River Interlinking: Environmental Disaster or Solution?
- 09 Jan 2025
Overview of the River Interlinking Concept
The concept of river interlinking in India traces its origins to the 19th century, when Sir Arthur Cotton first proposed inter-basin water transfer to address irrigation issues. Over time, this idea was refined by other experts. It evolved into the National Water Grid and, later, the River-Interlinking Project (ILR) under the Ministry of Water Resources. The goal is to transfer surplus water from rivers to drought-prone areas, aiming for water security, irrigation, and power generation.
Key Projects and Initiatives
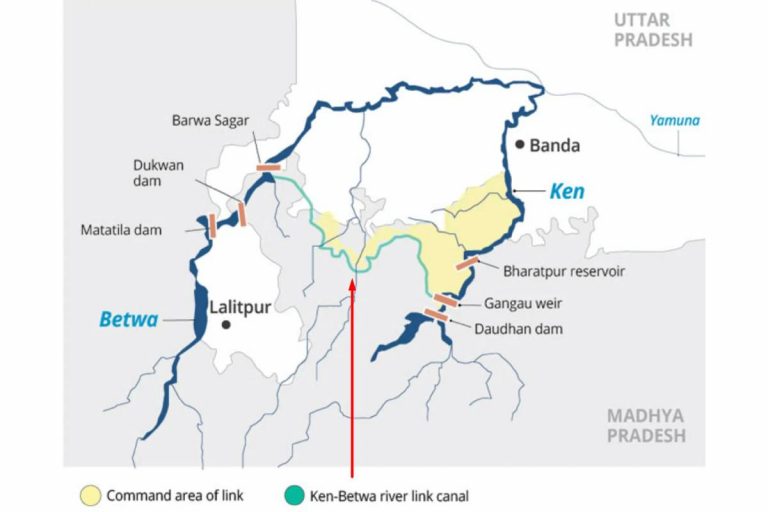
- Ken-Betwa River Link Project (KBLP): Launched in December 2024, the KBLP will link the water-surplus Ken River with the drought-stricken Betwa River. It aims to irrigate over 10 lakh hectares, supply drinking water to 62 lakh people, and generate hydropower and solar power. However, concerns over the environmental impact of building a dam within the Panna Tiger Reserve have been raised.
- National River Linking Project (NRLP): The NRLP, formally known as the National Perspective Plan, is an ambitious proposal that includes 30 river links—14 Himalayan and 16 Peninsular—to connect India's rivers and create a giant South Asian Water Grid.
Benefits of Interlinking Rivers
- Flood and Drought Mitigation: Redistributing water from surplus areas to drought-prone regions, such as Bundelkhand, will reduce the severity of floods and droughts.
- Agriculture and Irrigation: Expanding irrigation systems across 35 million hectares of land could significantly boost agricultural productivity and food security.
- Hydropower Generation: The interlinking project has the potential to generate up to 34 GW of hydropower, contributing to India's renewable energy targets.
- Economic Growth: Improving water availability can boost industries, provide drinking water, and support economic development in underdeveloped regions.
- Inland Waterways: The project will also contribute to the expansion of inland waterways, benefiting trade and reducing transportation costs.
Challenges and Concerns
- Environmental Impact:
- Biodiversity Loss: Projects like the Ken-Betwa project raise alarms about the destruction of ecologically sensitive areas, such as the Panna Tiger Reserve.
- River Ecosystem Disruption: Altering natural river courses can harm aquatic life, disrupt deltaic ecosystems, and degrade water quality. For instance, the Sardar Sarovar Dam's impact on the Narmada river system shows the long-term consequences of such projects.
- Pollution: The mixing of cleaner and more polluted rivers could exacerbate water contamination issues.
- Social and Financial Costs:
- Displacement: Large-scale interlinking projects will displace millions, especially marginalized communities and indigenous people, and disturb local livelihoods.
- High Financial Burden: The total estimated cost of the NRLP is ?5.5 lakh crore, which does not include environmental rehabilitation costs or the long-term maintenance of the infrastructure.
- Climate Change: Predictions suggest that climate change could affect river flows and the availability of surplus water. This might render the interlinking project ineffective in the long term.
- Inter-State Conflicts: Water-sharing disputes, like the long-standing issues over the Cauvery and Krishna rivers, could intensify with more interlinking projects.
- Infrastructural Challenges: Maintaining vast canal networks and reservoirs, managing sedimentation, and acquiring land for construction are logistical hurdles.
Alternative Approaches and Solutions
- Efficient Water Management:
- Integrated Watershed Management: Implementing a comprehensive approach to manage existing water resources can reduce the need for large-scale river transfers.
- Groundwater Recharge: Focusing on efficient groundwater management by identifying recharge mechanisms and regulating water use is crucial for sustainability.
- Modern Irrigation Techniques:
- Drip Irrigation: Israel’s success with drip irrigation, which reduces water use by 25%-75%, provides an example of how modern technologies can save significant amounts of water.
- Virtual Water: Emphasizing the import of water-intensive goods (like wheat) could save local water resources, which would otherwise be used for domestic agriculture.
- National Waterways Project (NWP): An alternative to the interlinking project, NWP aims to improve water management by creating navigation channels that double as water distribution networks with a fraction of the land use.
Way Forward
- Comprehensive Impact Assessments: The need for multidisciplinary studies to evaluate the environmental, social, and economic impacts of river interlinking projects cannot be overstated. Stakeholder engagement is crucial for equitable decision-making.
- Sustainable Water Policies: A national water policy should prioritize sustainable water practices, focusing on local solutions, such as water harvesting, watershed management, and smart irrigation.
- Focus on Regional Solutions: Smaller, state-specific projects should be prioritized to address water scarcity issues without triggering large-scale environmental degradation.
The Impact of Climate Change on Earth’s Water Cycle

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Climate change is significantly affecting Earth's water cycle, leading to extreme weather events such as intense floods and prolonged droughts. According to the 2024 Global Water Monitor Report, this disruption is increasingly evident, as seen in the devastating weather patterns experienced worldwide in 2024. The report, based on data from international researchers, highlights how these changes are directly linked to rising global temperatures and the resulting shifts in precipitation patterns.
Understanding the Water Cycle
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water in various forms—solid, liquid, and gas—throughout the Earth's atmosphere, land, and bodies of water. This cycle involves processes such as:
- Evaporation: Water from the surface of oceans, lakes, and rivers turns into vapor.
- Transpiration: Water is absorbed by plants from the soil and released as vapor.
- Precipitation: Water vapor condenses into clouds and falls as rain or snow, replenishing the Earth's surface.
- Runoff and Infiltration: Precipitation either flows into rivers or infiltrates the soil, contributing to groundwater.
The water cycle is vital for maintaining the planet’s ecosystems, regulating weather patterns, and providing water for all living organisms. However, climate change is intensifying these natural processes, with far-reaching consequences.
Impact of Climate Change on the Water Cycle
As global temperatures rise, climate change is having a profound impact on the water cycle. Warmer temperatures lead to:
- Increased evaporation: As air temperatures soar, more water evaporates into the atmosphere. For every 1°C rise in temperature, the atmosphere can hold about 7% more moisture, which exacerbates storms and increases the intensity of rainfall.
- More intense precipitation: With more moisture in the atmosphere, storms have become more intense, leading to severe flooding in various regions.
- Increased droughts: Warmer air also dries out the soil. This reduces the amount of water available for crops and plants, while also increasing the evaporation rate from soil, leading to longer and more intense droughts.
This disruption of the water cycle is already causing erratic weather patterns, as some regions face severe droughts, while others are experiencing extreme rainfall and floods.
Key Findings from the 2024 Global Water Monitor Report
The 2024 report presents several alarming statistics that highlight the growing impact of climate change on the water cycle:
- Water-related disasters: In 2024, these disasters caused over 8,700 fatalities, displaced 40 million people, and resulted in economic losses exceeding $550 billion globally.
- Dry months: There were 38% more record-dry months in 2024 than the baseline period (1995-2005), underlining the growing frequency of droughts.
- Intense rainfall: Record-breaking rainfall occurred 27% more frequently in 2024 compared to 2000, with daily rainfall records set 52% more often. This shows the growing intensity of precipitation events.
- Terrestrial water storage (TWS): Many dry regions faced ongoing low TWS levels, reflecting the scarcity of water in these areas, while some regions, such as parts of Africa, saw an increase in water storage.
- Future predictions: Droughts may worsen in regions like northern South America, southern Africa, and parts of Asia, while areas like the Sahel and Europe could experience increased flood risks in the coming years.
Conclusion
The findings of the 2024 report underscore the alarming impact of climate change on the global water cycle. As temperatures continue to rise, we can expect more frequent and severe weather events, including extreme flooding and devastating droughts. These changes will affect billions of people worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for action to mitigate climate change and adapt to its consequences. Addressing this challenge requires global cooperation to reduce emissions, enhance water management systems, and protect vulnerable regions from the intensifying effects of climate change.
Surge in E-Waste Generation in India
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
India has seen a significant increase in electronic waste (e-waste) generation, rising by 72.54% from 1.01 million metric tonnes (MT) in 2019-20 to 1.751 million MT in 2023-24. The sharpest rise occurred between 2019-20 and 2020-21, driven by increased electronic consumption due to the COVID-19 pandemic's work-from-home and remote learning arrangements.
Environmental and Health Concerns
E-waste contains hazardous substances like arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury. If not properly managed, these materials can severely impact human health and the environment, contaminating soil and water sources.
Government Efforts: E-Waste Management Rules, 2022
- Introduction of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): The government introduced the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, effective from April 1, 2023. These rules focus on making producers responsible for the recycling of e-waste. Producers are assigned recycling targets based on the quantity of e-waste generated or products sold and must purchase EPR certificates from authorized recyclers to meet these targets.
- Integration of Bulk Consumers: Public institutions and government offices, categorized as bulk consumers, are mandated to dispose of e-waste only through registered recyclers or refurbishers, ensuring proper treatment and recycling of the waste.
- Expansion of E-Waste Coverage: The updated rules expanded the scope to include 106 Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) items from FY 2023-24, up from 21 items previously covered under the 2016 E-Waste Rules.
Challenges in E-Waste Recycling and Disposal
- Low Recycling Rates: Although the share of e-waste recycled in India has increased from 22% in 2019-20 to 43% in 2023-24, a significant 57% of e-waste remains unprocessed annually. Informal sector practices, which dominate e-waste handling, often lack the necessary environmental safeguards, leading to improper disposal and environmental contamination.
- Lack of Infrastructure and Awareness: India faces challenges in building adequate infrastructure for e-waste collection and recycling, resulting in improper disposal in landfills. Furthermore, a lack of public awareness regarding proper disposal methods exacerbates the problem.
Global Context and India’s Position
- India ranks as the third-largest e-waste generator globally, following China and the United States. With an increasing rate of e-waste generation, the country faces an urgent need to improve recycling efficiency and adopt sustainable disposal methods.
International and National Conventions on E-Waste
- India is a signatory to several international conventions that govern hazardous waste management, including the Basel Convention, which regulates the transboundary movement of hazardous wastes, and the Minamata Convention, which focuses on mercury. At the national level, India has established the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, and other frameworks to manage and reduce e-waste effectively.
Strategic Recommendations for Effective E-Waste Management
- Harnessing the Informal Sector: India’s informal sector, which handles a significant portion of e-waste, must be integrated into the formal recycling systems. This can be achieved through training and financial support to ensure safe and environmentally responsible recycling practices.
- Technological Innovations: Encouraging research into advanced recycling technologies, such as AI and IoT-based solutions for efficient e-waste collection and tracking, will be crucial for improving the e-waste management system.
- Learning from Global Practices: Countries like the European Union (EU) and Japan have set strong examples. The EU’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive and Japan’s Home Appliance Recycling Law emphasize Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and provide models for India to adapt.
Conclusion
To address the growing e-waste challenge, India must improve its recycling infrastructure, integrate the informal sector, and adopt best practices from international models. With sustainable and effective strategies, India can mitigate the environmental and health risks posed by e-waste while promoting a circular economy.
Arctic Tundra: From Carbon Sink to Carbon Source

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The Arctic tundra, a frozen, treeless biome, has historically been a vital carbon sink, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO?) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). However, recent findings suggest that, for the first time in millennia, this ecosystem is emitting more carbon than it absorbs, a change that could have significant global consequences. This alarming shift was highlighted in the 2024 Arctic Report Card published by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The Arctic Tundra’s Role as a Carbon Sink
The Arctic tundra plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. In typical ecosystems, plants absorb CO? through photosynthesis, and when they die, carbon is either consumed by decomposers or released back into the atmosphere. In contrast, the tundra’s cold environment significantly slows the decomposition process, trapping organic carbon in permafrost—the permanently frozen ground that underpins much of the region.
Over thousands of years, this accumulation of organic matter has resulted in the Arctic storing an estimated 1.6 trillion metric tonnes of carbon. This figure is roughly double the amount of carbon in the entire atmosphere. As such, the tundra has served as a critical carbon sink, helping to mitigate global warming by trapping vast quantities of CO?.
Shifting Dynamics: Emission of Greenhouse Gases
Recent reports indicate a dramatic shift in the Arctic tundra’s role in the carbon cycle. Rising temperatures and increasing wildfire activity have disrupted the tundra’s balance, leading it to transition from a carbon sink to a carbon source.
Impact of Rising Temperatures
The Arctic region is warming at a rate approximately four times faster than the global average. In 2024, Arctic surface air temperatures were recorded as the second-warmest on record since 1900. This rapid warming is causing permafrost to thaw, which in turn activates microbes that break down trapped organic material. As this decomposition accelerates, carbon in the form of CO? and methane (CH?)—a more potent greenhouse gas—are released into the atmosphere.
The experts, explained the process by comparing thawing permafrost to meat left out of the freezer. Similarly, thawing permafrost accelerates the breakdown of trapped carbon.
The Role of Wildfires
In addition to warming temperatures, the Arctic has experienced a surge in wildfires in recent years. 2024 marked the second-highest wildfire season on record in the region, releasing significant amounts of GHGs into the atmosphere. Wildfires exacerbate the thawing of permafrost, creating a feedback loop where increased carbon emissions contribute further to warming, which, in turn, leads to more emissions.
Between 2001 and 2020, these combined factors caused the Arctic tundra to release more carbon than it absorbed, likely for the first time in millennia.
The Global Consequences of Emission
The transition of the Arctic tundra from a carbon sink to a carbon source is alarming, as it represents a significant amplification of global climate change. The release of additional CO? and CH? into the atmosphere further accelerates the greenhouse effect, leading to higher global temperatures. This warming is already having visible consequences around the world, from extreme weather events to rising sea levels.
If the Arctic tundra continues to emit more carbon than it absorbs, it could significantly exacerbate the climate crisis. The report underscores the urgency of addressing global emissions, as reducing greenhouse gases remains the most effective way to prevent further destabilization of this sensitive ecosystem.
Mitigating the Impact: The Path Forward
Despite the alarming trends, the Arctic Report Card suggests that it is still possible to reverse this process. By reducing global GHG emissions, it may be possible to slow the thawing of permafrost and allow the Arctic tundra to regain its role as a carbon sink. Scientists emphasize that mitigating climate change on a global scale is essential to prevent further emissions from the Arctic ecosystem.
Scientists, stressed the importance of emission reductions, stating, “With lower levels of climate change, you get lower levels of emissions from permafrost… That should motivate us all to work towards more aggressive emissions reductions.”
However, current trends suggest that achieving this goal may be challenging. A recent report from the Global Carbon Project indicates that fossil fuel emissions are likely to rise in 2024, with total CO? emissions projected to reach 41.6 billion tonnes, up from 40.6 billion tonnes in 2023.
How would a carbon market function?

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
COP29, the ongoing climate conference in Azerbaijan’s capital Baku, has given a fillip to the idea of using carbon markets to curb carbon emissions by approving standards that can help in the setting up of an international carbon market as soon as the coming year.
Introduction to Carbon Markets
- Carbon markets allow the buying and selling of the right to emit carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
- Governments issue certificates known as carbon credits, each representing the right to emit 1,000 kilograms of CO2.
- The total number of credits issued is capped to control carbon emissions. Companies and individuals who don’t have credits cannot emit CO2.
Trading of Carbon Credits
- Carbon Credit Trading: Companies holding more carbon credits than needed can sell them to others who need more, with the price determined by market forces.
- Carbon Offsets: Businesses can also purchase carbon offsets, often provided by environmental NGOs, which promise to reduce emissions (e.g., by planting trees). These offsets counterbalance the firm’s carbon emissions.
- The trading of both credits and offsets is designed to create financial incentives for companies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Advantages of Carbon Markets
- Addressing Externalities: Carbon emissions are a classic example of an economic externality, where the costs of pollution are not reflected in market prices.
- Market Efficiency: By allowing firms to buy and sell carbon credits, the system internalizes the cost of carbon emissions, encouraging businesses to reduce emissions to avoid higher costs.
- Incentive for Emission Reduction: Carbon markets aim to create a financial reason for companies to lower their emissions, thus helping mitigate climate change.
Voluntary vs. Government-Mandated Carbon Markets
- Voluntary Carbon Reporting: Many corporations prefer voluntary systems like the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) for reporting their emissions, fearing government-imposed restrictions.
- Market Flexibility: Corporations like ExxonMobil and General Motors argue that carbon markets with freely traded credits allocate carbon allowances more efficiently than government-imposed limits. This allows firms to purchase credits from others, optimizing resource allocation without restricting output.
- Corporate Resistance to Government Intervention: Firms are often reluctant to accept strict government budgets for carbon emissions, fearing increased operational costs and production limitations due to diverse supply chains.
Issues and Criticisms of Carbon Markets
- Government Manipulation of Credit Supply: Governments may increase the number of carbon credits issued, leading to lower prices and reduced incentives for emission reductions.
- Lack of Accountability in Carbon Offsets: Critics argue that some companies buy carbon offsets as a form of virtue signalling, without genuine concern for their environmental impact. This undermines the effectiveness of the offsets.
- Government Mismanagement: Political decision-making may lead to the over-restriction of carbon credits, potentially slowing economic growth by limiting available emissions allowances. The ability of governments to accurately determine the optimal supply of carbon credits is a contentious issue.
The Concept of Carbon Credits and Their History
- Introduction of Carbon Credits: Carbon credits were first introduced in the 1990s in the U.S., specifically through a cap-and-trade model designed to control sulfur dioxide emissions. This approach later expanded to include carbon emissions.
- Role of Carbon Markets: In essence, these markets aim to create a financial mechanism where firms can trade the right to pollute, ensuring a balance between economic growth and environmental protection.
Criticism of Carbon Offsets
- Effectiveness of Offsets: Experts are critical of carbon offsets, arguing that they do not always lead to meaningful reductions in emissions. For example, some companies may purchase offsets without ensuring that the projects are genuinely offsetting their emissions.
- Moral Hazard: Critics suggest that offset programs may lead to firms simply paying for the right to pollute, rather than actually reducing emissions in their operations.
Conclusion
- Carbon Markets as a Tool for Emission Reduction: Despite the criticisms, carbon markets remain a promising tool for mitigating climate change, provided they are carefully regulated and implemented.
- The Future of Carbon Trading: As discussions at COP29 evolve, the development of international standards for carbon trading could potentially enhance the effectiveness of these markets, offering a viable path to global emission reductions.
Reflections on Baku’s ‘NCQG Outcome’ at COP29
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The recently concluded COP29 in Baku, Azerbaijan, has brought the spotlight back to climate finance, particularly in relation to the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG). As the global community grapples with the escalating climate crisis, the discussions and outcomes from the COP29 summit are pivotal in shaping future climate action. However, the agreed-upon financial targets, which were expected to be a step towards transformative climate justice, have sparked significant concern, particularly among developing nations.
The Need for Climate Finance: A Global Responsibility
Climate finance is essential for supporting developing countries, which bear the brunt of climate change despite contributing minimally to global emissions. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has stressed the need to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, yet current policies could lead to a rise of up to 3.1°C. To counter this, developing nations require financial assistance to transition to green energy, adapt to climate impacts, and implement their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
The upfront costs of green technologies, such as renewable energy, are high, and while they offer long-term savings, their initial investments remain a significant barrier. Additionally, many developing countries face fiscal constraints, making it even more difficult to adopt climate-friendly technologies without external financial support.
The Role of NCQG in Addressing Climate Finance Gaps
The NCQG, an evolution of the 2010 $100 billion annual commitment, aims to provide clarity and accountability in climate financing. Established as a framework to ensure financial resources for climate action, the NCQG should ideally focus on the evolving needs of the Global South. However, at COP29, the target agreed upon was a mere $300 billion annually by 2035, far from the $1.3 trillion that developing countries had requested. This amount falls drastically short of what is necessary to meet the ambitious climate goals and fails to represent a transformative shift in financial flows.
Key Challenges and Discontent with the Outcome
Several challenges have been raised regarding the COP29 outcome:
- Equity and Responsibility: Developed nations are expected to bear a larger share of the financial burden, in line with the principle of 'Common but Differentiated Responsibilities' (CBDR). However, the NCQG outcome bypasses this principle, offering insufficient funds for climate action in developing countries.
- Types of Finance: There is debate over whether private finance should count towards the goal. Developing countries have stressed the importance of public finance over loans, which add to their debt burdens.
- Insufficient Commitment: While the $300 billion annual pledge is a step forward, it is far from adequate. The global climate finance needs, estimated at $5 trillion to $7 trillion by 2030, require bolder commitments from developed nations.
India's Position and Domestic Efforts
At COP29, India emphasized the need for developed countries to fulfill their financial commitments, advocating for at least $1.3 trillion annually until 2030. India, despite being a developing country, has also made significant strides in climate action through domestic policies. The 2024-25 Union Budget allocated substantial funds to renewable energy projects, including ?19,100 crore for the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy. These efforts demonstrate India’s commitment to climate goals, though the financial flow remains insufficient.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
The NCQG outcome at COP29 highlights the ongoing disparities in global climate finance commitments. While the $300 billion annual target is a step forward, it does not align with the urgency or scale required to tackle the climate crisis. To achieve a just and equitable transition to a sustainable future, future climate finance discussions must prioritize transparency, accountability, and fairness, ensuring that developed nations shoulder their fair share of the responsibility. The path forward requires unwavering international cooperation to ensure that developing countries receive the necessary support to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The 29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29), held in Baku, Azerbaijan, focused on enhancing climate finance, adaptation measures, and global cooperation.
Key Outcomes of COP29:
- Climate Finance: A new goal was set to triple climate finance for developing countries to USD 300 billion annually by 2035. The total climate finance target aims for USD 1.3 trillion annually by 2035.
- Carbon Markets: The conference operationalized Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, which establishes frameworks for carbon credit trading between countries. It also launched the Paris Agreement Crediting Mechanism, ensuring safeguards for human rights and the environment.
- Transparency and Adaptation: COP29 saw 13 countries submit their Biennial Transparency Reports, promoting greater accountability. The Baku Adaptation Roadmap was launched to speed up National Adaptation Plans (NAPs) in Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
- Gender and Inclusivity: A new Gender Action Plan was developed, and the Lima Work Programme on Gender was extended for another 10 years. Over 55,000 people, including civil society, Indigenous peoples, and youth, participated.
- Global Climate Action: The 2024 Yearbook of Global Climate Action highlighted the role of non-Party stakeholders like businesses and sub-national actors in combating climate change.
India’s Role at COP29: India played an active role in highlighting resilient infrastructure initiatives like the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) and advocated for financial resources to support Small Island Developing States (SIDS). India also pushed for solar energy adoption through the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and promoted gender-inclusive climate policies. India co-hosted the LeadIT summit with Sweden, focusing on industrial decarbonization.
Challenges at COP29:
- Inadequate Finance: Despite ambitious targets, many countries felt the financial commitments were insufficient and distant.
- Private Sector Dependency: The reliance on private sector contributions raised concerns about the reliability of funding.
- Emission Reduction Gaps: There was a lack of sufficient pledges to meet the 1.5°C global warming target, with rising emissions.
- Geopolitical Conflicts: Disputes over issues like the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) hindered progress.
India’s Carbon Credit Framework:
India introduced the Energy Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2022, establishing a domestic carbon market and setting a legislative framework for carbon credit trading. This aligns with India’s NDCs and aims to support sustainable growth while reducing emissions. However, concerns about the integrity of carbon credits and potential "greenwashing" need to be addressed through rigorous verification systems.
Conclusion:
COP29 marked progress in scaling up climate finance, carbon markets, and adaptation efforts, but significant challenges remain, especially in finance, emission reductions, and geopolitical cooperation. India's initiatives in carbon credit frameworks and resilience are steps toward a sustainable future. Moving forward, a collaborative, transparent, and adaptive approach is crucial to meet global climate goals.
Earning Instead of Burning
- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Paddy straw burning, prevalent in Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, contributes to severe air pollution, especially during the post-harvest period in October and November. Despite various government measures and subsidies to reduce stubble burning, it continues due to economic and operational constraints faced by farmers. To address this issue, innovative technologies for the productive use of paddy straw need to be explored.
Stubble Burning: Causes and Consequences
Reasons for Stubble Burning
- Short Crop Cycles: The narrow window between paddy harvest and wheat sowing forces farmers to burn straw to prepare fields quickly.
- Economic Constraints: High costs of alternative residue management methods.
- Lack of Awareness: Farmers are often unaware of sustainable alternatives.
- Limited Mechanization: Availability of crop residue management machinery is inadequate.
- Policy Gaps: Ineffective enforcement of regulations and insufficient incentives.
Consequences of Stubble Burning
- Air Pollution: Emission of harmful pollutants like PM2.5, CO2, and CO contributes to air quality degradation.
- Health Hazards: Increased respiratory illnesses due to the inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Soil Degradation: Loss of essential nutrients and organic matter.
- Climate Change: Stubble burning releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Economic Costs: Increased health care costs and loss of soil fertility.
Technologies for Paddy Straw Utilization
Large-Scale Technologies
- Direct Combustion:Burns rice straw under controlled conditions to generate heat for cooking and industrial uses. While its calorific value is lower than that of petrol and diesel, it is still viable for local energy generation.
- Pyrolysis and Gasification:
- Pyrolysis: Converts rice straw into bio-oil through heating at 200-760°C in the absence of oxygen.
- Gasification: Converts rice straw into syngas at higher temperatures (480-1,650°C) with limited oxygen. Challenges include low gas production and tar accumulation.
- Biochar Production:Rice straw is incinerated at lower temperatures to produce biochar, which is used as a soil conditioner to improve fertility, water retention, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Power Generation:Biomass-based power plants use rice straw to generate electricity, providing a sustainable energy source, especially for rural areas. States like Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh are scaling up such plants.
- Pellet Production:Rice straw is compressed into compact pellets, improving its density, transportability, and combustion efficiency. These pellets can partially replace coal in power plants, offering an alternative use for crop residue.
- Biofuels:Conversion of rice straw into biofuels like ethanol and biogas helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels and supports the renewable energy transition.
- Paper Production:Rice straw, with its high cellulose content, is used as an eco-friendly alternative to wood in the paper and pulp industry, reducing environmental impact.
Small-Scale Technologies
- Composting:Rice straw can be composted to produce organic fertilizer, enhancing soil health. Vermicomposting is another effective method, though awareness among farmers remains low.
- Mushroom Cultivation:Rice straw serves as an ideal substrate for growing mushrooms, particularly species like Volvariellavolvacea. This practice provides an additional income source for farmers.
- Silica Extraction:Rice straw contains high silica content, which can be extracted for industrial applications like construction and electronics.
- Fodder for Ruminants:Though rice straw is low in digestibility due to high silica content, it can be used as animal feed after pre-treatment, such as drying, grinding, or chemical processes to enhance its nutritional value.
- Adsorbent for Pollution Control:Rice straw can be used to remove heavy metals and toxins from contaminated water, showing promise in environmental cleanup efforts.
- Soil Incorporation:Instead of burning, rice straw can be incorporated directly into the soil to improve fertility, moisture retention, and crop yield. This practice is already being adopted in regions like Punjab and Haryana.
Conclusion: Path Forward
Stubble burning continues to be a significant environmental challenge, but the development and adoption of technologies for utilizing paddy straw can offer viable solutions. Both large- and small-scale technologies can convert rice straw into valuable products like biofuels, power, and fertilizers. To ensure widespread implementation, efforts must be made to increase awareness among farmers and stakeholders, coupled with strong policy support and infrastructural investment. A collaborative approach involving the government, industries, and farmers is essential for sustainable management of rice straw, benefiting both the environment and the economy.
Sustainable Path to Net-Zero for India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
India's commitment to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070 presents a significant challenge, with only 45 years remaining to reach this ambitious target. The path to net-zero requires a balancing act between economic development, energy security, and climate adaptation. India’s efforts to meet its climate goals will be shaped by multiple factors, including resource constraints, land use, and financial limitations.
Why Net-Zero at All?
- Scientific Consensus on Climate Change
- Climate change is a growing concern, with the global temperature rise already reaching 1.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- To avoid catastrophic impacts, the world needs to limit the temperature rise to 1.5°C. The remaining global carbon budget for this target is around 400-500 billion tonnes of CO?.
- Necessity of Sharp Emission Reductions
- Countries must drastically reduce emissions to stay within the carbon budget. Achieving net-zero emissions is essential for maintaining global climate stability.
Equity in Net-Zero Transitions
- Developed vs. Developing Countries
- Developed nations, historically responsible for a large share of emissions, are expected to lead the transition. However, they have not met the financial and technological support commitments for developing countries.
- Developing nations like India, with low per capita emissions, are under pressure to balance climate action with economic development.
- Climate Justice
- India’s per capita emissions are among the lowest globally, but the richest 10% of Indians contribute significantly to national emissions, exacerbating inequality.
- The impacts of climate change disproportionately affect the economically weaker sections, making the transition to net-zero not only an environmental challenge but a social justice issue as well.
The Challenge of Balancing Development and Sustainability
- Limits of India’s Resources
- India faces resource constraints, including land, water, and biodiversity, which limit the feasible expansion of renewable energy capacity.
- Meeting energy demands while ensuring food security, forest cover, and biodiversity preservation becomes increasingly challenging as energy requirements rise.
- Sustainable Consumption vs. Aspirational Lifestyles
- India’s aspiration to emulate the developed world’s lifestyle is unsustainable due to limited resources, which could lead to severe consequences like groundwater depletion, heat stress, and biodiversity loss.
- The focus should be on sufficiency consumption corridors, ensuring that consumption meets developmental goals without exceeding sustainable limits.
Projected Power Demand and Renewable Energy Targets
- Rising Power Demand
- India’s power demand could increase nine to ten-fold by 2070. Meeting this demand entirely via renewable energy requires significant expansion in energy generation capacity:
- 5,500 GW of solar energy
- 1,500 GW of wind energy
- India’s power demand could increase nine to ten-fold by 2070. Meeting this demand entirely via renewable energy requires significant expansion in energy generation capacity:
- Land Use Constraints
- To meet these targets, India must address land-use trade-offs. Expanding beyond 3,500 GW of solar and 900 GW of wind would require significant compromises in land availability for other uses, including agriculture and conservation.
Strategic Pathways to Net-Zero: Demand and Supply Measures
- Demand-Side Measures
- Energy-efficient construction: Use of better materials and passive designs to reduce cooling energy demand.
- Urban transport: Shift to public and non-motorized transport to reduce energy consumption in cities.
- Dietary choices: Promoting sustainable dietary practices to reduce the carbon footprint of food systems.
- Electrification: Focus on alternative fuels and energy-efficient appliances.
- Supply-Side Measures
- Decentralization of Energy Production: Expanding rooftop solar panels and solar pumps for agriculture.
- Nuclear Power Expansion: Increase nuclear energy to provide a low-carbon baseload and complement renewable sources like solar and wind, which are intermittent.
The Role of International Cooperation and Financial Support
- Global Cooperation
- Global climate action requires alignment between national interests, which may not always coincide, as seen in the context of the U.S. presidential election potentially influencing global climate policy.
- India’s path to net-zero depends heavily on international climate financing, technology transfer, and collaborative efforts to address climate justice.
- Equitable Financing for Developing Countries
- Developed countries are expected to provide financial support to developing nations like India to achieve climate goals. However, this support has been insufficient to date.
Conclusion: India’s Balancing Act
India faces a challenging balancing act as it seeks to provide quality of life for its growing population while achieving its climate adaptation and mitigation goals. The path to net-zero will require careful management of economic growth, energy production, and resource conservation. India must focus on demand-side strategies to reduce energy consumption and increase efficiency while expanding renewable energy infrastructure in a sustainable manner. Additionally, international cooperation and financial support will be crucial in ensuring that India’s transition to net-zero is equitable, efficient, and aligned with its developmental priorities.
Andhra Pradesh's Natural Farming Model

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
Andhra Pradesh's (AP) natural farming model presents a transformative opportunity to reshape the state’s agricultural landscape by 2050. An analysis by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in collaboration with the AP government, reveals how scaling natural farming could employ more farmers, increase incomes, and foster sustainable agricultural practices, potentially surpassing the benefits of conventional industrial agriculture.
AgroEco2050: Exploring Two Agricultural Futures
The AgroEco2050 initiative aimed to envision two possible futures for Andhra Pradesh’s agricultural systems by 2050:
- Industrial Agriculture Path: Focusing on intensification of conventional farming, relying heavily on chemicals, machinery, and monocultures.
- Natural Farming Path: Expanding agroecological practices, relying on regenerative, chemical-free farming methods to create more jobs, better livelihoods, and improve the environment.
The study compared these pathways, analyzing their impacts on employment, income, food production, biodiversity, and land use.
Key Findings: Natural Farming’s Impact on Employment and Income
- Employment Growth
- By 2050, natural farming would employ twice as many farmers as industrial agriculture: 10 million compared to 5 million.
- Unemployment in natural farming would decrease to 7%, in stark contrast to a projected 30% unemployment rate in the industrial agriculture scenario.
- Farmer Income
- Natural farming is expected to be more profitable for farmers due to lower input costs (seeds, fertilizers, machinery) and higher market prices for high-quality produce.
- The income gap between farmers and non-farmers, which stood at 62% in 2019, would decrease to 22% under natural farming by 2050, a sharp improvement compared to the 47% gap predicted under industrial agriculture.
What is Natural Farming?
Natural farming is an ecological, chemical-free farming system that emphasizes the use of locally available resources. Key practices include:
- Biodiversity-based pest management
- On-farm biomass recycling (e.g., mulching)
- Indigenous techniques like using cow dung and urine for soil fertility.
Globally recognized as a form of regenerative agriculture, it offers a sustainable alternative to industrial agriculture by sequestering carbon and restoring soil health.
Global Adoption
States like Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, and others are already adopting natural farming. While still evolving, its acceptance among farmers is steadily growing.
Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) in Andhra Pradesh
Origin and Growth
- In 2016, Andhra Pradesh launched the Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) initiative to offer a sustainable alternative to capital-intensive agriculture.
- This program, implemented by RythuSadhikaraSamstha, targets covering 6 million farmers across 6 million hectares.
National Recognition
The ZBNF approach gained national attention when it was featured in the 2019 Union Budget, aimed at doubling farmers' incomes by 2022. The central government now promotes this model under the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY).
Challenges in Scaling Natural Farming
- Farmer Training and Support
- Farmers need ongoing education and support to transition effectively to natural farming. Current training systems often fail to address the full scope of their needs.
- Certification Barriers
- The certification process for organic farming, including Participatory Guarantee Systems (PGS) and third-party certifications, is complex and costly, presenting a barrier for small-scale farmers.
- Marketing and Procurement Challenges
- There is a lack of effective marketing systems for organic products, which hampers the ability of farmers to sell their produce at fair prices.
- Without strong procurement or buy-back systems, farmers may struggle to find markets for their products.
- Policy and Funding Gaps
- Organic and natural farming programs still receive minimal funding compared to subsidies for chemical fertilizers, impeding large-scale adoption.
- Slow state-level implementation and a continued reliance on chemical inputs also delay the widespread shift to natural farming.
Moving Forward
- Scientific Research on Yields
- To address concerns about lower yields for staple crops, more scientific research is needed to assess the long-term viability of natural farming, especially for crops like wheat and rice, which are crucial for India’s food security.
- Localized Adoption
- Natural farming may be best suited for non-staple crops or localized farming, balancing sustainability with the need for food security.
- Risk Mitigation for Food Security
- Careful evaluation of natural farming’s impact on staple crop yields is necessary to avoid the food security risks witnessed in countries like Sri Lanka, where a sudden shift to organic farming led to reduced yields and increased prices.
Conclusion
The Andhra Pradesh natural farming model offers a promising alternative to industrial agriculture, with the potential to create jobs, improve farmers' incomes, and promote environmental sustainability. However, for this vision to become a reality, significant efforts must be made to address challenges related to training, certification, marketing, and funding. With continued research, policy support, and community involvement, natural farming can play a crucial role in feeding the future and promoting a more sustainable agricultural system.
Zeroing in on Methane Diplomacy, at COP29

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
From November 11 to 22, 2024, global leaders will gather in Baku, Azerbaijan, for the 29th Conference of Parties (COP29) under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). This year’s summit, known as the Finance COP, will focus on setting a new global climate finance target—the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG).
A key focus of the summit is the reduction of methane emissions, as countries aim to curb near-term temperature increases, which buys critical time for long-term CO2 reductions necessary for stabilizing climate change.
U.S.-China Collaboration and Methane Reduction
US-China Collaboration Despite Geopolitical Tensions
Despite ongoing geopolitical tensions, the United States and China have found common ground on the issue of methane reduction. Both nations recognize the importance of addressing methane emissions, which are more potent in the short term than CO2. They, along with the United Arab Emirates, organized a summit at COP28 to discuss methane and other non-CO2 pollutants.
China’s National Plan for Methane Emissions
In November 2023, China launched its first national methane reduction plan, emphasizing capacity-building efforts over explicit reduction targets. This plan marked a significant step in China’s climate policy, underscoring its commitment to mitigating methane emissions alongside the U.S.
Given that China and the U.S. are the two largest contributors to methane emissions globally, their collaboration presents a significant opportunity for global climate mitigation efforts. India, the third-largest emitter of methane, could benefit from this partnership by seeking financial support and technical expertise to address its methane challenges.
India’s Methane Emissions Profile and Challenges
Emissions Breakdown
India’s Third Biennial Update Report to the UNFCCC indicates that in 2016, India emitted approximately 409 million tons of CO2-equivalent methane. The major sources of these emissions include:
- Agriculture: 74% (mainly from livestock and rice cultivation)
- Waste: 14% (unmanaged organic waste in landfills and dumpsites)
- Energy: 11%
- Industrial processes: 1%
Due to the dominant role of agriculture, India has been cautious about committing to stringent methane reduction targets. Initiatives like the Global Methane Pledge, which calls for a 30% reduction from 2020 levels by 2030, have not been fully embraced.
Environmental and Health Impact of Methane Emissions
Methane-related fires at waste dumpsites, such as the Bhalswa dump in Delhi (2022), have highlighted the broader environmental and health risks of methane emissions. These fires contribute significantly to air pollution, making it urgent for India to address methane in its waste management and agricultural sectors.
India’s Initiatives for Methane Reduction
Waste Management Programs
- Comprehensive Waste Management Framework India’s waste management sector is a significant source of methane, contributing 14% of the nation’s total emissions. Although a comprehensive regulatory framework for waste management has been developed, implementation remains slow due to local capacity constraints and financial limitations.
- Innovative Solutions Indore, a city in Madhya Pradesh, has pioneered waste sorting and biomethane production. The city's initiative includes:
- Sorting organic waste
- Converting it into biogas to fuel city buses
This model has gained national attention and is being considered for replication in other cities.
- GOBARdhan Scheme Launched as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0, the Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) scheme encourages rural communities to convert cattle manure and other organic waste into biogas and compost, reducing methane emissions from livestock waste while providing additional income to rural households.
Agricultural and Livestock Emission Reduction
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) The NMSA promotes climate-resilient agricultural practices that reduce methane emissions. For example, Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) is a water-saving technique used in rice farming that reduces methane emissions by limiting anaerobic decomposition.
- National Livestock Mission Under the National Livestock Mission, practices such as improved fodder management, silage making, and Total Mixed Ration (TMR) feeding are being promoted. These practices reduce methane emissions from livestock by improving digestion and feed efficiency.
Opportunities for India at COP29
Leveraging U.S.-China Methane Partnership
COP29 offers India an opportunity to leverage the U.S.-China collaboration on methane reduction. By engaging with these two major emitters, India can seek:
- Financial support
- Technical assistance
- Capacity-building resources, particularly for its waste sector, which is a significant source of methane emissions.
Accurate data on methane emissions, such as satellite-based monitoring, can help India refine its emission inventories and enhance the effectiveness of its methane mitigation efforts.
Fast-Tracking India’s Methane Reduction Efforts
Although methane is not the primary focus at COP29, India has an opportunity to fast-track its efforts in methane reduction. The country's existing policies and initiatives, such as waste management programs and agricultural missions, provide a foundation upon which international collaboration can build.
Recent data from satellite monitoring in cities like Delhi and Mumbai shows that actual methane emissions from waste dumpsites may be 50%-100% higher than previously estimated, highlighting the urgency of addressing this issue.
Conclusion
Although methane may not dominate the COP29 agenda, it represents a critical pathway for India to accelerate its climate action. With the groundwork already laid through domestic policies and innovative solutions, India now requires enhanced financial and technical backing to scale up its methane reduction initiatives. By engaging proactively at COP29, India has a unique opportunity to secure the resources needed to tackle methane emissions, benefiting both its citizens and the global fight against climate change.
Key Takeaways from COP-16: Convention on Biological Diversity

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The 16th edition of the Convention of Biological Diversity (CBD) in Cali, Colombia was concluded.
Key Agreements at COP-16
- Establishment of the Cali Fund
- Purpose: To ensure equitable benefit-sharing from the use of Digital Sequence Information (DSI) on genetic resources.
- Focus on Indigenous Communities: At least 50% of the Cali Fund will support Indigenous peoples and local communities, with special emphasis on women and youth.
- Creation of a Permanent Subsidiary Body
- Inclusion of Indigenous Peoples: A new body will ensure the active participation of Indigenous groups in biodiversity conservation and policy discussions.
- Resource Mobilisation Strategy
- Target Funding: The conference agreed on a strategy to secure USD 200 billion annually by 2030 to support global biodiversity initiatives.
- Kunming Biodiversity Fund: A contribution of USD 200 million from China to support biodiversity funding.
- Management of Invasive Alien Species
- New Guidelines: Proposals for databases, cross-border trade regulations, and enhanced coordination with e-commerce platforms to manage invasive species.
- Identification of Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Areas (EBSAs)
- Enhanced Process: COP-16 agreed on an evolved process for identifying EBSAs, a critical aspect of marine conservation.
- Global Action Plan on Biodiversity and Health
- One Health Approach: Approval of a global action plan to curb zoonotic diseases, promote health, and safeguard ecosystems.
India’s Contribution at COP-16
Updated National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP)
- Financial Commitment: India plans to invest ?81,664 crore (USD 9.8 billion) from 2025-30 on biodiversity conservation.
- Focus Areas: India highlighted efforts such as the establishment of the International Big Cat Alliance, expansion of Ramsar sites, and increased spending on biodiversity from 2018-2022.
International Finance Support
- Global Partnerships: India emphasized the need for international finance to meet biodiversity targets, particularly under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Outcomes from COP-16
- New Mechanisms for Biodiversity Conservation
- Cali Fund: Ensures equitable benefit-sharing from genetic resources.
- Permanent Subsidiary Body: Facilitates the inclusion of Indigenous peoples in policy-making.
- Funding and Resource Mobilization
- USD 200 Billion Annually: Strategy to secure funding for biodiversity initiatives.
- Redirecting Harmful Subsidies: Agreement to redirect USD 500 billion in harmful subsidies by 2030.
- Biodiversity and Human Health
- Global Action Plan on Biodiversity and Health: Aimed at preventing zoonotic diseases and promoting human, animal, and environmental health.
Challenges in Biodiversity Protection
Key Threats to Biodiversity
- Population Growth and Resource Demand: Increasing population and demand for biological resources lead to over-exploitation.
- Habitat Degradation and Climate Change: Destruction of ecosystems and climate change threaten species globally.
- Invasive Species: Introduction of non-native species harms local biodiversity.
- Government Policies: Policies that prioritize development without environmental safeguards contribute to biodiversity loss.
Gaps in Global Biodiversity Framework
- Weak Legal Language: Concerns about insufficient legal protection for critical ecosystems.
- Lack of Implementation Mechanisms: Absence of mandatory review mechanisms for biodiversity targets.
Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF)
Framework Overview
- Adoption: Adopted at COP-15 in 2022, the KMGBF sets 23 action-oriented targets for biodiversity by 2030.
- Key Goals: Includes restoring 30% of degraded ecosystems and reducing the risk of invasive species by 50%.
- Living in Harmony with Nature: The framework envisions achieving biodiversity targets and living sustainably with nature by 2050.
Way Forward: Moving from Agreements to Action
- Participation of Stakeholders - Inclusive Approach: Ensuring the involvement of all relevant stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and local communities, in biodiversity conservation.
- Integrated Resource Management - Ecosystem Approach: Promoting a holistic approach to managing biodiversity and natural resources.
- Strengthening Governance - Good Governance Practices: Encouraging better governance to prevent unregulated exploitation of natural resources.
- International Financial Support - Alignment with Financial Institutions: Aligning global financial institutions and multilateral development banks with biodiversity conservation goals.
WWF Living Planet Report 2024

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- The WWF Living Planet Report 2024 highlights a drastic 73% decline in the average size of monitored wildlife populations globally from 1970 to 2020.
- The report underscores the urgent need for biodiversity conservation to maintain ecological balance, food security, and human health.
Key Findings of the 2024 Report
Wildlife Population Decline
- 73% Decline in monitored wildlife populations over the past 50 years (1970-2020).
- Freshwater species: Declined by 85%, the most significant drop.
- Terrestrial species: Declined by 69%.
- Marine species: Declined by 56%.
Main Threats to Wildlife
- Habitat Loss: Primary driver, particularly due to the expansion of food systems.
- Overexploitation: Over-hunting, fishing, and resource extraction.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species disrupt local ecosystems.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil contamination, especially in Asia-Pacific.
- Disease: Emerging diseases impacting wildlife populations.
Ecosystem Risks and Tipping Points
- Decline in wildlife signals risks of ecosystem tipping points.
- Critical ecosystems, like the Amazon and coral reefs, face potential irreversible damage.
- Impact on global food security and livelihoods due to ecosystem collapse.
India’s Wildlife Status
- Vulture populations in India remain critically endangered.
- Tiger populations have increased to 3,682 (2022).
- Snow leopards have been successfully monitored with 718 individuals recorded.
Case Study: Chennai’s Wetland Loss
- 85% reduction in Chennai’s wetlands due to urban expansion, exacerbating flood and drought risks.
- Initiatives like the Tamil Nadu Wetland Mission aim to restore these wetlands to improve ecosystem resilience.
Impacts of Wildlife Decline
- Ecosystem Imbalance
- Disruption in predator-prey relationships, pollination, and nutrient cycles due to species decline.
- Leads to ecosystem instability and potential collapse.
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Reduced genetic diversity makes ecosystems less resilient to environmental changes.
- Increases vulnerability to diseases, natural disasters, and climate change.
- Threats to Food Security
- Pollinators like bees and insects are essential for crop yields.
- Loss of pollinators threatens global food supply and agriculture.
- Human Health Implications
- Healthy ecosystems regulate disease by controlling pest populations.
- Declining biodiversity increases the risk of zoonotic diseases, such as COVID-19.
- Economic Consequences
- Agriculture, fisheries, and tourism industries depend on healthy ecosystems.
- Decline in wildlife can lead to job losses and economic instability.
- Cultural and Social Impacts
- Wildlife holds cultural, spiritual, and recreational value for societies worldwide.
- Loss of iconic species diminishes cultural identities and opportunities for nature-based tourism.
Challenges in Biodiversity Conservation
- Inadequate National Actions
- Despite global commitments (e.g., Global Biodiversity Framework, Paris Agreement, UN SDGs), national actions are insufficient to meet 2030 biodiversity targets.
- Risk of crossing tipping points that could lead to irreversible ecosystem degradation.
- Key Drivers of Biodiversity Loss
- Habitat Loss: Driven by agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure development.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, extreme weather, and altered precipitation patterns.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable hunting, fishing, logging, and resource extraction.
- Pollution: Industrial, agricultural, and plastic pollution disrupt natural habitats.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species outcompeting and threatening native populations.
- Lack of Funding: Inadequate financial resources for effective conservation.
- Weak Policy and Enforcement: Poorly implemented habitat protection laws.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Increased interactions between expanding human populations and wildlife.
- Genetic Diversity Loss: Reduced genetic diversity makes species vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes.
- Awareness Gaps: Insufficient public awareness on the importance of biodiversity.
Conclusion and Way Forward
Policy and Action Recommendations
- Expand protected areas and restore ecosystems to halt biodiversity loss.
- Engage Indigenous communities in conservation and land management practices.
- Promote sustainable farming, reduce food waste, and encourage plant-based diets to lessen food production impacts.
- Shift to renewable energy and reduce fossil fuel use to mitigate climate change.
- Redirect investments from environmentally harmful sectors to nature-friendly industries.
WWF-India’s Call for Collective Action
- WWF-India advocates for collective action to align climate, conservation, and sustainable development policies.
- The goal is to ensure a resilient and thriving future for both biodiversity and human societies.
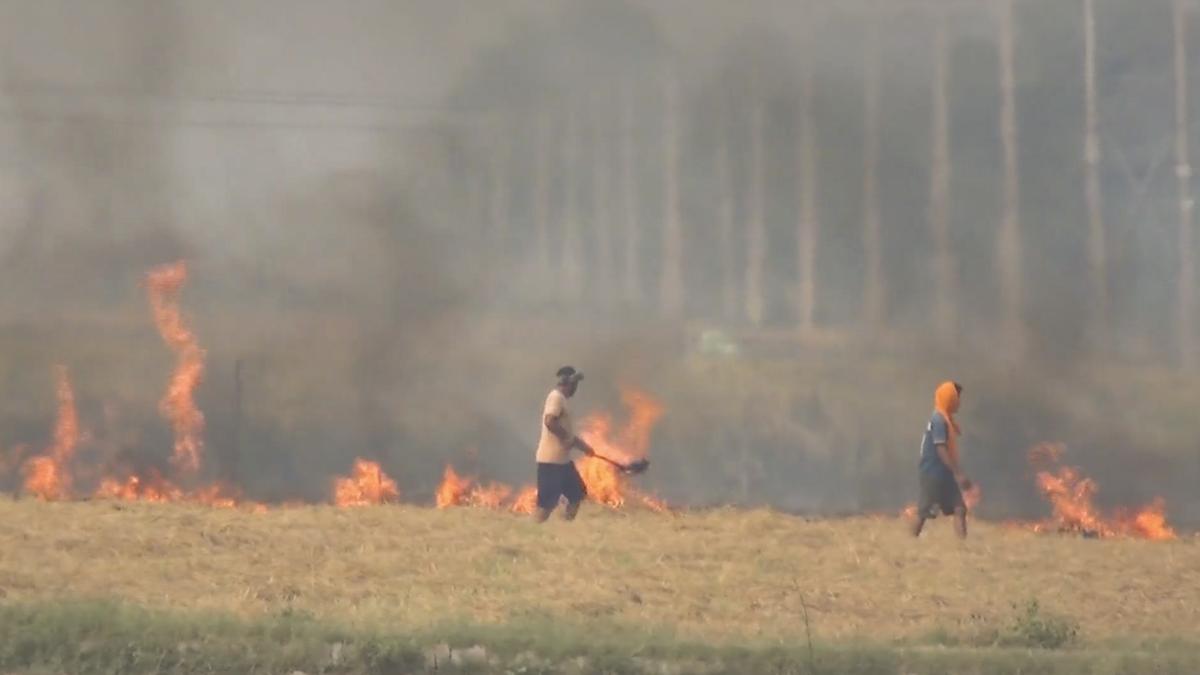
Stubble Burning and the Supreme Court's Ruling: Protecting the Right to a Pollution-Free Environment

- 24 Oct 2024
Introduction
Recently, the Supreme Court of India expressed serious concerns about the ongoing issue of stubble burning in the states of Punjab and Haryana. The Court criticized the selective enforcement of penalties for stubble burning and emphasized that such practices violate citizens' fundamental right under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, which guarantees the right to live in a pollution-free environment.
Court’s Observations on Stubble Burning
- The Supreme Court highlighted the failure of state governments in effectively implementing laws against stubble burning.
- Selective Enforcement: The Punjab and Haryana governments were accused of prosecuting only a few violators while allowing many others to escape punishment by paying a nominal fine.
- The Court observed that this approach is a blatant violation of the right to live in a pollution-free environment, which is guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
Right to a Pollution-Free Environment
- The Court emphasized that every citizen has the fundamental right to live in an environment free from pollution, as mandated by Article 21 of the Constitution.
- The Court questioned the effectiveness of current environmental regulations, specifically pointing out the lack of proper machinery to collect fines under Section 15 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Impact of Stubble Burning
Stubble burning, primarily in the northern states of India, exacerbates air pollution, especially in Delhi and surrounding regions. The seasonal spike in air pollution during the months of October and November is largely attributed to farm fires. This not only worsens the air quality but also has severe implications for public health.
Environmental and Health Consequences
- Air Pollution: The burning of crop residues significantly contributes to the rise in PM2.5 and PM10 levels, leading to hazardous air quality.
- Soil Health: Burning crop residues depletes essential nutrients from the soil, reducing organic carbon content and harming soil fertility.
Health Risks
- Exposure to pollutants like particulate matter (PM) can lead to respiratory problems, heart diseases, and other health complications for the population, especially in densely populated areas like Delhi.
Legal and Institutional Shortcomings
- Inadequate Implementation: Despite laws and penalties being in place, the lack of an effective enforcement mechanism has resulted in the persistence of stubble burning.
- Toothless Penalties: The Supreme Court criticized the amended Section 15 of the Environment Protection Act, 1986, which replaced criminal penalties with financial fines for environmental violations. However, the lack of rules and appointed adjudicating officers has rendered this provision ineffective.
- No Serious Enforcement: The failure of the Central government and state authorities to implement effective penalties has led to widespread non-compliance with environmental laws.
Government Actions and Responses
Centre’s Efforts:
- The Central Government has introduced a Central Sector Scheme to promote agricultural mechanization for in-situ management of crop residue in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Delhi.
- The government provides financial assistance of up to 50% for the purchase of machinery, such as the Happy Seeder, to manage paddy stubble without burning.
- A total of ?3,062 crore has been released from 2018 to 2023 to tackle stubble burning.
State-Level Actions:
- The Punjab government has introduced cash incentives for farmers who refrain from burning stubble. Additionally, the state is offering non-fiscal incentives, such as access to panchayat land for storing paddy straw.
- The Pusa Decomposer, developed by the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), is a bio-enzyme used to decompose crop residue. It helps in turning the stubble into manure within 20-25 days, enhancing soil health.
Challenges for Farmers:
- Many farmers still prefer burning stubble due to high costs associated with alternative methods of residue management.
- The Happy Seeder and other machinery remain expensive and are not affordable for most small-scale farmers, leading them to resort to burning as the most cost-effective option.
Court’s Directive and the Way Forward
- The Supreme Court directed the Centre and state governments to ensure better enforcement of laws related to air pollution, vehicular emissions, and industrial pollution.
- The Court also urged the Union Government to consider Punjab’s request for additional funds to tackle the stubble burning issue and to strengthen the enforcement mechanism.
- Urgency for Action: The Court’s observations suggest that the existing framework needs urgent reforms to protect citizens’ right to a pollution-free environment.
Constitutional Provisions Related to Environmental Protection
India’s Constitution provides several provisions to ensure the protection of the environment:
Article 21: Right to Life and Environment
- In the landmark case Subhash Kumar v. State of Bihar (1991), the Supreme Court held that the right to life under Article 21 includes the right to a wholesome environment.
- This view was reiterated in Virender Gaur v. State of Haryana (1994), further strengthening the legal framework for environmental protection.
Directive Principles of State Policy
- Article 48A: The State is mandated to protect and improve the environment and safeguard forests and wildlife.
- Article 39(e) and 47: These Articles place a duty on the State to promote public health and ensure environmental protection.
Fundamental Duties
- Article 51A(g) places a duty on citizens to preserve and protect the environment.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s ruling highlights the urgent need for better implementation of environmental laws and the protection of citizens’ fundamental rights under Article 21. While government schemes are in place, a more robust and consistent approach is required to address the issue of stubble burning and air pollution. Immediate reforms in the enforcement mechanisms and incentives for farmers are crucial to achieve a sustainable, pollution-free environment in India.
Biodiversity COP16

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), while historically overshadowed by climate change discussions, is now gaining increasing attention due to the growing recognition of the global biodiversity crisis. This evolving prominence highlights the need for urgent action to preserve ecosystems and halt biodiversity loss, which is intimately linked with the climate crisis.
Overview of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Origins and Objectives:
- The CBD emerged from the 1992 Rio Earth Summit, alongside the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Main Goals:
- Protect global biodiversity.
- Restore ecosystems.
- Ensure equitable distribution of the benefits derived from biological resources.
- COP16 and the Kunming-Montreal Framework:
- The 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) marks the first meeting following the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework adopted at COP15 in 2022.
- The framework sets out four key goals and 23 targets to be achieved by 2030, including:
- Protect 30% of global lands and oceans by 2030.
- Restore 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030.
The Growing Convergence Between Climate Change and Biodiversity
- Interlinkages Between Climate Change and Biodiversity:
- Mutual Impact:
- Climate change accelerates biodiversity loss by altering habitats and threatening species.
- In turn, ecosystem degradation contributes to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases (GHGs) from deforestation and soil degradation.
- Shared Drivers:
- Both crises are driven by unsustainable human activities, including over-exploitation of natural resources, deforestation, over-consumption, and pollution.
- Increasing Synergy:
- There is a growing realization of the need for integrated solutions that address both climate change and biodiversity loss simultaneously.
- Momentum for 30 x 30 Targets
- The 30 x 30 Commitment:
- The 30 x 30 targets are central to the Kunming-Montreal Framework, which includes:
- Conservation of 30% of the world's lands and oceans.
- Restoration of 30% of degraded ecosystems.
- These targets aim to ensure the preservation of biodiversity-rich areas and the restoration of degraded ecosystems globally by 2030.
- National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs):
- Countries are required to develop and submit their NBSAPs (akin to Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for climate change).
- As of now, only 32 countries have submitted their NBSAPs, with more expected during COP16.
- High Seas Treaty:
- A crucial agreement for achieving 30 x 30 targets is the High Seas Treaty (also called Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdictions (BBNJ)), which focuses on:
- Establishing protected marine areas in biodiversity-rich regions beyond national jurisdictions.
- Ensuring regulation of human activities in these areas.
Access and Benefit Sharing: The Case of Genetic Resources
- Genetic Resources and Their Exploitation:
- The oceans, along with terrestrial ecosystems, harbor a wide variety of genetic resources that can be exploited for medical, commercial, and scientific purposes.
- Advances in biotechnology and digital sequencing of genetic material have raised issues about the equitable sharing of benefits from these resources.
- Nagoya Protocol and Benefit Sharing:
- The Nagoya Protocol (2010) set out guidelines for the access and fair sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources.
- At COP16, discussions will center on how genetic sequences (used in products such as medicines, crops, etc.) can be used fairly, ensuring that indigenous communities, who may be the original custodians of these resources, benefit equitably.
Finance Mechanisms for Biodiversity Conservation
- Financial Targets:
- One of the key goals of the Kunming-Montreal Framework is to mobilize $200 billion per year by 2030 for biodiversity conservation globally.
- Developed countries are expected to contribute $20 billion annually to developing nations, increasing to $30 billion by 2030.
- Phasing Out Harmful Subsidies:
- Countries are urged to eliminate perverse incentives that harm biodiversity, such as subsidies for:
- Over-fishing.
- Deforestation.
- Fossil fuel consumption.
- The goal is to repurpose such incentives to support sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
- New Financial Mechanisms:
- COP16 discussions will also focus on creating innovative financial mechanisms, such as:
- A biodiversity fund.
- Biodiversity credits, similar to carbon credits, which would allow countries or organizations to offset their biodiversity loss by investing in conservation projects elsewhere.
Challenges and the Way Forward
- Implementation of 30 x 30 Targets:
- The main challenge lies in translating ambitious goals into actionable plans at the national and local levels. Countries must not only submit action plans but also implement and monitor them effectively.
- Increased Global Cooperation:
- Addressing biodiversity loss requires collaboration between countries, industries, and local communities to ensure that efforts are comprehensive and inclusive.
- Public Awareness and Engagement:
- It is crucial to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation and the urgent need for collective action to mitigate the combined threats of biodiversity loss and climate change.
Conclusion: The Need for Urgent Action
The discussions at COP16 signal an important shift in how the world addresses biodiversity and its links to climate change. As countries continue to recognize the interconnectedness of these two crises, the outcome of the CBD negotiations could play a pivotal role in shaping global environmental policy. However, meeting the ambitious goals set forth by the Kunming-Montreal Framework requires strong political will, adequate financing, and effective global cooperation.
