EC’s Model Code Needs Reform and India Needs Model Leadership

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Former Election Commissioner Ashok Lavasa points out that a significant gap in the present framework is that the Model Code of Conduct for elections has not spelled out the consequences of defaults, thus diluting its deterrent effect.
Context:
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) plays a pivotal role in India's electoral process, having evolved considerably since its inception to uphold fairness in elections.
- While originally crafted to regulate conduct during elections, the MCC faces new hurdles in today's dynamic political environment.
- Hence, it becomes imperative to delve into the historical progression of the MCC, identify existing deficiencies, and suggest strategies to bolster its implementation.
Evolution of the Model Code of Conduct (MCC):
- Kerala was the first state to adopt a code of conduct for elections.
- In 1960, ahead of the Assembly elections in the state, the administration prepared a draft code that covered important aspects of electioneering such as processions, political rallies, and speeches.
- It was only in 1974, just before the mid-term general elections, that the EC released a formal MCC.
- It also set up bureaucratic bodies at the district level to oversee its implementation.
- So the EC, just before the 1979 Lok Sabha elections, released a revised Model Code with seven parts, with one part devoted to the party in power and what it could and could not do once elections were announced.
- The MCC has subsequently evolved as an integral part of conducting fair and free elections.
Challenges Faced by the MCC and the Imperative for Strengthening Enforcement:
- Escalating Violations: Political parties and candidates routinely flout the MCC's regulations, engaging in activities like hate speech, vote-buying, and spreading misinformation, undermining the trust in the electoral process and compromising its fairness and transparency.
- Exploitation of Loopholes: In today's political landscape, there's a discernible trend of exploiting MCC loopholes to bypass its regulations.
- With the advent of technology and social media, political entities find novel ways to propagate propaganda and target voters, evading traditional MCC constraints and necessitating revisions to address these evolving challenges.
- Inadequate Deterrents: While the MCC sets ethical standards, it often lacks effective penalties for violations, resulting in politicians perceiving minimal risks in flouting its provisions.
- Strengthening the MCC entails imposing clear and proportionate penalties for transgressions to foster a culture of accountability.
- Complexity of Enforcement: India's vast and diverse electoral terrain, coupled with a surge in reported violations, strains the Election Commission's enforcement capabilities.
- Adjudicating MCC breaches can be arduous and resource-intensive, leading to accountability delays. Streamlining enforcement procedures and enhancing the EC's capacity is pivotal for ensuring prompt and efficient MCC implementation.
- Erosion of Public Trust: Widespread disregard for ethical norms and regulations can erode citizens' trust in the democratic process, fostering voter apathy and disenchantment.
- Restoring public confidence in elections necessitates robust measures to strengthen the MCC and underscore the EC's dedication to upholding electoral integrity.
Proposed Reforms to Enhance MCC Enforcement:
- Clear and Comprehensive Guidelines: The initial step towards MCC reform entails establishing clear and comprehensive guidelines delineating permissible and impermissible conduct during electoral campaigns.
- Regular updates to these guidelines are crucial to address evolving challenges and technological advancements, enabling political entities to navigate ethical standards effectively and prevent inadvertent violations.
- Strict Enforcement Mechanisms: Implementation of proportional penalties for infringements, such as fines, campaigning bans, and withdrawal of electoral symbols, constitutes a vital aspect of reform.
- Streamlining enforcement procedures by the Election Commission (EC) ensures swift adjudication of cases, bolstering the MCC's credibility and deterrent impact.
- Indirect Liability for Political Parties: Imposing penalties on parties for MCC violations, irrespective of individual culpability, incentivizes enhanced oversight over members' conduct.
- This fosters collective responsibility within political organizations, promoting greater accountability and ethical governance.
- Transparency and Public Accountability: Maintaining a publicly accessible database documenting all reported MCC violations and their dispositions empowers citizens to monitor regulatory compliance.
- This transparency holds political actors accountable for their actions, reinforcing public trust in the electoral process.
- Timely and Credible Adjudication: Prioritizing prompt resolution of violations and ensuring impartial decision-making by the EC are essential to uphold the MCC's deterrent effect.
- Timely adjudication prevents erosion of public confidence and underscores the EC's commitment to fair electoral practices.
- Continuous Evaluation and Revision: Vigilance in identifying areas for improvement and updating the MCC in response to emerging challenges and evolving electoral dynamics is crucial.
- This iterative approach ensures the MCC remains relevant and effective in safeguarding India's electoral integrity.
The Role of Political Parties and Election Commission in Safeguarding Electoral Integrity:
Political Leadership's Responsibility:
- Political leaders wield significant influence in upholding electoral integrity by adhering to ethical standards and fostering responsible conduct within their parties.
- By exemplifying ethical leadership, politicians can instill a culture of integrity and accountability among their supporters and party members.
- Effective self-regulation within political parties is imperative to minimize MCC violations and preserve the integrity of electoral campaigns.
- Through a commitment to fairness, transparency, and democratic principles, leaders can instill confidence in the electoral process and encourage civic engagement among voters.
The Election Commission's Mandate:
- As the guardian of electoral integrity, the Election Commission plays a pivotal role in impartially adjudicating MCC violations and enforcing electoral regulations.
- Timely and decisive enforcement of the MCC is crucial for deterring violations and upholding the integrity of electoral campaigns.
- Maintaining transparency in its actions and decisions related to MCC enforcement is essential for the EC to uphold public accountability.
- By providing regular updates on reported violations, adjudication outcomes, and enforcement measures, the EC fosters public trust in its ability to safeguard electoral integrity.
- Enhancing the EC's capacity for MCC enforcement is paramount for effectively addressing emerging challenges and ensuring the integrity of electoral processes.
- This includes investing in training programs, technological infrastructure, and human resources to enable the EC to adapt to evolving electoral dynamics and enforce regulations effectively.
Conclusion
While the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) serves as a crucial bulwark against electoral misconduct, its effectiveness hinges on vigorous enforcement and adaptability to evolving scenarios. Through the adoption of suggested reforms and the cultivation of ethical leadership, India can fortify the integrity of its democratic mechanisms, guaranteeing equitable and transparent elections for its populace.
Ensuring the Rights and Dignity of Senior Citizens
- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Policymakers should proactively address the overshadowing of the needs of the elderly population by the focus on the demographic dividend, and by establishing guidelines for home-based care to meet the challenges posed by an aging population.
Context:
- Amidst the discourse on India's demographic dividend, the growing population of older individuals is often overlooked.
- With projections indicating a significant rise in the elderly population, now reaching nearly 15% of the total population and expected to increase further, there is a pressing need to address the implications of this demographic shift.
- Declining fertility rates and longer life expectancy are key drivers of this transition, leading to smaller households and a greater demand for elder care, straining the existing health and social support systems.
- As the traditional family structure evolves, there's a growing reliance on external assistance for senior care at home, highlighting the need for a recalibration of healthcare and social welfare policies to meet the needs of this aging population.
What Legal Safeguards Exist for the Elderly Population?
- Constitutional provisions pertaining to the elderly are outlined in Article 41 and Article 46.
- While directive principles are not legally binding, they impose a positive obligation on the state during lawmaking processes.
- The Hindu Marriage and Adoption Act of 1956, in Section 20, mandates provisions for the maintenance of elderly parents.
- Under Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code, elder parents are entitled to claim maintenance from their children.
- The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act of 2007 formalizes the legal responsibility of children or heirs to provide maintenance for their parents or senior family members.
Key Issues Affecting Quality and Accessibility in Home-Based Care:
- Lack of Standardization and Defined Practices: Home-based care practices in India suffer from a lack of standardization and well-defined protocols, operating in a less regulated environment compared to institutional settings like hospitals or nursing homes.
- This variability in practices can result in inconsistencies in the quality of care provided to elderly individuals at home.
- Shortage of Trained Caregivers: A significant challenge in home-based care stems from the shortage of adequately trained caregivers.
- Caring for elderly individuals, particularly those with chronic illnesses or disabilities, demands specialized skills and knowledge.
- However, there is a scarcity of caregivers with the requisite training and expertise, exacerbating the quality of care provided and contributing to caregiver burnout.
- Mistreatment of Caregivers: Caregivers in home-based settings often face mistreatment or abuse from the families they serve, including verbal abuse, exploitation, or inadequate compensation for their services.
- The lack of legal protections and support mechanisms for caregivers leaves them vulnerable to exploitation, undermining the quality of care they can deliver.
- Financial Barrier: The cost of hiring a caregiver for home-based care can be prohibitively high for many families, particularly those from lower socio-economic backgrounds.
- This financial barrier limits access to quality home-based care services for elderly individuals in need, leading some families to forgo professional care altogether or rely on informal caregiving arrangements.
- The dominance of the Private Sector: The provision of home-based care services in India is predominantly controlled by the private, for-profit sector.
- While private agencies may offer a range of services, their services often come at a premium cost, exacerbating inequalities in access to care.
- Fragmented Regulatory Framework: The regulatory framework governing home-based care in India is fragmented and lacks comprehensive oversight.
- Standardized regulations or licensing requirements for home care agencies or individual caregivers are absent, leading to inconsistencies in the quality and safety of care provided and hindering efforts to ensure accountability and quality improvement.
Policy Interventions and Opportunities to Address Home-Based Care Challenges:
- Recognizing Home as a Viable Care Setting: An opportunity in home-based care lies in acknowledging the home environment as a feasible setting for providing care to elderly individuals, serving both as a place for care provision and employment for caregivers.
- Policymakers can pave the way for developing tailored policies and regulations to address the unique needs of home-based care.
- Tailoring Treatment Protocols to Home Environment: Policy interventions should focus on customizing treatment protocols and care plans to the home environment's specific challenges and opportunities, such as limited space, absence of medical equipment, and the presence of family members.
- This tailored approach can optimize care delivery and improve the experience for both caregivers and care recipients.
- Strengthening Caregiver Training and Support: Enhancing the training and support available to caregivers is crucial to meet the rising demand for home-based care services.
- Policy interventions should prioritize the standardization of vocational training programs, delineation of roles and responsibilities, and facilitation of career progression opportunities for caregivers.
- Investing in caregiver education and professional development can enhance the quality of care and alleviate caregiver shortages.
- Gender Considerations: Given the gender dimension of aging in India, with women typically outliving men, special attention is warranted for vulnerable elderly women, particularly widows.
- Policies should aim to empower them to lead dignified and independent lives in their later years.
Governmental and Legislative Initiatives to Enhance Home-Based Care:
- Policy Development and Implementation: The government holds a pivotal role in crafting and executing policies concerning home-based care for the elderly, with ministries such as the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, and Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship spearheading initiatives to address pertinent challenges and opportunities.
- Inter-Ministerial Coordination: Effective coordination among government ministries is indispensable for driving policy reforms in home-based care.
- Collaborative efforts enable the pooling of resources, expertise, and stakeholder perspectives to formulate comprehensive solutions tailored to the diverse needs of the elderly population and their caregivers.
- Legislative Frameworks: Legislative endeavors play a vital role in formalizing and regulating home-based care services.
- Legislation like the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens (Amendment) Bill, 2019, exemplifies efforts to standardize home care services and establish minimum standards for providers, thereby ensuring the legal protection, safety, and well-being of elderly individuals receiving such care.
- Regulatory Oversight: Government bodies like the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) contribute to regulatory oversight in home-based care services.
- These entities establish guidelines, standards, and licensing requirements for home care agencies and individual caregivers, ensuring adherence to quality and safety standards.
Conclusion
While India's emphasis on preparing its youth for the future is praiseworthy, it is equally crucial not to neglect the needs of its expanding elderly demographic. A resilient home-based care system enables economic participation and upholds society's ethical responsibility to support its aging citizens. By confronting challenges and embracing opportunities in home-based care, India can safeguard the well-being and dignity of its elderly population, fostering an inclusive and empathetic society for future generations.
Analysis of Curative Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court in Legal Dispute

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC), in the judgment of Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (DMRC) vs Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd (DAMEPL), set aside the arbitral award by exercising its curative jurisdiction.
Context:
- The Supreme Court of India holds a multifaceted role, serving as the apex court of appeal, a federal court, and an advisory body.
- One of its significant powers is the Curative Jurisdiction, established in 2002, which empowers the Court to rectify its judgments even after they have become final.
- However, the utilization of this jurisdiction has triggered discussions concerning its implications for judicial stability and the Supreme Court's role in shaping legal precedents.
What is the DMRC vs DAMEPL Case?
- The case dates back to 2008 when the DMRC entered into a PPP with the Delhi Airport Metro Express Private Limited (DAMEPL), a consortium led by Reliance Infrastructure Ltd, for the Delhi Airport Metro Express project.
- However, disputes arose between the two parties, leading to the termination of the agreement by DAMEPL in 2013.
- In 2017, an arbitration tribunal ruled in favor of DAMEPL and ordered DMRC to pay nearly Rs 8,000 crore.
- DMRC challenged this ruling in the Delhi High Court, which overturned the arbitral award in 2019.
- DAMEPL then appealed to the Supreme Court, which in September 2021 reversed the High Court's decision and upheld the arbitral award.
- However, in a recent judgment, the Supreme Court has now ruled in favor of DMRC, stating that there was a "fundamental error" in its previous judgment.
Significance of the Supreme Court’s Decision:
- Firstly, it underscores the importance of curative petitions in correcting grave injustices in legal judgments.
- Curative petitions are sparingly used and are only permitted on narrow, procedural grounds.
- The Supreme Court's decision to grant relief to DMRC highlights the court's commitment to rendering justice in its true sense.
- Secondly, the decision has implications for PPPs in infrastructure projects.
- PPPs play a crucial role in infrastructure development, but disputes between public and private entities can arise, leading to legal battles.
- The Supreme Court's decision provides clarity on the legal framework governing PPPs and sets a precedent for future disputes in similar projects.
- Lastly, the decision has implications for investor confidence.
- The Supreme Court's exercise of curative jurisdiction in this case, almost two and a half years after its final verdict, demonstrates the court's willingness to correct errors and ensure justice.
- This is likely to boost investor confidence in India's legal system and encourage investment in infrastructure projects.
Difference Between a Curative Petition and Curative Jurisdiction:
Curative Petition:
- A curative petition is a specific legal remedy available within the framework of curative jurisdiction.
- It is a petition filed by a party to the case that has exhausted all other legal remedies and seeks the correction of a judgment that may have resulted from a violation of principles of natural justice or a gross miscarriage of justice.
- The grounds for filing a curative petition typically include the discovery of new evidence or legal errors that were not apparent earlier.
- Curative petitions are relatively rare and are considered as a last resort to correct errors in judgment.
Curative Jurisdiction:
- Curative jurisdiction refers to the broader authority of the Supreme Court to review and rectify its judgments to prevent gross miscarriages of justice.
- It is a power vested in the Supreme Court to ensure that fundamental principles of justice and fairness are upheld, even after a judgment has become final.
- Curative jurisdiction allows the Supreme Court to revisit its decisions if it perceives a need to prevent manifest injustice or correct egregious errors that may have escaped earlier notice.
- While curative petitions are one mechanism through which curative jurisdiction is exercised, the Supreme Court may also suo motu invoke curative jurisdiction in exceptional cases without a formal petition being filed.
Impact and Implications of Curative Jurisdiction:
- Impact on Arbitral Awards' Integrity: A central apprehension surrounding curative jurisdiction is its potential to affect the integrity of arbitral awards.
- Arbitration relies on the conclusiveness and enforceability of awards for its efficacy.
- When the Court intervenes in arbitral decisions, particularly amid concerns of judicial overreach, it risks undermining arbitration's core principles, such as party autonomy and swift dispute resolution.
- Balancing Judicial Consistency and Flexibility: The dichotomy between judicial consistency and flexibility emerges concerning curative jurisdiction.
- While consistent legal interpretation fosters stability and predictability, it may stifle innovation. Conversely, excessive flexibility can breed uncertainty, eroding public trust in the judiciary.
- Examining the Scope of Judicial Review: Curative jurisdiction prompts queries about the extent of judicial review and its boundaries.
- While the Court's role as the ultimate legal interpreter is clear, intervening in its judgments without impinging on legislative or executive domains requires meticulous consideration.
- Implications for Legal Precedents: The significance of Supreme Court judgments in maintaining legal coherence is undeniable.
- However, curative jurisdiction may disrupt established precedents, casting doubt on the binding nature of judicial decisions.
- The Court must exercise judiciousness to rectify errors without compromising the legal framework's integrity.
- Public Perception and Judicial Trust: The Court's credibility hinges on its impartiality and integrity in dispensing justice.
- Excessive or arbitrary curative interventions may undermine public confidence in the judiciary, diminishing its authority as a legal arbiter.
- The Court must exercise curative powers prudently to maintain public trust in the judiciary.
Critical Analysis of Judicial Instability:
- Challenging Legal Certainty: Legal certainty, a cornerstone of the rule of law, demands consistency and predictability in legal outcomes.
- The use of curative jurisdiction, particularly in overturning final judgments, jeopardizes this certainty by casting doubt on the conclusiveness and enforceability of judicial decisions.
- Such uncertainty undermines parties' confidence in the stability of the legal framework, fostering confusion and mistrust in the judicial process.
- Diminishing Judicial Authority: Judicial stability is intrinsic to the authority and credibility of the judiciary.
- When the Supreme Court reverses its own judgments through curative measures, it risks appearing indecisive and inconsistent, eroding its status as the ultimate arbiter of the law.
- This erosion of authority undermines public trust in the judiciary, fostering skepticism about the fairness and impartiality of judicial proceedings.
- Disrupting Legal Precedent: The stability of legal precedent is vital for maintaining coherence and consistency in the legal system.
- However, the exercise of curative jurisdiction introduces the potential for disrupting established precedents and fostering inconsistency in judicial rulings.
- This undermines the reliability of legal principles, creating confusion among legal practitioners, litigants, and lower courts.
- Moreover, frequent reversals of judgments hinder the development of clear and consistent legal doctrines, impeding the evolution of the law.
- Risk of Judicial Overreach: Judicial stability acts as a safeguard against judicial overreach, ensuring that the judiciary respects its constitutional limits and upholds the separation of powers.
- However, the use of curative jurisdiction raises concerns about the Court's propensity to exceed its authority and intrude into the domains of the legislative and executive branches.
- By revisiting and overturning its own judgments, the Court risks overstepping its role and undermining the principles of checks and balances inherent in a democratic system.
Ways Forward for Balancing Judicial Oversight Stability:
- Fostering Judicial Accountability: Upholding judicial oversight, including the use of curative jurisdiction, is vital for ensuring judges are accountable and adhere to legal standards.
- It offers a mechanism to rectify errors and address any judicial misconduct.
- However, excessive oversight risks compromising judicial independence and impartiality, undercutting the judiciary's ability to fairly adjudicate disputes.
- Preserving Legal Stability: Legal stability is crucial for fostering predictability and confidence in the legal system.
- By upholding established precedents and minimizing disruptions to settled legal principles, the judiciary promotes legal stability.
- Nevertheless, the exercise of curative jurisdiction introduces uncertainty by allowing the Court to revisit and potentially reverse its judgments, challenging the stability of legal doctrine and the reliability of judicial decisions.
- Respecting the Separation of Powers: Striking a balance between judicial oversight and stability requires respecting the separation of powers and acknowledging the distinct roles of the judiciary, legislature, and executive.
- While the judiciary plays a critical role in interpreting and applying the law, it must exercise restraint to avoid intruding into the domains of other branches of government.
- The use of curative jurisdiction should be guided by principles of judicial deference and deference to legislative intent, particularly in matters where judicial intervention could undermine democratic processes or policy decisions.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court's Curative Jurisdiction is a potent mechanism for rectifying judicial mistakes, yet it presents hurdles to judicial stability and coherence. The DMRC vs DAMEPL case highlights the necessity for a balanced approach in reconciling judicial oversight with legal predictability. Ultimately, as the ultimate arbiter of the law, the Court must carefully wield its curative authority to uphold public trust in the legal system's integrity.
Supreme Court Affirms Women's Right To Child Care Leave

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On Monday, a Supreme Court bench headed by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud said, “Participation of women in the workforce is a matter not just of privilege but a constitutional entitlement protected by Article 15 of the Constitution.
Context:
- Recent data indicates that while 45% of India's graduates are women, only approximately 10% of educated women pursue long-term careers.
- However, amidst these challenges, there are instances of women advocating for their rights.
- For instance, a young mother from Himachal Pradesh recently petitioned the Supreme Court for the right to care for her child, who required her presence.
- Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud emphasized that women's participation in the workforce is a constitutional entitlement, and denying mothers childcare leave violates this principle.
- The petitioner, an assistant professor at a government college, highlighted that the Himachal Pradesh government had refused her childcare leave, despite her child's medical needs.
- The Supreme Court's intervention underscored that the state, as an employer, must address such concerns and uphold the rights of working mothers.
Protection Under the Constitution and Employer Responsibilities Concerning Women's Employment:
Constitutional Safeguards:
- Article 15 of the Indian Constitution stands as a pillar of gender equality, prohibiting discrimination based on sex and allowing for affirmative action to address historical disparities.
- The recent Supreme Court recognition of Article 15 underscores the constitutional imperative to foster a fair and inclusive society, particularly in matters of women's workforce participation.
- By affirming women's right to work without prejudice, the court reinforces the foundational principles of equality and non-discrimination enshrined in the Constitution.
Employer Responsibility:
- Employers, especially the government as role models, carry a significant duty to cultivate a supportive environment for female employees.
- Beyond mere legal compliance, employers must actively address the unique challenges women face in juggling work and caregiving responsibilities.
- The denial of childcare leave, as highlighted in the recent Supreme Court case, signifies a failure to acknowledge and respect women's rights in the workplace.
- The court's stance emphasizes that employers cannot overlook the specific needs of women employees and underscores the importance of proactive measures such as offering childcare assistance, flexible work arrangements, and gender-sensitive policies.
- By fulfilling these obligations, employers not only advance gender equality but also foster a more productive, inclusive, and supportive work culture.
Obstacles to Women's Participation in the Workforce:
Unbalanced Domestic Responsibilities:
- Women in India shoulder a disproportionate share of unpaid domestic and caregiving duties, including household chores and looking after family members.
- This unequal distribution of responsibilities consumes considerable time and effort, often hindering women's capacity to engage in paid employment outside their homes.
"Marriage" and "Motherhood" Setbacks:
- Women commonly encounter setbacks in their careers due to societal norms regarding marriage and motherhood.
- Marriage can lead to disruptions like relocation or increased household duties, affecting women's career trajectories and earning potential.
- Likewise, motherhood often results in temporary career breaks or reduced work hours to manage childcare, limiting opportunities for professional growth and financial independence.
Inadequate Support Infrastructure:
- The scarcity of affordable childcare options, along with insufficient support services like paid parental leave and flexible work arrangements, adds to the challenges faced by women in balancing work and family commitments.
- The absence of adequate support infrastructure may compel women to prioritize caregiving over employment, particularly when alternative care arrangements are lacking.
Legal Framework for Women’s Participation in the Workforce:
Legislative Advances:
- India has taken significant strides in enacting laws to uphold women's rights and foster gender equality in workplaces.
- These laws encompass provisions for maternity benefits, childcare services, and safeguards against gender discrimination in employment practices.
- Recent legislative changes have broadened maternity leave entitlements and mandated childcare facilities at workplaces, underscoring a commitment to bolstering women's engagement in the workforce.
Gender-Neutral Measures:
- Initiatives to render legal provisions gender-neutral represent a positive stride toward acknowledging caregiving duties as a shared responsibility among parents.
- By extending childcare benefits to all employees, regardless of gender, these reforms aim to challenge traditional gender norms and encourage greater equity in caregiving responsibilities within families.
Challenges in Implementing Legal Frameworks for Women's Workforce Participation:
Underfunded Welfare Schemes:
- Government-led initiatives, such as the National Crèches Scheme, face underfunding and inadequate infrastructure, limiting their ability to provide essential childcare services to marginalized communities.
- Without sufficient financial resources and institutional support, these schemes struggle to meet the demand for affordable and quality childcare services, particularly in underserved regions.
Lack of Enforcement and Monitoring:
- Effective enforcement mechanisms and regular monitoring of compliance are crucial for ensuring that employers adhere to legal requirements related to women's workforce participation.
- However, enforcement agencies often face challenges like limited resources, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and a lack of coordination between government departments, hindering their ability to enforce labour laws and address violations promptly.
Coverage Limitations:
- Existing laws often have a limited scope, with certain provisions only applying to formal sector establishments or workplaces with a minimum number of employees.
- This approach excludes many women working in the informal sector or smaller enterprises, leaving them without access to crucial maternity benefits and childcare support.
Way Forward
Collective Responsibility:
- State: The government plays a key role in setting legal and policy frameworks that promote gender equality.
- This includes enacting supportive laws, providing incentives for employers to adopt family-friendly policies, and investing in social infrastructure such as childcare facilities and education programs.
- Employers: Companies can significantly impact women's workforce participation through their practices and policies.
- Employers should adopt inclusive hiring practices, provide equal opportunities for career advancement, offer flexible work arrangements, and implement family-friendly policies like paid parental leave and on-site childcare facilities.
- Communities: Communities play a crucial role in challenging traditional gender norms and stereotypes.
- Community-based organizations, educational institutions, and grassroots initiatives can raise awareness, provide support for working mothers, and advocate for policy changes that promote gender equality.
Policy Integration:
- Integrating gender considerations into broader policy frameworks is essential for mainstreaming gender equality across all sectors of society.
- Key strategies include implementing gender-responsive budgeting, conducting gender impact assessments of policies and programs, and ensuring women's voices are heard in decision-making processes.
- By addressing these aspects, we can create a more inclusive society where women can fully participate in the workforce and achieve their potential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, achieving full participation of women in the workforce requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach involving the state, employers, and communities. By enacting supportive policies, promoting inclusive practices, challenging traditional gender norms, and integrating gender considerations into broader policy frameworks, we can create an enabling environment for women to thrive in their careers. It is through these concerted efforts that we can build a more equitable society and harness the immense potential that women bring to the workforce.
The Reality of the Swachh Bharat Mission

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A scheme fully owned by the state has become a toolkit for privatisation of public health services and continues caste discrimination.
Context:
- India was ranked right at the bottom of 180 countries in the Environment Performance Index (EPI) in 2022.
- This index evaluates countries based on their performance in addressing climate change, maintaining environmental health, and preserving ecosystem vitality.
- It assesses 40 performance indicators across 11 issue categories, encompassing areas like air quality, access to drinking water, and sanitation.
- In response to this ranking, the government expressed reservations, citing flaws in the methodology that, according to them, fail to accurately capture the Indian scenario.
- Over the past decade, the Modi government has launched several development campaigns, including the Swachh Bharat Mission, the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation, the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, and the National Clean Air Programme.
- These endeavors are geared towards enhancing living standards and addressing various socio-economic challenges.
- However, despite these efforts, there remains a noticeable rise in the population's vulnerability due to environmental issues like air and water pollution.
About Swachh Bharat Mission:
- Swachh Bharat Mission, the world’s largest sanitation initiative was launched by the Prime Minister of India in 2014 to achieve an Open Defecation Free India by October 2, 2019, as a tribute to Mahatma Gandhi.
- The programme led to the construction of over 10 crore individual household toilets, taking sanitation coverage from 39% in 2014 to 100% in 2019 when around 6 lakh villages declared themselves Open Defecation Free (ODF).
- The second phase of the mission aims to sustain the open defecation-free status and improve the management of solid and liquid waste, while also working to improve the lives of sanitation workers.
- The mission aimed at progressing toward target 6.2 of the Sustainable Development Goal Number 6 established by the United Nations in 2015.
- By achieving the lowest open defecation-free status in 2019, India achieved its Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6.2 health target in record time, eleven years ahead of the UN SDG target of 31 December 2030.
- The mission was split into two: rural and urban.
- In rural areas "SBM - Gramin" was financed and monitored through the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation (since converted to the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti) whereas "SBM - urban" was overseen by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The rural division has a five-tier mechanism: central, state, district, block panchayat, and gram panchayat.
- As part of the campaign, volunteers, known as Swachhagrahis, or "Ambassadors of cleanliness", promoted the construction of toilets using a popular method called Community-Led Total Sanitation at the village level.
Critique of the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM):
Discrepancy between Goals and Outcomes:
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) and its successor, SBM 2.0, set out ambitious objectives to achieve garbage-free cities, garnering political support across party lines.
- However, the reality on the ground paints a different picture.
- Despite government assertions of India achieving open defecation-free status, reports from the Comptroller and Auditor General in 2020 raised doubts about the program's effectiveness, highlighting issues such as substandard toilet construction and inadequate waste treatment.
- In urban areas, certain communities, particularly those residing in slums, continue to lack access to essential sanitation facilities, exacerbating existing inequalities.
- In rural and peri-urban regions, the lack of integration between toilet construction and waste management has led to environmental contamination and health hazards.
Perpetuation of Power Dynamics and Inequalities:
- Sanitation and waste management in India are deeply entrenched in caste dynamics, historically burdening marginalized communities with sanitation tasks.
- Despite attempts by SBM to promote the idea of shared responsibility, the underlying power dynamics persist.
- The introduction of capital-intensive technologies aimed at mechanizing waste management processes has not yielded the desired outcomes, resulting in health crises due to improper waste disposal practices.
- The outsourcing of sanitation work to private contractors, often employing members of marginalized communities, has further entrenched caste-based discrimination.
- Government emphasis on procuring expensive machinery for waste management, funded through public resources, has inadvertently facilitated the privatization of public health services, exacerbating existing inequalities.
Technological Solutions and Implementation Challenges:
- While the government has invested in technological solutions such as waste-to-energy plants and biological methanation, their effectiveness remains limited, with few success stories to showcase.
- Challenges persist in the implementation of these solutions, leading to a lack of tangible improvements in solid waste management across many towns and cities.
Gap in Sanitation Inspection Infrastructure:
- A significant gap in the sanitation inspection infrastructure exists within Himachal Pradesh, as revealed during a recent case in the State's High Court.
- On March 30, 2024, it was disclosed that the Shimla Municipal Corporation, consisting of 34 wards, has only five sanitation inspectors.
- Moreover, the decision to declare this cadre dead after retirement raises concerns about the State's commitment to addressing sanitation issues effectively.
- With more than 50 municipal bodies in Himachal Pradesh and only 20 sanitation inspectors available, it is clear that several municipalities lack essential sanitation inspection personnel.
The interconnectedness of Environmental Performance Index (EPI) and Development Campaigns:
- The EPI offers a comprehensive assessment of a country's environmental health and sustainability efforts.
- One critical aspect of the EPI is mapping, which exposes the shortcomings and unsustainability of current development processes.
- In light of a recent Supreme Court judgment acknowledging the links between climate change and basic human rights, it is evident that development models must be reevaluated and adjusted.
- The interconnectedness of the EPI and various development campaigns cannot be ignored, as the consequences of climate change directly impact human well-being and rights.
- With climate scientists attributing current environmental problems to anthropogenic and systemic factors, it is essential to consider the broader implications of the EPI when planning and implementing development initiatives.
Conclusion
To tackle India's environmental challenges, a comprehensive strategy prioritizing sustainability, equity, and social justice is essential. This involves reassessing development strategies, strengthening enforcement, and encouraging community participation in environmental governance. Addressing implementation issues and linking policies to human rights can improve India's EPI performance and foster a sustainable future.
Reversing the Global Democratic Recession

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Despite the disillusionment, for a variety of reasons, the need to fortify democratic foundations has to be ongoing and collaborative.
Context:
- India is in the midst of its most significant electoral exercise and it might be worthwhile to scrutinize people’s changing perceptions about their political ecosystems in both the largest democracy and other smaller democratic spaces elsewhere.
- Such an exercise may help us understand the prevailing global situation and work on the future course of action.
- Drawing insights from an extensive Pew Research Centre survey spanning 24 nations, examining the evolving attitudes toward democratic governance becomes imperative to grasp the broader global context and chart potential pathways forward.
Why Worldwide Decline in Confidence in Democratic Systems?
- According to the Pew Research Centre's extensive 2023 global survey, which included 30,861 participants, there is a notable decline in faith in democratic institutions across the globe.
- Although 77% of respondents still hold optimism for representative democracy, there is growing openness to alternative governance structures.
- Of concern is the diminishing support for representative democracy since 2017, juxtaposed with increased approval for direct democracy, rule by experts, and authoritarian regimes.
Regional Dynamics and Emerging Trends in Perceptions of Governance:
- Shifting Preferences Towards Expert Rule and Authoritarianism: A noticeable inclination towards endorsing rule by experts and authoritarian forms of governance is observed across different regions.
- This trend is particularly conspicuous in nations grappling with economic instability, political turbulence, or perceived inefficiencies within democratic structures.
- In such contexts, citizens often perceive democratic systems as sluggish and inadequate in addressing urgent challenges, fostering a growing appeal towards centralized authority and decisive leadership.
- Influence of Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic circumstances significantly shape preferences in governance.
- Individuals from lower-income countries with limited educational access tend to show support for authoritative leadership and military rule.
- This inclination may stem from a desire for stability and economic advancement, as authoritarian regimes are perceived as more effective in delivering immediate solutions to complex issues.
- Cultural and Historical Context: Variations in democratic perceptions are also influenced by cultural and historical backgrounds.
- Nations with past experiences of authoritarian rule or centralized governance structures may exhibit greater openness to authoritarian models.
- Additionally, cultural norms regarding leadership, hierarchy, and decision-making processes impact attitudes toward democracy and alternative governance models.
- Resistance to Authoritarian Trends in Certain Regions: Despite the rise in authoritarian sentiments in some areas, resistance to such ideologies persists in others.
- Regions with strong traditions of liberal democracy, including Canada, Europe, Scandinavia, and the United States, continue to prioritize democratic values and institutions.
- Here, a steadfast commitment to democratic principles, civil liberties, and the rule of law acts as a barrier against the erosion of democratic norms.
Evolution of Democratic Perceptions in India:
- Transition towards Strong Leadership: Recent years have witnessed a discernible transformation in Indian views on democracy, characterized by a diminishing preference for representative democracy and a growing inclination towards authoritative leadership.
- In 2017, 44% of Indians favored representative democracy, a figure that declined to 36% by 2023.
- Conversely, support for a commanding leader with substantial authority surged from 55% in 2017 to 67% in 2023.
- Rising Endorsement of Expert Governance: Mirroring global trends, Indian perspectives on governance have witnessed a notable uptick in backing for rule by experts and authoritarian models.
- Support for rule by experts skyrocketed from 65% to an impressive 82% during the same period.
- Of significant note is the remarkable preference for military rule or governance under an authoritarian figure, with a striking 85% of Indians expressing support for such models by 2023.
- Diverse Regional Outlooks: It's crucial to acknowledge the diversity in democratic perceptions across various regions and demographic cohorts within India.
- While certain segments may lean towards authoritarian leadership, others remain steadfast in their commitment to democratic principles and institutions.
- Factors such as education, socioeconomic status, and cultural heritage exert considerable influence on individuals' governance preferences.
Way Forward to Reinforce Democratic Foundations:
- Engaging Citizens in Governance: Central to a robust democracy is the active participation of citizens in decision-making processes.
- Governments should establish channels and platforms facilitating meaningful engagement in policymaking and public affairs.
- Initiatives like town hall meetings, participatory budgeting, citizen assemblies, and digital feedback platforms can foster citizen involvement.
- Ensuring Information Accessibility: Transparency and access to accurate information are cornerstone principles of democratic governance.
- Governments must ensure unhindered access to information about government actions and policies.
- Strengthening freedom of information laws, enhancing transparency mechanisms, and supporting investigative journalism can uphold government accountability.
- Upholding Accountability and Justice: Democratic institutions must remain accountable to the populace and uphold the rule of law.
- Governments should institute checks and balances, foster an independent judiciary, and implement effective oversight mechanisms to prevent power abuse.
- Additionally, efforts to promote equality before the law and safeguard the rights of marginalized groups are essential.
- Fostering Civic Engagement: Civil society organizations play a pivotal role in advocating for citizen rights and government accountability.
- Governments should create an enabling environment for civil society to operate freely, safeguarding freedoms of association, expression, and assembly.
- Collaboration between government and civil society can enhance democratic governance through dialogue and cooperation.
- Promoting Ethical Leadership: Ethical leadership and public service are vital for democratic integrity.
- Governments should cultivate a culture of ethical conduct among officials and public servants, implementing measures to combat corruption and promote transparency.
- Holding individuals accountable for misconduct reinforces democratic legitimacy.
- Embracing Responsive and Inclusive Policies: Democratic governments must prioritize policies addressing the needs of all citizens, especially marginalized groups.
- Proactive efforts to promote social justice, economic equality, and inclusivity in decision-making processes are crucial.
- Engaging diverse stakeholders and tailoring policies to ensure inclusivity is imperative for leaving no one behind.
Conclusion
The shifting democratic perceptions highlighted in both the Pew Research Centre survey and India's democratic context emphasize the importance of reevaluating global democratic systems. By acknowledging regional nuances, comprehending evolving attitudes, and emphasizing foundational reinforcement endeavors, nations can effectively address the complexities and potentials of democratic governance in the contemporary era.
Restoring Earth’s Right to ‘Good Health’

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Court of Human Rights found Switzerland guilty of violating the rights of women from KlimaSeniorinnen, stating that the government's emission control efforts were insufficient, failing to protect women from climate change impacts.
Context:
- Courts worldwide are increasingly tasked with addressing the nexus between climate change and human rights, as evidenced by significant rulings such as those from the European Court of Human Rights in Switzerland and the Supreme Court of India.
- These landmark decisions highlight the imperative of acknowledging climate change as a human rights issue and establishing crucial benchmarks for legal and policy responses to mitigate its detrimental effects on people and societies.
Legal Acknowledgment of Climate Change's Human Rights Impacts:
- Recent rulings by the European Court of Human Rights against the Government of Switzerland and the Supreme Court of India have underscored the failure to safeguard vulnerable populations from the effects of climate change.
- The European Court's decision highlighted the government's neglect in protecting elderly women from climate-related harm, while the Indian Supreme Court affirmed citizens' entitlement to freedom from adverse climate effects under constitutional guarantees.
- Citing Articles 14 (equality before the law) and 21 (right to life and personal liberty) of the Indian Constitution, the Supreme Court emphasized individuals' right 'to be free from the adverse impacts of climate change.'
- These legal judgments signify a significant step towards acknowledging climate change as a pivotal human rights concern.
The Escalating Human Rights Risks of the Global Climate Crisis:
- The global climate crisis presents an imminent threat to human rights, imperiling individuals and communities worldwide.
- The latest State of the Global Climate Report from the World Meteorological Organization presents compelling evidence of the intensifying impacts of climate change.
- In 2023, numerous climate indicators soared to unprecedented levels, marking it as the hottest year on record.
- This unparalleled warmth coincided with concerning trends such as heightened ocean heat accumulation, rising sea levels, diminishing Antarctic sea ice, and accelerated glacier retreat.
- These indicators underscore the severe strain on our planet, with profound implications for human welfare.
India's Climate Action and Vulnerability:
- Progress Amid Persistent Vulnerability: Despite notable advancements in climate action, India, among the world's fastest-growing economies, continues to confront significant vulnerability to climate change.
- Having met two of its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) targets—reducing emissions intensity by 33% to 35% and achieving 40% cumulative non-fossil fuel electricity capacity—well ahead of schedule, India demonstrates proactive measures.
- Nevertheless, the nation remains highly susceptible to climate-related adversities.
- Population Concentration in Disaster-Prone Areas: A primary concern is India's demographic distribution, with over 80% of its populace residing in regions prone to climate-induced calamities like floods, cyclones, droughts, and heatwaves.
- These events not only disrupt lives but also exacerbate existing socio-economic disparities, disproportionately impacting vulnerable groups such as small-scale farmers, rural communities, and marginalized populations.
- Intersecting Challenges of Climate Change: Climate change intersects with broader socio-economic and environmental issues, compounding their repercussions.
- Rapid urbanization and haphazard development intensify urban vulnerability to climate-driven disasters like flooding and landslides.
Frameworks to Strengthen India's Climate Action:
- Embracing Comprehensive Legislation: India's climate governance could benefit from the adoption of a comprehensive regulatory framework dedicated to climate change.
- This legislation would offer a unified structure for addressing diverse climate-related aspects, spanning mitigation, adaptation, finance, and capacity-building.
- By enshrining climate objectives, targets, and strategies in law, such a framework can furnish legal clarity and consistency, guiding sustained planning and investment.
- Insights from Global Climate Laws: Research from the London School of Economics and Political Science examined climate framework laws in 60 nations, spotlighting their pivotal role in shaping national climate agendas.
- Countries like Germany, Ireland, New Zealand, Finland, South Korea, South Africa, and the Philippines have instituted robust climate legislation surpassing mere compliance with international obligations.
- These laws have facilitated public resource mobilization, bolstered climate action capabilities, and fostered inter-sectoral cooperation.
Additional Measures for Enhanced Climate Governance in India:
- Integrated Climate Policies: India's climate strategies should embrace an integrated approach, embedding climate considerations into broader development frameworks and decision-making processes.
- This entails weaving climate adaptation and mitigation efforts throughout key sectors like agriculture, water management, energy, transportation, and urban development to foster a cohesive response to climate challenges.
- Localized Solutions and Cross-Sector Collaboration: Tailored, localized climate actions, coupled with collaborative efforts across sectors, are vital for addressing the diverse and context-specific impacts of climate change.
- Governments can craft targeted strategies to bolster resilience, mitigate risks, and advance sustainable development goals by engaging local stakeholders and fostering partnerships across sectors.
- Harmonizing Climate and Sustainable Development Goals: Localized climate initiatives often align with broader Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), such as poverty eradication, food security, access to clean water, and gender equity.
- Integrating climate considerations into local SDG agendas enables governments to leverage synergies, optimize resource use, and fortify community resilience and sustainability.
- Empowerment of Civil Society: Civil society organizations (CSOs) play a pivotal role in advocating for climate action, environmental equity, and governmental accountability.
- Empowering CSOs and fostering rights-based discourse on climate change are vital for fostering inclusive decision-making, transparency, and environmental justice.
- Fostering Inclusivity and Representation: Promoting diversity and inclusivity within civil society is imperative to ensure the voices and perspectives of marginalized communities are heard and heeded in climate policymaking.
- CSOs should aim to represent the interests of various stakeholders, including women, indigenous populations, youth, persons with disabilities, and other marginalized groups, in climate governance.
- Advancing Rights-Centric Discourse: A rights-based approach to climate action acknowledges that climate change disproportionately impacts vulnerable communities, infringing upon their basic human rights to life, health, food, water, and livelihoods.
- By framing climate change as a human rights issue, CSOs can advocate for policies that prioritize the needs of affected communities and champion environmental justice.
Conclusion
The alignment of legal rulings, scientific findings, and policy mandates emphasizes the pressing imperative to confront climate change as a human rights emergency.
By acknowledging the inseparable link between environmental health and human welfare, nations can pave the way toward climate resilience and equity.
Empowering communities, fortifying legal structures, and promoting cross-sectoral cooperation stand as pivotal measures in realizing a future liberated from the detrimental effects of climate change.
Legal Amendments Likely to Increase Medicine Costs without Improving Quality

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The amended rules will prolong the life of drugs on account of frivolous patenting, increase their prices, and make lives difficult for patients.
Context:
- India's healthcare system depends largely on accessible medications, with the generic pharmaceutical sector crucial for delivering quality drugs at affordable rates.
- The expense of medicines represents a substantial part of healthcare spending, with almost half of individuals' medical costs dedicated to purchasing prescriptions.
- Yet, the considerable expenses associated with medications, largely influenced by patenting, create significant hurdles for obtaining vital treatments.
What is the Role of Generic Pharmaceutical Companies?
- Generic pharmaceutical companies are pivotal in addressing the challenge of affordability by offering cost-effective alternatives to patented drugs.
- India's generic industry has earned global recognition for its role in providing essential medications at accessible prices.
- The development of India's patent laws has significantly influenced its pharmaceutical sector and its capacity to produce generic drugs.
- Initially, the Indian Patent Act of the early 1970s limited patent protection to the manufacturing processes rather than the products themselves.
- This approach facilitated the growth of the generic industry, positioning India as a major exporter of generic drugs by the late 1980s.
- However, recent revisions to the Indian Patent Law pose a threat to this ecosystem and jeopardize access to affordable healthcare.
What is the Impact of the TRIPS Agreement on India's Pharmaceutical Industry?
- The Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement, introduced in 1995, had a significant impact on India's pharmaceutical sector, shaping its development and global position. Key aspects of this impact include:
- Transition to Product Patents: A critical change brought by TRIPS was the requirement for member countries to grant patents for both products and processes, including pharmaceuticals.
- This shift from process to product patents posed challenges for India's thriving generic pharmaceutical industry, which had previously capitalized on producing affordable versions of patented drugs.
- Challenges for India's Generic Industry: The introduction of product patents threatened India's generic pharmaceutical sector, renowned for its capacity to manufacture low-cost essential medicines.
- These patents granted exclusive rights to inventors, restricting generic manufacturers' ability to produce and distribute affordable alternatives.
- Pressure to Comply with International Standards: The TRIPS Agreement pressured India to align its intellectual property laws with international standards, encompassing pharmaceutical patent protection.
- This necessitated amendments to India's Patent Act to comply with TRIPS obligations while preserving the interests of its generic pharmaceutical industry and public health priorities.
- Preserving Access to Medicines: Despite TRIPS challenges, India implemented measures to safeguard access to affordable medicines.
- Provisions like Section 3(d) of the Indian Patent Act, introduced in 2005, aimed to prevent granting frivolous patents for incremental innovations lacking significant therapeutic benefits.
- This ensured compliance with TRIPS requirements while maintaining access to affordable medicines.
- Balancing Innovation and Access: The TRIPS Agreement presented India with the challenge of balancing innovation and access to essential medicines.
- While patents incentivize innovation and investment in research and development, they can restrict access to life-saving treatments, particularly in developing countries with limited healthcare resources.
- Global Leadership in Generic Manufacturing: Despite the challenges posed by TRIPS, India emerged as a global leader in generic drug manufacturing.
- Leveraging its manufacturing capabilities and adherence to TRIPS flexibilities, the country's generic pharmaceutical industry continued to thrive, supplying affordable medicines domestically and globally.
What is Section 3(d) of India's Patent Act?
- Section 3(d) is a crucial provision in India's Patent Act that exemplifies the flexibilities embedded within the country's patent laws.
- It tackles concerns related to "evergreening"—a practice used by pharmaceutical companies to extend patent life through minor modifications or incremental innovations.
- The primary objective of Section 3(d) is to prevent the granting of patents for incremental innovations that lack significant therapeutic efficacy or novelty.
- By doing so, it aims to protect access to generic versions of essential medicines and promote affordability.
- Under Section 3(d), pharmaceuticals and chemical substances are eligible for patent protection only if they demonstrate enhanced efficacy compared to existing formulations.
- This requirement ensures that patents are granted for inventions representing genuine advancements in therapeutic efficacy rather than minor modifications or variations of existing drugs.
- Through Section 3(d), India's patent laws strike a balance between innovation and public health priorities, contributing to the overall well-being and access to medicines for its citizens.
What are the Contemporary Challenges in India's Patent Regime?
- India's patent regime currently faces several challenges, including issues related to pre-grant opposition, competition, international trade agreements, and flexibilities in patent law. These challenges have implications for access to affordable medicines, the financial burden on patent opponents, and drug availability.
- Threats to Pre-Grant Opposition: Amendments to the Indian Patent Rules have made filing opposition to patents at the pre-grant stage more challenging.
- This change could lead to granting patents for inventions lacking genuine novelty or therapeutic efficacy.
- Impact on Competition and Drug Prices: Limitations to the pre-grant opposition process may stifle competition in the pharmaceutical market and contribute to higher drug prices.
- By hindering generic manufacturers and civil society organizations from challenging frivolous patents, the amendments impede the availability of affordable generic drugs.
- Pressure from Pharma Majors and International Trade Agreements: These amendments reflect pressure from multinational pharmaceutical corporations, particularly Western and Japanese companies, seeking to align India's patent rules with their interests.
- Their lobbying efforts aim to weaken India's patent regime, facilitating patent grants for incremental innovations and extending market exclusivity for their products.
- Threats to Flexibilities in Patent Law: Amendments to India's patent rules threaten the flexibilities inherent in its patent law, including provisions such as Section 3(d) that set stringent patentability criteria based on enhanced efficacy.
- Weakening these provisions undermines India's capacity to protect public health priorities and promote access to affordable medicines.
- Financial Burden on Opponents of Patents: Imposing fees on patent opponents could deter patients, civil society organizations, and generic manufacturers from filing pre-grant oppositions.
- This financial burden limits stakeholders' ability to safeguard public health interests and promote affordable medicines.
- Impact on Compulsory Licensing and Drug Availability: The amendments also affect the issuance of compulsory licenses, crucial for ensuring access to medicines when patents hinder availability.
- By weakening provisions that enable compulsory licensing and limit evergreening, the amendments impede efforts to address healthcare disparities and promote equitable access to essential medicines.
Conclusion
Access to affordable medicines is vital for public health and universal healthcare. Policymakers must preserve patent law flexibilities, promote competition, and protect patient interests to ensure healthcare systems uphold affordability, accessibility, and quality. Amendments to India's Patent Rules should balance innovation, intellectual property rights, and societal well-being, mitigating negative impacts on essential medicines and public health outcomes.
How Can India Revive its Investment Cycle

- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Centre has been meeting its capex targets, but the trajectory of private sector and state governments is less certain.
Context:
- Policymakers in India are grappling with the imperative task of revitalizing the investment cycle. Despite the central government's success in meeting capital expenditure (capex) targets, uncertainty clouds the trajectory of investments from the private sector and state governments.
- Thus, a comprehensive examination of India's current investment landscape is essential, scrutinizing key indicators and trends to identify the hurdles and prospects in reigniting the investment momentum.
Overview of Investment Patterns:
- Fluctuating Investment Rates: The investment rate, representing gross fixed capital formation as a percentage of GDP, has shown variability in recent years.
- After dropping to 27.2% in 2020-21, there has been a slight improvement, with the rate climbing to 31.3% in 2023-24 from 30.8% in the preceding fiscal year.
- This increase suggests a possible resurgence in investment sentiment and activity, albeit starting from a relatively low level.
- Composition of Investments: Delving Deeper: Yet, a closer examination of investment composition reveals noteworthy nuances.
- A significant part of the recent uptick in capital formation stems from dwelling construction, supported by government initiatives to bolster the housing sector.
- While housing investments spur economic growth and job creation, diversification is essential for sustainable and equitable development.
- Declining Investment in Plant and Machinery: Of particular concern is the diminishing share of investments in plant and machinery, crucial for fostering productivity, innovation, and competitiveness across sectors.
- The allocation of investment to plant and machinery declined from 36% in 2017-18 to 30.7% in 2022-23, indicating a potential shift in investment priorities or hurdles in attracting investments in manufacturing and industrial domains.
Private Sector Investment:
- Insights from CMIE Data: Examining private sector investment trends often involves analyzing data provided by the Centre for Monitoring the Indian Economy (CMIE), offering valuable insights into the investment intentions and actions of private enterprises.
- Mixed Signals in Investment Intentions: Recent CMIE data reveals a nuanced picture of private sector investment in India.
- While new investment announcements dipped to Rs 27.1 lakh crore in 2023-24 from the previous year's Rs 39 lakh crore, they still represented the second-highest figures in a decade.
- However, it's essential to recognize that these announcements signify intentions rather than realized investments, potentially leading to disparities between planned projects and actual investments.
- Prevalence of Private Sector Intentions: The bulk of investment intentions—around 85%—originated from the private sector, underscoring its pivotal role in driving investment dynamics.
- Furthermore, foreign companies contributed 11% of the total investment intentions, reflecting a certain degree of confidence in India's business landscape among international investors.
Analyzing Investment Trends Across Sectors:
- Power Sector Dynamics: Investment inflows into the power sector have surged, reflecting a strategic focus on bolstering infrastructure, particularly in renewable energy projects like solar and wind power, driven by initiatives such as the Production Linked Investment (PLI) scheme.
- This expansion not only enhances energy security and environmental sustainability but also stimulates job creation and technological advancements.
- Transportation Sector Insights: Investment intentions in transportation services, notably aviation, have risen sharply due to ambitious expansion plans by major airlines.
- While these investments promise improved connectivity and economic growth, concerns persist about reliance on imported aircraft, emphasizing the need for initiatives to foster domestic manufacturing and technological capabilities.
- Diverse Industry Investment Trends: Various industries, including chemicals, machinery, metals, and automotive sectors, have attracted substantial investment commitments, reflecting a broad spectrum of opportunities for private sector investment.
- However, the absence of significant investments in consumer goods industries raises questions about the depth and breadth of sectoral investments.
- Challenges in Consumer Goods: Consumer goods industries face challenges such as excess capacity, subdued demand, and high inflation, which dampen investment enthusiasm despite government incentives like the PLI scheme.
- Lingering issues in job creation and rural demand further contribute to the subdued investment outlook in this segment.
- Impact of State Government Spending: Reduced capital expenditure by state governments in 2022-23 to meet fiscal targets poses a challenge to the investment cycle, given their significant contribution to overall investments.
- Budgetary constraints in state governments have a ripple effect on the broader investment landscape in the country.
Way Forward:
- Promoting Sustainable Growth: While the rise in capital formation is encouraging, ensuring its sustainability and fostering long-term growth hinges on achieving a balanced distribution of investments across sectors.
- Over-reliance on specific industries, like construction, may impede the economy's adaptability and hinder innovation and technological progress.
- Policy Imperatives for Investment Stimulus: Effective policy measures are imperative to stimulate private sector investment and cultivate a favorable investment environment.
- Streamlining regulatory frameworks, bolstering infrastructure, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship, and addressing sector-specific hurdles can incentivize private enterprises to invest in vital areas crucial for fostering economic growth and advancement."
Conclusion
Revitalizing India's investment cycle demands collaborative action from public and private stakeholders. Despite promising sectors, obstacles like sectoral disparities, muted consumer demand, and fiscal limitations at the state level impede a comprehensive rebound. Tackling these hurdles via tailored policies to spur demand, foster sectoral variety, and bolster the investment environment will be pivotal for nurturing enduring economic progress and advancement.
India’s Nuanced Approach in the South China Sea
- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In March 2024, India’s External Affairs Minister, S. Jaishankar, articulated, in a joint statement during his visit to Manila, India’s full support for the Philippines in upholding its national sovereignty concerning the South China Sea.
Context:
- During his visit to Manila in March 2024, India's External Affairs Minister reiterated India's steadfast support for the Philippines in safeguarding its national sovereignty amidst the ongoing South China Sea dispute.
- This statement came against the backdrop of heightened tensions and frequent maritime incidents in the region throughout 2023.
- Furthermore, a joint statement issued in 2023 by India and the Philippines emphasized the importance of China adhering to the rules-based maritime order and recognizing the 2016 ruling by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in favor of the Philippines.
- These statements reflect a notable shift in India's approach towards the South China Sea issue, departing from its previous stance of caution and neutrality.
- India's evolving position on the South China Sea underscores its broader strategic and economic interests on the global stage, with a renewed emphasis on upholding international maritime law, sovereignty, and sovereign rights in the region.
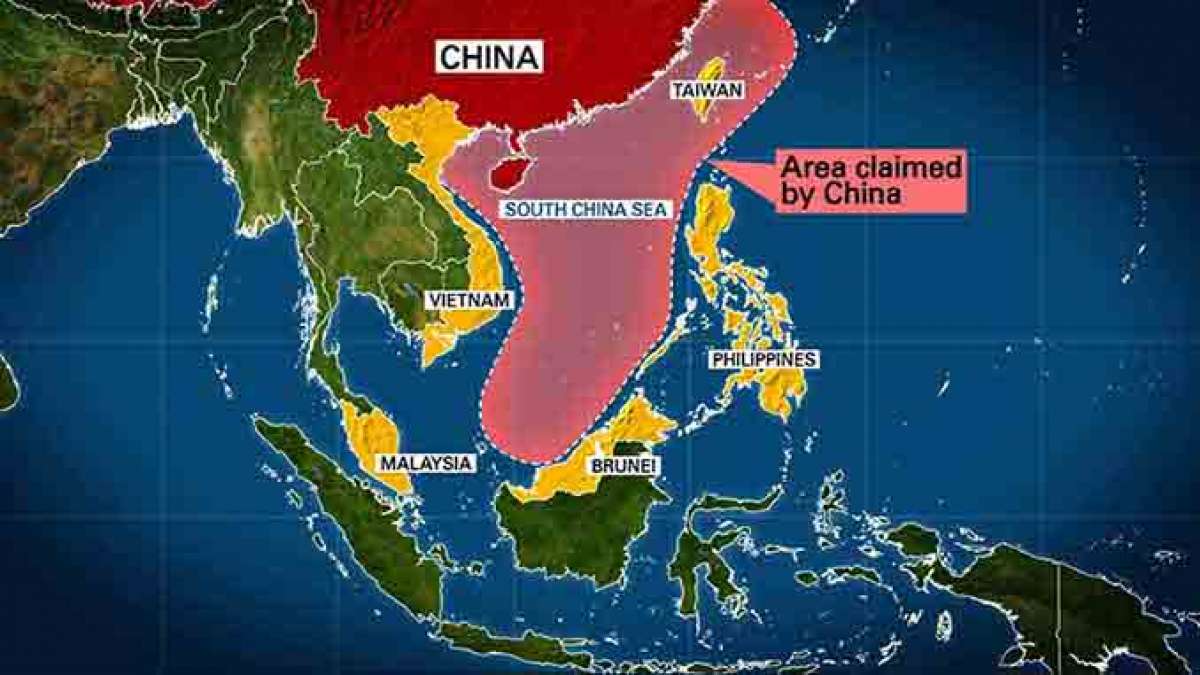
About the South China Sea (SCS):
- The South China Sea (SCS) is a pivotal body of water located in Southeast Asia, bordered by China to the north, Vietnam to the east and south, the Philippines to the west, and Borneo to the south.
- It encompasses a myriad of shoals, reefs, atolls, and islands, with notable features including the Paracel Islands, the Spratly Islands, and the Scarborough Shoal.
- Strategically situated, the SCS serves as a crucial maritime passage connecting the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean via the Strait of Malacca.
- It plays a vital role in global trade, with approximately one-third of all shipping traversing its waters annually, facilitating trillions of dollars in trade and serving as a linchpin for geopolitical dynamics.
- Rich in marine biodiversity, the SCS harbors a third of the world's marine species, providing essential fisheries that contribute to the food security of Southeast Asian nations.
- Additionally, the region is believed to possess vast reserves of oil and gas beneath its seabed, further heightening its economic significance.
- With an estimated $3.4 trillion worth of ship-borne commerce passing through its lanes each year, including crucial energy supplies to nations like the United States, Japan, and South Korea, the South China Sea stands as one of the busiest and most consequential waterways on the planet.
Various Ongoing Disputes in the South China Sea (SCS):
There are multiple ongoing disputes in the South China Sea (SCS) involving several countries. These disputes revolve around territorial and maritime claims over islands, reefs, banks, and other features in the region.
- Spratly Islands Dispute: The Spratly Islands are claimed by China, Taiwan, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei.
- These islands are strategically important due to their location in the middle of the South China Sea, as well as potential oil and gas reserves.
- Paracel Islands Dispute: The Paracel Islands are claimed by China, Taiwan, and Vietnam.
- China currently controls the islands, but Vietnam also asserts its sovereignty over them.
- Scarborough Shoal Dispute: The Scarborough Shoal is a disputed territory between China, Taiwan, and the Philippines.
- The shoal is rich in fishing resources and is strategically located near important shipping lanes.
- Gulf of Tonkin Dispute: This dispute involves China, Taiwan, and Vietnam, who have overlapping claims over the boundaries in the Gulf of Tonkin.
- Natuna Islands Dispute: Although geographically a part of the South China Sea, Indonesia claims sovereignty over the Natuna Islands, while China's "Nine-Dash Line" claim overlaps with Indonesia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) near the Natuna Islands.
- Senkaku Islands Dispute: In the East China Sea, the Senkaku Islands are disputed between China, Taiwan, and Japan, with Japan currently administering them.
- These disputes stem from historical claims, economic interests, and strategic considerations, leading to tensions between the involved parties.
India’s Policy Shift:
- Initially, India's engagement in the region was primarily motivated by economic considerations, in line with its Look East Policy.
- This policy sought to strengthen economic linkages with Southeast Asia and secure vital energy resources essential for India's growing economy.
- Demonstrating this economic focus, Indian state-owned enterprises like ONGC Videsh participating in oil and gas ventures in Vietnam's exclusive economic zones highlighted India's economic imperatives and its adherence to the principles of maritime resource exploration and exploitation within the framework of international law, particularly UNCLOS.
- India's policy trajectory has since evolved from Look East to Act East, indicating a shift towards a more proactive and strategic stance in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This shift reflects India's acknowledgment of the changing geopolitical landscape and the imperative for a comprehensive foreign policy approach.
- The Act East Policy places greater emphasis on economic integration and underscores the importance of forging strategic partnerships and enhancing security cooperation with countries in the Indo-Pacific, including Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, and the Philippines.
- Concurrently, India has augmented its capabilities through various measures such as forward deployment, mission-based operations, heightened maritime domain awareness, and the establishment of deep-water maritime infrastructure.
India's intricate dynamic with China:
- The assertive behavior exhibited by China in the South China Sea (SCS) and its gradual encroachment strategy across various maritime domains, including the Indian Ocean, have sparked apprehension within India.
- Chinese intelligence-gathering activities in the Eastern Indian Ocean have heightened India's vigilance, prompting a more proactive stance to address perceived threats to its maritime security.
- Against the backdrop of escalating geopolitical tensions in the SCS, largely driven by China's assertive territorial assertions and militarization efforts, India's approach has undergone a nuanced yet less cautious evolution.
- This transformation in India's stance toward the SCS is closely interlinked with its complex relationship with China.
- Both nations have a history of longstanding border disputes, which escalated following the Galwan Valley clash in 2020.
- China's periodic incursions into Indian territory and recent actions such as renaming Indian villages in Arunachal Pradesh further exacerbate these tensions.
- The Galwan Valley incident prompted India to deploy a frontline warship to the SCS, showcasing India's asymmetric deterrence capabilities.
- China's assertive stance and territorial claims in both the SCS and along India's land border pose significant challenges to regional stability.
- India's strategic engagements, including regular naval exercises and enhanced military cooperation with Southeast Asian nations, serve dual purposes: reaffirming India's commitment to regional security and acting as a counterbalance to China's contentious assertions.
The ASEAN Perspective:
- New Delhi's strategic recalibration stems from recognizing the critical importance of the South China Sea (SCS) for regional security and the global maritime order.
- The disputes involving China and various ASEAN nations in the SCS directly impact the principles of freedom of navigation and overflight, which are essential not only for India's trade and energy transport but also for countries worldwide.
- As an active participant in the Indo-Pacific region, India cannot afford to remain indifferent to such significant issues.
- Its central role in the Indo-Pacific extends beyond the Indian Ocean to the broader maritime domain, where China's rise challenges the established order in unforeseen ways.
- India's Indo-Pacific strategy prioritizes ASEAN centrality, despite internal differences within the regional grouping presenting challenges.
- India's advocacy for a rule-based international maritime order, particularly its steadfast support for UNCLOS, stands in opposition to unilateral actions that undermine regional stability.
- This principled stance, deeply rooted in India's foreign policy framework, indirectly counters China's expansive territorial claims and activities in the SCS, underscoring India's dedication to regional stability and security as a responsible stakeholder.
Navigating Challenges and Choices for India:
- India encounters complexities in managing the South China Sea (SCS) disputes, especially given the divergent interests within ASEAN.
- While ASEAN nations adopt varying approaches to disputes, India aims to strike a delicate balance between supporting regional partners and steering clear of direct entanglement in confrontational situations.
- India is exploring a spectrum of options, including initiatives to bolster capacity, cooperation in defense matters, infrastructure development, and advocating for the preservation of international law in the SCS.
Conclusion:
India's recalibrated approach to the South China Sea disputes arises from strategic necessities, evolving geopolitical landscapes, and regional intricacies. The nuanced stance adopted by India towards the South China Sea is emblematic of its broader strategy, aimed at safeguarding its interests while actively participating in collective endeavors to uphold peace, stability, and the rule of international law across the Indo-Pacific region.
Supreme Court's Directive Sets Delhi Metro Back on Course with Clear Roadmap

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The case involving DMRC (Delhi Metro Rail Corporation) and DAMEPL (Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd) which has been in and out of courts for over a decade, has concluded with the Supreme Court verdict on April 10.
Context:
- On April 10, the Supreme Court delivered its verdict on the case concerning the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) and Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd (DAMEPL), bringing it to a close.
- This ruling holds exceptional importance within the legal sphere, setting a notable precedent for arbitration tribunals and courts.
- Moreover, it carries significant implications for public service delivery via partnership models and demonstrates effective litigation strategies for infrastructure projects, contributing to India's future resilience.
What is the Dispute Between DMRC and DAMPEL?
- The dispute between the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) and Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt Ltd (DAMEPL) arises from the development and operation of the Airport Metro Express Line, a crucial infrastructure project in India's capital city, which began operations in 2011.
- The partnership between DMRC and DAMEPL followed a public-private partnership (PPP) model, where DMRC was responsible for constructing civil structures such as tunnels, viaducts, and station buildings, while DAMEPL was in charge of laying tracks, overhead equipment, signaling, and procuring rolling stock.
- Problems arose shortly after the line became operational.
- In 2012, DAMEPL suspended operations on the line, citing defects in the civil engineering works executed by DMRC.
- DAMEPL claimed that these defects compromised safety and functionality and demanded that DMRC rectify the issues within 90 days, threatening to treat the situation as a material breach of the agreement and terminate the contract if not addressed.
- DMRC attempted to resolve the issues through conciliation proceedings, but these efforts proved unsuccessful.
- Consequently, DAMEPL issued a notice of termination, asserting that DMRC had failed to remedy the defects.
- This led to a breakdown in the relationship between the two parties and prompted legal battles.
- Despite the challenges, DMRC and DAMEPL submitted a joint application in November 2012 to the commissioner of metro rail safety for inspection and permission to restart operations.
- Train services were eventually restored on the line by DAMEPL in 2013, with train speeds on the line increasing to 80 km/h. However, in June of the same year, DAMEPL announced its unwillingness to continue operating the line and ceased operations almost immediately.
- Recognizing the importance of the metro line for the public, DMRC stepped in to operate the nearly abandoned Airport Metro Express Line.
- DMRC resumed train operations and provided other ancillary services to maintain public transportation on the line.
- This intervention prevented a complete suspension of services and ensured continuity for commuters.
Findings of the Arbitration Tribunal:
- The tribunal awarded DAMEPL Rs 2,782 crore with interest after concluding that the termination notification was legitimate.
- In 2018, the Delhi High Court's single-judge bench maintained the award notwithstanding DMRC's protest.
- The Division Bench of the Delhi High Court, responding to DMRC's appeal, criticized the arbitral tribunal's methodology, pointing out errors such as failing to consider safety considerations and failing to read contractual provisions. As a result, the arbitration decision was revoked.
Supreme Court's Intervention and Final Judgement:
- Both DMRC and DAMEPL appealed to the Supreme Court through special leave petitions, leading to a significant legal process.
- Initially, the Supreme Court overturned the High Court's ruling and reinstated the arbitral award in 2021.
- However, following DMRC's curative petition, the Supreme Court revisited the case.
- After a thorough examination, considering various factors including factual background and tribunal decisions, the Court found significant errors in the arbitral award.
- Concluding that the award lacked coherence and resulted in serious injustice, the Court upheld the Division Bench's decision, deeming the award as flawed and illegal.
- This reversal of its earlier decision restored the parties to the status quo as per the Division Bench's judgment.
Importance of the Supreme Court Verdict:
- Establishing Precedent for Arbitration: The verdict sets a precedent for arbitration tribunals and courts, outlining the meticulous scrutiny required for arbitral awards.
- It underscores the importance of coherence and evidence-based reasoning in such decisions, ensuring fairness and consistency in dispute resolution.
- Ensuring Fairness and Justice: By reinstating the parties to the status quo as per the Delhi High Court Division Bench's judgment, the Supreme Court prioritizes fairness and justice in public-private partnership (PPP) projects.
- This safeguards public utilities from undue financial strain and upholds the interests of all stakeholders involved in contractual disputes.
- Promoting Accountability and Due Diligence: The ruling emphasizes accountability in infrastructure projects, stressing the need for due diligence and adherence to contractual obligations.
- It underscores the responsibility of all PPP participants to act in good faith, particularly in managing critical public infrastructure, thereby fostering transparency and integrity.
- Guiding Future Infrastructure Ventures: The judgment provides clarity for pending cases, especially in the infrastructure domain, offering a roadmap for handling disputes arising from PPP agreements.
- It ensures that future projects benefit from transparent and equitable dispute resolution mechanisms, enhancing the efficiency and credibility of infrastructure development efforts.
- Boosting Confidence in PPPs: By reaffirming the judiciary's commitment to legal integrity and fairness, the ruling instills confidence in both public and private entities engaging in PPPs.
- This confidence is essential for attracting investment in infrastructure projects, driving economic growth, and modernizing India's infrastructure landscape.
Conclusion
The prolonged legal conflict between DMRC and DAMEPL highlighted the complexities and challenges inherent in PPP projects, spanning over a decade with various assertions from both sides. This case serves as a testament to the judiciary's pivotal role in preserving equity and integrity within PPP ventures, crucial for advancing the nation's infrastructure. Furthermore, it underscores the significance of adhering to principles of fairness in contractual disagreements and the enduring influence of legal precedents on the trajectory of public-private collaborations
Left Wing Extremism/Naxalism in India

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least 29 Maoists were killed and three security personnel were injured in a gunbattle recently in a forest in Kanker district of Bastar division in Chhattisgarh.
Context:
- In a significant development, at least 29 Maoists were neutralized, and three security personnel sustained injuries during a fierce gun battle in a forested area of the Kanker district in Chhattisgarh's Bastar division.
- This successful joint operation, conducted by the District Reserve Guards (DRG) and the Border Security Force (BSF), marked the highest number of Maoist casualties recorded in a single operation within the Bastar region.
- The operation involved a strategic collaboration between the DRG, a specialized anti-Naxal force, and the BSF, with a well-executed plan that allowed them to engage and ultimately overpower the Maoists.
What is Left Wing Extremism?
- Left-Wing Extremism (LWE), also referred to as left-wing terrorism or radical left-wing movements, encompasses political ideologies and groups that aim to achieve substantial societal and political transformation through revolutionary methods.
- These groups may resort to targeting government institutions, law enforcement agencies, or private property to advance their objectives.
- India's LWE movement traces its origins back to the 1967 uprising in Naxalbari, West Bengal, which set the stage for the emergence of various left-wing extremist groups.
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs, LWE has impacted 90 districts across 10 states, with varying degrees of influence.
Maoist Presence Across India:
Maoist influence varies in intensity across different Indian states:
- Severely Affected States: Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, and Bihar face significant Maoist presence and activities, with frequent attacks on security forces and civilians.
- Partially Affected States: West Bengal, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh experience a more moderate Maoist presence, with occasional incidents and clashes.
- Slightly Affected States: Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh have a lower level of Maoist activity but are still considered areas of concern.
- The Communist Party of India (Maoist) has been attempting to expand its influence in the southern states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, aiming to connect the Western and Eastern Ghats.
- Additionally, incursions into Assam and Arunachal Pradesh have raised concerns about long-term strategic implications.
Factors Contributing to Left-Wing Extremism in India:
Several underlying factors contribute to the rise and persistence of Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) in India:
- Inequitable Development: Many LWE-affected regions are among India's least developed areas, characterized by high poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, malnutrition, and social exclusion rates.
- LWE groups often exploit the grievances of marginalized communities, particularly tribal populations, who have been deprived of land, forest, and mineral rights.
- Marginalization: Naxalites primarily consist of Dalits, Adivasis, and other marginalized sections of society.
- Maoist teachings deeply influence their leadership, with land reforms and economic development being key issues.
- Governance Deficit: LWE-affected areas often suffer from inadequate governance, administration, and service delivery.
- Weak or corrupt state institutions leave a vacuum that LWE groups can exploit.
- These groups also use violence and intimidation to disrupt democratic processes, including elections, local governance, and development schemes.
- Ideological Appeal: LWE groups claim to represent the interests of oppressed and exploited classes, promoting a radical ideology that rejects parliamentary democracy and advocates for armed revolution.
- Drawing inspiration from Mao Zedong and the 1967 Naxalbari uprising, these groups may also have links to other extremist and separatist movements in India and abroad.
- Globalization and Cultural Displacement: The impacts of globalization, such as cultural changes and displacement, can cause feelings of dislocation and alienation.
- Left-wing extremist movements may offer identity and purpose to individuals marginalized by global forces.
- Support Base: The Naxalite movement draws support from the landless, sharecroppers, agricultural laborers, Harijans, and tribals.
- As long as these groups continue to face exploitation and social injustice, the Naxalite support base will persist.
The Challenges Posed by Naxalites to India:
The Naxalite movement presents several challenges to India's stability and development:
- Vulnerability to External Threats: Naxalite activities expose India's internal vulnerabilities, potentially inviting external threats.
- The CPI (Maoist) has close ties with Northeast insurgent groups, many of which have links to external forces hostile to India.
- The CPI (Maoist) has also expressed solidarity with Jammu and Kashmir terrorist groups.
- Impediments to Economic Development: Focusing on India's poor and marginalized regions, Naxalite activities hinder economic development efforts crucial for improving these areas' conditions.
- Internal stability is essential for a nation's economic progress.
- Additional Internal Security Expenses: Scarce resources are diverted towards defense and internal security to counter Naxalite threats, which could be better utilized for social development initiatives.
- Adverse Impact on Governance: Naxalite domination in certain areas disrupts governance through violent tactics, such as killings, kidnappings, intimidation, and extortion.
- This hampers the delivery of essential services to citizens in affected regions.
Steps Taken by the Government to Counter Left-Wing Extremism:
To tackle the challenges posed by Left-Wing Extremism (LWE), the Indian government has implemented various strategies and initiatives:
- Deployment of Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs): CAPF battalions and Naga Battalions (BNs) are deployed to support state police forces in LWE-affected areas, providing additional security and resources.
- Security Related Expenditure (SRE) Scheme: The SRE scheme funds the recurring expenditures related to insurance, training, and operational needs of security forces, rehabilitation of surrendered LWE cadres, and awareness campaigns against violence.
- Review and Monitoring Mechanisms: The Ministry of Home Affairs regularly monitors the LWE situation at multiple levels through various review and monitoring mechanisms.
- Strengthening Intelligence Gathering: Intelligence capabilities at the central and state levels have been bolstered through measures like intelligence sharing via the Multi-Agency Centre (MAC) and State Multi-Agency Centre (SMAC) on a 24/7 basis.
- Inter-state Coordination: Given the cross-border nature of Maoist operations, the government facilitates frequent meetings and interactions between officials from bordering LWE-affected districts to enhance inter-state coordination.
- Countering Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs): As IEDs are a significant threat, the Home Ministry has developed a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) on explosives, IEDs, and landmines in affected areas, which has been shared with stakeholders for implementation.
- Enhanced Air Support: State governments and CAPFs have received increased air support, including UAVs and helicopters, for anti-Naxal operations and casualty evacuations.
Progress and Impact of the Measures:
- Over the past eight years, India has witnessed a substantial decrease in left-wing extremism violence and its geographical spread, thanks to the government's comprehensive measures:
- The number of left-wing extremism-related incidents dropped significantly in 2022 compared to 2013, totaling 413.
- Left-wing extremism-related deaths also experienced a substantial decline, with a 75% reduction from 397 in 2013 to 98 in 2022.
- The year 2022 saw a 33% decrease in resultant deaths and a 68% decrease in security forces' casualties compared to 2021.
Way Forward:
- Effective Implementation of PESA Act: Ensure proper and complete implementation of the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA) by issuing clear policy directives to empower gram sabhas.
- Align the Act with the historical and traditional tribal way of life and address implementation gaps that Maoists exploit.
- Tribal Empowerment and Representation: Foster tribal leadership by providing platforms for their voices to be heard and increasing representation in local governance structures and political processes.
- Address tribal communities' aspirations and ensure policies accommodate their unique needs and perspectives.
- Targeted Development Programs: Implement development programs addressing socio-economic issues faced by tribal communities, including infrastructure, healthcare, education, and employment opportunities. Involve local communities in participatory decision-making processes for initiatives.
- Counter Maoist Propaganda: Develop communication strategies to expose the gap between Maoist rhetoric and actions.
- Collaborate with local media, community leaders, and influencers to spread accurate information and counter misinformation.
- Negotiation and Conflict Resolution: Explore avenues for peaceful negotiation with moderate Maoist factions, identifying root causes of discontent and involving neutral mediators, civil society organizations, and respected community leaders in peacebuilding efforts.
- Human Rights Protection: Prioritize human rights protection in conflict zones, ensuring security measures align with the rule of law and minimizing collateral damage and civilian casualties.
- Long-term Strategic Planning: Develop a comprehensive, long-term strategy focused on sustainable development, social justice, and inclusive governance to address underlying issues contributing to the insurgency.
Conclusion
There is a widely acknowledged perspective that effectively addressing the Naxal issue requires a balanced approach involving both developmental and security measures. It's crucial not to solely consider it as a law and order challenge, as innocent tribal communities residing in remote forest areas often become targets of Naxal intimidation. Priority lies in re-establishing governance in Naxal-affected regions, fostering their development, and empowering marginalized communities to lead secure, dignified, and improved lives
New Data Law, a Barrier to Journalistic Free Speech

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In August 2023, India enacted its first comprehensive data protection law, the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, with the government currently in the process of formulating rules and regulations for its implementation, anticipated to conclude post the general election.
Context:
- In August 2023, India introduced its first comprehensive data protection law, the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023.
- While aimed at safeguarding personal data, its impact on journalistic freedom warrants examination, as the absence of exemptions for journalistic activities may threaten the foundational principles of a free press.
Provisions of Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act:
- The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 is a landmark legislation aimed at regulating the collection, processing, storage, and use of personal data in India.
- The Act establishes a comprehensive framework for lawful and transparent handling of personal data, seeking to safeguard individuals' privacy and data rights.
Key provisions of the DPDP Act, 2023 include:
- Definition of personal data: Any information capable of identifying an individual, directly or indirectly.
- Principles of data protection: Lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimisation, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, confidentiality, and accountability.
- Data handlers: Distinction between data fiduciaries (determining processing purpose and means) and data processors (processing data on behalf of fiduciaries).
- Consent: Requirement for explicit consent before processing personal data, with provisions for withdrawal.
- Individual rights: Access, correction, erasure, and transfer of personal data.
- Data localisation: Potentially mandating the storage and processing of certain sensitive data within India.
- Oversight: Establishment of a Data Protection Board to monitor compliance and resolve grievances.
- Non-compliance: Penalties and sanctions, including fines and legal consequences for violations.
- Cross-border data transfers: Ensuring data protection standards comparable to India's when transferring data across borders.
- Obligations for data fiduciaries and processors: Security measures, data breach notifications, and data impact assessments.
- The DPDP Act, 2023 represents a significant step towards upholding individual privacy rights in India and ensuring responsible data management by government entities, organisations, and individuals alike.
Journalistic Exemptions in Data Protection Laws:
- Traditionally, data protection laws include exemptions for journalistic activities, allowing journalists to access and report on personal data without consent for investigative purposes.
- These exemptions ensure freedom of the press and facilitate accountability in society.
- However, the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 does not provide such exemptions.
- Previous drafts of the Act, including versions released by an expert committee on data protection (2018), the government (2019), and a Joint Parliamentary Committee (2021), contained provisions for journalistic activities.
- The unexplained removal of these exemptions in the DPDP Act's final iterations (2022 and 2023) raises concerns over potential negative impacts on journalism and its role in maintaining transparency and accountability.
- Addressing this absence of journalistic exemptions will be crucial to upholding the freedom of the press and protecting the public's right to information.
Challenges for Journalists under the DPDP Act:
- Consent Requirements: Journalists are now obligated to secure consent from individuals before utilizing their personal data in news stories.
- This could impede investigative reporting, as subjects may refuse consent, thereby obstructing access to crucial information.
- Right to Erasure: The right to erasure permits individuals to demand the deletion of published stories containing their personal data.
- This provision may result in the removal of significant investigative work, undermining transparency.
- For instance, when reporting on a Member of Parliament (MP) and their activities, journalists often gather information such as meeting details, travel itineraries, and familial financial investments, all of which constitute personal data under the DPDP Act.
- This provision may result in the removal of significant investigative work, undermining transparency.
- Obtaining consent for such data usage poses challenges, and even after publication, MPs can invoke the right to erasure, compelling journalists to delete pertinent stories.
- Government Oversight: The Act grants the government authority to request information from data processors, potentially compromising the confidentiality of journalists' sources and research materials.
- This governmental oversight may curtail the press's capacity to hold the state accountable.
Addressing Concerns and Potential Solutions for Journalistic Freedoms under the DPDP Act:
- To ensure a balanced approach that protects personal data while preserving journalistic freedoms, addressing the concerns raised by the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act is essential.
- The following solutions could help achieve this goal:
- Transparent Consultation: The removal of exemptions for journalistic activities highlights the need for open and transparent public consultations.
- Although drafts of the DPDP Act were released for public input, the comments received were not made publicly available.
- Greater transparency in the consultation process would enable better comprehension of stakeholder perspectives and inform more effective law-making.
- Exemptions for Journalists: The central government should consider using its rule-making powers under the DPDP Act to exempt journalistic entities, including citizen journalists, from specific obligations within the Act.
- This exemption would protect the freedom of the press and encourage a transparent and open environment for journalism.
- Public Consultation: Implementing an open, transparent, and robust public consultation process could facilitate better understanding and consideration of various viewpoints.
- This approach would lead to a more balanced and effective data protection law that upholds both personal data privacy and freedom of the press.
Conclusion
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, is an essential step towards safeguarding personal data in India. However, its potential impact on journalistic free speech raises significant concerns that must be addressed.
To strike a balance between protecting individual privacy and upholding the fundamental principles of a free press, the government should consider implementing exemptions for journalists and fostering transparent consultation processes. These measures would enable a harmonious coexistence of personal data protection and journalistic freedoms, ensuring that both critical elements thrive in India's democratic landscape
Revealing Caste-based Inequalities in Indian Cities

- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Despite Dr. B.R. Ambedkar's hopeful vision for India's cities, the urban fabric continues to be profoundly fractured by enduring caste-based divisions.
Context:
- Caste has historically played a significant role in shaping the social fabric and geographical layout of communities throughout India.
- This influence is palpable in the organization of Indian cities, where caste often dictates spatial arrangements and societal dynamics.
- Despite entrenched obstacles, influential figures such as R. Ambedkar and Jyotirao Phule viewed urbanization as a potential catalyst for the liberation of Dalits.
- Consequently, it becomes imperative to delve into Ambedkar's perspective on urbanization, the enduring prevalence of caste-based discrimination within urban environments, and the ongoing hurdles encountered by Dalits and Muslims concerning housing and access to public services in urban areas.
What was B. R. Ambedkar’s View on Urbanization?
- A Pathway to Empowerment: B. R. Ambedkar, an eminent social reformer and advocate for Dalit rights, envisioned urbanization as a pathway to empowerment for marginalized communities in India.
- He posited that the traditional social structures prevailing in Indian villages were inherently oppressive due to the rigid caste system, which predetermined individuals' social status and opportunities based solely on their birth.
- Ambedkar contended that Indian villages served as the "working plant of the Hindu social order," perpetuating caste-based hierarchies that marginalized and subjugated Dalits.
- Viewing urbanization as a means of dismantling this entrenched caste-based order, he saw cities as spaces where individuals could blend into anonymity amidst a diverse population, transitioning from a caste-oriented society to one structured more around class.
- Disrupting Caste-Based Hierarchies: Ambedkar believed that this transition from a genealogy-based social structure to one centered on resource accumulation would weaken the systems of caste oppression that were deeply entrenched in rural areas.
- Urban environments, he argued, would offer Dalits access to diverse economic opportunities and avenues for skilled labor, enabling them to enhance their social and economic status.
- In cities, Dalits could potentially break free from the occupational constraints dictated by caste in villages, thereby fostering social mobility and economic independence.
- Additionally, Ambedkar saw urban areas as hubs of greater political and social awareness, with educational institutions and opportunities for civic engagement that could empower marginalized groups to assert their rights and actively participate in democratic processes.
- Urbanization Challenges and Ambedkar's Hope: Despite advocating for urbanization as a means of empowerment for marginalized communities, Ambedkar was cognizant of its inherent challenges.
- He acknowledged the persistent presence of caste-based discrimination within urban settings, drawing from his encounters with adversity.
- Ambedkar's personal experiences, such as his difficulties in securing housing in Baroda and encountering caste-based restrictions in textile mills, underscored the reality of caste-based biases in urban areas.
- However, rather than succumbing to disillusionment, he maintained an optimistic outlook regarding the transformative potential of cities.
- Ambedkar perceived urban environments as arenas where individuals could assert greater agency and autonomy in shaping their lives.
- Despite the hurdles presented by caste-based discrimination, he remained hopeful that cities could provide avenues for marginalized groups to transcend social barriers and realize their full potential.
Endurance of Caste-Based Bias in Urban Environments:
- Language of Purity-Pollution: Urban caste discrimination primarily manifests through the concept of purity-pollution, deeply ingrained in Hindu social practices.
- This notion labels specific foods, behaviors, and individuals as pure or impure based on caste.
- For instance, a 2021 survey revealed that non-vegetarian diets hinder rental housing access, reflecting prejudice against meat-eating castes.
- This notion labels specific foods, behaviors, and individuals as pure or impure based on caste.
- Caste Segregation in Housing: The purity-pollution concept extends to housing practices, with Dalits and other lower castes facing discrimination in renting or purchasing urban homes.
- Landlords and housing societies may reject them based on perceived cleanliness or dietary habits, leading to segregation and ghettoization.
- State-Sanctioned Policies: Government policies have also perpetuated urban caste-based discrimination.
- In March 2017, Uttar Pradesh restricted meat sales near religious places and mandated meat shops to conceal products from pedestrians.
- Similar measures in Gujarat targeted street food vendors selling meat-based items, citing religious concerns.
- These policies reinforce caste divisions by labeling meat as impure and associating it with certain castes.
Ambedkar's Vision, Discrimination's Impact, and Urban Space Inequity:
- Enduring Significance of Ambedkar's Vision: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar's vision of urbanization as a means for Dalit liberation remains relevant today, emphasizing the continuing pursuit of social justice and equality in Indian cities.
- His work highlights the need to address both historical and present-day caste-based discrimination to create inclusive urban environments.
- Spatial Consequences of Discrimination: Caste-based discrimination significantly affects urban spaces by segregating Dalits and other marginalized groups into specific areas or neighborhoods.
- These segregated zones often lack access to essential services and infrastructure, amplifying existing socioeconomic disparities within these communities.
- Influence on Public Spaces: Discrimination based on caste extends to public spaces, with restrictions on food sales limiting lower castes' economic and social participation in city life.
- Such policies contribute to exclusion and marginalization, shaping an environment detrimental to inclusivity and equity within urban landscapes.
Conclusion
Despite Ambedkar's hopeful vision of urbanization as a means to Dalit liberation, Indian cities have yet to fully realize this potential. While the shift to urban life has altered some aspects of caste oppression, new forms of discrimination have emerged and persisted, perpetuated by language, state policies, and institutional biases. This enduring struggle highlights the imperative of ongoing initiatives to combat caste-based discrimination and foster a more inclusive and equitable urban landscape in India.
A Reformed UNSC is not Possible Without India as a Permanent Member

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At a time when India is seriously advocating structural and functional reforms in the United Nations, the global forum’s president, Dennis Francis, has expressed optimism about India’s potential to secure a permanent seat on the UN Security Council.
Context:
- Amid India's active promotion of structural and functional reforms within the United Nations, Dennis Francis, the president of the global forum, has voiced optimism regarding India's ability to secure a permanent seat on the UN Security Council.
- The US and other Western countries sound extremely hollow when they pontificate on strengthening democracy and the fight against terrorism even as they keep India out of P5.
What is P5 Nations in the United Nations?
- P5 refers to the Permanent Five or Permanent Members of the United Nations Security Council.
- These are the five countries that have a permanent seat on the Security Council, granting them significant power within the UN.
The P5 members are:
-
- China
- France
- Russia
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Most of these countries were major victors of World War II and were seen as key players in maintaining international peace and security.
- They hold a special privilege within the Security Council: the right to veto any resolution.
- This means any one of these countries can single-handedly block a resolution, regardless of how many other countries support it.
- The P5's power and influence is a subject of some debate. Some argue that it's necessary to maintain stability, while others believe it gives these countries too much control and hinders the UN's effectiveness.
Urgent Need for Overhauling the United Nations (UN):
- Addressing the 76th UNGA in 2021, the Prime Minister of India underscored the imperative for 'comprehensive UN reforms,' stressing that 'outmoded structures' are inadequate to tackle contemporary challenges.
- Issues such as climate change, counterterrorism efforts, and the attainment of sustainable development goals (SDGs) were not prioritized when the UN was established seven decades ago.
- Today, they demand urgent attention.
- The aftermath of World War 2 has spawned numerous conflicts that persist, undermining global peace and economic advancement.
- The Covid-19 pandemic has laid bare the fragility of the world's healthcare systems.
- In today's multipolar world, the UN's polarized and antiquated structure is ill-suited to meet the demands of global governance.
- Cooperation among nations is essential to prevent the abuse of selective veto power by members pursuing hegemonic agendas.
Inconsistencies in Global Perceptions of India's UNSC Candidacy:
- In 2023, as India's G20 presidency drew to a close, the country's foreign minister noted a positive international reception to India's bid for a permanent seat on the UNSC.
- During bilateral discussions between the Prime Minister of India and the President of the USA, a joint statement emphasized India's stance on the need for a more inclusive and representative global governance structure through UN Security Council reform.
- In the same statement, the US expressed support for India's candidacy for a non-permanent seat on the UNSC for the term 2028-2029.
- Beyond the US, other voices echo the call for expanding non-permanent UNSC membership.
- The Uniting for Consensus (UFC) group, comprising twelve nations, advocates for increasing the number of non-permanent elected UNSC members from 15 to 26.
- Formed in 1990, the UFC opposes creating new permanent national seats, arguing that the current P5 arrangement stems from post-World War 2 circumstances, and creating additional privileged positions would be detrimental to UN membership's general interests.
- Critics point out the inconsistency of Western nations, notably the US, a permanent UNSC member, advocating for democracy and counterterrorism while simultaneously excluding India, one of the oldest UN members and the largest democracy, from the P5.
- China presents the primary obstacle to India's pursuit of a permanent UNSC seat.
China's Influence on UNSC Reform Efforts:
- Italy-China Collaboration within UFC: In 2023, the Deputy Prime Minister of Italy engaged in discussions with his Chinese counterpart, focusing on bilateral agreements and the situation in Ukraine.
- During this exchange, the Deputy Prime Minister of Italy commended the productive and consistent cooperation between China and Italy concerning UNSC reform, particularly their coordination within the Uniting for Consensus (UFC) group, where China holds an observer status.
- The presence of China as an observer suggests dim prospects for those advocating genuine reforms and expansion of the P5.
- China's Opposition to the G4 Group: Also in 2023, the G4 Group, consisting of India, Brazil, Japan, and Germany, convened during the 78th UNGA to deliberate on the UN reform process, particularly focusing on expanding the P5.
- Their objective is to modernize the UN's structure, which has its roots in the aftermath of World War 2.
- However, opposition from China, Russia, and South Korea regarding Japan's participation in the G4 due to historical issues stemming from World War 2 has caused friction and disagreement among the countries involved.
- Acknowledging India's Role: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru played a pivotal role in advocating for China's inclusion as a permanent member of the UN Security Council. Notably, both the US and the Soviet Union informally offered India the UNSC seat in the early 1950s.
- Nehru emphasized China's significance within the framework of his foreign policy.
- However, China's actions in Tibet and its conflict with India in 1962 shattered Nehru's perception of China's global role.
- India now stresses the importance of resolving issues such as Tibet and territories like Xinjiang and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- As a permanent UNSC member, China should remember the circumstances that led to its membership and acknowledge its responsibilities to India.
Conclusion
The international community must acknowledge that without comprehensive restructuring and democratization, untethered from its historical constraints, the United Nations (UN) will struggle to address the complexities of contemporary geopolitics and foster genuine multilateralism. Without these reforms, the aspirations for peace and prosperity will remain elusive. What's urgently required is a revamped, credible, and inclusive UN 2.0 that can effectively safeguard global peace and security.
United Nations Security Council:
- The Security Council has primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security.
- It has 15 Members, and each Member has one vote.
- Under the Charter of the United Nations, all Member States are obligated to comply with Council decisions.
- The Security Council takes the lead in determining the existence of a threat to the peace or act of aggression.
- It calls upon the parties to a dispute to settle it by peaceful means and recommends methods of adjustment or terms of settlement.
- In some cases, the Security Council can resort to imposing sanctions or even authorizing the use of force to maintain or restore international peace and security.
A Battle to Save Ladakh, and All of Humanity

- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
When climate activist Sonam Wangchuk took the stage in Leh, Ladakh recently, addressing a gathering of 30,000 individuals, his announcement of a 21-day climate fast resonated not only with the people of Ladakh but also with a global audience.
Context:
- The Himalayan region, situated between India's neighbors Pakistan and China, encompasses Ladakh, where 97% of the population comprises indigenous tribes whose livelihoods primarily depend on agriculture and animal husbandry.
- Despite its breathtaking beauty, this region grapples with various challenges, including the adverse effects of climate change, border tensions, and a surge in large-scale infrastructure projects.
- As climate activist Sonam Wangchuk leads protests and fasts, it becomes imperative to grasp the broader context of the Himalayan ecosystem's vulnerability.
The Climate Change Challenge in the Himalayan Region:
- Extreme Weather Events: Climate change manifests in more frequent and severe weather phenomena like heavy rainfall, cloudbursts, and flash floods.
- These events trigger landslides, wreaking havoc on mountain communities by damaging infrastructure, crops, and property, and endangering lives.
- Shifts in Monsoon Patterns: The region heavily relies on monsoon rains for agriculture and water supply.
- Climate change-induced alterations in monsoon patterns disrupt rainfall timing, intensity, and distribution, jeopardizing agricultural cycles and economic stability.
- Temperature Rise: Elevated temperatures impact both mountain and downstream ecosystems.
- Snowmelt patterns alter, local biodiversity faces disturbance, and traditional farming and animal husbandry practices suffer.
- Melting Glaciers: The Himalayas, often dubbed the Third Pole, harbor approximately 15,000 glaciers crucial to regional hydrology.
- These glaciers feed vital rivers like the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra, serving as lifelines for millions downstream.
- However, accelerated glacier melt due to global warming poses threats such as rising river levels, heightened flood risks, and potential water scarcity.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The Himalayan region hosts diverse flora and fauna, including many endemic species.
- Climate change threatens this unique biodiversity through habitat loss, altered migration routes, and ecosystem stress.
- Livelihood Impacts: Indigenous tribes and rural communities depend on farming and animal husbandry.
- Climate change-induced disruptions, such as erratic weather and natural disasters, challenge their traditional livelihoods.
National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem (NMSHE):
- The National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem (NMSHE) is one of the eight missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
- NMSHE is a multi-pronged, cross-cutting mission across various sectors.
- It contributes to the sustainable development of the country by enhancing the understanding of climate change, its likely impacts, and adaptation actions required for the Himalayas- a region on which a significant proportion of India’s population depends for sustenance.
- NMSHE seeks to facilitate the formulation of appropriate policy measures and time-bound action programs to sustain ecological resilience and ensure the continued provisions of key ecosystem services in the Himalayas.
- NMSHE intends to evolve suitable management and policy measures for sustaining and safeguarding the Himalayan ecosystem along with developing capacities at the national level to continuously assess its health status.
- Recognizing the importance of scientific and technological inputs required for sustaining the fragile Himalayan Ecosystem, the Ministry of Science and Technology has been given the nodal responsibility of coordinating this mission.
- However, the mission involves valuable cooperation of the Indian Himalayan States, the Planning Commission, and the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change to achieve its goals.
NMSHE's Role in Preserving the Himalayan Region:
- Accelerated Infrastructure Development: Since Ladakh transitioned to a Union Territory, numerous large-scale infrastructure projects have been rapidly implemented, including road expansions, bridge constructions, tunnel installations, railway lines, and solar energy initiatives.
- These endeavors, driven by entities such as the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) and the National Highways & Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd. (NHIDCL), focus on promoting tourism and industrial growth.
- Oversight of Previous Disasters: Despite past calamities in the Himalayan region, such as the catastrophic 2013 Kedarnath floods, and more recent incidents like the 2023 Joshimath disaster and the Silkyara tunnel collapse, there appears to be minimal reflection on previous warnings.
- Expert committees have advocated for limitations on pilgrim numbers and constraints on hydroelectric projects in ecologically fragile areas, but these recommendations have often been disregarded.
- Insufficient Attention to Concerns: Climate change activists have raised concerns about the inadequate consideration given to their suggestions, with little to no scrutiny conducted before approving multi-crore infrastructure projects.
- Worries regarding risk assessment, safety protocols, and geological evaluations seem to be overlooked in the pursuit of rapid development.
How to preserve the Himalayan Ecosystem Safe?
- Sustainable Development Practices: Conduct comprehensive environmental impact assessments before embarking on development projects to gauge potential ecosystem repercussions.
- Design projects with a focus on minimizing environmental harm and adhering to sustainability standards.
- Implement infrastructure projects with measures to reduce environmental disruption, such as using sustainable materials and employing low-impact construction methods.
- Focused Policies on Biodiversity Conservation: Expand and fortify protected areas like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries to safeguard the region's diverse flora and fauna.
- Establish and maintain wildlife corridors to facilitate safe animal migration and preserve genetic diversity, thus mitigating the risk of species extinction.
- Community Involvement: Integrate traditional knowledge and practices of local communities into conservation initiatives to ensure cultural relevance and long-term sustainability.
- Empower local communities to actively participate in conservation efforts, fostering greater engagement and ownership over preservation endeavors.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Implement strategies to curb greenhouse gas emissions, such as promoting renewable energy sources and combating deforestation, to mitigate climate change impacts.
- Support adaptation measures for local communities, including crop diversification and enhanced water management, to help them cope with evolving climate conditions.
- Research and Monitoring: Continuously monitor the Himalayan ecosystem, including its flora, fauna, and physical processes, to detect early signs of ecological changes and inform conservation strategies.
- Encourage interdisciplinary research on the region's ecology, climate, and geology to deepen understanding of ecosystem challenges and identify effective solutions.
Conclusion
It's crucial to recognize that while development is vital for economic progress, it should not be pursued at the cost of environmental harm and human well-being. The Himalayan region, renowned for its unparalleled biodiversity and rich cultural heritage, warrants thoughtful preservation and conservation efforts. It is incumbent upon all stakeholders to collectively assume the responsibility of safeguarding the future of this ecologically and culturally significant area.
The Advent Of A Holistic Approach To 'One Health'

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ‘National One Health Mission’ is the result of the recognition that only a coordinated approach will ensure a better response to disease outbreaks.
Context:
- In recent times, the intricate relationship among humans, animals, and the environment has gained significant attention, especially in light of the emergence of pandemics like COVID-19.
- This interconnectedness is underscored by the impact of diseases such as lumpy skin disease, which affects both livestock productivity and trade, bridging the gap between domesticated and wild animal health.
- Addressing these complex challenges, the Indian government has launched the 'National One Health Mission,' aimed at comprehensively tackling the interlinked domains of human, animal, and environmental health.
What is One Health?
- One Health is an integrating idea that brings different sectors together to solve the health, productivity, and conservation challenges and has major implications for India.
- It is a global topic and was endorsed during India's presidency of the G-20.
- India with its diverse wildlife, one of the largest livestock populations, and high density of human population, carries heightened risks for inter-compartmental spread of diseases.
- The Covid pandemic, recent outbreaks of Lumpy Skin Disease in cattle, and the constant threat of Avian Influenza show that it is not just about addressing diseases from the human health point of view (zoonosis) but we need to address the livestock and wildlife aspects.
- This also opens opportunities for leveraging the complementarity and strengths that are inherent in each sector and devising integrated, robust, and agile response systems.
What is the National One Health Mission?
- Initiated in July 2022, the National One Health Mission represents a comprehensive endeavor endorsed by the Prime Minister's Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC).
- With the participation of 13 ministries and departments, including the Department of Science and Technology, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), among others, this mission adopts a holistic approach towards One Health and pandemic preparedness.
- A pivotal achievement within this mission is the establishment of the National Institute for One Health in Nagpur.
- Functioning as the central coordinating body for both national and international One Health endeavors, this institute marks a significant milestone in the mission's implementation.
- On December 11, 2022, the foundation stone of the institute was laid by the Prime Minister, symbolizing the commitment to advancing the principles of One Health and enhancing pandemic preparedness.
Objectives and Approaches of The National One Health Mission:
- Seamless Surveillance Integration: The mission endeavors to establish an integrated surveillance system that seamlessly monitors health indicators across human, animal, and environmental sectors.
- By amalgamating data from these domains, it can swiftly identify potential health hazards and respond proactively.
- Coordinated Outbreak Management: Recognizing the necessity of a unified approach in outbreak response, the mission aims to institute protocols and frameworks facilitating collaboration among various sectors.
- This coordinated effort enables effective resource and information sharing to mitigate the impact of diseases affecting multiple domains.
- Collaborative Research and Development: Through fostering collaboration among scientific research institutions and government bodies, the mission fosters the development of innovative solutions for emerging health threats.
- This includes the creation of vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics critical for pandemic preparedness and response.
- Seamless Information Exchange: Effective communication and data sharing are imperative for a unified One Health approach.
- The mission endeavors to facilitate seamless information exchange between sectors and stakeholders, ensuring timely and informed actions.
- Preparedness for Future Pandemics: Building on past pandemic experiences, the mission seeks to develop strategies and frameworks to enhance the country's readiness for future health crises.
- This involves proactive planning for potential pandemics and emerging diseases such as avian influenza or Nipah virus.
- Resource Optimization: By leveraging the resources and expertise of multiple sectors and stakeholders, the mission aims to optimize resource utilization, including laboratory infrastructure, healthcare facilities, and scientific research capabilities.
- This collaborative effort enhances efficiency and cost-effectiveness in addressing health threats.
- Public Health Education and Awareness: The mission includes public education initiatives to raise awareness about the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
- Promoting an understanding of One Health principles encourages healthier behaviors and better preparedness for health emergencies.
Critical enabling activities of the One Health Mission:
- The outcomes of the One Health Mission will be supported by critical enabling initiatives.
- Many of these initiatives are ongoing and will be strengthened under the mission and several new activities that will facilitate the goals of the mission will be undertaken.?
Leveraging Laboratory Networks and Technological Integration in India's National One Health Mission:
- Establishment of High-Risk Pathogen Laboratories: The mission is dedicated to creating a nationwide network of laboratories equipped to handle high-risk pathogens classified under Biosafety Levels 3 and 4.
- These facilities provide a secure environment for studying infectious agents with pandemic potential.
- Departmental Collaboration: By consolidating laboratories managed by diverse departments, the mission aims to foster a cohesive network capable of coordinating resources and expertise across sectors.
- This integration enhances disease outbreak response, irrespective of its origin in human, animal, or environmental realms.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Pooling laboratory resources within a unified network ensures efficient utilization of infrastructure and personnel.
- This collaborative approach enables swift responses to outbreaks and other health crises, maximizing available resources.
- Interdisciplinary Research and Analysis: Encouraging collaboration among experts from various disciplines—including medicine, veterinary science, environmental science, and public health—the mission promotes comprehensive research and analysis of health threats across multiple sectors.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Harnessing the power of AI and machine learning, the mission enhances epidemiological capabilities by analyzing vast datasets to detect patterns, trends, and potential health risks.
- This technology enables timely interventions and enhances overall preparedness.
- Utilization of Disease Modelling: Advanced modeling techniques are employed to forecast disease spread and potential outbreaks.
- These models facilitate targeted measures for disease control and prevention.
- Expansion of Genomic Surveillance: The mission broadens genomic surveillance efforts beyond COVID-19, encompassing other infectious diseases.
- By analyzing genetic material from diverse sources like wastewater and animal congregations, scientists can monitor disease prevalence and identify emerging threats.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Emphasizing the importance of skill enhancement, the mission prioritizes capacity building across sectors in epidemiology, data analytics, and laboratory management.
- Training programs ensure that professionals possess the necessary skills to effectively utilize new technologies and methodologies.
Conclusion
The concept of One Health transcends mere disease management, encompassing broader realms such as antimicrobial resistance, food safety, plant diseases, and the consequential impacts of climate change. Addressing intersectoral issues like One Health necessitates active involvement not only from diverse governmental agencies but also from non-governmental organizations, academia, the private sector, and ordinary citizens. By adopting an actionable framework rooted in collaboration and comprehensive engagement, we can advance toward the overarching objectives of 'One Earth, One Health' and 'Health for All.
Climate Crisis is Not Gender Neutral

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The climate crisis is far from “gender neutral” as women and men are affected differently by weather and climate and therefore need gender-sensitive information and services.
Context:
- As the climate crisis intensifies, its disproportionate impact on women and girls becomes more evident, particularly in poverty-stricken regions.
- This calls for a critical examination of the gender dimensions of climate change, recognizing women's increased vulnerabilities and the importance of incorporating gender perspectives in climate action strategies.
- By doing so, we can develop effective solutions that address the unique challenges faced by women, ensuring a more equitable and sustainable approach to climate change mitigation and adaptation.
How Does Climate Change Impact Women?
- Rural Livelihood Dependence on Agriculture: In many regions, particularly rural India, women play a central role in agricultural activities, forming the backbone of their communities' livelihoods.
- However, the effects of climate change, such as erratic rainfall, droughts, and floods, pose significant threats to crop yields, directly impacting food security and income for these women.
- Compounded by limited access to essential resources like land, credit, and technology, women face heightened vulnerabilities in navigating climate-related risks.
- Health Risks Amplified by Climate Hazards: Women's health is uniquely susceptible to the challenges posed by climate change.
- For instance, prolonged heatwaves increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, including preterm birth and eclampsia.
- Moreover, exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollution exacerbates respiratory and cardiovascular diseases among women and unborn children, compromising their well-being.
- Gender Dynamics in Extreme Weather Events: The rise in the frequency of extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and cyclones, has profound implications, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Reports highlight that a significant portion of Indian districts are susceptible to such disasters, placing women and children at heightened risk.
- Emerging studies underscore a concerning correlation between these natural calamities and incidents of gender-based violence against women.
- Additionally, disruptions in water access due to climate-induced changes affect women's ability to engage in productive activities and access healthcare, intensifying their workload and compromising their overall welfare.
- Nutritional Challenges and Early Marriage: In regions prone to drought, women and girls face heightened risks of undernutrition due to food insecurity.
- Data indicates that women residing in these areas are more likely to experience underweight conditions and are at a higher risk of entering early marriages, perpetuating cycles of poverty and gender inequality.
How to Empower Women in Climate Action?
- Rich Tradition of Environmental Stewardship: Throughout history, women have been integral to environmental conservation efforts.
- Across various communities, they serve as primary custodians of natural resources, managing land, water, and forests with a deep-rooted understanding of sustainability.
- Their traditional knowledge and practices are invaluable assets for fostering biodiversity conservation and promoting climate-resilient agricultural techniques.
- Boosting Agricultural Productivity and Food Security: Providing women farmers with equitable access to resources such as land, credit, and agricultural inputs unleashes their potential to enhance agricultural productivity and adapt to climate change.
- Research indicates that closing the gender gap in agriculture could significantly increase crop yields and bolster food security.
- Women's innate connection to smallholder farming systems enables them to innovate with cost-effective, environmentally friendly farming methods, thereby fostering resilience in agricultural practices.
- Key Players in Local Adaptation Strategies: Women are pivotal to the success of community-based adaptation efforts, which prioritize building resilience to climate change at the grassroots level.
- Through women's groups and collectives like Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), communities mobilize, share knowledge, and implement adaptation measures.
- These grassroots initiatives empower women to advocate for their rights in decision-making processes concerning natural resource management and climate resilience.
- Inspiring Role Models and Catalysts for Change: Women leaders in climate action serve as inspirations and role models, paving the way for future generations of environmentalists and activists.
- Their prominence in climate solutions not only challenges gender norms but also encourages greater participation of women and girls in STEM fields and environmental leadership roles.
- By highlighting women's contributions to climate action, these role models empower others to pursue careers and opportunities in climate science, policy, and advocacy, fostering a more inclusive and impactful approach to addressing climate change.
Action Needed to Address the Gender Implications of Climate Change:
- Immediate Protection Against Health Risks: Swift action is imperative to safeguard vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women, outdoor laborers, children, and the elderly, from health risks exacerbated by extreme weather events like heat waves.
- Local authorities must develop and implement comprehensive heatwave response plans, incorporating early warning systems, establishing cooling centers, and adapting work and school schedules to mitigate heat-related illnesses and fatalities.
- Improved Access to Safe Drinking Water: Climate-induced disruptions to water sources escalate water scarcity and endanger public health.
- Immediate interventions are essential to enhance access to safe drinking water, particularly for women and girls responsible for water collection in many communities.
- Investments in water infrastructure, rainwater harvesting systems, and water purification technologies are vital to alleviate the impacts of water scarcity on vulnerable populations.
- Climate-Resilient Urban Planning: Urban areas face escalating vulnerabilities to climate-related hazards, including heatwaves, flooding, and air pollution.
- Urban planning strategies emphasizing green infrastructure—such as parks, green roofs, and tree-lined streets—can mitigate the urban heat island effect and minimize exposure to extreme temperatures.
- Moreover, measures to enhance air quality, like reducing vehicular emissions and promoting clean energy technologies, are crucial for safeguarding public health, particularly for women and children susceptible to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Community-Centered Adaptation Efforts: Community-based adaptation initiatives, engaging local communities, including women's groups and grassroots organizations, are pivotal in bolstering resilience to climate change at the grassroots level.
- These initiatives should prioritize the needs and aspirations of women and marginalized groups, empowering them in decision-making processes regarding adaptation planning and implementation.
- Investments in building the capacity of local institutions and community leaders can amplify the efficacy and sustainability of adaptation endeavors.
- Gender-Inclusive Climate Policies: National and sub-national climate policies must integrate gender-responsive approaches tailored to the distinct needs and priorities of women and girls.
- Recognizing women as agents of change and empowering their participation in climate decision-making at all levels is essential.
- Gender mainstreaming in climate policies ensures inclusivity, equity, and effectiveness in tackling the underlying drivers of vulnerability and inequality.
Conclusion
The disparities and vulnerabilities experienced by women and girls underscore the urgent need for inclusive and gender-responsive strategies in climate adaptation and mitigation endeavors.
By empowering women, we not only bolster resilience but also unlock innovative solutions crucial for combating the climate crisis. Thus, the integration of gender perspectives into climate action plans is imperative for forging a sustainable and equitable future for all
Indian Aviation, A Case of Air Safety at a Discount

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government introduced revised Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) Regulations, set to be implemented on June 1, 2024, but faced opposition from airline owners, prompting the DGCA to indefinitely defer the deadline.
Context:
- The aviation sector in India faces a pivotal moment, balancing rapid growth with pressing safety issues.
- The remarks from the Union Minister and the DGCA, highlighting safety as paramount, seem at odds with ongoing safety lapses.
- Given the significance of safety measures, it's imperative to examine safety protocols, parameters, challenges, and regulatory shortcomings.
Key Provisions in the Revised FDTL Regulations of January 2024:
- Extended Weekly Rest Periods for flight crew: The revised regulations mandate increased weekly rest periods from 36 hours to 48 hours for flight crew, thus ensuring sufficient time for recovery from cumulative fatigue.
- Night Duty: The definition of night has been amended, and it now covers the period of 0000-0600 hours in the revised regulations vis-à-vis the period of 0000-0500 hours under the previous regulations.
- This enhancement of one hour during the early morning will ensure adequate rest and also align the night duty period, which encompasses the Window of Circadian Low (WOCL) from 0200-0600 hours, i.e. the time during which the circadian body clock cycle is at its lowest in terms of alertness.
- Maximum Flight Time, Maximum Flight Duty Periods, and Number of Landings during Night: The revised regulations have taken into consideration different types of operations across time zones.
- The maximum flight time & maximum flight duty period for flight operations encroaching night have been restricted to 8 hours flight time & 10 hours flight duty period, respectively, and the number of landings has been limited to only two landings as compared to the maximum permissible 6 landings under previous regulations during night operations, thus enhancing flight safety.
- Quarterly fatigue reports: In addition, DGCA has mandated that all airline operators submit quarterly fatigue reports after analysis, including the Action Taken on such reports.
- Further, it has been stipulated that the fatigue reports shall follow a non-punitive and confidentiality policy.
What is the Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS)?
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is preparing to introduce a novel approach, known as the Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS), to handle fatigue among flight crew.
- The recent revision of Flight Duty Time Limitation (FDTL) regulations marks the initial phase of FRMS implementation in India.
- FRMS represents a data-driven strategy aimed at enhancing the monitoring and documentation of flight crew fatigue.
- The successful integration of FRMS hinges upon collaborative efforts from various stakeholders within the aviation sector, including regulators, airline operators, and flight crew, who must demonstrate readiness to embrace this new framework.
- This transition necessitates rigorous oversight, meticulous record-keeping, and comprehensive reporting to uphold compliance with the FRMS framework.
The Imperative for Implementing Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS):
- The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has mandated the adoption of the Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS) to address safety concerns.
- Extensive analysis of accidents and serious incidents attributed to fatigue has underscored the critical role of adequate rest and sleep deprivation in impairing pilots' reaction times.
- Countries like Japan, Singapore, and the United Kingdom prioritize flight crew fatigue management and emphasize regular rest periods to mitigate cumulative fatigue.
- These nations implement a system where pilots receive two days off each week to reset their circadian rhythm and recuperate from prolonged flying hours, with additional rest upon returning from long-haul flights.
- In contrast, existing Flight Duty Time Limitation (FDTL) regulations afford pilots only 30 days of annual leave and one day off per week, which pales in comparison to the leisure time granted to ground personnel.
- Airline schedules often overlook human performance limitations, neglecting the fact that pilots, like any other individuals, require time with their families.
- Thus, providing two days off per week is essential for maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Other concerns in the aviation sector:
- Runway End Safety Area (RESA): The absence of RESA at Kozhikode's Karipur airport has sparked warnings from the Minister for Civil Aviation about compromised passenger safety.
- Recommended by the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau following a 2020 air crash, the Ministry has threatened to curtail runway length unless land is handed over to the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- As of April 2024, no land has been provided, and flights remain unrestricted.
- Utilization of Pilots and Adherence to Safety Regulations: While the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) sets minimum crew requirements, airlines can opt for lower flight time and duty hours.
- Large aircraft orders often adhere to DGCA Civil Aviation Requirements for scheduled transport, which only specifies the minimum crew requirement.
- The crew requirement would more than double under the Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) CAR, but the DGCA does not monitor crew numbers based on these requirements.
- This is primarily due to the potential impact of positive media coverage and the reputation of India's aviation industry.
- Financial Stress on Pilots: Financial stress has been identified as a contributing factor to aircraft crashes, such as the Silkair crash in 1997 and the Egyptair crash in 1999.
- However, authorities in India often fail to adequately address the dangers of financial stress among pilots.
- A prime example is the recent merger of Vistara with Air India, where Vistara copilots faced a significant pay cut upon losing their command position, leading to increased financial strain.
Way Forward:
- Implementing ICAO Annex 1 Standards: A crucial step towards a more robust aviation sector involves adopting the International Civil Aviation Organization's (ICAO) Annex 1 standards, facilitating the recognition of foreign licenses and issuance of Indian licenses based on specific criteria.
- This streamlined process can attract experienced pilots, addressing shortages and elevating workforce competency.
- Harnessing Retired Pilots' Expertise: Utilizing retired pilots in training roles, particularly within simulator training centers, allows India to tap into their valuable experience and knowledge to mentor the next generation of aviators.
- By addressing training gaps and bolstering proficiency standards, this initiative enhances safety outcomes while supporting the professional growth of aspiring pilots.
- Strengthening Monitoring and Compliance: Regulatory bodies, such as the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), should fortify their monitoring mechanisms to ensure adherence to Flight Duty Time Limitations (FDTL) regulations and crew staffing requirements.
- This vigilance aids in identifying instances of non-compliance, mitigating fatigue-related risks, and fostering collaboration with airlines to manage crew resources effectively.
- Cultivating a Safety-Oriented Culture: Promoting a safety culture within the aviation industry is vital for achieving sustainable safety outcomes.
- Stakeholders should prioritize safety initiatives, invest in training programs, and encourage open communication channels for reporting concerns.
- This collaborative approach nurtures a safety-focused environment that benefits all parties and strengthens the overall aviation landscape.
Conclusion
The postponement of fatigue management regulations underscores the complexities of balancing safety concerns with commercial interests within India's aviation industry. To safeguard both flight safety and crew welfare, regulatory authorities must prioritize the implementation of rigorous fatigue management protocols and withstand industry pressures that jeopardize safety standards. It is only through a unified commitment to rectifying regulatory deficiencies and cultivating a culture of safety that India's aviation sector can maintain the utmost standards of flight safety and operational proficiency.
Shaping India’s path to inclusive health care

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
World Health Day, which is observed every year on April 7, unites us around health equity, an essential topic at the heart of global health and justice.
Context:
- World Health Day, commemorated every April 7th, underscores the significance of health equity, acknowledged as a basic human entitlement by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Hence, it is imperative to delve into the theme "My Health, My Right," delving into the hurdles and remedies in attaining health equity in India.
- As a country contending with multifaceted socioeconomic inequalities in healthcare access and results, this exploration becomes pivotal.
What is Health Equity?
- Health equity, as outlined by the WHO, embodies the principle that every person should have the opportunity to attain optimal health, irrespective of their social, economic, or environmental circumstances.
- It extends beyond mere healthcare access, addressing underlying factors such as poverty, discrimination, and resource imbalances.
- Considering Diverse Health Outcomes: A core tenet of health equity acknowledges that health results stem from a multifaceted interplay of elements, encompassing social, economic, and environmental determinants.
- Individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds often encounter obstacles like financial constraints, transportation limitations, and sparse healthcare facilities.
- The Vitality of Health Equity: Health equity holds paramount importance not only ethically but also from a public health standpoint.
- Research consistently indicates that societies fostering greater health equity typically enjoy superior health outcomes, marked by lower morbidity and mortality rates, reduced healthcare expenditures, and heightened life expectancy.
- Conversely, persistent health disparities may precipitate societal unrest, economic strains, and a squandered human potential.
Health Equity Challenges in India:
- Addressing Urban-Rural Disparities: India contends with pronounced healthcare inequalities between urban and rural regions, where urban areas typically boast superior healthcare infrastructure and services, while rural communities encounter obstacles like limited access to facilities, healthcare professionals, and infrastructure, resulting in inferior health outcomes compared to their urban counterparts.
- Navigating Overcrowded Urban Slums: Urban slums present profound challenges characterized by extreme poverty, overcrowding, unsanitary conditions, and inadequate access to clean water, fostering the spread of infectious diseases and escalating morbidity and mortality rates.
- Moreover, deficient healthcare infrastructure exacerbates health disparities as residents grapple with limited access to essential services.
- Tackling Socioeconomic and Caste Disparities: Marginalized groups, including Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and economically disadvantaged populations, confront elevated rates of illness and death due to restricted healthcare access, diminished health literacy, and societal prejudice.
- These disparities intertwine with broader determinants like education, employment, and housing, perpetuating disparities in health outcomes.
- Confronting the Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular ailments, diabetes, and cancer pose a mounting challenge to health equity in India, constituting a substantial portion of the disease burden.
- However, marginalized communities often face barriers to accessing preventive measures and NCD treatment, amplifying health inequalities and exacerbating existing socioeconomic gaps.
- Navigating Shortages in Healthcare Personnel: A severe shortage of healthcare professionals, with only 0.8 doctors per 1,000 individuals according to WHO data, exacerbates health challenges, particularly in rural areas where access to primary care is limited, resulting in delayed diagnoses, substandard treatment, and compromised health outcomes.
- Confronting Infrastructure and Resource Limitations: Inadequate healthcare infrastructure, insufficient funding, and resource limitations pose formidable obstacles to health equity in India, with many public facilities lacking essential equipment, medications, and skilled personnel.
- Furthermore, the unequal distribution of resources aggravates urban-rural healthcare disparities, exacerbating inequities in access to quality healthcare services.
Strategies and Measures to Advance Health Equity in India:
- Enhancing Primary Healthcare Services: A pivotal approach to fostering health equity in India involves bolstering primary healthcare provisions, especially in rural and marginalized regions.
- This entails augmenting the accessibility and availability of primary care facilities, fortifying the skills and capabilities of frontline healthcare personnel, and ensuring the delivery of essential health services encompassing preventive care, maternal and child healthcare, and management of chronic ailments.
- Initiatives such as the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) and the National Urban Health Mission (NUHM) strive to extend primary healthcare access and mitigate healthcare disparities between urban and rural locales.
- Advocating for Universal Health Coverage: Universal health coverage (UHC) stands as a cornerstone in ensuring equitable access to indispensable healthcare services devoid of financial strains.
- Endeavors like Ayushman Bharat, India's flagship health insurance program, aspire to furnish financial safeguarding to vulnerable segments by offering comprehensive coverage for hospitalization expenses.
- By broadening the reach of quality healthcare services and alleviating out-of-pocket costs, UHC endeavors to redress discrepancies in healthcare accessibility and enhance health outcomes for all citizens.
- Targeting Social Determinants of Health: Attaining health equity mandates a multifaceted approach that transcends healthcare interventions to address the underlying social determinants of health, encompassing poverty, education, housing, and employment.
- Initiatives geared towards poverty mitigation, augmenting educational and sanitation access, and fostering livelihood opportunities can wield a transformative impact on health outcomes and help ameliorate health disparities.
- Programs like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) furnish rural households with employment prospects, thereby fostering enhanced socioeconomic circumstances and superior health outcomes.
- Empowering through Health Literacy: Elevating health literacy assumes paramount significance in empowering individuals to make informed health decisions and pursue equitable healthcare access.
- Integration of health education within prevailing healthcare schemes can heighten public consciousness and advocate for preventive healthcare practices.
- Fostering Collaborative Endeavors: Efficacious collaboration among governmental bodies, civil society, healthcare providers, and international entities constitutes a linchpin in addressing health inequities.
- By harnessing their respective competencies and resources, these stakeholders can conceptualize culturally sensitive health initiatives tailored to the distinctive requisites of diverse communities.
Conclusion
Realizing health equity in India necessitates coordinated endeavors spanning various sectors and involving diverse stakeholders. Through targeted interventions addressing socioeconomic health determinants, bolstering healthcare infrastructure, and fostering collaborative alliances, India can progress towards a future where equitable access to superior healthcare becomes a universal norm. The pursuit of health equity transcends moral imperatives, emerging as a pivotal prerequisite for fostering sustainable development and societal advancement.
India Planning to Adopt ‘Living Wage’ Instead of ‘Minimum Wage’ by 2025

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India is reportedly poised to replace the minimum wage with the living wage system, with the transition anticipated to occur by next year.
Context:
- India is reportedly considering shifting from the minimum wage to the living wage by 2025.
- India has approached the International Labour Organization (ILO) to help it chalk out a framework to assess and operationalize the living wages.
- India has asked the ILO to help it in “capacity building, systemic collection of data and evidence of the positive economic outcomes resulting from the implementation of living wages”.
- Earlier in March, the United Nations agency forged an agreement on the living wage, which was also endorsed by its governing body.
- India, a founding member of the ILO and a permanent member of its governing body since 1922, passed the Code on Wages in 2019.
What is the Current Wage System in India?
- National Floor Level Minimum Wage (NFLMW): Established under the Code on Wages 2019, the NFLMW is determined by the government, requiring establishments to set minimum wages not below this level.
- Flexibility in Minimum Wage Standards: Section 5 of the Code on Wages 2019 prohibits employers from setting wages below the NFLMW, though states have the discretion to revise minimum wage rates as needed.
- Presently, the National Floor Wage stands at Rs 178 per day.
What’s a Living Wage?
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) defines the living wage as the level of remuneration “necessary to afford a decent standard of living for workers and their families, taking into account the country's circumstances and calculated for the work performed during the normal hours of work”.
- This decent standard of living includes being able to afford food, water, housing, education, healthcare, transportation, clothing, and other basic needs including a provision for contingencies, says the Global Living Wage Coalition.
- The goal of a living wage is to ensure the employees get an income enough for satisfactory living standards as well as reduce poverty.
What is Minimum Wage?
- Minimum wage refers to the legally mandated lowest level of compensation that employers must pay employees for their work over a specified period.
- While minimum wage endeavors to prevent low pay, living wage extends beyond by ensuring income is adequate to meet necessities like food, shelter, clothing, and other essentials, addressing the risk of workers falling below the poverty line despite earning minimum wages.
- In India, minimum wage calculation factors in variables such as the state of employment, the skill level of the worker, the nature of their job, and other pertinent factors.
Living Wage vs Minimum Wage:
- Definition: A living wage is the income required to meet basic needs and maintain a decent standard of living, while minimum wage is the lowest legally mandated compensation for workers.
- Purpose: A living wage seeks to address the risk of workers falling below the poverty line, while minimum wage aims to prevent low pay.
- Mandatory vs Voluntary: Minimum wages are legally required, whereas living wages are voluntary unless the government sets the minimum wage at the living wage level.
- Calculation: Living wages consider basic necessities and a decent standard of living, while minimum wages factor in variables like skill level, state of employment, and job nature.
Pros and Cons of Living Wages:
- Living wage is a divisive issue. Proponents of the living wage say people get paid more, leading to a rise in employee satisfaction.
- A boost in employee morale is likely to result in higher productivity.
- It also saves recruitment and training costs for companies as employee turnover falls.
- On the other hand, critics of the concept say companies may cut back on hiring if forced to pay increased wages, creating more job losses.
- Opponents also argue that imposing a living wage means creating a wage floor, which would hurt the economy by impacting businesses, especially those that cannot pay hiked salaries.
How Does Living Wage Benefit India?
- India has over 500 million (50-crore) workers, of which 90 percent are in the unorganized sector, noted ET.
- The national floor level minimum wage (NFLMW) – an amount below which no state government can fix the minimum wage – was Rs 178 per day or more depending on the location in 2023.
- This was set at Rs 176 per day in 2017 and has not been changed since then.
- Currently, some states pay workers in the unorganized sector even below the NFLMW.
- The Code on Wages, 2019 was passed by Parliament states that the minimum wage cannot be fixed below the national wage floor.
- However, this code, which is binding on all states, is yet to be implemented.
- If India replaces the minimum wages with living wages, workers are expected to earn more.
- According to the ILO, the living wage has to be calculated following its principles and wage-setting process.
Conclusion
India's pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030 hinges on strategic shifts, such as transitioning from minimum to living wages, to uplift millions from poverty while safeguarding their welfare. This is particularly pertinent against the backdrop of escalating income inequality, highlighting the imperative for a revamped wage system. As poverty rates decline yet inequality persists, a more equitable approach to wages becomes paramount, underscoring India's commitment to inclusive growth and social justice.
International Labor Organization (ILO):
- The International Labor Organization (ILO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations, founded in 1919 to promote social and economic justice through the establishment of international labor standards.
- The ILO operates with a unique tripartite structure, allowing governments, employers, and workers to engage in dialogue and decision-making on labor matters.
Key Roles and Functions:
- Setting International Standards: The ILO develops and adopts international labor standards in the form of conventions and recommendations, covering areas such as freedom of association, collective bargaining, child labor, forced labor, and non-discrimination.
- Technical Assistance and Capacity Building: The organization provides support to member states in enhancing their labor administration, labor inspection, employment policies, and social protection systems.
- Monitoring and Supervision: The ILO monitors the application of international labor standards in member states, offering guidance and assistance in their implementation.
- Research and Knowledge Sharing: The organization conducts research, collects data, and disseminates information on labor-related topics, facilitating evidence-based policy-making and dialogue.
- The ILO plays a critical role in promoting decent work, social justice, and labor rights worldwide, fostering cooperation among its 187 member states to address labor-related challenges and achieve sustainable development.
- The ILO headquarters are located in Geneva (Switzerland).
How the Government Can Generate Employment Through Universal Healthcare

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As India approaches the 2024 elections, highlighting healthcare as a strategic investment rather than a fiscal burden can drive employment generation, bolster economic growth, and foster sustainable development.
Context:
- With India gearing up for the upcoming general elections, recognizing healthcare as a crucial investment for national well-being and prosperity is essential.
- Despite its pivotal role, healthcare tends to be sidelined in political discussions, necessitating a shift in focus.
- Rather than perceiving healthcare as a financial burden, it should be considered a strategic investment.
- Embracing healthcare as an investment offers substantial returns, contributing to human capital development, economic progress, and sustainable development.
What is Universal Health Care (UHC)?
- Universal Health Care (UHC) embodies the principle that everyone should have access to quality healthcare regardless of financial situation.
- It is regarded as a fundamental measure for promoting human equity, security, and dignity.
- UHC has gained widespread acceptance as a primary goal of public policy globally, with numerous countries successfully implementing it, including wealthier nations and emerging economies like Brazil, China, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- World Health Organization (WHO) defines universal healthcare as “all people and communities can use the promotive, preventive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative health services they need, of sufficient quality to be effective, while also ensuring that the use of these services does not expose the user to financial hardship.”
Challenges in Implementing Universal Health Care (UHC):
- Inequitable Access to Health Insurance: Disparities in health insurance coverage persist, with the lowest wealth quintile and marginalized sections facing limited access to insurance, as indicated by NFHS-5 results.
- Lack of Financial Protection: Despite initiatives like Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, high out-of-pocket expenses, especially in urban areas, pose financial risks. NFHS data highlights significant disparities in expenditure across states.
- Inclusion and Exclusion Errors in Health Insurance Policies: Inaccuracies in health insurance policies, including PMJAY, lead to the inclusion of ineligible and exclusion of eligible households, affecting coverage effectiveness.
- Availability of Services: While PMJAY enlists hospitals, a significant portion is in the private for-profit sector, potentially limiting access to underserved areas.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Insufficient healthcare facilities, equipment, and medical supplies hinder UHC implementation, compounded by a shortage of specialists in CHCs.
- Poor Health Education: Limited awareness about preventive health measures contributes to preventable illnesses, emphasizing the need for improved health education and promotion.
Steps For Achieving Universal Health Care (UHC):
- Increase in Public Health Expenditure: Commitment to allocate 2.5% of GDP to health by 2025 is crucial.
- However, the current central budget allocation for 2024-25 falls short at 28%.
- Strategic Partnerships: The government must forge partnerships and incentivize the private sector to bridge healthcare gaps.
- Initiatives like Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) illustrate this collaborative approach, covering over 60 crore people.
- Reimbursement Rates Correction: Private sector participation is hindered by low reimbursement rates.
- Differential pricing based on clinical excellence and infrastructure investment can encourage participation.
- Infrastructure Development: Addressing the deficit of nearly 24 lakh hospital beds requires increased private sector investment, especially in tier 2 and 3 cities.
- National Priority Status for Healthcare: Designating healthcare as a national priority sector can unlock funding opportunities and incentives, fostering growth and development.
- Strengthening Primary Healthcare: Enhancing Health and Wellness Centers and including OPD care in health insurance coverage will improve health outcomes and reduce secondary and tertiary care burdens.
- Prevention and Control of NCDs: Prioritizing interventions at the primary healthcare level can significantly reduce the burden of non-communicable diseases, preventing complications and hospitalizations.
- Boosting Private Investment: Encourage and incentivize private sector investment in healthcare infrastructure, technology, and services to expand coverage and enhance healthcare accessibility and affordability for all citizens.
How Government can Generate Employment Through UHC in India?
Expanding the Healthcare Workforce: Universal healthcare will significantly increase the demand for healthcare professionals, creating millions of new jobs. This includes doctors, nurses, paramedics, technicians, pharmacists, and other support staff. The government can address this need by:
- Scaling Up Medical Education: Increased investment in medical colleges and nursing schools is crucial.
- This includes establishing new institutions, expanding existing ones, and introducing scholarship programs to attract talent.
- Standards for medical education must be maintained to ensure a high-quality workforce.
- Skill Development Initiatives: Developing a robust skill development ecosystem specific to healthcare is essential.
- This involves creating standardized training programs for various healthcare professions.
- Skill development should not be limited to clinical skills but also encompass areas like communication, empathy, and public health awareness.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Competitive salaries, loan repayment programs, and career progression opportunities can incentivize students to pursue healthcare careers.
- Additionally, considering the rural-urban divide, special incentives like higher pay and improved living conditions can attract healthcare professionals to serve in underserved areas.
Building a Robust Healthcare Infrastructure: Universal healthcare necessitates a well-developed healthcare infrastructure. This translates to significant job creation across various sectors:
- Infrastructure Development: Building new hospitals, clinics, diagnostic centers, and public health centers requires construction workers, engineers, architects, and technicians.
- Medical Equipment Manufacturing: Increased demand for medical equipment, from basic diagnostic tools to advanced technology, can incentivize local manufacturing.
- This can create numerous jobs in production, maintenance, and research & development.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Universal healthcare will significantly raise the demand for pharmaceuticals.
- This can boost domestic production, generating jobs in manufacturing, distribution, and research & development.
The Role of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs):
- The government cannot shoulder the entire responsibility alone. PPPs can play a vital role in expanding healthcare infrastructure and creating job opportunities:
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaboration with private hospitals and clinics can leverage existing infrastructure and expertise.
- The government can purchase services from the private sector, ensuring wider reach and quality care, while creating jobs within these institutions.
- Incentivizing Expansion: Tax breaks, subsidies, and streamlined licensing processes can incentivize private players to expand their facilities and hire more staff.
- This creates a multiplier effect, leading to job creation in construction, logistics, and other associated sectors.
Technology and its Role in Employment: Technology holds immense potential to improve healthcare delivery and create new job opportunities:
- Telehealth and Digital Health Records: Investment in telemedicine infrastructure and digital health records can create jobs in IT, data management, and cybersecurity.
- Additionally, telemedicine can bridge the gap in rural healthcare, requiring trained personnel to operate these services.
- Medical Informatics: The use of big data and analytics in healthcare will require skilled professionals to collect, analyze, and interpret data to improve healthcare delivery and outcomes.
Conclusion
Universal healthcare in India can be a transformative force, not just for public health, but also for the nation's economic landscape. By strategically investing in workforce development, fostering public-private partnerships, and embracing technological advancements, India can unlock a vast employment potential. This not only creates a win-win for job creation and healthcare access but also paves the way for a healthier and more prosperous future for all Indians.
India's Declining Fertility Rate: Unveiling Opportunities Amidst Change

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The projection by the UN Population Division is that India will have a population of close to 1.7 billion by 2065 before it starts declining.
Context:
- In recent findings, The Lancet has projected a decline in India's Total Fertility Rate (TFR) to 1.29 by 2051, contrasting with the government's technical group estimate of 1.94 for 2021-2025, and 1.73 for 2031-2035.
- Additionally, the UN Population Division predicts India's population will be near 1.7 billion by 2065, surpassing The Lancet's projections.
- These diverging forecasts suggest that India's population may stabilize below 1.7 billion well before 2065.
Insights into Demographic Projections:
- According to the UN Population Division, India is expected to approach a population of nearly 1.7 billion by 2065, followed by stabilization. In contrast, The Lancet report forecasts a decline in the total fertility rate (TFR) to 1.29 by 2051.
- These projections signal a significant evolution in India's population dynamics, suggesting broader implications beyond population size.
- Government projections and data from NFHS 5 further corroborate this trend, indicating a declining trajectory in the TFR and hinting at the possibility of population stabilization occurring sooner than expected.
Implications of Decreasing Total Fertility Rate (TFR):
- Economic Impact: The decline in TFR alters the age distribution, resulting in fewer children and more working-age adults.
- Initially, this demographic shift presents an economic opportunity, fostering growth through increased productivity and surplus income.
- Dependency Ratio: A reduced TFR lowers the dependency ratio, lessening the burden on the working-age population to support dependents.
- This enhances economic productivity and allows for better resource allocation towards development endeavors.
- However, aging populations may necessitate adjustments in healthcare and social welfare policies.
- Labour Market Dynamics: Demographic changes influence employment patterns and wage structures.
- A larger working-age cohort relative to dependents may increase labor supply, affecting wage levels.
- Shifts from agriculture to other sectors may alter employment opportunities and skill requirements.
- Social Welfare and Healthcare: Aging populations due to declining fertility rates require tailored social welfare and healthcare services.
- This includes pension schemes, long-term care facilities, and healthcare programs addressing age-related ailments, essential for ensuring the well-being of the elderly.
- Education and Human Capital: Decreasing TFR reduces the demand for primary and secondary education infrastructure.
- However, investments in higher education and skill development become crucial to equip the smaller cohort of young adults with the necessary skills for a competitive workforce.
How India’s Decreasing Fertility Rate Poses Advantages:
- Enhanced Labor Productivity: A declining total fertility rate (TFR) results in a demographic dividend, with a larger proportion of the population in the working-age bracket compared to dependents.
- This surplus labor force can drive heightened productivity across various sectors, fostering innovation, specialization, and overall economic growth.
- Capital Accumulation and Investment: Lower fertility rates prompt households to channel more resources towards the education and well-being of fewer children.
- This leads to increased savings and investment at the household level, facilitating capital formation and investments in critical areas such as infrastructure, technology, and human capital.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Decreasing TFR necessitates a shift in resource allocation away from childcare and education expenses for larger families towards investments in education, skill development, and healthcare for a smaller number of children.
- This reallocation optimizes the utilization of public funds and private investments, fostering human capital development and long-term productivity gains.
- Regional Development and Urbanization: Declining fertility rates often coincide with urbanization and regional development, with urban centers emerging as economic hubs.
- The concentration of populations in urban areas promotes economies of scale, knowledge sharing, and networking opportunities, stimulating entrepreneurship and industry growth.
- International Competitiveness: A transition to lower fertility rates enhances a nation’s international competitiveness by cultivating a younger, better-educated workforce.
- Such a workforce is more adept at adapting to technological advancements, competing in global markets, and attracting foreign investment.
- Additionally, a favorable demographic profile can strengthen a country’s creditworthiness, investor confidence, and long-term economic resilience.
Way Forward:
- Empowering Women and Marginalized Communities: Prioritize skill development initiatives, especially targeting women and underprivileged groups, to adapt to demographic shifts.
- While declining fertility rates may ease pressure on educational systems, efforts must focus on reducing dropout rates in higher education and promoting women's workforce participation.
- Sectoral and Geographical Workforce Redistribution: Respond to workforce transitions from agriculture to industrial and service sectors by implementing skill development programs, particularly for marginalized populations.
- Facilitate spatial redistribution of labor, especially north-south migration, to balance labor markets, enhance working conditions, and promote wage equality.
- Strengthening Healthcare Preparedness: With increasing life expectancy, anticipate challenges associated with an aging population and rising healthcare needs.
- Develop robust healthcare infrastructure and formulate policies tailored to address the requirements of the elderly, ensuring effective utilization of the demographic dividend.
Conclusion
India stands at a crucial crossroads in its socio-economic evolution marked by its demographic transition. Addressing the challenges and opportunities inherent in this transition demands strategic policy interventions, emphasizing skill development, gender equality, labor reallocation, and healthcare readiness. By navigating this transition with foresight and flexibility, India can unlock its full potential for long-term growth and development, positioning itself effectively on the global landscape.
Ensuring Democracy: When Governments Listen to the Election Commission
- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission (EC) is extremely reasonable in matters that affect public welfare and the Government, and investigative agencies must respect that.
Context:
- Recent concerns raised by two former heads of the poll panel have shed light on the actions of tax agencies during election periods.
- In a democracy, free and fair elections are fundamental, safeguarding citizens' rights to freely choose their representatives without external pressure.
- Given the significance of preserving the integrity of the electoral process, it is crucial to scrutinize actions that could potentially disrupt this process.
- Such actions include the issuance of tax demands or IT notices to political parties, prompting a closer examination of precedents where the Election Commission intervened to maintain a fair and balanced electoral environment.
Impact of IT Notices on Opposition During Election Period:
- Disruption of Level Playing Field (LPF) Through Financial Interference: The issuance of IT notices by tax agencies during election campaigns may be interpreted as efforts to undermine the democratic process by targeting specific political entities.
- Freezing accounts, debiting funds, or issuing notices during this crucial period can significantly disrupt the financial resources and operational capacities of certain parties, thereby skewing the electoral landscape in favor of others.
- Such interference compromises the core principles of democracy and electoral fairness, eroding public confidence in the integrity of the electoral process.
- Influence on Voter Perception: The timing of these actions raises concerns about their potential impact on voter perceptions and election outcomes.
- Voters may perceive such actions as politically motivated or aimed at influencing the electoral results, casting doubts on the fairness and impartiality of the electoral process.
- Preserving the principles of neutrality, transparency, and fairness is vital in upholding democratic ideals and ensuring elections truly reflect the will of the people.
- Operational Hurdles: Raids and enforcement activities by tax agencies pose significant operational challenges for political parties, diverting their focus and resources away from election campaigning.
- Parties may find themselves compelled to address legal matters, respond to inquiries, and navigate tax regulations complexities, detracting from their ability to engage with voters and advocate their platforms effectively.
- Undermining Confidence in the Electoral Process: The perception that tax agencies target specific parties or candidates during elections can undermine public trust in the fairness and impartiality of the electoral process.
- Such actions may be viewed as politically driven attempts to sway election outcomes, fostering skepticism about the legitimacy of the electoral process and the credibility of election results.
- Impact on Democratic Participation: Financial and operational challenges resulting from enforcement actions can discourage democratic engagement and participation among voters.
- Perceived unfairness or bias in the electoral process may lead citizens to disengage from the democratic process, fostering disillusionment and apathy toward democratic participation.
Why Actions Against CMs, Congress Can Wait?
- Traditionally, the Election Commission (EC) has adhered to the principle of postponing any actions that can be deferred until after the conclusion of elections.
- It prompts a crucial question: would there be any significant harm in postponing these actions?
- In the current scenarios involving the arrest of two chief ministers and the issuance of IT notices, including the freezing of accounts of an opposition party, delaying these actions until after the elections would likely result in no irreparable harm.
- Conversely, proceeding with these actions during the election period could inflict irreparable damage on the two affected parties by severely hampering their electoral campaigns, both physically and financially.
Actions Taken by the Elections Commission (EC) Against Governments and Central Agencies to Preserve Level Playing Field (LPF):
- Addressing Bias or Partiality: The EC has actively intervened to uphold fair and impartial elections, particularly in cases where central agencies faced allegations of bias or partiality.
- During the 2019 Lok Sabha elections, the EC urged the Enforcement Directorate (ED) to maintain impartiality following complaints from opposition parties about the perceived misuse of central agencies by the ruling party.
- Emphasizing Neutrality and Impartiality: The EC consistently underscores the principles of neutrality, impartiality, and non-discrimination in all enforcement actions during election periods.
- Its commitment to maintaining the integrity of the electoral process is evident through its insistence on fair treatment for all parties involved.
- Balancing Public Welfare with Electoral Neutrality: While ensuring fairness, the EC also demonstrates pragmatism in matters affecting public welfare.
- For instance, during state elections, it permitted the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas to announce a national reduction in petrol prices, deeming it beneficial to the wider public interest.
- However, proposals such as increases in minimum support prices of certain foodgrains, perceived as potentially influencing voters, are disallowed during election periods to maintain electoral neutrality.
- Promoting Transparency in the Electoral Environment: The EC's interventions aim to curtail the misuse of office by political leaders and ministers, fostering a transparent and equitable electoral environment.
- The Model Code of Conduct (MCC) serves as a pivotal instrument in this endeavor, imposing restrictions on ruling parties to prevent undue advantages.
- Providing Guidance to Political Entities: While primarily focusing on individuals, the EC also advises political parties to ensure adherence to the code of conduct.
- For example, during overlapping budget sessions and election periods, state governments are encouraged to adopt a "vote on account" approach to avoid contravening the MCC with new schemes or projects.
- EC's Influence in Goa By-Election, 2012: An illustrative instance of the EC's influence is its intervention in a by-election in Goa in 2012, where the Chief Minister intended to induct a probable candidate into the Council of Ministers before the election.
- Despite possessing constitutional authority, the Chief Minister deferred the induction upon the EC's advice, acknowledging the moral authority of the Model Code of Conduct.
- This exemplifies the delicate balance between various authorities in a parliamentary democracy, reinforcing India's electoral processes as models of integrity and fairness globally.
Conclusion
The Election Commission's proactive engagement with central agencies, advocating for the postponement of actions such as raids, freezing of accounts, and issuance of tax demands until after elections, serves as a cornerstone in upholding the principles of free and fair elections.
By intervening in such matters, the Election Commission reinforces its commitment to ensuring an impartial electoral process, reassuring voters of the integrity and fairness of elections.
Ultimately, safeguarding the integrity of elections is paramount to preserving democracy and fostering public trust in the electoral process.
Heat Waves and its Impacts in India

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecast a harsh and arid summer over a majority of regions of the country during April- June, with a high probability of heatwave episodes lasting as long as 10 to 20 days during the period.
Recent Prediction by India Meteorological Department (IMD):
- Extreme Heat Outlook: India is anticipated to face extreme heat from April to June, with central and western regions likely to be most affected.
- Expectations of 10 to 20 heatwave days across the country, exceed the normal range of four to eight days.
- Regions including Gujarat, central Maharashtra, north Karnataka, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, north Chhattisgarh, and Andhra Pradesh are forecasted to experience severe heatwaves in April.
- Pre-Monsoon Rainfall Performance: Below-average pre-monsoon rainfall is expected this month, particularly impacting coastal, eastern, and southern India.
- El Nino Conditions: El Nino conditions, marked by abnormal sea surface warming in the equatorial Pacific Ocean since last June, have the potential to reduce rainfall and increase temperatures, both locally in India and globally.
- Despite El Nino conditions easing after peaking in December, persistent warm conditions continue to elevate global temperatures.
- Recent Weather Conditions: February and March witnessed hotter-than-normal weather in southern India.
- Heatwave conditions were reported in Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Saurashtra-Kutch, and parts of Rajasthan during late March.
- Maximum temperatures soared to 42.6 degrees Celsius in areas such as Akola in Maharashtra and Phalodi in Rajasthan.
What are Heat Waves?
- Heatwaves entail prolonged periods of exceptionally hot weather, posing adverse effects on human health, the environment, and the economy.
- Given India's tropical climate, the nation is especially susceptible to heat waves, which have witnessed increased frequency and intensity in recent times.
What is the Criterion for Declaring a Heat Wave?
For Plains and Hilly Regions:
- Heatwave is recognized when the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C or higher for Plains and at least 30°C or higher for Hilly regions.
- Determined based on Departure from Normal Heat Wave:
- Departure from normal temperature ranges from 4.50°C to 6.40°C, with anything exceeding 6.40°C classified as a Severe Heat Wave.
- Alternatively, based on Actual Maximum Temperature Heat Wave:
- A heat wave is declared when the actual maximum temperature equals or exceeds 45°C, while a Severe Heat Wave is acknowledged if the actual maximum temperature equals or exceeds 47°C.
- Declaration occurs when the above criteria are met in at least 2 stations within a Meteorological subdivision for a minimum of two consecutive days, with the declaration taking effect on the second day.
For Coastal Areas:
- A heat wave may be identified when the maximum temperature departure from normal is 4.50°C or more, provided the actual maximum temperature registers at 37°C or higher.
Fatality Risk:
- While high temperatures alone may not be lethal, it's the conjunction of elevated temperatures and humidity, known as the wet bulb temperature, that renders heatwaves perilous.
- Increased moisture levels impede sweat evaporation and hinder body cooling mechanisms, leading to a rapid rise in internal body temperature, frequently resulting in fatal outcomes.
What are the Causes of Heatwaves?
- Global Warming: A primary factor driving heatwaves in India is global warming, a consequence of sustained increases in Earth's average temperature linked to human activities like fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial operations.
- Elevated temperatures and altered weather patterns can stem from this phenomenon.
- Rapid Urbanization: Rapid urban expansion and the proliferation of urban landscapes contribute to the "urban heat island effect."
- Urban areas, dense with population, structures, and concrete surfaces, absorb and retain heat, intensifying temperatures, particularly during heatwaves.
- El Nino Influence: El Nino events, characterized by Pacific Ocean warming, exert global climatic impacts, triggering shifts in temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
- The conclusion of a strong La Nina phase in the equatorial Pacific Ocean and the untimely onset of an El Nino event are anticipated factors contributing to the exceptionally hot forecast for the summer of 2023.
What are the Impacts?
- Health Effects: Swift escalation in heat exposure can disrupt the body's ability to regulate temperature, resulting in various ailments such as heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and hyperthermia, potentially leading to fatalities or hospitalizations.
- Water Resources Impact: Heatwaves exacerbate water scarcity issues in India, causing water bodies to dry up, diminishing water availability for agriculture and domestic use, and intensifying competition for water resources, fostering conflicts and influencing irrigation practices and water-reliant industries.
- Energy Impact: Elevated temperatures heighten demand for cooling, straining power grids and heightening the risk of blackouts, disrupting economic operations, reducing productivity, and adversely affecting vulnerable communities without reliable access to cooling amenities during heatwaves.
How to Mitigate Extreme Heat Wave Events?
- To mitigate the adverse effects of heat waves and climate change, a comprehensive action plan must be implemented at various levels:
- Heat Wave Action Plan: Develop a long-term plan to protect human lives, livestock, and wildlife by prioritizing effective adaptation strategies and robust disaster management policies.
- Ensure proper implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, with governments taking the lead and engaging multiple stakeholders.
- Implementing Climate Action Plans: Commit to the National Action Plan for Climate Change (NAPCC) for inclusive growth and ecological sustainability.
- Emphasize nature-based solutions that uphold ethical standards and promote intergenerational justice.
- Sustainable Cooling: Adopt passive cooling technology to create naturally ventilated buildings, reducing the urban heat island effect in residential and commercial areas.
- Consider adapting ancient Indian building designs, as recommended by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), to modern facilities.
- Heatwave Mitigation Plans: Implement measures to prevent heat-related fatalities, including providing access to water, oral rehydration solutions, shade in public spaces, flexible working hours, and accommodations for outdoor workers.
- Vigilant local administration and oversight by higher authorities are key to successful implementation.
- By implementing these strategies and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, we can create a more resilient future that effectively addresses the challenges posed by heat waves and climate change.
Indian Meteorological Department (IMD):
- India Meteorological Department is the country's National Meteorological Service.
- It deals with all matters relating to meteorology, seismology, and associated subjects.
- IMD is headquartered in Delhi and operates hundreds of observation stations across India and Antarctica.
- IMD units such as Forecasting Offices, Agrometeorological Advisory Service Centers, Hydro-meteorological Offices, Flood Meteorological Offices, Area Cyclone Warning Centers, and Cyclone Warning Centers are usually co-located with various observatories or meteorological centers.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
- It is responsible for forecasting, naming, and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northern Indian Ocean region, including the Straits of Malacca, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea, and the Persian Gulf.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Indian Government
India’s HIV/AIDS Response

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
April 1, 2004, marked a significant moment in India's fight against HIV/AIDS as Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) was introduced for Persons Living with HIV (PLHIV).
Context:
- April 1, 2004, stands as a landmark moment in India's approach to addressing the HIV/AIDS epidemic, as Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) was introduced for Persons Living with HIV (PLHIV).
- This initiative, conceived in response to the pressing issues of access and affordability, has emerged as a crucial intervention in the fight against the disease.
- As we commemorate this day, it is imperative to delve into the progression and significance of India's free ART program, shedding light on its transformative impact on the nation's response to the HIV/AIDS crisis.
HIV/AIDS's Emergence and Initial Challenges:
- Inception of a Global Health Crisis: The emergence of HIV/AIDS in the early 1980s signaled the onset of a widespread health emergency with profound implications for populations worldwide.
- Originally detected among groups in the United States, the disease swiftly traversed borders, reaching nations like India and beyond.
- This era was characterized by uncertainty, anxiety, and a lack of comprehension regarding the novel virus, initially dubbed GRID (Gay-Related Immune Deficiency), later renamed HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and its associated illness AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
- Absence of Effective Treatments Resulting in Dire Consequences: During the initial stages of the epidemic, HIV/AIDS was synonymous with a dire prognosis, largely due to the absence of viable treatment options.
- Marginalized communities, including men who have sex with men, intravenous drug users, and commercial sex workers, bore the brunt of the disease's impact.
- However, as time progressed, it became evident that HIV/AIDS transcended boundaries of gender, sexual orientation, and socioeconomic status, affecting individuals from diverse backgrounds.
- Pervasive Social Stigma: In addition to its grave health implications, HIV/AIDS precipitated significant social stigma and discrimination.
- Individuals living with HIV/AIDS encountered marginalization, employment loss, and social exclusion from both their communities and families.
- This pervasive stigma compounded the challenges associated with managing HIV/AIDS and impeded effective epidemic control efforts.
- Limited Treatment Accessibility and Exorbitant Costs of Available ART: Despite the escalating recognition of HIV/AIDS as a global health threat, access to treatment remained scant, particularly in low- and middle-income nations such as India.
- The approval of the first antiretroviral drug, AZT (zidovudine), by the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) in March 1987 marked a significant milestone.
- HAART (Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy) represented a breakthrough in disease management, combining multiple antiretroviral drugs to suppress viral replication and bolster immune response.
- However, the exorbitant expenses associated with HAART, reaching up to $10,000 annually per patient, rendered it inaccessible to the majority of individuals living with HIV/AIDS, especially those residing in resource-constrained settings.
The Introduction of Free ART in India and its Impact:
- In response to the pressing issues of limited access and affordability of HIV/AIDS treatment, the Indian government embarked on a significant initiative.
- On April 1, 2004, the government initiated the provision of Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) for Persons Living with HIV (PLHIV).
- The introduction of Free ART aimed to dismantle barriers to treatment and extend life-saving medication to all PLHIV, irrespective of their financial means.
- By offering ART at no cost, the government endeavored to ensure that access to treatment would not be hindered by financial constraints, thereby addressing a crucial gap in healthcare accessibility.
Its Role in Curbing the Epidemic
- Enhanced Treatment Accessibility: Over the past two decades, the initiative has undergone substantial expansion, witnessing a surge in the number of ART centers from less than 10 to approximately 700, catering to around 1.8 million PLHIV.
- This proliferation has facilitated heightened treatment access for individuals living with HIV/AIDS nationwide, including those residing in remote and underserved regions.
- A notable outcome of the Free ART endeavor has been the remarkable enhancement in health outcomes observed among PLHIV.
- Significant Reduction in Mortality Risk and Transmission Rates: Timely and effective treatment accessibility has transfigured HIV/AIDS from a dire prognosis to a manageable chronic ailment for many.
- By suppressing viral load and bolstering immune response, ART has not only extended the lifespan of PLHIV but also augmented their quality of life.
- Moreover, the Free ART initiative has played a pivotal role in curbing HIV transmission rates by ensuring treatment access for PLHIV, thereby thwarting virus dissemination within communities.
- Research indicates that efficacious ART can substantially mitigate HIV transmission risk, contributing to the overall decline in HIV prevalence.
- Broader Societal Benefits: Beyond its direct impact on individuals grappling with HIV/AIDS, the Free ART initiative has yielded wider societal advantages.
- By mitigating the disease burden and forestalling fresh infections, the initiative has alleviated the societal and economic repercussions of HIV/AIDS on families, communities, and healthcare systems.
- Supplementary Measures and Patient-Centric Approach: The success of India's ART program extends beyond free medication provision.
- Complementary initiatives, such as complimentary diagnostic services, prevention of parent-to-child transmission programs, and management of opportunistic infections, have played pivotal roles in curbing the HIV epidemic.
- Furthermore, the program has adopted a patient-centric strategy, furnishing stable PLHIV with two to three months' worth of medicines to minimize clinic visits and enhance treatment adherence.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
- Delayed Initiation and Attrition in Care: A notable portion of patients presents with advanced HIV illness, evidenced by low CD4 counts, impacting treatment efficacy.
- Furthermore, attrition in care remains a concern, as some patients discontinue treatment upon feeling well, leading to interruptions and potential drug resistance development.
- Logistical Hurdles and Infrastructure Deficiencies: Remote and underserved regions, including those with rugged terrain, encounter hurdles in accessing vital medications and healthcare provisions.
- Fortifying the logistical network and infrastructure for dispensing ART drugs is imperative to sustain uninterrupted treatment access for all PLHIV.
- Involvement of the Private Sector: While the public sector assumes a pivotal role in HIV/AIDS treatment provision, fostering collaboration with the private sector is crucial.
- Leveraging the resources and infrastructure of private healthcare entities can expand ART accessibility and reach marginalized populations, including urban dwellers.
- Interconnected Health Program Integration: Augmenting integration with other health initiatives, encompassing hepatitis, non-communicable ailments, and mental health, holds paramount importance.
- Given PLHIV's propensity for concurrent ailments, comprehensive and integrated healthcare services necessitate intersectoral collaboration within the healthcare spectrum.
- Realization of Ambitious NACP Phase 5 Objectives: The ongoing fifth phase of the National AIDS Control Programme (NACP) sets forth ambitious targets, envisaging an 80% reduction in annual new HIV infections and AIDS-related mortalities by 2025.
- Achieving these milestones demands concerted endeavors to escalate testing, enhance treatment coverage, and secure viral suppression among PLHIV.
Conclusion
India's free ART initiative has successfully combated HIV/AIDS, demonstrating the power of accessible healthcare. Its achievements emphasize the importance of political will, funding, community engagement, and patient-centered care in tackling infectious diseases. Lessons from this program will guide future public health endeavors, improving outcomes for all
