Extension of PM Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana (PMGKAY) (Indian Express)
- 06 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said that the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, the Centre’s free ration scheme that aids 80 crore poor, will be extended for five more years.
News Summary
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi, announced the extension of the free foodgrain provision under the National Food Security Act, 2013 for the next five years.
- The PM Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana (PMGKAY) scheme, which was originally set to end in December 2023, will now continue.
- This scheme was introduced in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic to provide free food grains to beneficiaries under the National Food Security Act, 2013.
What is Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Ann/Anna Yojana (PM-GKAY)?
- The Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) was launched in April 2020 as a part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative to help the poor people whose livelihoods were shuttered by a countrywide lockdown aimed at containing the spread of the Covid-19.
- It was a part of Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (PMGKP) to help the poor fight the battle against Covid-19.
- Under this scheme, about 80 crore beneficiaries covered under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) get free 5 kg foodgrains per person per month.
- This assistance is in addition to the subsidised ration provided under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), allowing families covered under the Public Distribution System (PDS) to access essential food items at a nominal cost ranging from Rs 1 to Rs 3 per kilogram.
- Objective of PM-GKAY: To feed India's poorest citizens by distributing food grain to all priority households—those with ration cards and those designated by the Antyodaya Anna Yojana scheme—through the Public Distribution System.
- The Antyodaya Anna Yojana is a centrally sponsored scheme that was introduced in 2000 with the goal of giving millions of the poorest households access to heavily subsidized food.
- To ensure the availability of protein, 1 kg of pulses were provided to families (as per regional preferences)
- Implementing Agency: Department of Food and Public Distribution, Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
Who is eligible for the scheme?
- Families eligible for PM-GKAY include those under the Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) and Priority Household (PHH) categories.
- PHH beneficiaries are identified by state governments and Union territory administrations based on their specific criteria.
- This ensures that households in most need receive the necessary support.
- AAY families, comprising widows, terminally ill persons, disabled individuals, elderly individuals without means of subsistence or societal support, primitive tribal households, and various vulnerable categories, are also eligible for the scheme.
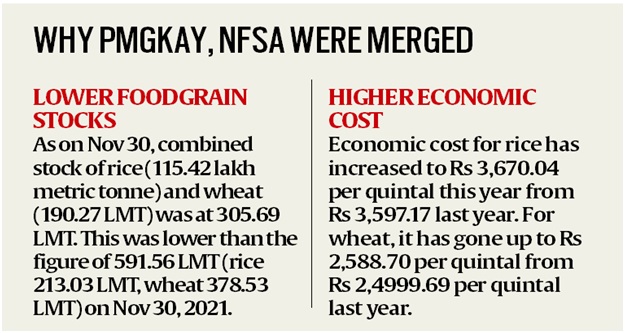
The merger of PMGKAY and NFSA:
- In January 2023, the government approved the integration of PM-GKAY benefits with the provisions of the NFSA Act.
- This integration will streamline the delivery of free food grains.
- It also ensures that families falling under the Antyodaya Ann Yojana (AAY) and priority households (PHH) categories receive free food grains according to their entitlement under NFSA.
- For the financial year 2023-24, the central government has allocated around 60 mt of food grain under the NFSA.
- This includes around 40 mt of rice, 19 mt of wheat, and 1 mt of coarse grains.
- The central issue price (CIP), the rate at which grains are made available to NFSA beneficiaries, is Rs 3 per kg for rice, Rs 2 per kg for wheat, and Rs 1 per kg for coarse cereals.
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (PMGKP) vs PMGKAY:
- The Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (PMGKP) was introduced in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic to provide economic relief to the vulnerable sections of society.
- Launched in March 2020, the scheme included various measures such as free food grains, cash transfers, and insurance coverage for healthcare workers, among others, to support those affected by the pandemic and the subsequent lockdown measures.
- The insurance scheme under PMGKP covered Rs 50 lakh per health worker fighting Covid-19.
- This insurance scheme was further extended by 180 days in April 2022.
What is National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013?
- The National Food Security Act (NFSA) was notified on 10th September, 2013.
- The objective of this scheme was to provide for food and nutritional security in the human life cycle approach, by ensuring access to adequate quantities of quality food at affordable prices for people to live a life with dignity.
- Coverage: 75% of the rural population and up to 50% of the urban population for receive subsidized food grains under the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- Overall, NFSA caters to 67% of the total population.
- State governments are tasked with identifying Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY - poorest of the poor) and priority households (PHH) beneficiaries within the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS)-covered population.
- Provisions: 5 Kg of foodgrains per person per month at Rs. 3/2/1 per Kg for rice/wheat/coarse grains.
- The existing AAY household will continue to receive 35 Kg of foodgrains per household per month.
- Meal and maternity benefits of not less than Rs. 6,000 to pregnant women and lactating mothers during pregnancy and six months after childbirth.
- Meals for children up to 14 years of age.
- Food security allowance to beneficiaries in case of non-supply of entitled foodgrains or meals.
- Setting up of grievance redressal mechanisms at the district and state levels.
What are the Challenges and the Issues?
- Inadequate Coverage: The National Food Security Act relies on data from the last census in 2011, leaving out a growing number of food-insecure individuals who have emerged since then.
- Financial Burden: Sustaining the program imposes a significant financial burden on the government, necessitating a continuous supply of affordable grains.
- In 2022, India had to impose restrictions on wheat and rice exports due to unpredictable weather conditions affecting harvests, adding pressure to food prices and unsettling global agricultural markets.
- Fiscal Deficit Concerns: The extension of the program could potentially jeopardize the government's goal of further reducing the fiscal deficit to 6.4% of the gross domestic product.
- Impact on Inflation: The program's continuation may also influence inflation rates, particularly in the case of rice and wheat, which contribute around 10% to India's retail inflation.
- Decreased production caused by factors like heatwaves and irregular monsoons has led to rising prices for these essential food items.
