Introduction to Dr. Manmohan Singh's Economic Reforms
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Dr. Manmohan Singh, a distinguished economist, played a crucial role in shaping India’s economic trajectory. His leadership, as Finance Minister (1991–96) and Prime Minister (2004–14), is particularly noted for the economic liberalization and reform policies that transformed India’s economy.
India’s Economic Crisis of 1991
- Economic Collapse: India faced a severe balance of payments crisis, with dwindling foreign reserves and rising inflation.
- Key Challenges: Fiscal deficit, industrial stagnation, and trade imbalances worsened by the collapse of the Soviet Union.
- Urgent Measures: Dr. Singh was appointed Finance Minister during this crisis and initiated bold reforms to stabilize and grow the economy.
Key Reforms in 1991
- Devaluation of the Rupee
- Aimed at making Indian exports competitive in global markets.
- Reduced import tariffs and liberalized foreign trade.
- Industrial Policy Reforms
- Abolition of Licence Raj: Deregulated the industrial sector, promoting private enterprises.
- Reduced state control and encouraged foreign investment, leading to industrial growth.
- Banking and Financial Reforms
- Reduced the statutory liquidity ratio (SLR) and cash reserve ratio (CRR).
- Allowed for more credit flow, fostering economic expansion and banking sector efficiency.
- Global Integration
- Introduced economic liberalization policies, integrating India with the global economy and attracting foreign investments.
Economic Growth and Social Welfare Initiatives
- Poverty Reduction: Reforms helped lift millions out of poverty by fostering job creation and industrial growth.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): Launched in 2005, providing 100 days of wage employment to rural households.
- Right to Information (RTI) and Right to Education (RTE)
- Empowered citizens by ensuring transparency and access to government information.
- RTE guaranteed free and compulsory education for children aged 6-14.
- Financial Inclusion: Aadhar project introduced to facilitate welfare delivery and financial inclusion.
Legacy of Economic Liberalization and Growth
- Economic Growth: Under his leadership, India’s GDP grew at an average rate of 8%, establishing India as one of the fastest-growing economies.
- Shift to a Market-Driven Economy: Reforms dismantled socialist controls, facilitating the rise of the private sector.
- Attracting Foreign Investment: Economic liberalization and policy reforms made India an attractive destination for foreign capital.
Leadership During Political and Economic Challenges
- Reluctant Prime Minister
- In 2004, Singh became Prime Minister despite initial reluctance, emerging as a unifying figure during coalition politics.
- His tenure saw India’s rise as a global economic power, particularly from 2004–2009.
- Challenges
- Singh’s second term was marred by allegations of corruption and policy paralysis, leading to criticism of his administration.
- However, his personal integrity remained intact, and he maintained focus on governance.
- Historic India-US Nuclear Deal (2008)
- The deal marked a significant shift in India’s foreign relations and energy policies, enabling civilian nuclear trade.
Conclusion
Dr. Manmohan Singh’s economic policies are central to India's modern economic framework. His vision transformed India from a closed, socialist economy to a vibrant, globalized economy, promoting inclusive growth and institutional reforms. Despite facing challenges and criticisms, his legacy remains a testament to strategic policymaking that continues to influence India’s economic landscape.
Sustainable Groundwater Management in India’s Agriculture

- 30 Dec 2024
Introduction: Groundwater Crisis and Agriculture
- India's Agricultural Dependence on Groundwater: India is a leading producer of water-intensive crops like rice, wheat, and pulses. The country’s agricultural sector heavily depends on groundwater for irrigation, especially for paddy cultivation.
- Over-exploitation of Groundwater: Groundwater extraction for irrigation is increasingly unsustainable, threatening agricultural sustainability in the long term.
Rising Groundwater Usage and Its Implications
- Population Growth and Groundwater Use: Between 2016 and 2024, global population grew from 7.56 billion to 8.2 billion, and India’s population rose from 1.29 billion to 1.45 billion. Concurrently, groundwater used for irrigation increased from 38% in 2016-17 to 52% in 2023-24, exacerbating the water crisis.
- Over-extraction in Major Paddy-Producing States: States like Rajasthan, Punjab, and Haryana have witnessed severe over-exploitation of groundwater for irrigation.
- Rajasthan: Highest groundwater salinisation (22%) despite receiving the highest average rainfall (608 mm) among these states.
- Punjab and Haryana: Lesser groundwater salinity due to canal irrigation and micro-irrigation systems.
Impact of Excessive Fertilizer Use on Groundwater Quality
- Soil Salinity and Groundwater Contamination: Excessive use of fertilizers, particularly for paddy cultivation, increases soil salinity and contributes to groundwater contamination.
- Toxic Chemicals in Groundwater: Nitrate contamination, caused by nitrogen-based fertilizers, and uranium contamination due to phosphate fertilizers are key concerns in states like Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Health Risks: Contaminated groundwater poses health risks such as thyroid disorders, cancer, and dental fluorosis, along with reduced agricultural productivity.
Projected Impact on Future Groundwater Availability
- Unsustainable Groundwater Levels: The Central Groundwater Board (CGWB) reports that if current practices continue, over half of the districts in Punjab could face groundwater depletion. Similarly, 21-23% of districts in Haryana and Rajasthan may experience a similar crisis.
- Population Growth and Water Scarcity: With India’s population expected to reach 1.52 billion by 2036, the need for sustainable groundwater management becomes even more critical.
Government Initiatives for Groundwater Management
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (2014): Promotes sustainable practices like zero tillage, cover cropping, and micro-irrigation for efficient water and chemical use.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (2015): Aims to boost irrigation efficiency through drip and sprinkler irrigation methods.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana (2019): Targets efficient groundwater management in water-stressed states like Gujarat, Haryana, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Success of Government Initiatives: CGWB data shows that the percentage of districts with unsustainable groundwater levels dropped from 23% in 2016-17 to 19% in 2023-24.
Role of State Governments in Groundwater Management
- State-Level Initiatives: States with unsustainable groundwater levels must take proactive measures to manage water resources efficiently.
- Example - Odisha: Odisha's Integrated Irrigation Project for Climate Resilient Agriculture emphasizes irrigation efficiency and climate-smart practices, supported by World Bank funding.
- Encouraging Resource-Efficient Agriculture: States with safe groundwater levels, like Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Telangana, and Odisha, should adopt water-efficient practices to protect groundwater resources.
Conclusion: Ensuring Agricultural Sustainability and Water Security
- Need for Urgent Action: Scaling up efforts to improve irrigation practices and groundwater management is crucial to securing India’s agricultural future.
- Global Food Security: Protecting groundwater resources will not only ensure water security within India but also contribute to global food security amid climate challenges.
- Blueprint for Sustainable Agriculture: States like Odisha are providing a model for sustainable water management, which can be replicated across water-stressed regions in India.
Surge in E-Waste Generation in India
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
India has seen a significant increase in electronic waste (e-waste) generation, rising by 72.54% from 1.01 million metric tonnes (MT) in 2019-20 to 1.751 million MT in 2023-24. The sharpest rise occurred between 2019-20 and 2020-21, driven by increased electronic consumption due to the COVID-19 pandemic's work-from-home and remote learning arrangements.
Environmental and Health Concerns
E-waste contains hazardous substances like arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury. If not properly managed, these materials can severely impact human health and the environment, contaminating soil and water sources.
Government Efforts: E-Waste Management Rules, 2022
- Introduction of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): The government introduced the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, effective from April 1, 2023. These rules focus on making producers responsible for the recycling of e-waste. Producers are assigned recycling targets based on the quantity of e-waste generated or products sold and must purchase EPR certificates from authorized recyclers to meet these targets.
- Integration of Bulk Consumers: Public institutions and government offices, categorized as bulk consumers, are mandated to dispose of e-waste only through registered recyclers or refurbishers, ensuring proper treatment and recycling of the waste.
- Expansion of E-Waste Coverage: The updated rules expanded the scope to include 106 Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) items from FY 2023-24, up from 21 items previously covered under the 2016 E-Waste Rules.
Challenges in E-Waste Recycling and Disposal
- Low Recycling Rates: Although the share of e-waste recycled in India has increased from 22% in 2019-20 to 43% in 2023-24, a significant 57% of e-waste remains unprocessed annually. Informal sector practices, which dominate e-waste handling, often lack the necessary environmental safeguards, leading to improper disposal and environmental contamination.
- Lack of Infrastructure and Awareness: India faces challenges in building adequate infrastructure for e-waste collection and recycling, resulting in improper disposal in landfills. Furthermore, a lack of public awareness regarding proper disposal methods exacerbates the problem.
Global Context and India’s Position
- India ranks as the third-largest e-waste generator globally, following China and the United States. With an increasing rate of e-waste generation, the country faces an urgent need to improve recycling efficiency and adopt sustainable disposal methods.
International and National Conventions on E-Waste
- India is a signatory to several international conventions that govern hazardous waste management, including the Basel Convention, which regulates the transboundary movement of hazardous wastes, and the Minamata Convention, which focuses on mercury. At the national level, India has established the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, and other frameworks to manage and reduce e-waste effectively.
Strategic Recommendations for Effective E-Waste Management
- Harnessing the Informal Sector: India’s informal sector, which handles a significant portion of e-waste, must be integrated into the formal recycling systems. This can be achieved through training and financial support to ensure safe and environmentally responsible recycling practices.
- Technological Innovations: Encouraging research into advanced recycling technologies, such as AI and IoT-based solutions for efficient e-waste collection and tracking, will be crucial for improving the e-waste management system.
- Learning from Global Practices: Countries like the European Union (EU) and Japan have set strong examples. The EU’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive and Japan’s Home Appliance Recycling Law emphasize Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and provide models for India to adapt.
Conclusion
To address the growing e-waste challenge, India must improve its recycling infrastructure, integrate the informal sector, and adopt best practices from international models. With sustainable and effective strategies, India can mitigate the environmental and health risks posed by e-waste while promoting a circular economy.
Glass Ceiling Cracks: Women's Rising Role in the 2024 Lok Sabha Elections
- 28 Dec 2024
Introduction:
The 2024 Lok Sabha elections marked a significant step forward for women’s participation in Indian politics. With 800 women candidates contesting across 390 constituencies, this was the highest ever since the 1957 general elections. This surge in women candidates has been a positive reflection of the evolving role of women in India's democratic processes.
Increase in Women Candidates:
- A total of 800 women candidates participated in the 2024 elections, up from 726 in 2019.
- The number of constituencies with no female candidate dropped to a historic low of 152, from 171 in 2019.
- However, despite the rise in participation, only 74 women won, while 629 forfeited their deposits.
Regional Variations:
- The highest number of women candidates were from Maharashtra (111), followed by Uttar Pradesh (80) and Tamil Nadu (77).
- Some constituencies, like Baramati, Secunderabad, and Warangal, saw the highest participation of women, with eight candidates each.
Voter Turnout and Gender Dynamics:
- Women voters surpassed men in voter turnout for the second consecutive time, with 65.78% women casting their vote in 2024, compared to 65.55% of men.
- Assam’s Dhubri recorded the highest female voter turnout at 92.17%, reflecting increased female engagement in the electoral process.
Electoral Data and Gender Insights:
- In 2024, there were 47.63 crore female electors out of 97.97 crore total voters, making up 48.62% of the electorate, a slight increase from 2019.
- The number of female electors per 1,000 male voters reached 946, up from 926 in 2019, showing growing electoral inclusivity.
Challenges and Progress:
- Despite the gains in women’s representation, there remain several constituencies without any female candidates, notably in states like Uttar Pradesh (30 constituencies), Bihar (15), and Gujarat (14).
- Though women's participation has risen, the number of women who win remains disproportionately low, reflecting the challenges they face in a patriarchal political landscape.
Inclusion and Diversity:
- The 2024 elections also saw greater inclusivity, with a rise in third-gender electors, which increased by 23.5% to 48,272.
- Voter turnout among transgender voters nearly doubled, reaching 27.09% compared to 14.64% in 2019.
- Additionally, the number of persons with disabilities (PwD) electors increased to 90.28 lakh, showcasing broader electoral inclusivity.
Conclusion:
The 2024 Lok Sabha elections witnessed a remarkable increase in women’s participation, both as voters and candidates. While the journey toward full gender parity in politics continues, the trends from these elections indicate a growing shift toward more inclusive electoral processes. The data released by the Election Commission further underlines this progress, showing the increasing role of women in shaping India’s democratic future.
Free Movement Regime
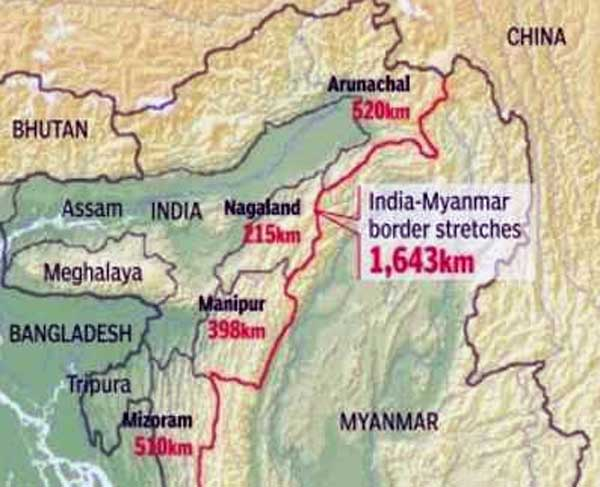
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government, through the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), has recently issued new guidelines to regulate the movement of people between India and Myanmar, especially along the border regions. These guidelines come after the suspension of the Free Movement Regime (FMR), which had previously allowed residents within a specified range of the border to move freely. The new protocol aims to enhance internal security and address concerns related to demographic shifts in India's northeastern states.
Background of the Free Movement Regime (FMR)
What is FMR?
The Free Movement Regime (FMR) is a bilateral arrangement between India and Myanmar that permits residents living in border areas to cross the international boundary without a visa. This agreement was established in 1968 to facilitate familial, cultural, and economic exchanges between people living on either side of the border.
Territorial Limits and Evolution
Initially, the FMR allowed free movement within a 40 km radius from the border. However, in 2004, this limit was reduced to 16 km, and additional regulations were introduced in 2016. The most recent development sees the limit further reduced to 10 km, with stricter regulations implemented to regulate the movement.
Recent Developments and New Guidelines
Suspension of FMR
In February 2023, Union Home Minister Amit Shah announced the suspension of the FMR along the India-Myanmar border, citing concerns about internal security and demographic changes, particularly in India's northeastern states. This decision came in the context of growing ethnic violence and political pressures, especially from states like Manipur.
Despite the announcement, the formal scrapping of the FMR is yet to be officially notified by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA). However, the MHA has issued new guidelines to regulate cross-border movement, focusing on enhancing security without completely discontinuing the regime.
Key Features of the New Guidelines
The updated protocols issued by the MHA include several measures aimed at improving the security and regulation of movement across the border:
- Reduced Movement Limit: The new guidelines reduce the free movement limit from 16 km to 10 km from the border on both sides.
- Border Pass System: Residents wishing to cross into Myanmar or return to India must obtain a "border pass" from the Assam Rifles. This pass allows a stay of up to seven days in the neighboring country.
- Document and Health Checks: Upon entry into India, individuals will undergo a document inspection by the Assam Rifles, followed by security and health checks conducted by state police and health authorities. Biometrics and photographs will be collected, and a QR code-enabled border pass will be issued for verification.
- Designated Entry Points: There will be 43 designated entry and exit points across the border, with biometric verification and health screening required at all points.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: The Assam Rifles will oversee the movement, ensuring that individuals comply with the new regulations. Violations of the movement protocol will result in legal action.
Infrastructure and Technology Implementation
The government plans to establish infrastructure, such as biometric machines and software for border pass issuance. Pilot entry and exit points will be operational soon, with a phased implementation for the remaining points.
Political Reactions and Opposition
Regional Concerns and Opposition
The suspension of the FMR has been a contentious issue in India's northeastern states. The governments of Nagaland and Mizoram have raised objections to the scrapping of the regime, citing the cultural and familial ties of border communities. The Nagaland Assembly passed a resolution opposing the government's decision, while political leaders in Manipur argued that the unregulated movement of people had contributed to ethnic violence in the region.
Specific Concerns in Manipur
The chief minister of Manipur, N. Biren Singh, attributed ongoing ethnic conflicts in the state to the unchecked movement of people across the border. This was particularly evident in the violent ethnic clashes that broke out in 2023. As a result, Singh urged the Home Ministry to cancel the FMR along the India-Myanmar border, and the new guidelines reflect the state's concerns.
Conclusion
The suspension of the Free Movement Regime along the India-Myanmar border, followed by the introduction of stricter guidelines, marks a significant shift in India's border management policy. While the formal scrapping of FMR is yet to occur, the new protocols aim to balance security concerns with the region's long-standing cultural ties. The implementation of biometric checks and designated entry points signifies the government’s focus on modernizing border control while addressing regional concerns. The outcome of this policy shift will have important implications for internal security, demographic dynamics, and bilateral relations between India and Myanmar.
Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 26, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi presided over the Veer Bal Diwas celebrations at the Bharat Mandap in New Delhi. This annual event commemorates the martyrdom of the sons of Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji and highlights the importance of nurturing the next generation. During the occasion, PM Modi also launched the ‘Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan,’ an initiative aimed at improving nutrition and well-being in rural India.
Veer Bal Diwas: Commemorating Sacrifice and Courage
Veer Bal Diwas was declared on January 9, 2022, by PM Modi to honor the sacrifices made by the young sons of Guru Gobind Singh Ji — Sahibzada Baba Zorawar Singh and Baba Fateh Singh — who were martyred in 1704. During the Mughal-Sikh battles, these two brave boys were captured and offered safety if they converted to Islam, which they refused. Their refusal to abandon their faith led to their brutal martyrdom by being bricked alive in the walls of a fort in Sirhind (Punjab). This act of resilience and unwavering faith is a cornerstone of Sikh history and culture.
Veer Bal Diwas not only commemorates their sacrifice but also serves as a reminder of the strength, faith, and courage demonstrated by all four of Guru Gobind Singh Ji’s sons. It underscores the Sikh ideals of sacrifice, courage, and dedication to faith.
Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan: Addressing Malnutrition in Rural Areas
On the same day, PM Modi launched the 'Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan', a nationwide mission focused on improving nutritional outcomes in rural areas. The initiative aims to enhance nutrition-related infrastructure and promote active community participation in tackling malnutrition. By encouraging village-level involvement, the program seeks to ensure that nutrition becomes a community-driven effort.
Key Objectives
- Malnutrition Eradication: The initiative focuses on combating malnutrition in rural communities by improving access to better nutrition.
- Healthy Competition: Encourages competition among villages to adopt best practices for nutrition and overall health.
- Sustainable Development: Promotes long-term, sustainable health practices that align with India's broader goals, such as the Poshan Abhiyan and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The program aims to make rural populations active participants in improving their own well-being, strengthening community-driven initiatives for better nutritional outcomes.
Engaging Children and Fostering Patriotism
In line with Veer Bal Diwas, various events were organized to engage young minds across the nation. These initiatives not only raised awareness about the significance of the day but also fostered a culture of courage, dedication, and patriotism.
- Online Competitions: Interactive quizzes were conducted through platforms like MyGov and MyBharat to encourage participation and understanding of Veer Bal Diwas.
- Creative Activities: Schools, Child Care Institutions, and Anganwadi centers organized storytelling, creative writing, and poster-making contests to engage children and promote nationalistic values.
Honoring Young Achievers: PMRBP Awardees
The event also saw the presence of the recipients of the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar (PMRBP), which recognizes children who have demonstrated exceptional abilities in various fields. The awardees, 17 in total, were presented with medals, certificates, and citation booklets by President Droupadi Murmu. These young achievers served as a source of inspiration, reinforcing the theme of celebrating youth potential on Veer Bal Diwas.
Conclusion: Strengthening the Foundation of India’s Future
The celebrations of Veer Bal Diwas and the launch of the Suposhit Gram Panchayat Abhiyan highlight the government’s commitment to nurturing India’s future by investing in its children and rural communities. By honoring historical sacrifices and fostering community-driven health and nutrition initiatives, these efforts contribute to building a resilient, prosperous India that can meet global challenges head-on. The twin focus on children’s development and rural well-being underscores India’s vision of a healthier, more inclusive society, aligned with national and global development goals.
India-Kuwait Ties

- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's two-day visit to Kuwait marks a significant milestone in India-Kuwait relations, being the first visit by an Indian Prime Minister in over four decades. This visit, undertaken at the invitation of Emir Sheikh Meshal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, aims to strengthen bilateral ties in key areas like trade, defense, energy, and cultural cooperation.
Strategic Partnership and Key Agreements
The visit elevated India-Kuwait relations to a 'Strategic Partnership,' with agreements covering diverse sectors. A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defense cooperation was signed, focusing on joint military exercises, coastal defense, and training. Furthermore, the two countries signed a Cultural Exchange Programme for 2025-2029 and an Executive Programme on Sports Cooperation for 2025-2028, enhancing cultural and people-to-people ties.
The establishment of a Joint Commission on Cooperation (JCC) will monitor bilateral relations, and new Joint Working Groups (JWGs) have been set up in areas like education, trade, and counter-terrorism. Both nations also agreed to deepen collaboration in emerging sectors such as semiconductors, artificial intelligence, e-governance, and technology sharing.
Economic and Energy Cooperation
India and Kuwait share strong economic ties, with bilateral trade reaching USD 10.47 billion in 2023-24. Kuwait is India’s sixth-largest crude oil supplier, meeting 3% of India's energy needs. The countries have also agreed to transition from a buyer-seller relationship in energy to a more comprehensive partnership, with focus areas including oil, gas, refining, and renewable energy. Kuwait’s membership in the International Solar Alliance (ISA) was welcomed by India, reflecting their growing collaboration in the energy sector.
Indian Diaspora and Labour Cooperation
The Indian community, numbering over 1 million, forms the largest expatriate group in Kuwait and plays a pivotal role in the country’s economy. Their contribution spans various sectors, including healthcare, engineering, retail, and business. Kuwait’s Vision 2035, which seeks to diversify its economy beyond oil, presents significant opportunities for collaboration with India, particularly in infrastructure, renewable energy, and technology.
The skilled workforce from India also aligns with Kuwait's developmental goals, offering further opportunities for labor cooperation, especially in sectors like healthcare, technology, and infrastructure.
Geopolitical and Multilateral Cooperation
India-Kuwait relations hold regional significance, particularly in West Asia. Kuwait's role in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) amplifies its geopolitical importance. India’s engagement with Kuwait helps maintain a balanced presence in the region, essential for its energy security and broader geopolitical interests. The GCC, which includes six Arab states, remains a key partner for India, contributing to significant trade and remittances. India also seeks to conclude a Free Trade Agreement with the GCC to enhance economic collaboration.
Cultural and Historical Ties
India and Kuwait’s relationship has deep historical roots, dating back to the pre-oil era when maritime trade was a cornerstone of Kuwait’s economy. Over the years, this relationship has grown, with India being a major trading partner and Kuwait contributing significantly to India's energy needs. The Indian Rupee was once the legal tender in Kuwait, underscoring the strength of their historical ties.
In conclusion, PM Modi's visit to Kuwait sets the stage for enhanced cooperation across several domains, reinforcing the strategic partnership between the two nations. It also highlights India's broader objectives in the West Asia region, balancing economic, geopolitical, and cultural interests.
Revitalization of India-China Relations: A Diplomatic Turning Point

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The 23rd meeting between India’s National Security Adviser (NSA) and China’s Foreign Minister, held as Special Representatives (SRs), marks a pivotal moment in the complex bilateral relationship between the two nations. This dialogue, which follows years of strain exacerbated by the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, signals a renewed commitment to restoring stability and fostering peace along the border.
Special Representatives Mechanism: A Foundation for Dialogue
The SR mechanism, established in the early 2000s, has long served as a key platform for addressing bilateral disputes, particularly the contentious boundary issue. Past rounds of discussions have facilitated troop disengagement and efforts to maintain peace along the Line of Actual Control (LAC). The recent meeting, following the 2023 BRICS summit discussions between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese President Xi Jinping, demonstrates a positive step towards de-escalation, with the resumption of talks providing hope for progress.
Key Outcomes of the 23rd SR Meeting
Several significant developments emerged from the meeting, focusing on cultural, economic, and strategic cooperation:
- Cultural and Economic Cooperation:
- Kailash-Mansarovar Yatra: The resumption of this religious pilgrimage represents a significant cultural exchange, fostering people-to-people ties.
- Border Trade Revival: Border trade in Sikkim has been reestablished, potentially revitalizing local economies and improving trade relations.
- Scientific and Environmental Cooperation:
- Trans-boundary River Data Sharing: China’s commitment to sharing crucial river data with India will aid in flood management, directly addressing India’s long-standing concerns over water security, particularly in light of China's upstream dam projects.
- Connectivity and Exchange Programs:
- Discussions on restarting direct flights and visa easements for students and businesses, along with enhanced journalist exchanges, signal a move toward greater normalization of relations.
- Commitment to Border Peace:
- Both sides have reiterated their intent to maintain peace along the border, a critical factor in reducing tensions. While China expressed a six-point consensus, India has cautiously framed the outcome as “positive directions,” reflecting a reserved optimism.
Challenges in India-China Relations
Despite the positive momentum, numerous challenges persist in the bilateral relationship:
- Boundary Dispute:
- The core irritant remains the unresolved border issue, with divergent perceptions of the LAC. While some disengagement has occurred, full de-escalation and demilitarization across the entire border have not yet been achieved.
- Trust Deficit:
- The 2020 Galwan clash has left a lasting scar on mutual trust. Additionally, China’s aggressive patrolling and policy shifts continue to raise concerns in India, necessitating vigilance in future negotiations.
- Economic Imbalances:
- India’s trade relationship with China remains lopsided, with a significant trade deficit. Moreover, China’s growing influence in India’s neighborhood, particularly in Pakistan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, challenges India’s strategic interests.
- Global Power Dynamics:
- India’s evolving alliances, particularly with the U.S., QUAD, and I2U2 group, alongside China’s assertive stance in Taiwan and the South China Sea, complicate bilateral relations and influence global perceptions.
The Way Forward
To navigate the challenges and harness opportunities, India must adopt a balanced approach, combining diplomatic engagement, economic resilience, and strategic vigilance:
- Confidence-Building Measures:
- Continued disengagement and de-escalation at the LAC, coupled with increased transparency in military activities, will be critical to maintaining peace.
- Broadening Cooperation:
- Exploring areas of mutual interest, such as climate change, public health, and infrastructure development, could foster deeper cooperation and help transcend contentious issues.
- Economic Realignment:
- India must address its trade deficit by pushing for greater market access for Indian products in China. Additionally, diversifying supply chains and promoting joint ventures in renewable energy and technology can reduce dependency.
- Multilateral Engagement:
- Engaging through global forums like BRICS, SCO, and G20, and strengthening regional alliances, will help mitigate tensions and counterbalance China's regional influence.
- Strategic Vigilance:
- Strengthening ties with regional allies, particularly in the Indo-Pacific, and enhancing military preparedness will safeguard India’s strategic interests in the face of China’s assertiveness.
Conclusion
The recent meeting between India and China represents a cautious but constructive step toward stabilizing their fraught relationship. By focusing on diplomacy, strengthening economic ties, and maintaining strategic vigilance, India can navigate its complex relationship with China in a rapidly shifting global context. A careful balance of engagement and vigilance will be crucial for India’s future dealings with its powerful neighbor.
India-Sri Lanka Diplomatic Engagement

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent visit of Sri Lankan President Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD) to India marked a significant moment in bilateral relations, as it was his first foreign trip since assuming office. The visit underscored key diplomatic exchanges and collaborations between the two countries, showcasing both areas of agreement and divergence.
Key Takeaways from AKD's Visit
Assurance on Anti-India Activities: One of the primary concerns for India was the use of Sri Lankan territory for activities detrimental to its security, particularly the presence of Chinese “research vessels” at Sri Lankan ports. President AKD assured Prime Minister Narendra Modi that Sri Lanka would not allow its territory to be used in ways that threaten India’s interests. This assurance is crucial, as it signals Sri Lanka's stance on maintaining regional stability, despite AKD’s perceived pro-China inclinations.
Tamil Minority Issue: Divergent Views: A notable divergence in their discussions was the issue of the Tamil minority in Sri Lanka. India has long advocated for the full implementation of the 13th Amendment to Sri Lanka’s Constitution, which would grant greater autonomy to the Tamil minority. However, AKD resisted this, reaffirming his opposition to the amendment’s full implementation. While India emphasized the importance of reconciliation and holding provincial elections, AKD focused on unity, sustainable development, and social protection, sidestepping any definitive commitments on the Tamil issue.
Sri Lanka's Assertive Diplomatic Posture: AKD’s strong parliamentary mandate has allowed him to adopt a more assertive diplomatic stance. This is evident not only in his handling of the Tamil issue but also in his approach to dealing with major powers like India and China. His administration appears to be prioritizing a more independent foreign policy, signaling a shift from previous administrations.
Bilateral Cooperation and Development Initiatives
The visit saw significant agreements on bilateral cooperation, particularly in development and connectivity. Both nations acknowledged the positive impact of India’s assistance in Sri Lanka’s socio-economic growth. Key projects discussed include:
- Indian Housing Project: Phases III and IV.
- Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects across three islands.
- High-Impact Community Development Projects.
- Digital collaborations, such as the implementation of Aadhaar and UPI systems in Sri Lanka.
Additionally, discussions focused on enhancing energy cooperation, including the supply of LNG, development of offshore wind power in the Palk Strait, and the high-capacity power grid interconnection. The resumption of passenger ferry services between key Indian and Sri Lankan ports was also a priority.
Defence and Security Cooperation
The two leaders agreed to explore a Defence Cooperation Framework and intensify collaboration on maritime surveillance, cyber security, and counter-terrorism. This aligns with India’s strategic interests in the region, as it seeks to ensure stability in the Indian Ocean and strengthen its defense ties with Sri Lanka.
Strategic Continuity Amid Leadership Change
Despite a change in leadership, the core strategic interests between India and Sri Lanka remain aligned. India views Sri Lanka’s stability as crucial to regional security, and both countries are focused on a mutually beneficial partnership. AKD’s emphasis on economic recovery and tackling corruption within Sri Lanka, as seen in his actions against political figures like Speaker Asoka Ranwala, further signals his determination to build a strong foundation for his government’s future.
Conclusion
President AKD’s visit highlighted the evolving dynamics of Sri Lanka’s foreign policy, marked by a more confident and independent approach in engaging with India. While challenges remain, especially regarding the Tamil issue, both countries have reaffirmed their commitment to deepening bilateral ties, with a focus on development, connectivity, and strategic cooperation.
Bank Credit to Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs)

- 21 Dec 2024
Introduction
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) is a flagship program by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) that aims to reduce poverty by empowering women, especially through Self-Help Groups (SHGs). These SHGs have been instrumental in improving financial inclusion, providing access to credit, and enhancing the economic and social status of women across India. The program has made significant strides in mobilizing women, improving their access to financial services, and facilitating entrepreneurial ventures in rural areas.
Key Features and Initiatives of DAY-NRLM
- Self-Help Groups (SHGs):
- Formation: DAY-NRLM supports the creation and strengthening of SHGs, primarily focusing on rural women from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Mobilization: As of 2024, over 10.05 crore women have been mobilized into 90.87 lakh SHGs across India.
- Objective: The main goal is to reduce poverty through empowerment by providing access to financial services and sustainable livelihoods.
- Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP):
- Support for Rural Enterprises: SVEP, a sub-scheme under DAY-NRLM, encourages SHG women and their families to set up small-scale businesses.
- Impact: As of October 2024, 3.13 lakh rural enterprises have been supported under this initiative.
- State-wise Distribution: The program has supported enterprises across various states, with notable contributions from Andhra Pradesh (27,651 enterprises), Kerala (34,569), and Uttar Pradesh (28,904).
- Banking Correspondent Sakhis:
- Role: Women in SHGs are trained as Banking Correspondent Sakhis to enhance access to banking services such as deposits, credit, remittances, pensions, and insurance in rural areas.
- Current Deployment: 1,35,127 Sakhis have been deployed under DAY-NRLM, empowering women to be financial intermediaries in their communities.
- Financial Support for SHGs:
- Revolving Fund: SHGs receive funds ranging from Rs. 20,000 to Rs. 30,000 to boost their operations and financial stability.
- Community Investment Fund: SHGs can avail of up to Rs. 2.50 lakh under the Community Investment Fund to strengthen their financial position.
- Interest Subvention: To make bank loans more affordable, DAY-NRLM provides interest subvention to SHGs, reducing their overall credit costs.
- Online Marketing Platform:
- www.esaras.in: This online platform allows SHGs to market their products, improving their access to broader markets and enhancing their income-generating potential.
Impact of DAY-NRLM and SHGs
- Financial Inclusion: SHGs play a vital role in financial inclusion by providing access to banking services, loans, and insurance to women, especially in rural and remote areas.
- Credit Mobilization: As of November 2024, SHGs have leveraged Rs. 9.71 lakh crore in bank credit, thanks to the capitalization support provided by DAY-NRLM, including Revolving Funds and Community Investment Funds.
- Empowerment of Women: SHGs have significantly contributed to the empowerment of women, providing them with financial independence, social support, and the ability to make decisions in their households and communities.
Challenges Faced by SHGs
- Beneficiary Identification: Ensuring that the most marginalized individuals are included in SHGs can be challenging.
- Training Gaps: There is a lack of quality training programs and expert trainers to build the capacity of SHG members.
- Financial Literacy: Many SHG members have limited knowledge of formal financial services, hindering effective financial management.
- Market Linkages: Poor integration with markets limits the growth potential of SHGs, especially in terms of product sales and business expansion.
- Community Support: Insufficient business environment support and value chain linkages pose challenges to SHG sustainability and growth.
Government Initiatives Supporting SHGs
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP): Launched by NABARD in 1992, this initiative aims to link SHGs with formal banking institutions, facilitating financial inclusion.
- Mission for Financial Inclusion (MFI): A broader initiative to ensure that rural populations have access to affordable financial services such as savings, credit, insurance, and pensions.
- Lakhpati Didi Initiative: Launched in 2023, this initiative empowers SHG women to adopt sustainable livelihood practices and aim for an annual household income exceeding Rs. 1 lakh.
Role of SHGs in Rural Development
- Women Empowerment: SHGs have emerged as a powerful tool for empowering women through financial independence, social security, and the ability to make informed decisions.
- Economic Growth: SHGs foster small-scale entrepreneurship, thereby creating local businesses that contribute to rural economic growth.
- Social Cohesion: By promoting collective action, SHGs provide a social support system that helps in addressing common issues faced by their members, such as health, education, and safety.
Future Prospects and Way Forward
- Technological Integration: SHGs should leverage advanced digital platforms for transaction management, record-keeping, and communication, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
- Reducing Informal Borrowing: Linking SHGs with formal financial institutions will reduce reliance on informal lenders, promoting financial inclusion.
- Inclusive Approach: SHGs should adopt an inclusive model to ensure that members from diverse socio-economic backgrounds are fairly represented and benefit equally.
- Training and Capacity Building: There is a need for more Community Resource Persons (CRPs) who can guide SHGs in beneficiary identification, financial management, and scaling their activities.
Supreme Court Directs Policy for Sacred Groves Protection

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court of India issued a significant judgment directing the Union Government to formulate a comprehensive policy for the protection and management of sacred groves across the country. These natural spaces, traditionally safeguarded by local communities, play a crucial role in preserving both ecological diversity and cultural heritage.
What are Sacred Groves?
Sacred Groves are patches of virgin forests that are protected by local communities due to their religious and cultural significance. They represent remnants of what were once dominant ecosystems and serve as key habitats for flora and fauna. Typically, sacred groves are not just ecological reserves, but also form an integral part of local traditions, often protected due to spiritual beliefs.
Key Features of Sacred Groves:
- Ecological Value: Sacred groves contribute significantly to biodiversity conservation.
- Cultural Significance: These groves are revered in various religious practices and are central to local traditions.
- Geographical Presence: Sacred groves are found in regions like Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and parts of Rajasthan.
Supreme Court's Directive
The court's judgment was based on a plea highlighting the decline of sacred groves in Rajasthan, particularly those being lost due to deforestation and illegal land-use changes. While the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 empowers state governments to declare community lands as reserves, the court recognized the need for a unified national policy to protect sacred groves as cultural reserves.
Recommendations:
- Nationwide Survey: The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) was instructed to conduct a nationwide survey to map and assess sacred groves, identifying their size and extent.
- Legal Protection: Sacred groves should be recognized as community reserves and protected under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- State-Specific Measures: The Rajasthan government was specifically directed to carry out detailed mapping (both on-ground and satellite) of sacred groves within the state, ensuring that the groves are recognized for their ecological and cultural significance.
The Role of Sacred Groves in Conservation
Sacred groves play a pivotal role in the conservation of biodiversity. They serve as refuges for various plant and animal species, and the traditional practices associated with these groves, such as tree worship, discourage destructive activities like logging and hunting.
Ecological and Cultural Importance:
- Sacred groves often act as critical biodiversity hotspots, preserving rare and indigenous species.
- They help maintain clean water ecosystems and act as carbon sinks, contributing to climate mitigation.
- Practices of non-interference with these areas have allowed flora and fauna to thrive over centuries.
Cultural Significance Across India
The importance of sacred groves is deeply embedded in India's diverse cultural heritage. They are considered the abode of deities, and various regions have unique names and rituals associated with these groves.
Examples of Sacred Groves in India:
- Himachal Pradesh: Devban
- Karnataka: Devarakadu
- Kerala: Kavu
- Rajasthan: Oran
- Maharashtra: Devrai
Piplantri Village Model
A key example highlighted in the judgment was the Piplantri village in Rajasthan, where the community undertook a remarkable transformation of barren land into flourishing groves. The initiative, driven by local leadership, involves planting 111 trees for every girl child born, which has led to several environmental and social benefits.
Impact of Piplantri's Community Efforts:
- Over 40 lakh trees have been planted, which has recharged the water table by 800-900 feet and lowered the local climate by 3-4°C.
- The initiative has contributed to the reduction of female foeticide and empowered women's self-help groups.
- The village now enjoys economic growth, better education opportunities, and increased local income.
Legal and Statutory Framework
Sacred groves are already recognized under existing Indian laws, notably the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, which allows states to declare sacred groves as community reserves. Additionally, the National Forest Policy of 1988 encourages the involvement of local communities in the conservation of forest areas, a principle supported by the Godavarman Case of 1996.
Key Legal Provisions:
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Empowers state governments to declare sacred groves as community reserves.
- National Forest Policy, 1988: Encourages community involvement in the conservation and protection of forests, including sacred groves.
- Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006: Suggests empowering traditional communities as custodians of sacred groves.
Looking Ahead: The Need for Action
The Supreme Court has scheduled further hearings to assess the progress of the survey and mapping efforts by Rajasthan. The court also stressed the importance of empowering traditional communities to continue their role as custodians of sacred groves, ensuring their sustainable protection for future generations.
By recognizing the ecological and cultural significance of sacred groves and encouraging community-driven conservation efforts, the Supreme Court’s ruling sets a precedent for more inclusive environmental policies in India. This could also inspire similar initiatives in other parts of the world, promoting the protection of sacred natural spaces for their critical role in maintaining biodiversity and fostering sustainable communities.
The Costly Push for 100% Electrification of Indian Railways

- 19 Dec 2024
Introduction
RITES Ltd., the consultancy arm of the Indian Railways, has secured two contracts to repurpose six broad gauge diesel-electric locomotives for export to African railways. These locomotives, originally designed for India’s broad gauge of 1,676 mm, will be modified for use on railways with the narrower Cape Gauge of 1,067 mm. While this is a commendable re-engineering effort, it also highlights a larger issue within Indian Railways: the unnecessary redundancy of functional diesel locomotives, leading to significant wastage of resources.
The Growing Problem of Idle Diesel Locomotives
As of March 2023, there were 585 diesel locomotives idling across the Indian Railways network due to electrification. This number has now reportedly grown to 760 locomotives, many of which still have more than 15 years of serviceable life. The root cause of this redundancy lies in the government’s mission to electrify the entire broad gauge network at an accelerated pace. This electrification push has resulted in the premature retirement of locomotives that could still serve the network for years, raising questions about the economic and environmental logic behind this decision.
The Justification for Electrification: Foreign Exchange and Environmental Concerns
The Indian government’s electrification drive is often justified on two primary grounds: saving foreign exchange by reducing the import of crude oil and reducing environmental pollution. Additionally, electrification is framed as a step toward a “green railway” powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind. However, the reality of these claims is more complicated.
Foreign Exchange Savings: A Small Impact on National Diesel Consumption
While electrification may reduce India’s diesel consumption, the impact on national fuel use is minimal. Railways account for just 2% of the country’s total diesel consumption. A report by AC Nielsen in 2014 indicated that the transport sector consumed 70% of the total diesel, with railways accounting for only 3.24%. Even with 100% electrification, the savings in foreign exchange would have little impact on the country’s overall diesel consumption, leaving other sectors like trucking and agriculture as the main contributors.
Environmental Concerns: Shifting Pollution, Not Reducing It
The environmental argument for electrification is also flawed. Electricity in India is still largely generated from coal-fired power plants, with nearly 50% of the country’s electricity coming from coal. Since the Indian Railways is heavily involved in transporting coal, switching from diesel to electric locomotives simply shifts pollution from the tracks to the power plants. This means that the transition to electric traction will not result in a cleaner environment unless the country significantly reduces its reliance on coal. Without a substantial increase in renewable energy generation, the push for a “green railway” remains unrealistic.
The Dilemma of Retaining Diesel Locomotives for Strategic Purposes
Despite the goal of 100% electrification, a significant number of diesel locomotives will remain in service. Reports indicate that 2,500 locomotives will be kept for “disaster management” and “strategic purposes,” although it is unclear why such a large fleet is necessary for these purposes. Additionally, about 1,000 locomotives will continue to operate for several more years to meet traffic commitments. This suggests that even with a fully electrified network, Indian Railways will continue to rely on thousands of diesel locomotives, many of which have substantial residual service life left.
Financial Sustainability and Coal Dependency
The financial sustainability of this transition remains a concern. Currently, the Indian Railways generates a significant portion of its freight revenue from transporting coal—40% of its total freight earnings in 2023-24. If the railways become fully electrified, it will need to find alternative revenue sources, as coal is a primary contributor. Until non-coal freight options can replace this income, the financial health of the railways may be at risk.
Conclusion: Wasted Resources and Unmet Goals
The mission to electrify the Indian Railways, while ambitious, is an example of how vanity projects can lead to colossal waste. Thousands of diesel locomotives are being discarded prematurely, despite their potential to continue serving the network. The environmental and financial justifications for 100% electrification, while appealing in theory, fail to account for the complexities of India’s energy landscape. As a result, the drive to create a “green railway” is likely to fall short, leaving behind a legacy of wasted taxpayer money and unfinished goals.
Arctic Tundra: From Carbon Sink to Carbon Source

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The Arctic tundra, a frozen, treeless biome, has historically been a vital carbon sink, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO?) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs). However, recent findings suggest that, for the first time in millennia, this ecosystem is emitting more carbon than it absorbs, a change that could have significant global consequences. This alarming shift was highlighted in the 2024 Arctic Report Card published by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The Arctic Tundra’s Role as a Carbon Sink
The Arctic tundra plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. In typical ecosystems, plants absorb CO? through photosynthesis, and when they die, carbon is either consumed by decomposers or released back into the atmosphere. In contrast, the tundra’s cold environment significantly slows the decomposition process, trapping organic carbon in permafrost—the permanently frozen ground that underpins much of the region.
Over thousands of years, this accumulation of organic matter has resulted in the Arctic storing an estimated 1.6 trillion metric tonnes of carbon. This figure is roughly double the amount of carbon in the entire atmosphere. As such, the tundra has served as a critical carbon sink, helping to mitigate global warming by trapping vast quantities of CO?.
Shifting Dynamics: Emission of Greenhouse Gases
Recent reports indicate a dramatic shift in the Arctic tundra’s role in the carbon cycle. Rising temperatures and increasing wildfire activity have disrupted the tundra’s balance, leading it to transition from a carbon sink to a carbon source.
Impact of Rising Temperatures
The Arctic region is warming at a rate approximately four times faster than the global average. In 2024, Arctic surface air temperatures were recorded as the second-warmest on record since 1900. This rapid warming is causing permafrost to thaw, which in turn activates microbes that break down trapped organic material. As this decomposition accelerates, carbon in the form of CO? and methane (CH?)—a more potent greenhouse gas—are released into the atmosphere.
The experts, explained the process by comparing thawing permafrost to meat left out of the freezer. Similarly, thawing permafrost accelerates the breakdown of trapped carbon.
The Role of Wildfires
In addition to warming temperatures, the Arctic has experienced a surge in wildfires in recent years. 2024 marked the second-highest wildfire season on record in the region, releasing significant amounts of GHGs into the atmosphere. Wildfires exacerbate the thawing of permafrost, creating a feedback loop where increased carbon emissions contribute further to warming, which, in turn, leads to more emissions.
Between 2001 and 2020, these combined factors caused the Arctic tundra to release more carbon than it absorbed, likely for the first time in millennia.
The Global Consequences of Emission
The transition of the Arctic tundra from a carbon sink to a carbon source is alarming, as it represents a significant amplification of global climate change. The release of additional CO? and CH? into the atmosphere further accelerates the greenhouse effect, leading to higher global temperatures. This warming is already having visible consequences around the world, from extreme weather events to rising sea levels.
If the Arctic tundra continues to emit more carbon than it absorbs, it could significantly exacerbate the climate crisis. The report underscores the urgency of addressing global emissions, as reducing greenhouse gases remains the most effective way to prevent further destabilization of this sensitive ecosystem.
Mitigating the Impact: The Path Forward
Despite the alarming trends, the Arctic Report Card suggests that it is still possible to reverse this process. By reducing global GHG emissions, it may be possible to slow the thawing of permafrost and allow the Arctic tundra to regain its role as a carbon sink. Scientists emphasize that mitigating climate change on a global scale is essential to prevent further emissions from the Arctic ecosystem.
Scientists, stressed the importance of emission reductions, stating, “With lower levels of climate change, you get lower levels of emissions from permafrost… That should motivate us all to work towards more aggressive emissions reductions.”
However, current trends suggest that achieving this goal may be challenging. A recent report from the Global Carbon Project indicates that fossil fuel emissions are likely to rise in 2024, with total CO? emissions projected to reach 41.6 billion tonnes, up from 40.6 billion tonnes in 2023.
Commitment to Eradicating Naxalism in Chhattisgarh by 2026

- 17 Dec 2024
Overview
Union Home Minister Amit Shah has reiterated India's commitment to eliminate Naxalism in Chhattisgarh by March 31, 2026. He emphasized the progress made in the fight against Naxalism, highlighting key successes and outlining the strategy for the coming years.
Key Pointers
- Government Commitment: Amit Shah emphasized the joint commitment of the Government of India and the Chhattisgarh state leadership to rid the state of Naxalism by 2026.
- Security Forces’ Success: Over the past year, Chhattisgarh police neutralized 287 Naxalites, arrested around 1,000, and saw 837 surrenders.
- Top Naxal Cadres Neutralized: The state forces successfully neutralized 14 high-ranking Naxal cadres.
- President’s Police Colour Award: Chhattisgarh Police received the President's insignia within 25 years, a significant achievement for the state.
The Three-Pronged Strategy for Eliminating Maoist Insurgency
- Security Measures (Force)
Deployment of Security Forces
- Enhanced Presence: Increased deployment of Central and State police forces in Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) areas.
- Joint Operations: Coordinated operations between state and central forces, including CRPF and COBRA units.
- Upgraded Technology: Incorporation of UAVs, solar lights, and mobile towers to enhance operational efficiency.
Operation SAMADHAN
- Key Elements:
- Smart Leadership: Leading with innovative strategies.
- Aggressive Strategy: Swift, decisive action against insurgents.
- Motivation and Training: Strengthening the capabilities of forces.
- Actionable Intelligence: Real-time intelligence for effective operations.
- Harnessing Technology: Using modern tech for strategic advantage.
2. Development Initiatives
Focused Development Schemes
- PMGSY: Rural road connectivity under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana.
- Aspirational Districts Program: Improving infrastructure in Naxal-affected areas.
- Skill Development: Targeted schemes in 47 LWE-affected districts to reduce unemployment.
Infrastructure Development
- Special Infrastructure Schemes: Building schools, roads, and bridges in remote areas to integrate them into the mainstream economy.
- Rehabilitation: Focus on providing rehabilitation for former Naxals through education and vocational training.
3. Empowerment (Winning Hearts and Minds)
Public Engagement
- Tribal Empowerment: Strengthening communication with tribal communities to reduce alienation and mistrust.
- Rehabilitation Policies: Surrender schemes offering incentives like education and financial aid to reintegrate former insurgents into society.
Maoism: Ideology and Background
What is Maoism?
- Origin: A form of communism developed by Mao Tse Tung, focusing on armed insurgency to capture state power.
- Core Beliefs: Maoists believe in violence and insurrection as legitimate means to overthrow the state and establish a People’s Democratic Republic.
- Indian Maoism: The Communist Party of India (Maoist), formed in 2004, leads the largest Maoist insurgency in India.
Recent Achievements in Combatting Maoist Insurgency
Key Successes in 2023
- Maoist-Free Villages: Villages in Dantewada declared "Maoist-free," a significant victory for the state.
- Reduction in Security Forces’ Casualties: 14 deaths in 2024, a dramatic decrease from 198 deaths in 2007.
- Infrastructure and Logistical Support: Enhanced use of helicopters and fortified police stations.
Government’s Commitment to Rebuilding
- Rehabilitation and Welfare: The government is implementing policies to improve the living standards of affected families, including 15,000 houses for Naxal-affected regions.
- Economic Development: Focus on building infrastructure and providing employment through skills training programs.
Challenges in Eliminating Naxalism
Socio-Economic Issues
- Exploitation of Tribals: Marginalization of tribals due to displacement for mining and forestry.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Basic amenities like roads, schools, and healthcare are absent in many areas.
- Centralized Naxal Command: The CPI (Maoist) retains a strong leadership, despite fragmentation of its forces.
Governance and Trust Issues
- Alienation of Local Populations: Ineffective governance and poor implementation of welfare schemes fuel local support for Naxal groups.
- Resource Conflict: The Naxals exploit rich mineral resources in the region to fund their insurgency.
Way Forward
Governance and Economic Reforms
- Tribal Empowerment: Form Tribal Advisory Councils as per the Fifth Schedule for better resource management.
- Land Redistribution: Enforce the Land Ceiling Act to reduce inequality.
- Livelihood Programs: Offer alternative livelihoods to reduce dependency on illegal activities.
Security Measures
- Paramilitary Deployment: Specialized forces to secure tribal areas and enable local governance.
- Resource Management: Ensure sustainable exploitation of natural resources, involving tribal communities in the decision-making process.
Peace Dialogues
- Inclusive Policies: Engage in dialogue with Naxals to facilitate their reintegration into mainstream society.
Conclusion
Naxalism in India, particularly in Chhattisgarh, is a complex issue rooted in socio-economic inequalities, lack of development, and historical alienation of tribal communities. The government's approach, encapsulated in the SAMADHAN strategy, combines security operations with developmental initiatives and a focus on empowerment to tackle the problem. With a clear commitment to eliminate Naxalism by 2026, the Indian government is making significant strides in reducing violence, improving governance, and integrating affected communities into the mainstream.
How would a carbon market function?

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
COP29, the ongoing climate conference in Azerbaijan’s capital Baku, has given a fillip to the idea of using carbon markets to curb carbon emissions by approving standards that can help in the setting up of an international carbon market as soon as the coming year.
Introduction to Carbon Markets
- Carbon markets allow the buying and selling of the right to emit carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
- Governments issue certificates known as carbon credits, each representing the right to emit 1,000 kilograms of CO2.
- The total number of credits issued is capped to control carbon emissions. Companies and individuals who don’t have credits cannot emit CO2.
Trading of Carbon Credits
- Carbon Credit Trading: Companies holding more carbon credits than needed can sell them to others who need more, with the price determined by market forces.
- Carbon Offsets: Businesses can also purchase carbon offsets, often provided by environmental NGOs, which promise to reduce emissions (e.g., by planting trees). These offsets counterbalance the firm’s carbon emissions.
- The trading of both credits and offsets is designed to create financial incentives for companies to reduce their carbon footprint.
Advantages of Carbon Markets
- Addressing Externalities: Carbon emissions are a classic example of an economic externality, where the costs of pollution are not reflected in market prices.
- Market Efficiency: By allowing firms to buy and sell carbon credits, the system internalizes the cost of carbon emissions, encouraging businesses to reduce emissions to avoid higher costs.
- Incentive for Emission Reduction: Carbon markets aim to create a financial reason for companies to lower their emissions, thus helping mitigate climate change.
Voluntary vs. Government-Mandated Carbon Markets
- Voluntary Carbon Reporting: Many corporations prefer voluntary systems like the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) for reporting their emissions, fearing government-imposed restrictions.
- Market Flexibility: Corporations like ExxonMobil and General Motors argue that carbon markets with freely traded credits allocate carbon allowances more efficiently than government-imposed limits. This allows firms to purchase credits from others, optimizing resource allocation without restricting output.
- Corporate Resistance to Government Intervention: Firms are often reluctant to accept strict government budgets for carbon emissions, fearing increased operational costs and production limitations due to diverse supply chains.
Issues and Criticisms of Carbon Markets
- Government Manipulation of Credit Supply: Governments may increase the number of carbon credits issued, leading to lower prices and reduced incentives for emission reductions.
- Lack of Accountability in Carbon Offsets: Critics argue that some companies buy carbon offsets as a form of virtue signalling, without genuine concern for their environmental impact. This undermines the effectiveness of the offsets.
- Government Mismanagement: Political decision-making may lead to the over-restriction of carbon credits, potentially slowing economic growth by limiting available emissions allowances. The ability of governments to accurately determine the optimal supply of carbon credits is a contentious issue.
The Concept of Carbon Credits and Their History
- Introduction of Carbon Credits: Carbon credits were first introduced in the 1990s in the U.S., specifically through a cap-and-trade model designed to control sulfur dioxide emissions. This approach later expanded to include carbon emissions.
- Role of Carbon Markets: In essence, these markets aim to create a financial mechanism where firms can trade the right to pollute, ensuring a balance between economic growth and environmental protection.
Criticism of Carbon Offsets
- Effectiveness of Offsets: Experts are critical of carbon offsets, arguing that they do not always lead to meaningful reductions in emissions. For example, some companies may purchase offsets without ensuring that the projects are genuinely offsetting their emissions.
- Moral Hazard: Critics suggest that offset programs may lead to firms simply paying for the right to pollute, rather than actually reducing emissions in their operations.
Conclusion
- Carbon Markets as a Tool for Emission Reduction: Despite the criticisms, carbon markets remain a promising tool for mitigating climate change, provided they are carefully regulated and implemented.
- The Future of Carbon Trading: As discussions at COP29 evolve, the development of international standards for carbon trading could potentially enhance the effectiveness of these markets, offering a viable path to global emission reductions.
Agrarian Crisis in India

- 15 Dec 2024
Introduction
- Supreme Court Committee Report: A high-level committee, appointed by the Supreme Court in September 2024, submitted its interim report on November 21, 2024, highlighting the severe distress in India's agricultural sector.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Income crisis faced by farmers
- Rising debt burden
- Farmer suicides
- Stagnation in agricultural growth
- Impact of climate change
Key Findings of the Supreme Court Committee Report
Income Crisis in Indian Agriculture
- Daily Earnings: Farmers earn an average of just Rs 27 per day from agricultural activities, a meager income that makes it impossible to sustain a decent standard of living.
- Average Household Income: Agricultural households have an average monthly income of Rs 10,218, far below the basic threshold for a decent life.
Escalating Debt Burden
- Institutional Debt: In 2022-23, Punjab's institutional debt was Rs 73,673 crore, and Haryana's was Rs 76,630 crore.
- Non-Institutional Debt: This burden is further exacerbated by non-institutional debt, contributing 21.3% of total debt in Punjab and 32% in Haryana.
Farmer Suicides
- High Suicide Rates: Over 400,000 farmers and agricultural workers have committed suicide since 1995, primarily due to escalating debt and financial despair.
- Survey Findings: In Punjab, a survey found 16,606 suicides among farmers and farm workers between 2000 and 2015.
Stagnation in Agricultural Growth
- Growth Rates: Between 2014-15 to 2022-23, Punjab's agricultural growth was a mere 2% per year, and Haryana’s was 3.38%, far below the national average.
Disproportionate Employment
- Workforce Participation: 46% of India’s workforce is employed in agriculture, but it contributes only 15% to national income. Many farmers face disguised unemployment and underemployment.
Impact of Climate Change
- Environmental Degradation: Climate change, water depletion, erratic rainfall, and soil degradation are further destabilizing the agricultural sector and threatening food security.
Challenges Faced by the Agricultural Sector
1. Limited Access to Credit and Finance
- Small Farmers: 86% of Indian farmers are small and marginal, struggling to access institutional credit, which limits their ability to invest in modern agricultural inputs.
2. Fragmented Landholdings
- Small Landholdings: The average landholding is 1.08 hectares, insufficient for large-scale, efficient farming, limiting the adoption of modern agricultural techniques.
3. Outdated Farming Practices
- Traditional Methods: Many farmers continue using traditional, inefficient farming practices due to limited access to modern technology.
4. Water Scarcity and Irrigation Issues
- Dependence on Monsoons: 60% of cropped area is rainfed, and only 52% of gross sown area is irrigated, exacerbating vulnerability to droughts and erratic rainfall.
5. Soil Degradation and Erosion
- Degraded Land: 30% of India's agricultural land is affected by soil degradation, leading to lower productivity and reduced resilience to pests.
6. Inadequate Agricultural Infrastructure
- Post-Harvest Losses: Insufficient storage, cold chain, and rural infrastructure result in 15-20% post-harvest losses, further reducing farmers' income.
Government Schemes for Farmers' Welfare
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana: Direct income support for farmers.
- PM Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Crop insurance scheme.
- PM Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY): Irrigation schemes to enhance water availability.
- e-NAM: National electronic market for better price realization.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund: Financial support for infrastructure development.
- Promotion of Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): Empowering farmers through collective marketing and production.
Recommendations for Addressing the Crisis
1. Loan Waivers and Debt Relief
- Debt Alleviation: Immediate measures to reduce the crushing debt burden through loan waivers, a key factor behind farmer suicides.
2. Legal Recognition of Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- MSP Protection: Granting legal backing to MSP to ensure farmers receive a fair price for their produce, reducing price volatility and income insecurity.
3. Promotion of Sustainable Farming
- Organic Farming: Encouraging organic farming and crop diversification to improve soil health and reduce dependency on a few staple crops.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Adopting water-efficient practices, drought-resistant crops, and sustainable farming techniques.
4. Agricultural Marketing Reforms
- Market Efficiency: Improving the agricultural marketing system by establishing farmer-friendly markets and reducing intermediaries to ensure better price realization.
5. Rural Employment Generation
- Diversification: Creating non-agricultural employment opportunities in rural areas through skill development and promoting agro-based industries.
6. Climate Adaptation Measures
- Water Management: Enhancing water management systems and promoting rainwater harvesting.
- Resilience to Climate Change: Investing in climate-resilient infrastructure and farming technologies.
Implications of the Findings
Economic Impact
- Agricultural Decline: Continued neglect of the agricultural sector poses a risk to India's economy, potentially leading to long-term economic instability and increased rural-urban migration.
Food Security
- Threat to National Food Security: Declining agricultural productivity, exacerbated by climate change and inadequate reforms, threatens the country’s ability to meet food demands.
Social Stability
- Farmer Suicides and Unrest: The ongoing crisis, marked by widespread suicides and growing despair, risks social instability and unrest, particularly in rural regions.
Conclusion: Urgent Need for Reform
The committee’s report underscores the critical need for comprehensive reforms in India’s agricultural sector to alleviate the crisis. Immediate action is required to address the debt burden, improve incomes, and ensure sustainable agricultural practices. Legal reforms like MSP recognition and debt relief, along with investments in infrastructure and climate resilience, are key to securing a stable future for Indian agriculture.
Artificial Solar Eclipse: Why Are Satellites Trying to Block the Sun?
- 14 Dec 2024
Introduction
The European Space Agency (ESA) has launched Proba-3, a mission that will create an artificial solar eclipse to study the Sun's atmosphere, known as the corona. This mission aims to demonstrate new technology and address unresolved questions about the Sun's outer layers.
What is an Artificial Solar Eclipse?
- Definition: An artificial solar eclipse mimics the natural phenomenon where the moon blocks sunlight, allowing detailed observation of the Sun’s corona.
- Created By: The eclipse is created by two satellites, which align to block the Sun's light and generate a controlled shadow for scientific study.
- Purpose: The goal is to study the Sun’s corona, particularly to understand why it is significantly hotter than the Sun’s surface.
How Does the Proba-3 Create an Eclipse?
Launch and Spacecraft
Proba-3 was launched on December 5 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India. The mission uses two satellites:
- Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC): This spacecraft guides the other satellite.
- Occulter Spacecraft (OSC): This satellite has a disk that creates a controlled shadow onto the CSC.
Formation Flying
Using Precise Formation Flying (PFF) technology, the two spacecraft maintain a precise distance of 150 meters (492 feet) apart, aligning perfectly with the Sun. This alignment mimics the effect of a solar eclipse.
Precision Requirements
The eclipse will need to maintain millimetre-level accuracy for up to six hours per orbit to provide scientists with stable observational conditions.
Mission Goals
- Demonstrating PFF Technology: One of the primary objectives of the Proba-3 mission is to demonstrate PFF technology. This involves using GPS and inter-satellite radio links for positioning, as well as maintaining a precise distance between the two spacecraft.
- Studying the Sun’s Corona: Another goal is to understand why the corona is hotter than the Sun's surface. The onboard instruments, including a coronagraph, will help with this research. The coronagraph will block out the Sun’s bright light, enabling clearer observations of the corona.
- ASPICCS Coronagraph: The Proba-3 coronagraph, named the Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun (ASPICCS), is designed to observe the corona in high detail, mimicking the observational conditions of a total solar eclipse.
Why Is This Such a Big Deal?
- Revealing the Sun’s Corona: The Sun’s corona is typically invisible because it is much less bright than the Sun’s surface. It can only be seen during a solar eclipse when the Moon blocks the Sun's light.
- Predicting Space Weather: Studying the corona helps scientists predict space weather and geomagnetic storms, which can disrupt satellites and other systems on Earth.
- Extended Observations: Unlike natural solar eclipses, which last only a few minutes, Proba-3 can provide six hours of observation time in each orbit (approximately 19 hours and 36 minutes), allowing for continuous study of the corona.
What is Precise Formation Flying (PFF) Technology?
- Definition: PFF technology allows satellites to maintain exact positions and orientations relative to each other in orbit.
- Mechanism: The technology uses GPS, inter-satellite radio links, and automated control systems to ensure alignment.
- Implementation in Proba-3: In the Proba-3 mission, the Coronagraph and Occulter spacecraft stay 150 meters apart, using PFF to maintain millimetre-level precision, which is crucial for simulating a solar eclipse.
- Benefits: PFF enhances mission accuracy and provides a platform for advanced observational techniques that will enable more detailed studies of the Sun's corona.
Conclusion
Proba-3 is a groundbreaking mission that will offer unprecedented insights into the Sun’s corona by simulating solar eclipses using advanced satellite technology. By studying the Sun’s outer layers, scientists aim to improve our understanding of space weather and the mysterious temperature anomaly of the corona.
India-Bhutan Relations

- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The December 2023 visit of Bhutan’s King and Queen to India highlights the enduring and strategic partnership between the two nations. Amidst growing Chinese influence and Bhutan’s domestic challenges, the visit holds significant geopolitical relevance, reinforcing India-Bhutan relations and underscoring Bhutan's critical role in India’s regional security.
Reaffirmation of India-Bhutan Relations
The visit reaffirmed the strong, time-tested partnership between India and Bhutan, rooted in mutual trust and cooperation. India reiterated its commitment to Bhutan's socio-economic development, increasing its financial aid for the 2024-2029 period from ?5,000 crore to ?10,000 crore. Notably, Bhutan’s flagship Gelephu Mindfulness City Project, championed by King Jigme Khesar, received strong Indian backing, reflecting India’s willingness to align with Bhutan’s developmental priorities.
Strategic Areas of Cooperation
Clean Energy and Hydropower
Bhutan remains central to India’s renewable energy strategy, particularly in hydropower, a vital part of Bhutan's economy. Bhutan exports the majority of its hydropower to India, reinforcing bilateral ties in the energy sector. This cooperation aligns with India’s regional energy security goals, with both nations seeking to strengthen clean energy initiatives.
Infrastructure Development
The visit also emphasized infrastructure projects, vital for enhancing Bhutan's connectivity. These projects are strategically significant, considering Bhutan's geostrategic importance in the Himalayas. Infrastructure development further strengthens the ties between the two nations, with a focus on mutual benefits and regional stability.
Geopolitical Context: China’s Growing Influence
China-Bhutan Border Disputes
The border issue with China has been ongoing since 1984. In 2023, Bhutan and China signed an agreement to expedite the settlement and demarcation of their borders. China’s push for resolution is part of its broader strategy to reduce India’s influence in Bhutan. The disputed areas, particularly those near India’s Siliguri Corridor, hold strategic importance for New Delhi. Any territorial adjustments could undermine India’s access to its Northeastern states.
Chinese Influence and Economic Engagement
China has been constructing villages along disputed border areas, altering ground realities and establishing civilian hubs that could serve as military outposts. Additionally, China is offering economic incentives to Bhutan, including promoting tourism and investing in Bhutan’s telecom sector, seeking to draw the country into closer economic and diplomatic alignment.
India’s Role in Bhutan’s Security and Sovereignty
Strategic Dependence on India
Bhutan's small military relies heavily on Indian support for training and defense. The 2017 Doklam standoff, where Indian forces intervened to prevent China from constructing a road in disputed territory, underscored India's crucial role in safeguarding Bhutan’s territorial integrity.
Friendship Treaty
The India-Bhutan Friendship Treaty is the cornerstone of their bilateral relations, ensuring Bhutan's sovereignty while reinforcing India's role in Bhutan’s foreign and defense policies. India's increased financial support aims to counter China’s economic influence in Bhutan.
Challenges for Bhutan
Balancing India and China
Bhutan is navigating a delicate balance between preserving its historical ties with India and engaging with China, which offers economic benefits. However, Bhutan’s sovereignty concerns limit its ability to make independent diplomatic decisions.
Domestic Issues
Bhutan faces challenges such as youth migration and limited economic diversification. Over-reliance on hydropower and a lack of industrial development make it vulnerable to external pressures, particularly from China.
The Strategic Importance of Bhutan to India
Geopolitical Buffer
Bhutan's location is vital for India’s security, especially in relation to the Siliguri Corridor, a narrow land link connecting India’s Northeast. Any Chinese presence in Bhutan’s disputed regions could disrupt access to this crucial corridor.
Hydropower Collaboration
Bhutan’s hydropower exports are central to India’s renewable energy strategy, and their cooperation in this area ensures mutual benefits.
Way Forward
India must continue to prioritize Bhutan’s development needs, ensuring robust financial and infrastructural support. Proactive engagement is necessary to address Bhutan’s concerns, particularly in light of China’s growing influence. Additionally, India should support Bhutan’s economic diversification to reduce reliance on external actors.
Impeachment of Judges
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent controversy surrounding remarks made by Justice Shekhar Kumar Yadav of the Allahabad High Court has prompted calls for his impeachment. During an event organized by the Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP), Justice Yadav made statements that were perceived as communal, leading to concerns over judicial impartiality. This incident has reignited discussions about the impeachment process for judges in India, highlighting the delicate balance between judicial independence and accountability.
Impeachment Process for Judges in India
In India, the impeachment process for judges, although not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution, serves as a mechanism to ensure judicial accountability while safeguarding judicial independence. The process is outlined under Articles 124 and 218 of the Indian Constitution, which govern the removal of Supreme Court and High Court judges, respectively.
Grounds for Impeachment
Judges in India can be removed on two grounds:
- Proved Misbehavior: Conduct that breaches the ethical standards of the judiciary.
- Incapacity: A judge’s inability to perform judicial duties due to physical or mental infirmity.
These grounds are clearly specified to prevent arbitrary removal, ensuring that the process remains fair and just.
Steps in the Impeachment Process
- Initiation of Motion: The process begins when a motion for impeachment is introduced in Parliament, either in the Lok Sabha or Rajya Sabha. The motion must be supported by at least 100 members of the Lok Sabha or 50 members of the Rajya Sabha. This ensures significant parliamentary backing before the motion proceeds.
- Formation of an Inquiry Committee: If the motion is admitted, a three-member inquiry committee is constituted. This includes a Supreme Court judge, the Chief Justice of a High Court, and a distinguished jurist. The committee conducts a thorough investigation into the allegations.
- Committee Report and Parliamentary Debate: Following the investigation, the committee submits its findings. If the judge is found guilty, the report is debated in Parliament. Both Houses must approve the motion by a special majority, which requires a two-thirds majority of members present and voting, as well as a majority of the total membership.
- Final Removal by the President: Once the motion is passed in both Houses, it is presented to the President, who issues the removal order.
Safeguards Against Misuse
The impeachment process includes several safeguards to prevent misuse:
- High Threshold for Initiation: The requirement for significant support from Parliament ensures that the process cannot be initiated frivolously.
- Objective Inquiry: The inquiry committee, comprising legal experts, guarantees an impartial investigation.
- Parliamentary Scrutiny: Both Houses of Parliament are involved, ensuring that the process undergoes democratic scrutiny.
Challenges and Precedents
Despite the rigorous process, no Supreme Court judge has been successfully impeached to date. Past attempts, such as those against Justice V. Ramaswami (1993) and Chief Justice Dipak Misra (2018), were unsuccessful. These instances demonstrate the complexities involved in the impeachment process.
Guidelines for Judges’ Public Statements
Judges in India are entitled to freedom of speech, but they are expected to exercise caution in public statements to maintain the dignity of their office. The Bangalore Principles of Judicial Conduct (2002) and the Restatement of Values of Judicial Life (1997) outline key principles for judicial conduct, including:
- Non-Interference in Political Matters: Judges should refrain from commenting on political issues to avoid any perception of bias.
- Impartiality: Judges must avoid statements that could prejudice ongoing cases or align them with specific ideologies.
Upholding Judicial Impartiality in a Diverse Society
To maintain impartiality, judges must interpret laws based on constitutional values of justice, equality, and secularism. Furthermore, the judiciary must ensure representation from diverse backgrounds to foster inclusivity and reduce systemic biases. Training programs focused on cultural competence and social diversity are essential to ensure that judges are sensitive to the needs of marginalized communities.
Conclusion
The impeachment process, while stringent, plays a critical role in maintaining judicial accountability in India. As seen in the case of Justice Yadav, judicial conduct, particularly public statements, must be carefully scrutinized to preserve the integrity of the judiciary. Upholding impartiality and adhering to constitutional values are paramount in ensuring that the judiciary continues to function as a neutral arbiter in India’s democracy.
Analysis of Female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) Trends in India: 2017-2023
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) recently released a working paper revealing critical insights into the trends of female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in India from 2017-18 to 2022-23. The report highlights an overall increase in female LFPR, with rural areas experiencing more significant growth compared to urban areas. This article delves into the key findings, regional disparities, influencing factors, and government initiatives aimed at promoting female workforce participation.
Key Findings on Female LFPR
The period between 2017-18 and 2022-23 witnessed a notable rise in female LFPR, both in rural and urban regions, though rural areas saw higher gains.
Rural female LFPR surged by approximately 69%, from 24.6% to 41.5%, while urban female LFPR increased from 20.4% to 25.4%. This consistent growth was observed even after excluding unpaid family workers or household helpers, reinforcing the long-term trend of increased female workforce participation across India.
However, a significant point of discussion in the report was the regional variations in female LFPR. States like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana have consistently reported low female LFPR, which is noteworthy considering that Punjab and Haryana are among India's wealthiest states, while Bihar is the poorest. This regional disparity suggests that economic prosperity does not automatically translate into higher female labour force participation, highlighting deeper socio-cultural and structural barriers.
Regional Disparities in Female LFPR
The report emphasizes the persistent challenges in northern and eastern India. Punjab and Haryana, despite their affluence, have struggled with low female LFPR. Cultural and societal norms in these regions may contribute to the underrepresentation of women in the workforce, particularly in rural areas where traditional gender roles are more entrenched.
On the other hand, Bihar, the poorest state in India, had the lowest female LFPR in the country, particularly in rural areas. However, there has been a significant improvement in recent years, especially among rural married women. This indicates a slow but positive shift in attitudes towards female employment in these states.
In contrast, northeastern states such as Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh have shown significant improvements in female LFPR, particularly in rural areas. These states have demonstrated that regional and cultural factors can also create conducive environments for female workforce participation.
Demographic Factors Affecting Female LFPR
Several demographic patterns influence female LFPR, including marital status and age. The report notes that married men consistently exhibit higher LFPR compared to women. Marriage, however, has a detrimental impact on female LFPR, particularly in urban areas, where women often face greater familial and societal pressures to prioritize domestic responsibilities over formal employment.
Age dynamics also play a crucial role in female LFPR trends. The data reveals a bell-shaped curve for female participation, peaking around the age of 30-40 years and sharply declining thereafter. This is in stark contrast to male LFPR, which remains almost universally high between the ages of 30-50 before gradually declining. These trends underscore the challenges women face in sustaining their participation in the workforce due to familial responsibilities, especially after marriage and childbirth.
Government Initiatives and the Rise in Female LFPR
The government's focus on women-led development is evident through various schemes aimed at increasing female workforce participation. Programs like Mudra Loans, the Drone Didi Scheme, and the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana have been particularly instrumental in empowering women, especially in rural areas. These initiatives provide women with access to financial resources, skill development opportunities, and avenues for entrepreneurship, all of which contribute to the rise in female LFPR.
The EAC-PM's analysis acknowledges the positive impact of these government schemes, but it also stresses the need for further research to evaluate their long-term effectiveness. While the descriptive analysis highlights a substantial increase in female LFPR between 2017-18 and 2022-23, especially in rural areas, there remains a need for continuous monitoring and assessment of these schemes to ensure their sustained impact.
Conclusion: A Positive Shift, but Challenges Remain
The increase in female LFPR across India from 2017-18 to 2022-23 signals a positive shift in employment trends, particularly in rural areas. However, regional disparities, societal norms, and demographic factors continue to pose challenges. The rise in female LFPR is encouraging, but it is essential to understand the deeper socio-economic factors that shape women's participation in the workforce.
Government schemes have contributed to this growth, but future research is necessary to gauge their long-term effects and ensure that women’s participation in the workforce is not just a short-term trend. It is crucial that the government continues to refine policies that support women in overcoming socio-cultural and economic barriers, especially in less prosperous states like Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana. Sustained efforts, including education, skill development, and gender-sensitive policies, will be key to ensuring that the rise in female LFPR is both inclusive and long-lasting.
The analysis by the EAC-PM provides an essential framework for policymakers to design more targeted interventions to address regional disparities and create a more inclusive labor market for women in India.
No-Confidence Motion Against Rajya Sabha Chairman

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
In December 2024, around 60 opposition MPs from the INDIA (Indian National Developmental, Inclusive Alliance) bloc submitted a notice to the Rajya Sabha Secretariat, seeking the removal of Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar from his position as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. This unprecedented move has sparked significant political debate, with the opposition accusing Dhankhar of partisanship and bias in the conduct of parliamentary proceedings.
The Charges Against Jagdeep Dhankhar
Allegations of Bias and Partisanship
The opposition has raised several allegations against Dhankhar since his appointment as the Rajya Sabha Chairman in August 2022. These include:
- Partiality towards the ruling government: The opposition claims that Dhankhar has shown bias in favor of the BJP, with accusations of repeatedly denying the Leader of the Opposition, Mallikarjun Kharge, the opportunity to respond to statements made by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and BJP President J.P. Nadda.
- Interference in Parliamentary Debates: Opposition MPs have accused Dhankhar of disrupting their speeches and allowing ruling party members to dominate parliamentary discussions.
- Unbecoming Remarks: The notice also refers to comments made by Dhankhar, including praising the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) and recalling his association with "so-called cultural organizations." These actions, according to the opposition, violate the non-partisan nature expected of the Chairman.
The Constitutional Framework for Removal of the Vice-President
Legal Provisions for Impeachment
The Vice-President of India, who also serves as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, is elected for a five-year term. Article 67 of the Indian Constitution outlines the procedure for his removal:
- Notice Requirement: A motion for the removal of the Vice-President must be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with a prior 14-day notice.
- Approval Process: The resolution must be passed by a majority in the Rajya Sabha and then approved by the Lok Sabha.
- Grounds for Removal: The Vice-President can only be removed through a resolution that is supported by a majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Opposition’s Plan and Challenges
Despite lacking the necessary numbers in the Rajya Sabha to succeed in the impeachment motion, the opposition's move is aimed at sending a political message to the BJP, expressing dissatisfaction with the functioning of the Parliament under Dhankhar’s leadership.
The current session of Parliament is scheduled to end on December 20, 2024, leaving little time for the motion to gain traction. The opposition also does not have the numbers needed for a majority in the Rajya Sabha, which complicates the chances of success for the motion.
Historical Precedents for Similar Resolutions
The last notable attempt to remove a parliamentary officer occurred in 2020 when the opposition moved a no-confidence motion against Rajya Sabha Deputy Chairman Harivansh. This motion was prompted by his decision to extend the session during the contentious farm Bills debate. Although the motion was discussed, it did not result in any significant change.
Similarly, there have been instances where motions to remove Lok Sabha Speakers have been moved but not passed, such as against G.V. Mavalankar in 1951, Sardar Hukam Singh in 1966, and Balram Jakhar in 1987.
Role and Significance of the Vice-President in India
Constitutional Role
The Vice-President of India holds the second-highest constitutional office, primarily functioning as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. His duties include:
- Presiding over Rajya Sabha Sessions: The Vice-President ensures the smooth functioning of the Rajya Sabha and maintains order during debates. He does not typically vote except in the case of a tie.
- Acting President: In the absence, resignation, or death of the President, the Vice-President assumes the role of the Acting President.
Removal Process Under Article 67
- Article 67(b) of the Constitution specifies the process for the removal of the Vice-President, requiring a 14-day notice and approval from both Houses of Parliament. This provision ensures that any such resolution receives due consideration and is not moved hastily.
Implications for Parliamentary Democracy
- Risks to Parliamentary Integrity: Opposition leaders have expressed concern that the current political environment is eroding the integrity of India’s parliamentary system. They argue that by misusing constitutional offices for partisan ends, the ruling government risks undermining the democratic foundations of the country.
Significance of the Move
- Although the opposition may not succeed in removing Dhankhar, the notice serves as a powerful symbol of resistance. The move underscores the opposition’s commitment to defending the principles of parliamentary democracy and the need for impartiality in the conduct of parliamentary affairs.
Conclusion
The opposition’s push to remove Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar from his position as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha highlights the growing political tensions in India’s Parliament. While the move may not succeed due to the lack of numerical support, it brings to the forefront critical issues regarding the independence of constitutional offices and the functioning of parliamentary democracy in India. The developments around this notice will continue to be a significant point of discussion as the winter session of Parliament draws to a close.
Beware of Digital Wedding Invites

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
In the peak wedding season, cyber fraudsters are increasingly exploiting digital wedding invitations to hack into mobile phones. These fraudulent invites, often disguised as PDF wedding cards shared on WhatsApp, contain embedded malware that allows cybercriminals to gain full access to the victim's phone. This includes access to sensitive financial data, making individuals vulnerable to fraud. The Lucknow Police Cyber Cell has issued a public warning, urging citizens to be cautious and avoid opening suspicious files.
How the Scam Works
The scam involves cybercriminals sending out malware-laden wedding invitations. Once the recipient opens the file, the malware infects their phone, enabling the fraudsters to remotely control the device. From there, they can access sensitive information, including bank account details, and may even transfer funds without the victim’s consent.
Preventive Measures and Cyber Hygiene
To protect against such scams, individuals should follow these preventive steps:
- Avoid Suspicious Files: Do not open files from unknown senders, particularly those with extensions like APK, PIF, or VBS. It is crucial to verify the sender's number—legitimate Indian numbers typically begin with +91.
- Turn Off Auto-Download: Disabling automatic downloads on platforms like WhatsApp can prevent files from being opened unknowingly.
- Enable Two-Step Verification: Strengthen security by activating two-step verification on your digital accounts and setting strong passwords.
- Report Fraud Immediately: In case of suspicious activity, contact the cybercrime helpline at 1930 or file a complaint on the official cybercrime portal (www.cybercrime.gov.in).
The Lucknow Police’s “Cyber Pathshala” campaign aims to raise awareness and educate the public on digital scams, particularly during the wedding season when these frauds are at their peak.
Cybersecurity Challenges in India
This emerging digital threat is part of a broader trend of sophisticated cybercrimes in India. Cyber fraudsters are increasingly using manipulative tactics, such as phishing, fake digital arrests, and malware attacks. In 2024, India witnessed a significant rise in ransomware attacks, frauds targeting financial institutions, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
India's legislative and institutional frameworks are evolving to address these challenges. Key measures include:
- The Information Technology Act, 2000, which lays the foundation for tackling cybercrimes.
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, which focuses on protecting personal data.
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), which coordinates national responses to cyber incidents.
Additionally, new frameworks like the National Cyber Security Policy, 2013, and initiatives such as Cyber Surakshit Bharat and the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), aim to fortify India's digital landscape and promote cybersecurity.
Emerging Cyber Threats
As India becomes more digitally connected, the threat landscape continues to evolve:
- Digital Arrest Scams: Fraudsters impersonate law enforcement to extort money from victims, claiming they are under investigation for fictitious crimes.
- Ransomware: Attacks on critical infrastructure, such as financial institutions and healthcare systems, have led to operational disruptions and financial losses.
- Deepfake Technology: The rise of AI-generated deepfakes poses significant risks, including misinformation and financial fraud.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities: The rapid adoption of IoT devices has created new security challenges, with many devices lacking adequate protection.
Strategic Recommendations for Enhancing Cybersecurity
To counter these evolving threats, India must focus on several strategic areas:
- Digital Literacy Campaigns: Nationwide efforts to improve digital literacy, particularly targeting vulnerable groups such as rural populations and senior citizens.
- Stronger IoT Security Protocols: Mandating secure design and certification for IoT devices.
- AI-Driven Threat Intelligence: Implementing AI-based tools for early threat detection and response in critical sectors.
- Mandatory Cybersecurity Audits: Regular audits of critical infrastructure, especially in sectors like healthcare, banking, and utilities.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships to address challenges such as cryptocurrency fraud, ransomware, and dark web-enabled crimes.
Conclusion
The rise of digital fraud, including the manipulation of wedding invitations for malicious purposes, highlights the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures in India. By improving public awareness, investing in technological solutions, and reinforcing legal and institutional frameworks, India can better protect its citizens from the growing threat of cybercrime. A proactive and informed approach is essential to secure the digital future of the nation.
Building on the Revival of the Manufacturing Sector
- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s manufacturing sector has shown remarkable signs of recovery and growth, thanks to strategic policy initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. To fully capitalize on this momentum and become a global manufacturing hub, however, deeper reforms are needed.
The Success of the PLI Scheme: A Catalyst for Growth
The government’s PLI scheme has been instrumental in revitalizing key sectors like electronics, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and textiles. It has not only boosted production but also increased exports and job creation. According to the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) 2022-23, manufacturing output grew by an impressive 21.5%, while gross value added (GVA) increased by 7.3%. Sectors such as basic metals, refined petroleum products, food products, and motor vehicles, which are beneficiaries of the PLI scheme, contributed 58% of total manufacturing output, registering growth of 24.5%.
This success underlines the potential of India’s manufacturing sector, with the PLI scheme acting as a key enabler. However, while the recovery is promising, there are significant challenges to overcome to sustain long-term growth.
Expanding PLI Incentives to New Sectors
The PLI scheme has largely benefitted traditional industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing. To further accelerate growth, the scope of the scheme must be extended to labour-intensive sectors such as apparel, footwear, and furniture, which hold immense potential for job creation. Additionally, emerging sectors like aerospace, space technology, and maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services offer new avenues for growth. By diversifying the incentive structure to these sectors, India could establish a more robust and resilient manufacturing ecosystem.
In sectors like capital goods, where India is heavily import-dependent, the potential for reducing supply chain vulnerabilities is significant. Moreover, promoting green manufacturing and advanced technologies could further bolster India’s competitiveness in global markets.
Addressing the Divergence Between Output and Value Addition
Despite a surge in production, India’s gross value added (GVA) has not kept pace with output growth. The ASI data shows that input prices soared by 24.4% in 2022-23, indicating that while production volumes are up, industries are grappling with high input costs. A more streamlined import regime could mitigate these costs. Simplifying tariffs into a three-tier system (for raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods) would reduce input costs, enhance competitiveness, and improve integration into global value chains.
Regional Imbalance: A Barrier to Inclusive Growth
The manufacturing sector’s growth is heavily concentrated in a few states such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Uttar Pradesh, which account for over 54% of manufacturing GVA. This concentration not only restricts equitable development but also hampers the overall growth potential of the sector. To address this, it is crucial that states actively participate in India's manufacturing growth story by implementing market reforms in land, labour, and power. Additionally, infrastructure development and investment promotion in less industrialized regions could help balance growth and ensure that the benefits of manufacturing reach all corners of the country.
Fostering MSME Growth and Enhancing Female Workforce Participation
Micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) contribute about 45% of India’s manufacturing GDP and employ around 60 million people. To scale these businesses and integrate them into global value chains, PLIs should be tailored to accommodate their needs, such as lowering capital investment thresholds and reducing production targets.
Equally important is the enhancement of female workforce participation. Studies suggest that India’s manufacturing output could increase by 9% if more women enter the workforce. The development of supportive infrastructure, such as hostels and childcare facilities, can play a pivotal role in enabling women’s participation, thus driving inclusive growth.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
To transform into a developed economy by 2047, India must continue to focus on strengthening its manufacturing sector. According to industry estimates, manufacturing’s share in Gross Value Added (GVA) can rise from 17% to 25% by 2030 and further to 27% by 2047. Achieving this will require sustained efforts to enhance competitiveness through business reforms, cost reduction, and policy support. India is well-positioned to harness its manufacturing potential, but timely and focused interventions are necessary to turn this vision into reality.
Reflections on Baku’s ‘NCQG Outcome’ at COP29
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The recently concluded COP29 in Baku, Azerbaijan, has brought the spotlight back to climate finance, particularly in relation to the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG). As the global community grapples with the escalating climate crisis, the discussions and outcomes from the COP29 summit are pivotal in shaping future climate action. However, the agreed-upon financial targets, which were expected to be a step towards transformative climate justice, have sparked significant concern, particularly among developing nations.
The Need for Climate Finance: A Global Responsibility
Climate finance is essential for supporting developing countries, which bear the brunt of climate change despite contributing minimally to global emissions. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has stressed the need to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, yet current policies could lead to a rise of up to 3.1°C. To counter this, developing nations require financial assistance to transition to green energy, adapt to climate impacts, and implement their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
The upfront costs of green technologies, such as renewable energy, are high, and while they offer long-term savings, their initial investments remain a significant barrier. Additionally, many developing countries face fiscal constraints, making it even more difficult to adopt climate-friendly technologies without external financial support.
The Role of NCQG in Addressing Climate Finance Gaps
The NCQG, an evolution of the 2010 $100 billion annual commitment, aims to provide clarity and accountability in climate financing. Established as a framework to ensure financial resources for climate action, the NCQG should ideally focus on the evolving needs of the Global South. However, at COP29, the target agreed upon was a mere $300 billion annually by 2035, far from the $1.3 trillion that developing countries had requested. This amount falls drastically short of what is necessary to meet the ambitious climate goals and fails to represent a transformative shift in financial flows.
Key Challenges and Discontent with the Outcome
Several challenges have been raised regarding the COP29 outcome:
- Equity and Responsibility: Developed nations are expected to bear a larger share of the financial burden, in line with the principle of 'Common but Differentiated Responsibilities' (CBDR). However, the NCQG outcome bypasses this principle, offering insufficient funds for climate action in developing countries.
- Types of Finance: There is debate over whether private finance should count towards the goal. Developing countries have stressed the importance of public finance over loans, which add to their debt burdens.
- Insufficient Commitment: While the $300 billion annual pledge is a step forward, it is far from adequate. The global climate finance needs, estimated at $5 trillion to $7 trillion by 2030, require bolder commitments from developed nations.
India's Position and Domestic Efforts
At COP29, India emphasized the need for developed countries to fulfill their financial commitments, advocating for at least $1.3 trillion annually until 2030. India, despite being a developing country, has also made significant strides in climate action through domestic policies. The 2024-25 Union Budget allocated substantial funds to renewable energy projects, including ?19,100 crore for the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy. These efforts demonstrate India’s commitment to climate goals, though the financial flow remains insufficient.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
The NCQG outcome at COP29 highlights the ongoing disparities in global climate finance commitments. While the $300 billion annual target is a step forward, it does not align with the urgency or scale required to tackle the climate crisis. To achieve a just and equitable transition to a sustainable future, future climate finance discussions must prioritize transparency, accountability, and fairness, ensuring that developed nations shoulder their fair share of the responsibility. The path forward requires unwavering international cooperation to ensure that developing countries receive the necessary support to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Scrapping of Windfall Gains Tax

- 05 Dec 2024
Introduction
On December 2, 2024, the Indian government withdrew the windfall gains tax on domestic crude oil production and fuel exports (diesel, petrol, and aviation turbine fuel - ATF). This tax, initially imposed in July 2022, was introduced in response to the surge in global oil prices following Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Its removal reflects the current global oil market stability and the improved fuel supply situation in India.
What is Windfall Gains Tax?
Definition
A windfall tax is a levy imposed on unexpected profits that result from extraordinary events, such as geopolitical crises or market disruptions. In the case of India, the tax was applied to the super-normal profits of oil producers and fuel exporters due to the global energy turmoil.
Key Features
- Domestic Crude Oil: The Special Additional Excise Duty (SAED) was imposed on domestic crude oil production.
- Fuel Exports: A combination of SAED and Road and Infrastructure Cess (RIC) was levied on diesel, petrol, and ATF exports.
Rationale Behind the Windfall Gains Tax
Immediate Context
The tax was introduced during a period of soaring global crude oil prices, driven by the Russia-Ukraine conflict. India, which imports over 85% of its oil, faced concerns about the availability of fuels and the impact of rising prices on domestic consumption. The tax was seen as a way to:
- Ensure Domestic Fuel Supply: By discouraging excessive fuel exports during a period of global supply chain disruptions.
- Increase Government Revenue: The tax aimed to capture windfall profits and offset the duty cuts on domestic fuel sales.
Global Context
Other countries also implemented similar windfall taxes during this period, as energy companies saw record profits due to the price surge.
Decline in Windfall Gains Tax Revenue
Revenue Collection
The windfall gains tax initially raised significant revenue, but the amount has decreased over time due to falling global oil prices:
- FY 2022-23: Rs 25,000 crore
- FY 2023-24: Rs 13,000 crore
- FY 2024-25 (so far): Rs 6,000 crore
This decline, combined with reduced oil prices, led to the tax being effectively inactive before its formal withdrawal.
Withdrawal of the Windfall Gains Tax
Reasons for the Withdrawal
- Global Stabilization: Crude oil prices, which had exceeded $100 per barrel, have now stabilized under $75 per barrel, with no immediate signs of a significant price surge.
- Domestic Fuel Availability: There is now a robust fuel supply in the domestic market, making the tax less necessary.
- Declining Revenues: With the tax generating diminishing returns, it was no longer economically viable for the government to maintain it.
Impact of the Scrapping
The government's move to scrap the windfall gains tax is seen as a signal of stability and predictability in the taxation regime. It assures the oil industry that the government is confident in the stability of global oil prices and supply chains.
Criticism of the Windfall Tax
Industry Opposition
The windfall tax faced opposition from the oil industry, which argued that it:
- Reduced Profitability: The tax limited the profits of publicly listed companies like ONGC and Reliance Industries.
- Discouraged Oil Production: By making the taxation environment unpredictable, it deterred investment in oil exploration and production in a country that is heavily dependent on oil imports.
- Created Uncertainty: Frequent revisions of the tax led to an unstable business environment.
Conclusion
The scrapping of the windfall gains tax is a significant policy shift. It not only provides relief to oil companies but also signals a more predictable and stable taxation regime. By withdrawing the tax, the government is fostering a conducive environment for future investments in domestic oil production and signaling its confidence in the stability of global oil prices. This move is a crucial step in ensuring that India’s energy policies remain adaptable and aligned with the evolving global market conditions.
Current Representation of Women in CAPFs

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) of India, comprising forces like CRPF, BSF, CISF, and others, play a crucial role in maintaining internal security. Women’s participation in these forces has been historically limited, but recent efforts have focused on increasing their representation. As of 2024, women constitute only 4.4% of the total personnel in CAPFs, highlighting the slow progress despite various initiatives.
Current Representation and Changes Over Time
- Overall Representation: Women make up 4.4% of the 9.48 lakh-strong CAPFs. Within this, the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) has the highest representation at 7.02%, followed by the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) at 4.43%, Border Security Force (BSF) at 4.41%, Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) at 4.05%, Assam Rifles at 4.01%, and Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) at 3.38%.
- Growth of Women Personnel: From 15,499 women in 2014, the number has tripled to 42,190 in 2024, reflecting a steady increase in recruitment. However, the percentage remains low despite these gains.
- Recruitment Trends: In 2024, 835 women were recruited, with 5,469 more in the process. In 2025, 4,138 women are expected to be recruited.
Government Efforts and Parliamentary Committee Recommendations
- Policy Measures: The government has introduced several steps to encourage women’s participation in CAPFs, such as reservations in constable-level positions: one-third for CRPF and CISF, and 14-15% for border forces like BSF, SSB, and ITBP.
- Challenges in Recruitment: Despite these policies, recruitment has not kept pace with the targets. The 2022 Parliamentary Committee on Home Affairs expressed disappointment over the “abysmally low” number of women in CAPFs, noting that women made up only 3.68% of the forces at that time.
- Recommendations by Parliamentary Committees:
- The Home Affairs Committee recommended fast-tracking phase-wise recruitment of women, particularly in CISF and CRPF.
- The Standing Committee on Personnel (2023) suggested “soft postings” for women to avoid difficult working conditions, especially in remote or strenuous terrains. It also called for reservations for transgender individuals.
- In 2024, further steps like fee waivers, relaxed physical standards, and provisions for maternity and child care leave were introduced to make the work environment more inclusive.
Reasons Behind Low Representation
- Cultural Barriers: Traditional gender roles and societal expectations deter many women from pursuing careers in security forces.
- Work Environment: The demanding nature of the job, which includes postings in remote areas and high-risk operations, makes it less appealing, especially for women with family responsibilities.
- Infrastructure Issues: Lack of adequate accommodation, sanitation facilities, and safety measures for women are deterrents to joining and retaining female personnel.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Although the representation of women in CAPFs has seen improvement, it remains below expectations due to persistent challenges. The government’s continuous focus on recruitment reforms, better working conditions, and policy incentives will be crucial to achieve gender parity in these forces. As societal attitudes evolve and the infrastructure improves, more women may be encouraged to serve in these vital security roles. Future efforts must include targeted recruitment drives and creating a more inclusive and supportive environment to enhance women’s participation in CAPFs.
India's Gig Economy: Growth and Impact on Employment

- 03 Dec 2024
Introduction
India’s gig economy is experiencing rapid growth, with projections indicating it will significantly contribute to the national economy and employment generation. A recent report by the Forum for Progressive Gig Workers estimates the gig economy could reach $455 billion by the end of 2024, growing at a 17% compounded annual growth rate (CAGR). By 2030, it may add 1.25% to India’s GDP and create 90 million jobs.
What is the Gig Economy?
- Definition: The gig economy refers to a labor market based on short-term, flexible jobs, typically facilitated by digital platforms. Gig workers, also called freelancers or independent contractors, are compensated for each task they complete.
- Key Features:
- Flexibility in work schedule and location.
- Task-based employment through digital platforms.
- Common sectors: e-commerce, transportation, delivery services, and freelance work.
Status of the Gig Economy in India
- Market Growth:
- In 2020-21, India had 7.7 million gig workers, which is expected to grow to 23.5 million by 2029-30.
- Key sectors contributing to growth include e-commerce, transportation, and delivery services.
- Driving Factors:
- Digital Penetration: With over 936 million internet subscribers and 650 million smartphone users, digital infrastructure is a key enabler of the gig economy.
- Startup and E-commerce Growth: The rise of startups and e-commerce platforms has increased demand for flexible labor.
- Changing Work Preferences: Younger generations seek work-life balance, opting for flexible gig work.
Gig Economy and Employment Generation
- Contribution to GDP: The gig economy is expected to contribute 1.25% to India’s GDP by 2030.
- Job Creation:
- The gig economy could create up to 90 million jobs by 2030.
- It is estimated that by 2030, gig workers will comprise 4.1% of India’s total workforce.
- Benefits:
- Women’s Empowerment: Gig work provides financial independence and flexibility, especially benefiting women in the workforce.
- Regional Growth: Tier-II and Tier-III cities are seeing accelerated growth in gig work opportunities.
Challenges Faced by Gig Workers
- Job Insecurity: Many gig workers experience instability in their employment, especially in low-skilled jobs.
- Income Volatility: Earnings are unpredictable, and workers face difficulty in financial planning.
- Regulatory Gaps: There is no comprehensive legal framework to protect gig workers’ rights and ensure fair working conditions.
- Delayed Payments: A significant number of workers face delayed payments, affecting their financial well-being.
- Skill Development: Many workers report a lack of opportunities for career advancement and skill development.
Government Initiatives for Gig Workers
- Code on Social Security, 2020: Recognizes gig workers and aims to extend social security benefits, though it lacks comprehensive coverage.
- e-Shram Portal & Welfare Schemes: Initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan Yojana and PMJJBY aim to provide financial security to gig workers.
- State-level Initiatives:
- Rajasthan’s Platform-Based Gig Workers Act (2023) focuses on registration and welfare.
- Karnataka’s bill mandates formal registration and grievance mechanisms.
The Way Forward
- Legal Reforms: India can draw from international models like California and the Netherlands, where gig workers are reclassified as employees to ensure protections such as minimum wages and regulated working hours.
- Portable Benefits System: Implementing a system where gig workers can access benefits like healthcare and retirement plans regardless of their employer.
- Skill Development: Strengthening collaborations with vocational institutions to enhance skills and improve earning potential.
- Technological Solutions: Establishing robust feedback mechanisms for workers to report exploitation and ensure fairness within the gig economy.
Conclusion
The gig economy in India is poised to become a significant driver of economic growth and job creation. However, addressing challenges such as income volatility, job insecurity, and regulatory gaps is crucial to ensuring sustainable growth.
NITI Aayog’s Framework for Future Pandemic Preparedness
- 02 Dec 2024
Introduction
In response to the evolving threat of pandemics, NITI Aayog has released an Expert Group report titled "Future Pandemic Preparedness and Emergency Response — A Framework for Action." The report offers a strategic blueprint for India to enhance its pandemic preparedness, drawing from the lessons learned during the COVID-19 crisis and global best practices. This framework aims to create a rapid, well-coordinated response system for future public health emergencies.
Rationale Behind the Expert Group
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of global and national health systems to emerging infectious diseases. As future pandemics are inevitable, especially with increasing zoonotic threats, India has taken a proactive step in planning for such eventualities. The WHO has warned that 75% of future pandemics may be zoonotic, caused by pathogens transmitted from animals to humans.
Key Findings from COVID-19 Response
India's response to COVID-19 highlighted several strengths and weaknesses in the public health system. Key efforts included developing vaccines, enhancing research and development frameworks, and deploying digital tools for data management across its 1.4 billion population. However, gaps were identified in governance, data management, and cross-sectoral coordination. These lessons have been integrated into the expert group’s framework for future preparedness.
The 100-Day Response Framework
A crucial aspect of the report is the emphasis on the first 100 days of a pandemic. The expert group argues that a rapid response within this period is essential for minimizing the impact of any outbreak. The framework outlines a detailed roadmap for preparedness, which includes tracking, testing, treating, and managing outbreaks efficiently. A robust system for quick deployment of countermeasures, including vaccines and treatments, is pivotal during these critical days.
Four Pillars of Pandemic Preparedness
The report's recommendations are organized around four pillars:
- Governance, Legislation, Finance, and Management:
- Proposes a new Public Health Emergency Management Act (PHEMA) to address modern pandemic needs.
- Creation of an empowered group of secretaries (EGoS) for rapid decision-making and coordination.
- Data Management, Surveillance, and Predictive Tools:
- Calls for a unified data platform to aggregate and analyze data for timely decision-making.
- Emphasizes strengthening genomic surveillance and establishing a national biosecurity network.
- Research, Innovation, and Infrastructure:
- Recommends a high-risk innovation fund to support research on diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics.
- Suggests enhancing manufacturing capacity and building biosafety containment facilities.
- Partnerships and Community Engagement:
- Stresses the importance of private sector involvement and community engagement in managing pandemics.
- Proposes a risk communication unit at the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) to manage public information and prevent misinformation.
International and National Collaboration
The report underscores the need for cross-border collaboration, aligning India’s efforts with international frameworks such as the WHO’s revised International Health Regulations and the Pandemic Accord negotiations. Collaboration with global institutions, academia, and the private sector is essential for sharing data, technology, and expertise during health crises.
Lessons from Past Epidemics
The report draws lessons from several past epidemics, including SARS, H1N1, and Ebola, which revealed the importance of timely diagnostics, coordinated surveillance, and rapid response. These lessons highlight the need for stronger international regulations, integrated data systems, and enhanced public-private partnerships in tackling future pandemics.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The framework offers actionable recommendations to strengthen India’s pandemic preparedness. From institutionalizing governance structures and creating a dedicated pandemic fund to enhancing surveillance and fostering innovation, these steps are designed to ensure rapid response and minimize the impact of future health crises. By focusing on governance, data management, research, and community partnerships, India aims to build a resilient health system capable of facing future challenges effectively.
Digital Arrests

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
In 2024, India has witnessed an alarming rise in cybercrime, particularly a new scam called "digital arrests." This type of fraud involves criminals impersonating law enforcement officials to extort money from victims. With more than 92,000 people targeted and ?2,141 crore defrauded from victims, these scams are rapidly becoming a significant concern for the public and law enforcement.
Nature of ‘Digital Arrests’
The modus operandi of digital arrest scams is sophisticated and emotionally manipulative. Cybercriminals contact victims through video calls, often using fake police officers' profiles and official documents to build credibility. They accuse victims of serious crimes such as money laundering or drug trafficking, claiming urgent action is needed to avoid arrest. The scammers create a false atmosphere of fear and urgency, convincing the victim to transfer large sums of money under the pretext of settling legal dues.
A notable example involves Ruchi Garg, who was targeted by scammers posing as police officers, falsely claiming her son was involved in a major scam. She was coerced into transferring ?80,000 before realizing it was a scam. Similar cases have affected hundreds, with perpetrators using AI-generated voices and fake visuals to amplify the deception.
The Growth of Cybercrime in India
Digital arrest scams are part of a broader increase in cybercrime in India. The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) has reported a rise in cyber fraud, with financial losses exceeding ?27,900 crore between 2021 and 2024. The most significant sources of these losses include stock trading scams, Ponzi schemes, and digital arrest frauds. As criminals adapt to emerging technologies and use social engineering tactics, the scale and complexity of scams are growing.
The surge in cybercrimes is fueled by vulnerabilities in India's digital landscape. With over 95 crore Internet users, many people, particularly the elderly or less tech-savvy, remain susceptible to such fraud. Cybercriminals often exploit this lack of awareness, combining fear and confusion to manipulate victims.
International Scope and Challenges
One of the challenges in combating digital arrests is the transnational nature of cybercrime. Scams often originate from countries like China, Cambodia, and Myanmar, where "scam compounds" run operations to train individuals in fraudulent techniques. These groups use virtual private networks (VPNs) and encrypted apps to conceal their identities and locations, making it difficult for Indian authorities to trace them.
Moreover, the involvement of mule bank accounts to launder defrauded money complicates investigations. Thousands of such accounts are identified and blocked regularly, but the flow of money continues through multiple channels, including cryptocurrencies.
Government Efforts and Preventive Measures
To address the growing menace of digital frauds, the Indian government has initiated several measures. The I4C, launched in 2020, aims to strengthen the response to cybercrimes by coordinating with various law enforcement agencies. The National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal allows citizens to report cyber fraud, while real-time alerts are sent to banks to prevent financial losses.
Additionally, the Cyber Crime Coordination Centre and other initiatives like Cyber Surakshit Bharat and CERT-In are working to enhance cybersecurity awareness and support victims. The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, also aims to regulate data security, which can reduce the sale of personal data on the dark web, a key enabler of these scams.
Conclusion
‘Digital arrests’ exemplify the evolving nature of cybercrimes in India. As digital threats become more complex and widespread, it is essential for citizens to remain vigilant and informed. Effective law enforcement, technological innovations, and public awareness are critical to reducing the impact of these scams and safeguarding the digital economy.
