Biomedical Waste Regulations

- 30 Nov 2024
The Emergence of HIV and Global Panic
In 1983, scientists Luc Montagnier and Robert Gallo independently identified the virus responsible for AIDS. By the mid-1980s, HIV/AIDS was perceived as a biological death sentence, with the virus primarily attacking immune cells, making medical intervention difficult. The epidemic quickly became associated with fear, ignorance, and stigma, as it was often linked to marginalized groups.
The "Syringe Tide" Incident and Public Outrage
In August 1987, the U.S. faced a public health crisis when discarded medical waste, including syringes and blood vials, washed up on beaches along the Atlantic coast. Known as the "Syringe Tide," this incident shocked the public and fueled anxiety, especially when children were seen playing with syringes. Traced to improper waste disposal in New York City, the event highlighted the hazardous nature of medical waste, which had been previously underestimated. Combined with the HIV/AIDS epidemic, this incident amplified public fear and economic losses of up to $7.7 billion due to the decline in tourism.
U.S. Response: Medical Waste Tracking Act of 1988
The widespread outrage led to the U.S. government passing the Medical Waste Tracking Act in 1988. This was the first law to formally categorize hospital waste as hazardous. The Act introduced stringent guidelines for the handling, transportation, and disposal of medical waste, establishing systemic regulation and oversight. It marked a significant turning point in both public health and environmental safety, changing how medical waste was managed in the healthcare sector.
India’s Journey in Biomedical Waste Management
Initial Steps and Delays
While the U.S. responded swiftly to the crisis, India’s approach to managing biomedical waste was slower. In 1986, India enacted the Environmental Protection Act, which marked the country’s first significant step towards environmental conservation. That same year, India identified its first HIV case. However, biomedical waste was not yet recognized as hazardous, and the Hazardous Waste (Management and Handling) Rules of 1989 failed to address the issue. As a result, local bodies were left to manage waste disposal, leading to inefficiencies.
Judicial Intervention and Legislative Action
In the 1990s, as pollution levels rose, particularly in urban areas like Delhi, the inadequacies of the system became apparent. In the landmark case Dr. B.L. Wadehra vs. Union of India (1996), the Supreme Court criticized Delhi’s waste management system, calling the city an "open garbage dump." This judgment led to a nationwide conversation on waste management and resulted in the Biomedical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules of 1998, marking the formal recognition of hospital waste as hazardous. The rules empowered the Central and State Pollution Control Boards to regulate waste disposal, ensuring accountability.
The Link Between HIV and Biomedical Waste Regulations
The HIV crisis highlighted the need for safe disposal practices to protect the environment and healthcare workers. While India charted its own course, the global response to HIV, particularly the U.S. model, influenced India’s approach to biomedical waste management. Over the years, India has made significant progress, with amendments to the rules in 2016 and 2020 to improve waste management technology and ensure safe disposal.
Current Challenges and Progress
- Ongoing Issues in Biomedical Waste Management: Despite significant progress, challenges remain, especially in rural and resource-limited areas. Mishandling of biomedical waste continues to pose risks, and healthcare professionals still face occupational hazards. Gaps in compliance and awareness persist, but the system’s progress is undeniable.
Conclusion
The HIV/AIDS epidemic, while tragic, indirectly led to significant improvements in healthcare waste management. As the crisis highlighted the dangers of improper waste disposal, it spurred legislative and systemic changes that have contributed to safer healthcare environments. The progress in biomedical waste management demonstrates that crises can often lead to long-term improvements.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet recently approved the launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF), marking a significant shift in the government's approach to agriculture. This initiative, a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, aims to promote natural farming across India, focusing on reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and promoting environmentally sustainable practices.
What is Natural Farming?
Natural farming, as defined by the Ministry of Agriculture, is a chemical-free agricultural method that relies on inputs derived from livestock and plant resources. The goal is to encourage farmers to adopt practices that rejuvenate soil health, improve water use efficiency, and enhance biodiversity, while reducing the harmful effects of fertilizers and pesticides on human health and the environment. The NMNF will initially target regions with high fertilizer consumption, focusing on areas where the need for sustainable farming practices is most urgent.
Evolution of Natural Farming Initiatives
The NMNF is not an entirely new concept but a scaled-up version of the Bhartiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhti (BPKP) introduced during the NDA government's second term (2019-24). The BPKP was part of the larger Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojna (PKVY) umbrella scheme, and natural farming was also promoted along the Ganga River under the NamamiGange initiative in 2022-23. With the renewed focus on natural farming following the 2024 elections, the government aims to extend the lessons learned from BPKP into a comprehensive mission mode, setting a clear direction for sustainable agriculture.
In Budget speech for 2024-25, it was announced a plan to initiate one crore farmers into natural farming over the next two years. The mission will be implemented through scientific institutions and willing gram panchayats, with the establishment of 10,000 bio-input resource centers (BRCs) to ensure easy access to the necessary inputs for natural farming.
Key Objectives
The NMNF aims to bring about a paradigm shift in agricultural practices by:
- Expanding Coverage: The mission plans to bring an additional 7.5 lakh hectares of land under natural farming within the next two years. This will be achieved through the establishment of 15,000 clusters in gram panchayats, benefiting 1 crore farmers.
- Training and Awareness: The mission will establish around 2,000 model demonstration farms at Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), Agricultural Universities (AUs), and farmers' fields. These farms will serve as hubs for training farmers in natural farming techniques and input preparation, such as Jeevamrit and Beejamrit, using locally available resources.
- Incentivizing Local Inputs: The creation of 10,000 bio-input resource centers will provide farmers with easy access to bio-fertilizers and other natural farming inputs. The mission emphasizes the use of locally sourced inputs to reduce costs and improve the sustainability of farming practices.
- Farmer Empowerment: 30,000 Krishi Sakhis (community resource persons) will be deployed to assist in mobilizing and guiding farmers. These trained individuals will play a key role in generating awareness and providing on-ground support to the farmers practicing natural farming.
- Certifications and Branding: A major aspect of the mission is to establish scientific standards for natural farming produce, along with a national certification system. This will help in creating a market for organically grown produce and encourage more farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
Targeting High Fertilizer Consumption Areas
The Ministry of Agriculture has identified 228 districts in 16 states, including Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Maharashtra, and West Bengal, where fertilizer consumption is above the national average. These districts will be prioritized for the NMNF rollout, as they have high fertilizer usage but low adoption of natural farming practices. By focusing on these areas, the mission seeks to reduce the over-dependence on chemical fertilizers and foster a transition to more sustainable farming practices.
Benefits of Natural Farming
The NMNF aims to deliver multiple benefits to farmers and the environment:
- Cost Reduction: Natural farming practices can significantly reduce input costs by decreasing the need for costly chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Soil Health and Fertility: By rejuvenating the soil through organic inputs, natural farming improves soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity, leading to long-term agricultural sustainability.
- Climate Resilience: Natural farming enhances resilience to climate-induced challenges such as drought, floods, and waterlogging.
- Healthier Produce: Reduced use of chemicals results in safer, healthier food, benefitting both farmers and consumers.
- Environmental Conservation: The promotion of biodiversity, water conservation, and carbon sequestration in soil leads to a healthier environment for future generations.
Conclusion
The launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming represents a critical step toward transforming India's agricultural practices into a more sustainable and environmentally friendly model. By targeting regions with high fertilizer usage, providing farmers with the tools and knowledge for natural farming, and creating a system for certification and branding, the government hopes to make natural farming a mainstream practice. As India continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, soil degradation, and health risks from chemical inputs, the NMNF provides a promising framework for sustainable agriculture that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.
India’s Urban Infrastructure

- 28 Nov 2024
Introduction
India’s urban population is projected to double from 400 million to 800 million by 2050. This demographic shift presents both challenges and opportunities for transforming the country’s urban infrastructure. To meet the growing needs of urban areas, India will require an investment of approximately ?70 lakh crore by 2036, a figure significantly higher than current spending levels.
Financial Challenges in Urban Infrastructure
- Investment Gap
- The current annual investment in urban infrastructure stands at ?1.3 lakh crore, which is only 28% of the ?4.6 lakh crore needed annually.
- A large portion of the existing investment, around 50%, is directed towards basic urban services, with the remainder allocated to urban transport.
- Municipal Finances
- Municipal finances have remained stagnant at 1% of GDP since 2002.
- Despite increased transfers from the central and state governments, municipal bodies face financial strain.
- The contribution of municipal own-revenue has decreased from 51% to 43%, indicating a reduced financial independence.
- Revenue Collection Inefficiencies
- Urban local bodies (ULBs) are collecting only a small fraction of their potential revenues, with property tax collections representing just 0.15% of GDP.
- Cost recovery for essential services like water supply and waste management ranges between 20% and 50%, pointing to a significant funding gap.
- Underutilization of Resources
- Cities like Hyderabad and Chennai utilized only 50% of their capital expenditure budgets in 2018-19.
- Central schemes such as AMRUT and the Smart Cities Mission also showed suboptimal fund utilization, with utilization rates of 80% and 70%, respectively.
- Decline in Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
- Investments through PPPs in urban infrastructure have seen a sharp decline, from ?8,353 crore in 2012 to ?467 crore in 2018.
- This drop is attributed to limited project-specific revenues and inadequate funding mechanisms.
Structural and Administrative Challenges
- Weak Governance and Fragmented Management
- Fragmented governance and limited administrative autonomy hinder effective urban planning and resource allocation.
- Municipal bodies often lack the ability to undertake long-term planning and project execution due to these governance challenges.
- Climate Vulnerability and Sustainability: Urban areas are increasingly vulnerable to climate risks like floods and heatwaves. However, many urban infrastructure projects fail to incorporate climate resilience in their planning, exacerbating the long-term vulnerability of investments.
- Inadequate Land Management
- There is poor coordination between land use planning and infrastructure development, resulting in urban sprawl and inefficient transportation systems.
- Opportunities to capitalize on the land value generated by metro and rail projects remain underutilized.
Measures for Transforming Urban Infrastructure
- Streamline Revenue Collection: Leverage technology to improve property tax collection systems and enhance cost recovery in essential services.
- Enhance Fund Utilization: Strengthen municipal capacities for effective project planning and incentivize the timely use of allocated grants.
- Scale Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Investments: Develop a pipeline of bankable projects and create risk-sharing mechanisms to attract private sector investments.
- Decouple Project Preparation from Funding: Ensure that infrastructure projects are thoroughly prepared for financial, social, and environmental sustainability before seeking funding.
- Promote Urban Innovation: Establish urban innovation labs and encourage public-private-academic collaborations to foster the adoption of advanced technologies.
- Empower Municipalities: Grant municipalities greater financial autonomy, enabling them to raise capital through municipal bonds and other debt mechanisms.
- Integrated Urban Planning: Align infrastructure development with land use, transport, and housing requirements, while integrating climate resilience into planning.
- Capacity Building: Invest in the training of municipal staff to improve governance and financial management capabilities.
Conclusion
India’s expanding urban population presents a major opportunity for economic growth. However, addressing the financial and structural challenges in urban infrastructure is crucial for harnessing this potential. By adopting a combination of short-term actions, medium-term strategies, and long-term reforms, India can create sustainable, resilient urban infrastructure that meets the growing needs of its cities, fostering inclusive development and long-term prosperity.
The Controversy around the Sambhal Mosque
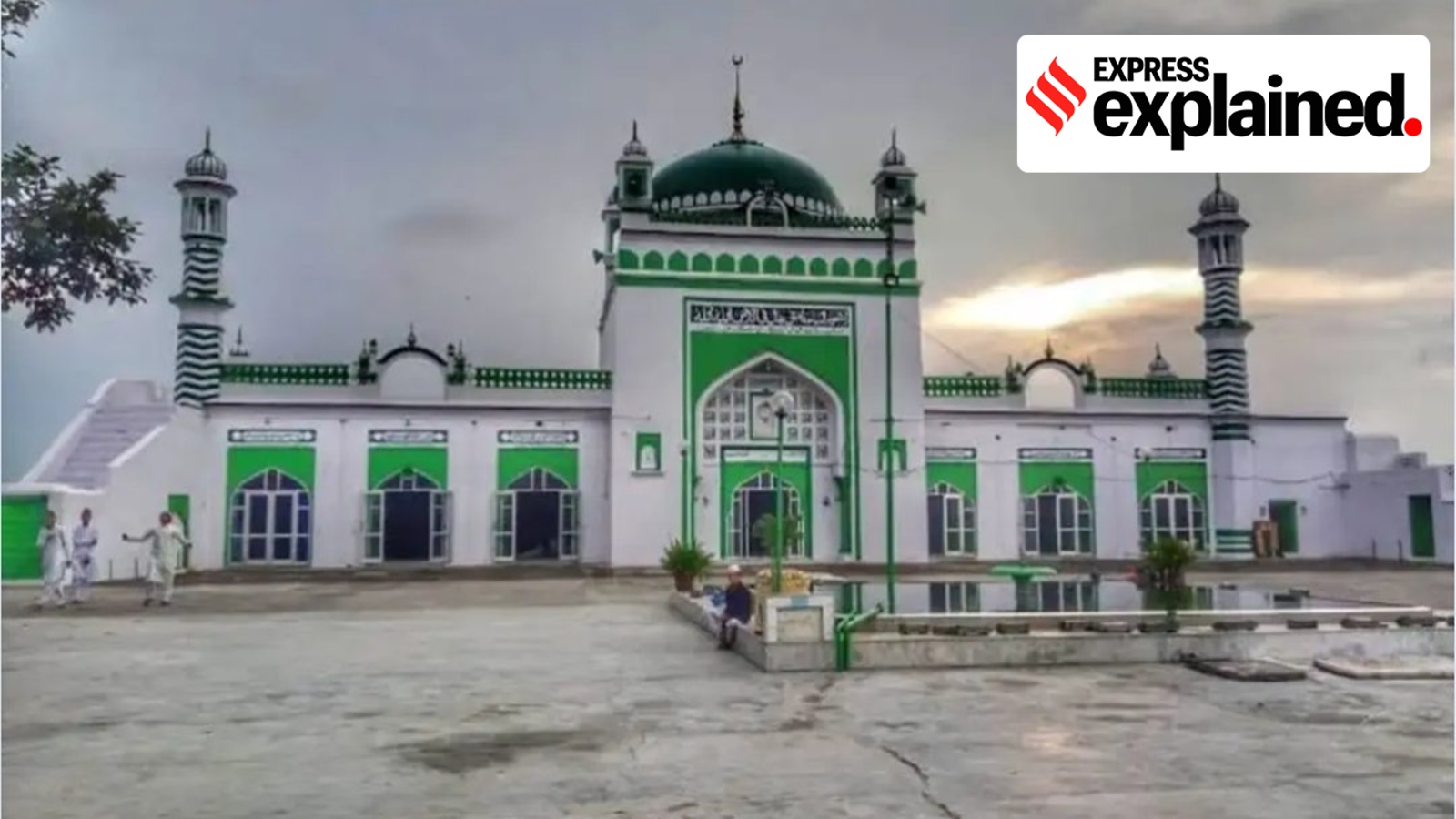

- 27 Nov 2024
Introduction
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has become a flashpoint in a larger religious and legal dispute after a petition was filed questioning its historical origins. Alleging that the mosque was built on the site of an ancient Hindu temple, the case has triggered both legal challenges and violent clashes, raising concerns about communal harmony and the protection of religious sites.
Background of the Dispute
On November 19, 2024, a petition was filed in the Sambhal district court, claiming that the 16th-century Jama Masjid was constructed over the site of an ancient Hari Har Mandir. This claim mirrors similar petitions filed in other parts of India, including Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have sought to alter the religious character of mosques they believe were built on temple sites. The petitioners in the Sambhal case include advocate Hari Shanker Jain, a key figure in the Gyanvapi and Mathura disputes.
Survey and Clashes
The Sambhal court ordered a survey of the mosque on November 19, 2024, to investigate the historical claims. The initial phase of the survey, conducted peacefully, involved mosque authorities and local police. However, a second survey on November 24 escalated tensions, as it was accompanied by a procession led by a local priest chanting Hindu slogans. Protests soon turned violent, leading to stone-pelting, police firing, and at least five deaths, including two teenagers. Locals accused the police of excessive force, while the police denied allegations of shooting.
The Mosque’s Historical Context
The Shahi Jama Masjid was built by Mughal Emperor Babur's general, Mir Hindu Beg, around 1528. It is one of the three mosques constructed during Babur's reign, the other two being in Panipat and Ayodhya. Architectural studies suggest it was constructed using stone masonry with plaster, and while some historians believe it was built on a pre-existing structure, the mosque’s historical context is complex. Local Hindu tradition holds that the site was originally a Vishnu temple, with the belief that Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu, will arrive there.
Legal Implications: The Places of Worship Act, 1991
The dispute touches upon the Places of Worship Act, 1991, which mandates the preservation of the religious character of all places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947. The Act was designed to prevent further disputes over religious sites, except for the Babri Masjid case, which was already under litigation at the time. The petitioners in the Sambhal case argue that the religious character of the mosque should be altered, contradicting the Act’s provisions.
Challenges to the Places of Worship Act
The Places of Worship Act has been criticized for barring judicial review and preventing any changes to the religious status of sites that existed before India’s independence. Some legal experts suggest that while an inquiry into the religious nature of a place might be permissible, changing that character would violate the Act. The ongoing legal challenges in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, and now Sambhal, highlight the complexities of reconciling India’s legal framework with communal sensitivities.
Conclusion
The Sambhal mosque dispute underscores the challenges in balancing India’s legal framework with religious and communal dynamics. While the Places of Worship Act aims to preserve the status quo, petitions challenging it have revived contentious debates over historical monuments and their religious significance. As the legal proceedings continue, the case will likely have far-reaching implications for India’s secular fabric and the preservation of communal harmony.
29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The 29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29), held in Baku, Azerbaijan, focused on enhancing climate finance, adaptation measures, and global cooperation.
Key Outcomes of COP29:
- Climate Finance: A new goal was set to triple climate finance for developing countries to USD 300 billion annually by 2035. The total climate finance target aims for USD 1.3 trillion annually by 2035.
- Carbon Markets: The conference operationalized Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, which establishes frameworks for carbon credit trading between countries. It also launched the Paris Agreement Crediting Mechanism, ensuring safeguards for human rights and the environment.
- Transparency and Adaptation: COP29 saw 13 countries submit their Biennial Transparency Reports, promoting greater accountability. The Baku Adaptation Roadmap was launched to speed up National Adaptation Plans (NAPs) in Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
- Gender and Inclusivity: A new Gender Action Plan was developed, and the Lima Work Programme on Gender was extended for another 10 years. Over 55,000 people, including civil society, Indigenous peoples, and youth, participated.
- Global Climate Action: The 2024 Yearbook of Global Climate Action highlighted the role of non-Party stakeholders like businesses and sub-national actors in combating climate change.
India’s Role at COP29: India played an active role in highlighting resilient infrastructure initiatives like the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) and advocated for financial resources to support Small Island Developing States (SIDS). India also pushed for solar energy adoption through the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and promoted gender-inclusive climate policies. India co-hosted the LeadIT summit with Sweden, focusing on industrial decarbonization.
Challenges at COP29:
- Inadequate Finance: Despite ambitious targets, many countries felt the financial commitments were insufficient and distant.
- Private Sector Dependency: The reliance on private sector contributions raised concerns about the reliability of funding.
- Emission Reduction Gaps: There was a lack of sufficient pledges to meet the 1.5°C global warming target, with rising emissions.
- Geopolitical Conflicts: Disputes over issues like the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) hindered progress.
India’s Carbon Credit Framework:
India introduced the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022, establishing a domestic carbon market and setting a legislative framework for carbon credit trading. This aligns with India’s NDCs and aims to support sustainable growth while reducing emissions. However, concerns about the integrity of carbon credits and potential "greenwashing" need to be addressed through rigorous verification systems.
Conclusion:
COP29 marked progress in scaling up climate finance, carbon markets, and adaptation efforts, but significant challenges remain, especially in finance, emission reductions, and geopolitical cooperation. India's initiatives in carbon credit frameworks and resilience are steps toward a sustainable future. Moving forward, a collaborative, transparent, and adaptive approach is crucial to meet global climate goals.
Challenges in Municipal Financing

- 25 Nov 2024
Introduction
Municipal corporations (MCs) in India are essential service providers in urban areas, but they face severe financial constraints, which hinder their ability to provide quality services. While urban India contributes almost 60% of the nation's economic output, MCs are heavily reliant on state and central government transfers, limiting their financial autonomy and operational capacity.
Key Issues in Municipal Financing
- Limited Revenue Generation
- Low Property Tax Revenues: Property tax, the main source of municipal revenue, contributes only 0.12% of GDP, a figure that reflects poor tax collection mechanisms and outdated property valuation systems.
- Revenue Concentration: Over 58% of municipal revenue comes from the top 10 cities, highlighting fiscal disparity between urban areas.
- Dependence on Government Transfers: Municipalities rely significantly on state and central transfers, constituting a large portion of their revenue. This reduces their ability to plan and execute long-term projects independently.
- Inefficiency in Tax and Fee Collection
- Ineffective Property Tax Systems: Existing tax formulas do not reflect actual property valuations, leading to under-taxation and revenue loss.
- Inadequate User Charges: Fees for essential services like water supply, sanitation, and waste management are not regularly adjusted, impacting cost recovery and service quality.
Strategies for Strengthening Urban Local Bodies (ULBs)
- Enhancing Revenue Sources
- Property Tax Reforms: Implementing GIS-based property tax mapping and linking tax rates to actual property valuations can improve tax compliance and revenue generation.
- Rationalising User Charges: Regular adjustments to service fees for water, sanitation, and waste management can ensure cost recovery and better service delivery.
- Reducing Dependence on Transfers
- State and Central Transfers: A rule-based framework for government transfers, accounting for inflation and city growth, can ensure predictability and adequate compensation for MCs.
- Boosting Non-Tax Revenues: MCs can increase income from user fees (e.g., for urban transport and waste management) and explore public-private partnerships (PPPs) to enhance service delivery.
- Leveraging Technology for Efficiency
- Digitalisation and Automation: Streamlining processes through technology can reduce inefficiencies, cut down on waste, and free up resources for capital expenditure.
- Monitoring Systems: Improved monitoring and reporting can reduce pilferage, enhance revenue collection, and ensure accountability.
Fiscal Management and Innovative Financing
- Municipal Bonds and Innovative Financing
- Larger MCs are already using municipal bonds to fund infrastructure projects. Smaller cities can adopt similar financing instruments to diversify funding sources and attract private investment.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Fostering partnerships in sectors like urban transport and waste management can attract private investment and reduce the financial burden on MCs.
- Resource Pooling for Infrastructure Projects
- MCs can collaborate to pool resources for large-scale projects, such as renewable energy or urban transport initiatives, overcoming fiscal constraints that individual corporations face.
Government Initiatives for Urban Governance
- Citizen-Centric Programs
- Swachh Sarvekshan (2017) promotes citizen participation to improve urban cleanliness.
- Swachh Bharat Idea Book empowers citizens to propose innovative solutions to urban challenges.
- Performance-Based Indices
- Ease of Living Index (2017) and the Municipal Performance Index (2019) assess urban quality of life, service delivery, and governance, encouraging better performance in ULBs.
Conclusion
Empowering urban local bodies is crucial for effective urban governance and development. By improving revenue generation through reforms, reducing dependence on transfers, and adopting innovative financing mechanisms, municipal corporations can enhance their capacity to meet the growing demands of urbanization. Collaborative efforts between the government, civil society, and academia are essential to ensure sustainable urban development and better living conditions for urban residents.
The Fight for Accessibility and Dignity in Indian Prisons

- 24 Nov 2024
Introduction
Prisons in India face numerous systemic issues, with overcrowding, abuse, and neglect being prevalent. For prisoners with disabilities, these challenges are magnified, as they struggle with basic needs and lack necessary accommodations. This issue is not only a human rights violation but also a failure in the implementation of legal protections.
Prison Conditions and Accessibility Issues for Disabled Inmates
- Challenges Faced by Disabled Prisoners: Disabled prisoners, such as Professor G.N. Saibaba, who spent a decade in prison before being exonerated, face severe challenges in performing everyday tasks like using toilets or taking baths. His experience of being physically lifted by fellow inmates due to the lack of wheelchair accessibility highlights the systemic neglect.
- Exclusion and Abuse: Prisoners with disabilities are particularly vulnerable to abuse, as their specific needs are ignored. The government does not track the number or conditions of disabled prisoners, which leads to neglect and mistreatment. Notably, Father Stan Swamy, who had Parkinson's disease, was denied essential items like a straw, affecting his ability to eat and drink.
Legal Framework and International Obligations
- Constitutional Protections: The Indian Constitution guarantees rights to prisoners, including protection from torture (Article 21) and the right to fair legal processes (Article 22). The Supreme Court has reinforced the need for humane treatment in prisons through various judgments.
- International Commitments: India has committed to international conventions such as the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and the Nelson Mandela Rules, which require reasonable accommodations for disabled prisoners. Despite these commitments, the practical enforcement of such rights remains minimal.
- Domestic Legislation: The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, mandates the protection of disabled individuals from abuse and exploitation. However, violations like the denial of basic assistive devices to prisoners show a gap in enforcement. The Ministry of Home Affairs has issued guidelines for prison accessibility, but they have yet to be widely implemented.
Systemic Failures and Lack of Political Will
- Overcrowding and Inadequate Infrastructure: Indian prisons house over 5.73 lakh prisoners, far exceeding their capacity. This overcrowding exacerbates the challenges faced by disabled prisoners, as the infrastructure is inadequate to meet their needs. A 2018 audit of Delhi’s prisons revealed significant accessibility gaps, such as inaccessible cells and toilets, making daily life for disabled prisoners even more difficult.
- Political Apathy and Public Indifference: Many believe that prisoners deserve their suffering, fueling a lack of urgency in addressing prison reforms. However, the state is responsible for ensuring the rights and dignity of all prisoners, including those with disabilities. There is a need for a shift in societal attitudes to ensure that these rights are upheld.
Reforms and the Way Forward
- Infrastructure and Accessibility: Prisons must implement universal design principles, ensuring that infrastructures are accessible to all, especially prisoners with disabilities. This includes accessible cells, toilets, and common areas, as well as functional wheelchairs.
- Judicial and Legal Reforms: The judicial system must expedite trials, especially for undertrials, and ensure that all prisoners have access to legal representation. This would help alleviate the overcrowding crisis and improve the overall functioning of the prison system.
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation and Welfare Programs: Prison systems need to focus on rehabilitation rather than mere punishment. Programs for skill development, education, and mental health support should be integrated into prison routines, providing prisoners with opportunities for personal growth and reintegration into society.
- Strengthening Oversight Mechanisms: There must be greater transparency in prison management through independent oversight bodies and regular audits. A whistleblower mechanism can help report violations of prisoner rights, ensuring greater accountability.
India’s Agricultural Sector

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
India’s agricultural sector, which employs 42.3% of the population, is crucial to the nation’s economy. However, it faces a range of challenges that need to be addressed to ensure long-term stability, food security, and sustainable growth.
Current Performance of India’s Agricultural Sector
- Key Agricultural Metrics and Growth
- Foodgrain Production: India produced 330.5 million metric tonnes (MT) of foodgrains in 2022-23, maintaining its position as the world’s second-largest producer.
- Horticulture Production: A record high of 351.92 million tonnes in horticultural production was achieved, marking a 1.37% increase from the previous year.
- Market Outlook
- India’s agricultural market is projected to reach USD 24 billion by 2025.
- The food and grocery retail sector is ranked as the sixth-largest globally, with 70% of its sales generated from retail.
- Investment and Export Trends
- FDI in Agriculture: From April 2000 to March 2024, the agricultural services sector attracted USD 3.08 billion in foreign direct investment, while the food processing industry garnered USD 12.58 billion.
- Agricultural Exports: India’s agricultural and processed food exports reached USD 4.34 billion in 2024-25, including products like marine products, rice, and spices.
Key Challenges Confronting India’s Agriculture
- Climate Change and Environmental Impact:Extreme weather events, such as heatwaves and erratic rainfall, continue to impact agricultural productivity. In 2023, India experienced its second-warmest year on record, contributing to crop damage and rising food prices.
- Water Stress and Irrigation Inefficiency: Agriculture consumes the majority of India’s water resources, but irrigation efficiency is still low. The country relies heavily on flood irrigation, which leads to significant water wastage. Only 11% of agricultural land is under micro-irrigation, far below global standards.
- Land Fragmentation and Declining Farm Sizes: The average size of agricultural farms has decreased from 1.08 hectares in 2016-17 to 0.74 hectares in 2021-22, hindering the adoption of modern farming practices and mechanization.
- Market Access and Price Realization: Farmers continue to face challenges in accessing fair market prices due to the dominance of intermediaries and inadequate market infrastructure. Despite reforms like e-NAM, price gaps between farm-gate and retail prices persist, leaving farmers with a smaller share of the final price.
- Technology Adoption and Digital Divide: Although agritech is growing in India, only 30% of farmers use digital tools in agriculture, and rural digital literacy is just 25%, which limits the widespread adoption of modern farming solutions.
Addressing Structural Issues in Indian Agriculture
- Soil Health and Sustainability:The excessive use of chemical fertilizers and mono-cropping practices has led to soil degradation. Approximately 30% of agricultural land in India is experiencing degradation, impacting productivity and sustainability. Stubble burning further exacerbates this issue, worsening air quality and soil health.
- Crop Diversification Challenges:Many farmers are locked into the wheat-rice cycle due to Minimum Support Price (MSP) guarantees, limiting the cultivation of other crops like pulses and oilseeds. Although India is the largest producer of pulses, the domestic production is insufficient to meet the growing demand.
- Feminisation of Agriculture:Women make up 63% of agricultural workers but own only 11-13% of the operational land, limiting their access to resources and decision-making power. This gender disparity hampers their economic security and limits their participation in agricultural development.
Conclusion
India’s agricultural sector holds immense potential but is facing significant structural challenges that must be addressed to ensure its long-term growth and sustainability. Urgent reforms are needed to address issues like climate vulnerability, inefficient irrigation, land fragmentation, and limited market access. Additionally, fostering technology adoption, improving infrastructure, and addressing gender disparities will be crucial for improving the sector's performance and securing India’s food security needs.
Janaagraha’s Report on Urban Local Bodies
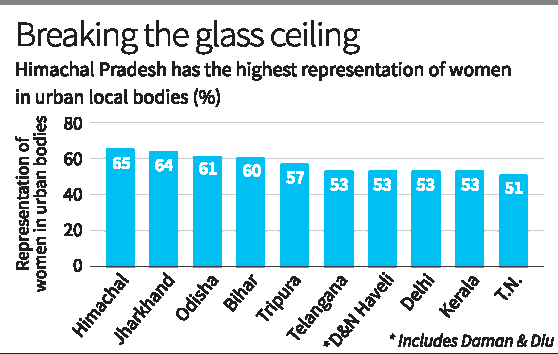
- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
46% of councillors in urban local bodies are women, says a report by Janaagraha, a not-for-profit organisation working to strengthen systems of governance in India’s cities.
Overview: Gender Representation in Urban Local Bodies
- Women Councillors in India: Around 46% of councillors in urban local bodies (ULBs) are women, according to a recent report by Janaagraha, a non-profit organization focused on strengthening urban governance systems.
- Capital Cities: In 19 out of 21 capital cities with active ULBs (such as Patna, Shimla, Ranchi, and Bhubaneswar), women councillors exceed 60% of the total councillor count.
Top States for Women Councillors
- Tamil Nadu stands out with the highest number of women councillors in the country, according to the "Roadmap for India’s City Systems Reforms" report by Janaagraha.
- Other States in the Top 10:
- Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Kerala, Bihar, and Chhattisgarh.
Women’s Reservation and Empowerment
- 50% Reservation: 17 states have legislated 50% women’s reservation in urban local bodies, surpassing the constitutional minimum of 33%.
Pathways for Urban Transformation
- Three Key Recommendations:
- Place-Based Governance: Advocates for governance focused on regional economies and local governments rather than sector-driven policies.
- Decentralised Participatory Governance: Emphasizes the need to strengthen urban local governments and increase citizen participation through the 74th constitutional amendment.
- Building State Capacities: Calls for a more effective role of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs and state urban departments focused on local self-government.
Rural-Urban Transition and Policy Reforms
- Urbanization of Villages: The report highlights that about 1,000 villages have already transitioned into urban areas since the 2011 Census, urging the need for a rural-urban transition policy.
- Reimagine Urban Ministries: Recommends restructuring urban ministries to focus on regional economies and the strengthening of local governance institutions.
Key Challenges in Urban Governance
- Delays in Elections: 61% of ULGs in 15 states have delayed council elections.
- Disempowered Local Bodies: Mayors and ULGs often lack autonomy, with control over only four out of 18 functions.
- Citizen Participation Gaps: There is a lack of formal platforms for citizen involvement in governance.
Skilling and Capacity Building
- Certification-Based Training: Proposes skilling programs for ULG staff, with a focus on improving municipal efficiency and project implementation.
- Shared Service Centres: Recommends creating municipal service centres to benefit smaller cities and enhance urban management.
Conclusion: Need for Place-Based Governance
- Strategic Shift: Srikanth Viswanathan, CEO of Janaagraha, emphasized the need to shift away from a sector-based governance model to a place-based governance approach, better suited to the urban challenges of modern India.
Earning Instead of Burning
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Paddy straw burning, prevalent in Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, contributes to severe air pollution, especially during the post-harvest period in October and November. Despite various government measures and subsidies to reduce stubble burning, it continues due to economic and operational constraints faced by farmers. To address this issue, innovative technologies for the productive use of paddy straw need to be explored.
Stubble Burning: Causes and Consequences
Reasons for Stubble Burning
- Short Crop Cycles: The narrow window between paddy harvest and wheat sowing forces farmers to burn straw to prepare fields quickly.
- Economic Constraints: High costs of alternative residue management methods.
- Lack of Awareness: Farmers are often unaware of sustainable alternatives.
- Limited Mechanization: Availability of crop residue management machinery is inadequate.
- Policy Gaps: Ineffective enforcement of regulations and insufficient incentives.
Consequences of Stubble Burning
- Air Pollution: Emission of harmful pollutants like PM2.5, CO2, and CO contributes to air quality degradation.
- Health Hazards: Increased respiratory illnesses due to the inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Soil Degradation: Loss of essential nutrients and organic matter.
- Climate Change: Stubble burning releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Economic Costs: Increased health care costs and loss of soil fertility.
Technologies for Paddy Straw Utilization
Large-Scale Technologies
- Direct Combustion:Burns rice straw under controlled conditions to generate heat for cooking and industrial uses. While its calorific value is lower than that of petrol and diesel, it is still viable for local energy generation.
- Pyrolysis and Gasification:
- Pyrolysis: Converts rice straw into bio-oil through heating at 200-760°C in the absence of oxygen.
- Gasification: Converts rice straw into syngas at higher temperatures (480-1,650°C) with limited oxygen. Challenges include low gas production and tar accumulation.
- Biochar Production:Rice straw is incinerated at lower temperatures to produce biochar, which is used as a soil conditioner to improve fertility, water retention, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Power Generation:Biomass-based power plants use rice straw to generate electricity, providing a sustainable energy source, especially for rural areas. States like Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh are scaling up such plants.
- Pellet Production:Rice straw is compressed into compact pellets, improving its density, transportability, and combustion efficiency. These pellets can partially replace coal in power plants, offering an alternative use for crop residue.
- Biofuels:Conversion of rice straw into biofuels like ethanol and biogas helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels and supports the renewable energy transition.
- Paper Production:Rice straw, with its high cellulose content, is used as an eco-friendly alternative to wood in the paper and pulp industry, reducing environmental impact.
Small-Scale Technologies
- Composting:Rice straw can be composted to produce organic fertilizer, enhancing soil health. Vermicomposting is another effective method, though awareness among farmers remains low.
- Mushroom Cultivation:Rice straw serves as an ideal substrate for growing mushrooms, particularly species like Volvariellavolvacea. This practice provides an additional income source for farmers.
- Silica Extraction:Rice straw contains high silica content, which can be extracted for industrial applications like construction and electronics.
- Fodder for Ruminants:Though rice straw is low in digestibility due to high silica content, it can be used as animal feed after pre-treatment, such as drying, grinding, or chemical processes to enhance its nutritional value.
- Adsorbent for Pollution Control:Rice straw can be used to remove heavy metals and toxins from contaminated water, showing promise in environmental cleanup efforts.
- Soil Incorporation:Instead of burning, rice straw can be incorporated directly into the soil to improve fertility, moisture retention, and crop yield. This practice is already being adopted in regions like Punjab and Haryana.
Conclusion: Path Forward
Stubble burning continues to be a significant environmental challenge, but the development and adoption of technologies for utilizing paddy straw can offer viable solutions. Both large- and small-scale technologies can convert rice straw into valuable products like biofuels, power, and fertilizers. To ensure widespread implementation, efforts must be made to increase awareness among farmers and stakeholders, coupled with strong policy support and infrastructural investment. A collaborative approach involving the government, industries, and farmers is essential for sustainable management of rice straw, benefiting both the environment and the economy.
Reimagining Governance with AI: The Promise of GovAI

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
India's rapid digital transformation, coupled with the advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), presents a unique opportunity to reimagine governance. The concept of GovAI—using AI to enhance public administration—holds the potential to revolutionize governance, improve efficiency, and create more responsive and inclusive public systems.
Digital Transformation in Governance
- Evolution of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
- Over the past decade, India has made significant strides in digital governance through the development of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). DPI has reduced inefficiencies, enhanced transparency, and improved service delivery, transforming India's governance landscape.
- Impact of AI on Governance
- As AI becomes a critical enabler in various sectors, its application to governance promises to deliver more efficient, inclusive, and responsive government services. The potential of AI lies in its ability to provide more with less, driving innovation across key public services.
Key Trends Driving GovAI
- Rapid Digitalization of India
- Currently, 90 crore Indians are connected to the Internet, with projections indicating 120 crore by 2026, positioning India as the most connected country globally.
- Digitalization serves as the backbone for AI-driven governance, enabling efficient data collection, analysis, and informed policy-making.
- Data as a Valuable Resource
- The rapid digitalization of India has led to the generation of vast amounts of data. This data serves as the fuel for AI models, which can be used to enhance governance.
- Programs like the IndiaDatasetsProgramme aim to harness government datasets for AI development while safeguarding data privacy through legislation.
- Demand for Efficient Governance
- The post-COVID world has underscored the need for governments to deliver better outcomes with fewer resources. AI has the potential to optimize the use of public resources, enabling more efficient and targeted governance.
India’s Leadership in AI-Driven Governance
- Positioning India as a Global Leader
- India’s digital governance initiatives have placed it at the forefront of AI adoption in the public sector. Through GovAI, India can solidify its position as a global leader in using technology for public good.
- As the Chair of the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI), India is advocating for the inclusive development of AI to ensure that it benefits all nations, not just a select few.
- Role of Innovation Ecosystem
- India’s innovation ecosystem, comprising startups, entrepreneurs, and tech hubs, can play a crucial role in driving the development of AI models, platforms, and apps for governance.
- A strong partnership between the government and private sector is essential to successfully deploy AI solutions across various sectors of governance.
Potential Benefits of GovAI
- Enhanced Efficiency and Service Delivery
- AI-powered tools, such as chatbots, can provide citizens with 24/7 assistance, streamlining public service delivery and reducing waiting times.
- AI can help in automating processes and improving the overall efficiency of government operations.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making
- AI can analyze large datasets to make informed policy decisions and design targeted interventions in sectors like healthcare, education, and social welfare.
- Data-driven insights can enhance the effectiveness of welfare schemes, improving outcomes for marginalized communities.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability
- AI can enhance transparency in governance by minimizing human intervention in processes, thus reducing corruption and ensuring efficient use of public resources.
- Predictive analytics and real-time data monitoring can enable proactive governance, preventing issues before they escalate.
Challenges and Drawbacks of GovAI
- Privacy Concerns
- The use of AI in governance requires the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about data privacy and surveillance.
- Robust data protection laws must be enforced to ensure citizens' data is handled responsibly.
- Accountability and Bias
- AI systems may produce biased outcomes depending on the data they are trained on. Ensuring accountability for decisions made by AI systems remains a challenge, particularly when errors or biases occur.
- Transparent mechanisms must be established to hold AI systems accountable for their actions.
- Increased State Control and Surveillance
- The integration of AI in governance could lead to increased state control, potentially compromising individual freedoms. Ensuring that AI is used responsibly to balance power between the government and citizens is critical.
- Digital Divide
- The benefits of AI in governance may not be evenly distributed across the population, exacerbating the digital divide.
- Efforts must be made to ensure that marginalized communities, without access to digital technologies or skills, are not left behind.
Conclusion
- Balancing Benefits and Risks
- The integration of AI into governance systems presents significant benefits, including enhanced efficiency, transparency, and proactive governance. However, there are challenges related to privacy, accountability, and state control.
- To ensure AI serves the public good, India must implement strong regulatory frameworks, promote transparency, and develop ethical AI systems that respect citizens’ rights and freedoms.
- Moving Toward Maximum Governance
- AI can help realize the vision of maximum governance, enabling more effective and targeted interventions across sectors like healthcare, security, education, and disaster management.
- The success of GovAI will depend on a trusted partnership between the government, private sector, and innovation ecosystem, ensuring that AI technology serves the larger public interest.
Sustainable Path to Net-Zero for India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
India's commitment to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070 presents a significant challenge, with only 45 years remaining to reach this ambitious target. The path to net-zero requires a balancing act between economic development, energy security, and climate adaptation. India’s efforts to meet its climate goals will be shaped by multiple factors, including resource constraints, land use, and financial limitations.
Why Net-Zero at All?
- Scientific Consensus on Climate Change
- Climate change is a growing concern, with the global temperature rise already reaching 1.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- To avoid catastrophic impacts, the world needs to limit the temperature rise to 1.5°C. The remaining global carbon budget for this target is around 400-500 billion tonnes of CO?.
- Necessity of Sharp Emission Reductions
- Countries must drastically reduce emissions to stay within the carbon budget. Achieving net-zero emissions is essential for maintaining global climate stability.
Equity in Net-Zero Transitions
- Developed vs. Developing Countries
- Developed nations, historically responsible for a large share of emissions, are expected to lead the transition. However, they have not met the financial and technological support commitments for developing countries.
- Developing nations like India, with low per capita emissions, are under pressure to balance climate action with economic development.
- Climate Justice
- India’s per capita emissions are among the lowest globally, but the richest 10% of Indians contribute significantly to national emissions, exacerbating inequality.
- The impacts of climate change disproportionately affect the economically weaker sections, making the transition to net-zero not only an environmental challenge but a social justice issue as well.
The Challenge of Balancing Development and Sustainability
- Limits of India’s Resources
- India faces resource constraints, including land, water, and biodiversity, which limit the feasible expansion of renewable energy capacity.
- Meeting energy demands while ensuring food security, forest cover, and biodiversity preservation becomes increasingly challenging as energy requirements rise.
- Sustainable Consumption vs. Aspirational Lifestyles
- India’s aspiration to emulate the developed world’s lifestyle is unsustainable due to limited resources, which could lead to severe consequences like groundwater depletion, heat stress, and biodiversity loss.
- The focus should be on sufficiency consumption corridors, ensuring that consumption meets developmental goals without exceeding sustainable limits.
Projected Power Demand and Renewable Energy Targets
- Rising Power Demand
- India’s power demand could increase nine to ten-fold by 2070. Meeting this demand entirely via renewable energy requires significant expansion in energy generation capacity:
- 5,500 GW of solar energy
- 1,500 GW of wind energy
- India’s power demand could increase nine to ten-fold by 2070. Meeting this demand entirely via renewable energy requires significant expansion in energy generation capacity:
- Land Use Constraints
- To meet these targets, India must address land-use trade-offs. Expanding beyond 3,500 GW of solar and 900 GW of wind would require significant compromises in land availability for other uses, including agriculture and conservation.
Strategic Pathways to Net-Zero: Demand and Supply Measures
- Demand-Side Measures
- Energy-efficient construction: Use of better materials and passive designs to reduce cooling energy demand.
- Urban transport: Shift to public and non-motorized transport to reduce energy consumption in cities.
- Dietary choices: Promoting sustainable dietary practices to reduce the carbon footprint of food systems.
- Electrification: Focus on alternative fuels and energy-efficient appliances.
- Supply-Side Measures
- Decentralization of Energy Production: Expanding rooftop solar panels and solar pumps for agriculture.
- Nuclear Power Expansion: Increase nuclear energy to provide a low-carbon baseload and complement renewable sources like solar and wind, which are intermittent.
The Role of International Cooperation and Financial Support
- Global Cooperation
- Global climate action requires alignment between national interests, which may not always coincide, as seen in the context of the U.S. presidential election potentially influencing global climate policy.
- India’s path to net-zero depends heavily on international climate financing, technology transfer, and collaborative efforts to address climate justice.
- Equitable Financing for Developing Countries
- Developed countries are expected to provide financial support to developing nations like India to achieve climate goals. However, this support has been insufficient to date.
Conclusion: India’s Balancing Act
India faces a challenging balancing act as it seeks to provide quality of life for its growing population while achieving its climate adaptation and mitigation goals. The path to net-zero will require careful management of economic growth, energy production, and resource conservation. India must focus on demand-side strategies to reduce energy consumption and increase efficiency while expanding renewable energy infrastructure in a sustainable manner. Additionally, international cooperation and financial support will be crucial in ensuring that India’s transition to net-zero is equitable, efficient, and aligned with its developmental priorities.
Andhra Pradesh's Natural Farming Model

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
Andhra Pradesh's (AP) natural farming model presents a transformative opportunity to reshape the state’s agricultural landscape by 2050. An analysis by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in collaboration with the AP government, reveals how scaling natural farming could employ more farmers, increase incomes, and foster sustainable agricultural practices, potentially surpassing the benefits of conventional industrial agriculture.
AgroEco2050: Exploring Two Agricultural Futures
The AgroEco2050 initiative aimed to envision two possible futures for Andhra Pradesh’s agricultural systems by 2050:
- Industrial Agriculture Path: Focusing on intensification of conventional farming, relying heavily on chemicals, machinery, and monocultures.
- Natural Farming Path: Expanding agroecological practices, relying on regenerative, chemical-free farming methods to create more jobs, better livelihoods, and improve the environment.
The study compared these pathways, analyzing their impacts on employment, income, food production, biodiversity, and land use.
Key Findings: Natural Farming’s Impact on Employment and Income
- Employment Growth
- By 2050, natural farming would employ twice as many farmers as industrial agriculture: 10 million compared to 5 million.
- Unemployment in natural farming would decrease to 7%, in stark contrast to a projected 30% unemployment rate in the industrial agriculture scenario.
- Farmer Income
- Natural farming is expected to be more profitable for farmers due to lower input costs (seeds, fertilizers, machinery) and higher market prices for high-quality produce.
- The income gap between farmers and non-farmers, which stood at 62% in 2019, would decrease to 22% under natural farming by 2050, a sharp improvement compared to the 47% gap predicted under industrial agriculture.
What is Natural Farming?
Natural farming is an ecological, chemical-free farming system that emphasizes the use of locally available resources. Key practices include:
- Biodiversity-based pest management
- On-farm biomass recycling (e.g., mulching)
- Indigenous techniques like using cow dung and urine for soil fertility.
Globally recognized as a form of regenerative agriculture, it offers a sustainable alternative to industrial agriculture by sequestering carbon and restoring soil health.
Global Adoption
States like Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, and others are already adopting natural farming. While still evolving, its acceptance among farmers is steadily growing.
Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) in Andhra Pradesh
Origin and Growth
- In 2016, Andhra Pradesh launched the Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) initiative to offer a sustainable alternative to capital-intensive agriculture.
- This program, implemented by RythuSadhikaraSamstha, targets covering 6 million farmers across 6 million hectares.
National Recognition
The ZBNF approach gained national attention when it was featured in the 2019 Union Budget, aimed at doubling farmers' incomes by 2022. The central government now promotes this model under the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY).
Challenges in Scaling Natural Farming
- Farmer Training and Support
- Farmers need ongoing education and support to transition effectively to natural farming. Current training systems often fail to address the full scope of their needs.
- Certification Barriers
- The certification process for organic farming, including Participatory Guarantee Systems (PGS) and third-party certifications, is complex and costly, presenting a barrier for small-scale farmers.
- Marketing and Procurement Challenges
- There is a lack of effective marketing systems for organic products, which hampers the ability of farmers to sell their produce at fair prices.
- Without strong procurement or buy-back systems, farmers may struggle to find markets for their products.
- Policy and Funding Gaps
- Organic and natural farming programs still receive minimal funding compared to subsidies for chemical fertilizers, impeding large-scale adoption.
- Slow state-level implementation and a continued reliance on chemical inputs also delay the widespread shift to natural farming.
Moving Forward
- Scientific Research on Yields
- To address concerns about lower yields for staple crops, more scientific research is needed to assess the long-term viability of natural farming, especially for crops like wheat and rice, which are crucial for India’s food security.
- Localized Adoption
- Natural farming may be best suited for non-staple crops or localized farming, balancing sustainability with the need for food security.
- Risk Mitigation for Food Security
- Careful evaluation of natural farming’s impact on staple crop yields is necessary to avoid the food security risks witnessed in countries like Sri Lanka, where a sudden shift to organic farming led to reduced yields and increased prices.
Conclusion
The Andhra Pradesh natural farming model offers a promising alternative to industrial agriculture, with the potential to create jobs, improve farmers' incomes, and promote environmental sustainability. However, for this vision to become a reality, significant efforts must be made to address challenges related to training, certification, marketing, and funding. With continued research, policy support, and community involvement, natural farming can play a crucial role in feeding the future and promoting a more sustainable agricultural system.
Khap Panchayats: Evolving Towards Modern Governance and Justice

- 17 Nov 2024
Why in the News?
Khap Panchayats have attracted attention due to their evolving role in addressing key socio-economic issues like unemployment, education, and rural development. Modernization efforts are underway to regulate these traditional councils, integrating them into formal Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) systems for better governance, accountability, and social justice.
What are Khap Panchayats?
Definition and Origin:
Khap Panchayats are community-based councils primarily found in North India, particularly in Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan. These informal bodies, composed of elders from kinship groups (Khaps), have historically served as local governance bodies that resolve disputes within their communities. Their origins trace back centuries and they function alongside formal legal systems, often prioritizing customary norms over constitutional law.
Historical Role:
Historically, Khap Panchayats have maintained social order in rural areas, acting as forums for dispute resolution related to marriage, property, and community matters. While their decisions were respected within their communities, they operated parallel to formal courts, and their influence was often seen as a stabilizing force in rural society. However, their structure has also contributed to the perpetuation of patriarchal practices and social exclusion.
Issues with Khap Panchayats
- Patriarchal Practices:Khap Panchayats have often been associated with gender inequality. They enforce rigid social norms that limit women's autonomy, particularly in matrimonial matters, inheritance rights, and personal freedoms. This has led to criticism for their role in suppressing women's rights.
- Honor Killings and Social Conservatism:Khap Panchayats are notorious for opposing inter-caste and same-gotra marriages, at times even endorsing honor killings to preserve social order. Such practices are violations of fundamental rights and personal freedoms guaranteed by the Indian Constitution.
- Legality Concerns:The decisions of Khap Panchayats often clash with constitutional values such as equality, personal liberty, and dignity. Their informal judgments lack legal validity and frequently violate the rule of law, raising significant concerns about their adherence to India’s legal framework.
- Caste-based Discrimination:Khap Panchayats have been criticized for reinforcing caste hierarchies, which leads to discrimination and exclusion of marginalized communities. Their focus on preserving traditional caste structures often results in the oppression of the vulnerable, particularly lower-caste groups.
Gender Dynamics and Evolving Roles of Khap Panchayats
In recent years, some Khap Panchayats have started to show more progressive and inclusive stances, particularly in promoting gender justice:
- Support for Women Athletes:Khap Panchayats have begun to recognize and celebrate the achievements of women, particularly in sports. Several Khap bodies have felicitated women sportspersons, contributing to a growing culture of sports among rural women. This marks a shift from their traditionally patriarchal stance.
- Promoting Gender Justice:Notably, the MehamChaubisiKhap in Haryana has played a significant role in advocating for women’s rights and gender equality. It was involved in supporting the 2023 wrestlers' protest against sexual harassment, demonstrating a shift towards gender-related activism and social reform.
Supreme Court Ruling on Khap Panchayats:
In the landmark Shakti Vahini v. Union of India case (2018), the Supreme Court of India addressed the issue of honor killings and inter-caste marriages. The Court emphasized that honor killings violate fundamental rights and called for strict measures to prevent such crimes. The Court further directed state governments to establish special protection cells for couples facing threats from their families and communities. This ruling underscored the importance of personal liberty and freedom of choice, regardless of community or caste.
What is Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)?
Definition and Importance:
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) refers to methods of resolving disputes without resorting to formal litigation. These methods include mediation, arbitration, and conciliation, all of which encourage cooperative problem-solving and mutually agreeable solutions. ADR is particularly important in India due to the overburdened judicial system, which faces a backlog of cases and delays.
ADR offers several advantages, including:
- Cost-effectiveness
- Confidentiality
- Flexibility
- Improved relationships between parties involved
Types of ADR Mechanisms:
- Arbitration: A formal process where an arbitrator resolves disputes and their decision is legally binding.
- Conciliation: A third-party neutral assists the parties in reaching an agreement, and the recommendations can be accepted or rejected.
- Mediation: A mediator facilitates communication between disputing parties, helping them reach a voluntary and mutually agreeable resolution.
- Negotiation: A direct negotiation between the parties without third-party involvement, aiming for a mutually acceptable settlement.
Integrating Khap Panchayats into the Formal ADR System
Given the potential of Khap Panchayats as community-based governance bodies, integrating them into the formal ADR framework can significantly enhance their role in dispute resolution. Here are some strategies for modernizing Khap Panchayats:
- Legal Recognition of ADR Role:Khap Panchayats can be legally recognized within the ADR framework, formalizing their role in mediation and dispute resolution, ensuring their decisions align with constitutional norms and human rights.
- Training and Capacity Building:Khap leaders can undergo training in ADR techniques such as mediation and arbitration, equipping them with skills to resolve conflicts impartially and in line with legal standards. This would help transition Khaps from informal bodies to more structured and legally compliant dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Legal Regulation and Oversight:Regulations can be put in place to define the scope and limitations of Khap Panchayats' authority, ensuring their decisions do not violate human rights or the constitution. Oversight mechanisms should be established to monitor their actions and prevent practices like honor killings or forced marriages.
- Shift Towards Developmental Roles:Some Khap Panchayats are already advocating for progressive reforms in areas like unemployment, education, and rural development. By focusing on these issues, Khap Panchayats can serve as agents of social change and contribute to community development.
- Awareness and Accountability:Awareness campaigns can educate rural communities about constitutional rights and the legal system, emphasizing the importance of formal legal frameworks and human rights. At the same time, Khap Panchayats should be held accountable for actions that undermine justice or equality.
- Collaboration with Formal Institutions:Khap Panchayats can collaborate with local governance bodies and judicial institutions, ensuring that their decisions align with the rule of law and contribute to social justice. This would enhance their role in inclusive decision-making and legally sound governance.
Conclusion
Khap Panchayats, with their deep-rooted history and influence, have the potential to evolve into modern governance institutions. By integrating them into the formal ADR framework, aligning their practices with constitutional values, and focusing on community development, they can contribute positively to dispute resolution and social reform in rural India. This transformation will require legal regulation, training, oversight, and awareness to ensure that Khap Panchayats function as effective, equitable bodies that respect the fundamental rights of all individuals.
Net Borrowing Ceiling

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
- In 2023, the central government imposed a Net Borrowing Ceiling (NBC) on Kerala, limiting its borrowing capacity to 3% of the projected Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) for the fiscal year 2023-24.
- Impact on Kerala’s Finances: This ceiling has significantly impacted Kerala’s ability to meet its expenditure needs and fund developmental activities, triggering political and legal disputes. Kerala has approached the Supreme Court of India, arguing that the imposition of NBC infringes upon its constitutional rights under Article 293 of the Indian Constitution.
Constitutional Provisions on Borrowing Powers
Article 292: Borrowing Powers of the Centre
- Central Government’s Borrowing: Article 292 grants the Central Government the authority to borrow money on the security of the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Limits on Borrowing: The extent of borrowing by the Centre is determined by laws enacted by Parliament.
Article 293: Borrowing Powers of the States
- State Borrowing: Article 293 allows State Governments to borrow within India against the Consolidated Fund of the State. However, it imposes certain conditions:
- If a State has outstanding loans or guarantees given by the Centre, the Centre’s consent is required to raise further loans.
- The Central government can impose conditions when granting such consent.
Centre’s Role in State Borrowing
- Article 293(3) allows the Centre to impose conditions on a state’s borrowing if it has existing liabilities or guarantees outstanding.
- The Centre has wide discretion in granting or denying consent, which has been a point of contention in Kerala’s case.
The Imposition of Net Borrowing Ceiling (NBC)
Scope of the NBC
- Comprehensive Coverage: The NBC encompasses all borrowing avenues, including open market loans, loans from financial institutions, and liabilities from State public accounts. To curb circumventing of the borrowing cap via State-owned enterprises, the NBC also covers borrowings by these entities.
Purpose of NBC
- Fiscal Discipline: The NBC is designed to regulate borrowing and prevent states from accumulating unsustainable levels of debt, thus ensuring financial stability.
- Transparency: By including all borrowing avenues, including off-budget borrowings by state-owned enterprises, the NBC aims to provide a clearer picture of a state’s financial health.
Arguments for the NBC
- Macroeconomic Stability: The NBC helps maintain macroeconomic stability by controlling the borrowing levels of states, thus protecting the national economy.
- Compliance with FRBM Act: The NBC aligns with the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, aiming to keep the fiscal deficit within prescribed limits.
- Equitable Resource Distribution: The NBC ensures that wealthier states do not disproportionately borrow, thus promoting balanced regional development.
Arguments Against the NBC
- Erosion of Fiscal Autonomy: Critics argue that the NBC undermines the fiscal autonomy of states, as guaranteed by Article 293, by restricting their ability to make independent financial decisions.
- Impact on Developmental Activities: States, particularly Kerala, contend that the borrowing cap restricts their ability to fund key infrastructure projects and social welfare activities.
- Legal Concerns: The NBC’s impact on the interpretation of Article 293 raises legal questions regarding the extent of the Centre’s authority over state borrowing powers.
Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act
Overview of the FRBM Act
- Objective: The FRBM Act, 2003 was enacted to promote fiscal discipline and ensure long-term financial stability in India.
- Key Features:
- Targets a 3% fiscal deficit of GDP for the Centre.
- Requires states to enact similar laws to control their fiscal deficit.
Amendments to FRBM Act
- 2018 Amendment: The FRBM Amendment Act required the central government to ensure that the fiscal deficit did not exceed 3% of GDP and total public debt remained under 60% of GDP.
- Fiscal Deficit Reduction: By 2025-26, the fiscal deficit is expected to be reduced to below 4.5% of GDP.
Way Forward: Strengthening Article 293
Guidelines for Borrowing Powers
- Transparency in Decision-Making: The Centre should ensure that the borrowing process is transparent, with clear standards and procedures for accepting or rejecting state borrowings.
- Consultative Process: The Centre should engage in consultations with states before imposing borrowing caps or conditions, fostering a cooperative federal structure.
- Equitable Treatment: Borrowing restrictions should apply uniformly to all states to avoid bias or favoritism.
Strengthening Fiscal Federalism
- Fiscal Autonomy: States should be given the flexibility to manage their finances in a way that reflects their unique economic needs and challenges.
- Periodic Reviews: The Net Borrowing Ceiling should be reviewed periodically to account for changing economic conditions and developmental priorities.
The Need for More Women in Politics
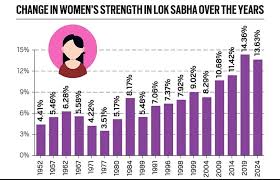
- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
India, the world's largest democracy, is at a crucial juncture where women’s active political participation is essential for holistic development and true democratic engagement. The year 2024 demands increased involvement of women in politics to address issues of gender inequality and ensure comprehensive policy representation.
Current Status of Women’s Political Representation in India
Women in Parliament
- Initial Representation: In 1952, women accounted for only 4.41% of the Lok Sabha. This gradually rose to around 14.36% in the 2019 elections.
- Recent Trends: In the 2024 elections, women made up approximately 16% of the Lok Sabha, with 74 women MPs, 43 of whom are first-time representatives.
Women in State Legislatures
- Representation in state legislative assemblies remains low, with the highest percentages in Chhattisgarh (14.4%), West Bengal (13.7%), and Jharkhand (12.4%).
Global Comparison
- According to the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), India ranks lower than many countries in terms of female representation in parliament, with global averages standing at 26.1%. India lags behind several African and South Asian nations.
Importance of Women’s Political Empowerment
- Enhancing Governance and Accountability: Political empowerment of women ensures better representation of gender-sensitive issues, promoting accountability in governance.
- Breaking Patriarchal Norms: Increasing women’s participation helps challenge the patriarchal structure that dominates Indian politics and promotes inclusive governance.
- Policy and Social Impact: Women in politics are more likely to advocate for policies that address issues like health, education, and gender equality, leading to improved societal welfare.
- Economic Benefits: Studies suggest that women in political leadership tend to improve economic outcomes for their constituencies by prioritizing social infrastructure.
Barriers to Women’s Political Participation
- Gender Gaps in Political Ambition: Women are less likely to pursue political careers due to gender conditioning, family pressures, and stereotypes about leadership abilities.
- Patriarchal Culture: A deeply ingrained patriarchal society hampers women’s political involvement, with male-dominated party structures and social norms limiting opportunities.
- High Election Costs: The financial burden of running for office often discourages women from contesting elections due to unequal access to resources.
- Male Gatekeepers in Politics: Political parties often show a preference for male candidates, especially for higher-profile positions, hindering the rise of women leaders.
- Criminalisation and Corruption in Politics: Growing criminalisation in politics and lack of political education further alienates women from the political process.
Key Legislative and Constitutional Measures for Women’s Political Empowerment
Legislative Measures
- Nari Shakti VandanAdhiniyam (2023): Provides 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and state assemblies.
- 73rd and 74th Amendments (1992): Introduced 33% reservation for women in Panchayats and Municipalities.
- Gender-Neutral Rules: Lok Sabha adopted gender-neutral rules in 2014, promoting inclusivity in legislative procedures.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 14 and 15: Ensure equality and non-discrimination, fundamental to women’s political participation.
- Article 243D: Mandates 33% reservation for women in Panchayats.
International Commitments
- CEDAW (1979): Advocates for women’s participation in political and public life.
- Beijing Platform (1995) and SDGs (2015): Call for removing barriers to women’s participation in politics.
Measures for Promoting Women’s Political Participation
- Quotas and Reservations: Ensuring mandatory quotas for women candidates in party tickets and legislative bodies can help bridge gender gaps.
- Capacity Building and Training: Offering political training programs for women can empower them with the skills and resources necessary for effective political participation.
- Strengthening Grassroots Movements: Support for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) can build leadership among women at the local level.
- Supportive Political Ecosystem: Political parties should be encouraged to nominate women for higher office positions, such as the Rajya Sabha or state legislative councils.
- Raising Public Awareness: Public awareness campaigns focusing on the importance of women in politics can shift societal attitudes and garner wider public support.
Conclusion:
As India moves forward, the active participation of women in politics is not merely a matter of equity but an essential building block for a vibrant, inclusive, and effective democracy. Through structural reforms, public awareness, and the promotion of female leadership, India can strengthen its democratic framework, ensuring that all citizens, regardless of gender, have an equal stake in shaping the nation's future.
Inter-State Council

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
The Inter-State Council, which works for Centre-State and interstate coordination and cooperation, has been reconstituted with Prime Minister Narendra Modi as its chairman, all chief ministers and nine Union ministers as members and 13 Union ministers as permanent invitees.
About the Inter-State Council (ISC)
Formation of ISC
- Establishment: Created on May 28, 1990, through a Presidential Order following the recommendations of the Sarkaria Commission (1988).
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
- Meetings: The Council has convened 12 times since its formation.
Constitutional Provisions
- Not a Constitutional Body: It was established under Article 263 of the Constitution, making it a non-permanent advisory body.
- Role: Article 263 empowers the President to create the ISC for improving coordination between States and the Union.
Powers and Functions
- Investigate and Discuss: The ISC discusses subjects of common interest between the Centre and States.
- Recommendations: It recommends measures for better coordination and addressing inter-state issues.
- Deliberations: The ISC also deliberates on matters referred by the Chairman.
Composition of the ISC
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India.
- Members:
- Chief Ministers of all States and Union Territories with legislative assemblies.
- Lieutenant Governors/Administrators of Union Territories without assemblies.
- 6 Union Cabinet Ministers nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Governors of States under President’s rule.
- Standing Committee:
- Chaired by the Union Home Minister.
- Includes 5 Union Cabinet Ministers and 9 Chief Ministers.
Functions and Role of the ISC
Role in Centre-State Cooperation
- Facilitates better coordination and cooperation between the Centre and States.
- Addressing disputes related to Centre-State and Inter-State relations.
Additional Functions
- Make Recommendations: Based on discussions, it recommends actions to align policies.
- Promote Social Legitimacy: Through consensus-driven decisions, ISC strengthens policy acceptance among states.
Key Bodies Related to Centre-State Relations
Zonal Councils
- Purpose: Promote interstate cooperation and coordination.
- Constitution: There are five Zonal Councils (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, Southern) and a separate North Eastern Council established in 1972.
River Water Dispute Tribunals
- Function: Set up under the Inter-State River Water Disputes Act, 1956, these tribunals resolve disputes over river water sharing between States.
GST Council
- Constitution: Established under Article 279A, the GST Council is responsible for decisions related to GST implementation, ensuring cooperative federalism.
Chief Justice of India

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
On November 11, 2024, Justice Sanjiv Khanna was sworn in as the 51st Chief Justice of India (CJI) at the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Delhi, marking a significant milestone in the Indian judiciary. He succeeds Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, who retired on November 10, 2024. Justice Khanna's term as CJI will last until May 13, 2025.
Background of Justice Sanjiv Khanna
Early Life and Legal Career
- Legal Practice: Justice Khanna began his legal career in 1983 after completing his law degree from Delhi University. He practiced in the District Courts of Delhi and handled cases in constitutional law, taxation, arbitration, and environmental law.
- Career in Delhi High Court: He was appointed as an Additional Judge to the Delhi High Court in 2005 and became a Permanent Judge in 2006.
- Appointment to the Supreme Court: Justice Khanna was appointed as a Supreme Court Judge in January 2019, without having served as a Chief Justice of a State High Court, and superseding 32 senior High Court judges.
Key Judicial Rulings of Justice Sanjiv Khanna
Major Constitutional Bench Decisions
- Abrogation of Article 370: Justice Khanna was part of the Bench that upheld the abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution, which revoked Jammu and Kashmir’s special status.
- Electoral Bonds Scheme: He also contributed to the ruling that struck down the 2018 Electoral Bonds scheme, raising questions about the transparency of political funding.
Support for EVMs
- Justice Khanna defended the use of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) and rejected calls to revert to paper ballots, emphasizing the need for technological progress and institutional trust.
Personal Liberty and Bail Decisions
- Arvind Kejriwal’s Interim Bail: Justice Khanna granted interim bail to Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal in the liquor policy case, underscoring personal liberty as a fundamental right.
- Judicial Review of Bail Conditions: He also initiated discussions on setting standards for bail conditions in cases involving significant political figures.
Role of the Chief Justice of India (CJI)
Appointment Process
- Article 124(2): A Supreme Court judge is appointed by the President of India, with the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court traditionally becoming the CJI.
- Qualifications: The CJI must be a citizen of India and have served as a judge in a High Court for at least five years or as an advocate in a High Court for ten years.
Powers and Responsibilities
- Master of the Roster: The CJI is the "Master of the Roster," responsible for assigning cases to specific benches and determining the court's schedule.
- Collegium System: The CJI, along with four senior judges, forms the Collegium that recommends judicial appointments for the Supreme Court and High Courts.
- Ad-Hoc Appointments: The CJI can also appoint ad-hoc judges to the Supreme Court under Article 127 of the Constitution.
Removal
- A CJI can only be removed through a process initiated in Parliament, requiring a special majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Appointment of CJI in Other Countries
United States
- The Chief Justice of the United States serves for life, with tenure continuing until impeachment or voluntary retirement.
United Kingdom
- The Lord Chief Justice in the UK is appointed by a special panel from the Appeal Court or the Supreme Court. The tenure is life, but mandatory retirement is set at 75 years of age.
Conclusion
Justice Sanjiv Khanna’s appointment as the 51st Chief Justice of India represents a significant moment in the country's judicial history. With his extensive experience and legal acumen, he faces numerous challenges, from dealing with case pendency to navigating sensitive constitutional issues. His tenure will likely shape the future trajectory of the Indian judiciary, with a focus on upholding justice and personal liberty while addressing the evolving needs of a democratic society.
Significance of LignoSat
- 12 Nov 2024
Introduction
- LignoSat is the world's first satellite constructed with wood, developed to test the viability of using timber as a sustainable material in space exploration.
- Launched on November 5, 2024, the satellite was sent to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard a SpaceX Dragon cargo capsule and will be released into orbit after a month for a six-month test.
What is LignoSat?
- Dimensions: LignoSat measures 4 inches (10 cm) on each side and weighs 900 grams.
- Material Composition: The satellite features panels made from magnolia wood using traditional Japanese craftsmanship, without screws or glue.
- Development Collaboration: LignoSat was developed by Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry, in collaboration with various researchers and space organizations.
Purpose and Objectives of the Mission
- Testing Timber in Space:
- The primary goal is to study how wood performs in the extreme conditions of space, where temperatures fluctuate dramatically between -100°C to 100°C.
- The satellite will also assess how wood interacts with space radiation and its potential to reduce the impact of radiation on sensitive electronics, such as semiconductors.
- Space Sustainability:
- LignoSat aims to demonstrate that wood can be a sustainable, renewable alternative to metals (like aluminium) traditionally used in spacecraft construction.
- The satellite will help determine if wood can be used in future space missions, potentially reducing reliance on non-renewable materials.
Testing the Durability of Wood in Space
- Challenges of Space Environment:
- Space is an extremely harsh environment with extreme temperature variations, exposure to radiation, and the lack of water and oxygen, all of which affect material durability.
- Unlike Earth, where wood decomposes due to moisture and oxygen, space's vacuum conditions could potentially preserve the wood's integrity, providing valuable insights into its durability.
- Previous Use of Wood in Space:
- Wood has already been tested in space applications: cork has been used on spacecraft to withstand re-entry conditions.
- The LignoSat mission builds on this knowledge, aiming to test wood's performance in space's high-radiation and vacuum environment.
Potential Advantages of Using Wood in Space Exploration
- Sustainability and Environmental Benefits:
- Unlike conventional aluminium satellites, which generate harmful pollutants upon re-entry (e.g., aluminium oxides), LignoSat's wooden components will degrade in a more environmentally friendly manner, minimizing atmospheric pollution.
- As space exploration increases, particularly with mega-constellations (e.g., SpaceX’s Starlink), space debris management becomes critical. Using wood could reduce the environmental impact of satellite disposal.
- Renewable Resource:
- Wood is a renewable resource, which offers a potential solution to the growing demand for materials used in space technology.
- Kyoto University researchers have long been exploring the idea of building habitats on the Moon and Mars using timber, with LignoSat seen as a stepping stone to proving the material's space-grade capabilities.
LignoSat's Design and Construction
- Hybrid Construction:
- While the outer panels of LignoSat are made from magnolia wood, the satellite still incorporates traditional aluminium structures and electronic components inside.
- The hybrid construction allows researchers to compare the performance of wood against conventional materials used in spacecraft.
- Testing Methods:
- LignoSat will orbit Earth for six months and monitor the wood’s reaction to space conditions, providing valuable data for future space missions.
- Sensors embedded in the satellite will track various environmental factors, such as radiation exposure, temperature fluctuations, and the structural integrity of the wood.
The Long-Term Vision: Building Timber Habitats in Space
- The research team, led by Takao Doi (astronaut and Kyoto University professor), envisions a future where timber is used for constructing space habitats on the Moon and Mars.
- The team’s ultimate goal is to plant trees in space and develop timber houses on extraterrestrial bodies, providing a sustainable, self-sufficient environment for humans in space.
Broader Implications for Space Exploration
- Sustainability in Space Missions:
- LignoSat represents an innovative step toward more sustainable space technologies by investigating eco-friendly materials that can minimize the environmental impact of space missions.
- It aligns with global efforts to make space exploration more sustainable, especially as space tourism and colonization plans grow.
- Future Prospects:
- If successful, LignoSat could pave the way for wood-based materials being used in spacecraft construction, not only for satellites but also for space stations and future human habitats in space.
Conclusion
- LignoSat’s mission marks a significant milestone in space exploration by exploring wood as a sustainable material in space technology.
- As the first wooden satellite, its results could pave the way for more eco-friendly, renewable materials in future space missions, aligning with global goals for sustainability and reducing space-related pollution.
What are the costs of population decline?

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
India has been witnessing significant demographic changes due to decades of family planning policies. This has led to declining fertility rates in certain States, particularly in the southern and smaller northern regions.
Introduction: Demographic Shift in India
- Southern States’ Fertility Trends: States like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana have fertility rates below the replacement level (around 1.4–1.5), while Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh have higher fertility rates (2.6–3).
- Ageing Population: Southern States face the challenge of an ageing population, with Kerala projected to have 22.8% of its population aged 60+ by 2036, while Bihar will have only 11%.
Economic and Health Impact of Population Decline
- Economic Consequences:
- Dependency Ratio: The old-age dependency ratio (the number of elderly for every 100 working-age individuals) has increased significantly in some States. Kerala, for example, had a ratio of 26.1 in 2021, signaling a crisis point.
- Loss of Demographic Dividend: States with declining fertility rates face the loss of a demographic dividend, i.e., the economic benefit from a large working-age population, which is increasingly burdened by elderly dependents.
- Health Expenditure: Rising healthcare costs, especially for cardiovascular diseases in southern States, will strain public health systems. The southern States, although comprising one-fifth of India's population, spent 32% of the country’s total out-of-pocket expenditure on cardiovascular diseases in 2017-18.
- Challenges of Low Fertility:
- Declining Labour Force Participation: Policies encouraging higher fertility may also reduce women’s labour force participation, undermining the economic growth of these States.
- Economic Pressures: Southern States, despite higher tax contributions, face a diminished share of central resources due to slower population growth. This is a point of concern in inter-State fiscal relations.
Political Implications of Uneven Population Growth
- Impact on Federal Structure:
- The uneven population growth across States will lead to significant changes in the delimitation of constituencies after the current freeze on seat allocation in Parliament expires in 2026.
- Redistribution of Lok Sabha Seats: Northern States like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar will likely gain more seats, while southern States like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh will lose seats due to their declining population shares.
- Challenges in Federal Relations:
- Southern States’ economic contributions through taxes are disproportionate to the resources they receive from the central pool, leading to growing tensions between high-growth and slow-growth regions.
- The shift in political power post-delimitation could increase regional disparities, potentially leading to political tensions between States.
Solutions and Policy Recommendations
- Pro-Natalist Policies:
- Southern States are considering pro-natalist policies to incentivize higher fertility rates. However, such measures have been largely unsuccessful internationally, especially when women’s economic independence and educational choices are restricted.
- International Experience: Attempts to incentivize childbearing, without addressing broader socio-economic factors like gender equality, have generally failed in other nations. Maternity benefits, gender-neutral parental leave, and childcare support are key to increasing fertility sustainably.
- Gender Equity and Work-Family Balance:
- Work-family policies that support paid maternity and paternity leaves, affordable childcare, and gender-neutral employment policies are essential to empower women to balance family and career.
- Studies indicate that countries with higher gender equity have better fertility rates because women are less likely to forgo childbearing for career reasons.
- Increasing Retirement Age:
- One way to reduce the old-age dependency ratio is to increase the retirement age, which would allow older workers to remain employed longer and support a sustainable economy.
- Social Security and pension reforms should also be considered to accommodate the ageing workforce and reduce the economic burden on younger generations.
- Managing Migration:
- Migration policies should be adjusted to manage the influx of economic migrants into southern States, who contribute to the economy but continue to be counted in their home States for fiscal and political purposes.
- Migration-based policy reforms could address the challenge of an ageing population in states with declining fertility while ensuring equitable resource distribution across States.
Bharat 6G Mission
- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
India aspires to lead the world in 6G technology by 2030 through the Bharat 6G Mission. This initiative builds upon the successful rollout of 5G, which reached 98% of districts in just 21 months.
Key Features of 6G Technology
- Terahertz (THz) Frequencies: 6G will utilize THz waves capable of transmitting significantly more data than 5G, offering ultra-fast data rates.
- Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output): Supports a large number of devices and simultaneous connections using multiple antennas, improving data transmission and reception.
- Network Slicing: Creates specialized, smaller networks tailored to specific traffic types, such as video streaming or industrial automation.
- Enhanced Security: Incorporates advanced encryption and authentication protocols to safeguard sensitive data.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC): Ensures ultra-low latency, critical for applications like industrial automation, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR).
- Integrated Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IIRS): Enhances signal strength and quality, particularly in areas with poor reception.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Supports data communication over hundreds of GHz or THz frequencies, facilitating faster transfer rates.
Government Initiatives for 6G Development
Bharat 6G Vision and Strategy
- Goal: To design, develop, and deploy 6G technologies, ensuring secure, intelligent, and pervasive global connectivity.
- Core Principles:
- Affordability, sustainability, and ubiquity aligned with the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India).
- Strategic Objectives:
- Promote R&D through startups, universities, and industries.
- Develop affordable 6G solutions and global IP contributions.
- Focus on transformative applications to enhance quality of life.
Technology Innovation Group (TIG) on 6G
- Established: November 1, 2021.
- Task Forces:
- Focus on multidisciplinary solutions, spectrum management, devices and networks, international standards, and R&D funding.
Bharat 6G Alliance
- A collaborative effort between Indian industry, academia, and research institutions to develop 5G advancements, 6G products, and patents.
- Global Alignment: Partners with organizations like the Next G Alliance (US), 6G Flagship (Finland), and South Korea’s 6G Forum.
Applications of 6G Technology
Application Area
Description
Healthcare
Real-time patient monitoring and AI-connected devices.
Agriculture
IoT and AI-driven predictive systems for crop health and irrigation.
Defense & Internal Security
Enhanced surveillance, communication, and unmanned operations.
Disaster Response
High-volume communication for emergency coordination.
Transportation
Ultra-low latency for urban air mobility and traffic management.
Education
High-speed remote learning, immersive AR/VR-enabled classrooms.
Metaverse
3D holographic displays and seamless virtual interactions.
Industrial Automation
Smart factories with enhanced operational efficiency through real-time data.
Smart Cities
Efficient urban infrastructure and real-time monitoring using IoT.
Entertainment & Media
Higher-quality streaming, immersive content delivery.
Environmental Monitoring
Real-time data collection for resource management and conservation.
Challenges in 6G Development
- Technical Complexity: Development of advanced components and subsystems makes 6G technology highly complex.
- Infrastructure Deployment: Significant investment and regulatory support are required for the necessary infrastructure upgrades.
- Spectrum Allocation: The limited availability of spectrum poses challenges in balancing competing demands for bandwidth.
- Security Concerns: High-speed data transmission increases vulnerability to cyber threats, necessitating robust security protocols.
- Standardization Issues: Achieving global consensus on standards for 6G interoperability can be slow and contentious.
- Global Collaboration: Effective international cooperation is critical for technological and regulatory alignment.
Conclusion
India’s Bharat 6G Mission represents a visionary approach to maintaining technological leadership in the rapidly evolving global digital landscape. By investing in research, fostering international collaborations, and pursuing policies aligned with Atmanirbhar Bharat, India can harness 6G to fuel socio-economic growth and strengthen global connectivity.
Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education Act, 2004

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
The Supreme Court recently upheld the constitutional validity of the Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education Act, 2004 (also called the Madarsa Act), while striking down certain provisions related to the granting of higher education degrees. The Court overturned the Allahabad High Court's previous decision, which had deemed the Act unconstitutional on the grounds that it violated the principle of secularism.
What is the Madarsa Act?
The Madarsa Act provides a legal framework for regulating madrasas (Islamic educational institutions) in Uttar Pradesh. The Act:
- Establishes the Uttar Pradesh Board of Madarsa Education, which oversees the curriculum and examinations for madrasas.
- Ensures that madrasas follow the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) curriculum for mainstream secular education alongside religious instruction.
- Empowers the state government to create rules for regulating madrasa education.
Allahabad High Court's Ruling
In March 2024, the Allahabad High Court declared the Madarsa Act unconstitutional, citing:
- Violation of secularism: The Court argued that the Act's emphasis on compulsory Islamic education, with modern subjects being optional, discriminated on religious grounds, violating the secular nature of the Constitution.
- Right to Education: The Court also claimed that the Act denied quality education under Article 21A, which guarantees free and compulsory education to children.
- Higher Education Degrees: The Act's provisions allowing the granting of Fazil and Kamil degrees were found to conflict with the University Grants Commission Act, 1956, which regulates higher education.
Supreme Court's Ruling
The Supreme Court overturned the Allahabad High Court's decision on several grounds:
- Basic Structure Doctrine: The Court clarified that the basic structure doctrine, which applies to constitutional amendments, does not apply to ordinary legislation like the Madarsa Act. Therefore, a law cannot be struck down simply for violating secularism unless explicitly prohibited by the Constitution.
- State's Authority to Regulate Education: The Court held that the state has the right to regulate education in minority institutions, as long as the regulation is reasonable and rational. It emphasized that the Madarsa Act does not deprive these institutions of their minority character.
- Right to Education for Minority Institutions: Referring to a 2014 decision, the Court ruled that the Right to Education Act (RTE) does not apply to minority institutions, as it would undermine their right to impart religious education and self-administer.
Striking Down Higher Education Provisions
While upholding most of the Act, the Supreme Court struck down the provisions related to higher education degrees (Fazil and Kamil). It ruled that:
- Section 9 of the Act, which allowed the Board to grant these degrees, is in conflict with the University Grants Commission Act, which only permits degrees to be awarded by universities recognized by the UGC.
Implications of the Ruling
- Regulation of Madrasa Education: The ruling affirms the state's authority to ensure quality education in madrasas, balancing religious instruction with secular subjects.
- Protection of Minority Rights: By upholding the Madarsa Act, the Court protected the rights of religious minorities to run educational institutions while ensuring they meet educational standards.
- Focus on Inclusivity: The judgment emphasizes the integration of madrasas within the broader educational framework, ensuring that madrasa students receive quality education.
In conclusion, the Supreme Court's decision supports the regulation of madrasa education while safeguarding the rights of minority institutions, except in areas related to the granting of higher education degrees, which remain under the jurisdiction of the UGC Act.
Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
Need for modification of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) amidst changing geopolitical, environmental, and demographic realities.
Background of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- About IWT:
- Signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank.
- Governs the sharing of the Indus River system waters.
- Historical Context:
- Origin in the Inter-Dominion Accord of 1948 post-partition.
- Finalized after negotiations facilitated by the World Bank in 1951.
- Key Provisions:
- Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) allocated to India.
- Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) allocated to Pakistan, with limited use allowed for India (e.g., hydropower, irrigation).
- Establishment of the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC) for cooperation and dispute resolution.
India’s Perspective
- Rationale for Modification:
- Increased demographic and agricultural demands.
- Need for sustainable water management.
- Acceleration of hydropower projects on western rivers permitted by the treaty.
- Security Concerns: Cross-border terrorism impacting trust in treaty operations.
Pakistan’s Concerns
- Dependence on Indus System: Critical for agriculture and drinking water as the lower riparian state.
- Potential Impacts of Modification:
- Fear of reduced water availability.
- Concerns over India’s hydropower projects altering water flow.
Current Challenges
- Hydropower Projects: Disputes over compliance with treaty provisions regarding hydropower construction.
- Technical Disputes: Divergent interpretations of treaty terms.
- Political Tensions: Strained bilateral relations with minimal diplomatic engagement.
- Climate Change Impacts: Altered precipitation patterns and glacial melt affecting water availability.
Arguments for Modifying the Treaty
- Addressing Contemporary Challenges: Climate change, technological advancements, and increased water demand.
- Securing National Interests:
- Clarifications on hydropower construction.
- Improved dispute resolution mechanisms.
Risks of Modifying the Treaty
- Escalation of Tensions: Perceived unilateral actions by Pakistan.
- Political Sensitivities: Domestic opposition in both countries.
Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
- Engagement and Dialogue: Bilateral discussions with potential third-party mediation (e.g., World Bank).
- Cooperation over Conflict: Recognizing mutual benefits of collaboration in water management.
- Adaptation Measures: Incorporate provisions addressing climate change and technological advances.
Zeroing in on Methane Diplomacy, at COP29

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
From November 11 to 22, 2024, global leaders will gather in Baku, Azerbaijan, for the 29th Conference of Parties (COP29) under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). This year’s summit, known as the Finance COP, will focus on setting a new global climate finance target—the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG).
A key focus of the summit is the reduction of methane emissions, as countries aim to curb near-term temperature increases, which buys critical time for long-term CO2 reductions necessary for stabilizing climate change.
U.S.-China Collaboration and Methane Reduction
US-China Collaboration Despite Geopolitical Tensions
Despite ongoing geopolitical tensions, the United States and China have found common ground on the issue of methane reduction. Both nations recognize the importance of addressing methane emissions, which are more potent in the short term than CO2. They, along with the United Arab Emirates, organized a summit at COP28 to discuss methane and other non-CO2 pollutants.
China’s National Plan for Methane Emissions
In November 2023, China launched its first national methane reduction plan, emphasizing capacity-building efforts over explicit reduction targets. This plan marked a significant step in China’s climate policy, underscoring its commitment to mitigating methane emissions alongside the U.S.
Given that China and the U.S. are the two largest contributors to methane emissions globally, their collaboration presents a significant opportunity for global climate mitigation efforts. India, the third-largest emitter of methane, could benefit from this partnership by seeking financial support and technical expertise to address its methane challenges.
India’s Methane Emissions Profile and Challenges
Emissions Breakdown
India’s Third Biennial Update Report to the UNFCCC indicates that in 2016, India emitted approximately 409 million tons of CO2-equivalent methane. The major sources of these emissions include:
- Agriculture: 74% (mainly from livestock and rice cultivation)
- Waste: 14% (unmanaged organic waste in landfills and dumpsites)
- Energy: 11%
- Industrial processes: 1%
Due to the dominant role of agriculture, India has been cautious about committing to stringent methane reduction targets. Initiatives like the Global Methane Pledge, which calls for a 30% reduction from 2020 levels by 2030, have not been fully embraced.
Environmental and Health Impact of Methane Emissions
Methane-related fires at waste dumpsites, such as the Bhalswa dump in Delhi (2022), have highlighted the broader environmental and health risks of methane emissions. These fires contribute significantly to air pollution, making it urgent for India to address methane in its waste management and agricultural sectors.
India’s Initiatives for Methane Reduction
Waste Management Programs
- Comprehensive Waste Management Framework India’s waste management sector is a significant source of methane, contributing 14% of the nation’s total emissions. Although a comprehensive regulatory framework for waste management has been developed, implementation remains slow due to local capacity constraints and financial limitations.
- Innovative Solutions Indore, a city in Madhya Pradesh, has pioneered waste sorting and biomethane production. The city's initiative includes:
- Sorting organic waste
- Converting it into biogas to fuel city buses
This model has gained national attention and is being considered for replication in other cities.
- GOBARdhan Scheme Launched as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0, the Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) scheme encourages rural communities to convert cattle manure and other organic waste into biogas and compost, reducing methane emissions from livestock waste while providing additional income to rural households.
Agricultural and Livestock Emission Reduction
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) The NMSA promotes climate-resilient agricultural practices that reduce methane emissions. For example, Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) is a water-saving technique used in rice farming that reduces methane emissions by limiting anaerobic decomposition.
- National Livestock Mission Under the National Livestock Mission, practices such as improved fodder management, silage making, and Total Mixed Ration (TMR) feeding are being promoted. These practices reduce methane emissions from livestock by improving digestion and feed efficiency.
Opportunities for India at COP29
Leveraging U.S.-China Methane Partnership
COP29 offers India an opportunity to leverage the U.S.-China collaboration on methane reduction. By engaging with these two major emitters, India can seek:
- Financial support
- Technical assistance
- Capacity-building resources, particularly for its waste sector, which is a significant source of methane emissions.
Accurate data on methane emissions, such as satellite-based monitoring, can help India refine its emission inventories and enhance the effectiveness of its methane mitigation efforts.
Fast-Tracking India’s Methane Reduction Efforts
Although methane is not the primary focus at COP29, India has an opportunity to fast-track its efforts in methane reduction. The country's existing policies and initiatives, such as waste management programs and agricultural missions, provide a foundation upon which international collaboration can build.
Recent data from satellite monitoring in cities like Delhi and Mumbai shows that actual methane emissions from waste dumpsites may be 50%-100% higher than previously estimated, highlighting the urgency of addressing this issue.
Conclusion
Although methane may not dominate the COP29 agenda, it represents a critical pathway for India to accelerate its climate action. With the groundwork already laid through domestic policies and innovative solutions, India now requires enhanced financial and technical backing to scale up its methane reduction initiatives. By engaging proactively at COP29, India has a unique opportunity to secure the resources needed to tackle methane emissions, benefiting both its citizens and the global fight against climate change.
Supreme Court Ruling on Property and Redistribution

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
A crucial 9-judge bench of the Supreme Court ruled on the scope of government powers over private property, with a focus on Articles 39(b) and 31C of the Constitution.
Key Issues Considered by the Court
- Article 31C: Whether it still protects laws giving effect to Articles 39(b) and 39(c), even after amendments and past rulings.
- Interpretation of Article 39(b): The meaning of “material resources of the community” and the limits on government acquisition.
Legal and Constitutional Background
- Article 31C and 39(b) Overview:
- Article 31C was introduced by the 25th Amendment (1971) to protect laws related to the distribution of resources for the common good.
- Article 39(b) (Directive Principle of State Policy) mandates that resources should be distributed to best serve the common good.
- Historical Context:
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973): The Supreme Court affirmed the Constitution’s "basic structure," impacting the interpretation of amendments to Article 31C.
- Minerva Mills Case (1980): The Court struck down further amendments to Article 31C.
The Supreme Court’s Ruling in 2024
- Restoration of the Post-Kesavananda Position: The Supreme Court clarified that the interpretation of Article 31C is restricted, and the protection under this article applies only to laws implementing Articles 39(b) and 39(c), not all directive principles.
- On Redistributing Private Property:
- The majority opinion held that not all privately owned properties can be considered “material resources of the community” for redistribution under Article 39(b).
- The Court dismissed the broad interpretation of "material resources" used in previous rulings (e.g., Justice Krishna Iyer’s dissent in the Ranganatha Reddy case, 1977).
Dissenting and Concurring Opinions
- Justice Nagarathna’s Concurring Opinion:
- Acknowledged that certain privately owned resources could be considered material resources (e.g., forests, wetlands), but emphasized a balanced approach.
- Distinguished between personal belongings and resources that could be considered part of the public domain.
- Justice Dhulia’s Dissent:
- Argued for a broader interpretation, in line with past rulings, that private resources could be considered material resources if they served the public good.
Interpretation of Article 39(b)
- Scope of the Article:
- Article 39(b) directs the State to ensure that the ownership of material resources is distributed to serve the common good.
- It imposes a positive obligation on the State to create policies for resource distribution, but does not authorize arbitrary expropriation of private property.
- Private Property as Material Resources:
- The Court clarified that private property cannot be deemed a material resource of the community unless specific conditions are met (e.g., scarcity, public welfare implications).
- The judgment emphasized a case-by-case analysis rather than a blanket approach.
Criteria for Assessing Material Resources
The Court provided criteria to evaluate whether a private property could be considered a “material resource of the community”:
- Nature of the Resource: What is the resource’s fundamental characteristic?
- Impact on Public Welfare: Does the resource impact the common good or public interest?
- Ownership Type: Is the resource privately owned or under state control?
- Scarcity: Is the resource scarce or in finite supply?
- Concentration of Ownership: Are the resources concentrated in the hands of a few private entities?
Implications of the Ruling
- Protection of Private Property Rights: The ruling strengthens protections against arbitrary State acquisition of private property, reinforcing the constitutional safeguards for property rights.
- Economic Implications: The Court noted that India’s economic trajectory has shifted from socialism to a market-based economy, and that resource redistribution policies should reflect this change.
- Policy Shifts: The ruling marks a shift away from a socialist economic ideology towards one that emphasizes private property rights, while still considering public welfare in resource distribution.
Conclusion
- Balancing Individual Rights with Public Welfare: The ruling underscores the importance of balancing private property rights with the need for equitable resource distribution to serve the common good.
- Implications for Constitutional Interpretation: This judgment marks a pivotal moment in the interpretation of property rights in India, affirming the evolving nature of the Constitution in response to dynamic economic and social policies.
Does Data Justify Subdivision of Quotas?
- 05 Nov 2024
Context
India's reservation system has long been a tool for uplifting historically marginalized communities, especially Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs). However, recent debates have questioned whether the system serves its intended purpose, particularly in light of disparities within the SC groups. The need for a ‘quota-within-quota’ system has been raised to ensure more equitable outcomes across different SC subgroups.
The Reservation System: Origins and Objectives
Purpose of Reservations
- Historical Background: Established to correct centuries of social and economic exclusion faced by SCs and STs.
- Mechanism for Equality: Aimed to create opportunities in education, government employment, and public offices for historically marginalized groups.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s Vision: Reservations were designed to transition from formal legal equality to substantive equality.
Challenges of the Current System
- Despite progress, certain SC subgroups seem to have benefited more than others.
- A Supreme Court ruling has led to calls for a 'quota-within-quota' to address intra-SC disparities.
Exploring Intra-SC Disparities: The Data Analysis
States Examined
- Key States: Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- Objective: To investigate whether some SC subgroups have disproportionately benefited from the reservation system.
Findings Across States
- Andhra Pradesh: Minor differences between SC groups (Malas vs. Madigas), with both groups showing similar socio-economic progress.
- Tamil Nadu: No significant disparity between Adi Dravida and Pallan groups, both benefiting equally from reservations.
- Punjab: Subdivision of quotas since 1975 has led to better outcomes for disadvantaged groups like Mazhabi Sikhs and Balmikis.
- Bihar: The Mahadalit category, introduced in 2007, failed due to political intervention, undermining the policy’s goals.
Key Insights
- In some states (e.g., Punjab), a subdivision of quotas has been effective in addressing intra-SC disparities.
- In other states, like Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, the benefits of reservations are already distributed fairly evenly among SC subgroups.
- The gap between SCs and upper-caste groups remains much larger than the gap within SCs.
The Issue of Access to Reservations
Caste Certificates as a Proxy for Access
- Data from IHDS: Less than 50% of SC households in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar report having caste certificates, limiting access to reserved positions.
- Better Access in Some States: Over 60-70% of SC households in Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh have caste certificates.
Core Issue: Ensuring Access
- Access Challenges: Without proper access to caste certificates, many SCs are excluded from the benefits of the reservation system.
- Priority Area: Ensuring that all eligible SCs have access to reservations is a critical concern before considering subdivision.
The 'Quota-within-Quota' Proposal
Concept and Potential Benefits
- Targeted Assistance: A ‘quota-within-quota’ would provide more focused help to the most disadvantaged SC subgroups, as seen in Punjab.
- Political Considerations: However, the political motivations behind quota subdivision, as seen in Bihar, can undermine the policy’s effectiveness.
Criticism and Limitations
- Uneven Need for Subdivision: In many states, the need for further subdivision is minimal, as the benefits of reservations are already fairly distributed.
- Political Exploitation: The policy risks becoming a political tool rather than a genuine means of achieving social justice, as political influence often determines who is categorized as the most disadvantaged.
Addressing Inequality Beyond Reservations
Income-Based Criteria and Monetary Benefits
- Current Approach: Monetary benefits (e.g., scholarships, lower fees) are a part of the affirmative action system.
- Income Criterion: Should be used to determine eligibility for monetary benefits to focus assistance on those most in need.
The "Creamy Layer" Debate
- Supreme Court’s Suggestion: The introduction of a "creamy layer" exclusion for SCs, akin to the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) model, remains contentious and requires stronger evidence.
Challenges of Economic Mobility
- Stigma and Discrimination: Economic progress does not necessarily eliminate social stigma or discrimination, especially for historically marginalized groups.
- Long-Term Goal: While reservations have contributed to creating a Dalit middle class, addressing stigma will require a gradual process.
The Need for Updated Data and Evidence-Based Policy
Data Deficiency
- Lack of Comprehensive Data: The absence of updated, reliable data on caste-based disparities limits the effectiveness of any policy reform.
- National Census Delay: India’s national Census, the only source of comprehensive data on caste, has been delayed, exacerbating the problem.
Evidence-Driven Reform
- Importance of Data: Robust and up-to-date data is essential to assess the true impact of reservations and to make informed policy decisions.
Conclusion: Reforming the Reservation System
- Reservations’ Success: The reservation system has played a significant role in improving the socio-economic status of SCs and STs.
- Intra-SC Disparities: While some subgroups benefit more than others, the broader gap between SCs and upper-caste groups remains far more pronounced.
- Focus on Access: The primary focus should be on improving access to reservations, ensuring that all eligible SCs benefit fully from affirmative action.
Key Takeaways from COP-16: Convention on Biological Diversity

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The 16th edition of the Convention of Biological Diversity (CBD) in Cali, Colombia was concluded.
Key Agreements at COP-16
- Establishment of the Cali Fund
- Purpose: To ensure equitable benefit-sharing from the use of Digital Sequence Information (DSI) on genetic resources.
- Focus on Indigenous Communities: At least 50% of the Cali Fund will support Indigenous peoples and local communities, with special emphasis on women and youth.
- Creation of a Permanent Subsidiary Body
- Inclusion of Indigenous Peoples: A new body will ensure the active participation of Indigenous groups in biodiversity conservation and policy discussions.
- Resource Mobilisation Strategy
- Target Funding: The conference agreed on a strategy to secure USD 200 billion annually by 2030 to support global biodiversity initiatives.
- Kunming Biodiversity Fund: A contribution of USD 200 million from China to support biodiversity funding.
- Management of Invasive Alien Species
- New Guidelines: Proposals for databases, cross-border trade regulations, and enhanced coordination with e-commerce platforms to manage invasive species.
- Identification of Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Areas (EBSAs)
- Enhanced Process: COP-16 agreed on an evolved process for identifying EBSAs, a critical aspect of marine conservation.
- Global Action Plan on Biodiversity and Health
- One Health Approach: Approval of a global action plan to curb zoonotic diseases, promote health, and safeguard ecosystems.
India’s Contribution at COP-16
Updated National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP)
- Financial Commitment: India plans to invest ?81,664 crore (USD 9.8 billion) from 2025-30 on biodiversity conservation.
- Focus Areas: India highlighted efforts such as the establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance, expansion of Ramsar sites, and increased spending on biodiversity from 2018-2022.
International Finance Support
- Global Partnerships: India emphasized the need for international finance to meet biodiversity targets, particularly under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Outcomes from COP-16
- New Mechanisms for Biodiversity Conservation
- Cali Fund: Ensures equitable benefit-sharing from genetic resources.
- Permanent Subsidiary Body: Facilitates the inclusion of Indigenous peoples in policy-making.
- Funding and Resource Mobilization
- USD 200 Billion Annually: Strategy to secure funding for biodiversity initiatives.
- Redirecting Harmful Subsidies: Agreement to redirect USD 500 billion in harmful subsidies by 2030.
- Biodiversity and Human Health
- Global Action Plan on Biodiversity and Health: Aimed at preventing zoonotic diseases and promoting human, animal, and environmental health.
Challenges in Biodiversity Protection
Key Threats to Biodiversity
- Population Growth and Resource Demand: Increasing population and demand for biological resources lead to over-exploitation.
- Habitat Degradation and Climate Change: Destruction of ecosystems and climate change threaten species globally.
- Invasive Species: Introduction of non-native species harms local biodiversity.
- Government Policies: Policies that prioritize development without environmental safeguards contribute to biodiversity loss.
Gaps in Global Biodiversity Framework
- Weak Legal Language: Concerns about insufficient legal protection for critical ecosystems.
- Lack of Implementation Mechanisms: Absence of mandatory review mechanisms for biodiversity targets.
Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF)
Framework Overview
- Adoption: Adopted at COP-15 in 2022, the KMGBF sets 23 action-oriented targets for biodiversity by 2030.
- Key Goals: Includes restoring 30% of degraded ecosystems and reducing the risk of invasive species by 50%.
- Living in Harmony with Nature: The framework envisions achieving biodiversity targets and living sustainably with nature by 2050.
Way Forward: Moving from Agreements to Action
- Participation of Stakeholders - Inclusive Approach: Ensuring the involvement of all relevant stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and local communities, in biodiversity conservation.
- Integrated Resource Management - Ecosystem Approach: Promoting a holistic approach to managing biodiversity and natural resources.
- Strengthening Governance - Good Governance Practices: Encouraging better governance to prevent unregulated exploitation of natural resources.
- International Financial Support - Alignment with Financial Institutions: Aligning global financial institutions and multilateral development banks with biodiversity conservation goals.
WWF Living Planet Report 2024

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- The WWF Living Planet Report 2024 highlights a drastic 73% decline in the average size of monitored wildlife populations globally from 1970 to 2020.
- The report underscores the urgent need for biodiversity conservation to maintain ecological balance, food security, and human health.
Key Findings of the 2024 Report
Wildlife Population Decline
- 73% Decline in monitored wildlife populations over the past 50 years (1970-2020).
- Freshwater species: Declined by 85%, the most significant drop.
- Terrestrial species: Declined by 69%.
- Marine species: Declined by 56%.
Main Threats to Wildlife
- Habitat Loss: Primary driver, particularly due to the expansion of food systems.
- Overexploitation: Over-hunting, fishing, and resource extraction.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species disrupt local ecosystems.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil contamination, especially in Asia-Pacific.
- Disease: Emerging diseases impacting wildlife populations.
Ecosystem Risks and Tipping Points
- Decline in wildlife signals risks of ecosystem tipping points.
- Critical ecosystems, like the Amazon and coral reefs, face potential irreversible damage.
- Impact on global food security and livelihoods due to ecosystem collapse.
India’s Wildlife Status
- Vulture populations in India remain critically endangered.
- Tiger populations have increased to 3,682 (2022).
- Snow leopards have been successfully monitored with 718 individuals recorded.
Case Study: Chennai’s Wetland Loss
- 85% reduction in Chennai’s wetlands due to urban expansion, exacerbating flood and drought risks.
- Initiatives like the Tamil Nadu Wetland Mission aim to restore these wetlands to improve ecosystem resilience.
Impacts of Wildlife Decline
- Ecosystem Imbalance
- Disruption in predator-prey relationships, pollination, and nutrient cycles due to species decline.
- Leads to ecosystem instability and potential collapse.
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Reduced genetic diversity makes ecosystems less resilient to environmental changes.
- Increases vulnerability to diseases, natural disasters, and climate change.
- Threats to Food Security
- Pollinators like bees and insects are essential for crop yields.
- Loss of pollinators threatens global food supply and agriculture.
- Human Health Implications
- Healthy ecosystems regulate disease by controlling pest populations.
- Declining biodiversity increases the risk of zoonotic diseases, such as COVID-19.
- Economic Consequences
- Agriculture, fisheries, and tourism industries depend on healthy ecosystems.
- Decline in wildlife can lead to job losses and economic instability.
- Cultural and Social Impacts
- Wildlife holds cultural, spiritual, and recreational value for societies worldwide.
- Loss of iconic species diminishes cultural identities and opportunities for nature-based tourism.
Challenges in Biodiversity Conservation
- Inadequate National Actions
- Despite global commitments (e.g., Global Biodiversity Framework, Paris Agreement, UN SDGs), national actions are insufficient to meet 2030 biodiversity targets.
- Risk of crossing tipping points that could lead to irreversible ecosystem degradation.
- Key Drivers of Biodiversity Loss
- Habitat Loss: Driven by agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure development.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, extreme weather, and altered precipitation patterns.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable hunting, fishing, logging, and resource extraction.
- Pollution: Industrial, agricultural, and plastic pollution disrupt natural habitats.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species outcompeting and threatening native populations.
- Lack of Funding: Inadequate financial resources for effective conservation.
- Weak Policy and Enforcement: Poorly implemented habitat protection laws.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Increased interactions between expanding human populations and wildlife.
- Genetic Diversity Loss: Reduced genetic diversity makes species vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes.
- Awareness Gaps: Insufficient public awareness on the importance of biodiversity.
Conclusion and Way Forward
Policy and Action Recommendations
- Expand protected areas and restore ecosystems to halt biodiversity loss.
- Engage Indigenous communities in conservation and land management practices.
- Promote sustainable farming, reduce food waste, and encourage plant-based diets to lessen food production impacts.
- Shift to renewable energy and reduce fossil fuel use to mitigate climate change.
- Redirect investments from environmentally harmful sectors to nature-friendly industries.
WWF-India’s Call for Collective Action
- WWF-India advocates for collective action to align climate, conservation, and sustainable development policies.
- The goal is to ensure a resilient and thriving future for both biodiversity and human societies.
Tackling Judicial Pendency and Adjournments in India

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
The issue of judicial delays and adjournments has become a significant concern in India’s judicial system. President Droupadi Murmu, while addressing the National Conference of District Judiciary in September 2024, emphasized the need to eliminate the culture of adjournments. These delays particularly affect the poor and rural populations, who often suffer in silence, avoiding court due to the fear of protracted justice.
Background of the Indian Judicial System
India’s judicial system has evolved under various legal frameworks, including the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC) and the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC). Initially, civil courts dealt with a wide range of cases, while criminal courts focused on criminal offenses. The establishment of the Supreme Court and High Courts further strengthened India’s judicial architecture to handle constitutional and appellate cases.
To address the growing caseload, the Indian government introduced the tribunal system through the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1976, aiming to manage specialized disputes. However, despite these reforms, case pendency continues to rise.
Key Issues Contributing to Judicial Delay and Pendency
- Judge-to-Population Ratio - India currently has 21 judges per million people, far below the recommended 50 judges per million as per the 120th Law Commission Report. The shortage of judges directly contributes to the growing backlog of cases.
- Vacant Judicial Positions - As of late 2024, 30% of High Court positions remain vacant, exacerbating the case pendency crisis. The delay in filling these vacancies has resulted in overburdened judges, further delaying case resolution.
- Legislative Overload - The enactment of laws without conducting prior judicial impact assessments leads to an increase in the number of cases, often without considering the capacity of the judiciary to handle them. This lack of foresight results in excessive pressure on courts.
- Overworked Judiciary - Judges often face a heavy workload, with some handling multiple responsibilities across different courts. This overburdening leads to mental fatigue, increased errors, and prolonged decision-making.
- Witness Delays - The absence of witnesses and delays in their appearance in court can significantly prolong the judicial process, contributing to case pendency.
Government Initiatives and Challenges
-
- National Judicial Infrastructure Plan (NJIP): The NJIP aims to modernize judicial infrastructure, improving court functioning and case processing. However, its full implementation across the country remains a work in progress.
- E-Courts Project: The E-Courts project aims to digitize the judicial process, including e-filing and virtual hearings. This initiative has shown promise in reducing procedural delays but still requires wider application.
- Tribunal System: While tribunals were introduced to reduce the burden on regular courts, their success has been limited, and the abolition of six tribunals in 2021 has added additional pressure on High Courts.
- Case Timeline Legislation: Laws prescribing time-bound adjudication for sensitive cases have been enacted, but due to inefficiencies in the system, deadlines are rarely met.
Recommendations for Reform
-
- Enhance Judicial Strength
-
- Increase the Judge-to-Population Ratio: The government should prioritize the appointment of judges to meet the 50 judges per milliontargets.
- Fill Vacant Positions: High Courts should fill vacant positions six months in advance to ensure a steady supply of judges.
-
- Judicial Impact Assessment
- Implement Judicial Impact Assessments: The Justice M. Jagannadha Rao Committee’s recommendation for judicial impact assessments should be made mandatory. Every new Bill should assess the likely increase in judicial workload, the required number of judges, and the necessary infrastructure.
- Promote Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
-
- Encourage ADR Mechanisms: Mediation and arbitration should be promoted as cost-effective alternatives to court proceedings. Public awareness campaigns and legal reforms can encourage the use of ADR.
-
- Strengthen Infrastructure and Technology
- Modernize Court Infrastructure: The judiciary should invest in technology such as e-filing and virtual hearings to reduce administrative burdens and expedite case resolutions.
- Streamline Administrative Processes: Technology can also help automate administrative tasks, thereby reducing the workload on judges and speeding up case processing.
- Limit Adjournments
- Stricter Norms for Adjournments: Judicial bodies should enforce stricter norms for granting adjournments, ensuring that they are not used excessively.
- Oversight Mechanism: An independent body can monitor the frequency of adjournments and take corrective action if needed.
Conclusion
Addressing the issue of judicial adjournments and case pendency requires a comprehensive approach involving structural reforms, better resource allocation, and the adoption of technology. Strengthening the judiciary’s infrastructure, increasing judicial appointments, and promoting alternative dispute resolution are vital steps toward ensuring quicker, fairer justice. The collaborative efforts of the judiciary, government, and society at large are essential to ensuring that India’s judicial system can meet the demands of justice in a timely and efficient manner.
