policymakers can capitalise on synergistic effects and enhance the efficacy of their interventions.
- For instance, initiatives promoting renewable energy can simultaneously advance climate action (SDG 13), foster economic growth (SDG 8), and improve access to clean water and sanitation (SDG 6).
- Customised Implementation Approaches: Moreover, the study stresses the importance of tailored strategies for SDG implementation tailored to regional and national contexts.
- Cookie-cutter solutions are unlikely to succeed given the varied socio-economic, political, and environmental landscapes in which the SDGs are being pursued.
- Instead, policymakers should identify context-specific entry points and leverage existing resources and capacities to drive progress.
- This may involve targeting specific sectors or geographic areas requiring interventions and engaging marginalized communities to ensure their voices and needs are addressed.
- Pragmatic Steps to Enhance Implementation: Additionally, the study provides pragmatic recommendations for bolstering SDG implementation.
- These encompass strengthening governance frameworks and accountability mechanisms, mobilising financial resources, fostering innovation and technology dissemination, and nurturing partnerships among governments, civil society, the private sector, and other stakeholders.
- By adopting a multi-faceted approach addressing political, economic, social, and environmental dimensions, policymakers can foster an enabling environment for transformative change.
Conclusion
The evaluation of SDG advancement highlights the imperative for swift and collaborative measures to overcome prevailing hurdles and hasten advancement. As 2024 heralds elections in numerous nations, incoming administrations have a chance to elevate sustainability as a focal point and harmonise domestic policies with the SDGs. By infusing sustainability tenets into governance structures and policy formulations, governments can play a pivotal role in expediting SDG attainment.
The Judiciary’s Shadow Over Standard-essential Patents

- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government must put in place measures to regulate standard essential patents before the judiciary causes further damage to India’s manufacturing dreams.
Context:
- The emergence of Standard Essential Patents (SEPs) and their implications for India's telecom manufacturing industry has become a significant policy issue.
- However, the utilization of SEPs by technology firms presents hurdles, potentially jeopardizing India's domestic manufacturing sector.
- Thus, it is crucial to delve into the intricacies of this matter, scrutinizing the role of SEPs, the regulatory challenges they present, and the necessity for regulatory action.
What are Standard Essential Patents (SEPs)?
- EPS are patents indispensable for implementing a technical standard, particularly prominent in industries like telecommunications reliant on standards such as 3G, 4G, and 5G for seamless device and network communication.
- Typically owned by entities or individuals, these patents are vital for guaranteeing the interoperability and compatibility of products and technologies adhering to specific standards.
- Critical for fostering interoperability and competitiveness in the cellular phone market, EPS covers technologies adopted as industry standards.
- Despite their significance, conflicts over EPS licensing and infringement are common, often resulting in legal disputes and negotiations between companies and patent holders to establish equitable licensing terms.
Significance of Essential Patents and Regulatory Hurdles:
- Essential Patents (EPs) such as CDMA, GSM, and LTE serve as the linchpin of technological standards in the telecom industry, ensuring seamless compatibility among various cellular phone brands.
- However, the standard-setting process, predominantly governed by private Standard Setting Organizations (SSOs), limits India's influence in shaping these standards.
- Consequently, owners of EPs may demand excessive royalties, resulting in the "patent holdup" dilemma.
- Although SSOs strive for fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory (FRAND) licensing, opacity and anti-competitive behaviours persist, as illustrated by substantial fines levied on companies like Qualcomm by multiple jurisdictions.
Judicial Response to Standard Essential Patents (SEPs) Issues:
- Competition Law Enforcement Inertia: The Competition Commission of India (CCI) commenced an inquiry in 2013 upon a complaint by Micromax against Ericsson, alleging SEP licensing abuse.
- However, Ericsson contested the CCI's jurisdiction, resulting in protracted legal wrangling.
- Despite a favourable ruling for the CCI in 2016, Ericsson's appeals prolonged the case until a final judgment in 2023.
- India, due to this prolonged litigation, remains the sole major economy yet to examine potential anti-competitive SEP licensing practices.
- Patent Infringement Cases and Judicial Engagement: While competition law matters linger, the Delhi High Court actively hears lawsuits by SEP owners against cellular phone manufacturers accused of patent infringement.
- These lawsuits entail intricate trials to ascertain patent validity, infringement, and damages.
- Rather than pausing proceedings pending competition law resolution, the court issues interim measures favouring SEP owners.
- Such measures often mandate manufacturers, many of them Indian, to deposit substantial sums with the court for ongoing production during trials.
- Unprecedented "Deposit" Orders: Issuing "deposit" orders, compelling manufacturers to deposit significant funds before trial, is unprecedented in commercial law.
- These orders, lasting throughout lengthy trials, impose heavy financial burdens on defendants, depriving them of vital working capital.
- While lacking legal foundation and fairness, the Delhi High Court justifies them using its "inherent powers to ensure justice."
- This judicial activism, while aimed at expediting legal proceedings, raises concerns about procedural fairness and equitable treatment of litigants.
Impact of Judicial Interventions and Legal Battles on India's Manufacturing Goals:
- Undermining Investor Confidence and Market Stability: Extended legal battles and judicial interventions sow uncertainty, denting investor trust in India's manufacturing sector.
- Foreign investors may perceive the unpredictable legal environment as a barrier to entering or expanding operations in the nation.
- Uncertainty regarding SEP licensing practices and potential adverse court rulings disrupts market stability, impeding long-term investment planning for both domestic and international enterprises.
- Stifling Growth and Innovation: SEP-related disputes divert attention and resources away from fostering innovation and technological progress in the telecom manufacturing domain.
- Rather than directing efforts towards research and development (R&D) or embracing new technologies, companies become entangled in legal disputes, hindering productive pursuits.
- This diversion of resources curtails innovation, obstructs product development, and undermines India's global competitiveness.
- Impact on Employment and Economy: The manufacturing sector is a vital source of employment and economic advancement, especially in emerging economies like India.
- However, uncertainties surrounding SEP-related litigation pose a threat to job stability and employment opportunities, particularly in the telecom manufacturing sector.
- Protracted legal proceedings and financial burdens may compel companies to downsize operations, leading to workforce reductions and inhibiting future investments.
- Policy Inconsistencies: Contradictions arise between judicial rulings favouring SEP owners and government initiatives to incentivize domestic manufacturing.
- While the government aims to attract investment and bolster indigenous production, SEP-related disputes undermine these objectives.
- The disconnect between supporting manufacturers and overlooking financial burdens imposed by SEP owners questions the coherence of policies promoting industrial growth.
- Long-term Industrial Landscape Implications: Unresolved tensions surrounding SEP licensing practices and judicial handling of disputes cast shadows over India's industrial future.
- Failure to address these issues may deter investors, jeopardize job creation, and impede India's transition to a knowledge-based economy.
- With regulatory intervention to streamline legal processes and ensure fairness, India can catch up to global peers in manufacturing prowess.
Way Forward:
- The European Parliament's proactive stance on regulating SEPs offers valuable lessons for global intervention in this arena.
- Given India's constrained influence in standard-setting and obligations to uphold patents of foreign tech firms, it presents a strong rationale for similar regulatory action.
- Enhancing regulatory frameworks to foster transparency, equity, and non-discriminatory practices in SEP licensing is essential to protect India's economic welfare and foster indigenous manufacturing.
Conclusion
The Indian government must prioritize resolving regulatory uncertainties regarding SEPs to protect domestic manufacturers' interests and drive industrial advancement. Regulatory actions should strive for a harmonious balance between technology firms' interests and overarching goals of economic progress, innovation, and consumer protection. Through decisive intervention, India can assert its autonomy, cultivate fair competition, and cultivate an environment conducive to investment and innovation.
Analysing Labour on a Warming Planet

- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The latest report from the International Labour Organization (ILO), titled 'Safeguarding Workers in a Changing Climate', underscores the pressing necessity to ensure the resilience of labour in the face of climate change.
Context:
- The International Labour Organisation (ILO) recently released a report titled "Ensuring Safety and Health at Work in a Changing Climate," highlighting the urgency of climate-proofing labour practices to protect workers' well-being.
- As the planet experiences warming, workplace environments evolve, and the ILO emphasizes the need to update occupational safety and health (OSH) regulations to address emerging risks.
- According to the report, over one-third of the global population is exposed to extreme heat each year, resulting in nearly 23 million work-related injuries.
- The ILO urges an overhaul of existing OSH laws and protections, as they have not kept pace with climate change-related hazards, leading to increased worker mortality and morbidity.
What Are the Emerging Climate-Related Risks?
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) has identified six primary impacts of climate change:
- Excessive heat
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation
- Extreme weather events
- Workplace air pollution
- Vector-borne diseases
- Agrochemicals
- These hazards can result in various health issues such as stress, stroke, and exhaustion. Particularly vulnerable to these risks are workers in sectors like agriculture, construction, urban conservation, transportation, and tourism.
- Of significant concern is the rising prevalence of gig employment globally, which is particularly susceptible to heat-related conditions.
- In India, gig workers, including ride-hailing app drivers, food and grocery delivery personnel, home repair technicians (electricians, plumbers, AC mechanics), and courier service employees, constitute approximately 1.5% of the total workforce, a figure projected to reach 4.5% by 2030 according to a Nasscom study.
- In the Indian context, the collective impact of these segments suggests that approximately 80% of the country's workforce, projected to be 600 million by 2023, is vulnerable to heat-related hazards.
- This staggering figure exceeds the entire current population of South America by 180 million.
Which Sectors Bear the Brunt of Climate Impact?
Agriculture Sector:
- Globally, agriculture stands out as the most heat-vulnerable sector, particularly in developing nations where informal farm labourers toil without adequate weather protection.
- In India, where agriculture and allied activities employed about 45.76% of the workforce in 2022-23 according to Union Agriculture Minister Arjun Munda, there's a concerning trend of decline from levels three decades ago.
- NSSO data from July 2018 to June 2019 reveals that nearly 90% of Indian farmers own less than two hectares of land, with incomes hovering around ?10,000 monthly on average.
- The situation is even direr in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal, where farmers' earnings can be as low as ?4,895, ?5,112, and ?6,762 respectively.
- Additionally, half of India's farmers are burdened with debt and lack access to modern agricultural technology, impeding their ability to adapt to a warming climate.
- Many communities have already adjusted work schedules to avoid peak heat hours, while the ILO recommends increased hydration facilities, breaks, and shaded rest areas in plantations.
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Sector:
- Following agriculture, India's MSME sector employs over 123 million workers, accounting for about 21% of the workforce.
- Despite its significant contribution to exports and manufacturing output, the sector's pervasive informality has led to minimal oversight of worker conditions by state Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) departments, rendering workers highly susceptible to heat-related risks.
Building & Construction Sector:
- The building and construction industry, with around 70 million workers constituting almost 12% of India's workforce, faces unique challenges exacerbated by urbanization.
- Workers in this sector contend with the urban heat island effect, heightened by rapid urban growth.
- Moreover, they are disproportionately exposed to physical injuries and air pollution-related health hazards, such as asthma, given the alarming pollution levels in many Indian cities.
Legislation Safeguarding Worker Rights in India:
- Central Laws: Integral to ensuring workplace safety in India are the Factories Act, the Workmen Compensation Act, and the Building and Other Construction Workers Act.
- These laws encompass various facets of labour rights and welfare, addressing conditions within factories and providing compensation for work-related injuries.
- Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020 (OSH Code, 2020): Introduced in 2020, the OSH Code represents a comprehensive effort to consolidate and revise existing legislation pertaining to workplace safety.
- Its primary objective is to streamline and strengthen the legal framework governing occupational safety and health nationwide.
- By amalgamating disparate regulations into a unified code, it aims to establish a more cohesive and effective system for ensuring workplace safety across diverse sectors and industries.
State Laws in Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra:
- Tamil Nadu: Tamil Nadu formulated its regulations under the Factories Act as early as 1950.
- These regulations stipulate a maximum wet bulb temperature of 30°C on shop floors and outline requirements for adequate air circulation.
- However, they lack specific provisions for thermal comfort tailored to varying activity levels or modern cooling solutions, indicating a need for updated standards.
- Maharashtra: Similarly, Maharashtra devised its rules under the Factories Act in 1963. Like Tamil Nadu, these regulations address maximum wet bulb temperatures and air circulation standards.
- Nevertheless, they also lack detailed provisions for contemporary cooling methods or adjustments for thermal comfort aligned with evolving production processes, underscoring the necessity for modernization.
Challenges in Addressing Heat Hazards:
- Regulatory Ambiguity: Existing regulations lack specificity regarding thermal comfort standards and the integration of air conditioning in workplaces.
- There's a pressing need to update regulations to accommodate modern cooling technologies and ensure the well-being and safety of workers.
- Impact of the Gig Economy: The burgeoning gig economy in India exacerbates workers' vulnerability to heat-related risks.
- Many gig workers, comprising a substantial portion of the workforce, often operate without adequate protections or support systems to mitigate extreme heat conditions.
- Pressures on Labor Unions: Labour unions face mounting pressures from management and bureaucratic entities, often prioritizing industry interests over worker welfare.
- This dynamic can result in the neglect of worker safety concerns pertaining to heat hazards and other climate-related risks.
- Effluent and Byproduct Management: The disposal of effluents and byproducts poses significant health risks, particularly with fluctuating temperatures, necessitating robust management strategies to safeguard worker health.
- Silicosis in Mining and Quarries: The escalating prevalence of silicosis, stemming from silica exposure in mines and quarries, presents a profound occupational health challenge that demands urgent attention and intervention.
- Shortcomings in Labor Inspection Departments: Vacancies and a lack of expertise within labour inspection departments undermine effective oversight of workplace safety measures, hindering the enforcement of regulations and exacerbating risks for workers.
Way Forward:
- Modernize Regulatory Frameworks: Revamp existing regulations to include clear guidelines on thermal comfort and air conditioning standards in workplaces.
- Integrate innovative cooling technologies to ensure the safety and well-being of workers.
- Empower Labor Unions: Strengthen labour unions and equip them with the resources needed to advocate for worker welfare and safety.
- Foster collaboration among unions, management, and governmental bodies to effectively tackle heat hazards.
- Enhance Labor Inspection Mechanisms: Boost staffing and training within labour inspection departments to enhance oversight of workplace safety.
- Conduct regular inspections and rigorously enforce safety regulations to shield workers from climate-related risks.
- Invest in Research and Development: Allocate funding for research initiatives focused on developing climate adaptation strategies tailored to various industries.
- Support studies assessing the efficacy of interventions and technologies in mitigating heat hazards and other climate-related risks.
- Raise Awareness and Education: Launch awareness campaigns to educate workers, employers, and the public about the health implications of climate change.
- Provide training programs on heat stress management and preventive measures to bolster resilience in vulnerable sectors.
Conclusion
Amidst the challenges posed by climate change, safeguarding workplace safety and health emerges as a critical imperative. The ILO report highlights a pressing call for a globally accepted regulatory framework to fortify workplaces against climate-related risks and safeguard workers. Achieving this necessitates concerted action from governments, industries, and workers alike to address evolving hazards and uphold the well-being of workers amidst the changing climate landscape.
Constitution and the Redistribution of Wealth

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
During the ongoing election campaign, there have been intense debates between the ruling government and the Opposition regarding wealth redistribution, while the SC has formed a nine-judge Bench to interpret the DPSP concerning ownership and control of material resources.
Context:
- Congress leader Rahul Gandhi during the Lok Sabha campaign said that there will be a financial survey to determine the distribution of wealth in the country for addressing the issue of inequality.
- The ruling BJP targeted Gandhi and alleged that Congress if elected, would bring back the "socialistic model" of economics and hinder India's growth as an economy.
What is Wealth Redistribution?
- The meaning of wealth redistribution is the transfer of wealth from one individual to another through a social mechanism such as taxation, charity, or public services.
- One biggest example of wealth redistribution would be income tax wherein higher earnings pay a higher percentage of tax compared to lower-income earners.
- Proponents of this exercise note that wealth redistribution is necessary to bridge the inequality gap between members of society.
- And in India, the gap between the rich and the poor is only growing further.
- As per a recent study, the country’s richest one per cent of the population now owns 40 per cent of the country’s wealth.
- According to the report titled Income and Wealth Inequality in India: The Rise of The Billionaire Raj, and published by The World Inequality Lab, “the inequality gap widened after the economy’s opening up in the early 1990s, but “between 2014-15 and 2022-23, the rise of top-end inequality has been particularly pronounced in terms of wealth concentration”.
- Based on figures from the World Inequality Database, India’s income inequality is among the very highest in the world, behind only Peru, Yemen and a few other small countries.
What Does India’s Constitution Say on Wealth Distribution?
- The Preamble to the Constitution aims to secure for all citizens social and economic justice, liberty and equality.
- Part III of the Constitution lists down the fundamental rights that guarantee liberty and equality while Part IV contains the DPSP.
- These are principles that the central and State governments should follow to achieve social and economic justice in our country.
- Unlike the fundamental rights in Part III, the DPSP is not enforceable in court.
- They are nevertheless fundamental in the governance of the country.
- Article 39(b) and (c) in Part IV contain principles that are aimed at securing economic justice.
- They provide that ownership and control of material resources of the society should be distributed to serve the common good and that the operation of the economic system does not result in the concentration of wealth to the common detriment.
- India’s Constitution-makers haven’t explicitly spoken of wealth redistribution.
- It’s noteworthy that when Article 39 (Draft Article 31) was being added to the Constitution, it was heavily debated.
- The economist KT Shah wanted the Constitution to outrightly prevent the creation of monopolies in industries.
- In agreement with him was Shibban Lal Saxena, who wanted it to be explicitly put down that the State shall control a few key industries.
- However, there were others Naziruddin Ahmad, who were not comfortable with the Constitution endorsing contested political and economic ideologies.
What is the Historical Context of the Redistribution of Wealth?
- The Constitution originally guaranteed the right to property as a fundamental right under Article 19(1)(f).
- It is provided under Article 31 that the state shall pay compensation in case of the acquisition of private property.
- It is pertinent to note that at the time of independence, the main property rights related to agricultural and other land.
- The government had to acquire the rights in such estates for carrying out land reforms and the construction of public assets.
- Considering the inadequate resources of the government and in order to provide greater flexibility in acquiring land for public welfare, various amendments were carried out curtailing the right to property.
- The Supreme Court in various cases has interpreted the relationship between fundamental rights and the DPSP.
- Most of these cases were against constitutional amendments made by the state that curtailed the right to property which was then a fundamental right.
- In the Golak Nath case (1967), the Supreme Court held that fundamental rights cannot be abridged or diluted to implement DPSP.
- Finally, in the Kesavananda Bharati case (1973), a thirteen-judge Bench of the Supreme Court upheld the validity of Article 31C but made it subject to judicial review.
- In the Minerva Mills case (1980), the Supreme Court ruled that the Constitution exists on a harmonious balance between fundamental rights and DPSP.
- In 1978, in order to avoid excessive litigation directly in the Supreme Court by the propertied class, the 44th Amendment Act omitted the right to property as a fundamental right and made it a constitutional right under Article 300A.
- The right to private property continues to be an important constitutional cum legal right.
- Any law to acquire private property by the state should be only for a public purpose and provide adequate compensation.
What is the Current Debate on the Redistribution of Wealth?
- The government of India in the first four decades after independence followed a “socialistic model” of economy.
- The economic policies resulted in the nationalisation of banking and insurance, extremely high rates of direct taxes (even up to 97%), estate duty on inheritance, tax on wealth etc.
- The rationale behind these measures during those times was to reduce inequality and redistribute wealth among the poorer sections that constituted the majority of the population.
- However, such measures stifled growth and also resulted in the concealment of income/wealth.
- Taxes like estate duty and wealth tax generated revenue that was much less than the cost incurred in administering them.
- The nineties saw the country move from a closed economy towards liberalisation, globalisation and privatisation.
- A new industrial policy was unveiled in 1991 with the objective of empowering market forces, improving efficiency and rectifying deficiencies in the country’s industrial structure.
- Estate duty was abolished in 1985 and wealth tax in 2016.
- The market-driven economy has resulted in additional resources for the government that has helped in bringing people out of abject poverty.
- Nonetheless, this economic system has also resulted in growing inequality.
- A report by the World Inequality Lab states that the top 10% of the country’s population have a share of 65% and 57% of the wealth and income respectively as of 2022-23.
- The bottom 50% on the other hand have a meagre share of 6.5% and 15% of the wealth and income respectively.
- The manifesto for the current Lok Sabha elections of the Congress promises that there will be a financial survey to ascertain the distribution of wealth among the people in the country and address the issue of inequality.
- The ruling party campaigners led by the PM have targeted the Opposition on this matter.
- The SC meanwhile has constituted a nine-judge Bench to interpret whether material resources under Article 39(b) include private resources as well.
Way Forward:
- Growing inequality is a worldwide problem of a liberalised open-market economic system.
- It is the responsibility of the government to protect the interest of the poorer classes who are most dependent on the state machinery for their livelihood.
- At the same time past policies of extremely high tax rates, estate duty, wealth tax etc., did not achieve their desired goals. Instead, they only led to the concealment of income and wealth.
- Innovation and growth should not be curtailed but the benefits of growth should reach all sections especially the marginalised.
- It's essential to design inclusive policies through informed debates, aligning with current economic models, to ensure that the benefits of growth reach marginalized sections, in line with the constitutional principle of economic justice for all.
Conclusion
The debate on wealth redistribution in India underscores the complex challenge of balancing economic growth with equitable resource allocation. While past policies have had mixed results, it remains essential for the government to protect vulnerable populations and promote inclusive growth. To achieve this, policymakers must foster innovation while ensuring the benefits reach marginalized communities. By designing policies aligned with current economic models and adhering to the constitutional principle of economic justice, India can work towards a future where growth and social equity coexist harmoniously.
EC’s Model Code Needs Reform and India Needs Model Leadership

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Former Election Commissioner Ashok Lavasa points out that a significant gap in the present framework is that the Model Code of Conduct for elections has not spelled out the consequences of defaults, thus diluting its deterrent effect.
Context:
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) plays a pivotal role in India's electoral process, having evolved considerably since its inception to uphold fairness in elections.
- While originally crafted to regulate conduct during elections, the MCC faces new hurdles in today's dynamic political environment.
- Hence, it becomes imperative to delve into the historical progression of the MCC, identify existing deficiencies, and suggest strategies to bolster its implementation.
Evolution of the Model Code of Conduct (MCC):
- Kerala was the first state to adopt a code of conduct for elections.
- In 1960, ahead of the Assembly elections in the state, the administration prepared a draft code that covered important aspects of electioneering such as processions, political rallies, and speeches.
- It was only in 1974, just before the mid-term general elections, that the EC released a formal MCC.
- It also set up bureaucratic bodies at the district level to oversee its implementation.
- So the EC, just before the 1979 Lok Sabha elections, released a revised Model Code with seven parts, with one part devoted to the party in power and what it could and could not do once elections were announced.
- The MCC has subsequently evolved as an integral part of conducting fair and free elections.
Challenges Faced by the MCC and the Imperative for Strengthening Enforcement:
- Escalating Violations: Political parties and candidates routinely flout the MCC's regulations, engaging in activities like hate speech, vote-buying, and spreading misinformation, undermining the trust in the electoral process and compromising its fairness and transparency.
- Exploitation of Loopholes: In today's political landscape, there's a discernible trend of exploiting MCC loopholes to bypass its regulations.
- With the advent of technology and social media, political entities find novel ways to propagate propaganda and target voters, evading traditional MCC constraints and necessitating revisions to address these evolving challenges.
- Inadequate Deterrents: While the MCC sets ethical standards, it often lacks effective penalties for violations, resulting in politicians perceiving minimal risks in flouting its provisions.
- Strengthening the MCC entails imposing clear and proportionate penalties for transgressions to foster a culture of accountability.
- Complexity of Enforcement: India's vast and diverse electoral terrain, coupled with a surge in reported violations, strains the Election Commission's enforcement capabilities.
- Adjudicating MCC breaches can be arduous and resource-intensive, leading to accountability delays. Streamlining enforcement procedures and enhancing the EC's capacity is pivotal for ensuring prompt and efficient MCC implementation.
- Erosion of Public Trust: Widespread disregard for ethical norms and regulations can erode citizens' trust in the democratic process, fostering voter apathy and disenchantment.
- Restoring public confidence in elections necessitates robust measures to strengthen the MCC and underscore the EC's dedication to upholding electoral integrity.
Proposed Reforms to Enhance MCC Enforcement:
- Clear and Comprehensive Guidelines: The initial step towards MCC reform entails establishing clear and comprehensive guidelines delineating permissible and impermissible conduct during electoral campaigns.
- Regular updates to these guidelines are crucial to address evolving challenges and technological advancements, enabling political entities to navigate ethical standards effectively and prevent inadvertent violations.
- Strict Enforcement Mechanisms: Implementation of proportional penalties for infringements, such as fines, campaigning bans, and withdrawal of electoral symbols, constitutes a vital aspect of reform.
- Streamlining enforcement procedures by the Election Commission (EC) ensures swift adjudication of cases, bolstering the MCC's credibility and deterrent impact.
- Indirect Liability for Political Parties: Imposing penalties on parties for MCC violations, irrespective of individual culpability, incentivizes enhanced oversight over members' conduct.
- This fosters collective responsibility within political organizations, promoting greater accountability and ethical governance.
- Transparency and Public Accountability: Maintaining a publicly accessible database documenting all reported MCC violations and their dispositions empowers citizens to monitor regulatory compliance.
- This transparency holds political actors accountable for their actions, reinforcing public trust in the electoral process.
- Timely and Credible Adjudication: Prioritizing prompt resolution of violations and ensuring impartial decision-making by the EC are essential to uphold the MCC's deterrent effect.
- Timely adjudication prevents erosion of public confidence and underscores the EC's commitment to fair electoral practices.
- Continuous Evaluation and Revision: Vigilance in identifying areas for improvement and updating the MCC in response to emerging challenges and evolving electoral dynamics is crucial.
- This iterative approach ensures the MCC remains relevant and effective in safeguarding India's electoral integrity.
The Role of Political Parties and Election Commission in Safeguarding Electoral Integrity:
Political Leadership's Responsibility:
- Political leaders wield significant influence in upholding electoral integrity by adhering to ethical standards and fostering responsible conduct within their parties.
- By exemplifying ethical leadership, politicians can instill a culture of integrity and accountability among their supporters and party members.
- Effective self-regulation within political parties is imperative to minimize MCC violations and preserve the integrity of electoral campaigns.
- Through a commitment to fairness, transparency, and democratic principles, leaders can instill confidence in the electoral process and encourage civic engagement among voters.
The Election Commission's Mandate:
- As the guardian of electoral integrity, the Election Commission plays a pivotal role in impartially adjudicating MCC violations and enforcing electoral regulations.
- Timely and decisive enforcement of the MCC is crucial for deterring violations and upholding the integrity of electoral campaigns.
- Maintaining transparency in its actions and decisions related to MCC enforcement is essential for the EC to uphold public accountability.
- By providing regular updates on reported violations, adjudication outcomes, and enforcement measures, the EC fosters public trust in its ability to safeguard electoral integrity.
- Enhancing the EC's capacity for MCC enforcement is paramount for effectively addressing emerging challenges and ensuring the integrity of electoral processes.
- This includes investing in training programs, technological infrastructure, and human resources to enable the EC to adapt to evolving electoral dynamics and enforce regulations effectively.
Conclusion
While the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) serves as a crucial bulwark against electoral misconduct, its effectiveness hinges on vigorous enforcement and adaptability to evolving scenarios. Through the adoption of suggested reforms and the cultivation of ethical leadership, India can fortify the integrity of its democratic mechanisms, guaranteeing equitable and transparent elections for its populace.
Ensuring the Rights and Dignity of Senior Citizens
- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Policymakers should proactively address the overshadowing of the needs of the elderly population by the focus on the demographic dividend, and by establishing guidelines for home-based care to meet the challenges posed by an aging population.
Context:
- Amidst the discourse on India's demographic dividend, the growing population of older individuals is often overlooked.
- With projections indicating a significant rise in the elderly population, now reaching nearly 15% of the total population and expected to increase further, there is a pressing need to address the implications of this demographic shift.
- Declining fertility rates and longer life expectancy are key drivers of this transition, leading to smaller households and a greater demand for elder care, straining the existing health and social support systems.
- As the traditional family structure evolves, there's a growing reliance on external assistance for senior care at home, highlighting the need for a recalibration of healthcare and social welfare policies to meet the needs of this aging population.
What Legal Safeguards Exist for the Elderly Population?
- Constitutional provisions pertaining to the elderly are outlined in Article 41 and Article 46.
- While directive principles are not legally binding, they impose a positive obligation on the state during lawmaking processes.
- The Hindu Marriage and Adoption Act of 1956, in Section 20, mandates provisions for the maintenance of elderly parents.
- Under Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code, elder parents are entitled to claim maintenance from their children.
- The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act of 2007 formalizes the legal responsibility of children or heirs to provide maintenance for their parents or senior family members.
Key Issues Affecting Quality and Accessibility in Home-Based Care:
- Lack of Standardization and Defined Practices: Home-based care practices in India suffer from a lack of standardization and well-defined protocols, operating in a less regulated environment compared to institutional settings like hospitals or nursing homes.
- This variability in practices can result in inconsistencies in the quality of care provided to elderly individuals at home.
- Shortage of Trained Caregivers: A significant challenge in home-based care stems from the shortage of adequately trained caregivers.
- Caring for elderly individuals, particularly those with chronic illnesses or disabilities, demands specialized skills and knowledge.
- However, there is a scarcity of caregivers with the requisite training and expertise, exacerbating the quality of care provided and contributing to caregiver burnout.
- Mistreatment of Caregivers: Caregivers in home-based settings often face mistreatment or abuse from the families they serve, including verbal abuse, exploitation, or inadequate compensation for their services.
- The lack of legal protections and support mechanisms for caregivers leaves them vulnerable to exploitation, undermining the quality of care they can deliver.
- Financial Barrier: The cost of hiring a caregiver for home-based care can be prohibitively high for many families, particularly those from lower socio-economic backgrounds.
- This financial barrier limits access to quality home-based care services for elderly individuals in need, leading some families to forgo professional care altogether or rely on informal caregiving arrangements.
- The dominance of the Private Sector: The provision of home-based care services in India is predominantly controlled by the private, for-profit sector.
- While private agencies may offer a range of services, their services often come at a premium cost, exacerbating inequalities in access to care.
- Fragmented Regulatory Framework: The regulatory framework governing home-based care in India is fragmented and lacks comprehensive oversight.
- Standardized regulations or licensing requirements for home care agencies or individual caregivers are absent, leading to inconsistencies in the quality and safety of care provided and hindering efforts to ensure accountability and quality improvement.
Policy Interventions and Opportunities to Address Home-Based Care Challenges:
- Recognizing Home as a Viable Care Setting: An opportunity in home-based care lies in acknowledging the home environment as a feasible setting for providing care to elderly individuals, serving both as a place for care provision and employment for caregivers.
- Policymakers can pave the way for developing tailored policies and regulations to address the unique needs of home-based care.
- Tailoring Treatment Protocols to Home Environment: Policy interventions should focus on customizing treatment protocols and care plans to the home environment's specific challenges and opportunities, such as limited space, absence of medical equipment, and the presence of family members.
- This tailored approach can optimize care delivery and improve the experience for both caregivers and care recipients.
- Strengthening Caregiver Training and Support: Enhancing the training and support available to caregivers is crucial to meet the rising demand for home-based care services.
- Policy interventions should prioritize the standardization of vocational training programs, delineation of roles and responsibilities, and facilitation of career progression opportunities for caregivers.
- Investing in caregiver education and professional development can enhance the quality of care and alleviate caregiver shortages.
- Gender Considerations: Given the gender dimension of aging in India, with women typically outliving men, special attention is warranted for vulnerable elderly women, particularly widows.
- Policies should aim to empower them to lead dignified and independent lives in their later years.
Governmental and Legislative Initiatives to Enhance Home-Based Care:
- Policy Development and Implementation: The government holds a pivotal role in crafting and executing policies concerning home-based care for the elderly, with ministries such as the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, and Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship spearheading initiatives to address pertinent challenges and opportunities.
- Inter-Ministerial Coordination: Effective coordination among government ministries is indispensable for driving policy reforms in home-based care.
- Collaborative efforts enable the pooling of resources, expertise, and stakeholder perspectives to formulate comprehensive solutions tailored to the diverse needs of the elderly population and their caregivers.
- Legislative Frameworks: Legislative endeavors play a vital role in formalizing and regulating home-based care services.
- Legislation like the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens (Amendment) Bill, 2019, exemplifies efforts to standardize home care services and establish minimum standards for providers, thereby ensuring the legal protection, safety, and well-being of elderly individuals receiving such care.
- Regulatory Oversight: Government bodies like the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) contribute to regulatory oversight in home-based care services.
- These entities establish guidelines, standards, and licensing requirements for home care agencies and individual caregivers, ensuring adherence to quality and safety standards.
Conclusion
While India's emphasis on preparing its youth for the future is praiseworthy, it is equally crucial not to neglect the needs of its expanding elderly demographic. A resilient home-based care system enables economic participation and upholds society's ethical responsibility to support its aging citizens. By confronting challenges and embracing opportunities in home-based care, India can safeguard the well-being and dignity of its elderly population, fostering an inclusive and empathetic society for future generations.
Analysis of Curative Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court in Legal Dispute

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC), in the judgment of Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (DMRC) vs Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd (DAMEPL), set aside the arbitral award by exercising its curative jurisdiction.
Context:
- The Supreme Court of India holds a multifaceted role, serving as the apex court of appeal, a federal court, and an advisory body.
- One of its significant powers is the Curative Jurisdiction, established in 2002, which empowers the Court to rectify its judgments even after they have become final.
- However, the utilization of this jurisdiction has triggered discussions concerning its implications for judicial stability and the Supreme Court's role in shaping legal precedents.
What is the DMRC vs DAMEPL Case?
- The case dates back to 2008 when the DMRC entered into a PPP with the Delhi Airport Metro Express Private Limited (DAMEPL), a consortium led by Reliance Infrastructure Ltd, for the Delhi Airport Metro Express project.
- However, disputes arose between the two parties, leading to the termination of the agreement by DAMEPL in 2013.
- In 2017, an arbitration tribunal ruled in favor of DAMEPL and ordered DMRC to pay nearly Rs 8,000 crore.
- DMRC challenged this ruling in the Delhi High Court, which overturned the arbitral award in 2019.
- DAMEPL then appealed to the Supreme Court, which in September 2021 reversed the High Court's decision and upheld the arbitral award.
- However, in a recent judgment, the Supreme Court has now ruled in favor of DMRC, stating that there was a "fundamental error" in its previous judgment.
Significance of the Supreme Court’s Decision:
- Firstly, it underscores the importance of curative petitions in correcting grave injustices in legal judgments.
- Curative petitions are sparingly used and are only permitted on narrow, procedural grounds.
- The Supreme Court's decision to grant relief to DMRC highlights the court's commitment to rendering justice in its true sense.
- Secondly, the decision has implications for PPPs in infrastructure projects.
- PPPs play a crucial role in infrastructure development, but disputes between public and private entities can arise, leading to legal battles.
- The Supreme Court's decision provides clarity on the legal framework governing PPPs and sets a precedent for future disputes in similar projects.
- Lastly, the decision has implications for investor confidence.
- The Supreme Court's exercise of curative jurisdiction in this case, almost two and a half years after its final verdict, demonstrates the court's willingness to correct errors and ensure justice.
- This is likely to boost investor confidence in India's legal system and encourage investment in infrastructure projects.
Difference Between a Curative Petition and Curative Jurisdiction:
Curative Petition:
- A curative petition is a specific legal remedy available within the framework of curative jurisdiction.
- It is a petition filed by a party to the case that has exhausted all other legal remedies and seeks the correction of a judgment that may have resulted from a violation of principles of natural justice or a gross miscarriage of justice.
- The grounds for filing a curative petition typically include the discovery of new evidence or legal errors that were not apparent earlier.
- Curative petitions are relatively rare and are considered as a last resort to correct errors in judgment.
Curative Jurisdiction:
- Curative jurisdiction refers to the broader authority of the Supreme Court to review and rectify its judgments to prevent gross miscarriages of justice.
- It is a power vested in the Supreme Court to ensure that fundamental principles of justice and fairness are upheld, even after a judgment has become final.
- Curative jurisdiction allows the Supreme Court to revisit its decisions if it perceives a need to prevent manifest injustice or correct egregious errors that may have escaped earlier notice.
- While curative petitions are one mechanism through which curative jurisdiction is exercised, the Supreme Court may also suo motu invoke curative jurisdiction in exceptional cases without a formal petition being filed.
Impact and Implications of Curative Jurisdiction:
- Impact on Arbitral Awards' Integrity: A central apprehension surrounding curative jurisdiction is its potential to affect the integrity of arbitral awards.
- Arbitration relies on the conclusiveness and enforceability of awards for its efficacy.
- When the Court intervenes in arbitral decisions, particularly amid concerns of judicial overreach, it risks undermining arbitration's core principles, such as party autonomy and swift dispute resolution.
- Balancing Judicial Consistency and Flexibility: The dichotomy between judicial consistency and flexibility emerges concerning curative jurisdiction.
- While consistent legal interpretation fosters stability and predictability, it may stifle innovation. Conversely, excessive flexibility can breed uncertainty, eroding public trust in the judiciary.
- Examining the Scope of Judicial Review: Curative jurisdiction prompts queries about the extent of judicial review and its boundaries.
- While the Court's role as the ultimate legal interpreter is clear, intervening in its judgments without impinging on legislative or executive domains requires meticulous consideration.
- Implications for Legal Precedents: The significance of Supreme Court judgments in maintaining legal coherence is undeniable.
- However, curative jurisdiction may disrupt established precedents, casting doubt on the binding nature of judicial decisions.
- The Court must exercise judiciousness to rectify errors without compromising the legal framework's integrity.
- Public Perception and Judicial Trust: The Court's credibility hinges on its impartiality and integrity in dispensing justice.
- Excessive or arbitrary curative interventions may undermine public confidence in the judiciary, diminishing its authority as a legal arbiter.
- The Court must exercise curative powers prudently to maintain public trust in the judiciary.
Critical Analysis of Judicial Instability:
- Challenging Legal Certainty: Legal certainty, a cornerstone of the rule of law, demands consistency and predictability in legal outcomes.
- The use of curative jurisdiction, particularly in overturning final judgments, jeopardizes this certainty by casting doubt on the conclusiveness and enforceability of judicial decisions.
- Such uncertainty undermines parties' confidence in the stability of the legal framework, fostering confusion and mistrust in the judicial process.
- Diminishing Judicial Authority: Judicial stability is intrinsic to the authority and credibility of the judiciary.
- When the Supreme Court reverses its own judgments through curative measures, it risks appearing indecisive and inconsistent, eroding its status as the ultimate arbiter of the law.
- This erosion of authority undermines public trust in the judiciary, fostering skepticism about the fairness and impartiality of judicial proceedings.
- Disrupting Legal Precedent: The stability of legal precedent is vital for maintaining coherence and consistency in the legal system.
- However, the exercise of curative jurisdiction introduces the potential for disrupting established precedents and fostering inconsistency in judicial rulings.
- This undermines the reliability of legal principles, creating confusion among legal practitioners, litigants, and lower courts.
- Moreover, frequent reversals of judgments hinder the development of clear and consistent legal doctrines, impeding the evolution of the law.
- Risk of Judicial Overreach: Judicial stability acts as a safeguard against judicial overreach, ensuring that the judiciary respects its constitutional limits and upholds the separation of powers.
- However, the use of curative jurisdiction raises concerns about the Court's propensity to exceed its authority and intrude into the domains of the legislative and executive branches.
- By revisiting and overturning its own judgments, the Court risks overstepping its role and undermining the principles of checks and balances inherent in a democratic system.
Ways Forward for Balancing Judicial Oversight Stability:
- Fostering Judicial Accountability: Upholding judicial oversight, including the use of curative jurisdiction, is vital for ensuring judges are accountable and adhere to legal standards.
- It offers a mechanism to rectify errors and address any judicial misconduct.
- However, excessive oversight risks compromising judicial independence and impartiality, undercutting the judiciary's ability to fairly adjudicate disputes.
- Preserving Legal Stability: Legal stability is crucial for fostering predictability and confidence in the legal system.
- By upholding established precedents and minimizing disruptions to settled legal principles, the judiciary promotes legal stability.
- Nevertheless, the exercise of curative jurisdiction introduces uncertainty by allowing the Court to revisit and potentially reverse its judgments, challenging the stability of legal doctrine and the reliability of judicial decisions.
- Respecting the Separation of Powers: Striking a balance between judicial oversight and stability requires respecting the separation of powers and acknowledging the distinct roles of the judiciary, legislature, and executive.
- While the judiciary plays a critical role in interpreting and applying the law, it must exercise restraint to avoid intruding into the domains of other branches of government.
- The use of curative jurisdiction should be guided by principles of judicial deference and deference to legislative intent, particularly in matters where judicial intervention could undermine democratic processes or policy decisions.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court's Curative Jurisdiction is a potent mechanism for rectifying judicial mistakes, yet it presents hurdles to judicial stability and coherence. The DMRC vs DAMEPL case highlights the necessity for a balanced approach in reconciling judicial oversight with legal predictability. Ultimately, as the ultimate arbiter of the law, the Court must carefully wield its curative authority to uphold public trust in the legal system's integrity.
Supreme Court Affirms Women's Right To Child Care Leave

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On Monday, a Supreme Court bench headed by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud said, “Participation of women in the workforce is a matter not just of privilege but a constitutional entitlement protected by Article 15 of the Constitution.
Context:
- Recent data indicates that while 45% of India's graduates are women, only approximately 10% of educated women pursue long-term careers.
- However, amidst these challenges, there are instances of women advocating for their rights.
- For instance, a young mother from Himachal Pradesh recently petitioned the Supreme Court for the right to care for her child, who required her presence.
- Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud emphasized that women's participation in the workforce is a constitutional entitlement, and denying mothers childcare leave violates this principle.
- The petitioner, an assistant professor at a government college, highlighted that the Himachal Pradesh government had refused her childcare leave, despite her child's medical needs.
- The Supreme Court's intervention underscored that the state, as an employer, must address such concerns and uphold the rights of working mothers.
Protection Under the Constitution and Employer Responsibilities Concerning Women's Employment:
Constitutional Safeguards:
- Article 15 of the Indian Constitution stands as a pillar of gender equality, prohibiting discrimination based on sex and allowing for affirmative action to address historical disparities.
- The recent Supreme Court recognition of Article 15 underscores the constitutional imperative to foster a fair and inclusive society, particularly in matters of women's workforce participation.
- By affirming women's right to work without prejudice, the court reinforces the foundational principles of equality and non-discrimination enshrined in the Constitution.
Employer Responsibility:
- Employers, especially the government as role models, carry a significant duty to cultivate a supportive environment for female employees.
- Beyond mere legal compliance, employers must actively address the unique challenges women face in juggling work and caregiving responsibilities.
- The denial of childcare leave, as highlighted in the recent Supreme Court case, signifies a failure to acknowledge and respect women's rights in the workplace.
- The court's stance emphasizes that employers cannot overlook the specific needs of women employees and underscores the importance of proactive measures such as offering childcare assistance, flexible work arrangements, and gender-sensitive policies.
- By fulfilling these obligations, employers not only advance gender equality but also foster a more productive, inclusive, and supportive work culture.
Obstacles to Women's Participation in the Workforce:
Unbalanced Domestic Responsibilities:
- Women in India shoulder a disproportionate share of unpaid domestic and caregiving duties, including household chores and looking after family members.
- This unequal distribution of responsibilities consumes considerable time and effort, often hindering women's capacity to engage in paid employment outside their homes.
"Marriage" and "Motherhood" Setbacks:
- Women commonly encounter setbacks in their careers due to societal norms regarding marriage and motherhood.
- Marriage can lead to disruptions like relocation or increased household duties, affecting women's career trajectories and earning potential.
- Likewise, motherhood often results in temporary career breaks or reduced work hours to manage childcare, limiting opportunities for professional growth and financial independence.
Inadequate Support Infrastructure:
- The scarcity of affordable childcare options, along with insufficient support services like paid parental leave and flexible work arrangements, adds to the challenges faced by women in balancing work and family commitments.
- The absence of adequate support infrastructure may compel women to prioritize caregiving over employment, particularly when alternative care arrangements are lacking.
Legal Framework for Women’s Participation in the Workforce:
Legislative Advances:
- India has taken significant strides in enacting laws to uphold women's rights and foster gender equality in workplaces.
- These laws encompass provisions for maternity benefits, childcare services, and safeguards against gender discrimination in employment practices.
- Recent legislative changes have broadened maternity leave entitlements and mandated childcare facilities at workplaces, underscoring a commitment to bolstering women's engagement in the workforce.
Gender-Neutral Measures:
- Initiatives to render legal provisions gender-neutral represent a positive stride toward acknowledging caregiving duties as a shared responsibility among parents.
- By extending childcare benefits to all employees, regardless of gender, these reforms aim to challenge traditional gender norms and encourage greater equity in caregiving responsibilities within families.
Challenges in Implementing Legal Frameworks for Women's Workforce Participation:
Underfunded Welfare Schemes:
- Government-led initiatives, such as the National Crèches Scheme, face underfunding and inadequate infrastructure, limiting their ability to provide essential childcare services to marginalized communities.
- Without sufficient financial resources and institutional support, these schemes struggle to meet the demand for affordable and quality childcare services, particularly in underserved regions.
Lack of Enforcement and Monitoring:
- Effective enforcement mechanisms and regular monitoring of compliance are crucial for ensuring that employers adhere to legal requirements related to women's workforce participation.
- However, enforcement agencies often face challenges like limited resources, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and a lack of coordination between government departments, hindering their ability to enforce labour laws and address violations promptly.
Coverage Limitations:
- Existing laws often have a limited scope, with certain provisions only applying to formal sector establishments or workplaces with a minimum number of employees.
- This approach excludes many women working in the informal sector or smaller enterprises, leaving them without access to crucial maternity benefits and childcare support.
Way Forward
Collective Responsibility:
- State: The government plays a key role in setting legal and policy frameworks that promote gender equality.
- This includes enacting supportive laws, providing incentives for employers to adopt family-friendly policies, and investing in social infrastructure such as childcare facilities and education programs.
- Employers: Companies can significantly impact women's workforce participation through their practices and policies.
- Employers should adopt inclusive hiring practices, provide equal opportunities for career advancement, offer flexible work arrangements, and implement family-friendly policies like paid parental leave and on-site childcare facilities.
- Communities: Communities play a crucial role in challenging traditional gender norms and stereotypes.
- Community-based organizations, educational institutions, and grassroots initiatives can raise awareness, provide support for working mothers, and advocate for policy changes that promote gender equality.
Policy Integration:
- Integrating gender considerations into broader policy frameworks is essential for mainstreaming gender equality across all sectors of society.
- Key strategies include implementing gender-responsive budgeting, conducting gender impact assessments of policies and programs, and ensuring women's voices are heard in decision-making processes.
- By addressing these aspects, we can create a more inclusive society where women can fully participate in the workforce and achieve their potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, achieving full participation of women in the workforce requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach involving the state, employers, and communities. By enacting supportive policies, promoting inclusive practices, challenging traditional gender norms, and integrating gender considerations into broader policy frameworks, we can create an enabling environment for women to thrive in their careers. It is through these concerted efforts that we can build a more equitable society and harness the immense potential that women bring to the workforce.
The Reality of the Swachh Bharat Mission

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A scheme fully owned by the state has become a toolkit for privatisation of public health services and continues caste discrimination.
Context:
- India was ranked right at the bottom of 180 countries in the Environment Performance Index (EPI) in 2022.
- This index evaluates countries based on their performance in addressing climate change, maintaining environmental health, and preserving ecosystem vitality.
- It assesses 40 performance indicators across 11 issue categories, encompassing areas like air quality, access to drinking water, and sanitation.
- In response to this ranking, the government expressed reservations, citing flaws in the methodology that, according to them, fail to accurately capture the Indian scenario.
- Over the past decade, the Modi government has launched several development campaigns, including the Swachh Bharat Mission, the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation, the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, and the National Clean Air Programme.
- These endeavors are geared towards enhancing living standards and addressing various socio-economic challenges.
- However, despite these efforts, there remains a noticeable rise in the population's vulnerability due to environmental issues like air and water pollution.
About Swachh Bharat Mission:
- Swachh Bharat Mission, the world’s largest sanitation initiative was launched by the Prime Minister of India in 2014 to achieve an Open Defecation Free India by October 2, 2019, as a tribute to Mahatma Gandhi.
- The programme led to the construction of over 10 crore individual household toilets, taking sanitation coverage from 39% in 2014 to 100% in 2019 when around 6 lakh villages declared themselves Open Defecation Free (ODF).
- The second phase of the mission aims to sustain the open defecation-free status and improve the management of solid and liquid waste, while also working to improve the lives of sanitation workers.
- The mission aimed at progressing toward target 6.2 of the Sustainable Development Goal Number 6 established by the United Nations in 2015.
- By achieving the lowest open defecation-free status in 2019, India achieved its Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6.2 health target in record time, eleven years ahead of the UN SDG target of 31 December 2030.
- The mission was split into two: rural and urban.
- In rural areas "SBM - Gramin" was financed and monitored through the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation (since converted to the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti) whereas "SBM - urban" was overseen by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The rural division has a five-tier mechanism: central, state, district, block panchayat, and gram panchayat.
- As part of the campaign, volunteers, known as Swachhagrahis, or "Ambassadors of cleanliness", promoted the construction of toilets using a popular method called Community-Led Total Sanitation at the village level.
Critique of the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM):
Discrepancy between Goals and Outcomes:
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) and its successor, SBM 2.0, set out ambitious objectives to achieve garbage-free cities, garnering political support across party lines.
- However, the reality on the ground paints a different picture.
- Despite government assertions of India achieving open defecation-free status, reports from the Comptroller and Auditor General in 2020 raised doubts about the program's effectiveness, highlighting issues such as substandard toilet construction and inadequate waste treatment.
- In urban areas, certain communities, particularly those residing in slums, continue to lack access to essential sanitation facilities, exacerbating existing inequalities.
- In rural and peri-urban regions, the lack of integration between toilet construction and waste management has led to environmental contamination and health hazards.
Perpetuation of Power Dynamics and Inequalities:
- Sanitation and waste management in India are deeply entrenched in caste dynamics, historically burdening marginalized communities with sanitation tasks.
- Despite attempts by SBM to promote the idea of shared responsibility, the underlying power dynamics persist.
- The introduction of capital-intensive technologies aimed at mechanizing waste management processes has not yielded the desired outcomes, resulting in health crises due to improper waste disposal practices.
- The outsourcing of sanitation work to private contractors, often employing members of marginalized communities, has further entrenched caste-based discrimination.
- Government emphasis on procuring expensive machinery for waste management, funded through public resources, has inadvertently facilitated the privatization of public health services, exacerbating existing inequalities.
Technological Solutions and Implementation Challenges:
- While the government has invested in technological solutions such as waste-to-energy plants and biological methanation, their effectiveness remains limited, with few success stories to showcase.
- Challenges persist in the implementation of these solutions, leading to a lack of tangible improvements in solid waste management across many towns and cities.
Gap in Sanitation Inspection Infrastructure:
- A significant gap in the sanitation inspection infrastructure exists within Himachal Pradesh, as revealed during a recent case in the State's High Court.
- On March 30, 2024, it was disclosed that the Shimla Municipal Corporation, consisting of 34 wards, has only five sanitation inspectors.
- Moreover, the decision to declare this cadre dead after retirement raises concerns about the State's commitment to addressing sanitation issues effectively.
- With more than 50 municipal bodies in Himachal Pradesh and only 20 sanitation inspectors available, it is clear that several municipalities lack essential sanitation inspection personnel.
The interconnectedness of Environmental Performance Index (EPI) and Development Campaigns:
- The EPI offers a comprehensive assessment of a country's environmental health and sustainability efforts.
- One critical aspect of the EPI is mapping, which exposes the shortcomings and unsustainability of current development processes.
- In light of a recent Supreme Court judgment acknowledging the links between climate change and basic human rights, it is evident that development models must be reevaluated and adjusted.
- The interconnectedness of the EPI and various development campaigns cannot be ignored, as the consequences of climate change directly impact human well-being and rights.
- With climate scientists attributing current environmental problems to anthropogenic and systemic factors, it is essential to consider the broader implications of the EPI when planning and implementing development initiatives.
Conclusion
To tackle India's environmental challenges, a comprehensive strategy prioritizing sustainability, equity, and social justice is essential. This involves reassessing development strategies, strengthening enforcement, and encouraging community participation in environmental governance. Addressing implementation issues and linking policies to human rights can improve India's EPI performance and foster a sustainable future.
Reversing the Global Democratic Recession

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Despite the disillusionment, for a variety of reasons, the need to fortify democratic foundations has to be ongoing and collaborative.
Context:
- India is in the midst of its most significant electoral exercise and it might be worthwhile to scrutinize people’s changing perceptions about their political ecosystems in both the largest democracy and other smaller democratic spaces elsewhere.
- Such an exercise may help us understand the prevailing global situation and work on the future course of action.
- Drawing insights from an extensive Pew Research Centre survey spanning 24 nations, examining the evolving attitudes toward democratic governance becomes imperative to grasp the broader global context and chart potential pathways forward.
Why Worldwide Decline in Confidence in Democratic Systems?
- According to the Pew Research Centre's extensive 2023 global survey, which included 30,861 participants, there is a notable decline in faith in democratic institutions across the globe.
- Although 77% of respondents still hold optimism for representative democracy, there is growing openness to alternative governance structures.
- Of concern is the diminishing support for representative democracy since 2017, juxtaposed with increased approval for direct democracy, rule by experts, and authoritarian regimes.
Regional Dynamics and Emerging Trends in Perceptions of Governance:
- Shifting Preferences Towards Expert Rule and Authoritarianism: A noticeable inclination towards endorsing rule by experts and authoritarian forms of governance is observed across different regions.
- This trend is particularly conspicuous in nations grappling with economic instability, political turbulence, or perceived inefficiencies within democratic structures.
- In such contexts, citizens often perceive democratic systems as sluggish and inadequate in addressing urgent challenges, fostering a growing appeal towards centralized authority and decisive leadership.
- Influence of Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic circumstances significantly shape preferences in governance.
- Individuals from lower-income countries with limited educational access tend to show support for authoritative leadership and military rule.
- This inclination may stem from a desire for stability and economic advancement, as authoritarian regimes are perceived as more effective in delivering immediate solutions to complex issues.
- Cultural and Historical Context: Variations in democratic perceptions are also influenced by cultural and historical backgrounds.
- Nations with past experiences of authoritarian rule or centralized governance structures may exhibit greater openness to authoritarian models.
- Additionally, cultural norms regarding leadership, hierarchy, and decision-making processes impact attitudes toward democracy and alternative governance models.
- Resistance to Authoritarian Trends in Certain Regions: Despite the rise in authoritarian sentiments in some areas, resistance to such ideologies persists in others.
- Regions with strong traditions of liberal democracy, including Canada, Europe, Scandinavia, and the United States, continue to prioritize democratic values and institutions.
- Here, a steadfast commitment to democratic principles, civil liberties, and the rule of law acts as a barrier against the erosion of democratic norms.
Evolution of Democratic Perceptions in India:
- Transition towards Strong Leadership: Recent years have witnessed a discernible transformation in Indian views on democracy, characterized by a diminishing preference for representative democracy and a growing inclination towards authoritative leadership.
- In 2017, 44% of Indians favored representative democracy, a figure that declined to 36% by 2023.
- Conversely, support for a commanding leader with substantial authority surged from 55% in 2017 to 67% in 2023.
- Rising Endorsement of Expert Governance: Mirroring global trends, Indian perspectives on governance have witnessed a notable uptick in backing for rule by experts and authoritarian models.
- Support for rule by experts skyrocketed from 65% to an impressive 82% during the same period.
- Of significant note is the remarkable preference for military rule or governance under an authoritarian figure, with a striking 85% of Indians expressing support for such models by 2023.
- Diverse Regional Outlooks: It's crucial to acknowledge the diversity in democratic perceptions across various regions and demographic cohorts within India.
- While certain segments may lean towards authoritarian leadership, others remain steadfast in their commitment to democratic principles and institutions.
- Factors such as education, socioeconomic status, and cultural heritage exert considerable influence on individuals' governance preferences.
Way Forward to Reinforce Democratic Foundations:
- Engaging Citizens in Governance: Central to a robust democracy is the active participation of citizens in decision-making processes.
- Governments should establish channels and platforms facilitating meaningful engagement in policymaking and public affairs.
- Initiatives like town hall meetings, participatory budgeting, citizen assemblies, and digital feedback platforms can foster citizen involvement.
- Ensuring Information Accessibility: Transparency and access to accurate information are cornerstone principles of democratic governance.
- Governments must ensure unhindered access to information about government actions and policies.
- Strengthening freedom of information laws, enhancing transparency mechanisms, and supporting investigative journalism can uphold government accountability.
- Upholding Accountability and Justice: Democratic institutions must remain accountable to the populace and uphold the rule of law.
- Governments should institute checks and balances, foster an independent judiciary, and implement effective oversight mechanisms to prevent power abuse.
- Additionally, efforts to promote equality before the law and safeguard the rights of marginalized groups are essential.
- Fostering Civic Engagement: Civil society organizations play a pivotal role in advocating for citizen rights and government accountability.
- Governments should create an enabling environment for civil society to operate freely, safeguarding freedoms of association, expression, and assembly.
- Collaboration between government and civil society can enhance democratic governance through dialogue and cooperation.
- Promoting Ethical Leadership: Ethical leadership and public service are vital for democratic integrity.
- Governments should cultivate a culture of ethical conduct among officials and public servants, implementing measures to combat corruption and promote transparency.
- Holding individuals accountable for misconduct reinforces democratic legitimacy.
- Embracing Responsive and Inclusive Policies: Democratic governments must prioritize policies addressing the needs of all citizens, especially marginalized groups.
- Proactive efforts to promote social justice, economic equality, and inclusivity in decision-making processes are crucial.
- Engaging diverse stakeholders and tailoring policies to ensure inclusivity is imperative for leaving no one behind.
Conclusion
The shifting democratic perceptions highlighted in both the Pew Research Centre survey and India's democratic context emphasize the importance of reevaluating global democratic systems. By acknowledging regional nuances, comprehending evolving attitudes, and emphasizing foundational reinforcement endeavors, nations can effectively address the complexities and potentials of democratic governance in the contemporary era.
Restoring Earth’s Right to ‘Good Health’

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Court of Human Rights found Switzerland guilty of violating the rights of women from KlimaSeniorinnen, stating that the government's emission control efforts were insufficient, failing to protect women from climate change impacts.
Context:
- Courts worldwide are increasingly tasked with addressing the nexus between climate change and human rights, as evidenced by significant rulings such as those from the European Court of Human Rights in Switzerland and the Supreme Court of India.
- These landmark decisions highlight the imperative of acknowledging climate change as a human rights issue and establishing crucial benchmarks for legal and policy responses to mitigate its detrimental effects on people and societies.
Legal Acknowledgment of Climate Change's Human Rights Impacts:
- Recent rulings by the European Court of Human Rights against the Government of Switzerland and the Supreme Court of India have underscored the failure to safeguard vulnerable populations from the effects of climate change.
- The European Court's decision highlighted the government's neglect in protecting elderly women from climate-related harm, while the Indian Supreme Court affirmed citizens' entitlement to freedom from adverse climate effects under constitutional guarantees.
- Citing Articles 14 (equality before the law) and 21 (right to life and personal liberty) of the Indian Constitution, the Supreme Court emphasized individuals' right 'to be free from the adverse impacts of climate change.'
- These legal judgments signify a significant step towards acknowledging climate change as a pivotal human rights concern.
The Escalating Human Rights Risks of the Global Climate Crisis:
- The global climate crisis presents an imminent threat to human rights, imperiling individuals and communities worldwide.
- The latest State of the Global Climate Report from the World Meteorological Organization presents compelling evidence of the intensifying impacts of climate change.
- In 2023, numerous climate indicators soared to unprecedented levels, marking it as the hottest year on record.
- This unparalleled warmth coincided with concerning trends such as heightened ocean heat accumulation, rising sea levels, diminishing Antarctic sea ice, and accelerated glacier retreat.
- These indicators underscore the severe strain on our planet, with profound implications for human welfare.
India's Climate Action and Vulnerability:
- Progress Amid Persistent Vulnerability: Despite notable advancements in climate action, India, among the world's fastest-growing economies, continues to confront significant vulnerability to climate change.
- Having met two of its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) targets—reducing emissions intensity by 33% to 35% and achieving 40% cumulative non-fossil fuel electricity capacity—well ahead of schedule, India demonstrates proactive measures.
- Nevertheless, the nation remains highly susceptible to climate-related adversities.
- Population Concentration in Disaster-Prone Areas: A primary concern is India's demographic distribution, with over 80% of its populace residing in regions prone to climate-induced calamities like floods, cyclones, droughts, and heatwaves.
- These events not only disrupt lives but also exacerbate existing socio-economic disparities, disproportionately impacting vulnerable groups such as small-scale farmers, rural communities, and marginalized populations.
- Intersecting Challenges of Climate Change: Climate change intersects with broader socio-economic and environmental issues, compounding their repercussions.
- Rapid urbanization and haphazard development intensify urban vulnerability to climate-driven disasters like flooding and landslides.
Frameworks to Strengthen India's Climate Action:
- Embracing Comprehensive Legislation: India's climate governance could benefit from the adoption of a comprehensive regulatory framework dedicated to climate change.
- This legislation would offer a unified structure for addressing diverse climate-related aspects, spanning mitigation, adaptation, finance, and capacity-building.
- By enshrining climate objectives, targets, and strategies in law, such a framework can furnish legal clarity and consistency, guiding sustained planning and investment.
- Insights from Global Climate Laws: Research from the London School of Economics and Political Science examined climate framework laws in 60 nations, spotlighting their pivotal role in shaping national climate agendas.
- Countries like Germany, Ireland, New Zealand, Finland, South Korea, South Africa, and the Philippines have instituted robust climate legislation surpassing mere compliance with international obligations.
- These laws have facilitated public resource mobilization, bolstered climate action capabilities, and fostered inter-sectoral cooperation.
Additional Measures for Enhanced Climate Governance in India:
- Integrated Climate Policies: India's climate strategies should embrace an integrated approach, embedding climate considerations into broader development frameworks and decision-making processes.
- This entails weaving climate adaptation and mitigation efforts throughout key sectors like agriculture, water management, energy, transportation, and urban development to foster a cohesive response to climate challenges.
- Localized Solutions and Cross-Sector Collaboration: Tailored, localized climate actions, coupled with collaborative efforts across sectors, are vital for addressing the diverse and context-specific impacts of climate change.
- Governments can craft targeted strategies to bolster resilience, mitigate risks, and advance sustainable development goals by engaging local stakeholders and fostering partnerships across sectors.
- Harmonizing Climate and Sustainable Development Goals: Localized climate initiatives often align with broader Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), such as poverty eradication, food security, access to clean water, and gender equity.
- Integrating climate considerations into local SDG agendas enables governments to leverage synergies, optimize resource use, and fortify community resilience and sustainability.
- Empowerment of Civil Society: Civil society organizations (CSOs) play a pivotal role in advocating for climate action, environmental equity, and governmental accountability.
- Empowering CSOs and fostering rights-based discourse on climate change are vital for fostering inclusive decision-making, transparency, and environmental justice.
- Fostering Inclusivity and Representation: Promoting diversity and inclusivity within civil society is imperative to ensure the voices and perspectives of marginalized communities are heard and heeded in climate policymaking.
- CSOs should aim to represent the interests of various stakeholders, including women, indigenous populations, youth, persons with disabilities, and other marginalized groups, in climate governance.
- Advancing Rights-Centric Discourse: A rights-based approach to climate action acknowledges that climate change disproportionately impacts vulnerable communities, infringing upon their basic human rights to life, health, food, water, and livelihoods.
- By framing climate change as a human rights issue, CSOs can advocate for policies that prioritize the needs of affected communities and champion environmental justice.
Conclusion
The alignment of legal rulings, scientific findings, and policy mandates emphasizes the pressing imperative to confront climate change as a human rights emergency.
By acknowledging the inseparable link between environmental health and human welfare, nations can pave the way toward climate resilience and equity.
Empowering communities, fortifying legal structures, and promoting cross-sectoral cooperation stand as pivotal measures in realizing a future liberated from the detrimental effects of climate change.
Legal Amendments Likely to Increase Medicine Costs without Improving Quality

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The amended rules will prolong the life of drugs on account of frivolous patenting, increase their prices, and make lives difficult for patients.
Context:
- India's healthcare system depends largely on accessible medications, with the generic pharmaceutical sector crucial for delivering quality drugs at affordable rates.
- The expense of medicines represents a substantial part of healthcare spending, with almost half of individuals' medical costs dedicated to purchasing prescriptions.
- Yet, the considerable expenses associated with medications, largely influenced by patenting, create significant hurdles for obtaining vital treatments.
What is the Role of Generic Pharmaceutical Companies?
- Generic pharmaceutical companies are pivotal in addressing the challenge of affordability by offering cost-effective alternatives to patented drugs.
- India's generic industry has earned global recognition for its role in providing essential medications at accessible prices.
- The development of India's patent laws has significantly influenced its pharmaceutical sector and its capacity to produce generic drugs.
- Initially, the Indian Patent Act of the early 1970s limited patent protection to the manufacturing processes rather than the products themselves.
- This approach facilitated the growth of the generic industry, positioning India as a major exporter of generic drugs by the late 1980s.
- However, recent revisions to the Indian Patent Law pose a threat to this ecosystem and jeopardize access to affordable healthcare.
What is the Impact of the TRIPS Agreement on India's Pharmaceutical Industry?
- The Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement, introduced in 1995, had a significant impact on India's pharmaceutical sector, shaping its development and global position. Key aspects of this impact include:
- Transition to Product Patents: A critical change brought by TRIPS was the requirement for member countries to grant patents for both products and processes, including pharmaceuticals.
- This shift from process to product patents posed challenges for India's thriving generic pharmaceutical industry, which had previously capitalized on producing affordable versions of patented drugs.
- Challenges for India's Generic Industry: The introduction of product patents threatened India's generic pharmaceutical sector, renowned for its capacity to manufacture low-cost essential medicines.
- These patents granted exclusive rights to inventors, restricting generic manufacturers' ability to produce and distribute affordable alternatives.
- Pressure to Comply with International Standards: The TRIPS Agreement pressured India to align its intellectual property laws with international standards, encompassing pharmaceutical patent protection.
- This necessitated amendments to India's Patent Act to comply with TRIPS obligations while preserving the interests of its generic pharmaceutical industry and public health priorities.
- Preserving Access to Medicines: Despite TRIPS challenges, India implemented measures to safeguard access to affordable medicines.
- Provisions like Section 3(d) of the Indian Patent Act, introduced in 2005, aimed to prevent granting frivolous patents for incremental innovations lacking significant therapeutic benefits.
- This ensured compliance with TRIPS requirements while maintaining access to affordable medicines.
- Balancing Innovation and Access: The TRIPS Agreement presented India with the challenge of balancing innovation and access to essential medicines.
- While patents incentivize innovation and investment in research and development, they can restrict access to life-saving treatments, particularly in developing countries with limited healthcare resources.
- Global Leadership in Generic Manufacturing: Despite the challenges posed by TRIPS, India emerged as a global leader in generic drug manufacturing.
- Leveraging its manufacturing capabilities and adherence to TRIPS flexibilities, the country's generic pharmaceutical industry continued to thrive, supplying affordable medicines domestically and globally.
What is Section 3(d) of India's Patent Act?
- Section 3(d) is a crucial provision in India's Patent Act that exemplifies the flexibilities embedded within the country's patent laws.
- It tackles concerns related to "evergreening"—a practice used by pharmaceutical companies to extend patent life through minor modifications or incremental innovations.
- The primary objective of Section 3(d) is to prevent the granting of patents for incremental innovations that lack significant therapeutic efficacy or novelty.
- By doing so, it aims to protect access to generic versions of essential medicines and promote affordability.
- Under Section 3(d), pharmaceuticals and chemical substances are eligible for patent protection only if they demonstrate enhanced efficacy compared to existing formulations.
- This requirement ensures that patents are granted for inventions representing genuine advancements in therapeutic efficacy rather than minor modifications or variations of existing drugs.
- Through Section 3(d), India's patent laws strike a balance between innovation and public health priorities, contributing to the overall well-being and access to medicines for its citizens.
What are the Contemporary Challenges in India's Patent Regime?
- India's patent regime currently faces several challenges, including issues related to pre-grant opposition, competition, international trade agreements, and flexibilities in patent law. These challenges have implications for access to affordable medicines, the financial burden on patent opponents, and drug availability.
- Threats to Pre-Grant Opposition: Amendments to the Indian Patent Rules have made filing opposition to patents at the pre-grant stage more challenging.
- This change could lead to granting patents for inventions lacking genuine novelty or therapeutic efficacy.
- Impact on Competition and Drug Prices: Limitations to the pre-grant opposition process may stifle competition in the pharmaceutical market and contribute to higher drug prices.
- By hindering generic manufacturers and civil society organizations from challenging frivolous patents, the amendments impede the availability of affordable generic drugs.
- Pressure from Pharma Majors and International Trade Agreements: These amendments reflect pressure from multinational pharmaceutical corporations, particularly Western and Japanese companies, seeking to align India's patent rules with their interests.
- Their lobbying efforts aim to weaken India's patent regime, facilitating patent grants for incremental innovations and extending market exclusivity for their products.
- Threats to Flexibilities in Patent Law: Amendments to India's patent rules threaten the flexibilities inherent in its patent law, including provisions such as Section 3(d) that set stringent patentability criteria based on enhanced efficacy.
- Weakening these provisions undermines India's capacity to protect public health priorities and promote access to affordable medicines.
- Financial Burden on Opponents of Patents: Imposing fees on patent opponents could deter patients, civil society organizations, and generic manufacturers from filing pre-grant oppositions.
- This financial burden limits stakeholders' ability to safeguard public health interests and promote affordable medicines.
- Impact on Compulsory Licensing and Drug Availability: The amendments also affect the issuance of compulsory licenses, crucial for ensuring access to medicines when patents hinder availability.
- By weakening provisions that enable compulsory licensing and limit evergreening, the amendments impede efforts to address healthcare disparities and promote equitable access to essential medicines.
Conclusion
Access to affordable medicines is vital for public health and universal healthcare. Policymakers must preserve patent law flexibilities, promote competition, and protect patient interests to ensure healthcare systems uphold affordability, accessibility, and quality. Amendments to India's Patent Rules should balance innovation, intellectual property rights, and societal well-being, mitigating negative impacts on essential medicines and public health outcomes.
How Can India Revive its Investment Cycle

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Centre has been meeting its capex targets, but the trajectory of private sector and state governments is less certain.
Context:
- Policymakers in India are grappling with the imperative task of revitalizing the investment cycle. Despite the central government's success in meeting capital expenditure (capex) targets, uncertainty clouds the trajectory of investments from the private sector and state governments.
- Thus, a comprehensive examination of India's current investment landscape is essential, scrutinizing key indicators and trends to identify the hurdles and prospects in reigniting the investment momentum.
Overview of Investment Patterns:
- Fluctuating Investment Rates: The investment rate, representing gross fixed capital formation as a percentage of GDP, has shown variability in recent years.
- After dropping to 27.2% in 2020-21, there has been a slight improvement, with the rate climbing to 31.3% in 2023-24 from 30.8% in the preceding fiscal year.
- This increase suggests a possible resurgence in investment sentiment and activity, albeit starting from a relatively low level.
- Composition of Investments: Delving Deeper: Yet, a closer examination of investment composition reveals noteworthy nuances.
- A significant part of the recent uptick in capital formation stems from dwelling construction, supported by government initiatives to bolster the housing sector.
- While housing investments spur economic growth and job creation, diversification is essential for sustainable and equitable development.
- Declining Investment in Plant and Machinery: Of particular concern is the diminishing share of investments in plant and machinery, crucial for fostering productivity, innovation, and competitiveness across sectors.
- The allocation of investment to plant and machinery declined from 36% in 2017-18 to 30.7% in 2022-23, indicating a potential shift in investment priorities or hurdles in attracting investments in manufacturing and industrial domains.
Private Sector Investment:
- Insights from CMIE Data: Examining private sector investment trends often involves analyzing data provided by the Centre for Monitoring the Indian Economy (CMIE), offering valuable insights into the investment intentions and actions of private enterprises.
- Mixed Signals in Investment Intentions: Recent CMIE data reveals a nuanced picture of private sector investment in India.
- While new investment announcements dipped to Rs 27.1 lakh crore in 2023-24 from the previous year's Rs 39 lakh crore, they still represented the second-highest figures in a decade.
- However, it's essential to recognize that these announcements signify intentions rather than realized investments, potentially leading to disparities between planned projects and actual investments.
- Prevalence of Private Sector Intentions: The bulk of investment intentions—around 85%—originated from the private sector, underscoring its pivotal role in driving investment dynamics.
- Furthermore, foreign companies contributed 11% of the total investment intentions, reflecting a certain degree of confidence in India's business landscape among international investors.
Analyzing Investment Trends Across Sectors:
- Power Sector Dynamics: Investment inflows into the power sector have surged, reflecting a strategic focus on bolstering infrastructure, particularly in renewable energy projects like solar and wind power, driven by initiatives such as the Production Linked Investment (PLI) scheme.
- This expansion not only enhances energy security and environmental sustainability but also stimulates job creation and technological advancements.
- Transportation Sector Insights: Investment intentions in transportation services, notably aviation, have risen sharply due to ambitious expansion plans by major airlines.
- While these investments promise improved connectivity and economic growth, concerns persist about reliance on imported aircraft, emphasizing the need for initiatives to foster domestic manufacturing and technological capabilities.
- Diverse Industry Investment Trends: Various industries, including chemicals, machinery, metals, and automotive sectors, have attracted substantial investment commitments, reflecting a broad spectrum of opportunities for private sector investment.
- However, the absence of significant investments in consumer goods industries raises questions about the depth and breadth of sectoral investments.
- Challenges in Consumer Goods: Consumer goods industries face challenges such as excess capacity, subdued demand, and high inflation, which dampen investment enthusiasm despite government incentives like the PLI scheme.
- Lingering issues in job creation and rural demand further contribute to the subdued investment outlook in this segment.
- Impact of State Government Spending: Reduced capital expenditure by state governments in 2022-23 to meet fiscal targets poses a challenge to the investment cycle, given their significant contribution to overall investments.
- Budgetary constraints in state governments have a ripple effect on the broader investment landscape in the country.
Way Forward:
- Promoting Sustainable Growth: While the rise in capital formation is encouraging, ensuring its sustainability and fostering long-term growth hinges on achieving a balanced distribution of investments across sectors.
- Over-reliance on specific industries, like construction, may impede the economy's adaptability and hinder innovation and technological progress.
- Policy Imperatives for Investment Stimulus: Effective policy measures are imperative to stimulate private sector investment and cultivate a favorable investment environment.
- Streamlining regulatory frameworks, bolstering infrastructure, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship, and addressing sector-specific hurdles can incentivize private enterprises to invest in vital areas crucial for fostering economic growth and advancement."
Conclusion
Revitalizing India's investment cycle demands collaborative action from public and private stakeholders. Despite promising sectors, obstacles like sectoral disparities, muted consumer demand, and fiscal limitations at the state level impede a comprehensive rebound. Tackling these hurdles via tailored policies to spur demand, foster sectoral variety, and bolster the investment environment will be pivotal for nurturing enduring economic progress and advancement.
India’s Nuanced Approach in the South China Sea
- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In March 2024, India’s External Affairs Minister, S. Jaishankar, articulated, in a joint statement during his visit to Manila, India’s full support for the Philippines in upholding its national sovereignty concerning the South China Sea.
Context:
- During his visit to Manila in March 2024, India's External Affairs Minister reiterated India's steadfast support for the Philippines in safeguarding its national sovereignty amidst the ongoing South China Sea dispute.
- This statement came against the backdrop of heightened tensions and frequent maritime incidents in the region throughout 2023.
- Furthermore, a joint statement issued in 2023 by India and the Philippines emphasized the importance of China adhering to the rules-based maritime order and recognizing the 2016 ruling by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in favor of the Philippines.
- These statements reflect a notable shift in India's approach towards the South China Sea issue, departing from its previous stance of caution and neutrality.
- India's evolving position on the South China Sea underscores its broader strategic and economic interests on the global stage, with a renewed emphasis on upholding international maritime law, sovereignty, and sovereign rights in the region.
About the South China Sea (SCS):
- The South China Sea (SCS) is a pivotal body of water located in Southeast Asia, bordered by China to the north, Vietnam to the east and south, the Philippines to the west, and Borneo to the south.
- It encompasses a myriad of shoals, reefs, atolls, and islands, with notable features including the Paracel Islands, the Spratly Islands, and the Scarborough Shoal.
- Strategically situated, the SCS serves as a crucial maritime passage connecting the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean via the Strait of Malacca.
- It plays a vital role in global trade, with approximately one-third of all shipping traversing its waters annually, facilitating trillions of dollars in trade and serving as a linchpin for geopolitical dynamics.
- Rich in marine biodiversity, the SCS harbors a third of the world's marine species, providing essential fisheries that contribute to the food security of Southeast Asian nations.
- Additionally, the region is believed to possess vast reserves of oil and gas beneath its seabed, further heightening its economic significance.
- With an estimated $3.4 trillion worth of ship-borne commerce passing through its lanes each year, including crucial energy supplies to nations like the United States, Japan, and South Korea, the South China Sea stands as one of the busiest and most consequential waterways on the planet.
Various Ongoing Disputes in the South China Sea (SCS):
There are multiple ongoing disputes in the South China Sea (SCS) involving several countries. These disputes revolve around territorial and maritime claims over islands, reefs, banks, and other features in the region.
- Spratly Islands Dispute: The Spratly Islands are claimed by China, Taiwan, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei.
- These islands are strategically important due to their location in the middle of the South China Sea, as well as potential oil and gas reserves.
- Paracel Islands Dispute: The Paracel Islands are claimed by China, Taiwan, and Vietnam.
- China currently controls the islands, but Vietnam also asserts its sovereignty over them.
- Scarborough Shoal Dispute: The Scarborough Shoal is a disputed territory between China, Taiwan, and the Philippines.
- The shoal is rich in fishing resources and is strategically located near important shipping lanes.
- Gulf of Tonkin Dispute: This dispute involves China, Taiwan, and Vietnam, who have overlapping claims over the boundaries in the Gulf of Tonkin.
- Natuna Islands Dispute: Although geographically a part of the South China Sea, Indonesia claims sovereignty over the Natuna Islands, while China's "Nine-Dash Line" claim overlaps with Indonesia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) near the Natuna Islands.
- Senkaku Islands Dispute: In the East China Sea, the Senkaku Islands are disputed between China, Taiwan, and Japan, with Japan currently administering them.
- These disputes stem from historical claims, economic interests, and strategic considerations, leading to tensions between the involved parties.
India’s Policy Shift:
- Initially, India's engagement in the region was primarily motivated by economic considerations, in line with its Look East Policy.
- This policy sought to strengthen economic linkages with Southeast Asia and secure vital energy resources essential for India's growing economy.
- Demonstrating this economic focus, Indian state-owned enterprises like ONGC Videsh participating in oil and gas ventures in Vietnam's exclusive economic zones highlighted India's economic imperatives and its adherence to the principles of maritime resource exploration and exploitation within the framework of international law, particularly UNCLOS.
- India's policy trajectory has since evolved from Look East to Act East, indicating a shift towards a more proactive and strategic stance in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This shift reflects India's acknowledgment of the changing geopolitical landscape and the imperative for a comprehensive foreign policy approach.
- The Act East Policy places greater emphasis on economic integration and underscores the importance of forging strategic partnerships and enhancing security cooperation with countries in the Indo-Pacific, including Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, and the Philippines.
- Concurrently, India has augmented its capabilities through various measures such as forward deployment, mission-based operations, heightened maritime domain awareness, and the establishment of deep-water maritime infrastructure.
India's intricate dynamic with China:
- The assertive behavior exhibited by China in the South China Sea (SCS) and its gradual encroachment strategy across various maritime domains, including the Indian Ocean, have sparked apprehension within India.
- Chinese intelligence-gathering activities in the Eastern Indian Ocean have heightened India's vigilance, prompting a more proactive stance to address perceived threats to its maritime security.
- Against the backdrop of escalating geopolitical tensions in the SCS, largely driven by China's assertive territorial assertions and militarization efforts, India's approach has undergone a nuanced yet less cautious evolution.
- This transformation in India's stance toward the SCS is closely interlinked with its complex relationship with China.
- Both nations have a history of longstanding border disputes, which escalated following the Galwan Valley clash in 2020.
- China's periodic incursions into Indian territory and recent actions such as renaming Indian villages in Arunachal Pradesh further exacerbate these tensions.
- The Galwan Valley incident prompted India to deploy a frontline warship to the SCS, showcasing India's asymmetric deterrence capabilities.
- China's assertive stance and territorial claims in both the SCS and along India's land border pose significant challenges to regional stability.
- India's strategic engagements, including regular naval exercises and enhanced military cooperation with Southeast Asian nations, serve dual purposes: reaffirming India's commitment to regional security and acting as a counterbalance to China's contentious assertions.
The ASEAN Perspective:
- New Delhi's strategic recalibration stems from recognizing the critical importance of the South China Sea (SCS) for regional security and the global maritime order.
- The disputes involving China and various ASEAN nations in the SCS directly impact the principles of freedom of navigation and overflight, which are essential not only for India's trade and energy transport but also for countries worldwide.
- As an active participant in the Indo-Pacific region, India cannot afford to remain indifferent to such significant issues.
- Its central role in the Indo-Pacific extends beyond the Indian Ocean to the broader maritime domain, where China's rise challenges the established order in unforeseen ways.
- India's Indo-Pacific strategy prioritizes ASEAN centrality, despite internal differences within the regional grouping presenting challenges.
- India's advocacy for a rule-based international maritime order, particularly its steadfast support for UNCLOS, stands in opposition to unilateral actions that undermine regional stability.
- This principled stance, deeply rooted in India's foreign policy framework, indirectly counters China's expansive territorial claims and activities in the SCS, underscoring India's dedication to regional stability and security as a responsible stakeholder.
Navigating Challenges and Choices for India:
- India encounters complexities in managing the South China Sea (SCS) disputes, especially given the divergent interests within ASEAN.
- While ASEAN nations adopt varying approaches to disputes, India aims to strike a delicate balance between supporting regional partners and steering clear of direct entanglement in confrontational situations.
- India is exploring a spectrum of options, including initiatives to bolster capacity, cooperation in defense matters, infrastructure development, and advocating for the preservation of international law in the SCS.
Conclusion:
India's recalibrated approach to the South China Sea disputes arises from strategic necessities, evolving geopolitical landscapes, and regional intricacies. The nuanced stance adopted by India towards the South China Sea is emblematic of its broader strategy, aimed at safeguarding its interests while actively participating in collective endeavors to uphold peace, stability, and the rule of international law across the Indo-Pacific region.
Supreme Court's Directive Sets Delhi Metro Back on Course with Clear Roadmap

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The case involving DMRC (Delhi Metro Rail Corporation) and DAMEPL (Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd) which has been in and out of courts for over a decade, has concluded with the Supreme Court verdict on April 10.
Context:
- On April 10, the Supreme Court delivered its verdict on the case concerning the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) and Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd (DAMEPL), bringing it to a close.
- This ruling holds exceptional importance within the legal sphere, setting a notable precedent for arbitration tribunals and courts.
- Moreover, it carries significant implications for public service delivery via partnership models and demonstrates effective litigation strategies for infrastructure projects, contributing to India's future resilience.
What is the Dispute Between DMRC and DAMPEL?
- The dispute between the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) and Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd (DAMEPL) arises from the development and operation of the Airport Metro Express Line, a crucial infrastructure project in India's capital city, which began operations in 2011.
- The partnership between DMRC and DAMEPL followed a public-private partnership (PPP) model, where DMRC was responsible for constructing civil structures such as tunnels, viaducts, and station buildings, while DAMEPL was in charge of laying tracks, overhead equipment, signaling, and procuring rolling stock.
- Problems arose shortly after the line became operational.
- In 2012, DAMEPL suspended operations on the line, citing defects in the civil engineering works executed by DMRC.
- DAMEPL claimed that these defects compromised safety and functionality and demanded that DMRC rectify the issues within 90 days, threatening to treat the situation as a material breach of the agreement and terminate the contract if not addressed.
- DMRC attempted to resolve the issues through conciliation proceedings, but these efforts proved unsuccessful.
- Consequently, DAMEPL issued a notice of termination, asserting that DMRC had failed to remedy the defects.
- This led to a breakdown in the relationship between the two parties and prompted legal battles.
- Despite the challenges, DMRC and DAMEPL submitted a joint application in November 2012 to the commissioner of metro rail safety for inspection and permission to restart operations.
- Train services were eventually restored on the line by DAMEPL in 2013, with train speeds on the line increasing to 80 km/h. However, in June of the same year, DAMEPL announced its unwillingness to continue operating the line and ceased operations almost immediately.
- Recognizing the importance of the metro line for the public, DMRC stepped in to operate the nearly abandoned Airport Metro Express Line.
- DMRC resumed train operations and provided other ancillary services to maintain public transportation on the line.
- This intervention prevented a complete suspension of services and ensured continuity for commuters.
Findings of the Arbitration Tribunal:
- The tribunal awarded DAMEPL Rs 2,782 crore with interest after concluding that the termination notification was legitimate.
- In 2018, the Delhi High Court's single-judge bench maintained the award notwithstanding DMRC's protest.
- The Division Bench of the Delhi High Court, responding to DMRC's appeal, criticized the arbitral tribunal's methodology, pointing out errors such as failing to consider safety considerations and failing to read contractual provisions. As a result, the arbitration decision was revoked.
Supreme Court's Intervention and Final Judgement:
- Both DMRC and DAMEPL appealed to the Supreme Court through special leave petitions, leading to a significant legal process.
- Initially, the Supreme Court overturned the High Court's ruling and reinstated the arbitral award in 2021.
- However, following DMRC's curative petition, the Supreme Court revisited the case.
- After a thorough examination, considering various factors including factual background and tribunal decisions, the Court found significant errors in the arbitral award.
- Concluding that the award lacked coherence and resulted in serious injustice, the Court upheld the Division Bench's decision, deeming the award as flawed and illegal.
- This reversal of its earlier decision restored the parties to the status quo as per the Division Bench's judgment.
Importance of the Supreme Court Verdict:
- Establishing Precedent for Arbitration: The verdict sets a precedent for arbitration tribunals and courts, outlining the meticulous scrutiny required for arbitral awards.
- It underscores the importance of coherence and evidence-based reasoning in such decisions, ensuring fairness and consistency in dispute resolution.
- Ensuring Fairness and Justice: By reinstating the parties to the status quo as per the Delhi High Court Division Bench's judgment, the Supreme Court prioritizes fairness and justice in public-private partnership (PPP) projects.
- This safeguards public utilities from undue financial strain and upholds the interests of all stakeholders involved in contractual disputes.
- Promoting Accountability and Due Diligence: The ruling emphasizes accountability in infrastructure projects, stressing the need for due diligence and adherence to contractual obligations.
- It underscores the responsibility of all PPP participants to act in good faith, particularly in managing critical public infrastructure, thereby fostering transparency and integrity.
- Guiding Future Infrastructure Ventures: The judgment provides clarity for pending cases, especially in the infrastructure domain, offering a roadmap for handling disputes arising from PPP agreements.
- It ensures that future projects benefit from transparent and equitable dispute resolution mechanisms, enhancing the efficiency and credibility of infrastructure development efforts.
- Boosting Confidence in PPPs: By reaffirming the judiciary's commitment to legal integrity and fairness, the ruling instills confidence in both public and private entities engaging in PPPs.
- This confidence is essential for attracting investment in infrastructure projects, driving economic growth, and modernizing India's infrastructure landscape.
Conclusion
The prolonged legal conflict between DMRC and DAMEPL highlighted the complexities and challenges inherent in PPP projects, spanning over a decade with various assertions from both sides. This case serves as a testament to the judiciary's pivotal role in preserving equity and integrity within PPP ventures, crucial for advancing the nation's infrastructure. Furthermore, it underscores the significance of adhering to principles of fairness in contractual disagreements and the enduring influence of legal precedents on the trajectory of public-private collaborations
Left Wing Extremism/Naxalism in India

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least 29 Maoists were killed and three security personnel were injured in a gunbattle recently in a forest in Kanker district of Bastar division in Chhattisgarh.
Context:
- In a significant development, at least 29 Maoists were neutralized, and three security personnel sustained injuries during a fierce gun battle in a forested area of the Kanker district in Chhattisgarh's Bastar division.
- This successful joint operation, conducted by the District Reserve Guards (DRG) and the Border Security Force (BSF), marked the highest number of Maoist casualties recorded in a single operation within the Bastar region.
- The operation involved a strategic collaboration between the DRG, a specialized anti-Naxal force, and the BSF, with a well-executed plan that allowed them to engage and ultimately overpower the Maoists.
What is Left Wing Extremism?
- Left-Wing Extremism (LWE), also referred to as left-wing terrorism or radical left-wing movements, encompasses political ideologies and groups that aim to achieve substantial societal and political transformation through revolutionary methods.
- These groups may resort to targeting government institutions, law enforcement agencies, or private property to advance their objectives.
- India's LWE movement traces its origins back to the 1967 uprising in Naxalbari, West Bengal, which set the stage for the emergence of various left-wing extremist groups.
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs, LWE has impacted 90 districts across 10 states, with varying degrees of influence.
Maoist Presence Across India:
Maoist influence varies in intensity across different Indian states:
- Severely Affected States: Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, and Bihar face significant Maoist presence and activities, with frequent attacks on security forces and civilians.
- Partially Affected States: West Bengal, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh experience a more moderate Maoist presence, with occasional incidents and clashes.
- Slightly Affected States: Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh have a lower level of Maoist activity but are still considered areas of concern.
- The Communist Party of India (Maoist) has been attempting to expand its influence in the southern states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, aiming to connect the Western and Eastern Ghats.
- Additionally, incursions into Assam and Arunachal Pradesh have raised concerns about long-term strategic implications.
Factors Contributing to Left-Wing Extremism in India:
Several underlying factors contribute to the rise and persistence of Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) in India:
- Inequitable Development: Many LWE-affected regions are among India's least developed areas, characterized by high poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, malnutrition, and social exclusion rates.
- LWE groups often exploit the grievances of marginalized communities, particularly tribal populations, who have been deprived of land, forest, and mineral rights.
- Marginalization: Naxalites primarily consist of Dalits, Adivasis, and other marginalized sections of society.
- Maoist teachings deeply influence their leadership, with land reforms and economic development being key issues.
- Governance Deficit: LWE-affected areas often suffer from inadequate governance, administration, and service delivery.
- Weak or corrupt state institutions leave a vacuum that LWE groups can exploit.
- These groups also use violence and intimidation to disrupt democratic processes, including elections, local governance, and development schemes.
- Ideological Appeal: LWE groups claim to represent the interests of oppressed and exploited classes, promoting a radical ideology that rejects parliamentary democracy and advocates for armed revolution.
- Drawing inspiration from Mao Zedong and the 1967 Naxalbari uprising, these groups may also have links to other extremist and separatist movements in India and abroad.
- Globalization and Cultural Displacement: The impacts of globalization, such as cultural changes and displacement, can cause feelings of dislocation and alienation.
- Left-wing extremist movements may offer identity and purpose to individuals marginalized by global forces.
- Support Base: The Naxalite movement draws support from the landless, sharecroppers, agricultural laborers, Harijans, and tribals.
- As long as these groups continue to face exploitation and social injustice, the Naxalite support base will persist.
The Challenges Posed by Naxalites to India:
The Naxalite movement presents several challenges to India's stability and development:
- Vulnerability to External Threats: Naxalite activities expose India's internal vulnerabilities, potentially inviting external threats.
- The CPI (Maoist) has close ties with Northeast insurgent groups, many of which have links to external forces hostile to India.
- The CPI (Maoist) has also expressed solidarity with Jammu and Kashmir terrorist groups.
- Impediments to Economic Development: Focusing on India's poor and marginalized regions, Naxalite activities hinder economic development efforts crucial for improving these areas' conditions.
- Internal stability is essential for a nation's economic progress.
- Additional Internal Security Expenses: Scarce resources are diverted towards defense and internal security to counter Naxalite threats, which could be better utilized for social development initiatives.
- Adverse Impact on Governance: Naxalite domination in certain areas disrupts governance through violent tactics, such as killings, kidnappings, intimidation, and extortion.
- This hampers the delivery of essential services to citizens in affected regions.
Steps Taken by the Government to Counter Left-Wing Extremism:
To tackle the challenges posed by Left-Wing Extremism (LWE), the Indian government has implemented various strategies and initiatives:
- Deployment of Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs): CAPF battalions and Naga Battalions (BNs) are deployed to support state police forces in LWE-affected areas, providing additional security and resources.
- Security Related Expenditure (SRE) Scheme: The SRE scheme funds the recurring expenditures related to insurance, training, and operational needs of security forces, rehabilitation of surrendered LWE cadres, and awareness campaigns against violence.
- Review and Monitoring Mechanisms: The Ministry of Home Affairs regularly monitors the LWE situation at multiple levels through various review and monitoring mechanisms.
- Strengthening Intelligence Gathering: Intelligence capabilities at the central and state levels have been bolstered through measures like intelligence sharing via the Multi-Agency Centre (MAC) and State Multi-Agency Centre (SMAC) on a 24/7 basis.
- Inter-state Coordination: Given the cross-border nature of Maoist operations, the government facilitates frequent meetings and interactions between officials from bordering LWE-affected districts to enhance inter-state coordination.
- Countering Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs): As IEDs are a significant threat, the Home Ministry has developed a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) on explosives, IEDs, and landmines in affected areas, which has been shared with stakeholders for implementation.
- Enhanced Air Support: State governments and CAPFs have received increased air support, including UAVs and helicopters, for anti-Naxal operations and casualty evacuations.
Progress and Impact of the Measures:
- Over the past eight years, India has witnessed a substantial decrease in left-wing extremism violence and its geographical spread, thanks to the government's comprehensive measures:
- The number of left-wing extremism-related incidents dropped significantly in 2022 compared to 2013, totaling 413.
- Left-wing extremism-related deaths also experienced a substantial decline, with a 75% reduction from 397 in 2013 to 98 in 2022.
- The year 2022 saw a 33% decrease in resultant deaths and a 68% decrease in security forces' casualties compared to 2021.
Way Forward:
- Effective Implementation of PESA Act: Ensure proper and complete implementation of the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA) by issuing clear policy directives to empower gram sabhas.
- Align the Act with the historical and traditional tribal way of life and address implementation gaps that Maoists exploit.
- Tribal Empowerment and Representation: Foster tribal leadership by providing platforms for their voices to be heard and increasing representation in local governance structures and political processes.
- Address tribal communities' aspirations and ensure policies accommodate their unique needs and perspectives.
- Targeted Development Programs: Implement development programs addressing socio-economic issues faced by tribal communities, including infrastructure, healthcare, education, and employment opportunities. Involve local communities in participatory decision-making processes for initiatives.
- Counter Maoist Propaganda: Develop communication strategies to expose the gap between Maoist rhetoric and actions.
- Collaborate with local media, community leaders, and influencers to spread accurate information and counter misinformation.
- Negotiation and Conflict Resolution: Explore avenues for peaceful negotiation with moderate Maoist factions, identifying root causes of discontent and involving neutral mediators, civil society organizations, and respected community leaders in peacebuilding efforts.
- Human Rights Protection: Prioritize human rights protection in conflict zones, ensuring security measures align with the rule of law and minimizing collateral damage and civilian casualties.
- Long-term Strategic Planning: Develop a comprehensive, long-term strategy focused on sustainable development, social justice, and inclusive governance to address underlying issues contributing to the insurgency.
Conclusion
There is a widely acknowledged perspective that effectively addressing the Naxal issue requires a balanced approach involving both developmental and security measures. It's crucial not to solely consider it as a law and order challenge, as innocent tribal communities residing in remote forest areas often become targets of Naxal intimidation. Priority lies in re-establishing governance in Naxal-affected regions, fostering their development, and empowering marginalized communities to lead secure, dignified, and improved lives
New Data Law, a Barrier to Journalistic Free Speech

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In August 2023, India enacted its first comprehensive data protection law, the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, with the government currently in the process of formulating rules and regulations for its implementation, anticipated to conclude post the general election.
Context:
- In August 2023, India introduced its first comprehensive data protection law, the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023.
- While aimed at safeguarding personal data, its impact on journalistic freedom warrants examination, as the absence of exemptions for journalistic activities may threaten the foundational principles of a free press.
Provisions of Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act:
- The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 is a landmark legislation aimed at regulating the collection, processing, storage, and use of personal data in India.
- The Act establishes a comprehensive framework for lawful and transparent handling of personal data, seeking to safeguard individuals' privacy and data rights.
Key provisions of the DPDP Act, 2023 include:
- Definition of personal data: Any information capable of identifying an individual, directly or indirectly.
- Principles of data protection: Lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimisation, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, confidentiality, and accountability.
- Data handlers: Distinction between data fiduciaries (determining processing purpose and means) and data processors (processing data on behalf of fiduciaries).
- Consent: Requirement for explicit consent before processing personal data, with provisions for withdrawal.
- Individual rights: Access, correction, erasure, and transfer of personal data.
- Data localisation: Potentially mandating the storage and processing of certain sensitive data within India.
- Oversight: Establishment of a Data Protection Board to monitor compliance and resolve grievances.
- Non-compliance: Penalties and sanctions, including fines and legal consequences for violations.
- Cross-border data transfers: Ensuring data protection standards comparable to India's when transferring data across borders.
- Obligations for data fiduciaries and processors: Security measures, data breach notifications, and data impact assessments.
- The DPDP Act, 2023 represents a significant step towards upholding individual privacy rights in India and ensuring responsible data management by government entities, organisations, and individuals alike.
Journalistic Exemptions in Data Protection Laws:
- Traditionally, data protection laws include exemptions for journalistic activities, allowing journalists to access and report on personal data without consent for investigative purposes.
- These exemptions ensure freedom of the press and facilitate accountability in society.
- However, the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 does not provide such exemptions.
- Previous drafts of the Act, including versions released by an expert committee on data protection (2018), the government (2019), and a Joint Parliamentary Committee (2021), contained provisions for journalistic activities.
- The unexplained removal of these exemptions in the DPDP Act's final iterations (2022 and 2023) raises concerns over potential negative impacts on journalism and its role in maintaining transparency and accountability.
- Addressing this absence of journalistic exemptions will be crucial to upholding the freedom of the press and protecting the public's right to information.
Challenges for Journalists under the DPDP Act:
- Consent Requirements: Journalists are now obligated to secure consent from individuals before utilizing their personal data in news stories.
- This could impede investigative reporting, as subjects may refuse consent, thereby obstructing access to crucial information.
- Right to Erasure: The right to erasure permits individuals to demand the deletion of published stories containing their personal data.
- This provision may result in the removal of significant investigative work, undermining transparency.
- For instance, when reporting on a Member of Parliament (MP) and their activities, journalists often gather information such as meeting details, travel itineraries, and familial financial investments, all of which constitute personal data under the DPDP Act.
- This provision may result in the removal of significant investigative work, undermining transparency.
- Obtaining consent for such data usage poses challenges, and even after publication, MPs can invoke the right to erasure, compelling journalists to delete pertinent stories.
- Government Oversight: The Act grants the government authority to request information from data processors, potentially compromising the confidentiality of journalists' sources and research materials.
- This governmental oversight may curtail the press's capacity to hold the state accountable.
Addressing Concerns and Potential Solutions for Journalistic Freedoms under the DPDP Act:
- To ensure a balanced approach that protects personal data while preserving journalistic freedoms, addressing the concerns raised by the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act is essential.
- The following solutions could help achieve this goal:
- Transparent Consultation: The removal of exemptions for journalistic activities highlights the need for open and transparent public consultations.
- Although drafts of the DPDP Act were released for public input, the comments received were not made publicly available.
- Greater transparency in the consultation process would enable better comprehension of stakeholder perspectives and inform more effective law-making.
- Exemptions for Journalists: The central government should consider using its rule-making powers under the DPDP Act to exempt journalistic entities, including citizen journalists, from specific obligations within the Act.
- This exemption would protect the freedom of the press and encourage a transparent and open environment for journalism.
- Public Consultation: Implementing an open, transparent, and robust public consultation process could facilitate better understanding and consideration of various viewpoints.
- This approach would lead to a more balanced and effective data protection law that upholds both personal data privacy and freedom of the press.
Conclusion
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, is an essential step towards safeguarding personal data in India. However, its potential impact on journalistic free speech raises significant concerns that must be addressed.
To strike a balance between protecting individual privacy and upholding the fundamental principles of a free press, the government should consider implementing exemptions for journalists and fostering transparent consultation processes. These measures would enable a harmonious coexistence of personal data protection and journalistic freedoms, ensuring that both critical elements thrive in India's democratic landscape
Revealing Caste-based Inequalities in Indian Cities

- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Despite Dr. B.R. Ambedkar's hopeful vision for India's cities, the urban fabric continues to be profoundly fractured by enduring caste-based divisions.
Context:
- Caste has historically played a significant role in shaping the social fabric and geographical layout of communities throughout India.
- This influence is palpable in the organization of Indian cities, where caste often dictates spatial arrangements and societal dynamics.
- Despite entrenched obstacles, influential figures such as R. Ambedkar and Jyotirao Phule viewed urbanization as a potential catalyst for the liberation of Dalits.
- Consequently, it becomes imperative to delve into Ambedkar's perspective on urbanization, the enduring prevalence of caste-based discrimination within urban environments, and the ongoing hurdles encountered by Dalits and Muslims concerning housing and access to public services in urban areas.
What was B. R. Ambedkar’s View on Urbanization?
- A Pathway to Empowerment: B. R. Ambedkar, an eminent social reformer and advocate for Dalit rights, envisioned urbanization as a pathway to empowerment for marginalized communities in India.
- He posited that the traditional social structures prevailing in Indian villages were inherently oppressive due to the rigid caste system, which predetermined individuals' social status and opportunities based solely on their birth.
- Ambedkar contended that Indian villages served as the "working plant of the Hindu social order," perpetuating caste-based hierarchies that marginalized and subjugated Dalits.
- Viewing urbanization as a means of dismantling this entrenched caste-based order, he saw cities as spaces where individuals could blend into anonymity amidst a diverse population, transitioning from a caste-oriented society to one structured more around class.
- Disrupting Caste-Based Hierarchies: Ambedkar believed that this transition from a genealogy-based social structure to one centered on resource accumulation would weaken the systems of caste oppression that were deeply entrenched in rural areas.
- Urban environments, he argued, would offer Dalits access to diverse economic opportunities and avenues for skilled labor, enabling them to enhance their social and economic status.
- In cities, Dalits could potentially break free from the occupational constraints dictated by caste in villages, thereby fostering social mobility and economic independence.
- Additionally, Ambedkar saw urban areas as hubs of greater political and social awareness, with educational institutions and opportunities for civic engagement that could empower marginalized groups to assert their rights and actively participate in democratic processes.
- Urbanization Challenges and Ambedkar's Hope: Despite advocating for urbanization as a means of empowerment for marginalized communities, Ambedkar was cognizant of its inherent challenges.
- He acknowledged the persistent presence of caste-based discrimination within urban settings, drawing from his encounters with adversity.
- Ambedkar's personal experiences, such as his difficulties in securing housing in Baroda and encountering caste-based restrictions in textile mills, underscored the reality of caste-based biases in urban areas.
- However, rather than succumbing to disillusionment, he maintained an optimistic outlook regarding the transformative potential of cities.
- Ambedkar perceived urban environments as arenas where individuals could assert greater agency and autonomy in shaping their lives.
- Despite the hurdles presented by caste-based discrimination, he remained hopeful that cities could provide avenues for marginalized groups to transcend social barriers and realize their full potential.
Endurance of Caste-Based Bias in Urban Environments:
- Language of Purity-Pollution: Urban caste discrimination primarily manifests through the concept of purity-pollution, deeply ingrained in Hindu social practices.
- This notion labels specific foods, behaviors, and individuals as pure or impure based on caste.
- For instance, a 2021 survey revealed that non-vegetarian diets hinder rental housing access, reflecting prejudice against meat-eating castes.
- This notion labels specific foods, behaviors, and individuals as pure or impure based on caste.
- Caste Segregation in Housing: The purity-pollution concept extends to housing practices, with Dalits and other lower castes facing discrimination in renting or purchasing urban homes.
- Landlords and housing societies may reject them based on perceived cleanliness or dietary habits, leading to segregation and ghettoization.
- State-Sanctioned Policies: Government policies have also perpetuated urban caste-based discrimination.
- In March 2017, Uttar Pradesh restricted meat sales near religious places and mandated meat shops to conceal products from pedestrians.
- Similar measures in Gujarat targeted street food vendors selling meat-based items, citing religious concerns.
- These policies reinforce caste divisions by labeling meat as impure and associating it with certain castes.
Ambedkar's Vision, Discrimination's Impact, and Urban Space Inequity:
- Enduring Significance of Ambedkar's Vision: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar's vision of urbanization as a means for Dalit liberation remains relevant today, emphasizing the continuing pursuit of social justice and equality in Indian cities.
- His work highlights the need to address both historical and present-day caste-based discrimination to create inclusive urban environments.
- Spatial Consequences of Discrimination: Caste-based discrimination significantly affects urban spaces by segregating Dalits and other marginalized groups into specific areas or neighborhoods.
- These segregated zones often lack access to essential services and infrastructure, amplifying existing socioeconomic disparities within these communities.
- Influence on Public Spaces: Discrimination based on caste extends to public spaces, with restrictions on food sales limiting lower castes' economic and social participation in city life.
- Such policies contribute to exclusion and marginalization, shaping an environment detrimental to inclusivity and equity within urban landscapes.
Conclusion
Despite Ambedkar's hopeful vision of urbanization as a means to Dalit liberation, Indian cities have yet to fully realize this potential. While the shift to urban life has altered some aspects of caste oppression, new forms of discrimination have emerged and persisted, perpetuated by language, state policies, and institutional biases. This enduring struggle highlights the imperative of ongoing initiatives to combat caste-based discrimination and foster a more inclusive and equitable urban landscape in India.
A Reformed UNSC is not Possible Without India as a Permanent Member

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At a time when India is seriously advocating structural and functional reforms in the United Nations, the global forum’s president, Dennis Francis, has expressed optimism about India’s potential to secure a permanent seat on the UN Security Council.
Context:
- Amid India's active promotion of structural and functional reforms within the United Nations, Dennis Francis, the president of the global forum, has voiced optimism regarding India's ability to secure a permanent seat on the UN Security Council.
- The US and other Western countries sound extremely hollow when they pontificate on strengthening democracy and the fight against terrorism even as they keep India out of P5.
What is P5 Nations in the United Nations?
- P5 refers to the Permanent Five or Permanent Members of the United Nations Security Council.
- These are the five countries that have a permanent seat on the Security Council, granting them significant power within the UN.
The P5 members are:
-
- China
- France
- Russia
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Most of these countries were major victors of World War II and were seen as key players in maintaining international peace and security.
- They hold a special privilege within the Security Council: the right to veto any resolution.
- This means any one of these countries can single-handedly block a resolution, regardless of how many other countries support it.
- The P5's power and influence is a subject of some debate. Some argue that it's necessary to maintain stability, while others believe it gives these countries too much control and hinders the UN's effectiveness.
Urgent Need for Overhauling the United Nations (UN):
- Addressing the 76th UNGA in 2021, the Prime Minister of India underscored the imperative for 'comprehensive UN reforms,' stressing that 'outmoded structures' are inadequate to tackle contemporary challenges.
- Issues such as climate change, counterterrorism efforts, and the attainment of sustainable development goals (SDGs) were not prioritized when the UN was established seven decades ago.
- Today, they demand urgent attention.
- The aftermath of World War 2 has spawned numerous conflicts that persist, undermining global peace and economic advancement.
- The Covid-19 pandemic has laid bare the fragility of the world's healthcare systems.
- In today's multipolar world, the UN's polarized and antiquated structure is ill-suited to meet the demands of global governance.
- Cooperation among nations is essential to prevent the abuse of selective veto power by members pursuing hegemonic agendas.
Inconsistencies in Global Perceptions of India's UNSC Candidacy:
- In 2023, as India's G20 presidency drew to a close, the country's foreign minister noted a positive international reception to India's bid for a permanent seat on the UNSC.
- During bilateral discussions between the Prime Minister of India and the President of the USA, a joint statement emphasized India's stance on the need for a more inclusive and representative global governance structure through UN Security Council reform.
- In the same statement, the US expressed support for India's candidacy for a non-permanent seat on the UNSC for the term 2028-2029.
- Beyond the US, other voices echo the call for expanding non-permanent UNSC membership.
- The Uniting for Consensus (UFC) group, comprising twelve nations, advocates for increasing the number of non-permanent elected UNSC members from 15 to 26.
- Formed in 1990, the UFC opposes creating new permanent national seats, arguing that the current P5 arrangement stems from post-World War 2 circumstances, and creating additional privileged positions would be detrimental to UN membership's general interests.
- Critics point out the inconsistency of Western nations, notably the US, a permanent UNSC member, advocating for democracy and counterterrorism while simultaneously excluding India, one of the oldest UN members and the largest democracy, from the P5.
- China presents the primary obstacle to India's pursuit of a permanent UNSC seat.
China's Influence on UNSC Reform Efforts:
- Italy-China Collaboration within UFC: In 2023, the Deputy Prime Minister of Italy engaged in discussions with his Chinese counterpart, focusing on bilateral agreements and the situation in Ukraine.
- During this exchange, the Deputy Prime Minister of Italy commended the productive and consistent cooperation between China and Italy concerning UNSC reform, particularly their coordination within the Uniting for Consensus (UFC) group, where China holds an observer status.
- The presence of China as an observer suggests dim prospects for those advocating genuine reforms and expansion of the P5.
- China's Opposition to the G4 Group: Also in 2023, the G4 Group, consisting of India, Brazil, Japan, and Germany, convened during the 78th UNGA to deliberate on the UN reform process, particularly focusing on expanding the P5.
- Their objective is to modernize the UN's structure, which has its roots in the aftermath of World War 2.
- However, opposition from China, Russia, and South Korea regarding Japan's participation in the G4 due to historical issues stemming from World War 2 has caused friction and disagreement among the countries involved.
- Acknowledging India's Role: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru played a pivotal role in advocating for China's inclusion as a permanent member of the UN Security Council. Notably, both the US and the Soviet Union informally offered India the UNSC seat in the early 1950s.
- Nehru emphasized China's significance within the framework of his foreign policy.
- However, China's actions in Tibet and its conflict with India in 1962 shattered Nehru's perception of China's global role.
- India now stresses the importance of resolving issues such as Tibet and territories like Xinjiang and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- As a permanent UNSC member, China should remember the circumstances that led to its membership and acknowledge its responsibilities to India.
Conclusion
The international community must acknowledge that without comprehensive restructuring and democratization, untethered from its historical constraints, the United Nations (UN) will struggle to address the complexities of contemporary geopolitics and foster genuine multilateralism. Without these reforms, the aspirations for peace and prosperity will remain elusive. What's urgently required is a revamped, credible, and inclusive UN 2.0 that can effectively safeguard global peace and security.
United Nations Security Council:
- The Security Council has primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- It has 15 Members, and each Member has one vote.
- Under the Charter of the United Nations, all Member States are obligated to comply with Council decisions.
- The Security Council takes the lead in determining the existence of a threat to the peace or act of aggression.
- It calls upon the parties to a dispute to settle it by peaceful means and recommends methods of adjustment or terms of settlement.
- In some cases, the Security Council can resort to imposing sanctions or even authorizing the use of force to maintain or restore international peace and security.
A Battle to Save Ladakh, and All of Humanity

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
When climate activist Sonam Wangchuk took the stage in Leh, Ladakh recently, addressing a gathering of 30,000 individuals, his announcement of a 21-day climate fast resonated not only with the people of Ladakh but also with a global audience.
Context:
- The Himalayan region, situated between India's neighbors Pakistan and China, encompasses Ladakh, where 97% of the population comprises indigenous tribes whose livelihoods primarily depend on agriculture and animal husbandry.
- Despite its breathtaking beauty, this region grapples with various challenges, including the adverse effects of climate change, border tensions, and a surge in large-scale infrastructure projects.
- As climate activist Sonam Wangchuk leads protests and fasts, it becomes imperative to grasp the broader context of the Himalayan ecosystem's vulnerability.
The Climate Change Challenge in the Himalayan Region:
- Extreme Weather Events: Climate change manifests in more frequent and severe weather phenomena like heavy rainfall, cloudbursts, and flash floods.
- These events trigger landslides, wreaking havoc on mountain communities by damaging infrastructure, crops, and property, and endangering lives.
- Shifts in Monsoon Patterns: The region heavily relies on monsoon rains for agriculture and water supply.
- Climate change-induced alterations in monsoon patterns disrupt rainfall timing, intensity, and distribution, jeopardizing agricultural cycles and economic stability.
- Temperature Rise: Elevated temperatures impact both mountain and downstream ecosystems.
- Snowmelt patterns alter, local biodiversity faces disturbance, and traditional farming and animal husbandry practices suffer.
- Melting Glaciers: The Himalayas, often dubbed the Third Pole, harbor approximately 15,000 glaciers crucial to regional hydrology.
- These glaciers feed vital rivers like the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra, serving as lifelines for millions downstream.
- However, accelerated glacier melt due to global warming poses threats such as rising river levels, heightened flood risks, and potential water scarcity.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The Himalayan region hosts diverse flora and fauna, including many endemic species.
- Climate change threatens this unique biodiversity through habitat loss, altered migration routes, and ecosystem stress.
- Livelihood Impacts: Indigenous tribes and rural communities depend on farming and animal husbandry.
- Climate change-induced disruptions, such as erratic weather and natural disasters, challenge their traditional livelihoods.
National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem (NMSHE):
- The National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem (NMSHE) is one of the eight missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
- NMSHE is a multi-pronged, cross-cutting mission across various sectors.
- It contributes to the sustainable development of the country by enhancing the understanding of climate change, its likely impacts, and adaptation actions required for the Himalayas- a region on which a significant proportion of India’s population depends for sustenance.
- NMSHE seeks to facilitate the formulation of appropriate policy measures and time-bound action programs to sustain ecological resilience and ensure the continued provisions of key ecosystem services in the Himalayas.
- NMSHE intends to evolve suitable management and policy measures for sustaining and safeguarding the Himalayan ecosystem along with developing capacities at the national level to continuously assess its health status.
- Recognizing the importance of scientific and technological inputs required for sustaining the fragile Himalayan Ecosystem, the Ministry of Science and Technology has been given the nodal responsibility of coordinating this mission.
- However, the mission involves valuable cooperation of the Indian Himalayan States, the Planning Commission, and the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change to achieve its goals.
NMSHE's Role in Preserving the Himalayan Region:
- Accelerated Infrastructure Development: Since Ladakh transitioned to a Union Territory, numerous large-scale infrastructure projects have been rapidly implemented, including road expansions, bridge constructions, tunnel installations, railway lines, and solar energy initiatives.
- These endeavors, driven by entities such as the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) and the National Highways & Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd. (NHIDCL), focus on promoting tourism and industrial growth.
- Oversight of Previous Disasters: Despite past calamities in the Himalayan region, such as the catastrophic 2013 Kedarnath floods, and more recent incidents like the 2023 Joshimath disaster and the Silkyara tunnel collapse, there appears to be minimal reflection on previous warnings.
- Expert committees have advocated for limitations on pilgrim numbers and constraints on hydroelectric projects in ecologically fragile areas, but these recommendations have often been disregarded.
- Insufficient Attention to Concerns: Climate change activists have raised concerns about the inadequate consideration given to their suggestions, with little to no scrutiny conducted before approving multi-crore infrastructure projects.
- Worries regarding risk assessment, safety protocols, and geological evaluations seem to be overlooked in the pursuit of rapid development.
How to preserve the Himalayan Ecosystem Safe?
- Sustainable Development Practices: Conduct comprehensive environmental impact assessments before embarking on development projects to gauge potential ecosystem repercussions.
- Design projects with a focus on minimizing environmental harm and adhering to sustainability standards.
- Implement infrastructure projects with measures to reduce environmental disruption, such as using sustainable materials and employing low-impact construction methods.
- Focused Policies on Biodiversity Conservation: Expand and fortify protected areas like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries to safeguard the region's diverse flora and fauna.
- Establish and maintain wildlife corridors to facilitate safe animal migration and preserve genetic diversity, thus mitigating the risk of species extinction.
- Community Involvement: Integrate traditional knowledge and practices of local communities into conservation initiatives to ensure cultural relevance and long-term sustainability.
- Empower local communities to actively participate in conservation efforts, fostering greater engagement and ownership over preservation endeavors.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Implement strategies to curb greenhouse gas emissions, such as promoting renewable energy sources and combating deforestation, to mitigate climate change impacts.
- Support adaptation measures for local communities, including crop diversification and enhanced water management, to help them cope with evolving climate conditions.
- Research and Monitoring: Continuously monitor the Himalayan ecosystem, including its flora, fauna, and physical processes, to detect early signs of ecological changes and inform conservation strategies.
- Encourage interdisciplinary research on the region's ecology, climate, and geology to deepen understanding of ecosystem challenges and identify effective solutions.
Conclusion
It's crucial to recognize that while development is vital for economic progress, it should not be pursued at the cost of environmental harm and human well-being. The Himalayan region, renowned for its unparalleled biodiversity and rich cultural heritage, warrants thoughtful preservation and conservation efforts. It is incumbent upon all stakeholders to collectively assume the responsibility of safeguarding the future of this ecologically and culturally significant area.
The Advent Of A Holistic Approach To 'One Health'

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ‘National One Health Mission’ is the result of the recognition that only a coordinated approach will ensure a better response to disease outbreaks.
Context:
- In recent times, the intricate relationship among humans, animals, and the environment has gained significant attention, especially in light of the emergence of pandemics like COVID-19.
- This interconnectedness is underscored by the impact of diseases such as lumpy skin disease, which affects both livestock productivity and trade, bridging the gap between domesticated and wild animal health.
- Addressing these complex challenges, the Indian government has launched the 'National One Health Mission,' aimed at comprehensively tackling the interlinked domains of human, animal, and environmental health.
What is One Health?
- One Health is an integrating idea that brings different sectors together to solve the health, productivity, and conservation challenges and has major implications for India.
- It is a global topic and was endorsed during India's presidency of the G-20.
- India with its diverse wildlife, one of the largest livestock populations, and high density of human population, carries heightened risks for inter-compartmental spread of diseases.
- The Covid pandemic, recent outbreaks of Lumpy Skin Disease in cattle, and the constant threat of Avian Influenza show that it is not just about addressing diseases from the human health point of view (zoonosis) but we need to address the livestock and wildlife aspects.
- This also opens opportunities for leveraging the complementarity and strengths that are inherent in each sector and devising integrated, robust, and agile response systems.
What is the National One Health Mission?
- Initiated in July 2022, the National One Health Mission represents a comprehensive endeavor endorsed by the Prime Minister's Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC).
- With the participation of 13 ministries and departments, including the Department of Science and Technology, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), among others, this mission adopts a holistic approach towards One Health and pandemic preparedness.
- A pivotal achievement within this mission is the establishment of the National Institute for One Health in Nagpur.
- Functioning as the central coordinating body for both national and international One Health endeavors, this institute marks a significant milestone in the mission's implementation.
- On December 11, 2022, the foundation stone of the institute was laid by the Prime Minister, symbolizing the commitment to advancing the principles of One Health and enhancing pandemic preparedness.
Objectives and Approaches of The National One Health Mission:
- Seamless Surveillance Integration: The mission endeavors to establish an integrated surveillance system that seamlessly monitors health indicators across human, animal, and environmental sectors.
- By amalgamating data from these domains, it can swiftly identify potential health hazards and respond proactively.
- Coordinated Outbreak Management: Recognizing the necessity of a unified approach in outbreak response, the mission aims to institute protocols and frameworks facilitating collaboration among various sectors.
- This coordinated effort enables effective resource and information sharing to mitigate the impact of diseases affecting multiple domains.
- Collaborative Research and Development: Through fostering collaboration among scientific research institutions and government bodies, the mission fosters the development of innovative solutions for emerging health threats.
- This includes the creation of vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics critical for pandemic preparedness and response.
- Seamless Information Exchange: Effective communication and data sharing are imperative for a unified One Health approach.
- The mission endeavors to facilitate seamless information exchange between sectors and stakeholders, ensuring timely and informed actions.
- Preparedness for Future Pandemics: Building on past pandemic experiences, the mission seeks to develop strategies and frameworks to enhance the country's readiness for future health crises.
- This involves proactive planning for potential pandemics and emerging diseases such as avian influenza or Nipah virus.
- Resource Optimization: By leveraging the resources and expertise of multiple sectors and stakeholders, the mission aims to optimize resource utilization, including laboratory infrastructure, healthcare facilities, and scientific research capabilities.
- This collaborative effort enhances efficiency and cost-effectiveness in addressing health threats.
- Public Health Education and Awareness: The mission includes public education initiatives to raise awareness about the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
- Promoting an understanding of One Health principles encourages healthier behaviors and better preparedness for health emergencies.
Critical enabling activities of the One Health Mission:
- The outcomes of the One Health Mission will be supported by critical enabling initiatives.
- Many of these initiatives are ongoing and will be strengthened under the mission and several new activities that will facilitate the goals of the mission will be undertaken.?
Leveraging Laboratory Networks and Technological Integration in India's National One Health Mission:
- Establishment of High-Risk Pathogen Laboratories: The mission is dedicated to creating a nationwide network of laboratories equipped to handle high-risk pathogens classified under Biosafety Levels 3 and 4.
- These facilities provide a secure environment for studying infectious agents with pandemic potential.
- Departmental Collaboration: By consolidating laboratories managed by diverse departments, the mission aims to foster a cohesive network capable of coordinating resources and expertise across sectors.
- This integration enhances disease outbreak response, irrespective of its origin in human, animal, or environmental realms.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Pooling laboratory resources within a unified network ensures efficient utilization of infrastructure and personnel.
- This collaborative approach enables swift responses to outbreaks and other health crises, maximizing available resources.
- Interdisciplinary Research and Analysis: Encouraging collaboration among experts from various disciplines—including medicine, veterinary science, environmental science, and public health—the mission promotes comprehensive research and analysis of health threats across multiple sectors.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Harnessing the power of AI and machine learning, the mission enhances epidemiological capabilities by analyzing vast datasets to detect patterns, trends, and potential health risks.
- This technology enables timely interventions and enhances overall preparedness.
- Utilization of Disease Modelling: Advanced modeling techniques are employed to forecast disease spread and potential outbreaks.
- These models facilitate targeted measures for disease control and prevention.
- Expansion of Genomic Surveillance: The mission broadens genomic surveillance efforts beyond COVID-19, encompassing other infectious diseases.
- By analyzing genetic material from diverse sources like wastewater and animal congregations, scientists can monitor disease prevalence and identify emerging threats.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Emphasizing the importance of skill enhancement, the mission prioritizes capacity building across sectors in epidemiology, data analytics, and laboratory management.
- Training programs ensure that professionals possess the necessary skills to effectively utilize new technologies and methodologies.
Conclusion
The concept of One Health transcends mere disease management, encompassing broader realms such as antimicrobial resistance, food safety, plant diseases, and the consequential impacts of climate change. Addressing intersectoral issues like One Health necessitates active involvement not only from diverse governmental agencies but also from non-governmental organizations, academia, the private sector, and ordinary citizens. By adopting an actionable framework rooted in collaboration and comprehensive engagement, we can advance toward the overarching objectives of 'One Earth, One Health' and 'Health for All.
Climate Crisis is Not Gender Neutral

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The climate crisis is far from “gender neutral” as women and men are affected differently by weather and climate and therefore need gender-sensitive information and services.
Context:
- As the climate crisis intensifies, its disproportionate impact on women and girls becomes more evident, particularly in poverty-stricken regions.
- This calls for a critical examination of the gender dimensions of climate change, recognizing women's increased vulnerabilities and the importance of incorporating gender perspectives in climate action strategies.
- By doing so, we can develop effective solutions that address the unique challenges faced by women, ensuring a more equitable and sustainable approach to climate change mitigation and adaptation.
How Does Climate Change Impact Women?
- Rural Livelihood Dependence on Agriculture: In many regions, particularly rural India, women play a central role in agricultural activities, forming the backbone of their communities' livelihoods.
- However, the effects of climate change, such as erratic rainfall, droughts, and floods, pose significant threats to crop yields, directly impacting food security and income for these women.
- Compounded by limited access to essential resources like land, credit, and technology, women face heightened vulnerabilities in navigating climate-related risks.
- Health Risks Amplified by Climate Hazards: Women's health is uniquely susceptible to the challenges posed by climate change.
- For instance, prolonged heatwaves increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, including preterm birth and eclampsia.
- Moreover, exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollution exacerbates respiratory and cardiovascular diseases among women and unborn children, compromising their well-being.
- Gender Dynamics in Extreme Weather Events: The rise in the frequency of extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and cyclones, has profound implications, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Reports highlight that a significant portion of Indian districts are susceptible to such disasters, placing women and children at heightened risk.
- Emerging studies underscore a concerning correlation between these natural calamities and incidents of gender-based violence against women.
- Additionally, disruptions in water access due to climate-induced changes affect women's ability to engage in productive activities and access healthcare, intensifying their workload and compromising their overall welfare.
- Nutritional Challenges and Early Marriage: In regions prone to drought, women and girls face heightened risks of undernutrition due to food insecurity.
- Data indicates that women residing in these areas are more likely to experience underweight conditions and are at a higher risk of entering early marriages, perpetuating cycles of poverty and gender inequality.
How to Empower Women in Climate Action?
- Rich Tradition of Environmental Stewardship: Throughout history, women have been integral to environmental conservation efforts.
- Across various communities, they serve as primary custodians of natural resources, managing land, water, and forests with a deep-rooted understanding of sustainability.
- Their traditional knowledge and practices are invaluable assets for fostering biodiversity conservation and promoting climate-resilient agricultural techniques.
- Boosting Agricultural Productivity and Food Security: Providing women farmers with equitable access to resources such as land, credit, and agricultural inputs unleashes their potential to enhance agricultural productivity and adapt to climate change.
- Research indicates that closing the gender gap in agriculture could significantly increase crop yields and bolster food security.
- Women's innate connection to smallholder farming systems enables them to innovate with cost-effective, environmentally friendly farming methods, thereby fostering resilience in agricultural practices.
- Key Players in Local Adaptation Strategies: Women are pivotal to the success of community-based adaptation efforts, which prioritize building resilience to climate change at the grassroots level.
- Through women's groups and collectives like Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), communities mobilize, share knowledge, and implement adaptation measures.
- These grassroots initiatives empower women to advocate for their rights in decision-making processes concerning natural resource management and climate resilience.
- Inspiring Role Models and Catalysts for Change: Women leaders in climate action serve as inspirations and role models, paving the way for future generations of environmentalists and activists.
- Their prominence in climate solutions not only challenges gender norms but also encourages greater participation of women and girls in STEM fields and environmental leadership roles.
- By highlighting women's contributions to climate action, these role models empower others to pursue careers and opportunities in climate science, policy, and advocacy, fostering a more inclusive and impactful approach to addressing climate change.
Action Needed to Address the Gender Implications of Climate Change:
- Immediate Protection Against Health Risks: Swift action is imperative to safeguard vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women, outdoor laborers, children, and the elderly, from health risks exacerbated by extreme weather events like heat waves.
- Local authorities must develop and implement comprehensive heatwave response plans, incorporating early warning systems, establishing cooling centers, and adapting work and school schedules to mitigate heat-related illnesses and fatalities.
- Improved Access to Safe Drinking Water: Climate-induced disruptions to water sources escalate water scarcity and endanger public health.
- Immediate interventions are essential to enhance access to safe drinking water, particularly for women and girls responsible for water collection in many communities.
- Investments in water infrastructure, rainwater harvesting systems, and water purification technologies are vital to alleviate the impacts of water scarcity on vulnerable populations.
- Climate-Resilient Urban Planning: Urban areas face escalating vulnerabilities to climate-related hazards, including heatwaves, flooding, and air pollution.
- Urban planning strategies emphasizing green infrastructure—such as parks, green roofs, and tree-lined streets—can mitigate the urban heat island effect and minimize exposure to extreme temperatures.
- Moreover, measures to enhance air quality, like reducing vehicular emissions and promoting clean energy technologies, are crucial for safeguarding public health, particularly for women and children susceptible to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Community-Centered Adaptation Efforts: Community-based adaptation initiatives, engaging local communities, including women's groups and grassroots organizations, are pivotal in bolstering resilience to climate change at the grassroots level.
- These initiatives should prioritize the needs and aspirations of women and marginalized groups, empowering them in decision-making processes regarding adaptation planning and implementation.
- Investments in building the capacity of local institutions and community leaders can amplify the efficacy and sustainability of adaptation endeavors.
- Gender-Inclusive Climate Policies: National and sub-national climate policies must integrate gender-responsive approaches tailored to the distinct needs and priorities of women and girls.
- Recognizing women as agents of change and empowering their participation in climate decision-making at all levels is essential.
- Gender mainstreaming in climate policies ensures inclusivity, equity, and effectiveness in tackling the underlying drivers of vulnerability and inequality.
Conclusion
The disparities and vulnerabilities experienced by women and girls underscore the urgent need for inclusive and gender-responsive strategies in climate adaptation and mitigation endeavors.
By empowering women, we not only bolster resilience but also unlock innovative solutions crucial for combating the climate crisis. Thus, the integration of gender perspectives into climate action plans is imperative for forging a sustainable and equitable future for all
Indian Aviation, A Case of Air Safety at a Discount

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government introduced revised Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) Regulations, set to be implemented on June 1, 2024, but faced opposition from airline owners, prompting the DGCA to indefinitely defer the deadline.
Context:
- The aviation sector in India faces a pivotal moment, balancing rapid growth with pressing safety issues.
- The remarks from the Union Minister and the DGCA, highlighting safety as paramount, seem at odds with ongoing safety lapses.
- Given the significance of safety measures, it's imperative to examine safety protocols, parameters, challenges, and regulatory shortcomings.
Key Provisions in the Revised FDTL Regulations of January 2024:
- Extended Weekly Rest Periods for flight crew: The revised regulations mandate increased weekly rest periods from 36 hours to 48 hours for flight crew, thus ensuring sufficient time for recovery from cumulative fatigue.
- Night Duty: The definition of night has been amended, and it now covers the period of 0000-0600 hours in the revised regulations vis-à-vis the period of 0000-0500 hours under the previous regulations.
- This enhancement of one hour during the early morning will ensure adequate rest and also align the night duty period, which encompasses the Window of Circadian Low (WOCL) from 0200-0600 hours, i.e. the time during which the circadian body clock cycle is at its lowest in terms of alertness.
- Maximum Flight Time, Maximum Flight Duty Periods, and Number of Landings during Night: The revised regulations have taken into consideration different types of operations across time zones.
- The maximum flight time & maximum flight duty period for flight operations encroaching night have been restricted to 8 hours flight time & 10 hours flight duty period, respectively, and the number of landings has been limited to only two landings as compared to the maximum permissible 6 landings under previous regulations during night operations, thus enhancing flight safety.
- Quarterly fatigue reports: In addition, DGCA has mandated that all airline operators submit quarterly fatigue reports after analysis, including the Action Taken on such reports.
- Further, it has been stipulated that the fatigue reports shall follow a non-punitive and confidentiality policy.
What is the Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS)?
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is preparing to introduce a novel approach, known as the Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS), to handle fatigue among flight crew.
- The recent revision of Flight Duty Time Limitation (FDTL) regulations marks the initial phase of FRMS implementation in India.
- FRMS represents a data-driven strategy aimed at enhancing the monitoring and documentation of flight crew fatigue.
- The successful integration of FRMS hinges upon collaborative efforts from various stakeholders within the aviation sector, including regulators, airline operators, and flight crew, who must demonstrate readiness to embrace this new framework.
- This transition necessitates rigorous oversight, meticulous record-keeping, and comprehensive reporting to uphold compliance with the FRMS framework.
The Imperative for Implementing Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS):
- The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has mandated the adoption of the Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS) to address safety concerns.
- Extensive analysis of accidents and serious incidents attributed to fatigue has underscored the critical role of adequate rest and sleep deprivation in impairing pilots' reaction times.
- Countries like Japan, Singapore, and the United Kingdom prioritize flight crew fatigue management and emphasize regular rest periods to mitigate cumulative fatigue.
- These nations implement a system where pilots receive two days off each week to reset their circadian rhythm and recuperate from prolonged flying hours, with additional rest upon returning from long-haul flights.
- In contrast, existing Flight Duty Time Limitation (FDTL) regulations afford pilots only 30 days of annual leave and one day off per week, which pales in comparison to the leisure time granted to ground personnel.
- Airline schedules often overlook human performance limitations, neglecting the fact that pilots, like any other individuals, require time with their families.
- Thus, providing two days off per week is essential for maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Other concerns in the aviation sector:
- Runway End Safety Area (RESA): The absence of RESA at Kozhikode's Karipur airport has sparked warnings from the Minister for Civil Aviation about compromised passenger safety.
- Recommended by the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau following a 2020 air crash, the Ministry has threatened to curtail runway length unless land is handed over to the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- As of April 2024, no land has been provided, and flights remain unrestricted.
- Utilization of Pilots and Adherence to Safety Regulations: While the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) sets minimum crew requirements, airlines can opt for lower flight time and duty hours.
- Large aircraft orders often adhere to DGCA Civil Aviation Requirements for scheduled transport, which only specifies the minimum crew requirement.
- The crew requirement would more than double under the Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) CAR, but the DGCA does not monitor crew numbers based on these requirements.
- This is primarily due to the potential impact of positive media coverage and the reputation of India's aviation industry.
- Financial Stress on Pilots: Financial stress has been identified as a contributing factor to aircraft crashes, such as the Silkair crash in 1997 and the Egyptair crash in 1999.
- However, authorities in India often fail to adequately address the dangers of financial stress among pilots.
- A prime example is the recent merger of Vistara with Air India, where Vistara copilots faced a significant pay cut upon losing their command position, leading to increased financial strain.
Way Forward:
- Implementing ICAO Annex 1 Standards: A crucial step towards a more robust aviation sector involves adopting the International Civil Aviation Organization's (ICAO) Annex 1 standards, facilitating the recognition of foreign licenses and issuance of Indian licenses based on specific criteria.
- This streamlined process can attract experienced pilots, addressing shortages and elevating workforce competency.
- Harnessing Retired Pilots' Expertise: Utilizing retired pilots in training roles, particularly within simulator training centers, allows India to tap into their valuable experience and knowledge to mentor the next generation of aviators.
- By addressing training gaps and bolstering proficiency standards, this initiative enhances safety outcomes while supporting the professional growth of aspiring pilots.
- Strengthening Monitoring and Compliance: Regulatory bodies, such as the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), should fortify their monitoring mechanisms to ensure adherence to Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) regulations and crew staffing requirements.
- This vigilance aids in identifying instances of non-compliance, mitigating fatigue-related risks, and fostering collaboration with airlines to manage crew resources effectively.
- Cultivating a Safety-Oriented Culture: Promoting a safety culture within the aviation industry is vital for achieving sustainable safety outcomes.
- Stakeholders should prioritize safety initiatives, invest in training programs, and encourage open communication channels for reporting concerns.
- This collaborative approach nurtures a safety-focused environment that benefits all parties and strengthens the overall aviation landscape.
Conclusion
The postponement of fatigue management regulations underscores the complexities of balancing safety concerns with commercial interests within India's aviation industry. To safeguard both flight safety and crew welfare, regulatory authorities must prioritize the implementation of rigorous fatigue management protocols and withstand industry pressures that jeopardize safety standards. It is only through a unified commitment to rectifying regulatory deficiencies and cultivating a culture of safety that India's aviation sector can maintain the utmost standards of flight safety and operational proficiency.
Shaping India’s path to inclusive health care

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
World Health Day, which is observed every year on April 7, unites us around health equity, an essential topic at the heart of global health and justice.
Context:
- World Health Day, commemorated every April 7th, underscores the significance of health equity, acknowledged as a basic human entitlement by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Hence, it is imperative to delve into the theme "My Health, My Right," delving into the hurdles and remedies in attaining health equity in India.
- As a country contending with multifaceted socioeconomic inequalities in healthcare access and results, this exploration becomes pivotal.
What is Health Equity?
- Health equity, as outlined by the WHO, embodies the principle that every person should have the opportunity to attain optimal health, irrespective of their social, economic, or environmental circumstances.
- It extends beyond mere healthcare access, addressing underlying factors such as poverty, discrimination, and resource imbalances.
- Considering Diverse Health Outcomes: A core tenet of health equity acknowledges that health results stem from a multifaceted interplay of elements, encompassing social, economic, and environmental determinants.
- Individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds often encounter obstacles like financial constraints, transportation limitations, and sparse healthcare facilities.
- The Vitality of Health Equity: Health equity holds paramount importance not only ethically but also from a public health standpoint.
- Research consistently indicates that societies fostering greater health equity typically enjoy superior health outcomes, marked by lower morbidity and mortality rates, reduced healthcare expenditures, and heightened life expectancy.
- Conversely, persistent health disparities may precipitate societal unrest, economic strains, and a squandered human potential.
Health Equity Challenges in India:
- Addressing Urban-Rural Disparities: India contends with pronounced healthcare inequalities between urban and rural regions, where urban areas typically boast superior healthcare infrastructure and services, while rural communities encounter obstacles like limited access to facilities, healthcare professionals, and infrastructure, resulting in inferior health outcomes compared to their urban counterparts.
- Navigating Overcrowded Urban Slums: Urban slums present profound challenges characterized by extreme poverty, overcrowding, unsanitary conditions, and inadequate access to clean water, fostering the spread of infectious diseases and escalating morbidity and mortality rates.
- Moreover, deficient healthcare infrastructure exacerbates health disparities as residents grapple with limited access to essential services.
- Tackling Socioeconomic and Caste Disparities: Marginalized groups, including Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and economically disadvantaged populations, confront elevated rates of illness and death due to restricted healthcare access, diminished health literacy, and societal prejudice.
- These disparities intertwine with broader determinants like education, employment, and housing, perpetuating disparities in health outcomes.
- Confronting the Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular ailments, diabetes, and cancer pose a mounting challenge to health equity in India, constituting a substantial portion of the disease burden.
- However, marginalized communities often face barriers to accessing preventive measures and NCD treatment, amplifying health inequalities and exacerbating existing socioeconomic gaps.
- Navigating Shortages in Healthcare Personnel: A severe shortage of healthcare professionals, with only 0.8 doctors per 1,000 individuals according to WHO data, exacerbates health challenges, particularly in rural areas where access to primary care is limited, resulting in delayed diagnoses, substandard treatment, and compromised health outcomes.
- Confronting Infrastructure and Resource Limitations: Inadequate healthcare infrastructure, insufficient funding, and resource limitations pose formidable obstacles to health equity in India, with many public facilities lacking essential equipment, medications, and skilled personnel.
- Furthermore, the unequal distribution of resources aggravates urban-rural healthcare disparities, exacerbating inequities in access to quality healthcare services.
Strategies and Measures to Advance Health Equity in India:
- Enhancing Primary Healthcare Services: A pivotal approach to fostering health equity in India involves bolstering primary healthcare provisions, especially in rural and marginalized regions.
- This entails augmenting the accessibility and availability of primary care facilities, fortifying the skills and capabilities of frontline healthcare personnel, and ensuring the delivery of essential health services encompassing preventive care, maternal and child healthcare, and management of chronic ailments.
- Initiatives such as the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) and the National Urban Health Mission (NUHM) strive to extend primary healthcare access and mitigate healthcare disparities between urban and rural locales.
- Advocating for Universal Health Coverage: Universal health coverage (UHC) stands as a cornerstone in ensuring equitable access to indispensable healthcare services devoid of financial strains.
- Endeavors like Ayushman Bharat, India's flagship health insurance program, aspire to furnish financial safeguarding to vulnerable segments by offering comprehensive coverage for hospitalization expenses.
- By broadening the reach of quality healthcare services and alleviating out-of-pocket costs, UHC endeavors to redress discrepancies in healthcare accessibility and enhance health outcomes for all citizens.
- Targeting Social Determinants of Health: Attaining health equity mandates a multifaceted approach that transcends healthcare interventions to address the underlying social determinants of health, encompassing poverty, education, housing, and employment.
- Initiatives geared towards poverty mitigation, augmenting educational and sanitation access, and fostering livelihood opportunities can wield a transformative impact on health outcomes and help ameliorate health disparities.
- Programs like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) furnish rural households with employment prospects, thereby fostering enhanced socioeconomic circumstances and superior health outcomes.
- Empowering through Health Literacy: Elevating health literacy assumes paramount significance in empowering individuals to make informed health decisions and pursue equitable healthcare access.
- Integration of health education within prevailing healthcare schemes can heighten public consciousness and advocate for preventive healthcare practices.
- Fostering Collaborative Endeavors: Efficacious collaboration among governmental bodies, civil society, healthcare providers, and international entities constitutes a linchpin in addressing health inequities.
- By harnessing their respective competencies and resources, these stakeholders can conceptualize culturally sensitive health initiatives tailored to the distinctive requisites of diverse communities.
Conclusion
Realizing health equity in India necessitates coordinated endeavors spanning various sectors and involving diverse stakeholders. Through targeted interventions addressing socioeconomic health determinants, bolstering healthcare infrastructure, and fostering collaborative alliances, India can progress towards a future where equitable access to superior healthcare becomes a universal norm. The pursuit of health equity transcends moral imperatives, emerging as a pivotal prerequisite for fostering sustainable development and societal advancement.
India Planning to Adopt ‘Living Wage’ Instead of ‘Minimum Wage’ by 2025

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India is reportedly poised to replace the minimum wage with the living wage system, with the transition anticipated to occur by next year.
Context:
- India is reportedly considering shifting from the minimum wage to the living wage by 2025.
- India has approached the International Labour Organization (ILO) to help it chalk out a framework to assess and operationalize the living wages.
- India has asked the ILO to help it in “capacity building, systemic collection of data and evidence of the positive economic outcomes resulting from the implementation of living wages”.
- Earlier in March, the United Nations agency forged an agreement on the living wage, which was also endorsed by its governing body.
- India, a founding member of the ILO and a permanent member of its governing body since 1922, passed the Code on Wages in 2019.
What is the Current Wage System in India?
- National Floor Level Minimum Wage (NFLMW): Established under the Code on Wages 2019, the NFLMW is determined by the government, requiring establishments to set minimum wages not below this level.
- Flexibility in Minimum Wage Standards: Section 5 of the Code on Wages 2019 prohibits employers from setting wages below the NFLMW, though states have the discretion to revise minimum wage rates as needed.
- Presently, the National Floor Wage stands at Rs 178 per day.
What’s a Living Wage?
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) defines the living wage as the level of remuneration “necessary to afford a decent standard of living for workers and their families, taking into account the country's circumstances and calculated for the work performed during the normal hours of work”.
- This decent standard of living includes being able to afford food, water, housing, education, healthcare, transportation, clothing, and other basic needs including a provision for contingencies, says the Global Living Wage Coalition.
- The goal of a living wage is to ensure the employees get an income enough for satisfactory living standards as well as reduce poverty.
What is Minimum Wage?
- Minimum wage refers to the legally mandated lowest level of compensation that employers must pay employees for their work over a specified period.
- While minimum wage endeavors to prevent low pay, living wage extends beyond by ensuring income is adequate to meet necessities like food, shelter, clothing, and other essentials, addressing the risk of workers falling below the poverty line despite earning minimum wages.
- In India, minimum wage calculation factors in variables such as the state of employment, the skill level of the worker, the nature of their job, and other pertinent factors.
Living Wage vs Minimum Wage:
- Definition: A living wage is the income required to meet basic needs and maintain a decent standard of living, while minimum wage is the lowest legally mandated compensation for workers.
- Purpose: A living wage seeks to address the risk of workers falling below the poverty line, while minimum wage aims to prevent low pay.
- Mandatory vs Voluntary: Minimum wages are legally required, whereas living wages are voluntary unless the government sets the minimum wage at the living wage level.
- Calculation: Living wages consider basic necessities and a decent standard of living, while minimum wages factor in variables like skill level, state of employment, and job nature.
Pros and Cons of Living Wages:
- Living wage is a divisive issue. Proponents of the living wage say people get paid more, leading to a rise in employee satisfaction.
- A boost in employee morale is likely to result in higher productivity.
- It also saves recruitment and training costs for companies as employee turnover falls.
- On the other hand, critics of the concept say companies may cut back on hiring if forced to pay increased wages, creating more job losses.
- Opponents also argue that imposing a living wage means creating a wage floor, which would hurt the economy by impacting businesses, especially those that cannot pay hiked salaries.
How Does Living Wage Benefit India?
- India has over 500 million (50-crore) workers, of which 90 percent are in the unorganized sector, noted ET.
- The national floor level minimum wage (NFLMW) – an amount below which no state government can fix the minimum wage – was Rs 178 per day or more depending on the location in 2023.
- This was set at Rs 176 per day in 2017 and has not been changed since then.
- Currently, some states pay workers in the unorganized sector even below the NFLMW.
- The Code on Wages, 2019 was passed by Parliament states that the minimum wage cannot be fixed below the national wage floor.
- However, this code, which is binding on all states, is yet to be implemented.
- If India replaces the minimum wages with living wages, workers are expected to earn more.
- According to the ILO, the living wage has to be calculated following its principles and wage-setting process.
Conclusion
India's pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030 hinges on strategic shifts, such as transitioning from minimum to living wages, to uplift millions from poverty while safeguarding their welfare. This is particularly pertinent against the backdrop of escalating income inequality, highlighting the imperative for a revamped wage system. As poverty rates decline yet inequality persists, a more equitable approach to wages becomes paramount, underscoring India's commitment to inclusive growth and social justice.
International Labor Organization (ILO):
- The International Labor Organization (ILO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations, founded in 1919 to promote social and economic justice through the establishment of international labor standards.
- The ILO operates with a unique tripartite structure, allowing governments, employers, and workers to engage in dialogue and decision-making on labor matters.
Key Roles and Functions:
- Setting International Standards: The ILO develops and adopts international labor standards in the form of conventions and recommendations, covering areas such as freedom of association, collective bargaining, child labor, forced labor, and non-discrimination.
- Technical Assistance and Capacity Building: The organization provides support to member states in enhancing their labor administration, labor inspection, employment policies, and social protection systems.
- Monitoring and Supervision: The ILO monitors the application of international labor standards in member states, offering guidance and assistance in their implementation.
- Research and Knowledge Sharing: The organization conducts research, collects data, and disseminates information on labor-related topics, facilitating evidence-based policy-making and dialogue.
- The ILO plays a critical role in promoting decent work, social justice, and labor rights worldwide, fostering cooperation among its 187 member states to address labor-related challenges and achieve sustainable development.
- The ILO headquarters are located in Geneva (Switzerland).
How the Government Can Generate Employment Through Universal Healthcare

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As India approaches the 2024 elections, highlighting healthcare as a strategic investment rather than a fiscal burden can drive employment generation, bolster economic growth, and foster sustainable development.
Context:
- With India gearing up for the upcoming general elections, recognizing healthcare as a crucial investment for national well-being and prosperity is essential.
- Despite its pivotal role, healthcare tends to be sidelined in political discussions, necessitating a shift in focus.
- Rather than perceiving healthcare as a financial burden, it should be considered a strategic investment.
- Embracing healthcare as an investment offers substantial returns, contributing to human capital development, economic progress, and sustainable development.
What is Universal Health Care (UHC)?
- Universal Health Care (UHC) embodies the principle that everyone should have access to quality healthcare regardless of financial situation.
- It is regarded as a fundamental measure for promoting human equity, security, and dignity.
- UHC has gained widespread acceptance as a primary goal of public policy globally, with numerous countries successfully implementing it, including wealthier nations and emerging economies like Brazil, China, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- World Health Organization (WHO) defines universal healthcare as “all people and communities can use the promotive, preventive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative health services they need, of sufficient quality to be effective, while also ensuring that the use of these services does not expose the user to financial hardship.”
Challenges in Implementing Universal Health Care (UHC):
- Inequitable Access to Health Insurance: Disparities in health insurance coverage persist, with the lowest wealth quintile and marginalized sections facing limited access to insurance, as indicated by NFHS-5 results.
- Lack of Financial Protection: Despite initiatives like Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, high out-of-pocket expenses, especially in urban areas, pose financial risks. NFHS data highlights significant disparities in expenditure across states.
- Inclusion and Exclusion Errors in Health Insurance Policies: Inaccuracies in health insurance policies, including PMJAY, lead to the inclusion of ineligible and exclusion of eligible households, affecting coverage effectiveness.
- Availability of Services: While PMJAY enlists hospitals, a significant portion is in the private for-profit sector, potentially limiting access to underserved areas.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Insufficient healthcare facilities, equipment, and medical supplies hinder UHC implementation, compounded by a shortage of specialists in CHCs.
- Poor Health Education: Limited awareness about preventive health measures contributes to preventable illnesses, emphasizing the need for improved health education and promotion.
Steps For Achieving Universal Health Care (UHC):
- Increase in Public Health Expenditure: Commitment to allocate 2.5% of GDP to health by 2025 is crucial.
- However, the current central budget allocation for 2024-25 falls short at 28%.
- Strategic Partnerships: The government must forge partnerships and incentivize the private sector to bridge healthcare gaps.
- Initiatives like Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) illustrate this collaborative approach, covering over 60 crore people.
- Reimbursement Rates Correction: Private sector participation is hindered by low reimbursement rates.
- Differential pricing based on clinical excellence and infrastructure investment can encourage participation.
- Infrastructure Development: Addressing the deficit of nearly 24 lakh hospital beds requires increased private sector investment, especially in tier 2 and 3 cities.
- National Priority Status for Healthcare: Designating healthcare as a national priority sector can unlock funding opportunities and incentives, fostering growth and development.
- Strengthening Primary Healthcare: Enhancing Health and Wellness Centers and including OPD care in health insurance coverage will improve health outcomes and reduce secondary and tertiary care burdens.
- Prevention and Control of NCDs: Prioritizing interventions at the primary healthcare level can significantly reduce the burden of non-communicable diseases, preventing complications and hospitalizations.
- Boosting Private Investment: Encourage and incentivize private sector investment in healthcare infrastructure, technology, and services to expand coverage and enhance healthcare accessibility and affordability for all citizens.
How Government can Generate Employment Through UHC in India?
Expanding the Healthcare Workforce: Universal healthcare will significantly increase the demand for healthcare professionals, creating millions of new jobs. This includes doctors, nurses, paramedics, technicians, pharmacists, and other support staff. The government can address this need by:
- Scaling Up Medical Education: Increased investment in medical colleges and nursing schools is crucial.
- This includes establishing new institutions, expanding existing ones, and introducing scholarship programs to attract talent.
- Standards for medical education must be maintained to ensure a high-quality workforce.
- Skill Development Initiatives: Developing a robust skill development ecosystem specific to healthcare is essential.
- This involves creating standardized training programs for various healthcare professions.
- Skill development should not be limited to clinical skills but also encompass areas like communication, empathy, and public health awareness.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Competitive salaries, loan repayment programs, and career progression opportunities can incentivize students to pursue healthcare careers.
- Additionally, considering the rural-urban divide, special incentives like higher pay and improved living conditions can attract healthcare professionals to serve in underserved areas.
Building a Robust Healthcare Infrastructure: Universal healthcare necessitates a well-developed healthcare infrastructure. This translates to significant job creation across various sectors:
- Infrastructure Development: Building new hospitals, clinics, diagnostic centers, and public health centers requires construction workers, engineers, architects, and technicians.
- Medical Equipment Manufacturing: Increased demand for medical equipment, from basic diagnostic tools to advanced technology, can incentivize local manufacturing.
- This can create numerous jobs in production, maintenance, and research & development.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Universal healthcare will significantly raise the demand for pharmaceuticals.
- This can boost domestic production, generating jobs in manufacturing, distribution, and research & development.
The Role of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs):
- The government cannot shoulder the entire responsibility alone. PPPs can play a vital role in expanding healthcare infrastructure and creating job opportunities:
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaboration with private hospitals and clinics can leverage existing infrastructure and expertise.
- The government can purchase services from the private sector, ensuring wider reach and quality care, while creating jobs within these institutions.
- Incentivizing Expansion: Tax breaks, subsidies, and streamlined licensing processes can incentivize private players to expand their facilities and hire more staff.
- This creates a multiplier effect, leading to job creation in construction, logistics, and other associated sectors.
Technology and its Role in Employment: Technology holds immense potential to improve healthcare delivery and create new job opportunities:
- Telehealth and Digital Health Records: Investment in telemedicine infrastructure and digital health records can create jobs in IT, data management, and cybersecurity.
- Additionally, telemedicine can bridge the gap in rural healthcare, requiring trained personnel to operate these services.
- Medical Informatics: The use of big data and analytics in healthcare will require skilled professionals to collect, analyze, and interpret data to improve healthcare delivery and outcomes.
Conclusion
Universal healthcare in India can be a transformative force, not just for public health, but also for the nation's economic landscape. By strategically investing in workforce development, fostering public-private partnerships, and embracing technological advancements, India can unlock a vast employment potential. This not only creates a win-win for job creation and healthcare access but also paves the way for a healthier and more prosperous future for all Indians.
India's Declining Fertility Rate: Unveiling Opportunities Amidst Change

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The projection by the UN Population Division is that India will have a population of close to 1.7 billion by 2065 before it starts declining.
Context:
- In recent findings, The Lancet has projected a decline in India's Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to 1.29 by 2051, contrasting with the government's technical group estimate of 1.94 for 2021-2025, and 1.73 for 2031-2035.
- Additionally, the UN Population Division predicts India's population will be near 1.7 billion by 2065, surpassing The Lancet's projections.
- These diverging forecasts suggest that India's population may stabilize below 1.7 billion well before 2065.
Insights into Demographic Projections:
- According to the UN Population Division, India is expected to approach a population of nearly 1.7 billion by 2065, followed by stabilization. In contrast, The Lancet report forecasts a decline in the total fertility rate (TFR) to 1.29 by 2051.
- These projections signal a significant evolution in India's population dynamics, suggesting broader implications beyond population size.
- Government projections and data from NFHS 5 further corroborate this trend, indicating a declining trajectory in the TFR and hinting at the possibility of population stabilization occurring sooner than expected.
Implications of Decreasing Total Fertility Rate (TFR):
- Economic Impact: The decline in TFR alters the age distribution, resulting in fewer children and more working-age adults.
- Initially, this demographic shift presents an economic opportunity, fostering growth through increased productivity and surplus income.
- Dependency Ratio: A reduced TFR lowers the dependency ratio, lessening the burden on the working-age population to support dependents.
- This enhances economic productivity and allows for better resource allocation towards development endeavors.
- However, aging populations may necessitate adjustments in healthcare and social welfare policies.
- Labour Market Dynamics: Demographic changes influence employment patterns and wage structures.
- A larger working-age cohort relative to dependents may increase labor supply, affecting wage levels.
- Shifts from agriculture to other sectors may alter employment opportunities and skill requirements.
- Social Welfare and Healthcare: Aging populations due to declining fertility rates require tailored social welfare and healthcare services.
- This includes pension schemes, long-term care facilities, and healthcare programs addressing age-related ailments, essential for ensuring the well-being of the elderly.
- Education and Human Capital: Decreasing TFR reduces the demand for primary and secondary education infrastructure.
- However, investments in higher education and skill development become crucial to equip the smaller cohort of young adults with the necessary skills for a competitive workforce.
How India’s Decreasing Fertility Rate Poses Advantages:
- Enhanced Labor Productivity: A declining total fertility rate (TFR) results in a demographic dividend, with a larger proportion of the population in the working-age bracket compared to dependents.
- This surplus labor force can drive heightened productivity across various sectors, fostering innovation, specialization, and overall economic growth.
- Capital Accumulation and Investment: Lower fertility rates prompt households to channel more resources towards the education and well-being of fewer children.
- This leads to increased savings and investment at the household level, facilitating capital formation and investments in critical areas such as infrastructure, technology, and human capital.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Decreasing TFR necessitates a shift in resource allocation away from childcare and education expenses for larger families towards investments in education, skill development, and healthcare for a smaller number of children.
- This reallocation optimizes the utilization of public funds and private investments, fostering human capital development and long-term productivity gains.
- Regional Development and Urbanization: Declining fertility rates often coincide with urbanization and regional development, with urban centers emerging as economic hubs.
- The concentration of populations in urban areas promotes economies of scale, knowledge sharing, and networking opportunities, stimulating entrepreneurship and industry growth.
- International Competitiveness: A transition to lower fertility rates enhances a nation’s international competitiveness by cultivating a younger, better-educated workforce.
- Such a workforce is more adept at adapting to technological advancements, competing in global markets, and attracting foreign investment.
- Additionally, a favorable demographic profile can strengthen a country’s creditworthiness, investor confidence, and long-term economic resilience.
Way Forward:
- Empowering Women and Marginalized Communities: Prioritize skill development initiatives, especially targeting women and underprivileged groups, to adapt to demographic shifts.
- While declining fertility rates may ease pressure on educational systems, efforts must focus on reducing dropout rates in higher education and promoting women's workforce participation.
- Sectoral and Geographical Workforce Redistribution: Respond to workforce transitions from agriculture to industrial and service sectors by implementing skill development programs, particularly for marginalized populations.
- Facilitate spatial redistribution of labor, especially north-south migration, to balance labor markets, enhance working conditions, and promote wage equality.
- Strengthening Healthcare Preparedness: With increasing life expectancy, anticipate challenges associated with an aging population and rising healthcare needs.
- Develop robust healthcare infrastructure and formulate policies tailored to address the requirements of the elderly, ensuring effective utilization of the demographic dividend.
Conclusion
India stands at a crucial crossroads in its socio-economic evolution marked by its demographic transition. Addressing the challenges and opportunities inherent in this transition demands strategic policy interventions, emphasizing skill development, gender equality, labor reallocation, and healthcare readiness. By navigating this transition with foresight and flexibility, India can unlock its full potential for long-term growth and development, positioning itself effectively on the global landscape.
Ensuring Democracy: When Governments Listen to the Election Commission
- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission (EC) is extremely reasonable in matters that affect public welfare and the Government, and investigative agencies must respect that.
Context:
- Recent concerns raised by two former heads of the poll panel have shed light on the actions of tax agencies during election periods.
- In a democracy, free and fair elections are fundamental, safeguarding citizens' rights to freely choose their representatives without external pressure.
- Given the significance of preserving the integrity of the electoral process, it is crucial to scrutinize actions that could potentially disrupt this process.
- Such actions include the issuance of tax demands or IT notices to political parties, prompting a closer examination of precedents where the Election Commission intervened to maintain a fair and balanced electoral environment.
Impact of IT Notices on Opposition During Election Period:
- Disruption of Level Playing Field (LPF) Through Financial Interference: The issuance of IT notices by tax agencies during election campaigns may be interpreted as efforts to undermine the democratic process by targeting specific political entities.
- Freezing accounts, debiting funds, or issuing notices during this crucial period can significantly disrupt the financial resources and operational capacities of certain parties, thereby skewing the electoral landscape in favor of others.
- Such interference compromises the core principles of democracy and electoral fairness, eroding public confidence in the integrity of the electoral process.
- Influence on Voter Perception: The timing of these actions raises concerns about their potential impact on voter perceptions and election outcomes.
- Voters may perceive such actions as politically motivated or aimed at influencing the electoral results, casting doubts on the fairness and impartiality of the electoral process.
- Preserving the principles of neutrality, transparency, and fairness is vital in upholding democratic ideals and ensuring elections truly reflect the will of the people.
- Operational Hurdles: Raids and enforcement activities by tax agencies pose significant operational challenges for political parties, diverting their focus and resources away from election campaigning.
- Parties may find themselves compelled to address legal matters, respond to inquiries, and navigate tax regulations complexities, detracting from their ability to engage with voters and advocate their platforms effectively.
- Undermining Confidence in the Electoral Process: The perception that tax agencies target specific parties or candidates during elections can undermine public trust in the fairness and impartiality of the electoral process.
- Such actions may be viewed as politically driven attempts to sway election outcomes, fostering skepticism about the legitimacy of the electoral process and the credibility of election results.
- Impact on Democratic Participation: Financial and operational challenges resulting from enforcement actions can discourage democratic engagement and participation among voters.
- Perceived unfairness or bias in the electoral process may lead citizens to disengage from the democratic process, fostering disillusionment and apathy toward democratic participation.
Why Actions Against CMs, Congress Can Wait?
- Traditionally, the Election Commission (EC) has adhered to the principle of postponing any actions that can be deferred until after the conclusion of elections.
- It prompts a crucial question: would there be any significant harm in postponing these actions?
- In the current scenarios involving the arrest of two chief ministers and the issuance of IT notices, including the freezing of accounts of an opposition party, delaying these actions until after the elections would likely result in no irreparable harm.
- Conversely, proceeding with these actions during the election period could inflict irreparable damage on the two affected parties by severely hampering their electoral campaigns, both physically and financially.
Actions Taken by the Elections Commission (EC) Against Governments and Central Agencies to Preserve Level Playing Field (LPF):
- Addressing Bias or Partiality: The EC has actively intervened to uphold fair and impartial elections, particularly in cases where central agencies faced allegations of bias or partiality.
- During the 2019 Lok Sabha elections, the EC urged the Enforcement Directorate (ED) to maintain impartiality following complaints from opposition parties about the perceived misuse of central agencies by the ruling party.
- Emphasizing Neutrality and Impartiality: The EC consistently underscores the principles of neutrality, impartiality, and non-discrimination in all enforcement actions during election periods.
- Its commitment to maintaining the integrity of the electoral process is evident through its insistence on fair treatment for all parties involved.
- Balancing Public Welfare with Electoral Neutrality: While ensuring fairness, the EC also demonstrates pragmatism in matters affecting public welfare.
- For instance, during state elections, it permitted the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas to announce a national reduction in petrol prices, deeming it beneficial to the wider public interest.
- However, proposals such as increases in minimum support prices of certain foodgrains, perceived as potentially influencing voters, are disallowed during election periods to maintain electoral neutrality.
- Promoting Transparency in the Electoral Environment: The EC's interventions aim to curtail the misuse of office by political leaders and ministers, fostering a transparent and equitable electoral environment.
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) serves as a pivotal instrument in this endeavor, imposing restrictions on ruling parties to prevent undue advantages.
- Providing Guidance to Political Entities: While primarily focusing on individuals, the EC also advises political parties to ensure adherence to the code of conduct.
- For example, during overlapping budget sessions and election periods, state governments are encouraged to adopt a "vote on account" approach to avoid contravening the MCC with new schemes or projects.
- EC's Influence in Goa By-Election, 2012: An illustrative instance of the EC's influence is its intervention in a by-election in Goa in 2012, where the Chief Minister intended to induct a probable candidate into the Council of Ministers before the election.
- Despite possessing constitutional authority, the Chief Minister deferred the induction upon the EC's advice, acknowledging the moral authority of the Model Code of Conduct.
- This exemplifies the delicate balance between various authorities in a parliamentary democracy, reinforcing India's electoral processes as models of integrity and fairness globally.
Conclusion
The Election Commission's proactive engagement with central agencies, advocating for the postponement of actions such as raids, freezing of accounts, and issuance of tax demands until after elections, serves as a cornerstone in upholding the principles of free and fair elections.
By intervening in such matters, the Election Commission reinforces its commitment to ensuring an impartial electoral process, reassuring voters of the integrity and fairness of elections.
Ultimately, safeguarding the integrity of elections is paramount to preserving democracy and fostering public trust in the electoral process.
Heat Waves and its Impacts in India

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecast a harsh and arid summer over a majority of regions of the country during April- June, with a high probability of heatwave episodes lasting as long as 10 to 20 days during the period.
Recent Prediction by India Meteorological Department (IMD):
- Extreme Heat Outlook: India is anticipated to face extreme heat from April to June, with central and western regions likely to be most affected.
- Expectations of 10 to 20 heatwave days across the country, exceed the normal range of four to eight days.
- Regions including Gujarat, central Maharashtra, north Karnataka, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, north Chhattisgarh, and Andhra Pradesh are forecasted to experience severe heatwaves in April.
- Pre-Monsoon Rainfall Performance: Below-average pre-monsoon rainfall is expected this month, particularly impacting coastal, eastern, and southern India.
- El Nino Conditions: El Nino conditions, marked by abnormal sea surface warming in the equatorial Pacific Ocean since last June, have the potential to reduce rainfall and increase temperatures, both locally in India and globally.
- Despite El Nino conditions easing after peaking in December, persistent warm conditions continue to elevate global temperatures.
- Recent Weather Conditions: February and March witnessed hotter-than-normal weather in southern India.
- Heatwave conditions were reported in Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Saurashtra-Kutch, and parts of Rajasthan during late March.
- Maximum temperatures soared to 42.6 degrees Celsius in areas such as Akola in Maharashtra and Phalodi in Rajasthan.
What are Heat Waves?
- Heatwaves entail prolonged periods of exceptionally hot weather, posing adverse effects on human health, the environment, and the economy.
- Given India's tropical climate, the nation is especially susceptible to heat waves, which have witnessed increased frequency and intensity in recent times.
What is the Criterion for Declaring a Heat Wave?
For Plains and Hilly Regions:
- Heatwave is recognized when the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C or higher for Plains and at least 30°C or higher for Hilly regions.
- Determined based on Departure from Normal Heat Wave:
- Departure from normal temperature ranges from 4.50°C to 6.40°C, with anything exceeding 6.40°C classified as a Severe Heat Wave.
- Alternatively, based on Actual Maximum Temperature Heat Wave:
- A heat wave is declared when the actual maximum temperature equals or exceeds 45°C, while a Severe Heat Wave is acknowledged if the actual maximum temperature equals or exceeds 47°C.
- Declaration occurs when the above criteria are met in at least 2 stations within a Meteorological subdivision for a minimum of two consecutive days, with the declaration taking effect on the second day.
For Coastal Areas:
- A heat wave may be identified when the maximum temperature departure from normal is 4.50°C or more, provided the actual maximum temperature registers at 37°C or higher.
Fatality Risk:
- While high temperatures alone may not be lethal, it's the conjunction of elevated temperatures and humidity, known as the wet bulb temperature, that renders heatwaves perilous.
- Increased moisture levels impede sweat evaporation and hinder body cooling mechanisms, leading to a rapid rise in internal body temperature, frequently resulting in fatal outcomes.
What are the Causes of Heatwaves?
- Global Warming: A primary factor driving heatwaves in India is global warming, a consequence of sustained increases in Earth's average temperature linked to human activities like fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial operations.
- Elevated temperatures and altered weather patterns can stem from this phenomenon.
- Rapid Urbanization: Rapid urban expansion and the proliferation of urban landscapes contribute to the "urban heat island effect."
- Urban areas, dense with population, structures, and concrete surfaces, absorb and retain heat, intensifying temperatures, particularly during heatwaves.
- El Nino Influence: El Nino events, characterized by Pacific Ocean warming, exert global climatic impacts, triggering shifts in temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
- The conclusion of a strong La Nina phase in the equatorial Pacific Ocean and the untimely onset of an El Nino event are anticipated factors contributing to the exceptionally hot forecast for the summer of 2023.
What are the Impacts?
- Health Effects: Swift escalation in heat exposure can disrupt the body's ability to regulate temperature, resulting in various ailments such as heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and hyperthermia, potentially leading to fatalities or hospitalizations.
- Water Resources Impact: Heatwaves exacerbate water scarcity issues in India, causing water bodies to dry up, diminishing water availability for agriculture and domestic use, and intensifying competition for water resources, fostering conflicts and influencing irrigation practices and water-reliant industries.
- Energy Impact: Elevated temperatures heighten demand for cooling, straining power grids and heightening the risk of blackouts, disrupting economic operations, reducing productivity, and adversely affecting vulnerable communities without reliable access to cooling amenities during heatwaves.
How to Mitigate Extreme Heat Wave Events?
- To mitigate the adverse effects of heat waves and climate change, a comprehensive action plan must be implemented at various levels:
- Heat Wave Action Plan: Develop a long-term plan to protect human lives, livestock, and wildlife by prioritizing effective adaptation strategies and robust disaster management policies.
- Ensure proper implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, with governments taking the lead and engaging multiple stakeholders.
- Implementing Climate Action Plans: Commit to the National Action Plan for Climate Change (NAPCC) for inclusive growth and ecological sustainability.
- Emphasize nature-based solutions that uphold ethical standards and promote intergenerational justice.
- Sustainable Cooling: Adopt passive cooling technology to create naturally ventilated buildings, reducing the urban heat island effect in residential and commercial areas.
- Consider adapting ancient Indian building designs, as recommended by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), to modern facilities.
- Heatwave Mitigation Plans: Implement measures to prevent heat-related fatalities, including providing access to water, oral rehydration solutions, shade in public spaces, flexible working hours, and accommodations for outdoor workers.
- Vigilant local administration and oversight by higher authorities are key to successful implementation.
- By implementing these strategies and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, we can create a more resilient future that effectively addresses the challenges posed by heat waves and climate change.
Indian Meteorological Department (IMD):
- India Meteorological Department is the country's National Meteorological Service.
- It deals with all matters relating to meteorology, seismology, and associated subjects.
- IMD is headquartered in Delhi and operates hundreds of observation stations across India and Antarctica.
- IMD units such as Forecasting Offices, Agrometeorological Advisory Service Centers, Hydro-meteorological Offices, Flood Meteorological Offices, Area Cyclone Warning Centers, and Cyclone Warning Centers are usually co-located with various observatories or meteorological centers.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
- It is responsible for forecasting, naming, and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northern Indian Ocean region, including the Straits of Malacca, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea, and the Persian Gulf.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Indian Government
India’s HIV/AIDS Response

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
April 1, 2004, marked a significant moment in India's fight against HIV/AIDS as Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) was introduced for Persons Living with HIV (PLHIV).
Context:
- April 1, 2004, stands as a landmark moment in India's approach to addressing the HIV/AIDS epidemic, as Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) was introduced for Persons Living with HIV (PLHIV).
- This initiative, conceived in response to the pressing issues of access and affordability, has emerged as a crucial intervention in the fight against the disease.
- As we commemorate this day, it is imperative to delve into the progression and significance of India's free ART program, shedding light on its transformative impact on the nation's response to the HIV/AIDS crisis.
HIV/AIDS's Emergence and Initial Challenges:
- Inception of a Global Health Crisis: The emergence of HIV/AIDS in the early 1980s signaled the onset of a widespread health emergency with profound implications for populations worldwide.
- Originally detected among groups in the United States, the disease swiftly traversed borders, reaching nations like India and beyond.
- This era was characterized by uncertainty, anxiety, and a lack of comprehension regarding the novel virus, initially dubbed GRID (Gay-Related Immune Deficiency), later renamed HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and its associated illness AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
- Absence of Effective Treatments Resulting in Dire Consequences: During the initial stages of the epidemic, HIV/AIDS was synonymous with a dire prognosis, largely due to the absence of viable treatment options.
- Marginalized communities, including men who have sex with men, intravenous drug users, and commercial sex workers, bore the brunt of the disease's impact.
- However, as time progressed, it became evident that HIV/AIDS transcended boundaries of gender, sexual orientation, and socioeconomic status, affecting individuals from diverse backgrounds.
- Pervasive Social Stigma: In addition to its grave health implications, HIV/AIDS precipitated significant social stigma and discrimination.
- Individuals living with HIV/AIDS encountered marginalization, employment loss, and social exclusion from both their communities and families.
- This pervasive stigma compounded the challenges associated with managing HIV/AIDS and impeded effective epidemic control efforts.
- Limited Treatment Accessibility and Exorbitant Costs of Available ART: Despite the escalating recognition of HIV/AIDS as a global health threat, access to treatment remained scant, particularly in low- and middle-income nations such as India.
- The approval of the first antiretroviral drug, AZT (zidovudine), by the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) in March 1987 marked a significant milestone.
- HAART (Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy) represented a breakthrough in disease management, combining multiple antiretroviral drugs to suppress viral replication and bolster immune response.
- However, the exorbitant expenses associated with HAART, reaching up to $10,000 annually per patient, rendered it inaccessible to the majority of individuals living with HIV/AIDS, especially those residing in resource-constrained settings.
The Introduction of Free ART in India and its Impact:
- In response to the pressing issues of limited access and affordability of HIV/AIDS treatment, the Indian government embarked on a significant initiative.
- On April 1, 2004, the government initiated the provision of Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) for Persons Living with HIV (PLHIV).
- The introduction of Free ART aimed to dismantle barriers to treatment and extend life-saving medication to all PLHIV, irrespective of their financial means.
- By offering ART at no cost, the government endeavored to ensure that access to treatment would not be hindered by financial constraints, thereby addressing a crucial gap in healthcare accessibility.
Its Role in Curbing the Epidemic
- Enhanced Treatment Accessibility: Over the past two decades, the initiative has undergone substantial expansion, witnessing a surge in the number of ART centers from less than 10 to approximately 700, catering to around 1.8 million PLHIV.
- This proliferation has facilitated heightened treatment access for individuals living with HIV/AIDS nationwide, including those residing in remote and underserved regions.
- A notable outcome of the Free ART endeavor has been the remarkable enhancement in health outcomes observed among PLHIV.
- Significant Reduction in Mortality Risk and Transmission Rates: Timely and effective treatment accessibility has transfigured HIV/AIDS from a dire prognosis to a manageable chronic ailment for many.
- By suppressing viral load and bolstering immune response, ART has not only extended the lifespan of PLHIV but also augmented their quality of life.
- Moreover, the Free ART initiative has played a pivotal role in curbing HIV transmission rates by ensuring treatment access for PLHIV, thereby thwarting virus dissemination within communities.
- Research indicates that efficacious ART can substantially mitigate HIV transmission risk, contributing to the overall decline in HIV prevalence.
- Broader Societal Benefits: Beyond its direct impact on individuals grappling with HIV/AIDS, the Free ART initiative has yielded wider societal advantages.
- By mitigating the disease burden and forestalling fresh infections, the initiative has alleviated the societal and economic repercussions of HIV/AIDS on families, communities, and healthcare systems.
- Supplementary Measures and Patient-Centric Approach: The success of India's ART program extends beyond free medication provision.
- Complementary initiatives, such as complimentary diagnostic services, prevention of parent-to-child transmission programs, and management of opportunistic infections, have played pivotal roles in curbing the HIV epidemic.
- Furthermore, the program has adopted a patient-centric strategy, furnishing stable PLHIV with two to three months' worth of medicines to minimize clinic visits and enhance treatment adherence.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
- Delayed Initiation and Attrition in Care: A notable portion of patients presents with advanced HIV illness, evidenced by low CD4 counts, impacting treatment efficacy.
- Furthermore, attrition in care remains a concern, as some patients discontinue treatment upon feeling well, leading to interruptions and potential drug resistance development.
- Logistical Hurdles and Infrastructure Deficiencies: Remote and underserved regions, including those with rugged terrain, encounter hurdles in accessing vital medications and healthcare provisions.
- Fortifying the logistical network and infrastructure for dispensing ART drugs is imperative to sustain uninterrupted treatment access for all PLHIV.
- Involvement of the Private Sector: While the public sector assumes a pivotal role in HIV/AIDS treatment provision, fostering collaboration with the private sector is crucial.
- Leveraging the resources and infrastructure of private healthcare entities can expand ART accessibility and reach marginalized populations, including urban dwellers.
- Interconnected Health Program Integration: Augmenting integration with other health initiatives, encompassing hepatitis, non-communicable ailments, and mental health, holds paramount importance.
- Given PLHIV's propensity for concurrent ailments, comprehensive and integrated healthcare services necessitate intersectoral collaboration within the healthcare spectrum.
- Realization of Ambitious NACP Phase 5 Objectives: The ongoing fifth phase of the National AIDS Control Programme (NACP) sets forth ambitious targets, envisaging an 80% reduction in annual new HIV infections and AIDS-related mortalities by 2025.
- Achieving these milestones demands concerted endeavors to escalate testing, enhance treatment coverage, and secure viral suppression among PLHIV.
Conclusion
India's free ART initiative has successfully combated HIV/AIDS, demonstrating the power of accessible healthcare. Its achievements emphasize the importance of political will, funding, community engagement, and patient-centered care in tackling infectious diseases. Lessons from this program will guide future public health endeavors, improving outcomes for all
Prioritizing Africa in India's Global South Perspective
- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As Africa houses three-fourths of humanity and over 39 percent of the global GDP, there's a growing call to reform existing structures towards a more inclusive and representative system focused on development.
Context:
- President of India, Droupadi Murmu's trip to Mauritius underscored the significance of India's ties with African nations, particularly emphasizing Mauritius' role as a pivotal partner in the Indian Ocean Region.
- This visit reflects India's expanding involvement in Africa, characterized by joint initiatives in community development and the inauguration of critical infrastructure projects.
- As India endeavors to bolster its standing within the Global South, it becomes imperative to comprehend the diverse facets of the India-Africa relationship, analyzing the potential opportunities it offers and the necessity for enhanced collaboration.
Analyzing India's Comprehensive Engagement with Africa:
- Investments and Trade: India's commitment to Africa is evidenced by its burgeoning investments, which soared to $98 billion in 2023, reflecting its confidence in Africa's economic potential and its dedication to nurturing enduring partnerships.
- Bilateral trade between India and Africa has surged to $100 billion, spanning diverse sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, technology, and services, catalyzing economic growth and diversification in both regions.
- Developmental Projects: India's involvement in Africa extends to diverse developmental initiatives, encompassing infrastructure, healthcare, education, agriculture, and renewable energy sectors.
- By spearheading such projects, India not only fosters economic progress in Africa but also cements diplomatic ties and goodwill.
- Export of Scalable Solutions: Drawing on its expertise in cost-effective and scalable solutions, India has played a pivotal role in addressing various challenges confronting African nations.
- Through initiatives spanning from eco-friendly housing to solar energy technology, Indian entities contribute to poverty alleviation and sustainable development, bolstering India's reputation as a dependable partner committed to mutual progress.
- Mutual Prosperity and Development: India and Africa mutually benefit by capitalizing on each other's strengths and resources.
- While India's investments stimulate economic growth, generate employment, and facilitate technology transfer in Africa, African markets offer India access to vital natural resources, new markets, and strategic collaborations.
- This symbiotic relationship fosters economic resilience, innovation, and inclusive growth in both regions.
The Strategic Significance of India's Advocacy for Africa's Representation in Global Arenas:
- Enhancing Africa's Representation and Influence India's active advocacy for Africa's presence in global governance platforms underscores its dedication to amplifying the voices of developing nations.
- Recognizing Africa's substantial population and economic contribution, India emphasizes the necessity of its representation for a fairer and more inclusive international system.
- Initiatives like supporting the African Union's inclusion in the G20 highlight India's acknowledgment of Africa's pivotal role in shaping global agendas.
- Driving Reform and Adaptation Amidst evolving global challenges, there's a growing impetus for adapting governance structures to address emerging issues and foster sustainable development.
- India's push for Africa's participation in global forums reflects its commitment to reforming institutions like the United Nations, International Monetary Fund, and World Bank to better reflect the interests of developing nations.
- Fostering Strategic Partnerships India's advocacy for Africa's representation in global governance is not only driven by altruism but also strategic considerations.
- Recognizing Africa's increasing influence, India seeks to cultivate strategic partnerships with African nations to advance its global interests.
- By supporting Africa's involvement in decision-making processes, India enhances its diplomatic influence and strengthens its position as a leading voice in the Global South.
- Advancing Development Goals: Aligned with its broader development agenda, India's advocacy for Africa's representation in global governance focuses on priorities such as poverty alleviation, sustainable development, and inclusive growth.
- By championing Africa's interests in international forums, India aims to address systemic inequalities and advocate for policies benefiting vulnerable populations.
- This advocacy spans various domains, including trade, finance, climate change, and peace and security, reflecting India's commitment to fostering a more equitable world order.
Exploring India Africa's Rich Historical Bonds and Charting a Path for Future Collaboration:
- Legacy of Colonialism and Struggle for Liberation: India's historical relationship with Africa is deeply rooted in its fight against colonialism, with both regions sharing similar experiences of exploitation and oppression under European rule.
- India's support for African liberation movements during the colonial era solidified a bond based on shared values of freedom and sovereignty.
- Cultural Exchange and People-to-People Connections: Centuries of interaction between Indian traders, scholars, and missionaries with African societies have left enduring cultural legacies, enriching both regions' traditions and languages.
- Today, vibrant Indian communities contribute to Africa's cultural diversity and economic vitality, fostering mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Commitment to Development and Capacity-Building: India's engagement with Africa in development cooperation dates back to its early days of independence, with a focus on providing technical assistance and capacity-building support.
- Continued collaboration in sectors such as education, healthcare, agriculture, and infrastructure underscores India's enduring commitment to Africa's progress and prosperity.
- Exploring Economic Opportunities and Innovation: With Africa emerging as a dynamic economic hub, India stands poised to deepen its economic ties by leveraging historical bonds and cultural affinities.
- Opportunities abound for enhanced trade, investment, and technology exchange, benefiting both regions and driving sustainable development.
- Forging Strategic Partnerships in a Changing Global Landscape: Amid geopolitical shifts, India and Africa have the chance to strengthen strategic alliances grounded in shared values and interests.
- By aligning diplomatic efforts and leveraging their collective strengths, both regions can wield greater influence on global issues like climate change, terrorism, and pandemics, fostering a more equitable and inclusive world order.
Conclusion
The multifaceted partnership between India and Africa presents abundant prospects for economic, political, and social collaboration. In India's pursuit of leadership within the Global South, fostering closer ties with African nations emerges as imperative. Amidst the swiftly evolving global landscape, the alignment between India and Africa signifies a potential for mutual prosperity and advancement
Understanding India’s Coal Imports

- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In recent years, the combination of unpredictable weather patterns and rapid economic growth has resulted in significant spikes in electricity demand, posing a challenge to reliably meet the escalating requirements.
Background:
- India has grappled with the looming threat of electricity shortages in recent years, particularly exacerbated by rising temperatures amplifying the power demand.
- While discussions on this matter typically revolve around the deficit in domestic thermal coal and the need for imports, a more thorough investigation uncovers intricate challenges concerning logistics and regulatory interpretation.
- Therefore, it is imperative to delve into these dimensions, shedding light on the complexities of the situation and seeking solutions to tackle the root causes.
What are the Primary Causes of Domestic Thermal Coal Shortages?
- Transportation Infrastructure Deficiencies: A critical challenge lies in the inadequacy of transportation infrastructure, notably the railway network, which predominantly facilitates coal transportation across India.
- Despite substantial coal production, the limited capacity of railways often hampers timely delivery to power plants, contributing to delays and inefficiencies in the coal supply chain.
- Geographical Disparities: Complicating matters, the distribution of coal mines and power plants across diverse regions adds another layer of complexity to logistics.
- Power plants situated far from coal mines encounter heightened logistical hurdles, facing difficulties in securing a consistent coal supply due to increased transportation time and costs.
- Storage and Handling Limitations: Insufficient storage and handling infrastructure at both mines and power plants exacerbate challenges in managing demand and supply fluctuations.
- Inadequate storage capacity can lead to stockpiling issues, exacerbating delays and hindering efficient coal delivery.
Balancing Alternative Domestic Sources and Imports:
- Exploration of Alternative Domestic Sources: While alternative coal sources, like auctions organized by Coal India Ltd., present a viable domestic option, they often receive less attention compared to imports.
- These auctions enable power plants to procure coal domestically, albeit potentially at higher prices, yet remain overlooked in favor of imported coal.
- However, auctions offer a feasible alternative, particularly for plants not hindered by logistical constraints in accessing coal from auction sites.
- Narrow Focus on Imports: The discourse tends to prioritize imports as the default solution for coal shortages, neglecting the potential of domestic alternatives and failing to consider the broader implications of heavy reliance on imported coal.
- Cost Implications: Importing coal entails additional costs, including transportation, handling, and import duties, resulting in higher variable costs for coal-based electricity.
- These expenses are often transferred to consumers through elevated electricity tariffs, burdening both households and industries.
- Regulatory Interpretation: Misinterpretation of Ministry of Power advisories recommending coal imports as mandates further blur the distinction between alternative sources and imports.
- While these advisories may propose importing a certain percentage of coal, they should not be perceived as obligatory requirements but rather as guidelines to be tailored to each power plant's unique circumstances.
- Less Emphasis on Domestic Procurement Enhancement: The emphasis on imports sidelines opportunities to improve domestic coal procurement and distribution processes.
- Addressing logistical hurdles and streamlining administrative procedures could enhance the efficiency and reliability of India's domestic coal supply chain, potentially reducing the reliance on costly imports.
Regulatory Frameworks Influencing Responses to Electricity Shortages and Coal Procurement Strategies:
- Clarifying Advisory Interpretations: An ongoing challenge in regulatory considerations involves clarifying interpretations of advisories from government entities like the Ministry of Power.
- While these advisories may offer recommendations for addressing coal shortages, particularly through import suggestions, they should not be misconstrued as mandates.
- Misinterpretation can lead to unnecessary costs and burdens on consumers, as power plants may feel compelled to comply with import recommendations, disregarding potentially viable domestic alternatives.
- Forward-Thinking Regulatory Decision-Making: Regulatory bodies overseeing electricity generation and distribution must adopt a forward-thinking approach to decision-making.
- This entails comprehensive assessments of regulatory measures' implications on stakeholders, including consumers, power producers, and distribution utilities.
- Analysis should weigh the costs and benefits of various coal procurement strategies, encompassing factors like transportation costs, import duties, and environmental impacts.
- Customized Approaches for Diverse Plant Settings: Recognizing the varied challenges among power plants regarding coal shortages, regulatory bodies should tailor measures to each plant's specific circumstances.
- Pit-head plants, closer to coal mines, may have easier access to domestic coal and encounter fewer logistical constraints compared to plants situated farther away, necessitating heavier reliance on imports.
- Regulatory interventions should thus be nuanced and adaptable rather than uniformly applied.
- Balancing Cost-Efficiency and Reliability: Regulators face the critical task of balancing cost and reliability in electricity supply.
- While imports may offer prompt solutions to coal shortages, they incur substantial costs affecting consumers.
- Therefore, regulators must meticulously evaluate the potential cost savings of domestic procurement against the reliability and security of imported coal supply, ensuring transparency and equity in decision-making.
- Long-Term Planning and Sustainability Integration: Regulatory considerations should encompass long-term planning and sustainability objectives alongside immediate coal shortage mitigation.
- While addressing immediate needs is crucial, regulators must also contemplate the broader ramifications of coal procurement strategies on energy security, environmental sustainability, and renewable energy transition.
- This necessitates a forward-looking approach aligning short-term actions with long-term sustainability objectives, facilitating India's transition to a resilient and sustainable energy framework.
Conclusion
Addressing electricity shortages in India necessitates a nuanced approach that considers both logistical hurdles and regulatory complexities. While importing coal may offer a temporary solution, it does not tackle the fundamental logistics inefficiencies. India can better navigate the challenges of power generation by addressing root causes and implementing tailored solutions, ensuring a more effective response to evolving weather patterns and increasing demand for electricity
WTO’s Investment Facilitation Negotiations Are Not Illegal

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
One significant event during the 13th Ministerial Conference (MC13) of the World Trade Organization (WTO) in Abu Dhabi was the inability to ratify the agreement concerning investment facilitation for development (IFD). Despite garnering backing from over 70% of the membership, approximately 120 member countries, the agreement remained unadopted.
Context:
- The recent 13th Ministerial Conference (MC13) of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) in Abu Dhabi unfolded a notable occurrence as the agreement on investment facilitation for development (IFD) failed to gain adoption.
- Despite substantial backing from approximately 120 member countries, the IFD Agreement encountered resistance, particularly from India and South Africa.
- In light of these events, it becomes imperative to delve into India's opposition to the IFD Agreement and its apprehensions regarding its alignment with WTO principles, especially concerning the intertwining of investment with trade and the procedural aspects of negotiation surrounding the agreement.
What is the IFD agreement?
- The Investment Facilitation for Development (IFD) Agreement is a legally binding framework that aims to enhance investment flows and promote transparency in regulatory processes.
- Finalized in November 2023, the agreement is the result of plurilateral negotiations initiated by 70 countries under the Joint Statement Initiative at the WTO in 2017.
- Despite initial opposition from some countries, including India, the IFD Agreement gained significant support, with 120 nations pushing for its inclusion as a plurilateral agreement within Annex 4 of the WTO Agreement.
- Although the WTO is primarily a multilateral trade organization, the allowance for plurilateral agreements under Article II.3 of the WTO Agreement sets the stage for binding commitments among participating WTO member countries.
Key objectives of the IFD Agreement include:
- Regulatory Transparency: Increasing openness in investment policies and procedures to instill confidence and predictability in the investment landscape.
- Streamlined Administrative Procedures: Simplifying investment-related processes and reducing red tape to attract and facilitate foreign investment inflows.
- By creating a stable and transparent environment for international investments, the IFD Agreement aims to contribute to economic growth and development, catalyzing cooperation among participating WTO members without imposing obligations on non-signatory countries.
What are India’s Concerns?
- India's resistance to the Investment Facilitation for Development (IFD) Agreement stems from concerns regarding its alignment with the WTO framework and the process undertaken to integrate it into the WTO rulebook.
- Given the WTO's dispute settlement mechanism, which solely permits state-to-state legal claims, incorporating Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) appears infeasible.
- This challenge contributed to India and South Africa's significant efforts to prevent the IFD Agreement from becoming an official component of WTO regulations.
India's primary apprehensions surrounding the IFD Agreement:
- Integrating Investment into the WTO: India questions the compatibility and relevance of investment policies within the WTO's scope, particularly when considering existing platforms dedicated to investment negotiations.
- Process-related Concerns: India argues that the procedure for incorporating the IFD Agreement into the WTO rulebook must be carefully scrutinized, ensuring adherence to established protocols and consensus-building among all member nations.
- While the actual content of the IFD Agreement does not appear to be India's primary concern, the nation's stance underscores the importance of considering the broader implications of such agreements within the global trade and investment landscape.
- As the international community navigates the complexities of investment facilitation and regulatory reform, the debate surrounding the IFD Agreement will continue to shape the future of multilateral cooperation and the evolution of the WTO's mandate.
Is Investment a Suitable Component of the WTO Framework?
- India posits that investment's integration into the World Trade Organization (WTO) may not inherently translate to increased cross-border trade, contrasting with scholarly perspectives emphasizing the interconnectedness of trade and investment.
- Citing the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), it is highlighted that a substantial portion—70%—of international trade occurs within global value chains, underscoring the symbiotic relationship between trade and investment.
- Contemporary free trade agreements like the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership exemplify this integration, featuring comprehensive investment provisions encompassing facilitation and protection measures.
- Intriguingly, India's recent trade pact with the European Free Trade Association, despite including investment provisions focused on facilitation and promotion, underscores a pragmatic approach to incorporating investment elements, albeit with limitations.
Negotiating Process of the IFD Agreement:
- India has emphasized the absence of a negotiating mandate regarding investment discussions.
- India contends that the WTO's General Council's decision in 2004 ruled out talks on the nexus between trade and investment, a facet categorized under the 'Singapore issues' introduced during the 1996 WTO Singapore ministerial conference.
- These discussions were explicitly excluded from the Doha round of negotiations initiated in 2001.
- Additionally, India has pointed to the 2015 WTO Nairobi ministerial decision, which stipulates that launching negotiations on new issues multilaterally necessitates unanimous agreement among all member states.
- India argues that since consensus wasn't reached among all nations to commence negotiations on an IFD Agreement, the ensuing negotiations and the resultant text presented for adoption are deemed illegitimate.
Key Questions Surrounding the IFD Agreement:
- India's assertion of a negative mandate against initiating negotiations on the trade and investment relationship raises two critical queries warranting clarification.
- Firstly, does this negative mandate extend to all facets of investment, including facilitation?
- Notably, the shelved investment agreement proposed during the 1996 Singapore ministerial primarily addressed market access and investment protection, leaving ambiguity regarding whether the negative mandate encompasses all investment-related aspects within the WTO.
- Secondly, does the negative mandate solely pertain to launching negotiations on new issues in a multilateral context?
- The inquiry arises as to whether this prohibition extends to negotiations commenced on a plurilateral basis.
- The negotiations for an IFD agreement were instigated on a plurilateral, not multilateral, basis.
- Although Article X.9 of the WTO Agreement stipulates that adding an agreement to the existing set of Plurilateral Agreements listed in Annex 4 necessitates consensus exclusively, the agreement lacks provisions mandating consensus for initiating negotiations for a Plurilateral Agreement.
Way forward:
- As the primary regulatory body for international trade, the World Trade Organization (WTO) is responsible for updating existing rules and establishing new ones.
- However, reaching a consensus on decision-making within the WTO remains a significant challenge, often leading to legislative deadlock.
- In this context, Preferential Agreements (PAs), such as the proposed Investment Facilitation for Development (IFD) Agreement, can serve as catalysts for reinvigorating the WTO's legislative function.
- By fostering cooperation among subsets of WTO members, Preferential Agreements (PAs) can help circumvent the challenges of consensus-building within the broader organization.
- As India continues its ascent to become the world's third-largest economy, it is increasingly critical for the nation to reassess its defensive posture toward PAs.
- By recognizing the potential benefits of agreements like the IFD, India has the opportunity to demonstrate leadership on the global stage, support the revitalization of the WTO's legislative function, and contribute to a more collaborative and effective approach to international trade regulation.
Conclusion
The failure to ratify the IFD agreement at MC13 underscores the formidable challenges encountered by the WTO in navigating intricate matters such as investment facilitation. It underscores the divergent perspectives among member nations regarding the scope and nature of the WTO's role in governing global economic interactions. Closing these divergences becomes imperative for the WTO to adeptly address the evolving landscape of international trade and investment
Employment Scenario in India Grim - ILO

- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to the India Employment Report 2024 by the ILO and IHD, nearly 83% of the unemployed workforce comprises youth, with the percentage of educated unemployed youth more than doubling from 35.2% in 2000 to 65.7% in 2022.
India Employment Report 2024:
- The India Employment Report 2024, the third installment in the series of publications by the Institute for Human Development focusing on labor and employment concerns, is conducted in collaboration with the International Labour Organization (ILO).
- This report delves into the issue of youth employment, analyzing the evolving economic, labor market, educational, and skills landscapes in India over the past twenty years.
- It sheds light on recent trends in the Indian labor market, showcasing both positive advancements and enduring challenges, including those exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Key Insights from the India Employment Report 2024:
- Drawing from data sourced from National Sample Surveys and Periodic Labour Force Surveys spanning 2000 to 2022, the report offers a comprehensive analysis of employment trends and the present landscape.
Employment Trends & Current Scenario:
- Female labor market participation, after a notable decline in previous years, exhibited accelerated growth post-2019, particularly in rural regions.
- A noticeable trend in the Indian labor market is the gradual shift of the workforce from agriculture to non-farm sectors.
- Self-employment and casual employment dominate India's employment landscape, with approximately 82% of the workforce engaged in the informal sector, and nearly 90% informally employed.
- While wages for casual laborers saw modest growth from 2012 to 2022, real wages for regular workers stagnated or declined.
- Official surveys inadequately capture migration levels in India, expected to significantly rise along with urbanization in the future, reaching around 40% migration rate and a 607 million urban population by 2030.
Challenges of Youth Employment:
- Despite a sizable working-age population, India's youth demographic, accounting for 27% of the total population in 2021, is projected to decline to 23% by 2036.
- Each year, approximately 7-8 million youths join the labor force, presenting an opportunity for India to capitalize on the demographic dividend.
- Youth labor market participation has historically been lower than adults, primarily due to higher education enrollment rates.
- Youth unemployment witnessed a notable increase from 5.7% in 2000 to 17.5% in 2019, declining to 12.1% in 2022 post-lockdowns.
Recommendations:
- The report underscores five key policy domains for comprehensive action, focusing on both general employment enhancement and youth-specific interventions:
- Promoting job creation
- Enhancing employment quality
- Addressing labor market disparities
- Strengthening skills and active labor market policies
- Bridging knowledge gaps on labor market dynamics and youth employment.
What is the International Labour Organization (ILO)?
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations (U.N.) agency.
- The goal of the ILO is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labor standards.
- The ILO has 187 member states and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with approximately 40 field offices around the world.
- The standards upheld by the ILO are broadly intended to ensure accessible, productive, and sustainable work worldwide in conditions of freedom, equity, security, and dignity.
Understanding the ILO
- It was founded in 1919 under the League of Nations and incorporated into the U.N. as a specialized agency in 1946.
- The ILO is the first and oldest specialized agency of the U.N.
- The organization’s goal is to serve as a uniting force among governments, businesses, and workers.
- It emphasizes the need for workers to enjoy conditions of freedom, equity, security, and human dignity through their employment.
- The ILO promotes international labor standards through its field offices in Africa, Latin America, the Caribbean, the Arab States, Asia and the Pacific, and Europe and Central Asia.
- The organization provides training on fair employment standards, offers technical cooperation for projects in partner countries, analyzes labor statistics and publishes related research, and regularly holds events and conferences to examine critical social and labor issues.
- The ILO was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1969.
- The organization was recognized for improving fraternity and peace among nations, pursuing decent work and justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to developing nations.
- The labor standards set forth by the ILO have been published in 190 conventions and six protocols.
- These standards recognize the right to collective bargaining, attempt to eliminate forced or compulsory labor abolish child labor, and eliminate acts of discrimination concerning employment and occupation.
- As a result, the protocols and conventions of the ILO are a major contributor to international labor law.
Structure:
- A unique feature of the ILO is its tripartite character.
- The membership of the ILO ensures the growth of the tripartite system in the Member countries.
- At every level in the Organization, Governments are associated with the two other social partners, namely the workers and employers.
- All three groups are represented in almost all the deliberative organs of the ILO and share responsibility for conducting its work.
- The work of the Conference and the Governing Body is supplemented by Regional Conferences, Regional Advisory Committees, Industrial and Analogous Committees, Committee of Experts, Panels of Consultants, Special Conference and meetings, etc.
The three organs of the ILO are:
- International Labour Conferences: General Assembly of the ILO – Meets every year in June.
- Governing Body: Executive Council of the ILO. Meets three times a year in March, June, and November.
- International Labour Office: A permanent secretariat.
India & ILO:
- India is a founder member of the International Labour Organization, which came into existence in 1919.
- At present the ILO has 187 Members.
About the Institute of Human Development (IHD):
- Founded in 1998 under the patronage of the Indian Society of Labour Economics (ISLE), the Institute of Human Development (IHD) is dedicated to fostering a society that embraces an inclusive social, economic, and political framework, devoid of poverty and deprivation.
- IHD's core mission revolves around conducting research in diverse domains such as labor and employment, livelihood, gender, health, education, and various facets of human development.
- Through its endeavors, IHD seeks to generate knowledge and insights that contribute to the advancement of human welfare and societal well-being.
TB-Mukt Bharat India's Fight Against Tuberculosis
- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even though World TB Day (March 24) has passed, recognizing the needs and interests of patients and communities must form the basis of disease elimination.
What is Tuberculosis?
- Tuberculosis (TB) is an airborne bacterial infection caused by a type of bacteria called mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- The infection primarily attacks our lungs and if not treated early, permanent lung damage can result.
- Tuberculosis can also spread to other parts of the body such as the intestines, bones and joints, brain, skin, and other tissues of the body.
- It can be classified into two categories:
- Active tuberculosis (TB) and
- Latent tuberculosis (TB).
Causes of Tuberculosis (TB):
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis usually spreads from person to person through airborne droplets, which are produced when the infected person coughs, sneezes, speaks, or sings.
Signs & symptoms of Tuberculosis (TB):
- A person with latent Tuberculosis (TB) cannot spread the infection to others as it is not contagious and may not show symptoms because their immune system is protecting them from getting sick.
- However, latent TB can develop into active TB if that individual’s immune system cannot stop the bacteria from growing and starts showing symptoms such as:
- Bad cough that lasts for 3 weeks or longer
- Pain in chest
- Coughing blood or sputum
- Fever or night sweats
- Weight loss or no appetite
- Chills
- Weakness
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis (TB):
- Tuberculosis (TB) can be tested in two ways, namely skin test and blood test.
- These two tests only tell if a person has TB or not; if the test is positive then other tests are needed to check if it is latent TB or active TB, such as chest X-ray or CT, or acid-fast bacillus tests (sputum tests).
Treatment of Tuberculosis (TB)
- Both latent TB and active TB can be effectively treated with antibiotics, albeit requiring different durations of treatment.
- Complete adherence to medication is imperative for curing TB; failure to complete the prescribed course may lead to the recurrence of illness and increased difficulty in recovery.
- For latent TB, treatment typically involves a course lasting 3-9 months, comprising 1-2 antibiotics.
- While active TB necessitates a more extensive regimen, with doctors prescribing 2 to 4 or more antibiotics for 6-9 months or longer.
- Ensuring proper medication adherence is crucial for individuals with latent TB to prevent its progression to active TB.
- In many cases, significant improvement is observed within weeks of initiating treatment, with the infection becoming non-contagious.
- Therefore, completing the full course of medication is essential to safeguard oneself and others from tuberculosis.
What is drug-resistant Tuberculosis (TB)?
- Drug-resistant TB is when the bacteria that causes TB becomes resistant to some or all the medications.
- Once drug-resistant TB is developed, it is very difficult to treat it.
- It may require more and different medications with a longer period of treatment.
- Some injectable drugs can cause loss of hearing and balance problems.
Status of TB in India:
- India bears approximately 27% of the global burden of tuberculosis (TB), making it the country with the highest TB burden worldwide.
- Government of India aims to eliminate tuberculosis (TB) by 2025.
- The theme for World Tuberculosis Day (March 24) in 2024 was the same as in 2023 “Yes, we can end TB”, which reflects the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to eliminate TB by 2030.
Challenges Confronting India in TB Elimination:
- Drug-resistant TB Cases: India grapples with a substantial burden of drug-resistant TB, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB), necessitating more expensive, specialized drugs and prolonged treatment durations.
- Diagnostics and Case Detection: Accurate and timely TB diagnosis remains a challenge, particularly in areas lacking access to modern diagnostic tools, leading to reliance on older, less reliable methods.
- Poor Primary Healthcare and Infrastructure: Limited access to healthcare facilities, especially in rural and remote regions, results in delayed diagnosis and treatment, facilitating TB transmission within communities.
- Stigma and Awareness: Stigma surrounding TB may deter individuals from seeking timely healthcare, while inadequate awareness about the disease perpetuates its prevalence.
- Private Sector Engagement: With a significant portion of healthcare services provided by the private sector, effective TB control necessitates coordinated efforts and standardized treatment protocols between the public and private sectors.
- Treatment Adherence: Ensuring patient adherence to the full course of TB treatment, which involves prolonged antibiotic courses, poses a significant challenge.
- Vulnerable Populations: Certain demographics, such as migrant workers, urban slum dwellers, and individuals residing in overcrowded conditions, face heightened TB risks, requiring targeted interventions.
Initiatives by the Government of India to Eradicate TB:
- National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP): A National Strategic Plan (2017-25) aims to eliminate TB from India by 2025.
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (PMTBMBA): Introduced in 2022, this initiative provides community support to TB patients, offering nutritional, diagnostic, and vocational assistance.
- Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP): Launched in 1997, RNTCP has been continuously revised and strengthened to combat TB effectively.
- Universal Drug Susceptibility Testing (DST): Efforts have been intensified to ensure universal access to drug susceptibility testing, enabling early detection of drug-resistant TB strains for tailored treatment.
- Ni-kshay Portal: An online platform established to monitor notified TB cases effectively.
- Introduction of New Drugs: Drugs like Bedaquiline and Delamanid for treating drug-resistant TB are provided free of cost to TB patients.
- Research and Development (R&D) for Treatment: Studies are ongoing to explore shorter anti-tubercular drug courses, aiming to reduce treatment duration.
- Vaccine Development: Trials are being conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of vaccines such as Immuvac and VPM1002 in preventing TB, offering promising avenues for future TB prevention strategies.
Global Efforts to Eradicate TB:
- End TB Strategy: spearheaded by the World Health Organization (WHO), it provides a roadmap for countries to reduce TB incidence by 80%, and TB deaths by 90%, and eliminate catastrophic costs for TB-affected households by 2030.
- World Development Report (1993): Published by WHO, it highlighted TB treatment for adults as the most cost-effective among all developmental interventions.
- The Global Fund: a global initiative aimed at defeating HIV, TB, and malaria, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable future worldwide.
- The Stop TB Partnership: a collaborative effort involving expertise from diverse country, regional, and global partners, dedicated to transforming the TB landscape and achieving the goal of ending TB by 2030.
- Sustainable Development Goal 3: part of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, it targets to end the TB epidemic by 2030, reflecting a commitment to global health and well-being.
Way Forward:
- Development and Widespread Adoption of an Adult TB Vaccine: Prioritizing the research and development of an effective vaccine against TB for adults.
- Ensuring widespread distribution and utilization of the vaccine to bolster TB prevention efforts globally.
- Cost Reduction of Anti-TB Drugs: Implementing strategies to lower the production costs of essential anti-TB medications.
- Making these drugs more accessible and affordable to all individuals in need, regardless of economic status.
- Innovation in TB Treatment: Investing in research and development to create injection-free and orally-administered TB medications.
- Expanding treatment options to enhance patient compliance and improve treatment outcomes.
- Integration of AI-Assisted Radiology: Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) technology to facilitate rapid and accurate TB diagnosis.
- Promoting the use of handheld radiology devices equipped with AI algorithms, allowing for quick TB detection with high accuracy rates, thereby streamlining diagnostic processes and improving patient care.
Navigating the Global Waterscape, and Its Challenges

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the context of climate change-related pressures, the world also needs to foster improved cooperation over water-sharing.
Context:
- The global water crisis remains a critical issue, with roughly two billion people lacking access to clean water, threatening individual and collective well-being.
- Water has been a determining factor in civilizations' prosperity and decline throughout history.
- Ancient Mesopotamian cities experienced conflicts over fertile land and water resources, illustrating the age-old struggle for water.
- As the 31st World Water Day approaches in 2024, themed "Leveraging Water for Peace," the United Nations emphasizes the significance of water diplomacy to tackle contemporary water challenges and secure a sustainable future for all.
Water Diplomacy in a Time of Extremities:
- Encouraging Collaborative Governance: Water diplomacy underscores the necessity of collaborative governance mechanisms to effectively tackle shared water challenges.
- By uniting relevant stakeholders—governments, local communities, NGOs, and international agencies—collaborative governance frameworks foster dialogue, information exchange, and joint decision-making.
- These mechanisms pave the way for sustainable water management policies and strategies that prioritize the needs and interests of all involved parties.
- Ensuring Fair Water Allocation: At the core of water diplomacy lies the principle of equitable water allocation among riparian states.
- Acknowledging that water resources transcend political boundaries, water diplomacy advocates for fair distribution, considering the needs, rights, and vulnerabilities of all stakeholders.
- Through negotiated agreements and treaties, riparian states can establish frameworks for sharing water resources, managing competing demands, and peacefully resolving disputes.
- Promoting Regional Stability and Peace: Effective water diplomacy contributes to regional stability and peace by mitigating conflicts over shared water resources.
- By fostering cooperation and understanding among neighboring states, water diplomacy builds trust, enhances security, and reduces tensions stemming from water-related disputes.
- Additionally, collaborative water management initiatives foster cross-border cooperation, economic integration, and diplomatic relations, bolstering broader efforts to uphold peace and stability in conflict-prone regions.
- Embracing Inclusive Approaches: Inclusive water diplomacy involves engaging a diverse array of stakeholders, including indigenous communities, civil society organizations, academia, and the private sector.
- Recognizing the importance of marginalized groups' contributions and perspectives, inclusive approaches promote social equity and transparency in decision-making processes.
- By integrating local knowledge, cultural practices, and community priorities, inclusive water diplomacy enhances the legitimacy and efficacy of governance frameworks.
- Preventing and Resolving Conflicts: Water diplomacy plays a pivotal role in preventing and resolving conflicts arising from competing water interests.
- Through proactive diplomacy, early warning systems, and confidence-building measures, riparian states can address potential sources of tension and defuse conflicts before they escalate.
- Moreover, mechanisms for peaceful dispute resolution, such as arbitration and mediation, enable states to resolve water-related disputes through dialogue and negotiation, averting coercive or confrontational measures.
Strategic Approaches for Tackling Rural Water Challenges in India:
- Enhancing Infrastructure: A primary strategy involves developing water infrastructure like wells, hand pumps, boreholes, and piped systems to improve access to safe water and sanitation facilities in rural areas.
- Investment in constructing and maintaining such infrastructure can reduce waterborne diseases, leading to better health outcomes.
- Encouraging Community Engagement: Engaging local communities in planning, implementing, and managing water projects is crucial for their sustainability and success.
- Empowering rural residents through participatory water management committees and user associations can promote ownership of water resources, efficient practices, and conflict resolution.
- Conservation and Management Practices: Promoting conservation and management practices is vital for maximizing water efficiency in rural areas.
- Techniques like rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, watershed management, and soil moisture conservation can reduce reliance on unpredictable water sources and build climate resilience.
- Incorporating Technological Innovations: Leveraging technology can significantly improve water access and management in rural areas.
- Solar-powered pumps, drip irrigation systems, and water-efficient technologies can enhance agricultural productivity, while monitoring applications and remote sensing can enable real-time resource management.
- Policy Support and Interventions: Government support is essential in addressing rural water needs through adequate funding, regulatory frameworks for equitable water distribution, and legislation to protect water resources and promote sustainable practices.
- Policy coherence across the agriculture, health, and environment sectors is crucial for tackling the interconnectedness of water, food security, and rural development.
Addressing Transboundary Water Challenges:
- Highlighting the Significance of Transboundary Waters: The report underscores the prominence of transboundary waters, noting that a substantial portion of the world's freshwater resources, including those in India, are shared across borders.
- India's extensive landmass boasts a network of long rivers, vital not only for its own needs but also shared with neighboring countries.
- However, the South Asian region has witnessed a significant deterioration in water quality in recent years, particularly in rivers like the Meghna, Brahmaputra, Ganga, and Indus, as highlighted in the 2024 report.
- The Need for Sophisticated Cross-Border Water Governance: Addressing these challenges requires a sophisticated approach to cross-border water governance, promoting effective and equitable allocation of water resources among nations that share them.
- It is imperative to develop robust mechanisms for cooperation and coordination to manage shared waters sustainably.
- Global Perspective on Transboundary Cooperation: According to a 2021 UNESCO progress report on Sustainable Development Goal indicator 6.5.2, titled "Progress on transboundary water cooperation," out of UNESCO's 194 member states and 12 associate members, 153 countries are classified as water-sharing nations.
- Remarkably, transboundary waters account for 60% of the world's freshwater flows.
- However, only 24 of these 153 countries have achieved a 100% cooperation agreement on their shared waters, indicating the pressing need for enhanced collaboration.
- Ensuring Collective Well-being and Peace: While significant progress has been made in fostering peace over time, the scarcity of freshwater poses a threat to our collective well-being and peace.
- This issue is not only crucial for achieving the 2030 Agenda and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) but also for maintaining stability and harmony among nations.
- Effective transboundary cooperation in the sustainable management of water resources is essential to realize benefits across various sectors, including health, food and energy security, disaster resilience, education, improved standards of living, employment, economic development, and the preservation of ecosystem services.
Conclusion
As the global struggle for clean water access continues for approximately two billion people, the ever-increasing demand for this precious resource directly impacts our collective well-being and peace. In order to build a sustainable future, we must prioritize water conservation efforts that transcend political boundaries, fostering regional cooperation and stability. By recognizing the urgency of this challenge, we can work together to ensure a secure and equitable water supply for generations to come.
Inter-Ministerial Joint Workshop on “Blue Economy”

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) organized a consultative workshop in New Delhi today on the Blue Economy Pathways study report status.
Context:
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) has collaborated with the World Bank to conduct a technical study and compile a report titled 'India’s Blue Economy: Pathways for resource-efficient, inclusive, and resilient growth in India.'
- This report aims to explore global best practices in Blue Economy implementation, develop an ocean accounting framework, enhance institutional capacity, and propose innovative finance mechanisms in alignment with India's Blue Economy Policy framework.
What is the Blue Economy?
- The blue economy, or the ocean economy, is a term used to describe the economic activities associated with the oceans and seas.
- The World Bank? defines the blue economy as the “sustainable use of ocean resources to benefit economies, livelihoods, and ocean ecosystem health”.
- The activities? commonly understood to represent the blue economy include maritime shipping, fishing and aquaculture, coastal tourism, renewable energy, water desalination, undersea cabling, seabed extractive industries and deep sea mining, marine genetic resources, and biotechnology.
- The blue economy is estimated to be worth more than US$1.5 trillion? per year globally.
- It provides over 30 million jobs and supplies a vital source of protein to over three billion people.
How do the Oceans Contribute to Sustainable Development?
- There is a Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) dedicated to oceans: number 14, ‘Life Below Water?’ aims to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources.
- It sets out seven targets for a sustainable ocean economy by 2030. So far, progress toward reaching these goals has been limited?.
- There have been some small improvements in the sustainability of fisheries and an expansion of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), but these cover only around 7.5% of the oceans.
How are the Oceans Governed?
- Governance of the ocean and the blue economy is both complex and potentially difficult to implement, which has led to fragmented approaches to the sharing of marine resources between nations and impeded understanding of the environmental impacts of the blue economy.
- Ocean-related regulations apply to Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs), which include territorial waters, archipelagos, and the area of sea that extends 200 nautical miles out from countries’ coastlines.
- The remaining area is called the High Seas? (or ‘open ocean’) and accounts for 64% of the world’s oceans.
Importance of the Blue Economy:
- Economic Prosperity: The Blue Economy offers substantial avenues for economic advancement across various sectors including fisheries, aquaculture, tourism, maritime transport, renewable energy, and biotechnology.
- Sustainable Resource Management: It advocates for the responsible and sustainable utilization of marine resources such as fish stocks, minerals, and energy sources, ensuring their availability for present and future generations.
- Renewable Energy Development: By fostering the exploration of renewable energy sources like offshore wind, wave, and tidal energy, the Blue Economy reduces reliance on fossil fuels, thereby combating climate change.
- Tourism Boost: Coastal and marine tourism serves as a cornerstone of the Blue Economy, stimulating revenue generation, and job creation, and bolstering local economies in coastal areas.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Healthy oceans play a pivotal role in regulating the planet's climate.
- Through conservation efforts and sustainable practices, the Blue Economy aids in mitigating climate change impacts by preserving coastal ecosystems and reducing carbon emissions.
- Biodiversity Protection: Through the promotion of sustainable practices and responsible resource management, the Blue Economy contributes to the conservation of marine biodiversity, safeguarding endangered species and habitats.
Challenges Facing the Blue Economy:
- Pollution and Environmental Degradation: India's coastal regions confront significant pollution stemming from industrial discharge, untreated sewage, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste.
- This pollution adversely impacts marine ecosystems, biodiversity, and the long-term sustainability of marine industries.
- Overexploitation of Marine Resources: Illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing practices exacerbate resource depletion, leading to diminished fish stocks and jeopardizing the livelihoods of coastal communities.
- Climate Change Impacts: The effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and alterations in oceanic conditions, pose threats to fisheries, aquaculture, coastal infrastructure, and marine biodiversity.
- Maritime Security Challenges: India's maritime security faces multifaceted challenges including piracy, illegal trafficking, maritime terrorism, and territorial disputes, necessitating robust security measures.
- Limited Institutional Capacity and Infrastructure: Effective management and sustainable development of the blue economy require robust institutional frameworks, governance mechanisms, and infrastructure.
- However, India grapples with capacity constraints, inadequate funding, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and regulatory gaps, hindering optimal resource management and development.
India's Blue Economy:
- India's Blue Economy, encompassing its vast coastline and Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), holds immense potential for driving sustainable growth and development.
- With a coastline stretching 7,517 km and an EEZ covering over two million square kilometers, India is endowed with abundant living and non-living resources.
- Although currently contributing approximately 4% to the nation's GDP, India's Blue Economy is projected to experience significant expansion with improved mechanisms and infrastructure.
- Furthermore, the coastal economy plays a crucial role in sustaining the livelihoods of over four million fisherfolk and other coastal communities.
Four key industries are poised to propel India's Blue Economy forward:
- Fishing: Leveraging the rich marine resources to enhance fisheries production and promote sustainable fishing practices.
- Aquaculture: Developing innovative techniques to foster the cultivation of aquatic organisms, contributing to food security and livelihood opportunities.
- Ports: Investing in port infrastructure and capacity building to facilitate maritime trade, cargo handling, and logistics efficiency.
- Shipping: Strengthening the shipping industry to support global commerce, transportation, and connectivity while ensuring environmental sustainability
Government Initiatives Promoting Blue Economy:
- Sagarmala Programme: The Sagarmala Programme, a flagship initiative, focuses on modernizing India's ports, improving port connectivity, and driving port-led development.
- It prioritizes logistics optimization, coastal shipping promotion, and the establishment of coastal economic zones to stimulate economic expansion and employment generation.
- National Policy Framework: The government has devised a comprehensive National Policy Framework for the Blue Economy, outlining a strategic path for the sustainable development and management of marine resources.
- It aims to integrate sectors like fisheries, aquaculture, shipping, tourism, and renewable energy to foster holistic growth.
- National Marine Fisheries Action Plan (NMFAP): This plan encompasses strategies to enhance fishery resources assessment, upgrade infrastructure and technology in the fisheries sector, and encourage aquaculture development.
- Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM): The government has initiated the Integrated Coastal Zone Management Program to foster sustainable development and conservation of coastal ecosystems.
- Blue Economy Cell: The Ministry of Earth Sciences has instituted a dedicated Blue Economy Cell to streamline research, policy formulation, and implementation of Blue Economy endeavors.
- Marine Spatial Planning (MSP): India is actively developing Marine Spatial Planning frameworks to ensure the efficient and sustainable utilization of marine space.
Conclusion
India's Blue Economy is on the brink of substantial expansion in the coming years.
With the government's proactive Blue Economy Mission, there's potential for this sector to emerge as a key economic driver, contingent upon effective policy implementation.
Aligned with the government's broader vision outlined in the 'Vision of New India by 2030', the Blue Economy policies are geared towards securing enduring economic benefits, fostering job creation, promoting equity, and safeguarding environmental sustainability.
India's Bhutan Policy: Balancing Regional Allies in the Shadow of Dragon
- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Bhutan decided on Wednesday to postpone a state visit by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Thimphu this week because of bad weather.
Context:
- The planned visit to Bhutan on 21-22 March by the Indian prime minister however had to be postponed due to inclement weather conditions over Paro airport.
- Notwithstanding the sudden intervention by nature, the visit which was otherwise planned amid an electioneering time, showcases the importance that New Delhi is imparting to an important friend and neighbour.
- The importance of Bhutan for India can be immediately gauged from the manner in which China is seeking to woo its southern neighbour away from the ambit of Indian influence.
Background of India-Bhutan Relations:
- India and Bhutan have maintained a special bilateral relationship based on mutual trust, goodwill, and understanding.
- This unique partnership is founded upon the Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation, first signed in 1949 and subsequently renewed in 2007.
- The treaty has provided a strong framework for the two nations to develop close political, economic, and cultural ties.
- A significant aspect of the enduring bond between India and Bhutan lies in their spiritual kinship.
- Bhutan regards India as the "gyagar," acknowledging its role as the sacred birthplace of Buddhism.
- This deep cultural and religious connection has helped foster resilience and camaraderie between the two nations, further cementing their historical friendship.
Why does Bhutan Hold Significant Importance for India?
- India and Bhutan have maintained strong bilateral relations rooted in shared cultural heritage, political cooperation, economic ties, and social connections.
Cultural Bonds:
- Buddhist Heritage: With India being the birthplace of Lord Buddha, Bhutanese monks frequently visit significant Buddhist sites such as Nalanda, Bodh Gaya, and Rajgir, fostering spiritual connections.
- Open Border Policy: The open border encourages regular exchanges of travellers for work, tourism, shopping, and medical care, further strengthening cultural ties.
Political Cooperation:
- High-Level Visits: Frequent political exchanges at the ministerial level, including visits by the Indian Prime Minister and the King of Bhutan, sustain and strengthen bilateral relations.
- Doklam Crisis: During the 2017 crisis, Bhutan granted access to Indian army personnel to resist Chinese incursions, demonstrating mutual trust and cooperation.
- Civilian Award: Bhutan conferred its highest civilian award on Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2021, recognizing his contributions to the friendship between the two nations.
Economic Partnerships:
- Financial Assistance: India has provided financial aid to Bhutan since the 1960s, supporting its five-year plans, for agriculture, irrigation, health, industrial development, road transport, energy, and education.
- Trade and Commerce: The 1972 Agreement on Trade and Commerce, revised in 2016, promotes free trade, with India being Bhutan's largest trading partner, exceeding $1422 million in bilateral trade in 2021-22.
- Vaccine Maitri Initiative: Bhutan was the first country to receive Indian-made Covishield vaccines, with 550,000 doses gifted during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Hydropower Collaboration: A vital cooperation area generating significant revenue, hydroelectric projects are covered under a 2006 bilateral agreement, with four operational projects supplying 2136 MW of electricity to India and two more under construction.
Social Connections:
- Education: Approximately 1,000 scholarships are provided annually to Bhutanese students in Indian universities for engineering and medicine, fostering knowledge exchange.
- Indian Diaspora: 50,000 Indians working in Bhutan contribute to fields such as education, arts, and health.
Environmental Importance:
- Carbon-Neutral Commitment: As one of the few countries committed to carbon neutrality, Bhutan has found a key partner in India to achieve this goal through renewable energy, forest conservation, and sustainable tourism initiatives.
New Cooperation Areas:
- Space: Joint development of the India-Bhutan SAT small satellite aims to help manage Bhutan's natural resources, promoting scientific collaboration.
- Fintech: Launching the RuPay Card enables full interoperability, with Bhutan as the second country to launch India's BHIM app for cashless payments.
- E-learning: Integrating Bhutan's DrukRen with India's National Knowledge Network facilitates information access for universities and research institutions in both countries, fostering educational cooperation.
What are the Challenges in India-Bhutan Relations?
- Despite their close ties, India-Bhutan relations face several challenges that must be addressed to maintain a strong partnership.
China's Growing Influence:
- Chinese Presence: China's increasing influence in Bhutan, particularly near the disputed Bhutan-China border, has raised concerns in India, traditionally Bhutan's closest ally.
- While Bhutan and China have not established diplomatic relations, their friendly exchanges can potentially shift the balance of power in the region.
Border Disputes:
- Incidents of Incursions: While the 699 km India-Bhutan border has been largely peaceful, recent incursions by Chinese forces have created flashpoints, such as the 2017 Doklam standoff in the India-China-Bhutan tri-junction.
- Any escalation of these border disputes could strain India-Bhutan relations and challenge their traditional security cooperation.
Hydropower Projects:
- Bhutan's hydropower sector is a key economic pillar, with India playing a significant role in its development.
- However, some Bhutanese have expressed concerns over the perceived disproportionate benefits for India.
- These concerns have led to public opposition in Bhutan against Indian involvement in the sector, which could impact bilateral relations.
Trade Issues:
- Trade Imbalance: India accounts for over 80% of Bhutan's imports and exports, raising concerns about the significant trade deficit.
- Bhutan seeks greater access to the Indian market for its products to reduce the trade deficit, which could require further negotiation and collaboration between the two countries.
- To navigate these challenges, both India and Bhutan must address these concerns through open dialogue, strategic cooperation, and mutually beneficial agreements to maintain their strong and enduring partnership.
Strategies for Strengthening Indo-Bhutan Relations:
- To further enhance the bilateral ties between India and Bhutan, several approaches can be adopted to address potential challenges and promote mutual growth such as:
- Diplomatic Engagement: India should regularly discuss with Bhutan to comprehend its evolving foreign policy objectives and concerns.
- Continual support for Bhutan's sovereignty and development needs is vital to allay any apprehensions of India as a threat.
- Expanded Economic Assistance: India can provide increased economic aid, trade advantages, and infrastructural development to shield Bhutan from succumbing to China's debt-trap tactics.
- Fortifying Defense Collaboration: India should address existing impediments in the relationship and reinforce defence and security cooperation with Bhutan to ensure mutual safety and counter potential Chinese influence effectively.
- Promoting Regional Cooperation: India and Bhutan are members of various regional organizations like SAARC, BIMSTEC, and BBIN.
- Strengthening regional cooperation mechanisms will ensure Bhutan's interests are adequately represented in these forums, enhancing overall regional stability and prosperity.
Conclusion
Bhutan is perhaps one of the most important allies that India has in its neighbourhood. Time has proven its relationship with India. However, recent times have witnessed changing dynamics in the Himalayan kingdom’s polity. Focusing on diplomatic engagement, bolstering economic support, strengthening military ties, and fostering regional cooperation will pave the way for a prosperous and secure future. Also, corrective and course-correction measures that are being undertaken by India to implement its Neighbourhood First policy are laudable.
Key Facts about Bhutan:
- Geography: Nestled between India and China, Bhutan is a landlocked country characterized by majestic mountains and verdant valleys.
- Thimphu is the capital city of Bhutan.
- Political System: Bhutan transitioned to democracy in 2008, following its inaugural democratic elections. The King of Bhutan serves as the Head of State.
- Official Name: Referred to as the 'Kingdom of Bhutan', its Bhutanese name is Druk Gyal Khap, translating to the 'Land of the Thunder Dragon'.
- River: The Manas River, stretching over 376 km, holds the title of Bhutan's longest river. It flows through the Himalayan foothills, forming a transboundary river between southern Bhutan and India.
- Government system: Bhutan follows a parliamentary monarchy system.
- Borders: Bhutan shares borders with only two countries: India and Tibet (an autonomous region of China).
Addressing the Persistent Issue of Gender Pay Disparity

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent World Bank Group report highlighted that women globally earn only 77 cents for every dollar earned by men, underscoring the persistent gender pay gap where women, on average, earn less than men.
Context:
- The World Bank Group's recent report sheds light on the persistent issue of the gender pay gap, revealing that women globally earn only 77 cents for every dollar their male counterparts earn.
- This disparity has been a contention, with critics sometimes questioning its existence.
- However, the International Labour Organisation regards the gender pay gap as a tangible indicator of inequality between men and women.
- While various reports present different figures, it is crucial to acknowledge the underlying factors that contribute to this gap and work towards eradicating them to achieve equitable pay for all individuals, regardless of gender.
How is the Gender Pay Gap Calculated?
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) defines the gender pay gap as the difference between the average wage levels of all working women and men in the labor market, whether they are paid a monthly salary, hourly wage, or daily wage.
- It is crucial to note that this gap does not exclusively represent the wage disparity between men and women with similar qualifications and job responsibilities.
- Rather, it encompasses the overall earnings difference between all working women and men.
- While the concept of "equal pay for equal work" advocates for equitable compensation for men and women with the same qualifications and job duties, the gender pay gap reflects broader income disparities.
- There is no single, universally agreed-upon method for calculating the gender pay gap.
- Different organizations and studies may produce varying figures due to their distinct approaches.
- Understanding the various factors contributing to the gender pay gap and addressing them through appropriate policies and initiatives is vital for achieving gender equality in the workforce and ensuring fair compensation for all workers.
Methodological Differences and the Persistence of the Gender Pay Gap:
- The variation in reported gender pay gaps can be attributed to the distinct methodologies employed by different organizations and studies.
- For instance, Pew Research used hourly wages to calculate the disparity. At the same time, the US Bureau of Labor Statistics utilized weekly wages, considering only full-time workers, defined as those working at least 35 hours per week.
- Such differences in approach can lead to varying estimates of the gender pay gap.
- Despite these discrepancies in methodology, it is essential to recognize that the gender pay gap is a persistent issue in most countries and industries.
- While the extent of the gap may differ across studies, the underlying reality is that income disparities between men and women continue to be a prevalent challenge.
What are the Root Causes of the Gender Pay Disparity?
- The gender pay gap can be attributed to several interconnected factors that perpetuate income inequality between men and women.
- Firstly, women's lower labor force participation rate is influenced by prevailing gender stereotypes and societal expectations about gender roles.
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that the global labor force participation rate for women stands at just under 47%, compared to 72% for men.
- In India, the 2011 Census reported a workforce participation rate of 25.51% for women, against 53.26% for men.
- Secondly, even when women join the workforce, they are often concentrated in lower-paying sectors or job roles.
- The ILO's Women in Business and Management report found that fewer women occupy management and leadership positions, particularly at higher levels.
- They are more likely to work in support functions such as human resources and financial administration, leading to a lower average salary compared to male managers.
- A Georgetown University survey in 2013 further highlighted that the top 10 highest-paying professions, primarily in engineering and computer science, were dominated by men, while women were overrepresented in the 10 lowest-paying professions, such as arts and education.
- Additionally, women are more likely to work part-time due to limited full-time employment opportunities and family responsibilities.
- In 73 countries, based on 2018 data, women outnumbered men as part-time workers.
- The ILO explains that part-time work often lacks proportional benefits to full-time positions, impacting women's overall remuneration over time.
- Other institutional and socioeconomic factors, such as the traditional view of men as breadwinners, lower investments in women's education, and concerns over safety in commuting and the workplace, also contribute to the gender pay gap.
- Addressing these underlying issues and promoting gender equity in the workforce is essential to bridging the gender pay gap and achieving fair compensation for all individuals.
Understanding the Implications of the Gender Pay Gap:
- Analyzing the gender pay gap through various demographic factors reveals patterns that provide valuable insights into income disparities between men and women.
- For example, women in their mid-30s and 40s often experience a decline in earnings compared to men in similar positions and professions.
- Critiques of the 77% statistic argue that it overlooks the "motherhood penalty," where unmarried women earn 95 cents or more for every dollar a man makes.
- This penalty suggests that women face career growth setbacks when they take breaks to raise children, highlighting an area requiring attention to promote equal opportunities.
- The 2023 Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences winner, Claudia Goldin, extensively researched pay equality and argued that traditional gender roles force men to "step up" in their careers while women "step back" for family responsibilities.
- This dynamic ultimately disadvantages both genders, as men miss out on family time, and women sacrifice their careers.
- Efforts to close the gender pay gap, such as implementing maternity and paternity leave policies and flexible work arrangements, have shown promise in reducing income disparities.
- However, the pace of progress varies, emphasizing the need for continued attention and innovation in promoting equal opportunities for all workers.
Conclusion
The gender pay gap continues to pose significant challenges across nations and industries. Examining demographics and career stages reveals important patterns that underline disparities between men's and women's earnings. Addressing inequalities, such as the "motherhood penalty," and transforming traditional work structures are vital for achieving equal opportunities. While policies like parental leave and flexible work arrangements have shown promise, sustained commitment to innovation and reform is crucial for fostering lasting progress and a more equitable professional environment.
The Role of NFHS Data in Formulating Policies for Women's Financial Inclusion

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Financial inclusion awareness programmes must give special attention to women in households not headed by women.
Context:
- Financial inclusion is a key driver for realizing a more sustainable and inclusive future, as it directly influences the achievement of eight out of the 17 United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Despite its importance, inequalities continue to exist, with India's subpar performance in the Global Gender Gap Report 2023 underscoring significant gaps in the economic realm.
- To address these disparities, particularly for women in India, it is vital to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the complex aspects of financial inclusion.
- Insights can be drawn from multiple sources such as the World Bank's Global Findex Database and the National Family Health Survey (NFHS), ultimately paving the way for targeted interventions and improved financial access for all.
What is Financial Inclusion?
- Financial inclusion is a method of offering banking and financial services to individuals.
- It aims to include everybody in society by giving them basic financial services regardless of their income or savings.
- It focuses on providing financial solutions to the economically underprivileged.
- The term is broadly used to describe the provision of savings and loan services to the poor in an inexpensive and easy-to-use form.
- It aims to ensure that the poor and marginalized make the best use of their money and attain financial education.
- With advances in financial technology and digital transactions, more and more startups are now making financial inclusion simpler to achieve.
The Role of Financial Inclusion in Advancing Women's Empowerment:
- Financial inclusion not only facilitates women's access to bank accounts but also drives broader economic participation and empowerment.
- By offering women avenues for savings, credit, and investment, financial inclusion empowers them to manage risks, build assets, and seize socio-economic opportunities.
- In doing so, it bolsters women's resilience to economic uncertainties, fosters greater household welfare, and promotes economic stability, thereby illustrating its pivotal role in driving gender equity and sustainable development.
Insights from NFHS Data on Women's Financial Inclusion Progress:
- The NFHS data offers a comprehensive understanding of the multi-faceted dimensions of financial inclusion among women in India.
- Over the past two decades, several indicators point towards a significant improvement in women's economic empowerment and access to financial services including:
Financial Autonomy and Decision-making:
- A notable aspect highlighted by the NFHS surveys is the increasing financial autonomy among women.
- There has been a marked shift towards greater control over financial resources, with more women possessing self-operated bank accounts and playing an active role in financial decision-making within their households.
- This trend signifies a positive step towards women's economic independence, contributing to their overall empowerment and well-being.
Awareness and Utilization of Micro-Credit Programs:
- Micro-credit schemes have emerged as a key facilitator of financial assistance for women entrepreneurs and small business owners in rural India.
- The NFHS data indicates a growing awareness of these programs among women, with an increasing number utilizing micro-credit facilities to support their economic activities.
- This underscores the importance of targeted interventions and support mechanisms in promoting women's access to formal credit sources, fostering entrepreneurship, and generating income at the grassroots level.
Access and Utilization of Formal Banking Services:
- An analysis of factors such as education, occupation, and household characteristics reveals key determinants of women's financial inclusion.
- The NFHS data emphasizes the pivotal role of education in enabling women's awareness and utilization of financial services.
- Similarly, occupation and access to electronic media also significantly influence women's access to formal banking channels and digital financial tools.
- These insights underscore the need for targeted interventions and policy measures to address disparities and barriers, ensuring inclusive financial access, particularly among marginalized and vulnerable groups of women.
Advances in Global Financial Inclusion and India:
- Financial inclusion has become a key enabler of economic growth and development worldwide, with India demonstrating substantial progress in this arena.
- According to the World Bank's Global Findex Database, there has been a significant increase in adult ownership of bank accounts globally between 2011 and 2020.
- India's commendable growth of 42 percentage points during this period exemplifies the success of targeted interventions promoting financial access, particularly for marginalized communities such as women.
- This upward trend emphasizes the importance of continued efforts in fostering inclusive financial systems to ensure sustainable development and shared prosperity.
The Influence of Government Initiatives on Financial Inclusion:
- India's commitment to advancing financial inclusion has resulted in substantial progress, particularly in reducing the gender gap in account ownership.
- The introduction of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) in 2014 played a pivotal role in this achievement, offering universal access to banking services, including savings accounts, remittances, and overdrafts to underserved communities such as women in rural and urban areas.
- By January 2024, PMJDY had facilitated the opening over 28 crore accounts for women, significantly contributing to bridging the gender gap in financial access.
- Furthermore, government initiatives like the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana and the National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM) have been instrumental in fostering women's economic empowerment and participation in the formal financial sector.
- These schemes provide opportunities for skill development, entrepreneurship training, and access to credit, enabling women to establish and sustain livelihoods.
- In addition, social protection programs such as the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana and Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana offer financial assistance and support during critical life stages such as pregnancy and homeownership.
- Collectively, these initiatives have played a vital role in promoting women's economic independence and overall well-being, underscoring the importance of continued efforts towards inclusive financial systems.
Challenges and Way Forward:
- While significant progress has been made in advancing financial inclusion, several challenges remain, requiring concerted efforts and multi-stakeholder collaboration to address. Key areas of focus include:
- Enhancing Financial Literacy: Despite the expansion of banking services, a significant proportion of the population, particularly in rural and marginalized communities, lack adequate knowledge and understanding of financial products and services.
- By promoting targeted education and awareness campaigns, we can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions and fully utilize available resources.
- Bridging the Digital Divide: The potential of digital financial services to enhance access and convenience is immense.
- However, disparities in internet connectivity, smartphone ownership, and digital literacy create barriers to their effectiveness.
- Expanding digital infrastructure and promoting digital literacy initiatives are critical to ensuring equitable access to digital financial services for all segments of society.
- Promoting Inclusivity of Marginalized Communities: Systemic barriers continue to hinder the meaningful participation of marginalized communities, including women, minorities, and persons with disabilities in the financial ecosystem.
- These barriers are multifaceted, encompassing social, cultural, and economic factors.
- To overcome these challenges, tailored interventions and affirmative action programs are necessary, fostering an enabling environment that promotes their inclusion and empowerment.
- Advancing through Collaboration: A collaborative approach involving multiple stakeholders, including government agencies, financial institutions, civil society organizations, and grassroots initiatives, is indispensable in advancing financial inclusion.
- By coordinating efforts, leveraging resources, and implementing holistic solutions, we can collectively navigate the path ahead, overcoming challenges, and ensuring inclusive and sustainable financial systems for all.
Conclusion
Advancing financial inclusion for women in India is essential for fostering inclusive growth and sustainable development. While initiatives like PMJDY and DAY-NRLM have made significant strides, concerted action is necessary to tackle remaining disparities and fully leverage women's economic potential. By emphasizing education, digital literacy, and tailored awareness initiatives, India can unlock fresh opportunities for women's economic empowerment, thereby advancing the agenda of inclusive growth and prosperity.
Many elections, AI’s dark dimension

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
With a series of elections to be held across the world in 2024, the potential of AI to disrupt democracies cannot be dismissed.
Context:
- The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) marks a significant turning point in human history.
- With the rise of Generative AI (GAI), the possibility of achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) becomes increasingly feasible, raising questions about its potential to mimic human abilities.
- Thus, exploring AI's profound influence on human life, particularly within electoral contexts and broader societal realms, is imperative.
What is Generative AI (GAI)?
- Generative AI, short for Generative Artificial Intelligence, represents a branch of artificial intelligence focused on creating new content rather than simply processing or analyzing existing data.
- Unlike traditional AI systems, which are designed to recognize patterns or make predictions based on historical data, generative AI models have the capability to generate new data that resembles real-world examples.
- These models work by learning patterns and structures from large datasets and then using that knowledge to create new content.
- They can produce various types of content, including images, text, audio, and even video.
- For example, a generative AI model trained on a dataset of human faces can generate realistic-looking images of faces that have never existed before.
- They can produce various types of content, including images, text, audio, and even video.
- One of the key technologies behind generative AI is deep learning, particularly a type of neural network called a generative adversarial network (GAN).
- In a GAN, two neural networks are pitted against each other: a generator and a discriminator.
- The generator creates new data samples, while the discriminator tries to distinguish between real and fake data.
- Through this adversarial process, the generator learns to produce increasingly realistic content.
- Generative AI has a wide range of applications across various industries.
- In the field of art and design, it can be used to generate new artwork, music, or even fashion designs.
- In entertainment, it can create realistic characters and environments for video games and movies.
- In healthcare, it can generate synthetic medical images for training diagnostic algorithms.
- However, the technology also raises ethical concerns, such as the potential for misuse, copyright issues, and the creation of fake content.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Shaping Electoral Landscapes:
- A Transformative Influence- AI's Ascendancy in Politics: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into electoral processes represents a profound transformation in global political dynamics.
- As nations gear up for elections, the incorporation of AI technologies introduces new variables that require a reassessment of conventional campaign methodologies and voter outreach strategies.
- In the context of upcoming elections, including India's extensive seven-phase general election, AI emerges as a decisive factor influencing electoral trajectories.
- The deployment of Generative AI, with its ability to conduct dynamic simulations and replicate real-world interactions, presents unprecedented opportunities and challenges for political stakeholders and the electorate.
- Harnessing AI for Campaign Innovation and Voter Engagement: Political entities and candidates are leveraging AI-driven tools to analyze vast datasets, craft targeted messaging, and optimize campaign blueprints.
- AI-powered predictive analytics empower parties to pinpoint swing voters, tailor messages to specific demographics, and deploy resources more precisely.
- Additionally, AI-enabled sentiment analysis of social media platforms furnishes real-time insights into voter attitudes and emerging concerns, informing campaign narratives and responsiveness strategies.
- Moreover, AI's impact extends beyond campaign frameworks to encompass voter engagement and mobilization endeavors.
- Through AI-driven chatbots, personalized interactions with voters are facilitated, addressing inquiries, disseminating information, and fostering voter participation.
What are the Concerns Regarding AI's Impact on Electoral Integrity?
- Challenges Posed by Deep Fakes: The expanding presence of AI within electoral arenas prompts apprehensions regarding its implications for democratic processes and the integrity of elections.
- The emergence of 'Deep Fake' technology, capable of generating convincingly realistic yet fabricated audio, video, and textual materials, presents a formidable obstacle in identifying and combatting misinformation and disinformation campaigns.
- Deep fakes produced by AI possess the capacity to deceive voters, manipulate public opinion, and erode trust in democratic institutions, thus distorting the integrity of electoral outcomes.
- Impact on Public Discourse and Decision-making: Moreover, the utilization of AI-powered algorithms in social media platforms for content curation and recommendation purposes raises concerns regarding filter bubbles, echo chambers, and algorithmic bias.
- These algorithms, driven by AI, may inadvertently amplify divisive content, perpetuate existing biases, and contribute to the segmentation of public discourse, consequently influencing voter perceptions and decision-making processes.
What are AI Influences its challenges, and Mitigation Strategies?
- As artificial intelligence (AI) permeates various spheres of society, including electoral contexts, addressing the concept of AI influence becomes increasingly critical.
- AI influence refers to the ability of AI-driven tactics to shape human behavior and decision-making processes, often without individuals' explicit awareness or consent.
- Challenges in Addressing AI Influence: A primary challenge in addressing AI influence is mitigating its impact on electoral dynamics.
- AI-powered algorithms can analyze extensive data sets to predict and influence voter behavior, potentially affecting electoral outcomes in ways that may not align with democratic principles or voter preferences.
- To counter this, safeguards must be implemented to prevent undue AI-driven influence on electoral processes and outcomes.
- Promoting Transparency and Accountability: Transparency and accountability are crucial in addressing AI influence.
- Electoral authorities and policymakers should establish clear guidelines and regulations governing the use of AI in political campaigns and voter engagement efforts.
- This includes mandates for disclosing the use of AI-driven algorithms, data sources, and methodologies in campaign strategies, enhancing public awareness and understanding of AI's role in elections.
- Protecting Democratic Values: Efforts to combat AI influence should prioritize safeguarding democratic values and electoral integrity.
- Measures must be implemented to detect and mitigate AI-driven manipulation, such as disinformation campaigns, deep fakes, and algorithmic bias.
- Collaborative approaches involving electoral authorities, technology firms, civil society organizations, and academia are essential to develop effective tools and techniques for detecting and countering AI-driven threats to electoral integrity.
- Empowering Voter Literacy: Promoting media literacy and digital literacy among voters is crucial for combating AI influence.
- By equipping voters with the skills to critically evaluate information sources, distinguish fact from fiction, and identify manipulation tactics, individuals can resist the influence of AI-driven propaganda and make informed voting decisions.
- Educational initiatives, public awareness campaigns, and media literacy programs are vital for enhancing voter resilience against AI-driven misinformation and manipulation.
Additional Measures for Ensuring Electoral Integrity:
- Incorporating Ethical Guidelines into AI Governance: Furthermore, the ethical dimensions of AI governance should inform the development and application of AI technologies within electoral contexts.
- Ethical AI governance frameworks should prioritize principles such as fairness, transparency, accountability, and adherence to democratic values.
- This entails conducting comprehensive risk assessments, ensuring transparency and explainability in algorithms, and establishing mechanisms for independent oversight and accountability.
- Adopting Proactive Strategies: Policymakers, electoral authorities, and civil society actors should embrace proactive strategies to uphold electoral integrity and democratic principles in the age of AI.
- Implementing robust regulatory frameworks, transparency mandates, and oversight mechanisms is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with AI-driven manipulation and disinformation campaigns.
- Furthermore, investments in digital literacy initiatives and media literacy programs can empower voters to critically assess information sources, distinguish between fact and fiction, and resist manipulation efforts.
Way Forward:
- The risks associated with AI pose a substantial threat, surpassing concerns regarding biases in its design and development.
- AI systems inherently tend to manifest adversarial traits, for which effective mitigation strategies have yet to be fully realized.
- Beyond electoral implications, India's position as a digital frontrunner necessitates a cautious approach towards AI adoption, recognizing both its potential advantages and disruptive capabilities.
- While AI offers numerous benefits, it is imperative for the nation and its leaders to acknowledge its potential for malevolence.
- India's prominence in digital innovation presents both opportunities and challenges, as the advancement of AI, including AGI, brings both advantages and risks.
- Addressing the complexities of AI policy requires amplifying democratic voices and resisting the tendency to cede policymaking authority to a select few tech conglomerates.
Conclusion
The emergence of AI marks a significant milestone in human evolution, impacting electoral dynamics and social harmony in profound ways. While AI offers remarkable progress, it demands careful oversight to minimize its disruptive effects and uphold democratic values. As we venture into the realm of AI, wise decision-making and forward-thinking are essential to steer toward a future characterized by ethical AI governance and conscientious innovation.
Model Code of Conduct comes into force: Lok Sabha Elections 2024

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI) announced that the country would vote in seven phases from April 19 to June 1 and the results will be announced on June 4. With this, the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) comes into effect.
What is the Model Code of Conduct (MCC)?
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) is a set of guidelines published by the Election Commission of India (EC) for political parties and candidates to set standards of conduct during the election campaign and polling.
- It also explains how parties can lodge complaints to the EC observers in case of dispute and instructs how the Ministers of the parties in power must conduct themselves when the MCC is in force.
- In 2019, a new addition regarding election manifestos was added, instructing parties to not issue promises which were ‘repugnant to the ideals of the Constitution’.
Is the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) Legally Binding?
- The MCC evolved as part of the ECI’s drive to ensure free and fair elections and was the result of a consensus among major political parties.
- It has no statutory backing.
- Simply put, this means anybody breaching the MCC can’t be proceeded against under any clause of the Code.
- Everything is voluntary.
- The EC uses moral sanction or censure for its enforcement.
- The ECI can issue a notice to a politician or a party for an alleged breach of the MCC either on its own or based on a complaint by another party or individual.
- Once a notice is issued, the person or party must reply in writing, either accepting fault and tendering an unconditional apology or rebutting the allegation.
- In the latter case, if the person or party is found guilty subsequently, he/she can attract a written censure from the ECI, something that many see as a mere slap on the wrist.
- However, several actions are listed as ‘electoral offenses’ and ‘corrupt practices’ under the Indian Penal Code (now known as Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita) and the Representation of the People Act, 1951 such as:
- Causing tension between castes, religious or linguistic communities
- Appealing to caste or communal feeling to secure votes
- Using places of worship for election propaganda
- Bribing/intimidating/impersonating voters
- Canvassing within 100 meters of polling booths
- Transporting voters to and from polling stations
- Disrupting public meetings
- Serving or distributing liquor on polling day
- Holding public meetings 48 hours before the closing of polls
- These actions will attract appropriate punishment as per these laws.
Previous Model Code of Conduct ‘Violations’:
- During the 2023 Madhya Pradesh Assembly elections, Priyanka Gandhi Vadra was questioned by the ECI for alleging that Prime Minister Narendra Modi favored his "big industrialist friends" during an election rally.
- In 2017, both BJP and Congress accused each other of violating the MCC during the Gujarat polls.
- In 2014, Amit Shah and Azam Khan were banned from campaigning by the ECI during the Lok Sabha polls under Article 324 of the Constitution for inflammatory speeches, which was lifted after they apologized and pledged to follow the Code.
When Does MCC Come Into Force and End?
- The MCC comes into force immediately when the election schedule is announced by the Election Commission and remains in operation till the election process is complete, i.e. results are announced.
- The MCC applies to all elections to the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies.
- It is also applicable for State Legislative Council elections from Local Bodies, and Graduates’ and Teachers’ Constituencies.
- It is enforced throughout India in case of General elections, and the State up for polls in case of Legislative Assembly elections.
Who Is Bound by It?
- All organizations, committees, corporations, and commissions (e.g. Transport authorities, Jal boards) funded wholly or partially by the Centre or State are bound by the MCC.
- While listed political parties and candidates are bound to follow the MCC, even non-political organizations that hold campaigns favoring a political party or candidate are bound to follow specific guidelines mentioned by the EC.
How is the MCC Enforced?
- Before holding polls for the General or State Assembly elections, the Election Commission issues guidelines to the government to shift out all officers including police who are posted in their home district, and who have completed/completed three out of four years in that district to ensure no interference.
- The MCC is then implemented by the newly appointed officials and nodal EC officers monitor compliance.
- No election campaigning is allowed within the constituency 48 hours before the close of polls.
What Restrictions Does the Model Code of Conduct Impose?
- The MCC contains eight provisions dealing with general conduct, meetings, processions, polling day, polling booths, observers, the party in power, and election manifestos.
- As soon as the code kicks in, the party in power, whether at the Centre or in the states, should ensure that it does not use its official position for campaigning.
- Hence, no policy, project, or scheme can be announced that can influence voting behavior.
- The party must also avoid advertising at the cost of the public exchequer or using official mass media for publicity on achievements to improve chances of victory in the elections.
- The code also says the ministers must not combine official visits with election work or use official machinery for the same.
- The ruling party cannot use government transport or machinery for campaigning.
- It should also ensure that public places such as maidans etc., for holding election meetings, and facilities like the use of helipads are provided to the opposition parties on the same terms and conditions on which they are used by the party in power.
- The issue of advertisement at the cost of the public exchequer in the newspapers and other media is also considered an offense.
- The ruling government cannot make any ad-hoc appointments in government, public sector undertakings, etc., which may influence the voters.
- Political parties or candidates can be criticized based only on their work record and no caste and communal sentiments can be used to lure voters.
- Mosques, Churches, Temples, or any other places of worship should not be used for election campaigns.
- Bribing, intimidating, or impersonation of voters is also barred.
- Holding public meetings during the 48 hours before the hour fixed for the closing of the poll is also prohibited.
- The 48 hours is known as “election silence”.
- The idea is to allow a voter a campaign-free environment to reflect on events before casting her vote.
What are the Guidelines for Poll Manifestos?
- Manifestos must not contain anything repugnant to the ideals enshrined in the Constitution.
- They must reflect the rationale for welfare scheme promises and indicate ways to meet the financial requirements for it.
- The manifesto documents must not be released during the prohibitory period (when MCC kicks in).
How are Violations Dealt With?
- Any complaint regarding elections should be brought to EC observers, the Returning Officer, the local magistrate, the Chief Electoral Officer, or the Election Commission itself.
- In response, any directions issued by the EC, Returning Officer, or District Election Officer shall be strictly complied with.
In issuing AI advisory, MEITY becomes a deity

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) reportedly issued an advisory on 1 March 2024 (Advisory) to “intermediaries” and “platforms” hosting artificial Intelligence (AI) including generative AI-based models.
Context:
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MEITY), previously recognized as the Department of Electronics and IT (DEITY), has come under scrutiny regarding its endeavors to govern technology and the Internet.
- It is imperative to examine MEITY's recent advisory regarding generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), exploring its legal foundation, uncertainties, and repercussions for technology regulation in India.
What is the Recent Advisory by MEITY on AI Regulation?
- Regarding the Regulation of AI Technologies: The advisory urges tech firms to ensure that their AI models, including Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI, prevent users from hosting or displaying unlawful content, addressing concerns about potential misuse.
- Quality Assurance and Testing: It stresses the use of reliable and tested AI models while cautioning against deploying under-tested or unreliable ones without explicit permission from the Government of India, aiming to uphold quality standards and mitigate associated risks.
- Advisory on Transparency and Accountability: The advisory highlights the importance of transparency and accountability in AI deployment, recommending appropriate labeling of AI models to acknowledge potential fallibility or unreliability, reflecting a broader commitment to ethical AI practices and user awareness of associated limitations and risks.
Analysis of Ambiguity Regarding the Legal Status of Government Advisory:
- Lack of Statutory Authority: The uncertainty surrounding the legal status of MEITY's advisories is a key issue in assessing the government's regulatory power and its impact on stakeholders.
- Unlike established regulatory bodies such as SEBI, MEITY lacks explicit statutory powers to issue binding directives or advisories.
- This absence of a specific legal framework leads to interpretation challenges and questions about the enforceability of MEITY's directives.
- Uncertainty on MEITY’s Advisory Power: The IT Act of 2000, which primarily governs technology regulation in India, does not grant MEITY the authority to issue advisories on emerging technologies like AI.
- While the IT Act addresses electronic records, digital signatures, and cybersecurity, it does not specify MEITY's mandate to regulate AI or other technological advancements.
- Lack of Defined Terms and References: The term "advisory" lacks a precise definition under the IT Act or other relevant legislation, allowing MEITY to issue directives that carry the weight of official recommendations without a clear legal foundation.
- This ambiguity leaves stakeholders, including technology firms and legal experts, uncertain about the legal consequences of non-compliance with MEITY's advisories.
- Furthermore, MEITY's advisories often lack explicit citations of legal authority or references to specific legislative provisions, contributing to perceptions of arbitrary regulatory actions.
- Compliance Challenges: In the absence of clear penalties or enforcement mechanisms tied to MEITY's advisories, compliance becomes discretionary rather than obligatory.
- This situation underscores the ambiguity surrounding the legal standing of MEITY's regulatory directives, raising concerns about accountability and procedural fairness in technology regulation.
Additional Concerns Regarding Government’s Advisory on AI:
- Transparency Issues and Hasty Policymaking: MEITY's advisories, particularly those related to AI regulation, exhibit a pattern of expedited policymaking driven by media events, lacking thorough evaluation or stakeholder input.
- Released with limited transparency, these advisories fail to provide comprehensive information, undermining the credibility of MEITY's regulatory decisions.
- Ambiguous Terminology and Ministerial Clarifications: The recent AI advisory introduces vague terms like "bias prevention" and proposes an AI model licensing system without clear definitions or legal framework.
- Ministerial clarifications on social media platforms add to the confusion, leaving terms undefined and enforcement mechanisms uncertain.
- This ambiguity contributes to stakeholder uncertainty and undermines legal clarity.
- The decline in Administrative Standards and Overreach: MEITY's reliance on advisory regulations marks a decline in administrative standards, sidestepping formal legislative processes and stakeholder consultations.
- The extension of IT Rules, 2021, to regulate digital content further illustrates regulatory overreach.
- Additionally, the influence of social media metrics on policy decisions reflects a departure from deliberative governance.
- Threat to Freedom of Expression: MEITY's regulatory actions, including AI governance advisories and social media content moderation directives, risk infringing on online freedom of expression.
- The vague and arbitrary nature of these directives may lead to self-censorship among individuals and organizations, fearing repercussions for expressing dissent or challenging government policies.
- This suppression of free speech undermines democratic discourse and diversity in the digital realm.
- Expansion of Surveillance and Control Measures: Digital authoritarianism often entails expanding state surveillance and control over online activities.
- MEITY's regulatory efforts, such as implementing IT Rules, 2021, and proposing AI governance measures, could facilitate heightened government surveillance and online content censorship.
- This erosion of digital privacy rights jeopardizes individual autonomy and fosters a climate of apprehension and self-censorship among internet users.
- Impact on Innovation and Technological Advancement: MEITY's regulatory overreach and legal ambiguity pose substantial obstacles to innovation and technological progress in India.
- Uncertainty surrounding compliance obligations and enforcement mechanisms discourages investment and innovation in emerging fields like AI.
- Moreover, burdensome regulatory requirements may stifle entrepreneurship and impede the growth of India's technology sector.
Why Regulate the AI Sector?
- The regulation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) represents an evolving landscape as governments navigate the potential benefits and pitfalls of this influential technology.
Reasons for Regulation:
- Risk Management: AI carries the potential for bias, discrimination, privacy breaches, and safety concerns. Regulations serve to mitigate these risks effectively.
- Transparency and Understandability: Many AI systems operate opaquely, complicating comprehension of their decision-making processes. Regulations can foster transparency and clarity.
- Establishing Accountability: Regulatory frameworks can delineate clear lines of responsibility for the creation, deployment, and utilization of AI systems.
- Building Public Confidence: Well-defined regulations can instill public confidence in AI technologies, promoting their conscientious development and application.
Way Forward:
- Unified Effort: Combating the challenges posed by digital authoritarianism demands a unified effort to uphold democratic principles, foster transparency and accountability, and protect fundamental rights in the digital realm.
- Scrutiny of MEITY’s Regulatory Measures: MEITY's regulatory initiatives must undergo thorough scrutiny and oversight to ensure alignment with democratic norms and respect for individual liberties.
Conclusion
MEITY's advisory regulations raise pertinent questions regarding its legal jurisdiction, transparency, and impact on technological advancement in India. The ambiguity in terminology, swift policy formulation, and reliance on social media for dissemination weaken the credibility and efficacy of regulatory measures. Addressing these concerns necessitates a reassessment of MEITY's regulatory strategy and a commitment to transparent, inclusive governance practices.
India’s R&D Funding, Breaking Down the Numbers
- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The announcement in the interim Budget for 2024-25, of a corpus of ?1 lakh crore to bolster the research and innovation ecosystem within the country, has sparked enthusiasm within the scientific and research communities.
Context:
- In the current scenario, the recent allocation of a substantial ?1 lakh crore in India's Interim Budget for 2024-25 to enhance the research and innovation ecosystem underscores the nation's dedication to advancing scientific pursuits.
- Additionally, the decision to expand the iconic slogan 'Jai Jawan Jai Kisan' to 'Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan, Jai Vigyan, Jai Anusandhan' signifies a renewed focus on research and innovation as essential elements of development.
- Evaluating the present state of India's research and development (R&D) landscape, including its funding, output, and the potential impact of recent initiatives on nurturing a conducive environment for research and innovation, is imperative.
Current Outlook of India's R&D Landscape:
- Gross Expenditure on Research and Development: India's R&D sector has witnessed substantial growth, with Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD) increasing from ?6,01,968 million in 2010-11 to ?12,73,810 million in 2020-21.
- Despite this growth, India's research investment as a percentage of GDP remains at 0.64%, lagging behind major developed and emerging economies like China (2.4%), Germany (3.1%), South Korea (4.8%), and the United States (3.5%).
- Academic Talent: Despite the relatively lower GDP allocation for R&D, India has emerged as a key producer of academic talent, annually producing an impressive 40,813 PhDs, ranking third globally after the United States and China.
- Research Output: India's research output remains substantial, ranking third globally with over 3,00,000 publications in 2022, showcasing the nation's robust research ecosystem and its dedication to advancing knowledge across various fields.
- Innovation: India demonstrates commendable performance in patent grants, securing the sixth position globally with 30,490 patents granted in 2022.
- While this number is lower compared to the U.S. and China, it reflects India's evolving innovation landscape and its potential for further growth in intellectual property creation.
- Major Sponsors: In India, GERD is primarily driven by the government sector, including the central government (43.7%), State governments (6.7%), Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) (8.8%), and the public sector industry (4.4%), with the private sector industry contributing only 36.4% during 2020–21.
- Investment in R&D: According to R&D statistics (2022-23) from the Department of Science and Technology, India's total investment in R&D reached $17.2 billion in 2020-21.
- Within this sum, 54% ($9.4 billion) is allocated to the government sector, predominantly utilized by four key scientific agencies — the DRDO (30.7%), the Department of Space (18.4%), ICAR (12.4%), and the Department of Atomic Energy (11.4%).
Major Challenges Facing R&D:
- Private Sector Inertia: Despite India's significant Gross Expenditure on Research and Development (GERD), private industries contribute only 37% of the country's R&D funding, reflecting a discrepancy compared to the global trend where business enterprises typically contribute over 65%.
- Low Participation by Higher Education Institutions (HEIs): HEIs play a minor role in R&D investment, contributing only 8.8% ($1.5 billion), limiting their potential contribution to research and innovation.
- Brain Drain: Talented researchers often migrate to countries with better research infrastructure and funding opportunities, leading to a loss of skilled manpower and hindering R&D progress.
- Inadequate Education and Training: The education system may fail to adequately equip students with the requisite skills and knowledge needed to excel in R&D, posing a challenge to innovation and scientific advancement.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Complex procedures and bureaucratic red tape can impede research initiatives, delaying progress and discouraging potential investors from engaging in R&D activities.
- Limited Collaboration with Academia: A gap exists between academic research and industry needs, hampering the effective transfer of knowledge and technology, and inhibiting the development of innovative solutions to real-world problems.
Proposed Measures:
- Embrace a Collaborative Approach: Fostering collaboration among the government, business enterprises, and Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) is imperative to harness the full potential of science, technology, and innovation for driving economic growth and technological progress.
- Promote Public-Private Partnerships: Encouraging collaboration between academia and industry can facilitate the translation of research findings into commercial applications, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical implementation.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Directing resources towards safeguarding intellectual property rights and addressing technical challenges can unlock new markets and spur innovation.
- Provide Government Subsidies to Stimulate Private Sector Investment: Implementing government initiatives such as tax incentives and grants can incentivize increased private sector investment in Research and Development (R&D), bolstering India's R&D ecosystem and fostering stronger industry-academia partnerships for knowledge exchange and innovation.
- Prioritize Skill Development: Reforms in education that prioritize the development of critical thinking, problem-solving, and research skills are essential to nurture a workforce capable of driving innovation and scientific advancement.
- Streamline Bureaucratic Processes: Simplifying regulatory procedures and regulations can expedite research projects, attract investments, and create a conducive environment for R&D activities.
- Incentivize Innovation: Introducing government schemes and awards to recognize and reward innovative research endeavors can incentivize scientists, researchers, and businesses to pursue groundbreaking innovations that contribute to societal progress and economic development.
Government Initiatives:
- National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP): Recent initiatives, such as the National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP) and the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) Act, signal a strong commitment to fostering research and innovation.
- The NDTSP aims to incentivize private sector engagement in R&D, while the ANRF Act seeks to bridge the R&D investment gap and nurture a robust research culture within HEIs.
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) Act: Enacted to address India's persistent R&D investment gap, this legislation aims to cultivate a thriving research culture within Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) and drive innovation across various sectors.
- UchhatarAvishkarYojana (UAY): Geared towards promoting innovation that addresses industry needs and enhances India's manufacturing competitiveness, UAY fosters collaboration between academia and industry, both domestically and internationally, to drive advancements in research and technology.
- Impacting Research Innovation & Technology (IMPRINT): This initiative endeavors to tackle pressing engineering challenges by facilitating interdisciplinary research collaborations and translating knowledge into practical solutions across ten designated technology domains.
- Establishment of Research Parks: Research parks established at premier institutes such as IIT Delhi, IIT Guwahati, and IIT Kharagpur serve as platforms for fostering collaboration between academia, industry, and entrepreneurial ventures, facilitating the establishment of R&D units, and promoting innovation.
- Impact of Recent Initiatives: These initiatives, coupled with the allocation in the interim Budget, are poised to drive India's research and innovation agenda forward, particularly in burgeoning industries.
Way Forward:
- India's technological and manufacturing ambitions rely on a pivotal transformation within its R&D domain, necessitating a dual-pronged strategy:
- Encouraging active participation from the private sector, alongside
- Strengthening the research infrastructure within academia.
- Embracing a multifaceted approach that engages a spectrum of stakeholders is imperative to confront the challenges and unlock the full potential of R&D, fostering India's economic expansion and global competitiveness.
- Drawing insights from the R&D frameworks of developed nations while leveraging India's inherent strengths in agile decision-making and strategic alignment could catalyze a formidable evolution within its R&D landscape.
Conclusion
While significant strides have been made, there is a need for increased funding, stronger industry-academia collaboration, and policy measures to incentivize private sector involvement. Recent initiatives such as the NDTSP and the ANRF Act represent positive steps towards realizing India's potential as a powerhouse of research and innovation. By creating a conducive environment for research and innovation, India can pave the way for sustainable development and prosperity in the years to come.
CAA Rules go against equality, federalism and India’s Constitution

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Although protecting persecuted individuals is commendable, the ideal solution is to grant refugee status to all, irrespective of their religious affiliation.
Context:
- India has been engaged in heated discussions over the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) since its inception in 2019.
- The recent issuance of Rules under the CAA by the Union government has sparked renewed debates concerning its impact on India's constitutional secularism.
- Amid these discussions, it is crucial to assess the CAA's provisions, their effects on citizenship, and the wider socio-political consequences they carry.
Concerns Surrounding the Citizenship Amendment Act:
- Selective Approach to Citizenship: The Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) of 2019 amends India's Citizenship Act of 1955 and introduces a selective approach to granting citizenship.
- This selective approach is a significant point of contention, as it differentiates between individuals based on their religious identity.
- Preferential Treatment for Certain Religious Groups: The CAA expedites the citizenship process for undocumented immigrants belonging to Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Jain, Parsi, and Christian communities from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh.
- However, the Act explicitly excludes Muslims from these provisions, which has led to considerable debate and criticism.
- Violation of Secular Principles: Critics argue that the CAA violates the secular principles enshrined in India's Constitution.
- Secularism, a foundational tenet of India's democratic ethos, mandates that the state remain neutral in matters of religion and guarantee equal rights and protections to all citizens, regardless of their faith.
- Discriminatory Nature: The CAA's exclusion of Muslims from its purview has been perceived as discriminatory and runs counter to India's historical commitment to religious pluralism and tolerance.
- This discriminatory nature has sparked widespread protests and highlighted deep divisions within Indian society regarding citizenship, identity, and secularism.
- Upholding Constitutional Principles: The protests against the CAA underscore the importance of upholding constitutional principles and safeguarding the rights of all citizens, irrespective of their religious affiliation.
- This controversy serves as a reminder of the need for inclusive and non-discriminatory policies that respect the diversity of India's population.
Potential Implications of the Notified Rules under the Citizenship Amendment Act:
- Streamlined Citizenship Process: The notified Rules streamline the citizenship application process by providing clear procedures and documentation requirements.
- This standardization can potentially expedite the citizenship-granting process, allowing eligible individuals to secure legal status more efficiently.
- Lenient Proof Requirements: The Rules offer leniency in requirements for proof of nationality and residence, accepting various documents as evidence.
- This flexibility may enable more individuals to establish their eligibility for citizenship under the CAA.
- Centralisation of Authority: The notified Rules centralize the citizenship-granting process at the national level, with an empowered committee formed by the Union government now responsible for processing applications.
- This centralisation consolidates power at the national level, potentially reducing the role of local authorities in decision-making and grassroots-level accountability.
- Legal and Constitutional Challenges: The Rules are likely to face legal and constitutional challenges, particularly regarding their compatibility with India's constitutional principles and international legal standards.
- Critics argue that the CAA and its accompanying Rules violate the constitutional guarantee of equality before the law (Article 14) by discriminating based on religion.
- Contradictions and Regional Discontent: The implementation of the CAA has exposed internal contradictions within India's citizenship laws, particularly in the case of Assam.
- The discrepancy between Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955, and the provisions of the CAA has fuelled discontent among local communities and complicated the citizenship landscape.
- Overall, the notified Rules under the Citizenship Amendment Act have significant implications for the citizenship-granting process, the balance of power between national and local authorities, and the interpretation of constitutional principles.
- As the legal and societal debates surrounding the CAA continue, these implications will likely shape the discourse on citizenship and belonging in India.
Moving Toward Inclusive Solutions: Addressing the Concerns Raised by the Citizenship Amendment Act:
- To address the concerns raised by the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) and its accompanying Rules, it is crucial to adopt a more inclusive approach that aligns with international humanitarian norms and India's commitment to secularism.
Here are some steps that can be taken:
- Inclusive Protection for Persecuted Individuals: Instead of granting citizenship based on religious affiliation, India should consider offering refugee status to all persecuted individuals, regardless of their religion.
- This approach would be in line with international humanitarian norms and would uphold the principle of secularism enshrined in India's Constitution.
- Ratification of International Conventions: Ratifying international conventions such as the Geneva Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees would demonstrate India's commitment to protecting vulnerable populations and ensuring their rights.
- This step would also bring India in line with global standards for refugee protection.
- Reevaluation of the Citizenship Amendment Act: Given the concerns surrounding the CAA's compatibility with constitutional principles and its potential for discrimination, it is essential to reevaluate the Act's provisions.
- This process should involve a thorough examination of the CAA's impact on vulnerable communities and its alignment with India's democratic values.
- Upholding Constitutional Values: To ensure that the CAA and other legislation adhere to India's core values, it is crucial to reaffirm the principles of equality, non-discrimination, and secularism as outlined in the Constitution.
- Policies and laws should be crafted to uphold these principles and protect the rights of all individuals, irrespective of their religious affiliation.
- By taking these steps, India can work toward addressing the concerns raised by the Citizenship Amendment Act and foster a more inclusive approach to citizenship that aligns with the nation's historical commitment to diversity and pluralism.
Centre notifies implementation of Citizenship Amendment Act Rules

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
More than four years after Parliament passed The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019, the Ministry of Home Affairs on Monday notified the Rules to implement the law.
Context:
- The Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) of 2019 amended the Citizenship Act of 1955 to provide a pathway to Indian citizenship for migrants belonging to Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Jain, Parsi, or Christian communities who entered India before December 31, 2014, from Pakistan, Afghanistan, or Bangladesh.
- The law was enacted amidst nationwide protests, particularly in Assam, and was officially notified on January 10, 2020.
- However, the implementation of the CAA was delayed due to the absence of accompanying rules and regulations.
- To address this issue, the Union government issued an order on May 28, 2021, empowering district collectors in 13 districts with significant migrant populations to accept citizenship applications from the groups specified in the 2019 amendment.
- The CAA has been a subject of controversy and criticism, with opponents arguing that it violates the secular principles of the Indian constitution by excluding Muslims from its purview.
- Supporters of the law contend that it offers relief to persecuted minorities from neighboring countries.
- As the rules for the CAA have now been put in place, its implementation is anticipated to be a significant development in the ongoing discussions surrounding citizenship and immigration in India.
About the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) 2019:
- The Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) of 2019 is a significant amendment to India's Citizenship Act of 1955.
- It aims to provide a pathway to citizenship for Hindu, Sikh, Parsi, Buddhist, Jain, and Christian immigrants from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh who have faced religious persecution and have been residing in India without documentation.
- The CAA reduces the residency requirement for citizenship from 11 years to 5 years for eligible immigrants who entered India before December 31, 2014.
- The Act also includes provisions for the cancellation of Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) registration in cases where the individual has violated any provision of the Citizenship Act or other applicable laws.
- The CAA applies to individuals who have been compelled to seek shelter in India due to religious persecution.
- However, the Act does not apply to certain areas, such as regions covered by the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution (which deals with autonomous tribal-dominated regions in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram) and states with an inner-line permit regime (Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, and Mizoram).
- The implementation of the CAA has faced delays due to opposition in several states, including Assam and Tripura.
- The Act has sparked protests and legal challenges, with critics arguing that it violates the secular principles of the Indian Constitution and excludes certain persecuted groups, such as the Rohingya from Myanmar, Tibetan Buddhists from China, and Tamils from Sri Lanka.
- The CAA has been a subject of intense debate, with supporters claiming it offers relief to persecuted minorities and opponents asserting that it discriminates against Muslims and undermines India's secular fabric.
- The Supreme Court is currently considering multiple petitions challenging the constitutional validity of the CAA.
Citizenship Amendment Rules, 2024:
- The Citizenship Amendment Rules, 2024 lay out a clear process for eligible refugees from Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh to seek Indian citizenship through registration or naturalization.
- The process begins with the submission of an application, along with an affidavit confirming the accuracy of the information provided and an affidavit from an Indian citizen vouching for the applicant's character.
- Applicants must also provide a declaration of their familiarity with one of the languages listed in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- The application is to be submitted electronically to an empowered committee via a district-level committee, as notified by the central government.
- The district-level committee, headed by a designated officer, is responsible for verifying the submitted documents and administering the oath of allegiance to the applicant.
- Supporting documents that must be provided by applicants include:
- A passport issued by the governments of Pakistan, Afghanistan, or Bangladesh
- A birth certificate
- Any form of identity document
- Land or tenancy records; or any document proving that the applicant's parents, grandparents, or great-grandparents were citizens of one of the three countries.
- These documents remain valid even beyond their expiration dates.
- Proof of entry into India before December 31, 2014, is also required.
- Acceptable supporting documents for this include:
- visa and immigration stamp
- A registration certificate from the Foreigners Regional Registration Officer (FRRO)
- A slip issued by the Census enumerators in India
- A government-issued license or certificate
- A permit in India (including a driving license
- Aadhaar number, or ration card), or a marriage certificate issued in India.
- Once an application is approved, the applicants will be issued a digital certificate, granting them Indian citizenship.
- These rules provide a structured pathway for eligible refugees from the specified countries to obtain citizenship in India, offering them a chance at a new beginning and a sense of belonging in their adopted homeland.
The Mains issues and challenges associated with the CAA of 2019:
- Legal challenge: The CAA has been challenged in the Supreme Court by the Indian Union Muslim League (IUML) and others on the grounds of discrimination and violation of fundamental rights.
- Right to equality: Critics argue that using religion as a criterion for citizenship eligibility violates Article 14 of the Constitution, which guarantees equality before the law and equal protection under the law.
- Targeting of Muslims: Concerns have been raised that the CAA, in conjunction with the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam, may disproportionately affect Muslims and lead to their exclusion from citizenship.
- Secularism: The use of religion as a basis for citizenship is seen by some as a violation of the principle of secularism, which is a fundamental feature of the Indian Constitution.
- Conflict with Assam Accord: The CAA's cutoff date for determining citizenship contradicts the Assam Accord of 1985, which set a different date for identifying foreigners in the state, leading to protests and opposition in Assam and other northeastern states.
- Widespread protests: The CAA has sparked protests across India, reflecting the complexities and sensitivities surrounding the issue of citizenship and the challenge of balancing the needs of persecuted minorities with upholding constitutional principles and addressing regional concerns.
What is the Government’s Stand?
- The government's position on the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) is that Muslims have been excluded from the list of "persecuted" minorities because they constitute the majority in the Islamic countries of Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh.
- According to the government, the CAA aims to provide citizenship to those who have faced religious persecution in these countries.
- However, this rationale is subject to scrutiny, as there are other persecuted minorities in these countries and elsewhere who have not been included in the CAA.
- For instance, Tamil Hindus in Sri Lanka, Rohingya Muslims in Myanmar, and minority Muslim sects like Ahmadiyyas and Hazaras in Pakistan and Afghanistan also face persecution in their respective countries.
- The exclusion of these groups from the CAA raises questions about the criteria used to determine which minorities are considered persecuted and eligible for Indian citizenship under the Act.
What’s Next?
- The court will have to look into two issues:
- Whether the special treatment given to the so-called “persecuted minorities” from the three Muslim-majority neighboring countries only is a reasonable classification under Article 14 of the constitution for granting citizenship, and
- Whether the state is discriminating against Muslims by excluding them.
- The Supreme Court has earlier held that the law has to clear two legal hoops to pass the equality test when it is challenged on the grounds of Article 14.
- First, any differentiation between groups of persons must be founded on an “intelligible differentia”, and
- Second, “that differentia must have a rational nexus to the object sought to be achieved by the Act”.
- The SC can strike down a classification if it is found to be arbitrary. The court recently struck down the electoral bonds scheme on the ground that it was “manifestly arbitrary” — that is, “irrational, capricious or without an adequate determining principle”.
Voters must know who funds political parties. This is the right that Supreme Court has protected

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court of India has recently mandated the public disclosure of all pertinent information regarding corporate funding of political parties, with the State Bank of India and other entities directed to comply with the court's directive.
Context:
- The recent landmark ruling by the Supreme Court's Constitution Bench, led by the Chief Justice of India, represents a pivotal moment in Indian democracy.
- This ruling specifically addresses the legality of the Electoral Bond Scheme (EBS) initiated through the Finance Act of 2017.
- Beyond its immediate implications, the verdict underscores fundamental principles such as equality, transparency, and proportionality concerning corporate contributions to election funding.
What is the Supreme Court verdict on the Electoral Bond Scheme?
- Nullification of Electoral Bond Scheme: The Supreme Court declared the Electoral Bond Scheme (EBS) unconstitutional, citing concerns over unrestricted donations, anonymity of contributions via promissory notes, and exemption of corporate donors from disclosure obligations.
- This underscores the imperative of transparency in corporate election financing, aligning with constitutional rights outlined in Article 14 (equality) and Article 19(1)(a) (right to information).
- Immediate Cessation of Electoral Bonds and Disclosure Mandates: The Court mandated the immediate cessation of electoral bonds and directed all pertinent authorities to disclose relevant information dating back to April 12, 2019.
- The State Bank of India's request for an extension was met with skepticism, prompting a contempt petition against them for non-compliance.
- Guidelines on Legislative Passage via Money Bill Route: While the verdict didn't specifically address the Speaker's authority to classify bills as money bills, it offered guidance suggesting that not all legislative determinations qualify as financial or economic decisions.
- This challenges the presumption of constitutionality and underscores the need for a nuanced approach in evaluating bills passed via the money bill route.
What is the Reason Behind SC's Scrutiny of Electoral Bond Scheme (EBS)?
- Elimination of Donation Caps: The court closely examined the EBS due to its elimination of donation caps imposed on political parties, as outlined in the Finance Act 2017.
- This removal of restrictions allowed for unrestricted inflow of funds into electoral campaigns, posing a potential threat to the democratic principle of a level playing field.
- Anonymity of Donations via Promissory Notes: An area of concern highlighted by the court was the provision in the EBS allowing for anonymous donations to political parties through promissory notes issued by recognised banks.
- This mechanism raised significant issues regarding transparency and accountability, as it enabled substantial financial backing to political entities without disclosing the identity of the contributors.
- Exemption of Corporate Donors from Disclosure Requirements: The EBS faced scrutiny for exempting corporate donors from the obligation to disclose their contributions in balance sheets, a highly contentious feature.
- This exemption created opacity surrounding corporate funding of political parties, undermining the transparency necessary for a robust democratic process.
SC’s Analysis of the Proportionality Doctrine: Its Implications on Legislative Goals and the Restriction of FR
- Evolution of the Proportionality Doctrine: The judgment highlights the proportionality doctrine as a tool for self-discipline in constitutional judicial review, aimed at balancing governmental powers with individual rights
- Serving as a foundational aspect of constitutional discipline, it establishes parameters applicable to all governance institutions.
- Differentiation Between Manifest Arbitrariness and Reasonable Exercise of Power: A crucial distinction is drawn between manifest arbitrariness and the reasonable exercise of power, with the court emphasizing that restricting a fundamental right does not equate to abrogating it entirely.
- This distinction safeguards against arbitrary exercise of governmental authority, stressing the necessity for reasonable and proportionate limitations on rights.
- Legitimate Goals and Appropriate Means: Applying the proportionality test, the court scrutinizes the legislative objectives behind the Electoral Bond Scheme, mandating that any restriction on a fundamental right must serve a legitimate goal and utilize suitable means.
- Questions are raised regarding the legitimacy of curbing black money as a specific ground under Article 19(2), emphasizing the need for the state to justify its actions with reasonable objectives.
- Nexus Between Law and Stated Objectives: Introducing the concept of a reasonable nexus, the court holds that laws should demonstrate a rational connection between means employed and objectives sought to be achieved.
- This requirement ensures that restrictions on fundamental rights are directly related to their intended purpose, avoiding arbitrary infringements.
- Balancing Conflicting Rights: A notable development is the introduction of the double proportionality test, addressing conflicts between equal rights such as donor privacy and voter information and influence.
- The court mandates a secondary proportionality assessment to ensure that any infringement on one right is justified and not disproportionate in impact.
- Alternative Measures and Judicial Restraint: While advocating proportionality, the court suggests alternative measures to achieve legislative goals, such as setting up electoral trusts or imposing caps on corporate funding.
- Additionally, it exercises judicial restraint, respecting the autonomy and powers of the executive and legislative branches.
- Chief Justice M C Chagla's Warning: The judgment recalls Chief Justice M C Chagla's 1958 caution regarding the influential role of big business and money in democracy, highlighting a long-standing concern about corporate influence.
- Chagla's foresight underscores the judiciary's role in preventing improper or corrupt influence, emphasizing the need to safeguard democratic values.
- Historical Perspectives by the CJI: Chief Justice Chandrachud's historical perspective underscores the judiciary's responsibility to prevent improper influences on democracy, advocating for a proactive role in safeguarding democratic values.
- The court's assertion aligns with the idea of acting as a check against attempts to compromise the democratic process, particularly by powerful corporate entities.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court's nullification of the Electoral Bond Scheme is a staunch defense of democratic principles. By rejecting elements that undermine transparency, equality, and accountability, the court reaffirms core democratic values. This landmark ruling signifies a crucial juncture in India's legal narrative, establishing a precedent for safeguarding democracy against opaque financial influences.
Gender equality as the plank of sustainable development

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Though women have a crucial role in energy access, production, and consumption, they face barriers that limit their participation and impact in the energy sector.
Context:
- Gender equality and women's empowerment discussions have surged in recent times.
- Yet, the interconnectedness of gender equality and sustainable energy development is frequently neglected.
- Hence, there's a crucial need to delve into the intricate relationship between these areas, recognizing their pivotal contribution to attaining Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The Crucial Role of Gender Equality in Sustainable Energy:
Gender equality is not just a matter of social justice; it is also a prerequisite for sustainable development. Women play a crucial role in energy access, production, and consumption. Yet, they often face significant barriers that limit their participation and impact in the energy sector. This gender disparity not only hampers individual opportunities but also hinders overall economic growth and environmental sustainability.
- Foundational Role in SDGs: Gender equality is intricately linked with SDGs like SDG5 (gender equality), SDG7 (clean energy), and SDG12 (climate action), serving as a cross-cutting enabler for overall SDG success.
- Impact on Clean Energy Access: Studies consistently demonstrate that gender equality and women's empowerment are essential for achieving universal access to sustainable energy.
- Recognizing women's active participation in the energy sector is crucial for devising inclusive policies and strategies for clean energy access.
- Strategic Alignment with Climate Action: Gender equality is integral to climate action, as reflected in its inclusion in SDG12.
- Empowering women in the energy sector fosters sustainable and climate-resilient practices, supporting efforts to combat environmental degradation.
- Social Justice and Economic Development: Gender equality in sustainable energy transcends SDGs, embodying principles of social justice.
- Addressing gender disparities in energy access not only aligns with moral imperatives but also drives broader economic growth and prosperity.
Gender Equality in Energy Access:
- Household Responsibilities: Women predominantly manage household energy tasks like cooking, heating, and lighting.
- However, energy infrastructure tends to reach women last, leading to a lack of access to modern energy sources, forcing reliance on harmful alternatives like biomass and kerosene.
- Disproportionate Impact: The absence of clean and reliable energy sources exposes women and children to household air pollution, contributing to 3.2 million premature deaths annually, with 60% affecting women and children, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Energy Poverty: Limited access to modern energy perpetuates energy poverty, exacerbating health risks associated with household air pollution and hindering socio-economic development.
- Gender Disparity in the Energy Sector: Despite representing 48% of the global labor force, women constitute only 32% of full-time employees in the renewable energy sector and a mere 22% in the overall energy sector.
- Educational Barriers: Gender disparities in educational access hinder women from acquiring technical skills and training necessary for employment in the energy sector, further perpetuating gender inequality.
- Limited Opportunities: Women face restricted opportunities to pursue technical roles within the energy sector, contributing to the underrepresentation of women in positions of leadership and decision-making.
- Inequitable Policies: Company policies within the energy sector often fail to promote gender diversity and equality, perpetuating systemic barriers to women's advancement and participation in the industry.
What are the Economic Benefits of Empowering Women in the Energy Sector?
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency: Empowering women in the energy sector can lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Diverse teams that include women bring different perspectives, problem-solving approaches, and innovative ideas, enhancing overall productivity in the workplace.
- Enhanced Decision-Making and Problem-Solving: Women's inclusion in decision-making processes within the energy sector can lead to more effective problem-solving and decision-making.
- Research indicates that diverse teams, including gender-diverse ones, tend to make better decisions by considering a wider range of perspectives and factors.
- Talent Retention and Recruitment: Promoting gender diversity and inclusion in the energy sector can help attract and retain top talent.
- Organizations that prioritize gender equality are often perceived as more desirable workplaces, leading to improved recruitment and retention rates.
- Access to Untapped Talent Pool: Empowering women in the energy sector provides access to an untapped talent pool, thereby addressing skills shortages and labor market gaps.
- By tapping into the skills and expertise of women, energy companies can enhance their competitiveness and adaptability in a rapidly evolving industry.
- Economic Growth and Sustainable Development: Gender equality in the energy sector contributes to broader economic growth and sustainable development.
- Women's participation in the workforce, particularly in high-growth sectors like energy, stimulates economic activity, drives innovation, and fosters inclusive growth.
- Increased Financial Performance: Companies with greater gender diversity at all levels, including leadership positions, tend to outperform their less diverse counterparts financially.
- Research suggests that organizations with diverse leadership teams achieve higher financial returns, indicating a positive correlation between gender diversity and financial performance.
- Reduction in Gender Pay Gap: Empowering women in the energy sector can help reduce the gender pay gap and promote equitable compensation practices.
- By ensuring equal pay for equal work and addressing barriers to women's advancement, energy companies can create fairer and more inclusive workplaces.
Way Forward:
- Address Gender Disparity in the Energy Sector: Transform perceptions regarding women's roles in the energy sector and integrate gender considerations into energy policies at all levels.
- Stakeholders including governments, non-state actors, international institutions, and philanthropic organizations must collaborate to create an enabling environment and implement innovative solutions.
- This approach not only enhances access to clean energy but also fosters women's meaningful participation in the sustainable energy transition.
- Promote Entrepreneurship and Collective Initiatives: Support initiatives like the Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge (ENTICE) that empower individuals, particularly women, to initiate entrepreneurial ventures and drive collective action for sustainable energy.
- Explore opportunities in Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) initiatives, which are being implemented by various state governments in India in partnership with philanthropic organizations.
- DRE initiatives can rapidly deliver affordable energy access, alleviate women's daily burdens, and enhance their productivity.
- Leverage Inspirational Initiatives: Draw inspiration from initiatives such as Solar Mamas launched by Barefoot College in India, which empowers illiterate women to become solar engineers.
- These initiatives not only bring clean energy solutions to communities but also promote women's economic empowerment and leadership in the energy sector.
Conclusion
It is important to recognise that the dialogue on gender and energy has clearly shifted from women being identified as part of vulnerable groups to acknowledging them as key agents of change and decision makers across the energy sector. Gender-responsive and women-led initiatives have been successful in the clean energy space. That is why, this is the right time to harness the power of women and energy to create a more inclusive, prosperous, and sustainable world for present and future generations.
Can a justice system without women bring justice to women?

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The latest India Justice Report (IJR) points out that the gender gap remains wide in each of the subsystems that make up the justice delivery system — police, judiciary, prisons, legal aid, and human rights commissions.
Background:
- Diversity stands as a fundamental cornerstone of institutional efficacy globally, with gender inclusivity serving as a pivotal measure of dedication to this principle.
- As International Women’s Day is celebrated today (8th March), it becomes imperative to assess the status of gender diversity within India's justice delivery system, as underscored in the recent findings of the India Justice Report (IJR).
- The data underscores a stark gender disparity within different subsystems, prompting inquiries into the extent of justice institutions' dedication to cultivating inclusivity.
Gender Disparities in India's Justice Delivery System as Revealed by the India Justice Report (IJR):
- Systemic Inequities: The IJR underscores pervasive gender gaps within every facet of the justice delivery system, encompassing the police, judiciary, prisons, legal aid, and human rights commissions.
- This comprehensive analysis illuminates the systemic nature of the issue, indicating that gender disparities are not isolated incidents but rather entrenched throughout the justice system.
- Quotas and Limited Progress: While quotas have aided in women's inclusion, their impact appears concentrated in lower-level positions within the justice system.
- Despite affirmative action measures, women's representation in higher-ranking roles remains disproportionately low.
- Numerical Underrepresentation: The IJR's analysis reveals a stark reality, with only approximately three lakh women active in the justice delivery system.
- This numerical underrepresentation not only indicates inadequate representation but also suggests underlying structural barriers hindering women's full participation.
- Gender Disparity in the Judiciary: Within the judiciary, data indicates a concerning trend where women's presence diminishes significantly as one ascends the hierarchy.
- While women comprise 35% of subordinate judges, this percentage drastically declines to 13% in high courts, with a notable lack of women in the Supreme Court.
- Leadership Void: The absence of a female Chief Justice of India, despite decades of existence, underscores persistent barriers preventing women from ascending to the highest echelons of the judiciary.
- Similarly, women's representation in chief justice positions in high courts remains disproportionately low.
- NHRC's Gender Imbalance and Limited Women Representation: The NHRC, entrusted with upholding fairness and justice, demonstrates a glaring lack of gender diversity, having never had a female commissioner.
- This absence of women in decision-making roles within a human rights commission highlights institutional disregard for gender representation.
- Similar gender imbalances extend to state commissions, with few women serving as members or holding leadership positions, emphasizing the systemic nature of gender disparity within these crucial institutions.
What are the Potential Factors Contributing to Disparity?
- Institutional Apathy and Lack of Initiative: The absence of women in pivotal roles within these commissions reflects not only a numerical deficit but also a lack of proactive efforts to address and rectify this imbalance.
- Findings from the IJR suggest a notable apathy within these institutions, where fostering gender diversity is often overlooked or relegated to a secondary concern.
- Complacency: State commissions, akin to the NHRC's shortcomings, fail to exemplify gender inclusivity.
- The IJR's data paints a discouraging picture, with only a few commissions demonstrating a willingness to appoint women to decision-making positions.
- The absence of proactive measures perpetuates an institutional culture indifferent to the value of diverse perspectives and experiences.
- Deflection of Responsibility: Decision-makers within these institutions often deflect responsibility instead of addressing the root causes of gender disparity.
- Excuses citing "difficulties" in "accommodating" more women serve as common deflection tactics, diverting attention from the urgent need to challenge existing institutional structures and cultures hindering women's entry and retention.
What are the Possible Benefits of Diversity Within the Justice Delivery System?
- Global Research Insights: Research worldwide consistently highlights the positive outcomes of diverse and inclusive work environments.
- The IJR echoes this global perspective, emphasizing that the integration of women and other diversities can reshape institutional culture within the justice system.
- It challenges conventional practices by introducing fresh perspectives, experiences, and methodologies that contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of complex issues.
- Internal Cultural Transformation: Incorporating women into traditionally male-dominated institutions disrupts established norms and cultivates a culture of openness.
- This transformation extends beyond numerical representation, fostering the integration of diverse viewpoints, communication styles, and problem-solving approaches.
- Women, as essential contributors, can drive a shift towards more collaborative, empathetic, and innovative decision-making processes.
- Improved Public Perception: Inclusive institutions not only benefit internally but also enhance public trust and perception.
- A justice delivery system that mirrors the diverse population it serves becomes more responsive, credible, and reflective of societal values.
- This alignment between the institution and the public fosters trust and inclusivity, strengthening the legitimacy and effectiveness of the justice system.
Way Forward:
- Institutional Readiness: Initiating institutional change necessitates preparedness. Justice administrators are urged to proactively tackle systemic obstacles impeding women's inclusion.
- This entails conducting a thorough assessment of current structures, policies, and practices to identify and dismantle barriers obstructing women's full and equitable participation at all levels of the justice system.
- Leading Through Example: The absence of a female Chief Justice of India and the scarcity of women in judiciary leadership roles underscore the imperative for a transformative shift.
- Institutions must actively advocate for and facilitate women's ascension to leadership positions, challenging entrenched biases and breaking the glass ceiling that historically hindered their advancement.
- Reassessing Recruitment and Retention Strategies: There is a pressing need to critically reassess recruitment and retention practices within the justice delivery system.
- This entails a comprehensive review of hiring procedures, promotion criteria, and initiatives to ensure gender-equitable treatment throughout individuals' careers.
Conclusion
To achieve justice, barriers must be dismantled, equal opportunities ensured, and the institutional biases perpetuating gender disparities acknowledged. Upholding equality mandates justice institutions to address systemic impediments hindering women's inclusion, transcending superficial measures. Decision-makers must lead by example, reassess practices, and implement strategies fostering gender balance and inclusivity within the justice system.
The National Credit Framework makes education system more flexible

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The evolving academic landscape necessitates exploration of credit system challenges and transformative impacts of initiatives like the National Credit Framework (NCrF) and the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC).
Context:
- In the realm of academia, the credit system serves as a cornerstone for quantifying students' learning endeavors and accomplishments.
- Consequently, as the educational landscape evolves, it becomes imperative to delve into the importance of credits, address challenges stemming from credit incompatibility, and examine the transformative potential of initiatives such as the National Credit Framework (NCrF) and the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC).
What is the Need for the National Credit Framework (NCrF)?
- The limitations encountered by the pre-NEP credit system highlighted the urgent need for a more adaptable and versatile approach to earning credits.
- It became evident that existing credit systems, although a progression towards flexible education, did not sufficiently cater to the modern demand for interdisciplinary studies and the diverse goals of students.
- As a pivotal move towards reshaping the educational paradigm, the University Grants Commission (UGC) unveiled the National Credit Framework (NCrF) in April 2023.
What is the National Credit Framework (NCrF)?
- The National Credit Framework (NCrF) heralds a paradigm shift in academic structuring, redefining the traditional notion of the academic year and credit allocation.
Framework Components:
- The NCrF comprises three principal verticals:
- The National School Education Qualification Framework (NSEQF),
- The National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF), and
- The National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
Provisions:
- Integration of Academic and Vocational Education: The NCrF emphasizes the integration of academic and vocational education, aligning with the National Education Policy (NEP) to ensure equivalence and coherence between the two education streams.
- Credit System: A credit system based on 'notional learning hours' is introduced, wherein students must accrue a minimum of 40 credits per year, with each semester accounting for 20 credits.
- Notional hours encompass various academic activities, including attending classes, studying for assessments, and completing assignments and homework.
- Students are expected to accumulate a total of 160 credits over their schooling period, with 120 credits attainable upon completion of a three-year bachelor's degree and 320 credits upon completion of a Ph.D.
- Credit Acquisition Mechanisms: The NCrF introduces various mechanisms for credit acquisition, extending beyond traditional academic pursuits.
- Credits can be earned through participation in Olympiads, science quizzes, internships, and employment during college.
- Credit Levels: The framework delineates credit levels ranging from level 1 to level 8, with specific levels associated with different stages of education.
- Higher education spans levels 4.5 to 8, while vocational education and training encompass levels 1 through 8.
- Aadhaar-Enabled Student Registration: An Aadhaar-enabled student registration system is implemented, providing students with an Academic Bank of Credit (ABC) account for depositing degrees and credits.
- This system includes a knowledge locker akin to DigiLocker, ensuring secure storage of academic credentials.
What is the Significance of Credits in Students' Academic Journey”?
- Capturing Learning Effort and Achievement: Credits serve as tangible markers of students' academic journeys, encapsulating not just the knowledge acquired but also the dedication and effort invested in their educational pursuits.
- By assigning numerical values to credits, institutions can systematically evaluate students' engagement and accomplishments.
- Linkage to Curricular Activities: Beyond conventional classrooms, credits extend their influence to encompass various curricular activities such as internships, research projects, and community service.
- Acting as a unifying thread, credits seamlessly integrate these diverse experiences into the broader academic narrative, ensuring that students' educational endeavors embrace practical applications and real-world scenarios.
- Acknowledgment of Skill Acquisition and Development: Recognizing that education encompasses more than just the accumulation of facts, credits play a crucial role in acknowledging skill acquisition and development.
- Whether it involves honing critical thinking abilities, enhancing communication skills, or mastering technical expertise, credits become a measure of students' holistic growth.
- This emphasis on skills not only prepares students for professional challenges but also aligns education with the evolving demands of the contemporary workforce.
- Systematic Monitoring and Assessment: Credits serve as a guiding compass for both students and educational institutions, offering a systematic mechanism to monitor and assess academic progression.
- Through credit-based systems, institutions can quantify learning outcomes within a structured qualification framework.
- This systematic approach enables a nuanced understanding of academic advancement, allowing institutions to identify strengths, address weaknesses, and tailor educational strategies accordingly.
- Measurement of Quantification within a Qualification Framework: One of the primary roles of credits is to provide a quantifiable measure within a qualification framework.
- This facilitates the standardization of educational achievements and enables easy comparison and recognition of academic accomplishments.
- Credits thus serve as a universal language that transcends institutional boundaries, fostering a cohesive understanding of academic excellence.
Challenges Encountered by the Pre-NEP Credit-Based System (Choice Based Credit System [CBCS]):
- Compatibility Issues between CBCS and Semester System: Despite efforts by the University Grants Commission (UGC) to address rigid educational structures through the implementation of CBCS and semester systems, challenges arose in their compatibility.
- These initiatives aimed to introduce flexibility but faced hurdles in implementation and effectiveness.
- Incompatibilities within the CBCS model and semester mechanisms hindered seamless student mobility between educational institutions and programs.
- Lack of Exploratory Educational Experience: Despite intending to offer students a varied and exploratory educational experience, CBCS faced criticism for perceived inflexibility.
- Critics argued that it limited students' ability to delve into a wide range of learning objectives.
- The rigid structure of CBCS was viewed as a constraint rather than an enabler, raising concerns about fostering interdisciplinary learning and accommodating diverse academic pursuits.
- Shortcomings in Providing Student Autonomy: Another challenge was the perceived inadequacy in providing autonomy to students.
- Pre-NEP credit systems did not effectively empower students to participate in diverse academic pursuits.
- Constraints imposed by existing credit structures hindered students' ability to customize their educational journeys based on individual interests, thereby limiting the realization of a personalized and dynamic learning experience.
Conclusion
The integration of the NCrF and ABC signifies a monumental shift in the Indian education landscape, emphasizing flexibility, inclusivity, and holistic learning. This transformative initiative resonates with the objectives of the National Education Policy, heralding a future of dynamic and adaptable education systems tailored to meet the diverse needs and aspirations of both students and educators.
Green jobs and the problem of gender disparity

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Increasing women’s representation in green jobs will lead to benefits such as boosting a low-carbon and environmentally sustainable economy
Context:
- The worldwide movement towards low-carbon development presents India with a distinctive opportunity for progress.
- Nevertheless, this transition brings forth a gender disparity challenge, as men tend to transition to green jobs more rapidly than women.
- Hence, it's crucial to delve into the gender aspects of India's green transition, highlighting the imperative for women's empowerment and gender equality in climate initiatives.
What are Green Jobs?
- Green jobs represent a category of employment directly benefiting the planet and contributing to overall environmental well-being.
- These roles are geared towards mitigating the negative environmental impact of various economic sectors and advancing the creation of a low-carbon economy.
- Occupations involving renewable energy, resource conservation, and the promotion of energy-efficient practices fall under this umbrella.
- The International Labour Organization characterizes green jobs as 'decent jobs that contribute to the preservation or restoration of the environment.'
- They encompass diverse sectors such as manufacturing, construction, renewable energy, energy efficiency, and automobiles, historically characterized by lower female representation.
Gender Disparity in Green Jobs:
- Globally, men tend to transition to green jobs at a faster pace than women.
- Despite India's significant increase in renewable energy capacity by 250% between 2015 and 2021, women constitute only 11% of workers in the solar rooftop sector.
- The Annual Survey of Industries 2019-20 reveals that women workers are predominantly concentrated in industries like apparel, textile, leather, food, and tobacco.
- According to a Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) 2019 report, men make up 85% of the workforce in sectors such as infrastructure, transport, construction, and manufacturing.
- A 2023 study by the Skill Council for Green Jobs indicated that 85% of green skills training was provided to men, with over 90% of women expressing belief that social norms hinder their participation in such training.
- Restrictive social norms contributing to this disparity include perceptions that women are unsuitable for certain technical roles, safety concerns, lower representation in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects, and familial constraints.
Advantages of Women's Engagement in Green Jobs:
- Addressing Gender Bias in the Labour Market: Increased representation of women in green jobs acts as a potent remedy to entrenched gender biases in the labor market.
- By entering traditionally male-dominated sectors like manufacturing, construction, and renewable energy, women challenge stereotypes and reshape societal perceptions of gender roles.
- Expanded Economic Opportunities: Women's greater involvement in green jobs opens up expanded economic avenues for them.
- Participation in sectors such as renewable energy and energy efficiency enables women to access high-growth industries, fostering both economic growth and personal financial stability.
- Beyond economic benefits, engagement in green jobs offers opportunities for women's advancement in technical and social spheres, exposing them to innovative technologies, sustainable practices, and networking opportunities.
- Empowerment of Women's Agency: The transition to green jobs empowers women by granting them agency over their economic destinies.
- In roles contributing to environmental preservation or restoration, women find alignment with a broader sense of purpose, fostering a deeper connection to their work and its societal impact.
- Contribution to Long-Term Gender Empowerment: Participation in green jobs extends beyond immediate economic gains, contributing to the enduring empowerment of women.
- By breaking into historically imbalanced sectors, women pave the way for future generations, inspiring young girls to pursue careers in STEM fields.
- Promotion of Environmental Stewardship: Women's involvement in green jobs resonates with their recognized role as custodians of the environment.
- With a nuanced understanding of the interconnectedness of social and ecological systems, women offer unique perspectives to the development and implementation of sustainable practices within green industries.
Way Forward:
- Addressing Data Gaps: Rectifying the lack of data is imperative to understand the landscape of women's participation in green jobs in India.
- Initiatives should focus on mapping emerging areas for green growth and collecting sex-disaggregated data on green jobs to enhance women's engagement.
- Conducting gender analysis, gathering gender statistics through periodic labor force surveys, and mobilizing additional resources can shed light on the present and future impact of low-carbon transitions on women workers and entrepreneurs.
- Supporting Women Entrepreneurs: Gender-targeted financial policies and products tailored to the needs of women entrepreneurs can catalyze their entry into the green transition market.
- Measures such as collateral-free lending, financial literacy training, and establishing supportive networks are crucial to unlock their potential.
- Developing appropriate tools to assess creditworthiness, facilitate loan disbursement, and reduce operational costs for women-owned businesses is essential.
- Promoting a Gender-Just Transition: A comprehensive strategy for a gender-just transition encompasses employment, social protection, reduction of care work burden, and skill development.
- Collaboration among government, private sectors, and stakeholders is essential to harness innovation, technology, and finance for women entrepreneurs and workers.
- Businesses must prioritize gender justice to mitigate barriers and promote equitable job opportunities for a fair transition.
Conclusion
As India navigates its green transition, prioritizing women's empowerment and gender equity in climate actions is essential for unlocking the co-benefits of a low-carbon and environmentally sustainable economy. Bridging the gender gap in green jobs requires concerted efforts to address social norms, collect gender-disaggregated data, and implement inclusive policies. This is not only an economic imperative but a crucial step towards building a socially equitable and inclusive future for all.
India's Journey to Net-Zero Amidst Mineral Shortages and Technological Challenges

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
By 2030, India wants to set up 500 GW of non-fossil fuel power generating capacity but the problem is that the availability of the minerals is not enough. One needs to process it and manufacture the final product which also means access to technology.
Background:
- As the world shifts towards decarbonization and faces growing demand for critical minerals, governments worldwide are strategically securing access to these vital resources.
- In alignment with this trend, the Indian government has amended mining laws to encourage private sector involvement in the extraction and processing of critical minerals.
Importance of Critical Minerals:
- Driving Decarbonization and Clean Energy Technologies: Critical minerals are pivotal for clean energy technologies such as solar PV plants, wind farms, and electric vehicles, essential for global decarbonization efforts.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), a substantial portion of minerals like copper, rare earths, nickel, cobalt, and lithium will be crucial for meeting Paris Agreement targets.
- Transforming the Transportation Sector: Electric vehicles (EVs) rely heavily on critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel for their battery production.
- As countries shift towards EV adoption, the demand for these minerals is expected to soar, driving sustainable transportation initiatives.
- Essential in Consumer Electronics: Critical minerals are vital for producing consumer electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
- Rare earth elements and other minerals enable the miniaturization and enhanced performance of electronic devices.
- Supporting the Construction Industry: Critical minerals contribute to the production of high-strength alloys, cement, and other building materials in the construction sector.
- These minerals enhance the durability and efficiency of construction materials, promoting sustainability in infrastructure projects.
- Ensuring Defence and National Security: In the defense sector, critical minerals are indispensable for advanced weaponry and communication systems.
- Securing a stable supply of these minerals is critical for maintaining national security and technological superiority.
- Vital for Fertilizers and Agriculture: Minerals like phosphorus and potassium are essential components in fertilizers, crucial for enhancing crop yields and ensuring global food security.
- Crucial for Industrial Magnets: Neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, critical minerals, are crucial for manufacturing magnets used in various industries.
- These magnets are integral components in technologies ranging from electric motors to medical devices.
Geopolitical Dynamics of Critical Minerals and Global Ramifications:
- Economic Dynamics: The geographical concentration of critical mineral resources in select countries like Australia, China, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Indonesia, and Chile fosters economic dependencies.
- Nations with substantial reserves enjoy advantages in revenue generation, job creation, and overall economic development, potentially leading to global economic disparities.
- Geopolitical Power Play: The strategic significance of critical minerals turns their extraction and processing into geopolitical instruments, enabling nations to wield influence on the global stage.
- China, notably, has leveraged its dominance in rare earths to exert political pressure, exemplified by restrictions on exports to countries such as the US and Japan.
- China's control over critical minerals, coupled with its monopolized processing capacity, carries significant geopolitical implications, prompting international collaborations like the US-led Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) to secure supply chains and reduce dependence on authoritarian regimes.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: The concentration of critical mineral resources in specific regions raises concerns about the vulnerability of global supply chains.
- Political instability, trade conflicts, or other geopolitical events in major producing nations can disrupt the supply of critical minerals, adversely affecting industries reliant on them.
India's Objectives and Hurdles in Acquiring Critical Minerals:
- Pursuit of Decarbonization Goals and Energy Transition: India has outlined ambitious objectives for decarbonization, aiming for net-zero emissions by 2070 and establishing 500 GW of non-fossil fuel power generation capacity by 2030.
- Embracing renewable energy sources, electric vehicles, and sustainable practices underscores India's dedication to combatting climate change.
- Heavy Reliance on Imports: Despite possessing identified reserves, India heavily depends on imports to meet its demand for critical minerals.
- This import dependency presents significant challenges, exposing the nation to global market fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, and potential geopolitical tensions.
- Strategic Agreements for Exploration: Acknowledging the necessity to reduce import reliance, India has forged strategic agreements, such as the one with Australia, to jointly explore critical minerals like lithium and cobalt.
- Collaborations with resource-rich nations aim to secure access to raw materials and diversify sources beyond traditional suppliers.
- Lack of Domestic Processing Capacity: Identifying critical minerals marks only the initial step; subsequent processing and manufacturing require advanced technology and infrastructure.
- India encounters challenges in building domestic processing capacity, contributing to an extended gestation period before achieving self-reliance.
- Apart from raw material availability, accessing advanced processing technology remains crucial, emphasizing the importance of technology transfer and collaborative ventures with proficient countries.
- Participation in International Collaborations: India's engagement in the US-led MSP illustrates its dedication to fostering strategic partnerships for securing the critical minerals supply chain.
- The MSP encompasses countries with critical mineral deposits and access to processing technology, fostering a collective endeavor to surmount challenges.
Noteworthy Actions Undertaken by the Indian Government:
- Identification of Critical Minerals: In July 2023, India took a significant stride by identifying a list of 30 critical minerals, distinct from rare earths.
- Each mineral was selected based on criteria such as disruption potential, substitutability, cross-cutting usage, import reliance, and recycling rates.
- The identified minerals are predominantly concentrated in states and union territories, including Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Jammu and Kashmir.
- Amendment of Existing Mining Laws: Subsequently, in November 2023, the Indian government amended existing mining laws to facilitate private sector participation in the auction of 20 blocks containing critical minerals and rare earths.
- This amendment signifies a notable shift in India's mineral sector, unlocking opportunities for private enterprises to engage in the extraction and processing of these vital resources.
Conclusion
There is a mounting concern that the limited access to critical minerals could pose a substantial obstacle to India's ambitious journey towards decarbonization. The achievement of decarbonization objectives hinges on surmounting challenges associated with import reliance, processing capabilities, and technological advancements.
A women’s urban employment guarantee act

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, there has been growing concern about the urban employment scenario for women in India, revealing a significant gap between the demand for employment and the opportunities available to urban women.
Context:
- According to the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), there has been a notable rise in women's workforce participation in India, increasing from 22% in 2017-18 to 35.9% in 2022-23.
- Despite this growth, India's female labor force participation rate (FLFPR) remains lower than the global average of 47% and lags behind countries like China, which boasts an FLFPR of 60%.
- While there has been progress, the FLFPR in India still presents a considerable gap.
Rural Areas:
- The FLFPR in rural areas has shown significant improvement, rising to 41.5% in 2022-23 from 24.6% in 2017-18.
Urban Areas:
- In urban regions, the FLFPR has also experienced growth, increasing to 25.4% in 2022-23 from 20.4% in 2017-18.
- However, women's employment rates in urban areas stood at 22.9% in the last quarter of 2023.
What is the Current Situation (Unmet Employment Demand)?
- The current landscape highlights a substantial unmet demand for employment among urban women, indicating a disparity between urban and rural areas.
- Urban areas exhibit a notably higher proportion of unemployed women actively seeking employment compared to their rural counterparts, with an unemployment rate of 9% in urban regions versus 4% in rural regions.
Two Categories of Unemployment:
- Unemployment manifests in two forms: individuals actively seeking employment and those desiring to work but not engaging in active job-seeking.
- Underutilized Potential: Approximately 25% of urban women have attained higher secondary education, a stark comparison to the 5% in rural areas, suggesting significant untapped potential.
- The low urban employment rates among women underscore the underutilization of their skills and qualifications.
- Role of MGNREGA and Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM): Initiatives like MGNREGA and DAY-NRLM have played a vital role in empowering women financially in rural settings, with over half of the MGNREGA workforce comprising women.
- However, urban settings present unique challenges. Social norms, safety concerns, and inadequate transportation options pose significant barriers to urban women's workforce participation.
Causes of Urban Unemployment Among Women in India:
- Challenges of Social Norms and Safety: Urban women face barriers to entering the workforce due to entrenched social norms, safety concerns, and inadequate transportation options, which hinder their participation.
- Gender-Based Occupational Segregation: Gender-based segregation of occupations and sectors persists in India, leading to limited growth in job opportunities for women and reduced participation rates.
- Economic Impacts: The rapid adoption of new technologies in response to the pandemic has resulted in widespread unemployment, particularly due to business closures and job losses.
- This has widened the skill gap among job seekers.
- Population Growth: The increasing population and labor force contribute to rising unemployment in India, making it challenging for economic growth to keep pace with population expansion.
- Insufficient Investment: Insufficient investment in unorganized sectors, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), and rural development exacerbates unemployment among women.
- Combined with safety concerns and regressive social norms, this leads to underemployment or unemployment.
- Financial Burden: Calculations suggest that funding 150 days of work per year at ?500 daily wages would cost around 1.5% of the GDP. Factoring in material and administrative expenses, this could increase to around 2%.
Proposed Solutions:
- Government Initiatives: The government has introduced protective provisions in labor laws to ensure equal opportunities and a supportive work environment for women.
- Need for Women's Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA): To address urban unemployment comprehensively, there is a call for a national-level Women's Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA) and a Decentralized Urban Employment and Training Scheme akin to MGNREGA for rural women.
Vision for Women's Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA):
- The vision for WUEGA entails women comprising at least 50% (ideally 100%) of the program management staff, fostering gender inclusivity and empowerment at all levels of decision-making.
- Involving women and local communities in program management can enhance the constitutional principle of decentralization, ensuring grassroots participation and ownership.
- Every worksite under WUEGA would be equipped with essential facilities, including childcare services, to support working mothers and promote their participation in the workforce.
- Job opportunities provided by WUEGA will be accessible within a 5-km radius of each participant's residence, with free public transportation available for women, ensuring ease of access to employment opportunities
What are Some Key Urban Employment Initiatives?
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY): Launched under Atmanirbhar Bharat package 3.0, ABRY incentivizes employers to create new employment opportunities while providing social security benefits and addressing employment loss during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan (PMGKRA): PMGKRA focuses on providing immediate employment and livelihood opportunities to distressed individuals, emphasizing the creation of public infrastructure and livelihood assets in rural areas.
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM): DAY-NULM aims to alleviate poverty and vulnerability among urban poor households by facilitating access to self-employment and skilled wage employment opportunities.
- Women-led Waste Management: In Karnataka, women-led initiatives in waste management have empowered women to manage waste collection and drive 'Swacch' vehicles, leading to successful outcomes and increased acquisition of driving licenses among women.
- Pradhan Mantri Rojgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY): PMRPY incentivizes employers to generate new employment opportunities, thereby contributing to job creation across various sectors.
- National Career Service (NCS) Project: NCS offers comprehensive career-related services including job matching, career counseling, vocational guidance, and information on skill development courses, internships, and apprenticeships.
- PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi): PM SVANidhi provides collateral-free working capital loans up to ?10,000 with a one-year tenure to approximately 50 lakh street vendors, enabling them to restart their businesses post the Covid-19 lockdown.
Way Forward:
- Existing urban work opportunities, such as plantation and harvesting reeds on floating wetlands, should be expanded and tailored to local needs through inclusive community consultations.
- Introducing incentives, such as automatic inclusion in welfare boards, can serve as a mechanism to provide essential benefits like maternity entitlements, pensions, and emergency funds, thereby promoting economic security and social welfare for women.
- Closing gender gaps and empowering women align with the Sustainable Development Goals, underscoring not just ethical and constitutional obligations but also the potential for women's increased workforce participation to drive economic growth.
- Addressing societal norms and challenges that hinder women's workforce participation is crucial for fostering an inclusive and equitable work environment.
- Furthermore, the implementation of additional initiatives and policies aimed at promoting women's participation in the workforce will play a pivotal role in advancing the female labor force participation rate in India.
India's Surprising GDP Growth Rate

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's gross domestic product (GDP) growth for the third quarter (October-December) of the fiscal year 2023-24 has surpassed expectations, coming in at 8.4% compared to the estimated 6.7%.
News Summary:
- India's economy saw a growth of 8.4% in the December quarter compared to the same period last year, surpassing the 7.6% growth recorded in the previous quarter and the forecast of 6.7% as per a Reuters poll of economists.
- Further, the NSO pegged a higher GDP growth rate of 7.6% for the entire fiscal year, up from the initial estimate of 7.3%.
- To comprehend India’s unexpected growth, it is imperative to delve into the diverse aspects of the country's economic landscape, and evaluating the factors underpinning this surprising growth is equally crucial, including consumption patterns, savings dynamics, and investment trends.
What are the Factors Driving India’s Growth Surplus?
- Enhanced Economic Momentum: Initially estimated at 7.3 percent, the GDP growth set a promising tone for the fiscal year.
- However, the subsequent second advance estimate, incorporating third-quarter data, surpassed expectations.
- This signals a bolstered economic momentum, notably fueled by increased net taxes contributing significantly to the growth trajectory.
- Impact of Rising Net Taxes and Subsidies: An essential aspect of this growth narrative is the comparison between gross value added (GVA) and GDP growth.
- While GDP growth stands impressively at 7.6 percent, GVA, excluding net tax effects, registers a slightly lower 6.9 percent.
- This nuanced distinction underscores the influence of net taxes and subsidies on overall economic performance.
- Furthermore, with an average growth rate of 8.2 percent for the first three quarters, extrapolations suggest a projected fourth-quarter growth of approximately 5.9 percent.
- Effective Policy Measures and Financial Resilience: Despite GDP figures still below pre-pandemic levels, concerted domestic efforts and policy initiatives have steered the economy toward a 7 percent growth trajectory.
- A significant factor contributing to this progress is the reinforced state of banking and corporate balance sheets, indicative of the efficacy of strategic policy interventions.
Assessment of Challenges and Expected Downturn:
- Impact of High-Interest Rates: The enduring prevalence of high interest rates presents a formidable obstacle to sustained economic advancement.
- Elevated interest rates have the potential to deter borrowing and investment, thereby affecting both consumer expenditure and corporate expansion initiatives.
- This concern is further compounded by the limited effectiveness of monetary policy, given that inflation projections persist above the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) 4% target.
- Normalisation of Net Tax Effects: The current fiscal period has significantly contributed to GDP growth from the escalation of net taxes (taxes minus subsidies).
- However, there is an anticipation that the net tax influence on GDP will revert to normal levels in the upcoming year.
- This normalization implies that the impetus provided by the net tax element to the economic growth rate may diminish, potentially leading to a slowdown.
- Influence of Global Economic Conditions: India's economic performance is intricately intertwined with global economic circumstances.
- Uncertainties prevailing in the global market, such as trade tensions, geopolitical dynamics, and external disruptions, could trigger spill-over ramifications on India's economy.
- Consequently, external factors beyond the nation's jurisdiction may exert influence on the overall economic outlook.
Private Consumption, Household Savings, and Evolving Trends:
- Disparities in Growth: The growth disparity between rural and urban areas is notable, with rural consumption likely trailing urban consumption.
- This discrepancy can be attributed primarily to the disproportionate impact of high food inflation on rural households.
- The sluggish growth of agriculture, at a mere 0.7%, underscores the challenges faced by the rural economy, where food inflation significantly affects discretionary spending.
- Impact of Food Inflation: High food inflation has exerted a considerable influence on consumption patterns, particularly in rural regions.
- Nominal food consumption spending surged by 13% last year, indicative of the inflationary pressure on essential commodities.
- This trend is expected to persist, impacting purchasing power and discretionary spending across both rural and urban landscapes.
- Shifting Consumption Patterns: Household consumption expenditure data reflects a gradual shift towards non-food items over time, mirroring rising per capita income and evolving consumer preferences.
- This transition underscores the necessity to recalibrate weights in the consumer price index basket, which currently reflects consumption patterns from 2011-12.
- Household Savings: Disaggregated data reveals that household savings constitute a substantial portion, comprising 61% of total savings in the economy.
- Despite its prominence, the share of household savings in GDP declined to 18.4% in 2022-23, indicating changing trends in savings composition.
- Household savings are further categorized into financial and physical savings, with financial savings, including bank deposits and securities, witnessing a significant decline to 5.3% of GDP in 2022-23.
- Conversely, physical savings, driven by borrowings for assets like houses, have increased, reflecting evolving preferences and market dynamics.
Analysis of Investment Trends: Public, Corporate, and Household:
- Private Corporate Investment Patterns: The data indicates a stagnant trajectory in private corporate investments, with no clear signs of revival evident in the fiscal year 2022-23.
- This stagnation raises concerns, as private sector investments play a pivotal role in propelling economic growth, fostering job creation, and stimulating innovation.
- Public and Household Investment Dynamics: In contrast to private corporate investments, both public and household investments have exhibited substantial growth during the fiscal year 2022-23.
- Public investments, often influenced by government policies and infrastructure projects, contribute significantly to economic development.
- On the other hand, household investments, encompassing expenditures on residences and durable goods, serve as indicators of consumer confidence and economic stability.
Way Forward:
- Mitigating Policy Uncertainty: The government must mitigate policy uncertainty and streamline compliance costs.
- A stable and foreseeable policy landscape is indispensable for fostering private-sector investments.
- Addressing these concerns is paramount to cultivating an environment conducive to long-term corporate strategizing and sustained economic expansion.
- Encouraging a Comprehensive Revival of Private Investments: Recognizing the pivotal role of a comprehensive revival of private investments in sustaining high growth rates over the medium term is imperative for the government.
- While the government's emphasis on infrastructure development and targeted initiatives like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme has yielded positive outcomes, a more holistic approach is warranted to invigorate investments across diverse sectors of the economy.
Conclusion
India's unexpected GDP growth, underpinned by resilient domestic fundamentals and strategic policy emphasis, necessitates a nuanced examination of various economic facets. As India traverses through these multifaceted dimensions, focused attention on private corporate investments, consumption trends, and savings dynamics emerges as pivotal for achieving sustained and inclusive economic progress. Furthermore, the government's role in ensuring policy stability and minimizing compliance burdens emerges as a decisive factor in unlocking the full potential of India's economic prowess.
Understanding the World of the Informal Waste Picker

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
1st March is celebrated as International Waste Pickers Day in memory of the massacre in Colombia in which 11 workers were brutally killed at the University of Barranquilla.
Context:
- 1st March is celebrated as International Waste Pickers Day in memory of the massacre in Colombia in which 11 workers were brutally killed at the University of Barranquilla.
- While these individuals play vital roles in waste management, they endure systematic marginalization, health risks, and a lack of legal safeguards.
- Hence, delving into the often unnoticed realm of informal waste pickers in India becomes imperative to grasp their indispensable yet overlooked contributions to waste management systems.
What is the Informal Sector in Waste Management?
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) defines the informal sector in waste management as ‘individuals or small and micro-enterprises that intervene in waste management without being registered and without being formally charged with providing waste management services’.
- These workers are the primary collectors of recyclable waste, playing a critical role in waste management and resource efficiency by collecting, sorting, trading, and sometimes even reinserting discarded waste back into the economy.
- Yet, they face systemic marginalization due to non-recognition, non-representation, and exclusion from social security schemes and legal protection frameworks.
What Does the Data Reveal?
- Although precise figures on informal waste pickers are elusive, the Centre for Science and Environment suggests that approximately 5%–2% of the urban population worldwide is involved in the informal waste economy.
- A significant portion comprises vulnerable demographics such as women, children, and the elderly, many of whom are disabled, residing within the most impoverished urban communities. Tragically, they frequently endure instances of violence and sexual harassment.
- According to the Periodic Labour Force Survey 2017-18, India's urban workforce includes nearly 1.5 million waste pickers, with approximately half a million being women.
What are the Challenges Faced by Informal Waste Pickers?
- Systemic Marginalization: Informal waste pickers, predominantly consisting of women, children, and the elderly, face profound marginalization within the waste management ecosystem.
- According to the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2017-18, India's urban workforce includes nearly 1.5 million waste pickers, with half being women.
- Engaging in hazardous work, these individuals collect an average of 60 kg to 90 kg of waste daily without adequate safety measures.
- Their marginalized position within the caste hierarchy exacerbates their vulnerability, leading to health issues such as dermatological and respiratory problems, as well as frequent injuries.
- Economic Instability: Irregular employment, low wages, and susceptibility to exploitation contribute to a cycle of poverty that is challenging to break.
- The 2023 report from the Alliance of Indian Waste Pickers (AIW) underscores the impact of private sector involvement in municipal solid waste management.
- With the adoption of expensive machinery and competitive rates offered to waste generators, private entities marginalize informal pickers, forcing them into hazardous waste collection activities such as scavenging in dump sites.
- This not only heightens health risks but also undermines their income and social standing.
- Lack of Recognition and Representation: The invisibility of informal waste pickers within policy and legal frameworks exacerbates their plight.
- Despite playing a vital role in waste management systems, they are often overlooked in decision-making processes.
- Their contributions are not acknowledged, and they lack representation in discussions regarding waste management policies, leaving them without legal protections, social security, and a voice in shaping the systems they contribute to.
- Exclusion from Formal Waste Management Systems: The involvement of private entities in municipal solid waste management, while introducing technological advancements, further isolates informal waste pickers.
- Dump sites are frequently restricted, limiting their access and pushing them into greater vulnerability.
- As highlighted by the AIW, the privatization of waste management sidelines informal pickers, posing threats to their health, income, and overall well-being.
- This exclusionary approach deepens the gap between formal and informal waste management sectors.
What is the Significance of Informal Waste Pickers in Plastic Management?
- Global Impact: Waste pickers play a pivotal role in plastic waste management worldwide, responsible for collecting and recovering up to 60% of all plastic waste, as emphasized in the 2022 World Economic Forum report.
- Underrecognized Contribution: Despite their vital role in sustainable recycling efforts, waste pickers' contributions often go unacknowledged, and they struggle to secure adequate livelihoods.
- Quantifiable Contribution: Reports from the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and Pew indicate that informal waste pickers gathered 27 million metric tonnes of plastic waste in 2016 alone, constituting 59% of all plastic material collected for recycling. This significant effort prevents plastic from ending up in landfills or oceans.
- Relevance in India: With increasing per capita plastic waste generation in India, the role of waste pickers becomes even more crucial. India is among the top 12 countries responsible for 52% of the world's mismanaged waste, according to a recent CPCB report.
- Utilizing Traditional Knowledge: Waste pickers possess valuable traditional knowledge about waste handling, which could greatly enhance the effectiveness of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) systems if incorporated effectively.
- Rethinking EPR Frameworks: Given their substantial contribution, it is imperative to reassess the formulation of EPR norms to ensure the inclusion and empowerment of millions of informal waste pickers within the new legal framework.
What is the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)?
- EPR presents a hopeful framework by shifting the burden of waste management from municipal bodies to commercial waste producers.
- It marks a departure from conventional "end-of-the-pipe" waste management strategies, incentivizing producers to embrace environmentally friendly practices, minimize waste production, and engage in recycling initiatives.
- In principle, EPR can promote social inclusivity by recognizing the contributions of informal waste pickers and grassroots stakeholders.
Challenges and Considerations Regarding EPR with Informal Waste Pickers:
- Implementation Challenges: Despite its positive aims, the practical application of EPR has raised concerns about its impact on the informal waste sector.
- Globalizing and Organizing Women in Informal Employment (WIEGO) notes that EPR guidelines often redirect waste away from the informal sector, jeopardizing the livelihoods of informal waste pickers and potentially leading to widespread displacement.
- The aspiration for social inclusion through EPR faces a harsh reality, where the informal sector, vital to waste management, risks marginalization.
- Neglect of Informal Waste Pickers: The Alliance of Indian Waste Pickers (AIW) has observed a significant oversight in both the formulation and execution of EPR guidelines in India.
- While stakeholders identified in the guidelines include various entities such as the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), producers, brand owners, industry associations, civil society organizations, and citizens, there is a glaring absence of specific inclusion of informal waste pickers or their representative organizations.
- This omission contradicts the principles of social justice and sustainability that EPR aims to uphold.
- Conflict Between Solid Waste Management Rules and EPR Guidelines: A conflict arises between the Solid Waste Management Rules of 2016 and the EPR Guidelines of 2022, exacerbating the challenges faced by informal waste pickers.
- While the former mandates the involvement of waste pickers in municipal solid waste management systems, the latter fails to prioritize their participation.
- This discrepancy highlights the necessity for a cohesive and integrated approach to waste management policies, wherein the rights and contributions of informal waste pickers are duly recognized and safeguarded.
Way Ahead:
- Revisiting EPR Policies: To realize the potential of EPR in achieving sustainable waste management and social equity, a reevaluation of its policies is essential.
- Acknowledging the traditional knowledge held by waste pickers and involving them in decision-making processes can augment the efficacy of EPR frameworks.
- Furthermore, stakeholders, including producers and policymakers, should actively collaborate with informal waste pickers and their representative bodies to facilitate a fair and equitable transition.
- Plastic Treaty and Equitable Transition: On a global scale, waste pickers play a significant role in sustainable recycling, collecting, and recovering up to 60% of all plastic waste.
- Despite their invaluable contributions, their labour is often undervalued, and they struggle to sustain themselves financially.
- As the global community prepares for the imminent Plastic Treaty aimed at addressing plastic pollution, it is imperative to ensure a just transition for these workers.
- This entails recognizing their contributions and safeguarding their livelihoods, thereby fostering a more inclusive and equitable approach to plastic management.
Conclusion
As India grapples with escalating plastic waste generation, the imperative of integrating informal waste pickers into waste management frameworks becomes ever more pronounced.
Given the valuable traditional knowledge held by these workers, there is a clear opportunity to bolster the effectiveness of EPR systems through a reevaluation of EPR norms and the active engagement of millions of informal waste pickers within a legal framework. It is essential for international collaboration and local endeavours to intersect, prioritizing the recognition, protection, and empowerment of these often overlooked workers. This convergence holds the potential to foster a more inclusive and robust waste management ecosystem.
Are States getting funds they are entitled from the Centre?

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The recent agitations by the governments of Kerala and Karnataka, and the support extended by several State governments, have highlighted many disquieting issues in the practice of fiscal federalism in India.
Context:
- The recent protests by the governments of Kerala and Karnataka, supported by several other state governments, have brought to light several concerning issues regarding fiscal federalism in India.
- These protests underscore the pressing need for the newly constituted 16th Finance Commission (FC) to approach the matter with seriousness and innovation to address grievances related to growing vertical and horizontal inequalities in resource allocation.
What is Fiscal Federalism?
- Fiscal federalism refers to the distribution of financial authority and obligations among various tiers of government within a nation.
- It encompasses considerations like determining the roles and responsibilities of the central and state governments in delivering services, devising mechanisms for revenue generation and allocation among these entities, and establishing fair and efficient systems for transfers or grants distribution to promote equity and effectiveness.
Fiscal Federalism in India:
- The framers of the Constitution stipulated that the Central government would share its tax revenues with the states and provide grants from the Consolidated Fund based on a formula determined by the Finance Commission every five years.
- India operates under a three-tier federal tax system, delineating the powers of the Central government, state governments, and local bodies to levy taxes.
- The Central government possesses the authority to impose taxes on individual and corporate incomes, along with indirect taxes like central goods and services tax (CGST), integrated goods and services tax (IGST), and customs duties. Additionally, it collects surcharges and cesses on various taxes.
- State governments are responsible for levying state goods and services tax (SGST), stamp duties, land revenue, state excise duties, and professional taxes.
- Local bodies exercise jurisdiction over taxes such as property or house taxes, tolls, and utility taxes on services like electricity and water.
What are the Constitutional Provisions?
- The Constitution of India outlines the taxation authority of both the Union and States, categorizing them into the Union List and the State List respectively (as outlined in the Seventh Schedule under Article 246).
- Initially, there was no taxation provision in the Concurrent List.
- However, with the introduction of GST, the need for a concurrent taxation framework arose, leading to the insertion of Article 246A (as the 101st Amendment in August 2016).
- This amendment empowered the Union to legislate for CGST (Central GST) and IGST (Integrated GST), while the States were granted the authority to enact SGST laws.
- Article 270 of the Constitution outlines the mechanism for distributing net tax proceeds collected by the Union government among the Centre and the States.
What are the Concerns with the States?
- Growing Vertical and Horizontal Inequalities: States have raised concerns about increasing disparities both vertically, pertaining to the sharing of resources between the Union and States, and horizontally.
- The Union government's inclination to retain a larger share of its proceeds outside the divisible pool has exacerbated these inequalities.
- Retention of Proceeds: The Union government's practice of withholding a greater portion of its proceeds from the divisible pool has diminished the share allocated to States, contravening mandates from successive Finance Commissions.
- Proliferation of Cesses and Surcharges: Various cesses and surcharges, such as the Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess, have been introduced by the Union government, leading to an expansion of these revenue streams.
- This expansion has resulted in a larger portion of the gross tax revenue being excluded from net proceeds, thereby depriving States of their rightful share.
- Financial Exclusion of States: Over the period from 2009-10 to 2023-24, the Union government collected a substantial cumulative amount of ?36.6 lakh crore through cesses and surcharges, all of which remained unshared with the States.
- The imposition of cesses and surcharges has faced criticism from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG), further highlighting concerns about their impact on state finances.
Way Forward
- Rectifying disparities in resource sharing and addressing the proliferation of cesses and surcharges are critical imperatives for the 16th Finance Commission (FC).
- The FC should proactively address historical imbalances in vertical devolution by compensating States appropriately and ensuring accurate estimates of "net proceeds" in budgetary documents.
- Moreover, it should consider providing lump sum untied grants to States to offset shortfalls in devolution over the past decade.
- Simultaneously, legislative measures must be enacted by the Union government to impose strict limits on the collection of cesses and surcharges, ensuring their automatic expiration after a defined period and preventing their rebranding under different names.
- Furthermore, States must adhere to the principles of fiscal federalism by allocating sufficient resources to local bodies and promoting dynamic and transparent development initiatives at the grassroots level.
What is the Finance Commission?
- The Finance Commission is constituted by the President under Article 280 of the Constitution, mainly to give its recommendations on the distribution of tax revenues between the Union and the States and amongst the States themselves.
- Two distinctive features of the Commission’s work involve redressing the vertical imbalances between the taxation powers and expenditure responsibilities of the center and the States respectively and equalization of all public services across the States.
Functions of the Finance Commission:
- It is the duty of the Commission to make recommendations to the President as to the distribution between the Union and the States of the net proceeds of taxes which are to be:
- Divided between them and the allocation between the States of the respective shares of such proceeds;
- The principles which should govern the grants-in-aid of the revenues of the States out of the Consolidated Fund of India;
- The measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the Panchayats in the State based on the recommendations made by the Finance Commission of the State;
- The measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the Municipalities in the State based on the recommendations made by the Finance Commission of the State;
- Any other matter referred to the Commission by the President in the interests of sound finance.
- The Commission determines its procedure and has such powers in the performance of its functions as Parliament may by law confer on them.
Appointment of the Finance Commission and Qualifications for Members:
- The Finance Commission is appointed by the President under Article 280 of the Constitution.
- As per the provisions contained in the Finance Commission Act, 1951 and The Finance Commission (Salaries & Allowances) Rules, 1951, the Chairman of the Commission is selected from among persons who have had experience in public affairs, and the four other members are selected from among persons who:
- (a) are, or have been, or are qualified to be appointed as Judges of a High Court; or
- (b) have special knowledge of the finances and accounts of the Government; or
- (c) have had wide experience in financial matters and administration; or
- (d) have special knowledge of economics
How are the recommendations of the Finance Commission implemented?
- The recommendations of the Finance Commission are implemented as under:
- Those to be implemented by an order of the President:
- The recommendations relating to the distribution of Union Taxes and Duties and Grants-in-aid fall in this category.
- Those to be implemented by executive orders:
- Other recommendations to be made by the Finance Commission, as per its Terms of Reference
When was the first Commission Constituted and how many Commissions have been Constituted so far?
- The First Finance Commission was constituted under the chairmanship of Shri K.C. Neogy on 6th April 1952.
- 15th Finance Commissions have been Constituted so far at intervals of every five years.
- The 16th Finance Commission was constituted on 31 Dec 2023 with Shri Arvind Panagariya, former Vice-Chairman, NITI Aayog as its Chairman.
- The 16th Finance Commission is required to submit its recommendations by October 31st, 2025.
- However, the recommendations of the 15th FC cover the six years up to 31st March 2026.
Sustainable Practices and Urging for Eco-Friendly Elections in India

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In August 2023, ahead of the Assembly elections in five States, the Election Commission of India (ECI) voiced its concern over the environmental risks associated with the use of non-biodegradable materials in elections.
Context:
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) has emphasized the environmental impact of traditional election materials, urging a shift towards eco-friendly practices, particularly given India's status as the world's largest democracy.
- India must prioritize environmental sustainability in its electoral procedures, recognizing successful eco-friendly initiatives in Kerala, Sri Lanka, and Estonia, and strategizing a comprehensive green transition involving diverse stakeholders.
Why Conducting Elections Require a Paradigm Shift?
- Unrecognized Environmental Impact of Elections: The emissions generated by campaign flights in the 2016 US presidential elections underscore the substantial carbon footprint linked to conventional election methodologies.
- Conventional election practices, marked by paper-based materials, energy-intensive rallies, and disposable items, contribute to environmental harm and affect public health.
- Given the colossal scale of India's elections, these concerns become more pressing, calling for a shift towards eco-friendly election processes.
- Startling Research Findings: Recent research from Estonia (2023) pinpoints transportation to and from polling booths as the primary contributor to carbon emissions in elections, closely followed by the operational footprint of polling booths.
- Adopting digital voting systems has the potential to slash the overall carbon footprint by as much as 40%.
What are Some Successful Models of Eco-Friendly Elections?
- Pioneering Initiatives in Kerala and Goa: During the 2019 general election, the Kerala State Election Commission spearheaded efforts to eliminate single-use plastic materials from campaign activities.
- Subsequently, the Kerala High Court enforced a ban on non-biodegradable materials, leading to the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives like paper posters and wall graffiti.
- Collaborative endeavors between government bodies and district administrations in Thiruvananthapuram ensured the implementation of green election practices, including training sessions for election workers in rural areas.
- In 2022, the Goa State Biodiversity Board showcased eco-friendly election booths crafted from biodegradable materials by local artisans during the Assembly elections.
- Innovative Strategies from Sri Lanka: In 2019, the Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna (SLPP) party initiated the world's first carbon-sensitive, environmentally friendly election campaign.
- This groundbreaking campaign measured carbon emissions from campaign vehicles and electricity usage, offsetting them by planting trees across districts with public participation.
- By addressing the immediate carbon footprint of the campaign and raising awareness about the importance of forest cover, Sri Lanka set a notable example for sustainable election practices.
- Estonia's Digital Voting Model: Estonia pioneered digital voting as an online alternative, significantly enhancing voter participation while reducing environmental impact.
- The success of Estonia's approach underscores the feasibility of digital voting, complemented by stringent security measures, as an eco-friendly and voter-centric solution.
A Roadmap for Sustainable Green Elections:
- Political Leadership and Digital Campaigning: Political parties should enact legislation mandating eco-friendly election practices, integrating them into the Model Code of Conduct governing campaign activities.
- Encouraging the adoption of digital platforms for campaigning and door-to-door outreach can substantially reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional public rallies.
- Incentivizing Sustainable Practices and Infrastructure Development: Offering incentives for political parties to use sustainable materials like natural fabrics and recycled paper in place of plastic and paper-based campaign materials, alongside supporting waste management and local artisans.
- Government investment in digital voting infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, ensures reliable internet access and accessible digital devices for all voters.
- Role of the Election Commission of India (ECI) with Government Backing: The ECI can advocate for digital voting systems, highlighting their environmental benefits and addressing security concerns through comprehensive measures.
- Public Awareness and Civil Society Engagement: Civil society organizations can lead public awareness campaigns, educating citizens about the environmental impact of traditional election methods and advocating for eco-friendly alternatives.
- Monitoring the implementation of green initiatives and advocating for transparency and accountability in the electoral process.
- Media's Advocacy Role: Media outlets can spotlight the environmental consequences of conventional election methods through investigative reporting and by showcasing successful eco-friendly initiatives.
- Global Collaboration for Sustainable Elections: Collaborating with countries like Sri Lanka and Estonia, which have successfully implemented eco-friendly election practices, to share insights and support international platforms for exchanging best practices in sustainable electoral initiatives.
Hurdles and Potential Solutions for Conducting Eco-Friendly Elections:
- Technology Barriers: Ensuring a seamless transition to digital voting demands robust technological infrastructure, particularly in remote regions where connectivity may be sparse.
- Upholding the integrity and security of digital systems is paramount, requiring comprehensive safeguards against cyber threats and manipulation to uphold public trust.
- Financial Impediments: Embracing eco-friendly materials and technologies entails significant initial investments, posing challenges for governments constrained by budgetary limitations.
- Competing priorities may hinder the allocation of funds toward sustainable electoral practices, despite their long-term environmental advantages.
- Cultural Shifts and Public Doubts: Cultural norms often associate physical polling booth presence with democratic participation, necessitating efforts to shift perceptions towards digital methods.
- Addressing public skepticism regarding new technologies, particularly concerns about security and reliability, requires proactive measures to build trust and confidence.
- Promoting Transparency and Accountability: The adoption of eco-friendly and digital strategies must be accompanied by transparent processes and robust auditing mechanisms.
- Establishing clear protocols for auditing new practices fosters accountability and addresses concerns about fairness and impartiality, enhancing public trust.
- Tackling Logistical Complexities: Executing large-scale electoral reforms demands meticulous planning and coordination across various stages.
- From sourcing eco-friendly materials to training personnel, addressing logistical challenges systematically is essential for smooth implementation.
Conclusion
Adopting environmentally conscious electoral practices represents not only an imperative for India but also a chance to lead by example on the global stage. Harmonizing high-level policies with ground-level efforts and engaging various stakeholders—political entities, Election Commissions, governments, citizens, media, and civil society—can position India as a trailblazer in conducting sustainable elections. This transformative approach not only integrates environmental responsibility but also reinforces the connection between ecological stewardship and the core tenets of democracy.
An expansive land management policy is overdue

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The global economic impact of land degradation on ecosystem services amounts to an estimated $6 trillion annually.
Context:
- Land plays a crucial role across various human endeavors, offering ecological, economic, social, and cultural benefits.
- However, the multi-faceted nature of land is often overlooked in management practices, leading to heightened stress, degradation, and environmental strain.
- Globally, land degradation results in annual losses of ecosystem services estimated at USD 6 trillion.
- The 14th Conference of Parties (COP14) of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), held in New Delhi in 2019, highlighted the widespread challenge of land degradation faced by different nations and emphasized the importance of achieving Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN).
What is Land Degradation?
- Land degradation refers to the deterioration of the quality and productivity of land resources, typically caused by human activities and natural processes.
- It involves the loss of soil fertility, reduction in vegetation cover, depletion of water resources, and overall decline in the capacity of the land to support various ecosystem functions and human activities.
- Land degradation can take various forms, including soil erosion, desertification, deforestation, salinization, and contamination by pollutants.
- It poses significant environmental, economic, and social challenges, impacting agricultural productivity, food security, biodiversity, and the livelihoods of millions of people around the world.
- Addressing land degradation is crucial for sustainable land use, environmental conservation, and the well-being of present and future generations.
What is the Current Status of Land Degradation in India?
- From 2015 to 2019, UNCCD data reported that 30.51 million hectares of India's land had degraded, accounting for 9.45% of the nation's total landmass by 2019, up from 4.42% in 2015.
- During this period, 251.71 million Indians, constituting 18.39% of the population, were exposed to land degradation, with 854.4 million individuals experiencing drought from 2015 to 2018.
- According to the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India, published by the Space Applications Centre (SAC) of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the extent of land degradation and desertification in India reached 97.84 million hectares in 2018-19.
- This atlas offers state-wise data on degraded land, aiding in the planning and execution of initiatives aimed at land restoration by providing crucial data and technical insights.
Global Scenario:
- Land degradation exhibits significant regional variations, with Sub-Saharan Africa, Western and Southern Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean witnessing degradation rates surpassing the global average between 2015 and 2019.
- In Eastern and Central Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean, over 20% of the total land area faced severe degradation by 2019.
- Since 2015, Sub-Saharan Africa saw its degraded land increase from 6.7% to 14.63%, while Western Asia and Northern Africa experienced a rise from 3.78% to 7.18%.
What are the Different Causes of Land Degradation?
- Deforestation: Driven by population growth and resource demand, deforestation weakens soil structure, making it prone to erosion by wind and water.
- Deforestation is particularly rampant in areas like Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- Mineral Processing: Industries such as limestone grinding and ceramic production release substantial dust, settling in surrounding areas and contributing to land degradation.
- Soil Erosion: Processes like water flow, wind, rainfall, and landslides strip away the fertile topsoil layer, leaving behind less fertile subsoil, and rendering land unsuitable for cultivation and agriculture.
- Overgrazing: Excessive grazing by animals removes grass cover, making soil susceptible to erosion by wind and water.
- This phenomenon, common in hilly areas like Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat, disrupts soil structure and fertility.
- Over-Irrigation: In states like Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, excessive irrigation leads to soil salinity and alkalinity, diminishing its fertility and suitability for agriculture.
- Mining Sites: After mining activities, abandoned sites leave deep scars and harmful materials that degrade the soil, rendering it unsuitable for productive use.
- Deforestation due to mining in states like Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha exacerbates land degradation.
- Industrial Effluents: Waste disposal from industries is a significant source of land and water pollution, contributing to land degradation.
- Mining and Developmental Projects: Large-scale clearing of forests for mining and construction projects further accelerates land degradation under the guise of development.
- Commercial Exploitation of Forests: High-value trees and plants are harvested for economic gain, disrupting soil-plant interactions essential for soil stability.
- Overgrazing, mining, agricultural expansion, floods, and forest fires are key drivers of deforestation, exacerbating land degradation.
- Desertification: Human activities and climate change contribute to desert-like conditions in arid or semi-arid regions, leading to the spread of sand onto fertile agricultural lands, reducing soil fertility, and hampering agricultural productivity.
Challenges in the Management of Land Degradation in India:
- India with only 2.4% of the world’s geographical area and more than 17% of the world's population experiences several land management challenges.
- Arable land in India is around 55% of the total geographical area and forest cover accounts for another 22%.
- The rest is desert, mountains, etc.
- Around 30% of the total geographical area is degraded land.
- Access to agricultural land continues to be an important livelihood issue as a significant share of the population depends on agriculture for their sustenance.
- Development targets and the demand for land to accommodate the growing population, infrastructure, rapid urbanization, and social, cultural, and environmental aspects are placing unprecedented pressure on land.
- This is resulting in more competition among farmers and between agriculture and other land resource-based sectors, as well as land use conflicts, escalation of land prices, and changing land rights.
- Across the country, natural areas are being squeezed and ecological functions are being lost.
- Not only does this adversely affect the livelihood opportunities of the people who directly depend on environmental resources, but also the buffering effects of natural ecosystems in the face of disasters such as floods and droughts, temperature rise, and environmental pollution are severely compromised.
- Climate change has brought with it another set of challenges.
- In India, current land management practices are sectoral with each department following its own approach.
- Land management falls under the purview of State governments.
- Further, cultural land is privately owned and land-use decisions are constitutionally vested with the owner.
- Apart from this administrative complexity, the challenges to adopting and implementing appropriate land management practices in the country include knowledge gaps, a short-term planning bias, a fragmented approach, a lack of action for unforeseen events, and regulatory barriers.
What Steps Need to be Taken for Land Management?
- Set up a Multi-stakeholder Platform: As a critical mechanism to achieving sectoral integration and addressing these challenges, it is imperative to set up a multi-stakeholder platform at the district and sub-district levels to bring together farmers, other land managers, policymakers, civil society organizations, business leaders, and investors under a common platform.
- Article 243ZD (1) of the Constitution provides for district planning committees to consolidate plans from panchayats and municipalities.
- This committee may be activated in the direction of preparing a land management plan, covering both agricultural and non-agricultural sectors.
- Landscape Approach: A landscape approach will be useful in this context as it will provide deep insights to assess the potential of land and the scope of allocation and reallocation of land for appropriate uses.
- This will help with evaluation, negotiation, trade-off, and decision-making.
- A climate-smart landscape approach will contribute to climate objectives, increased agricultural production, improved local livelihoods, and the conservation of biodiversity.
Government Initiatives to Combat Land Degradation and Desertification in India:
- Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India, published by Space Applications Centre (SAC) Indian Space Research Organisation, Ahmedabad, which provides the extent of land degradation and desertification in India, states that the land degradation and desertification in the country has been estimated to be 97.84 million hectares in 2018-19.
- It provides state-wise areas of degraded land which is helpful in the planning and implementation of schemes aimed at the restoration of land by providing important data and technical inputs.
- An online portal has been developed with the help of Space Application Center(SAC), Ahmedabad for visualization of degraded areas of land with the processes causing degradation.
- A Centre of Excellence has been envisaged at the Indian Council for Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) Dehradun for enhanced South-South Cooperation.
- It aims at knowledge sharing, promotion of best practices, sharing India’s experiences with cost-effective and sustainable land management strategies, developing ideas for transformative projects and programs, and capacity building.
Way Forward:
- Advancing Integrated Landscape Management: Despite existing on-ground experiences, there is a lack of systematic institutional support for this approach, highlighting the need for concerted efforts to promote it.
- Embracing the Value of Landscape: Echoing the European Landscape Convention's recognition of landscape as vital for individual and societal well-being, greater emphasis should be placed on understanding and preserving landscapes.
- Recognizing the Role of Sustainable Land Management: Reports like the U.K. Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology's assessment underscore the importance of managing land sustainably for environmental benefits, including addressing climate change, ensuring food security, and mitigating biodiversity loss.
- Parliamentary Action in India: Indian lawmakers can spearhead discussions on the evolving challenges of integrated land management practices and play a pivotal role in crafting policies for long-term sustainability.
- This necessitates the involvement of stakeholders at all levels, fostering collaboration horizontally and vertically across the spectrum.
Preserving Democratic Integrity Through Privacy Safeguards in the Digital Age

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The big data economy, powered by massive datasets and unprecedented levels of personal information has fundamentally altered how a country conducts elections, and how people vote.
Background:
- The emergence of the big data economy has significantly altered the landscape of elections and individual voting patterns, offering both benefits and challenges.
- As the general elections approach in two months, it becomes imperative to delve into the far-reaching effects of extensive datasets on political scenarios.
- Equally important is a comprehensive understanding of the privacy implications, emphasizing the critical necessity for robust data protection measures, especially in anticipation of the upcoming elections in India.
What are the Challenges Arising from Big Data's Influence on Elections?
- Precision Targeting and Tailoring: Big data enables political campaigns to engage in micro-targeting, tailoring messages and campaign content to specific demographics or individual voters.
- By analyzing extensive datasets, candidates gain insights into voters' preferences, behaviors, and opinions, facilitating highly customized outreach efforts across various communication channels.
- Lack of Transparency and Consent: A significant concern is the opacity surrounding collecting, processing, and utilizing personal information.
- Voters often lack awareness of databases containing detailed personal data and the extent to which it's used for political purposes.
- Informed consent becomes elusive, as individuals are unaware of how their data is harnessed, limiting their ability to control its usage.
- Reinforcement of Power Dynamics: The abundance of data amplifies the power of political entities to influence voters through targeted messaging and strategic communication.
- Candidates can craft narratives tailored to specific groups, addressing issues and concerns discerned from data analysis.
- This sophisticated targeting extends beyond demographic attributes, delving into personal preferences and habits.
- Risks of Manipulation and Exploitation: While big data offers campaign efficiency and targeted communication, it also presents risks of manipulation and exploitation.
- Unethical practices, such as the strategic dissemination of misinformation to exploit voter sentiments, can undermine the integrity of the electoral process.
- Information asymmetry between political entities and voters raises concerns about privacy invasion and democratic principles.
What are the Consequences of Social Media and Networks Effects?
- Network Effect: The network effect, central to social media platforms, describes the increasing value and utility of a network as more users join.
- Larger user bases offer enhanced connectivity, content creation, and interaction opportunities, drawing individuals to these platforms.
- Profound Data Collection and User Profiling: Social media platforms thrive on comprehensive data collection, going beyond basic demographics to create detailed user profiles.
- Users' interactions provide valuable insights into their preferences, behaviors, and associations, enabling targeted advertising and personalized content delivery.
- Lack of Transparency in Data Practices: Users often lack awareness of the extent and granularity of data collected by social media platforms, raising concerns about privacy invasion and potential misuse.
- Limited transparency results in minimal user control over data utilization, highlighting the need for greater transparency and accountability.
- Algorithmic Personalization and Decision-Making: Algorithms drive personalized user experiences on social media platforms, curating content based on collected data.
- While personalization enhances user satisfaction, it also introduces concerns regarding algorithmic biases and selective information presentation, influencing user perspectives and behaviors.
- Commercialization and Data Exploitation: Social media platforms monetize user data through direct sales or personalized advertising, leveraging extensive user profiling for targeted marketing.
- While this practice benefits platforms economically, it sparks ethical debates surrounding the commercialization and commodification of user information.
The Indian Data Protection Act has Critical Flaws.:
- India’s Data Protection Act has not yet come into force. Its critical flaws include:
- Absence of Limitations on Government’s Powers to Access Data: The Act lacks clear limitations on governmental powers to access data, raising concerns about potential misuse and infringing on citizens' right to privacy.
- This ambiguity undermines the fundamental principle of safeguarding individuals from unwarranted surveillance.
- Lack of Independence for the Data Protection Board: The absence of proper checks and balances compromises the independence and effectiveness of the Data Protection Board, leaving it vulnerable to external influences and pressures.
- Instances of withholding information by authorities, citing the Data Protection Act, underscore the potential for confusion and misuse during this transitional phase.
- Challenges in Enforcement and Redressal: The non-functional status of the Data Protection Board exacerbates challenges in enforcement and redressal mechanisms.
- Individuals lack a reliable channel for seeking recourse in privacy violations, further complicating the protection of individual rights.
- Deficiencies in Actionable Rights: The Act needs to adequately address individual rights, notably omitting essential provisions such as the right to compensation.
- This limitation restricts individuals' ability to seek appropriate remedies for privacy infringements, weakening the overall efficacy of the data protection framework.
Way Forward:
- Seizing the Opportunity for Improvement: The forthcoming rules to operationalize the Data Protection Act represent a pivotal moment to address existing shortcomings and enhance privacy safeguards.
- Engaging stakeholders through multi-stakeholder consultations is imperative to ensure a comprehensive and diverse range of perspectives informs the regulatory framework.
- Placing Individuals at the Core: Prioritizing the impact on individuals is paramount in shaping the rules.
- By emphasizing individuals' rights and privacy concerns, the regulatory framework can better serve the needs and interests of citizens.
- Sustained and inclusive consultation processes must remain ongoing, fostering an environment conducive to incorporating feedback from diverse stakeholders.
- The urgency for Legislative Reforms: While the rules offer avenues for corrective action, the imperative for legislative reforms cannot be overstated.
- Foundational flaws, particularly concerning governmental powers and the independence of the Data Protection Board, necessitate substantive changes at the legislative level.
- Striking a delicate balance between feasibility and inclusivity is essential to avoid hasty amendments that may compromise the integrity and effectiveness of the data protection regime.
Conclusion
As India approaches elections, the need for a people-centric data protection framework becomes evident, striking a delicate balance between the advantages of digitization and the preservation of privacy and democratic values. Emphasizing inclusive and rights-based models is crucial in effectively addressing the complexities presented by the big data landscape, fostering a resilient and equitable digital future that cannot be underestimated.
Paradigm Shift: Unleashing Local Wisdom for Sustainable Economic Growth

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India’s policymakers must free themselves from Western-dominated theories of economics and in this, local solutions are the way to solve global systemic problems.
What is Economic Growth?
- Economic growth denotes the expansion of a nation's economy over a defined duration.
- This expansion is commonly quantified by the aggregate output of goods and services within the economy, known as gross domestic product (GDP).
Key Points:
- GDP Measurement: Gross domestic product serves as the primary metric for assessing economic growth, reflecting the overall economic activity within a nation.
- GDP represents the total monetary value of all finalized goods and services generated within a country's borders during a specified timeframe.
- Definition of Economic Growth: Economic growth signifies the sustained increase in a country's real national income and per capita income over an extended period.
- This progression indicates an expansion in the nation's economic output and its citizens' earning potential.
- Long-term Perspective: Economic growth is characterized by its longitudinal nature, emphasizing continuous advancement in a nation's economic prosperity over time.
- It underscores the importance of sustained increases in productivity, income levels, and overall economic well-being.
Current Economic Analysis:
- GDP as a Benchmark: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth has emerged as the predominant yardstick for evaluating the overall well-being of economies worldwide.
- It serves as a comprehensive measure of a nation's economic output, encompassing the total value of goods and services produced within its borders over a specific period.
- Paradigm Shift: There has been a notable shift in economic ideology, prioritizing the expansion of the economic "pie" before addressing issues of income distribution.
- This paradigmatic change has supplanted previous socialist models that emphasized addressing socio-economic disparities at the grassroots level.
- Historical Economic Focus: Since the liberalization of India's economy in 1991, successive governments have placed considerable emphasis on fostering GDP growth as a primary driver of economic development.
- This policy orientation has underscored the significance of achieving robust GDP expansion as a cornerstone of national economic policy.
- Projected Growth Trajectory: The First Advance Estimates of National Income for the fiscal year 2023-24 indicate a projected Real GDP growth rate of 7.3 percent for India.
- This forecast, as outlined in the Macro-Economic Framework Statement 2024-25, reflects the anticipated trajectory of India's economic growth in the near term.
- Global Economic Projections: According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), India is poised to ascend to the rank of the third-largest economy globally by 2027, measured in terms of market exchange rate.
- Additionally, the IMF anticipates a substantial increase of 200 basis points in India's contribution to global economic growth over the next five years.
Addressing Challenges and Considerations:
- Beyond GDP: Limitations in Assessing Well-being: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) fails to comprehensively measure a nation's overall standard of living or well-being.
- It overlooks critical aspects that contribute to general welfare, such as environmental sustainability and quality of life indicators.
- External Costs and Trade-offs: While GDP growth may signify increased economic output, it can also entail adverse consequences, including environmental degradation and societal trade-offs.
- For instance, heightened industrial activity may lead to environmental harm or infringe upon individuals' leisure time.
- Socioeconomic Inequality: The distribution of GDP among a country's populace significantly impacts its citizens' quality of life.
- India's economic progress, marred by increasing inequality, underscores the importance of addressing disparities in wealth distribution to foster inclusive growth.
- Unemployment Challenges: Despite remarkable GDP growth, India grapples with persistent challenges in providing adequate employment opportunities.
- The discrepancy between economic expansion and job creation highlights the need for targeted interventions to address unemployment concerns.
- Reimagining Economic Progress: Rethinking traditional metrics of economic success is imperative to address the multifaceted challenges facing nations today.
- Embracing alternative indicators that prioritize sustainability, social equity, and inclusive growth can pave the way for a more holistic approach to economic development.
Inclusive and Sustainable Development:
- Traditional economic models advocate for linear development paths, prioritizing urbanization and industrialization.
- However, India's slow progress in these areas raises concerns, especially amidst global climate challenges.
- The reliance on fossil fuels for growth further complicates matters, requiring a reevaluation of development paradigms.
- India must pioneer inclusive and environmentally sustainable growth models to address these challenges effectively.
- This necessitates a shift towards alternative pathways that prioritize both economic advancement and environmental stewardship.
- By fostering innovation and collaboration, India can lead the way towards a more sustainable future for itself and the world.
Fossil Fuels and the Modern Economy:
- ??Fossil fuels play a crucial role in the global economy, serving as vital resources for various sectors.
- These include coal, oil, and natural gas, which contribute significantly to the production and distribution of essential materials for modern society, including steel, concrete, plastics, and food.
- While fossil fuels have fueled industrialization and economic growth, their adverse effects on both human health and the environment raise significant concerns.
- Balancing their economic importance with the need for sustainable alternatives poses a challenge for modern society.
Way Forward:
- Addressing the Global Climate Crisis: India must confront the pressing challenge of the global climate crisis while simultaneously advancing its own economic growth to bridge the gap with developed nations.
- Embracing a New Paradigm: India should strive to forge a new paradigm of progress that prioritizes inclusive and environmentally sustainable growth, benefiting both its citizens and the global community.
- Diversifying Economic Perspectives: Policymakers in India ought to liberate themselves from the dominance of Western economic theories, fostering a more diverse and contextually relevant approach to economic development.
- Harnessing Rural Potential: Rural India has the potential to serve as a hub of innovation, generating novel solutions in institutions and policies conducive to inclusive and sustainable growth, with relevance beyond national borders.
- Local Solutions for Global Challenges: Systems science underscores the efficacy of locally crafted solutions, collaboratively developed by communities in their own locales, as effective remedies for global systemic issues such as climate change and inequitable economic growth.
- Prioritizing Economic Development: A concerted focus on economic development is essential, encompassing efforts by policymakers and communities to enhance the standard of living and economic conditions across the country.
- Holistic Approach to Development: Economic development encompasses not only material prosperity but also the overall quality of life of the population, encompassing factors such as education, healthcare, and nutrition.
- Enhancing Living Standards: The advancement of a nation's economic development correlates with improvements in the living standards of its people, reflecting better access to education, healthcare, and other essential amenities.
Upholding Constitutional Values: A Call Beyond Celebration

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
While SC judgments on electoral bonds and Chandigarh mayoral election are welcome, they ought not to merely be an episodic legitimisation of the façade of constitutionalism.
Recent Indian Supreme Court Rulings Questioning Government Actions:
- Invalidating the Electoral Bonds Scheme: The Supreme Court ruled the electoral bonds scheme unconstitutional, posing a challenge to a major government initiative concerning political funding.
- AAP Victory in Chandigarh Mayoral Election: The Court affirmed the Aam Aadmi Party's (AAP) victory in the Chandigarh mayoral race, overturning a local electoral outcome and directly challenging administrative actions in the election process.
Analyzing the Supreme Court's Balancing Act:
- Observe the Executive's Activities to Sustain Its Own Lawfulness: The Supreme Court of India, as the highest judicial authority, bears the weighty responsibility of interpreting and upholding the Constitution.
- In fulfilling this duty, it frequently engages in a precarious balancing act, striving to negotiate the intricacies of challenging executive decisions while safeguarding its own credibility.
- This intricate dance between the judiciary and the executive mirrors the broader constitutional framework, wherein checks and balances play a pivotal role in preventing the dominance of any single branch.
- Significance of Upholding Legitimacy: A fundamental aspect of this delicate balancing act is the imperative to avoid antagonizing the executive to the extent that it imperils the Court's legitimacy.
- The Court recognizes that maintaining this delicate equilibrium is indispensable for the institution’s continued existence.
- A collapse in the Court's credibility could undermine the very fabric of the constitutional order it endeavours to uphold.
- This consideration often influences the Court's deliberations, prompting careful consideration of the potential ramifications for its stature.
What are the Issues with the Court's Balancing Act Against the Executive?
- The Court grapples with the intricate balance between its roles as a legal arbiter and guardian of constitutional integrity, particularly when confronted with executive actions that may encroach upon constitutional principles.
- Recent decisions, like invalidating the electoral bonds scheme, highlight the Court's assertion in safeguarding democratic norms while cautiously avoiding confrontation to preserve its legitimacy.
- However, concerns arise when the Court's reluctance to challenge the executive overshadows its commitment to constitutional values, potentially legitimizing authoritarian agendas.
- Maintaining a facade of constitutionalism can lead to questions regarding the Court's consistent commitment to curbing executive power.
- The Court must uphold constitutional principles robustly, even if it means challenging the executive's authority uncomfortably, to ensure justice and democracy prevail.
- Success in this delicate balancing act lies not only in the decisions rendered but also in the Court's unwavering dedication to justice and democracy, despite formidable executive pressures.
Analysing Political Culture, Public Sentiment, and the Court's Influence:
- Disparity Between Legal Pronouncements and Public Opinion: Recent Supreme Court rulings against government initiatives, such as invalidating the electoral bonds scheme, fail to resonate as significant concerns within public sentiment, highlighting a disconnection between legal decisions and public perception.
- Normalization of Institutional Decline: The lack of public outcry over decisions challenging government actions reflects a worrying normalization of institutional decay, where issues like electoral malpractice are perceived as minor errors rather than threats to democracy.
- Aestheticization of Politics: Rather than prompting political concern, events like the Chandigarh mayoral race are often viewed as entertainment, illustrating a shallow engagement with political developments that overlook their implications for governance.
- Opposition Fragmentation and Political Dynamics: The Opposition's fragmented state impedes its ability to leverage judicial decisions against the government, weakening efforts to hold the ruling party accountable and allowing it to diminish the significance of adverse legal rulings.
- Courts' Influence on Political Culture: While the Court delivers commendable decisions, it operates within a political culture seemingly immune to the erosion of democratic norms, limiting its ability to shape broader perceptions.
- Legal victories, though sound, struggle to spark the necessary public mobilization to impact the prevailing political climate.
Way Ahead:
- Embracing Civic Courage and Critical Inquiry: Amidst institutional erosion and a dearth of political engagement, there is a pressing need for civic courage, critical thinking, and a commitment to holding the government to account.
- Instances of institutional impropriety, whether through overreach, repression, or communalisation, often fail to provoke a robust public response.
- The reluctance to critically engage with such issues perpetuates a political climate where even pro-democracy decisions are seen as rare anomalies rather than normative outcomes.
- As such, the public's reception of these rulings becomes pivotal in shaping their enduring impact.
- Calling for a Reassessment of Institutional Roles: Recent legal verdicts must be part of a broader effort to challenge the consolidation of authoritarianism and communalism.
- The prevailing political climate necessitates critically reassessing institutional roles in fostering genuine accountability.
Conclusion
Recent Supreme Court rulings, while potentially positive, warrant cautious consideration amid broader institutional challenges. Navigating issues like legitimacy balancing, fragmented opposition, and institutional normalization presents formidable obstacles. The enduring impact of these decisions hinges on both public reception and the Court's steadfast dedication to constitutional principles, determining whether they signify substantive progress or fleeting glimpses of hope amidst broader democratic challenges in India.
India Allows 100% Foreign Direct Investment in Space Sector

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the government of India has approved the amendment in the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy for the space sector.
Context:
- India’s space industry, though nascent compared to global leaders such as the US, Russia, and China, has made significant strides in cutting-edge technologies, as evidenced by successful missions like Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and XpoSat.
- These achievements have not only demonstrated India’s economic prowess in space technology but have also positioned the Country favourably on the global map.
- However, the sector faces challenges, particularly in funding.
- Despite the sector’s expansion from 10 to 150 startups within three years, the absence of a substantial domestic investor pool interested in space ventures, which are inherently slow to yield returns, has hindered growth.
- The only other way out was to look at Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy.
- According to experts, “India stands at a critical juncture in its space journey.
- With strategic investments in infrastructure and manufacturing, alongside fostering innovation and education, India can achieve its goal of a US$44 billion space economy by 2033, enhancing its position as a global leader in space technology and services.
What is the Current Status of India’s Space Sector?
- India's expertise in the space sector is globally acknowledged, with achievements ranging from cost-effective satellite construction to launching foreign satellites.
- Aligned with its commitment to the Geneva Conference on Disarmament (1979), India advocates for the peaceful and civilian utilization of outer space, opposing any militarization efforts.
- The Indian Space Economy is valued at approximately $8.4 billion, constituting around 2-3% of the global space economy.
- ISRO stands as the 6th largest space agency globally, boasting an impressive success rate.
- India also ranks 5th worldwide in the number of private space companies, with over 400 such entities.
- Budgetary Allocation: The Department of Space has witnessed a nominal 4% increase in its allocation in the Interim Union Budget for 2024-25, rising from ?12,545 crore to ?13,043 crore.
- Future Projections: Implementation of the Indian Space Policy 2023 could propel the Indian space economy to reach $44 billion by 2033.
- Growth in Space Start-Ups: The number of Space Start-Ups has surged from just 1 in 2014 to 189 in 2023, as reported by the DPIIT Start-Up India Portal.
- Investment in Indian Space Start-Ups has concurrently risen to $124.7 million in 2023.
Key Changes in FDI Policy:
- With the privatization of space launches, India aims for a significant five-fold increase in its share of the global launch market.
- The recent changes in the FDI policy reflect a more welcoming approach to foreign investment.
- Specifically, the satellite sector which used to have strict rules has now been split into different parts each with its own limits on how much foreign investment is allowed.
- Launch Vehicles and Associated Systems/Subsystems: Foreign investment up to 49% is permitted under the automatic route with government approval mandated for anything beyond this threshold.
- This includes activities related to the establishment of spaceports for spacecraft launches and receptions.
- Satellite Manufacturing and Operation: The automatic route allows for up to 74% FDI covering satellite manufacturing, operation, satellite data products and both the Ground Segment and User Segment.
- Approval from the government is required for FDI exceeding 74% in these activities.
- Manufacturing of Components and Systems/Subsystems: Foreign investors are now allowed to invest up to 100% in manufacturing components and systems for satellites, ground segments and user segments through the automatic route.
- The decision to liberalize FDI norms in the space sector stems from a strategic vision outlined in the Indian Space Policy 2023.
- By fostering a more investor-friendly environment the government aims to tap into the potential of non-government entities (NGEs) encouraging them to invest in Indian companies within the space domain.
- This move is expected to drive technological advancements, scale up operations globally and boost India's position in the global space economy.
Recent Advancements in the India’s Space Sector:
- Indian Space Policy 2023: This policy delineates the roles and responsibilities of entities like ISRO, NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), and private sector players with the aim of bolstering involvement from research, academia, startups, and industry.
- Strategic Proposals by SIA: The Space Industry Association – India (SIA-India) has recommended in its Pre-Budget Memorandum for FY 2024-25 a substantial increase in India's space budget.
- Defence Space Agency (DSA): India inaugurated its Defence Space Agency (DSA) alongside the Defence Space Research Organisation (DSRO), tasked with developing space-based weapons to counter adversaries.
- Defence Space Mission Launch: The Indian Prime Minister unveiled the Defence Space Mission during the Defence Expo 2022 in Gandhinagar.
- Expansion of Satellite Manufacturing: India's satellite manufacturing sector is forecasted to grow to USD 3.2 billion by 2025, up from USD 2.1 billion in 2020.
- SAMVAD Program: ISRO introduced the SAMVAD Student Outreach Program at its Bengaluru facility, aimed at fostering space research among young minds.
- The objective is to bolster India's expanding space program, encourage private sector participation, drive technological innovation, and position the nation as a prominent player in the global space landscape.
Importance of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the Space Sector:
- Advancement in Space Missions: India's achievements in space missions have positioned it as a reliable provider of cost-effective space solutions globally, with FDI expected to further enhance technological capabilities and expand operations.
- Boost to Manufacturing: Encourages the establishment of manufacturing facilities within India, aligning with the government's 'Make In India' initiative and bolstering domestic manufacturing capabilities.
- Private Sector Engagement: FDI facilitates greater private sector involvement in India's space endeavours, transitioning from ISRO-driven initiatives to leveraging space technology for commercial applications and fostering industry participation.
- Integration into Global Value Chains: Expected to integrate Indian companies into global value chains, enabling them to contribute significantly to the global space economy.
- Technology Uptake and Global Collaboration: FDI promotes the absorption of advanced technology and facilitates global integration, enabling companies to enhance product sophistication, scale operations globally, and increase their share in the global space economy.
- Enhanced Business Environment: FDI policy reforms improve the Ease of Doing Business in India, attracting greater FDI inflows and fostering investment, income, and employment growth.
- Stimulus for Research and Innovation: FDI in the space sector stimulates technology transfer, fosters research collaborations, and encourages innovation, driving advancements in space technology and applications.
What are the Challenges?
- Limited Investor Engagement: Investors show limited interest in the later stages of space tech development, likely due to perceived high risks and long-term investment horizons.
- Talent Shortage: The space tech sector faces a shortage of skilled professionals, highlighting the need for expanded talent development initiatives.
- Policy Ambiguity: Ambiguous policies in the space sector create uncertainty, necessitating clear and consistent regulatory frameworks to attract foreign investment.
- Streamlining FDI Procedures: Simplification of foreign direct investment processes is essential to remove barriers and encourage investor participation in the space industry.
- High Capital Requirements: Space technology ventures demand substantial capital investments, posing challenges for startups and smaller enterprises in accessing necessary funds.
- Competition Concerns with ISRO: Foreign investors express reservations due to competition concerns with ISRO, highlighting the importance of addressing perceived conflicts of interest to instil investor confidence.
Conclusion
The amendment in the FDI policy on the space sector heralds a new era of growth and opportunity for India’s space industry. By opening doors to foreign investment, India aims to leverage private sector participation to enhance its space capabilities, drive innovation, and foster economic development. The policy reform underscores India’s commitment to becoming a global leader in space exploration and technology.
Having panchayats as self-governing institutions

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
There is a need to educate elected representatives and the public on the significance and the need for panchayats to be able to survive on its own resources
Context:
- Three decades have passed since the enactment of the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts, designed to institutionalize local bodies as entities of local self-government.
- Presently, the degree of devolution in India's Panchayati Raj institutions exhibits variations among states, with some making substantial strides and others trailing behind.
- Therefore, there is a pressing need to scrutinize the fiscal devolution dimension, underscoring the pivotal role of state government commitment in enhancing the effectiveness of Panchayati Raj institutions at the grassroots level.
What is the Local Self Government?
- The system of local self-government, more commonly known as ‘panchayats’, had been established to empower the grassroots of democracy in India.
- Panchayats or local-self rule is a three-tier system in each state which has elected bodies at the village, taluk and district levels.
- The concept of panchayats has been present in Indian society since ancient times.
- Over the centuries the concept has undergone various changes and modifications and in the recent past has taken the form of panchayati raj institutions after decentralization reforms in the early 1990s.
- These institutions for grassroots-level democracy were formally included in the Constitution through the 73rd and 74th Amendments Act in 1993.
- The constitutional amendments also ensured the reservation of one-third of all elected positions for women in both rural and urban areas.
- Derived from the Central Act, various State Panchayati Raj Acts have incorporated provisions for taxation and revenue collection.
- The main idea of setting up local-self government institutions was to enable and empower the local people to manage their affairs by being a part of the decision-making process and participating in the implementation of policies in a more effective manner.
The Present State of Fiscal Devolution of Panchayats:
- Reliance on External Funds: The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments Acts underscored the importance of fiscal devolution, urging Panchayati Raj institutions and urban local bodies to achieve financial self-sufficiency.
- These amendments explicitly stated the necessity for local bodies to generate their own revenues to reduce reliance on grants from higher levels of government.
- However, the current scenario indicates that Panchayati Raj institutions still heavily depend on external funding, with only 1% of their revenue originating from taxes.
- Panchayats' Struggle to Generate Revenue Through Taxation: The data highlights the challenge that, despite constitutional provisions, Panchayats are not effectively utilizing taxation as a primary revenue source.
- Merely 1% of revenue is generated through taxes, while a significant 80% is sourced from the Central government and 15% from the States.
- This disparity raises concerns about the commitment of state governments to decentralization and the overall efficacy of devolution initiatives implemented over the past three decades.
- Centralization of Financial Resources Despite Constitutional Emphasis on Fiscal Devolution: Despite the constitutional emphasis on fiscal devolution, the centralization of financial resources remains a persistent issue.
- Panchayats are envisioned as self-governing entities with the authority to raise their own revenue, yet the reality paints a different picture.
- The disproportionate distribution of revenue indicates a lack of fiscal empowerment at the grassroots level, undermining the fundamental principles of local self-government.
What are the Challenges Faced by Panchayati Raj Institutions in Revenue Generation?
- Dependency on Grants: The reliance on grants is exacerbated by the heightened allocations from Central Finance Commissions (CFC).
- A comparative analysis reveals a significant increase in grants disbursed through the 14th and 15th CFCs, amounting to ?2,00,202 crore and ?2,80,733 crore, respectively.
- This substantial influx of grants has inadvertently diminished incentives for generating own-source revenue.
- Panchayats, buoyed by augmented financial assistance, have gradually shifted focus away from revenue generation, fostering a culture of dependence on external funds.
- The Culture of Entitlement: A prevalent cultural mindset fosters resistance to taxation, with individuals expecting a range of services and benefits without contributing financially to the sustenance of Panchayats.
- This aversion to taxation arises from the belief that public services should be provided without imposing a direct financial burden on the local populace.
- Dilemma of Elected Representatives: Elected representatives, crucial to the functioning of Panchayati Raj institutions, grapple with their own set of challenges.
- There exists a tangible apprehension among these representatives that levying taxes might adversely affect their popularity and electoral prospects.
- This fear often results in hesitancy to take decisive steps towards revenue generation.
- Addressing this challenge necessitates targeted efforts to educate elected representatives about the enduring benefits of financial self-sufficiency and its positive impact on local development endeavours.
- Decline in Tax Collection: Tax collection, which stood at ?3,12,075 lakh in 2018-19, dwindled to ?2,71,386 lakh by 2021-2022.
- This downward trend raises concerns, signalling a waning commitment to financial autonomy at the local level.
- Similarly, non-tax revenue also experienced a decline from ?2,33,863 lakh to ?2,09,864 lakh during the same period.
- These patterns underscore the imperative for revitalized efforts in revenue generation and a departure from grant dependency.
Government's Efforts to Implement Constitutionally Mandated Fiscal Devolution:
- Establishment of an Expert Committee: To address this challenge, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj constituted an expert committee tasked with examining the own source of revenue (OSR) of rural local bodies.
- The committee's findings delineate various revenue-generating avenues accessible to Panchayati Raj institutions through State Acts.
- These mechanisms include property tax, land revenue cess, stamp duty surcharge, tolls, professional tax, advertisement tax, and user charges for essential services like water, sanitation, and lighting.
- While these avenues exist, their effective implementation is imperative for Panchayats to attain financial autonomy.
- Focus on Effective Taxation Mechanisms: The report underscores the significance of establishing an enabling environment for taxation, encompassing decisions on tax and non-tax bases, enactment of robust tax management and enforcement laws, etc.
- This strategic approach aims to empower Panchayats to fully leverage their revenue generation potential.
- While taxation constitutes a vital aspect of fiscal devolution, the report also acknowledges the potential of non-tax revenue streams, including Fees, rent, income from investment sales and hire charges,
- Along with revenue from innovative initiatives such as rural business hubs, commercial ventures, renewable energy projects, carbon credits, CSR funds, and donations.
- Diversification of revenue sources can bolster the financial resilience of Panchayati Raj institutions, reducing their reliance on grants.
The Role of Gram Sabhas:
- Gram sabhas have a significant role in fostering self-sufficiency and sustainable development at the grass-roots level by leveraging local resources for revenue generation.
- They can be engaged in planning, decision-making, and implementation of revenue-generating initiatives that range from agriculture and tourism to small-scale industries.
- They have the authority to impose taxes, fees, and levies, directing the funds towards local development projects, public services, and social welfare programmes.
- Through transparent financial management and inclusive participation, gram sabhas ensure accountability and foster community trust, ultimately empowering villages to become economically independent and resilient.
- Thus, gram sabhas need to promote entrepreneurship, and foster partnerships with external stakeholders to enhance the effectiveness of revenue generation efforts.
Way Forward:
- Education and Awareness: There is a pressing need to raise awareness among elected representatives and the public about the importance of revenue generation for developing Panchayats as self-sustaining institutions.
- Ultimately, the dependency syndrome for grants has to be minimised and in due course, panchayats will be able to survive on their own resources.
- Achieving this goal requires concerted efforts at all levels of governance, including the state and central levels.
- Promotion of Entrepreneurship: Gram Sabhas plays a crucial role in promoting entrepreneurship and fostering partnerships with external stakeholders to bolster revenue generation efforts.
- Encouraging entrepreneurial ventures within local communities can stimulate economic growth and reduce dependency on external funding.
- Collaboration and Support: Panchayats need to collaborate closely with higher tiers of governance and external stakeholders to enhance their revenue generation capabilities.
- This collaborative approach can facilitate the implementation of innovative initiatives and the efficient utilization of resources, thereby fostering financial self-reliance among Panchayats.
Greece’s gateway to Asia, India’s gateway to Europe

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The state visit by Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis to India will be another important step in building a strategic relationship between India and Greece — a process which began with the historic visit of the Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, to Greece in August 2023.
Context:
- The upcoming state visit of Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis to New Delhi signifies a pivotal milestone in the ongoing initiatives to forge a strategic partnership between Greece and India.
- This diplomatic initiative follows the landmark visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Greece in August 2023, which generated enthusiasm among Greek political and business circles.
- The anticipation surrounding the visit of the Greek Prime Minister underscores the mutual dedication to enhancing bilateral relations and collaboration across diverse sectors.
Historical Connections:
- India and Greece share a rich historical bond spanning more than 2500 years, characterized by cultural exchanges and a mutual embrace of democratic values.
- Presently, their bilateral relations are multifaceted, covering political, economic, and military cooperation.
- Trade Routes: Ancient maritime trade routes linked the Indus Valley Civilization with the Aegean region, facilitating the exchange of commodities such as spices, textiles, and intellectual ideas.
- Archaeological evidence, including the discovery of Indus seals in Mesopotamia, suggests the existence of trade connections between the two civilizations.
- Alexander the Great (326 BCE): Alexander's conquest of parts of northwest India fostered cultural and diplomatic exchanges between Greece and India.
- Greek philosophies and ideologies potentially influenced various aspects of Indian art, mathematics, and astronomy during this period.
- Indo-Greek Kingdoms (2nd century BCE – 1st century CE): Hellenistic kingdoms established in northwest India witnessed a fusion of Greek and Indian cultures.
- This blending is evident in Gandhara art, which exhibits Greco-Buddhist influences and serves as a testament to the cultural interplay between the two civilizations.
The Current Status of Bilateral Relations between India and Greece:
- Steady Progress in Bilateral Relations: While India and Greece share a historical connection and mutual enthusiasm, the pace of their bilateral cooperation has been characterized by gradual progress.
- In this context, it is essential to delve into the various facets of collaboration, recognizing both the positive developments and the need for enhanced momentum.
- Military Cooperation: Over time, military collaboration between the two nations has witnessed notable advancements.
- Joint exercises involving the Indian Navy, Indian Air Force, and the Greek armed forces have been conducted, underscoring a shared commitment to fostering mutual understanding and coordination.
- Reciprocal exercises are in the pipeline, illustrating an ongoing endeavour to deepen military bonds.
- These joint military endeavours not only bolster regional security but also signify an increasing level of confidence and collaboration between the armed forces of Greece and India.
- Economic Engagement: On the economic front, there have been significant instances of collaboration signalling a burgeoning partnership.
- For instance, an Indian construction company has joined forces with a prominent Greek construction firm to undertake a significant project: the construction of a new airport on the island of Crete.
- Such initiatives highlight the potential for cross-border investments and partnerships that can contribute to economic development and diversification.
Advancing Economic Reforms And Greece's Role:
- Greece's proactive stance in promoting deeper EU-India relations adds another layer of importance to ongoing economic reforms.
- As Greece endeavours to swiftly finalize the EU-India bilateral trade and investment agreement (BTIA), it underscores its dedication to establishing a conducive environment for heightened economic cooperation.
- The BTIA is poised to act as a catalyst, providing a structured framework for trade and investment, thereby nurturing closer economic bonds between the EU and India.
A Path to Closer Ties: Economic Reforms in Greece
- The economic facet of the Greece-India relationship assumes greater prominence as Greece, under the leadership of Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis, embarks on substantial economic reforms.
- Over the past half-decade, the Mitsotakis administration has implemented measures aimed at steering the Greek economy towards a more sustainable growth trajectory.
- This transformation positions Greece not only as a dependable eastern frontier of the European Union (EU) but also as a potential linchpin in broader geopolitical and economic strategies.
IMEEC Corridor: A Vision of Significance
- As Greece solidifies its role in the Eastern Mediterranean, the concept of establishing the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) emerges as a compelling vision.
- The IMEEC embodies a comprehensive economic initiative aimed at seamlessly connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe, thereby stimulating trade, investment, and economic collaboration.
- This ambitious proposition aligns with the shared vision of both nations to deepen their economic bonds and explore novel avenues for cooperation.
The Geopolitical Significance of the Indo-Greek Relationship:
- A Robust Foundation Rooted in Historical Bonds: The historical backdrop of the evolving ties between Greece and India (with diplomatic relations established in 1950) enriches their contemporary diplomatic endeavours.
- Furthermore, these diplomatic exchanges acquire significance amidst India's ascent as a global power, being perceived not only as an enduring ally but also as a dynamic and influential player on the world stage.
- Contemporary Diplomacy: The momentous visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Greece in August 2023 served as a watershed, laying the groundwork for enhanced collaboration.
- The enthusiasm witnessed in Greece, particularly among political and business circles, underscores the perceived opportunities in forging a strategic partnership with India.
- Strategic Importance of Both Nations' Locations: The geopolitical relevance of this burgeoning relationship is amplified by the strategic locations of Greece and India.
- Situated in regions pivotal to the global system, both nations grapple with geopolitical complexities and volatility.
- Recent events in the Red Sea highlight the interconnectedness of the East Mediterranean, where Greece is positioned, and the Indian Ocean region, accentuating the imperative for collaboration to promote security, stability, and prosperity.
- A Strategic Vision: Gateway to Europe and Asia: The Greek Prime Minister's assertion that "India will find no better gateway to Europe than my country, and for Greece, there is no better gateway to Asia than a close strategic relationship with India" encapsulates the acknowledgement of each nation's unique role in bridging the other's region.
- This pragmatic understanding not only acknowledges geographical realities but also reflects a strategic vision to leverage mutual strengths for collective advancement.
Way Forward to Enhance Indo-Greek Relations:
- Promoting Cross-Cultural Understanding: By expanding university student exchange programs, deliberate steps will be taken to familiarize the younger generation with the cultures, traditions, and educational systems of both nations.
- This fosters not only cross-cultural appreciation but also establishes a groundwork for future collaborations and friendships.
- Fostering Cultural Exchanges: Cultural exchanges serve as a cornerstone in fortifying the bonds between Greece and India.
- Through the promotion of cultural events, exhibitions, and festivals, both countries create platforms for their citizens to immerse themselves in and celebrate the richness of each other's cultural heritage.
- These initiatives act as bridges, connecting hearts and minds, and nurturing a sense of shared identity and mutual respect for cultural diversity.
- Media Collaboration: Bridging Information Gaps: Media collaboration emerges as a pivotal avenue to bridge geographical distances and keep the citizens of both nations abreast of developments, cultural nuances, and societal trends.
- Joint efforts in media, including co-productions, cultural documentaries, and news coverage, facilitate a nuanced understanding of each other's realities.
Conclusion
The swift exchange of visits between the political leadership of Greece and India underscores their commitment and the urgency in advancing their strategic partnership. As the world navigates through a pivotal year in 2024, the onus lies on policymakers and businesses to capitalize on this momentum and fortify the strategic partnership between Greece and India.
With elections in at least 83 countries, will 2024 be the year of AI freak-out?

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Regulatory panic could do more harm than good. Rather than poor risk management today, rules should anticipate the greater risks that lie ahead.
Context:
- The year 2024 will see 4.2 billion people go to the polls, which, in the era of artificial intelligence (AI), misinformation and disinformation may not be the democratic exercise intended.
- The Global Risks Report 2024 named misinformation and disinformation a top risk, which could destabilise society as the legitimacy of election results may be questioned.
- Therefore, it is crucial to scrutinise the possible drawbacks of swiftly formulated regulations to counter AI-driven disinformation during this crucial period.
What are the Major Challenges Arising from Hasty Regulatory Responses to AI?
Escalation of Disinformation: Unintended Ramifications of Resource Allocation
- The surge in disinformation, demonstrated by manipulated videos impacting political figures, presents a formidable obstacle.
- For instance, consider the case of Tarique Rahman, a leader of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party, whose manipulated video suggested a reduction in support for Gaza's bombing victims—an action with potential electoral repercussions in a Muslim-majority country.
- Meta, the parent company of Facebook, exhibited delayed action in removing the fabricated video, raising concerns about the effectiveness of content moderation.
- Moreover, the reduction in content moderation staff due to widespread layoffs in 2023 exacerbates the challenge.
- The pressure to prioritize interventions in more influential markets may leave voters in less prominent regions, such as Bangladesh, vulnerable to disinformation, potentially leading to a global surge in disinformation due to the focus on catching misinformation from powerful governments.
Reinforcement of Industry Dominance: Amplifying Concentration and Ethical Concerns
- While well-intentioned, AI regulations risk bolstering industry concentration. Mandates such as watermarking (which are not foolproof) and red-teaming exercises (which are expensive) may inadvertently favour tech giants, as smaller companies encounter compliance obstacles.
- Such regulations could further entrench the power of already dominant players by erecting barriers to entry or rendering compliance unfeasible for startups.
- This concentration not only consolidates power but also raises apprehensions regarding ethical lapses, biases, and the centralization of consequential decisions within a select few entities.
Navigating Ethical Quagmires: Pitfalls of Sincere Guidelines
- The formulation of ethical frameworks and guidelines introduces its own complexities.
- The question of whose ethics and values should underpin these frameworks gains prominence in polarized times. Divergent perspectives on prioritizing regulation based on risk levels add layers of complexity, with some viewing AI risks as existential threats while others emphasize more immediate concerns.
- The absence of laws mandating audits of AI systems raises transparency issues, leaving voluntary mechanisms vulnerable to conflicts of interest.
- In the Indian context, members of the Prime Minister's Economic Advisory Council have even argued that the concept of risk management itself is precarious concerning AI, given its non-linear, evolving, and unpredictably complex nature.
Navigating the Complexity of AI Regulation: Strategies for Policymakers
- Acknowledge and Address Democracy's Inherent Challenges Alongside AI Threats:
- Before delving into the intricacies of AI-related risks, policymakers must acknowledge the persistent challenges facing democracy globally.
- Instances of unjust political imprisonments, threats to electoral processes, and disruptions to communication networks underscore the vulnerability of democratic systems.
- Furthermore, the enduring issues of vote-buying and ballot-stuffing tarnish the integrity of elections.
- These entrenched challenges within the democratic process provide context for evaluating the novelty of AI threats.
- Strike a Balance Between Addressing AI Risks and Implementing Sensible Regulation:
- The rush among regulators to enact AI regulations ahead of the 2024 elections, following the AI fervour of 2023, underscores the need for caution.
- While it is essential to confront the emerging threats posed by AI, hastily devised regulations may inadvertently worsen the situation.
- Policymakers must carefully consider the potential for unintended consequences and the complexities inherent in regulating a swiftly evolving technological landscape.
- It is crucial for regulators to appreciate the delicate balance required to manage AI risks without unintentionally creating new challenges or hindering democratic processes.
- Prepare for Future Challenges: Policymakers must adopt a forward-thinking approach to AI regulation, anticipating and formulating rules that not only address current risks but also proactively tackle future challenges.
- Recognizing the rapid evolution of technology, regulatory frameworks must evolve accordingly.
- By planning several steps ahead, regulators can contribute to the resilience of democratic processes, ensuring that voters in elections beyond 2024 benefit from an adaptive, proactive, and effective regulatory environment.
How Major Tech Companies Join Hands to Combat AI Misuse in Elections?
- On February 16th, 2024, a major step was taken in the fight against AI misuse in elections.
- 20 tech giants, including Microsoft, Google, Meta, and Adobe, signed a voluntary agreement called the "Tech Accord to Combat Deceptive Use of AI in 2024 Elections."
- This agreement marks a significant step towards collective action against the potential manipulation of democratic processes through deepfakes and other AI-generated content.
Key features of the Tech Accord:
- Collaborative detection and labelling: Companies pledge to develop tools and techniques for identifying and labelling deepfakes, fostering transparency and facilitating content removal.
- Transparency and user education: The accord emphasizes transparency in company policies regarding deepfakes and aims to educate users on identifying and avoiding them, raising public awareness about the technology's capabilities and limitations.
- Rapid response and information sharing: The signatories commit to sharing information and collaborating on takedown strategies for identified deepfakes, aiming for faster removal and a unified front against malicious actors.
- Additional measures: The agreement includes further commitments to invest in threat intelligence, empower candidates and officials with reporting tools, and collaborate on open standards and research.
However, critical analysis reveals potential limitations:
- Voluntary nature: The accord's voluntary character raises concerns about its enforceability and long-term effectiveness.
- Companies may prioritize competing interests over their goals.
- Technical challenges: Deepfake detection remains an evolving field with limitations.
- Continuous innovation by malicious actors can outpace detection capabilities.
- Potential for bias: Concerns exist about potential biases in detection algorithms, particularly regarding marginalized groups, further complicating the issue.
- Freedom of expression and censorship: Balancing the need for content moderation with upholding freedom of expression requires careful consideration and potential legal challenges.
Conclusion
Balancing immediate concerns with long-term implications, and addressing AI-related electoral risks requires careful regulatory foresight. While the Tech Accord offers promise in combatting AI-driven election interference, its effectiveness depends on rigorous implementation and continuous adaptation to evolving threats. Ongoing research and dialogue are crucial to address ethical concerns and ensure a balanced approach to safeguarding democracy and individual rights.
The Cost of Legal MSP is Greatly Exaggerated (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Farmers have resumed protests without a specific trigger, unlike their previous march against contentious farm laws. Their main demand is a legal guarantee for Minimum Support Prices (MSP).
Context:
- The renewed protest by farmers, advocating for a legal assurance of Minimum Support Prices (MSP), underscores the enduring battle for agricultural sector stability.
- Amidst this, it's crucial to delve into the intricacies of MSP, address prevailing misconceptions, and explore the advantages of formalising this system.
What is the Minimum Support Price (MSP)?
- MSP (Minimum Support Price) is the cost at which the government buys crops from the farmers, to guarantee farmers against any sharp fall in agricultural income.
- It is declared by the Government based on the proposal of the Commission for Agricultural Cost and Prices (CACP), at the start of the planting season.
- This mechanism aims to protect small and marginal farmers from financial losses and ensure an adequate supply of food grains for public distribution across India.
- Since its inception in 1966-67 for wheat, the MSP framework has expanded to cover various essential food crops, facilitating their availability to the public through subsidized rates under the public distribution system.
- However, only a small percentage, approximately 6% or less, of farmers are able to sell their produce at prices higher than the MSP.
Is the MSP Different in different states?
- Because of the variety in irrigation and wages, the expense of a similar yield changes from one state to another.
- However, there is no draft of the local Minimum Support Price, so there is one MSP for the whole country.
Significance of Minimum Support Price:
- Fixed Remunerations: The farmers are financially insured against the impulses of price fall in the market.
- It gives security to farmers from crop loss and price uncertainty.
- Help in Decision Making: MSPs are reported toward the start of the planting season, this assists farmers with settling on the best choices of crop that they should plant.
- This development data assists the farmer with settling on the best choice with regards to which yield to plant for the most extreme monetary advantage inside the restrictions of his agricultural land size, environment, and irrigation framework.
- Crop Diversification: The MSP declared by the Government of India without precedent for 1966-67 for wheat has reached out to around 24 crops at the present.
- This has urged the farmers to develop these different crops to maximize their agricultural income.
- Price Limitations for Private Purchasers: MSP conveys a value message to advertise that if vendors don’t offer higher than MSP costs the farmer may not sell them his produce.
- In this manner, it goes about as an anchor or benchmark for agricultural produce.
- It guarantees the market costs won’t be radically lower than the Minimum Support Price.
- Commercial Crops: MSP is utilized as an instrument to boost the creation of explicit food crops which is short in supply.
- MSP spurs farmers to develop commercial crops and expand creation on a commercial basis.
- Purchasing Power Enhancement: MSP provides fixed amounts in framers’ hands which makes them financially stable.
- It helps in upgrading the buying limit and updating the style of living of farmers and their families.
Challenges in Implementation of MSP:
- Selective Intervention and Limited Coverage: Despite the annual announcement of MSP for 23 crops, actual implementation tends to be selective, primarily focusing on major crops like rice and wheat.
- This limited coverage undermines the broader objective of ensuring stability across various agricultural commodities.
- MSP Implementation Bias: The unequal application of MSP, favouring specific crops, marginalizes farmers cultivating other essential commodities.
- This bias exacerbates regional disparities and impacts the economic well-being of farmers engaged in non-major crop cultivation.
- Disconnect Between Market Price and MSP: The disparity between market prices and MSP poses a significant challenge, as government intervention is triggered primarily when market prices fall below the MSP.
- Inconsistent intervention exacerbates uncertainties for farmers, leading to financial distress during market downturns.
- Perceived Government Apathy: Farmers perceive a lack of genuine interest or urgency from the government in effectively implementing MSP.
- This perceived apathy breeds distrust and frustration among farmers, fueling demands for a legal guarantee to ensure consistent and widespread implementation.
- Political Hesitation and Decision-Making Delays: While there is political consensus supporting a legal guarantee for MSP, successive governments have hesitated to formalize this mechanism.
- Delayed decision-making perpetuates uncertainties in the agricultural sector, undermining the effectiveness of MSP as a stabilizing force.
What Does a Legal Guarantee of MSP Mean and What Obstacles in Legalising MSP?
- It means that anyone paying less than the price set by the government for crops could be criminally charged.
- Currently, there is an MSP for 23 crops.
- However, the highest procurement by the government is of wheat and rice.
- According to experts, if MSP is legally guaranteed, the government will have to pay it regardless of supply and demand dynamics.
- At the moment, about 60 per cent of the total field crop production in India comes from wheat and paddy.
- Fiscal Concerns: Misconceptions regarding the fiscal implications of guaranteeing MSP have posed obstacles to its legalization.
- Despite the political consensus, concerns over perceived excessive fiscal burdens have deterred governments from formalizing MSP.
- Prevalent Misconceptions: There is a prevalent misconception that legalizing MSP necessitates government procurement of all agricultural produce, which is inaccurate.
- Government intervention is required only when market prices dip below MSP, and it does not entail the procurement of the entire marketable surplus.
- Misunderstanding of Procurement Costs and Subsidies: The cost of procuring rice and wheat is often misconstrued as the cost of the MSP program, whereas it primarily serves as a subsidy to consumers rather than farmers.
- For other crops, government procurement is not a cost unless sold with a subsidy, with the actual cost being the difference between economic cost and issue price.
Potential Advantages of Legalising MSP:
- Ensuring Uniform Implementation: Formalizing Minimum Support Prices (MSP) establishes a clear legal framework, ensuring consistent application across all crops.
- This move addresses current issues of selective intervention, providing farmers with a dependable safety net.
- Promoting Inclusive Agricultural Growth: Expanding MSP coverage to various crops ensures that price stability benefits all segments of the farming community.
- Small and marginal farmers cultivating diverse crops can access MSP protection, fostering inclusive agricultural development.
- Reducing Farmer Vulnerability: Formalizing MSP reduces farmers' susceptibility to market fluctuations by guaranteeing a minimum income for their produce.
- This assurance enables farmers to navigate uncertainties with confidence, knowing that government intervention is assured during price downturns.
- Boosting the Rural Economy: A secured MSP contributes to farmers' economic well-being, leading to increased rural income.
- This upliftment stimulates the rural economy by generating demand for goods and services, fostering growth across multiple sectors.
- Clarifying Consumer Subsidies: Formalization helps distinguish between procurement costs and consumer subsidies, often conflated as MSP program expenses.
- This clarity aids policy discussions and ensures targeted subsidy allocation, benefiting both farmers and consumers.
- Facilitating Strategic Government Operations: A legal framework empowers the government to conduct strategic operations in domestic and international markets.
- Through controlled sales during periods of high market prices, the government can manage inflation, ensuring price stability for consumers.
Conclusion
The legalization of MSP presents a holistic remedy to the agricultural sector's woes.
Beyond ensuring uniform application, it fosters diversification, inclusivity, and economic robustness, ultimately benefiting farmers and bolstering rural prosperity. By dispelling misconceptions and tackling apprehensions, policymakers can pave the way toward a more secure and prosperous future for our farmers.
WTO Pressure on Indian Farm Subsidies Amid Farmer's Protest for MSP (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government might find it challenging to meet the protesting farmers' demand for a legal guarantee of (MSP) due to India's farm subsidies being scrutinised at the (WTO), especially with criticism from a group of 19 influential agricultural exporting countries.
Background:
- After independence, our country struggled to produce enough food for its large population as the agriculture sector was in a poor state.
- To address this challenge, we either had to import grains, which incurred significant costs, or rely on aid from other nations.
- In 1960, the government took steps toward self-sufficiency. They introduced high-yielding seeds, promoted the use of fertilisers, and improved agricultural machinery.
- At the same time, the government supported rice and wheat cultivation by offering farmers a Minimum Support Price (MSP).
- This ensures that farmers receive a fair price; if they can't sell their crops for a better price in the market, the government will buy them at a favourable rate.
- However, there's currently tension between India and the WTO regarding these subsidies.
Green Revolution
- The Green Revolution, initiated in the 1960s, aimed to enhance agricultural productivity and bolster the nation's economy.
- India embraced technological and industrial advancements in agriculture during this era.
- This included the adoption of high-yield seeds, modern farming equipment, irrigation systems, pesticides, and fertilisers to transform the agricultural landscape.
- The green revolution helped India move from a state of importing grains to a state of self-sufficiency.
Causes of Tensions Between India and the WTO:
- India's actions in this realm have stirred discontent among other nations, who perceive India's practices as unfair trade manoeuvres.
- The government's practice of procuring crops from farmers at low prices and subsequently exporting them at reduced rates to global markets has drawn criticism.
- Developed countries have lodged complaints, alleging multiple instances of India breaching WTO regulations by providing subsidies amounting to 60-70% of the total crop value.
- While the WTO permits governments to offer subsidies to farmers, it imposes restrictions, allowing developed countries to provide up to 5% and developing countries up to 10% of the total value in subsidies.
What are the WTO Regulations on Farm Subsidies?
- The WTO regulations on farm subsidies aim to promote fair competition and prevent global trade distortion.
- These regulations establish limits on the types and levels of subsidies that member countries can offer to their agricultural sectors.
- Levels of Subsidies:
Green Box:
- These subsidies have minimal impact on trade distortion.
- They are not specific to particular products and are generally permissible under WTO rules.
- Examples include funding for research, environmental conservation, and direct income support for farmers facing challenges such as crop loss or natural disasters.
Amber Box:
- These subsidies promote excessive production and distort international trade.
- Examples include input subsidies like those for seeds, fertilisers, and Minimum Support Price (MSP).
- WTO restricts these subsidies, capping them at 5% for developed countries and 10% for developing countries.
Blue Box:
- These subsidies, akin to Amber Box subsidies, aim to limit production.
- Currently, only a few countries, such as Norway and Iceland, utilise these subsidies.
- The WTO does not impose any limits on these subsidies.
Why India's Agricultural Subsidy Programs Encounter Challenges in the WTO?
- India's agricultural subsidies face hurdles at the WTO due to the organisation's rules, which do not consider subsidies on a per-farmer basis, disadvantageous to developing countries like India.
- For instance, although India's per-farmer subsidy is significantly lower compared to countries like the US, the WTO regulations focus on total subsidy amounts.
- In 2019-20, India's subsidies exceeded the 10% limit relative to its total rice production, despite the per-farmer subsidy being relatively modest at $300 compared to the US's $40,000 per farmer.
- While India is safeguarded by the 'Peace Clause' established during the WTO's Bali ministerial in 2013, certain ambiguities in the clause leave India vulnerable to disputes.
- Consequently, new schemes must adhere to the 10% subsidy ceiling, foregoing protection under the 'Peace Clause'.
Criticism of India’s Agricultural Subsidies by Influential Agricultural Exporting Countries:
- The Cairns Group, which includes countries like Australia, Brazil, and Canada, has raised concerns about the level of subsidisation in India’s public stockholding (PSH) program.
- They argue that India's agricultural support measures are significantly subsidised, leading to distortions in global food prices and negatively impacting food security in other nations.
- Last year, the group circulated a comprehensive proposal aimed at reducing trade-distorting agricultural support among WTO members, advocating for a halving of the total global entitlement/subsidies.
- This proposal sparked tensions among developing nations, with India among those affected.
- Essentially, the Cairns Group is advocating for India to either dismantle or scale back its Minimum Support Price (MSP) scheme, prompting India to seek stronger legal protection for its MSP program.
Upcoming Challenges for the Government of India:
- In pursuit of greater flexibility in providing agricultural support, India is actively advocating for a permanent solution at the forthcoming inter-ministerial summit in Abu Dhabi.
- However, the entrenched impasse on politically sensitive issues between developed and developing nations makes resolution unlikely.
- Farmers' groups in India advocate for removing agriculture from the purview of the WTO, but this approach could present challenges and hinder India and other developing nations from regulating subsidies provided by developed countries.
- The government faces a dilemma, as it grapples with peer pressure at the WTO while simultaneously facing demands for Minimum Support Price (MSP) from farmers.
- The call for better MSP support isn't limited to Punjab farmers; farmers across the nation are seeking similar assurances.
- Furthermore, if farmers in Punjab and Haryana shift away from agriculture, it could pose a threat to the country's food security.
Way Forward
- While India currently avoids disputes on the subsidy matter at the WTO due to the non-functionality of the Dispute Settlement Body (DSB), member countries will continue to scrutinise India's adherence to subsidy limits.
- As a result, India must advocate not only for adjustments to the formula used to calculate the food subsidy cap within the WTO but also for the inclusion of programs implemented after 2013 under the protection of the 'Peace Clause'.
Inauguration of BAPS Temple in UAE by PM Modi: Exploring Its Unique Features, Architecture, and Significance (Indian Express)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
During his two-day visit to UAE, Prime Minister Modi will inaugurate the BAPS Swaminarayan temple in Abu Dhabi, the first Hindu temple in the Gulf nation.
Context:
- Prime Minister Modi on Wednesday inaugurated the (BAPS) temple, the first-ever Hindu temple in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- The iconic stone temple is located in Abu Mureikhah, near Al Rahba off the Dubai-Abu Dhabi Sheikh Zayed Highway.
- The inauguration of the 108-ft high temple marks a significant moment for the Hindu community in UAE and the two countries’ bilateral ties.
What is BAPS?
- Bochasanwasi Shri Akshar Purushottam Swaminarayan Sanstha (BAPS) is a socio-spiritual Hindu organisation founded on the principles of practical spirituality.
- The temple was built by the organisation, a denomination of the Swaminarayan Sampradaya, a Vaishnav sect of Hinduism.
- With over 3,850 centres globally, BAPS has garnered national and international recognition, including affiliation with the United Nations.
- Through vows of abstinence and purity, BAPS fosters a foundation for humanitarian endeavours, caring for societies, families, and individuals.
What Does BAPS Do?
- The BAPS Swaminarayan Sanstha views spirituality as its core mission. Through gradual steps, it strives to draw individuals closer to God.
- In collaboration with BAPS Charities, the organization extends its outreach globally, addressing diverse humanitarian needs.
- From education to healthcare and environmental concerns, practical solutions are offered to real-world problems, impacting lives on both macro and micro scales.
- BAPS has a network of around 1,550 temples across the world, including the Akshardham temples in New Delhi and Gandhinagar, and Swaminarayan temples in London, Houston, Chicago, Atlanta, Toronto, Los Angeles, and Nairobi.
Who is Swami Narayan?
- Bhagwan Swaminarayan’s life and work have not only influenced communities in Gujarat, India but have affected change throughout the world.
- He reestablished Hindu Sanatan Dharma, cleansing traditions and rituals of the impurities that had seeped in over time.
- His contributions have been hailed by Hindus and dignitaries of other faiths as truly transforming the lives of millions of individuals.
- He improved societal standards and, most importantly, the innate nature of people, eradicating them from lust, anger, greed, and envy.
- Bhagwan Swaminarayan’s teachings transcended borders, rejuvenating Hindu traditions worldwide.
What are the Features of the (BAPS) Temple?
- The Abu Dhabi temple is a traditional stone Hindu temple with seven shikhars.
- Built in the traditional Nagar style, the temple’s front panel depicts universal values, stories of harmony from different cultures, Hindu spiritual leaders and avatars.
- Spread over 27 acres, the temple complex is on 13.5 acres
- The 13.5 acres of land was gifted by Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the President of the UAE in 2019.
- The height of the temple is 108 ft, its length 262 ft and its width 180 ft.
- While the external facade uses pink sandstone from Rajasthan, the interior uses Italian marble.
- A total of 20,000 tonnes of stones and marble were shipped in 700 containers for the temple.
- More than Rs 700 crore was spent on the temple’s construction.
- The temple has two central domes, Dome of Harmony and Dome of Peace, emphasizing human coexistence through the carvings of earth, water, fire, air, and plants.
- A Wall of Harmony, one of the largest 3D-printed walls in the UAE, features a video showcasing key milestones of the temple’s construction.
- The word ‘harmony’ has been written in 30 different ancient and modern languages.
- The seven shikhars (spires) are representative of the seven Emirates of the UAE.
- Other amenities include an assembly hall with a capacity of 3,000 people, a community centre, exhibitions, classrooms, and a majlis venue.
What are the Key Architectural Features?
- The temple was judged the Best Mechanical Project of the Year 2019 at the MEP Middle East Awards, and the Best Interior Design Concept of the Year 2020.
- Among the key architectural features are 96 bells and galumphs installed around the path leading to the temple.
- These 96 bells are a tribute to Pramukh Swami Maharaj’s 96 years of life.
- Nano tiles have been used, which will be comfortable for visitors to walk on even in the hot weather.
- On the top left of the temple is a stone carving of the scene of Pramukh Swami Maharaj envisioning the temple in Abu Dhabi in 1997.
- Non ferrous material (which is more vulnerable to corrosion) has been used in the temple.
- While many different types of pillars can be seen in the temple, such as circular and hexagonal, there is a special pillar, called the ‘Pillar of Pillars’, which has around 1,400 small pillars carved into it.
- Buildings surrounding the temple are modern and monolithic, with their colour resembling sand dunes.
- Deities from all four corners of India have been featured in the temple.
- These include Lord Ram, Sita, Lakshman and Hanuman, Lord Shiv, Parvati, Ganpati, Kartikeya, Lord Jagannath, Lord Radha-Krishna, Akshar-Purushottam Maharaj (Bhagwan Swaminarayan and Gunatitanand Swami), Tirupati Balaji and Padmavati and Lord Ayappa.
- The temple also has some special features, like a ‘holy river’ surrounding it, for which waters from Ganga and Yamuna have been brought in.
- The river Saraswati has been depicted in the form of white light.
- A Varanasi-like ghat has been created where the ‘Ganga’ passes.
- Apart from 15 value tales from Indian civilisation, stories from the Maya civilisation, Aztec civilisation, Egyptian civilisation, Arabic civilisation, European civilisation, Chinese civilisation and African civilisation have been depicted.
What is the Significance of the Temple?
- A Muslim king donated land for a Hindu Mandir, where the lead architect is a Catholic Christian, the project manager a Sikh, the foundational designer a Buddhist, the construction company a Parsi group, and the director comes from the Jain tradition.
Religious Significance:
- First Hindu stone temple in Abu Dhabi: This marks a historic milestone for the Hindu community in the UAE, providing them with a dedicated place of worship and cultural centre.
- Symbol of religious tolerance: The temple's inauguration signifies the UAE's growing acceptance and appreciation of religious diversity, fostering interfaith dialogue and understanding.
Cultural Significance:
- Strengthens India-UAE ties: The temple stands as a symbol of the strong cultural and diplomatic relations between India and the UAE, promoting mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Promotes Indian culture: The temple serves as a platform to educate the UAE community about Indian art, architecture, and traditions, fostering cultural exchange and appreciation.
Social Significance:
- Provides a sense of belonging: The temple offers a space for the Hindu community to gather, celebrate festivals, and connect with their cultural roots, fostering a sense of belonging and identity.
- Promotes social integration: The temple's open-door policy welcomes people of all faiths, encouraging social interaction and understanding between different communities in the UAE.
- Strengthens social fabric: The temple's emphasis on values like compassion, service, and community engagement contributes to strengthening the social fabric of UAE society.
Overall, the BAPS Swaminarayan Mandir in Abu Dhabi represents a significant step forward in religious tolerance, cultural exchange, and community building in the UAE. It serves as a testament to the growing understanding and appreciation between India and the UAE, and its impact will be felt for generations to come.
Gender Gap In STEMM and Government Efforts to Address It (Indian Express)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Principal Scientific Advisor to the Government of India Prof Ajay Kumar Sood launched Science for Women-A Technology & Innovation (SWATI), a portal aimed at representing girls in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics & Medicine).
Background:
- Gender inequality in the science sector has persisted as a significant issue, prompting a series of interventions to rectify this imbalance.
- Hence, delving into the trajectory of endeavours to narrow the gender divide in Indian science becomes crucial, particularly with the introduction of SWATI (Science For Women- A Technology & Innovation).
- This portal seeks to establish an extensive repository of female scientists across the nation, marking a significant milestone in this ongoing journey.
What is the SWATI Portal?
- SWATI Portal is a pioneering initiative aimed at establishing a unified online platform dedicated to showcasing Indian Women and Girls in STEMM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics & Medicine).
- The database hosted on the SWATI Portal serves as a valuable resource for informing policy decisions aimed at addressing gender disparities in STEMM fields.
- Developed, hosted, and maintained by the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), New Delhi, SWATI Portal stands out as the first-of-its-kind initiative in India.
Objectives:
- To significantly expand the scope of representation, encompassing every Indian woman in science across various career stages and disciplines, spanning both academia and industry.
- Facilitating robust and enduring research on equality, diversity, and inclusivity issues in India through the establishment of a comprehensive and searchable database.
- Sections within the portal include categories such as Icons (Padma/Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar/Stree Shakti Science Samman awardees), Directors, Secretaries, Academy Presidents, Faculty from Indian Universities, and personnel from autonomous organizations including S&T Ministry, CSIR, DBT, DST, MHRD, UGC, GATI, and KIRAN.
The 2004 INSA Report and the Systematic Discrimination in Indian Science:
- Recognition of Disparity: In 2004, the Indian National Science Academy (INSA) released a pivotal report that reshaped discussions on gender disparities in Indian science.
- This landmark document departed from conventional discourse by not only highlighting the gender gap but also delving into the complex layers of discrimination, including caste-related issues.
- Notably, the report garnered governmental endorsement, marking a significant acknowledgement of the imperative to investigate and rectify gender imbalances in the scientific domain.
- A nuanced Approach to Gender Disparity: The report transcended simplistic narratives, unveiling evidence of workplace bias rooted not only in gender but also in caste dynamics.
- This holistic perspective offered insights into the multifaceted challenges encountered by women in science, challenging prevalent assumptions that attributed the gender gap solely to familial responsibilities.
- Of particular significance was the collaboration between scientists and social scientists, fostering a deeper understanding of the societal dimensions of gender disparities within the scientific realm.
- This interdisciplinary synergy represented a departure from the traditional isolation of the scientific community from social science discourse on gender equality.
- Proposed Solutions and Recommendations: Advocating for proactive measures, the report underscored the need for collective action from policymakers, academia, and the scientific community to redress gender imbalances.
- By providing a comprehensive analysis of the hurdles faced by women in science, the INSA report laid the groundwork for subsequent initiatives, transcending surface-level assessments.
- Its recommendations influenced the trajectory of gender-related endeavours in the Indian scientific landscape, catalyzing a series of initiatives aimed at fostering inclusivity and equity.
Next Steps and Obstacles: Handling the Complicated Environment:
- National Conference of Women Scientists: Concurrently, the Department of Science and Technology (DST) convened a national conference in 2008, gathering over a thousand women scientists in response to the INSA report.
- During this event, the Science and Technology Minister unveiled ambitious support measures, including flexible work arrangements, childcare facilities, research grants, and housing options.
- However, the execution of these pledges encountered obstacles, with the envisioned standing committee failing to materialize, resulting in the delayed realization of promised advancements.
- IASc Report on Women's Attrition in Science: In 2010, IASc conducted a comprehensive survey on the factors contributing to women leaving the scientific field.
- The findings, based on responses from approximately 800 scientists, unveiled a multifaceted array of reasons, with women emphasizing organizational challenges alongside familial and societal pressures.
- These challenges included inflexible schedules, inadequate infrastructure, and pervasive discrimination, underscoring the necessity for systemic reforms rather than attributing departures solely to individual choices.
- Launch of "Lilavati's Daughters": Following the INSA report, the Indian Academy of Sciences (IASc) published "Lilavati's Daughters" in 2008, a compilation aimed at spotlighting the accomplishments of women in science and dispelling stereotypes.
- Discrepancies Between Intentions and Actions: The disparity between announced initiatives and their implementation underscored bureaucratic obstacles impeding progress.
- The stalling of the proposed standing committee exemplified bureaucratic hurdles that hindered the translation of well-intentioned policies into tangible outcomes for women in science.
Newer Strategies to Tackle Gender Disparity in Indian Science:
- Gender Advancement for Transforming Institutions (GATI): GATI introduces a progressive approach to addressing gender disparities, departing from conventional methods.
- Its charter, reflecting evolving gender discourse, embraces more inclusive language and practices.
- Recognizing transgender identities and advocating for gender-neutral parental leave, GATI acknowledges the diverse spectrum within the scientific community.
- Science, Technology, and Innovation Policy (STIP) 2020: The draft STIP 2020 signifies a shift towards a more inclusive science policy paradigm.
- By integrating provisions for transgender inclusion and advocating for gender-neutral parental leave, STIP 2020 aims to foster an environment supportive of scientists across genders.
- SWATI: Science for Women- A Technology & Innovation: SWATI, unveiled on International Women's Day 2021 by the former Department of Biotechnology (DBT) chief, Renu Swarup, promises to be a pioneering platform.
- Initially described as a portal dedicated to women scientists in DBT and its Autonomous Institutions, SWATI holds potential as a vital resource for advancing gender equality in the scientific sphere.
- However, detailed information about SWATI has been scarce until recent developments.
Is SWATI a Fresh Start or a Familiar Cycle?
- The introduction of SWATI signifies a commitment to integrating women into the domains of science and technology, recognizing their invaluable contributions.
- However, scepticism arises from past initiatives that initially generated excitement but ultimately faltered.
- Despite this, several aspects of SWATI instill optimism. The platform's inclusivity extends to all genders beyond the male binary, emphasizing support for scientists with diverse gender identities.
- Unlike previous endeavours, SWATI adopts a flexible approach, eschewing rigid criteria such as mandatory PhD qualifications, and acknowledging the diverse roles women play in science, regardless of formal degrees.
Conclusion
While the introduction of SWATI offers hope for progress in gender equity within Indian science, it's crucial to maintain a balance of optimism and caution. The effectiveness of SWATI will be determined by its transformation from a concept into a resilient and transparent platform capable of comprehensively addressing the multifaceted challenges confronting women in the scientific realm.
A Privileged Strategic Partnership, Without a Gulf (The Hindu)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi is scheduled to pay an official visit to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) from February 13-14, 2024 which will include inaugurating a temple built by the Bochasanwasi Shri Akshar Purushottam Swaminarayan Sanstha in Abu Dhabi.
Background:
- The upcoming official visit of the Indian Prime Minister to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) scheduled for February 13-14, 2024, signifies a pivotal moment in the evolving rapport between the two countries.
- This visit offers an opportunity to examine the diverse dimensions of the strategic partnership between India and the UAE, encompassing diplomatic, economic, cultural, and geopolitical connections that have matured over time.
- The Prime Minister will address the World Government Summit in Dubai as the ‘Guest of Honour’.
The Nature of India-UAE Special Diplomatic Relations:
- Elevated Diplomatic Engagements and Mutual Gestures: The essence of the India-UAE strategic partnership in diplomacy is marked by a sequence of notable visits, reciprocal actions, and joint endeavours, underscoring the depth of their association.
- The forthcoming seventh visit of the Indian Prime Minister to the UAE, scheduled for February 13-14, 2024, reinforces the diplomatic bonds between the two countries.
- Personal Connection: The close and amicable bond between Prime Minister Modi and UAE President Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan serves as a cornerstone in diplomatic interactions.
- This personal connection has evolved through frequent encounters, discussions, and collaborative initiatives across various domains.
- Their shared vision acts as a catalyst for expanding cooperation across diverse sectors.
- Special Collaborative Ventures: The diplomatic cooperation extends beyond regular interactions to encompass special events and joint initiatives that highlight the importance of their partnership.
- For instance, the felicitation of the UAE President in Gandhinagar during the Vibrant Gujarat Summit is a notable instance.
- This reciprocal gesture underscores the mutual respect and camaraderie between the leaders.
- Global Environmental Endeavours: Both nations actively contribute to global endeavours addressing climate change.
- Their joint involvement in the Global Green Credit Initiative underscores their dedication to environmental sustainability.
- This shared commitment to global issues demonstrates a diplomatic convergence that transcends bilateral interests, positioning India and the UAE as responsible global participants.
- Strategic Partnerships: The strategic alignment between India and the UAE is evident in their engagement in various international forums and alliances.
- Their participation in the West Asian Quad (I2U2) and the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor highlights a shared commitment to regional stability and economic progress.
- These partnerships further solidify their diplomatic collaboration in shaping geopolitical dynamics.
- Crisis Management: The diplomatic ties between India and the UAE are tested during critical junctures, such as the ongoing conflict in Gaza.
- The scheduled visit presents an opportunity for both leaders to discuss pressing regional issues, showcasing their dedication to addressing challenges and preserving regional stability.
- People-Centric Diplomacy: Cultural exchanges and people-to-people connections significantly contribute to diplomatic relations.
- Instances like the UAE conferring the Order of Zayed on Prime Minister Modi and India's role as the 'Guest of Honour' at the Abu Dhabi Festival underscore the cultural aspects of the partnership.
- Such gestures foster mutual understanding and goodwill among the citizens of both nations.
Additional Highlights of the UAE-India Strategic Partnership:
- Energy Security: The UAE's role as a vital partner in India's energy security is underscored by agreements on strategic oil reserves stored in India and collaborations on crude oil storage facilities.
- The partnership between Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserves Ltd and the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company reflects a shared commitment to securing energy resources.
- Defence and Security Collaboration: Both nations actively engage in defence and security cooperation, demonstrating mutual trust and a dedication to regional stability.
- Instances such as India's special invitation to the OIC Foreign Ministers’ Meeting and the UAE's participation in the G-20 summit under India’s presidency exemplify a unique level of diplomatic understanding.
- Cultural and People-to-People Connections: Cultural exchanges, exemplified by India's role as the 'Guest of Honour' at the Abu Dhabi Festival and the conferral of the Order of Zayed on PM Modi, strengthen people-to-people bonds.
- Initiatives like the establishment of the IIT Delhi Abu Dhabi campus and the opening of a UAE consulate in Hyderabad further enrich the cultural and educational facets of the partnership.
- The BAPS temple: Constructed on a generous donation of a 27-acre land parcel by the UAE President
- It stands as the UAE's second prominent Hindu temple, following the inauguration of the Hindu Temple in Dubai in 2022.
- Geopolitical Alignment: Both countries' participation in significant groupings like I2U2 and the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor underscores their shared geopolitical interests.
- The UAE's involvement in the corridor, aimed at linking India to Europe, presents a potential alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- Fintech: The RuPay card, an integral part of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), has been operational in the UAE since 2019. Starting from July 2023, transactions using the Indian rupee have been facilitated at Dubai’s airports.
- Regional Dynamics: The ongoing conflict in Gaza introduces an additional layer of complexity to regional dynamics, offering an opportunity for leaders to address pressing issues.
Way Forward:
- Both nations maintain close coordination within the region and participate in several significant groupings, including the I2U2.
- The UAE's involvement in the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) infrastructure project, established during the G-20 summit in Delhi, aims to link India to Europe via the Arabian peninsula.
- This corridor presents a potential alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- India boasts numerous strategic partnership agreements globally, yet none exhibit the depth of convergence and mutual respect as the one with the UAE.
- While India acknowledges and appreciates the UAE’s regional role, the UAE also acknowledges India's forthcoming 'global leadership' role.
- Both nations anticipate the continued strengthening of this privileged strategic partnership in the years to come.
Conclusion
The India-UAE strategic partnership exemplifies the extensive and varied connections that have developed over time. Spanning diplomatic, economic, and cultural spheres, as well as shared geopolitical goals, this relationship serves as a paradigm of harmony and mutual regard.
With a shared vision for continued advancement, the privileged strategic partnership is positioned for further enhancement in the future.
Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024 (Indian Express)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024, was introduced in Lok Sabha on 5th Feb which aims to prevent “unfair means” in order to “bring greater transparency, fairness and credibility to the public examinations system”.
Context:
- The Centre recently tabled the draft of the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024 in Parliament.
- This legislative proposal aims to prevent unfair means in public examinations and common entrance tests held across the country.
- In a bid to tighten the noose on public examinations, the proposed law provides for punishment, including imprisonment, in instances of malpractice in these tests.
- The Bill serves as a model draft for states to adopt at their discretion, aiding them in preventing criminal elements from disrupting the conduct of their state-level public examinations.
- At present, there is no specific substantive law to deal with unfair means adopted or offenses committed by various entities involved in the conduct of public examinations by the Central Government and its agencies.
- Therefore, it is imperative that elements that exploit vulnerabilities of the examination system are identified and effectively dealt with by a comprehensive Central legislation.
Which Exams are “Public Examinations” as Defined in the Bill?
- Under Section 2(k) of the Bill, a “public examination” is defined as any examination conducted by a “public examination authority” listed in the Schedule of the Bill, or any “such other authority as may be notified by the Central Government”.
- The schedule lists five public examination authorities:
- (i) the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC), which conducts the Civil Services Examination, Combined Defence Services Examinations, Combined Medical Services Examination, Engineering Services Examination, etc.;
- (ii) the Staff Selection Commission (SSC), which recruits for Group C (non-technical) and Group B (non-gazetted) jobs in the central government;
- (iii) the Railway Recruitment Boards (RRBs), which recruit Groups C and D staff in the Indian Railways;
- (iv) the Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS), which hires at all levels for nationalized banks and regional rural banks (RRBs); and
- (v) National Testing Agency (NTA), which conducts the JEE (Main), NEET-UG, UGC-NET, the Common University Entrance Test (CUET), etc.
- Apart from these designated public examination authorities, all “Ministries or Departments of the Central Government and their attached and subordinate offices for recruitment of staff” will also come under the purview of the new law.
- The central government can add new authorities in the schedule through a notification as and when required.
What is Meant by the Use of “Unfair Means” in an Examination?
- Section 3 of the Bill lists at least 15 actions that amount to using unfair means in public examinations “for monetary or wrongful gain”.
- These acts include:
- Leakage of question paper or answer key or part thereof and colluding in such leakage;
- Accessing or taking possession of question paper or an Optical Mark Recognition response sheet without authority”;
- Tampering with answer sheets including Optical Mark Recognition response sheets.
- Providing solution to one or more questions by any unauthorized person during a public examination, and
- Directly or indirectly assisting the candidate” in a public examination.
- The section also lists:
- Tampering with any document necessary for short-listing of candidates or finalizing the merit or rank of a candidate.
- Tampering with the computer network or a computer resource or a computer system.
- Creation of a fake website” and “conduct of fake examination, issuance of fake admit cards or offer letters to cheat or for monetary gain” as illegal acts.
What Punishment does the Proposed Law Provide for Violations?
- Section 9 of the Bill states that all offenses shall be cognizable, non-bailable, and non-compoundable — which means that an arrest can be made without a warrant and bail will not be a matter of right; rather, a magistrate will determine whether the accused is fit to be released on bail.
- A non-compoundable offense is one in which the case cannot be withdrawn by the complainant even when the complainant and the accused have reached a compromise, and a trial must necessarily follow.
- Punishment for “any person or persons resorting to unfair means and offenses” can be three to five years in prison, and a fine up to Rs 10 lakh.
- If the convict fails to pay the fine, “an additional punishment of imprisonment shall be imposed, as per the provisions of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023,” Section 10(1) of the Bill says.
- Under Section 10(2), a service provider who is engaged to provide “support of any computer resource or any material, by whatever name it may be called” for the conduct of the examination can be fined up to Rs 1 crore, along with other penalties.
- The Bill provides for harsher punishment in cases of organized paper leaks, where “organized crime” is defined as unlawful activity by a group of persons colluding in a conspiracy “to pursue or promote a shared interest for wrongful gain in respect of a public examination”.
- Section 11(1) says the punishment for organized crime will be “imprisonment for a term not less than five years but which may extend to ten years” and a fine “which shall not be less than one crore rupees”.
Why has the Government Brought this Bill?
- In recent years, there has been a significant rise in cases of question paper leaks during recruitment exams nationwide.
- An investigation uncovered at least 48 instances of paper leaks across 16 states over the past five years, disrupting the hiring process for government jobs and affecting approximately 1.51 crore applicants for about 1.2 lakh posts.
- The Statement of Objects and Reasons of the Bill highlights that malpractices in public examinations lead to delays and cancellations, adversely affecting millions of youth.
- Currently, there is no specific substantive law addressing unfair means or offenses committed during these examinations.
- It is crucial to identify and effectively deal with elements exploiting vulnerabilities in the examination system through comprehensive Central legislation.
- The primary objective of the Bill is to enhance transparency, fairness, and credibility in public examination systems, ensuring that sincere efforts of youth are duly rewarded and their future is secure.
- It aims to deter individuals, organized groups, or institutions from engaging in unfair practices that undermine the integrity of public examinations for monetary or wrongful gains.
- The Bill explicitly states that candidates, as defined within its scope, will not be subject to its provisions and will continue to be governed by existing administrative provisions of the relevant public examination authority.
- Once enacted, the Bill will also serve as a model draft for states to adopt at their discretion.
- This provision is expected to assist states in preventing criminal elements from disrupting the conduct of their state-level public examinations.
How to restore WTO’s authority (Indian Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Since the end of 2019, WTO’s crown jewel, the appellate body (AB) stands crippled because the US has single-handedly blocked the appointment of new members.
Context:
- The 13th ministerial meeting of the World Trade Organization (WTO) is scheduled in Abu Dhabi, presenting a chance to tackle the persistent crisis in the Dispute Settlement Mechanism (DSM).
- The effectiveness of WTO's key component, the DSM, has diminished since late 2019, mainly due to the United States obstructing the appointment of new Appellate Body (AB) members.
- Despite the implications of this crisis, there exist specific options for developing countries that could offer potential solutions to rejuvenate the DSM.
What is the World Trade Organization (WTO)?
- The WTO is an international institution responsible for overseeing global trade rules among nations.
- With 164 member countries (including Liberia and Afghanistan, the most recent additions in 2016) and 25 observer countries and governments, it officially commenced operations on January 1, 1995, replacing the 1948 General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in accordance with the 1994 Marrakesh Agreement.
Organizational Structure:
- The highest authority within the WTO is the Ministerial Conference, comprising all member states, typically meeting biennially with a consensus-driven decision-making approach.
- Daily operations are managed by three bodies, sharing the same membership:
- General Council:
- Functions as the primary decision-making body.
- Convenes as the Dispute Settlement Body (DSB) when addressing disputes between WTO members.
- Dispute Settlement Body (DSB):
- Empowered to establish dispute settlement panels.
- Refers matters to arbitration.
- Adopts reports from panels, Appellate Body, and arbitration.
- Monitors the implementation of recommendations and rulings, authorizing concession suspension in cases of non-compliance.
- Exclusive authority to make decisions, while panels and the Appellate Body can only offer recommendations.
- Trade Policy Review Body:
- Operates with terms of reference distinct from the General Council and DSB.
- Assesses the trade policies of member countries through periodic reviews.
- This structure ensures effective governance and dispute resolution within the WTO framework, emphasizing consensus in decision-making processes.
The Importance of the Appellate Body (AB):
- Enforceable Decision-Making:nThe Appellate Body (AB) holds the authority to review and, if necessary, overturn legal findings and interpretations by WTO panels.
- This enforceable nature ensures a conclusive resolution to trade disputes, fostering stability and predictability in international trade relations.
- Mandatory Jurisdiction: The AB's jurisdiction spans all WTO member countries, creating a mandatory framework for resolving disputes.
- Member nations are obligated to participate in the AB process, reinforcing the foundation of a rules-based international trading system.
- Advocacy for Equitable Practices: By addressing disputes and upholding compliance with WTO rules, the AB contributes to the promotion of fair and equitable trade practices.
- This approach establishes a level playing field for both developed and developing nations, supporting inclusivity and sustainable economic growth.
Challenges in the Dispute Settlement Mechanism (DSM):
- Appellate Body's Paralysis: Since late 2019, the AB, integral to the DSM, has been practically non-functional due to the blockage of new member appointments, primarily led by the United States dissatisfied with previous dispute outcomes.
- This obstruction erodes the binding nature of the dispute resolution process, creating a legal void.
- Evasion of Compliance: With the AB inoperable, countries have found a loophole to evade compliance with WTO panel rulings.
- Nations can appeal into the void, rendering the DSM ineffective and contradicting its purpose of providing a binding and enforceable resolution to trade disputes.
- Prolonged Dispute Resolution: The absence of a functioning AB leads to delays in resolving trade disputes.
- Without a binding appellate process, disputes may linger, contributing to economic uncertainties and potential retaliatory actions among trading partners.
- Undermining Rules-Based Trade: The DSM crisis jeopardizes the concept of a rules-based international trading system.
- The inability to enforce agreed-upon rules diminishes predictability and stability crucial for global economic growth through trade.
Potential Measures for Developing Countries to Sustain a Functional Two-Tiered DSM:
- Participation in the European Union-led MPIA: Developing countries can explore joining the European Union-led multi-party Interim Appeal Arbitration Arrangement (MPIA) as an initial option.
- This arrangement formalizes the arbitration mechanism already available under the WTO, providing appellate review for panel reports.
- However, the MPIA's voluntary nature poses challenges, leading to ad hoc tribunals and limited adoption of awards by all WTO members.
- Creation of a Restricted AB with Limited Powers: Considering the opposition to the AB by the United States, an alternative is formulating a diluted AB with constrained powers.
- Limiting the AB's authority in various ways, such as deference to parties in dispute and non-persuasive value of rulings, may be explored.
- However, a diluted AB could contradict the intended role of the DSM in providing security and predictability to the multilateral trading regime.
- Resurrecting the AB with an Opt-Out Provision: Scholars Robert Howse and Wenhua Ji propose resurrecting the AB with a critical modification—allowing countries to opt out of compulsory AB jurisdiction.
- Countries opting out would be excluded from participating in the appellate process, settling disputes solely through a single-tier panel jurisdiction.
- Critics express reservations about altering the intrinsic nature of a two-tier binding DSM but acknowledge the need to safeguard the AB's integrity.
Conclusion
In addressing the WTO DSM crisis, developing countries, including India, confront a complex decision-making process.
While restoring the AB to its original form is ideal, the suggested resurrection with an opt-out provision offers a pragmatic compromise, recognizing challenges while preserving the AB's legitimacy.
As WTO member countries gather in Abu Dhabi, the way forward requires thoughtful consideration of trade-offs to balance DSM effectiveness with accommodating diverse interests in the global trade landscape.
Major Takeaways From Interim Budget (2024-25) (The Hindu)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented her sixth Union Budget for the next financial year (2024-25), which differed from previous budgets as it was an interim budget.
What is the Interim Budget?
- The Interim Budget serves as a transitional financial plan presented by the incumbent government in an election year, bridging the period between the dissolution of the Parliament and the formation of a new government.
- This budgetary measure is necessitated by constitutional requirements outlined in Article 112 of the Indian Constitution, which mandates the submission of an annual financial statement to both Houses of Parliament.
- This statement outlines the anticipated receipts and expenditures of the Government of India for the upcoming fiscal year and requires approval from both Houses.
- However, in an election year, the prospect of a change in government following the polls prevents the presentation of a full-fledged budget by the incumbent administration.
- Consequently, the need arises for an interim budget to address the financial requirements during the transitional period.
- While there is no specific constitutional provision for an interim budget, the government seeks approval from the Lower House for the funds necessary for the transition period (April - July) through the votes on account provision.
Features and Components of Interim Budget:
- During the presentation of an interim budget, the Finance Minister provides an overview of the current state of the Indian economy, including its fiscal status and revised estimated growth for the upcoming year.
- This presentation encompasses details of both planned and non-planned government expenditures and revenues.
- While the government refrains from introducing major schemes that could sway voters or presenting an Economic Survey, it retains the authority to revise tax rates within the framework of the interim budget.
- Similar to the Union budget, the interim budget is presented to both Houses of Parliament on February 1 by the Finance Minister, subjected to debate and voting in the Lok Sabha, and subsequently forwarded for Presidential approval.
- Despite its interim nature, the interim budget remains valid for the entire fiscal year, serving as a crucial transitional arrangement until the presentation of a full-fledged budget by the new government.
What is Vote on Account?
- Article 116 of the Constitution empowers the Lower House to authorize advance grants for estimated expenditures during a portion of a financial year through legislative approval.
- This mechanism, known as a vote on account, facilitates the continuity of government operations during transitional periods.
- A typical vote on account encompasses the allocation of funds for essential expenses such as salaries, ongoing projects, and other necessary expenditures of the Central government.
- Notably, it does not entail modifications to tax rates.
- Additionally, a standard vote on account remains effective for a period of two months, with the possibility of extension for up to four months as required.
Major Takeaways from the Interim Budget (2024-25) - Part I:
- No Change in Taxation: The Interim Budget maintains existing tax rates without proposing any changes to direct or indirect taxes, including import duties.
- Withdrawal of Outstanding Direct Tax Demands: A significant initiative in the Interim Budget is the proposal to withdraw outstanding direct tax demands, benefiting taxpayers with demands up to Rs. 25,000 for the period up to the financial year 2009-10, and up to Rs. 10,000 for financial years 2010-11 to 2014-15.
- This measure is expected to benefit approximately one crore taxpayers.
- Tripled Direct Tax Collections: Over the past decade, direct tax collections have more than tripled, accompanied by a substantial increase in the number of return filers.
- The new tax regime ensures no tax liability for taxpayers with income up to Rs. 7 lakh.
- Additionally, corporate tax rates for existing domestic companies have been reduced from 30% to 22%, and for certain new manufacturing companies to 15%.
- Improvements in Taxpayer Services: The government's focus on enhancing taxpayer services has led to a transformation in the assessment system and simplified tax return filing processes.
- The average processing time for returns has been significantly reduced from 93 days to just 10 days.
- GST Compliance Relief: The implementation of GST has streamlined compliance for trade and industry, resulting in a reduction in logistics costs and taxes, and ultimately lowering prices for consumers.
- The GST base has doubled, with monthly gross GST collections nearly doubling to Rs. 1.66 lakh crore.
- Customs Facilitation Measures: Several steps have been taken in customs to facilitate international trade, including a substantial decrease in import release times at Inland Container Depots, air cargo complexes, and seaports over the last four years.
- White Paper Announcement: The government will release a white paper to provide insights into the period until 2014, aiming to draw lessons from past challenges and policy decisions.
Interim Budget (2024-25)- Part II:
- Increased Capital Expenditure: The Interim Budget allocates an 11.1% increase in capital expenditure for the upcoming year, amounting to Rs. 11,11,111 crore, representing 3.4% of the GDP.
- This investment aims to build on previous capital expenditure growth and stimulate economic growth and employment.
- Projected Real GDP Growth: India's Real GDP is projected to grow at 7.3% in FY 2023-24, reflecting the economy's resilience and healthy macroeconomic fundamentals despite global challenges.
- International agencies forecast India's continued growth between 6.1% and 6.7% in 2024-25.
- Robust GST Collection and Revenue Outlook: Strong economic activity has bolstered revenue collections, with gross GST revenues surpassing the Rs. 1.6 lakh crore mark for the seventh time.
- Total receipts, excluding borrowings, are estimated at Rs. 30.80 lakh crore, reflecting strong growth momentum and formalization in the economy.
- Support for State Governments: The Interim Budget extends support to state governments through schemes such as interest-free loans for capital expenditure and provisions for milestone-linked reforms.
- Fiscal Consolidation and FDI Inflow: Efforts towards fiscal consolidation aim to reduce the fiscal deficit to below 4.5% by 2025-26, with market borrowings estimated to be lower than the previous fiscal year.
Additionally, the government highlights a significant increase in FDI inflows over the past decade.
- Developmental Achievements: The Interim Budget underscores various developmental initiatives, including poverty alleviation programs, support for entrepreneurs through schemes like PM Mudra Yojana, housing initiatives, and promotion of startups through financial assistance.
- Infrastructure Development in Railways and Aviation: The budget outlines plans for major economic railway corridor programs and enhancements in aviation infrastructure, reflecting the government's commitment to improving transportation and connectivity.
- Committee on Population Growth Challenges: A high-powered committee will be formed to address challenges arising from rapid population growth and demographic changes, aligning with the goal of 'Viksit Bharat' (Developed India).
What are Other Announcements and Strategies in the Budget?
- During the presentation of the Interim Budget, Union Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman unveiled plans to increase the capital expenditure outlay for the next year by 11.1 percent to approximately Rs. 11 lakh crore, constituting 3.4 percent of the GDP.
- The Interim Budget introduces a range of announcements and strategies, signaling the trajectory and developmental approach aimed at realizing the vision of a 'Viksit Bharat' (Developed India) by 2047.
- In a series of announcements, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman underscored the government's commitment to empowering the eastern region and its populace, positioning it as a significant catalyst for India's overall economic growth which includes:
- Boost in the Technology Sector: A corpus of Rs 1 lakh crore will be established through a fifty-year interest-free loan to facilitate long-term financing or refinancing for research and innovation in emerging technology domains.
- This initiative aims to incentivize the private sector to significantly enhance research and innovation efforts.
- Railway Infrastructure Development: The budget outlines plans for three major economic railway corridor programs focusing on energy, mineral, and cement corridors, port connectivity corridors, and high-traffic density corridors.
- Additionally, the conversion of forty thousand normal rail bogies to Vande Bharat standards will enhance safety, convenience, and passenger comfort.
- Aviation Sector Expansion: With the number of airports doubling to 149, and five hundred and seventeen new routes serving 1.3 crore passengers, the aviation sector demonstrates significant growth.
- Indian carriers have proactively placed orders for over 1000 new aircraft, indicating a robust expansion in the aviation industry.
- MGNREGA Allocation: A substantial increase in allocation for the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) scheme is proposed in the Interim Budget for 2024-25, with Rs. 86,000 crore allocated compared to Rs. 60,000 crore in the previous fiscal year.
- Subsidy Rationalization: The interim budget aims to reduce the subsidy bill on essential commodities like food, fertilizer, and fuel, with the projected subsidy falling to a five-year low of approximately Rs. 3.8 lakh crore in 2024-25.
- Notably, the fertilizer subsidy is being reduced with expectations of improvements in the global situation and increased domestic production.
- Demographic Challenges Addressed: Recognizing the challenges posed by rapid population growth and demographic changes, the government announces the formation of a high-powered committee.
- Tasked with comprehensive consideration and recommendations, this committee aligns with the goal of 'Viksit Bharat' (Developed India) by addressing demographic challenges effectively.
Conclusion
The Interim Budget serves as a transitional financial plan presented by the government during an election year, addressing various sectors such as railways, tourism, healthcare, technology, aviation, green energy, aquaculture, and housing. However, it is important to note that the incoming government will present its comprehensive budget after the newly elected Lok Sabha, delineating the government's financial strategy for the entire fiscal year.
Navigating the Risks and Benefits Associated with Internationalisation of Government Bonds (The Hindu)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
There is a serious underestimation of the risks involved in the internationalisation of bond markets and currencies of emerging economies.
Context:
- In recent times, there have been noticeable changes in the global financial landscape, specifically regarding the inclusion of government bonds from emerging economies in global indices.
- It is crucial to evaluate the actions taken by J.P. Morgan, Bloomberg, and FTSE Russell in incorporating Indian local currency government bonds (LCGBs) into global indices amidst these developments.
- Exploring the reasons behind these moves and understanding the potential advantages and risks associated with such initiatives is essential.
J.P. Morgan's Influence on India's Financial Landscape:
- The inclusion of Indian local currency government bonds (LCGBs) in J.P. Morgan's Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) Global index suite in September 2023 marked a significant milestone.
- This step not only underscored India's financial stature but also raised expectations within the Indian financial sector.
- It spurred interest from other major index providers such as Bloomberg-Barclays and FTSE Russell.
- Subsequently, Bloomberg Index Services announced in January 2024 that India's fully accessible route (FAR) bonds would be incorporated into the Bloomberg Emerging Market Local Currency Index, further bolstering this trend.
- All eyes are now on FTSE Russell, highlighting the increasing influence and anticipation of reforms in India's government bond market.
What is the Process of Opening Local Bond Markets?
- Opening local bond markets to foreign investors is a strategic move by emerging economies to bolster their global financial integration.
- In India, this journey began in 2019 and gained momentum by 2020 with the introduction of the fully accessible route (FAR).
- Despite facing challenges like delays due to government policies on capital gains taxes and local settlement, the core policy remained unchanged, showcasing a dedication to promoting global financial inclusivity.
Advantages of Internationalising Bond Markets:
- Reduced Reliance on Domestic Institutions: By integrating local currency government bonds into global indices, emerging economies like India aim to lessen their dependence on domestic financial institutions.
- This diversified funding base can contribute to financial stability.
- Stability in Funds Tracking Indices: Inclusion in global indices can result in a more stable inflow of funds, as funds tracking indices typically have a longer investment horizon compared to short-term speculative flows.
- This stability can help mitigate volatility in local financial markets, providing a secure environment for both domestic and foreign investors.
- Lower Cost of Public Borrowing: Increased demand for local currency government bonds from global investors may lead to a decrease in domestic interest rates.
- As a result, the cost of public borrowing for the government can decline.
- Relief for Local Financial Institutions: Higher participation by foreign investors in local bond markets can alleviate the balance sheets of local financial institutions holding these bonds.
- This increased liquidity may encourage more lending and private investment.
- Mitigation of "Original Sin": Bond market internationalization helps mitigate the "original sin" problem faced by emerging economies, where they are unable to borrow internationally in their currencies.
- By issuing bonds in their currencies, these countries shift the exchange rate risk onto international lenders, potentially avoiding widespread private insolvencies during sharp currency declines.
Risks Involved with Internationalising Bond Markets:
- Loss of Control and Heightened Interest Rate Risks: Internationalizing bond markets poses the risk of losing control over long-term interest rates, leaving emerging economies more vulnerable to global interest rate fluctuations.
- This can negatively impact domestic bond markets and overall economic stability.
- Exchange Rate Volatility and Spillover Effects: Increased participation by foreign investors exposes local currency bond markets to exchange rate volatility.
- During periods of global risk aversion or liquidity challenges, adverse spillover effects can occur, as seen in events like the Lehman collapse in 2008 and recent shifts in U.S. monetary policy.
- Volatility in Inflows of Local Currency Bonds: Instances such as the rapid exit of investors from local currency assets in Malaysia during 2014-15 and the total withdrawal of foreigners from the bond market in Türkiye since Spring 2018 underscore the unpredictability of capital flows.
- These sudden stops and exits can lead to large reserve losses and currency declines, highlighting the potential for rapid market fluctuations.
Efforts by the Inter-Departmental Group (IDG) and RBI to Integrate Government Bonds into Global Indices:
- Indian LCGBs Integration into Global Indices: The RBI's journey towards internationalization commenced in October 2022 with an Inter-Departmental Group (IDG) report outlining efforts to integrate Indian local currency government bonds (LCGBs) into global indices.
- Diversification of Funding Channels: The inclusion of Indian LCGBs in global indices aims not only to attract foreign capital but also to diversify funding sources, reducing reliance on domestic institutions and tapping into large international resources.
- Stability Enhancement and Investment Allocation: The IDG report highlights the potential benefits of LCGB inclusion in global indices, such as enhancing the stability of funds tracking these indices.
- This stability can foster a more predictable investment environment, attracting long-term investors and improving investment allocation within the Indian financial market.
- Rupee Internationalization Beyond Bonds: Integrating LCGBs into global indices is just one aspect of a broader effort to internationalize the Indian rupee, as outlined in the IDG report.
- Another crucial component involves allowing banking services in the rupee (INR) outside the country.
Moving Forward:
- Striking a Delicate Balance: While the opening of local bond markets presents abundant opportunities, it necessitates careful balancing.
- Countries must balance the attraction of foreign capital with the management of potential risks.
- Drawing from Past Experiences: The experiences of Malaysia and Türkiye offer valuable lessons, emphasizing proactive management of offshore markets to prevent excessive speculation and maintain currency stability.
- These lessons underscore the importance of regulatory vigilance, timely interventions, and a balanced approach to fostering internationalization while preserving macroeconomic stability.
Conclusion
The process of opening local bond markets marks a crucial stride for emerging economies aiming for deeper integration into the global financial realm.
Recent developments involving J.P. Morgan, Bloomberg, and FTSE Russell underscore the growing recognition of India's financial market potential.
As India embarks on this journey, it must adeptly navigate complexities, carefully weigh risks and benefits, and adapt to the evolving global financial landscape for enduring success and stability.
The Evolution and Powers of the Deputy Chief Minister (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Currently, there are 26 deputy CMs across 14 states. The post, not mentioned in the Constitution, is nevertheless a long-standing feature of Indian politics.
Context:
- The tradition of appointing a deputy CM in Indian politics is a well-established practice, typically arising from political negotiations, especially in coalition governments or situations where a single leader lacks undisputed authority within the ruling party or support across key interest groups in the state.
- This trend is gaining prominence, evident in the four out of five states that underwent elections in November—Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Telangana, and Chhattisgarh—all currently having deputy CMs.
- With the exception of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, most major states also feature the position of deputy CM.
What is the Post of Deputy CM?
- Article 163(1) of the Constitution says “There shall be a Council of Ministers with the Chief Minister at the head to aid and advise the Governor in the exercise of his functions”.
- Neither Article 163 nor Article 164 mentions the post of Deputy Chief Minister.
- The post of Deputy CM is understood as being equivalent in rank to that of Cabinet Minister (in the state).
- The Deputy CM enjoys the same pay and perks as a Cabinet Minister.
Across Various States:
- At least 13 other states in the country apart from Bihar currently have Deputy CMs.
- The other states include:
- Maharashtra, Haryana, UP, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Telangana, Himachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh
- The highest of these is in Andhra Pradesh, with Chief Minister Y S Jagan Mohan Reddy having five Deputy CMs.
A Brief History of the Deputy CM Post:
- Perhaps the first Deputy CM in India was Anugrah Narayan Sinha, who was the most important leader of the Congress in Bihar after the first Chief Minister of the state, Dr Srikrishna Singh (Sinha).
- Deputy CMs were seen in more states, especially after the reduction of Congress’s near-total dominance in national politics after 1967.
- Bihar: Anugrah Narayan Sinha remained Deputy CM until his death in 1957.
- Karpoori Thakur became the second Deputy CM of Bihar in 1967, in the state’s first non-Congress government led by Mahamaya Prasad Sinha.
- Uttar Pradesh: Ram Prakash Gupta of the Bharatiya Jana Sangh (BJS) became Deputy Chief Minister in the Samyukta Vidhayak Dal (SVD) government that came to power in 1967 with Chaudhary Charan Singh as Chief Minister.
- This experiment was repeated in the next government under Chief Minister Chandra Bhanu Gupta of the Congress — when Kamalapati Tripathi was sworn in as Deputy CM in February 1969.
- Both Ram Prakash Gupta and Tripathi went on to become CMs themselves.
- Madhya Pradesh: Virendra Kumar Saklecha of the BJS became Deputy CM in the SVD government led by Govind Narain Singh who came to power in July 1967.
- Haryana: Haryana has had a tradition of Deputy CMs; Chaudhary Chand Ram, a Jat leader from Rohtak, was the first to hold this position in the short-lived government led by Rao Birender Singh.
What are the Powers of the Deputy CM?
- More than the post of deputy chief minister, it is the nature of portfolios allocated to a deputy chief minister that decides how much weight the person carries in the cabinet.
- Chief ministers are often seen to keep most of the important portfolios like home and vigilance with themselves.
- If it's a coalition government, then senior leaders of the largest coalition partner usually get finance and revenue.
- The chief minister is also the sole authority on the transfer and posting of Class-I officers in the state.
- The deputy chief minister does not have a say in this matter.
- The deputy chief minister gets the same pay and perks as enjoyed by other cabinet-rank ministers in the government.
- They, however, enjoy tax-free pay and perks.
- In the matters of administration, the deputy chief minister holds no authority to see the files earmarked for the chief minister.
- In fact, the deputy chief minister is required to route all files pertaining to the portfolios allocated to her to the chief minister for clearance.
- The deputy chief minister cannot claim to preside over a cabinet meeting on her own or issue directions to other departments than allocated to her by the chief minister.
- The deputy chief minister, like any other minister, needs to seek clearance from the chief minister for expenditure over and above the budget allocated to her departments.
- Yet, deputy chief ministers are politically significant.
- It conveys the political weight the party - in the case of the coalition government - or the leader carries in the ruling dispensation.
- This is virtually a declaration that the leader who is appointed as deputy chief minister is Number 2 in the government.
- This aside, the number of deputy chief ministers in a government reflects factions in the ruling dispensation that need to be balanced for survival or the government's hitch-free run.
- Even in oath-taking, the Constitution does not provide for a separate oath for the deputy chief minister or deputy minister.
What are the Concerns?
- Lack of constitutional backing and unclear roles can allow the Chief Minister to exploit the position arbitrarily.
- Unlimited appointments of Deputy CMs may lead to excessive appeasement of coalition partners.
- Duplication of roles with Cabinet ministers could create governance and administrative challenges.
What Lies Ahead?
- There's a need to clearly define the roles and responsibilities of Deputy CMs.
- Implementing a limit on the number of Deputy CMs per Chief Minister could streamline the role.
- It's essential to raise political awareness among Indian citizens about this position.
Deputy Prime Ministers:
- India has also seen several Deputy Prime Ministers — a post that was first held by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel when Jawaharlal Nehru was Prime Minister.
- Nehru and Patel were the two tallest leaders of the Congress at the time and were also seen as representing two different streams of thinking within the party.
- Among those who held the position subsequently were Morarji Desai, Charan Singh, Chaudhary Devi Lal, and Lal Krishna Advani.
- Devi Lal’s appointment as Deputy PM in VP Singh’s government in 1989 was challenged in court on the ground that “the oath administered to him as such was not…in accordance with the prescription of the Constitution”.
- In K M Sharma vs Devi Lal and Ors (1990), the Supreme Court upheld Devi Lal’s appointment “in view of the clear statement made by the learned Attorney General that Respondent No. 1 (Devi Lal) is just a Minister like other members of the Council of Ministers, though he has been described as Deputy Prime Minister.
- The description of him as Deputy Prime Minister does not confer on him any powers of the Prime Minister”.
Optimizing Logistics Costs in India and the Critical Role of Accurate Data (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Logistics has been talked about for a long time and India has also focused on improving performance. We are now getting some precise data on measurement and quantification.
Context:
- The logistics sector plays a vital role in shaping a nation's economic dynamics, and its intricacies are of paramount importance.
- India's steady progress in the Logistics Performance Index (LPI) rankings reflects positive advancements in its logistics sector, showcasing a dedicated effort to boost global competitiveness and streamline trade logistics efficiency.
- Consequently, a comprehensive examination of India's logistics landscape, involving the analysis of key indicators, methodologies, and recent reports, becomes essential for a nuanced comprehension of its achievements and hurdles.
The Logistics Performance Index (LPI):
- Developed by the World Bank, the Logistics Performance Index (LPI) stands as a crucial tool for evaluating a country's trade logistics efficiency and effectiveness.
- Comprising six key dimensions—customs, infrastructure, international shipments, logistics competence, tracking and tracing, and timeliness—the LPI offers a comprehensive insight into a nation's logistical capabilities.
India's Position in the LPI:
- Despite inherent methodological considerations in survey-based indices, the 2023 LPI places India at the 38th position out of 139 countries, showcasing an improvement from its 2014 rank of 54.
- This positive trajectory aligns with India's 2022 vision to reduce logistics costs, enhance LPI rankings, and establish a data-driven decision support mechanism.
- Furthermore, the introduction of PM Gati Shakti in 2021, though its impact is not immediately reflected in the LPI 2023 due to understandable time lags.
Assessing Logistics Costs in India:
- Economic Survey 2022-23: The Economic Survey 2022-23 reveals a consistent range of logistics costs in India, hovering between 14-18% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- This starkly contrasts with the global benchmark of 8%, highlighting the challenges in achieving optimal efficiency in India's logistics operations.
- The survey emphasizes the need for strategic interventions to address the significant gap between India's logistics costs and international standards.
- Dun and Bradstreet (D&B) 2018 Report: An in-depth examination of seaport business costs by a Dun and Bradstreet (D&B) 2018 report indicates that the cost is approximately 15-16% of the consignment value.
- Notably, there is considerable variation across ports, emphasizing the necessity of a nuanced approach in evaluating logistics costs within specific segments of the supply chain.
- NCAER Report (December 2023): The National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) introduces a fresh perspective in its report on logistics costs in India.
- Acknowledging the absence of official estimates, the report references various private sector and academic institutions' estimates.
- Employing meticulous methodology, including supply and use tables, the report provides a nuanced and precise estimation.
- According to this report, logistics costs in 2021-22 ranged between 7.8% and 8.9% of GDP, showcasing a decline over time with a transient increase in 2017-18 and 2018-19.
- CII-Arthur D Little Report (2020): Delving into logistics costs throughout the supply chain, the CII-Arthur D Little Report (2020) estimates them to be around USD 400 billion, equivalent to 14% of India's GDP.
- Comparative assessments with global peers, including the United States, Europe, and China, expose a competitiveness gap of USD 180 billion.
- The report underscores the urgency of addressing these high logistics costs to bolster India's economic competitiveness globally.
Logistics Cost Performance Across States:
- As per the Commerce Ministry's LEADS (Logistics Ease Across Different States) report for 2023:
- States are categorized into four groups - coastal, landlocked, north-east, and Union Territories.
- States exhibiting strong performance are termed achievers.
- States with moderate performance are referred to as fast movers.
- States with below-average performance are labelled as aspirers.
- Performance of Coastal States:
- Approximately 75% of export cargo is traced back to coastal states.
- Among coastal states, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu are notably successful.
- However, lagging behind in performance are Goa, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- While most states, including Goa and Odisha, have implemented a state-level logistics policy, West Bengal, ranking lowest in the coastal category, lacks one.
Difficulties and Variations for Policymakers in Developing a Successful Plan for India's Logistics Sector:
- Methodological Variations: A key challenge in deciphering logistics cost reports stems from the diverse methodologies employed across different studies.
- These reports adopt varied approaches, ranging from consignment value percentages to supply and use tables, to estimate logistics costs.
- The resulting disparities in methodologies contribute to variations in reported figures, necessitating careful consideration when drawing conclusions.
- India's Global Competitiveness: The consistent comparison with global benchmarks, particularly the 8% GDP threshold for logistics costs, prompts questions about India's competitiveness on the international stage.
- Reports consistently highlight a competitiveness gap, with logistics costs surpassing global averages.
- This has implications for India's capacity to attract investment, participate in global trade, and position itself advantageously in the interconnected world economy.
Shifting Perspectives on India’s Logistics Costs:
- Reassessing Established Views: The evolving discourse on logistics costs in India challenges conventional perceptions regarding the country's logistics expenses.
- As methodologies advance and newer reports offer more accurate estimations, the narrative may transition from a broad acknowledgement of high costs to a more nuanced comprehension of the sector's intricacies.
- This evolving narrative carries implications for businesses, investors, and policymakers, prompting them to stay informed of the latest data and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Encouraging Trends Amid Challenges: While challenges persist, positive trends also emerge from the data.
- The improvement in India's Logistics Performance Index (LPI) rankings over time and the downward trend in logistics costs, as highlighted by the NCAER report, present a more optimistic outlook.
- These positive signals indicate that endeavors to enhance logistics efficiency and reduce costs may be gaining momentum, pointing towards a positive trajectory for India's logistics landscape.
Conclusion
The logistics landscape in India is intricate, featuring indices like LPI, varied cost assessments, and state-level nuances that collectively contribute to a holistic understanding.
The recent NCAER report establishes a crucial methodological groundwork for future deliberations, challenging existing perceptions and emphasizing the importance of accurate measurement in assessing India's logistics capabilities.
In the pursuit of elevating its global position in logistics, India must adopt a nuanced approach that considers both macro and micro perspectives. This approach is vital for fostering sustainable growth and driving efficiency improvements throughout the nation.
Raj Bhavan Needs Radical Reforms (The Hindu)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, during a visit to the Calicut University campus, the Governor of Kerala referred to activists from the Students’ Federation of India as 'criminals.' This incident raises concerns about the conduct of Governors in states led by opposition parties and underscores the need to examine the legal implications of such statements.
Context:
- In Kerala, the State Assembly passed a Bill to abolish the Governor’s chancellorship.
- The Governor did not give assent to it and referred the Bill, along with others, to the President.
- This happened after he sat on the Bills for a long time and after the government moved the Supreme Court to pray for gubernatorial assent.
- It was in this context that he visited the University as Chancellor, against the will of the Assembly.
- This action lacked democratic legitimacy.
Role of Chancellor in State Public Universities:
- State public universities are established through state legislation, with the Governor typically designated as the Chancellor in most laws.
- As Chancellor, the Governor serves as the head of public universities and holds the authority to appoint the Vice-Chancellor.
- The Chancellor possesses the power to invalidate any university proceedings not in accordance with existing laws.
Governor's Discretion as Chancellor:
- In 1997, the Supreme Court clarified that the Governor, in the capacity of Chancellor, is not bound by the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers when performing duties related to a separate statutory office.
- Both the Sarkaria and Punchhi Commissions acknowledged the Governor's independence in discharging statutory functions, emphasizing that the Governor is not legally obligated to follow the advice of the Council of Ministers.
- However, consultation with the concerned Minister may be beneficial for the Governor
Limits to immunity:
- Article 361 of the Constitution provides only a limited and conditional immunity for the Governors.
- It says that Governors shall not be answerable to any court for the exercise and performance of the powers and duties of their office or for any act done or purported to be done by them in their official capacity.
- This does not mean that Governors are not liable for their misbehaviour unconnected with their official duty.
- In Rameshwar Prasad v. Union of India (2006), after finding that the Governor abused power in recommending Presidential rule in Bihar, the Supreme Court said that the motivated and whimsical conduct of the Governor is amenable to judicial review.
- Yet, the question of whether Governors can claim immunity for extra-constitutional gestures and utterances was not a matter of issue in Rameshwar Prasad.
- However, the Court said that “right persons” should be chosen as Governors to maintain “the sanctity of the post”.
Legal Implications of Derogatory Comments by Public Functionaries:
- Kaushal Kishor v. State of Uttar Pradesh (2023): The court emphasized that the freedom of expression for public functionaries should only be restricted by 'reasonable restrictions' outlined in Article 19(2) of the Constitution.
- Regarding ministers, Justice B.V. Nagarathna highlighted that if a public functionary's statement contradicts the government's stance, the minister is personally responsible and can face consequences for the remarks.
- While there was agreement on the personal liability of public functionaries for actions unrelated to their public duty, there were varying opinions on the enforcement of fundamental rights against non-state actors.
- This implies that public functionaries do not enjoy statutory or constitutional immunity if they commit a crime, including offences like defamation, especially when the act is unrelated to or conflicts with their official duties.
Commission reports:
- The Sarkaria Commission Report (1988) lamented that “some Governors have failed to display the qualities of impartiality and sagacity expected of them”.
- It added that “many Governors, looking forward to further office under the Union or [an] active role in politics after their tenure came to regard themselves as agents of the Union”. Since then, the situation has only worsened.
- The Commission’s recommendation that the “(Governor) should be a detached figure and not too intimately connected with the local politics of the State” remains wishful thinking.
- The Justice M.M. Punchhi Commission report (2010) said that “to be able to discharge the constitutional obligations fairly and impartially, the Governor should not be burdened with positions and powers which are not envisaged by the Constitution.”
- It said that conferring statutory power on Governors by posting them as chancellors of the universities will have the potential to expose Raj Bhavan to “controversies or public criticism”.
Way Forward:
- Legal Prohibition: The state legislative requires systemic changes regarding the office of the Governor, necessitating a legal prohibition against further appointments of Governors in any official capacity.
- Constitutional Amendment: The central government should consider amending Article 155 of the Constitution, involving consultation with the Chief Minister, as recommended by the Sarkaria Commission.
- Establishing an independent body for Governor selection, with a significant role for the Chief Justice of India, could enhance the quality of the selection process.
- Constitutional Morality: While the Constitution may not regulate individual behaviour, emphasizing the notion of constitutional morality is crucial.
- In the NCT of Delhi v. Union of India (2018) case, the Supreme Court highlighted the importance of identifying the "moral values of the Constitution" based on a notion of "constitutional culture."
- It stressed that "constitutional morality places responsibilities and duties on individuals who occupy constitutional institutions and offices."
Conclusion
While the office of the Governor is entrusted with defending the Constitution and advising elected regimes, it is essential to prevent the potential misuse of powers in the absence of a defined time frame for decision-making. Establishing a reasonable time frame for Governors to decide on Bills passed by the Assembly is imperative to safeguard the principles of federalism in the country.
Important Constitutional Provisions Related to the Governor:
- Article 153 stipulates that each state shall have a Governor, with one person who can be appointed as Governor for two or more states.
- The Governor of a State shall be appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal (Article 155).
- A person to be eligible for appointment as Governor should be a citizen of India and have completed an age of 35 years (Article 157).
- Article 156 of the Indian Constitution deals with the Term of office of Governor.
- It further states that the Governor shall hold office during the pleasure of the President.
- Article 161 grants the Governor the power to grant pardons, reprieves, etc.
- However, the Supreme Court clarified that the Governor exercises this power in consultation with the State government, being bound by its advice.
- Article 163 establishes a council of ministers headed by the Chief Minister to aid and advise the Governor in performing functions, with certain exceptions for discretion.
- Article 164: The Chief Minister shall be appointed by the Governor and the other Ministers shall be appointed by the Governor on the advice of the Chief Minister, and the Ministers shall hold office during the pleasure of the Governor.
- Article 174: The Governor can also summon, prorogue, and dissolve the Legislative Assembly.
- By convention, he does this on the advice of the Council of Ministers while they enjoy the confidence of the Assembly
Discretionary powers include:
- Appointment of a Chief Minister in the absence of a clear majority in the state legislative assembly
- Handling situations like no-confidence motions
- Addressing the failure of constitutional machinery in the state (Article 356)
- The Governor's authority concerning the passage of bills is delineated by Article 200 and Article 201. The Governor may:
- Give assent, turning the bill into law
- Withhold assent, rejecting the bill
- Return the bill (if not a money bill) to the state legislature for reconsideration, with or without specific recommendations
- If the bill is reconsidered and passed again, the Governor cannot withhold assent.
- The Governor may also reserve the bill for the President's consideration, who can assent, withhold assent, or direct the Governor to return the bill to the state legislature for further review.
Centre Wants to End Free Movement Regime With Myanmar (Indian Express)
- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre has decided to scrap the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB), which was implemented in 2018 as part of India’s Act East policy.
What is the Free Movement Regime?
- The FMR is a mutually agreed pact between India and Myanmar that allows tribes dwelling along the border on either side to travel up to 16 km inside the other country without a visa.
- The members of hill tribes have to produce a border pass, which is valid for a year and can stay in the other country for about two weeks per visit.
- The FMR was introduced in 2018 as part of the government’s ‘Act East Policy’ when relations between India and Myanmar were on the rise.
- The agreement aimed to facilitate people-to-people ties between the countries as residents in the region enjoy strong ethnic and familial relations on both sides of the border.
- The FMR was also brought to provide impetus to local trade and business.
- Originally planned for 2017, its implementation was delayed due to the Rohingya refugee crisis that emerged in August of that year.
Background and Purpose:
- The boundary delineation by the British in 1826 separated people of the same ethnicity and culture into two nations without their opinion.
- The FMR sought to address this historical division, allowing ethnically similar communities across borders to move freely without visa requirements.
- Initially designed to boost local trade and business, the FMR has faced criticism for inadvertently facilitating issues such as illegal immigration, drug trafficking, and gun-running.
Why it is being removed?
- India and Myanmar share a mostly unfenced border.
- The IMB goes through forested terrain which is difficult to monitor.
- In Manipur, just 10 km of its border with Myanmar is fenced.
- Mizoram has a 510-km-long porous border with Myanmar.
- Nagaland shares a 215 km boundary with the Southeast Asian nation and
- Arunachal Pradesh has a 520 km-long boundary with Myanmar.
- Since the ethnic conflict erupted in Manipur last year, the free movement regime has come into the spotlight.
- The Meiteis have blamed the illegal migration of tribal Kuki-Chin peoples from Myanmar for stirring up tensions in the state.
- On the other hand, the Kukis in Manipur have accused the Meiteis and Chief Minister N Biren Singh of using this as an excuse for “ethnic cleansing”.
- The alleged illegal migration via the FMR has emerged as a key issue between local leaders in Manipur.
- The FMR was suspended several times in the past, including in 2020 during COVID-19.
- Since the military coup in Myanmar on 1 February 2021, a large number of tribals fleeing violence in their country have crossed over to India, especially into Manipur and Mizoram.
- Over 40,000 refugees belonging to the Kuki-Chin-Zo ethnic group took shelter in Mizoram, while about 4,000 migrants are said to have entered Manipur.
- There are allegations that these refugees took shelter on Indian soil and then got involved in illegal activities such as drug smuggling.
Is ending FMR the solution?
- Many insurgent groups such as the United National Liberation Front (UNLF), the People’s Liberation Army (PLA), the United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA), the National Socialist Council of Nagaland (NSCN), and small groups of Kukis and Zomis have constructed camps in Myanmar’s Sagaing Division, Kachin State and Chin State.
- “They took shelter there, obtained arms, trained cadres, and, most importantly, engaged in illegal activities such as smuggling drugs and selling weapons to raise funds.
- This is possible because of the porous borders and frequent misuse of FMR.
- Therefore, managing and administering the border areas effectively is pertinent for reducing drug trafficking and illegal cross-border movement on unfenced borders.
Conclusion
The Indo-Myanmar border, spanning 1,643 km, presents challenges related to secessionist movements, insurgency, and narcotics smuggling. Neither cancelling the FMR nor completely fencing the border is the solution as it could affect livelihoods, education and essential travel for health care. It is imperative for India to tackle the issue by pursuing the ‘killing the snake without breaking the stick’ stance. A collaborative and multifaceted approach is crucial to addressing these challenges and ensuring stability in the region.
Indo-Myanmar Border:
- The Indo-Myanmar border spans 1,643 km, with Arunachal Pradesh (520 km), Nagaland (215 km), Manipur (398 km), and Mizoram (510 km) sharing common borders with Myanmar.
- Demarcation of the Border: Approximately 1,472 km of the border has been demarcated, leaving only two sections unmarked:
- Lohit sub-sector in Arunachal Pradesh (136 km) and
- Kabaw Valley in Manipur (35 km).
Security Challenges
- Secessionist Movements: The Greater Nagaland movement, encompassing areas in both India and Myanmar, has heightened instability along the border.
- Support to Insurgents: Insurgents in India's Northeastern states maintain ties with groups in Myanmar, offering political support, economic aid, logistics, military training, or arms supplies.
- Narcotics Smuggling: Proximity to the Golden Triangle, a hub for drug production, contributes to rampant drug trafficking, with concerns about synthetic drug trafficking to and from Myanmar.
Border Management
- Security Forces: The Assam Rifles, known as the "Friends of the North East People," safeguards the Indo-Myanmar border in the North East.
- Modern Surveillance Equipment: Modern tools like Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), Battlefield Surveillance Radar (BFSR), and Laser Range Finders enhance border security.
- Border Fencing: To curb infiltration and illegal activities, the Indian government is implementing fencing measures along the Indo-Myanmar border.
- Comprehensive Border Infrastructure Project: A comprehensive project aims to enhance infrastructure on the India-Myanmar border.
- Integrated Check Posts (ICPs): Major entry points on land borders are designated as Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) for efficient management.
- Border Area Development Programme (BADP): The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) undertakes various developmental initiatives under the Border Area Development Programme (BADP) for a holistic approach to border development.
XPoSat: ISRO’s New X-ray Eye in Space (Indian Express)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) put its first polarimetry mission X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) in a precise circular orbit of 650 km on Monday (January 1) after a 21-minute flight.
Context:
- As the world welcomed the first morning of 2024, ISRO's launch vehicle successfully placed a new X-ray payload, XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite), into orbit for astronomical research.
- XPoSat is the world’s second satellite-based mission dedicated to making X-ray polarimetry measurements.
- If the mission proceeds as planned, this entirely indigenous instrument in design and fabrication will mark another significant achievement for Indian astronomers.
What is XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite)?
- X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) is India’s first and world’s second mission dedicated to analysing the polarisation of X-rays emanating from bright celestial sources in the medium frequency band.
- XPoSat comprises two payloads, including Indian X-ray Polarimeter (POLIX) and X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing (XSPECT).
- They have been built by Raman Research Institute and UR Rao Satellite Centre, both located in Bengaluru.
- The spacecraft is designated for observation from low earth orbit (~ 650 km, low inclination of ~ 6 degree).
- It has an estimated mission life of about five years during which XPoSat will observe sources that emit polarised X-rays.
- The observations will be done when the magnetars or neutron stars (they are highly magnetic and display a wide array of X-ray activity) are in transit through the Earth’s shadow, for instance, during the eclipse period.
What are the Two Scientific Payloads Onboard XPoSat?
- POLIX: It is the world’s first instrument designed to operate in the medium X-ray of 8 to 30 kilo electron Volt (keV) energy band.
- It comprises a collimator, which is the key component to filter light originating from bright sources in the field of view.
- Moreover, there is a scatterer consisting of four X-ray proportional counter detectors (that prevent the trapped light from escaping).
- It will observe a few tens of astronomical sources. It was conceived, designed, and built at RRI.
- XSPECT: It is designed to conduct fast timing and high spectroscopic resolution in a soft X-ray energy band (0.8-15 keV).
- It will observe a variety of sources like X-ray pulsars, black hole binaries, low-magnetic field neutron stars, active galactic nuclei or AGNs (a compact region at the centre of a galaxy that emits a significant amount of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum) and magnetars.
Why is the XPoSat Mission Significant?
- Till now, astronomers have largely used and depended on spectroscopic, imaging and timing–based data obtained from either ground-based telescopes or satellite-based missions from the optical to the radio frequency band of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Polarisation of celestial sources was done either in the optical or radio bands.
- XPoSat, however, will be a game-changer and facilitate X-ray polarisation measurements possible from bright sources, that too, in the medium energy band (8-30 keV) energy range – which has never been attempted ever before.
- The XPoSat team has identified several tens of sources radiating X-rays.
- XPoSat will observe two kinds of sources:
- Persistent sources (targeted and known sources) and
- Transient sources (pulsars, active galactic nuclei, magnetars).
- Out in space, X-rays get polarised due to multiple causes.
- For example, X-rays when subject to strong magnetic fields or due to the interactions with material present around black holes.
- So, by studying the polarised X-rays emanating from excellent sources like magnetars, black holes and their surrounding environments, and neutron stars, scientists can probe the nature of the radiations and the multitudes of processes involved in the generation of these radiations.
- POLIX will undertake important measurements like the degree and angle of polarisation of X-ray photons from the environment surrounding black holes, neutron stars, and other such cosmic entities.
- These two additional parameters, along with the spectrographic, timing and imaging data, will aid researchers to overall improve the present understanding of the celestial bodies and ultimately unravel some of the unknown mysteries of the Universe.
What is the Polarisation of X-rays and Why Study It?
- X-rays comprise electric and magnetic waves that are constantly in motion.
- Being sinusoidal waves, they do not follow a patterned direction of motion.
- Whereas, a polarised X-ray is both organised and has two waves vibrating in the same direction.
- When magnetars or black holes emit X-rays, they encounter a wide variety of materials in the Universe.
- As X-rays pass through the thick cloud of materials, the electric component of the X-ray emits a photon in a changed direction, as it has now undergone scattering.
- In the process, the new photon has got polarised in a direction perpendicular to the plane formed between the original and scattered photon.
- The polarisation measurements – angular and degree of polarisation – are believed to provide clues about the bright X-ray emitting sources the nature of these radiations and the complex process they undergo.
- X-rays are electromagnetic radiation whose wavelength is 0.01-10 nanometres (where 1 nanometre is one-billionth of a metre), corresponding to energies of 100-100,000 electron-volt (eV).
- Electromagnetic radiation is characterised by an electric field and a magnetic field vibrating perpendicular to each other.
- The polarisation of electromagnetic radiation refers to the orientation of these two fields as the radiation moves through space.
- X-rays can be polarised when they get scattered.
- For example, when an X-ray travelling through space encounters an atom, the electric field of the X-ray can energise an electron, which will then emit a photon.
- Since X-rays are also photons, the new photon will give the impression that an X-ray photon has been scattered.
- Polarised X-rays are also produced when the path of a fast-moving charged particle is bent by a magnetic field.
- Studying these X-rays can reveal which way the magnetic field is pointing, and tracking how these X-rays evolve in time can reveal many things about the body producing such fields, like a pulsar.
How Does XPoSat Compare With X-ray Experiments or Missions Globally?
- Missions on X-ray polarisation measurements have been a handful, the world over.
- Some like HX-POL and XL-Calibur have been balloon-based and short-duration experiments by NASA and collaborators.
- Indian astronomers, using AstroSat which is India’s first astronomy-based space mission launched in September 2015 — performed timing and broadband spectroscopy of X-ray sources but no polarisation studies were performed.
- The lack of development of highly sensitive and precise instruments makes missions for polarisation measurements of X-rays extremely challenging, thus fewer missions have been attempted so far.
- In 2021, NASA launched Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE).
- It has been designed to operate and perform X-ray polarisation measurements within the soft X-ray band (2 to 8 keV energy band).
- Besides complementing IXPE, XPoSat’s payload POLIX will offer an expanded observational energy band, as it is designated to perform X-ray polarisation in the medium X-ray band (8 to 30 keV).
Conclusion
The accomplished launch of XPoSat and the deployment of POLIX mark a substantial advancement in India's commitment to excelling in space-based X-ray astronomy. With the inventive design of POLIX and its capability to investigate lower energy X-rays, coupled with its collaboration with NASA's instrument, Indian astronomers find themselves at the forefront of unravelling the enigmas surrounding pulsars and black holes. As XPoSat embarks on its cosmic scanning mission, the scientific community is eagerly anticipating the valuable insights it is poised to deliver.
Arvind Panagariya to Head 16th Finance Commission (ET)

- 01 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government appointed former NITI Aayog Vice-Chairman Arvind Panagariya Chairman of the 16th Finance Commission, which will recommend the tax revenue sharing formula between the Centre and States for the five-year period beginning April 2026.
Constitution of the 16th Finance Commission:
- The Government of India, with the approval of the President of India, has constituted the 16th Finance Commission, in pursuance to Article 280(1) of the Constitution.
- Dr Arvind Panagariya, former Vice-Chairman, of NITI Aayog, and Professor, at Columbia University will be the Chairman.
- Members of the 16th Finance Commission would be notified separately.
- Shri Ritvik Ranjanam Pandey has been appointed as Secretary to the Commission.
- The 16th Finance Commission shall make recommendations as to the following matters, namely:
- The distribution between the Union and the States of the net proceeds of taxes which are to be, or maybe, divided between them under Chapter I, Part XII of the Constitution and the allocation between the States of the respective shares of such proceeds;
- The principles which should govern the grants-in-aid of the revenues of the States out of the Consolidated Fund of India and the sums to be paid to the States by way of grants-in-aid of their revenues under Article 275 of the Constitution for the purposes other than those specified in the provisos to clause (1) of that article; and
- The measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a State to supplement the resources of the Panchayats and Municipalities in the State on the basis of the recommendations made by the Finance Commission of the State.
- The 16th Finance Commission may review the present arrangements on financing Disaster Management initiatives, with reference to the funds constituted under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 (53 of 2005), and make appropriate recommendations thereon.
- The 16th Finance Commission has been requested to make its report available by the 31st day of October 2025 covering a period of five years commencing on the 1st day of April 2026.
15h Finance Commission Recommendations (Effective from 2021 to 2026):
- Tax Proceeds Allocation: The Commission advocates for an equitable distribution of tax proceeds between the central government and states, fostering a well-balanced fiscal sharing mechanism.
- Assessment of GST Impact: The FC underscores the importance of analyzing the impact of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on the economy.
- This evaluation aims to comprehend the implications of GST implementation across various sectors.
- Performance-Linked Incentives: Proposed incentives are tied to states' efforts in addressing key issues like population control, ease of doing business, and other pertinent factors.
- Financial Assistance to States: The FC suggests the provision of revenue deficit grants, grants to local bodies, and disaster management grants to states.
- These grants are intended to bolster the financial requirements of the states and promote effective governance.
Proposed Recommendations for the 16th Finance Commission:
- Review of the 2018 Amendment to the Centre’s FRBM: This proposal aligns with the suggestion made by the 15th Finance Commission.
- In the fiscal year 2020-21, the combined debt-GDP ratio of the central and state governments reached 89.8%.
- While these figures have started declining, they remain significantly higher than the corresponding Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) norms of 40% and 20% established in the 2018 amendment.
- With the Centre’s fiscal deficit at 9.2% of GDP and that of states at 4.1% in 2020-21, it becomes imperative to re-examine the 2018 amendment to the Centre’s FRBM, especially considering the deviations from established norms.
- Limiting Freebies: Some state governments exhibit relatively higher debt and fiscal deficit figures compared to their Gross State Domestic Products (GSDPs).
- Two primary concerns arise in this context: the widespread distribution of subsidies and the reintroduction of the previous pension scheme in states without a clear identification of funding sources and the resultant fiscal burdens.
- Often, these subsidies are financed by increasing the fiscal deficit. While advocating for safety nets for the poor is essential in a country facing economic challenges, a prudent approach is crucial.
- The next Finance Commission should provide explicit guidelines to ensure long-term fiscal sustainability and responsible spending on gratuities.
Freebies Must Be Restricted Through Reform:
- An innovative approach to address this issue is the establishment of a loan council, as suggested by the 12th Finance Commission.
- This independent body would monitor the scale and profiles of loans taken by both the central and state governments.
- The 16th Finance Commission should thoroughly scrutinize non-merit subsidies.
- It is crucial for the Finance Commission to enforce strict adherence to fiscal deficit limits by states.
- Incentives should be provided for states maintaining fiscal discipline, potentially integrating fiscal performance as a criterion in horizontal distribution.
- Conversely, measures should be imposed on states exceeding fiscal deficit limits, with appropriate actions taken on their borrowing capacities.
Conclusion
During the pre-reform era, Finance Commission recommendations held less significance, given alternative methods the Centre employed to compensate states. However, with the abolition of the Planning Commission, the Finance Commission has emerged as the primary architect of India's fiscal federalism, shouldering substantial responsibility and wielding significant influence. The recommendations provided by the 16th Finance Commission will be critical as India progresses towards becoming the world's third-largest economy.
Finance Commission:
- The Finance Commission is a constitutional body responsible for providing recommendations on the distribution of tax revenues among the Union and the States, as well as among the States themselves.
- Composition: Constituted by the President under Article 280 of the Constitution, the Finance Commission is formed at the end of every fifth year or earlier, as deemed necessary.
- Parliament has the authority to establish the requisite qualifications for commission members and determine the selection process, as enacted by The Finance Commission (Miscellaneous Provisions) Act, 1951.
- Mandate: The Commission is tasked with making recommendations to the President on various aspects, including the distribution of net tax proceeds between the Union and the States, principles governing grants-in-aid to State revenues, measures to augment a State's Consolidated Fund, and other matters referred to it by the President in the interest of sound finance.
- Composition: The Finance Commission comprises a Chairman and four other members appointed by the President.
- The Chairman is selected from individuals with experience in public affairs, while the other members may have qualifications related to judiciary, financial expertise, administration, or economics.
- Tenure: Each member serves a term specified by the President and is eligible for reappointment.
- Independence: The recommendations of the Finance Commission, although significant, are not binding on the government.
Rebel Group ULFA Signs Peace Accord With Centre, Assam Govt (Indian Express)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), the Assam government and the pro-talks faction of the United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA) signed a memorandum of settlement on Friday.
News Summary:
- The pro-talks faction of the United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA) has officially signed a tripartite Memorandum of Settlement recently with the Central government and the Assam government.
- Chairperson Arabinda Rajkhowa led the ULFA pro-talks faction, which initiated peace talks with the government on September 3, 2011, following the signing of an agreement for the Suspension of Operations with the central and state governments.
- This Memorandum of Settlement signifies the formal commitment of the ULFA faction to renounce violence and integrate into the mainstream.
- It's noteworthy that the hardline faction of ULFA, led by Paresh Baruah, remains outside the purview of the peace accord, and Baruah is reportedly residing along the China-Myanmar border.
- As part of the agreement, Assam will receive a substantial development package, marking a significant step in the peace process.
- Over the past five years, there have been 9 peace and border-related agreements signed in the Northeast region.
- In November 2023, a peace agreement was successfully negotiated with the United National Liberation Front (UNLF) in Manipur, a separatist group representing the Meitei community.
Insurgency in Assam: Causes and Dynamics
- Assam has grappled with insurgency since the 1980s, even after the formation of separate states like Nagaland, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The primary demand of many militant groups in the region has been increased political autonomy, often articulated through calls for separate statehood.
Factors Driving the Insurgency in Assam:
- Ethnic Complexities: Assam is marked by historical tensions among its indigenous ethnic groups.
- Autonomous districts like Karbi Anglong and North Cachar Hills are home to 15 recognized tribes, while the rest of the state has 14 tribes.
- Bodo, Mishing, Karbi, Rabha, Sonowal Kachari, Lalung, Garo, and Dimasa are major tribes, with sustained autonomy movements, especially among Bodo groups.
- Immigration Challenges: Large-scale immigration of Bengali-speaking Muslims from Bangladesh has fueled tension.
- Assamese residents perceive this migration as a threat to their identity, culture, and economic stability.
- Political Dynamics: Movements advocating sub-regional aspirations have clashed with State Governments and Autonomous Councils.
- Example: The All Bodo Students' Union (ABSU) intensified its movement in 1987, seeking a separate state of Bodoland on the North Bank of the Brahmaputra.
- Economic Concerns: The region's economic isolation after partition has adversely impacted its economy.
- The central government’s perception of resource exploitation has fueled sentiments supporting the insurgency.
- Understanding these complex dynamics is crucial for addressing the longstanding insurgency issues in Assam.
The Dynamic Landscape of Insurgent Groups in Assam:
- United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA): ULFA was established in April 1979 with Assamese nationalism as its guiding principle.
- It promised to free Assam and create an autonomous region called Swadin Asom (Independent Assam) that would be home to the Assamese-speaking ethnic group.
- Bodo Movement in Assam: The 1960s saw the emergence of the Bodo political movement, advocating for a homeland known as Udyachal for Assam plains tribal communities.
- The All-Bodo Students Union (ABSU), formed in 1967, became a key advocate for the Bodo cause.
- Post the Assam Accord in 1985, the ABSU played a pivotal role in reviving the movement, eventually supported by armed groups like the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB).
- Bodo Accords (1993, 2003, 2020): Three accords were signed, leading to the formation of the Bodoland Autonomous Council (1993), Bodo Territorial Council (2003), and a truce with NDFB factions (2020).
- The accords granted legislative, administrative, executive, and financial powers to the councils, recognizing Bodo as an associate official language.
- Karbi Insurgency: Five major militant groups in Karbi Anglong, including:
- Karbi People’s Liberation Tiger,
- People’s Democratic Council of Karbi Longri (PDCK),
- Karbi Longri NC Hills Liberation Front (KLNLF),
- Kuki Liberation Front (KLF), and
- United People’s Liberation Army (UPLA).
- The insurgency by these groups revolved around the demand for an autonomous state and had taken off in the 1980s.
- A settlement in 2021 granted greater autonomy, special packages, and a Rs 1,000 crore development package over five years for the Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council.
- Dimasa Uprising: DNLA, the latest group in Dima Hasao district, engaged in a tripartite agreement.
- The settlement mirrors the provisions of the Karbi Anglong agreement, focusing on autonomy and special development packages for the Dimasa community.
These insurgent movements, rooted in regional aspirations, have undergone transformations through accords and settlements, aiming at greater autonomy, linguistic recognition, and developmental packages for the respective ethnic communities in Assam.
In conclusion, the recent Memorandum of Settlement between the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, the Assam government, and the pro-talks faction of ULFA is a positive stride towards peace. However, historical patterns warn of potential challenges post-negotiations. To holistically manage the region, establishing a North East Security Council is vital. The persistent demand for sovereignty by the Paresh Baruah-led ULFA (I) remains a significant hurdle, necessitating a nuanced and sustained approach to lasting peace.
What is the Assam Accord?
- The Assam Accord inked on 15 August 1985, stands as a pivotal Memorandum of Settlement (MoS) resulting from extensive negotiations between the Government of India and representatives of the Assam Movement.
- This historic accord materialized after a six-year-long agitation, commencing in 1979, led by the All Assam Students’ Union (AASU).
- The core demand of the protestors, primarily driven by concerns about the influx of Bangladeshi immigrants, was the identification and expulsion of illegal foreigners.
- In the presence of then-Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi in New Delhi, the accord marked a turning point.
- The leaders of the Assam Movement, cognizant of the issue’s complexity, reached a consensus to accept migrants who had entered Assam before 1 January 1966.
- In a reciprocal gesture, the Government of India acknowledged and addressed the political, social, cultural, and economic apprehensions of the Assamese people.
- As a significant commitment, the government pledged to review the electoral database, aligning it with the aforementioned date.
- Additionally, the accord underscored the government's commitment to the identification and deportation of refugees and migrants who entered Assam after 25 March 1971.
- Thus, the Assam Accord, born out of a prolonged struggle, aimed to address the multifaceted concerns surrounding immigration and safeguard the interests of the indigenous population in Assam.
Broadcast Regulation 3.0, Commissions and Omissions (The Hindu)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) has taken a significant step in broadcasting regulation by releasing the Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill 2023. This bill is part of a series of efforts to regulate broadcasting in an integrated manner.
Context:
The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India has proposed a draft Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023. The draft Bill provides for a consolidated framework to regulate the broadcasting services in the country and seeks to replace the existing Cable Television Networks (Regulation) Act, 1995, and other Policy Guidelines currently governing the broadcasting sector in the country.
The Bill streamlines regulatory processes, extends its purview to cover Over-the-Top(OTT) content and digital news, and introduces contemporary definitions and provisions for emerging technologies. It seeks to provide Content Evaluation Committees and a Broadcast Advisory Council for self-regulation, different program and advertisement codes for different Broadcasting Network Operators, Accessibility measures for persons with disabilities, and statutory penalties, etc.
Key Highlights of the draft Broadcasting Services (Regulation) Bill, 2023:
- Consolidation and Modernization: It addresses a long-standing need to consolidate and update the regulatory provisions for various broadcasting services under a single legislative framework.
- This move streamlines the regulatory process, making it more efficient and contemporary.
- It extends its regulatory purview to encompass broadcasting over-the-top (OTT) content and digital news and current affairs currently regulated through IT Act, 2000 and regulations made there under.
- Contemporary Definitions and Future-Ready Provisions: To keep pace with the evolving technologies and services, the bill introduces comprehensive definitions for contemporary broadcasting terms and incorporates provisions for emerging broadcasting technologies.
- Strengthens the Self-Regulation Regime: It enhances self-regulation with the introduction of ‘Content evaluation committees and evolves the existing Inter-Departmental Committee into a more participative and broader ‘Broadcast Advisory Council’.
- Differentiated Programme Code and Advertisement Code: It allows for a differentiated approach to Programme and Advertisement Codes across various services and requires self-classification by broadcasters and robust access control measures for restricted content.
- Accessibility for Persons with Disabilities: The bill addresses the specific needs of persons with disabilities by providing enabling provisions for the issue of comprehensive accessibility guidelines.
- Statutory Penalties and Fines: The draft Bill introduces statutory penalties such as advisory, warning, censure, or monetary penalties, for operators and broadcasters. Provision for imprisonment and/or fines remains, but only for very serious offenses, ensuring a balanced approach to regulation.
- Equitable Penalties: Monetary penalties and fines are linked to the financial capacity of the entity, taking into account their investment and turnover to ensure fairness and equity.
- Infrastructure Sharing, Platform Services, and Right of Way: The bill also includes provisions for infrastructure sharing among broadcasting network operators and carriage of platform services.
- Further, it streamlines the Right of Way section to address relocation and alterations more efficiently, and establishes a structured dispute resolution mechanism.
Arguments in Support of the Bill:
- Revamped Legal Framework: This legislation signifies a departure from the Cable Television Networks Regulation Act of 1995.
- The Information & Broadcasting Minister lauds it as a "crucial law" designed to modernize the regulatory framework, aligning with the dynamic landscape of OTT, digital media, DTH, IPTV, and emerging technologies.
- Additionally, it incorporates comprehensive accessibility guidelines for the Divyangjan community.
- Empowerment of Broadcasters: The bill introduces provisions aimed at empowering broadcasters through self-regulation mechanisms.
- Striving for a delicate balance between regulatory oversight and industry autonomy is a key objective.
- Tailored Approach to Codes: The draft Bill permits a "differentiated approach" to Programme and Advertisement Codes across diverse services.
- This approach enables the tailoring of regulations to accommodate the unique nature of linear and on-demand content, providing content creators with increased flexibility and relevance.
- Equitable Measures: Monetary penalties under this bill are intricately tied to the entity's investment and turnover, ensuring fairness.
- Penalties are proportionally determined based on the financial standing of the entity, meaning that larger corporations with higher investments and turnovers may face more substantial fines compared to smaller entities with limited financial capacity.
- Inclusive Stakeholder Participation: The bill emphasizes stakeholder involvement through public consultation, a move applauded by the industry.
- The government's initiative to establish a unified law is welcomed, with expectations that it will streamline compliance and enforcement processes.
Arguments Against the Bill:
- Concerns about Control and Regulation: There are concerns surrounding whether the bill's emphasis is truly on public service or if it leans more towards expanding government control and regulation.
- Some worry that the bill might amplify government control over digital infrastructure and influence citizens' viewing choices.
- Ambiguities in Draft Provisions: Specifically, point 36 in the draft raises concerns about its broad and ambiguous language, providing authorities with the power to restrict content.
- Questions arise regarding the role of "authorized officers" working under government direction.
- Potential Impact on Minority Communities: Apprehensions exist that the bill could lead to the erasure or selective representation of Indian minority communities.
- The draft's vague language may be susceptible to exploitation, promoting a universal majority identity for India.
- Challenges with Cable Regulation: The Cable Television Networks (Regulation) Act of 1995, initially targeting illegal cable operators, faced transparency issues due to a nexus involving operators, politicians, entrepreneurs, and broadcasters.
- The new bill fails to address loopholes and problems in implementing the existing Act, including conflicts of interest and opaque practices within the Indian media industry.
- Government's Trust Deficit: Critics point to the government's recent history with media regulation, highlighting a pattern of unfulfilled promises and questionable outcomes.
- The bill is compared to the controversial IT Rules of 2021 introduced for national welfare.
- Concerns about Oligopolistic Media Ownership: Amid debates on "cultural invasion" and "anti-national" programming, some argue that the connection between government officials and media houses may foster oligopolistic media ownership.
Notable Omissions from the Bill:
- Lack of Regulation on Ownership: The bill overlooks concerns related to ownership within the media landscape, mirroring the oversights in the TRAI paper.
- Despite placing emphasis on audience measurement methodologies, the absence of provisions regulating cross-media and vertical ownership is apparent.
- Cross-media ownership, previously identified as a threat to diversity by TRAI, consolidates media power, with interconnected interests of cable and DTH distributors, news broadcasters, and telecom companies potentially restricting the array of available news sources.
- Absence of an Independent Broadcast Regulator: The bill remains silent on the establishment of an independent broadcast regulator, a concept previously endorsed in the 'airwaves' judgment of 1995, the 1997 Broadcasting Bill, and reiterated in the 2007 iteration.
- Instead of proposing an independent regulator, the bill introduces a 'Broadcast Advisory Council' tasked with addressing viewer grievances and violations of the Programme Code and Advertisement Code.
- Concerns arise about the Council's ability to handle grievances from a broad audience and questions surface regarding its autonomy.
The Way Ahead: Urgent Requirement for Conflict of Interest Regulation
- The Indian government has not effectively managed conflicts of interest in the media industry, especially the connections between MSOs (Multi-Service Operators), politicians, and vertical integration.
- As this has led to a loss of trust, a regulation on conflicts of interest is the need of the hour.
Conclusion
The essence of Broadcasting Regulation goes beyond mere compliance; it revolves around fostering an environment conducive to growth, and innovation, and ensuring fair access to communication services. Striking the right balance between regulatory oversight and industry autonomy is crucial for India to strategically position itself for sustained success in the rapidly evolving telecommunications sector.
Severe Drought in the Amazon Rainforests (Indian Express)
- 19 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Hundreds of fish dead, no drinking water, food or other supplies — the latest spell of drought in the Amazon rainforest has disrupted the lives of tens of thousands of Indigenous people.
Amazon Rainforest Drought:
- In the period from July 2023 to September 2023, eight Brazilian states experienced the lowest rainfall in over four decades.
- Projections indicate that rainfall is expected to remain below average until the year's end.
- This recent calamity further contributes to the ongoing destruction of the Amazon, often referred to as the planet's lungs due to its role in storing over 150 billion metric tonnes of carbon.
Impact of the Drought:
- Depletion of Water Bodies: The Rio Negro, among the world’s largest rivers, registers a historic low of 13.59 meters.
- The Madeira River, a crucial Amazon tributary, experiences a decline, causing the suspension of operations at the Santo Antonio hydroelectric dam due to exceptionally low water levels.
- Loss of Marine Life: Elevated mortality among fish and river dolphins (Boto) results from the drought's impact on water levels.
- Carcasses contaminate water sources, compelling residents to use compromised water for essential activities like cooking, bathing, and drinking.
- State of Emergency and Humanitarian Concerns: Brazilian authorities express apprehension about approximately 500,000 people being affected by the end of October.
- Manaus, the largest city in Amazonas, declares states of emergency in 55 out of 62 municipalities due to acute water shortages.
- Escalation of Wildfires: The rainforest, now more susceptible due to extreme dry conditions, witnesses a surge in wildfires.
- Amazonas state records an unprecedented 2,700 blazes this month, marking the highest for October in the past 25 years.
- Deteriorating Air Quality in Manaus: Smoke from wildfires adversely impacts air quality in Manaus, a city of two million in the heart of the Amazon.
- Hazardous pollution levels pose health risks, leading to respiratory issues for children and older residents, prompting hospitalisations.
What are the Reasons Behind this Drought?
- Droughts are not unprecedented in the Amazon, with the most notable recent instance occurring in 2021, marking the driest period in at least 90 years.
- The current drought, however, appears to be even more severe, attributable to two simultaneous natural phenomena impeding cloud formation and exacerbating the already diminished rainfall levels in the region.
- Influence of El Niño: El Niño denotes an abnormal warming of surface waters in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- This weather pattern tends to elevate the likelihood of setting temperature records and induces heightened heat extremes across various global regions, including the ocean.
- Elevated Water Temperatures in the Atlantic Ocean: The other contributing factor is the unusually high water temperatures observed in the northern tropical Atlantic Ocean.
- Elevated ocean temperatures prompt the ascent of heated air into the atmosphere, reaching the Amazon rainforest.
- The warmth inhibits cloud formation, resulting in a substantial reduction in rainfall.
Studies Highlighting Concerns for the Future of the Amazon Rainforests:
- Numerous studies over the years have consistently warned that the Amazon faces an increased risk of prolonged and more frequent droughts due to escalating global temperatures.
- A 2022 research publication in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) projected that if current fossil fuel consumption rates persist, the rainforest could endure significant droughts in 9 out of every 10 years by 2060.
- Another study, featured in the journal Nature in 2022, disclosed a concerning trend: Amazon's diminished ability to recover from prolonged droughts over the last two decades, bringing it dangerously close to a tipping point.
- Crossing this threshold could result in the transformation of the lush green forest into a drier open savanna, releasing substantial stored carbon and contributing to further global warming.
- With 17 to 20 percent of the Amazon destroyed in the past five decades, urgent measures are imperative to combat deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions, and where feasible, undertake reforestation initiatives in the depleted areas, as advocated by experts.
About Amazon Rainforests:
- Amazon is the world’s largest tropical rainforest covering over 5.5 million square kilometres.
- Tropical forests are closed-canopy forests growing within 28 degrees north or south of the equator.
- Due to the thickness of the canopy (the top branches and leaves of the trees), the Amazon floor is in permanent darkness.
- Tropical forests are very wet places, receiving more than 200 cm of rainfall per year, either seasonally or throughout the year.
- The Amazon is found in South America, spanning across Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana.
- Running through the north of the rainforest is the Amazon River — a network of many hundreds of waterways that stretches 6,840km.
- Around 400-500 indigenous Amerindian tribes call the Amazon rainforest home.
- It’s believed that about fifty of these tribes have never had contact with the outside world!
- The Amazon has an incredibly rich ecosystem – there are around 40,000 plant species, 1,300 bird species, 3,000 types of fish, 430 mammals and a whopping 2.5 million different insects. Wow!
- The Amazon is home to a whole host of fascinating – and deadly! – creatures, including electric eels, flesh-eating piranhas, poison dart frogs, jaguars and some seriously venomous snakes.
- This area of immense natural beauty plays an important role in limiting climate change. This is because the rich vegetation takes carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) out of the air and releases oxygen.
Large Ozone Hole Detected Over Antarctica (The Hindu)
- 13 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
As part of the EU’s environmental monitoring program, the European Space Agency Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite detected a giant hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica recently.
What is an Ozone Hole?
- An ozone hole refers to a region in the stratosphere above Antarctica where the ozone layer experiences significant depletion.
- Contrary to the term "hole," it doesn't imply a complete absence of ozone; rather, scientists use the term metaphorically to indicate an area where ozone concentrations fall below the historical threshold of 220 Dobson Units.
- The dimensions of the ozone hole over Antarctica fluctuate annually, typically forming in August and dissipating by November or December, driven by distinct climatic conditions in the region.
Mechanism Behind Ozone Hole Formation:
- The emergence of the ozone hole is linked to the Earth's rotation, creating specific winds over the enclosed Antarctic landmass.
- The polar vortex, characterized by robust winds around the poles, is a key factor in the dynamics of the ozone hole.
- During winter, the polar vortex forms due to temperature variations, acting as a barrier that separates polar air from warmer air at lower latitudes.
- This isolation fosters the formation of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs), triggering reactions leading to ozone depletion.
- Chemical processes occurring on the surface of PSCs activate chlorine and bromine compounds, particularly chlorine, acting as catalysts in ozone-depleting reactions.
- When exposed to sunlight, these compounds catalyze the breakdown of ozone molecules.
- The size and intensity of the polar vortex directly influence the extent of ozone depletion.
- As the vortex weakens in spring, the mixing of polar air with warmer air from lower latitudes gradually closes the ozone hole, contributing to the restoration of the ozone layer.
What Caused the Giant Ozone Hole in 2023?
- Scientists believe this year’s big ozone hole could be due to the volcanic eruptions at Hunga Tongain Tonga during December 2022 and January 2023.
- In contrast to typical volcanic eruptions that release gases primarily within the lower atmosphere, this specific event ejected a substantial quantity of water vapour into the stratosphere.
- The presence of water vapour, along with other ozone-depleting elements such as bromine and iodine, had repercussions on the ozone layer through chemical reactions, ultimately modifying its heating rate.
Human-caused Ozone Holes:
- While this year’s Antarctic ozone hole was likely due to a volcanic eruption, scientists became aware that human activities were creating huge ozone holes in the 1970s.
- Ground and satellite-based measurements detected the holes, which were caused by the widespread use of chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons.
- “The culprit behind ozone depletion was not aerosols in aerosol cans, but the propellants we use as gases to propel the solutions inside.
- These gaseous propellants contain chlorine, which is released high in the stratosphere and depletes the ozone.
- The world took action after scientists raised alarm over the ozone holes, and quickly.
- In 1987, The Montreal Protocol was created to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of these harmful substances.
- The protocol was effective as ozone holes got smaller in the decades after ozone-depleting gas emissions were controlled.
Is there any Relation Between Climate Change and Ozone Holes?
- Ozone depletion is not considered a primary catalyst for global climate change.
- Nevertheless, there are indications that the rising global temperatures associated with climate change may impact the dynamics of ozone holes.
- Recent instances of substantial ozone holes have been associated with climate change, particularly the escalation of wildfires.
- The heightened frequency and intensity of wildfires, often exacerbated by climate change, release more smoke into the stratosphere, potentially contributing to additional ozone depletion.
- While ozone holes may yield a cooling effect by diminishing the greenhouse gas impact (as the loss of ozone allows slightly more heat to escape into space from that region), they can also disrupt the normal progression of seasons, leading to prolonged wintertime conditions.
What is Ozone (O3)?
- Formation: Ozone molecules result from the interaction of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun with O2 molecules.
- During this process, an O2 molecule is split, and the two liberated oxygen atoms combine with other O2 molecules, forming O3 molecules.
- While oxygen (O2) constitutes 21% of Earth's atmosphere, ozone makes up less than 0.001%.
- Ozone Layer: The ozone layer, crucial for life on Earth, is primarily generated in the stratosphere where UV radiation is more intense due to thinner air at higher altitudes.
- This region, known as the 'ozone layer,' spans approximately 10 to 40 km in altitude, with a peak of around 25 km.
- Significance of Ozone Layer: The ozone layer plays a vital role in protecting life on Earth by absorbing the most harmful type of UV radiation, UV-B radiation, with wavelengths between 280 and 315 nanometres.
- Shielding against UV rays is significant in reducing skin cancer rates, as most skin cancers are linked to excessive UV radiation exposure.
- As UV radiation is absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere, it leads to the heating of the surrounding air, creating the stratospheric temperature inversion.
- Measurement of Stratospheric Ozone: Stratospheric ozone is quantified as the total amount present in an atmospheric column in Dobson units.
- One Dobson unit represents the amount of ozone that would form a layer 0.01 mm thick at average sea-level pressure and temperature.
- Ozone Production: Most stratospheric ozone is produced at tropical latitudes, and high-altitude winds disperse it globally.
- Ozone undergoes continual formation and breakdown, with its distribution across the planet being neither uniform nor constant.
- Natural processes historically balanced ozone formation and breakdown, but human activities in recent decades have accelerated ozone depletion.
- Ground-level ozone formation contributes to 'photochemical smog,' posing a health hazard when ozone levels become elevated due to its toxic nature.
Qatar court drops death penalty for 8 Indians, Govt says sentences reduced (Indian Express)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A Qatar court has reduced the death sentences awarded to eight former Indian Navy personnel last month in connection with an alleged case of espionage.
What is the Case?
- Arrest of Eight Navy Personnel: On August 30, 2022, eight former Indian Navy personnel, accompanied by two others, were apprehended under undisclosed charges and subsequently placed in solitary confinement.
- These individuals were affiliated with Al Dahra Global Technologies and Consultancy Services, a defense services provider company.
- Sources indicate that the Indian nationals were privately engaged with the company to supervise the induction of Italian small stealth submarines U2I2.
- The company's previous website, now defunct, mentioned its provision of training, logistics, and maintenance services to the Qatari Emiri Naval Force (QENF).
- Charges Against the Men: The specific charges against the individuals have not been publicly disclosed; however, media reports suggest that the eight Indians are accused of espionage on behalf of Israel.
- Death Penalty for Navy Veterans: In March 2023, after multiple unsuccessful bail pleas, the trial for the Navy veterans commenced, culminating on October 26, 2023, with the imposition of the death sentence on all eight men.
- India's Appeal: In November 2023, the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) announced the filing of an appeal, revealing that its legal team possessed details of the charges.
- The Indian ambassador in Doha visited the incarcerated individuals on December 3, providing consular access.
- This access occurred shortly after Prime Minister Modi met Qatar’s Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al-Thani during the COP28 summit in Dubai on December 1.
What Options Has India Explored?
- One avenue involves legal challenges, a step that has been acknowledged and has temporarily mitigated the sentence.
- Concurrently, India has actively utilized diplomatic channels to engage with the Qatari authorities.
- The families have submitted a mercy plea to the Emir of Qatar, leveraging the tradition of pardons granted during Ramadan and Eid, with support from the Indian government.
India-Qatar Bilateral Relations:
- Economic Ties: In recent years, the trade volume between India and Qatar has witnessed fluctuations.
- During the fiscal year 2015-2016, trade between the two nations reached an impressive $10 billion.
- However, recent years have seen a slight decline in trade due to falling gas and oil rates in the international market.
- Trade Statistics and Import Dependence: In the fiscal year 2022-23, India's total imports from Qatar amounted to $16.81 billion, primarily in fossil fuels like liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), plastics, and petrochemical products.
- Conversely, India's exports to Qatar during the same fiscal year were valued at $1.97 billion, covering items such as cereals, copper articles, iron and steel products, vegetables, fruits, spices, and processed food items.
- Investment Interests and Collaborative Projects: Qatari authorities, particularly the Qatar Investment Authority, express interest in investing in India, focusing on infrastructure development, roads, highways, economic corridors, and projects related to gas and fertilizers.
- India reciprocates with a keen interest in direct investments in liquefied natural gas, chemical industries, fertilizer production, urea, petrochemicals, and infrastructure projects.
- India's Growing Energy Needs: India, with its growing energy needs, has a robust energy partnership with Qatar, dating back to a 1990 agreement.
- This commitment involves India purchasing 7.5 million tonnes of LNG annually for 25 years.
- The collaboration was further strengthened in December 2015, with Qatar agreeing to augment its LNG supply to India by an additional one million tonnes annually.
- Collaboration in Defence Affairs: India's defense collaboration with Qatar focuses on training, mutual participation in conferences and events, and visits by Indian Navy and Coast Guard vessels.
- Notably, the joint naval exercise 'Zair-Al-Bahr' showcases significant cooperation between the Indian and Qatari Navies.
- Both nations are committed to combating the financing of terrorism.
- Cultural Interaction: The Indian Cultural Centre (ICC) plays a crucial role in overseeing Indian community associations in Doha.
- Qatar's role as a co-sponsor of the United Nations General Assembly Resolution designating June 21 as the International Day of Yoga is highly valued by India.
- Indian Diaspora in Qatar: The Indian community in Qatar, numbering approximately 700,000, constitutes the largest expatriate group.
- Their contributions span diverse sectors, including projects related to the Qatar 2022 FIFA World Cup, and annual remittances to India are estimated at around 750 million dollars.
- Indispensable Role of Qatar as an LNG Supplier: The cornerstone of the bilateral trade relationship lies in liquefied natural gas (LNG), where Qatar plays a pivotal role by meeting 80% of India's LNG requirements.
- India imported a total of 19.85 million tonnes of LNG in the fiscal year 2022-23, with approximately 54% of this LNG.
- This significant reliance on Qatar, both through long-term contracts and spot purchases, underscores the challenge of diversifying India’s sources of LNG.
Challenges in India-Qatar Bilateral Relations:
- BJP Spokesperson's Controversy: The initial strain in the relationship arose in June 2022 when BJP spokesperson Nupur Sharma made derogatory references to the Prophet on a TV show.
- Qatar was the first country to object and demanded a public apology from India.
- Jailing of Navy Personnel: The second significant challenge involves the imprisonment of eight ex-Navy personnel.
- This development caught New Delhi off guard, particularly given the substantial Indian expatriate community in Qatar, where 800,000 Indians live and work.
- Israeli-Gaza Conflict: The news of the death penalty for the Indians coincided with heightened tensions in the Middle East due to the Israeli bombardment of Gaza.
- Qatar, with its strong sympathy for the Palestinians, has played a mediating role, including securing the release of American hostages from Hamas captivity.
- Qatar's diplomats are actively engaged as regional mediators in the ongoing crisis.
Maximizing Opportunities for Strengthened Relations:
- Safeguarding Expatriate Workers: India must engage in negotiations aimed at ensuring the protection of the rights and well-being of its expatriate workers in Qatar, who have encountered various labour-related challenges.
- Cultural Exchange and Soft Power: Recognizing the widespread popularity of Bollywood among Qataris, India should actively explore diverse avenues for cultural exchange to amplify its soft power influence.
- This cultural diplomacy can serve as a bridge for deeper understanding between the two nations.
- Cooperation in the Education Sector: The presence of esteemed Western universities in Qatar presents an opportunity for Indian students to access quality education abroad without the usual constraints of long distances and high living costs.
- Strengthening cooperation in the education sector can further elevate the resilience and depth of the India-Qatar relationship, even in the face of seemingly intractable diplomatic challenges.
- Collaborative Environmental Sustainability: India and Qatar can forge a collaborative path towards fostering a cleaner and more energy-efficient environment.
- Joint efforts in environmental sustainability can contribute to shared global goals.
India-Maldives Relations Amidst Chinese Influence (Indian Express)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Following the recent presidential elections in Maldives, there are concerns about the potential impact on India-Maldives relations due to the 'India-Out' campaign led by President-elect Mohamed Muizzu.
Context:
- The recent election in Maldives resulted in the victory of a candidate perceived as Pro-China for the presidential role, sparking apprehensions for India.
- Maldives had a historical shift from an Executive Presidency system dating back to 1968 to a multi-party democracy in 2008.
- The absence of a re-elected incumbent president since 2008 is causing concern for India on this occasion.
Geographical Bonds Between India and Maldives:
- The Maldives is an archipelago spread across 90,000 square kilometres, predominantly comprising 99.6% of the ocean, leaving the remaining land scattered among over 1,200 islands.
- A concerning forecast by experts suggests that by 2050, 80% of the Maldives may face submersion due to the effects of 'Global Boiling.'
- In this geographical tapestry, India emerges as the closest neighbour, positioned just 70 nautical miles away.
- In times of crisis, it is India alone that stands as Maldives' immediate and unwavering ally.
- The profound words of Ibn Khaldun, the Tunisian philosopher, find resonance in the destiny woven by geography between these two nations.
- As he asserted, geography plays a pivotal role, and in the case of India and the Maldives, it s
How Has India Assisted the Maldives in the Past?:
- Essential Support and Communication Dependence: Historically, Maldives has leaned on India for essentials and communication, with India standing as a consistent and indispensable factor in the island nation's development.
- Even during the British protectorate years (1887-1965), Maldives relied on India for essentials and as a gateway to the outside world.
- State Bank of India's Role in Tourist Economy: India played a pivotal role in shaping Maldives' tourist economy, with the State Bank of India serving as a major financier in building the foundation of the country's tourism sector.
- This enduring support positions the State Bank of India as the largest bank in the Maldives to this day.
- Non-Interference in Internal Developments: Crucially, India has refrained from interfering in Maldives' internal affairs, offering support during critical moments such as the attempted coup in 1988 and subsequent assistance in various forms over the decades.
- The profound dependence of Maldives on India, coupled with India's unconditional support, has played a pivotal role in the island nation's emergence as the highest per capita country in South Asia.
- India's Prompt Response in Crises: During three major crises in 1988 (coup), 2004 (tsunami), and 2014 (water shortage), India emerged as the first responder, exemplifying its commitment to Maldives' well-being.
- Critical Role of Indian Professionals: In education and health, Indian teachers and doctors continue to play crucial roles, extending their influence even to remote inhabited islands.
- Strategic Defense Cooperation: The strategic defence cooperation between India and Maldives goes beyond material assistance, focusing on capacity building through joint exercises like Ekuverin and Ekatha, as well as collaboration in surveillance assets, training 1,400 MNDF trainers in recent years, and disaster management efforts.
What is the Current Situation of India-Maldives Bilateral Relations?
- India stands as the predominant partner in various sectors, be it trade or tourism.
- Demonstrating commitment to elevating Maldives' infrastructure, India is actively engaged in projects such as enhancing connectivity in Greater Male.
- India plays a vital role in supplying a diverse range of essential commodities in bulk, including rice, wheat flour, sugar, potatoes, onions, eggs, vegetables, and even special dispensations like river sand and construction materials.
India's Strategic Interests in Maldives:
- Strategic Significance: Maldives holds paramount importance for India as a primary line of defense against various threats, including terrorism, piracy, drug trafficking, narcotics, and maritime crimes.
- Geographically, Maldives is strategically positioned merely 70 nautical miles from Minicoy and 300 nautical miles from India's West coast.
- It serves as a pivotal point within the commercial sea lanes traversing the Indian Ocean.
- Geo-Political Alignment: India's interests in Maldives align on various fronts, encompassing:
- Securing sea lanes of communication.
- Combating piracy and sea-based terrorism.
- Transforming the Indian Ocean into a conflict-free zone, restoring its status as a peaceful maritime region.
- Exploring the potential of the blue economy and enhancing trade relations.
- Internal Security Concerns: Maldives' proximity and shared maritime borders have direct implications for India's internal security.
- The upsurge in Maldivians joining terrorist groups, such as the Islamic State (IS), poses a significant challenge.
- Political instability and socio-economic uncertainties contribute to the growth of Islamist radicalism, raising concerns about the potential use of remote Maldivian islands as launch pads for terror attacks against India and its interests.
What are the Challenges to India-Maldives Bilateral Relations?
- Rising Islamic Radicalization: The Maldives has witnessed an alarming increase in per capita numbers of individuals joining foreign terrorist groups in Syria and Iraq.
- A 2020 report by the European Foundation for South Asian Studies highlights the challenge of growing Islamic radicalization among the Maldivian population.
- India Out Campaign: The India Out campaign, supported by Maldives' opposition leader Abdulla Yameen and the newly elected president, projects a sceptical view of India's investments and defence partnerships.
- Allegations include concerns about compromising the sovereignty of the island nation by allowing Indian military presence, fostering a negative sentiment towards India's role as a net-security provider.
- The China Factor: China's engagement in the region is perceived as self-serving, characterized by debt financing leading to potential debt traps and China's expanding influence.
- Concerns arise over China's interference in Maldives' internal politics and support for conservative elements, posing a threat to the development of a vibrant democracy.
- There are apprehensions that elements aligning with China may perpetuate a legacy of controlled regimes from the Gayoom era, potentially compromising the nation's long-term interests.
Way Ahead for India-Maldives Relations: Detrimental Effects of Anti-India Campaigns
- India remains steadfast in its commitments to the Maldives, consistently investing in efforts to strengthen bilateral relations.
- Any hasty attempts to unravel this carefully nurtured partnership are poised to inflict more harm on the Maldives than on India itself.
- A telling example is the 2012 'GMR out' campaign, which cost Maldives a substantial $270 million payout to GMR.
- The Yameen era, marked by a pro-China policy, plunged Maldives into a debt crisis, underscoring the potential pitfalls of such geopolitical shifts.
Conclusion
Throughout the decades, India has been a reliable source of security assistance for Maldives, extending a hand of friendship and trust. It is anticipated that the newly elected President Muizzu will likely refrain from taking drastic measures that could alter the fabric of relations with India. While elections are often driven by emotions and promises, the pragmatic realities of governance may lead him to recognize the potential repercussions of undermining the longstanding ties with India.
Demand for Special Category State Status for Bihar (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar on Sunday urged Union Home Minister Amit Shah to give Bihar the status of Special Category State, during the meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council (EZC) in Patna.
Context:
- During the 26th meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council on 10th Dec. which was chaired by Home Minister Amit Shah, Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar urged the Home Minister to give Bihar the status of Special Category State.
- He also demanded that the Centre should place two amendment bills raising the quota for deprived castes from 50 to 65% in state government jobs and educational institutions in the 9th Schedule of the Constitution to make them to make them immune to legal scrutiny.
- The Ninth Schedule of the Constitution includes a list of Central and state laws that cannot be challenged in courts.
- In 1992, the Supreme Court capped reservations for the backward classes at 50 per cent.
- Regarding Caste Based Survey, he said the Central government never had any intention of creating hurdles in the caste-based survey.
What is a Special Category Status (SCS)?
- It is a classification granted by the Centre to assist the development of States that face geographical or socio-economic disadvantages.
- The SCS was introduced in 1969 on the recommendation of the Fifth Finance Commission (FC).
- Five factors such as:
- (i) hilly and difficult terrain
- (ii) low population density and/or sizeable share of tribal population
- (iii) strategic location along international borders
- (iv) economic and infrastructural backwardness and
- (v) non-viable nature of state finances, are considered before granting SCS.
- In 1969, three States — Jammu & Kashmir, Assam and Nagaland — were granted the SCS.
- Subsequently, eight more States including Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand were given the SCS by the erstwhile National Development Council.
What are the Benefits of Special Status?
- The SCS States used to receive grants based on the Gadgil-Mukherjee formula, which earmarked nearly 30% of the total central assistance for States to the SCS States.
- However, after the abolition of the Planning Commission and the recommendations of the 14th and 15th FC, this assistance to SCS States has been subsumed in an increased devolution of the divisible pool funds for all States (increased to 41% in the 15th FC from 32%).
- Additionally, in the SCS States, the Centre-State funding of centrally sponsored schemes is divided in the ratio of 90:10, far more favourable than the 60:40 or 80:20 splits for the general category States.
- Besides, there are several other incentives available to the SCS States in the form of concession in customs and excise duties, income tax rates and corporate tax rates to attract investments to set up new industries etc.
Why is Bihar demanding the Special Category Status (SCS)?
- The demand for SCS for Bihar has been made by various political parties of the State time and again.
- The poverty and backwardness of the State are argued to be because of the lack of natural resources, continuous supply of water for irrigation, regular floods in the northern region and severe droughts in the southern part of the State.
- Simultaneously, the bifurcation of the State led to the shifting of industries to Jharkhand and created a dearth of employment and investment opportunities.
- With a per-capita GDP of around ?54,000, Bihar has consistently been one of the poorest States.
Is Bihar’s demand justified?
- Although Bihar meets most of the criteria for the grant of SCS, it does not fulfil the requirement of hilly terrain and geographically difficult areas, which is considered to be the primary reason for difficulty in infrastructural development.
- In 2013, the Raghuram Rajan Committee set up by the Centre, placed Bihar in the “least developed category” and suggested a new methodology based on a ‘multi-dimensional index’ for devolving funds instead of an SCS, which can be revisited to address the State’s socio-economic backwardness.
Do other States also want Special Category Status (SCS)?
- Since its bifurcation in 2014, Andhra Pradesh has asked for a grant of SCS on the grounds of revenue loss due to Hyderabad going to Telangana.
- Additionally, Odisha has also been requesting for the SCS, highlighting its vulnerability to natural calamities such as cyclones and a large tribal population (nearly 22%).
- However, the Central government citing the 14th FC report, which made a recommendation to the Centre that no State be accorded the SCS, has repeatedly denied their demands.
What are the Challenges Associated with Special Category Status (SCS)?
- Resource Allocation: The provision of Special Category Status (SCS) involves extending additional financial aid to the state, potentially straining the central government's resources.
- Balancing fund allocation among states becomes crucial, raising concerns about disparities or dissatisfaction among non-SCS states.
- Dependency on Central Assistance: States awarded SCS often develop a heavy reliance on central assistance, potentially discouraging efforts toward self-sufficiency and independent economic growth.
- Implementation Challenges: Even after receiving SCS, challenges may arise in effectively utilizing funds due to administrative inefficiencies, corruption, or inadequate planning. Ensuring the allocated funds serve their intended purposes remains a significant hurdle.
The Way Forward:
There is a necessity to review and refine the criteria for granting SCS to ensure fairness and transparency. Clearly defining eligibility parameters based on socio-economic indicators, infrastructure development, and other relevant factors is crucial.
Encourage states to formulate comprehensive development plans focused on sustainable growth, job creation, infrastructure development, and human capital enhancement. SCS should be part of a broader strategy for holistic development.
Implement policies that gradually reduce states' dependence on central assistance, promoting self-sufficiency and economic diversification. States should be encouraged to generate their revenue streams.
Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2023 and the Legend of Sammakka and Sarakka (NewsOnAir)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Lok Sabha on Wednesday (6th December 2023) took up the Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2023 for consideration and passing. The Bill amends the Central Universities Act, 2009, which establishes central universities for teaching and research in various states.
News Summary:
- Recently, the Lok Sabha took up the Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2023 for consideration and passing.
- The Bill amends the Central Universities Act, 2009, which establishes central universities for teaching and research in various states.
- The Bill seeks to establish a Central Tribal University in Telangana which will be named ‘Sammakka Sarakka Central Tribal University’.
Background:
- This legislative proposal aligns with the commitments outlined in the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014.
- The 2014 Reorganisation Act resulted in the division of the former state of Andhra Pradesh into Telangana and the remaining Andhra Pradesh state.
- As per this act, both Andhra Pradesh and Telangana were promised support to establish a tribal university each.
Key Features:
- Amendment to Central Universities Act, 2009: The bill involves amendments to the Central Universities Act, 2009, a legislation enacted to establish and incorporate universities dedicated to teaching and research across various states.
- Name of the Central Tribal University: The university is named as a tribute to the legendary mother-daughter duo, Sammakka and Sarakka.
- Addressing Regional Aspirations: The establishment of the Sammakka Sarakka Central Tribal University is poised to address and fulfil regional aspirations for the foreseeable future.
- Focus on Tribal Population: The university's primary objective is to offer avenues for higher education and research facilities, with a special emphasis on serving the tribal population of India.
About the Legend of Sammakka and Sarakka:
- As per the legends, Sammakka was married to a feudal chief of the Kakatiyas dynasty, Pagididda Raju who ruled over the Warangal region.
- She had two daughters and one son - Sarakka or Saralamma, Nagulamma and Jampanna, respectively.
- In the 13th century, Saralamma succumbed in a battle against local rulers protesting tax imposition, while Sammakka vanished into the hills.
- The local (Koya) tribals believed she transformed into a vermillion casket.
The Sammakka Saralamma Jatara:
- The Sammakka Sarakka Jathara, also known as Medaram Jathara, is a biennial festival that commemorates the 13th-century battle where the mother-daughter duo actively protested against local rulers imposing taxes on the Koya tribe.
- Sammakka and Sarakka are revered as protectors of the Koya tribe, and the festival is distinctively free from Vedic or Brahmanic influences.
- During the festival, devotees take a holy dip in Jampanna Vagu, a stream and tributary of the River Godavari.
- Commencing from Medaram, situated in the Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary within the Dandakaranya forest, the Jathara involves Koya tribe priests performing rituals.
- Various tribal and non-tribal communities from Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Jharkhand actively participated in the event.
- Recognized as the second-largest fair in India and often likened to the Kumbh Mela for tribals, the festival holds the status of a state festival declared by the Telangana government.
Political and Cultural Significance of the Sammakka Saralamma Jatara:
- The festival attracts participation from the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Telangana state government, including the Chief Minister.
- Funding has been released for community shelters and infrastructure, and the Ministry of Tourism allocated Rs. 75.88 crore for the integrated development of a tribal circuit under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme.
- This circuit encompasses Mulugu, Laknavaram, Medavaram, Tadvai, Damaravi, Mallur, and Bogatha Waterfalls, where the Sammakka-Sarakka temple is located.
- Mulugu, a reserved Scheduled Tribes (ST) assembly seat with a population of approximately 2.6 lakhs (2011 Census), holds political and cultural significance with a 75% ST population.
- The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Ramappa Temple is situated about 15 km from Mulugu.
Koya Tribe
- The Koya tribe, recognized as the largest Adivasi tribe in Telangana, holds Scheduled Tribe status in the region.
- They are dispersed across the Telugu-speaking states of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
- The Koyas commonly refer to themselves as Dorala Sattam (Lords group) and Putta Dora (original lords).
- In their dialect, akin to Gonds, they identify as "Koitur."
- Habitat and Livelihood: The Godavari and Sabari rivers, integral to their habitat, significantly shape the economic, social, and cultural aspects of Koya life.
- Primarily settled cultivators, they engage in the cultivation of crops like Jowar, Ragi, Bajra, and various millets.
- Language: While some Koya individuals have adopted Telugu as their primary language, others in different regions still speak the Koya dialect.
- Religion and Festivals: Key deities in Koya religious practices include Lord Bhima, Korra Rajulu, Mamili, and Potaraju.
- Major festivals for the Koyas include Vijji Pandum (seeds charming festival) and Kondala Kolupu (festival to appease Hill deities).
- Cultural Practices: During festivals and marriage ceremonies, the Koyas showcase a vibrant and robust dance known as Permakok ata (Bison horn dance).
Supreme Court Upholds Abrogation of Article 370 (Indian Express)
- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court in a 5-0 unanimous ruling upheld the Centre’s abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution on December 11.
News Summary:
- A five-member Constitution bench of the Supreme Court, headed by Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, unanimously upheld on December 11 the abrogation of Articles 370 and 35A and the carving out of Ladakh as constitutionally valid.
- The SC noted that Article 370 was a temporary provision and that the erstwhile State of Jammu and Kashmir had no internal sovereignty.
- The top court has directed the Election Commission to ensure elections are held to the J&K assembly by September 30, 2024.
- The court has also recommended the government form a truth and reconciliation commission to record the human rights abuses in Jammu and Kashmir by both state and non-state actors.
Key Highlights from the Judgment:
- Regarding the 'unique' and 'special status' of Jammu and Kashmir: The Supreme Court clarified that J&K lost its sovereignty after acceding to India in 1947.
- Despite an initial proclamation by Maharaja Hari Singh expressing intent to retain sovereignty, his successor, Karan Singh, declared that the Indian Constitution would prevail.
- This proclamation, issued on November 25, 1949, repealed the Government of India Act, 1935, and made the Constitution of India applicable to J&K, essentially merging it with India.
- On Jammu and Kashmir being an integral part of India: Chief Justice Chandrachud cited Section 3 of the J&K Constitution, along with Articles 1 and 370 of the Indian Constitution.
- Article 3 of the J&K Constitution explicitly states that the state is an integral part of the Union of India.
- The court emphasized that having its own Constitution did not confer special status; it aimed at everyday governance, while Article 370 intended integration with India.
- On the restoration of statehood: The court deemed the reorganization into Union Territories in 2019 as temporary and directed the Centre to restore statehood and conduct Legislative Assembly elections.
- Article 370 - temporary or permanent: The Supreme Court affirmed that Article 370 is a temporary, transitional provision, originally meant for the specific circumstances during the state's accession to India in 1947.
- Concerning the effective abrogation of Article 370: The Court upheld both presidential proclamations of August 2019, including the redefinition of the 'constituent assembly of Jammu and Kashmir' as the 'Legislative Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir.'
- It referred to the 'SR Bommai v Union of India' ruling, asserting that actions taken during the President's rule were not prima facie malafide.
- Truth and Reconciliation Commission: Justice Sanjay Kaul proposed establishing a Truth and Reconciliation Commission to investigate alleged human rights violations by both state and non-state actors in J&K.
- Such a commission would officially acknowledge and disclose past wrongdoings to address and resolve historical conflicts.
What is Article 370 of the Constitution of India?
- On October 17, 1949, Article 370 became part of the Indian constitution as a 'temporary provision.'
- This article granted special privileges to Jammu & Kashmir, allowing it to create its own constitution and limiting the legislative powers of the Indian Parliament in the state.
- Origin: N Gopalaswami Ayyangar introduced Article 370 as Article 306 A in the draft constitution.
- Provisions: Under Article 370, the Constituent Assembly of Jammu & Kashmir had the authority to recommend which articles of the Indian Constitution should be applicable to the state.
- After drafting the state's constitution, the J&K Constituent Assembly was dissolved.
- Clause 3 of Article 370 gives the President of India the power to amend its provisions and scope.
- Article 35A: Stemming from Article 370, Article 35A was introduced in 1954 through a Presidential Order based on the J&K Constituent Assembly's recommendation.
- It empowers the Jammu & Kashmir legislature to define the state's permanent residents and their special rights and privileges.
Abrogation of Article 370:
- On August 5, 2019, the Government of India, repealed nearly all provisions of Article 370 in the Indian constitution.
- The President issued The Constitution (Application to Jammu And Kashmir) Order, 2019 on the same day.
- This order substituted the term ‘Constituent Assembly’ in Article 370(3) with ‘Legislative Assembly [of Jammu & Kashmir].’
- It's important to note that the Order technically modified the interpretation clause of Article 367, not Article 370 itself; it utilized Article 370(1) for this purpose.
- Subsequently, a Statutory Resolution was presented in the Rajya Sabha, leading to the abrogation of the majority of Article 370.
- This action was possible without the concurrence of the Jammu & Kashmir Legislative Assembly as the State was under the President’s rule.
- On August 6, Parliament approved the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Bill, 2019, dividing the State into two Union Territories: Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh, with the former being provided with a legislative assembly.
The Supreme Court’s ruling is in line with what the Centre had argued during the hearing. The Union government had said the 1949 proclamation accepted the supremacy of the Indian Constitution and surrendered sovereignty to it, where the sovereign was ‘We the people of India’.
Why India cannot Afford to Repeat its Nuclear Weapons Mistakes with AI (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
As India hosts the GPAI summit 2023, discussions are raised on the comparison of the nuclear revolution with advancement in Artificial Intelligence.
Context:
- As India prepares to host the GPAI summit next week, the current discourse on the geopolitics of Artificial Intelligence inevitably revolves around the nuclear experience.
- India, with its complex nuclear history, now has the opportunity to reflect on and apply lessons from its nuclear journey in addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by AI.
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the development of computer systems that emulate human intelligence, encompassing tasks like learning, reasoning, and problem-solving.
- Significance in Healthcare: AI aids in disease diagnosis, treatment planning, and data-driven healthcare solutions.
- Economic Impact: AI optimizes financial processes, enhancing trading strategies, risk management, and overall efficiency in various industries.
- Automation and Efficiency: In manufacturing and logistics, AI-driven automation streamlines processes, improving productivity.
- Personalized Experiences: AI enhances user experiences through personalized content recommendations, virtual assistants, and language translation.
- Research and Development: AI accelerates scientific discoveries, innovation, and problem-solving across diverse fields.
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI contributes to the development of autonomous vehicles, improving safety and efficiency in transportation.
- Global Impact: AI is a transformative force with the potential to reshape industries, and decision-making, and address complex challenges, underlining its significance in the technological and societal landscape.
Despite its benefits, ethical concerns include data privacy, bias, and potential job displacement, requiring careful management.
Comparisons Between Nuclear Revolution and Ongoing AI Revolution:
- Profound Consequences: While inherently distinct, the nuclear revolution characterized by atomic bombs in 1945 shares notable similarities with the ongoing AI revolution.
- Both revolutions carry far-reaching implications, with AI being perceived as potentially exerting even more sweeping and transformative impacts on the economy, society, and polity.
- Resembling Governance Challenges: Issues surrounding AI governance closely parallel those faced at the onset of the nuclear age.
- Common challenges encompass managing geopolitical implications, preventing misuse, and establishing international norms and institutions to govern AI.
- Military AI Regulation Advocacy in Both Contexts: Similar to the nuclear era, there are calls to regulate military applications of AI, including proposals for a freeze on research and development pending a thorough assessment.
- Despite these concerns, rapid advances in AI persist, echoing the historical trajectory of nuclear technology.
- AI Dominance Race Discourse: In the discourse on AI, the US and China, akin to the US-Soviet dominance in the nuclear era, emerge as central figures.
- Agreements between the US and China on AI are considered crucial for navigating the technological revolution.
Actions Taken to Tackle AI Governance Challenges:
- Efforts to Navigate Competition: The United States is actively addressing competition in military AI with China, initiating discussions on regulatory measures.
- This includes implementing restrictions on the supply of advanced chips to China, with the aim of slowing down AI development.
- Proposals for Establishing International Norms and Initiatives: In response to potential negative consequences of the AI revolution, there is a proposal for the creation of international norms, drawing inspiration from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) established for nuclear energy regulation.
- Concepts such as the 'International Agency for Artificial Intelligence' (IAAI) and initiatives like the Global Partnership for Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) have been put forward.
- Formation of Coalitions and Emphasis on Military Deterrence: The United States is actively building coalitions with like-minded partners to discuss AI development and effectively manage its impacts.
- Initiatives such as GPAI, comprising 28 members, are integral to broader efforts, and alliances are being strengthened for military deterrence, particularly in relation to Russia and China.
- Global Partnership on AI (GPAI): GPAI, a multi-stakeholder initiative launched in June 2020 with 15 members, seeks to bridge the gap between theory and practice in AI.
- It supports cutting-edge research and applied activities on AI-related priorities and has since expanded to 29 members, including India.
- The OECD serves as its secretariat.
- Recent London AI Summit: The summit, held recently, aimed to harness the potential of AI for new knowledge, economic growth, advancements in human capabilities, and problem-solving.
- A discussion paper released by the British government highlighted AI-related risks, from the spread of disinformation to potential misuse for harmful purposes.
- The British Prime Minister emphasized the direct addressing of these concerns, assuring people that their safety would be prioritized while seizing the opportunities for a better future offered by AI.
Guiding Principles for India: Drawing Insights from Nuclear History to Navigate the AI Landscape
- Pragmatic Stance over Idealism: India's historical pursuit of the "time-bound elimination of nuclear weapons" incurred significant costs, emphasizing the need for a pragmatic and strategic approach in dealing with the complexities of AI.
- Seizing Collaborative Opportunities: Learning from past missed opportunities in nuclear cooperation, India should actively foster partnerships, particularly with the US, capitalizing on the existing momentum in joint efforts related to AI and emerging technologies.
- Avoiding Exceptionalism: India's historical inclination towards exceptionalism and pursuing a third way in technological development poses challenges.
- In the context of AI, recognizing the universality of science and technology is essential, promoting collaboration over isolationist postures.
- Empowering the Private Sector: Unlike the government-led progress in nuclear and space endeavours, AI's evolution is primarily driven by the private sector in the West.
- India must enhance the role of the private sector in AI research, development, and innovation for sustained growth.
- Urgent Reforms for Global Competitiveness: While recent efforts to open up science and technology sectors are commendable, India must prioritize urgent and comprehensive reforms to strengthen its position in the global AI landscape.
Conclusion
When it comes to AI, India's policy is not characterized by the disarmament idealism that shaped its approach to nuclear weapons. Emphasizing pragmatic strategies and harnessing international partnerships are crucial elements that should underpin India's strategic approach to AI development. Recognizing the strategic significance of AI, it is imperative for India to avoid replicating past mistakes made in the realm of nuclear weapons with regard to AI.
The Case for Caste Census in India (The Hindu)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Bihar government unveiled the outcomes of its caste survey within the state, revealing that the combined representation of Extremely Backward Classes (EBCs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) exceeds 63%.
Context:
- In a recent development, the Bihar government published the findings of its caste survey, indicating that the combined percentage of Extremely Backward Classes (EBCs) and Other Backward Classes (OBCs) surpasses 63%.
- This survey has sparked a nationwide discussion, emphasizing the need for a thorough examination of socio-economic data and a consideration of arguments both in support of and against a caste-based survey on a national scale.
What Does the Socio-Economic Data Reveal?
- Manifestation of Caste-Linked Deprivation in Indian Society: In rural areas during 2011-12, the average monthly per capita consumption expenditures (MPCE) for Scheduled Tribes (ST), Scheduled Castes (SC), and Other Backward Classes (OBC) households were 65%, 73%, and 84% respectively compared to the general category.
- Urban areas witnessed average MPCE for ST, SC, and OBC households at 68%, 63%, and 70% of the general category.
- Inequality Persists Across Caste Groups in Multidimensional Poverty Metrics:
- Multidimensional poverty estimates from the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4/2015-16) highlight the enduring inequality across caste categories in India.
- Despite constituting around 73% of the population, STs, SCs, and OBCs collectively accounted for 84% of the country’s impoverished individuals.
- The OBC category alone comprised over 50% of India’s multidimensionally poor.
- According to the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI), the combined share of STs, SCs, and OBCs in the country's poor rose from 77.6% in 2005-06 to nearly 84% in 2015-16.
- The Sachar Committee report (2006) estimated that 31% of Muslims were categorized as 'Below the Poverty Line.'
- These findings underscore the evident causal relationship between caste-based discrimination and exclusion, particularly affecting STs, SCs, and OBCs, as well as religion (particularly Muslims), and the prevalence of poverty and deprivation.
Education and Employment Dynamics Across Caste Groups:
- Educational Disparities Based on Caste: Significant educational disparities exist, with the general category boasting a notably higher percentage of literate, secondary and high school graduates, as well as those with undergraduate and postgraduate degrees compared to OBCs, SCs, and STs.
- According to the NSS 75th round (2017-18), the proportion of graduates is 12% in the general category, while it stands at 3% for STs, 4% for SCs, and 6% for OBCs.
- Postgraduate representation is over 3% in the general category, approximately 1% among OBCs, and less than 1% for both SCs and STs.
- Employment Landscape: Analyzing employment status based on PLFS 2021-22 data reveals that over 30% of the general category workforce holds regular jobs, contrasting with around 20% for OBCs and SCs, and just over 12% for STs.
- Conversely, nearly 29% of STs, 38% of SCs, and 20% of OBCs work as casual labourers, compared to only 11.2% in the general category.
- The informal sector is predominantly occupied by STs, SCs, and OBCs, while the general category has a disproportionately large presence in formal employment.
- The Central government, a major formal sector employer with over 18.78 lakh employees as of January 2021, sees 52.7% belonging to the general category.
- Within the most qualified and highest-paid employee groups (Group A), the general category constitutes over 64%.
- These findings underscore that despite the Mandal Commission recommendations being officially implemented three decades ago, the persistent caste-based educational inequalities continue to replicate a similar pattern in skilled, formal employment.
Historical Overview of Caste-Based Surveys:
- During the Pre-Independence Era: The British colonial administration introduced caste-wise enumeration of the population in 1881, a practice that persisted until the 1931 census.
- Post-Independence Surveys: Following independence, successive Indian governments refrained from conducting comprehensive caste enumeration due to concerns that it might reinforce caste divisions and perpetuate the caste system.
- Despite the absence of a caste census, official surveys and statistics have revealed the persistent existence and growth of the caste system in independent India, along with its associated discriminatory and exclusionary consequences.
- The Mandal Commission Report: In 1980, the Backward Classes Commission, chaired by B.P. Mandal, submitted a pivotal report to the President of India.
- The report began with the dictum, "There is equality only among equals. To equate unequal is to perpetuate inequality."
- Drawing on caste/community-wise population figures from the 1931 census, the Mandal Commission estimated that the combined population of Hindu and non-Hindu Other Backward Classes (OBCs) constituted 52% of India's population.
- The commission crucially concluded that caste should be considered a class of citizens.
- If an entire caste is socially and educationally backwards, reservation can be implemented in its favour, justifying it as a socially and educationally backward class of citizens under Article 15(4) of the Constitution.
- This article empowers the state to make special provisions for the advancement of socially and educationally backward classes of citizens.
Reservation in Public Services and Indra Sawhney Judgment:
- In 1990, the V.P. Singh government introduced a 27% reservation for Other Backward Classes (OBCs) in public services.
- This decision faced legal scrutiny, leading to the landmark Indra Sawhney & others versus the Union of India judgment in 1992, where the Supreme Court validated the government's stance.
- The court made a noteworthy observation, stating that the identification of a group based on criteria other than caste, such as a combination of occupation, social status, education, and economic factors leading to caste, might not be deemed invalid.
- This crucial interpretation paved the way for the implementation of OBC reservations in both public employment and educational institutions across India.
Arguments Against a Nationwide Caste-Based Survey:
- Opposition to a comprehensive caste census has centred on the apprehension that unveiling the precise population proportions of Other Backward Classes (OBCs) at 52% or above could lead to calls for an expansion of the existing 27% reservation quota for OBCs.
- This concern gained traction with the initiation of demands following the enactment of the Constitutional (103rd Amendment) Act, 2019.
- This legislation introduced a 10% reservation for Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) within the general category, impacting admissions to both public and private educational institutions and civil posts and services.
- Despite facing legal challenges due to breaching the 50% reservation ceiling, the law was ultimately upheld by a majority judgment of the Supreme Court in 2022.
The Path Forward:
- Comprehensive Caste Enumeration: Given the significant variation in OBC population estimates from different official sample surveys—ranging from 41% to 46% between 2015-16 and 2021-22—only a thorough caste enumeration can provide an accurate assessment.
- More crucially, identifying the numbers and proportions of individual castes within the OBC category is essential for implementing effective reservations and other benefits.
- For instance, the Bihar caste survey revealed that 122 smaller caste groups within the Extremely Backward Classes (EBC) category constituted 36% of the state's population, marking the largest share among social categories.
- Build on Justice Rohini Commission Report: The Justice Rohini Commission, formed in 2017 to scrutinize the sub-categorization of OBCs in the Central list, presented its findings in 2023.
- A nationwide socio-economic caste census is imperative to formulate scientific criteria for such sub-categorization.
- This is equally crucial for all states with their individual State-level OBC lists due to the diverse caste compositions.
Conclusion
Caste remains a significant issue in Indian society, acknowledged by a broad spectrum of thinkers, ideologies, and political parties, all advocating for the eradication of the caste system and its inequalities. Given this apparent societal concern, a nationwide caste survey emerges as the initial step towards investigating and addressing the complexities associated with caste-related issues.
Baiga Tribal Group Gets Habitat Rights in Chhattisgarh (Indian Express)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of Assembly elections in Chhattisgarh, the Baiga Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) recently became the second to get habitat rights in the state, after the Kamar PVTG.
Context:
- Chhattisgarh has granted habitat rights to the Baiga Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG), marking them as the second PVTG to receive such rights in the state, following the Kamar PVTG.
- This development affects seven PVTGs residing across 17 districts in Chhattisgarh, namely Kamar, Baiga, Pahadi Korba, Abujhmadiya, Birhor, Pando, and Bhujia.
- Specifically, 19 Baiga villages, home to 6,483 individuals across 2,085 families, have been granted these habitat rights.
About the Baiga Tribe:
- The Baiga Tribe stands among the Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) and is distributed across Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Traditionally, the Baiga led a semi-nomadic lifestyle and engaged in slash-and-burn cultivation.
- Presently, their livelihood primarily hinges on minor forest produce.
- Their agricultural practices include a form of shifting cultivation known as "Bewar."
- Notably, ‘Mahua’ holds significance in Baiga cuisine and beverages, as it is an intoxicant derived from fermenting and distilling the flowers of the Mahua tree.
- Tattooing plays a pivotal role in Baiga culture, with specific tattoos designated for different ages and body parts, reflecting the cultural richness and diversity of the community.
What are Habitat Rights?
- Habitat rights recognition entails granting a community authority over their customary habitation territory, encompassing socio-cultural practices, economic and livelihood activities, intellectual knowledge of biodiversity and ecology, and traditional wisdom in utilizing natural resources.
- These rights also encompass protecting and conserving both natural and cultural heritage.
- Recognising habitat rights serves to safeguard and enhance traditional livelihoods and ecological knowledge that have been transmitted through generations.
- Additionally, it facilitates the integration of diverse government schemes and initiatives from various departments, empowering Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) to foster the development of their habitats.
What Does ‘Habitat’ Mean?
- According to Section 2(h) of the Forest Rights Act (FRA), “Habitat includes the area comprising the customary habitat and such other habitats in reserved forests and protected forests of primitive tribal groups and pre-agricultural communities and other forest dwelling Scheduled Tribes.
Under What Law Are Such Rights Granted?
- Habitat rights are given to PVTGs under section 3(1) (e) of The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- It is also known as the Forest Rights Act (FRA).
The Forest Rights Act of 2006
- The Forest Rights Act of 2006, also referred to as the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, stands as a significant legal milestone in India.
- Its primary purpose is to acknowledge and confer forest rights, including the occupation of forest land, to forest-dwelling Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers.
- This legislation is designed to address historical injustices inflicted upon these communities and to duly recognize their contributions to forest conservation.
How Does the Government Fix a Habitat?
- The procedure is based on a detailed guideline given for this purpose in 2014 by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA).
- Based on the MoTA guidelines, the traditional tribal leaders of the tribe are consulted about the extent of their culture, traditions, and occupation.
- It is corroborated by the government and then a habitat is declared.
How Many States Have Recognised Habitat Rights?
- Out of 75 PVTGs in India, only three have habitat rights.
- The Bharia PVTG in Madhya Pradesh was the first, followed by the Kamar tribe and now the Baiga tribe in Chhattisgarh.
Significance of Granting Habitat Rights:
- Preservation of Cultural and Heritage Richness: The granting of habitat rights plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the distinctive cultural, social, and traditional heritage of tribal communities.
- This recognition enables them to uphold their unique languages, rituals, customs, and traditional knowledge systems.
- Conservation of Biodiversity: Tribal communities possess unique knowledge about their local ecosystems, flora, fauna, and sustainable resource management.
- Recognition of their rights plays a vital role in preserving biodiversity and facilitating the sustainable management of natural resources.
- Fostering Sustainable Development: By acknowledging the rights of tribal communities, governments can foster sustainable development.
- Indigenous practices often prioritize sustainability and conservation, crucial for environmental well-being and the overall prosperity of society.
- Empowerment and Advancement of Social Justice: Bestowing habitat rights empowers tribal communities through legal recognition, ensuring their active participation in decision-making processes that impact their lives.
- This rectification of historical injustices contributes to the establishment of a more equitable and just society.
- Safeguarding Livelihoods: Many tribal communities rely on their natural surroundings for sustenance.
- Granting rights to lands and resources ensures the continuity of their traditional occupations such as hunting, gathering, fishing, and farming, thereby supporting their economic well-being.
Can Habitat Rights be Used to Stop Activities Like Mining?
- The habitat rights will help the PVTG protect their habitat from developmental activities harmful to them.
- The title may not be an ownership title in the nature of a private property owner, but consent and consultation of the gram sabha will be needed for any developmental activity.
- Forest Rights have legal protection under the Forest Conservation Act, the Land Acquisition Law of 2013, and even the SC/ST Prevention of Atrocities. Act.
- The grant of habitat rights under the Forest Rights Act provides an additional layer of legal protection.
- If any kind of development activity is hampering their habitat rights, the tribal group concerned can take up the matter with the administration under the Forest Rights Act, and if not resolved, the matter can be taken to court.
What is a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG)?
- According to the Ministry of tribal affairs, tribal communities that are technologically backward, have stagnant or declining population growth, extremely low levels of literacy, and a subsistence level of economy are declared as PVTG.
- PVTGs have low health indices and largely reside in isolated, remote, and difficult areas in small and scattered hamlets/habitats.
- The ministry has identified 75 PVGTs in 18 states and one Union Territory.
- In 2019, the MoTA started a scheme for their protection and improvement in terms of social indicators like livelihood, health, nutrition and education to decrease their vulnerability.
Government Initiatives for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs):
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs administers a program titled 'Development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs),' which operates as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme with 100% Central assistance extended to 18 states and the Union Territory of Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- The primary objective of this initiative is to foster the comprehensive socio-economic development of PVTGs while preserving their rich cultural heritage.
- Under the Development of PVTGs scheme, State Governments execute projects tailored to address key sectors such as education, health, and livelihood, with the overarching goal of ensuring the holistic well-being of PVTG communities.
Gandhi's Perspectives on Jewish Nation-state in Palestine (Indian Express)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Mahatma was deeply sympathetic to the plight of the Jewish people in Europe. But he was against Zionists and the attempt to create a state of their own by force in Palestine, which was already inhabited by the Palestinian Arab people.
What was Mahatma Gandhi’s Views on Jews and A Separate Jewish Homeland?
Gandhi was deeply sympathetic to the Jewish people.
- The Mahatma always made it clear that he had deep sympathies for the Jewish people who had historically been unjustly persecuted for their religion.
- In his article ‘The Jews’ he said, “My sympathies are all with the Jews. They have been the untouchables of Christianity. Religious sanction has been invoked for the justification of the inhuman treatment meted out to them.”
- He further said that the German persecution of the Jews seems to have no parallel in history and expressed his concern with Britain’s policy of placating Adolf Hitler at the time (before World War II broke out).
- He wrote that“If there ever could be a justifiable war in the name of and for humanity, a war against Germany, to prevent the wanton persecution of a whole race, would be completely justified.
Yet, he did not support a Zionist state in Palestine.
- Gandhi opposed the establishment of a Zionist State in Palestine, contending that imposing Jews on the Arabs was both wrong and inhumane. He considered it a crime against humanity to diminish the dignity of the proud Arabs by restoring Palestine, either in part or wholly, as the national home for the Jews.
What are the Reasons Behind His Opposition to A Jewish Homeland?
- Religious Text as a Pretext: Mahatma Gandhi contended that the creation of a separate state based on religious grounds was unjustified.
- He believed that Palestine already belonged to Arab Palestinians, and the British-facilitated settlement of Jews was inherently violent.
- In his view, a religious act, such as Jews returning to Palestine, should not involve the use of force through the bayonet or the bomb.
- Goodwill of Arabs: Gandhi asserted that for Jews to settle in Palestine, it was essential to have the goodwill of the Arabs.
- He argued that this goodwill could only be achieved by forgoing the use of the British bayonet in the process.
- Contradiction to Global Struggle: Gandhi opposed the concept of a Jewish homeland, seeing it as contradictory to the broader struggle for increased rights that Jews were pursuing across the globe.
- He wasn't alone in holding this view, as it was shared by others during that period.
- Forced Relocation Concerns: He questioned the practicality of confining Jews to Palestine, wondering if they would appreciate being compelled to leave other parts of the world where they had settled.
- Gandhi expressed the concern that the Jewish claim for a national home could be seen as providing a justifiable reason for the expulsion of Jews, as witnessed in Germany.
Impact of Mahatma Gandhi’s Views on Indian Foreign Policy
- Shaping India's Foreign Policy through Gandhi's Influence on Nehru: Mahatma Gandhi's perspectives and his staunch anti-imperialism significantly influenced Jawaharlal Nehru, India's inaugural Prime Minister, shaping the nation's foreign policy for decades.
- Nehru, in many ways, inherited and embraced this perspective from Gandhi.
- Rejection of the Two-Nation Solution and Support for the Palestinian Cause: India's political stance toward Israel took firm shape shortly after gaining independence in 1947.
- Both Jawaharlal Nehru and Mahatma Gandhi advocated for the Palestinian cause and firmly rejected the concept of two nations based on religious criteria.
- While expressing sympathy for the Jews, they believed that a state founded on religious exclusivity lacked moral and political sustainability, aligning with their opposition to the partition of India.
- India's Anti-Israel Votes at the UN: India's position on Palestine reflected not only its alignment with the Arab world but also resonated with the principles of the Non-Aligned Movement and the United Nations.
- During the UN vote on the partition of Palestine, India, along with Arab countries, cast its vote against the proposal.
- Similarly, when Israel sought admission to the UN, India once again voted against the move.
- Recognition of Israel as a Nation with Limited Diplomatic Relations: India officially acknowledged Israel's status as a nation on September 17, 1950, following similar recognitions by two Muslim-majority countries, Turkey and Iran.
- In 1953, Israel gained permission to establish a consulate in Mumbai, yet it was not granted diplomatic representation in New Delhi.
- Engagement with Palestinian Leadership under Yasser Arafat: During the late 1960s and early 1970s, the Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) emerged as the representative body for the people of Palestine under the leadership of Yasser Arafat.
- India fostered connections with the primary political faction within the PLO, Al Fatah.
- Recognition of PLO as the Legitimate Representative of the Palestinian People: On January 10, 1975, India took a significant step by officially recognizing the PLO as the exclusive and legitimate representative of the Palestinian people.
- Furthermore, India permitted the PLO to establish an independent office in New Delhi.
- While India was among the last non-Muslim states to recognize Israel, it achieved the distinction of becoming the first non-Arab state to acknowledge the legitimacy of the PLO.
Conclusion
Mahatma Gandhi maintained his perspectives on the Palestine-Israel issue throughout his life, emphasizing his disapproval of the unjust treatment of Jews. Simultaneously, he consistently reaffirmed his longstanding opposition to the creation of a separate nation for the Jewish community.
For numerous decades, Gandhi's viewpoints significantly influenced Indian foreign policy. However, in more recent times, India has undergone a shift in approach, decoupling its relations with Israel and Palestine. Establishing robust ties with Israel marks a departure from the historical hyphenation of India-Israel-Palestine relations, reflecting a changing dynamic in India's diplomatic engagements.
That many of these unapproved or banned FDCs contain antibiotics is cause for concern given the growing antibacterial microbial resistance in India (The Hindu)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A group of academics from India, Qatar and the United Kingdom recently published a worrying new study in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice on the volume of unapproved and even banned fixed dose combinations (FDC) of antibiotics being sold in India.
News Summary:
- In the Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice, a group of academics from India, Qatar, and the United Kingdom recently released a concerning new study on the amount of antibiotics that are being sold in India that are not allowed or even prohibited as fixed dosage combinations (FDCs).
- The analysis, which makes use of pharmaceutical industry sales data, shows that in 2020, 60.5% of FDCs containing antibiotics (or 239 formulations) were unapproved, and another 9.9% containing 39 formulations were being distributed in the nation even though they were prohibited.
- The fact that antibiotics are present in so many of these illicit or prohibited FDCs is concerning given the rising incidence of antimicrobial microbial resistance (AMR) in India.
What are the Fixed Dose Combinations (FDCs) Drugs?
- FDCs are combinations of one or more known drugs and can be useful in treating some diseases since the combination can improve patient compliance.
- For instance, if a patient has to take three different medications for a particular treatment, she may forget to take one.
- But if all three medications are combined into one tablet or one syrup, the chance of her forgetting to take one or two of the drugs is reduced.
- For diseases such as AIDS, it is well documented that FDCs have proven to be very useful in improving patient compliance, which at the end of the day improves treatment outcomes.
Concerns with FDCs Drugs?
- Making FDCs is not an easy job, even though most consist of drugs with known safety and efficacy profiles.
- All drugs have side effects. When formulated together, there is a possibility that the active ingredient or excipients (inactive ingredients) may affect how each drug functions.
- For example, the drugs may interact in a way to reduce the therapeutic efficacy of each active ingredient, or, worse, the drugs may interact with each other to create a more toxic element, often called metabolites.
- This is why all FDCs must go through a scientifically designed approval process where such interactions can be evaluated.
Advantages of Fixed Dose Combinations:
- FDCs increase patient adherence, streamline treatment, and optimize the advantages of the combined therapeutic actions of the two medications.
- Treatment for infectious diseases: A significant portion of India's population is afflicted with infectious diseases.
- FDCs are very helpful in the treatment of infectious disorders when it is customary to administer numerous antimicrobial drugs, such as HIV, malaria, and tuberculosis.
- Additionally useful in chronic diseases, FDCs are especially beneficial when co-occurring disorders are common.
- Affordability and accessibility: FDCs have particular benefits over single entity preparations, including improved efficacy, a lower likelihood of side effects, potentially lower costs, and easier distribution logistics that are pertinent to resource-constrained scenarios like those in India.
Challenges Associated with Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs):
- Increased Risk of Side Effects: Combining multiple active ingredients in FDC drugs heightens the risk of adverse drug interactions and increases susceptibility to side effects.
- Patients may exhibit heightened sensitivity or allergic reactions to specific components, posing challenges in identification and management due to the fixed combination.
- For instance, a single FDC drug containing Paracetamol, Bromhexine, Phenylephrine, Chlorpheniramine, and Guaiphenesin may elevate the risk of side effects like drowsiness, dizziness, and increased blood pressure.
- Regulatory Challenges: Regulating FDC drugs prove challenging due to the complexities associated with evaluating the safety and efficacy of multiple active ingredients in a single formulation.
- Maintaining quality control and standardization for FDC drugs becomes more demanding compared to single-component medications.
- Overuse and Misuse: FDC drugs can contribute to the overuse and misuse of medications.
- Patients might unknowingly consume multiple active ingredients unnecessarily or in inappropriate combinations, leading to potential health risks.
- Lack of Evidence-based Clinical Data: Approval of some FDC drugs may be based on limited or insufficient clinical evidence supporting their efficacy and safety profiles.
- The absence of robust scientific data raises concerns about the appropriateness and reliability of FDC drugs for specific medical conditions.
Why are FDCs banned in India?
- Patients may not need that many drugs; thus, they are subjected to additional side effects.
- Some drug doses have to be individualized based on the patient's condition.
- This is not possible when using FDCs.
- Some companies have been selling FDCs in India under this pretext without consulting the central government, as seen with the cefixime-azithromycin combination, which has already been banned.
- These non-essential FDCs, therefore, do more harm than good by encouraging irrational and indiscriminate prescribing of multiple drugs than necessary.
Some Examples of (Banned Fixed-Dose Combination) Drugs in India:
- Fixed dose combination of Aceclofenac + Paracetamol + Rabeprazole
- Fixed dose combination of Nimesulide + Diclofenac
- Fixed dose combination of Nimesulide + Cetirizine + Caffeine
How is the Pharmaceutical Industry Exploiting Loopholes in India's Legal Framework?
- Pharmaceutical companies in India use these FDCs to escape liability under multiple laws without much concern for public health.
- One such law is the Drugs (Prices Control) Order (DPCO), under which the government fixes the prices of individual drugs.
- Since drug combinations were traditionally not covered under the DPCO, the pharmaceutical industry decided that making FDCs provided an easy way to escape the remit of the DPCO.
- Motivated solely by market-driven pragmatism rather than a commitment to public health, the Indian pharmaceutical industry introduced an extensive array of FDCs lacking any discernible medical rationale.
- For example, anti-inflammatory drugs were combined with vitamins, anti-histamines were combined with anti-diarrhoeal agents, penicillin was combined with sulphonamides, and vitamins were combined with analgesics.
- These were combinations not found in any other country.
The pharmaceutical industry benefited in two ways.
- Firstly, the wide range of FDCs in the market meant no standards were set by bodies like the Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission, shielding manufacturers from quality testing and potential legal consequences.
- Essentially, the pharmaceutical industry could dictate its testing standards when FDCs were sampled for government testing.
- Second, the FDC approach provides companies with a justification for higher drug prices. For instance, if multiple companies sell azithromycin individually, they must compete and lower prices.
- However, combining it with another drug in an FDC allows them to market it as a unique solution, justifying higher prices until competitors introduce similar products.
- This system rewards pseudo-innovation rather than true medical breakthroughs, allowing dubious FDCs to command elevated prices, supported by doctors who may presume regulatory oversight.
Is there any Regulatory Framework Addressing the Issue of FDCs?
- The FDC problem has been on the regulatory radar since 1978 when the first government committee studied the issue and admitted that we had a problem on our hands.
- At the time, there was no system under the colonial-era Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 to vet drugs for safety and efficacy before their sale in India.
- This meant that each State drug controller could hand out manufacturing licences for any drug formulation and there was little that the central government could do to stop their sale.
- In 1982, Parliament changed the law to give the central government the power to “prohibit” the manufacture of specific drugs that lack therapeutic value or justification.
- Later in 1988, the central government amended the rules to introduce a new requirement for manufacturers of all “new drugs”, including FDCs, to submit proof of safety and efficacy to the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) who heads the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO).
- These amendments also made it clear that State drug controllers could not grant “manufacturing licences” for “new drugs” that are not approved for safety and efficacy by the DCGI.
Is Unabated Licensing Undermining FDC Regulation in India?
- Despite clear legal provisions, State drug controllers continue to overlook regulations, issuing manufacturing licenses for Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs) not approved by the DCGI with impunity.
- Manufacturers selling these unapproved FDCs technically expose themselves to prosecution by the Central government for violating the law.
- Rather than pursuing criminal prosecutions, the Ministry of Health is engaged in a reactive approach, frequently utilizing its powers under Section 26A to prohibit the manufacturing of specific FDCs.
- Since 1983, 444 orders have been issued under this provision, primarily targeting FDCs. Many of these orders have become entangled in intricate legal disputes, with inconsistent court decisions further complicating the regulatory landscape.
Conclusion
The fact that these academics have discovered 239 unapproved FDCs being sold in 2020 in just one category of FDCs more than 42 years after the problem was first flagged is an astonishing indictment of the incompetence of the drug regulatory framework in India. As they point out in their paper, unregulated FDCs may end up contributing to the AMR problem in India. The Ministry of Health needs to take immediate action.
Today, India is poised at the moment and GDP that China was in in 2007. Does it have the same gumption? (Indian Express)
- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
If India slowly but steadily raises its development cooperation budget to less than 0.5 per cent of its GDP by 2030, it will still have put around $70 billion into the global system. India is already the voice of the Global South; it will become the bank of the Global South.
Context:
- In 2007, China's GDP stood at approximately $3.6 trillion. Fast-forward to the present, India's GDP has reached $3.7 trillion or potentially more, framing a significant context for a crucial juncture in Indian diplomacy under the current leadership.
- As India wraps up its transformative diplomatic year in 2023, highlighted by its G20 presidency, it becomes imperative to reflect on the geopolitical lessons drawn from China's rise post the 2008 financial crisis.
Global South and India:
- Global South represent a group of countries primarily located in Asia, Africa, and Latin America which are referred to as "developing" or "underdeveloped".
- Global North on the other hand is completely opposite to this- developed, high per capita income, higher life expectancy and having a strong voice in various multilateral organizations.
Significance of the Global South:
- Economic Projections: By 2030, three out of the four largest economies are anticipated to emerge from the Global South (China, India, Japan, Indonesia).
- BRICS Dominance: The GDP of BRICS nations, measured in terms of purchasing power, now surpasses that of the G7 countries.
- Increased Intra-South Trade: Intra-South trade has surged, constituting over a quarter of global trade.
- Addressing Global Challenges: Collaborating with Global South nations is crucial for tackling issues like climate change, inequality, malnutrition, and energy security.
- Foreign Direct Investment: Outflows of foreign direct investment from the South contribute significantly to global flows.
India's Initiatives as a Global South Leader:
- Multilateral Reforms: India advocates for the reform of multilateral institutions to enhance inclusivity.
- Aarogya Maitri Project: Providing medical supplies to disaster-affected countries.
- Global South Diplomacy: Initiatives like the Global South Young Diplomat Forum and the Global South Centre of Excellence for R&D.
- Educational Support: Offering Global South Scholarships for students pursuing higher education in India.
- While India possesses the potential and political will to lead the Global South, it must also strive to narrow the gap between the Global North and South, aligning with its vision of 'Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam'—The World is One Family."
The Rise of China to Geoeconomic Prominence: An Analysis
- China's Strategic Moves During the Financial Crisis: Back in 2007, China had not yet achieved the geo-economic prominence it now holds.
- However, despite having a GDP lower than India's today, it swiftly emerged as a pivotal nation during the global financial crisis in 2008.
- Countries worldwide sought to deepen their ties with China, aiming to secure a special standing in their diplomatic relations with the People's Republic.
- China's strategic advantage lies in its provision of institutional and geo-economic responses.
-
- These responses included the establishment of a development bank, the initiation of a cross-continental lending program, and the catalyzation of infrastructure projects without the legacy constraints associated with Western agencies.
- This marked the beginning of what later evolved into the Belt and Road Initiative.
- China's Role as a Crucial Non-Western Alternative: In 2008, China capitalized on its economic potential to amass significant economic and political influence, a position it has maintained ever since.
- This was achieved by positioning itself as a vital addition to the global order.
- While the US grappled with post-crisis recovery and the Eurozone faced internal challenges, China emerged as a symbol of stability and economic dynamism.
- The world, in search of an extra engine for growth and an additional source of investment, welcomed China as a crucial alternative outside the Western world.
- Hence, China's adept strategic manoeuvres not only offered a remedy during the financial crisis but also solidified its status as an indispensable centre of geopolitical power on the global stage.
Does India Possess Enough Resources to Continue China's Ascent the Path?
- Unleashing India's Potential for Global Influence: India is in a similar position and has a comparable GDP. This is the foundation that Indians must comprehend in order to grasp their current position in the world as we approach 2024.
- Recent history shows us that a $4 trillion economy, comparable to India's, can have a significant impact.
- It can make a place for itself beside economies that are four or five times larger than its own, such as the US, the EU, and China, with foresight and deft diplomacy.
- A Unique Opportunity for India: In 2024, as Europe stagnates, the US withdraws, and China faces internal issues and sees a nominal decline in its share of the global economy, there is real potential for India.
What Additional Advantages India Can Provide Along China's Lines?
- Momentum-Focused Additionalities: Unlike China's case, India's aspirations for additionalities require momentum more than extraordinariness.
- With its trajectory set on a green and digital future, in contrast to China's manufacturing dominance, India aims to leverage its $4 trillion economy to wield influence comparable to a $15 trillion economy.
- Systematic Approach to Additionalities: India's quest for additionalities should emulate China's approach from 15 years ago, emphasizing a systematic roadmap.
- This roadmap, outlining India's unique proposition, signals that its economy is positioned to exert significant influence globally.
- Dedicated Development Finance Institution: To meet global corporate needs beyond trade finance, India should establish an outward-focused development finance corporation, mirroring China's China Development Bank.
- This institution should carry a distinct global imagery and play a pivotal role as a major source of development finance.
- Strategic External Engagement: Collaborating with like-minded partners, India should strategically map priority infrastructure, connectivity routes, business hubs, and developmental projects.
- This external engagement approach aligns with the vision for India's global role and positions 2024 as the year to articulate a comprehensive world map reflecting this vision.
Priorities for India's Upcoming Government in the Years Ahead:
- Information Technology (IT) and Innovation: Demonstrate India’s global potential, following the model set by China in 2007 and during the 2008 financial crisis.
- Leverage the established status as a global IT hub to propel software services and technology exports to new heights.
- Entrepreneurship and Start-ups: Sustain and enhance the flourishing start-up ecosystem through supportive policies and funding.
- Capitalize on the growing number of Unicorns (over 100) as a testament to India's entrepreneurial prowess.
- Strategic Location: Leverage India's strategic geographical location as a gateway between the Middle East, Europe, and Asia for enhanced international trade.
- Strengthen India's role in the India-Middle East Europe corridor, offering an alternative trade route to the Middle East and Europe.
- Key Reforms and Policies: Continue the momentum of economic reforms aimed at improving the business environment and ease of doing business.
- Build on initiatives such as Make in India and Goods and Services Tax (GST) to streamline processes and stimulate economic activity.
- These strategic focus areas can propel India’s global standing, foster innovation, and contribute to sustained economic growth.
As India enters a transformative phase in 2024, its capacity to translate economic momentum into global influence becomes pivotal for its role in the changing geopolitical scenario.
Drawing insights from China's ascent, a strategic roadmap, systematic methodologies, and visionary diplomacy emerge as crucial elements for reshaping the global order.
India's trajectory toward becoming the bank of the Global South hinges on its ability to contribute significantly to global growth, institutions, and security through strategic additions.
Manipur's UNLF Signs Peace Pact with Govt. (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union and Manipur governments have signed a peace agreement with the United National Liberation Front (UNLF), a banned Meitei extremist organisation which is also the oldest armed group based in the Manipur valley, Union Home Minister Amit Shah said on Wednesday.
News Summary:
- Manipur's oldest valley-based armed group UNLF that has been fighting for a sovereign land following the post-independence merger of the erstwhile kingdom with India has now signed a tripartite peace deal with Centre and the Manipur Govt.
- It is a significant step towards lasting peace in Manipur, which shares a long border with junta-ruled Myanmar and serves as India's main surface transport gateway to Southeast Asia, thus playing a key role in national security.
- The Centre in the announcement of the peace agreement described the UNLF as a "valley-based" armed group to indicate its origins in the state capital Imphal Valley and other districts not classified as hill areas.
- Similarly, at least 25 hill-based insurgent groups are already under a tripartite peace deal called the suspension of operations (SoO) agreement.
Key Highlights of the Peace Deal:
- While the details of the deal haven't been disclosed publicly, experts indicate that the current agreement predominantly revolves around the suspension of operations (SoO).
- This means that both the UNLF and security forces will refrain from engaging in operations against each other.
- In the upcoming stages, specific areas will be designated to establish camps for UNLF within the valley.
- In these camps, UNLF members will reside alongside their arms and ammunition, all supervised by the Manipur government and armed forces.
- The discussions for a comprehensive peace accord between the government and UNLF will persist, with the focus on advancing after the successful implementation of the SoO arrangements.
What is the United National Liberation Front (UNLF)?
- Formation: The UNLF was formed in November 1964 by Khalanlang Kamei as president, Thangkhopao Singsit as vice president, and A Somarendro Singh as general secretary.
- It set up its armed wing the Manipur Peoples' Army (MPA) in February 1990.
- Objectives: The UNLF favoured a long-term program to secede from India under the leadership of Arembam Samarendra Singh, form an alliance mainly with China and gradually capture political power with the help of an indoctrinated young population and the intelligentsia.
- It aimed at reclaiming the Kabow Valley in Myanmar.
- Personnel And Weapons: The UNLF split into two factions due to internal differences.
- Jointly, the two factions are estimated to have 400-500 personnel with over 500 weapons of mixed types.
- Links With Other Valley-Based Armed Groups: The UNLF was a constituent of the Coordination Committee, known as CorCom, which is an umbrella body of earlier six and currently four groups - RPF/PLA, PREPAK, and PREPAK/PRO.
- The UNLF is an "unlawful association" under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act.
- The UNLF had been carrying out its activities, including violence and propaganda jointly in consultation with the other constituents of CorCom.
- The close association of these constituents was one of the reasons for valley-based armed groups not responding to offers of coming overground and joining the mainstream.
- Areas Of Operation: All valley districts of Manipur - Imphal East, Imphal West, Thoubal, Bishnupur, Jiribam, and Kakching, and some Kuki and Vapiphei-dominated villages in the hill districts of Manipur.
- The UNLF's camps, training centers, hideouts, and safehouses are in the Sagaing region of Chin State and Rakhine State in Myanmar.
- The UNLF had been able to operate freely within Myanmar allegedly due to its close links with officials of the Myanmar military.
- Linkages and Front Organisations: The UNLF, being the oldest valley-based armed group, had wielded a significant influence on public issues.
- Most of the impact was through the front organisations that it used to mobilise public protests on key matters.
- Return To Mainstream: The senior leaders of the UNLF responded favourably to the Centre's offer to join the mainstream for the first time in 2020.
- More than 400 personnel with an equal number of weapons joined the peace process, which will have a significant impact on the security scenario of Manipur and the northeast region.
Insurgency in Manipur:
- Manipur is currently experiencing an armed conflict between India and various separatist rebel groups.
- This insurgency is a part of the broader Insurgency in Northeast India, encompassing aspects of both a national liberation war and an ethnic conflict.
- Historical Background of Manipur: Post the brief Anglo-Manipur War of 1891, the Kingdom of Manipur came under British rule and became a British protectorate.
- In October 1949, Manipur joined India and achieved separate statehood in 1972.
- Rise of Insurgency: Manipur's integration into India led to the emergence of several insurgent organizations advocating for an independent state within Manipur's borders, rejecting the merger with India as involuntary.
- The insurgency issue arose in the late 1960s and 1970s, contrasting with the peaceful merger period.
- The United National Liberation Front (UNLF), the first separatist faction, was established in November 1964.
- Currently, the region faces challenges from multiple insurgent groups.
What are the Factors Behind the Rise of Insurgency in Manipur?
- Forced Merger with India: The roots of separatist insurgency in Manipur can be traced to perceived discontent arising from the alleged "forced" merger of Manipur with the Union of India.
- The delay in granting full-fledged statehood further fueled dissatisfaction.
- Despite merging in 1949, Manipur attained statehood only in 1972.
- Rise of Militancy: Subsequent years witnessed the formation of various militant groups, including the People’s Liberation Army (PLA), People’s Revolutionary Party of Kangleipak (PREPAK), Kangleipak Communist Party (KCP), and Kanglei Yawol Kanna Lup (KYKL). These valley-based outfits advocate for an independent Manipur.
- Ethnic Conflict: Despite the hills comprising nine-tenths of Manipur's geographical area, they are sparsely populated.
- The majority of the state's population resides in the valley, with the Meitei community dominating.
- While the surrounding hill districts are inhabited by Nagas and Kukis.
- Ethnic clashes between Nagas and Kukis in the early 1990s led to the formation of several Kuki insurgent groups.
- Over time, their demand shifted from a separate Kuki state to a Territorial Council.
- This conflict's continuation gave rise to smaller outfits like the Zeliangrong United Front (ZUF), People’s United Liberation Front (PULF), and other splinter groups.
- Greater Nagalim Demand: The Nagalim or Greater Nagaland demand encompasses Naga-inhabited areas of Manipur, while the Meitis strive to preserve the historical integrity of a single geographic entity that has endured for centuries.
- Insufficient Socio-Economic Progress: Due to its challenging topography, the state has faced persistent challenges in achieving economic development and socio-economic transformation.
- Throughout the years, persistent corruption, fund mismanagement, and the neglect to empower the general populace have contributed to a growing sense of discontent.
What are the Steps Taken by the Government?
Military Measures:
- AFSPA Implementation: In 1980, the entire Manipur was declared a "disturbed area," prompting the imposition of the contentious Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA).
- This act, aimed at suppressing insurgency, remains in effect to date.
- Operation All Clear: The Assam Rifles and the army executed "Operation All Clear" in the hill areas, neutralizing many militant hideouts.
- However, some relocated to the valley.
Ceasefire Arrangements:
- In 1997, the National Socialist Council of Nagaland-IM (Isak-Muivah) initiated a ceasefire agreement with the Government of India, and ongoing peace talks persisted.
- Kuki Outfits: Under the Kuki National Organisation (KNO) and United People’s Front (UPF), Kuki outfits signed tripartite Suspension of Operation (SoO) pacts with the Governments of India and Manipur on August 22, 2008.
- Some smaller outfits have entered SoO agreements with the state government, leading to rehabilitation programs.
- Valley-Based Militant Outfits: Significant valley-based militant groups like UNLF, PLA, and KYKL, among others, have not yet participated in negotiations with the government.
What is the Current Situation?
- One faction of the UNLF, led by Koireng, remains resistant to engaging in talks.
- Withdrawal from Suspension of Operations (SoO): In 2008, a tripartite Suspension of Operations (SoO) agreement involving the Centre, Manipur state, and Kuki-Zomi insurgent groups was established.
- The primary goal was to facilitate political dialogue. However, in March 2023, the Manipur government withdrew from the agreement with the Zomi Revolutionary Army and the Kuki National Army.
- The decision was attributed to their alleged influence in fostering agitation among forest encroachers.
Way Forward
- Effective Border Management: Prior to implementing any counter-insurgency policies or operations, proper management of the Indo-Myanmar international border is imperative.
- Promoting Economic Development: Following good governance, economic development should be pursued through participation from government, semi-government, and private entrepreneurship.
- Establishing Good Governance: Instituting good governance in the state necessitates a transparent government, a fair judiciary system, adherence to the rule of law, and ensuring basic amenities like hospitals, schools, and police stations.
- Political sincerity and equitable fund distribution for both valley and hill development are crucial.
- Community Engagement: Enhancing connectivity and interaction among Manipur's diverse communities and mainland India is vital for fostering national integration.
- Utilizing Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs), women's associations and cultural programs can play a significant role in rebuilding confidence among the valley and hill populations.
RBI Increases Risk Weights on Unsecured Loans (Business Standard)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently issued regulatory measures to banks and NBFCs to increase risk weights associated with consumer credit and bank credit by an additional 25 percentage points.
- Currently, at 100% risk weight, loans to consumers will see an increase to 125%, excluding loans for housing, education, vehicles, and against gold.
- This would be applicable to unsecured personal loans, credit cards, and lending to NBFCs.
- The directions are expected to result in higher capital requirements for lenders and thereby, an increase in lending rates for consumers.
What is ‘Risk Weights'?
- Risk weight is capital required to be set aside, stipulated by the Reserve Bank of India for Banks, or National Housing Bank for housing finance companies, that has to be made by banks for giving the loan.
- In other words, it is the amount (depicted as a percentage of loan disbursed) that institutions need to set aside for assets.
- The risk weight is a function of the risk perception the apex bank has on loans for different sectors.
- It is applicable to all categories of retail (personal, home, car, and education loans) as well as corporate lending.
- The one that often impacts borrowers directly, and the most, is the risk weight on home loans.
- It is an essential tool for banks to manage this risk.
Why do risk weights matter?
- Risk weights are pivotal in banking regulation, as they dictate the capital set aside for different loan types, reflecting their risk profiles.
- Unsecured loans, perceived as riskier, have higher weights, thus requiring more capital.
- Home loans, for instance, attract a risk weight of 35-50%, depending on the size of the loan.
- In comparison, personal loans will now have a risk weight of 125%.
Why were the Changes by RBI Deemed Necessary?
- Governor Shaktikanta Das had flagged concerns about the “high growth” in “certain components of consumer credit.” while presenting the monetary policy statement in October this year.
- He advised banks and NBFCs to “strengthen their internal surveillance mechanisms, address the build-up of risks, if any, and institute suitable safeguards, in their own interest.”
- The governor said these were being closely monitored by the apex banking regulator for “any signs of incipient stress.”
- Rating agency Moody’s also put forth that higher risk weights are intended to “dampen lenders’ consumer loan growth appetite.”
- The unsecured segment, it adds, has grown rapidly in the past few years, exposing financial institutions to a potential spike in credit costs in the event of a sudden economic or interest rate shock.
- RBI’s latest figures stipulate that unsecured personal loans have increased approximately 23% on a year-over-year basis, as of September 22 this year.
- Outstanding loans from credit cards increased by about 30% during the same period.
- Major concerns emerge for loans below Rs 50,000 – these carry the utmost default risk.
- Delinquencies in this segment stood at 5.4% as of June this year.
- Ratings agency S&P in their assessment held that borrowers in this segment are often highly leveraged and may have other lending products.
- According to Moody’s, several NBFCs that until now focused on secured lending categories (such as infrastructure, real estate, and vehicle loans) have pivoted to riskier segments.
What are the main concerns?
- The primary concerns are about how these changes might affect the amount of money banks have and how well they can make a profit.
- Having enough money, called capital adequacy, is crucial for banks.
- It helps them handle unexpected problems or risks in their business without losing too much money.
- A recent report from S&P, which is a group that studies these things, says that if banks are more careful and focus on managing risks, it could make their loans safer.
- However, it predicts that a measure called Tier-1 capital adequacy, which is like the best kind of money banks have, might go down a bit—about 60 basis points.
- This is important because Tier-1 capital helps banks deal with losses right away.
- S&P thinks that this might make banks that don't have a lot of this kind of money think about getting more.
- Also, it noticed that government-owned banks generally have less of this important money than big private banks.
- But, the report says that finance companies might face the biggest impact because they could end up borrowing more from banks, and it might affect how much good money they have.
How It will affect Consumers?
- As the risk weightage goes up, banks may become more careful about giving loans to consumers, especially those seen as having a higher risk.
- This could make it harder for some people to get credit cards or personal loans.
- Even those who still qualify for credit might face stricter terms and conditions.
- Experts suggest that by increasing the risk weightage, the RBI is trying to handle the increasing number of people not repaying their loans and the risks connected to unsecured loans.
- Lenders will now have to consider the higher credit risk in this type of loan, which could make lending more expensive.
- As a result, borrowers taking out these loans may face higher costs.
Way Forward
Banks and NBFCs may need to review their approaches to risk and lending specifically for unsecured loans. This could involve placing greater emphasis on evaluating creditworthiness and exploring alternative strategies to effectively handle risk while still providing loans. Financial institutions might also consider diversifying their loan portfolios by placing more emphasis on secured lending or exploring other creditworthy segments. This approach aims to balance the effects of the heightened risk-weighting associated with unsecured loans.
What is the Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)?
- The Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is a financial metric used to evaluate a bank's stability and risk management.
- Calculated as a percentage, it compares a bank's capital—comprising Tier-1 and Tier-2 capital—to its risk-weighted assets.
- Tier-1 capital includes core elements like common equity
- Tier-2 capital consists of supplementary items.
- Regulatory authorities, such as the RBI, establish minimum CAR requirements to ensure banks can absorb potential losses.
- A higher CAR reflects greater financial resilience, emphasizing a bank's ability to navigate economic challenges and adhere to regulatory standards.
Rat-Hole Mining in Uttarkashi Tunnel Rescue (Indian Express)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Experts in Uttarakhand have resorted to ‘rat-hole’ mining to help rescue 41 workers trapped inside the collapsed Silkyara tunnel.
Context:
- Rat hole mining, a controversial and outlaw mining practice is back in the spotlight nearly 9 years after it was banned by the National Green Tribunal (NGT) over severe environmental impacts and unsafe labour conditions.
- The rat hole mining technique is being used to extract the 41 construction workers trapped inside a collapsed Uttarakhand tunnel after modern machinery failed to execute the rescue operation.
- The attempt to free 41 trapped workers in the collapsed Silkyara-Barkot tunnel encountered a significant setback as the auger joint of the debris-drilling machine broke.
What is Rat-hole Mining?
- Rat hole mining is a method of extracting coal from narrow, horizontal seams, prevalent in Meghalaya.
- The term “rat hole” refers to the narrow pits dug into the ground, typically just large enough for one person to descend and extract coal.
- Once the pits are dug, miners descend using ropes or bamboo ladders to reach the coal seams.
- The coal is then manually extracted using primitive tools such as pickaxes, shovels, and baskets.
- The rat-hole mining is broadly of two types.
- The first type is a side-cutting procedure, in the side-cutting procedure, narrow tunnels are dug on the hill slopes and workers go inside until they find the coal seam.
- The coal seam in the hills of Meghalaya is very thin, less than 2 m in most cases.
- In the other type of rat-hole mining, called box-cutting, a rectangular opening is made, varying from 10 to 100 sqm, and through that a vertical pit is dug, 100 to 400 feet deep.
- Once the coal seam is found, rat-hole-sized tunnels are dug horizontally through which workers can extract the coal.
Environmental and Safety Concerns Associated with Rat-hole mining:
- Rat hole mining poses significant safety and environmental hazards.
- The mines are typically unregulated, lacking safety measures such as proper ventilation, structural support, or safety gear for the workers.
- Additionally, the mining process can cause land degradation, deforestation, and water pollution.
- This method of mining has faced severe criticism due to its hazardous working conditions, environmental damage, and numerous accidents leading to injuries and fatalities.
- Despite attempts by authorities to regulate or ban such practices, they often persist due to economic factors and the absence of viable alternative livelihoods for the local population.
When and Why was Rat-hole Mining Banned?
- This rat-mining method has faced severe criticism due to its hazardous working conditions, environmental damage, and numerous accidents leading to injuries and fatalities.
- Experts have opined that the mines are typically unregulated, lacking safety measures such as proper ventilation, structural support, or safety gear for the workers, thereby creating a rather harmful environment for the rat-miners.
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned the practice in 2014 and retained the ban in 2015.
- The NGT observed, “It is also informed that there is umpteen number of cases where by virtue of rat-hole mining, during the rainy season, water flooded into the mining areas resulting in the death of many individuals including employees/workers."
How Rat-hole Mining has Helped in Uttarakhand Tunnel Rescue Operation?
- The state-of-the-art American auger machine drilled roughly 47-48 meters of a horizontal tunnel.
- After that, it’s driller tool broke inside the drilled passage and authorities said that the damage was beyond repair.
- The rescue teams then resorted to manual drilling – a safer but time-consuming option. However, they brought in a team of rat hole mining experts who completed the remaining task in less than two days.
- The rat hole miners went inside the steel pipe being pushed inside the rubble through which trapped workers were pulled out and drilled a horizontal passage.
- The process was somewhat similar to the digging of a narrow tunnel for coal mining.
What are the Other Methods Used to Rescue the Trapped Workers in the Silkyara Tunnel?
- Vertical drilling: Vertical drilling is done through a boring machine, digging straight down from the ground using electrical tools and equipment.
- In the case of the Uttarakhand tunnel collapse, a vertical drill had been boring into the ground and an 800-mm pipe had been inserted to bring out the trapped workers.
- Auger mining (horizontal drilling): A horizontal auger machine or a directional drill is a specialised tool designed to drill horizontal bores or create underground tunnels without disturbing the ground.
- These machines are used to lay down water and gas pipes and to dig a tunnel.
- However, the auger machine in the case of the Uttarakhand tunnel collapse failed to free the trapped workers as it hit metal obstructions and eventually broke down, beyond repair.
What is a Horizontal Auger Machine?
- A horizontal auger machine, also known as a horizontal boring machine or directional drill, is a specialized tool designed for creating horizontal bores or underground tunnels without causing surface disruption.
- It typically features a rotating helical screw blade, referred to as an auger, attached to a central shaft or drill, facilitating penetration through rotation.
- Applications: Widely utilized in construction, utility installations (such as laying pipes or cables), and various infrastructure projects.
- Working Mechanism: Positioned at the starting point of the bore, often on the surface, the machine comprises a drill head with an auger or a drill string.
- The rotating auger at the front of the machine cuts through soil, rock, or other underground materials.
- The rotation is powered by hydraulic or mechanical systems.
- As the auger progresses, it removes the material from the tunnel.
- The removal process is usually facilitated by a drilling fluid or mud pumped through the drill string.
- The drilling fluid serves multiple purposes, including lubricating the drilling process, cooling the cutting head, and transporting excavated material back to the surface.
The President of India Advocates for the “All India Judicial Service” (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
President Draupadi Murmu on Sunday called for the creation of an all-India judicial service to recruit judges, saying this will help make the judiciary diverse by increasing representation from marginalised social groups.
News Summary:
- President Draupadi Murmu in her inaugural address, advocates for the establishment of an all-India judicial service during the Supreme Court’s Constitution Day celebrations on 26th Nov.
- November 26th is observed as Constitution Day to commemorate the adoption of the Constitution of India by the Constituent Assembly in 1949.
- The creation of an all-India judicial service is proposed to diversify the judiciary, increasing representation from marginalized social groups.
- She also discusses gender and caste representation, emphasizing the need for accessible justice and suggested a merit-based, competitive, and transparent process for recruiting judges from varied backgrounds.
- The President envisions an all-India judicial service selecting talented individuals from across the country, providing opportunities to less-represented social groups.
- She calls for removing colonial remnants from all domains as part of India's continued democratization.
- She highlights India's democratic strides post-independence, celebrating diverse leadership across genders and socially disadvantaged groups.
About All-India Judicial Service:
- The concept of the All-India Judicial Service was initially introduced in the 14th Report of the Law Commission of India in 1958.
- This service envisions the central recruitment of district judges through an all-India examination, with subsequent allocation to each state, mirroring the organizational structure of other All-India Services such as IAS and IPS.
- The primary objective is to establish a transparent and efficient recruitment method, aiming to attract the finest legal talent in India.
- The idea was again proposed in the Law Commission Report of 1978, which discussed delays and arrears of cases in the lower courts.
- In 2006, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice in its 15th Report backed the idea of a pan-Indian judicial service and also prepared a draft Bill.
- Currently, the appointment of district judges is carried out by the state governor based on the recommendations of the chief justice of the respective state's high court.
What is the procedure to set up an All-India Service?
- The 42nd Constitutional Amendment (1976) brought about modifications to Article 312(1), granting the Parliament the authority to legislate for the establishment of one or more All-India Services.
- Following this, as per Article 312(1) of the Constitution, the Rajya Sabha must pass a resolution with the support of at least two-thirds of its members present and voting.
- Subsequently, Parliament can amend Article 233 and Article 234 by a simple majority to institute an All-India Judicial Service (AIJS).
- The recruitment procedures and terms for individuals appointed to All India services are subject to regulation by Parliament through the enactment of the All India Service Act, 1951.
- Importantly, this process does not necessitate a constitutional amendment under Article 368.
Arguments Setting of the All-India Judicial Service (AIJS):
- Enhanced Judicial Efficiency: Implementation of the All-India Judicial Service (AIJS) ensures an efficient subordinate judiciary by addressing issues such as different pay scales, faster vacancy fulfillment, and standardized training across states.
- Vacancies and Pendency of Cases: As of July 2023, the subordinate judiciary's working strength was 19,858, with 5,000 posts remaining vacant against the sanctioned strength of 25,246.
- Over 85% of the 5 crore pending cases, especially in district courts, contribute to a significant backlog, with more than one lakh cases pending for over 30 years.
- Balancing Judges To Population Ratio: The AIJS aligns with a Law Commission report (1987) suggesting a judge-to-population ratio of 50 judges per million people, a considerable increase from the then-existing 10.50 judges.
- Despite progress, the current figure of 20 judges in terms of sanctioned strength remains comparatively lower than the U.S. (107) and the U.K. (51) ratios.
- Enhanced Representation for Marginalized Sections: The AIJS is advocated by the government as an optimal solution for achieving equitable representation of marginalized and deprived sections of society within the judiciary.
- Addressing Corruption and Nepotism: A bottoms-up approach to recruitment through the AIJS is seen as a strategy to tackle issues like corruption and nepotism prevalent in the lower judiciary.
- Absence of career growth: Currently, less than 25% of judicial officers have the chance to ascend to High Court judgeship, primarily reaching the rank of district judges towards the end of their careers.
- The remaining 75% quota is allocated for High Court judge recruitment from the Bar Association of India.
- The establishment of an All-India Judicial Service (AIJS) would ensure a richer talent pool with a younger age profile for selection by High Courts and the Supreme Court, offering a remedy to the issue of limited career growth.
Criticism Against Setting up an All-India Judicial Service:
- Centralization and State Power Concerns: The adoption of a centralized recruitment process is criticized as infringing on federalism, and encroaching on the constitutional powers granted to states.
- Language Barrier Challenge: An argument against AIJS is that judges recruited through this process may lack proficiency in the local languages of the States where they are posted.
- Given that civil and criminal court proceedings are conducted in languages prescribed by respective State governments, this language barrier is a significant concern.
- Impact on Local Reservations: Centralized testing may potentially dilute reservations based on caste, rural backgrounds, or linguistic minorities, undermining localized efforts to ensure representation.
- Conflict with Separation of Powers: Opposition stems from constitutional principles of the separation of powers.
- Centralized testing raises concerns about the executive gaining influence in the appointment of district judges, potentially diminishing the role of High Courts.
- Limited Impact on Structural Issues: Critics argue that the creation of the All-India Judicial Service (AIJS) fails to address inherent structural challenges in the lower judiciary.
- Uniformity in pay scales, as addressed by the Supreme Court in the 1993 All India Judges Association case, is seen as a more effective approach.
- Alternative Solutions Over Central Exam: Experts contend that addressing structural issues involves increasing pay universally and ensuring that a portion of High Court judges are selected from the lower judiciary.
- This approach is seen as more effective than relying solely on a central exam to attract quality talent.
Supreme Court’s Stand:
- In 1992, the Supreme Court (SC) issued a directive in the case of All India Judges’ Association v. The Union of India, instructing the Centre to establish an All India Judicial Service (AIJS).
- However, during a review of this judgment in 1993, the court granted the Centre the freedom to take the lead on the AIJS matter.
- In 2017, the SC independently addressed concerns about the appointment of district judges, suggesting the exploration of a Central Selection Mechanism.
- Senior advocate Arvind Datar, acting as amicus curiae (friend of the court), circulated a concept note to all states proposing a common examination instead of separate state exams.
- The merit list from this common examination would guide High Courts in conducting interviews and appointing judges.
- Datar emphasized that this approach would not alter the constitutional framework or diminish the authority of states or High Courts.
Way Forward
Despite the prolonged debate spanning decades, numerous States and High Courts have expressed reservations regarding the creation of an All-India Judicial Service (AIJS). Therefore, it is imperative to foster a comprehensive consensus among the Centre, States, and the Judiciary before the Parliament proceeds with establishing the AIJS. In the meantime, efforts should be concentrated on implementing more targeted and immediate solutions to effectively address the challenges faced by the Indian judiciary.
Violence Against Women (United Nations)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
- The International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women is observed worldwide on November 25 each year, as designated by the United Nations General Assembly.
- 2023 theme of Elimination of Violence against Women: This year’s theme, "UNITE! Invest to prevent violence against women and girls", emphasises the need to fund prevention strategies proactively to stop gender-based violence.
Violence Against Women:
- According to United Nations (UN) data, one in three women worldwide experience physical or sexual violence, mostly by an intimate partner, affecting approximately 736 million women globally.
- This alarming trend extends beyond traditional settings, seeping into workplaces and online spaces, further exacerbated by post-pandemic repercussions, conflicts, and climate change.
- Violence against women and girls is a human rights violation, and the immediate and long-term physical, sexual, and mental consequences for women and girls can be devastating, including death.
- Violence negatively affects women’s general well-being and prevents women from fully participating in society.
- It impacts their families, their community, and the country at large.
- It has tremendous costs, from greater strains on health care to legal expenses and losses in productivity.
Statistics on Violence against Women in India:
- Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) is recognised as a pervasive social issue and a significant public health challenge.
- Recent global estimates indicate that over 25% of women of reproductive age, who have ever been in a relationship, have faced physical, sexual, or both forms of IPV—reaching an average of 35% in South Asia.
- According to the National Library of Medicine, 32% of ever-married Indian women reported experiencing physical, sexual, or emotional violence from their husbands.
- In India, the prevalent spousal violence are physical (28%), emotional (14%) and sexual (6%).
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reported 428,278 cases of crimes against women in 2021, marking a 15.3% increase from 2020 (371,503 cases).
- The majority of these cases under the Indian Penal Code were classified as:
- "cruelty by husband or his relatives" (31.8%)
- "assault on women with intent to outrage her modesty" (20.8%)
- "kidnapping and abduction of women" (17.6%), and "rape" (7.4%).
- The crime rate, registered per lakh women population, rose to 64.5 in 2021 from 56.5 in 2020.
History of Elimination of Violence against Women:
- It dates back to 1981 when women’s rights activists began marking 25 November as a day against gender-based violence.
- This day pays homage to the Mirabal sisters—three Dominican political activists brutally murdered in 1960 by order of the country’s ruler, Rafael Trujillo (1930-1961).
- In a significant stride towards combating violence against women, the UN General Assembly, in December 1993, adopted the Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women, laying the groundwork for global efforts to eradicate such violence.
- In February 2000, the UN General Assembly, officially designated 25 November as the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women.
- This resolution urged governments, international organizations and NGOs to unite in organizing activities annually on this date, fostering public awareness and collective action to address and eliminate violence against women and girls worldwide.
Factors Influencing Violence:
- Men's Predisposing Factors: Men are more likely to engage in violence if they have low education, a history of maltreatment in childhood, witnessed domestic violence against their mothers, misuse alcohol, hold unequal gender views supporting violence, and possess a sense of entitlement over women.
- Women's Vulnerability Factors: Women are more likely to face intimate partner violence if they have lower education, witnessed their mothers being abused, experienced childhood abuse, and hold attitudes accepting violence, male privilege, and the subordinate status of women.
- Effective Interventions: Advocacy and empowerment counseling, along with home visitation, show promise in preventing or reducing intimate partner violence against women.
- Impact of Conflict and Displacement: Situations of conflict, post-conflict, and displacement can worsen existing violence, including by intimate partners and non-partner sexual violence.
Root Causes of Violence Against Women:
- Gender Disparity: Gender inequality deeply ingrained in society exposes women to various forms of violence.
- Discriminatory gender norms and stereotypes contribute to structural inequality.
- Psychiatric Morbidity: Psychiatric morbidity encompasses both physical and psychological deterioration due to mental or psychological conditions, often linked to alcohol consumption.
- Regular alcohol consumption by husbands correlates strongly with poor mental health in women. Alcohol serves as a situational factor, heightening the risk of violence by diminishing inhibitions and impairing judgment.
- Sociodemographic Factors: Patriarchy is a significant contributor to violence against women.
- Higher economic status and perceived power of women to challenge traditional gender roles increase the risk of violence.
- Family Factors: Exposure to harsh physical discipline and witnessing parental violence during childhood predicts victimization and perpetration of violence in adulthood.
- Traditional and Cultural Practices: Female genital mutilation leads to severe physical and psychological consequences.
- Acid attacks, driven by family disputes or rejection of marriage proposals, cause disfigurement and trauma.
- "Honour killings" in various countries uphold the family reputation, justifying violence for reasons like alleged adultery or disapproved relationships.
- Early marriages, with or without consent, undermine the health and autonomy of girls, constituting a form of violence.
- Judiciary and Law Enforcement: An insensitive, inefficient, and corrupt judicial system and law enforcement machinery fail to deter various forms of crimes.
- Sociocultural Factors: Deep-rooted stereotypes confining women to primary roles of marriage and motherhood persist.
- The stigma associated with unmarried, separated, or divorced status perpetuates gender-based violence.
- The custom of dowry remains prevalent in Indian marriages, contributing to the problem
Impact of Violence Against Women:
- Health Ramifications: Violence, regardless of its form, profoundly affects women's physical, mental, sexual, and reproductive health.
- Adverse consequences extend to self-esteem, work capacity, and decision-making abilities concerning fertility.
- Economic Implications: Violence against women carries significant economic repercussions for both individual households and the nation.
- Direct Costs: These include the loss of income, productivity, healthcare expenses, and the cost of social services.
- Indirect Costs: Impact on child well-being, female and child mortality, and the intergenerational social and psychological toll.
- Development Challenges: Violence acts as a barrier to women's participation in development and planning programs at both micro and macro levels.
- It restricts women's freedom to act or move freely, hindering their access to and experience of the benefits of development.
- Violence poses a challenge to poverty alleviation programs, impeding the equitable distribution of resources.
- Rights Impediment: Any form of violence against women obstructs the realization of their fundamental rights as outlined in Article 14, 21, 19, and 32 of the Indian Constitution.
Way Forward to Addressing Gender-Based Violence:
- Gender-Based Legislation: Enact and rigorously enforce legislation that promotes gender equality, addressing discrimination against women in marriage, divorce, custody laws, inheritance laws, and asset ownership.
- Financial Empowerment: Enhance women's access to paid employment opportunities, fostering financial independence.
- National Plans and Policies: Develop and allocate resources for national plans and policies dedicated to addressing violence against women comprehensively.
- Enhanced Crime Surveillance: Improve the systems for collecting crime surveillance data specifically related to violence against women.
- Capacity Building and Training: Provide comprehensive training to service providers and law enforcement officers, enabling them to effectively handle cases of violence against women.
- Prevention of Recurrence: Implement strategies to prevent the recurrence of violence by early identification of women and children experiencing abuse and offering appropriate referrals and support.
- Promotion of Egalitarian Norms: Integrate the promotion of egalitarian gender norms into life skills and comprehensive sexuality education curricula for young people.
- Gender-Based Surveys: Generate evidence on effective strategies and the magnitude of the issue by conducting population-based surveys.
- Include violence against women in demographic and health surveys, surveillance, and health information systems.
25 years of the International Space Station (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The International Space Station (ISS) celebrated its 25th anniversary on November 20, 2023. It was launched in 1998, the first module marked the beginning of a remarkable journey. With over 140,000 Earth orbits and a quarter-century milestone, the ISS remains a symbol of peaceful collaboration for scientific endeavors.
What is the International Space Station (ISS)?
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a space station that was assembled in low earth orbit (LEO) by the United States and Russia, with assistance and components from a multinational consortium.
- It is a collaborative effort between multiple space agencies, including the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the Federal Space Agency of Russia (Roscosmos), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
- The ISS has been inhabited continuously and serves as an important platform for research and exploration in space.
- The success of the ISS is largely due to the implementation of various space standards and agreements, which help to ensure that the station is designed, operated, and maintained safely and efficiently.
- ISS is the longest continuous human presence in space, amounting to around 25 years.
- However, it is not the first-ever manned space station as Salyut, Almaz, Mir, and Skylab preceded it in this regard.
- Moreover, ISS is divided into two zones, the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) and the United States Orbital Segment (USOS).
- ROS is where Russia’s cosmonauts work, whereas USOS is where space crews from the US, Japan, Canada, and Europe collaborate.
When did the International Space Station launch?
- The first segment of the ISS — the Zarya Control Module — was Russian and launched on November 20, 1998.
- Zarya supplied fuel storage and battery power, and served as a docking zone for other space vehicles arriving at the ISS.
- One month later, on December 4, 1998, the US launched the Unity Node 1 module.
- Together, the two modules were the start of a functioning space laboratory.
- Over the course of 42 assembly flights, the ISS became what it is today.
- Among the first “live-in” astronauts were Bill Shepherd of NASA and Roscosmos cosmonauts Yuri Gidzenko and Sergei Krikalev.
- Since then, the ISS has been continuously inhabited.
Characteristics of ISS:
- Size and Composition: Weighing around 460 tons, the ISS boasts a habitable volume comparable to a Boeing 747 aircraft's interior.
- Comprising interconnected modules, laboratories, living quarters, and docking ports, forming a complex structure in space.
- Orbit and Circulation: Travels at a speed of 8 kilometers (5 miles) per second, completing an orbit around Earth every 90 minutes.
- Generates 16 sunrises and sunsets in a 24-hour cycle, passing overhead multiple times daily.
- Mission Durations: Standard missions last approximately six months, though crew members may have shorter or longer stays.
- During their tenure, astronauts and cosmonauts conduct experiments, maintain systems, and perform essential tasks for the station's functioning.
- Presence of International Crew: The ISS is continuously occupied by a diverse crew hailing from various nations.
- Rotating crews of astronauts and cosmonauts live and work on the station, contributing to scientific research and station upkeep.
- Scientific Endeavors: Provides a unique environment for scientific experiments in microgravity, spanning biology, physics, astronomy, and materials science.
- Serves as a testbed for technologies crucial for future deep-space exploration.
- Global Symbol of Unity: The ISS stands as a testament to international collaboration in space exploration, fostering unity among participating nations.
- It exemplifies the peaceful coexistence of astronauts from different backgrounds in the pursuit of shared scientific goals.
Why Is the Space Station Important?
- The significance of the Space Station lies in its role as a platform for diverse scientific research and experiments in the distinctive microgravity setting of space.
- Microgravity, also known as near-zero gravity or weightlessness, provides a unique environment for researchers worldwide to explore various fields, including biology, physics, astronomy, and Earth sciences.
- Through the ISS, valuable insights have been gained in areas such as human health in space, materials science, and climate change.
- The station serves as a continuous habitat for human presence in space, marking a sustained human presence since the arrival of the first crew.
What do astronauts do onboard the ISS?
- When ISS astronauts not conducting scientific experiments, they go on regular spacewalks to add new components to the station, such as robotic arms, or run maintenance.
- There have been times when astronauts have had to inspect or fix holes that were created by space debris.
- The astronauts are also on a strict health regimen. They have to mitigate the loss of muscle and bone mass, which is caused by microgravity in space.
- That includes working out on specially designed machines, including treadmills, for at least two hours a day.
- But the astronauts’ daily exercise is used to improve our scientific understanding of the effects of space on our bodies.
What scientific discoveries on the ISS have benefited life on Earth?
- Astronauts have conducted hundreds of scientific experiments on the ISS.
- Sometimes they experiment on themselves, monitoring their general health, nutrition, or the effects of solar radiation and sometimes they conduct experiments for scientists on Earth.
- These experiments have led to numerous scientific breakthroughs.
- From Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease to cancer, asthma, and heart disease — it’s all been studied in space.
- Scientists say some medical experiments are best done in space because cells behave in microgravity more like they do inside the human body, but it’s difficult to recreate such conditions on Earth.
- There have been discoveries to benefit drug development, new water purification systems, methods to mitigate muscle and bone atrophy, and those that have led innovations in food production.
How long will the ISS be operational?
- Plans for the future operation of the ISS were thrown into uncertainty with the start of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in early 2022.
- Both the European Space Agency and national bodies withdrew from international collaborations with Russia, and Russia said it was leaving the ISS to build its own space station.
- Also, old and new spacefaring nations want to make an independent mark on space.
- They include Japan, China, India, the United Arab Emirates and others.
- The US and Europe have said they remain committed to the International Space Station through 2030.
- But plans are afoot for a post-ISS world, as well: NASA is almost entirely focused on its Artemis program and plans to populate the moon and ESA is working toward a new space station, which it is calling Starlab.
India and Japan Converge in Southeast Asia (The Hindu)
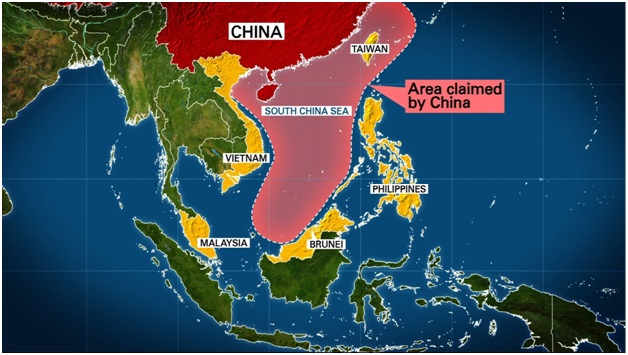
- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Philippines is now exploring Japan and India as alternative partners for development and security cooperation.
Concerns between the China and Philippines:
- The relationship between the Philippines and China has been strained for decades due to long-standing territorial disputes in the South China Sea.
- The Philippines claims sovereignty over several islands and reefs in the South China Sea, while China maintains a sweeping claim over the entire area, known as the "nine-dash line."
- These competing claims have led to numerous incidents of Chinese vessels blocking or harassing Philippine fishing boats and military vessels.
- In 2012, the Philippines filed an arbitration case against China under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) challenging the legality of China's nine-dash line claim.
- In 2016, the Permanent Court of Arbitration ruled in favor of the Philippines, finding that China's nine-dash line claim had no legal basis.
- However, China has refused to accept the ruling.
- The South China Sea is a strategically important waterway, with an estimated $3.3 trillion in trade passing through it annually.
- It is also believed to be rich in natural resources, including oil and gas.
- The ongoing territorial disputes have raised tensions in the region and have the potential to escalate into conflict.
- In addition to the territorial disputes, there have been other issues that have strained relations between the Philippines and China including China's militarization of the South China Sea, its fishing practices in Philippine waters, and its human rights record.
Bilateral Relations Between India and the Philippines:
India and the Philippines have enjoyed a warm and cordial relationship since establishing diplomatic ties in 1949, shortly after both countries gained independence. The relationship is rooted in shared values of democracy, pluralism, and the rule of law, as well as a growing economic partnership.
Political and Strategic Cooperation:
- India and the Philippines have maintained regular high-level visits and engagements, fostering a strong political and strategic partnership.
- The two countries have cooperated on a range of issues, including maritime security, counterterrorism, and defense.
- Intensification of relations with the Philippines resulted from India’s Look East Policy (1992) and further diversified with the Act East Policy (2014).
Economic Partnership:
- India and the Philippines have a growing economic partnership, with bilateral trade reaching over $3 billion in 2022.
- India is currently the Philippines' fifteenth-largest trading partner.
- The two countries have signed several agreements to enhance economic cooperation, including the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), which is expected to further boost trade and investment.
Cultural and People-to-People Exchanges:
- Both countries have active diaspora communities that contribute to cultural exchange and people-to-people linkages.
- India and the Philippines have signed agreements on cultural cooperation and education exchange.
Recent Developments:
- In recent years, India and the Philippines have elevated their relationship to a "Strategic Partnership."
- This reflects the growing convergence of their interests in the Indo-Pacific region and their commitment to promote a rules-based international order.
Key Areas of Cooperation:
- Maritime Security: India and the Philippines have a shared interest in maintaining peace and stability in the maritime domain.
- The two countries have conducted joint naval exercises and collaborated on maritime surveillance and information sharing.
- Counterterrorism: India and the Philippines have pledged to cooperate in combating terrorism and preventing the spread of violent extremism.
- They have shared intelligence and expertise in counterterrorism operations and training.
- Defense Cooperation: Key developments include the BrahMos missile deal, the establishment of a resident Defense Attache office in Manila, and the consideration of India's proposal for a concessional Line of Credit to fulfill the defense needs of the Philippines.
- Additionally, collaboration extends to maritime domain awareness (MDA), joint patrols, and the exchange of information.
- The two countries have also conducted joint military exercises to enhance interoperability and strengthen defense ties.
Japan and India's Involvement in Southeast Asia:
- Free and Open Indo-Pacific: A joint effort to counter China's growing assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Free and Open Indo-Pacific is an umbrella term that encompasses Indo-Pacific-specific strategies of countries with similar interests in the region.
- Japan's Free and Open Indo-Pacific aligns with India's Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative.
- Partnership with ASEAN: Strengthening economic, political, and cultural ties with ASEAN member nations.
- Infrastructure Development: Japan's Partnership for Quality Infrastructure involvement in Southeast Asian projects (ports, roads, and energy facilities).
- India also expresses interest in regional infrastructure projects.
- Connectivity Projects: Both nations actively promote connectivity, with India contributing through projects like the Trilateral Highway (connecting India, Myanmar, and Thailand).
- Economic Assistance: Providing economic assistance and development aid to support socio-economic growth in Southeast Asia.
- Assistance includes financial support, capacity building, and technology transfer.
- Security Cooperation: Engaging in security dialogues and joint military exercises with Southeast Asian countries.
- Collaborating on common security challenges such as maritime security and counter-terrorism.
- Human Resource Development: Joint efforts in human resource development programs, including scholarships and training opportunities.
- Aimed at enhancing skills and knowledge across various sectors.
- Regional Forums: Active participation in regional forums like the East Asia Summit (EAS) and ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF).
- Addressing regional challenges and fostering dialogue on a variety of issues.
India-Japan Relations:
The roots of the relationship trace back to ancient times when Buddhism was introduced to Japan in the 6th century. A robust partnership emerged from India's Look East Policy, evolving into a 'Special Strategic and Global Partnership' in 2014.
- Economic Cooperation: Strong trade and investment ties with significant bilateral investments.
- Initiatives like Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) and Neemrana Industrial Park for Japanese firms.
- Collaboration in the automobile sector, exemplified by Maruti Suzuki.
- Infrastructure Investment: Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) plays a pivotal role in investing in India's infrastructure projects.
- Contributions range from the Delhi Metro to water and sanitation projects.
- Strategic Cooperation: Shared commitment to a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- Highlighted in Japan's National Security Strategy (NSS-2022) and 2021 Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement (ACSA).
- Defence Collaboration: Steadily growing cooperation in response to regional security challenges.
- Initiatives like the 2015 Agreements on the transfer of defence Equipment and Technology..
- In terms of security, India and Japan constantly engage in varied platforms ranging from regular bilateral military exercises and two-plus-two meetings to multilateral frameworks such as the Quad and the G20.
- Technology Partnership: Collaboration on cutting-edge technologies like robotics, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy.
- Examples include the India-Japan Digital Partnership (I-JDP) and cooperation in nuclear technology.
- Regional and Global Cooperation: Active collaboration on climate change, counterterrorism, and United Nations reforms.
- Joint development of the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor for economic collaboration and capacity-building in African countries.
- Cultural and People-to-People Ties: Promotion of tourism, educational exchanges, and scholarships.
- Initiatives like the Japan Exchange and Teaching (JET) Programme and the India-Japan Global Partnership Summit foster personal bonds between citizens.
Accordingly, as India is significantly deepening and broadening its ties with Southeast Asian countries, such as the Philippines, India should consider taking its third-country developmental model with Japan into the sub-region of the greater Indo-Pacific at a time when resident countries are looking for alternative sources of development and security amidst the polarising dynamics of the U.S.-China power competition.
OECD Report About Climate Finance (The Hindu)
- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A new report, published by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), showed that economically developed countries fell short of their promise to jointly mobilise $100 billion a year, towards the climate mitigation and adaptation needs of developing countries, in 2021 – one year past the 2020 deadline.
What is the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)?
- The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is an association of 38 nations in Europe, the Americas, and the Pacific.
- Its members and key partners represent 80% of world trade and investment.
- The goal of the OECD is to promote the economic welfare of its members.
- It also coordinates its efforts to aid developing countries outside of its membership.
- As a result, its programs help promote reform in more than 100 countries worldwide.
- The OECD's main headquarters is located in Paris (France)
- The OECD collects, analyzes, and reports on economic growth data for its members.
- This gives them the knowledge to further their prosperity and fight poverty. It also balances the impact of economic growth on the environment.
- Committees within the OECD analyze the data and make policy recommendations.
- It's up to each member country to decide how to use OECD recommendations.
- The OECD publishes mainly two reports:
- International Migration Outlook
- Programme for International Student Assessment
Key Findings of the OECD Report Ahead of COP 28:
- The OECD has released a report titled 'Climate Finance Provided and Mobilised by Developed Countries in 2013-2021.'
- This comprehensive report highlights the collective patterns in annual climate finance contributed and mobilized by developed nations for developing countries during the period from 2013 to 2021.
- In-depth analyses are presented, offering insights into climate themes, sectors, financial instruments, and regional distributions specifically for the years 2016 to 2021.
- Additionally, the report offers essential recommendations for international providers to enhance financial support for adaptation efforts and to more efficiently engage private finance in climate action.
Major Takeaways from the Report Published by OECD:
- Failure to Meet Commitments: The report revealed that the economically developed countries had failed to meet their commitment to together raise $100 billion annually by 2021, one year after the 2020 deadline, to help developing nations with their climate adaptation and mitigation needs.
- According to the report, affluent nations raised $89.6 billion in 2021, however, the amount of money allocated for adaptation decreased by 14% from 2020 to 2021.
- The ability of developing nations to meet their needs for climate adaptation and mitigation is lowered when sufficient climate funding is not raised.
- It also weakens confidence in the industrialized world's sincerity in addressing the climate catastrophe among the world's poorer nations.
- Loan-Centric Climate Finance: According to the OECD study, $49.6 billion in loans were given out of the $73.1 billion that the public sector raised in 2021 through bilateral and multilateral channels.
- It illuminates the degree to which wealthy nations must rely on loans at market rates in order to meet their climate finance commitments.
- For instance, a research team's evaluation of the worldwide flows of climate finance from 2011 to 2020 revealed that 61% of the funding came from loans.
Issue With 'Additionality'
- Another issue in the OECD report pertains to additionality.
- The UNFCCC states that developed countries “shall provide new and additional financial resources to meet the agreed full costs incurred by developing country Parties in complying with their obligations under the convention”.
- This means developed countries can’t cut overseas development assistance (ODA) in order to finance climate needs because that would effectively rob Peter to pay Paul.
- In the real world, it could cut off support for healthcare in order to reallocate that money to, say, install solar panels.
- The “new and additional finance” also means developed countries can’t double-count.
- For example, a renewable energy project could contribute to both emission reductions and overall development in a region.
- As per the U.N. Convention, however, donor countries can’t categorise such funding as both ODA and climate finance because it wouldn’t fulfill the “new and additional” criterion.
- A few years ago, European Union officials admitted to double-counting development aid as climate finance.
What Counts as Climate Finance?
- At present, there is no commonly agreed definition of ‘climate finance’ because developed countries have endeavored repeatedly to keep it vague.
- For example, at the COP 27 in Egypt last year, Australia and the U.K. even sought to end discussions to define ‘climate finance’.
- In the run-up to the COP 26 in Glasgow, the U.S. led an effort to block debate on a common definition, alongside Switzerland, Sweden, and some other developed countries.
- The lack of definitional clarity has reportedly led to strange situations like funding for chocolate and gelato stores in Asia and a coastal hotel expansion in Haiti being tagged as climate finance.
- The ambiguity works in favour of richer countries because it leaves the door open to arbitrarily classify any funding, including ODA and high-cost loans, as climate finance and escape the scrutiny that a clearer definition might bring.
- So while developed countries can claim they have provided billions in climate finance, the actual flows need to be checked for whether they actually went into climate mitigation and adaptation in developing countries or something else.
How much do developing countries need?
- According to the OECD assessment, climate investments for developing nations are expected to reach approximately $1 trillion year by 2025 and $2.4 trillion annually between 2026 and 2030.
- In contrast, the $100 billion objective is insufficient and even more so given that it has not yet been reached.
What role can the private sector play?
- To meet the scale of the challenge, people like the U.S. climate envoy John Kerry and World Bank president Ajay Banga have routinely emphasised the role the private sector could play.
- But the OECD report shows that private financing for climate action has stagnated for a decade.
- The problem is particularly worse for climate adaptation because investment in this sector can’t generate the sort of high returns that private investors seek.
- There also haven’t yet been signs that the private sector is interested in massively scaling up its climate investments.
What is Climate Change?
- Climate change is the result of long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns.
- Natural variations, like those influenced by changes in the solar cycle, can contribute to these shifts.
- However, since the 1800s, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas, have emerged as the primary driver of climate change.
- The combustion of fossil fuels produces greenhouse gas emissions, creating a metaphorical blanket around the Earth.
- This 'blanket' traps the sun's heat, leading to an increase in temperatures.
- The rising temperatures, a consequence of climate change, accelerate the melting of ice.
- This, in turn, contributes to elevated sea levels, resulting in flooding and erosion.
Uttarakhand Tunnel Collapse (Indian Express)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
On November 12, the under-construction Silkyara-Barkot tunnel on the Yamunotri National Highway in Uttarakhand’s Uttarkashi district collapsed.
News Summary:
- On November 12, 2023, the Silkyara Bend - Barkot tunnel, which was under construction, collapsed in the Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
- The collapse trapped at least 40 workers inside the tunnel.
- The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), the State Disaster Response Force (SDRF), and the police promptly initiated and led the rescue operations.
- The tunnel is a part of the Char Dham all-weather road project which commenced in 2016.
What is the Char Dham All Weather Road Project?
- It is a central govt. Project to improve the existing condition of Highways in the state of Uttarakhand.
- In this project, the govt. will upgrade and develop the road which connects all four 'Dhams' i.e.
- Gangotri, Yamunotri, Kedarnath, and Badrinath in the upper Himalayas.
- The 12,000-crore dream project will turn 1100 km of damaged highways of Uttarakhand into all-season roads.
About the Silkyara Tunnel which Collapsed:
- The tunnel, designed to connect Silkyara to Dandal gaon in Uttarkashi district, spans a total length of 4.5 km.
- As part of the Char Dham all-weather road project, this double-lane tunnel is recognized as one of the longest and aims to reduce the journey from Uttarkashi to Yamunotri Dham by 26 kilometers.
- Construction progress includes 2.3 km completed from the Silkyara side and 1.6 km from the Barkot end. Approximately, a 400m stretch of the tunnel is yet to be constructed.
- Regarding the incident:
- The Silkyara Tunnel, located on Uttarkashi-Yamnotri Road, became the site of the accident where workers are currently trapped. The collapse occurred approximately 270m from the entrance on the Silkyara side.
What are the Tunnel Excavation Techniques Utilised in India?
In India, two primary methods of Tunnel Excavation are employed: the drill and blast method (DBM) and tunnel-boring machines (TBMs).
- Tunnel-boring machines (TBMs): TBMs bore into the rock from the front using a rotating head.
- The excavated tunnel section is supported by installing precast concrete segments.
- TBMs are preferred when the rock cover is up to 400 meters in height.
- Notably, the TBM method was applied in constructing tunnels for the Delhi Metro.
- Drill and Blast Method (DBM): DBM involves drilling holes into the rock and loading them with explosives.
- Upon detonation, the rock breaks apart.
- DBM is the chosen method for mountains ranging from 1000 to 1200 meters in height.
- This method is commonly used for tunnel construction in the Himalayas, Jammu & Kashmir, and Uttarakhand.
What could be the Possible Causes of the Tunnel Collapse in Uttarakhand?
- Presence of Fractured or Fragile Rock: Fractured rocks with numerous joints are weaker, making them susceptible to collapse under significant overhead weight, possibly leading to tunnel collapse.
- Water Seepage: Over time, water seepage can erode loose rock particles, creating a void on the top of the tunnel, which might contribute to the tunnel caving in.
- Landslide-Prone Young Himalayan Rock System: The proximity of the incident site to the Main Central Thrust (MCT)/Barkot thrust of the Himalayas raises the possibility that seismic waves could trigger a landslide in the tunnel.
- Improper Study of Shear Zone and Lack of Protection Measures: Experts suggest that the lack of adequate geological mapping studies of the shear zone and failure to implement protective measures, such as steel ribs, rock bolts, or shotcrete, may have contributed to the collapse due to insufficient monitoring.
In addition to these, expert-provided reasons, concerns have been raised about the Himalayas' fragility in supporting massive infrastructure projects like the Char-Dham project and large-scale hydroelectric power projects.
What Measures Have Been Taken to Ensure Safe Tunnel Construction in India?
- Establishment of Tunnel Zone Department in the MoRTH: A dedicated Tunnel Zone department has been set up in the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- Its primary role is to enhance tunneling capabilities and formulate guidelines for the design and construction of tunnels.
- Formation of Expert Committee on Tunnel: An Expert Committee on Tunnel has been constituted to address technical challenges arising during the implementation of tunnel projects across the country.
- Indian Standard Code for Tunnel Construction: The issuance of Indian Standard Codes, specifically IS 15026 (2002) and IS 4756 (1978), provides comprehensive guidelines for tunnel design, lighting, and ventilation.
- Implementation of IRC Codes for Tunnels: The implementation of the IRC code for tunnels in 2019 ensures that road tunnels adhere to international standards.
- Adherence to Standard Codes in Tunnel Construction: Ensuring compliance with various standard codes, including Integrated Tunnel Control Systems (ITCS), The Work in Compressed Air Regulations 1996, Emergency Evacuation and Rescue Plans for tunnels, and guidelines from the Research Designs and Standards Organisation (RDSO).
- Incorporation of International Tunnelling and Underground Space Association Safety Practices: Following safety practices outlined by the International Tunnelling and Underground Space Association, emphasizing specific escape routes marked by signs and the development of contingency plans for emergency situations during tunnel construction.
What Steps Should Be Taken for Ensuring Safe Tunnel Construction?
- Enhanced Geotechnical Studies: In India, the simultaneous design and construction of tunnel projects should be accompanied by more detailed geotechnical studies, including petrographic analysis.
- This information is crucial for incorporating precise design and construction elements into the tunnel project.
- Ongoing Monitoring by Specialist Geologists: Independent specialist geologists should regularly visit construction sites to conduct thorough inspections.
- This practice ensures the early identification of potential failures and helps determine the stand-up time of the rock. (Rock stand-up time refers to the duration for which a rock can remain stable without support.)
- Testing Adequacy of Tunnel Supports: All tunnel supports, such as shotcrete, rock bolts, steel ribs, and tunnel pipe umbrellas, need rigorous testing to ensure their adequacy in preventing tunnel collapse.
- This proactive approach helps in maintaining the stability and integrity of the tunnel structure.
- Emergency Evacuation Arrangements: Robust arrangements for safe evacuation in the event of a collapse are imperative.
- Deployment of National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) personnel, along with the provision of proper safety equipment, is essential. Construction companies bidding for projects should submit comprehensive safety plans as part of their project proposals.
High Court Quashes Haryana Govt's 75% Quota in Private Sector Jobs (Indian Express)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Punjab and Haryana High Court on Nov 17 quashed a law passed by the Haryana government in 2020 that provided 75% reservation in private jobs to residents of the state.
Context:
- The Punjab and Haryana high court on Friday struck down a Haryana law that reserved 75% private sector jobs, paying up to ?30,000 a month, for local candidates.
- The court found it unconstitutional and stated that the 2021 law violated fundamental rights as per the Constitution, emphasizing that individual rights should align with the Constitution's text and spirit, not popular or majoritarian notions.
Key Provisions of Haryana State Employment of Local Candidates Act 2020:
- The Act is applicable to all private companies, societies, partnership firms, trusts, any person employing ten or more persons in Haryana, or any other entity as may be notified by the Government.
- The Act requires private sector employers to reserve 75% of job posts that offer a salary of less than INR 30,000 for individuals who are domiciled in Haryana.
- The Government of Haryana has also made the residency (domicile) requirement to 5 years for a person to obtain a residency certificate.
- The Act enables the Haryana Government to focus on securing employment opportunities for domiciled individuals.
- However, domiciled linked reservations are not a new concept since other States have also introduced similar laws.
- For instance, the Government of Andhra Pradesh notified the Andhra Pradesh Employment of Local Candidates in the Industries / Factories Act, 2019 which provided for reservation of 75% of posts in existing and upcoming factories, industries, joint ventures, and public-private partnership projects for local candidates.
- However, central or state governments or any organisation owned by them were kept outside the ambit of this Act.
- Employers can seek an exemption if enough local candidates with required skills are unavailable; the Designated Officer decides based on an inquiry.
- The law was made applicable for 10 years but was stayed by the high court last year.
Haryana was also one of several states that have enacted laws in recent years to provide reservations for local residents in the private sector. These include Maharashtra (up to 80% quota), Karnataka (75%), Andhra Pradesh (75%) and Madhya Pradesh (70%). However the validity of most of these laws has been challenged before the Supreme Court and high courts.
Who challenged the law and on what grounds?
- The Faridabad Industries Association and other Haryana-based associations went to court, contending that Haryana wanted to create reservations in the private sector by introducing a policy of “sons of the soil”, which was an infringement of the constitutional rights of employers.
- The petitioners argued that private sector jobs are purely based on skills and an analytical bent of mind, and employees have a fundamental right to work in any part of India.
- Therefore, they argued, “The act of the respondent (government) forcing the employers to employ local candidates in the private sector vide this impugned Act is the violation of the federal structure framed by the Constitution of India, whereby the government cannot act contrary to the public interest and cannot benefit one class”.
- The Haryana government argued that it had the power to create such reservations under Article 16(4) of the Constitution, which says that the right to equality in public employment does not prevent the State from “making any provision for the reservation of appointments or posts in favour of any backward class of citizens which, in the opinion of the State, is not adequately represented in the services under the State”.
What was the ruling of the High Court?
- The High Court ruled that the law violates Part III of the Constitution (Fundamental Rights) and declared it ineffective "from the date it came into force."
- It expressed concerns that certain provisions, such as the obligation for employers to submit quarterly reports and the authorization for officers to request documents or verification, resembled an "Inspector Raj" situation.
- The court concluded that the state's actions constituted an "absolute control over a private employer," leading to violations of an individual's right to engage in occupation, trade, or business under Article 19(1)(g) of the Constitution.
- The judges held that notions about individual rights have to be in accordance with the text and spirit of the Constitution and not popular or majoritarian notions.
- The court also said that:
- “The state cannot direct the private employers to do what has been forbidden to do under the Constitution of India.
- It cannot do such discrimination against the individuals on account of the fact that they do not belong to a certain state and have a negative discrimination against other citizens of the country”.
The Structure and Development of Reservations in Public Employment in India:
- Reservation in public employment was initially limited to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Later extended to include Other Backward Classes (OBCs) based on Mandal Commission recommendations (1980).
- Mandal Commission's Recommendations:
- The Mandal Commission proposed a 27% reservation for OBCs in central services and public sector undertakings.
- This was an addition to the existing reservation for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Constitutional Perspective: Reservation is not a fundamental right.
- While the constitution emphasizes non-discrimination in public employment, the state has the authority to promote specific societal sections through reservation in education or employment.
- Basis for Reservation: Reservation can be based on factors such as domicile (residence) or backwardness.
- Parliamentary Authority: Parliament can enact laws regarding employment to a state office, specifying requirements like residence within that state (Article 16(3)).
- State's Authority: The State has the power to advance socially and educationally backward classes or Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Article 15(4)).
- Provisions can be made to reserve posts for backward classes not adequately represented in the State services (Article 16(4)).
Some Important Judgements related to Reservation:
- Indra Sawhney v. Union of India Case (1992):
- The court affirmed the constitutionality of 27% reservation but set a 50% cap on public employment reservation.
- The court recommended excluding advanced sections within OBCs (creamy layer) from reservation benefits.
- M.Nagaraj v. Union Of India Case (2006 ):
- The Supreme Court validated the constitutional legitimacy of the 77th Amendment, allowing the state to reserve posts for underrepresented backward classes.
- It emphasized excluding the creamy layer from the reservation, extending this principle to Scheduled Castes and Tribes.
- Dr. Jaishri Laxmanrao Patil vs Chief Minister Case (2021):
- The Supreme Court reaffirmed the Indra Sawhney decision and invalidated Section 4(1)(a) and Section 4(1)(b) of the Act.
- These sections provided 12% reservation for Marathas in educational institutions and 13% reservation in public employment.
- This judicial decision sent a strong message, highlighting instances where certain state governments exceeded the prescribed limits on reservations without any justifiable exceptional circumstances.
- Janhit Abhiyan (EWS) Case (2022):
- The Supreme Court upheld the validity of the 103rd Constitutional Amendment, providing 10% reservation for Economically Weaker Sections (EWS).
- The court clarified that the EWS quota doesn't breach the 50% reservation cap, as it falls within the non-reserved category.
India, UK Proposed Free Trade Agreement (FTA) (Indian Express)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
India and the UK officials are expected to soon hold the next round of talks for the proposed free trade agreement (FTA) to iron out differences on issues such as social security pact, automobiles, medical devices, and the movement of professionals.
Context:
- External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar discussed the India-UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with Britain’s Prime Minister Rishi Sunak and Foreign Secretary David Cameron recently.
- These talks were held as the bilateral trade between India and the UK increased to USD 20.36 billion in 2022-23 from USD 17.5 billion in 2021-22.
- When signed, the India-UK FTA will serve as a template for an agreement with India’s second-largest trade partner, the European Union (EU).
- Breaking from the look east policy for trade deals under the UPA that saw widening deficits with Japan, South Korea, and ASEAN countries, the government is counting on economic integration with Western and African nations to fuel export growth.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is a deal between two or more countries aimed at lessening obstacles to the exchange of imports and exports.
- In a free trade arrangement, goods and services can move across borders with minimal government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or prohibitions.
- This concept stands in contrast to trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs can take various forms, such as Preferential Trade Agreements, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements, and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPAs).
Expectations from the India-UK Free Trade Agreement:
- Merchandise Trade: Indian products like petroleum, medicines, diamonds, machine parts, airplanes, and wooden furniture worth $6 billion already enjoy tariff-free access to the UK, even without the FTA, so there might be limited additional benefits.
- Services: India aims for immediate advantages, such as obtaining priority visas for Indian professionals on short-term assignments in the UK.
- However, acquiring a substantial number of short-duration business visas may be challenging, given the UK's cautious approach post-Brexit, associating visas with immigration.
- Rules of Origin: Ensuring that products from third countries receive FTA benefits only if they undergo significant transformation in the exporting country.
- India's preference for conservative rules of origin may lead to prolonged discussions and negotiations.
- Government Procurement: Allowing UK producers to sell to India’s government procurement sector would create a level playing field.
- Conversely, Indian firms may face a competitive and restricted government procurement market in the UK, necessitating a cautious approach.
- Labour Standards, Gender, Environment, Digital Trade, IPRs: India should establish domestic rules/standards before committing to these aspects under the FTAs.
- Until then, India must avoid undertaking burdensome obligations on non-trade issues.
Factors Behind the India-UK Free Trade Agreement:
- The China Factor: Disruptions in supply chains during the pandemic highlighted the risks of excessive reliance on China, leading Western companies to adopt a 'China-plus one' approach.
- Australia's tensions with China and the complementary nature of the Indian economy created a compelling case for a trade deal between India and the UK.
- India's RCEP Exit: Following its withdrawal from the China-dominated Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), India has been actively pursuing trade agreements with the UK, Australia, and the EU to balance its regional engagement against China.
- Brexit Impact: The UK, facing a challenging election in early 2025, sees a trade deal with India as crucial.
- The negotiations are influenced by the post-Brexit landscape as the UK seeks to strengthen its economic ties globally.
What India will Gain from this FTA?
- India’s labour-intensive sectors such as apparel and gems and jewellery have seen a steep decline in market share over the last five years.
- Indian textile exports face tariffs walls as high as 10% in the UK; a trade deal could put India on par with competition such as Bangladesh, and revive textile exports.
- However, the British Parliament has been warned in a report that granting zero-duty access to Indian textiles under the FTA could bring stress on Least Developed Countries such as Bangladesh.
UK Gain in this Deal:
- Past deals with Japan and the ASEAN countries have shown that the elimination of duty does not automatically result in export growth.
- Also, many Indian exports to the UK already enjoy low or zero tariffs, while British exports to India such as cars, Scotch whisky, and wines, face considerable tariffs of 100-150%.
- Tariff reductions on these goods will potentially offer them deeper access into Indian markets.
- Notably, the average tariff on goods imported from India into the UK is 4.2% but the average tariff in India on goods imported from the UK is 14.6%
What are the Challenges in the India-UK FTA?
- Non-tariff barriers: Modern FTAs go beyond tariff reduction. India could use the negotiations to eliminate non-tariff barriers (NTBs) that have historically been a concern for exporters, especially for agri exports.
- NTBs often come in the form of regulations, standards, testing, certification, or pre-shipment inspection that are aimed at protecting human, animal, or plant health and the environment.
- Vegetable and fruit exporters often face strict limits imposed by European economies on pesticides and other contaminants in agri imports.
- In manufacturing too, Indian products face high rejection based on conformity assessments and technical requirements.
- Issue of carbon tax: Like the EU, the UK is looking to impose a levy on metal imports based on carbon emissions.
- An EU-style carbon border adjustment mechanism (CBAM) will hurt India’s exports to the UK even if India wins significant removal of tariffs.
- The UK’s carbon tax could be harsh, as one of its aims is to reduce dependence on Russian energy imports.
Sub-categorisation Within Castes (The Hindu)
- 17 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
In an election rally in Telangana, Prime Minister Narendra Modi promised to look into the sub-categorisation of Scheduled Castes (SCs) to identify and help the most backward among them.
Context:
- During an election rally in Telangana, Prime Minister Narendra Modi pledged to examine the sub-categorization of Scheduled Castes (SCs) to identify and support the most backward among them.
- This move is perceived as the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) aiming to attract the Madiga community.
- The Madigas, the largest among all SC communities in the State, have asserted that another SC community, the Malas, is occupying their rightful share of representation.
Is Sub-categorisation within Castes legal?
- Historical Context: The issue arose in 1996 when the Andhra Pradesh government formed a one-man Commission under Justice Ramachandra Raju.
- The Commission recommended sub-categorization of SCs in the state based on evidence of varying backwardness and representation among communities.
- The attempt to implement this recommendation led to legal challenges, reaching the Supreme Court in 2004.
- The Supreme Court then ruled that states lack the power to unilaterally sub-categorize communities in the SCs or Scheduled Tribes (STs) list.
- Legality of Sub-categorization: Over the past two decades, states like Punjab, Bihar, and Tamil Nadu have attempted to enact reservation laws at the state level for sub-categorizing SCs.
- Legal proceedings have ensued, with the Supreme Court establishing a larger Constitution Bench to make a decision on the matter.
- Contradictory Judgments: In a 2020 judgment, a five-judge Bench, led by Justice Arun Mishra, stated that deciding on the benefits in the SCs/STs lists would not be considered "tinkering," and states could proceed.
- This contradicts the 2004 Supreme Court ruling and has led to the 2020 judgment being referred to a larger Bench for clarification.
What is the Union Government’s Stand?
- The Union government established a National Commission to investigate the sub-categorization of Scheduled Castes (SCs) in Andhra Pradesh.
- The Cabinet at that time proposed an amendment to Article 341 of the Constitution of India to facilitate sub-categorization.
- Both the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) and the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) expressed the view that a constitutional amendment was unnecessary.
- They pointed out that Article 16(4) of the Constitution already empowered states to formulate special laws for any backward classes they deemed under-represented.
Arguments in favour of Sub-Categorization within SCs:
- From the Justice Raju Commission to the National Commission, the principal argument for sub-categorisation of SCs has been the graded inequalities among SC communities.
- The Justice Raju Commission was formed by the Andhra Pradesh state government in 1996 to look into the matter.
- The thrust of it has been that even among the marginalised, there are communities that have lesser access to basic facilities.
- As a result, the relatively more forward communities among them have managed to avail benefits consistently while crowding the more backward ones out.
- The solution, therefore is to sub-categorise the communities and provide separate reservations to the more backward communities within the reservation meant for SCs.
Arguments Against Sub-Categorisation within SCs:
- Both the SC and ST Commissions have noted that allotting separate reservations within the categories would not really address the root cause of the problem.
- In an internal note prepared by the NCST, it explained that the most backward SCs are lagging so far behind forward SC communities that a separate quota would not help.
- It said that the idea was to ensure representation at all levels.
- But given the disparity, even if posts were reserved at higher levels, these most backward SCs would not have enough candidates to be considered for it in the first place.
- Both the NCSC and the NCST had thus recommended that existing schemes and government benefits should first reach these sections before any sub-categorisation.
Legal experts emphasize the crucial need for substantial data to substantiate the sub-categorization initiative. But what is primarily needed is concrete population numbers of each community and sub-community and their respective socio-economic data, which are the only thing that can provide a reasonable ground to decide how castes can be categorised, how much percentage should be given, etc.
National Commission for Scheduled Castes:
- The National Commission for Scheduled Castes is a constitutional body established with a view to providing safeguards against the exploitation of Scheduled Castes and Anglo-Indian communities to promote and protect their social, educational, economic, and cultural interests, special provisions were made in the Constitution.
- Article 338 of the Indian constitution deals with National Commission for Scheduled Castes.
- Historical Evolution:
- Initially, Article 338 of the Constitution provided for the appointment of a Special Officer, known as the Commissioner for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- 65th Amendment Act, 1990 replaced the single-member system with the establishment of a multi-member National Commission for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST).
- The 89th Amendment Act, 2003 resulted in the creation of two separate commissions in 2004:
- National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC)
- National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST)
Composition:
- The NCSC comprises a Chairperson, a Vice-Chairperson, and three additional Members, appointed by the President through a warrant under his hand and seal.
- The President of India also determines their conditions of service and tenure of office.
Functions:
- The NCSC is entrusted with several key responsibilities, including:
- Investigating and monitoring matters related to constitutional and legal safeguards for the SCs.
- Inquiring into specific complaints regarding the deprivation of rights and safeguards of the SCs.
- Participating in and advising on the planning process for the socioeconomic development of the SCs.
- Evaluating the progress of SC development under the Union or a state.
- Presenting annual reports to the President on the functioning of these safeguards.
- Making recommendations for effective implementation of safeguards and other measures for the protection, welfare, and socioeconomic development of the SCs.
- Evolution of Responsibilities:
- Until 2018, the NCSC also addressed similar functions concerning the Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
- However, the 102nd Amendment Act, 2018, relieved the commission of this responsibility.
National Commission for Scheduled Tribes:
- It was formed in 2004 by amending Article 338 and introducing Article 338A through the 89th Constitution Amendment Act, making it a constitutional body.
- Objective:
- Article 338A empowers the NCST to oversee the implementation of safeguards for Scheduled Tribes (STs) under the Constitution, prevailing laws, and government orders, and to assess the effectiveness of these safeguards.
- Composition:
- Comprises a Chairperson, a Vice-Chairperson, and three Members appointed by the President through warrant.
- Mandated that at least one Member must be a woman.
- Term of office for the Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson, and Members is three years.
- Chairperson holds the rank of Union Cabinet Minister, Vice-Chairperson as Minister of State, and other Members as Secretary to the Government of India.
- Members are ineligible for appointments beyond two terms.
- Duties and Functions:
- Investigation and Monitoring: Examine and monitor all matters concerning safeguards for STs under the Constitution, existing laws, and government orders.
- Complaint Inquiry: Investigate specific complaints regarding the denial of rights and safeguards for STs.
- Advisory Role: Participate and advise in the planning of socio-economic development for STs, evaluating their progress.
- Annual Reports: Submit annual reports on the operation of safeguards to the President, including necessary recommendations.
- Presidential Rule: The President, following parliamentary laws, may assign additional functions related to the protection, welfare, development, and advancement of STs.
What Is Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) And Why India Is Not A Member (Live Mint)
- 16 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister Piyush Goyal is attending the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation meeting in the United States today, which will also see US President Joe Biden and his Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping hold their second in-person dialogue since Mr. Biden assumed office in 2021, amid tensions and a trust deficit between the two countries.
What is Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)?
- The Asia-Pacific Economic Co-operation (APEC) is a regional economic forum and was formed in 1989.
- It is a grouping of economies around the Pacific Ocean that aims to promote trade, investment, and economic development in the region.
- The bloc is looking to “leverage the growing interdependence of the Asia-Pacific and create greater prosperity for the people of the region through regional economic integration”.
- APEC started with 12 members in 1989 but has over the years grown to 21, which includes the US, China, Russia, Japan, and Australia.
- The other members include Brunei, Hong Kong, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, Indonesia, South Korea, Canada, Mexico, Peru, Chile, Malaysia, Vietnam, Singapore, Thailand and Taiwan.
- Taiwan and Hong Kong, which China stakes claim to as its territory, participate separately in the forum.
- APEC accounts for about 62 percent of global GDP and almost half of global trade and around 2.9 billion citizens.
- As of 2018, they represented 48 percent of global trade.
- It operates based on non-binding commitments with decisions reached by consensus and commitments undertaken voluntarily.
Why is India not a member of the APEC Group?
- India attempted to join APEC in 1991, the year the Indian economy was liberalised.
- A majority of the members of the grouping were in favour of India’s inclusion but some opposed it.
- They had reservations about India’s “protectionist instincts” and cited its records on the economic reforms.
- There was also a freeze on membership since 1997.
- However, it was not extended in 2012.
- In 2016, then Union Minister for Commerce and Industry Nirmala Sitharaman told Parliament that the request to join was based on India’s geographical location, the potential size of the economy, and the degree of trade interaction with the Asia-Pacific.
- India remains an observer of APEC and has been expanding trade and investment ties in the region since the 2000s.
- Among other factors, India’s lack of a Pacific coastline has worked against its membership in APEC, but the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) is clearly meant to give India a more central position, given the US focus on creating alternatives and counterweights to China’s economic influence.
How can India benefit from APEC membership?
- “Becoming an APEC member would bring several benefits for India, such as promoting closer economic relations, facilitating trade and investment flows, and opening market access to major economies.
- Aligning with APEC by simplifying and harmonizing trade procedures and regulations could boost India’s exports, attract foreign direct investment, and support domestic initiatives like ‘Make in India‘.
- A membership could encourage the country to “adopt best practices, streamline trade processes and reduce transaction costs”.
- It could facilitate “technology transfer” in important areas like information technology, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, renewable energy and manufacturing.
- The membership will be helpful for improving flows of knowledge, capital, and goods within the region through better coordination of policies.
- Economies such as Japan and South Korea (members of both APEC and IPEF) are also important for India in terms of the technological and production know-how they can provide, as is Taiwan, which is only a member of APEC.
What is the Significance of APEC?
- Since its formation, the grouping championed the lowering of trade tariffs, free trade, and economic liberalisation.
- As per the US State Department, “During its first five years of operation, APEC established its core objectives.
- In the 1991 Seoul Declaration, APEC member economies proclaimed the creation of a liberalised free trade area around the Pacific Rim as the principle objective of the organisation.”
- The experts at the think tank Centre for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), stated, “The dynamic growth attributable to APEC initiatives contributed significantly to the development of a growing middle class in the developing Asia-Pacific region.
Conclusion
India must independently pursue trade liberalization, excluding China to ease concerns. Multilateral coordination, more efficient than bilateral deals, is crucial. Empirical evidence emphasizes the clear positive impact of trade liberalization on Indian economic growth, surpassing other policy reforms. India's anxieties about trade openness may impede growth.
Engagement in institutions such as APEC and IPEF provides a platform for addressing and isolating these concerns. India's focused approach to trade liberalization is pivotal for navigating economic complexities and fostering meaningful international collaborations.
Mount Etna Eruption: What is a Volcano and How do they erupt? (Indian Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
- Mount Etna, Europe's tallest and most active volcano, erupted again on the island of Sicily on Sunday, November 12, 2023.
- The eruption sent a lava fountain into the air and ash miles into the sky.
- The ash fell on the nearby city of Catania, causing some disruption to air travel.
About Mount Etna:
- Mount Etna is a large stratovolcano on the eastern coast of Sicily, Italy.
- It is the highest and most active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world.
- Its recorded volcanic activity dates back to 1500 B.C. Since then, it has erupted more than 200 times.
- Mount Etna is a complex volcanic system, made up of several different lava domes and craters.
- The summit crater, known as the Voragine, is a large depression that is often filled with lava.
- The volcano also has several calderas, which are large, sunken depressions that are formed by the collapse of the volcano's summit.
- In recent years, Mount Etna has become increasingly active, with several eruptions in the past decade. The most recent eruption began in 2022 and has produced a number of lava flows and ash clouds.
- The eruption has also caused a number of earthquakes, some of which have been felt in nearby towns and cities.
Other volcanoes erupt for much longer than Etna:
- One of the most famous long-term eruptions was the Kilauea volcano in Hawaii.
- Its spewing spree in 1983 continued — almost nonstop — for 35 years until 2018, only to start again in 2021. The eruption is still ongoing.
- Dukono in Indonesia started erupting in August 1933 and is still continuing.
- Santa Maria in Guatemala began erupting in June 1922 and continues to this day.
- Yasur in Vanuatu first rumbled to life in about 1270 (± 110 years) and as of June 2023, was still erupting.
- Lava domes: Lava domes are formations created by the slow extrusion of viscous lava, typically rhyolitic or andesitic, forming a steep-sided mound or dome-shaped structure near a volcano's vent.
- Crater: A volcanic crater is a bowl- or funnel-shaped depression that usually lies directly above the vent from which volcanic material is ejected.
What is a volcano?
- Volcanoes are openings, or vents where lava, tephra (small rocks), and steam erupt onto the Earth’s surface.”
- Volcanoes can be on land and in the ocean.
- They are, in part, a result of their own eruptions but also the general formation of our planet, as tectonic plates move.
- Mountain ranges like the Andes in South America and the Rockies in North America, as well as volcanoes, formed through the movement and collision of tectonic plates.
- How do volcanoes erupt?
- Essentially, it’s a case of magma, or molten rock, below the surface of the Earth, bubbling up, rising, and overflowing, like boiling milk out of a pot on a stove.
- The magma finds its way to vents in the volcano and gets spewed across the land and into the atmosphere.
- When magma erupts from a volcano, it is called lava.
- There are four main types of volcanoes:
- Cinder cones
- Composite or stratovolcanoes
- Shield volcanoes and
- Lava domes
- Their type is determined by how the lava from an eruption flows and how that flow affects the volcano, and, as a result, how it affects its surrounding environment.
- Each volcano is unique and can vary in size and composition, but a crucial aspect of these mountains is the amount of silicon dioxide present in the magma and rocks below the surface.
- A high silica content can lead to violent eruptions that are categorized as explosive.
- Silica makes magma preventing it from readily flowing.
- Eruptions such as Alaska’s Novarupta in 1912 and Washington’s Mount St. Helens in 1980 all were composed of high amounts of silica.
- When silica values are low, eruptions are categorized as effusive with magma that is thinner and tends to be less explosive.
Types of Volcanoes:
- Cinder Cones: Cinder cones are considered to be the most common and simplest type of volcano in the world.
- Their structures are typically small, so their footprint doesn’t cover much terrain.
- Many are considered by volcanologists to be monogenetic and only erupt once during their lifespan.
- Once a cinder cone volcano becomes dormant, it usually never erupts again.
- Composite Volcanoes: Composite volcanoes are some of the largest and the most picturesque of any mountain in the world.
- Eruptions can be explosive and produce devastating impacts.
- Unlike a cinder volcano, composite volcanoes are usually active over a period of thousands of years.
- Mount St. Helens, Krakatoa, Mount Pinatubo, and Hunga-Tonga-Hunga-Ha’apai are all considered to be composite volcanoes, which also can be known as stratovolcanoes.
- The last significant composite volcano eruption was in Tonga in early 2022.
- Shield Volcanoes: This type of volcano is typically the largest on Earth and covers a broad swath of terrain.
- Hawaii’s Mauna Loa and K?lauea are classic examples of shield volcanoes and are among the most active in the world.
- Mauna Loa, from the sea floor base to its top elevation, is more than 33,000 feet tall.
- The great width of these volcanoes is a result of thin lava flows.
- Eruptions are not considered to be eruptive and usually rank low on the VEI.
- Threats from landslides and volcanic smog are usually significant with these types of volcanoes.
- Lava Domes: Lava dome features are usually quite small and due to thick magma, the lava doesn’t have wide impacts.
- These types of volcanoes can be explosive and are frequently found in the craters of composite volcanoes.
- Domes tend to grow from material that builds up over time by hardening lava from eruptions.
- Explosive eruptions can occur with little warning, which makes these features dangerous, if in the immediate area.
Volcanoes that are particularly active in the Pacific Ring of Fire:
- Some of the most active volcanoes are located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, which includes New Zealand, Southeast Asia, Japan, and the western coast of the Americas.
- About 90% of all earthquakes worldwide strike within this region.
Can scientists predict volcanic eruptions?
- Scientists are capable of predicting volcanic eruptions hours, or sometimes several days, in advance.
- This is not the case with earthquakes, which are much harder to predict.
- Scientists use seismographic data from earthquakes and other tremors, because those can be a precursor to volcanic eruptions.
- They monitor the ground for signs of deformation, which may be caused by the movement of magma.
- They also take readings of volcanic gas emissions, and changes in gravity and magnetic fields.
Community Rights & Forest Conservation (The Hindu)
- 14 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023, marks a noteworthy evolution in the environmental legal landscape of India, amending the pivotal Forest (Conservation) Act of 1980. Despite its substantial implications for forest conservation, the recent amendment has garnered limited attention and scant discussion concerning its potential impact on both forests and their inhabitants.
What is a community forest resource?
- The community forest resource area is the common forest land that has been traditionally protected and conserved for sustainable use by a particular community.
- The community uses it to access resources available within the traditional and customary boundary of the village; and for seasonal use of landscape in case of pastoralist communities.
- Each CFR area has a customary boundary with identifiable landmarks recognised by the community and its neighboring villages.
- It may include a forest of any category – revenue forest, classified & unclassified forest, deemed forest, DLC land, reserve forest, protected forest, sanctuary and national parks, etc.
What are Community Forest Resource rights?
- The Community Forest Resource Rights are mentioned under Section 3(1)(i) of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act.
- It is commonly referred to as the Forest Rights Act or the FRA.
- It provides for recognition of the right to “protect, regenerate or conserve or manage” the community forest resource.
- These rights allow the community to formulate rules for forest use by itself and others and thereby discharge its responsibilities under Section 5 of the FRA.
- CFR rights, along with Community Rights (CRs) under Sections 3(1)(b) and 3(1)(c), which include nistar rights and rights over non-timber forest products, ensure sustainable livelihoods of the community.
- (Nistar means the concession granted to agriculturists and Villagers for removal from forest coupes on payment at stipulated rates for specified forest produce for bonafide domestic use, but not for barter sale.)
- These rights give the authority to the Gram Sabha to adopt local traditional practices of forest conservation and management within the community forest resource boundary.
Why is the recognition of CFR rights important?
- Aimed at undoing the “historic injustice” meted out to forest-dependent communities due to curtailment of their customary rights over forests, the Forest Rights Act or the FRA came into force in 2008.
- It is important as it recognises the community’s right to use, manage and conserve forest resources, and to legally hold forest land that these communities have used for cultivation and residence.
- It also underlines the integral role that forest dwellers play in the sustainability of forests and the conservation of biodiversity.
- It is of greater significance inside protected forests like national parks, sanctuaries and tiger reserves as traditional dwellers then become a part of the management of the protected forests using their traditional wisdom.
- But while CFR rights are an important empowerment tool, getting a consensus amongst various villages about their traditional boundaries often proves a challenge.
Key Provisions of the Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
- Land under the Act: The amended law exclusively applies to areas classified under the Forest Act, 1927, and those designated as such on or after October 25, 1980.
- Notably, it excludes forests converted for non-forest use after December 12, 1996.
- The amendments streamline the Act's application to recorded forest lands, private forest lands, plantations, etc.
- Exempted Categories of Land: To encourage afforestation and plantation outside forests, the Bill proposes exemptions, such as providing 0.10 ha of forest land for connectivity along roads and railways, allocating up to 10 ha for security-related infrastructure, and allowing up to 5 ha in Left Wing Extremism Affected Districts for public utility projects.
- Exemptions also cover strategic projects related to national security within 100 km of international borders.
- Leasing of Forest Land: The Act mandates prior approval from the central government for the assignment of forest land to any entity, whether government-controlled or not.
- This condition now applies to all entities, with approval subject to terms and conditions specified by the central government.
- Permitted Activities in Forest Land: Restrictions on de-reservation or non-forest use of forest land may be lifted with prior approval from the central government.
- The Act outlines specific activities exempt from non-forest purposes, including those related to the conservation, management, and development of forests and wildlife.
- Expansion of Delegated Legislation Power: The amendment broadens the Central Government's power for delegated legislation.
- In addition to making Rules, it now includes the authority to issue "directions" to central government authorities, state governments, union territories, or any recognized organization, entity, or body, ensuring effective implementation of the Act's provisions.
Key Concerns with the Amendment:
- Redefining Forests: The amendment introduces a contradiction to the established definition of forests by the Supreme Court in 1996.
- This change, making any tree patches recorded as forest in government records deemed as forests, jeopardizes legal safeguards for approximately one-fifth to one-fourth of India's forests, as reported by the Public Action Committee (PAC) in Punjab.
- Infrastructure Encroachment: The exemption of land near border areas for national security projects raises concerns about adverse effects on forest cover and wildlife in northeastern states.
- Broad exemptions for projects like zoos, eco-tourism facilities, and reconnaissance surveys may also negatively impact forest land and wildlife.
- Neglect of Tribal Rights: The amendment removes the requirement for prior consent from tribal grama sabhas for alterations to forests for non-forest purposes.
- Allowing private companies to use forest land for ecotourism could prioritize corporate interests over tribal communities' livelihoods, potentially leading to the erosion of local cultures and traditions due to mass tourism.
- Top-Down Authority: Concerns have been raised about potential forest exploitation by profit-driven private companies and the consolidation of power in the central government, potentially neglecting the concerns of state governments.
- This shift in authority could lead to imbalances and adverse consequences for forest management.
- Human-Animal Conflicts: Allowing infrastructure development on forest land without addressing the growing issue of human-animal conflicts in tribal hamlets poses threats to both livelihoods and wildlife.
- The amendment lacks provisions to mitigate or prevent such conflicts, potentially exacerbating the situation.
The Path Ahead:
- Empowerment of Local Communities: Empower local communities, especially tribal groups, by involving them in decision-making processes, recognizing traditional knowledge, and ensuring equitable benefits from forest resources.
- Reinforce legal safeguards to protect indigenous communities' rights and heritage.
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): Strengthen the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process to comprehensively assess proposed projects' environmental impact.
- This ensures sustainable development while minimizing ecological damage and informs decision-makers.
- Stakeholder Consultation: Conduct extensive consultations with environmental experts, tribal communities, local stakeholders, and NGOs to address concerns and integrate diverse perspectives.
- Prioritize inclusiveness, local participation, and transparency in decision-making processes.
- Capacity Building: Invest in capacity building for relevant authorities to ensure effective implementation of the Act, adherence to guidelines, and competent decision-making.
- This enhances the capability of authorities to manage and regulate the Act efficiently.
- Transparency in Decision-Making: Ensure transparency in decision-making regarding forest land use, exemptions, and infrastructure projects to foster trust among stakeholders.
- Transparent processes enhance accountability and public trust.
- Periodic Review Mechanism: Establish a robust periodic review mechanism to evaluate the Act's impact on forests, biodiversity, and local communities.
- Adjustments should be made based on findings, considering feedback and evolving circumstances.
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Establish efficient conflict resolution mechanisms to address disputes arising from the Act.
- Provide a fair platform for all stakeholders to voice concerns and seek resolution, promoting constructive dialogue.
- Scientific Research and Monitoring: Promote scientific research to monitor the Act's impact on forest ecosystems, biodiversity, and climate goals.
- Use data-driven insights for informed policy adjustments and develop adaptive management strategies for unforeseen challenges.
These comprehensive steps collectively form a holistic approach to navigating the complexities of forest management, ensuring sustainability, equity, and the preservation of environmental integrity.
Digital Advertisement Policy, 2023 (Indian Express)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government recently announced that it had approved a new policy allowing its advertising wing, the Central Bureau of Communication (CBC), to undertake advertisement campaigns on social media, OTT platforms, and other digital media.
News Summary:
- The government has introduced a digital advertising policy, facilitating websites with a minimum of 2.5 lakh unique users per month, OTT platforms, and podcasts to participate in publicity campaigns.
- Released by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, the policy empowers the Central Bureau of Communication (CBC) to conduct digital media campaigns.
- The policy incorporates competitive bidding for rate discovery, ensuring transparency for three years.
Key Provisions of the Digital Advertisement Policy, 2023:
- Empowerment for Digital Campaigns: The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting has formally sanctioned the implementation of the "Digital Advertisement Policy, 2023." This landmark decision aims to empower the Central Bureau of Communication, facilitating the execution of comprehensive campaigns within the Digital Media Space.
- Mission Alignment with Evolving Media Landscape: In response to the dynamic changes in the media landscape, this policy marks a significant milestone in CBC's mission.
- It focuses on disseminating information and raising awareness about various government schemes, programs, and policies.
- Expansion into Digital Platforms: The policy extends CBC's reach into the realm of digital advertising by allowing the empanelment of agencies and organizations in the Over-The-Top (OTT) and Video on Demand Space.
- Leveraging Podcasts and Digital Audio: CBC can now capitalize on the growing number of listeners on Podcasts and Digital Audio platforms.
- Empanelment of Digital Audio platforms facilitates the dissemination of government messages to a broader audience.
- Mobile Application Outreach: For the first time, CBC has the capability to channelize public service campaign messages through Mobile Applications.
- This diversifies the channels through which government communication can reach the public.
- Streamlined Advertisement on Social Media: Recognizing the popularity of Social Media Platforms as channels for public conversations, the policy simplifies the process for CBC to place advertisements for government clients on these platforms.
- Enhanced Outreach with Digital Media Agencies: The policy empowers CBC to panel Digital Media Agencies, further expanding its outreach through various digital platforms.
- This enhances the ability to effectively communicate government initiatives.
- Embracing Innovation and Transparency: The policy acknowledges the dynamic nature of the digital landscape and allows CBC to onboard New and Innovative Communication Platforms within the Digital Space.
- The approval process involves a duly constituted committee.
- Competitive Bidding and Rate Discovery: An important aspect of the policy is the introduction of competitive bidding for rate discovery, ensuring transparency and efficiency in the selection of advertising rates.
- Rates discovered through this process remain valid for three years and are applicable to all eligible agencies.
Why is there a need for the Digital Advertisement Policy?
Digital advertising is the promotion of products and services via online platforms like streaming media, websites, and more. Digital advertisements are available in text, image, audio, and video formats.
- Impact of Digital India Initiative: The government's Digital India initiative has significantly increased the country's internet connectivity, leading to a substantial rise in the number of people engaged with online and social media platforms.
- Substantial Internet Penetration: Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) reports internet penetration in India surpassing 880 million as of March 2023, highlighting the extensive reach and potential of digital media.
- Consultative Policy Formation: The Digital Advertisement Policy 2023 has been formulated after extensive discussions involving various stakeholders, ensuring a comprehensive and inclusive approach to its design.
- Enhancing Citizen Outreach: This policy serves as a roadmap for amplifying the Government of India's digital outreach efforts, aiming to enhance information dissemination to its citizens, aligning with the evolving digital landscape.
About Central Bureau of Communication:
- Central Bureau of Communication (CBC) is a unit of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- It has the mandate of providing 360 degrees communication solutions to Ministries, Departments, Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), and autonomous bodies.
- It was set up in December 2017 by the integration of the erstwhile Directorate of Advertising and Visual Publicity (DAVP), Directorate of Field Publicity (DFP), and Song & Drama Division (S&DD).
- With 23 Regional Offices (ROs) and 148 Field Offices (FOs), CBC is engaged in the process of educating people, both rural and urban, about the Government’s policies and programmes to evoke their participation in developmental activities.
- As an advisory body to the government on media strategy, CBC aims to elevate the government's image as the key enabler of public empowerment, adapting policies to match the evolving media landscape.
- CBC comprises divisions such as the Advertising and Visual Communication Division, Folk Communication Division, and Field Communication Division, each employing different forms of communication—ranging from traditional media to live performances—to maximize outreach and understanding of government schemes among the populace.
- CBC orchestrates comprehensive and integrated communication campaigns that transcend singular advertising efforts, employing a diverse range of communication channels to disseminate information and engage with the public extensively.
Ben Gurion Canal: An Alternative to the Suez Canal (Indian Express)
- 11 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Speculation suggests that Israel's desire to control the Gaza Strip, including the elimination of Hamas, may be tied to a long-debated economic opportunity, the Ben Gurion Canal Project.
Historical Context: Ben Gurion Canal Project:
- This ambitious project aims to chart a course from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean, echoing historic initiatives such as the Suez Canal, which has long been a pivotal maritime route since its completion in the 19th century.
- The proposed Ben Gurion Canal not only signals Israel’s aspirations to claim a stake in global trade dynamics but also reflects the ongoing quest to expand its geopolitical influence, a narrative that has been part of the region’s history since Israel’s establishment in 1948.
A Rivalry Revived
- The Ben Gurion Canal, if completed, would challenge the supremacy of the Suez Canal, potentially diverting commerce and reshaping economic currents.
- The strategic move can be seen as a continuation of the historical tensions that saw Israel and Egypt at odds during the Suez Crisis in 1956, where control over this critical passageway was a central issue.
About the Ben Gurion Canal Project:
- The Ben Gurion Canal Project, named after Israel’s founding father David Ben-Gurion (1886-1973), remains one of the most ambitious infrastructure projects ever planned on paper.
- It was first envisioned in the 1960s to create an alternative route to the Suez Canal, potentially enhancing economic prospects in the region.
- Estimated cost may exceed $100 billion.
- The idea is to cut a canal through the Israeli-controlled Negev Desert from the tip of the Gulf of Aqaba — the eastern arm of the Red Sea that juts into Israel’s southern tip and south-western Jordan — to the Eastern Mediterranean coast.
Historical Significance of Suez Canal:
- Upon its 1869 opening, the Suez Canal transformed global maritime trade.
- Linking the Mediterranean and Red Seas via the Isthmus of Suez, it facilitated direct ship passage between Europe and Asia, circumventing the need to navigate around the entirety of Africa.
- The canal significantly reduced the travel distance between London and Bombay (now Mumbai) by over 41 percent.
- During the 2022-23 fiscal year, approximately 26,000 vessels traversed the Suez Canal, contributing to nearly 13 percent of global shipping.
What are the Issues with the Suez Canal?
- The Suez Canal, stretching 193 km in length, 205 m in width, and 24 m in depth, stands as the world's largest shipping bottleneck.
- Despite being widened and deepened over the years, it remains perennially congested, with long queues at either end.
- In March 2021, the mammoth cargo ship Ever Given got stuck in the canal, blocking passage for more than a week.
- It was estimated that the resulting “traffic jam” held up an estimated $ 9.6 billion of goods every day.
- Also, Egypt’s control over the waterway has been a source of conflict for almost 70 years now.
- In 1956, after President Gamal Abdel Nasser (1918-70) decided to nationalise the canal, war broke out, with the UK, France, and Israel attacking Egypt in order to regain control.
- The Suez Crisis ended in a military victory for the aggressors but an overwhelming political victory for Egypt, which kept control over the canal, which was shut for more than six months due to the conflict.
- This was also a pivotal moment in the Cold War, with Soviet threats of intervention key to stopping the allied aggression against Egypt.
- The Suez Canal was also the focal point of both the 1967 and 1973 Arab-Israeli wars, and was shut from 1967-75.
- However, the canal holds immense significance for Egypt's economy.
- The Suez Canal Authority collects all toll revenue generated, along with the local economic advantages it provides.
- In the 2022-23 fiscal year, toll revenues reached a record $9.4 billion for Egypt's Suez Canal Authority, contributing to almost 2 percent of Egypt's GDP, which stood at $476.8 billion, as per the World Bank.
Thus, for the West, a shipping lane through Israel would be ideal:
- The idea of a new shipping route through Israel has long interested the West.
- A declassified 1963 US government memo proposed using nuclear explosives to create a 160-mile sea-level canal across Israel, connecting the Mediterranean to the Gulf of Aqaba.
- This alternative to the Suez Canal was seen as strategically important and potentially beneficial for regional economic development.
What is preventing Israel from constructing the canal?
- Cost and Complexity: One of the primary obstacles was the immense cost and complexity of such an endeavor.
- Estimates suggested a price tag of up to $100 billion, significantly higher than the potential cost of widening the existing Suez Canal to address its traffic issues.
- Consideration of Nuclear Excavation: Due to the high cost of conventional excavation, planners explored the controversial concept of using nuclear explosives for construction, as indicated in a declassified 1963 US government memorandum.
- Of course, this is also a very dangerous choice due to the possibility of radioactive fallout.
- Geographical Limitations: The proposed route faced challenges due to the topography and terrain, resulting in a planned canal that was over 100 kilometers longer than the Suez Canal.
- Economic Viability and Preference for Shorter Routes: Even if the project were to be realized, concerns existed about the economic viability as many ships might continue to favor the shorter, established route via the Suez Canal.
- Geopolitical Challenges: The region's ongoing military threats, including the constant risk from conflicts and attacks, presented significant concerns for the feasibility and security of a canal carrying billions of dollars in freight daily.
Cash For Query Charges: Mahua Moitra To Be Barred From The LS (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Ethics Committee of Lok Sabha, which inquired into the cash-for-query allegations leveled by BJP MP Nishikant Dubey against TMC MP Mahua Moitra, adopted its draft report Thursday, recommending her expulsion from the 17th Lok Sabha for “unethical conduct” and “serious misdemeanors.”
Cash-for-Query (Mahua Moitra) News Summary:
- The report recommending Moitra's expulsion was labeled 'prejudiced and incorrect' by 4 opposition panel members.
- They accused the Ethics Committee chairman and BJP members of breaching rules by leaking panel proceedings.
- Next Steps: Former Lok Sabha Secretary General P. D. T. Achary states that the speaker now holds the authority to decide whether the report will be made public.
- In the upcoming parliamentary session, the committee's chairperson will present the report, sparking a debate and a subsequent vote on the member's expulsion.
- This event could mark a historic moment as it might be the first time the Lok Sabha Ethics Committee suggests an MP's expulsion.
- A prior 'cash-for-query' case in 2005 saw 11 MPs facing expulsion, but it was the Rajya Sabha Ethics Committee and a Lok Sabha Inquiry Committee that proposed those expulsions.
The 2005 Cash-for-Query Scandal:
- Back in 2005, a hidden camera sting operation exposed the involvement of 11 Members of Parliament who were allegedly willing to use their positions to promote a company and ask questions in the House in exchange for money.
- As a result of the parliamentary committee's investigations, 10 Members of Lok Sabha faced expulsion from the lower house.
- Furthermore, the Rajya Sabha conducted its own inquiry through the Ethics Committee, leading to the expulsion of 1 of its members.
- In 2007, the Supreme Court upheld these expulsions, asserting that the authority to expel members was within the privileges and immunities of Parliament.
- This landmark decision was made in the case of Raja Ram Pal v/s The Hon'Ble Speaker.
About the Lok Sabha’s Ethics Committee:
- Committee Formation:
- The Speaker appoints members to the Ethics Committee for a one-year term.
- This 15-member Committee is responsible for investigating complaints about unethical behavior by Lok Sabha Members referred by the Speaker, offering recommendations accordingly.
- Historical Insight:
- The concept of ethics panels for both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha was first discussed at a 1996 conference in Delhi.
- Vice President K. R. Narayanan established the Rajya Sabha's Ethics Committee in 1997 to oversee moral conduct and examine misconduct cases.
- The idea for a Lok Sabha Ethics Committee emerged in 1997 but was officially recommended during the 13th Lok Sabha by the Committee of Privileges.
- An ad hoc Ethics Committee was formed in 2000 by the late Speaker G. M. C. Balayogi, eventually becoming a permanent House fixture in 2015.
- Handling Complaints:
- Anyone, through a Lok Sabha MP, can file a complaint against a Member, supported by evidence and a statement verifying the complaint's validity.
- The Committee also considers self-complaints by Members without the need for an affidavit.
- The Speaker refers complaints against MPs to the Committee after a preliminary inquiry.
- Function and Scope:
- The Committee examines complaints but does not entertain those solely based on media reports or matters under legal consideration.
- It presents its findings to the Speaker, seeking approval for the report's consideration.
- There's provision for a brief discussion on the report in the House.
Ethics Committee vs. Privileges Committee: A Comparison
- Overlap in Responsibilities: The roles of the Ethics Committee and the Privileges Committee often coincide, leading to some shared functions.
- The regulations, such as those outlined in the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in the Lok Sabha, that are applicable to the Committee of Privileges also extend to the Ethics Committee.
- Handling Allegations: When an allegation of corruption involving an MP arises, it can be directed to either committee. Typically, more severe accusations are referred to the Privileges Committee.
- Privileges Committee's Mandate: The primary role of the Privileges Committee is to protect the "freedom, authority, and dignity of Parliament."
- These privileges apply to individual Members as well as the entire House, ensuring their collective and individual dignity and authority.
- Breach of Privilege: MPs can be investigated for breaching privilege, and individuals who are not MPs can also face allegations of breaching privilege for actions that challenge the authority and dignity of the House.
- Ethics Committee's Focus: In contrast, the Ethics Committee's main responsibility is addressing cases of misconduct involving Members of Parliament only.
What Lies Ahead?
The time taken by a Committee depends on the complexity of the case it's handling. However, the Committee lacks the authority to refer cases to investigative agencies like the CBI or the Police. It also doesn't possess executive powers to directly penalize a Member.
Instead, the Committee can recommend the suspension of a Member for a defined period. These recommendations are then presented to the House for approval or rejection, including the suggested punishment. In the event of claims related to unconstitutionality, gross illegality, or denial of natural justice, a Member has the option to challenge the decision in a court of law.
India Has the Highest Cases Of TB in The World: Global TB Report 2023 (NDTV)
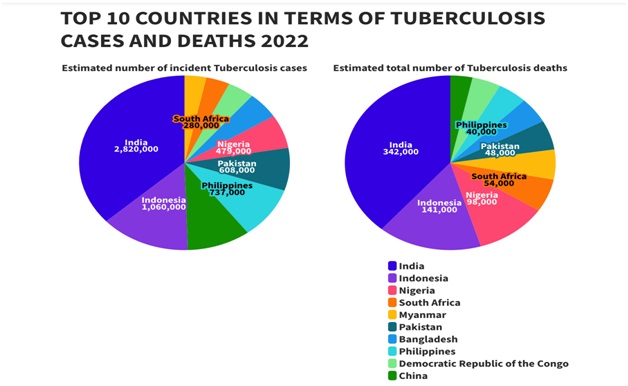
- 09 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
According to the Global TB Report 2023 by the World Health Organisation, India had the highest number of Tuberculosis (TB) cases in the world in 2022.
What is the Global Tuberculosis Report?
- The Global Tuberculosis Report published by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- It provides a comprehensive and up-to-date assessment of the TB epidemic and progress in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of the disease at global, regional, and country levels.
- This is done in the context of global TB commitments, strategies, and targets.
- This report is based primarily on data gathered by WHO from national ministries of health in annual rounds of data collection.
Key Findings of the Global Tuberculosis Report 2023?
- India had the highest number of Tuberculosis (TB) cases in the world in 2022.
- The country accounted for 27 percent of the total TB cases in the world.
- The report revealed that 30 nations accounted for 87 percent of the world's TB cases.
- India was followed by Indonesia (10 per cent), China (7.1 per cent), the Philippines (7.0 per cent), Pakistan (5.7 per cent), Nigeria (4.5 per cent), Bangladesh (3.6 per cent), and the Democratic Republic of Congo (3.0 per cent).
- In the Case of the Fatality Ratio (the measure of how severe a disease is), India stood at 12 percent, which means 12 out of 100 patients died of the disease.
- Singapore had the lowest score of 1 percent while China stood at the 14th spot with 4 percent.
- While TB is curable, death can occur when it is diagnosed late.
- The report also highlights a recovery trend in TB diagnosis and treatment services in 2022, signaling a potential reversal of the COVID-19 impact on TB control efforts.
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
- Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease primarily caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- It mainly affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body such as the pleura (lining around the lungs), lymph nodes, intestines, spine, and brain.
- Transmission:
- TB spreads through the air when an infected person with active TB disease coughs, sneezes, or even talks.
- The bacteria can travel through the air and be inhaled by people who are nearby.
- Symptoms:
- Common symptoms include a persistent cough lasting three weeks or more, chest pain, unintentional weight loss, fatigue, and fever.
- The symptoms may develop gradually, making early detection crucial.
- Treatment for TB:
- TB is treated with a course of antibiotics, typically lasting six to nine months.
- It's crucial to complete the full course to ensure the bacteria are completely eradicated and to prevent drug resistance.
- Prevention:
- Prevention involves vaccination with the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, particularly in regions with high TB prevalence.
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals helps prevent transmission.
- Drug-resistant TB:
- Drug-resistant TB occurs when the TB bacteria in a person's body don't respond to, or are resistant to, one or more of the primary TB drugs.
- There are two main categories of drug-resistant TB:
- MDR (multidrug-resistant) TB and
- XDR (extensively drug-resistant) TB.
- MDR TB is characterized by bacteria resistant to at least two vital TB drugs, isoniazid and rifampicin. These drugs are among the most effective in treating TB.
- On the other hand, XDR TB takes resistance a step further. In addition to being resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin, XDR TB strains are also resistant to any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs: amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin.
- This makes XDR TB more challenging to treat, as it doesn't respond to a broader range of medications commonly used against TB.
- The World Health Organization's END TB Strategy, initiated in 2014, sets a goal to globally eradicate the TB epidemic by 2035.
- The strategy targets a 95% reduction in TB-related deaths compared to 2015, a 90% decrease in TB incidence rates by 2035 compared to 2015, and the ambitious aim of ensuring that no families face catastrophic costs due to TB by the year 2035.
Global Initiatives to Combat Tuberculosis:
- The World Health Organization (WHO), in collaboration with the Global Fund and Stop TB Partnership, has introduced the joint initiative "Find. Treat. All. #EndTB."
- The release of the Global Tuberculosis Report by WHO serves as a crucial tool in assessing and addressing the global TB situation.
Initiative by Government of India to Tackle Tuberculosis:
- National TB Elimination Programme: Prioritizing TB elimination by allocating additional resources under the National Health Mission, intensifying efforts towards achieving the goal of a TB-free India.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Mission: It emphasizes the integration of technology by introducing digital health IDs for TB patients.
- This initiative aims to guarantee the availability of accurate diagnostics and appropriate treatment through digital means.
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan: It's an initiative of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW) to accelerate the country’s progress towards TB elimination by 2025.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana: It provides Rs 500 support through direct benefit transfer to eligible patients.
- Currently, two vaccines VPM (Vaccine Projekt Management) 1002 and MIP (Mycobacterium Indicus Pranii) have been developed and identified for TB, and are under Phase-3 clinical trial.
Way Forward
- Specialized Active Case Finding Drives: Launch targeted campaigns to actively identify and diagnose TB cases in specific populations.
- Scaling Up of Molecular Diagnostics to Block Levels: Expanding the use of molecular diagnostic techniques to the grassroots level for efficient and accurate TB detection.
- Decentralization of Screening Services through Ayushman Bharat Health & Wellness Centres: Extending screening services to local health and wellness centers under the Ayushman Bharat initiative, making TB detection more accessible.
- Private Sector Engagement: Collaborating with the private sector to enhance TB case identification and treatment.
- Newer Patient-Centric Initiatives: Introducing innovative models like the Family Caregiver Model and Differentiated Care to reduce mortality and improve treatment success rates.
What are the Pollutants in Our Air, and How They Impact Health (Indian Express)
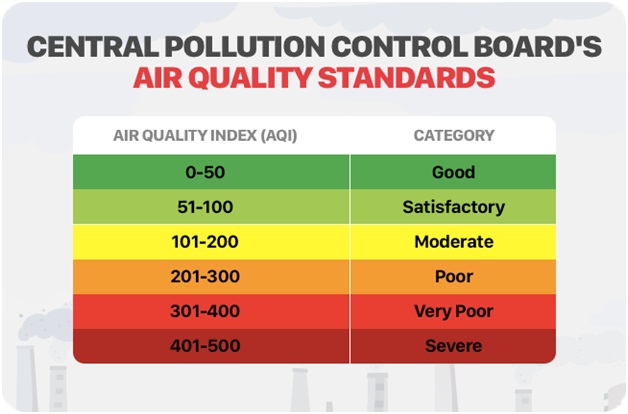
- 08 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Rising pollution levels in north India have led to focus returning on the Air Quality Index (AQI) score, a measure of air pollution.
Context:
- The escalating pollution in northern India has once again drawn attention to the Air Quality Index (AQI) score, which gauges air pollution levels.
- On Monday, Delhi, for instance, registered an AQI score exceeding 400.
- This categorizes the air quality as 'severe,' with any reading above 100 indicating at least a moderate level of pollution on the index.
What is the Air Quality Index (AQI)?
- AQI is a number, which is a measure of air quality.
- The higher the AQI, the worse the air.
- The color-coded AQI index was launched in India in 2014, and it helps the public and the government understand the condition of the air and what subsequent measures are to be taken to combat the situation, based on its severity.
- According to the Central Pollution Control Board, part of the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change, the AQI transforms complex air quality data of various pollutants into a single number (index value), nomenclature, and color.
- The pollutants measured include PM 10, PM 2.5, Nitrogen Dioxide, Ozone, Carbon, etc.
- There are six categories of AQI, namely ‘Good’ (0-50), ‘Satisfactory’ (51-100), ‘Moderately polluted’ (101-200), ‘Poor’ (201-300), ‘Very Poor’ (301-400), and ‘Severe’ (401-500).
How Pollutants Impact Our Health?
PM 10 and PM 2.5
- These are extremely fine particulate matter (PM) particles, with the digits accompanying them referring to their diameter.
- So, PM 10 and PM 2.5 are smaller than 10 and 2.5 microns in their diameter, respectively.
- One micron is about a thousandth of a millimeter and this tiny size has a role to play in how they impact human health.
- The finer the particles are, the more difficult it gets to protect oneself from them.
- Due to their size, the PM 2.5 particles can easily bypass the nose and throat and can enter the circulatory system.
- The particles can also lead to chronic diseases such as asthma, heart attack, bronchitis, and other respiratory problems.
- Byproducts of emissions from factories, vehicular pollution, construction activities, and road dust, such particles are not dispersed and stay suspended in the air that we breathe.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) gets in the air from the burning of fuel, with sources including emissions from vehicles and power plants.
- Short-term exposure to high levels of NO2 can aggravate respiratory diseases like asthma, and lead to other problems such as coughing or difficulty in breathing.
- Long-term exposure may also contribute to the development of asthma and could increase susceptibility to respiratory infections.
Ozone (O3)
- Ozone is a gas that is present in the upper layers of the atmosphere, protecting human health from the impact of the Sun’s UV rays.
- However, surface-level ozone is among the most significant air pollutants. It is formed by the reaction of atmospheric pollutants in the presence of sunlight.
- According to the International Journal of Medical Public Health, with the increase in surface ozone levels, there is a likelihood of an increase in the risk of hospital admissions for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD) and the number of cardiovascular and respiratory deaths.
Sulphur Dioxide (SO2)
- The largest source of SO2 in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels by power plants and other industrial facilities.
- Additional sources are industrial processes and natural sources such as volcanoes.
- As with other gases, SO2 exposure is harmful to the cardiovascular system and can lead to the development of respiratory illnesses.
- SO2 can also react with other compounds to form particulate matter.
- At high concentrations, gaseous SOx can harm trees and plants by damaging foliage and decreasing growth.
Ammonia (NH3)
- A 2017 NASA-funded study said that in India, “A broad increase in fertilizer use coupled with large contributions from livestock waste have resulted in the world’s highest concentrations of atmospheric ammonia.”
- While gaseous ammonia is a natural part of Earth’s nitrogen cycle, excess ammonia is harmful to plants and reduces air and water quality.
- In the troposphere –where all weather takes place and where people live – ammonia gas reacts with nitric and sulfuric acids to form nitrate-containing particles.
- Those particles contribute to aerosol pollution that is damaging to human health.
- Ammonia gas can also fall back to Earth and enter lakes, streams, and oceans, where it contributes to harmful algal blooms and “dead zones” with dangerously low oxygen levels.
Lead (Pb)
- Lead is a naturally occurring toxic metal found in the Earth’s crust. But in increased quantities, exposure to it becomes extremely dangerous to health.
- Important sources of environmental contamination come from mining, smelting, manufacturing and even recycling activities.
- Young children are particularly vulnerable to lead poisoning because they absorb four to five times as much ingested lead as adults from a given source.
- Children who survive severe lead poisoning may be left with permanent intellectual disability and behavioral disorders.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- A toxic, colorless, and odorless gas, it is given off when fuel containing carbon, such as wood, coal, and petrol, is burned.
- If CO levels are high enough, a person may become unconscious and die. Long-term exposure has been linked with an increased risk of heart disease.
Power of the Governor Over State Bills (The Hindu)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Punjab have approached the Supreme Court to decide a time frame for which Governors have to either return or grant assent to Bills passed by Legislatures
News Summary:
- Punjab government led by Aam Aadmi Party had filed a petition in the Supreme Court, challenging the delay by Governor Banwarilal Purohit in giving assent to the bills passed by the State assemblies or proposed to be tabled by them.
- The recent feud between Purohit and Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann-led government pertains to three money bills that were proposed to be tabled by the State during a Special Session of the fourth Budget Session on October 20.
- The governor's approval is needed to table money bills in the House.
- Tamil Nadu has also accused Governor R.N. Ravi of toying with the citizens’ mandate by sitting on the Bills by neither assenting nor returning them.
- It said the Governor has positioned himself as a “political rival” who has caused a “constitutional deadlock” by simply sitting on the Bills for months together.
- Kerala, in its separate petition, said that eight proposed laws passed by its Legislative Assembly were pending with the Governor, not for months, but years.
- Of the eight, three Bills were waiting for the Governor’s word for over two years.
Observation by the Supreme Court:
- The Supreme Court on Monday expressed acute displeasure at Governors holding back key Bills, especially in Opposition-ruled States such as Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Telangana, until State governments approach the top court for judicial intervention.
- The court also questioned the Assembly’s action to reconvene three months after the Vidhan Sabha was adjourned sine die in March.
- “The Assembly was summoned on March 3 and adjourned sine die, without being prorogued, on March 22. The Speaker then reconvenes the Assembly three months later!
- The Supreme Court also said that Governors must remember that they are not the elected representatives of states and have limited power over the legislative actions of an elected government.
The process of granting assent:
- Article 200 of the Constitution covers the options before the Governor when a Bill passed by both Houses of the Legislature is presented to him.
- The first proviso to the Article says the Governor could either declare his assent to the Bill or withhold the assent if it is not a Money Bill or reserve the law for the consideration of the President if he thinks the Bill derogates from or endangers the power of judicial review of the High Court.
- In case the Governor chooses to withhold assent, he should return the Bill “as soon as possible” with a message requesting the Legislative Assembly to reconsider the proposed law or any specified provisions or suggest amendments.
- The Assembly would reconsider and pass the Bill, and this time, the Governor should not withhold his assent.
- In short, the constitutional head of the State would bow to the considered decision of the elected representatives of the people.
Do Governors have discretion?
- Governors did have the discretion to return Bills before the first proviso in the draft Article 175 (now Article 200).
- This was amended by the Constituent Assembly in 1949.
- Though it was thought that the Governor’s exercise of discretion would act as a “potential check on disruptive legislative tendencies” by States, Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, while introducing the amended proviso, said, “in a responsible government there can be no room for the Governor acting on discretion”.
- T. T. Krishnamachari, a Constituent Assembly member from Madras and later Finance Minister, approved of the amendment, saying “The Governor cannot act on his own, he can only act on the advice of the Ministry.
- When a Governor sends a Bill back for further consideration, he does so expressly on the advice of his Council of Ministers”.
- Mr. Krishnamachari explained that if the Bill passed by the Legislative Assembly needs modification or has garnered adverse public opinion, the government uses the Governor to return the Bill to the Lower House as quickly as possible for re-legislation.
- The first proviso to Article 200 is thus a “saving clause” and retains the discretion over the fate of the Bill solely in the hands of the State Cabinet.
- Article 163 of the Constitution makes it clear the Governor is not expected to act independently.
- The Supreme Court in the Shamsher Singh case verdict has held that as a formal head of the State, a “Governor exercises all his powers and functions conferred on him by or under the Constitution on the aid and advice of his Council of Ministers save in spheres where the Governor is required by or under the Constitution to exercise his functions in his discretion.”
- The assent or return of the Bill does not involve the discretion of individuals occupying the Governor’s post.
By when should Bills be returned?
- The first proviso of Article 200 says it should be “as soon as possible”.
- The Constitution is silent on what exactly this phrase means.
- The Supreme Court has interpreted “as soon as possible” in the proviso to mean “as early as practicable without avoidable delay” in its 1972 judgment in Durga Pada Ghosh versus the State of West Bengal.
- Justice (now retired) Rohinton F. Nariman, in his 2020 judgment in the Keisham Megha Chandra Singh case, said a ‘reasonable time’ would mean three months.
- The States have urged the court to interpret the phrase in the proviso and fix a time limit by which Governors should assent or return a Bill.
- The 1988 Sarkaria Commission report on Centre-State relations had suggested consultation with the Governor while drafting the Bill and fixing a deadline for its disposal.
What Efforts Have Been Made to Address Concerns Regarding Governors' Alleged Partisan Role?
- Proposal by Sarkaria Commission: The Sarkaria Commission, set up in 1983 to look into Centre-state relations, proposed that the Vice President of India and the Speaker of Lok Sabha should be consulted by the Prime Minister in the selection of Governors.
- National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2000): The Commission recommended significant changes in the selection of Governors.
- The Commission suggested that the “Governor of a State should be appointed by the President, after consultation with the Chief Minister of that State”.
- Punchhi Committee Proposal: The Justice Madan Mohan Punchhi Committee, constituted in 2007 on Centre-state relations.
- The committee proposed in its report that a committee comprising the Prime Minister, Home Minister, Vice President, Speaker, and the concerned Chief Minister should choose the Governor.
- The Punchhi Committee recommended deleting the “Doctrine of Pleasure” from the Constitution but backed the right of the Governor to sanction the prosecution of ministers against the advice of the state government.
- It also argued for a provision for impeachment of the Governor by the state legislature.
The Way Forward
- While Governors may hold differing views on the content of a Bill and have constitutional options at their disposal, they should refrain from using their authority to obstruct legislation they personally disagree with.
- It's essential to put into practice the principle recommended by the Punchhi Commission, which assessed Centre-State relations and proposed that Governors should not be burdened with the role of Chancellors.
- Governors sometimes appear to have an overly elevated perception of their constitutional roles. Their primary duty is to uphold the Constitution and, if necessary, advise elected governments to align with its provisions. However, this responsibility does not grant them the authority to operate as an independent power center by exploiting the absence of a specific time frame for decision-making and their discretionary powers.
Extension of PM Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana (PMGKAY) (Indian Express)
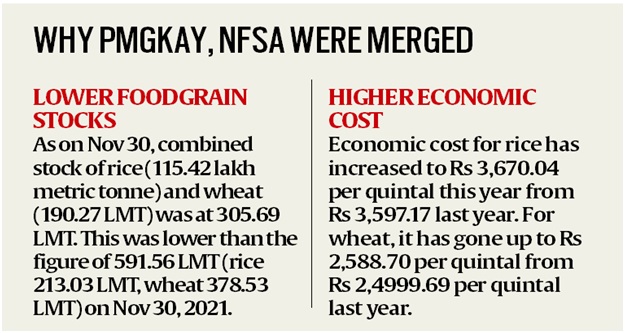
- 06 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said that the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, the Centre’s free ration scheme that aids 80 crore poor, will be extended for five more years.
News Summary
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi, announced the extension of the free foodgrain provision under the National Food Security Act, 2013 for the next five years.
- The PM Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana (PMGKAY) scheme, which was originally set to end in December 2023, will now continue.
- This scheme was introduced in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic to provide free food grains to beneficiaries under the National Food Security Act, 2013.
What is Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Ann/Anna Yojana (PM-GKAY)?
- The Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) was launched in April 2020 as a part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative to help the poor people whose livelihoods were shuttered by a countrywide lockdown aimed at containing the spread of the Covid-19.
- It was a part of Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (PMGKP) to help the poor fight the battle against Covid-19.
- Under this scheme, about 80 crore beneficiaries covered under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) get free 5 kg foodgrains per person per month.
- This assistance is in addition to the subsidised ration provided under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), allowing families covered under the Public Distribution System (PDS) to access essential food items at a nominal cost ranging from Rs 1 to Rs 3 per kilogram.
- Objective of PM-GKAY: To feed India's poorest citizens by distributing food grain to all priority households—those with ration cards and those designated by the Antyodaya Anna Yojana scheme—through the Public Distribution System.
- The Antyodaya Anna Yojana is a centrally sponsored scheme that was introduced in 2000 with the goal of giving millions of the poorest households access to heavily subsidized food.
- To ensure the availability of protein, 1 kg of pulses were provided to families (as per regional preferences)
- Implementing Agency: Department of Food and Public Distribution, Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
Who is eligible for the scheme?
- Families eligible for PM-GKAY include those under the Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) and Priority Household (PHH) categories.
- PHH beneficiaries are identified by state governments and Union territory administrations based on their specific criteria.
- This ensures that households in most need receive the necessary support.
- AAY families, comprising widows, terminally ill persons, disabled individuals, elderly individuals without means of subsistence or societal support, primitive tribal households, and various vulnerable categories, are also eligible for the scheme.
The merger of PMGKAY and NFSA:
- In January 2023, the government approved the integration of PM-GKAY benefits with the provisions of the NFSA Act.
- This integration will streamline the delivery of free food grains.
- It also ensures that families falling under the Antyodaya Ann Yojana (AAY) and priority households (PHH) categories receive free food grains according to their entitlement under NFSA.
- For the financial year 2023-24, the central government has allocated around 60 mt of food grain under the NFSA.
- This includes around 40 mt of rice, 19 mt of wheat, and 1 mt of coarse grains.
- The central issue price (CIP), the rate at which grains are made available to NFSA beneficiaries, is Rs 3 per kg for rice, Rs 2 per kg for wheat, and Rs 1 per kg for coarse cereals.
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (PMGKP) vs PMGKAY:
- The Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (PMGKP) was introduced in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic to provide economic relief to the vulnerable sections of society.
- Launched in March 2020, the scheme included various measures such as free food grains, cash transfers, and insurance coverage for healthcare workers, among others, to support those affected by the pandemic and the subsequent lockdown measures.
- The insurance scheme under PMGKP covered Rs 50 lakh per health worker fighting Covid-19.
- This insurance scheme was further extended by 180 days in April 2022.
What is National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013?
- The National Food Security Act (NFSA) was notified on 10th September, 2013.
- The objective of this scheme was to provide for food and nutritional security in the human life cycle approach, by ensuring access to adequate quantities of quality food at affordable prices for people to live a life with dignity.
- Coverage: 75% of the rural population and up to 50% of the urban population for receive subsidized food grains under the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- Overall, NFSA caters to 67% of the total population.
- State governments are tasked with identifying Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY - poorest of the poor) and priority households (PHH) beneficiaries within the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS)-covered population.
- Provisions: 5 Kg of foodgrains per person per month at Rs. 3/2/1 per Kg for rice/wheat/coarse grains.
- The existing AAY household will continue to receive 35 Kg of foodgrains per household per month.
- Meal and maternity benefits of not less than Rs. 6,000 to pregnant women and lactating mothers during pregnancy and six months after childbirth.
- Meals for children up to 14 years of age.
- Food security allowance to beneficiaries in case of non-supply of entitled foodgrains or meals.
- Setting up of grievance redressal mechanisms at the district and state levels.
What are the Challenges and the Issues?
- Inadequate Coverage: The National Food Security Act relies on data from the last census in 2011, leaving out a growing number of food-insecure individuals who have emerged since then.
- Financial Burden: Sustaining the program imposes a significant financial burden on the government, necessitating a continuous supply of affordable grains.
- In 2022, India had to impose restrictions on wheat and rice exports due to unpredictable weather conditions affecting harvests, adding pressure to food prices and unsettling global agricultural markets.
- Fiscal Deficit Concerns: The extension of the program could potentially jeopardize the government's goal of further reducing the fiscal deficit to 6.4% of the gross domestic product.
- Impact on Inflation: The program's continuation may also influence inflation rates, particularly in the case of rice and wheat, which contribute around 10% to India's retail inflation.
- Decreased production caused by factors like heatwaves and irregular monsoons has led to rising prices for these essential food items.
Delhi Air Pollution: Causes, Impact & Measures (The Hindu)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The air quality in Delhi-NCR declined over the past week due to a gradual drop in temperatures, calm winds that trap pollution, and a surge in post-harvest paddy straw burning across Punjab and Haryana.
Context:
- The air quality in Delhi has plummeted to hit the ‘severe’ category for the first time this season, with the AQI breaching the 450 mark according to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- The State government implemented restrictions, including banning construction and demolition activities.
- Over the last few years, Delhi and its surrounding areas have been subject to hazardous smog, which conincides with the winter months rolling in.
- Smoke from farmers burning crop stubble, vehicle exhaust and factory emissions combine every winter to blanket the region in a toxic haze.
What is Pollution?
- Pollution refers to the contamination of the earth's environment with materials that interfere with human health, quality of life or the natural functioning of the ecosystems.
- The major forms of pollution include water pollution, air pollution, noise pollution and soil contamination.
- Other less-recognised forms include thermal pollution and radioactive hazards.
What are the Reasons behind Rising Air Pollution in Delhi?
- Delhi is one of the most polluted capital cities in the world for a variety of factors, including location (landlocked city), traffic patterns, dust, and farm fires.
- However, weather also has a significant impact.
- Typically, Delhi experiences deteriorating air quality from October to November, with improvements occurring from March to April.
- Unlike the winter season, the current weather conditions are not unfavorable.
- During winter, cool and calm weather tends to trap and intensify daily pollution, especially in northern India within the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- In addition to local emissions, the decline in air quality is primarily attributed to an increase in fire incidents, largely resulting from the burning of wheat crop stubble in northern India especially Punjab and Haryana.
- Air Pollution in Delhi-NCR and the Indo-Gangetic Plains is a complex issue influenced by a variety of factors.
- Location: Delhi is a landlocked city compared to Mumbai and Kolkata so the level of pollution is more as the level of particulate matter and pollutants is not able to get discharged into the surrounding areas.
- Wind Direction: In October, the monsoons withdraw from Northwest India, bringing northwesterly winds.
- During summers, northwesterly winds transport dust from northern Pakistan and Afghanistan.
- Reduced Wind Speed: Winters see lower wind speeds compared to summers, making the region more susceptible to pollution.
- Delhi's landlocked position doesn't benefit from the sea breeze that disperses pollutants in other parts of the country.
- Stubble Burning: Burning crop stubble in states like Punjab, Rajasthan, and Haryana adds to the winter smog.
- This practice releases harmful gases like methane, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
- Vehicular Pollution: Vehicular emissions significantly contribute to declining air quality in Delhi during winter, accounting for about 20% of the problem.
- Dust Storms: Dust storms from Gulf countries worsen the existing pollution levels.
- Dry and cold weather results in dusty conditions from October to June, contributing to PM10 and PM2.5 pollutants.
- Temperature Drop: Lower temperatures reduce the inversion height, concentrating pollutants in the lower atmosphere.
- The inversion height is the layer beyond which pollutants cannot disperse upward.
- Firecrackers: Despite bans on firecracker sales, Diwali celebrations with fireworks contribute to air pollution.
- Construction Activities and Open Waste Burning: Large-scale construction projects in Delhi-NCR increase dust and pollution.
- Landfill sites and open waste burning also add to air pollution concerns.
Impact of Air Pollution on health:
- Respiratory Issues: Air pollution is a major cause of respiratory problems, including asthma, bronchitis, and lung infections.
- It can exacerbate existing conditions and increase the risk of developing them.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Poor air quality is linked to heart problems, including heart attacks and stroke, as it can lead to the buildup of plaque in blood vessels and raise blood pressure.
- Cancer Risk: Long-term exposure to certain air pollutants is associated with an increased risk of lung and other types of cancer.
- Neurological Effects: Emerging research suggests that air pollution may have adverse effects on the central nervous system and could be linked to cognitive decline and mental health issues.
- Reduced Life Expectancy: Prolonged exposure to air pollution is associated with a shortened life expectancy, as it contributes to a range of health problems that can be life-threatening.
Impact of Air Pollution on Economic Growth:
- Healthcare Costs: Air pollution increases medical expenses due to illnesses, reducing economic growth.
- Lower Productivity: Poor air quality impairs worker productivity, hampering economic output.
- Tourism and Investment: Severe pollution deters tourists and investors, affecting local economies.
- Agricultural Losses: Air pollution harms crops, impacting food production and livelihoods.
- Environmental Cleanup Costs: Funds spent on pollution control divert resources from productive sectors, hindering economic growth.
What Steps Should Be Taken to Address Pollution in Delhi?
- Congestion Charge: Introducing a congestion charge for private vehicles during peak hours can alleviate traffic congestion and promote public transport or carpooling.
- Revenue generated from this charge can support green projects or subsidize electric vehicles, encouraging eco-friendly choices.
- Cap-and-Trade for Industrial Emissions: Implementing a cap-and-trade system sets emission limits for industries, fostering a market-driven approach to pollution reduction.
- This incentivizes industries to lower emissions and invest in cleaner technologies, ultimately reducing pollution.
- Drones for Pollution Control: Utilizing drones to detect and mitigate pollution hotspots is a proactive measure for managing air quality.
- Drones provide real-time air quality data with high resolution, allowing for public accessibility and targeted intervention.
- Vertical Gardens: Incorporating vertical gardens in urban areas enhances aesthetics and air quality.
- They absorb carbon dioxide, release oxygen, and create habitats for wildlife, contributing to urban biodiversity.
- Rewards for Low-Carbon Lifestyles: Promoting low-carbon living through a rewards system, such as points, vouchers, or tax benefits for eco-friendly choices like public transport or carpooling, encourages environmentally conscious behavior, reducing carbon footprints.
Government Measures to Combat Pollution in Delhi:
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP): Aims to reduce PM10 and PM2.5 particles by at least 20% by 2024 compared to 2017 levels.
- Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP): As per a Supreme Court order, GRAP outlines actions based on different Air Quality Index categories, addressing air quality in Delhi and the National Capital Region.
- Stubble Burning Mitigation: Various short-term solutions, both in-situ and ex-situ, have been introduced to address crop stubble burning, such as Subsidy to farmers for Turbo happy seeders and bio-decomposers.
- Turbo Happy Seeder (THS) is a machine mounted on a tractor that cuts and uproots the stubble, in order to reduce stubble burning.
- Mobile Enforcement Teams: Enforce regulations against vehicular pollution, complemented by public awareness campaigns and investments in mass rapid transport systems. Phasing out old commercial vehicles is also underway.
- Cleaner Transport: The introduction of BS-VI vehicles, push for electric vehicles (EVs), Odd-Even as an emergency measure and construction of the Eastern and Western Peripheral Expressways to reduce vehicular pollution.
- Improved Farming Practices: Encouraging better disposal of crop residue and exploring cost-effective solutions, like chemical decomposition by the Indian Agricultural Research Institute, are essential for tackling stubble burning.
- "Green War Room": This initiative uses satellite data to identify sources of smog, particularly farm fires in Punjab and Haryana, and takes necessary action.
In response to a growing environmental and health crisis, antipollution measures are being strengthened. However, to ensure success, government bodies at various levels must need to gather the political will to boost investment, foster cross-boundary cooperation, and motivate both citizens and businesses to make their contributions.
CAR-T Cell Therapy (Indian Express)
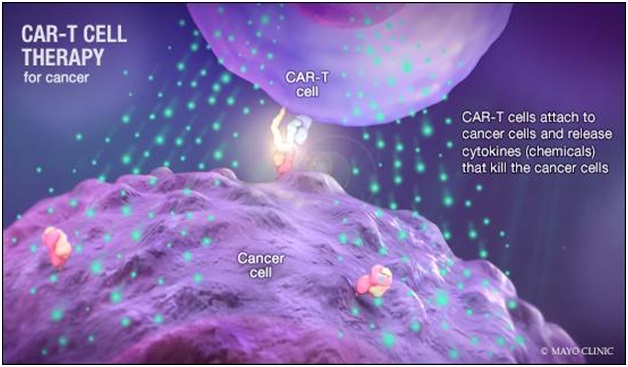
- 03 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The drugs regulator has granted market authorisation to India's breakthrough CAR-T cell therapy for patients with B-cell lymphomas who didn't respond to standard treatments like chemotherapy.
News Summary:
- India’s first indigenously developed Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T Cell T therapy, a cutting-edge treatment for specific types of cancer patients, has shown promising results and could be the safest therapy in this category so far, researchers have said.
- The therapy was tested on six paediatric patients of Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia and 10 adults suffering from B-cell lymphoma as part of phase one clinical trials by researchers associated with the Tata Memorial Hospital in Mumbai and the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay.
What is CAR-T cell therapy, and how do CAR-T cells find and destroy cancer cells?
- CAR-T is a revolutionary therapy that modifies immune cells, specifically T-cells, by turning them into potent cancer fighters known as CAR-T cells.
- T-cells are special cells (white blood cells that find and fight illness and infection) whose primary function is cytotoxic, meaning they can kill other cells.
- In CAR-T therapy, we genetically modify them into cancer-fighting cells. These supercharged cells are then put back into the body, and they go after cancer cells — especially in blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphomas.
Here's how CAR-T cell therapy works?
- Collection: First, a patient's T cells are taken from their blood through a process called "leukapheresis."
- Genetic Modification: These T cells are then sent to a laboratory where they are genetically modified to make them better at attacking cancer.
- Preparation: Before the modified T cells are returned to the patient, the patient typically undergoes several days of chemotherapy.
- This chemotherapy helps create the right environment in the body for the modified T cells to work against the cancer.
- Infusion: Once the environment is ready, the patient receives an infusion of the modified T cells.
- This process is similar to receiving a blood transfusion and takes about 30 to 90 minutes.
- Activation: The CAR-T cells become active and start to attack the cancer cells.
- However, this activation process can lead to side effects, such as a high fever, a fast heart rate, low blood pressure, and low blood oxygen levels.
- Some patients may also experience temporary neurological effects like confusion, tremors, and difficulty communicating.
- Recovery typically occurs within two weeks after one cycle of the treatment.
- Approximately 70% of patients respond to the treatment, with variations between leukaemia and lymphoma cases.
- About 50% of these responsive patients achieve a complete response.
How effective and different is this from other cancer treatments like, say, chemotherapy?
- While chemotherapy and immunotherapy may add a few months or years to a cancer patient’s life, cell-and-gene therapy is designed to cure and provide lifelong benefits.
- It makes treatment easier with a one-time therapy [unlike several sessions of chemotherapy] that can be truly transformative [for a patient].
- It’s a lifeline for non-responsive cancer patients.
What is NexCAR19?
- NexCar19 is a type of CAR-T and gene therapy developed indigenously in India by ImmunoACT, which is a company incubated at IIT Bombay.
- This therapy is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein.
- This protein acts like a flag on cancer cells, which allows CAR-T cells to recognise and attach themselves to the cancer cells and start the process of elimination.
- India is now one of the first developing countries to have its indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform.
- Even some developed nations don’t have their own CAR-T therapies; they import them from the United States or Europe.
Who is eligible for the NexCAR19 therapy?
- This therapy is for people with B-cell lymphomas who didn’t respond to standard treatments like chemotherapy, leading to relapse or recurrence of the cancer.
- B-cell lymphoma is a kind of cancer that begins in white blood cells called lymphocytes.
- Lymphocytes produce antibodies, which are proteins that aid in the fight against infections.
- They are frequently discovered in lymph nodes and other lymphoid organs, like the spleen.
Are the children eligible for this therapy too?
- B-cell leukaemia is most common among children.
- The paediatric trial phase is currently underway at the Tata Memorial Hospital, in collaboration with IIT-Bombay.
- Although the therapy for children will not be any different, for now, ImmunoACT has received CDSCO approval for use in patients aged 15 years and older.
Is there any side-effects of this therapy?
- It significantly reduces drug-related toxicities, causing minimal harm to neurons and the central nervous system—a condition known as neurotoxicity.
- Neurotoxicity can occasionally occur when CAR-T cells recognize the CD19 protein and access the brain, potentially leading to life-threatening situations.
- Additionally, the therapy results in minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), characterized by inflammation and hyperinflammation in the body due to the death of a substantial number of tumor cells.
Conclusion
The treatment is not intended for someone who is newly diagnosed. Instead, it’s an alternative for those who already have gone through other more conventional cancer therapy, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy, and that treatment has been unsuccessful.
A considerable amount of research is underway to see if CAR-T cell therapy could be appropriate as a treatment for different forms of cancer, too, including other blood cancers such as multiple myeloma. So if a patient has a type of cancer that hasn’t responded well to traditional treatment, it may be worthwhile to explore the possibility of enrolling in a clinical research trial that’s using CAR-T cell therapy.
Maratha Quota Protest (The Hindu)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Residents in many villages of Maharashtra’s Dharashiv district on November 1 launched a ‘jail bharo’ (court arrest) protest in support of the Maratha quota agitation.
News Summary:
- The Maratha quota agitation intensified in Maharashtra after activist Manoj Jarange started an indefinite hunger strike to press the quota demand.
- The demand for OBC reservation emerged with the Supreme Court's May 2021 ruling that invalidated the Maratha quota established by the state's Socially and Educationally Backward Class (SEBC) Act, 2018.
- The Marathas want to be recognized as Kunbis, which would entitle them to benefits under the Other Backward Classes (OBC) quota.
- The State Govt. on asked officials to issue fresh Kunbi caste certificates to eligible Maratha community members from Marathwada, paving the way for them to avail reservation benefits under the Other Backward Classes (OBC) category.
- However, Mr. Jarange opposed the move saying the entire Maratha community should be given reservation.
Historical Background of the Maratha Community:
- The Marathas, historically identified as a “warrior” caste, comprise mainly peasant and landowning groups and makeup 33 per cent of the population in Maharashtra.
- The Maratha Kshatriyas have surnames like Deshmukh, Bhonsle, More, Shirke and Jadhav while most others belong to Kunbi, a predominantly agrarian sub-caste.
- The Kshatriya-Kunbi difference existed till the days of the Maratha empire.
- Now, most Marathas are engaged in farming activities.
Difference between Marathas and Marathis:
- While all Marathas are Marathis, not all Marathis are Marathas. Maratha signifies a group of castes, while Marathi is the language spoken by several communities in Maharashtra and some neighbouring areas of other states.
- A maximal circle of 96 clans is said to include all true Maratha, but the lists of these 96 clans are highly varied and disputed.
What is the issue of Maratha Reservation?
- The Marathas have been the politically dominant community in Maharashtra — since the formation of the state in 1960 as 12 of its 20 Chief Ministers have been Marathas.
- However, with a divide in holdings and problems in the farming sector, there has been a decline in the prosperity of middle and lower-middle-class Marathas.
- The demand for the Maratha reservation has been going on for decades now.
- The demand for quota for Marathas began in 1981 when Mathadi Labour Union leader Annasaheb Patil staged a morcha in Mumbai in support of the proposal.
- The Maratha Mahasangh and the Maratha Seva Sangh organized a strong movement for the Maratha reservation in government jobs and educational institutions in 1997.
- The issue was brought up again in 2000.
Timeline of Maratha Reservation Issue:
- June 2017: An 11-member commission led by retired Justice M. G. Gaikwad was formed.
- The commission recommended providing Maratha reservation rights under the category of Socially and Educationally Backward Class (SEBC).
- November 2018: Maharashtra legislature passed a bill proposing a 16% reservation in education and government jobs for the Maratha community, declared as a socially and educationally backward class by the government.
- June 2019: The Bombay High Court upholds the constitutional validity of the Maratha quota under the Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (SEBC) Act, 2018.
- It reduces the quota from 16% to 12% in education and 13% in government jobs, following the recommendations of the Maharashtra State Backward Class Commission.
- May 2021: The Supreme Court invalidated the Maratha reservation in 2021, citing the 1992 cap of 50% on all reservations. (Indira Sawhney judgment 1992)
- The total reservation ceiling was raised to 64% and 65%, respectively, by the Maratha reservations of 12% and 13% in employment and education, respectively.
Indira Sawhney judgment 1992
- In the Indira Sawhney judgment (1992), the Supreme Court made it clear that 50% reservations should generally be the rule, and the limit could only be relaxed in specific exceptional situations, typically in remote areas, to include them in mainstream opportunities.
- The Supreme Court stated that there were no such "exceptional circumstances" or "extraordinary situations" in Maharashtra to exceed the 50% reservation limit.
- Additionally, the court ruled that the state government couldn't grant socially and economically backward status to a community.
- Only the president has the authority to make changes to the central list of socially and backward classes; states can only provide suggestions.
- While the Bench unanimously upheld the constitutional validity of the 102nd Constitution Amendment, there was a difference of opinion on whether it affected the states' power to identify Socially and Economically Backward Classes (SEBCs).
- The Supreme Court emphasized that a separate reservation for the Maratha community goes against Articles 14 (right to equality) and 21 (due process of law).
- November 2022: After the SC struck down the Maratha reservation and upheld the 10 per cent quota for the Economically Weaker Sections, the Maharashtra government said that until the issue of the Maratha reservation is resolved, economically weaker members of the community can benefit from the EWS quota.
- April 2023: The state government declared that it will file a curative petition and establish a new panel to conduct a thorough assessment of the community's "backwardness" following the SC's denial of its review plea.
Maharashtra Government's Stance:
- The Maharashtra government has approved the issuance of Kunbi caste certificates to Marathas from Marathwada, based on historical documents from the Nizam era that recognize them as Kunbis.
- The main goal is to grant Marathas Kunbi caste certificates, which would classify them as Other Backward Classes (OBCs) and grant them access to the benefits reserved for OBCs.
- To ensure a standardized process, the government has formed a committee consisting of five members, led by former Justice Sandeep Shinde.
- This committee will create the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for issuing Kunbi caste certificates.
Who are Kunbis?
- Kunbis, a community traditionally involved in farming, are categorized as Other Backward Classes (OBC) in Maharashtra.
- During the period when Marathwada was part of the Hyderabad province, the community in that area was recognized as Kunbis, known for their farming activities.
- However, when Marathwada became part of Maharashtra, this community was categorized as Marathas.
- In 1967, Punjab Rao Deshmukh requested OBC status for Marathas in the Vidarbha region, and in 2004, the Maharashtra government issued a Government Resolution (GR) granting Kunbi status to Marathas from that area.
What is the reaction from OBC Organizations?
- Opposition to Maratha Demand: OBC organizations strongly disagree with the Maratha request for OBC reservations, fearing it might affect their existing quota.
- Reservation Concerns: OBC leaders argue that the Maratha reservation should not reduce or compromise the existing OBC reservation.
- They highlight that OBCs in Maharashtra already have a 19% reservation, which is higher than the national average of 27%.
Conclusion
In the current social and political situation, it is becoming increasingly clear that a potential conflict between the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) and the Marathas will emerge big if the problem is not addressed and managed amicably. To ensure social harmony and avoid potential conflicts, stakeholders and policymakers must engage in constructive dialogue and find fair solutions to the OBC and Maratha reservation issue.
Biofuels and Global Biofuels Alliance (TOI)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Global Biofuel Alliance, formed during the recent G20 summit in India, aims to support the development and deployment of sustainable biofuels.
What are Biofuels?
- Biofuels are sustainable fuels made from a variety of organic materials (e.g. wood, crops, oil, algae, organic residues, etc.) called biomass.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), biofuels are liquid fuels derived from biomass.
- It can be used as an alternative to fossil fuel-based liquid transportation fuels such as gasoline, diesel and aviation fuels.
How are Biofuels Produced?
- Biofuels can be produced from several methods or production pathways, including transesterification, hydrotreating, gasification, Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, fermentation and pyrolysis.
- Biofuels are generally divided into four categories – or generations – according to feedstock – or the type of biomass – used.
- First-generation biofuels, known as conventional biofuels, are produced from agricultural food crops, vegetable oil, and food waste.
- Higher carbon content and emit greenhouse gases.
- Second-generation biofuels, called advanced biofuels, are made from energy crops, agricultural or forest residue, known as lignocellulosic biomass.
- Greenhouse content less than 1st generation biofuel
- Third-generation biofuels are made from the byproducts of microorganisms, such as algae, natural organisms that can be rapidly produced with little energy and without disrupting ecosystems.
- Carbon Neutral (CO2 emitted=CO2 sequestered)
- 4th Generation biofuels are produced from genetically engineered crops like GM crops, pyrolysis, gasification etc. and are Carbon Negative.
What are the advantages of Biofuels?
- Biofuel Availability: Biofuels can be produced in multiple locations and from diverse sources, making global production and distribution realistic.
- Renewable Energy: Biofuels come from plants, so we can keep growing them, making biofuels a sustainable energy source.
- Energy Independence: Using biofuels means we rely less on foreign oil, saving money on imports and boosting our energy security.
- Cleaner Environment: Biofuels produce fewer harmful gases compared to fossil fuels, which helps keep our environment cleaner.
- Income for Farmers: Biofuels can give farmers extra income, which aligns with the goal of doubling their earnings.
- Plenty of Biofuel Sources: We can make biofuels from different things like plants, waste, and algae, so there's a lot of it available.
What are the disadvantages of Biofuels?
- Biofuel sustainability: End-to-end sustainability is a key question, as biofuels must come from a green supply chain, starting with sustainable biomass production.
- Land used for biofuel production needs to be closely monitored, ensuring sustainable management practices and avoiding crop displacement.
- Resource Demand: Making biofuels needs a lot of land and water.
- In countries like India, where there's not much extra land for farming, it might not be a good idea to use it for biofuels.
- Competition with Food: Biofuel production and food production sometimes fight for the same land and resources.
- This can lead to higher food prices and make it hard for people to get enough to eat.
- Greenhouse Gases: Surprisingly, some biofuels can produce even more greenhouse gases than regular fossil fuels.
- This happens when we use land that was once covered in forests to grow crops for biofuels.
Are Biofuels a Replacement for Fossil Fuels?
- There is a difference between biofuels and sustainable biofuels according to experts.
- While 1G ethanol is considered a biofuel, experts categorize 2G ethanol as sustainable biofuels.
- The problem has gained significant attention recently due to the acceleration of climate change, raising worries about the threat to food security and the increasing loss of forests and biodiversity as a result of the increased area required for farming.
- Estimates show that far over half of all vegetated land is currently under cultivation, making agriculture one of the primary global sources of carbon emissions.
- The Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA) has said unequivocally that producing 2G ethanol would be its primary objective.
Biofuels and the Energy Shift:
When it comes to changing our energy sources, biofuels play a role:
- Right now, most biofuels are mixed with regular gasoline or diesel to some extent.
- India, for example, is increasing the use of 20% ethanol-blended petrol across the country by 2025.
- Some experts think that electric vehicles (EVs) and green hydrogen are the main focus for our energy future.
- But others believe that 2G ethanol can help in the transition. It can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and keep internal combustion engines in use longer.
- This gives time for new alternatives to develop, helps farmers, and creates jobs.
What is the Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA)?
- The Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) is an initiative by India as the G20 Chair.
- The Alliance intends to expedite the global uptake of biofuels through facilitating technology advancements, intensifying the utilization of sustainable biofuels, and shaping robust standard setting and certification through the participation of a wide spectrum of stakeholders.
- The alliance will also act as a central repository of knowledge and an expert hub.
- GBA aims to serve as a catalytic platform, fostering global collaboration for the advancement and widespread adoption of biofuels.
- This transition aims to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, create employment opportunities, and stimulate economic growth.
- Members: The GBA has already gained support from 19 countries and garnered the interest of 12 international organizations.
- Notably, seven G20 countries, including Argentina, Brazil, Canada, India, Italy, South Africa, and the United States, are actively supporting the GBA
- Additionally, four G20 invitee countries (Bangladesh, Singapore, Mauritius, UAE) are also backing this initiative.
- Furthermore, eight non-G20 countries (Iceland, Kenya, Guyana, Paraguay, Seychelles, Sri Lanka, Uganda, and Finland) have agreed to be initiated members of the GBA.
- International organizations including, the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, World Economic Forum, World LPG Organization, UN Energy for All, UNIDO, Biofutures Platform, International Civil Aviation Organization, International Energy Agency, International Energy Forum, International Renewable Energy Agency, World Biogas Association.
How the GBA Operate?
- The GBA has a multifaceted approach to support the global development and deployment of sustainable biofuels.
- It provides capacity-building exercises across the entire biofuel production value chain and offers technical support for national biofuel programs.
- Moreover, the GBA aims to foster knowledge sharing regarding policy best practices among its members.
- The GBA plans to establish a virtual marketplace that helps industries, countries, ecosystem participants, and key stakeholders connect by mapping the demand and supply of biofuels.
- It will also facilitate the development, adoption, and implementation of internationally recognized standards, codes, sustainability principles, and regulations.
- These efforts are designed to incentivize the adoption and trade of biofuels on a global scale.
Significance for India:
- The GBA holds particular significance for India.
- It is a tangible outcome of India's G20 presidency, reinforcing the nation's global presence.
- Collaboration within the alliance provides additional opportunities for Indian industries, allowing them to export technology and equipment related to biofuels.
- This collaboration also accelerates existing Indian biofuel programs, such as PM-JIVAN Yojna, SATAT, and the GOBARdhan scheme.
- By doing so, it contributes to increasing farmers' income, creating job opportunities, and fostering overall development within the Indian ecosystem.
Steps taken by GOI to promote biofuels:
- Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN Yojana (2019): This scheme aims to create a system for commercial projects and boost Research and Development in 2G Ethanol production.
- GOBAR DHAN Scheme (2018): This scheme focuses on managing cattle dung and farm waste to create useful compost, biogas, and bio-CNG.
- This not only keeps villages clean but also increases the income of rural households.
- It was launched under the Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin).
- Ethanol Blending: The 2018 Biofuel Policy set a goal to reach 20% ethanol blending and 5% biodiesel blending by 2030.
- However, the government now plans to achieve the 20% ethanol blending target by 2025-26 instead of 2030.
- National Policy on Biofuels (2018): This policy classifies biofuels into "Basic Biofuels" like 1G bioethanol and biodiesel and "Advanced Biofuels" like 2G ethanol, converting municipal solid waste into drop-in fuels, 3G biofuels, and bio-CNG.
- It provides financial and fiscal incentives to promote each category of biofuels.
- Repurpose Used Cooking Oil (RUCO): This initiative, launched by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), aims to collect and convert used cooking oil into biodiesel.
Conclusion
While biofuels hold potential in the fight against climate change, their practical viability remains uncertain. In countries like India, where agricultural surplus is limited, their role as a major energy source may be challenging. Nevertheless, biofuels can still contribute to a greener future through sustainable production and consumption practices. The success of the GBA will determine the extent to which biofuels can play a meaningful role in addressing climate change and energy needs.
Vision document to make India a $30 trillion economy by 2047 (TOI)

- 31 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
India will aim to become a ‘developed nation’ by 2047, with an economy of $30 trillion in its 100th year of independence, which will be propelled by radical policy changes and reforms in governance by 2030.
News Summary:
- The 'Viksit Bharat @2047' document, which outlines this vision, is nearing completion, following its inception in December 2021 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Ten sectoral groups of secretaries (SGoSs) were entrusted with the task of preparing sector-specific visions, and these are nearly finalized.
- Niti Aayog will consolidate these sectoral visions into a single comprehensive document by December, following consultations with SGoSs and thought leaders, including industry leaders.
- Prime Minister Modi is expected to unveil this vision document in December or January.
What is the Current State of the Indian Economy?
- India’s economy was $3.5 trillion in FY23, but currently with a GDP of $3.7 trillion, it is estimated to be the 5th largest economy in the world and according to some projections, India's GDP will surpass that of Germany and Japan by 2030.
- The country’s per capita income was estimated at around $2,500 in FY23.
- Nations with per capita income beyond a threshold of $17,000 are considered as developed.
- This rapid rate of economic expansion would result in India becoming the second-largest economy in the Asia-Pacific region.
NITI Aayog Vision India@2047 Document:
- The process of shaping the Vision India@2047 document commenced in December 2021.
- To ensure comprehensive coverage, ten groups of secretaries were assembled, each focused on distinct sectors such as rural and agriculture, infrastructure, social vision, welfare, technology, governance, security, foreign affairs, and more.
- This document will provide a blueprint for achieving the ambitious goal of transforming India into a $30-trillion developed economy by 2047, with a per-capita income ranging from $18,000 to $20,000.
- It will encompass a range of crucial elements, including re-engineering government processes, implementing reforms, and streamlining the efforts of various ministries and departments to eliminate redundancy.
- Expect insights into India's global involvement in areas like trade, investment, technology, capital flows, and research and development.
- Furthermore, the document will shed light on which Indian companies are poised to lead on the global stage and the strategic approach for nurturing the ecosystem required to realize this vision.
- It will also delve into matters related to human capital development, leveraging the nation's vast market size, and addressing regional disparities.
- The vision document will also provide a roadmap, delineating where India aims to be in 2030 and, ultimately, in 2047."
What are the obstacles ahead in implementing the Vision India@2047?
- NITI Aayog is assisting Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh in preparing their vision documents in order to bring them into compliance with the national vision document.
- While other states, such as Uttarakhand, Goa, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh, are working on their own documents.
- Middle-income trap: The plan will include safeguards to make sure the economy stays out of the "middle-income trap".
What is the middle-income trap?
- According to the World Bank, the term "middle-income trap" describes a scenario in which a nation with a middle-class income is unable to make the transition to a high-income economy because of growing expenses and a decrease in its competitiveness.
- It's when per capita income reaches around $5,000 to $6,000, and then progress slows down.
- Low-income countries often tend to transition faster to middle-income levels, driven by low wages, cheap labour and basic technology catch-up.
- However, only a few countries manage to achieve high-income status.
What are the reasons for the middle-income trap?
- An example of what is known as the "middle-income trap" is when labour wages become so high that a middle-income nation is unable to compete on a global scale in the production of standardized, labour-intensive goods.
- But because of its relatively low productivity, it is also unable to compete on a large enough scale in higher value-added activities.
- As a result, growth is slowing, wages are stagnant or falling, and the informal economy is expanding.
Countries that are stuck in the middle-income trap:
- Historically, some evidence suggests that Latin American and Middle Eastern countries suffered middle-income traps for at least four or five decades.
- According to a World Bank report, out of 101 middle-income countries in 1960, only 13 countries achieved high-income status by 200
- The most recent examples are Brazil and Mexico, which were touted to transition to developed economies but failed to achieve the same success as Japan or some countries in Eastern Europe.
What Strategies Can Help India Overcome Middle-Income Traps?
- Investment: India should aim for an investment-to-GDP ratio of 35%. Achieving this goal requires boosting savings to 32% of GDP.
- In the fiscal year 2022, savings and investment rates were 30.2% and 29.6%, respectively, indicating the need for further growth.
- Balancing Fiscal Consolidation with Growth: India faces a challenge with a general public debt of 83% of GDP and high fiscal deficits.
- Balancing fiscal consolidation while meeting targets set under the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) framework is crucial.
- Structural Reforms: The Asian Development Bank (ADB) emphasizes the need for structural reforms in India to address issues like structural bottlenecks, declining investment, and an increasing current account deficit.
- Notable reforms include the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), which has strengthened the country's banking systems.
- Education and Skill Development: Skill development is vital for enhancing labour productivity and promoting inclusive growth.
- Recent reports suggest that employability among young people needs improvement, emphasizing the importance of education and skill enhancement programs.
- Research, Development, and Innovation: Innovation plays a significant role in transforming India's economy. India's progress in the Global Innovation Index reflects its potential.
- Initiatives like the CoWin platform for monitoring vaccination programs and the development of data ecosystems through platforms like UPI and Aadhaar are driving India's growth.
- Climate Change Adaptation: India should focus on developing and customizing adaptation technologies and solutions to address climate-induced vulnerabilities.
- This includes addressing challenges in agricultural production, food security, disaster risks, resource access (water, power, coastal resources), and human health in the face of climate change.
Kerala Blast: Who are Jehovah’s Witnesses (Indian Express)

- 30 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
- Two people were killed and scores injured after a series of blasts at a Sunday prayer convention of the Jehovah’s Witnesses sect near Kochi.
- The incident took place at the Zamra International Convention and Exhibition Centre at Kalamassery, where around 2,500 faithful from across the state had gathered for a prayer session.
- Dominic Martin, an estranged member of Jehovah’s Witnesses, who is now in police custody, posted a video on social media taking responsibility for the act.
Who are Jehovah’s Witnesses?
- Jehovah’s Witnesses are a Christian sect with a distinctive monotheistic belief system.
- They do not adhere to the Holy Trinity doctrine, which sees God as existing in three equal persons: the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ), and the Holy Spirit.
- Origins in the 1870s:
- The sect's origins trace back to the Bible Student movement initiated in the 1870s by American pastor Charles Taze Russell.
- Today, the Governing Body of Jehovah’s Witnesses is headquartered in Warwick, New York.
- The primary organization responsible for disseminating the sect's doctrines is the Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society of Pennsylvania, also headquartered in Warwick.
- Worship of Jehovah:
- They worship Jehovah as "the one true and Almighty God, the Creator."
- Jehovah is viewed as the God of key biblical figures, including Abraham, Moses, and Jesus.
- Their places of worship are called "Kingdom Halls," which are plain, functional buildings resembling small conference centers.
- View of Jesus Christ:
- Jehovah’s Witnesses recognize Jesus Christ as the "King of God’s Kingdom in heaven" but not as the Almighty God.
- Their beliefs are solely based on the text of the Bible, which they consider to be the word of God.
- Rejection of Traditional Festivals:
- They do not celebrate Christmas or Easter, as they believe these festivals have roots in Pagan traditions.
- Evangelical Work and End-Times Beliefs
- Door-to-Door Evangelism:
- Jehovah’s Witnesses are well-known for their evangelical work, which involves going door to door to share their religious teachings, often referred to as "The Truth."
- They believe that the end of the world is imminent.
- According to their teachings, the "Kingdom of God" will replace human governments and fulfill God's purpose for the Earth.
- Religious Isolation:
- Jehovah’s Witnesses tend to keep a distance from other religious groups.
- They maintain strict neutrality in political affairs and avoid affiliation with other religions.
- Despite their own religious isolation, they respect the choices made by individuals in matters of religion and politics.
- Political Neutrality:
- Jehovah’s Witnesses are well-known for their political neutrality, which sets them apart from many other religious groups.
- While they accept government authority in many matters and pay taxes, they do not vote in elections, serve in the military, or salute the flag.
- They believe that engaging in such acts compromises their primary loyalty to God.
Jehovah’s Witnesses: A History of Persecution
- Jehovah’s Witnesses have no political affiliations, and they renounce violence. However, they make an easy target for governments looking for internal enemies, as they refuse to bow down to government symbols. Many nationalists call them “enemies of the state.”
- As a result, they have often suffered persecution throughout history in many parts of the world.
- In Nazi Germany, they were killed in concentration camps.
- African Jehovah’s Witnesses faced violence for refusing to support dictators.
Jehovah’s Witnesses in India:
- Jehovah’s Witnesses have been present in India since 1905.
- They established an office in 1926 in Bombay (now Mumbai), and obtained legal registration in 1978.
- The Jehovah’s Witnesses website (jw.org) mentions that their members in India have at times been accused of trying to convert people due to their evangelical work.
Jehovah’s Witnesses and National Anthem Case:
- Bijoe Emmanuel & Ors vs State Of Kerala & Ors
- In 1985, three Jehovah’s Witness students in Kerala faced suspension for refusing to sing the national anthem on religious grounds.
- Their case reached the Supreme Court in 1986, emphasizing the freedom of conscience enshrined in Article 25 of the Constitution.
- The Supreme Court ruled that respectfully standing, without vocal participation, during the anthem did not violate the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act of 1971.
- This landmark case balanced religious freedom with national symbols, setting a significant precedent in India's legal history.
India-Qatar Relations: Death Sentence to Eight Former Indian Navy Officers (Indian Express)

- 28 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a setback to India’s efforts at securing their release, eight former personnel of the Indian Navy, arrested in an alleged case of espionage, were handed the death sentence by a court in Qatar.
About India- Qatar Relations:
- Economic Cooperation: Economic cooperation is a cornerstone of the India-Qatar relationship.
- Qatar exports products like LNG, LPG, chemicals, petrochemicals, fertilizers, plastics, and aluminum articles to India.
- India exports cereals, copper articles, iron and steel articles, vegetables, and fruits to Qatar.
- In 2021, India ranked among the top four largest export destinations for Qatar and is among the top three sources of Qatar's imports, with bilateral trade totaling approximately $15 billion.
- The India-Qatar Start-up Bridge is a collaborative initiative to connect the startup ecosystems of both nations.
- Energy Partnership: Qatar is a significant supplier of LNG to India, and this energy partnership has grown over the years.
- India's total imports from Qatar in FY2022-23 were valued at $16.81 billion, of which LNG imports alone were worth $8.32 billion.
- Political and Diplomatic Relations: Both countries maintain strong political ties. High-level visits by leaders from both sides have led to the signing of various agreements and Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) covering diverse areas, including defense, trade, and investment.
- For instance, former PM Manmohan Singh’s visit in November 2008
- In November 2022, Vice President Jagdeep Dhankar traveled to Doha for the FIFA World Cup and addressed the Indian diaspora.
- Cultural and People-to-People Exchanges: The cultural aspect of the relationship is strengthened by the presence of a large Indian community in Qatar.
- An extensive Indian community of over 800,000 individuals resides in Qatar, fostering strong ties between the two nations through expatriates.
- The Qatar Fund for Development (QFFD) provided COVID-19 medical relief materials to India.
- Defense Collaboration: The two countries have explored defense collaboration and joint military exercises, strengthening their defense ties and strategic partnerships.
- For instance, Joint military exercises, such as the Za’ir-Al-Bahr (Roar of Sea) naval exercise, promote cooperation between the Indian and Qatari Navies.
- The 2008 Defense Cooperation Agreement is a pivotal aspect of India-Qatar relations, involving mutual training and visits, notably for the Qatari Emiri Naval Forces in India.
- Maritime collaboration includes interactions between Indian and Qatari ports.
- Education and Skill Development: Qatar has also partnered with India in the field of education and skill development, providing opportunities for Indian workers to enhance their skills and employability.
- For instance, 14 Indian schools in Qatar are offering CBSE curricula.
What are the challenges associated with the India-Qatar relationship?
- Detention of 8 Ex-Navy Personnel: Eight former Indian Navy personnel are imprisoned in Qatar, with some facing the death sentence.
- This is a significant concern, particularly as a large Indian expatriate community resides in Qatar.
- Strained Relations Post-2017 Qatar Blockade: India's engagement with nations like Saudi Arabia and the UAE has strained its relationship to some extent with Qatar due to the Gulf blockade in 2017.
- Geopolitical Complexities within OIC: Qatar, in collaboration with Turkey, Pakistan, and Malaysia, has challenged the UAE and Saudi Arabia within the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), raising concerns for India.
- Support for Militant Groups: Qatar's alignment with Iran and its support for groups like the Muslim Brotherhood and Hamas have caused tensions with India.
- Historical Rivalry with Israel: Qatar and Israel have a historical enmity, and India's growing ties with Israel have not been well-received by the Qatari leadership.
- Controversy Over Prophet Comments: Controversy arose due to comments by an Indian ruling party spokesperson against the Prophet.
- Qatar demanded a public apology, which was resolved after the spokesperson was removed from their position.
- Media Concerns About Minorities: Qatar's media (i.e. Al Jazeera) has expressed concerns about the treatment of minorities by the ruling government, further impacting bilateral relations.
- Participation in US-Led Initiatives: India's involvement in U.S.-led initiatives like I2U2 and the IMEEEC has contributed to strained relations with Qatar, particularly in light of the Hamas attacks and the Abraham Accords.
Why is Qatar important to India's Look West Policy despite these challenges?
- Geopolitical Significance: Qatar hosts leaders from various opposition and militant movements, including Hamas, the Muslim Brotherhood, and the Taliban, positioning itself as a key player in the intricate dynamics of the Islamic world.
- Global and Regional Interests: Qatar houses American and Turkish military bases while maintaining diplomatic ties with Iran, which significantly influences the geopolitics of the region.
- Soft Power Influence: Qatar wields substantial soft power through the government-owned Al Jazeera broadcaster, allowing it to shape opinions across the region.
- GCC Membership: Qatar's membership in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) holds strategic importance for India, especially concerning regional matters such as Kashmir.
- UNSC Support: Qatar's support is crucial for India's pursuit of a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council.
- Business Relationships: Numerous major Indian companies operate in Qatar, fostering economic ties between the two nations.
- Gulf Stability: The stability of the Gulf region is of paramount importance to India's energy and maritime security, underscoring the significant role Qatar plays in this context.
What are the options available for India in the present case?
- Legal Recourse and Diplomatic Pressure: In response to the verdict, India is actively pursuing a range of legal options and retains the possibility of escalating the matter to the International Court of Justice (ICJ) if due process is not followed.
- Transfer of Sentenced Persons: There exists a bilateral agreement for the transfer of sentenced prisoners, enabling Indian nationals sentenced in Qatar to serve their sentences in India.
- Economic Influence: India's substantial market for Qatar's LNG stands as a potent economic leverage.
- Given India's sustained growth and energy demands, Qatar maintains a vested interest in nurturing a robust economic relationship.
- This opens avenues for potential concessions and a review of trade agreements that could mutually benefit both nations.
- Prudent Diplomacy: Effectively navigating challenges and engaging in constructive dialogue underscores the importance of diplomacy in resolving international disputes.
- For instance, India is dedicated to providing consular and legal support and has raised the verdict issue with Qatari authorities, particularly in light of families filing a mercy plea with the Emir of Qatar.
Conclusion
The situation involving the 8 Indian citizens and former naval servicemen necessitates a concerted effort involving legal, diplomatic, and humanitarian actions. The government must place a strong emphasis on negotiations with Qatari authorities, potentially warranting high-level intervention. At this juncture, a swift and diplomatic approach, rather than brinkmanship, is of utmost importance.
Provisions Regarding Surrogacy in India (The Hindu)

- 27 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Two-judge Bench comes to the rescue of a woman suffering from the rare medical condition of Mayer Rokitansky Kuster Hauser syndrome by staying the operation of a law that threatened to wreck her hopes of becoming a mother.
What was the case, and why did the woman approach the Supreme Court?
- There was a woman who had the Mayer Rokitansky Kuster Hauser (MRKH) syndrome.
- Medical board records showed she has absent ovaries and an absent uterus, hence she cannot produce her eggs/oocytes.
- The couple had begun the process of gestational surrogacy, through a donor, last year.
- However, a government notification (on March 14 this year) amended the law, banning the use of donor gametes.
- It said “intending couples” must use their gametes for surrogacy.
- The petition was filed in the SC challenging the amendment as a violation of a woman’s right to parenthood.
What are Gametes?
- Gametes are reproductive cells that fuse during fertilization to form a new organism.
- They are haploid cells, meaning they contain only one copy of each chromosome. This ensures that the offspring has the correct number of chromosomes from both parents.
- In animals, the male gamete is called a sperm cell and the female gamete is called an egg cell.
- Sperm cells are small and motile, while egg cells are large and nonmotile.
- Gametes are produced through a process called meiosis, which reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell by half.
- This process is essential for sexual reproduction.
What were the petitioner’s arguments?
- The woman said that she started the surrogacy procedure months before the amendment took effect, so it cannot be implemented retrospectively.
- She and her spouse were unable to proceed with the surrogacy procedure in order to become parents because the Surrogacy (Regulation) Rules 2022 amendment prohibited the use of donor eggs.
- The Surrogacy Act 2021, which recognized situations where a couple would have to choose gestational surrogacy in order to become parents due to a medical condition, is in conflict with the amendment.
- The medical or congenital conditions listed in the Surrogacy Rules allowed a woman to choose to become a mother through gestational surrogacy.
- These included not having a uterus, having one that is missing, having an abnormal uterus, or having had surgery to remove the uterus because of a medical condition like gynecological cancer.
- It was explicitly stated in the Surrogacy Rules that the woman had the final say in the matter.
- Government's argument: According to the law, surrogacy cannot be used unless the intended couple and the child are "genetically related." This made using donor eggs exempt.
What was the Supreme Court’s (SC’s) Verdict?
- The Surrogacy Act's main provisions, both in form and content, imply that the amendment is prima facie contrary to their intended meaning.
- It was a "woman-centric" law that allowed gestational surrogacy.
- The woman's incapacity to become a mother due to her ailment or birth defect was the sole reason for choosing to have a surrogate child.
- Among these conditions were the lack of a uterus, multiple pregnancies, recurrent miscarriages, or an illness that would make the pregnancy dangerous or impossible for her to carry to term.
- The amendment cannot be in conflict with the Rules, which expressly identify the lack of a uterus or any related condition as a medical necessity for gestational surrogacy.
- The court emphasized that the surrogate child would be related to the husband in response to the government's argument that the child should be "genetically related" to the couple.
- It should be noted in this context that the phrase "genetically" related to the prospective couple must be interpreted as referring to the husband.
What is surrogacy?
- Surrogacy is the act of bearing and delivering a child on behalf of a different individual or couple (i.e., intended parents).
- A woman who bears a child on behalf of another woman is known as a surrogate mother. This can be done either naturally (traditional surrogacy) or by implanting a fertilized egg from another woman into her womb (gestational surrogates).
- The biological mother of the child serves as a traditional surrogate. Because it was their egg that was fertilized by the father's sperm.
- Eggs from the mother (or an egg donor) can now be collected, and fertilized with sperm from the father (or a sperm donor), and the embryo can be placed into the uterus of a gestational surrogate thanks to a process known as "in vitro fertilization" (IVF). Gestational surrogates are genetically unrelated to the child because their egg was not used in the process.
Provisions regarding the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021:
- Prohibition of commercial surrogacy: The Act prohibits commercial surrogacy, meaning that no monetary or other material benefit can be given to the surrogate mother, except for medical expenses and insurance coverage.
- Permissibility of altruistic surrogacy: The Act only allows altruistic surrogacy, where the surrogate mother is a close relative of the intending couple or intending woman, and does not receive any financial or other material benefit, except for medical expenses and insurance coverage.
- Eligibility criteria for intending couples and surrogate mothers: Intending couples must be legally married and have a medical condition that necessitates surrogacy.
- Surrogate mothers must be between the ages of 25 and 35 years, have at least one child of their own, and be medically and psychologically fit for surrogacy.
- Registration of surrogacy clinics and assisted reproductive technology (ART) banks: All surrogacy clinics and ART banks must be registered with the National Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy Board.
- Establishment of National and State Boards: The Act establishes a National Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy Board and State Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy Boards to regulate the practice of surrogacy and to ensure the welfare of surrogate mothers and children born through surrogacy.
- Penalties for violations: The Act prescribes penalties for violations of its provisions, including imprisonment for up to 10 years and fines up to Rs. 10 lakhs.
Women, Marriage and Labour Market Participation (The Hindu)

- 26 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
- With the high percentage of married women in the working-age population, there is growing concern about the economic impact of their non-participation in India's workforce.
- Women who work have better economic opportunities and more household decision-making authority.
- The work of Nobel laureate Claudia Goldin draws attention to differences in women's employment outcomes.
What is the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR)?
- The Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) is an important indicator in labor market studies because it represents the proportion of a country's working-age population that is either employed or actively looking for work.
- The female labor force participation rate (FLFPR) is the percentage of working-age women who are currently employed or looking for work.
Data on Women’s Labour Participation:
- In 2022, the global LFPR for women was 47.3%.
- Women's LFPR decreased in developing nations;
- For example, in India it fell from 28% in 1990 to 24% in 2022.
- Based on data from India's NSSO Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) for individuals aged 25 to 49, the following trends have been noted::
- Compared to the Usual Principal and Subsidiary Status (UPSS) status, married women exhibit a significantly lower employment proportion under the Usual Principal Status (UPS) status.
- Marriage has a significant impact on women's labor-force outcomes.
- The female labor force participation rate (FLFPR) among married women between the ages of 25 and 49 decreased by 5% in 2022–2023.
- The FLFPR for this group decreased to 45% in 2022–2023 from 50% in 2004–05.
- Most of the FLFPR decline is concentrated in the 25–29 age range.
What is the Periodic Labour Force Survey?
- The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) was introduced by the NSO in April 2017 in response to the growing need for labor force data to be available at more frequent intervals.
- PLFS aims to accomplish two main goals:
- to estimate, for the urban areas only in the CWS, the major employment and unemployment indicators (i.e., the worker population ratio, labor force participation rate, and unemployment rate) in a brief period of three months.
- to annually estimate the indicators of employment and unemployment in both CWS and usual Status in both rural and urban areas.
What is NSSO?
- The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) is an organization within the Government of India's Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- It is in charge of carrying out extensive nationwide sample surveys on a range of socioeconomic topics.
- The NSSO was established in 1950 to meet the data needs of post-independence India.
- The National Sample Survey (NSS) Commission, which is composed of state officials, academics, and subject-matter experts, provides overall direction for the organization's operations.
- Regular "rounds" of surveys are carried out by the NSSO, and they typically last for a year. These rounds are usually named after the year they begin, such as "68th round" or "75th round."
- In 2019, the NSSO merged with the Central Statistics Office (CSO) to form the National Statistical Office (NSO) in order to streamline and consolidate the country's statistical system.
What is the reason behind the decline/low participation rate of women in labor force?
- Movement of Production: According to economist Claudia Goldin (1994), adult women's LFPR shows a U-shaped pattern during periods of economic expansion.
- She also mentioned that the shift in production from the family farm, small business, and home to the larger market is the reason for the initial drop in the participation rate.
- Marriage Issues: When married women indicate a desire to enter the workforce, the problem gets worse.
- Women's LFPR tends to decline after marriage for a variety of reasons.
- When comparing the Usual Principal Status (UPS) to the Usual Principal and Subsidiary Status (UPSS), married women exhibit a significantly lower employment proportion, according to the PLFS data (25 to 49 years).
- The age range of 25 to 29 is where the majority of the decline in the female LFPR is found.
What are the Problems Faced by Married Women?
- Growing Family Obligations: Due to women's lower educational attainment and restricted mobility, there is a growing social disapproval of women working outside the home, which in turn leads to an increase in family obligations.
- Marriage Increases Domestic Responsibilities: In addition to increasing women's domestic responsibilities, the institution of marriage places numerous social and cultural constraints on them that limit their ability to engage in the workforce.
- Social Elements: Women's limited labor participation is also influenced by a number of other societal factors, including their location and affiliations with particular castes and religions.
- The level of wealth in their home and the social norms that are in place regarding women working outside the home also influence how many women enter the workforce.
Other challenges faced by married women:
- When women choose to return to the workforce after marriage, they typically show a preference for jobs that are located close to their homes and provide more flexibility.
- Due to a number of social restrictions, women also face gender-asymmetrical professional costs.
- It causes gender differences in decisions about fertility, age at marriage, income inequality, and premarital career choices.
- It has been noted that women in higher social classes typically fulfill home duties in order to conform to strict social norms.
- Women from lower socioeconomic classes are more likely to work, mainly due to financial limitations brought on by poverty.
- When compared to their more educated counterparts, women who are illiterate are more likely to enter the workforce following marriage.
- According to empirical research on the distribution of female labor across various industry sectors in India, the agricultural sector continues to be the most popular choice for women seeking employment.
What can be solutions to promote greater participation of married women in the labour market?
- Offering Child Care Services: By helping women handle their caregiving duties, this program will allow them to dedicate enough time to gainful employment.
- It is also crucial to invest in the establishment of childcare services in office buildings through cooperative models and in industrial corridors with industry associations.
- Public crèches can be run in worksite clusters like labor nakas, close to markets, industrial areas, and densely populated low-income residential areas.
- Additionally, the establishment of work environments that give precedence to the requirements and welfare of female employees, the supply of safe modes of transportation, and the growth of opportunities for part-time employment would function as inducers for increased female participation in the Indian labor market.
Government Initiatives to increase female labor participation rate:
The government has targeted the issue by taking various prominent steps to increase the female labour participation rate which includes:
- Enactment of the Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017 which provides for enhancement in paid maternity leave from 12 weeks to 26 weeks.
- Provisions for mandatory crèche facility in establishments having 50 or more employees.
- Issue of an advisory to the States under the Factories Act, 1948 for permitting women workers in the night shifts with adequate safety measures.
Conclusion
- Married women's lower participation in the labor force and their propensity to leave the workforce after marriage are caused by a variety of factors.
- In light of this, it is critical to consider appropriate strategies for advancing women's empowerment during this period of rapid economic expansion.
- Empowering women in the workforce is not only economically necessary, but also a crucial first step toward achieving gender equality and inclusive economic growth.
Canada-India Standoff and Vienna Convention (Indian Express)

- 25 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
- Relationships between India and Canada, which were already tense, have gotten worse as a result of Canada's most recent accusation that India has unilaterally revoked the diplomatic immunity of Canadian diplomats based in India.
- According to Canada, India has violated both the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (VCDR) and international law.
Context:
- The recent diplomatic dispute between India and Canada arose due to controversial comments by Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau linking Indian agents to the killing of a Khalistani separatist leader.
- In response, India demanded that Canada withdraw 41 of its diplomats to ensure parity in diplomatic representation.
- India cited provisions of the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations to justify its demand.
- The convention allows the receiving state to limit the size of a diplomatic mission to a reasonable number.
- Canada complied with India's demand, withdrawing the 41 diplomats, but expressed concerns about potential violations of the Vienna Convention.
- This ongoing dispute between India and Canada has brought attention to the Vienna Convention and its rules governing diplomatic relations between states.
What is the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations?
- The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961) is a United Nations treaty that set some common principles and terms on how countries must treat each other’s diplomatic representatives, in order to ensure friendly relations and maintain proper communication channels between countries.
- It was approved on April 14, 1961, at the Neue Hofburg in Vienna, Austria, during the United Nations Conference on Diplomatic Intercourse and Immunities.
- 193 nations have ratified the convention as of right now.
- India ratified it through the Diplomatic Relations (Vienna Convention) Act of 1972.
Major Provisions of the Vienna Convention:
- Diplomatic immunity is one of the Convention's guiding principles.
- It guarantees that ambassadors can carry out their responsibilities without intimidation, fear, or threat.
- Diplomats are exempt from arrest and detention under Article 29 of the Convention.
- The host nation is obliged to treat the diplomatic agent with due respect and to take all reasonable precautions to shield the diplomat's person, liberty, or dignity from any harm or violation.
Does India Have the Right to Ask Any Country to Reduce the Size of its Mission?
- Yes, India has every right to make unilateral decisions and it’s actions are entirely compliant with the parity clause.
- According to the Ministry of External Affairs, India's action is consistent with Article 11(1) of the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (VCDR).
- According to Article 11.1 of the Convention, the host nation may set reasonable and suitable restrictions on the size of a foreign diplomatic mission, taking into account the specific needs of the mission as well as the conditions and circumstances that currently exist in the host country.
- The receiving State may, at any time and without cause, declare the head of the mission or any member of the diplomatic staff persona non grata, or unwelcome, in accordance with Article 9 of the Convention.
- According to MEA, India feels that a reciprocal diplomatic presence in both nations is necessary due to the significantly greater number of Canadian diplomats in India and their ongoing meddling in (India's) internal affairs.
- People with diplomatic privileges and immunities are required by Article 41(1) of the VCDR to refrain from meddling in the domestic affairs of the receiving state.
- Therefore, it would be a violation of Canada's VCDR if these Canadian diplomats were meddling in internal matters in India.
- Additionally, this may be cause to revoke or limit diplomatic immunity.
- In Line with India’s Diplomatic Relations Act of 1972,
- India passed this law in accordance with the Diplomatic Relations Act of 1972 to give the VCDR effect.
- According to Section 4 of this Act, if a nation violates the VCDR, the central government may limit diplomatic privileges and immunities granted to that nation.
International Precedents and Legal Grounds for India's Actions:
- UK's Restriction on the Soviet Mission: The United Kingdom imposed restrictions on the Soviet Union's mission in the UK due to the discovery of Russian diplomats involved in unacceptable activities.
- The UK invoked Article 11 of the VCDR to substantiate its decision.
- US Measures against the Iranian Mission (1979): In 1979, the United States exercised its authority to limit the number of Iranian diplomats stationed in Washington.
- Estonia and Moldova's Approach to the Russian Mission: Earlier this year, Moldova and Estonia both requested Russia to reduce the size of its mission, emphasizing the principle of parity.
- In justifying their actions, both Moldova and Estonia relied on Article 11 of the VCDR.
- Moldova alleged the involvement of Russian diplomats in destabilizing Moldova's internal situation, while Estonia argued that Russian diplomats were actively undermining its security.
Conclusion
Beyond the legal aspects, a larger issue is the current lack of trust between Ottawa and New Delhi. Both sides should focus on adopting confidence-building measures to address this issue.
Allegations of breaching international law could further strain the situation and hinder diplomatic relations.
Allocation of Election Symbols to Political Parties in India (Indian Express)

- 24 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
- The Supreme Court declined to hear a petition that the ruling Telangana's Bharat Rashtra Samiti (BRS) party filed challenging the attribution of election symbols to two other parties.
- BRS contended that the symbols 'road roller' and 'chapatti roller' given to 'Yuga Thulasi Party' and 'Alliance of Democratic Reforms Party' resembled BRS's car symbol, potentially causing confusion among voters during elections.
- The Supreme Court declined the petition, expressing confidence in voters' ability to distinguish between the symbols.
How are Election Symbols Allotted to Political Parties in India?
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) is responsible for symbol allotment, operating under The Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968.
- This order aims to specify, reserve, choose, and allocate symbols for elections in Parliamentary and Assembly Constituencies, primarily for recognized political parties.
- Symbols can be either reserved for exclusive use by recognized political parties or 'free' for unrecognised registered parties.
- Unrecognized registered parties or candidates can choose from 'free' symbols because they have not secured enough percentage of votes to fulfill the prescribed criteria to become a recognised party.
- Once selected by parties, these symbols become 'free' for others to choose in subsequent elections.
- Recognized national and state parties receive exclusive symbols.
- For instance, the Samajwadi Party leader Mulayam Singh Yadav chose the symbol of a bicycle for the 1993 Uttar Pradesh Assembly polls.
- The ECI announces party symbols through notifications published in the Gazette of India.
- As per recent notifications, there are six national parties, 26 state parties, and 2,597 registered unrecognised parties in India.
Do political parties get to state their preferences?
- The 1968 order empowers the Election Commission (EC) to manage the specification, reservation, choice, and allocation of symbols for parliamentary and assembly elections, particularly for recognizing political parties.
- Unregistered parties are required to provide a list of ten symbols in order of preference from the set of free symbols published by the EC.
- Parties have the option to propose up to three new symbols of their choice.
- These proposals should include names and clear designs, ranked in order of preference.
- The EC may consider these proposals for allocation as a common symbol if no objections arise.
- Proposed symbols must not resemble existing reserved or free symbols, have no religious or communal connotations, and should not depict birds or animals.
What happens when a recognised political party splits?
- When a recognised political party splits, the Election Commission takes the decision to assign the symbol.
- For instance, the Congress party, in the first elections of 1952, had a pair of bulls as its symbols. Following splits in the party over the years, the current symbol of hand eventually went to the party.
- More recently, the EC allowed the Eknath Shinde faction of the Shiv Sena to retain the party’s traditional bow and arrow symbol, while the Udbhav Tackeray faction was allotted a flaming torch.
- The factions had asked for the trident (Trishul) and the mace (Gada), which were rejected citing religious connotations.
- Both factions had also wanted the ‘rising sun’, which the EC pointed out was the DMK’s election symbol.
- In case of a split, the EC is empowered to decide on the claims of opposing factions under Paragraph 15 of the Symbols Order, 1968.
- After considering all of the relevant information, considering the circumstances of the case, and consulting with the parties' representatives, the EC makes a decision.
- All of these rival sections or groups are bound by the Commission's decision.
- When registered but unrecognized parties split, the ECI usually advises the warring factions to settle their differences internally or go to court.
Sadiq Ali Case
- In the Sadiq Ali v. Election Commission of India (1971), it was decided that in matters of disputes among groups of a political party, the test of majority support among members of the party's "organizational and legislative wings" was the critical test to decide the dispute.
- It includes the Party Constitution Test, Party Constitution Aims and Objectives Test, and Majority Test.
What happens to the faction that doesn't receive the symbol of the parent party?
- Before 1997, the Election Commission recognized the group not obtaining the symbol based on specific criteria defined in Paras 6 and 7 of the Symbols Order.
- This recognition depended on whether the breakaway party had the support of a sufficient number of MPs/MLAs according to those criteria, leading to their recognition as a National or State Party.
- However, in 1997, the Election Commission determined that merely having MPs and MLAs was insufficient.
- This was because these elected representatives had contested and won elections on the tickets of their parent (undivided) parties.
- Consequently, the Election Commission introduced a new rule.
- Under this rule, the splinter group of the party, different from the group that received the party symbol, was required to register itself as a separate political party.
- These newly registered parties could only attain national or state party status based on their performance in elections at the state or central level following their registration.
Registration of Political Parties:
- According to the Election Commission of India (ECI), any party seeking registration must submit an application to the Commission within 30 days of the date of its formation in accordance with the Commission's rules.
- It acts in accordance with Article 324 of the Indian Constitution and Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- According to Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act of 1951, all political parties must register before participating in elections.
Dam Safety Act (The Hindu)

- 23 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
- India has nearly 6,000 large dams, 80% of which are over 25 years old and pose safety risks.
- A new Dam Safety Act (DSA) was enacted in late 2021.
- On October 4, 2023, the Teesta III dam at Chungthang, one of the largest hydropower projects in India, was destroyed by a glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) in North Sikkim's South Lhonak Lake.
- Since then, reports have shown there were no early warning systems, risk assessments, or preventive measures implemented as required by the Act.
What are the provisions of the Dam Safety Act, 2021?
- The Dam Safety Act was introduced in the Rajya Sabha in December 2021 in response to inadequate surveillance and maintenance, which resulted in dam failure-related disasters.
- The Act outlined important duties and required the creation of bodies at the federal and state levels to carry them out.
- Key provisions:
- Dam safety policies and rules would be supervised by a National Committee on Dam Safety;
- State-level disputes would be handled by a National Dam Safety Authority, which would also be responsible for implementation;
- The Chairman of the Central Water Commission (CWC) would be in charge of dam safety protocols on a national scale.
- There would be a State Committee on Dam Safety (SCDS) and a State Dam Safety Organization (SDSO).
What do the States need to do?
- States are required by provisions to: categorize dams according to risk of hazards; carry out routine inspections; develop emergency action plans; implement emergency flood warning systems; and carry out safety reviews and period risk assessment studies.
- States were asked to report and document incidents of dam failures.
- Until now, no statutory provision required systemic reporting of failures, and no single agency was in charge of tracking this information.
- The CWC maintains a list, but it is not consistently updated.
Is there any action taken for failing to comply?
- Any provision of the Act that is broken is punishable by imprisonment and/or monetary penalties.
- The entity shall be punished with imprisonment for a term which may extend to two years if such obstruction or refusal to comply with directions results in the loss of lives or imminent danger.
- For failing to comply with the Dam Safety Act, the Sikkim High Court ordered the Gati Hydropower Project company to pay two widowed mothers 70 lakh in February 2023.
What are the challenges?
- Blind spots in the implementation of the law
- The Dam Safety Act (DSA) fails to encourage transparency and does not support risk-based decision-making.
- Such disasters occur frequently, and their size reveals a pattern of neglect.
- Access to Information
- A strong Dam Safety Act (DSA) should make it simple for various stakeholders to access information, but India's framework falls short.
- Safety at dams serves a public purpose.
- The general public should have immediate access to all information regarding dam safety, including the roles played by all institutions, committees, and authorities, as well as their reports, decisions, minutes, and agendas.
- Nothing is, however, in the public domain.
- Absence of a cyclical review
- Periodic reviews are frequently not carried out, or if they are, the results are not readily accessible to the public.
- Comprehensive dam safety evaluations are mandated by the Act for dam builders. The failure's analysis and reporting, however, are not standardized.
How is dam safety undertaken?
Dam safety is a function of many parts:
- Design and Construction: Building dams with safety margins is the initial step.
- Dams should be designed and constructed to withstand potential hazards.
- Maintenance and Operation: Dams need regular upkeep and should be operated following safety guidelines to ensure their long-term stability.
- Real-Time Data: Continuous monitoring and recording of dam data in an easily accessible format is crucial for prompt action in case of emergencies.
- Hazard Forecasting: Being prepared for hazardous events is key. This includes forecasting potential risks and having emergency plans in place.
- The incident in Sikkim revealed poor compliance with safety measures, ranging from dam design to the capacity of spillways that manage water release.
- Hazard Profiling: Regular assessment and profiling of potential hazards are mandated.
- Hazards can change due to factors like climate change, urbanization, and water usage patterns.
- Periodic Reviews: Periodic reviews are essential to update inundation maps and dam reservoir capacity rules.
- This contributes to downstream safety.
- Review Frequency: Spillway capacity and safety metrics should be reviewed approximately every five years.
- However, these reviews may not be conducted as required.
- Dam Safety Evaluations: The Act requires comprehensive dam safety evaluations by dam builders.
- Unfortunately, there's a lack of standardization in how failure analysis and reporting are carried out.
- Non-Compliance: In certain cases, such as the July-August floods in Himachal Pradesh, dam builders were found guilty of non-compliance with dam safety regulations, leading to government notices.
Manual Scavenging in India (The Hindu)

- 21 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court, in a judgment, said claims of fraternity, equality, and dignity among citizens remain a mere illusion if a sizeable section of society is forced to enter sewers for a living and die trapped in them even a decade after the outlawing of the inhuman practice of manual scavenging.
What is Manual Scavenging?
- The practice of manually cleaning, handling, and disposing of human excreta and other waste materials from dry latrines, open drains, and sewers is known as manual scavenging.
- Although it has been formally prohibited since 1993, manual scavenging has long been a problem in India.
Manual Scavenging in India:
- According to the 2011 Census of India, there were over 740,000 households in India where manual scavenging was still practiced.
- The National Commission for Safai Karamcharis reports that between 2016 and 2019, 482 manual scavengers lost their lives while clearing septic tanks and sewers throughout India.
- An advocacy group fighting to end manual scavenging, the Safai Karamchari Andolan, calculates that there are still roughly 1.8 million manual scavengers in India.
- Many manual scavengers suffer from a variety of health issues, including skin diseases, respiratory problems, and even death, as a result of their exposure to toxic fumes in septic tanks and sewer lines.
- From 2019 to 2022, a total of 233 people died as a result of accidents while performing hazardous sewer and septic tank cleaning.
- Haryana had the most deaths (13), followed by Maharashtra (12) and Tamil Nadu (10).
Why does manual scavenging still occur frequently in India?
- Ineffective sewage management system: In India, the majority of municipalities lack the newest sewage cleaning equipment, necessitating the entry of sewage workers through manholes into the underground sewerage systems.
- However, because they are much less expensive to hire, contractors illegally hire unskilled laborers and pay them a daily wage.
- Social stratification based on caste: Manual scavenging has long been connected to India's caste system, where some castes have been marginalized and compelled to work in fields that are deemed "unclean" or "polluting."
- Manual scavenging as a source of income for these marginalized communities continues as a result of the persistence of caste-based discrimination and social stigma.
- Lack of Alternative Livelihood Opportunities: Manual scavenging is common in affected communities due to a lack of alternative employment opportunities.
- Many manual scavengers are trapped in a cycle of poverty and exclusion, with no access to education or skill development programs that could provide them with alternative means of subsistence.
- Due to a lack of economic alternatives, they must continue to engage in manual scavenging for survival.
What Are the Consequences of Manual Scavenging?
- Health Effects: Manual scavengers face significant health risks as a result of direct exposure to human waste and hazardous substances.
- They are especially vulnerable to diseases like cholera, typhoid, hepatitis, and various respiratory infections.
- The lack of protective equipment and poor sanitation conditions exacerbate the health risks, leading to an increase in illnesses and premature deaths among manual scavengers.
- Dignity and Human Rights Violations: Manual scavenging is a clear violation of the individual’s dignity and human rights.
- They live in deplorable and inhumane conditions, handling human waste with their bare hands and without access to basic sanitation facilities.
- This occupation reinforces caste-based oppression by perpetuating social stigma, discrimination, and marginalization of affected communities.
- Psychological and Emotional Trauma: Manual scavenging can have serious psychological and emotional consequences for those involved.
- Their mental health suffers as a result of their constant exposure to filth, the humiliation of their work, and the discrimination they face.
- Manual scavengers frequently suffer from feelings of shame, low self-esteem, and depression, which can lead to long-term psychological trauma.
Steps Taken by Government to Reduce Manual Scavenging:
- In an effort to prevent deaths caused by hazardous cleaning of sewers and septic tanks, the government created the NAMASTE scheme or National Action Plan for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem.
- The Employment of Manual Scavengers and Construction of Dry Latrines (Prohibition) Act, 1993 was enacted to prohibit manual scavenging.
- The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and Their Rehabilitation Act of 2013 was passed to strengthen the ban and provide for the rehabilitation of manual scavengers.
Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013:
- It was passed in 2013 to make provisions for the banning of employment as manual scavengers and the rehabilitation of manual scavengers and their families.
- The act's main goals are to get rid of unhygienic latrines, forbid hiring manual scavengers, forbid dangerous manual cleaning of septic and sewer tanks, and keep track of manual scavengers and their rehabilitation.
- Provisions:
- No person or organization may hire or engage any person to perform manual scavenging.
- Anyone who engages in manual scavenging in violation of the provisions of the MS Act, 2013, faces imprisonment for up to two years, a fine of up to one lakh rupees, or both.
- It outlines the measures taken to help sanitation workers and their families get back on their feet.
- Following a survey of manual scavengers, the local administration must issue them with a photo identity card containing information about their family members as well as monetary compensation.
- Their children must receive a government scholarship, as well as a residential plot and the funds necessary to build on it.
- It is also illegal for a person to clean a sewer or septic tank without the employer providing protective gear and cleaning devices and following safety precautions.
- Every local authority is required by the Act to ensure that there are no insanitary latrines in its jurisdiction and that no manual scavengers are employed.
- A municipality or a panchayat is a local authority that is in charge of sanitation in its jurisdiction.
- Local governments must build community sanitary latrines (that do not require manual removal of human excreta) and make plans for their sanitary upkeep at all times.
- They must also ensure that technological appliances are used to clean sewers, septic tanks, and other similar spaces in their jurisdictions.
- Despite legal prohibitions and government efforts to eliminate manual scavenging, the practice continues in various parts of the country.
Way Forward
- Technology-Driven Solutions: Innovative tools and machinery that can take the place of manual scavenging work must be developed.
- For instance, septic tanks and sewer lines can be cleaned by automated robots, eliminating the need for human intervention in potentially dangerous situations.
- Encourage Entrepreneurship and Skill Development: There is a need to encourage affected individuals' training and skill development, allowing them to explore alternative livelihood opportunities.
- To assist former manual scavengers in transitioning to safer and more dignified professions, governments and non-governmental organizations can provide vocational training in areas such as plumbing, electrical work, computer literacy, and entrepreneurship.
- Upgrades to Sanitation Infrastructure: Invest in sanitation infrastructure development and improvement, such as the construction of modern toilets, sewage treatment plants, and efficient waste management systems.
- These improvements will reduce the need for manual scavenging and provide safer waste disposal options.
10 Years of China's Visionary Belt and Road Initiative (The Hindu)
- 20 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently Chinese President Xi Jinping commemorated the 10th anniversary of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
What is the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)?
- The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), also known as the One Belt, One Road (OBOR) initiative, is a massive infrastructure and economic development project launched by China.
- It was introduced by Chinese President Xi Jinping in 2013 and aims to enhance trade and investment connectivity between China and various countries in Asia, Europe, Africa, and beyond.
- The initiative comprises two main components:
- The Silk Road Economic Belt: This land-based component envisions the construction of a network of roads, railways, and pipelines connecting China to Europe through Central Asia, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe.
- Maritime Silk Road: This sea-based component focuses on developing a network of ports and coastal infrastructure, linking China to Southeast Asia, South Asia, Africa, and Europe via the Indian Ocean and South China Sea.
What are the objective of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)?
- The BRI aims to stimulate economic development, improve trade relationships, and foster cultural exchanges across participating countries.
- It involves extensive investments in infrastructure, including roads, railways, ports, and energy projects, with the goal of boosting economic growth and connectivity.
- The initiative has been met with both enthusiasm and scrutiny, as it has the potential to reshape global trade and geopolitical dynamics.
- It is scheduled to be finished in 2049, to coincide with the centennial of the People's Republic of China.
Geographic Corridors:
The land-based Silk Road Economic Belt envisions six key development corridors:
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- New Eurasian Land Bridge Economic Corridor.
- China-Indochina Peninsula Economic Corridor.
- China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor.
- China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor.
- China-Myanmar Economic Corridor.
What is India's position on BRI?
- India objects to the project on the grounds of transparency and national sovereignty. India has boycotted China's BRI summits in 2017 and 2019 and has not endorsed the BRI joint statements issued by the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
- The main reason India opposes the BRI is that it includes the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), which passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK), which India claims as its own territory.
- India also contends that BRI projects must adhere to international norms, the rule of law, and financial sustainability, and must not create debt traps or environmental and social risks for host countries.
- India has instead advocated for other connectivity programs, such as the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), a G7 program to finance infrastructure projects in developing nations.
What are the concerns related to the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)?
- Debt burden: The debt sustainability and transparency of BRI projects, particularly in countries with weak governance, high corruption, and low credit ratings.
- Some critics have accused China of engaging in "debt-trap diplomacy" by lending money to countries like Sri Lanka and Zambia that eventually find themselves unable to repay, and then seizing strategic assets or extracting political concessions in exchange.
- Geostrategic Concerns: The Belt and Road Initiative has raised geopolitical concerns, particularly about China's growing influence and control over critical infrastructure in partner countries.
- Because of these concerns, some countries have reconsidered their participation in the initiative.
- Political Tensions: Geopolitical rivalries and disputes, such as the India-China border dispute, have hampered BRI project implementation in some regions.
- The progress of the initiative could be hampered by these political tenses.
- Multilateral Governance: The BRI is not a multilateral initiative, but rather a collection of mostly bilateral projects. This decentralized approach may cause coordination and governance issues.
- Unlike initiatives such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), the BRI lacks a centralized governing structure, making collective action difficult.
- Environmental and social concerns: The BRI's infrastructure development projects have been criticized for their potential environmental and social impacts.
- It is difficult to ensure that BRI projects are environmentally sustainable and take into account the well-being of local communities.
Alternatives to BRI concerns include:
- Blue Dot Network (BDN): A multi-stakeholder initiative led by the United States, Japan, and Australia to promote high-quality global infrastructure development standards.
- B3W Initiative: The B3W Initiative, led by the G7, seeks to address the infrastructure gap in developing and low-income countries.
- Global Gateway: The European Union launched the Global Gateway to compete with BRI, focusing on various sectors such as climate change, digitalization, health, and education.
- PGII (Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment): A rebranded version of B3W. It is a G7 initiative to fund infrastructure projects in developing countries. India is in favor of it.
- India's Efforts:
- India's counter to BRI, supported by Lines of Credit (LOCs) to countries in Asia, Africa, the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), and Latin America.
- It includes projects such as IMEC and INSTC.
- During the recent G20 summit, India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) initiative
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) connecting India to the Middle East and Russia
To protect its own interests, China has established a network of investments that has left several low- and middle-income countries in severe debt; thus, global initiatives have provided a counter-block for monopoly and taken steps to focus on more inclusive and sustainable development.
Supreme Court’s Same-sex Marriage Verdict (Indian Express)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
A five-judge Constitution Bench led by Chief Justice of India (CJI) D Y Chandrachud unanimously rejected same-sex marriage recognition. In a 3-2 majority decision, the Bench also refused to authorize civil unions for non-heterosexual couples.
What is the Supreme Court's Observation?
The Denial of Marriage as a Fundamental Right:
- All five judges on the Bench agreed that there's no fundamental right to marry in the Constitution.
Limitations on Modifying the Special Marriage Act (SMA), 1954:
- They also unanimously agreed that changing the Special Marriage Act (SMA) of 1954 using gender-neutral language to allow same-sex marriage isn't possible.
- The petitioners wanted the Supreme Court to interpret the word marriage as being between spouses instead of man and woman.
- Alternatively, they asked for removing the gender-restrictive provisions of the SMA.
- The Chief Justice of India (CJI) said that striking down the SMA provisions would impact the legal framework for interfaith and inter-caste couples.
- Interpreting the SMA in a gender-neutral way, he added, would be like making new laws from the judiciary, which goes against the separation of powers.
Rejection of Civil Unions for Non-Heterosexual Couples:
- The bench ruled 3:2 against allowing civil unions for non-heterosexual couples.
- The minority judges believed that the right to form unions comes from the fundamental right to freedom of speech and expression, and the right to life.
- They argued that the right to enter into a union shouldn't be restricted based on sexual orientation, as it's a violation of Article 15 of the Constitution.
- The majority view was that it's the legislature's role, not the Court's, to recognize and grant legal status to non-heterosexual relationships formally.
- Regarding rights for non-heterosexual couples, all five judges noted that a high-level Cabinet committee will consider the rights that can be given to non-heterosexual couples.
- This could include joint bank accounts, same-sex spouses being beneficiaries for provident funds, pensions, inheritance, and making medical decisions for the other spouse.
Considerations on Adoption Rights of Children:
- On the rights to adopt children, the Supreme Court unanimously agreed that one's sexual orientation shouldn't determine one’s suitability to be adoptive parents.
- However, in a 3:2 split verdict, the Court upheld the existing regulations that deny unmarried couples, including queer individuals, the right to adopt a child as a couple.
- Since same-sex marriage isn't legal in India, they also cannot adopt children as a couple.
- In 2022, the Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) issued new Adoption Regulations, requiring a couple to be in a stable marital relationship for two years to be eligible for adoption.
- This made it impossible for queer couples to adopt, as it prohibited individuals in live-in relationships from adopting children.
- The minority view by CJI Chandrachud and Justice Kaul argued that CARA's guidelines discriminate against unconventional, unmarried couples seeking to adopt children.
What is the Legal Status of Same-Sex Marriages in India?
- The right to marry isn't explicitly recognized as a fundamental or constitutional right in the Indian Constitution; instead, it's a statutory right.
- However, the recognition of marriage as a fundamental right has evolved through judicial decisions by India's Supreme Court.
- These legal declarations are binding on all courts throughout India under Article 141 of the Constitution.
Earlier Views of the Supreme Court on Same-Sex Marriages:
- Marriage as a Fundamental Right (Shafin Jahan v. Asokan K.M. and others 2018):
- The Supreme Court, while referring to Article 16 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the Puttaswamy case, determined that the right to marry a person of one's choice is an integral aspect of Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Article 16 (2) in the Indian Constitution prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth, residence, or any of these factors.
- The right to marry is an inherent part of the liberty guaranteed by the Constitution as a fundamental right, as it pertains to individuals' ability to make decisions crucial to their pursuit of happiness, including matters of belief and faith.
- LGBTQ Community's Entitlement to Constitutional Rights (Navtej Singh Johar and others v. Union of India 2018):
- The Supreme Court ruled that members of the LGBTQ community "are entitled, just like all other citizens, to the complete spectrum of constitutional rights, including the liberties protected by the Constitution."
- They have the right to equal citizenship and "equal protection of the law.
What are the Arguments Supporting Same-Sex Marriage?
- Equal Rights and Protection Under the Law: Every person, regardless of their sexual orientation, has the fundamental right to marry and build a family.
- Parity in Legal Rights: Same-sex couples should enjoy the same legal rights and safeguards as heterosexual couples.
- Combating Discrimination: The non-recognition of same-sex marriage constitutes discrimination that undermines the dignity of LGBTQIA+ couples.
- Strengthening Families and Communities: Marriage offers social and economic advantages to couples and their families, which are equally valuable to same-sex couples.
- Cohabitation as a Fundamental Right: The Chief Justice of India (CJI) has recognized cohabitation as a fundamental right, emphasizing the government's responsibility to legally acknowledge the societal significance of such relationships.
- Challenging Absolute Biological Gender: The Supreme Court of India acknowledges that biological gender is not an absolute concept and that gender is more intricate than merely one's physical characteristics.
- The understanding of a man or woman is not fixed.
- Global Acceptance: Same-sex marriage is legally recognized in many countries worldwide.
- Denying this right to individuals in a democratic society contradicts global principles. Notably, same-sex marriage is legal in 32 countries.
What are the Arguments Opposing Same-Sex Marriage?
- Religious and Cultural Beliefs: Many religious and cultural communities uphold the belief that marriage should exclusively involve a man and a woman.
- They contend that altering the traditional definition of marriage would contradict their fundamental religious and cultural principles.
- Procreation: Some argue that the primary purpose of marriage is procreation, and same-sex couples are unable to have biological children.
- Consequently, they believe that permitting same-sex marriage contradicts the natural order of reproduction.
- Legal Concerns: There are apprehensions that legal issues may arise if same-sex marriage is allowed, including complications related to inheritance, taxation, and property rights.
- Some argue that modifying existing laws and regulations to accommodate same-sex marriage would be overly complex.
- Adoption Challenges: When queer couples adopt children, it can lead to societal stigma, discrimination, and potential negative effects on the emotional and psychological well-being of the child.
- This is particularly relevant in Indian society, where universal acceptance of the LGBTQIA+ community is not yet achieved.
What Can Be the Way Forward?
- Promoting Awareness: Conduct awareness campaigns to foster equality and acceptance of all sexual orientations, broadening public understanding of the LGBTQIA+ community.
- Legal Reforms: Consider amending the Special Marriage Act of 1954 to permit same-sex couples to legally marry and access the same rights and privileges as heterosexual couples.
- In the interim, establishing contract-like agreements can provide similar rights for LGBTQIA+ individuals.
- Dialogue and Engagement: Initiate conversations with religious leaders and communities to bridge the gap between traditional beliefs and contemporary attitudes regarding same-sex relationships.
- Legal Challenges: The Indian LGBTQIA+ community can legally challenge the constitutionality of existing laws that prohibit same-sex marriage.
- Such challenges can set a legal precedent, potentially leading to the legalization of same-sex marriage.
- Collaboration: Achieving the legalization of same-sex marriage necessitates a collective effort involving various stakeholders, including the LGBTQIA+ community, government, civil society, and religious leaders.
- Collaboration is key to creating a more inclusive society where everyone has the freedom to love and marry whomever they choose, regardless of their gender.
What is the Special Marriage Act (SMA) 1954?
In India, all marriages can be registered under their respective personal laws, such as the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955, or the Muslim Marriage Act, 1954. Alternatively, couples can choose the Special Marriage Act, 1954, for their marriage registration, ensuring the protection of the rights of both partners.
About:
- The Special Marriage Act, 1954, is legislation enacted by the Parliament of India that provides for civil marriages, open to Indian citizens and nationals abroad, regardless of their religious or faith affiliations.
- This act enables individuals from diverse religious backgrounds to unite in matrimony and outlines the procedures for both solemnizing and registering the marriage.
Key Provisions:
- Advance Notice to the Marriage Officer: Couples are required to provide a notice to the Marriage Officer, along with the necessary documents, 30 days prior to the intended wedding date.
- Registration Process: After the submission of documents, both parties must be present for the issuance of a public notice, inviting objections.
- The registration takes place 30 days after the notice date, following the resolution of any objections that may have arisen during that period, overseen by the Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM).
- Presence of Parties and Witnesses: On the registration day, both parties, along with three witnesses, must be present to complete the marriage registration process.
Women Reservation Bill 2023 (Times Now)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Congress leader Dr. Jaya Thakur on Monday filed a PIL in the Supreme Court for implementing the Women's Reservation bill before the 2024 general elections. Former congress president Sonia Gandhi also alleges BJP govt of creating anti-women policies and deprived women of their rights.
What Are the Main Provisions of the Women’s Reservation Bill?
- Reservation for Women in the Lower House: The Bill introduces Article 330A to the constitution, borrowing inspiration from Article 330, which focuses on seat reservations for SCs/STs in the Lok Sabha.
- The Bill proposes the rotation of reserved seats for women among different constituencies in states or Union Territories.
- For seats designated for SCs/STs, the Bill aims to reserve one-third for women in a rotational manner.
- Reservation for Women in State Legislative Assemblies: The Bill introduces Article 332A, making it mandatory to reserve seats for women in every state Legislative Assembly.
- Additionally, one-third of the seats reserved for SCs and STs must be specifically allocated to women, and one-third of the total seats filled through direct elections in the Legislative Assemblies will also be reserved for women.
- Reservation for Women in NCT of Delhi (New Clause in 239AA): The Bill amends Article 239AA of the constitution, which grants special status to the Union Territory of Delhi as the national capital concerning its administrative and legislative functions.
- The amendment specifies that laws enacted by the parliament shall apply to the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- Commencement of Reservation (New Article - 334A): The reservation for women will take effect after the census conducted following the Bill's commencement has been published.
- Subsequently, delimitation will occur to allocate reserved seats for women. This reservation will initially be implemented for a 15-year period.
- However, it will persist until a later date, as determined by a law passed by Parliament.
- Rotation of Seats: Seats reserved for women will undergo rotation after each delimitation, in accordance with a law enacted by Parliament.
What Is the Historical Background of Women's Reservation in Indian Politics?
- The roots of women's reservation in Indian politics can be traced back to the Indian national movement.
- In 1931, leaders Begum Shah Nawaz and Sarojini Naidu, representing three women's organizations, submitted a joint official memorandum to the British Prime Minister.
- This memorandum addressed the status of women in the new Constitution.
- The National Perspective Plan for Women, proposed in 1988, recommended reserving seats for women at various political levels, starting from the panchayat and extending to Parliament.
- These recommendations paved the way for the groundbreaking 73rd and 74th amendments to the Constitution.
- These amendments mandated that all State governments reserve one-third of seats for women in Panchayati Raj Institutions and one-third of chairperson positions at all levels of Panchayati Raj Institutions, as well as in urban local bodies.
- Within these reserved seats, one-third were specifically allocated for Scheduled Caste/Scheduled Tribe women.
- In 2001, the National Policy for the Empowerment of Women expressed the idea of considering reservations in higher legislative bodies.
- In May 2013, the Ministry of Women and Child Development established a committee on the status of women, which recommended ensuring a minimum of 50% reservation of seats for women in various governmental bodies, including local bodies, State Legislative Assemblies, Parliament, ministerial positions, and all government decision-making bodies.
- In 2015, the Report on the Status of Women in India highlighted the inadequate representation of women in state assemblies and Parliament.
- It recommended reserving at least 50% of seats for women in local bodies, State Legislative Assemblies, Parliament, ministerial positions, and all government decision-making bodies.
What Are the Supporting Arguments for the Bill?
- Historical Underrepresentation: Despite some progress, the number of women Members of Parliament remains relatively low.
- Research has shown that women elected under reservation policies invest more in public goods closely related to women's concerns.
- Reservations in local bodies have enabled women to make meaningful contributions.
- Gender Equality: Enhancing women's representation in politics is a crucial step toward achieving gender equality.
- However, India's ranking in the Global Gender Gap Report 2022, at 48th out of 146 in Political Empowerment, suggests room for improvement, with a score of 0.267, notably lower than top-ranking countries like Iceland and Bangladesh.
- Women's Right to Self-representation and Self-determination: Ensuring proportional representation for underrepresented groups in the political system is vital for their ability to influence policy-making.
- The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women underscores the need to eliminate discrimination in political and public life.
- Diverse Perspectives: A more diverse legislature, including a substantial number of women, can bring a broader range of perspectives to decision-making.
- This diversity can lead to more effective policy formulation and governance.
- Empowerment of Women: Women's reservation in politics empowers them at various levels, encouraging their participation in politics and inspiring them to take on leadership roles in other sectors.
- Promotion of Women's Issues: Women in politics often prioritize and advocate for issues directly affecting women, such as gender-based violence, women's health, education, and economic empowerment.
- Their presence can lead to the prioritization of these issues in policy discussions.
- Role Models: Women leaders in politics can serve as role models for young girls, encouraging them to aspire to leadership positions in various fields.
- Representation in politics can break stereotypes and inspire future generations.
- Examples include Indira Gandhi, India's first and only female Prime Minister, who served from 1966 to 1977, and Sushma Swaraj, the second woman External Affairs Minister of India after Indira Gandhi.
What Are the Arguments Against the Bill?
- Exclusion of Separate OBC Reservation: The Bill, while providing separate reservation for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes women within the existing one-third quota, does not include separate reservations for Other Backward Classes (OBC) women, who constitute a significant portion of the female population.
- No Reservation in the Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils: The Bill does not extend the reservation to women in the Rajya Sabha and legislative councils, which limits the scope of its impact.
- Dependence on Census and Delimitation: The implementation of reservation for women in Parliament relies on the census and delimitation processes.
- The delay in conducting the census and the potential political sensitivity of delimitation, particularly in regions with slower population growth, could hinder the bill's effectiveness.
- Concerns of Women as Proxies: The phenomenon of 'Panchayat Patis' in local governments, where husbands use their wives as proxy candidates for reserved seats, has raised concerns.
- With an extension of reservations to women in Parliament, there is a fear of the emergence of 'MP and MLA Patis,' where husbands wield real power.
- Challenges to Equality Principles: Opponents argue that the bill contradicts the principles of equality enshrined in the Constitution.
- Some believe it may perpetuate the unequal status of women, as they might not be perceived as competing on merit.
- Diverse Interests of Women: Women do not constitute a homogenous group, unlike caste-based groups.
- As a result, the arguments used to justify caste-based reservations may not be directly applicable to reservations for women.
- Women's interests cannot be isolated from other social, economic, and political strata.
- Restriction of Voter Choice: Some opponents of the Bill argue that seat reservations for women would limit voter choice.
- They propose alternative methods such as reservations for women within political parties and the implementation of dual-member constituencies.
- Lack of Widespread Consultation: The bill was introduced through a "supplementary list" in a hastily organized Parliament session.
- Critics argue that such a vital constitutional amendment for women's reservations should have been introduced following extensive discussion and analysis.
How Can Effective Implementation of Women's Representation be Achieved?
- Strengthen Independent Decision Making: Establishing independent monitoring systems or committees that explicitly prevent family members from exerting influence on the decision-making process of women representatives.
- This can be achieved by reducing the impact of patriarchal mindsets.
- Increasing Awareness and Education: Disseminate awareness among women about their rights and the significance of their participation in politics.
- Educational programs and awareness campaigns are instrumental in raising women's political engagement.
- Addressing Gender-based Violence and Harassment: Gender-based violence and harassment are significant barriers to women's involvement in politics.
- Address these issues through policy and legal measures to create a safer and more supportive environment for women in politics.
- Electoral Process Reforms: Implement reforms, such as introducing proportional representation and preferential voting systems, to enhance women's representation in politics.
- These reforms ensure that more women can be elected.
These are only a few strategies to increase the number of women in Indian politics. Achieving lasting change necessitates a multifaceted approach that tackles various challenges simultaneously.
Electoral Bonds Case Referred to 5-Judge Constitution Bench for Hearing (The Hindu)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
- Electoral Bonds Case Referred to 5-Judge Constitution Bench for Hearing on October 31 by Supreme Court.
- Two NGOs, Common Cause and Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR), have filed petitions challenging the electoral bonds scheme.
- The petitioners argue that anonymous funding through these bonds promotes corruption and infringes on citizens' right to a corruption-free nation.
What Are Electoral Bonds (EBs)?
- Electoral bonds, introduced by the Government of India in 2018, serve as a financial instrument to facilitate anonymous political donations.
Key Points:
- An electoral bond is a bearer instrument, akin to a promissory note, allowing the bearer to make contributions to political parties.
- Eligibility to Receive Electoral Bonds: Only registered political parties qualify to receive electoral bonds. Specific criteria apply:
- Recognition: The party must be registered under Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- Recent Election Performance: The party must have secured at least 1% of the votes polled in the most recent Lok Sabha or State Assembly election.
- Available Denominations: The Government has specified various denominations for electoral bonds, ranging from Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 1 crore.
- Authorized Bank: The State Bank of India (SBI) is the sole authorized institution for the sale of electoral bonds.
How They Work:
- Eligibility to Purchase: Indian citizens or entities incorporated in India are eligible to buy these bonds.
- Denominations: Electoral bonds are available in various denominations, such as Rs. 1,000, Rs. 10,000, Rs. 1,00,000, Rs. 10,00,000, and Rs. 1,00,00,000.
- Lifespan: These bonds have a short life of 15 days, during which they can be used solely for making donations to registered political parties.
- Availability: Electoral bonds can be purchased during specific periods, typically 10 days in the months of January, April, July, and October as specified by the Central Government.
- Encashment: Eligible political parties can encash these bonds through a designated bank account with the authorized bank.
- Disclosure: Political parties are required to disclose the amount received from electoral bonds to the Election Commission.
Key Features of Electoral Bonds:
- Anonymity: Electoral bonds ensure donor anonymity by keeping the identity of the donor confidential, both to the public and the recipient’s political party.
- Purchase and Redemption: These bonds can be purchased from authorized banks using legal tender.
- They are available in fixed denominations, with the minimum value set by the government.
- Redemption is exclusive to registered political parties within a specified time frame.
- Validity: Electoral bonds have limited validity, typically 15 days, during which they can be utilized for making donations to eligible political parties.
- Exclusivity: Only political parties that have garnered at least 1% of the votes in the most recent Lok Sabha or State Assembly election are qualified to receive electoral bond donations.
- Transparency: While donor identities are kept confidential, political parties receiving electoral bond donations are obligated to disclose donation details in their financial statements submitted to the Election Commission of India.
What are the Reasons for Introducing Electoral Bonds?
- Promoting Digital Transactions: The electoral bond scheme was introduced to encourage the transition from cash-based political donations to digital transactions.
- This shift aimed to reduce the use of unaccounted or black money in political funding.
- Ensuring Donor Anonymity: The scheme's objective was to safeguard donor anonymity.
- The donor's name is not disclosed on the bond. Donors contributing less than Rs 20,000 to political parties through the purchase of electoral bonds are not required to provide identity details like PAN, enhancing protection against potential backlash due to their political affiliations.
- Formalizing Political Contributions: Electoral bonds aimed to formalize political contributions by routing donations through the banking system.
- This formalization establishes a documented record of donations, making the process more transparent and accountable.
- Enhancing Transparency: While donor identities are shielded, the electoral bond scheme sought to enhance transparency in political funding.
- This is achieved by mandating political parties to disclose the details of electoral bond donations in their financial statements.
Criticisms of Electoral Bonds:
- Lack of Transparency: While political parties must disclose the amount of donations received through electoral bonds, the identity of donors remains confidential.
- Potential for Money Laundering: Critics argue that the anonymity provided by electoral bonds can be exploited for money laundering or funneling black money into the political system.
- Unequal Advantage to Ruling Parties: The sale of such bonds via a government-owned bank (SBI) raises concerns that the government could discern who is funding its opponents.
- This may create opportunities for extortion or victimization of companies that don't support the ruling party.
- Bypassing Election Commission Scrutiny: Unlike other forms of political funding, electoral bonds do not necessitate approval or verification by the Election Commission of India (ECI), potentially undermining the ECI's oversight role in regulating political funding and ensuring a level playing field.
- No Upper Limit on Funding: The removal of the cap on corporate donations to political parties has raised concerns about unlimited corporate funding.
- Concerns by RBI and EC: Both the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the ECI have expressed concerns about electoral bonds, highlighting the potential for increased black money circulation, money laundering, counterfeiting, and forgery.
- They also worry about setting a precedent for money laundering, eroding trust in Indian banknotes, undermining central banking legislation, legitimizing opacity in election funding, and facilitating money laundering for shell companies and foreign donations.
What are the Challenges Associated with Electoral Bonds?
- Compromising the Right to Know: Electoral bonds, by concealing the identities of donors and recipients, may pose challenges to the right to know, which is a component of the right to freedom of expression under Article 19 of the Constitution.
- Government Access to Donor Data: The risk of anonymity compromise arises from government access to donor data, enabling the government in power to exploit this information, potentially impacting the fairness of elections.
- Unauthorized Donations Violating Regulations: There is a risk of unauthorized donations violating existing regulations and guidelines.
- Crony Capitalism and Black Money: Electoral bonds may create a risk of crony capitalism, which entails mutually beneficial relationships between business leaders and government officials. It also opens the door to the infusion of black money into political funding.
- Loopholes in Corporate Transparency and Donation Limits: Concerns arise from loopholes regarding transparency for corporate entities and the removal of the 7.5% clause in the Companies Act 2013. This change raises concerns about the potential use of shell companies for political funding, including the circulation of black money.
Way forward
- Enhance Transparency: Take steps to improve transparency within the Electoral Bond Scheme.
- Stricter Regulation and Disclosure: Enforce more stringent regulations for political parties, mandating full disclosure and permitting the Election Commission of India (ECI) to scrutinize donations, both in terms of bonds and expenditure.
- Address Loopholes: Identify and rectify any existing loopholes in the Electoral Bond system to mitigate the potential for misuse, violation of donation limits, and risks like crony capitalism and the infusion of black money.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Review: Establish a system for continuous monitoring and review of the Electoral Bond Scheme.
- This can be achieved through judicial oversight, periodic assessments, and engagement with the public.
- This approach will help address emerging concerns and adapt to evolving political landscapes, ultimately promoting a more inclusive decision-making process.
Key Findings from the Association of Democratic Reforms (ADR) Report:
Donations and Funding Sources Analysis:
- The highest donations from Electoral Bonds, amounting to ?3,438.8237 crore, were received in the year 2019-20, coinciding with the general elections.
- In 2021-22, a year with 11 Assembly elections, donations through Electoral Bonds reached ?2,664.2725 crore.
- Out of the total donations of ?16,437.635 crore received by the 31 political parties analyzed, 55.90% came from Electoral Bonds, 28.07% from the corporate sector, and 16.03% from other sources.
National Parties:
- National parties experienced a significant surge in donations through Electoral Bonds, with a 743% increase from FY 2017-18 to FY 2021-22.
- In contrast, corporate donations to national parties increased by only 48% during the same period.
Regional Parties and Electoral Bond Contributions:
- Regional parties also witnessed a substantial proportion of their donations coming from Electoral Bonds.
Power-Biased Donations via Electoral Bonds:
- The BJP, as the ruling party, received the highest donation among national political parties, with more than 52% of its total donations sourced from Electoral Bonds, totaling ?5,271.9751 crore.
- The Congress secured the second-highest Electoral Bond donations, with ?952.2955 crore, constituting 61.54% of its total donations.
- The Trinamool Congress received ?767.8876 crore through Electoral Bonds, accounting for 93.27% of its total donations.
Digital India Act, 2023
- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The recent announcement of the Digital India Act, 2023 (DIA) marks a substantial step forward in constructing a forward-looking legal framework for India's thriving digital environment. This development is particularly timely, coinciding with the nation's ongoing digital transformation. The proactive approach by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) harmonizes with India's ambitious 'Digital India' initiative.
Current Status of Internet Usage in India:
- As of May 2023, India boasted a substantial 759 million Internet users.
- According to Statista, the Internet penetration rate in India reached 47.0% of the total population in early 2022.
- India stands as the second-largest online market across the globe, following China.
- This achievement is attributed to the growing affordability of smartphones, the extensive reach of mobile broadband networks, and the government's initiatives to bolster digital literacy.
- The character of internet usage has also transformed, with the rise of various intermediaries and the proliferation of new forms of user harm, including cyberstalking, trolling, and doxing.
What is the Digital India Act, 2023?
Objectives:
- To establish adaptable regulations that align with the evolving trends in technology and are amenable to updates according to the nation's digital infrastructure requirements.
- To provide a readily accessible adjudication mechanism for addressing online civil and criminal offenses.
- To ensure timely remedies for citizens, resolving cyber disputes and upholding the rule of law on the internet.
- To create a legislative framework grounded in overarching guiding principles to ensure compliance.
Key Components:
- Open Internet: As envisioned by the Indian government, an open internet should embody elements such as choice, competition, online diversity, fair market access, ease of doing business, and streamlined compliance for startups.
- These attributes serve to prevent the concentration of power and gatekeeping.
- Online Safety and Trust: The Act places a significant focus on protecting users from cyber threats, including issues like revenge porn, defamation, and cyberbullying.
- It aims to advocate for digital rights such as the Right to be Forgotten and the Right to Digital Inheritance (the passing down of digital assets to designated beneficiaries), safeguard minors and their data from addictive technology, and moderate the spread of fake news on social media platforms.
- Accountable Internet: The Act seeks to enhance accountability in internet use and activities.
- It introduces legal mechanisms for addressing complaints, upholds constitutional rights in cyberspace, promotes algorithmic transparency, periodic risk assessments, and disclosure norms for data collected by intermediaries.
Salient Features:
- The Digital India Act, 2023 (DIA) will serve as a replacement for the Information Technology Act of 2000 (IT Act), which has become inadequate in addressing the evolving challenges and opportunities brought about by the rapid growth of the internet and emerging technologies.
- DIA's framework will prioritize crucial aspects including online safety, fostering trust, ensuring accountability, upholding the principles of an open internet, and regulating cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain.
- DIA will collaborate with other pertinent laws and policies, encompassing the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, Digital India Act Rules, National Data Governance Policy, and amendments to the Indian Penal Code pertaining to Cyber Crimes.
- DIA will reassess the 'safe harbor' principle, which provides legal protection to online platforms such as Twitter and Facebook against liability for user-generated content.
- DIA introduces stringent Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements for wearable devices used in retail sales, backed by criminal law provisions and penalties.
- DIA aligns with the Digital India Goals for 2026, aimed at cultivating a USD 1 trillion digital economy and shaping the trajectory of global technologies.
Why the Digital India Act is Necessary?
- Outdated Regulations: The current IT Act of 2000 was conceived during a time when the internet had a mere 5.5 million users and is now inadequate to address the complexities of today's internet landscape.
- With 850 million users, numerous intermediaries, and emerging issues like cyberstalking and doxing, the IT Act falls short of addressing these modern challenges.
- Inadequacy of Existing Regulations: Despite the presence of regulatory components such as Intermediary Guidelines, Digital Media Ethics Code, and data protection rules, they prove insufficient in governing cutting-edge technologies.
- Adapting to Technological Advancements: With advancements like AI, Blockchain, and IoT, the legal framework must evolve to effectively address their distinctive challenges.
- This entails enhancing cybersecurity measures, fortifying data protection, and regulating emerging tech sectors.
- Addressing E-commerce and Online Content: The surge in e-commerce, digital transactions, and online content sharing necessitates up-to-date regulations.
- The Digital India Act will handle matters concerning consumer protection, electronic contracts, and content moderation on social media platforms.
- Global Alignment and Best Practices: To actively engage in the global digital landscape, India's regulations must be in harmony with international standards and best practices.
Challenges in Implementing Digital India Act (DIA), 2023:
- Balancing regulation with innovation and economic growth: Tighter regulations, especially in emerging tech sectors, might unintentionally hinder entrepreneurial endeavors and discourage foreign investments.
- Freedom of Expression: The review of the 'safe harbor' principle for online platforms has the potential to affect freedom of expression.
- Balancing regulatory needs without curbing this fundamental right is a delicate task.
- Resource and Infrastructure Requirements: Effective enforcement of the DIA will demand substantial resources, expertise, and infrastructure.
- Investments in these areas are essential.
- Balancing Stakeholder Interests: Striking a balance between the interests of various stakeholders, including tech giants and citizens' rights, presents a significant challenge.
- Ensuring that all perspectives are considered in the implementation process is crucial.
- Surveillance and Privacy Concerns: Critics argue that certain provisions of the act may grant excessive surveillance powers to the government, potentially compromising privacy rights.
- Strong safeguards should be integrated to prevent abuse of power and privacy violations.
- Data Localization and Cross-Border Data Flows: The act's stance on data localization is a contentious issue.
- While localization can enhance data protection and security, it may disrupt cross-border data flows, impacting global businesses reliant on efficient data transfers.
How Other Countries Approach Data Privacy Regulation:
- Approximately 70% of countries globally have implemented data protection legislation, as reported by the United Nations trade agency UNCTAD.
- The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted in 2018, is often considered the most stringent privacy and security law globally and serves as a global standard.
- Various nations, including China and Vietnam, have recently strengthened regulations concerning the cross-border transfer of personal data.
- In 2018, Australia enacted a bill that granted law enforcement access to encrypted data.
Way Forward for Effective Implementation of Digital India Act (DIA), 2023:
- Stakeholder Involvement: Engage all relevant stakeholders, including government bodies, tech companies, legal experts, and civil society, in the drafting and execution of the act.
- This collaborative effort will lead to a balanced and comprehensive legal framework.
- Balancing Regulation and Innovation: While stricter regulations, particularly in emerging tech fields, are essential, they should be carefully designed to avoid unintentionally stifling entrepreneurship and deterring foreign investments.
- Striking the right balance between regulation and innovation is imperative.
- Collaboration and Capacity Enhancement: Invest in building the capacity of law enforcement agencies, the judiciary, and regulatory bodies to ensure effective enforcement of the DIA.
- International Alignment: Collaborate with other countries and international organizations to align the DIA with global best practices and standards in the digital sphere.
- Public Awareness: Conduct public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about their rights and responsibilities in the digital realm, promoting a culture of digital literacy.
Conclusion
The effectiveness of the Digital India Act, 2023 will hinge on its practical implementation. Striking the right balance between enforceability, privacy protection, and fostering innovation is key. Addressing these considerations with care, this act holds the promise of sculpting a digital environment that benefits not only individuals and businesses but the entire nation.
Israel-Palestine Conflict
- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
- In a recent onslaught, Hamas, the ruling militant group in Gaza, launched a fierce attack on Israel via land, air, and sea, resulting in numerous casualties and reigniting the century-old Israel-Palestine Conflict.
- This has prompted global and regional powers to intervene.
- Israel, which had recently solidified peace agreements with neighboring nations like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, faces potential strain due to this attack.
- Moreover, Israel declared a state of war as Palestinian militants launched a barrage of rockets into the southern and central regions, combining a breach of security barriers and rocket attacks.
- The assault occurred on the 50th anniversary of the Yom Kippur War, with the goal of reclaiming territory lost during the 1967 conflict, prompting the Israel Defense Forces to initiate airstrikes on Hamas targets in Gaza.
What is the History of Israel-Palestine Conflict?
Early phase:
- In the 19th century, the land of Palestine was home to a diverse population, with approximately 86% Muslims, 10% Christians, and 4% Jews, living together in harmony.
- However, in the late 1800s, a European group called the Zionists decided to colonize this land with the aim of establishing a Jewish homeland. Initially, they explored various locations in Africa and the Americas but eventually settled on Palestine.
- The rise of Hitler to power in Europe led to a significant increase in Jewish immigration to Palestine. This influx of Jewish people contributed to the escalation of conflict in the region.
Balfour Declaration:
- The British government issued this historic document in 1917, endorsing the concept of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
- This declaration triggered a significant increase in Jewish immigration to the region.
Establishment of Palestine:
- As a result of the inability to control the escalating conflict between Arabs and Jews, Britain withdrew its forces from Palestine in 1948.
- This decision transferred the responsibility for resolving the conflicting claims to the newly formed United Nations.
- The UN proposed a partition plan to create independent Jewish and Arab states within Palestine. However, it faced widespread rejection by most Arab nations.
1948 Arab-Israeli Conflict:
- In 1948, the declaration of Israel's independence by the Jewish community led to an attack by neighboring Arab states.
- By the war's end, Israel had gained control of approximately 50% more territory than what the UN partition plan had originally anticipated.
UN Partition Plan:
- In 1947, the United Nations decided to step in, but it didn't adhere to the principle of 'self-determination of peoples.'
- Under significant Zionist influence, the UN proposed allocating 55% of Palestine for a Jewish state.
- This decision was made, despite the fact that the Jewish population represented only around 30% of the total population and owned less than 7% of the land.
1947-1949 Conflict
- Hostilities erupted almost immediately after the approval of the November 1947 Resolution.
- On May 14, 1948, just one day before the expiration of the British Mandate (as Palestine was a British colony), Britain announced the 'establishment of a Jewish State in Eretz-Israel, to be named the State of Israel.'
- This declaration ignited a large-scale conflict known as the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
- By the war's conclusion, Israel had gained control over 78 percent of Palestine, resulting in the redrawing of the map."
The Suez Crisis of 1956:
- In 1956, Israel, France, and the United Kingdom initiated a military operation against Egypt in response to the nationalization of the Suez Canal.
- In the course of this conflict, Israel gained control of the Sinai Peninsula and the Gaza Strip. However, due to international pressure, these territories were relinquished, and Israel withdrew in 1957.
1967 War - The Six-Day War:
- Often referred to as the Six-Day War, this conflict began with a highly effective surprise attack by Israeli forces on Egypt.
- During this war, Israel took control of the remaining 22% of Palestine that had evaded its grasp in 1948, including the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
- Additionally, Israel occupied parts of Egypt (which were later returned) and still retains control over areas in Syria.
Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO):
- The PLO was established with the goal of liberating Palestine from Israeli control and Jewish dominance while seeking to establish the influence of the Muslim Brotherhood in the Arab world.
- In 1975, the United Nations granted the PLO observer status and acknowledged the right of Palestinians to self-determination.
Camp David Accords (1978):
- The U.S.-brokered 'Framework for Peace in the Middle East' provided the foundation for peace negotiations between Israel and its neighboring countries, aiming to resolve the 'Palestinian problem.'
- Unfortunately, these efforts ultimately went unfulfilled.
The Rise of Hamas:
- In 1987, Hamas was established as a violent offshoot of Egypt's Muslim Brotherhood, with the intention of advancing its agenda through armed conflict or 'jihad.'
- The U.S. government has designated Hamas as a terrorist organization.
- Notably, in 2006, Hamas achieved success in the Palestinian Authority's legislative elections.
- Subsequently, in 2007, it ousted Fatah from Gaza, leading to a geographical split in the Palestinian movement.
- The year 1987 also witnessed escalating tensions in the occupied territories of the West Bank and Gaza, resulting in the First Intifada, which evolved into a minor conflict between Palestinian militants and the Israeli army.
The Oslo Accords:
- In 1993, the Oslo Accords marked an agreement between Israel and the PLO to officially acknowledge each other and renounce the use of violence.
- These accords also led to the creation of the Palestinian Authority, which gained limited autonomy in the Gaza Strip and certain areas of the West Bank.
- By 2005, Israel initiated a one-sided withdrawal of Jewish settlements from Gaza, while still maintaining strict control over all border crossings, effectively establishing a blockade.
- In 2012, the United Nations elevated Palestinian representation to that of a 'non-member observer state.
Repeated Clashes and Ceasefires:
- Israel and Hamas have been involved in several significant conflicts, including Operation Cast Lead (2008-2009), Operation Pillar of Defense (2012), and Operation Protective Edge (2014).
- These conflicts resulted in substantial casualties on both sides.
- In 2021, tensions escalated due to Israeli policies in Jerusalem, including the proposed eviction of Palestinian families from Sheikh Jarrah and restrictions on access to the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound.
- In response, Hamas launched rocket attacks on Jerusalem and other Israeli cities, and Israel carried out airstrikes on Gaza.
- These hostilities led to the loss of over 250 Palestinian lives and 12 Israeli lives.
- A ceasefire was eventually brokered by Egypt, with support from the United States and other international parties.
Possible Implications of the Israel-Palestine Conflict on India:
- Trade Relations: An escalation in the conflict might have consequences for India's trade ties with Israel, particularly in critical sectors like defense equipment.
- Israel is a major supplier of defense technology to India, and any disruptions in this trade partnership could impact India's defense capabilities.
- Diplomatic Complexities: India has traditionally pursued a balanced foreign policy approach, maintaining relations with both Israel and Arab nations.
- If the conflict escalates and involves other Arab countries, it could pose diplomatic challenges for India.
- Striking a balance between its ties with Israel and maintaining positive relations with Arab nations could become more intricate.
- Economic and Strategic Links with the Middle East: India's economic and strategic ties with the Middle East have gained significance, especially concerning initiatives like the India-Middle East-Europe economic corridor.
- If the conflict intensifies and includes other regional actors like Hezbollah and Iran, it may lead to instability in the West Asian region, affecting India's interests.
- Energy Supplies: The West Asian region serves as a crucial source of energy imports for India.
- Any disruption in the stability of the region could potentially impact India's energy supply, resulting in economic challenges.
- Welfare of Indian Expatriates: India hosts a substantial expatriate population working in various Middle Eastern countries.
- The safety and well-being of these Indian citizens could be jeopardized if the conflict escalates, making it imperative for India to ensure their protection.
India's Position on the Israel-Palestine Conflict:
- In November 1947, India was one of the few countries that opposed the UN's partition plan, reflecting its own recent experience with independence. In the following decades, India's political leadership actively supported the Palestinian cause and maintained limited diplomatic relations with Israel.
Recognizing Palestine:
- India recognized Israel in 1950, making it one of the first non-Arab countries to do so.
- However, India also holds the distinction of being the first country to recognize the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole representative of the Palestinian people.
- Moreover, India was among the early nations to recognize Palestine's statehood in 1988.
UNHRC Engagement:
- In 2014, India supported a UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC) resolution that aimed to investigate Israel's human rights violations in Gaza.
- Despite endorsing this probe, India abstained from voting against Israel in the UNHRC in 2015.
De-Hyphenation Policy:
- As part of its 'Link West Policy' in 2018, India de-hyphenated its relationship with Israel and Palestine, treating both countries as independent and exclusive partners.
UN Vote on Palestinian NGO:
- In June 2019, India voted in favor of a decision introduced by Israel in the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) that objected to granting consultative status to a Palestinian non-governmental organization.
Balancing Act:
- India has endeavored to maintain its historical image as a moral supporter of Palestinian self-determination while simultaneously engaging in military, economic, and other strategic relations with Israel.
Advocating Peace:
- India firmly advocates dialogue and diplomacy as the only viable means to resolve the Israel-Palestine conflict.
- India also supports the role of the Quartet, composed of the US, Russia, the EU, and the UN, along with other regional and international actors, in facilitating peace talks between Israel and Palestine.
- In recent years, India’s position has also been perceived as pro-Israel.
Potential Solutions for the Israel-Palestine Conflict
- The need for a peaceful solution in the Israel-Palestine conflict is paramount, and it's incumbent on the global community to come together to facilitate it. However, the reluctance exhibited by the Israeli government and other involved parties has only exacerbated the issue. Therefore, adopting a balanced approach is crucial to maintain positive relations with both Arab countries and Israel.
- The Two-State Solution: One of the most broadly endorsed proposals is the two-state solution, which envisions the establishment of an independent and sovereign Palestinian state alongside Israel, with mutually agreed and internationally recognized borders.
- This approach seeks to address the fundamental issues at the heart of the conflict, including matters like Jerusalem, refugees, settlements, security, and water resources.
- It has garnered support from numerous global leaders, including countries like India, the United States, and China.
- The Abraham Accords: The recent normalization agreements, such as the Abraham Accords, between Israel and the UAE, Bahrain, Sudan, and Morocco, signify steps in the right direction.
- It's imperative for all regional powers to envision a peaceful resolution between Israel and Palestine, following the model of the Abraham Accords
- India's Role in Multilateral Organizations: India, in its role within multilateral organizations, should work diligently in collaboration with all relevant stakeholders to achieve security and stability in the Middle East and West Asia.
- With its substantial 90 lakh-strong Indian community in the region and its strategic connectivity to both West Asia and Europe, is well-positioned to engage with all sides in the complex West Asian landscape.
- Having been re-elected to the United Nations Human Rights Council for 2022-24, India should leverage these multilateral platforms to act as a mediator in resolving the Israel-Palestine issue.
- Genuine normalization between Israel and Palestine can only occur when past annexations and other contentious issues are effectively addressed.
Disputed Territories:
- Gaza Strip - Residence to approximately 2 million Palestinians, a significant portion of whom were displaced during or after the War of Independence in Israel.
- West Bank - This area is home to about 3 million Palestinians, primarily comprising Muslim Arabs. It also encompasses several Jewish holy sites that draw thousands of pilgrims annually.
- East Jerusalem - Jerusalem itself stands as a city marked by division and dispute. Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli conflict, it was physically divided into two parts. The western side was administered by Israel, while the eastern section was under Jordanian control. However, Israel seized control of the entire city during the Six-Day War in 1967.
The figures of Sammakka-Sarakka, their significance (Indian Express)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union cabinet has given its approval for the establishment of the Sarakka Central Tribal University in Telangana. This university will be located in the Mulugu district, with a budget of Rs 889 crore allocated for its development. During a recent visit to Telangana, the Prime Minister of India announced that the university would be named after Sammakka-Sarakka, a respected mother-daughter duo within the local tribal community.
News regarding the Sarakka Central Tribal University:
- The Central government had committed to establishing the Tribal University as part of the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014.
- This Act resulted from the division of the former state of Andhra Pradesh into Telangana and the remaining Andhra Pradesh state, following the Telangana movement.
- According to the Act, both Andhra Pradesh and Telangana were entitled to support for the creation of a tribal university each.
- However, the Telangana tribal university faced significant challenges, primarily related to the timely allocation of 500-600 acres of land.
About the Legend of Sammakka and Sarakka:
- The Legend of Sammakka and Sarakka tells the story of Sammakka, who was married to Pagididda Raju, a feudal chief of the Kakatiyas, a Deccan dynasty that ruled the Warangal area.
- They had two daughters, Sarakka (also known as Saralamma) and Nagulamma, as well as a son named Jampanna.
- In the 13th century, a battle against local rulers erupted due to the imposition of taxes.
- Tragically, Saralamma lost her life in the conflict, while Sammakka disappeared into the hills.
- The local Koya tribals held a belief that Sammakka transformed into a vermillion casket.
The Sammakka Saralamma Jatara:
- Mulugu hosts a biennial festival known as the Sammakka Saralamma Jatara, often referred to as the tribal version of the Kumbh Mela.
- This event commemorates the courageous stand of the mother-daughter duo against the taxation imposed on the Koya people.
- Over time, this festival has grown significantly in importance, and it is believed that after the Kumbh Mela, the Sammakka Saralamma Jatara attracts the largest number of devotees in the country.
- Approximately 1.5 crore devotees, hailing from various tribal and non-tribal communities, participate in this festival, including people from Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and other regions.
- Due to the immense turnout, the Samakka-Sarakka Jatara was designated as a state festival in 1996.
The Political and Cultural Significance of the Sammakka Saralamma Jatara:
- This festival receives consistent participation from both the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs and the Telangana state government, including the Chief Minister.
- The Central Government allocated Rs 6.25 crore for the yatras held in 2018, 2020, and 2022, with additional funds set aside for the construction of community shelters and other essential infrastructure.
- Furthermore, the Ministry of Tourism approved a substantial sum of Rs. 75.88 crore for the comprehensive development of a tribal circuit under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme.
- This tribal circuit encompasses Mulugu, Laknavaram, Medavaram, Tadvai, Damaravi, Mallur, and Bogatha Waterfalls, where the Sammakka-Sarakka temple is situated.
- Mulugu, an assembly seat reserved for Scheduled Tribes (ST), boasts a population of approximately 2.6 lakhs as per the 2011 Census, with a 75% ST population.
- Notably, the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Ramappa Temple is located just around 15 km from Mulugu.
How to read the NCRB 2022 report on crime in India (Indian Express)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released its annual report on crime in India for the year 2022 on Sunday (December 3).
- The report is a compilation of data on reported crime from across the country, and provides the big picture of broad trends in crime registration.
- Reports by the NCRB, which functions under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, include statistics on offences ranging from crimes against women to economic and financial crimes.
What does the 2022 NCRB report say?
- Overall Crime Statistics: In 2022, a total of 58,24,946 cognizable crimes, including 35,61,379 Indian Penal Code (IPC) crimes and 22,63,567 Special & Local Laws (SLL) crimes, were officially recorded.
- This marked a 4.5% decrease in case registrations compared to the challenging pandemic year of 2021.
- The crime rate has declined: The crime rate, indicating crimes registered per lakh population, saw a decline from 445.9 in 2021 to 422.2 in 2022.
- This shift is considered a more insightful indicator, recognizing that absolute crime numbers tend to rise with population growth.
- Increase in crime against women: Crime against women witnessed an uptick in 2022, with 4,45,256 reported cases, reflecting a 4% increase from the figures recorded in 2021.
- Notably, the major share of these crimes under IPC sections included 'Cruelty by Husband or His Relatives' (31.4%), 'Kidnapping & Abduction of Women' (19.2%), and 'Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage her Modesty' (18.7%).
- Increase in reporting of cybercrime: Cybercrime reporting witnessed a substantial surge, increasing by 24.4 percentage points compared to 2021, with a total of 65,893 cases.
- Predominantly, 64.8% of these cases involved fraud, followed by extortion (5.5%), and sexual exploitation (5.2%).
- Significant increase in suicides cases: Suicides reported during 2022 increased by 4.2% compared to 2021, totaling 1,70,924 cases.
- Major contributing factors were 'Family Problems (other than marriage-related problems)' (31.7%), 'Marriage Related Problems' (4.8%), and 'Illness' (18.4%), collectively accounting for 54.9% of total suicides.
- The overall male-to-female ratio of suicide victims stood at 71.8:28.2.
What are the headline trends in state-wise data in the report?
- The states/ UTs reporting the highest chargesheeting rate under IPC crimes are Kerala (96.0%), Puducherry (91.3%), and West Bengal (90.6%).
- This is the percentage of cases in which the police reached the stage of framing charges against the accused, out of the total true cases (where a charge sheet was not laid but a final report submitted as true, plus the total cases chargesheeted).
Does this mean that these states are more crime-prone than others?
-
Not necessarily. The NCRB report underlines that the data record the incidence of registered crime, not the actual occurrence of crime.
- This is an important distinction — and also an acknowledgement of the fact that there are limitations to the data.
- So, when reported crimes against women in Delhi rose significantly in the aftermath of the 2012 bus gangrape case, it may have been a reflection of increased awareness about the need for registering crimes, both among those affected and the police, rather than an actual increase in the incidence of crime against women.
What are the limitations to the data compiled by NCRB?
- Data Reflects Registered Crimes, Not Actual Occurrence: The NCRB report captures registered crimes, not the actual occurrence of crime.
- Instances like the reported rise in crimes against women in Delhi post the 2012 bus gangrape may indicate increased awareness rather than an actual surge in crime.
- Limitations Due to Principal Offence Rule: NCRB employs the Principal Offence Rule, counting the most severe crime in a single FIR.
- This may lead to undercounting, as in cases like 'Murder with Rape' being categorized as 'Murder' rather than rape.
- Local-Level Inefficiencies Impact Report Accuracy: Inefficiencies at the local level influence report accuracy as the NCRB data relies on submissions from local sources.
- The recording of details in an FIR, for example in suicide cases, depends on the understanding of the local police officer visiting the scene.
- Socio-Economic Causative Factors Not Captured: The NCRB acknowledges the omission of socio-economic causative factors or reasons for crimes in its data compilation.
- Important factors influencing criminal behavior may be overlooked.
- Factors Affecting Data Collection: Certain groups may refrain from reporting crimes due to reasons such as fear of an uncooperative or hostile response from the police.
- Shortage of police officers or unfilled vacancies at the local level can hinder effective data collection.
- These limitations underscore the need for a nuanced interpretation of NCRB data, recognizing the potential biases and gaps inherent in its compilation process.
About National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB):
- The NCRB was established in January 1986 as a body mandated to compile and keep records of data on crime.
- It’s headquartered is in New Delhi and is part of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Government of India.
- It was set up based on the recommendation of the National Police Commission, 1977 and a Task force, 1985.
Function of the NCRB:
- The NCRB functions as a crucial repository, aiding investigators in tracing crimes and criminals.
- It serves as a national warehouse for fingerprint records, encompassing both Indian and foreign criminals.
- This facilitates the identification and tracking of interstate criminals through fingerprint searches.
- Entrusted in 2009, the NCRB is responsible for monitoring, coordinating, and implementing the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS) project.
- In 2017, the NCRB introduced the National Digital Police Portal, empowering police officers to search for criminals or suspects in the CCTNS database.
- Additionally, it provides citizens with services like online complaint filing.
Reports Published:
- Apart from the esteemed Crime in India report, the NCRB publishes:
- Prisons Statistics India Report.
- Accidental Deaths and Suicides
- Prison Statistics
- Reports on Missing Women and children in India
Compilation of Data for NCRB Reports:
- For the NCRB’s flagship annual Crime in India reports, information is obtained from the police forces of 36 states and Union Territories.
- Similar data are furnished for 53 cities with populations exceeding 10 lakh each as per the 2011 Census, by respective state-level crime records bureaus.
- The information is entered by state/UT police at the level of the local police station, and is validated at the levels of the district and state, and finally, by the NCRB.
How to Enhance the Effectiveness of NCRB's Operations:
- States should leverage NCRB's data in crafting their annual police strategies, ensuring its multi-dimensional use in crime control to achieve tangible outcomes.
- Despite the connection of 16,390 police stations on CCTNS, it's crucial for central agencies like the CBI, NCB, and NIA to integrate with it, fostering comprehensive data sharing.
- It is imperative for all agencies to promptly join the CCTNS, striving for 100 percent completeness in data to enhance the network's efficiency.
- With the conclusion of phase 2 of ICJS, there is an opportunity to augment its utility further.
- This can be achieved through the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, analytical tools, and an enhanced fingerprint system.
Controversies Arising from a Potential Nobel Prize for mRNA COVID Vaccines (The Hindu)
- 05 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
The 2023 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine has been granted to Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman in recognition of their contribution to the development of mRNA vaccine technology. While the Nobel Prizes are intended to honor achievements that have benefited humanity, a strict assessment of scientific accomplishments raises questions about whether the subset of mRNA vaccines used during the COVID-19 pandemic fully aligns with these standards.
What is an mRNA Vaccine?
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA crucial for protein synthesis.
- It is synthesized from a DNA template during the transcription process.
- mRNA vaccines function by introducing a specific mRNA fragment that corresponds to a viral protein, often a segment of a protein located on the virus's outer surface.
- When this mRNA enters cells, it instructs them to produce the viral protein.
- As part of the body's natural immune response, the immune system recognizes this foreign protein and generates specialized proteins known as antibodies.
- Antibodies play a vital role in defending the body against infections by identifying individual viruses or pathogens, binding to them, and marking them for elimination.
- Even after the body has cleared the pathogen, these antibodies persist in the body, providing long-lasting immunity and enabling a rapid response if the same pathogen is encountered again.
Challenges Surrounding Nobel Recognition for mRNA Vaccines:
Prioritizing Profit over Ethics
- Katalin Karikó and Dr. Weissman initiated their collaboration on mRNA technology while at the University of Pennsylvania in the late 1990s.
- The University granted patents for this technology to mRNA RiboTherapeutics, which subsequently sublicensed them to CellScript.
- CellScript, in turn, sublicensed the technology to Moderna and BioNTech for substantial sums of $75 million each.
- Karikó joined BioNTech as a senior vice president in 2013, leading to the company's partnership with Pfizer to develop an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine in 2020.
Substantial Research Supported by Public Funds
- A considerable portion of the research underpinning many new drugs and vaccines is conducted with funding from governments and public resources.
- This phase of drug development is both risky and time-consuming, involving the exploration of potential biomolecular targets within the body that can be targeted by drugs to treat specific ailments, as well as the identification of suitable chemical candidates.
- The estimated costs and timeframes for this stage typically range from $1 billion to $2.5 billion and several decades, respectively.
Later Commercialization of Publicly Funded Research by Private Entities
- Private companies then proceed to commodify and commercialize the outcomes of this research, often reaping substantial profits—frequently at the expense of the very taxpayers who funded the initial research.
- For instance, when Moderna and Pfizer began manufacturing their mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, they prioritized securing ample supplies for themselves before allowing exports to the global community.
- Furthermore, the use of these vaccines in other countries, including India, faced complications due to protracted negotiations related to pricing and liability.
The Challenges Encountered by the COVAX Program:
The COVAX Program
- The COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access program, abbreviated as COVAX, was a global initiative with the goal of ensuring fair access to COVID-19 vaccines. It was led by the GAVI vaccine alliance.
- COVAX constituted one of the four essential components of the Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator, initiated in 2020 by the WHO, the European Commission, and the government of France in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- This initiative orchestrated international efforts to provide equitable access to COVID-19 tests, treatments, and vaccines for low- and middle-income countries.
- UNICEF played a crucial role as the primary delivery partner, leveraging its extensive experience as the world's largest vaccine purchaser.
- UNICEF was responsible for procuring COVID-19 vaccine doses, managing logistics, ensuring country readiness, and overseeing in-country vaccine distribution.
- As of October 19, 2020, 184 countries had become participants in the COVAX program.
Challenges Faced by the COVAX Program
- Unfortunately, the COVAX program encountered significant obstacles in achieving its objectives.
- Notably, India, Russia, and China were notable exporters of billions of vaccine doses.
- However, their efforts faced issues related to the potential overestimation of manufacturing capacity in India, as well as concerns about the quality of vaccines from Russia and China.
- Moreover, there were reports of several African countries having to discard large quantities of vaccine doses due to their proximity to expiration dates when they were exported.
The Corbevax Initiative: Contrasting Dr. Karikó's Journey
- A team of researchers from the Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, among others, pioneered the development of a protein sub-unit vaccine called Corbevax.
- This vaccine was subsequently licensed to India's Biological E for production, notably without pursuing a patent.
- In February 2022, a Texas politician penned a letter recommending the vaccine's creators for the Nobel Peace Prize.
- They were acknowledged for their remarkable efforts in developing and distributing an affordable COVID-19 vaccine worldwide, free from patent constraints.
- Kenya's Ambassador to the United Nations also lauded these researchers for providing essential ethical and scientific guidance on a global scale.
In Conclusion
- Scientists should not be faulted for seeking to benefit from their research.
- However, the narrative of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic has raised questions about this selflessness.
- Throughout the pandemic, this technology had the potential to benefit everyone but faced certain limitations.
- Therefore, it is essential for history to accurately record the events that unfolded during the pandemic, contrasting with what the 2023 Nobel Prize in Medicine signifies.
Cancer Screening in India (The Hindu)
- 04 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
As only a handful of Indian districts currently meet the Health Ministry's cancer screening standards, the ICMR is preparing to address this issue.
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has called for Expressions of Interest to advance research aimed at speeding up cancer screening, early diagnosis, and treatment.
About Cancer:
Cancer is a complex and devastating group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
- Cellular Aberration: At its core, cancer begins with mutations in the DNA of normal cells.
- These mutations disrupt the intricate mechanisms that regulate cell growth and division.
- Uncontrolled Growth: Cancer cells multiply uncontrollably, forming a mass of tissue known as a tumor. Not all tumors are cancerous; benign tumors are non-cancerous and do not invade nearby tissues.
- Malignant Tumors: Cancerous or malignant tumors are invasive and can infiltrate nearby tissues and even spread to distant parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
- This process is called metastasis.
- Diverse Types: There are over 100 different types of cancer, each originating in specific cell types or tissues.
- Common types include breast, lung, prostate, and colon cancer.
- Risk Factors: Several factors can increase the risk of developing cancer, including genetics, exposure to carcinogens (such as tobacco and UV radiation), poor diet, lack of physical activity, and certain infections.
- Survival Rates: Cancer survival rates have improved over the years due to advances in research and treatment.
- Early diagnosis and prompt intervention often lead to better outcomes.
Cancer incidence and mortality in India:
- Cancer's Impact in India: Cancer is a formidable public health concern in India, where it stands as the third-highest country for cancer incidence, following China and the United States.
- Future Trends: Projections from the Global Cancer Observatory indicate a noteworthy 57.5% surge in cancer cases in India between 2020 and 2040.
Trends in cancer incidence and their contributing factors:
- Divergent Trends in Cancer Incidence: In India, there are varying trends in cancer incidence.
- Notably, cervical cancer rates have dropped from 45 to 10 cases per 100,000 people over the past five decades.
- In contrast, breast cancer rates are on the rise, especially in urban areas like Hyderabad, where it stands at 45 cases per 100,000.
- Factors Behind the Trends: Cervical cancer's decline can be attributed to factors like delayed marriages, smaller family sizes, improved hygiene practices, and the introduction of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine.
- The increase in breast cancer cases is linked to late marriages, delayed childbirth, reduced breastfeeding, and diets high in protein.
- Unlike cervical cancer, there's no known specific cause for breast cancer, which makes screening crucial.
- Tobacco-related cancers, such as oral and esophageal cancer, have seen a decrease thanks to tobacco control laws that have curbed public smoking.
- Lung cancer, driven by both pollution and smoking, remains a concern.
- In regions like Arunachal Pradesh, indoor fires during winter contribute to high lung cancer rates.
- Unfortunately, lung cancer often goes undiagnosed until advanced stages, resulting in a low survival rate.
Improvements in cancer treatments and the infrastructure challenges in India:
- Advancements in Cancer Treatments: Progress in cancer treatment can be measured by examining cure rates for different types of cancers.
- For instance: Over the past half-century, the cure rate for pancreatic cancer has doubled, moving from 3% to 6%.
- The cure rate for prostate cancer has seen significant improvement, rising from 60% to 100%.
- Newer treatments have substantially boosted breast cancer survival rates, elevating them from 50% to 90%.
- Challenges in Cancer Care Infrastructure: Despite these treatment advancements, India faces challenges in its cancer care infrastructure, encompassing seven critical pillars: prevention, surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, imaging, laboratory diagnostics, and palliative care.
- In developing countries, including India, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends one radiotherapy machine per million people. Given India's population of 1.4 billion, this would require 1,400 machines. However, the country currently has only 700 such machines, highlighting a substantial deficit in cancer care infrastructure.
Steps required to reduce overall cancer mortality in India, similar to the approach in the US:
- Prioritize Screening: The initial step should focus on widespread cancer screening.
- The government has already initiated this process by upgrading health and wellness centers to screen for the three most prevalent cancers in India - breast, cervical, and oral (which together account for 34% of cancer cases).
- Accessible and Affordable Treatment: Effective screening should seamlessly lead to accessible and affordable hospital treatment.
- Ensuring that cancer care is within reach for all is crucial.
- Expand Cancer Care Facilities: The existing ratio of one cancer care facility for every 5 crore people in India must be improved.
- Increasing the number of facilities is essential to guarantee timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Early Diagnosis and Prompt Treatment: The key goal is to ensure early cancer diagnoses and prompt treatment to improve survival rates.
- Enhanced Coordination: Coordination is vital. Currently, various government programs operate independently and in isolation.
- Streamlining and synchronizing these efforts can enhance the overall impact of cancer control initiatives in India.
ICMR Project to Enhance Cancer Screening at the District Level:
- This project is scheduled to run for four years, including six months for preparatory activities and another six months for analysis and interpretation.
- It encompasses formative phases, implementation, and evaluation.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) aims to enhance both the coverage and quality of cancer screening within the existing healthcare system, employing established and validated methods.
- The plan involves engaging non-specialist physicians and other healthcare personnel within a supportive healthcare framework to conduct cancer and precancerous condition screenings.
- A key objective is to ensure that individuals testing positive are promptly connected to facilities for early diagnosis and treatment.
- Active involvement of local communities is crucial to motivate the target population to undergo screening for early detection and treatment.
- For instance, research has shown that frontline health workers like Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) can promote and perform home-based cancer screening, which has led to higher participation rates due to the privacy and convenience it offers.
Mains Question:
- What strategies can be implemented to improve cancer screening rates and access to timely treatment in India, especially considering the existing deficit in cancer care facilities and the need for coordinated efforts? (10M)
Why the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Is Expected to Sustain the Repo Rate Pause: Insights into RBI's Policy (Indian Express)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
- The Reserve Bank of India's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is going to meet from October 4 to 6.
- During this meeting, it is expected that the MPC will not change the repo rate, which is currently at 6.5 percent.
- This will be the fourth time in a row that they keep it the same.
- The reason for this decision is that inflation, which is measured using the consumer price index (CPI), is staying high.
- Additionally, it's likely that the central bank will stick to its plan of reducing the amount of money in the economy, which is known as a 'withdrawal of accommodation' stance.
- This is done to control inflation and prevent it from getting worse.
- On the other hand, if they were to take an 'accommodative stance,' it would mean that the central bank is willing to increase the money supply in order to boost economic growth.
Why is RBI likely to keep things the same in its policy?
Domestic Challenges:
- Consumption Concerns: There are worries about people buying less due to high food prices.
- Monsoon Trouble: The monsoon season hasn't been consistent, which is affecting crops like kharif.
- Higher Interest Rates: Interest rates are up, which can impact borrowing and spending.
- Inflation is still high, at 6.8 percent. While it's expected to drop, there's some concern about the kharif crop, especially pulses, which could make prices go up.
- The RBI Governor has also pointed out that frequent food price increases can make it harder to control inflation.
External Challenges:
- Rising Oil Prices: Oil prices worldwide have gone up, averaging nearly $89 per barrel. This is a 12.6 percent increase since the last policy.
- Russia-Ukraine War: The conflict between Russia and Ukraine is causing problems in the supply chains for many goods.
Is there going to be a revision in the GDP growth prediction?
- According to experts, it's unlikely that the RBI will alter its GDP forecast in the upcoming monetary policy announcement.
- The basic factors supporting growth still look positive, but there's a significant question mark regarding how a poor monsoon might affect agricultural production.
- Additionally, there's anticipation of an ongoing economic slowdown in Europe and China, which could lead to reduced exports and potential challenges for rural demand due to this year's weak monsoon.
Will there be any announcements regarding liquidity measures?
- According to experts, it's unlikely that the RBI will introduce any specific liquidity measures at this time, as the current liquidity situation is already tight.
- Furthermore, the RBI is in the process of reversing the incremental cash reserve ratio (I-CRR), which was introduced in the August policy.
- I-CRR is an extra cash reserve that banks have to maintain on top of the standard cash reserve ratio (CRR), which is the portion of deposits that banks must keep with the RBI.
- The RBI declared the discontinuation of I-CRR on September 8.
- However, despite the gradual withdrawal of I-CRR, there has been a liquidity deficit in the system since mid-September due to quarterly tax outflows and GST payments.
- Additionally, interventions in the foreign exchange market aimed at supporting the rupee may have slightly absorbed some rupee liquidity.
What is the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
- According to Section 45ZB of the revised RBI Act of 1934, the central government has the authority to establish a six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
- The MPC's main responsibility is to decide the policy interest rate necessary to achieve the inflation target. The first MPC was formed in September 2016.
- Members of MPC
- As per the amended RBI act, the MPC is composed of the following members:
- The RBI Governor, who serves as its ex officio chairperson.
- The Deputy Governor responsible for monetary policy.
- An officer from the Bank nominated by the Central Board.
- Three individuals appointed by the central government.
Functions of MPC:
- Setting Policy Interest Rates: The primary role of the MPC is to determine policy interest rates, specifically the repo rate.
- Inflation Targeting: The government has set a current inflation target, which is a Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation goal of 4% with a tolerance range of +/- 2%.
- Economic Analysis and Forecasting: The MPC conducts comprehensive analysis and forecasting of various economic indicators, including inflation, GDP growth, employment, fiscal conditions, and global economic trends.
- Decision-Making: The MPC convenes at least four times a year to assess the direction of monetary policy.
Presidential Election in Maldives and India (The Hindu)

- 02 Oct 2023
Why is it in the News?
Mohamed Muizzu, the leading candidate from the Opposition, has secured the position of President in the Maldives. He emerged victorious in a closely contested election, defeating the incumbent Ibrahim Mohamed Solih, who had friendly relations with India.
News Summary About Maldives Presidential Election:
- The Maldives has chosen Mohamed Muizzu as its new president, ousting the incumbent Ibrahim Mohamed Solih, known for his pro-India stance.
- President Solih faced criticism from the Opposition for his 'India first' policy.
Key Points:
- In the second round of the Presidential Election, Mr. Muizzu secured approximately 54% of the vote, while Mr. Solih garnered nearly 46%.
- The run-off election witnessed a higher voter turnout of 86%, surpassing the 79.85% recorded in the first round, which was the lowest in Maldivian presidential election history.
- The initial round did not produce a clear winner, as no candidate managed to obtain more than 50% of the votes.
Electoral System in the Maldives:
- Parliament Name: The legislative body in the Maldives is known as Majlis or People's Majlis.
- Parliament Structure: Maldives follows a unicameral parliamentary structure.
- First-Past-the-Post Majority System: In the Maldives, both Parliament and Council elections utilize the first-past-the-post majority system, where voters cast their ballots for a single candidate.
- Term Duration: The Majlis consists of 87 members, each directly elected for a five-year term from 87 individual single-member constituencies.
- Two-Round System: The President of the Maldives is elected using a two-round system.
- If no candidate secures more than 50% of the votes in the first round, a second round or run-off is conducted.
- 2023 Maldives Election: The initial round of the election featured eight candidates, marking the highest number of candidates so far.
- The Maldives has a population of approximately 5.2 lakh people.
- As per the Election Commission of the Maldives, there are 2.8 lakh eligible voters, with around 1.6 lakh being members of various political parties.
Evolution of the Executive Presidency System in the Maldives:
- Single-Party System Until 2008: The Maldives operated under an Executive Presidency system since 1968.
- It adhered to a single-party system until 2008, where the President was elected for a five-year term through a referendum.
- Maumoon Abdul Gayoom's 30-Year Rule: Ibrahim Naseer served as the first executive President from 1968 to 1978.
- Due to political protests in 1978, Naseer did not seek re-election for a third term.
- In 1978, the Maldivian parliament selected Maumoon Abdul Gayoom as the succeeding President.
- Gayoom led the nation for an astonishing 30 years, until 2008, effectively managing protests and famously thwarting a coup attempt with India's assistance in 1988.
- Era of the Multi-Party System: In response to protests by various factions, Gayoom initiated political reforms in 2004.
- Political parties were officially registered in 2005, and a new Constitution was adopted in 2008.
- These changes paved the way for Presidential elections every five years, embracing a multi-party system.
India's Engagement with Maldivian Politics:
- India's relationship with Maldivian politics has been a blend of experiences, with the Solih government being the most favorable thus far.
- India collaborated closely with Abdul Gayoom's administration for three decades.
- When Mohamed Nasheed assumed power in 2008, India expressed its support through then Vice President Hamid Ansari's attendance at his inauguration ceremony.
- Tensions arose in 2012 when the Maldivian government terminated the GMR contract for the Maldives' airport, straining the bilateral relationship significantly.
- Following Yameen's rise to power in 2013, he pursued a more aggressive courtship with China.
- During his tenure, the Maldives joined President Xi Jinping's Belt and Road Initiative.
- When India and Western lenders hesitated to extend loans to Yameen's government due to allegations of human rights violations, he turned to Beijing, which provided funding without stringent conditions.
- Solih's victory in the 2018 elections was met with relief in Delhi.
- Prime Minister Modi even attended Solih's swearing-in ceremony during his visit to the Maldives.
Potential Shift in Maldives' Foreign Policy:
- The victory of Muizzu might indicate a possible adjustment in the Maldives' foreign policy.
- He enjoys the support of former President Abdulla Yameen, known for his pro-China stance and 'India out' campaign.
- Despite this, local observers in the Maldives believe that Mr. Muizzu is unlikely to abruptly sever ties with India.
- The newly elected leader is expected to pursue a balanced approach in managing India-China relations.
- Meanwhile, India hopes for the continuity of its various infrastructure projects in the Maldives.
- India's recent initiatives in the Maldives encompass a wide range of projects, including water and sanitation in 34 islands, road construction, land reclamation as part of the Addu development project, a cancer hospital, a port project, a cricket stadium, two airport development projects, the Greater Male connectivity project with bridges, causeways, and roads, social housing projects, mosque renovations, and the establishment of the national college for police.
- Estimates indicate that Indian aid to the Maldives from 2018 to 2022 exceeded Rs 1,100 crore, more than double the amount provided in the preceding five-year period (approximately Rs 500 crore).
Mains Question:
- Evaluate the potential shifts in the Maldives' foreign policy under President Mohamed Muizzu, and elucidate the impact on its relationship with India, given historical dynamics and infrastructure projects. (15M)
Law Commission against lowering the age of consent under the POCSO Act (The Hindu)

- 30 Sep 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Law Commission advises maintaining the current age of consent at 18 years under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act. Reducing it could harm efforts to combat child marriage and trafficking.
Context:
- The Law Commission, led by Justice (Retired) Ritu Raj Awasthi, submitted Report No. 283 to the Law Ministry.
Key Points from the 22nd Law Commission Report:
- It advises against lowering the age of consent, citing potential negative impacts on combating child marriage and trafficking.
- The panel recommends amendments to the POCSO Act, 2012, addressing cases where 16 to 18-year-olds give tacit approval, not legal consent.
- Courts are advised to handle adolescent love cases with caution to maintain a balanced approach, prioritizing the child's best interests.
- The Law Commission also proposed phased implementation of e-FIR registration, starting with offenses carrying up to three years of imprisonment. This move aims to address delays in FIR registration and enable real-time reporting of crimes.
The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act:
- POCSO Act, enacted in 2012 and administered by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, is India's first comprehensive law addressing child sexual abuse.
- It aims to safeguard children from sexual assault, harassment, and pornography and establishes Special Courts for such cases.
- In 2019, amendments were made to enhance penalties for specific offenses, discouraging perpetrators and promoting a dignified upbringing.
- Key Features:
- Gender-neutral definition: The Act defines a child as "any person" below 18 years.
- Non-reporting as an offense: Those responsible for institutions must report sexual offenses involving subordinates, with penalties for failure to do so.
- No time limit for reporting abuse: Victims can report offenses at any time, even years later.
- Confidentiality of victim's identity: The Act prohibits the disclosure of the victim's identity in any media without authorization from special courts.
- Challenges:
- Rising abuse, especially during the Covid-19 pandemic, with the emergence of new forms of cybercrime.
- Lack of awareness among minors, parents, and society.
- Concerns about the criminalization of consensual sexual activity among adolescents prompted calls for legislative review by CJI D Y Chandrachud.
The Issue of Minors Facing Legal Action for Consensual Acts:
- Minors aged 16 to 18 engaging in consensual activities that could be considered sexual under the law face potential bookings under POCSO.
- Even though these cases of adolescent consensual activity may not always lead to the conviction of a minor, the legal framework could lead to the denial of bail and prolonged detention.
- A study revealed that in West Bengal, Assam, and Maharashtra, one in every four cases under the POCSO Act involved what could be termed as "romantic cases," where the victim was in a consensual relationship with the accused.
What Does 'Age of Consent' Mean?
- The 'age of consent' is the legal threshold at which a person is deemed capable of giving consent for sexual activities. Before the POCSO Act, this age was set at 16.
- Under the POCSO Act, any sexual activities involving individuals under 18 are classified as criminal offenses, regardless of whether mutual consent exists among minors.
- This determination is rooted in the legal assumption that individuals under 18 lack the capacity to provide consent within the legal framework.
China Rejects Expanding CPEC Cooperation in Energy, Water, and Climate with Pakistan (The Hindu)

- 29 Sep 2023
Why is it in the News?
China has refused to further expand cooperation in the areas of energy, water management, and climate change under the multi-billion dollar China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), it emerged on September 25, signalling a strain in the 'ironclad' friendship between the two all-weather allies.
Summary of News: Challenges Arise as China Rejects Pakistan's CPEC Expansion Proposals:
- In a significant development, Beijing has declined multiple investment proposals from Islamabad, spanning various sectors like energy, tourism, water management, and climate change, all within the ambit of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- These decisions were revealed through the minutes of the 11th Joint Cooperation Committee (JCC) meeting, where the future of CPEC projects is discussed.
- The JCC serves as a pivotal decision-making body for CPEC matters.
- China's reluctance to expand cooperation in these specific areas within the CPEC framework highlights the current challenges faced by both nations in their efforts to further strengthen their economic partnership.
What is CPEC?
- CPEC, short for the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, is a vast network of infrastructure projects spanning 3,000 kilometers.
- It connects China's northwest Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region to the Gwadar Port in Pakistan's western province of Balochistan.
- This initiative represents a bilateral partnership between Pakistan and China, designed to enhance connectivity within Pakistan through the development of highways, railways, pipelines, as well as energy and industrial infrastructure projects.
- The primary objective of CPEC is to enable China to establish access to the Middle East and Africa via the Gwadar Port, providing a strategic link to the Indian Ocean.
- In return, China actively supports various development projects in Pakistan, addressing the country's energy shortages and assisting in stabilizing its economic situation.
- It's important to note that CPEC is an integral part of the broader Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), initiated in 2013.
- The BRI aims to create an extensive network of land and sea routes connecting Southeast Asia, Central Asia, the Gulf region, Africa, and Europe, fostering international economic cooperation and development.
What are the Implications of CPEC for India?
- Challenges to Sovereignty: India has consistently voiced opposition to the CPEC project because it passes through the Pakistan-occupied Kashmir territory of Gilgit-Baltistan, a disputed region claimed by both India and Pakistan.
- The corridor is also perceived as a potential alternative economic route for the Indian-administered Kashmir Valley.
- Regional Optimism: Despite India's official stance, key stakeholders in the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir have expressed optimism about the potential benefits of the CPEC project.
- Some local business and political leaders have even proposed declaring both sides of the Line of Control (LoC) in Kashmir as a 'Special Economic Zone.'
- Territorial Implications: The success of CPEC could bolster Gilgit-Baltistan's international recognition as part of Pakistani territory, undermining India's claim over this region, which spans 73,000 square kilometers and is home to over 1.8 million people.
- China's Maritime Influence: Once fully operational, CPEC could offer China a more efficient trade route to major U.S. ports on the East Coast, potentially reshaping international trade dynamics.
- This could grant China greater influence over global goods movement between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
- China's 'String of Pearls': CPEC aligns with China's broader strategy of expanding its presence in the Indian Ocean, often referred to as the 'String of Pearls.'
- This involves establishing a network of airfields and ports in countries surrounding India.
- Gwadar port's control would solidify China's dominance in the Indian Ocean region.
- Pakistan's Economic Boost: CPEC has the potential to accelerate Pakistan's economic development.
- With easier access to Chinese raw materials, Pakistan's textile and construction material industries could become regional leaders, potentially impacting Indian exports in similar sectors.
- Strengthening BRI and Chinese Influence: CPEC is a significant component of China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), aimed at enhancing trade connectivity with Eurasia.
- A more integrated China in the global economy may challenge India's aspirations for a permanent seat on the UN Security Council.
Way forward
- India has the opportunity to capitalize on its strategic positioning by collaborating with like-minded nations and actively engaging in multilateral endeavors such as:
- Asia-Africa Growth Corridor: This India-Japan economic cooperation agreement holds significant promise for India's strategic interests and serves as a potential counterbalance to China's influence.
- Blue Dot Network: Championed by the United States, the Blue Dot Network is a multi-stakeholder initiative that unites governments, the private sector, and civil society in the pursuit of establishing high-quality, trustworthy standards for global infrastructure development.
- It is poised to become a globally recognized system for evaluating and certifying infrastructure projects, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region.
Renewed Dispute Over Cauvery Water Sharing (Indian Express)
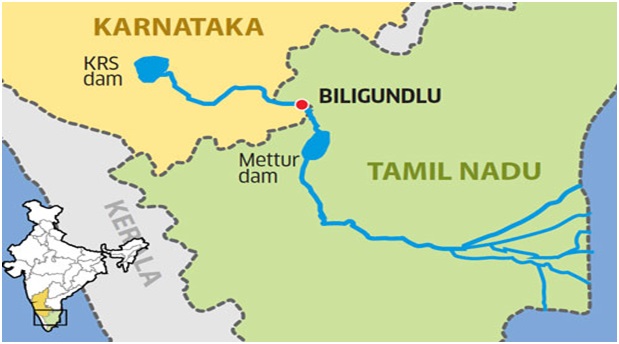
- 28 Sep 2023
Why is it in the News?
The resurgence of the Cauvery water-sharing conflict between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, despite the Supreme Court's 2018 ruling on the longstanding dispute, is primarily due to inadequate rainfall in Karnataka's Cauvery river catchment area.
A Historical Overview of the Cauvery Water Dispute
- Origin of the Dispute Before Independence: The origins of the Cauvery water dispute trace back to 1892 during the British colonial era, involving the Madras Presidency and the Princely state of Mysore.
- In 1924, an agreement was reached between Mysore and Madras, with a validity period of 50 years.
- Post-Independence Dispute: The agreement signed between the Madras Presidency and the Princely state of Mysore concluded in 1974.
- Starting in 1974, Karnataka began diverting water into its four newly constructed reservoirs without obtaining consent from Tamil Nadu, leading to a post-independence dispute.
Supreme Court's Ruling on the Cauvery Water Dispute:
- Clear Allocation of Water Quantities to TN and Karnataka: In 2018, the Supreme Court made a definitive decision to allocate an additional 14.75 TMC (Thousand Million Cubic Feet) of water to Karnataka while reducing Tamil Nadu's share by the same amount.
- Karnataka's additional allocation was primarily designated for addressing the drinking water needs in southern Karnataka.
- As per this ruling, out of the total annual Cauvery water share of 740 TMC, Tamil Nadu was granted 404.25 TMC, Karnataka received 284.75 TMC, and Kerala obtained 30 TMC.
- Furthermore, the court allocated 7 TMCs to Puducherry and reserved 14 TMCs for environmental conservation and preventing waste into the sea.
- Establishment of CWMA (Cauvery Water Management Authority): The Supreme Court also mandated the establishment of the Cauvery Water Management Authority (CWMA) along with the Cauvery Water Regulatory Committee (CWRC) to resolve inter-state disputes according to the court's directives.
- The CWMA operates as a primarily non-political body operating under the supervision of the Union Water Resources Ministry.
- It serves as the central agency responsible for regulating disputes between the two states.
Reasons for the Ongoing Dispute:
- Political parties in both Karnataka and Tamil Nadu argue that the 2018 Supreme Court order delineated water-sharing guidelines solely for typical monsoon years, not accounting for scenarios of water scarcity.
- The present monsoon season is unfolding as deficient, with rainfall measuring more than 30 percent below the usual levels.
- In particular, the months of August and September, within the four-month monsoon period that commenced in June, have experienced the lowest rainfall in Karnataka in 123 years.
How the Current Crisis Has Unfolded?
- Karnataka's Reduced Water Release: Per the 2018 Supreme Court verdict, Karnataka is obligated to release 123.14 TMC (Thousand Million Cubic Feet) of water to Tamil Nadu between June and September during a normal monsoon year.
- For August and September in a typical monsoon season, Karnataka should release a combined total of 82.71 TMC.
- However, this year, Karnataka had only released 40 TMC of water by September 23, citing an ongoing distress situation in the state.
- Tamil Nadu's Engagement with CWMA: In August, Tamil Nadu turned to the Cauvery Water Management Authority (CWMA) to ensure regular water supplies.
- The Cauvery Water Regulatory Committee (CWRC), functioning under the CWMA, noted that rainfall in the Cauvery basin in Karnataka was 26 percent below normal by early August.
- The committee also observed that Karnataka had only released 30.252 TMC of water from June 1 to August 28, far less than the usual 80.451 TMC in a typical year.
- CWMA's Decision: In accordance with the committee's advice, the CWMA initially ordered the release of approximately 13 TMC of water for 15 days at a rate of 12,000 cubic feet per second (cusecs) per day, despite Tamil Nadu's request for 25,000 cusecs per day.
- Subsequently, after reviewing the monsoon situation once more, the CWRC and CWMA decreased Karnataka's water release to 5,000 cusecs per day, while Tamil Nadu sought 12,000 cusecs.
- Supreme Court's Verdict on CWMA's Decision: Both Tamil Nadu and Karnataka appealed to the Supreme Court to contest the CWMA's orders.
- However, the Supreme Court upheld the release of 5,000 cusecs of water until September 26.
- The Karnataka government has stated its intention to adhere to the Supreme Court's order until September 26 and then reassess the situation.
Karnataka's Arguments:
- Reliance on Southwest Monsoon: Karnataka contends that Tamil Nadu predominantly receives its significant rainfall during the retreating northeast monsoon period, typically occurring between October and November.
- In contrast, Karnataka heavily depends on rainfall during the southwest monsoon months from June to September.
- Protesters argue that water is being directed to Tamil Nadu as the southwest monsoon season nears its end, resulting in critically low storage levels in the Cauvery basin reservoirs in Karnataka.
- The Cauvery River serves as the primary source of drinking water for Bengaluru and for irrigation purposes in the Mandya region of the state.
- Mekedatu Check Dam Project Implementation: The Karnataka government is advocating for the execution of the Mekedatu Check Dam project on the Cauvery River.
- This project is designed to serve as a reservoir for Bengaluru's drinking water needs and to release surplus water to Tamil Nadu during crisis situations, such as the current one.
The Storage Status of Cauvery Basin Reservoirs in Karnataka:
- As of September 23, the four reservoirs located in the Cauvery basin – Krishna Raja Sagar, Kabini, Hemavathy, and Harangi – were at 50% of their storage capacity.
- Collectively, these reservoirs held 51.1 TMC (Thousand Million Cubic Feet) of water, compared to their total capacity of 104.5 TMC.
- According to the Karnataka government, the state's water requirements are estimated at 112 TMC (79 TMC for crop irrigation and 33 TMC for supplying Bengaluru's drinking water needs) until June 2024.
- Given that the southwest monsoon season in Karnataka is concluding, the Karnataka government asserts that the remaining water in the Cauvery basin reservoirs must be preserved for essential drinking water and agricultural irrigation purposes.
Is the Current Situation Unique?
- The current Cauvery water crisis bears similarities to previous crises that occurred in 1991, 2002, 2012, and 2016.
- What sets this crisis apart is that it has arisen after the Supreme Court's final resolution of the dispute in 2018.
- Furthermore, historical protests related to the Cauvery issue have sometimes escalated into violence, often driven by mainstream political parties attempting to gain favor with voters by adopting chauvinistic stances.
- In recent years, however, Karnataka's politicians have adopted a more conciliatory approach.
- Notably, in the Mandya region, farmers have shifted towards cultivating less water-intensive crops, and younger generations are increasingly moving away from agriculture.
- As a result, the Cauvery issue is no longer as emotionally charged as it was three decades ago.
In Conclusion
- The Cauvery River, often referred to as the 'Dakshina Ganga,' has long been recognized as the economic lifeline of the states it traverses, with its most significant impact being felt in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- Although the contest over Cauvery's waters can be traced back to the 11th century AD, contemporary Tamil Nadu and Karnataka have grappled with disagreements regarding the sharing of Cauvery's waters.
- It is imperative for the states to shift away from a regional-centric approach and embrace cooperation and coordination as genuine solutions, transcending conflicts for the benefit of all.
Mains Question:
- How has the Cauvery River played a pivotal role in the economic development of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, and what are the contemporary challenges and potential cooperative solutions in managing its water resources? (15M)
Parliament Panel Findings on the New Education Policy, 2020 (The Hindu)

- 27 Sep 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Education Committee of the Parliament has just presented a report about how the National Education Policy (NEP) from 2020 is being put into action in higher education.
Assessment in the report:
- The report checks how well the National Education Policy (NEP) from 2020 is being used in higher education and what progress has been made.
- In India, there are currently 1043 universities.
- Most of them, around 70%, are run by state laws, while about 18% are managed by the Central Government.
- When it comes to students, 94% of them study at state or private institutions, and only 6% are in central institutions.
- The report says that more students are going to college now compared to a few years ago. This is measured using something called Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER), which has gone up from 24.1% in 2016-17 to 27.3% in 2020-21. It's also improved for ST and SC students during this time.
- GER is like a way to see how many students in the right age group (18-23 years) are in higher education compared to the total population.
Report's Status of Implementation:
- Things are going well with the implementation of NEP 2020, thanks to different initiatives like PM Schools for Rising India (PM SHRI), e-VIDHYA, and NIPUN Bharat. The goal is to change higher education to be more inclusive, flexible, and meet global standards.
- Jammu and Kashmir is leading the way by being one of the first places in India to start using NEP 2020 in all Higher Education Institutions starting from 2022.
- NEP 2020 wants students to become more creative and innovative. It encourages connections between colleges and industries and works on joint programs.
- Indian universities will get more freedom to set up campuses in other countries and welcome top 100 universities from around the world to work in India.
- NEP 2020 also allows students more flexibility with something called "Multi Entry and Multiple Exit (MEME)" options, which gives them more choices in their education.
Issues Related to NEP:
- Accessibility: Some students in economically disadvantaged areas can't easily access higher education because of money problems, where they live, and because they might feel like they don't belong due to stereotypes.
- Multiple Entry And Multiple Exit (MEME)System: Even though the MEME system seemed flexible, the report suggests it might not work as well in India as it does in Western countries.
- Language Barrier: Most higher education institutions use English to teach, but not many teach in local languages. This can be a problem for students who are more comfortable in their local language.
- Lack of Funding: India needs to spend more on education. Right now, it's only about 2.9% of the country's total income (GDP), but experts say it should be 6%. This means there's not enough funding for education.
Way Forward
- By 2030, the goal is to have at least one multi-purpose higher education institution in every district in India. And by 2035, they want 50% of students to be in higher education, including vocational training.
- They want to focus more on research and innovation to help India file more patents and improve its global ranking.
- To get more money for education, Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA) should look for funds from sources other than the government, like private companies, foundations, and international banks.
- They plan to make better use of technology in education. Creating a National Educational Technology Forum (NETF) will help expand digital resources and make India a top place for knowledge.
- They also want to make it easier for students who study different subjects to get credit for their work. This will help them move between schools and colleges more smoothly.
National Education Policy (NEP) 2020:
- The National Education Policy, created in July 2020, shows what India's new education system will look like.
- A group led by Shri K. Kasturirangan made this policy.
- NEP 2020 has five important ideas: making education affordable, easy to access, high-quality, fair for everyone, and making sure everyone is responsible for learning.
- It's like a big plan to change both basic and higher education in India by 2040.
- This is the third big education plan since India became independent. The earlier ones were made in 1968 and 1986.
- The new policy focuses on things like studying different subjects, using technology, writing well, solving problems, thinking logically, and getting experience in different jobs.
The Geopolitical Significance of the Israel Link in an Economic Corridor (The Hindu)
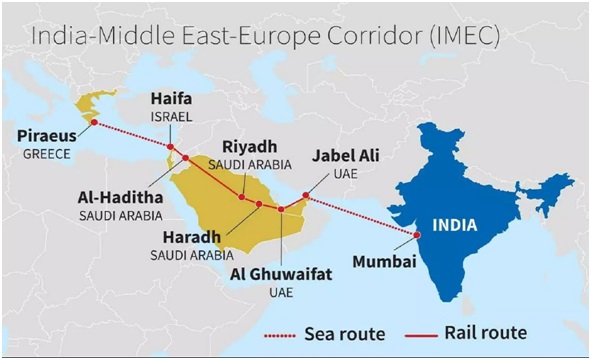
- 26 Sep 2023
Why is it in the News?
The G-20 Summit in 2023, hosted by India, achieved remarkable success despite the group's focus on economic matters in addressing global complexities. The global media recognized India's accomplishments during this summit for its diverse outcomes.
The significance of the G20 Delhi Declaration:
- A Collaborative Consensus: The declaration achieved a rare consensus among countries with diverse perspectives and interests.
- Balancing Act: The Delhi Declaration strikes a delicate balance by addressing global challenges without directly singling out specific nations for their actions.
- For instance, it refrains from naming Russia's aggression against Ukraine but underscores the importance of upholding the United Nations charter and principles of territorial sovereignty.
- Tailored to Diverse Interests: This balanced approach enables each member to identify elements in the declaration that align with their interests, contributing to its overall success.
- Showcasing India's Diplomatic Expertise: The declaration's significance lies in its ability to secure agreement from major world leaders, even in the midst of international power dynamics.
- Despite the absence of China's President Xi Jinping and Russian President Vladimir Putin at the summit, India demonstrated its diplomatic skill in bridging divides and fostering consensus among a diverse array of nations.
What is India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC)?
- One of the most significant outcomes of the G20 summit was the unveiling of the ambitious India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, IMEEC.
- This corridor features a rail and sea route designed to facilitate the transportation of goods from India to Europe, passing through the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Israel.
- The project's implications extend beyond economic matters; it has the potential to reshape geopolitics in the future.
- Notably, it presents an intriguing challenge to China's Belt and Road Initiative, although this is just one aspect of its broader significance.
- The U.S. President hailed IMEEC as 'a truly monumental development,' emphasizing its transformative potential for all parties involved and the global community at large.
- The prompt endorsement of this project by the Israeli Prime Minister underscores Israel's eagerness to participate in this remarkable endeavor.
The Significance of IMEEC: A Game-Changer in Global Trade
- A Transformative Impact: IMEEC is poised to be a potential game-changer in the realm of global trade, offering an alternative to China's extensive strategic infrastructure investments.
- Enhancing Prosperity: This corridor promises to boost prosperity in the participating countries by facilitating the flow of energy and digital communications.
- It addresses the pressing need for infrastructure in lower- and middle-income nations, fostering economic growth.
- Strengthening Regional Ties: The improved infrastructure will not only drive economic growth but also promote closer ties among Middle Eastern countries.
- Countering China's Influence:
- IMEEC arrives at a juncture when Saudi Arabia and the UAE, traditional U.S. allies, have been strengthening their connections with China and the rapidly growing Eastern economies.
- China's role in the Middle East has expanded, including its involvement in brokering regional agreements.
- A Response to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): Washington views IMEEC as an ambitious endeavor to counter China's Belt and Road Initiative, which aimed to enhance global connectivity with China's economy.
- Recent challenges, such as rising loan defaults and slowed investments, have cast doubts on the viability of China's BRI.
- Strategic Significance for India: For India, IMEEC holds immense geopolitical and trade importance.
- Concerns arose over China's connectivity projects in the region, and India faced hurdles, including Pakistan's refusal to grant overland access.
- India's attempts to establish credible connectivity through Iran faced challenges due to geopolitical complexities.
- IMEEC provides a solution by offering connectivity to both the Arabian Peninsula and Europe, addressing India's strategic concerns.
The Role of Israel in the Economic Corridor
- The U.S. initiative is designed to reshape the geoeconomic landscape of the Middle East through connectivity projects like IMEEC.
- The United States believes that these projects can address concerns among Gulf countries, reaffirm its commitment to the region, reduce tensions with Iran, and strengthen its leadership in the Gulf.
- However, achieving these strategic objectives hinges on advancing the normalization agenda outlined in the Abraham Accords, particularly with Saudi Arabia.
- Furthermore, the normalization of relations between Israel and Saudi Arabia is a critical prerequisite for the realization of this economic corridor.
Why Israel Wasn't Part of the Corridor Launch
- Unprecedented Middle Eastern Presence: India made history within the G20 by inviting the largest number of Middle Eastern countries ever to participate as guests in the summit.
- However, notably, India's strategic partner from the region, Israel, did not receive a similar invitation.
- Regional Considerations: India's decision to exclude Israel from the guest list may have been influenced by regional sensitivities, particularly regarding the preferences of Arab countries.
- U.S. Influence: The U.S. administration's avoidance of engaging with the Israeli Prime Minister for several months due to domestic politics may have played a role in Israel's role at the summit.
- Domestic Political Factors: In his statement following the corridor's launch, the Israeli Prime Minister expressed gratitude to the U.S. President but did not mention the Indian Prime Minister.
- This omission could be linked to Netanyahu's domestic political challenges and his previous inattention to U.S. foreign policy goals.
The Path Ahead
- Normalization of Saudi-Israel Relations: Saudi Arabia is open to ending its diplomatic boycott of Israel, but it comes with conditions.
- Saudis expect Israel to commit to the two-state solution and the well-being of the Palestinian people, even if the occupation persists for some time.
- Resolution of Israel-Palestine Conflict: Currently, on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly, Saudi Arabia, along with the Arab League and the EU, is collaborating with Egypt and Jordan to launch a 'Peace Day Effort.'
- This initiative aims to encourage Israelis and Palestinian leaders to find compromises.
- Achieving peace in the Israel-Palestine conflict is a formidable challenge, especially considering the rise of extremism on both sides.
- Waiting for Progress: The realization of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor may need to await progress in the Israel-Palestine situation.
The IMEEC plan faces a significant hurdle with Israel's aspiration for normalized relations with Saudi Arabia, which Riyadh does not currently endorse. Despite not formally joining, the new IMEEC effectively brings Saudi Arabia into the fold. With time, the corridor could create the economic and psychological conditions necessary for normalization.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the role of regional dynamics and international influences in the potential normalization of relations between Israel and Saudi Arabia, and how this could impact the progression of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC). (15M)
The NIA and its Authority Regarding Property Seizure (Indian Express)

- 25 Sep 2023
Why is it in the News?
The National Investigation Agency (NIA) seized property, including land and a portion of a house owned by Gurpatwant Singh Pannu, the founder and attorney of the banned Sikhs for Justice based in the United States, in Amritsar and Chandigarh.
Why Was the National Investigation Agency Established?
- In recent decades, India has faced significant acts of terrorism originating from beyond its borders.
- Many of these attacks have intricate connections across states and international boundaries, possibly linked to activities like arms and drug smuggling, as well as the circulation of counterfeit Indian currency.
- Recognizing these challenges, there arose a need to establish a central-level agency dedicated to investigating terrorism-related offenses and certain other acts with nationwide implications.
- Various experts and committees, including the Administrative Reforms Commission in its report, had proposed the creation of such an agency.
About the National Investigation Agency:
- The National Investigation Agency (NIA) came into existence with the enactment of the National Investigation Agency Act in 2008.
- This Act empowers the NIA to:
- Take proactive notice of terrorist activities anywhere in India and initiate investigations.
- Enter any state without requiring permission from the state government.
- Conduct investigations and make arrests.
- The NIA is India's primary Central Counter-Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency.
Objectives:
- Establish high standards of excellence in national-level counter-terrorism and other security-related investigations by developing a highly skilled, collaborative workforce.
- Act as a deterrent to both existing and potential terrorist groups or individuals.Jurisdiction:
- The provisions of the NIA Act apply throughout India and extend to Indian citizens residing outside the country.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Supervising Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs
Roles of NIA:
- Conducting thorough, expert investigations of scheduled offenses utilizing state-of-the-art forensic techniques, and establishing high investigative standards to guarantee the detection of all cases assigned to the NIA.
- Facilitating efficient and prompt legal proceedings.
- Fostering professional and cooperative interactions with the governments of States, Union Territories, and other law enforcement agencies, in accordance with the legal requirements of the NIA Act.
- Providing assistance to all States and other investigative bodies in handling terrorist cases.
- Establishing a comprehensive database containing all pertinent terrorist-related information and sharing this database with States and other relevant agencies.
Is the NIA Authorized to Carry Out Searches and Asset Seizures?
- Under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Act (UAPA), enacted in 2019, NIA officers have the authority to conduct searches and confiscate properties suspected of being associated with terrorist activities.
- NIA is not obligated to obtain permission from a state's Director General of Police.
- The investigating officer only needs approval from the Director General of NIA.
What Changes Were Introduced by the NIA (Amendment) Act 2019?
- Offenses Beyond Borders:
- Initially, the NIA had jurisdiction over crimes solely within India.
- However, the amended Act extends its authority to investigate crimes committed outside of India, provided it adheres to international treaties and the laws of the respective countries involved.
- If the Central Government believes that a crime committed abroad falls within the Act's jurisdiction, it can direct the NIA to investigate it as if it occurred in India.
Expanded Scope of Legal Authority:
- The NIA can investigate offenses listed in the Schedule of the NIA Act.
- Originally, this Schedule included Acts such as The Atomic Energy Act, 1962, The Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967, and The Anti-Hijacking Act, 1982, among others.
- With the amendment, the NIA can now also probe cases related to:
- Human Trafficking
- Counterfeit currency or banknotes
- Prohibited arms
- Cyber-terrorism
- Crimes under the Explosive Substances Act, 1908
Establishment of Special Courts:
- The 2008 Act established Special Courts for the trial of cases under the Act.
- The 2019 amendment grants the central government the authority to designate Sessions Courts as Special Courts for the trial of Scheduled Offenses under the Act.
- Before doing so, the central government must consult with the Chief Justice of the relevant High Court.
- In cases where multiple Special Courts exist in an area, the most senior judge will assign cases.
- Additionally, state governments have the power to designate Sessions Courts as Special Courts to try scheduled offenses.
Non-performing Assets (NPAs) and Wilful Defaulters (Indian Express)

- 23 Sep 2023
Why is it in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has put forth a proposal that requires lenders to categorize a borrower as a "wilful defaulter" within six months of their account being declared a non-performing asset (NPA). Previously, the RBI did not have a specific timeframe for identifying such borrowers.
Context:
- The RBI defines wilful defaulters as individuals or entities that have the means to repay a bank's dues but deliberately do not, or divert bank funds.
- A "large defaulter" refers to someone with outstanding dues of Rs 1 crore or more, whose account has been categorized as doubtful or a loss.
- A "wilful defaulter" is a borrower or guarantor who has committed wilful default, with an outstanding amount of Rs 25 lakh or more.
According to the RBI's draft guidelines:
- Lenders must assess the "wilful default" aspect for all accounts with outstanding amounts of Rs 25 lakh and above or as per RBI notifications.
- The process of classifying or declaring a borrower as a wilful defaulter should be completed within six months of the account becoming an NPA.
- An Identification Committee, established by lenders, must scrutinize evidence of wilful default.
- Lenders must investigate the wilful default aspect thoroughly before transferring the credit facility to other lenders or asset reconstruction companies (ARCs).
Other aspects of the RBI's draft guidelines include:
- No additional credit facility should be extended by any lender to a wilful defaulter or any entity associated with them.
- This prohibition on additional credit lasts for up to one year after the wilful defaulter's name is removed from the List of Wilful Defaulters (LWD) by the lenders.
- Wilful defaulters are ineligible for credit facility restructuring.
- These guideline revisions come after reviewing instructions and considering various judgments and orders from the Supreme Court and High Courts.
What is Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)?
- Non-Performing Assets, often referred to as NPAs, represent loans or advances for which the principal or interest payments have remained overdue for a period of 90 days or more.
- For banks, loans are considered assets because the interest they generate is a significant source of income.
- However, when customers, whether individuals or corporations, are unable to make interest payments, these assets become "non-performing" for the bank as they cease to generate income.
- Therefore, the RBI defines NPAs as assets that no longer generate income for banks. Banks are required to disclose their NPA figures to the public and report them to the RBI periodically.
- Classification of Assets: According to RBI guidelines, banks must further categorize NPAs into three types:
- Substandard assets: These are assets that have been NPAs for less than or equal to 12 months.
- Doubtful assets: Assets that have remained in the substandard category for 12 months.
- Loss assets: These are considered uncollectible and of such minimal value that keeping them as bankable assets is not justified, although some minimal recovery value may exist.
- NPA Provisioning: Provisioning for a loan refers to setting aside a certain percentage of the loan amount as a reserve. The standard rate of provisioning in Indian banks ranges from 5-20%, depending on the business sector and the borrower's repayment capacity. However, in the case of NPAs, 100% provisioning is required in accordance with Basel-III norms.
- GNPA and NNPA: Two key metrics help us understand a bank's NPA situation.
- GNPA (Gross Non-Performing Assets) represents the total value of gross NPAs a bank has in a specific quarter or financial year.
- NNPA (Net Non-Performing Assets) subtracts the provisions made by the bank from the gross NPA, providing the exact value of NPAs after specific provisions.
- NPA Ratios: NPAs can also be expressed as percentages of total advances, indicating the proportion of advances that are not recoverable.
- For instance:
- GNPA ratio is the ratio of the total GNPA to the total advances.
- NNPA ratio uses net NPA to calculate the ratio to the total advances.
Impact of NPAs and the Current Situation with Future Projections for India:
- Effects of NPAs: Banks face a shortage of funds for lending to other productive sectors in the economy.
- To maintain their profit margins, banks may need to raise interest rates.
- Reduced investments could lead to an increase in unemployment rates.
- Banks have the option to retain NPAs in their books with hopes of recovery, make provisions for them, or write off the loans entirely as bad debt.
- Present State of NPAs in India: According to the latest RBI Financial Stability Report, the gross NPA ratio of scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) reached a 10-year low of 3.9% in March 2023.
- Both gross and net NPA ratios have declined significantly from their peak levels of 11.5% and 6.1% in March 2018 to 3.9% and 1.0% in March 2023, respectively.
- A contributing factor to the reduction in gross NPAs in 2022-23 was the substantial write-offs undertaken by banks.
- Future Projection for India: Based on stress test results, it is anticipated that the GNPA ratio for all SCBs may improve to 3.6% by March 2024.
- However, in the event of a deterioration in the macroeconomic environment, leading to medium or severe stress scenarios, the GNPA ratio could potentially rise to 4.1% and 5.1%, respectively.
Mains Question:
- Evaluate the impact of rising NPAs on the Indian economy, including effects on bank lending, interest rates, and employment. Elucidate the current NPAs situation in India and discuss future projections in light of recent trends. (10M)
The Shift to Eurasia: Global Order Changes with the G20-IMEC Plan (Indian Express)

- 21 Sep 2023
Why is it in News?
- At the 18th G20 Summit held in New Delhi, the US President, along with leaders from India, Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, Italy, and the European Commission, introduced the expansive India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC) project.
- This ambitious initiative aims to establish robust connections for India, including sea routes to the Arabian Gulf and a northern pathway connecting Saudi Arabia to Europe through Jordan and Israel.
Importance of the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC):
- Shared Vision Embodied: The IMEC embodies a collective vision uniting nations with a combined GDP of approximately $47 trillion, constituting roughly 40 percent of the world's total GDP.
- This vision extends beyond trade, energy, and digital resilience.
- Pathway to an Interconnected Transoceanic System: The Corridor paves the way for a more interconnected transoceanic system, stretching from the Mediterranean region through West Asia into the vast Indo-Pacific.
- Recognition of Non-Western Powers: The IMEC signifies recognition by the US and EU of the ascent of non-Western powers and the undeniable shift of the global economic and geopolitical center eastward.
- It underscores the need to allocate more substantial global leadership roles to India, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, key actors reshaping the future economic and geopolitical landscape in Eurasia.
- Influence of Emerging Powers: Abu Dhabi, Riyadh, New Delhi, and other emerging powers in Eurasia will wield significant influence in recalibrating broader power dynamics across the supercontinent.
How Will IMEC Impact the Global Order in Eurasia?
- Facilitating Diplomacy Between Hostile Nations: An often overlooked aspect of IMEC is how its very existence, along with its design and operational challenges, serves as another step toward bringing Saudi Arabia and Israel closer together.
- This initiative aligns with ongoing US-backed attempts to secure a normalization agreement between the two nations.
- Promoting Equitable Power Dynamics in Eurasia: IMEC aligns with the US's Eurasian strategy in a post-hegemonic era, aiming to establish a more balanced power structure across the wider Eurasian landscape.
- The objective is to prevent a loose coalition of states, including China, Russia, and Iran, from dominating the supercontinent.
- Instead, it seeks to bolster the influence of countries like India, Saudi Arabia, and Japan, enabling them to project economic and geopolitical power and contribute actively to a balanced Eurasian power structure.
- Europe Embracing Multipolarity Beyond Its Borders: Particularly for Europe, the Corridor represents a significant effort to attain geopolitical relevance and unity beyond the European continent in a new multipolar reality.
- Countries such as Italy, Germany, and France are aligning their efforts with the United States and Asian powers, aiming to move beyond occasional maritime exercises in the Indo-Pacific and integrate their economic systems into high-growth markets in the East.
How Will IMEC Serve India's Geopolitical Interests?
- Enhancing Strategic Engagement with the Arab World: The Indian government now has a unique opportunity to establish enduring connectivity between India and the Arabian region.
- This initiative will reassert India's role as a driving force in shaping regional connectivity.
- Bypassing Pakistan's Veto: For decades, Pakistan had staunchly opposed granting India access to land-locked Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- The successful implementation of this project will provide India with an alternative route to connect with Central Asia and Europe, circumventing Pakistan's objections.
- Strengthening US-India Cooperation in the Middle East: While conventional wisdom suggested that India and the United States primarily collaborated in the Indo-Pacific, with limited common interests in the Middle East, this perception changed when India and the US, alongside Israel and the UAE, established the I2U2 forum to develop joint economic projects.
- The India-Arabia-Europa corridor could prove to be even more impactful.
IMEC and Its Relationship with China:
- The US and EU might be inclined to present IMEC as a potential counterpart to China's Belt and Road Initiative.
- For Delhi, Abu Dhabi, and Riyadh, whether as existing (in India's case) or new members (in the case of Saudi Arabia and the UAE) of the BRICS group, IMEC symbolizes the emergence of a West Asian framework.
- Within this framework, countries like India, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Oman, and Egypt are steadily expanding their integration, encompassing aspects beyond energy, remittances, and ideology.
Way Forward
- Preserving the Significance of the Corridor Launch: The symbolism associated with the Corridor's launch in New Delhi and the absence of Russia and China at the Summit should not be underestimated. It's crucial to avoid drawing misguided conclusions from this symbolism by the US and EU.
- Embracing a Balanced Approach: For countries like India, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, the pursuit of a balanced Eurasian structure doesn't necessitate forming a coalition aimed at containing China and Russia.
- The Russian President's statement that the IMEC complements Russia's North-South project should be considered in this context.
- Ensuring IMEC Success: The success of IMEC hinges on several critical factors, including conducting a pragmatic assessment of each nation's motivations for participation, advancing the project beyond a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), addressing logistical challenges, and prioritizing elements like electricity, digital connectivity, and clean hydrogen during the Corridor's initial phases.
- Addressing Security Concerns: The IMEC nations should also proactively address potential security challenges that may arise due to increased Eurasian connectivity.
- The inauguration of IMEC represents a noteworthy step in the evolving global power dynamics, with a clear shift towards the East.
- It underscores the dedication of the US, Europe, and emerging players like India, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE to foster a more equitable and interconnected Eurasian arrangement.
- The success of IMEC has the potential to set a precedent for future transcontinental initiatives seeking to establish a more balanced Eurasian framework.
Mains Question:
- Elaborate on the implications of the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC) launch for the global power shift, highlighting the potential influence on India including global power dynamics and future transcontinental initiatives. (15M)
Women’s Reservation Bill Introduced in Loksabha (Indian Express)

- 20 Sep 2023
Why is it in News?
The One Hundred Twenty-Eight Amendment Bill 2023, also known as the Women Reservation Bill, has been presented in the Lok Sabha. This bill aims to allocate one-third of all seats for women in both the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies.
The Historical Background of the Women's Reservation Bill:
- The demand for political reservation for women has been a longstanding one, dating back to the pre-independence era.
- Various committees have advocated for women's political reservation.
A Brief Journey of Women's Political Reservation:
- During the National Movement, in 1931, three women's organizations sent a letter to the British Prime Minister requesting political reservation for women.
- In the Constituent Assembly debates, the issue of women's reservation was discussed.
- However, it was rejected on the premise that a democracy should provide representation to all groups.
- In 1971, the Committee on the Status of Women in India and in 1988, the National Perspective Plan for Women both recommended reserving seats for women in local bodies.
- These recommendations led to the 73rd and 74th amendments to the Constitution, which mandate that all State governments reserve one-third of seats for women in local bodies.
- Nonetheless, the matter of reservation in the Parliament and Legislative Assemblies remained unresolved until the introduction of the Women's Reservation Bill.
Historical Progression of the Women's Reservation Bill:
- 1996: The Women's Reservation Bill made its debut in 1996 as the 81st Constitutional Amendment Bill under the Deve Gowda government.
- It was referred to a parliamentary select committee led by Geeta Mukherjee. However, the Bill expired with the dissolution of the Lok Sabha due to a lack of consensus, particularly regarding reservation for OBC women.
- 1999: The NDA government revived the Bill in the 13th Lok Sabha and presented it twice in 2003.
- Unfortunately, these attempts to pass the bills were unsuccessful, resulting in their expiration.
- 2004: The UPA government incorporated the reservation bill into its Common Minimum Programme and placed it in the Rajya Sabha to prevent it from lapsing once more.
- 2010: The Women's Reservation Bill, initially introduced as the 108th Constitutional Amendment Bill in 2008, was successfully passed in the Rajya Sabha but lapsed in the Lok Sabha.
- Its most vocal opponents included the RJD, the JD(U), and the SP, who advocated for 33% reservation for backward groups within the 33% women's quota.
Arguments in Support of the Bill:
- Enhancing Women's Political Representation: India ranks lower than 140 other nations in terms of women's representation in national legislatures, as per the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) 'Women in Parliament' Report (2021).
- Despite some increase in women's representation in the Lok Sabha since independence (around 16% in the 17th Lok Sabha), India lags behind several African and South Asian countries like Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- Empowering Women's Leadership for Change: Studies on panchayats have demonstrated the positive impact of women's reservation on women's empowerment and resource allocation.
- For instance, a former woman Sarpanch of Dhani Mayan Khan GP in Haryana established a training center for women and ensured that every village child attended school.
- Advancing the Decriminalization of Politics: Reserved seats for women could contribute to the decriminalization of Indian politics.
- Currently, in the Lok Sabha, 159 MPs have declared serious criminal cases against them, including rape, murder, attempted murder, kidnapping, and crimes against women.
- Addressing Crimes Against Women: The Women's Reservation Bill can play a role in addressing crimes against women in society, potentially leading to a decrease in cases like the Nirbhaya Rape Case.
- Aligning Representation with Vote Share: Despite an increase in women's vote share, their representation in political positions has not kept pace.
- Women in India vote at a rate similar to men, but their representation in political roles remains significantly lower.
- Breaking the Patriarchal Nature of Indian Politics: Indian politics has traditionally been patriarchal, with top party positions and positions of power predominantly held by men.
- The Women's Reservation Bill has the potential to challenge and transform this patriarchal aspect of Indian politics.
- Challenging Stereotypes: An increase in women politicians can help break stereotypes that limit women to the role of 'homemakers,' fostering a broader acceptance of women as lawmakers.
Arguments Opposing the Bill:
- Lack of Separate OBC Reservation: The Bill reserves seats separately for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes women within the existing one-third quota of seats.
- However, it does not provide separate reservation for OBC women, who constitute 60% of the female population.
- Exclusion from Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils: The Bill does not extend reservations to women in the Rajya Sabha and the Legislative Councils, limiting its scope.
- Potential Misuse with Proxy Candidates: Some argue that the introduction of women's reservations could lead to the emergence of 'MP and MLA Patis,' where individuals use their wives as proxy candidates for reserved seats, wielding the actual power.
- Contradiction with Equality Principles: Opponents contend that the idea of women's reservation contradicts the principle of equality enshrined in the Constitution.
- They argue that such reservations could perpetuate the unequal status of women, as they might not be perceived as competing based on merit.
- Heterogeneity of Women: Women are a diverse group with varied backgrounds and interests, unlike caste groups.
- Consequently, the same arguments used to justify caste-based reservations may not be directly applicable to women.
- Women's interests are interconnected with other social, economic, and political strata.
- Restricting Voter Choice: Critics argue that reserving seats for women could limit voter choices.
- Instead of reservations, opponents of the Bill have proposed alternative approaches, such as women's reservation within political parties and the implementation of dual-member constituencies, where each constituency has two MPs, with one being a woman.
Key Provisions of the Women Reservation Bill 2023:
- Reservation of one-third of all seats for women in the Lok Sabha, state legislative assemblies, and the legislature of the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- Within this allocation, one-third of the seats will be reserved for scheduled castes and scheduled tribes.
- The reservations will remain in effect for 15 years from the law's commencement.
- However, Parliament has the authority to extend the reservation period beyond 15 years through legislation.
- Reserved seats may be subject to rotation.
- This means that seats designated for women will not remain fixed but will rotate after each election cycle.
- The provisions will come into effect only after a delimitation exercise is carried out for this purpose.
- Delimitation will be based on the data collected in the first census conducted after the bill's passage.
- The amendment will be implemented following the dissolution of the respective house or legislative assembly and will not impact any existing representation.
- For instance, even after the Bill's passage, one-third women's representation will not be immediately applicable.
- It will become effective as each state completes its assembly term and holds elections.
What Steps Can Be Taken Moving Forward?
In addition to the Women's Reservation Bill, India should consider implementing the following reforms to enhance the political empowerment of women:
- Institutionalizing Intra-Party Democracy: Encourage intra-party democracy to broaden the pool of women candidates within political parties.
- Strengthening Women's Agencies and Organizations: Support and reinforce women's agencies and organizations to contribute to the creation of a progressive society with equal opportunities for all citizens.
- Promoting Women's Participation at the Panchayat Level: Enhance women's participation at the panchayat level by strengthening women's self-help groups.
- Encouraging Girls' Participation in College/University Politics: Promote the active involvement of girls in college/university student political parties and political debates to nurture future women leaders.
Mains Question:
- What are the key provisions and potential challenges associated with the Women's Reservation Bill 2023, and how can these challenges be addressed to ensure effective implementation and increased political empowerment of women in India? (15M)
Enhancing the Benefits of Research for Basmati Rice in India (Indian Express)

- 19 Sep 2023
Why is it in News?
Over the past three decades, the yearly exports of Basmati Rice have surged from 0.3-0.35 million tonnes (valued at $200-250 million) to 4.5-4.6 million tonnes, with a value of $4.7-4.8 billion.
Transforming the Rice Industry in India:
- Until the late 1980s, Indian farmers cultivated traditional tall basmati rice varieties, which reached heights of 150-160 cm.
- However, these tall plants were susceptible to lodging, bending over when laden with well-filled grains, and they produced a meager 10 quintals of paddy per acre over a lengthy period of 155-160 days, from nursery sowing to harvesting.
- Some of these traditional varieties included Taraori (also known as Karnal Local or HBC-19) and Dehraduni (Type-3).
- The turning point occurred when the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) introduced Pusa Basmati-1 (PB-1), an improved variety released in 1989.
- By the early 21st century, India was exporting 0.6-0.7 million tonnes of basmati rice, generating annual revenues of $400-450 million, with PB-1 accounting for approximately 60% of this success.
Evolution of the Rice Sector in India:
- The first significant change occurred with the introduction of Pusa Basmati-1 (PB-1), which led to a doubling of India's basmati exports.
- However, the true transformation took place in 2003 when Pusa Basmati-1121 (PB-1121) was released.
- PB-1121's standout feature was its grain quality: each kernel averaged 8 mm in length but elongated 2.7 times to approximately 21.5 mm when cooked.
- One cup of milled PB-1121 grains yielded 4.5 cups of cooked rice, compared to 4 cups for PB-1 and 3.7 cups for Taraori.
- Following the introduction of PB-1121, India's basmati rice exports surged from 0.7 million tonnes to 3.7 million tonnes and from $390 million to $4.9 billion in value terms between 2001-02 and 2013-14.
- Another significant development occurred in 2013 when the IARI released Pusa Basmati-1509 (PB-1509).
- PB-1509 had a shorter seed-to-grain duration of just 115-120 days, making it advantageous for farmers as they could cultivate an extra crop.
- After harvesting PB-1509, farmers began adopting various crop combinations, including planting a three-month potato crop in early October, followed by sunflower, sweet corn, or onion in early January, all of which matured in 90-100 days.
Enhancing Disease Resistance in Basmati Rice:
- In recent years, scientists at IARI have been dedicated to safeguarding the improved yield of their basmati varieties by introducing genes for disease resistance.
- An example is PB-1121, which became vulnerable to bacterial leaf blight. To combat this, IARI introduced Pusa Basmati-1885 and Pusa Basmati-1847.
- These varieties were essentially PB-1121 and PB-1509 but equipped with "built-in resistance" to both bacterial blight and rice blast fungal disease.
- The incorporation of resistance traits through marker-assisted backcross breeding eliminates the need for farmers to use fungicides.
- This reduction in the application of crop protection chemicals not only promotes sustainable farming but also preserves the premium reputation of Indian basmati in the global market.
Challenges Faced by Basmati Rice:
- Basmati Rice encounters two primary challenges:
- Lack of Minimum Support Price (MSP): Unlike other crops, basmati paddy does not have a minimum support price (MSP) established by the government, which can affect the income security of farmers.
- Export Dependency: The majority of basmati rice is exported, with a limited domestic market. This export-centric nature exposes farmers to market fluctuations and government export policies.
- For instance, the Union government recently imposed restrictions, disallowing basmati shipments priced below $1,200 per ton.
India's Rice Exports in 2023:
- India holds the title of the world's largest rice exporter, commanding a substantial 45% share of the global rice market.
- During April-May 2023, the nation's rice exports surged by 21.1% compared to the same period in the previous fiscal year.
- In May 2023, the export of Basmati rice experienced a notable increase of 10.86% compared to its exports in May 2022.
- Non-Basmati rice shipments have been consistently growing for the past three years, and the export of Basmati rice in 2022-2023 exceeded the figures of the previous year.
- Government data up to August 17, 2023, reveals that total rice exports (excluding broken rice) reached 7.3 million tonnes, marking a 15% increase compared to the 6.3 million tonnes exported during the corresponding period last year.
India-Canada FTA Stalled (Indian Express)

- 18 Sep 2023
Why is it in the News?
Negotiations for a bilateral free trade agreement between India and Canada have been temporarily halted. This decision followed Prime Minister Modi's concerns about anti-India activities by extremist groups in Canada, which he discussed with Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau during the G20 Summit.
Context:
- Negotiations on the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) between India and Canada have been temporarily suspended due to political differences.
- Talks are expected to resume once these issues are resolved.
Possible Reasons for the pause:
- Strained Relations: The relationship between the two countries has become tense due to concerns related to pro-Khalistan groups operating in Canada.
- Diplomatic Actions: In July, India summoned the Canadian envoy and issued a formal demarche after posters naming senior Indian diplomats in Canada surfaced.
- Strong Response: Following a meeting between Prime Ministers Modi and Trudeau during the G20 Summit, India released a strongly-worded statement.
India-Canada Relations:
- Diplomatic relations between India and Canada were formally established in 1947. However, the partnership took a significant step forward when it was elevated to a strategic level during Prime Minister Modi's visit to Canada in 2015.
Commercial Relations:
- Bilateral Trade: The economic relationship between the two nations has witnessed substantial growth. India has become Canada's 10th largest trading partner.
- Trade Figures: In the fiscal year 2022-23, India's total exports to Canada amounted to US$ 4.10 billion, showing an increase from US$ 3.76 billion in the previous year.
- Simultaneously, India's imports from Canada reached US$ 4.05 billion in 2022-23, up from US$ 3.13 billion in 2021-22.
- Key Exports and Imports: The bilateral trade consists of a range of items. India exports gems, pharmaceutical products, ready-made garments, among others.
- In contrast, India imports commodities like pulses, newsprint, wood pulp, asbestos, potash, iron scrap, copper, minerals, and industrial chemicals from Canada.
- Investment: Canadian Pension Funds have made cumulative investments of around US$ 55 billion in India.
- Additionally, the cumulative Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) from Canada since the year 2000 amounts to approximately US$ 4.07 billion.
- CEPA/EPTA Negotiations: In March 2022, both countries agreed to re-launch negotiations for the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- Furthermore, they explored the possibility of an interim agreement called the Early Progress Trade Agreement (EPTA), which could bring mutual commercial benefits.
- Negotiations on CEPA and EPTA resumed in April 2022 and continued through nine rounds of talks until July of the same year.
Nuclear Cooperation:
- Canada's nuclear aid to India began in 1956 and saw collaboration until 1974, when India conducted its nuclear test, Smiling Buddha.
- Canada was among the earliest participants in India's nuclear power program, notably contributing to the construction of CIRUS, India's first research reactor.
- The restoration of nuclear cooperation between the two countries occurred in June 2010 with the signing of a Nuclear Cooperation Agreement (NCA).
Science and Technology:
- Bilateral collaboration extends to various sectors, including joint research projects in healthcare, agri-biotech, and waste management under the IC-IMPACTS program.
- Furthermore, the Department of Earth Science and Polar Canada initiated a program for the exchange of knowledge and scientific research focused on Cold Climate (Arctic) Studies.
Cooperation in Space:
- Notably, the commercial arm of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), ANTRIX, has successfully launched several nanosatellites from Canada.
- In a significant milestone, ISRO included Canada's first Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite on its 100th satellite PSLV launch in January 2018.
Development Cooperation:
- After 55 years of bilateral programming in India with a total aid of $2.39 billion, Canada's bilateral development assistance program came to an end in 2006.
- This change resulted from a shift in Indian government policy regarding aid.
- Presently, Canada supports various projects in India through Grand Challenges Canada.
- The main programming sector of the Partnerships for Development Innovation Branch focuses on maternal, newborn, and child health, including support for early childhood development.
Cooperation in Indo-Pacific:
- In November 2022, Canada unveiled its Indo-Pacific strategy.
- Although Canada is the last G7 nation to formally embrace the concept of the Indo-Pacific, its strategy emphasizes India's strategic importance.
- The document highlights India as a key partner and calls for close collaboration with the country.
People-to-People Relation:
- Canada is home to one of the largest Indian diasporas globally, numbering 1.6 million individuals (comprising Persons of Indian Origin - PIOs and Non-Resident Indians - NRIs), which constitutes more than 4% of its total population.
- In the political arena, the present Canadian House of Commons, with a total strength of 338, includes 22 Members of Parliament of Indian origin.
- Additionally, there has been an encouraging cultural exchange, symbolized by a commemorative Diwali stamp jointly issued by Canada Post and India Post in 2017.
- Furthermore, Diwali celebrations on Parliament Hill have been a tradition for 18 years.
Challenges in India-Canada Relation:
- Khalistani Groups: A significant challenge lies in Canada providing a safe haven for separatist Khalistani groups.
- New Delhi has expressed concerns regarding the Liberal Party's alleged alignment with these groups for political support.
- Some members of the Sikh diaspora, backed by pro-Khalistan groups, are politically active in Canada.
- Anti-India Elements: Concerns have also arisen about Canada's perceived slow response to address anti-India elements operating on its soil.
- Instances such as the vandalization of a Hindu temple near Toronto and the defacement of Indian symbols with anti-India graffiti have added to these concerns.
- Diplomatic Tensions: Occasional diplomatic tensions have arisen due to issues such as Canadian comments regarding India's farmer protests and India's subsequent cancellation of diplomatic talks in response.
- India-Canada relations are multifaceted, encompassing trade, investment, scientific collaboration, and more. However, they also face challenges related to certain groups and diplomatic issues."
Apple support for NavIC prompts consideration of mandatory adoption and extra incentives by the government. (Indian Express)
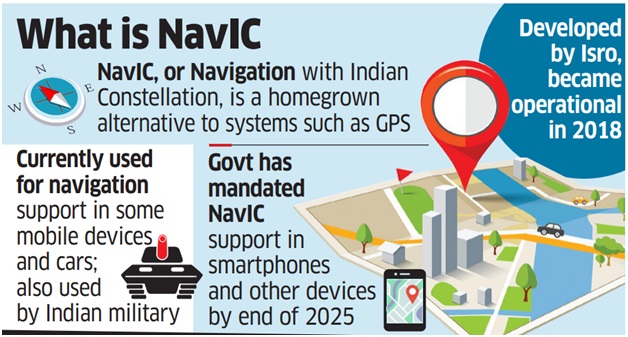
- 16 Sep 2023
Why it is in News?
- Following Apple's adoption of the NavIC navigation technology in select iPhone 15 models, the government is contemplating a mandate for all smartphones sold in India to incorporate this homegrown GPS alternative.
- According to the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), this requirement would apply to all 5G phones by January 1, 2025, and other phones by December 2025.
Context:
- Currently, only a few smartphone brands like Poco, Vivo, and Xiaomi incorporate NavIC support.
- To encourage wider adoption of this indigenous navigation system, the government is contemplating additional incentives for smartphone manufacturers.
- These incentives may be included in the upcoming round of the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme if manufacturers utilize chips designed or produced in India that support NavIC technology.
- As an example, the existing IT hardware PLI offers cashback incentives to companies employing India-designed or -manufactured chips in their systems.
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) aims to make it nearly mandatory, similar to the automobile sector, for all GPS-enabled devices to include NavIC chipsets, alongside other technologies like GPS.
- Apple's recent announcement of NavIC support in its latest iPhone models marks the company's first inclusion of this technology, potentially driving its mainstream acceptance.
- The achievements of ISRO, including the successful lunar mission (Chandrayaan 3), the maiden solar mission (Aditya L1), and the growing recognition of NavIC technology, demonstrate India's expanding capabilities in the realm of space technology.
What is NavIC?
- NavIC, also known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), is an independent and self-reliant navigation satellite system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Initially approved in 2006 with a budget of $174 million, NavIC was anticipated to be completed by 2011 but became operational in 2018.
- Comprising seven satellites, NavIC covers the entirety of India's landmass and extends up to 1,500 km beyond its borders.
- Its primary objective is to reduce dependence on foreign navigation satellite systems, particularly for critical sectors.
- Currently, NavIC is utilized in India for:
- Public vehicle tracking, ensuring emergency alerts for fishermen in remote deep-sea areas with no terrestrial network connectivity.
- Tracking and disseminating information related to natural disasters.
- India's next goal is to integrate NavIC into smartphones, aligning with the draft satellite navigation policy of 2021, which outlines plans to expand coverage from regional to global.
What are the Benefits of a Regional Navigation System?
- India is the sole country with its regional satellite-based navigation system.
- Four global satellite navigation systems exist: the American GPS, Russian GLONASS, European Galileo, and Chinese Beidou.
- Japan also has a four-satellite system similar to India's GAGAN (GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation) that can enhance GPS signals over its territory.
- When fully operational, NavIC (supported by ground stations in Japan, France, and Russia for improved signal triangulation) will provide highly accurate open signals, up to 5 meters, and even more precise restricted signals (comparable to GPS's ~20 meters accuracy).
- Unlike GPS, NavIC employs satellites in high geostationary orbits, ensuring they remain fixed relative to Earth and continuously cover the same Earth region.
- NavIC signals approach India at a 90-degree angle, enhancing their reach to devices located in congested urban areas, dense forests, or mountainous terrain.
Comparison Between Old and New (2nd-Generation) NavIC Satellites:
- The existing seven satellites in the IRNSS constellation were launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), which is ISRO's reliable launch rocket.
- In 2018, the IRNSS-1I satellite joined the constellation, replacing an older, partially malfunctioning satellite. It was ISRO's ninth satellite for NavIC, although it's often considered the eighth due to the loss of IRNSS-1H in 2017 when the payload's heat shield failed to open on schedule.
- The 2nd-generation satellite, NVS-01, launched in May 2023, belongs to ISRO's NVS series and is notably heavier.
- NVS-01 features an onboard Rubidium atomic clock, a significant indigenous development for precise object location determination.
- Currently, only four IRNSS satellites offer location services, while others are designated for messaging services.
- The 2nd-generation satellites will introduce signals in a third frequency, L1 (in addition to the existing L5 and S frequencies), enhancing interoperability and supporting use in wearable devices.
- These upgraded satellites will also boast a longer mission lifespan, exceeding 12 years, in contrast to the 10-year mission life of the existing satellites.
Mains Question:
- How has the implementation of NavIC benefited India's navigation autonomy and strategic importance, and what are the key challenges and planned enhancements, particularly regarding mobile phone compatibility and signal security? (15M)
India's Supply Chain Opportunity (Indian Express)

- 15 Sep 2023
Why it is in News?
Nevertheless, the declaration made during the G20 Leaders' Summit about the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has the capability to position India as a key player in the Asian segment of global supply chains. This holds substantial importance as part of endeavors to reduce reliance on supply chains centered around China.
What Are Supply Chains?
- A supply chain encompasses all the stages involved in delivering a final product or service to the customer, starting from raw material producers.
- It involves strategically locating various production stages (like design, production, assembly, marketing, and service activities) in a cost-effective manner.
- Global supply chains have been the dominant model of industrial production since the 1980s, shaping the trajectory and character of globalization and regionalization.
- These global supply chains are prevalent in a wide spectrum of industries, from simpler ones like textiles, food processing, and consumer goods to more intricate sectors such as automobiles, aircraft, machinery, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Why Are Global Supply Chains Shifting Away from China?
- Presently, China plays a significant role in global value chains, contributing to nearly 20% of global manufacturing trade and a substantial share of key inputs required for production within global value chains.
- Nevertheless, even before the Covid-19 pandemic, Western companies were progressively reducing their dependence on China as a sourcing market, and its appeal among Western buyers was waning.
- This shift was driven, in part, by increasing labor costs and supply chain challenges within China, along with concerns among investors about tighter regulation of foreign businesses.
- Additionally, the trade disputes between China and the US prompted multinational companies to reconsider their global sourcing strategies.
- Certain segments of Chinese supply chains, especially those reliant on labor-intensive processes, were relocating to more cost-effective locations.
- However, complete relocation from China is challenging due to the substantial costs associated with shifting supply chains, including establishing new facilities and recruiting and training workers, among other factors.
Why are India and Southeast Asia Considered Favorable Supply Chain Destinations?
- Southeast Asia has been successful in luring foreign companies due to its combination of low labor costs, tax incentives, and enhanced logistical capabilities.
- Notably, countries like Vietnam and Thailand have emerged as prominent choices for supply chain relocation.
- India, however, is poised to become an accompanying manufacturing hub in Asia alongside China by leveraging foreign technology transfers and creating value-added employment opportunities. This is evident in various developments:
- Increased production of iPhones within India.
- Early-stage technology transfer for the technologically advanced Mercedes Benz EQS to India.
- Foxconn Technology Group's establishment of a chip-making fabrication plant in Gujarat.
- India's existing manufacturing sectors, including automobiles, pharmaceuticals, and electronics assembly, already possess sophistication and are likely to excel in this competition.
- Foreign investors are drawn to India due to both geopolitical and economic considerations.
- India's services sector, encompassing ICT, back-office functions, financial and professional services, as well as transport and logistics, is also positioned for success.
Initiatives Taken by India to Strengthen its Supply Chain Network:
- Since 2022, the Indian government has prioritized preferential trade through various bilateral agreements with trading partners.
- The UAE-India Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement became effective in May 2022.
- Ongoing discussions aim to finalize the Australia-India free trade agreement (FTA) by the close of 2023. Negotiations are also underway for UK-India and EU-India FTAs.
- The Indian Prime Minister's visit to Washington DC in June 2023 underscored the pivotal role of supply chains in India-United States relations.
- These new agreements with Western trading partners signify a commitment to extensive economic integration, surpassing India's previous FTAs, which primarily focused on goods trade and related measures.
Path Ahead for India - Drawing Lessons from China's Success:
- Encouraging foreign direct investment (FDI) with an export focus remains a key strategy for engaging in supply chains.
- Local businesses must devise strategic approaches to integrate into global supply networks.
- Large conglomerates can allocate resources and costs effectively among their business units.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can play pivotal roles as industrial suppliers and subcontractors for major exporters.
- Strategic moves such as mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations with multinational corporations and prominent domestic enterprises are sensible steps.
- Investing in domestic technological capabilities to meet international benchmarks for price, quality, and timeliness is crucial.
- Identifying and targeting multinational corporations involved in industries where India holds a potential comparative advantage, coupled with improved coordination between central and state governments, is essential.
- Investing in higher education in fields like science, technology, engineering, and mathematics is a forward-looking approach.
- Caution should be exercised when contemplating the adoption of China's interventionist state model, as it carries significant risks of government failures.
- Engaging with think tanks to gain insights into effective strategies is a prudent course of action.
- India stands at a pivotal moment in history to foster industrialization in South Asia, which would enhance regional stability, create employment opportunities, and reduce susceptibility to Chinese influence.
- To promote regional supply chains, the Indian government should consider the following policy actions:
- Expanding the Make in India Programme into a broader Make in South Asia Programme.
- Establishing a comprehensive bilateral Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with Bangladesh.
- Enhancing the Indo-Sri Lanka FTA to bolster regional trade and investment based on established rules.
- Without forging connections within South Asia, India's appeal to the Global South remains limited. The emerging supply chain opportunities with the United States offer India a promising pathway to embark on its journey of global integration, while maintaining a 'Neighbourhood First' approach.
Latest NSO Data on Inflation in India (The Hindu)

- 14 Sep 2023
Why it is in News?
- Recent data from the National Statistical Office (NSO) reveals that India's retail inflation rate decreased to 6.83% in August.
- This decline came after hitting a 15-month high of 7.44% in July 2023, primarily because of falling prices of food items, particularly vegetables.
- However, it's worth noting that the inflation rate still remains above the upper limit of the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) medium-term inflation target range of 4+/-2%.
Key Points from the Recent NSO Data:
- In August 2023, retail inflation stood at 6.83%, marking the fourth instance this year and the seventh since August 2022 where it exceeded the upper limit of the target.
- Policymakers are increasingly concerned about high inflation rates.
- In its recent monetary policy review, the RBI maintained the key repo rate at 6.50% but raised the inflation projection for FY2024 from 5.1% to 5.4%.
- In the Index of Industrial Production (IIP), manufacturing showed improvement, rising to 141.2 in July from 135 a year ago and 141.1 in the previous month.
- Of concern, consumer durables contracted by 2.7% year-on-year in July 2023, indicating weaknesses and imbalances in consumption demand.
Key Insights from the Recent NSO Data:
- Consumer Confidence Declines: In August 2023, consumer sentiment dropped by 1.5%, breaking a streak of continuous increases since January 2023.
- This decline can impact the Indian economy and businesses, particularly in anticipation of the upcoming festive season.
- A significant contributor to this drop is a decrease in consumers' intentions to buy consumer durables like cars and TVs.
- This pessimism is not only due to stagnant perceived incomes but also concerns about future earnings.
- Persistent Inflation: According to RBI projections, inflation is expected to remain above 5% until the first quarter of 2024-25, with the likelihood of reaching 6.2% in the current quarter (July-September), which is beyond the RBI's comfort zone.
- Although overall food inflation has moderated, certain food items like cereals, pulses, and milk are experiencing upward price momentum.
- Factors such as irregular rainfall and low reservoir levels pose further risks to food inflation.
- Additionally, the recent surge in global crude oil prices is a cause for concern. However, the continuing deflation in the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) will have a delayed impact on Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation.
- The government's decision to reduce cooking gas prices by Rs 200 per cylinder is expected to benefit domestic LPG consumers and those under the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY).
- India's GDP Growth Prospects: India's potential GDP growth rate has steadily decreased from around 8% just before the Global Financial Crisis of 2008-09 to 6% before the Covid pandemic.
- The potential GDP growth rate represents the rate at which an economy can expand without causing high inflation.
- The temporary increase in India's GDP growth rates in 2020-21 was primarily due to a lower base.
- The Indian economy faces various challenges, including a slowing global economy, elevated oil prices, and climate change. Economists estimate that, under a business-as-usual scenario, India's economy cannot grow more than 5% over the next decade.
- While this growth rate may be attractive from a global perspective, it may not be sufficient to meet the employment needs of India's large youth population.
What is Inflation?
- Inflation signifies an increase in prices, resulting in a decrease in the purchasing power of money over time.
- The rate at which purchasing power diminishes is measured by tracking the average price increase of a specific set of goods and services over a specified period.
- This price hike, typically expressed as a percentage, signifies that a unit of currency can purchase fewer goods and services compared to previous periods.
- In contrast, deflation occurs when prices fall, leading to an increase in purchasing power.
What are the causes of inflation?
- Demand-Pull Inflation: This occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds their supply.
- When demand is high and supply is limited, businesses often raise prices, leading to inflation.
- It's often associated with strong economic growth.
- Cost-Push Inflation: In this scenario, rising production costs, such as increased wages or the cost of raw materials, force businesses to raise prices to maintain their profit margins.
- Oil price spikes are a classic example of cost-push inflation.
- Built-In Inflation: Sometimes called wage-price inflation, this happens when workers consistently demand higher wages to keep up with rising prices.
- Businesses then raise prices to cover increased labor costs, creating a cycle of inflation.
Categories:
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): This index calculates the weighted average of prices for a basket of goods and services at the consumer or retail level.
- Wholesale Price Index (WPI): The WPI monitors price changes for goods in stages before reaching the retail level.
Inflation Targeting in India:
- The RBI Act of 1934 establishes a legal and institutional framework for ensuring price stability while also considering growth objectives.
- In 2016, the Finance Act amended the RBI Act to establish a Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
- The MPC issues a bi-monthly Monetary Policy Report to set India's benchmark interest rate, enhancing transparency and accountability in the country's monetary policy.
- The current mandate of the MPC is to maintain an annual inflation rate of 4% (with a tolerance range of +/-2%).
- If inflation exceeds this range for three consecutive quarters, the committee is accountable to the Government of India.
Mains Question:
- How does the RBI's inflation targeting framework impact India's economic stability and growth? Discuss the tools and effectiveness of RBI's strategies in controlling inflation. (10 M)
Ridding India of Food Insecurity (The Hindu)

- 13 Sep 2023
Why it is in News?
- While India is currently the world's fastest-growing major economy, it is also grappling with a rapid increase in food-price inflation.
- The surge in food prices began to intensify notably in 2019 and has continued to rise in most subsequent years.
- In July of this year, annual inflation surpassed 11%, reaching its highest level in the past decade.
- One consequence of this sustained high food-price inflation is the possibility that a portion of the population may encounter difficulties in accessing food with sufficient nutritional value.
Key Findings of Concern:
- The 'State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World' report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) assesses the percentage of people in different countries who cannot afford a nutritious diet.
- Approximately 74% of the population is unable to afford a healthy diet.
- This likely results in decreased food consumption due to reduced purchasing power.
- Food prices in India have been on a consistent upward trend since 2019, with annual inflation exceeding 11% in July 2023, the highest rate in a decade.
- There has been a notable increase in the prevalence of anaemia, with over 50% of adult women estimated to be affected according to the latest National Family Health Survey conducted between 2019 and 2021.
- Critics argue that macroeconomic policies, including the Reserve Bank of India's focus on inflation control through measures like inflation targeting, are ineffective in addressing food inflation, which is primarily driven by supply-side factors.
Importance of Food Security:
- Enhanced Health and Nutrition: Food security plays a crucial role in improving the health and well-being of individuals by preventing malnutrition and its associated health issues, including stunted growth, cognitive impairment, and increased susceptibility to diseases.
- It's worth noting that malnutrition is responsible for the deaths of approximately 3.1 million children each year, accounting for nearly half of all child deaths under the age of 5.
- Economic and Social Stability: Food security contributes to the economic and social stability of individuals and nations by enabling increased productivity, income generation, and participation in trade.
- According to a World Bank study, the global cost of undernutrition, in terms of lost productivity and human capital, amounts to USD 3.5 trillion per year.
- Additionally, a United Nations report highlighted that food insecurity played a pivotal role in 58% of conflicts between 2017 and 2019.
- Poverty Alleviation: Food security is instrumental in reducing poverty as it enables people to afford and access nutritious food while also investing in other essential needs such as education and healthcare.
- These factors help break the cycle of poverty.
- National Security: Food security bolsters national security by ensuring a reliable food supply that is not vulnerable to external factors like global food prices or supply chain disruptions.
- Food insecurity can make nations susceptible to such factors, compromising their sovereignty.
- Sustainable Development: Food security aligns with sustainable development goals, particularly Goal 2: Zero Hunger.
- It also supports related goals such as poverty reduction, improved health, gender equality, and environmental sustainability, contributing to a holistic approach to sustainable development.
Causes of Food Insecurity:
- Impact of Russia-Ukraine Conflict: The Russia-Ukraine conflict has disrupted the global supply chain due to trade-related policies imposed by countries, exacerbating the global food crisis.
- Several nations have implemented food trade restrictions to bolster domestic supply and reduce prices.
- Rising Domestic Inflation: Many countries are grappling with domestic food inflation, which has intensified the issue of food insecurity.
- For instance, India has imposed bans on wheat and rice exports to support its domestic population.
- Climate Variability and Extremes: Climate change has significantly affected the availability and quality of critical resources like water, land, and biodiversity essential for food production.
- It has also led to shifts in the patterns and severity of pests, diseases, and natural disasters, resulting in reduced crop yields and livestock productivity.
- The Global Report on Food Crises highlights that weather and climate extremes were the primary drivers of acute food insecurity in 12 countries in 2021, impacting nearly 57 million people.
- Economic Slowdowns and Downturns: Economic slowdowns have diminished the income and job prospects of vulnerable populations, who typically allocate a substantial portion of their income to food purchases.
- These economic shocks have disrupted both the supply and demand for food, leading to increased food prices and reduced food quality.
Learning from the Green Revolution:
- India boasts a rich historical backdrop of the Green Revolution, a transformative period during the 1960s.
- The government initiated a supply-side approach, providing farmers with high-yield seeds, accessible credit, and guaranteed prices through procurement.
- This initiative achieved remarkable success, swiftly liberating India from dependence on food imports and fulfilling its ambition of self-sufficiency.
- However, certain strategic errors were made during this period.
- Excessive use of chemical fertilizers resulted in soil degradation.
- An overemphasis on procurement prices, rather than prioritizing productivity to enhance farm incomes, contributed to inflation.
- The policy primarily focused on cereals, neglecting pulses, a vital source of protein for the majority of Indians.
The Path Ahead: Suggested Actions
- Enhanced Agricultural Investment: Evaluate and optimize public expenditure on irrigation to improve its efficiency.
- Revitalize Research Institutes: Revamp India's network of public agricultural research institutes to rekindle their pivotal role, reminiscent of their contributions during the 1960s.
- Reinvigorate the Role of Local Village Representatives (Gram Sevak): Empower and elevate the role of the gram sevak in villages, making them instrumental in disseminating best agricultural practices.
- Boost Protein-Based Crop Production: Implement a comprehensive program to significantly increase protein production by incorporating various initiatives.
- Foster Cooperative Federalism: Encourage states to actively contribute to enhancing agricultural productivity rather than relying solely on food allocations from the central pool for their Public Distribution System.
- Ensure Permanent Access to a Balanced Diet: Prioritize measures consistent with ecological sustainability to ensure that all Indians have continuous access to a nutritious diet.
- Supply-Side Interventions: Implement interventions on the supply side to stabilize food prices by improving land yield.
- Focus on Cost Reduction: Concentrate on the specific objective of reducing food production costs.
- Multifaceted Approach: Extend irrigation coverage to 100% of the net sown area, eliminate land leasing restrictions, accelerate agricultural research efforts, and reinstate agricultural extension services.
Mains Question:
- Examine the key agricultural issues in India today, encompassing food security, sustainability, and economic stability. Propose a holistic approach that integrates government funding, research, inter-state collaboration, and supply-side interventions to pave the way for a resilient and prosperous future in Indian agriculture. (15M)
Strategic Partnership Council (SPC) Meeting Between India & Saudi Arabia (Indian Express)

- 12 Sep 2023
Why it is in News?
Saudi Arabia’s Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman Al Saud and Prime Minister Narendra Modi held extensive talks on Monday, agreeing to expand trade and security ties. The leaders also co-chaired the first summit-level meeting of the India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council (SPC).
What is India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council (SPC)?
- The agreement to create the SPC was inked during Prime Minister Modi's official visit to Saudi Arabia in October 2019. This partnership was conceived to establish a top-tier council to guide and enhance the Indo-Saudi relationship.
- Key Pillars:
- The SPC operates through two primary pillars:
- Committee on Political, Security, Social, and Cultural Cooperation.
- Committee on Economy and Investments.
- These sub-committees engage at four distinct levels:
- Summit Level (Involving the Prime Minister and Crown Prince)
- Ministerial Level
- Senior Officials' Meetings
- Joint Working Groups (JWGs)
Key Highlights From the Recent Meeting Between Saudi's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and PM Modi:
- Notable Developments:
- Advancing the $50-billion West Coast refinery project, a massive undertaking with a capacity of 60 million tonnes.
- It will be a refinery and petrochemical complex situated on the Maharashtra coast.
- Identifying energy, defense, semiconductors, and space as sectors where cooperation will be intensified.
- Recognizing various other areas of collaboration, including security, education, technology, transportation, healthcare, tourism, and culture.
- Expanding the Relationship:
- Both parties agreed to transform their existing hydrocarbon relationship into a more comprehensive energy partnership.
- Signed Agreements:
- Additionally, eight agreements were formally signed to enhance cooperation in various domains, encompassing digitization and investment.
India-Saudi Arabia Bilateral Relations:
- India and Saudi Arabia share warm and amicable bilateral relations that are a testament to their deep-rooted economic and socio-cultural connections spanning centuries.
- These relations were formalized with the establishment of diplomatic ties in 1947, and since then, both nations have engaged in high-level exchanges and visits.
The Economic Cooperation Between India and Saudi Arabia:
Trade:
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, the bilateral trade volume between India and Saudi Arabia surged to a historic high of $52.75 billion.
- India's exports to Saudi Arabia saw significant growth, reaching $10.7 billion, compared to $8.8 billion in 2021-22.
- India stands as the second-largest trading partner for Saudi Arabia, while Saudi Arabia ranks as the fourth-largest trading partner for India.
Investment:
- Indian investments in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia have now reached approximately USD 2 billion.
- Saudi Arabia, on the other hand, is recognized as the 18th largest investor in India, with investments amounting to $3.14 billion as of March 2022.
- During the visit of the Saudi Crown Prince to India in February 2019, he made a significant announcement of the Kingdom's plans to invest a substantial sum of US $100 billion across various sectors in India.
Energy Partnership Between India and Saudi Arabia:
Vital Energy Collaboration:
- Energy collaboration stands as a foundational element of the bilateral relationship between India and Saudi Arabia, playing a crucial role in ensuring India's energy security.
- Saudi Arabia maintains its position as one of India's key partners in the sourcing of crude oil and petroleum products.
Crucial Import Destination:
- During the fiscal year 2022-23, Saudi Arabia retained its status as India's third-largest supplier of crude oil and petroleum products.
- India imported a substantial 39.5 million metric tonnes (MMT) of crude oil from Saudi Arabia in FY23, constituting 16.7% of its total crude oil imports.
LPG Contribution:
- India also benefitted from Saudi Arabia as a significant source of LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) imports, with 7.85 MMT of LPG imported from Saudi Arabia in FY23. This accounted for 11.2% of India's total petroleum product imports during that fiscal year.
Defense Partnership Between India and Saudi Arabia:
High-Level Engagement:
- In a significant diplomatic move, General Manoj Mukund Naravane, the Chief of Naval Staff of India, paid a landmark visit to Saudi Arabia in December 2020.
Naval Exercises:
- The two nations have successfully conducted two editions of their bilateral naval exercise titled 'Al Mohed al Hindi.'
Collaborative Defense Endeavors:
- India and Saudi Arabia are actively engaged in fostering collaboration within the realm of defense industries and capacity building, further strengthening their partnership in the defense domain.
Indian Community Living in Saudi Arabia:
- Prominent Expatriate Community:
- The Indian community in Saudi Arabia is a substantial one, numbering around 2.2 million people.
- This makes it the largest expatriate community within the Kingdom.
- Economic Contribution:
- Indians constitute approximately 7% of Saudi Arabia's total population, and they play a significant role in driving the country's economic growth.
- Migration Process Enhancement:
- During Prime Minister Modi's visit to Riyadh in October 2019, a noteworthy development was announced. India's e-Migrate system would be integrated with Saudi Arabia's e-Thawtheeq system, streamlining the migration process for workers.
- Hajj Pilgrimage:
- The annual Hajj pilgrimage holds immense importance in the Indo-Saudi bilateral relationship.
- During the visit of the Saudi Crown Prince to New Delhi in February 2019, it was revealed that India's Hajj quota would be expanded by 24,975 in 2019, allowing 200,000 Indians to partake in the Hajj pilgrimage in August 2019.
Recent Diplomatic Engagements:
- In 2019, the then Indian Prime Minister, Manmohan Singh, undertook a significant visit to Saudi Arabia, culminating in the signing of the 'Riyadh Declaration.'
- This landmark agreement elevated the bilateral relationship between the two nations to the status of a 'Strategic Partnership.'
- During Prime Minister Modi's visit to Saudi Arabia in 2016, King Salman bestowed upon him the Kingdom's highest civilian honor.
- In February 2019, Crown Prince Salman of Saudi Arabia visited India and announced the Kingdom's decision to invest approximately US$100 billion in India.
Later in the same year, during Prime Minister Modi's visit to Riyadh, the two nations signed the Strategic Partnership Council (SPC) Agreement, marking a pivotal moment in their diplomatic relations.
African Union Joined G20 (G20 Becomes G21) (The Hindu)

- 11 Sep 2023
Why it is in News?
At the 18th G20 Summit in India, the African Union (AU) became a new member of the G20, just three months after India proposed the idea of their inclusion.
Context:
- In June of this year, Prime Minister Modi suggested to G20 leaders that the African Union should be granted full membership at the upcoming G20 Summit in Delhi.
- This idea was born after the 'Voice of the Global South' Summit in January 2023, which saw participation from most of the African Union's 55 member countries.
- Up to that point, only one country from the African Union, South Africa, was a part of the G20.
- Several African leaders had emphasized that Europe had representation from five countries and the European Union (EU) within the G20, and they believed the African Union deserved similar representation.
What is the African Union (AU)?
- The African Union (AU) is a group of 55 member states representing the countries of the African Continent.
- In essence, it's a union that has various objectives aimed at enhancing the well-being of its member countries, both on their own and as a collective.
- It was formally established in 2002, succeeding the Organisation of African Unity (OAU, 1963-1999).
- The AU's main offices are located in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Vision of the African Union (AU):
- The AU is driven by its vision of "A united, prosperous, and peaceful Africa, led by its own people and serving as a dynamic force on the global stage."
- To accomplish this mission, a target year of 2063 has been established, marking the 100th anniversary of the OAU's establishment.
- Agenda 2063's key objectives include:
- Fostering prosperity in Africa through inclusive growth and sustainable development.
- Achieving a politically unified and integrated continent, inspired by the principles of Pan-Africanism.
- Cultivating a Africa characterized by good governance, democracy, human rights, justice, and the rule of law.
- To realize the aims outlined in Agenda 2063, the AU has devised a series of five 10-year plans, with the initial plan spanning from 2014 to 2023.
Objectives of the African Union (AU):
- The AU dedicates its efforts and resources to fostering stronger unity and solidarity among African nations and their citizens.
- Its goal is to expedite the political and socio-economic integration of the continent, addressing the diverse social, economic, and political challenges faced by African nations.
- Additionally, the AU actively works to promote peace, stability, and security throughout the region.
The Role of the AU in Promoting Peace on the Continent:
- The AU strongly believes that resolving conflicts is essential for achieving prosperity.
- In pursuit of this goal, it established a Peace and Security Council in 2004.
- This council has the authority to intervene in conflicts, replacing the principle of non-interference with one of non-indifference.
- It can deploy military forces in situations involving genocide and crimes against humanity and can authorize peacekeeping missions.
- The AU also oversees the New Partnership for Africa's Development (Nepad), an anti-poverty plan that offers a partnership with the West.
- It promotes good political and economic practices in exchange for increased aid and investment.
- Many of the AU's peacekeeping missions have been instrumental in helping governments combat terrorism across Africa, from the Sahel to northern Mozambique.
- Diplomatic efforts by the AU have also successfully resolved conflicts in Africa, such as brokering a peace deal between the Ethiopian Government and the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) in South Africa in 2022.
- Another notable achievement is the establishment of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which became operational in 2021.
- With 54 member countries as signatories, AfCFTA is the world's largest new free trade area since the creation of the WTO in 1994.
- Its aim is to boost intra-African trade by implementing deeper trade liberalization and improved regulatory harmonization.
- The AfCFTA is projected to increase Africa's income by $450 billion by 2035 and elevate intra-African exports by more than 81%.
Limitations of the African Union (AU):
- The AU has faced challenges in preventing coups in Africa, with over 200 coups occurring on the continent since the 1960s. Some of the most recent ones happened in Gabon and Niger.
- Another issue is the AU's struggle to ensure that its member nations fulfill their annual financial obligations.
- This has led to financial constraints, forcing the organization to rely on external funding, which can affect its independence.
Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan 2023 (Indian Express)

- 09 Sep 2023
Why in the News?
The second year of the Swachh Vayu Survekshan, carried out by the ministry based on self-assessments submitted by 130 identified cities under the National Clean Air Programme, saw Agra in Uttar Pradesh securing the second rank, followed by Thane in Maharashtra on the third spot.
About Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan:
- In September 2022, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change published rules for 'Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan - Ranking of Cities' as part of the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
- The idea behind Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan is to rank 131 cities in India based on how well they follow City Action Plans from NCAP.
- These plans are meant to reduce air pollution by up to 40% by 2025-26.
How Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan works?
- The Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan methodology categorizes 131 cities into three groups based on population:
- The first group includes 47 cities with a population exceeding 10 lakhs.
- The second group comprises 44 cities with a population ranging from 3 to 10 lakhs.
- The third group consists of 40 cities with a population less than 3 lakhs.
- Cities are required to perform self-assessments using the framework available on the PRANA online portal, which stands for "Portal for Regulation of Air-pollution in Non-Attainment Cities."
- The assessment focuses on key components, including solid waste management, road dust control, management of construction and demolition waste, and the control of emissions from vehicles and industries.
- Cash awards will be given to the top three performing cities in each group, fostering a spirit of competitive federalism.
- This Sarvekshan serves as a valuable tool for cities to plan and execute actions aimed at improving air quality.
- It's important to note that this ranking is not based on direct measurements of air quality parameters but on the proactive measures taken by cities to enhance air quality across various domains.
About Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan 2023:
- The Union Environment, Forest and Climate Change Minister, Bhupender Yadav, recently announced awards for the Swachh Vayu Sarvekshan 2023, which is a survey aimed at assessing clean air.
- In the first category, which includes cities with a population of more than 10 lakhs, Indore secured the top spot, followed by Agra and Thane.
- Indore achieved the highest score of 187 out of 200.
- In the second category, which covers cities with populations between 3-10 lakhs, Amravati took the first position, with Moradabad and Guntur following closely.
- Similarly, in the third category, which comprises cities with populations less than 3 lakhs, Parwanoo (Himachal Pradesh) secured the first rank, with Kala Amb (Himachal Pradesh) and Angul (Odisha) in the second and third positions, respectively.
- The assessment considered eight categories, including biomass and municipal solid waste burning, road dust, dust from construction and demolition waste, vehicular emissions, emissions from industries, other emissions, IEC activities (public awareness), and improvement in PM10 concentrations.
- Urban local bodies submitted self-assessment reports with supporting documents to determine the rankings.
- Notably, in the 2022 survey, Lucknow, Prayagraj, and Varanasi were the top three cities in the million-plus population category, but they ranked lower in the current year's survey.
What is National Clean Air Programme?
- The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP), initiated in 2019, stands as India's primary initiative to improve air quality significantly.
- This program was introduced as a comprehensive, time-bound, national-level strategy aimed at addressing the widespread issue of air pollution throughout the country.
- The primary objective is to achieve a reduction of 20% to 30% in Particulate Matter concentrations by 2024, with 2017 serving as the baseline year.
- NCAP has identified 132 non-attainment cities nationwide. These cities have consistently failed to meet the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for over five years.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change serves as the nodal ministry responsible for overseeing NCAP's implementation.
Measurement of Unemployment in India? (The Hindu)

- 08 Sep 2023
Why in the News?
- Based on the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), India's unemployment rate reached a peak of 6.1% in 2017, which was the highest ever recorded.
- However, the latest PLFS data from 2021-22 indicates a decrease to 4.1% in unemployment.
- This article underscores the challenges in accurately measuring unemployment in India.
- While there has been a reduction in unemployment from 2017 to 2022, it is still higher than the rates observed in some developed economies, such as the United States, where it hovers around 3.5%.
What is the Meaning of Unemployment:
- As per the International Labour Organisation (ILO), unemployment involves being without a job, being ready to accept a job, and actively seeking employment.
- In other words, if someone loses their job but doesn't actively seek another, they are not considered unemployed. Hence, unemployment is distinct from being without a job.
Measuring the Unemployment Rate:
- The unemployment rate is calculated by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the total labor force.
- The labor force is the combined count of both employed and unemployed individuals.
- People who are neither employed nor unemployed, like students and those involved in unpaid domestic work, are categorized as outside the labor force.
- It's important to note that the unemployment rate may also decrease when an economy doesn't create sufficient jobs or when individuals choose not to actively seek employment.
Challenges in Measuring Unemployment in India:
- Cultural Factors: Social norms and cultural constraints influence job search decisions in developing economies like India.
- A definition of unemployment that relies on active job seeking may underestimate the true situation.
- Informal Work: In contrast to developed economies, individuals in India often hold informal, intermittent jobs.
- This means someone might be unemployed one week but engaged in various roles over time, such as casual labor or farming.
- Varying Methodologies: Different organizations use distinct methodologies to measure unemployment.
- For instance, the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy categorizes individuals based on their daily activity preceding the interview, leading to variations in unemployment rates and labor force participation rates.
- Data Timing: Timing can also impact unemployment rates.
- For example, the lockdown in March 2020 had a profound effect on the Indian economy, but this disruption was not immediately reflected in the PLFS unemployment rates, which cover a period from July of one year to June of the next.
- Trade-offs: Developing economies face trade-offs in choosing reference periods for data collection.
- Shorter periods yield higher unemployment rates and lower employment rates, while longer periods tend to show the opposite.
- This dilemma is less common in developed nations with more consistent, year-round employment.
Differences in Rural and Urban Unemployment Rates in India:
- The lenient criteria for categorizing someone as employed contribute to the lower unemployment rates in rural regions compared to urban areas.
- Agricultural economies provide individuals with opportunities like family farming or occasional agricultural work, increasing the likelihood of finding some form of employment in rural settings.
- While these definitions may seem to 'underestimate' unemployment, they were primarily crafted to account for the substantial informal economy prevalent in these areas.
Classifying Employment Status in India:
- The National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO) employs two primary methods for this purpose: Usual Principal and Subsidiary Status (UPSS) and Current Weekly Status (CWS).
- UPSS determines an individual's primary employment status based on their predominant activity during the previous year, whether employed, unemployed, or out of the labor force.
- For instance, even if someone's principal status is not that of a worker, they would still be considered employed under UPSS if they engaged in economic activity in a subsidiary role for a period of not less than 30 days.
- CWS, on the other hand, uses a shorter reference period of one week. An individual is counted as employed if they worked for at least one hour on at least one day during the seven days leading up to the survey date.
- UPSS unemployment rates consistently tend to be lower than CWS rates because it is more likely that individuals will find employment over the course of a year compared to just one week.
Unemployment is becoming a significant issue in the upcoming election. To address it effectively, it's crucial to grasp how unemployment is defined and measured in a developing economy like India.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the challenges associated with measuring unemployment in India and how these measurement methods impact our understanding of the employment situation in the country. (15M)
At G20, the Eend of Old Multilateralism – and the Beginning of a New Order (Indian Express)

- 07 Sep 2023
Why in the News?
Delhi’s current emphasis is on building bridges between developing and developed countries. Many in the developed world are waking up to the importance of greater cooperation between the North and the South amidst the breakdown of relations between the East and the West.
What are the factors contributing to the weakening of global cooperation in the post-Cold War era?
- Russian Conflicts: International relations have been strained due to Russia's aggressive actions, notably its annexation of Ukraine's Crimean Peninsula in 2014 and the ongoing conflict with Ukraine.
- China's Territorial Ambitions: Concerns have arisen from China's territorial disputes with neighboring Asian countries, including India, Japan, the Philippines, and Vietnam.
- Economic Leverage: China's attempts to leverage its economic power for political and strategic purposes have led to growing distrust among nations worldwide.
- Change in Chinese Policies: A shift in Chinese policies under Xi Jinping, departing from the peaceful periphery and shared prosperity approach of the 1980s, has had adverse effects on regional and global institutions.
How is Asia reacting to China's actions?
- Security Institutions: New security coalitions such as the Quad, comprising India, the United States, Japan, and Australia, have been formed to counterbalance China's growing influence in the region.
- AUKUS Pact: The establishment of the AUKUS alliance, which includes Australia, Britain, and the United States, is a direct response to China's expanding military presence in the area.
- Questioning ASEAN's Role: China's assertive territorial expansion has raised concerns about the effectiveness of ASEAN-led regional organizations in maintaining stability.
- Bilateral Relationships: Many Asian nations are reinforcing bilateral ties to deter China's unilateral actions. For instance, the trilateral agreement involving the United States, Japan, and South Korea aims to enhance security in Northeast Asia.
- Economic Diversification: Countries like Japan and the United States are actively seeking to reduce their economic reliance on China by diversifying their trade partnerships.
How is India's role undergoing transformation?
- Central Player: India is increasingly assuming a central role in shaping both regional and global dynamics, evident in its active participation in forums such as the Indo-Pacific Quadrilateral Forum.
- G20's Evolution: India is advocating for the G20 to address the concerns of the Global South, indicating its aspiration to have a more significant role in global economic discussions.
- Shifting Alliances: While historically aligned with Moscow and Beijing for a multipolar world, India's focus has shifted due to China's growing assertiveness, leading it closer to nations like Australia, Japan, and the United States.
- Embracing the Indo-Pacific: India has embraced the Indo-Pacific concept and revitalized the Quad alliance to counterbalance China's influence in the region.
What are the key elements of India's new approach to multilateralism?
- Quad Collaboration: During the Jakarta summit, the Prime Minister of India emphasized the Quad's role in complementing ASEAN's efforts and promoting regional stability.
- Re-globalization Focus: India's External Affairs Minister, S Jaishankar, advocates for a diversified and democratic form of globalization that moves away from a production model centered around China.
- Collective Solutions: Despite the challenges faced in multilateralism, India remains committed to seeking collective solutions to various global issues, including the modernization of the global tax regime.
Global South Concerns: India places a strong emphasis on addressing the concerns of the Global South within the G-20 agenda, with a goal of fostering greater cooperation between developed and developing nations, rather than reviving past confrontational politics.
