Why Farmers Deserve Price Security
- 11 Jan 2025
Introduction:
The future of Indian agriculture is at a crossroads. With the shrinking of the agricultural workforce and the diversion of fertile farmlands for urbanization, ensuring the sustainability of farming is a strategic imperative. Among the various support mechanisms for farmers, the Minimum Support Price (MSP) remains a central point of debate. Should there be a legal guarantee for MSP? This question has gained prominence, especially with the rising challenges in agriculture, from unpredictable climate patterns to volatile market prices.
The Decline of Agriculture and Its Impact
India’s agricultural sector faces a dual crisis: loss of both land and human resources. Prime agricultural lands across river basins, such as the Ganga-Yamuna Doab or the Krishna-Godavari delta, are being repurposed for real estate, infrastructure, and industrial projects. Additionally, the number of "serious farmers" – those deriving at least half of their income from agriculture – is dwindling. The number of operational holdings may be 146.5 million, but only a small fraction of these farmers remains committed to agriculture.
This decline threatens the future of India’s food security, as the country will need to feed a population of 1.7 billion by the 2060s. To sustain farming and ensure long-term food security, we must secure farmers' livelihoods. Price security, particularly through MSP, plays a crucial role in this context.
The Role of MSP in Securing Farmers
MSP is the government-mandated price at which it guarantees the purchase of crops if market prices fall below a certain threshold. It provides a safety net for farmers against price volatility. The process of fixing MSP involves recommendations by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), which takes into account factors such as the cost of production and market trends. Once approved by the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), MSP is set for various crops, including rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
For farmers to stay in business, there must be a balance between production costs and returns. Farming is a risky business – yield losses can occur due to weather anomalies, pest attacks, or other natural factors. However, price risks can be mitigated with a guaranteed MSP. This would encourage farmers to invest in their land and adopt modern farming technologies, which would boost productivity and reduce costs.
Arguments for and Against Legal MSP Guarantee
Supporters of a legal MSP guarantee argue that it would provide financial security to farmers, protecting them from unpredictable market conditions. It would also promote crop diversification, encourage farmers to shift from water-intensive crops to those less dependent on irrigation, and inject resources into rural economies, thus addressing distress in rural areas.
However, critics highlight several challenges with a legal guarantee for MSP. The most significant concern is the fiscal burden it would impose on the government, potentially reaching Rs. 5 trillion. Furthermore, such a system could distort market dynamics, discouraging private traders and leading to a situation where the government becomes the primary buyer of agricultural produce. This could be economically unsustainable, especially for crops with low yields. Additionally, legal MSP guarantees could violate World Trade Organization (WTO) subsidy principles, adversely impacting India’s agricultural exports.
The Way Forward: A Balanced Approach
Given the challenges associated with a legal MSP guarantee, alternative measures should be explored. Price Deficiency Payment (PDP) schemes, such as those implemented in Madhya Pradesh and Haryana, could be expanded at the national level. These schemes compensate farmers for the difference between market prices and MSP, ensuring price security without the fiscal burden of procurement.
Additionally, the government can focus on improving agricultural infrastructure, such as cold storage facilities, to help farmers better access markets and increase price realization. Supporting Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) could also help farmers by enhancing collective bargaining power and ensuring better prices for their produce. Moreover, gradual expansion of MSP coverage to include a wider range of crops would encourage diversification, reducing the dominance of rice and wheat.
Government Extends Special Subsidy on DAP

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian government has decided to extend the special subsidy on Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) fertilizer for another year, a decision aimed at stabilizing farmgate prices and addressing the challenges posed by the depreciation of the Indian rupee.
Key Government Decision
- Extension of Subsidy: The Centre has extended the Rs 3,500 per tonne special subsidy on DAP from January 1, 2025 to December 31, 2025.
- Objective: This extension aims to contain farmgate price surges of DAP, India’s second most-consumed fertilizer, which is being impacted by the fall in the rupee's value against the US dollar.
Fertilizer Price Dynamics and Impact
- MRP Caps on Fertilizers: Despite the decontrol of non-urea fertilizers, the government has frozen the maximum retail price (MRP) for these products.
- Current MRPs:
- DAP: Rs 1,350 per 50-kg bag
- Complex fertilizers: Rs 1,300 to Rs 1,600 per 50-kg bag depending on composition.
- Current MRPs:
- Subsidy on DAP: The subsidy includes Rs 21,911 per tonne on DAP, plus the Rs 3,500 one-time special package.
- Impact of Currency Depreciation:
- The rupee's depreciation has made imported fertilizers significantly more expensive.
- The landed price of DAP has increased from Rs 52,960 per tonne to Rs 54,160 due to the rupee falling from Rs 83.8 to Rs 85.7 against the dollar.
- Including additional costs (customs, port handling, insurance, etc.), the total cost of imported DAP is now Rs 65,000 per tonne, making imports unviable without further subsidy or MRP adjustments.
- The rupee's depreciation has made imported fertilizers significantly more expensive.
Industry Concerns and Viability Issues
- Import Viability:
- Fertilizer companies face significant cost pressures due to rising import prices and the current MRP caps.
- Without an increase in government subsidies or approval to revise MRPs upwards, imports will be unviable.
- Even with the extended subsidy, companies estimate a Rs 1,500 per tonne shortfall due to currency depreciation.
- Stock Levels and Supply Challenges:
- Current stock levels for DAP (9.2 lakh tonnes) and complex fertilizers (23.7 lakh tonnes) are below last year's levels.
- With inadequate imports, there are concerns about fertilizer supply for the upcoming kharif season (June-July 2025).
Government’s Strategy and Fiscal Implications
- Compensation for Imports:
- In September 2024, the government approved compensation for DAP imports above a benchmark price of $559.71 per tonne, based on an exchange rate of Rs 83.23 to the dollar.
- With the rupee falling below Rs 85.7, these previous compensation calculations have become outdated.
- Fiscal Impact:
- The extended subsidy will cost the government an additional Rs 6,475 crore. Despite this, political implications of raising the MRP are minimal, as only non-major agricultural states are facing elections in 2025.
Future Outlook and Priorities
- Immediate Priority: The government’s primary concern is securing adequate fertilizer stocks for the kharif season, focusing on ensuring sufficient imports of both finished fertilizers and raw materials.
- Balancing Factors: The government will need to navigate the complex balance of maintaining fertilizer affordability for farmers, ensuring the viability of fertilizer companies, and managing fiscal constraints.
As the subsidy extension is implemented, all eyes will be on the government's ability to ensure a stable supply of fertilizers while safeguarding both farmer interests and economic sustainability in the face of an increasingly challenging exchange rate environment.
Introduction to Dr. Manmohan Singh's Economic Reforms
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Dr. Manmohan Singh, a distinguished economist, played a crucial role in shaping India’s economic trajectory. His leadership, as Finance Minister (1991–96) and Prime Minister (2004–14), is particularly noted for the economic liberalization and reform policies that transformed India’s economy.
India’s Economic Crisis of 1991
- Economic Collapse: India faced a severe balance of payments crisis, with dwindling foreign reserves and rising inflation.
- Key Challenges: Fiscal deficit, industrial stagnation, and trade imbalances worsened by the collapse of the Soviet Union.
- Urgent Measures: Dr. Singh was appointed Finance Minister during this crisis and initiated bold reforms to stabilize and grow the economy.
Key Reforms in 1991
- Devaluation of the Rupee
- Aimed at making Indian exports competitive in global markets.
- Reduced import tariffs and liberalized foreign trade.
- Industrial Policy Reforms
- Abolition of Licence Raj: Deregulated the industrial sector, promoting private enterprises.
- Reduced state control and encouraged foreign investment, leading to industrial growth.
- Banking and Financial Reforms
- Reduced the statutory liquidity ratio (SLR) and cash reserve ratio (CRR).
- Allowed for more credit flow, fostering economic expansion and banking sector efficiency.
- Global Integration
- Introduced economic liberalization policies, integrating India with the global economy and attracting foreign investments.
Economic Growth and Social Welfare Initiatives
- Poverty Reduction: Reforms helped lift millions out of poverty by fostering job creation and industrial growth.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): Launched in 2005, providing 100 days of wage employment to rural households.
- Right to Information (RTI) and Right to Education (RTE)
- Empowered citizens by ensuring transparency and access to government information.
- RTE guaranteed free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14.
- Financial Inclusion: Aadhar project introduced to facilitate welfare delivery and financial inclusion.
Legacy of Economic Liberalization and Growth
- Economic Growth: Under his leadership, India’s GDP grew at an average rate of 8%, establishing India as one of the fastest-growing economies.
- Shift to a Market-Driven Economy: Reforms dismantled socialist controls, facilitating the rise of the private sector.
- Attracting Foreign Investment: Economic liberalization and policy reforms made India an attractive destination for foreign capital.
Leadership During Political and Economic Challenges
- Reluctant Prime Minister
- In 2004, Singh became Prime Minister despite initial reluctance, emerging as a unifying figure during coalition politics.
- His tenure saw India’s rise as a global economic power, particularly from 2004–2009.
- Challenges
- Singh’s second term was marred by allegations of corruption and policy paralysis, leading to criticism of his administration.
- However, his personal integrity remained intact, and he maintained focus on governance.
- Historic India-US Nuclear Deal (2008)
- The deal marked a significant shift in India’s foreign relations and energy policies, enabling civilian nuclear trade.
Conclusion
Dr. Manmohan Singh’s economic policies are central to India's modern economic framework. His vision transformed India from a closed, socialist economy to a vibrant, globalized economy, promoting inclusive growth and institutional reforms. Despite facing challenges and criticisms, his legacy remains a testament to strategic policymaking that continues to influence India’s economic landscape.
Analysis of Female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) Trends in India: 2017-2023
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) recently released a working paper revealing critical insights into the trends of female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in India from 2017-18 to 2022-23. The report highlights an overall increase in female LFPR, with rural areas experiencing more significant growth compared to urban areas. This article delves into the key findings, regional disparities, influencing factors, and government initiatives aimed at promoting female workforce participation.
Key Findings on Female LFPR
The period between 2017-18 and 2022-23 witnessed a notable rise in female LFPR, both in rural and urban regions, though rural areas saw higher gains.
Rural female LFPR surged by approximately 69%, from 24.6% to 41.5%, while urban female LFPR increased from 20.4% to 25.4%. This consistent growth was observed even after excluding unpaid family workers or household helpers, reinforcing the long-term trend of increased female workforce participation across India.
However, a significant point of discussion in the report was the regional variations in female LFPR. States like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana have consistently reported low female LFPR, which is noteworthy considering that Punjab and Haryana are among India's wealthiest states, while Bihar is the poorest. This regional disparity suggests that economic prosperity does not automatically translate into higher female labour force participation, highlighting deeper socio-cultural and structural barriers.
Regional Disparities in Female LFPR
The report emphasizes the persistent challenges in northern and eastern India. Punjab and Haryana, despite their affluence, have struggled with low female LFPR. Cultural and societal norms in these regions may contribute to the underrepresentation of women in the workforce, particularly in rural areas where traditional gender roles are more entrenched.
On the other hand, Bihar, the poorest state in India, had the lowest female LFPR in the country, particularly in rural areas. However, there has been a significant improvement in recent years, especially among rural married women. This indicates a slow but positive shift in attitudes towards female employment in these states.
In contrast, northeastern states such as Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh have shown significant improvements in female LFPR, particularly in rural areas. These states have demonstrated that regional and cultural factors can also create conducive environments for female workforce participation.
Demographic Factors Affecting Female LFPR
Several demographic patterns influence female LFPR, including marital status and age. The report notes that married men consistently exhibit higher LFPR compared to women. Marriage, however, has a detrimental impact on female LFPR, particularly in urban areas, where women often face greater familial and societal pressures to prioritize domestic responsibilities over formal employment.
Age dynamics also play a crucial role in female LFPR trends. The data reveals a bell-shaped curve for female participation, peaking around the age of 30-40 years and sharply declining thereafter. This is in stark contrast to male LFPR, which remains almost universally high between the ages of 30-50 before gradually declining. These trends underscore the challenges women face in sustaining their participation in the workforce due to familial responsibilities, especially after marriage and childbirth.
Government Initiatives and the Rise in Female LFPR
The government's focus on women-led development is evident through various schemes aimed at increasing female workforce participation. Programs like Mudra Loans, the Drone Didi Scheme, and the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana have been particularly instrumental in empowering women, especially in rural areas. These initiatives provide women with access to financial resources, skill development opportunities, and avenues for entrepreneurship, all of which contribute to the rise in female LFPR.
The EAC-PM's analysis acknowledges the positive impact of these government schemes, but it also stresses the need for further research to evaluate their long-term effectiveness. While the descriptive analysis highlights a substantial increase in female LFPR between 2017-18 and 2022-23, especially in rural areas, there remains a need for continuous monitoring and assessment of these schemes to ensure their sustained impact.
Conclusion: A Positive Shift, but Challenges Remain
The increase in female LFPR across India from 2017-18 to 2022-23 signals a positive shift in employment trends, particularly in rural areas. However, regional disparities, societal norms, and demographic factors continue to pose challenges. The rise in female LFPR is encouraging, but it is essential to understand the deeper socio-economic factors that shape women's participation in the workforce.
Government schemes have contributed to this growth, but future research is necessary to gauge their long-term effects and ensure that women’s participation in the workforce is not just a short-term trend. It is crucial that the government continues to refine policies that support women in overcoming socio-cultural and economic barriers, especially in less prosperous states like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana. Sustained efforts, including education, skill development, and gender-sensitive policies, will be key to ensuring that the rise in female LFPR is both inclusive and long-lasting.
The analysis by the EAC-PM provides an essential framework for policymakers to design more targeted interventions to address regional disparities and create a more inclusive labor market for women in India.
Building on the Revival of the Manufacturing Sector
- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s manufacturing sector has shown remarkable signs of recovery and growth, thanks to strategic policy initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. To fully capitalize on this momentum and become a global manufacturing hub, however, deeper reforms are needed.
The Success of the PLI Scheme: A Catalyst for Growth
The government’s PLI scheme has been instrumental in revitalizing key sectors like electronics, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and textiles. It has not only boosted production but also increased exports and job creation. According to the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) 2022-23, manufacturing output grew by an impressive 21.5%, while gross value added (GVA) increased by 7.3%. Sectors such as basic metals, refined petroleum products, food products, and motor vehicles, which are beneficiaries of the PLI scheme, contributed 58% of total manufacturing output, registering growth of 24.5%.
This success underlines the potential of India’s manufacturing sector, with the PLI scheme acting as a key enabler. However, while the recovery is promising, there are significant challenges to overcome to sustain long-term growth.
Expanding PLI Incentives to New Sectors
The PLI scheme has largely benefitted traditional industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing. To further accelerate growth, the scope of the scheme must be extended to labour-intensive sectors such as apparel, footwear, and furniture, which hold immense potential for job creation. Additionally, emerging sectors like aerospace, space technology, and maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services offer new avenues for growth. By diversifying the incentive structure to these sectors, India could establish a more robust and resilient manufacturing ecosystem.
In sectors like capital goods, where India is heavily import-dependent, the potential for reducing supply chain vulnerabilities is significant. Moreover, promoting green manufacturing and advanced technologies could further bolster India’s competitiveness in global markets.
Addressing the Divergence Between Output and Value Addition
Despite a surge in production, India’s gross value added (GVA) has not kept pace with output growth. The ASI data shows that input prices soared by 24.4% in 2022-23, indicating that while production volumes are up, industries are grappling with high input costs. A more streamlined import regime could mitigate these costs. Simplifying tariffs into a three-tier system (for raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods) would reduce input costs, enhance competitiveness, and improve integration into global value chains.
Regional Imbalance: A Barrier to Inclusive Growth
The manufacturing sector’s growth is heavily concentrated in a few states such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Uttar Pradesh, which account for over 54% of manufacturing GVA. This concentration not only restricts equitable development but also hampers the overall growth potential of the sector. To address this, it is crucial that states actively participate in India's manufacturing growth story by implementing market reforms in land, labour, and power. Additionally, infrastructure development and investment promotion in less industrialized regions could help balance growth and ensure that the benefits of manufacturing reach all corners of the country.
Fostering MSME Growth and Enhancing Female Workforce Participation
Micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) contribute about 45% of India’s manufacturing GDP and employ around 60 million people. To scale these businesses and integrate them into global value chains, PLIs should be tailored to accommodate their needs, such as lowering capital investment thresholds and reducing production targets.
Equally important is the enhancement of female workforce participation. Studies suggest that India’s manufacturing output could increase by 9% if more women enter the workforce. The development of supportive infrastructure, such as hostels and childcare facilities, can play a pivotal role in enabling women’s participation, thus driving inclusive growth.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
To transform into a developed economy by 2047, India must continue to focus on strengthening its manufacturing sector. According to industry estimates, manufacturing’s share in Gross Value Added (GVA) can rise from 17% to 25% by 2030 and further to 27% by 2047. Achieving this will require sustained efforts to enhance competitiveness through business reforms, cost reduction, and policy support. India is well-positioned to harness its manufacturing potential, but timely and focused interventions are necessary to turn this vision into reality.
Scrapping of Windfall Gains Tax

- 05 Dec 2024
Introduction
On December 2, 2024, the Indian government withdrew the windfall gains tax on domestic crude oil production and fuel exports (diesel, petrol, and aviation turbine fuel - ATF). This tax, initially imposed in July 2022, was introduced in response to the surge in global oil prices following Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Its removal reflects the current global oil market stability and the improved fuel supply situation in India.
What is Windfall Gains Tax?
Definition
A windfall tax is a levy imposed on unexpected profits that result from extraordinary events, such as geopolitical crises or market disruptions. In the case of India, the tax was applied to the super-normal profits of oil producers and fuel exporters due to the global energy turmoil.
Key Features
- Domestic Crude Oil: The Special Additional Excise Duty (SAED) was imposed on domestic crude oil production.
- Fuel Exports: A combination of SAED and Road and Infrastructure Cess (RIC) was levied on diesel, petrol, and ATF exports.
Rationale Behind the Windfall Gains Tax
Immediate Context
The tax was introduced during a period of soaring global crude oil prices, driven by the Russia-Ukraine conflict. India, which imports over 85% of its oil, faced concerns about the availability of fuels and the impact of rising prices on domestic consumption. The tax was seen as a way to:
- Ensure Domestic Fuel Supply: By discouraging excessive fuel exports during a period of global supply chain disruptions.
- Increase Government Revenue: The tax aimed to capture windfall profits and offset the duty cuts on domestic fuel sales.
Global Context
Other countries also implemented similar windfall taxes during this period, as energy companies saw record profits due to the price surge.
Decline in Windfall Gains Tax Revenue
Revenue Collection
The windfall gains tax initially raised significant revenue, but the amount has decreased over time due to falling global oil prices:
- FY 2022-23: Rs 25,000 crore
- FY 2023-24: Rs 13,000 crore
- FY 2024-25 (so far): Rs 6,000 crore
This decline, combined with reduced oil prices, led to the tax being effectively inactive before its formal withdrawal.
Withdrawal of the Windfall Gains Tax
Reasons for the Withdrawal
- Global Stabilization: Crude oil prices, which had exceeded $100 per barrel, have now stabilized under $75 per barrel, with no immediate signs of a significant price surge.
- Domestic Fuel Availability: There is now a robust fuel supply in the domestic market, making the tax less necessary.
- Declining Revenues: With the tax generating diminishing returns, it was no longer economically viable for the government to maintain it.
Impact of the Scrapping
The government's move to scrap the windfall gains tax is seen as a signal of stability and predictability in the taxation regime. It assures the oil industry that the government is confident in the stability of global oil prices and supply chains.
Criticism of the Windfall Tax
Industry Opposition
The windfall tax faced opposition from the oil industry, which argued that it:
- Reduced Profitability: The tax limited the profits of publicly listed companies like ONGC and Reliance Industries.
- Discouraged Oil Production: By making the taxation environment unpredictable, it deterred investment in oil exploration and production in a country that is heavily dependent on oil imports.
- Created Uncertainty: Frequent revisions of the tax led to an unstable business environment.
Conclusion
The scrapping of the windfall gains tax is a significant policy shift. It not only provides relief to oil companies but also signals a more predictable and stable taxation regime. By withdrawing the tax, the government is fostering a conducive environment for future investments in domestic oil production and signaling its confidence in the stability of global oil prices. This move is a crucial step in ensuring that India’s energy policies remain adaptable and aligned with the evolving global market conditions.
India's Gig Economy: Growth and Impact on Employment

- 03 Dec 2024
Introduction
India’s gig economy is experiencing rapid growth, with projections indicating it will significantly contribute to the national economy and employment generation. A recent report by the Forum for Progressive Gig Workers estimates the gig economy could reach $455 billion by the end of 2024, growing at a 17% compounded annual growth rate (CAGR). By 2030, it may add 1.25% to India’s GDP and create 90 million jobs.
What is the Gig Economy?
- Definition: The gig economy refers to a labor market based on short-term, flexible jobs, typically facilitated by digital platforms. Gig workers, also called freelancers or independent contractors, are compensated for each task they complete.
- Key Features:
- Flexibility in work schedule and location.
- Task-based employment through digital platforms.
- Common sectors: e-commerce, transportation, delivery services, and freelance work.
Status of the Gig Economy in India
- Market Growth:
- In 2020-21, India had 7.7 million gig workers, which is expected to grow to 23.5 million by 2029-30.
- Key sectors contributing to growth include e-commerce, transportation, and delivery services.
- Driving Factors:
- Digital Penetration: With over 936 million internet subscribers and 650 million smartphone users, digital infrastructure is a key enabler of the gig economy.
- Startup and E-commerce Growth: The rise of startups and e-commerce platforms has increased demand for flexible labor.
- Changing Work Preferences: Younger generations seek work-life balance, opting for flexible gig work.
Gig Economy and Employment Generation
- Contribution to GDP: The gig economy is expected to contribute 1.25% to India’s GDP by 2030.
- Job Creation:
- The gig economy could create up to 90 million jobs by 2030.
- It is estimated that by 2030, gig workers will comprise 4.1% of India’s total workforce.
- Benefits:
- Women’s Empowerment: Gig work provides financial independence and flexibility, especially benefiting women in the workforce.
- Regional Growth: Tier-II and Tier-III cities are seeing accelerated growth in gig work opportunities.
Challenges Faced by Gig Workers
- Job Insecurity: Many gig workers experience instability in their employment, especially in low-skilled jobs.
- Income Volatility: Earnings are unpredictable, and workers face difficulty in financial planning.
- Regulatory Gaps: There is no comprehensive legal framework to protect gig workers’ rights and ensure fair working conditions.
- Delayed Payments: A significant number of workers face delayed payments, affecting their financial well-being.
- Skill Development: Many workers report a lack of opportunities for career advancement and skill development.
Government Initiatives for Gig Workers
- Code on Social Security, 2020: Recognizes gig workers and aims to extend social security benefits, though it lacks comprehensive coverage.
- e-Shram Portal & Welfare Schemes: Initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana and PMJJBY aim to provide financial security to gig workers.
- State-level Initiatives:
- Rajasthan’s Platform-Based Gig Workers Act (2023) focuses on registration and welfare.
- Karnataka’s bill mandates formal registration and grievance mechanisms.
The Way Forward
- Legal Reforms: India can draw from international models like California and the Netherlands, where gig workers are reclassified as employees to ensure protections such as minimum wages and regulated working hours.
- Portable Benefits System: Implementing a system where gig workers can access benefits like healthcare and retirement plans regardless of their employer.
- Skill Development: Strengthening collaborations with vocational institutions to enhance skills and improve earning potential.
- Technological Solutions: Establishing robust feedback mechanisms for workers to report exploitation and ensure fairness within the gig economy.
Conclusion
The gig economy in India is poised to become a significant driver of economic growth and job creation. However, addressing challenges such as income volatility, job insecurity, and regulatory gaps is crucial to ensuring sustainable growth.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet recently approved the launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF), marking a significant shift in the government's approach to agriculture. This initiative, a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, aims to promote natural farming across India, focusing on reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and promoting environmentally sustainable practices.
What is Natural Farming?
Natural farming, as defined by the Ministry of Agriculture, is a chemical-free agricultural method that relies on inputs derived from livestock and plant resources. The goal is to encourage farmers to adopt practices that rejuvenate soil health, improve water use efficiency, and enhance biodiversity, while reducing the harmful effects of fertilizers and pesticides on human health and the environment. The NMNF will initially target regions with high fertilizer consumption, focusing on areas where the need for sustainable farming practices is most urgent.
Evolution of Natural Farming Initiatives
The NMNF is not an entirely new concept but a scaled-up version of the Bhartiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhti (BPKP) introduced during the NDA government's second term (2019-24). The BPKP was part of the larger Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojna (PKVY) umbrella scheme, and natural farming was also promoted along the Ganga River under the NamamiGange initiative in 2022-23. With the renewed focus on natural farming following the 2024 elections, the government aims to extend the lessons learned from BPKP into a comprehensive mission mode, setting a clear direction for sustainable agriculture.
In Budget speech for 2024-25, it was announced a plan to initiate one crore farmers into natural farming over the next two years. The mission will be implemented through scientific institutions and willing gram panchayats, with the establishment of 10,000 bio-input resource centers (BRCs) to ensure easy access to the necessary inputs for natural farming.
Key Objectives
The NMNF aims to bring about a paradigm shift in agricultural practices by:
- Expanding Coverage: The mission plans to bring an additional 7.5 lakh hectares of land under natural farming within the next two years. This will be achieved through the establishment of 15,000 clusters in gram panchayats, benefiting 1 crore farmers.
- Training and Awareness: The mission will establish around 2,000 model demonstration farms at Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), Agricultural Universities (AUs), and farmers' fields. These farms will serve as hubs for training farmers in natural farming techniques and input preparation, such as Jeevamrit and Beejamrit, using locally available resources.
- Incentivizing Local Inputs: The creation of 10,000 bio-input resource centers will provide farmers with easy access to bio-fertilizers and other natural farming inputs. The mission emphasizes the use of locally sourced inputs to reduce costs and improve the sustainability of farming practices.
- Farmer Empowerment: 30,000 Krishi Sakhis (community resource persons) will be deployed to assist in mobilizing and guiding farmers. These trained individuals will play a key role in generating awareness and providing on-ground support to the farmers practicing natural farming.
- Certifications and Branding: A major aspect of the mission is to establish scientific standards for natural farming produce, along with a national certification system. This will help in creating a market for organically grown produce and encourage more farmers to adopt sustainable practices.
Targeting High Fertilizer Consumption Areas
The Ministry of Agriculture has identified 228 districts in 16 states, including Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Maharashtra, and West Bengal, where fertilizer consumption is above the national average. These districts will be prioritized for the NMNF rollout, as they have high fertilizer usage but low adoption of natural farming practices. By focusing on these areas, the mission seeks to reduce the over-dependence on chemical fertilizers and foster a transition to more sustainable farming practices.
Benefits of Natural Farming
The NMNF aims to deliver multiple benefits to farmers and the environment:
- Cost Reduction: Natural farming practices can significantly reduce input costs by decreasing the need for costly chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Soil Health and Fertility: By rejuvenating the soil through organic inputs, natural farming improves soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity, leading to long-term agricultural sustainability.
- Climate Resilience: Natural farming enhances resilience to climate-induced challenges such as drought, floods, and waterlogging.
- Healthier Produce: Reduced use of chemicals results in safer, healthier food, benefitting both farmers and consumers.
- Environmental Conservation: The promotion of biodiversity, water conservation, and carbon sequestration in soil leads to a healthier environment for future generations.
Conclusion
The launch of the National Mission on Natural Farming represents a critical step toward transforming India's agricultural practices into a more sustainable and environmentally friendly model. By targeting regions with high fertilizer usage, providing farmers with the tools and knowledge for natural farming, and creating a system for certification and branding, the government hopes to make natural farming a mainstream practice. As India continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, soil degradation, and health risks from chemical inputs, the NMNF provides a promising framework for sustainable agriculture that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.
India’s Urban Infrastructure

- 28 Nov 2024
Introduction
India’s urban population is projected to double from 400 million to 800 million by 2050. This demographic shift presents both challenges and opportunities for transforming the country’s urban infrastructure. To meet the growing needs of urban areas, India will require an investment of approximately ?70 lakh crore by 2036, a figure significantly higher than current spending levels.
Financial Challenges in Urban Infrastructure
- Investment Gap
- The current annual investment in urban infrastructure stands at ?1.3 lakh crore, which is only 28% of the ?4.6 lakh crore needed annually.
- A large portion of the existing investment, around 50%, is directed towards basic urban services, with the remainder allocated to urban transport.
- Municipal Finances
- Municipal finances have remained stagnant at 1% of GDP since 2002.
- Despite increased transfers from the central and state governments, municipal bodies face financial strain.
- The contribution of municipal own-revenue has decreased from 51% to 43%, indicating a reduced financial independence.
- Revenue Collection Inefficiencies
- Urban local bodies (ULBs) are collecting only a small fraction of their potential revenues, with property tax collections representing just 0.15% of GDP.
- Cost recovery for essential services like water supply and waste management ranges between 20% and 50%, pointing to a significant funding gap.
- Underutilization of Resources
- Cities like Hyderabad and Chennai utilized only 50% of their capital expenditure budgets in 2018-19.
- Central schemes such as AMRUT and the Smart Cities Mission also showed suboptimal fund utilization, with utilization rates of 80% and 70%, respectively.
- Decline in Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
- Investments through PPPs in urban infrastructure have seen a sharp decline, from ?8,353 crore in 2012 to ?467 crore in 2018.
- This drop is attributed to limited project-specific revenues and inadequate funding mechanisms.
Structural and Administrative Challenges
- Weak Governance and Fragmented Management
- Fragmented governance and limited administrative autonomy hinder effective urban planning and resource allocation.
- Municipal bodies often lack the ability to undertake long-term planning and project execution due to these governance challenges.
- Climate Vulnerability and Sustainability: Urban areas are increasingly vulnerable to climate risks like floods and heatwaves. However, many urban infrastructure projects fail to incorporate climate resilience in their planning, exacerbating the long-term vulnerability of investments.
- Inadequate Land Management
- There is poor coordination between land use planning and infrastructure development, resulting in urban sprawl and inefficient transportation systems.
- Opportunities to capitalize on the land value generated by metro and rail projects remain underutilized.
Measures for Transforming Urban Infrastructure
- Streamline Revenue Collection: Leverage technology to improve property tax collection systems and enhance cost recovery in essential services.
- Enhance Fund Utilization: Strengthen municipal capacities for effective project planning and incentivize the timely use of allocated grants.
- Scale Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Investments: Develop a pipeline of bankable projects and create risk-sharing mechanisms to attract private sector investments.
- Decouple Project Preparation from Funding: Ensure that infrastructure projects are thoroughly prepared for financial, social, and environmental sustainability before seeking funding.
- Promote Urban Innovation: Establish urban innovation labs and encourage public-private-academic collaborations to foster the adoption of advanced technologies.
- Empower Municipalities: Grant municipalities greater financial autonomy, enabling them to raise capital through municipal bonds and other debt mechanisms.
- Integrated Urban Planning: Align infrastructure development with land use, transport, and housing requirements, while integrating climate resilience into planning.
- Capacity Building: Invest in the training of municipal staff to improve governance and financial management capabilities.
Conclusion
India’s expanding urban population presents a major opportunity for economic growth. However, addressing the financial and structural challenges in urban infrastructure is crucial for harnessing this potential. By adopting a combination of short-term actions, medium-term strategies, and long-term reforms, India can create sustainable, resilient urban infrastructure that meets the growing needs of its cities, fostering inclusive development and long-term prosperity.
RBI brings back 102 tonnes gold from BoE; 60 per cent reserves in India

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
England over the past two-and-a-half years, reflecting a strategic shift in its approach to safeguarding gold reserves. This move marks a significant increase in the RBI's domestic gold holdings.
Rise in the RBI's Domestic Gold Holdings
- Current Status (September 2024):The RBI's domestic gold reserves have grown to 510.46 metric tonnes, up from 295.82 metric tonnes in March 2022.
- Reduction in Gold Held Abroad:The gold held under the custodianship of the Bank of England has decreased to 324 metric tonnes from 453.52 metric tonnes in March 2022.
- Gold as a Share of Foreign Exchange Reserves:The proportion of gold in India's total foreign exchange reserves increased from 8.15% in March 2024 to 9.32% in September 2024.
Gold Kept in the Bank of England
- Overview of the Bank of England's Gold Vault:The Bank of England is home to one of the largest gold vaults in the world, second only to the New York Federal Reserve, housing around 400,000 bars of gold.
- India’s Gold Held Abroad:The RBI continues to retain 324 metric tonnes of its gold with the Bank of England and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS).
- Additional Gold Management:Around 20 tonnes of gold are managed through gold deposit schemes.
- Strategic Role of London’s Gold Market:Storing gold in London provides immediate access to the global London bullion market, enhancing liquidity for India’s gold assets.
Historical Context of India’s Gold Holdings
- 1991 Balance of Payments Crisis:During a financial crisis in 1991, India had to send 47 tonnes of gold to the Bank of England to secure loans for repaying international creditors.
RBI’s Strategy to Bring Gold Back to India
- Global Trend of Central Banks Buying Gold:Since the imposition of U.S. sanctions on Russia in 2022, central banks globally have been increasing their gold reserves as a hedge against inflation and to reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar. India has outpaced other G20 nations in this trend, surpassing Russia and China in gold purchases.
- De-dollarisation:This shift is part of a broader strategy of de-dollarisation, aiming to diversify away from the U.S. dollar amidst rising gold prices and growing geopolitical tensions.
Significance of Repatriating Gold to India
- Sign of Economic Strength
- Recovery from the 1991 Crisis:The decision to repatriate gold reflects a significant improvement in India's economic position, a stark contrast to the 1991 economic crisis when India had to pledge gold for financial survival.
- Optimizing Financial Resources
- Reducing Storage Costs:Storing gold domestically allows the RBI to save on storage fees paid to foreign custodians, such as the Bank of England.
- Strategic Significance
- Enhanced Resilience Amid Global Instability:By repatriating its gold, India enhances its strategic autonomy and strengthens its economic position in a world of rising uncertainties and currency volatility.
RBI's Capacity to Safeguard Gold Domestically
- Increasing Domestic Storage Capacity:The RBI has been increasing its domestic capacity for gold storage to accommodate rising reserves and reduce dependence on foreign gold safekeeping facilities.
- Current Foreign Exchange Reserves:As of October 2024, India’s total foreign exchange reserves stand at $684.8 billion, sufficient to cover over 11.2 months of imports.
Diversification of Foreign Exchange Reserves
- Mitigating Currency Risks:By increasing gold reserves, India diversifies its foreign exchange holdings, reducing reliance on any single currency and shielding itself from global currency fluctuations and economic volatility.
- Gold as a Stable Asset:Gold serves as a stable asset, providing a safeguard against global economic shocks, and balances India’s reserves portfolio.
Gold as a Hedge against Inflation
- Preserving Wealth amid Inflation:Gold is traditionally viewed as a hedge against inflation, maintaining or appreciating in value when other currencies weaken. By increasing its gold reserves, India positions itself to better withstand the adverse effects of inflation and ensure long-term financial stability.
Conclusion
The repatriation of gold by the RBI reflects a strategic move to bolster India's economic strength and diversify its financial assets. The decision to bring gold back to India not only signifies an improvement in India's economic fundamentals but also aligns with global trends of central banks increasing their gold reserves to ensure long-term stability and reduce reliance on the U.S. dollar.
Analysis of Growing Economic Divide in India
- 29 Oct 2024
Overview
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM)'s report titled "Relative Economic Performance of Indian States: 1960-61 to 2023-24" highlights an alarming trend of widening economic disparities across India's states, which is increasingly threatening the principles of federalism and national unity. The findings reveal significant regional imbalances in terms of contributions to the national income, per capita income, and overall economic development. This analysis delves into the key insights from the report and explores the broader implications for India's federal structure, governance, and policy approaches.
Key Insights from the Report
- Regional Economic Disparities:
- Western and Southern States' Dominance: States such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka have consistently outperformed others. These states have benefited from higher private investments, better infrastructure, and a more business-friendly environment. They also enjoy proximity to international markets, especially coastal regions like Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, which have access to ports and export markets.
- Underperformance of Northern and Eastern States: On the other hand, northern states (with exceptions like Delhi and Haryana) and eastern states like Bihar, Odisha, and West Bengal lag behind in economic performance. These regions face challenges such as poor infrastructure, low levels of investment, and weak governance structures, which hinder their growth potential.
- Impact of Liberalization (1991):
- The 1991 economic reforms marked a shift toward market-oriented growth, benefiting states that were already more industrialized or had better urban infrastructure. Southern states, in particular, adapted well to the liberalized environment, attracting higher levels of private investment and expanding their economies.
- The liberalization process disproportionately favored urban centers like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Bengaluru, where investments were channelized into growing service sectors, technology, and industries, creating a feedback loop of wealth accumulation in these hubs. Meanwhile, the hinterland remained underdeveloped due to insufficient public investment and the lack of private sector interest in these regions.
- Investment Disparities:
- Private Investment: Wealthier states attract a disproportionate share of private investment, which is driven by profitability and market opportunities. These states have better infrastructure, which reduces transaction costs and increases returns on investment. In contrast, underdeveloped states struggle to attract investment due to poor governance, inadequate infrastructure, and perceived higher risks.
- Public Investment: While the public sector still plays a role in investment, the New Economic Policies (NEP) since 1991 have shifted the focus towards private sector-driven growth. This has further widened the investment gap, as the poorer states receive less public investment relative to their needs.
- Role of Infrastructure and Governance:
- The availability and quality of infrastructure are significant determinants of economic performance. States with better roads, energy supply, ports, and communication networks tend to attract more investments. Additionally, good governance, characterized by reduced corruption, better policy implementation, and transparency, also plays a critical role in fostering economic development.
- In contrast, states with weaker governance structures and poor infrastructure struggle to create an enabling environment for businesses, further compounding regional disparities.
- Impact on Federalism:
- The growing economic divide is leading to tensions between the Centre and state governments, particularly in wealthier states that contribute significantly to national income but feel short-changed in resource allocation. These states argue that they are not receiving a fair share of national resources in return for their contributions, leading to growing dissatisfaction with the federal system.
- The tension is exacerbated by political factors, such as accusations from opposition-led states that the Centre uses public investment to favor states aligned with the ruling party. The growing perception of politicization of resource allocation has the potential to undermine the spirit of cooperative federalism.
Structural Causes of Regional Inequality
- Economic and Investment Magnetism:
- Wealthier states attract more private investments, as they offer better returns due to established markets, skilled labor, and urbanization. Cities like Mumbai, Delhi, and Bengaluru serve as economic magnets, drawing talent, technology, and capital, which further consolidates their economic dominance.
- In contrast, states without such economic hubs or access to global markets struggle to attract investment. The absence of urban agglomerations and the concentration of wealth and resources in a few states perpetuate regional disparities.
- Policy and Investment Bias:
- Post-liberalization policies have disproportionately benefited the organized sector, often at the expense of the unorganized sector, which is more prevalent in poorer states. The emphasis on industrial growth and infrastructure development has largely bypassed the rural and informal sectors, which are critical in underdeveloped states.
- The organized sector has also benefited from government support, such as tax concessions and subsidized infrastructure, which have enabled these industries to thrive in already developed regions. This has widened the gap between the haves and the have-nots.
- Cronyism and the Black Economy:
- Crony capitalism and the prevalence of the black economy in poorer states further exacerbate regional imbalances. In some cases, political patronage and corruption divert resources and investments from areas that need them most. This weakens the investment climate, especially in states with higher levels of informal and illegal economic activity.
Implications for Federalism
The growing economic disparity poses a serious threat to India's federal structure. The increasing dissatisfaction of wealthier states with the current fiscal arrangements and the growing demand for fairer resource allocation challenge the spirit of cooperative federalism. A well-functioning federal system relies on equitable distribution of resources and opportunities for all regions to develop.
Policy Recommendations
To address these disparities and strengthen India's federal framework, several policy measures need to be implemented:
- Enhancing Governance and Infrastructure in Lagging States:
- Improved governance and reducing corruption are essential in attracting both private and public investments. Additionally, there must be a focus on developing critical infrastructure, such as roads, energy, and health facilities, which are essential for economic growth.
- States need to increase public investment in sectors like education, healthcare, and social security to improve human capital and productivity.
- Focus on the Unorganized Sector:
- A significant portion of the labor force in poorer states is employed in the unorganized sector. Policies should aim to formalize this sector by providing social security benefits, improving labor rights, and increasing productivity through skill development. This could help raise incomes and stimulate local demand, attracting more private investment.
- Balancing the Organized and Unorganized Sectors:
- While the organized sector has benefited from liberalization, more attention should be given to the unorganized sector, which forms the backbone of the economy in many poorer states. A balanced approach to economic growth, which includes both organized and unorganized sectors, can help reduce disparities.
- Shifting Focus from Urban Centers to Hinterlands:
- Private sector investment must be incentivized in underdeveloped regions through tax breaks, subsidies, and targeted infrastructure projects. This will encourage businesses to expand beyond the major urban centers, thus promoting a more balanced distribution of economic activities.
Conclusion
The widening economic divide in India, as revealed by the EAC-PM report, poses a significant challenge to the country's federalism and unity. To ensure inclusive and balanced development, policy reforms must focus on reducing regional disparities by improving governance, infrastructure, and investment in lagging states. A shift towards equitable growth, addressing the needs of both the organized and unorganized sectors, is essential to promoting national cohesion and ensuring sustainable economic progress across all regions.
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- 27 Oct 2024
Introduction
The Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 8, 2015, with the aim of providing financial support to non-corporate, non-farm small and micro enterprises in India. Through this initiative, loans are provided to individuals and small businesses who are unable to access formal institutional finance.
In the Union Budget 2024-25, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced an increase in the loan limit under PMMY from ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh, with the introduction of a new loan category, Tarun Plus, aimed at fostering growth in the entrepreneurial sector.
Key Features of the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
Loan Limit Increase
- Loan Limit Raised: The loan limit has been increased from ?10 lakh to ?20 lakh for eligible entrepreneurs.
- New Loan Category: The newly introduced Tarun Plus category caters to entrepreneurs who have previously availed and successfully repaid loans under the Tarun category.
- Credit Guarantee: The Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU) will cover these enhanced loans, further ensuring the security of micro-enterprises.
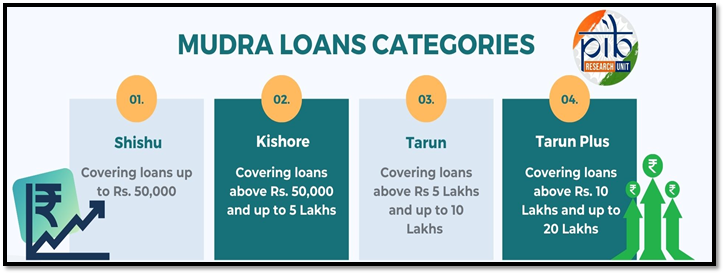
Categories of MUDRA Loans
PMMY provides collateral-free loans through financial institutions like Scheduled Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks (SFBs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), and Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs). These loans are provided for income-generating activities in sectors like manufacturing, trading, services, and allied agriculture activities.
Objectives of PMMY
- Financial Inclusion: PMMY targets marginalized and socio-economically neglected sections of society, promoting financial inclusivity.
- Support to Small Businesses: By providing affordable loans, the scheme encourages small-scale entrepreneurs, particularly women and minority groups, to establish and expand their businesses.
- Fostering Entrepreneurship: PMMY aims to unlock the potential of India’s entrepreneurial spirit, especially in rural and underserved areas.
MUDRA: The Institutional Backbone
Role of Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Ltd. (MUDRA)
MUDRA is the primary institution set up by the Government of India to manage and implement the Mudra Yojana. It acts as a refinancing agency that provides financial support to small and micro-enterprises by working through financial intermediaries, such as banks and micro-finance institutions.
Funding Sources
- Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Small Finance Banks (SFBs)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
Application Process
Applicants can avail loans through any of the aforementioned financial institutions or apply online via the Udyami Mitra Portal.
Benefits of Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
- Collateral-free Loans: No security is required to obtain loans, which reduces the financial burden on borrowers.
- Easily Accessible: PMMY loans are available across India, making them accessible to entrepreneurs in both rural and urban areas.
- Quick and Flexible Loans: Loans can be disbursed quickly with flexible repayment terms (up to 7 years).
- Empowering Women Entrepreneurs: The scheme offers special incentives for women entrepreneurs, helping them to establish and grow their businesses.
- Support to Rural Areas: Special emphasis on empowering rural enterprises and reducing regional disparities.
- MUDRA Card: The MUDRA Card is a RuPay debit card that allows borrowers to access funds through an overdraft facility, enhancing liquidity for businesses.
- No Default Penalty: In case of loan defaults due to unforeseen circumstances, the government will step in to reduce the burden on entrepreneurs.
Categories of Loans Under PMMY
1. Shishu Category: Loans up to ?50,000
- Targeted at micro-enterprises at the initial stage of their business journey.
2. Kishore Category: Loans between ?50,000 and ?5 lakh
- Targeted at enterprises looking to expand their operations and upgrade their infrastructure.
3. Tarun Category: Loans between ?5 lakh and ?10 lakh
- For established businesses that are in need of funds to scale up.
4. Tarun Plus: Loans between ?10 lakh and ?20 lakh
- A new category designed for entrepreneurs who have repaid loans under the Tarun category and wish to further expand their business.
Achievements of PMMY (2023-24)
- Total Loans Sanctioned: ?5.4 trillion across 66.8 million loans in FY 2023-24.
- Loans Disbursed: Significant amounts were disbursed under each category:
- Shishu: ?1,08,472.51 crore
- Kishore: ?1,00,370.49 crore
- Tarun: ?13,454.27 crore
- Women Borrowers: A large share of loans have gone to women entrepreneurs, ensuring gender inclusivity.
- Minority Borrowers: The scheme also emphasizes financial empowerment of minority communities.
- NPA Reduction: The Non-Performing Assets (NPA) in Mudra loans have reduced to 3.4% in FY 2024, compared to higher levels in earlier years.
Digital Tools and Support Systems
MUDRA MITRA App
The MUDRA MITRA mobile app helps users access information about the PMMY scheme, loan application procedures, and other resources. The app is available for download on Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
Online Loan Application
Entrepreneurs can apply for loans online via portals such as PSBloansin59minutes and Udyamimitra, providing greater convenience and accessibility.
Steps to Improve Implementation
- Handholding Support: Assistance in submitting loan applications is available for applicants.
- Intensive Awareness Campaigns: The government conducts publicity campaigns to raise awareness about PMMY.
- Simplified Loan Process: The loan application forms have been simplified to encourage wider participation.
- Performance Monitoring: Regular monitoring of PMMY implementation to ensure its success.
- Interest Subvention: A 2% interest subvention is offered for prompt repayment of Shishu loans.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana has been a transformative scheme in fostering entrepreneurship and ensuring financial inclusion for small and micro-businesses across India. With the recent increase in loan limits and the addition of the Tarun Plus category, the scheme continues to empower emerging entrepreneurs and provides a crucial lifeline for business growth and sustainability. By supporting women, minorities, and new entrepreneurs, PMMY has contributed significantly to economic upliftment and inclusive growth in the country.
What are the stress factors for Indian Railways?
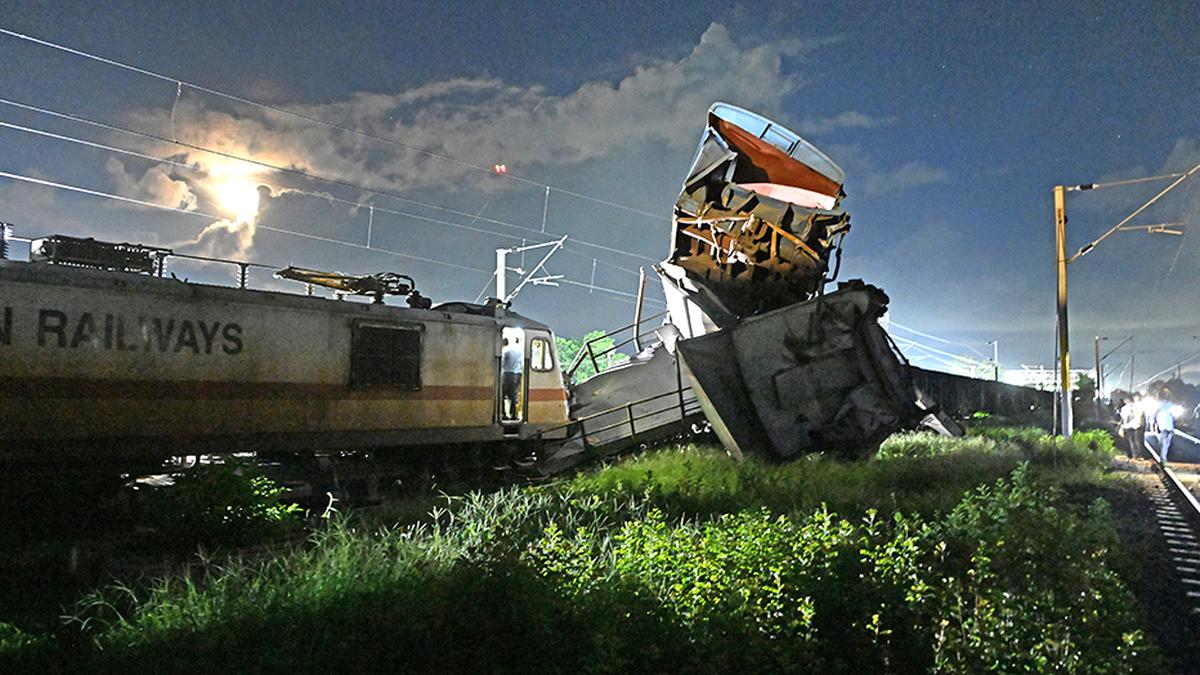

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
On October 17, eight coaches of the Agartala-Lokmanya Tilak Express derailed in Assam with no casualties. On October 11, a passenger train rear-ended a stationary goods train near Chennai, also with no casualties. Indian trains have been involved in multiple accidents of late. The Balasore accident on June 2, 2023, had the greatest death toll, more than 275, yet pressure on the Railways to improve safety competes with pressures straining its subsistence.
Railway Accident Trends
- Decline in Accidents Over Time:
- From 1,390 accidents per year in the 1960s, railway accidents have reduced to about 80 accidents per year in the last decade.
- Recent Consequential Accidents:
- 34 accidents in 2021-2022
- 48 accidents in 2022-2023
- 40 accidents in 2023-2024
- Primary Causes of Accidents:
- 55.8% due to staff errors (railway personnel).
- 28.4% due to non-staff errors.
- 6.2% due to equipment failure.
- Role of Signalling Failures:
- Major accidents, such as Balasore and Kavaraipettai, were attributed to signalling system failures.
Key Safety Technologies and Measures
- Kavach System:
- Kavach is an automatic train protection system designed to prevent collisions by monitoring train positions and activating alarms or braking.
- As of February 2024, Kavach was implemented on only 2% (1,465 route km) of the railway network, limiting its effectiveness.
- Signalling System Overhaul:
- Outdated and faulty signalling systems contribute significantly to accidents. Both Balasore and Kavaraipettai incidents were linked to failures in signalling infrastructure.
Financial Strain on Indian Railways
- Operating Ratio (OR):
- The Operating Ratio (OR) in 2024-2025 is estimated to be ?98.2, indicating that the Railways spends ?98.2 for every ?100 earned.
- A higher OR reduces available funds for safety improvements and infrastructure upgrades.
- Budgetary Constraints:
- The 2023-24 budget showed a 7.2% reduction in capital outlay for track renewal and a 96% decrease in the Depreciation Reserve Fund, which is used to replace aging assets.
- Revenue Imbalance:
- Freight services account for 65% of Railways’ revenue but face capacity constraints, with 30% of the network operating at over 100% capacity.
- Passenger services, however, continue to incur significant losses, with ?68,269 crore loss in 2021-22.
Challenges in Rail Infrastructure
- Slow Infrastructure Development:
- The government's Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs), intended to alleviate congestion, are severely delayed:
- The Eastern DFC is the only fully operational corridor.
- Other corridors, including the Western DFC and additional planned routes, remain incomplete.
- Track and Equipment Maintenance:
- Ongoing delays in upgrading and maintaining essential infrastructure (tracks, wagons, signalling) contribute to the rising number of accidents.
Loco Pilot Working Conditions
- Extended Working Hours:
- Loco pilots often work 12-hour shifts due to manpower shortages, leading to fatigue and increased risk of human error.
- Stress and exhaustion are significant contributors to accidents caused by human error, including Signal Passed at Danger (SPAD).
Recommendations for Improving Railway Safety
- Loco Pilot Vacancies:Immediate recruitment to fill the 18,799 vacant loco pilot positions to prevent overworking and reduce fatigue-related errors.
- Expand Kavach Deployment:Accelerate the nationwide installation of the Kavach system, particularly on high-risk and high-traffic routes, to enhance safety.
- Complete Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs):Expedite the completion of DFCs to ease congestion and increase freight movement efficiency.
- Independent Railway Safety Authority:Establish an independent Railway Safety Authority with statutory powers, as recommended by the Kakodkar Committee (2012), to enforce safety standards and monitor implementation.
- Improve Signal Infrastructure:Invest in advanced and reliable signalling systems to prevent errors stemming from outdated or malfunctioning infrastructure.
- Regulate Working Hours:Enforce strict work hour limits to reduce fatigue among railway staff and ensure proper rest between shifts.
- Strengthen Trackside Infrastructure:Install fencing along tracks in high-risk areas to prevent cattle run-overs, a common cause of derailments in rural and semi-urban areas.
Conclusion
- Indian Railways faces a complex set of challenges, balancing safety requirements with financial constraints. Despite technological advancements like Kavach, its limited deployment and outdated infrastructure continue to present significant risks.
- A holistic approach to reform is needed, including addressing manpower shortages, upgrading safety technologies, and investing in infrastructure development. This will be essential for reducing accidents, improving safety, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of India’s vast railway network.
