India-Sri Lanka Diplomatic Engagement

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent visit of Sri Lankan President Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD) to India marked a significant moment in bilateral relations, as it was his first foreign trip since assuming office. The visit underscored key diplomatic exchanges and collaborations between the two countries, showcasing both areas of agreement and divergence.
Key Takeaways from AKD's Visit
Assurance on Anti-India Activities: One of the primary concerns for India was the use of Sri Lankan territory for activities detrimental to its security, particularly the presence of Chinese “research vessels” at Sri Lankan ports. President AKD assured Prime Minister Narendra Modi that Sri Lanka would not allow its territory to be used in ways that threaten India’s interests. This assurance is crucial, as it signals Sri Lanka's stance on maintaining regional stability, despite AKD’s perceived pro-China inclinations.
Tamil Minority Issue: Divergent Views: A notable divergence in their discussions was the issue of the Tamil minority in Sri Lanka. India has long advocated for the full implementation of the 13th Amendment to Sri Lanka’s Constitution, which would grant greater autonomy to the Tamil minority. However, AKD resisted this, reaffirming his opposition to the amendment’s full implementation. While India emphasized the importance of reconciliation and holding provincial elections, AKD focused on unity, sustainable development, and social protection, sidestepping any definitive commitments on the Tamil issue.
Sri Lanka's Assertive Diplomatic Posture: AKD’s strong parliamentary mandate has allowed him to adopt a more assertive diplomatic stance. This is evident not only in his handling of the Tamil issue but also in his approach to dealing with major powers like India and China. His administration appears to be prioritizing a more independent foreign policy, signaling a shift from previous administrations.
Bilateral Cooperation and Development Initiatives
The visit saw significant agreements on bilateral cooperation, particularly in development and connectivity. Both nations acknowledged the positive impact of India’s assistance in Sri Lanka’s socio-economic growth. Key projects discussed include:
- Indian Housing Project: Phases III and IV.
- Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects across three islands.
- High-Impact Community Development Projects.
- Digital collaborations, such as the implementation of Aadhaar and UPI systems in Sri Lanka.
Additionally, discussions focused on enhancing energy cooperation, including the supply of LNG, development of offshore wind power in the Palk Strait, and the high-capacity power grid interconnection. The resumption of passenger ferry services between key Indian and Sri Lankan ports was also a priority.
Defence and Security Cooperation
The two leaders agreed to explore a Defence Cooperation Framework and intensify collaboration on maritime surveillance, cyber security, and counter-terrorism. This aligns with India’s strategic interests in the region, as it seeks to ensure stability in the Indian Ocean and strengthen its defense ties with Sri Lanka.
Strategic Continuity Amid Leadership Change
Despite a change in leadership, the core strategic interests between India and Sri Lanka remain aligned. India views Sri Lanka’s stability as crucial to regional security, and both countries are focused on a mutually beneficial partnership. AKD’s emphasis on economic recovery and tackling corruption within Sri Lanka, as seen in his actions against political figures like Speaker Asoka Ranwala, further signals his determination to build a strong foundation for his government’s future.
Conclusion
President AKD’s visit highlighted the evolving dynamics of Sri Lanka’s foreign policy, marked by a more confident and independent approach in engaging with India. While challenges remain, especially regarding the Tamil issue, both countries have reaffirmed their commitment to deepening bilateral ties, with a focus on development, connectivity, and strategic cooperation.
India-Bhutan Relations

- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The December 2023 visit of Bhutan’s King and Queen to India highlights the enduring and strategic partnership between the two nations. Amidst growing Chinese influence and Bhutan’s domestic challenges, the visit holds significant geopolitical relevance, reinforcing India-Bhutan relations and underscoring Bhutan's critical role in India’s regional security.
Reaffirmation of India-Bhutan Relations
The visit reaffirmed the strong, time-tested partnership between India and Bhutan, rooted in mutual trust and cooperation. India reiterated its commitment to Bhutan's socio-economic development, increasing its financial aid for the 2024-2029 period from ?5,000 crore to ?10,000 crore. Notably, Bhutan’s flagship Gelephu Mindfulness City Project, championed by King Jigme Khesar, received strong Indian backing, reflecting India’s willingness to align with Bhutan’s developmental priorities.
Strategic Areas of Cooperation
Clean Energy and Hydropower
Bhutan remains central to India’s renewable energy strategy, particularly in hydropower, a vital part of Bhutan's economy. Bhutan exports the majority of its hydropower to India, reinforcing bilateral ties in the energy sector. This cooperation aligns with India’s regional energy security goals, with both nations seeking to strengthen clean energy initiatives.
Infrastructure Development
The visit also emphasized infrastructure projects, vital for enhancing Bhutan's connectivity. These projects are strategically significant, considering Bhutan's geostrategic importance in the Himalayas. Infrastructure development further strengthens the ties between the two nations, with a focus on mutual benefits and regional stability.
Geopolitical Context: China’s Growing Influence
China-Bhutan Border Disputes
The border issue with China has been ongoing since 1984. In 2023, Bhutan and China signed an agreement to expedite the settlement and demarcation of their borders. China’s push for resolution is part of its broader strategy to reduce India’s influence in Bhutan. The disputed areas, particularly those near India’s Siliguri Corridor, hold strategic importance for New Delhi. Any territorial adjustments could undermine India’s access to its Northeastern states.
Chinese Influence and Economic Engagement
China has been constructing villages along disputed border areas, altering ground realities and establishing civilian hubs that could serve as military outposts. Additionally, China is offering economic incentives to Bhutan, including promoting tourism and investing in Bhutan’s telecom sector, seeking to draw the country into closer economic and diplomatic alignment.
India’s Role in Bhutan’s Security and Sovereignty
Strategic Dependence on India
Bhutan's small military relies heavily on Indian support for training and defense. The 2017 Doklam standoff, where Indian forces intervened to prevent China from constructing a road in disputed territory, underscored India's crucial role in safeguarding Bhutan’s territorial integrity.
Friendship Treaty
The India-Bhutan Friendship Treaty is the cornerstone of their bilateral relations, ensuring Bhutan's sovereignty while reinforcing India's role in Bhutan’s foreign and defense policies. India's increased financial support aims to counter China’s economic influence in Bhutan.
Challenges for Bhutan
Balancing India and China
Bhutan is navigating a delicate balance between preserving its historical ties with India and engaging with China, which offers economic benefits. However, Bhutan’s sovereignty concerns limit its ability to make independent diplomatic decisions.
Domestic Issues
Bhutan faces challenges such as youth migration and limited economic diversification. Over-reliance on hydropower and a lack of industrial development make it vulnerable to external pressures, particularly from China.
The Strategic Importance of Bhutan to India
Geopolitical Buffer
Bhutan's location is vital for India’s security, especially in relation to the Siliguri Corridor, a narrow land link connecting India’s Northeast. Any Chinese presence in Bhutan’s disputed regions could disrupt access to this crucial corridor.
Hydropower Collaboration
Bhutan’s hydropower exports are central to India’s renewable energy strategy, and their cooperation in this area ensures mutual benefits.
Way Forward
India must continue to prioritize Bhutan’s development needs, ensuring robust financial and infrastructural support. Proactive engagement is necessary to address Bhutan’s concerns, particularly in light of China’s growing influence. Additionally, India should support Bhutan’s economic diversification to reduce reliance on external actors.
Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
Need for modification of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) amidst changing geopolitical, environmental, and demographic realities.
Background of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)
- About IWT:
- Signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank.
- Governs the sharing of the Indus River system waters.
- Historical Context:
- Origin in the Inter-Dominion Accord of 1948 post-partition.
- Finalized after negotiations facilitated by the World Bank in 1951.
- Key Provisions:
- Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) allocated to India.
- Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) allocated to Pakistan, with limited use allowed for India (e.g., hydropower, irrigation).
- Establishment of the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC) for cooperation and dispute resolution.
India’s Perspective
- Rationale for Modification:
- Increased demographic and agricultural demands.
- Need for sustainable water management.
- Acceleration of hydropower projects on western rivers permitted by the treaty.
- Security Concerns: Cross-border terrorism impacting trust in treaty operations.
Pakistan’s Concerns
- Dependence on Indus System: Critical for agriculture and drinking water as the lower riparian state.
- Potential Impacts of Modification:
- Fear of reduced water availability.
- Concerns over India’s hydropower projects altering water flow.
Current Challenges
- Hydropower Projects: Disputes over compliance with treaty provisions regarding hydropower construction.
- Technical Disputes: Divergent interpretations of treaty terms.
- Political Tensions: Strained bilateral relations with minimal diplomatic engagement.
- Climate Change Impacts: Altered precipitation patterns and glacial melt affecting water availability.
Arguments for Modifying the Treaty
- Addressing Contemporary Challenges: Climate change, technological advancements, and increased water demand.
- Securing National Interests:
- Clarifications on hydropower construction.
- Improved dispute resolution mechanisms.
Risks of Modifying the Treaty
- Escalation of Tensions: Perceived unilateral actions by Pakistan.
- Political Sensitivities: Domestic opposition in both countries.
Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
- Engagement and Dialogue: Bilateral discussions with potential third-party mediation (e.g., World Bank).
- Cooperation over Conflict: Recognizing mutual benefits of collaboration in water management.
- Adaptation Measures: Incorporate provisions addressing climate change and technological advances.
16th BRICS Summit
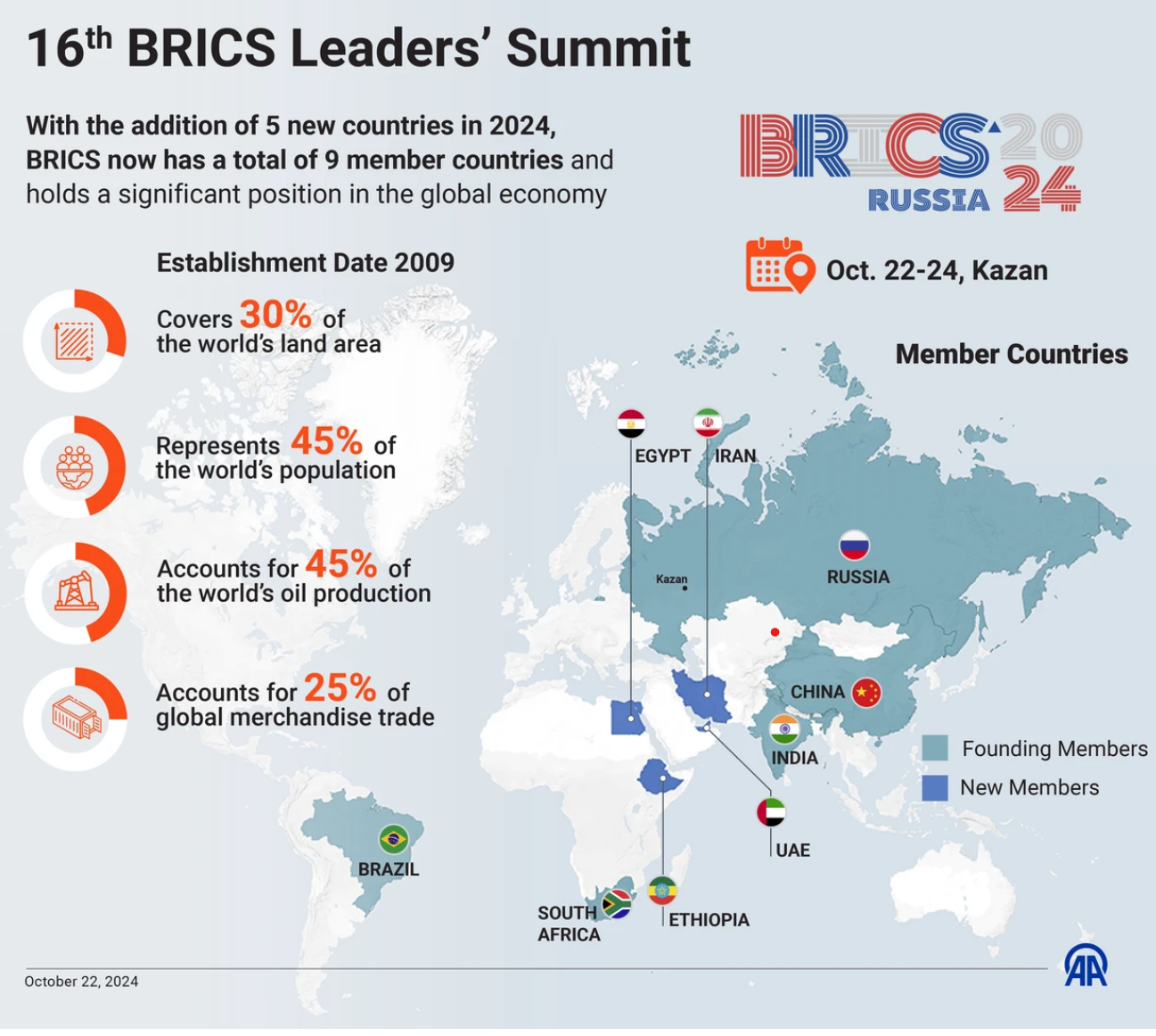
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the 16th BRICS Summit was held in Kazan, Russia.
Key Highlights:
Overview of the Bilateral Meeting between PM Modi and President Xi
- Location & Context: The meeting took place on the sidelines of the 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan, Russia (October 23, 2024), marking the first bilateral interaction between PM Modi and President Xi Jinping in nearly five years.
- Significance: The meeting focused on India-China relations, specifically the border dispute that arose following the 2020 standoff in Ladakh.
- Agreement on Border Disengagement: Both leaders welcomed an agreement for "complete disengagement" along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), which could pave the way for the resolution of issues that emerged after the Galwan Valley clashes in June 2020.
Key Points of the India-China Border Pact
- Resolution of Border Issues: The agreement addresses longstanding disputes, including in Depsang Plains and Demchok, where Chinese forces had encroached on Indian territory.
- Restoration of Patrolling: Both nations agreed to restore patrols to old patrolling points (PPs) along the LAC in these disputed areas.
- Next Steps: The Special Representatives (SRs) on the India-China boundary will meet soon to oversee the management of peace and tranquility in the border areas and explore mutually acceptable solutions.
- Diplomatic Mechanisms: Dialogue mechanisms at the foreign ministers and other official levels will be utilized to stabilize and rebuild bilateral relations, contributing to regional and global stability.
Strategic Importance of the Bilateral Meeting
- Maintaining Peace and Stability: PM Modi emphasized that differences between India and China should be managed carefully to ensure that broader peace and tranquility are maintained.
- Global Impact: Both leaders affirmed that stable India-China relations would have a positive impact on regional and global peace and contribute to a multipolar world.
- Long-Term Strategic Perspective: The leaders discussed progressing bilateral relations from a strategic perspective, enhancing communication, and exploring cooperation to address developmental challenges.
Key Takeaways from the 16th BRICS Summit
- Expansion and New Membership: The summit saw the inclusion of five new members—Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia (pending formalization). This expansion reflects BRICS’s growing influence as a forum representing the Global South.
- Focus on Multilateralism: Leaders emphasized multilateral cooperation to address challenges such as global security, economic growth, and sustainable development.
- Kazan Declaration: The declaration touched upon key issues:
- Geopolitical Conflicts: It called for dialogue and diplomacy to resolve disputes like the Ukraine crisis and the West Asia conflict.
- Sanctions and Trade: Criticized unilateral sanctions and their disruptive effects on global trade and development goals.
- Grain Exchange: A proposal was made to establish a BRICS Grain Exchange, aimed at improving agricultural trade among member states.
- Financial Integration: There was a push for greater financial integration through the use of local currencies for trade, exemplified by India’s UPI system as a successful model.
Importance of BRICS in the Global Context
- Global Influence: BRICS continues to be a key player in global geopolitics, representing 40% of the world’s population and 26% of global GDP (as of 2023).
- Strategic Goals: BRICS has consistently called for reform of international institutions like the UNSC, IMF, and World Bank, advocating for a more equitable global governance structure.
- Economic Collaboration: The New Development Bank (NDB), established in 2015, continues to play a vital role in funding development projects across BRICS countries, though the group’s influence in global finance remains limited compared to the World Bank.
Challenges Facing BRICS Expansion
- Geopolitical Contradictions: The inclusion of diverse new members (e.g., UAE, Egypt, Iran) could complicate decision-making due to geopolitical rivalries.
- Decision-Making Hurdles: Achieving consensus among an expanding membership will become more challenging. The expansion may dilute the cohesiveness of the group, as seen in other multilateral forums like the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and G77.
- De-Dollarisation Efforts: While BRICS aims to de-dollarize trade and reduce reliance on the SWIFT system, efforts to develop alternatives like a BRICS payment system and BRICS currency are still in nascent stages.
- Economic Disparities: Economic gaps among members—China’s GDP is significantly larger than the combined GDP of other members—could also create imbalances in decision-making.
India’s Role and Strategic Positioning in BRICS
- Geopolitical Balancing: India's participation in BRICS is a strategic maneuver to balance its global position and strengthen ties with emerging economies, particularly in the Global South.
- Diplomatic Relations with Russia: India continues to prioritize its relationship with Russia, which remains crucial for regional security and energy cooperation.
- India-China Ties: The agreement on the India-China border represents a significant shift in relations, with potential for a reset in Sino-Indian ties.
Key Themes in the Kazan Declaration
- Global Governance: Calls for reforming global institutions to give developing nations more representation.
- Energy and Sustainability: Proposals for strengthening energy cooperation, including the creation of energy corridors and the promotion of sustainable energy practices.
- Security: Emphasized the need for universal security by addressing the security concerns of all nations and promoting dialogue over confrontation.
Conclusion: Future of India-China and BRICS Relations
- India-China Relations: The border disengagement pact is a critical step towards stabilizing the India-China relationship, with potential positive impacts on regional security and global geopolitics.
- BRICS’s Growing Influence: As BRICS expands, it faces internal challenges but remains a potent voice for the Global South, aiming to reshape global governance and financial systems.
- India’s Strategic Positioning: India is likely to play a pivotal role in BRICS, especially as the group’s focus shifts towards regional stability, economic cooperation, and de-dollarization in the coming years.
